Transformers documentation
YOLOS
YOLOS
Overview
The YOLOS model was proposed in You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu. YOLOS proposes to just leverage the plain Vision Transformer (ViT) for object detection, inspired by DETR. It turns out that a base-sized encoder-only Transformer can also achieve 42 AP on COCO, similar to DETR and much more complex frameworks such as Faster R-CNN.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Can Transformer perform 2D object- and region-level recognition from a pure sequence-to-sequence perspective with minimal knowledge about the 2D spatial structure? To answer this question, we present You Only Look at One Sequence (YOLOS), a series of object detection models based on the vanilla Vision Transformer with the fewest possible modifications, region priors, as well as inductive biases of the target task. We find that YOLOS pre-trained on the mid-sized ImageNet-1k dataset only can already achieve quite competitive performance on the challenging COCO object detection benchmark, e.g., YOLOS-Base directly adopted from BERT-Base architecture can obtain 42.0 box AP on COCO val. We also discuss the impacts as well as limitations of current pre-train schemes and model scaling strategies for Transformer in vision through YOLOS.
Tips:
- One can use YolosImageProcessor for preparing images (and optional targets) for the model. Contrary to DETR, YOLOS doesn’t require a
pixel_maskto be created.
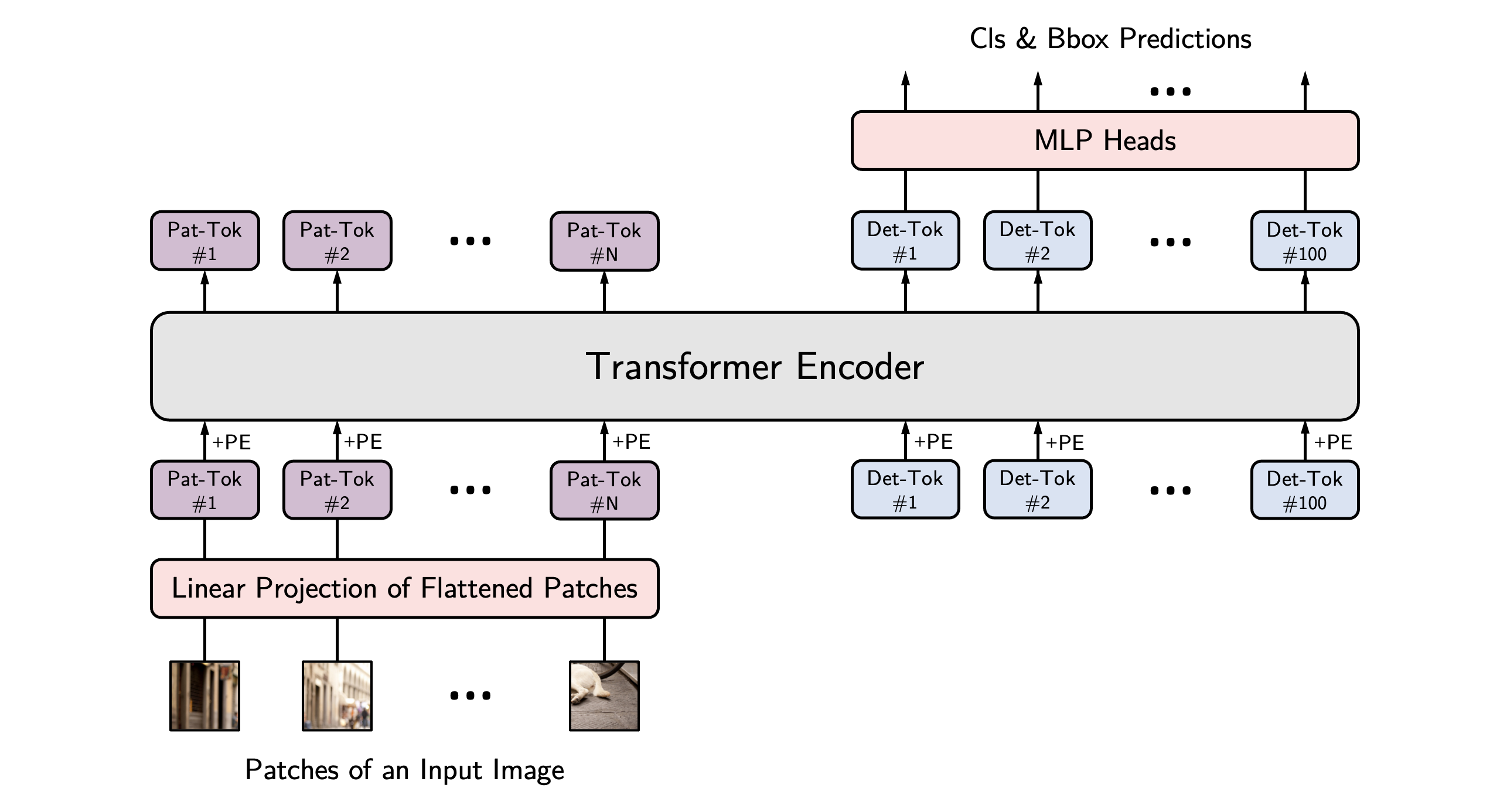 YOLOS architecture. Taken from the original paper.
YOLOS architecture. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with YOLOS.
- All example notebooks illustrating inference + fine-tuning YolosForObjectDetection on a custom dataset can be found here.
If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
YolosConfig
class transformers.YolosConfig
< source >( hidden_size = 768 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 intermediate_size = 3072 hidden_act = 'gelu' hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 image_size = [512, 864] patch_size = 16 num_channels = 3 qkv_bias = True num_detection_tokens = 100 use_mid_position_embeddings = True auxiliary_loss = False class_cost = 1 bbox_cost = 5 giou_cost = 2 bbox_loss_coefficient = 5 giou_loss_coefficient = 2 eos_coefficient = 0.1 **kwargs )
Parameters
-
hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. -
num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. -
num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. -
intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. -
hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported. -
hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probabilitiy for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler. -
attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. -
initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. -
layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. -
image_size (
List[int], optional, defaults to[512, 864]) — The size (resolution) of each image. -
patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to16) — The size (resolution) of each patch. -
num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to3) — The number of input channels. -
qkv_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to add a bias to the queries, keys and values. -
num_detection_tokens (
int, optional, defaults to100) — The number of detection tokens. -
use_mid_position_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to use the mid-layer position encodings. -
auxiliary_loss (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether auxiliary decoding losses (loss at each decoder layer) are to be used. -
class_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — Relative weight of the classification error in the Hungarian matching cost. -
bbox_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 5) — Relative weight of the L1 error of the bounding box coordinates in the Hungarian matching cost. -
giou_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 2) — Relative weight of the generalized IoU loss of the bounding box in the Hungarian matching cost. -
bbox_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 5) — Relative weight of the L1 bounding box loss in the object detection loss. -
giou_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 2) — Relative weight of the generalized IoU loss in the object detection loss. -
eos_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Relative classification weight of the ‘no-object’ class in the object detection loss.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a YolosModel. It is used to instantiate a YOLOS model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the YOLOS hustvl/yolos-base architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import YolosConfig, YolosModel
>>> # Initializing a YOLOS hustvl/yolos-base style configuration
>>> configuration = YolosConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the hustvl/yolos-base style configuration
>>> model = YolosModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configYolosImageProcessor
class transformers.YolosImageProcessor
< source >( format: typing.Union[str, transformers.models.yolos.image_processing_yolos.AnnotionFormat] = <AnnotionFormat.COCO_DETECTION: 'coco_detection'> do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Dict[str, int] = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2> do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float]] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float]] = None do_pad: bool = True **kwargs )
Parameters
-
format (
str, optional, defaults to"coco_detection") — Data format of the annotations. One of “coco_detection” or “coco_panoptic”. -
do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. -
size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"shortest_edge" -- 800, "longest_edge": 1333}): Size of the image’s (height, width) dimensions after resizing. Can be overridden by thesizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. -
resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toPILImageResampling.BILINEAR) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. -
do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. -
rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod. do_normalize — Controls whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. -
image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN) — Mean values to use when normalizing the image. Can be a single value or a list of values, one for each channel. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod. -
image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD) — Standard deviation values to use when normalizing the image. Can be a single value or a list of values, one for each channel. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod. -
do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to pad the image to the largest image in a batch and create a pixel mask. Can be overridden by thedo_padparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a Detr image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]] annotations: typing.Union[typing.List[typing.Dict], typing.List[typing.List[typing.Dict]], NoneType] = None return_segmentation_masks: bool = None masks_path: typing.Union[str, pathlib.Path, NoneType] = None do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Union[typing.Dict[str, int], NoneType] = None resample = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float, NoneType] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None do_pad: typing.Optional[bool] = None format: typing.Union[str, transformers.models.yolos.image_processing_yolos.AnnotionFormat, NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, str, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> **kwargs )
Parameters
-
images (
ImageInput) — Image or batch of images to preprocess. -
annotations (
List[Dict]orList[List[Dict]], optional) — List of annotations associated with the image or batch of images. If annotionation is for object detection, the annotations should be a dictionary with the following keys:- “image_id” (
int): The image id. - “annotations” (
List[Dict]): List of annotations for an image. Each annotation should be a dictionary. An image can have no annotations, in which case the list should be empty. If annotionation is for segmentation, the annotations should be a dictionary with the following keys: - “image_id” (
int): The image id. - “segments_info” (
List[Dict]): List of segments for an image. Each segment should be a dictionary. An image can have no segments, in which case the list should be empty. - “file_name” (
str): The file name of the image.
- “image_id” (
-
return_segmentation_masks (
bool, optional, defaults to self.return_segmentation_masks) — Whether to return segmentation masks. -
masks_path (
strorpathlib.Path, optional) — Path to the directory containing the segmentation masks. -
do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image. -
size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to self.size) — Size of the image after resizing. -
resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults to self.resample) — Resampling filter to use when resizing the image. -
do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image. -
rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults to self.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to use when rescaling the image. -
do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image. -
image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults to self.image_mean) — Mean to use when normalizing the image. -
image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults to self.image_std) — Standard deviation to use when normalizing the image. -
do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_pad) — Whether to pad the image. -
format (
strorAnnotionFormat, optional, defaults to self.format) — Format of the annotations. -
return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional, defaults to self.return_tensors) — Type of tensors to return. IfNone, will return the list of images. -
data_format (
strorChannelDimension, optional, defaults to self.data_format) — The channel dimension format of the image. If not provided, it will be the same as the input image.
Preprocess an image or a batch of images so that it can be used by the model.
pad
< source >( images: typing.List[numpy.ndarray] return_pixel_mask: bool = False return_tensors: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, str, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Optional[transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = None )
Parameters
-
image (
np.ndarray) — Image to pad. -
return_pixel_mask (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to return a pixel mask. -
input_channel_dimension (
ChannelDimension, optional) — The channel dimension format of the image. If not provided, it will be inferred from the input image. -
data_format (
strorChannelDimension, optional) — The channel dimension format of the image. If not provided, it will be the same as the input image.
Pads a batch of images to the bottom and right of the image with zeros to the size of largest height and width in the batch and optionally returns their corresponding pixel mask.
post_process_object_detection
< source >(
outputs
threshold: float = 0.5
target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = None
)
→
List[Dict]
Parameters
-
outputs (
YolosObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model. -
threshold (
float, optional) — Score threshold to keep object detection predictions. -
target_sizes (
torch.TensororList[Tuple[int, int]], optional) — Tensor of shape(batch_size, 2)or list of tuples (Tuple[int, int]) containing the target size(height, width)of each image in the batch. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
List[Dict]
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model.
Converts the raw output of YolosForObjectDetection into final bounding boxes in (top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y) format. Only supports PyTorch.
YolosFeatureExtractor
Preprocess an image or a batch of images.
pad
< source >( images: typing.List[numpy.ndarray] return_pixel_mask: bool = False return_tensors: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, str, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Optional[transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = None )
Parameters
-
image (
np.ndarray) — Image to pad. -
return_pixel_mask (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to return a pixel mask. -
input_channel_dimension (
ChannelDimension, optional) — The channel dimension format of the image. If not provided, it will be inferred from the input image. -
data_format (
strorChannelDimension, optional) — The channel dimension format of the image. If not provided, it will be the same as the input image.
Pads a batch of images to the bottom and right of the image with zeros to the size of largest height and width in the batch and optionally returns their corresponding pixel mask.
post_process_object_detection
< source >(
outputs
threshold: float = 0.5
target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = None
)
→
List[Dict]
Parameters
-
outputs (
YolosObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model. -
threshold (
float, optional) — Score threshold to keep object detection predictions. -
target_sizes (
torch.TensororList[Tuple[int, int]], optional) — Tensor of shape(batch_size, 2)or list of tuples (Tuple[int, int]) containing the target size(height, width)of each image in the batch. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
List[Dict]
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model.
Converts the raw output of YolosForObjectDetection into final bounding boxes in (top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y) format. Only supports PyTorch.
YolosModel
class transformers.YolosModel
< source >( config: YolosConfig add_pooling_layer: bool = True )
Parameters
- config (YolosConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare YOLOS Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >(
pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None
output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None
return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None
)
→
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
-
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See YolosImageProcessor.call() for details. -
head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
-
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. -
output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. -
return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (YolosConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The YolosModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, YolosModel
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-small")
>>> model = YolosModel.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-small")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 3401, 384]YolosForObjectDetection
class transformers.YolosForObjectDetection
< source >( config: YolosConfig )
Parameters
- config (YolosConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
YOLOS Model (consisting of a ViT encoder) with object detection heads on top, for tasks such as COCO detection.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >(
pixel_values: FloatTensor
labels: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Dict]] = None
output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None
output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None
return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None
)
→
transformers.models.yolos.modeling_yolos.YolosObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
-
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See YolosImageProcessor.call() for details. -
head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
-
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. -
output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. -
return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. -
labels (
List[Dict]of len(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the bipartite matching loss. List of dicts, each dictionary containing at least the following 2 keys:'class_labels'and'boxes'(the class labels and bounding boxes of an image in the batch respectively). The class labels themselves should be atorch.LongTensorof len(number of bounding boxes in the image,)and the boxes atorch.FloatTensorof shape(number of bounding boxes in the image, 4).
Returns
transformers.models.yolos.modeling_yolos.YolosObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.yolos.modeling_yolos.YolosObjectDetectionOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (YolosConfig) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsare provided)) — Total loss as a linear combination of a negative log-likehood (cross-entropy) for class prediction and a bounding box loss. The latter is defined as a linear combination of the L1 loss and the generalized scale-invariant IoU loss. - loss_dict (
Dict, optional) — A dictionary containing the individual losses. Useful for logging. - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_classes + 1)) — Classification logits (including no-object) for all queries. - pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, 4)) — Normalized boxes coordinates for all queries, represented as (center_x, center_y, width, height). These values are normalized in [0, 1], relative to the size of each individual image in the batch (disregarding possible padding). You can usepost_process()to retrieve the unnormalized bounding boxes. - auxiliary_outputs (
list[Dict], optional) — Optional, only returned when auxilary losses are activated (i.e.config.auxiliary_lossis set toTrue) and labels are provided. It is a list of dictionaries containing the two above keys (logitsandpred_boxes) for each decoder layer. - last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the decoder of the model. - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The YolosForObjectDetection forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, AutoModelForObjectDetection
>>> import torch
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-tiny")
>>> model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("hustvl/yolos-tiny")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # convert outputs (bounding boxes and class logits) to COCO API
>>> target_sizes = torch.tensor([image.size[::-1]])
>>> results = image_processor.post_process_object_detection(outputs, threshold=0.9, target_sizes=target_sizes)[
... 0
... ]
>>> for score, label, box in zip(results["scores"], results["labels"], results["boxes"]):
... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()]
... print(
... f"Detected {model.config.id2label[label.item()]} with confidence "
... f"{round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}"
... )
Detected remote with confidence 0.994 at location [46.96, 72.61, 181.02, 119.73]
Detected remote with confidence 0.975 at location [340.66, 79.19, 372.59, 192.65]
Detected cat with confidence 0.984 at location [12.27, 54.25, 319.42, 470.99]
Detected remote with confidence 0.922 at location [41.66, 71.96, 178.7, 120.33]
Detected cat with confidence 0.914 at location [342.34, 21.48, 638.64, 372.46]