datasets:
- garage-bAInd/Open-Platypus
- Open-Orca/OpenOrca
inference: false
language:
- en
library_name: transformers
license: cc-by-nc-4.0
model_creator: Open-Orca
model_link: https://huggingface.co/Open-Orca/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B
model_name: OpenOrca Platypus2 13B
model_type: llama
pipeline_tag: text-generation
quantized_by: TheBloke

TheBloke's LLM work is generously supported by a grant from andreessen horowitz (a16z)
OpenOrca Platypus2 13B - GPTQ
- Model creator: Open-Orca
- Original model: OpenOrca Platypus2 13B
Description
This repo contains GPTQ model files for Open-Orca's OpenOrca Platypus2 13B.
Multiple GPTQ parameter permutations are provided; see Provided Files below for details of the options provided, their parameters, and the software used to create them.
Repositories available
- GPTQ models for GPU inference, with multiple quantisation parameter options.
- 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8-bit GGUF models for CPU+GPU inference
- 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8-bit GGML models for CPU+GPU inference (deprecated)
- Open-Orca's original unquantised fp16 model in pytorch format, for GPU inference and for further conversions
Prompt template: Alpaca-InstructOnly
### Instruction:
{prompt}
### Response:
Licensing
The creator of the source model has listed its license as cc-by-nc-4.0, and this quantization has therefore used that same license.
As this model is based on Llama 2, it is also subject to the Meta Llama 2 license terms, and the license files for that are additionally included. It should therefore be considered as being claimed to be licensed under both licenses. I contacted Hugging Face for clarification on dual licensing but they do not yet have an official position. Should this change, or should Meta provide any feedback on this situation, I will update this section accordingly.
In the meantime, any questions regarding licensing, and in particular how these two licenses might interact, should be directed to the original model repository: Open-Orca's OpenOrca Platypus2 13B.
Provided files and GPTQ parameters
Multiple quantisation parameters are provided, to allow you to choose the best one for your hardware and requirements.
Each separate quant is in a different branch. See below for instructions on fetching from different branches.
All recent GPTQ files are made with AutoGPTQ, and all files in non-main branches are made with AutoGPTQ. Files in the main branch which were uploaded before August 2023 were made with GPTQ-for-LLaMa.
Explanation of GPTQ parameters
- Bits: The bit size of the quantised model.
- GS: GPTQ group size. Higher numbers use less VRAM, but have lower quantisation accuracy. "None" is the lowest possible value.
- Act Order: True or False. Also known as
desc_act. True results in better quantisation accuracy. Some GPTQ clients have had issues with models that use Act Order plus Group Size, but this is generally resolved now. - Damp %: A GPTQ parameter that affects how samples are processed for quantisation. 0.01 is default, but 0.1 results in slightly better accuracy.
- GPTQ dataset: The dataset used for quantisation. Using a dataset more appropriate to the model's training can improve quantisation accuracy. Note that the GPTQ dataset is not the same as the dataset used to train the model - please refer to the original model repo for details of the training dataset(s).
- Sequence Length: The length of the dataset sequences used for quantisation. Ideally this is the same as the model sequence length. For some very long sequence models (16+K), a lower sequence length may have to be used. Note that a lower sequence length does not limit the sequence length of the quantised model. It only impacts the quantisation accuracy on longer inference sequences.
- ExLlama Compatibility: Whether this file can be loaded with ExLlama, which currently only supports Llama models in 4-bit.
| Branch | Bits | GS | Act Order | Damp % | GPTQ Dataset | Seq Len | Size | ExLlama | Desc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| main | 4 | 128 | No | 0.1 | wikitext | 4096 | 7.26 GB | Yes | 4-bit, without Act Order and group size 128g. |
| gptq-4bit-32g-actorder_True | 4 | 32 | Yes | 0.1 | wikitext | 4096 | 8.00 GB | Yes | 4-bit, with Act Order and group size 32g. Gives highest possible inference quality, with maximum VRAM usage. |
| gptq-4bit-64g-actorder_True | 4 | 64 | Yes | 0.1 | wikitext | 4096 | 7.51 GB | Yes | 4-bit, with Act Order and group size 64g. Uses less VRAM than 32g, but with slightly lower accuracy. |
| gptq-4bit-128g-actorder_True | 4 | 128 | Yes | 0.1 | wikitext | 4096 | 7.26 GB | Yes | 4-bit, with Act Order and group size 128g. Uses even less VRAM than 64g, but with slightly lower accuracy. |
| gptq-8bit--1g-actorder_True | 8 | None | Yes | 0.1 | wikitext | 4096 | 13.36 GB | No | 8-bit, with Act Order. No group size, to lower VRAM requirements. |
| gptq-8bit-128g-actorder_True | 8 | 128 | Yes | 0.1 | wikitext | 4096 | 13.65 GB | No | 8-bit, with group size 128g for higher inference quality and with Act Order for even higher accuracy. |
How to download from branches
- In text-generation-webui, you can add
:branchto the end of the download name, egTheBloke/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B-GPTQ:main - With Git, you can clone a branch with:
git clone --single-branch --branch main https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B-GPTQ
- In Python Transformers code, the branch is the
revisionparameter; see below.
How to easily download and use this model in text-generation-webui.
Please make sure you're using the latest version of text-generation-webui.
It is strongly recommended to use the text-generation-webui one-click-installers unless you're sure you know how to make a manual install.
- Click the Model tab.
- Under Download custom model or LoRA, enter
TheBloke/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B-GPTQ.
- To download from a specific branch, enter for example
TheBloke/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B-GPTQ:main - see Provided Files above for the list of branches for each option.
- Click Download.
- The model will start downloading. Once it's finished it will say "Done".
- In the top left, click the refresh icon next to Model.
- In the Model dropdown, choose the model you just downloaded:
OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B-GPTQ - The model will automatically load, and is now ready for use!
- If you want any custom settings, set them and then click Save settings for this model followed by Reload the Model in the top right.
- Note that you do not need to and should not set manual GPTQ parameters any more. These are set automatically from the file
quantize_config.json.
- Once you're ready, click the Text Generation tab and enter a prompt to get started!
How to use this GPTQ model from Python code
Install the necessary packages
Requires: Transformers 4.32.0 or later, Optimum 1.12.0 or later, and AutoGPTQ 0.4.2 or later.
pip3 install transformers>=4.32.0 optimum>=1.12.0
pip3 install auto-gptq --extra-index-url https://huggingface.github.io/autogptq-index/whl/cu118/ # Use cu117 if on CUDA 11.7
If you have problems installing AutoGPTQ using the pre-built wheels, install it from source instead:
pip3 uninstall -y auto-gptq
git clone https://github.com/PanQiWei/AutoGPTQ
cd AutoGPTQ
pip3 install .
For CodeLlama models only: you must use Transformers 4.33.0 or later.
If 4.33.0 is not yet released when you read this, you will need to install Transformers from source:
pip3 uninstall -y transformers
pip3 install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
You can then use the following code
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline
model_name_or_path = "TheBloke/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B-GPTQ"
# To use a different branch, change revision
# For example: revision="main"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,
device_map="auto",
trust_remote_code=False,
revision="main")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, use_fast=True)
prompt = "Tell me about AI"
prompt_template=f'''### Instruction:
{prompt}
### Response:
'''
print("\n\n*** Generate:")
input_ids = tokenizer(prompt_template, return_tensors='pt').input_ids.cuda()
output = model.generate(inputs=input_ids, temperature=0.7, do_sample=True, top_p=0.95, top_k=40, max_new_tokens=512)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0]))
# Inference can also be done using transformers' pipeline
print("*** Pipeline:")
pipe = pipeline(
"text-generation",
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.95,
top_k=40,
repetition_penalty=1.1
)
print(pipe(prompt_template)[0]['generated_text'])
Compatibility
The files provided are tested to work with AutoGPTQ, both via Transformers and using AutoGPTQ directly. They should also work with Occ4m's GPTQ-for-LLaMa fork.
ExLlama is compatible with Llama models in 4-bit. Please see the Provided Files table above for per-file compatibility.
Huggingface Text Generation Inference (TGI) is compatible with all GPTQ models.
Discord
For further support, and discussions on these models and AI in general, join us at:
Thanks, and how to contribute
Thanks to the chirper.ai team!
Thanks to Clay from gpus.llm-utils.org!
I've had a lot of people ask if they can contribute. I enjoy providing models and helping people, and would love to be able to spend even more time doing it, as well as expanding into new projects like fine tuning/training.
If you're able and willing to contribute it will be most gratefully received and will help me to keep providing more models, and to start work on new AI projects.
Donaters will get priority support on any and all AI/LLM/model questions and requests, access to a private Discord room, plus other benefits.
- Patreon: https://patreon.com/TheBlokeAI
- Ko-Fi: https://ko-fi.com/TheBlokeAI
Special thanks to: Aemon Algiz.
Patreon special mentions: Russ Johnson, J, alfie_i, Alex, NimbleBox.ai, Chadd, Mandus, Nikolai Manek, Ken Nordquist, ya boyyy, Illia Dulskyi, Viktor Bowallius, vamX, Iucharbius, zynix, Magnesian, Clay Pascal, Pierre Kircher, Enrico Ros, Tony Hughes, Elle, Andrey, knownsqashed, Deep Realms, Jerry Meng, Lone Striker, Derek Yates, Pyrater, Mesiah Bishop, James Bentley, Femi Adebogun, Brandon Frisco, SuperWojo, Alps Aficionado, Michael Dempsey, Vitor Caleffi, Will Dee, Edmond Seymore, usrbinkat, LangChain4j, Kacper Wikieł, Luke Pendergrass, John Detwiler, theTransient, Nathan LeClaire, Tiffany J. Kim, biorpg, Eugene Pentland, Stanislav Ovsiannikov, Fred von Graf, terasurfer, Kalila, Dan Guido, Nitin Borwankar, 阿明, Ai Maven, John Villwock, Gabriel Puliatti, Stephen Murray, Asp the Wyvern, danny, Chris Smitley, ReadyPlayerEmma, S_X, Daniel P. Andersen, Olakabola, Jeffrey Morgan, Imad Khwaja, Caitlyn Gatomon, webtim, Alicia Loh, Trenton Dambrowitz, Swaroop Kallakuri, Erik Bjäreholt, Leonard Tan, Spiking Neurons AB, Luke @flexchar, Ajan Kanaga, Thomas Belote, Deo Leter, RoA, Willem Michiel, transmissions 11, subjectnull, Matthew Berman, Joseph William Delisle, David Ziegler, Michael Davis, Johann-Peter Hartmann, Talal Aujan, senxiiz, Artur Olbinski, Rainer Wilmers, Spencer Kim, Fen Risland, Cap'n Zoog, Rishabh Srivastava, Michael Levine, Geoffrey Montalvo, Sean Connelly, Alexandros Triantafyllidis, Pieter, Gabriel Tamborski, Sam, Subspace Studios, Junyu Yang, Pedro Madruga, Vadim, Cory Kujawski, K, Raven Klaugh, Randy H, Mano Prime, Sebastain Graf, Space Cruiser
Thank you to all my generous patrons and donaters!
And thank you again to a16z for their generous grant.
Original model card: Open-Orca's OpenOrca Platypus2 13B
🐋 The First OrcaPlatypus! 🐋
OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B
OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B is a merge of garage-bAInd/Platypus2-13B and Open-Orca/OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B.
This model is more than the sum of its parts! We are happy to be teaming up with the Platypus team to bring you a new model which once again tops the leaderboards!
Want to visualize our full (pre-filtering) dataset? Check out our Nomic Atlas Map.
We are in-process with training more models, so keep a look out on our org for releases coming soon with exciting partners.
We will also give sneak-peak announcements on our Discord, which you can find here:
Evaluation
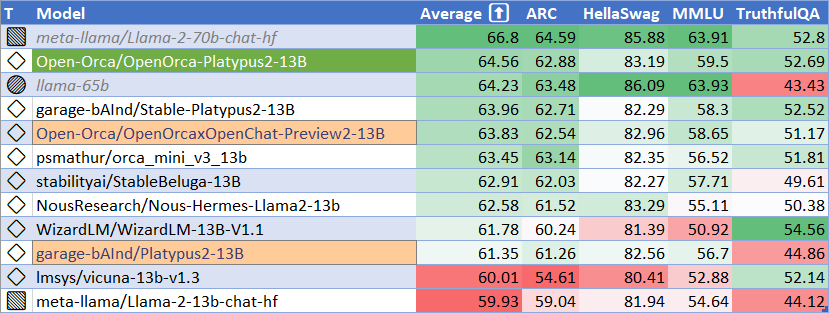
HuggingFace Leaderboard Performance
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| MMLU (5-shot) | 59.5 |
| ARC (25-shot) | 62.88 |
| HellaSwag (10-shot) | 83.19 |
| TruthfulQA (0-shot) | 52.69 |
| Avg. | 64.56 |
We use Language Model Evaluation Harness to run the benchmark tests above, using the same version as the HuggingFace LLM Leaderboard.
Please see below for detailed instructions on reproducing benchmark results.
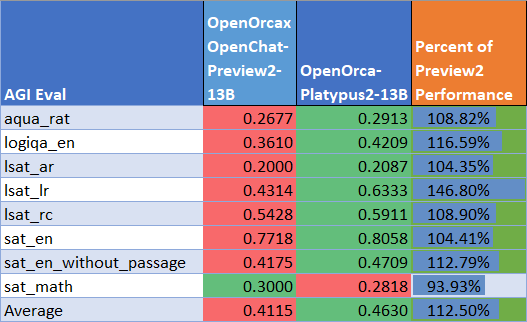
AGIEval Performance
We compare our results to our base Preview2 model (using LM Evaluation Harness).
We find 112% of the base model's performance on AGI Eval, averaging 0.463. A large part of this boost is the substantial improvement to LSAT Logical Reasoning performance.
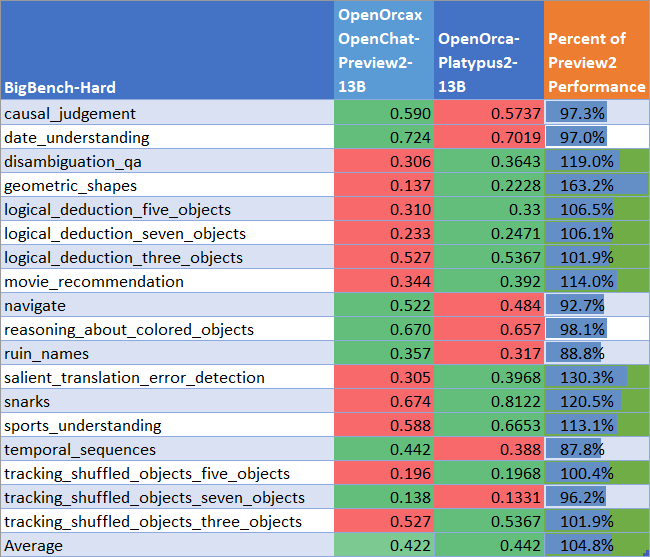
BigBench-Hard Performance
We compare our results to our base Preview2 model (using LM Evaluation Harness).
We find 105% of the base model's performance on BigBench-Hard, averaging 0.442.
Model Details
- Trained by: Platypus2-13B trained by Cole Hunter & Ariel Lee; OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B trained by Open-Orca
- Model type: OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B is an auto-regressive language model based on the Lllama 2 transformer architecture.
- Language(s): English
- License for Platypus2-13B base weights: Non-Commercial Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-4.0)
- License for OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B base weights: Llama 2 Commercial
Prompting
Prompt Template for base Platypus2-13B
### Instruction:
<prompt> (without the <>)
### Response:
Prompt Template for base OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B
OpenChat Llama2 V1: see OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B for additional information.
Training
Training Datasets
garage-bAInd/Platypus2-13B trained using STEM and logic based dataset garage-bAInd/Open-Platypus.
Please see our paper and project webpage for additional information.
Open-Orca/OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B trained using a refined subset of most of the GPT-4 data from the OpenOrca dataset.
Training Procedure
Open-Orca/Platypus2-13B was instruction fine-tuned using LoRA on 1x A100-80GB.
For training details and inference instructions please see the Platypus GitHub repo.
Supplemental
Reproducing Evaluation Results (for HuggingFace Leaderboard Eval)
Install LM Evaluation Harness:
# clone repository
git clone https://github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness.git
# change to repo directory
cd lm-evaluation-harness
# check out the correct commit
git checkout b281b0921b636bc36ad05c0b0b0763bd6dd43463
# install
pip install -e .
Each task was evaluated on a single A100-80GB GPU.
ARC:
python main.py --model hf-causal-experimental --model_args pretrained=Open-Orca/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B --tasks arc_challenge --batch_size 1 --no_cache --write_out --output_path results/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B/arc_challenge_25shot.json --device cuda --num_fewshot 25
HellaSwag:
python main.py --model hf-causal-experimental --model_args pretrained=Open-Orca/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B --tasks hellaswag --batch_size 1 --no_cache --write_out --output_path results/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B/hellaswag_10shot.json --device cuda --num_fewshot 10
MMLU:
python main.py --model hf-causal-experimental --model_args pretrained=Open-Orca/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B --tasks hendrycksTest-* --batch_size 1 --no_cache --write_out --output_path results/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B/mmlu_5shot.json --device cuda --num_fewshot 5
TruthfulQA:
python main.py --model hf-causal-experimental --model_args pretrained=Open-Orca/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B --tasks truthfulqa_mc --batch_size 1 --no_cache --write_out --output_path results/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B/truthfulqa_0shot.json --device cuda
Limitations and bias
Llama 2 and fine-tuned variants are a new technology that carries risks with use. Testing conducted to date has been in English, and has not covered, nor could it cover all scenarios. For these reasons, as with all LLMs, Llama 2 and any fine-tuned varient's potential outputs cannot be predicted in advance, and the model may in some instances produce inaccurate, biased or other objectionable responses to user prompts. Therefore, before deploying any applications of Llama 2 variants, developers should perform safety testing and tuning tailored to their specific applications of the model.
Please see the Responsible Use Guide available at https://ai.meta.com/llama/responsible-use-guide/
Citations
@software{hunterlee2023orcaplaty1
title = {OpenOrcaPlatypus: Llama2-13B Model Instruct-tuned on Filtered OpenOrcaV1 GPT-4 Dataset and Merged with divergent STEM and Logic Dataset Model},
author = {Ariel N. Lee and Cole J. Hunter and Nataniel Ruiz and Bleys Goodson and Wing Lian and Guan Wang and Eugene Pentland and Austin Cook and Chanvichet Vong and "Teknium"},
year = {2023},
publisher = {HuggingFace},
journal = {HuggingFace repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://huggingface.co/Open-Orca/OpenOrca-Platypus2-13B},
}
@article{platypus2023,
title={Platypus: Quick, Cheap, and Powerful Refinement of LLMs},
author={Ariel N. Lee and Cole J. Hunter and Nataniel Ruiz},
booktitle={arXiv preprint arxiv:2308.07317},
year={2023}
}
@software{OpenOrcaxOpenChatPreview2,
title = {OpenOrcaxOpenChatPreview2: Llama2-13B Model Instruct-tuned on Filtered OpenOrcaV1 GPT-4 Dataset},
author = {Guan Wang and Bleys Goodson and Wing Lian and Eugene Pentland and Austin Cook and Chanvichet Vong and "Teknium"},
year = {2023},
publisher = {HuggingFace},
journal = {HuggingFace repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://https://huggingface.co/Open-Orca/OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B},
}
@software{openchat,
title = {{OpenChat: Advancing Open-source Language Models with Imperfect Data}},
author = {Wang, Guan and Cheng, Sijie and Yu, Qiying and Liu, Changling},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.8105775},
url = {https://github.com/imoneoi/openchat},
version = {pre-release},
year = {2023},
month = {7},
}
@misc{mukherjee2023orca,
title={Orca: Progressive Learning from Complex Explanation Traces of GPT-4},
author={Subhabrata Mukherjee and Arindam Mitra and Ganesh Jawahar and Sahaj Agarwal and Hamid Palangi and Ahmed Awadallah},
year={2023},
eprint={2306.02707},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
@misc{touvron2023llama,
title={Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models},
author={Hugo Touvron and Louis Martin and Kevin Stone and Peter Albert and Amjad Almahairi and Yasmine Babaei and Nikolay Bashlykov and Soumya Batra and Prajjwal Bhargava and Shruti Bhosale and Dan Bikel and Lukas Blecher and Cristian Canton Ferrer and Moya Chen and Guillem Cucurull and David Esiobu and Jude Fernandes and Jeremy Fu and Wenyin Fu and Brian Fuller and Cynthia Gao and Vedanuj Goswami and Naman Goyal and Anthony Hartshorn and Saghar Hosseini and Rui Hou and Hakan Inan and Marcin Kardas and Viktor Kerkez and Madian Khabsa and Isabel Kloumann and Artem Korenev and Punit Singh Koura and Marie-Anne Lachaux and Thibaut Lavril and Jenya Lee and Diana Liskovich and Yinghai Lu and Yuning Mao and Xavier Martinet and Todor Mihaylov and Pushkar Mishra and Igor Molybog and Yixin Nie and Andrew Poulton and Jeremy Reizenstein and Rashi Rungta and Kalyan Saladi and Alan Schelten and Ruan Silva and Eric Michael Smith and Ranjan Subramanian and Xiaoqing Ellen Tan and Binh Tang and Ross Taylor and Adina Williams and Jian Xiang Kuan and Puxin Xu and Zheng Yan and Iliyan Zarov and Yuchen Zhang and Angela Fan and Melanie Kambadur and Sharan Narang and Aurelien Rodriguez and Robert Stojnic and Sergey Edunov and Thomas Scialom},
year={2023},
eprint= arXiv 2307.09288
}
@misc{longpre2023flan,
title={The Flan Collection: Designing Data and Methods for Effective Instruction Tuning},
author={Shayne Longpre and Le Hou and Tu Vu and Albert Webson and Hyung Won Chung and Yi Tay and Denny Zhou and Quoc V. Le and Barret Zoph and Jason Wei and Adam Roberts},
year={2023},
eprint={2301.13688},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI}
}
@article{hu2021lora,
title={LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models},
author={Hu, Edward J. and Shen, Yelong and Wallis, Phillip and Allen-Zhu, Zeyuan and Li, Yuanzhi and Wang, Shean and Chen, Weizhu},
journal={CoRR},
year={2021}
}