Datasets:
The full dataset viewer is not available (click to read why). Only showing a preview of the rows.
Error code: JobManagerCrashedError
Need help to make the dataset viewer work? Make sure to review how to configure the dataset viewer, and open a discussion for direct support.
text
string | id
string | dump
string | url
string | date
string | file_path
string | language
string | language_score
float64 | token_count
int64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How AP reported in all formats from tornado-stricken regionsMarch 8, 2012
When the first serious bout of tornadoes of 2012 blew through middle America in the middle of the night, they touched down in places hours from any AP bureau. Our closest video journalist was Chicago-based Robert Ray, who dropped his plans to travel to Georgia for Super Tuesday, booked several flights to the cities closest to the strikes and headed for the airport. He’d decide once there which flight to take.
He never got on board a plane. Instead, he ended up driving toward Harrisburg, Ill., where initial reports suggested a town was destroyed. That decision turned out to be a lucky break for the AP. Twice.
Ray was among the first journalists to arrive and he confirmed those reports -- in all formats. He shot powerful video, put victims on the phone with AP Radio and played back sound to an editor who transcribed the interviews and put the material on text wires. He then walked around the devastation with the Central Regional Desk on the line, talking to victims with the phone held so close that editors could transcribe his interviews in real time.
Ray also made a dramatic image of a young girl who found a man’s prosthetic leg in the rubble, propped it up next to her destroyed home and spray-painted an impromptu sign: “Found leg. Seriously.”
The following day, he was back on the road and headed for Georgia and a Super Tuesday date with Newt Gingrich’s campaign. The drive would take him through a stretch of the South that forecasters expected would suffer another wave of tornadoes.
To prevent running into THAT storm, Ray used his iPhone to monitor Doppler radar, zooming in on extreme cells and using Google maps to direct himself to safe routes. And then the journalist took over again.
“When weather like that occurs, a reporter must seize the opportunity to get the news out and allow people to see, hear and read the power of nature so that they can take proper shelter,” Ray says.
So Ray now started to use his phone to follow the storms. He attached a small GoPro camera to his steering wheel in case a tornado dropped down in front of the car somewhere, and took video of heavy rain and hail with his iPhone. Soon, he spotted a tornado and the chase was on. He followed an unmarked emergency vehicle to Cleveland, Tenn., where he was first on the scene of the storm's aftermath.
Again, the tornadoes had struck in locations that were hours from the nearest AP bureau. Damage and debris, as well as a wickedly violent storm that made travel dangerous, slowed our efforts to get to the news. That wasn’t a problem in Tennessee, where our customers were well served by an all-formats report that included this text story.
“CLEVELAND, Tenn. (AP) _ Fierce wind, hail and rain lashed Tennessee for the second time in three days, and at least 15 people were hospitalized Friday in the Chattanooga area.”
The byline? Robert Ray.
For being adept with technology, chasing after news as it literally dropped from the sky and setting a standard for all-formats reporting that put the AP ahead on the most competitive news story of the day, Ray wins this week’s $300 Best of the States prize.
© 2013 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. Terms and conditions apply. See AP.org for details. | <urn:uuid:d66bc6fe-8477-4adf-b430-f6a558ccc8ff> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://%20jwashington@ap.org/Content/Press-Release/2012/How-AP-reported-in-all-formats-from-tornado-stricken-regions | 2013-05-18T05:48:54Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.972142 | 717 |
Did you know you have two little yellow, nine-volt-battery-sized adrenal glands in your body, just chilling out, maxin’, relaxin’ all cool on top of your kidneys? Someone told me this and I checked it out. Turns out it’s true.
It seems as though your adrenal glands are kind of like those British Royal Guards with the big, black fuzzy hats who stand like statues in front of Buckingham Palace. They just stand there quietly, not doing much really, just enjoying the brown, slippery beach that is your kidneys.
However, if anything startling should happen that requires your attention — like say you’re about to give a speech at a wedding or your hear a twig crack outside your tent or your doorbell rings in the middle of the night — then they leap into action, jumping out of their peaceful slumber to squeeze out a big dose of adrenaline right into your body, pumping you up, and turning you into a primal, warrior-like version of yourself.
When tension runs high and adrenaline is secreted into your body some crazy things can happen — sometimes called the fight-or-flight response:
- Your heart rate increases. And specifically, your body starts sending blood to all your big muscles and diverts it away from “non-critical” parts of your body, like your brain, immune system, and digestive system. I guess someone figured you could digest the sandwich after you killed the bear.
- Your pupils dilate and you get tunnel vision. Quite literally, adrenaline also reduces your peripheral vision, which together with your big, wide pupils helps you focus on what lies ahead. You can’t quite see through walls, but if a crow is diving at your eyes you might be able to swat it away better.
- Your body gets ready to boot it. In addition to the rising heart rate, your body starts turning lots more stuff into sugar, raising your blood sugar level and filling you with energy. You might not even feel pain as easily, so the raspberry bushes that shred your legs when you’re running out of the forest won’t slow you down.
But what’s also great about adrenalin is that, first of all, you don’t have to control it. It just sort of kicks it into high gear when it figures you could use a boost. I think it’s kind of cool knowing that your body will help you out when you need it most. Punch me in the face and suddenly my internal British Royal Guard tosses away his fuzzy, black cap, cracks his neck, and rolls up his sleeves.
And really, isn’t it that little dose of adrenalin that helps you do a better job when you need it most? It’s a natural upper, helping you nail the big speech, ace the final exam, or perhaps flee both of those scenes.
There’s a reason some people become adrenaline junkies. The boost you get from your adrenal glands waking up and getting out of bed is intoxicating. Sure, it fuzzes up your thinking a bit and sends your intestines on sabbatical, but it sure does pump you up. And remember: when something important in your life is about to happen, you can count on your good pal adrenaline to be there, juicing you up, helping you fight the good fight.
Jian Ghomeshi is the host of my favorite radio show. It’s called Q and broadcasts across North America every morning. Jian is a big friend and fan of 1000 Awesome Things and The Book of Awesome and I’m really excited because he just released his first book. It’s called 1982 and is a beautifully written memoir about growing up in the suburbs of Toronto and trying to fit in. (My kind of book!) For those of you who love reading, I think he’s a fantastic writer and am really excited to recommend this book. | <urn:uuid:803e14c3-dc2e-43d6-b75d-6fb3981c4fe6> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1000awesomethings.com/2012/09/24/934-adrenaline/ | 2013-05-18T08:11:45Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.947991 | 821 |
Car Wash For Clara!
Now is your chance to help! 2 year old Clara Woodward has Cancer! Clara can’t say “Neuroblastoma” but she knows how it feels. You can help!!
A Car Wash will be held Saturday July 23, 11am-2pm at Java Jet on the corner of Edison & Canal Drive in Kennewick.
There is also an account set up in Clara’s name. Her family lives in Pasco and is travelling to Spokane for treatment.
For further information contact” Kelly Gammon at 509-380-2321 | <urn:uuid:ac1bbfff-9519-4967-9c64-3dc3a4b471ec> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1027kord.com/car-wash-for-clara/ | 2013-05-18T06:49:55Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.911518 | 125 |
Listeners Get Sky-high View of Missoula From Hot Air Balloons
On Friday, June 1, during the Graduation Matters carnival, Townsquare Media – Missoula offered hot air balloon rides to members of the community at the Missoula County Fairgrounds.
Thank you to all of our sponsors, including Southgate Mall and Town Pump.
Here are some of the photos we took at the event:
Check out a few more below from the gallery we posted during the event: | <urn:uuid:c1445c58-b111-4c4e-badd-1e43ec317df7> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1075zoofm.com/listeners-get-sky-high-view-of-missoula-from-hot-air-balloons/ | 2013-05-18T06:25:20Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.956516 | 103 |
Log In Please enter your ECode to log in.
Forgotten your eCode? If you created your login but do not remember your eCode please enter your e-mail address in the box below and click on E-mail My Login Info. This will e-mail your login info to you
Copyright 2007, a2z, Inc. All rights reserved. | <urn:uuid:e5829f7d-b944-4468-9573-61b7cb3078cc> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1105govinfoevents.com/enterprisearchitectureevent/public/MyBriefcasef671.html?ID=563&sortMenu=103001&exp=1%2F26%2F2009+3%3A27%3A46+PM | 2013-05-18T05:27:01Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.798235 | 75 |
spotlight provides a convenient rechargeable LED light for work play and everyday life. choose from many vibrant colors to match your car, home, or personal style.
- high power 0.5 watt LED bulb (35+ lumens)
- colorful anodized aluminum body
- 180+ minutes of light per charge
- water resistant / submersible
- red glow ‘charging’ indicator
- rechargeable Ni - MH battery
- shines 50 meter / 150 feet | <urn:uuid:6bfca20f-ea67-41ba-b995-b7081b4a8b15> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://12vspotlight.com/ | 2013-05-18T06:49:17Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.754259 | 102 |
K-State put themselves in sole position of first place in the Big 12 with their 79-70 over Iowa State on Saturday, and K-State is now #10 in the AP poll heading into Monday night’s Sunflower Showdown. With losses last week at TCU and Oklahoma, KU drops nine spots to #14. Oklahoma State has won five straight including at Texas on Saturday, and is now #17, up five spots from last week’s poll.
K-State and KU tip off on Monday night at 8:00pm at Allen Fieldhouse. Coverage on SportsRadio 1350 KMAN and 101.5 K-Rock begins at 7:00 from the K-State Sports Network with Wyatt Thompson and Stan Weber.
Stay connected to all things KSU on the go just text EMAW to 88474
For full video wrap-ups, including analysis, highlights, coaches & player interviews of K-State Football & Basketball check out PowerCatGameday.com | <urn:uuid:dc9d9fd8-5a21-4ab0-bbb2-9718720e1cc2> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1350kman.com/k-state-now-in-top-10/ | 2013-05-18T07:19:46Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.945918 | 204 |
Five Reasons I Love Boston
1. The water.
The Atlantic Ocean, as deep and true as denim, so blue it melts into the sky, horizonless. And the Charles River. Years from now, I’ll remember riding the Red Line from Boston into Cambridge at night – the way the lights streak across the black water like crayons lined up in a box.
After my childhood in Seattle to my college years in Boston, I don’t think I could live anywhere but a coast.
2. The seasons.
I always come back to school right at the tail end of summer. Heat sinks into the subway stations like poisonous gas, and whatever you wear, it’s too much fabric. With October right around the corner, though, fall settles in. I love the way golden light fans out from behind buildings and through alleyways. Yellow leaves get stuck in the rain currents along the sidewalk. It’s my favorite time of year.
Boston has also taught me the true meaning of winter. Winter is wet hair freezing solid on the way to class, two pairs of socks, ears tucked into scarves. Torrential flurries of snowflakes that burn skin. Frankly, winter is miserable.
But then there’s that one morning – and it’s always a morning, and you’re never quite prepared for it – when you step outside and every tree in Boston has bloomed. Cherry blossoms opened like pale pink popcorn, blue skies, tender green leaves. It’s such a miracle that this can happen despite the sheets of ice and crazy wind tunnels, it makes everything worthwhile.
3. The quirkiness.
I love the farmer’s markets all over the city, the narrow brick alleys begging to be explored, the late night restaurants in Chinatown. Boston constantly surprises me. Today I discovered the food trucks – why didn’t I know that Boston has food trucks??
4. The history.
A handful of the founding fathers are buried mere blocks from campus. I walk through the oldest park in America to get to my boyfriend D-’s apartment in Beacon Hill, a neighborhood of gas lamps and weathered brick. Everywhere you look, historic churches stand between skyscrapers. The contrast is astonishing.
5. These amazing people.
Sure, most of them aren’t from Boston. A-’s from Colorado, C-’s from LA, and S- is all the way from Guam. But nine months of the year, they’re all mine. They make Boston feel like home.
Why do you love _______? | <urn:uuid:64f968bf-14bc-48bd-a1bb-a43b3f4a3c3d> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://17andbaking.com/2012/09/30/five-reasons-i-love-boston/?like=1&source=post_flair&_wpnonce=fd9f0e7c6a | 2013-05-18T07:25:34Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.92668 | 550 |
TRIBE CHIEF TRIS DAZZLES AT DISH, FLUBS IN FIELD IN SIXTH STRAIGHT TIGER WIN
By Calvin J. Butterworth
June 19, 1924
Ty Cobb can tell you. Personally causing your team's loss when you are managing said team can be a devastating turn of events. Players who look to you for leadership and support are left in a rudderless abyss and often need to find dry morning land on their own.
Such was the case at Navin Field today, as the suddenly resurgent Indians re-visited our neighborhood, fresh from taking three of four from the Yankees and before that, four straight from Boston. It was their misfortune, though, to run into the Earl of Whitehill, who has been spinning masterpieces of hurling lately. Skipper Speaker doubled off him with two outs in the 1st, but Riggs Stephenson, back from an ailment, left him there with a short fly. Joe Sewell and Speaker singled with two outs again two innings later, but this time Riggs grounded out.
Meanwhile Harry Heilman, hero of yesterday, was stranding runners aplenty for our side, failing after three straight Fred Haney hits off Joe Shaute. The game remained scoreless through the first six frames, a remarkable achievement when one considers the power of these clubs' collective clout.
With one out in the Tiger 7th, though, Frank O'Rourke reached on his third single. Whitehill then lofted a fly straight out to Speaker. The sun had been playing peek-and-seek all afternoon behind thin clouds, and as the ball reached its pinnacle it was evident Tris was having trouble locating it. Sure enough, he threw up his mitt at the last moment and was as stunned as the thousands of witnesses were to have it nick off the top and bound insanely toward the deep fence. By the time he tracked down the sphere, O'Rourke had scampered home and Whitehill was standing on third base. Shaute was visibly unnerved, threw a muffin-ball to Rigney, and Topper rammed it into the corner for a double and 2-0 lead!
Egg still dripping down his face, Speaker singled with one out in the 8th, Stephenson followed with one of his own, but the Earl induced a twin killing off the bat of George Burns to end the threat. Another minor disturbance went by the wayside in the 9th, Whitehill had his tidy 10-hit shutout, and Detroit had won six games in a row.
Cobb was thrilled later about the result. "Home runs? Who needs 'em? We got more line hits in our bureau than a buccaneer's got dubloons in the sand." Someone mentioned the error by Speaker was a lucky break and Cobb froze the reporter with a baleful stare before ducking into the nearest shower stall.
CLE 000 000 000 - 0 10 1
DET 000 000 20x - 2 8 0
Only other American League game today:
at BROWNS 10-14-0, WHITE SOX 8-10-2
One of the more thrilling spectacles of this or any year, and no one expected it. The Chicagos have had their way with St. Louis all season, and with Sloppy Thurston staked to a 6-2 after three on the horrific Ray Kolp, Brownie fans were already making their dinner plans. It was actually 8-2 in the last of the 6th when four Browns singles and a key flub from Bill Barrett gave St. Louis four runs and put them back in the contest. A Pat Collins single in the 8th pulled them to 8-7, as great relief twirling from George Grant and Hub Pruett kept matters close. But after Tobin and pinch-hitter Severeid both singled to begin the last of the 9th, up stepped famous batsman George Sisler. He picked out a Thurston curve, swung mightily and cracked it on a magnificent arc out to right. Hooper gave chase but ran out of room as the ball dropped into the Sportsman Park pavilion amidst a gaggle of celebrating fans.
Washington will be in Shibe Park tomorrow, now with a 2-game advantage, while the Red Sox will take their losing streak into Yankee Stadium.
|AMERICAN LEAGUE through Thursday, June 19|
|Chicago White Sox||38||25||.603||2|
|New York Yankees||31||31||.500||8.5|
|St. Louis Browns||27||36||.429||13|
|Boston Red Sox||24||37||.393||15| | <urn:uuid:2c08e1d4-9706-41d8-84dc-ee2939758c81> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1924andyouarethere.blogspot.com/2009_07_01_archive.html | 2013-05-18T05:54:12Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.964752 | 979 |
|Tommy Pi - Trance Experience|
|Written by Paul|
Tommy Pi started DJing at small private parties at the age of 13. He was always into music, so it was no surprise when he went on and bought his first equipment, some Omnictronic Turntables and a small Gemini mixer. From that day on he always used any chance he got to play at parties, and it wasn't long before his day would come, for him play on a big stage in front of more than 50 people! There was a big party in his home town of Minden (North Germany) with DJ's like Monika Kruse, Alex Lück and others and Tommy thought that it would be great to play there. So he went straight to the promotor and said 'Hey man, I'm from here, I'm a DJ, too so can I play?'Not thinking that this would ever be possible, the promotor said, 'Ok, just come here tomorrow, and you can play for an hour'. That was the birth of DJ Tommy Pi.
From then on, Tommy played in clubs like PW1 in Porta Westfalica, or Go!Parc in Herford. He also played the Go!Parc on Tour Events alongside Alex Lück and others. The biggest day was yet to come! On 21st of October 2000 Tommy and his mate Dee-B had the chance to play alongside Piet Blank at the Einslive Party in Minden, invited by Piet himself. It was a big party and Tommy was very nervous and shaking as he put the needle on the vinyl for the first record 'DJ Culture'. He played on that evening and the crowd were fantastic and it was a lot of fun for both, Tommy and Dennis.
The crowning Glory for Tommy was in 2002 when he was voted as 'Best DJ' by the local magazine 'Stadtgeflüster'. Tommy was the second DJ to win this trophy, after Timo Maas won it the year before.
In 2003 Tommy started his weekly Radio Show 'Trance Experience' on PureDJ. The show is streamed every Monday from 8-10 pm CET. Now, 1Mix is rebroadcasting the show from October 2008 Tuesdays from 4-6pm.
In February 2005 Tommy's second Radio Show 'Trance Experience ETN Edition' was started on ETN.fm as a monthly one-hour radio show.
All of Tommy's mixes and Radio Shows are now available as a Podcast on iTunes,podcast.de or mypodcast.com. | <urn:uuid:7e6216ca-0a01-498d-85f7-7d4aed299c98> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1mix.co.uk/trance-shows/tommy-pi-trance-experience.html | 2013-05-18T05:54:17Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.985657 | 527 |
When I found out we would be getting a PopATot for review I was excited! I knew before we even had it that we would like it, but I had no idea how much we would LOVE it! I am so excited to share this amazing product with you all!
PopATot was created by parents, Evan and Stacy, who have 5 children! I personally think this idea is wonderful. When I was trying to describe to my husband what was coming in the mail for Ladybug, I described it as a cross between a card table, an exersaucer, and a fabric folding chair. He sort of got it, but when he finally saw it he totally understood my references!!!
I will let our many photos of Ladybug speak mostly for themselves (she is 5 1/2-6 months in all of these photos). We use this thing every day now, and in many different places throughout each day-it is that easy to move around.
My absolute favorite use for the PopATot is in our schoolroom. We have a fairly small schoolroom and I only need to have Ladybug in there sometimes, so I don't want a big baby item in there. PopATot is perfect because I can set it up and take it down quickly!
My bedroom is another of those places! She hangs out in my room often like this now!!
We have a 2nd story deck off of our bedroom, and the PopATot is perfect for the deck!!! We can't fit anything else out the small door, let alone leave something big out there in the weather. This is wonderful!
I set Ladybug up in the middle and the boys ride all around her on their riding toys!
She's all smiles and cuteness!!!
Pac Man likes the PopATot too ;)
I am so excited that one of YOU is going to win this awesome baby item, just in time for the holiday season. Won't this be wonderful to have for Thanksgiving or Christmas, when you are away from home? I am looking forward to bringing ours with us to visit family for Christmas this year! It folds up so small and fits in it's own sling bag so it is very portable!
Visit PopATot and leave a comment here telling why you'd love to own a PopATot.
After you do that, you can gain some extra entries by any of the following, remember to leave an extra comment for each item so they will count as entries...
- If you have a baby who you'd love to have this for, tell how old your baby is in a comment for an extra entry.
- If you will take a photo of your baby in his/her new PopATot and write a post on your blog about your win and PopATot, give yourself an extra entry (also an honor thing).
- Watch this video featuring the creator telling all about it...be sure to watch the entire segment to gain this extra entry!
- Go here and tell about one of the photos you think is a great idea for a use of the PopATot, for an extra entry!
- Become a Fan of PopATot on Facebook, for an extra entry!
- If you Follow/Subscribe to Lil' Ladybug give yourself an extra entry (go here and look on the right sidebar for subscriber info).
*International can pay actual shipping
I will select a winner using Random.org, so be sure you leave a separate comment for each entry, I will also be moderating comments to check that your entries are valid-please be honest! You MUST leave an email in your comment or have it enabled via your profile, or you CANNOT win.
Contest ENDS November 1, 2009. Winner will be announced here, and emailed (your email MUST be in each comment/or enabled in blogger). Winner must reply to my email within 48 hours or another winner will be chosen.
See general 1000 Subscribers Celebration Guidelines Here! This is our final giveaway for the celebration!! | <urn:uuid:0868921d-8323-4a3d-b012-51c15c046cc1> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://1plus1plus1equals1reviews.blogspot.com/2009/10/grand-finale-4-popatot.html?showComment=1256068362402 | 2013-05-18T06:19:38Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.953971 | 826 |
2012 Indy Info
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
giving it all away...
where the illusions of scarcity meet the reality of abundance
Don't believe a word "THEY" tell you !
All Themes around Ascension 2012, Sirius and the Galactic Federation of Light
Geologic and Earthchanges News events
Helping others, particularily baby boomers, access and implement new creative skills.
Insights for the journey home
"We Are The Ones We Have Been Waiting For"
Guidance from an elder brother | <urn:uuid:b7319126-5fdb-4ae0-a17b-584c071b561c> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://2012indyinfo.com/category/sfhs/ | 2013-05-18T08:07:40Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.837776 | 123 |
Iran’s Wild Card for Defense Stocks In 2012 … Dividends Hang in the Balance (ATK, GD, LLL, LMT, RTN)December 28, 2011 by Jon C. Ogg
It is no secret that Iran is a saber-rattling nation. The country wants to be relevant on the global stage so much that it keeps up with its nuclear ambitions regardless of global trading sanctions and regardless of efforts from the Western nations trying to stop it. And now the big news is not the nuclear front, but an Iranian minister claiming that Iran could effectively block the flow of traffic through the Gulf of Hormuz easier than drinking a glass of water.
In the age of austerity and military budgets being slashed to deal with deficits, Iran has a chance of turning 2012 accidentally into the year of defense stocks. Alliant Techsystems Inc. (NYSE: ATK), General Dynamics Corp. (NYSE: GD), L-3 Communications Holdings Inc. (NYSE: LLL), Lockheed Martin Corporation (NYSE: LMT) and Raytheon Co. (NYSE: RTN) could all hang in the balance. With operations all but gone in Iraq and with the trend in Afghanistan being one of leaving, Iran is the obvious wild card.
If anything real ever comes out of Iran’s religious political leadership other than how neat it is to stone people over adultery, how it denies that alternative lifestyles exist in Iran, or about how it wants nuclear power for peace, this may end up making the sell-off seen in defense stocks a bargain of the century. If (or when) Iran ever announces that it has built a nuclear bomb, it likely is going to be difficult for Western nations to slash and burn too far on the defense spending. Before running out and loading up on warfare stocks, please remember … this is all “If, Then.”
Alliant Techsystems Inc. (NYSE: ATK) trades at $56.15 and the 52-week trading range is $51.26 to $78.17. Thomson Reuters has a consensus price target of $71.70, implying upside of roughly 28%. Alliant Tech currently has a lower dividend yield against peers with only a payout rate of about 1.4% and shares are up about 4% since the Thanksgiving break. Alliant is highly dependent on the business of selling bullets and it no longer has the booster-rocket business from Space Shuttle launches.
General Dynamics Corp. (NYSE: GD) trades at $66.15 and the 52-week trading range is $53.95 to $78.27. Thomson Reuters has a consensus price target of $76.16, implying upside of about 15%. General Dynamics currently yields about 2.9%.
L-3 Communications Holdings Inc. (NYSE: LLL) trades at $66.85 and the 52-week trading range is $58.30 to $88.55. Thomson Reuters has a consensus price target of $71.64, implying upside of only about 7%. L-3 yields about 2.7% in its dividend and shares are up about 5% from the Thanksgiving break.
Lockheed Martin Corp. (NYSE: LMT) trades at $81.25 and the 52-week trading range is $66.36 to $82.43. Thomson Reuters has a consensus price target of $80.12, implying that the stock is above a full-value price. Its dividend yield is quite high at about 5% and shares are up almost 5% since its $1.00 dividend was reflected in the stock in late November.
Raytheon Co. (NYSE: RTN) trades at $48.50 and the 52-week trading range is $38.35 to $53.12. Thomson Reuters has a consensus price target of $49.53, implying upside of only about 2%. Its dividend yield is currently about 3.7% and shares are up about 14% since the Thanksgiving break.
Unless something new comes out of North Korea, or unless there is more unrest in the Middle East, Iran is the big worry for the country today. With such high payouts from some defense contractors, it is worth wondering just how high some of the payouts can rise during the proliferation of austerity.
JON C. OGG | <urn:uuid:9185d0b6-7b1f-4e81-a97b-43a69978ba4f> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://247wallst.com/2011/12/28/irans-wild-card-for-defense-stocks-in-2012-dividends-hang-in-the-balance-atk-gd-lll-lmt-rtn/print/ | 2013-05-18T07:25:54Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.946137 | 885 |
personalized baby Gifts | site map | personalized name trains | new affiliates | privacy |personalized children's music | personalized children's books |personalized children's clocks | personalized lovies | personalized baby's first christmas gifts| personalized first birthday gifts | Children's Valentine's Day Gifts | Children's Easter Gifts | Kids Easter Gifts | Easter Baskets | Easter Bunny | Baby Bibs | Comfy Cozy Baby Gund | Get Well Gifts for Kids|Sesame Street Characters |Elmo Dolls |Sesame Street Dolls |Sesame Street Gifts |Sesame Street Elmo |Sesame Street Big Bird|Sesame Street Cookie Monster|Personalized Kids Music |Easter Baskets for Infants |Easter Baskets for Kids |Kids Christmas Gifts |Childrens Christmas Gifts |Unique Baby Blankets |Personalized Children's Books |Baby Christmas Baskets |Christmas Baby Gifts |Boston Red Sox Baby Gifts2Blockheads.com Personalized Children's Gifts
"Where Kids are Stars"
1786 St. Peters Road
Pottstown, PA 19465
Phone: 484 824-8500
Hours of Operation: Monday - Friday 8AM-5PM EST
Not an affiliated company of Gund, Inc. or Sesame Workshop. The representations made on this website are those of 2Blockheads Baby Store. Gund Images © Gund, Inc. Gund®, babyGund® and Gotta Getta Gund® are trademarks of Gund, Inc. Sesame Workshop, Sesame Street are owned and licensed by Sesame Workshop. Copyright Sesame Workshop. All Rights Reserved. | <urn:uuid:22c08026-31e6-4edc-9fad-ffcd216a7e09> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://2blockheads.com/inc/comments/post/IAEHTOCAJJYZTRLBZABAA | 2013-05-18T06:56:04Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.793657 | 326 |
San Francisco 49ers cornerback Shawntae Spencer will miss the rest of the season with a torn ligament in his left knee.
Spencer, a fifth-year pro, will be placed on injured reserve soon after undergoing surgery Wednesday to repair the ligament. He injured his knee late in the 49ers’ road victory at Seattle on Sept. 14, and missed last week’s victory over Detroit.
Tarell Brown and Donald Strickland will compete to replace Spencer with the 49ers, who kept 12 defensive backs on their 53-man roster to start the season. Brown, a second-year pro, got his first career interception last weekend while filling in for Strickland, who also sat out with a knee injury. | <urn:uuid:100d293c-7eea-4a56-93ef-88c64b25a9a2> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://49ersnews.com/2008/09/spencer-done/ | 2013-05-18T06:20:38Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.961929 | 153 |
In Suzanne Collins’s wildly popular Hunger Games books, children are chosen by lottery to serve as gladiators who fight to the death. The Games are televised for the entertainment of the general population. Collins models her games on ancient Rome, where gladiators fought to the death and slaves were fed to the lions. She even names her dystopian world Panem, after the Latin word for bread, as in bread and circuses, panem et circenses. Bread and circuses refers to the cheap trick of persuading the masses to cheer for a lion or a slave, for one gladiator or another, rather than participating in or observing or acting to change the political arena. Keep the general population fed with the most basic of food and keep their minds off of rebellion with the distractions of entertainment.
As I read through Lenore Skenazy’s blog and watched her appearances on various chat shows, I kept thinking, “Bread and circuses.” There is so much air time to fill, so television producers and headline writers make news of the Mommy Wars. Free Range Parenting vs. Helicopter Parenting. Stay-at-home Mothers vs. Working Mothers. Breast vs. Bottle. Sleep Training vs. Attachment Parenting. Blah, blah, blah. In one blogger’s take on the issue, she asks, “Free range parenting versus helicopter parenting: which team are YOU on?” Really? We have to pick teams? These issues are so much more complex than x vs. y, but so much easier to digest if packaged in a familiar us vs. them format.
In one clip, Skenazy and another parent appear on Anderson Cooper to replay how Skenazy was able to help this woman who is so much of the helicopter persuasion that in public washrooms she feels it necessary to go right into the bathroom stall with her daughter. “Doesn’t everybody?” this mother quips, when the audience gasps. They feed this woman to the lions, then they rescue her, undo her public shame with a public reformation of her extreme and errant ways.
Unless it’s extreme, it’s not entertainment, so we have thown up on the screen all kind of wild and wacky folk on reality shows who hoard or dumpster dive for coupons for hundreds of free sticks of deodorant, saving up against Armageddon.
What good does any of this do? Silly distractions from the reality lived in the murky middle ground.
I respect Skenazy and her husband’s decision to let their son ride the subway alone. I respect her desire to move away from a culture where kids are kept bubble wrapped. I respect her initiative to create a television show that capitalizes on the buzz that her son’s subway ride generated. But I resent the circus atmosphere of telling the stories of bubble wrapped or free range kids.
Why do mothers keep feeding each other to the lion of artificially polarized public opinion? | <urn:uuid:1ac6d51e-62f3-46ac-b505-0adc65876218> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://4mothers1blog.com/2012/04/24/a-big-silly-distraction/ | 2013-05-18T06:19:05Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.937658 | 620 |
I tend to specialise in shallow depth of field commercial and editorial images, recently I have been involved in portraiture and fashion as the technical challenges have been interesting to me.
Most of my work is conducted on site and is taken "free style". I prefer to work this way, I "find" the image at the time of the event. I am passionate about the "feel" of an image, I love to produce images that evoke an emotion or question from the viewer. If you have something special and creative you wish to produced or take part in then please make contact.
Above all the wordy bits.... I just love taking pictures ... Send me an email if your interested in working with me. | <urn:uuid:b2e8b652-5aba-48fc-bf8a-4f92e6aff885> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://500px.com/SimonPeckham/following?page=42 | 2013-05-18T06:23:26Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.953902 | 145 |
there's always been a fascination of black and white photography. his first ever, a Fujifilm S1000fd. a bridge camera with full manual controls. there were plenty of land/sea scapes, still life, animals, cars, street and a bit of food and architecture.
things changed after his first and only photography workshop by world renowned master photographer Manuel Librodo. portraiture was never this interesting.
he got his hands on a Canon 350D kit and a 50mm f/1.8. it was a good training camera. mark now has the camera that works best for
him, a Nikon D90.
...with hopes of becoming a semi-professional photographer one day.
photography, i love. | <urn:uuid:a53df88a-2c5e-41b4-a920-14fc3bcef9fb> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://500px.com/mdeguzman?page=3 | 2013-05-18T07:17:10Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.974644 | 153 |
It's be kind of a rough week photographically. My TS-E 24mm f/3.5L ii broke on the outing where I made this image (the shift locking knob fell right off) and someone stole my crampons when I left the outside this cave.
The very next day, I went on a great hike across the Mt Juneau ridge carrying a camera body, three lenses, and a tripod. What I wasn't carrying was a memory card of any type (iphone photos only on that trip...despite the sore shoulders). Still, I laughed out loud when I saw the LCD on my camera read "No CF Card". | <urn:uuid:2ebe4832-5f0b-4303-9419-503100c09029> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://500px.com/photo/12134207?from=popular | 2013-05-18T05:50:44Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.957076 | 133 |
This temporary Starter account, Explorer, was automatically created for you.
A Starter account can do almost everything a normal account can do such as Liking and Favoriting photos, but it will expire after a while.
To rename this account and keep it for yourself just enter your email address in the header dropdown above.
It's that easy.
Feel free to checkout my photos, it would be really nice to read your feedback
Instantly log in to vote, fave, comment, or upload.
old stories by Mister Mark
Copy the code to your website | <urn:uuid:52f65f41-fd41-4912-805b-aee725c85379> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://500px.com/photo/28398153 | 2013-05-18T05:08:44Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.944431 | 117 |
(Fort Worth, TX) On Sunday, March 4th, The 5Choir from Saint Andrew Catholic Church in Fort Worth appeared at the 2012 Spirit Games at Nolan Catholic High School. The Stephen Breen Memorial Foundation brought together Fort Worth's Catholic kids of all ages for the fifth annual SPIRIT GAMES, a day of competition and fun. The Stephen Breen Memorial Foundation is committed to offering financial aid to local children who seek the strength and values of a Catholic education and to those courageous children and their families whose lives are afflicted with cancer.
The 5Choir played and sang for the Mass with Bishop Kevin Vann, and played a short set of songs after Mass. The band covered songs featured on local Christian station KLTY, such as "Your Grace is Enough" and "The Revelation Song" as well as Catholic favorites like "Here I Am, Lord". For the Ordinary of the Mass, they played selections from the new Mass of St. Frances Cabrini by Kevin Keil, director of Liturgy and Music at Holy Cross Catholic Church in The Colony.
The members of the 5Choir are: Jed Chatterton, Mike Hyry & John Costlow, guitars; Gerard Bowsher, drums; Brian Benison, bass, keyboards and director; Athena Meyer, flute, keyboard & vocals and David Lyles, Victor Meyer, Honey Rae, Aimee Pietzsch, Peggy Spears, Mark Trance & Kimberly Ward, vocals. Sound at the Spirit Games by Opie Odom.
Asked about the 2012 Spirit Games, 5Choir director Brian said, "I was thrilled when Jim Breen, President of The [Stephen Breen Memorial] Foundation called and asked if the 5Choir could play at the Spirit Games. Jim heard us play at the 5PM Mass at Saint Andrew and thought we were a good fit. I have been working with the 5Choir for 2 years, and everyone in the group is fantastic and full of enthusiasm for this musical outreach. Can't wait to do it again!"
All photographs by Bob Lee.
High resolution photo files available on request. | <urn:uuid:42538bef-63d4-4ffb-a170-123b48640da9> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://5choir.com/spiritgames/ | 2013-05-18T06:01:27Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.959478 | 430 |
Residents Oppose Rezoning to Make Way for Walmart
It’s no secret the Bentonville-based retail behemoth would love to put a Walmart store of some sort in Bella Vista, as it continues to scour the country for more real estate amid a very saturated landscape.
But several Bella Vista residents in the chosen neighborhood oppose the rezoning of 6.4 acres of residential and surrounding woodlands which would become eligible for commercial use by Walmart.
Walmart has a pending contract to purchase the corner lot at Oldham Drive and U.S. 71 which is already zoned commercial, but the deal is contingent on the Bella Vista City Council approving a motion to re-zone 6.4 acres of woodland behind the narrow frontage lots. Click here to read the full story from our partners at TheCityWire.com. | <urn:uuid:fe99f8da-2da5-412e-8077-09b672b7a4f1> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://5newsonline.com/2012/05/23/residents-oppose-rezoning-to-make-way-for-walmart/ | 2013-05-18T05:13:38Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.94856 | 171 |
Times Tables = Fun
Stripes - Cosmetic Bag
3 in 1 Plastic Fruit Vegetable Skin Rotary Blade Rotating Peeler
Women's Weekly Smart Food Cookbook
Veggie Magic Twister
Be the first to receive our daily deals.
Register to 6Shooter and be in the draw to win 1 of 5 $100.00 6Shooter credits. Spend at least $50.00 on 6Shooter from 3rd September - 30th November and be in the draw to WIN $500.00 credit. Uhh yes please! Please click on T&C at the bottom of the site. | <urn:uuid:63196bdb-c05d-44c5-8815-a1fb4dd3ea37> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://6shooter.co.nz/ | 2013-05-18T08:08:26Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.896743 | 126 |
Now This Is a Unique Motorcycle Trick [VIDEO]
Here we have a man about to take his brand new motorcycle for a spin. Or so you think. Actually, the fellow does take the bike for a pretty intense ride, but just not in the way you’d expect.
Check it out below:
[via The Daily What] | <urn:uuid:7a4a8c4c-ab2b-4c94-87f0-b9c22728607e> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://929jackfm.com/now-this-is-a-unique-motorcycle-trick-video/ | 2013-05-18T05:30:11Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.928798 | 72 |
Banks To Start Adding Debit Card Fees; Bank of America and More
Starting soon, maybe as soon as tomorrow, if you’re like me and use your debit card to buy everything from gum to groceries to video games, you may have to pay a monthly fee for the convenience of not carrying cash everywhere.
Albeit not much, five dollars, that’s five more dollars that we never used to have to spend just to put our money in a bank. I first heard about Bank of America doing this yesterday, but now I’m learning that other banks like Chase and Wells Fargo may be doing it as well. Not that I’m surprised. A lot of national chain banks are starting to have fees for just about everything else you do.
Here’s what the New York Times said on this:
Bank of America joins banks including SunTrust and Regions in charging the fees. Other institutions, like Wells Fargo and Chase, are testing them, too. And over all, bank fees have crept up to record levels, a recent survey found.
The added fees have come even though the limit on the merchant fees wasn’t as low as banks initially had feared. (The Federal Reserve originally considered a cap of 12 cents, or half of what it finally set.)
Looks like I may be back to carrying cash on me once again. How about you? Tell us what you think in the comments below.
Read More at New York Times | <urn:uuid:909fd7fd-fa58-48fa-996c-51a0be8b6bc2> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://929thebull.com/banks-to-start-adding-debit-card-fees-bank-of-america-and-more/ | 2013-05-18T05:18:47Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.960721 | 303 |
WATD Local News
WATD Local Weather
TotalTraffic Boston on Twitter
- TotalTrafficBOS: #Chelmsford ramps blocked on Rt 495 Both NB/SB at EX 34 - Rt 110 and EX 35 - Rt 3 #traffic http://t.co/AoTr5OsSgQ Twitter / TotalTrafficBOS
- TotalTrafficBOS: #Needham ramp restrictions on Rt 128 SB at EX 18 - Great Plain Ave #traffic http://t.co/AoTr5OsSgQ Twitter / TotalTrafficBOS
- TotalTrafficBOS: #Andover ramp restrictions on I-93 SB at EX 44 - Rt 495 #traffic http://t.co/AoTr5OsSgQ Twitter / TotalTrafficBOS
Posted on January 20, 2013 | No CommentsIt’s Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Day. It’s also the Inauguration Day for President Obama. Just read an article from ABC News we wanted to share called 5 Ways to Honor Martin Luther King, Jr.: http://abcnews.go.com/US/ways-honor-martin-luther-king-jr/story?id=18221627 Jeff and Ilene Hills from Healthy Appetites Natural Foods in Plymouth will join us... | <urn:uuid:b18d28af-5f1d-4044-b63c-7284d9900f11> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://959watd.com/ssmorningnews/tag/jr/ | 2013-05-18T07:00:17Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.789456 | 291 |
Insurance Company Declares Living Man Dead
George Johannesen is very much alive. Which is why it was so surprising when the Canadian man received a letter addressed “To the Estate of George Johannesen.” Even more surprising is that it came from his insurance company, who should really be on top of such things.
Now this wouldn’t have been so terrible if Manitoba Public Insurance was giving Johannesen’s estate a fat check for his passing away. But that’s not what happened. Instead the letter was to inform the estate that, since George was dead, his driver license and auto insurance had been cancelled in October.
This poses a problem for Johannesen because, being alive, he continues to drive his car.
“I don’t understand how this could have happened,” he told the Toronto Sun. “For me to be declared dead, someone would have to present a death certificate. For someone to get that, I guess I must have died sometime in October.”
Now the 59-year-old worries that he will stop getting his pension and other government benefits. The Manitoba Public Insurance Company says they are trying to resolve the issue. They also claim they weren’t the ones who determined Johannesen was dead, but cryptically can’t reveal the source of the confusion for confidentially reasons. Perhaps a pesky ghost is behind the mix up? | <urn:uuid:6945b6ac-1063-4b03-84fa-8e5a540d4787> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://961wodz.com/insurance-company-dead-man/ | 2013-05-18T04:55:48Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.989102 | 292 |
If you travel to Destin Florida from Acadiana over the Summer you are going to travel by at least three outlet malls that I know of. I guess you could say four if you count the one in Gonzales Louisiana but who takes I-10 through New Orleans to get to the beach? Let's assume a man is driving and you are taking the shortest route possible. There is the outlet mall in Gulfport Ms, The one in Foley Alabama and my personal favorite Silver Sands in Destin. So what is the real truth about outlet mall shopping? | <urn:uuid:00b68b86-7bcb-4294-b841-e50bad844e9a> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://973thedawg.com/tags/outlet-malls/ | 2013-05-18T05:49:37Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.953757 | 111 |
Cajuns Surpass Last Year’s NO Bowl Ticket Sales.
Last year’s R+L Carriers New Orleans Bowl set a new attendance record, due in no small part to the more than 18.000 Cajuns fans who purchased tickets through the UL athletics department.
This year, another record could easily be set.
It was announced today over 20,000 tickets have been sold through the UL ticket office, with ticket sales continuing throughout the weekend. The box office is open 10am-6pm Monday through Friday.
Monday at 6pm is the deadline to buy tickets at the UL ticket office.
The increased ticket sales has led NO Bowl officials to open the Terrace level to the Mercedes Benz Superdome for the first time in bowl history.
The Cajuns and East Carolina will meet Saturday, December 22 at 11:00am. | <urn:uuid:71433555-1327-4e0f-8c2d-e4e9fe52819c> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://999ktdy.com/cajuns-surpass-last-years-no-bowl-ticket-sales/ | 2013-05-18T06:50:26Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.953375 | 180 |
Cupertino had its Apple Campus 2 Environmental Impact meeting this evening. Apple was represented by Campus 2 Project Manager Terry Reagan.
The City of Cupertino will be the lead agency and will prepare an Environmental Impact Report (EIR) for the Apple Campus 2 Project
While most Cupertino residents seem pretty excited about the idea, some are voicing concerns that traffic and other environmental impacts of the huge building could adversely affect their town. Notable from the video above:
- Contrary to previous reports, Mayor Gilbert Wong said the project wasn’t a “done deal”
- Apple Campus 2 Project Manager Terry Reagan (1.21) is no Steve Jobs when it comes to presenting Apple’s case. | <urn:uuid:6cefe004-e23f-4708-a1d1-2bb648511d0e> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://9to5mac.com/tag/environmental-impact-statement/ | 2013-05-18T06:34:29Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.941652 | 148 |
40th Parliament, 3rd Session
March 3, 2010 -
March 26, 2011
About this Committee
Like other standing committees, the Standing Committee on Health is appointed under the Standing Orders of the House of Commons for the life of a specific Parliament. It was first established in this form in 1994 to reflect the fact that the Department of Health and Welfare had been separated into two components: Health and Human Resources Development. By November 1995, this departmental restructuring was formally recognized in Bill C-95 (Department of Health Act).
The House of Commons Standing Committee on Health is empowered to study and report on all matters relating to the mandate, management, and operation of Health Canada. This includes its responsibilities for the operations of the internal body called the Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA).
The Committee is also responsible for the oversight of five agencies that report to Parliament through the Minister of Health:
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR);
- Patented Medicine Prices Review Board (PMPRB);
- Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission (HMIRC);
- Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC);
- Assisted Human Reproduction Canada (AHRC)
The mandate of the Standing Committee on Health also includes reviewing and reporting on matters referred to it by Orders of Reference from the House of Commons relating to Health Canada and its associated agencies. | <urn:uuid:d3966269-01e6-4b57-94f8-f40e83294d91> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://Ignatieff.M@parl.gc.ca/CommitteeBusiness/AboutCommittees.aspx?Cmte=HESA&Language=E&Mode=1&Parl=40&Ses=3 | 2013-05-18T06:50:06Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.947484 | 278 |
Stateside Footy presents an Australian Rules Football Championship match, played on October 14, 2012 at the USAFL Nationals Tournament in Mason, Ohio. This game features the Womens Division Final between the Boston Lady Demons and the two-time defending champion Denver Lady Bulldogs (Guest Commentator: Brian Barrish of the Philadelphia Hawks). The second half features a look back at the Boston Demons 2012 season. Stateside Footy is a cable access TV show produced with the assistance of WCTV - Wilmington Community Television in Wilmington, MA. It features Aussie Rules Football as it is played in the U.S.A.
Stateside Footy is a Cable Access program produced in the New England region of the United States. It is the only American Cable Access Program featuring Australian Rules Football as it is played in the United States. Episodes feature game telecasts of footy matches played in the Boston area, as well as news and stories about Aussie Football in America. Visit our web site at http://www.statesidefootytv.com | <urn:uuid:6680090d-661c-4d6b-96b0-485b114a6c67> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://a.blip.tv/statesidefootytv/stateside-footy-episode-12-16-usafl-womens-final-and-2012-in-review-6540732 | 2013-05-18T05:01:49Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.957332 | 211 |
Chang-an Jiang, Kim-leng Poh, and Tze-yun Leong
It is a frequently encountered problem that new knowledge arrived when making decisions in a dynamic world. Usually, domain experts cannot afford enough time and knowledge to effectively assess and combine both qualitative and quantitative information in these models.Existing approaches can solve only one of two tasks instead of both.We propose a four-step algorithm to integrate multiple probabilistic graphic models, which can effectively update existing models with newly acquired models. In this algorithm, the qualitative part of model integration is performed first, followed by the quantitative combination. We illustrate our method with an example of combining three models. We also identify the factors that may influence the complexity of the integrated model. Accordingly, we identify three factors that may influence the complexity of the integrated model. Accordingly, we present three heuristic methods of target variable ordering generation. Such methods show their feasibility through our experiments and are good in different situations. Finally, we provide some comments based on our experiments results. | <urn:uuid:f20540ee-fafb-422d-9d76-a6fc554293b7> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://aaai.org/Library/Symposia/Spring/2005/ss05-02-009.php | 2013-05-18T08:02:49Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.928985 | 209 |
No. 24; Updated March 2011
Click here to download and print a PDF version of this document.
Parents are usually the first to recognize that their child has a problem with emotions or behavior. Still, the decision to seek professional help can be difficult and painful for a parent. The first step is to gently try to talk to the child. An honest open talk about feelings can often help. Parents may choose to consult with the child's physicians, teachers, members of the clergy, or other adults who know the child well. These steps may resolve the problems for the child and family.
Following are a few signs which may indicate that a child and adolescent psychiatric evaluation will be useful.
- Marked fall in school performance
- Poor grades in school despite trying very hard
- Severe worry or anxiety, as shown by regular refusal to go to school, go to sleep or take part in activities that are normal for the child's age
- Frequent physical complaints
- Hyperactivity; fidgeting; constant movement beyond regular playing with or without difficulty paying attention
- Persistent nightmares
- Persistent disobedience or aggression (longer than 6 months) and provocative opposition to authority figures
- Frequent, unexplainable temper tantrums
- Threatens to harm or kill oneself
- Marked decline in school performance
- Inability to cope with problems and daily activities
- Marked changes in sleeping and/or eating habits
- Extreme difficulties in concentrating that get in the way at school or at home
- Sexual acting out
- Depression shown by sustained, prolonged negative mood and attitude, often accompanied by poor appetite, difficulty sleeping or thoughts of death
- Severe mood swings
- Strong worries or anxieties that get in the way of daily life, such as at school or socializing
- Repeated use of alcohol and/or drugs
- Intense fear of becoming obese with no relationship to actual body weight, excessive dieting, throwing up or using laxatives to loose weight
- Persistent nightmares
- Threats of self-harm or harm to others
- Self-injury or self destructive behavior
- Frequent outbursts of anger, aggression
- Repeated threats to run away
- Aggressive or non-aggressive consistent violation of rights of others; opposition to authority, truancy, thefts, or vandalism
- Strange thoughts, beliefs, feelings, or unusual behaviors
See other Facts for Families:
#25 Where to Seek Help for Your Child
#52 Comprehensive Psychiatric Evaluation
#57 Normal Adolescent Development, Middle School, and Early High School Years
#58 Normal Adolescent Development, Late High School Year and Beyond
#00 Definition of a Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist
The American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) represents over 8,500 child and adolescent psychiatrists who are physicians with at least five years of additional training beyond medical school in general (adult) and child and adolescent psychiatry.
Facts for Families© information sheets are developed, owned and distributed by AACAP. Hard copies of Facts sheets may be reproduced for personal or educational use without written permission, but cannot be included in material presented for sale or profit. All Facts can be viewed and printed from the AACAP website (www.aacap.org). Facts sheets may not be reproduced, duplicated or posted on any other website without written consent from AACAP. Organizations are permitted to create links to AACAP's website and specific Facts sheets. For all questions please contact the AACAP Communications & Marketing Coordinator, ext. 154.
If you need immediate assistance, please dial 911.
Copyright © 2012 by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. | <urn:uuid:673b1bf6-2c30-40ae-992b-c387d00a836a> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://aacap.org/page.ww?name=When+to+Seek+Help+for+Your+Child§ion=Facts+for+Families | 2013-05-18T06:26:22Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.927742 | 755 |
According to reports, Mr Jammeh recently told supporters he would “cut off the head” of any homosexual caught in the Gambia.
1. The Gambia is ruled by President Yahya Jammeh, an army officer who seized power in 1994.
In the past, he has also claimed he could cure anyone with the Aids virus in three days.
2. A British couple who have spent the past 12 years working as Christian missionaries in the the Gambia have been jailed after being charged with sedition. (British missionaries jailed in Gambia )
Banjul from http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:000000f2.JPG
3. Scary Tales of Tiny Gambia Being the Headquarters of the Mafia World
By Bubacarr Ceesay
December 13, 2005
The Gambia is the international limelight again as the center of an international mafia ring.
In a masterpiece investigative report, The Wayne Madsen Report unraveled a network of weapons smugglers and mobsters operating in the heart of the Gambian Capital, working hand in hand with the Gambian leader, President Yahya Jammeh.
In reference to the Gambia, the report stated thus:
"There is also now interest in the activities of Richard T. Hines, the head of the powerful Republican lobbying firm RTH Consulting, Inc.
"Hines, a South Carolina native and a protege of the late GOP dirty trickmeister Lee Atwater, was one of the architects of the dirty tricks campaign by Bush against John McCain in the 2000 South Carolina primary.
"A confederate of Abramoff in the 1980s Reagan administration's covert support network for the Nicaraguan contras, Angolan UNITA guerrillas, and Afghan mujaheddin, Hines is active in various Confederacy resurgence organizations, many of which have clear racist agendas.
"However, that has not prevented Hines from becoming the lobbyist for Gambian dictator Yahya Jammeh, a military officer who overthrew Gambia's democratically-elected President Sir Dawda K. Jawara in a 1994 military coup supported by the United States Navy.
"Hines inherited the lobbying contract for Gambia from the eclectic Washington lobbyist Edward von Kloberg III, an individual who represented Mobutu Sese Seko of Zaire, Liberia's Samuel K. Doe, Nicolae Ceausescu of Romania, Congolese leader Laurent Kabila, the exiled King Kigeli V of Rwanda, and Saddam Hussein.
"Last May, von Kloberg took a swan dive off of a castle in Rome, allegedly committing suicide after a spat with a gay partner.
"The connections between Hines and Gambia are important since the small narrow West African country is also a major base of operations for notorious Russian international arms smuggler Viktor Bout.
"The Gambia is the headquarters for one of many of Bout's front companies -- companies that are used to smuggle everything from weapons to diamonds and mercenaries to international relief supplies.
Bout, reportedly in a Bangkok jail since March 2008
"In fact, Bout was the character on whom fictional arms smuggler Yuri Orlov, played by Nicolas Cage in the movie Lord of War, was largely based.
"Bout's connections with the Christian Right do not end with Gambia.
"Bout was Liberian dictator Charles Taylor's primary arms and diamond smuggler.
"Bout and his associates were given Liberian diplomatic passports and, with Taylor's blessing and protection, they registered a number of their front companies in Monrovia, the Liberian capital.
"Taylor, who is now in exile in Nigeria, was a business partner with Christian Coalition founder Pat Robertson.
"Robertson's organization mentored both Ralph Reed and Richard Hines.
"According to British and Israeli intelligence sources, Taylor also enabled Al Qaeda to launder blood diamonds for cash through Liberia.
"Liberia and neighboring Sierra Leone were where Israeli mobsters engaged in business with Israeli gangsters who operated under the full protection of the Israeli Likud government.
"Before Likud began purging Mossad of experienced intelligence officers with ties to the Israeli Labor Party, the Israeli-Al Qaeda diamond financial connection in West Africa was being pointed out by those officers as suicidal for Israeli interests.
"However, Taylor and Bout had powerful interests in the United States: a combination of the Christian Right and pro-Likud organizations like the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC), both of which ignored and continue to ignore Israeli organized crime connections to Al Qaeda and terrorism.
"Robertson and Taylor were business partners in a Cayman Islands front company called Freedom Gold, Ltd.
"In fact, Freedom Gold bas headquartered at Robertson's CBN offices in Virginia Beach, Virginia. Robertson's African interests also crossed paths with Bout's in another country -- the former Zaire.
"Robertson's African Development Company used the cover of Robertson's tax-exempt "Operation Blessing" to ferry conflict diamonds out of civil war-ravaged Zaire (now Congo).
"A UN Security Council report dated November 30, 2005, lists Bout's Gambia New Millennium Air Company as having its address at the residence of Hines' client Jammeh: State House, Banjul, Gambia.
"The UN report states, 'The Director of this firm is Baba Jobe, who is already listed on the Liberia Sanctions Committee's assets freeze list. According to a commercial aviation database, the firm acted as a cover for Victor Bout's operations. Its one aircraft, a Russian-made passenger jet, was acquired from Centrafrican Airlines.'
"It is noteworthy that Hines's client, President Jammeh, just took possession of the Russian-made VIP presidential passenger jet, an Ilyushin IL-62 (C5-GNM) [Gambia] (formerly CCCP-86511 [USSR], RA-86511 [Russia], 3D-RTI [Swaziland], TL-ACL [Central African Republic]).
"And also of interest is the owner of the presidential aircraft: it is none other than Gambia New Millennium Air, the Bout-owned company listed on the UN Security Council freeze list and which is headquartered at Jammeh's State House in Banjul, the Gambian capital.
"In fact, the plane had been previously registered to Bout front companies in Swaziland and the Central African Republic.
" Bout, who flew arms and passengers from Dubai and other locations to Taliban-controlled Afghanistan prior to 9-11, is now providing air services in post-Taliban Afghanistan as well as U.S.-occupied Iraq.
"Bout's transactions with the Taliban were handled by Vial, Inc., a firm based in Delaware.
"One of Bout's closest associates is the Russian-Israeli Odessa-born crime boss Leonid Minin, an Israeli national who, according to the UN Security Council, travels on forged German passports as well as legal Israeli, Russian, Greek, and Bolivian passports under at least ten aliases.
"It is also noteworthy that many of Bout's operations are based in Eastern European countries that have been mentioned in association with the rendition and transporting of CIA prisoners.
"Bout's numerous Russian-built cargo and passenger planes have been seen at the same airports used by CIA flights.
"For example, Bright Aviation, a suspected Bout front, is based at Sofia Airport in Bulgaria.
"Bulgaria is believed to be one of the countries used by the CIA to house secret prisoners.
"Another Bout front, Moldtransavia SRL, is based in Chisinau, Moldova, another suspected stopover point for CIA flights.
"One Chisinau, Moldova-based Bout front company, Aerocom, which also does business as Air Mero, is contracted to fly for Kellogg, Brown & Root in Iraq and elsewhere.
"Aerocom has also been cited in UN and DEA reports for being involved in drug smuggling in Belize.
"Some law enforcement officials in the United States and Europe believe that the covert flights being operated by CIA contractors and Bout's companies in support of secret prisoner movement are also involved in smuggling drugs.
"After being subjected to news reports, Aerocom quickly changed its name last year."
Highly dependable sources in Banjul also informed AllGambian about recent arms purchase by the Jammeh regime from an undisclosed country, amounting to 4.3 million dalasis.
This comes at the heels of a hard-hitting border impasse between the Gambia and Senegal.
The stand-off almost paralyzed the Gambian economy and caused untold hardship on the average Gambian. Observers wondered how the Gambia gov can afford to spend on presidential jets and military hardware at this junction when the economy is in shambles. | <urn:uuid:052280ae-4e57-401f-95a0-23a58b01b11a> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://aangirfan.blogspot.ca/2008/12/gambia-and-organised-crime.html | 2013-05-18T07:19:30Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.947875 | 1,848 |
Ragdoll Kittens Available Now!
All babies are spoken for, but we have some on the way if you would like to get on our waiting list.
Waiting List With Deposit
Sheila Any color Girl
Riley Family Seal Mink Boy
Our kittens are avialable for delivery. We like to have our kittens driven to their new families when going a long distance or flying with them when we can. You are welcome to pick up your new baby. We are in the Knoxville TN area and are an easy drive from GA, NC, SC, KY, AL, VA and West Virginia. One of our delivery drivers is in NY so having them delivered to NY, MA, RI, CT, OH, PA and FL are very easily arranged.
We are a TICA Registered Cattery
Available Ragdoll Kittens | <urn:uuid:91f06c24-12da-4694-9582-138bb3e0139a> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://aaronsragdollkittens.com/ | 2013-05-18T07:14:11Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.932954 | 174 |
Previous abstract Next abstract
Session 40 - The Interstellar Medium.
Display session, Tuesday, June 09
Gamma Ray Burst (GRB) explosions can make kpc-size shells and holes in the interstellar media (ISM) of spiral galaxies if much of the energy heats the local gas to above 10^7 K. Disk blowout is probably the major cause for energy loss in this case, but the momentum acquired during the pressurized expansion phase can be large enough that the bubble still snowplows to a kpc diameter. This differs from the standard model for the origin of such shells by multiple supernovae, which may have problems with radiative cooling, evaporative losses, and disk blow-out. Evidence for giant shells with energies of \sim10^53 ergs are summarized. Some contain no obvious central star clusters and may be GRB remnants, although sufficiently old clusters would be hard to detect. The expected frequency of GRBs in normal galaxies can account for the number of such shells.
Program listing for Tuesday | <urn:uuid:e2300ad5-01dd-4e80-92b3-7ec88785cc9d> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://aas.org/archives/BAAS/v30n2/aas192/abs/S040015.html | 2013-05-18T06:20:41Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.912641 | 208 |
Very pleased with the Meta Targa SR2. Fitting on the Skoda Octavia took me a while as the wires had to fed up through the tailgate, but once installed it worked a treat. Top marks !
Hubby bought one of these for my Golf. Absolutely brilliant will never back into a skip again.
Been using the Meta reversing sensors for almost a year now. This really is a super simple item to fit, it looks good even better than some factory fit items fitted in the bumber, in actual fact you have to look hard to even notice them. Works brilliantly, not a single scratch on me rear. This item has definitely saved my marriage. Top product from a top supplier (this should guarantee a discount on my next purchase) | <urn:uuid:5e405767-37f9-4945-aa00-44f157892072> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abacuscaralarms.co.uk/alarmshop/index.php?act=viewProd&productId=94&ccSID08d9c7843f5fd94eef9876bc9b24ddb5=554e874dfdb57748d9d8a7477300dda3 | 2013-05-18T06:26:06Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.947041 | 155 |
Everyone wishes for something. And lots of people believe they know how to make their wishes come true with magical thinking.
What is it? "Magical thinking is a belief in forms of causation, with no known physical basis," said Professor Emily Pronin of Princeton. "So, for example, there's no known physical basis for how carrying a fluffy pink rabbit's foot in your pocket is going to increase your odds of winning the lottery."
For magical thinkers, it's more about the power of their wishes, their feelings and their positive thinking to affect their lives directly.
Twenty-seven-year-old aspiring actress Lindsay Lioz relies on magical thinking to further her showbiz career -- starting with visualizing every audition in advance. "It makes me feel like I've had rehearsal," she said. "It makes me feel prepared."
Lioz also uses magical thinking to improve her love life. She's written a list of the qualities she wants in a man -- and she sleeps with that list under her pillow every night. How has it worked so far? "I have great men in my life, I do. I'm very happy with how it's working out."
Magical thinkers call that idea "the law of attraction." It's a key element of the bestselling book "The Secret," which has been hailed by Oprah Winfrey and bought by millions worldwide.
"'The Secret' is telling people that if you think positive thoughts, positive things will happen, even at a very specific level," Pronin said. "If you visualize getting a parking space, you will get one. If you want to get thin, just stop having fat thoughts."
Magical thinking is not a religion. It's a different kind of faith -- a faith in the power of positive thoughts and feelings. Yet as unscientific as magical thinking sounds, Pronin said studies have shown there are times when it seems to have a real effect: "There was a study where people in their mid-20s were measured in terms of their optimism," she said, "and then, 50 years later, those who were more optimistic, were actually more likely to still be alive. So it's not always magical to believe that your positive thoughts are having a positive effect."
Magical thinking starts in childhood. At the University of Texas, Professor Jacqui Woolley has examined how children who know the difference between what's real and what's not believe that wishing can cause a penny to appear in what has just been shown to be an empty box. "We find that, by about the age of 4, most of the kids we test seem to really believe that wishing works," said Woolley. "So that would be an example of magical thinking."
Nick Barber spent his childhood wishing for riches, focusing on something his father gave him. "I was about 8 or 9 when my dad came home and gave me a fake million dollar bill," he said. "And that became something that represented my goals. I've hung on to it every since."
Barber would even sleep with the bill under his mattress. Now, at 27, he runs a multimillion dollar real estate company in Dallas called UMoveFree, and he still has that million dollar bill in his wallet. How did that bill help him get to this point? "It allowed me to believe in myself at a very young age," Barber said, "not to pay attention to those that said you can't, and to always believe that I can." | <urn:uuid:97684525-19c7-48da-a302-c2da701993dd> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/2020/story?id=3160862&page=1 | 2013-05-18T07:15:02Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.990037 | 716 |
Do you drive a picop? Eat sándwiches de rosbif? Do you still own any cederrones? If these words don't sound familiar to you, that's because yesterday, the Associated Press released their first-ever Spanish language style guide, and set us all straight on the proper usage of some of Español's newest words.
In case there's any confusion, picop is AP's official Spanish-language word for what many call a camioneta or pick-up truck, rosbif is their official spelling for "roast beef" in Spanish. And cederrón? That means CD-ROM. Duh.
Gathered in the auditorium of the prestigious Columbia Journalism School, some of the leading Spanish-language journalists sat down on Monday evening to discuss the finer points of the "language of Cervantes" and the AP stylebook -- which they describe as the "journalist's bible." Debate over the AP's continued use of term "illegal immigrant" dominated much of the event. But the most lively part of the evening was the presentation of words with roots in modern-day English -- or "estadunidismos," as the new Stylebook calls them.
If the Spanish-language style guide is to be our bible, then Monday evening's Moses was surely Argentine journalist Jorge Ignacio Covarrubias who has worked with the AP for more than 40 years and helped put together the new stylebook. The white-haired Covarrubias handed down to us such words as zapeo for channel surfing, cibersitio for website, pipermín for peppermint, ofimática for computer system for office management (like Word), and vermú for vermouth -- all in the form of a PowerPoint presentation. (Can we please call it a Powerrpoín?)
But not all Spanglish words are fair game, according to Covarrubias. For example, the AP recommends against using parada to mean parade. The word "parada" has historically been used to mean "stop", but many modern-day Spanish speakers have started using it to also mean parade. The AP suggests that writers instead use "desfile."
Many regionalisms are also discouraged. Autobús is the preferred term for bus, although some countries use guagua and others say colectivo. But, after lengthy discussion of the Spanish word for "drinking straw," (pajita vs. popote vs. canuto), no consensus has yet been reached, said Covarrubias.
Not everybody was happy about all of the AP's decisions. Laura Martínez, a bilingual blogger who writes about Hispanic media, tweeted "Cervantes is probably revolcándose en la tumba tras escuchar el tema ése del "cederrón"," which translates to "Cervantes is probably turning over in his grave after hearing the thing about the 'cederrón'" | <urn:uuid:cd3169e8-c0b9-4e0a-9e29-ee6c8330ed11> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/ABC_Univision/ap-spanish-language-stylebook-introduces-technical-spanglish/story?id=17769035 | 2013-05-18T06:21:24Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.921005 | 619 |
The recent news that Bristol Palin and Levi Johnston were engaged came as a shock to many.
After all, here's a couple whose relationship imploded on the world stage and turned into a bitter family feud involving Palin's mother Sarah Palin, the former vice presidential candidate.
Following their breakup, the pair traveled very different paths: Bristol Palin went on to be a spokeswoman for teen abstinence; Levi Johnston posed for Playgirl.
But like star-crossed lovers, Palin and Johnston found a way to come back together, reuniting for the sake of their year-old son, Tripp.
"It's like Romeo and Juliet in Wasilla," Joy Behar said on "The View."
And while their relationship may seem rife with reality TV-like drama, according to Thomas Van Flein, the Palin family attorney, there's no plan for the young mom to chroncile her romance anytime soon.
"There is a lot of public speculation that Bristol and Levi have signed up for a reality show about their relationship," he said in a statement to ABC News today. "They have not. While several networks have pitched different concepts, Bristol has not agreed to participate in any show. Her focus remains on doing what is best for Tripp and her family."
Though they announced their engagement last week on the cover of US Weekly, senior editor Lindsay Powers said the news shouldn't come as a total surprise.
"About a month ago we saw the relationship thawing between them," Powers told ABCNews.com.
That's when Palin told "Good Morning America" that she was getting back together with Johnston for Tripp's sake.
"I am doing my best to raise a happy, active and healthy boy," Palin said. "I believe that wherever possible, if the parents can cooperate and co-parent in a positive way, the child will benefit. Levi and I are turning a new page here as co-parents to this wonderful boy and putting aside the past because doing so is in Tripp's best interest."
They certainly wouldn't be the first couple to reunite for the kids and they certainly won't be the last. But will other celebrity couples who have split up follow in their footsteps? Last week, several former couples made headlines. ABCNews.com thought it would be fun to take a look at their chances of getting back together. Powers ranked them from most to least likely.
Jesse James and Sandra Bullock | <urn:uuid:3f4afc77-d75c-4fb4-a68d-86fd538bd977> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/Entertainment/bristol-palin-levi-johnston-reunite-celebrity-couple-follow/story?id=11171769 | 2013-05-18T04:59:06Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.977646 | 499 |
After this story aired on "Good Morning America," K-Mart contacted the Hayes family to give them two $50 gift certificates to the store to help out with the sextuplets' many needs.
Sept. 14 means there's a birthday in the Hayes household, six times over. Three years ago, Eric and Elizabeth Hayes gave birth to sextuplets.
Then they were six bundles of joy, now they are six individual toddlers with distinct personalities.
Rachel's the Curious George of the group, E.J. is the shy one, and Ryan's the most outgoing, who believes in sharing, until push comes to bite. While Tara prefers her alone time, Connor, the resident drama king, enjoys his time at center stage.
Rebecca is the only sextuplet who is struggling -- she has cerebral palsy -- raising all the questions about the consequences of fertility medicine.
The Hayes already had three boys and one girl when they decided to give parenthood one more shot, in hopes of a sister for their daughter.
"And, you know, we hit the jackpot," Eric said. He explained that originally they thought they were having triplets, possibly quintuplets, but never sextuplets, until the third doctor's visit when he held up six fingers to tell the lucky parents what they had to look forward to.
Even with the shocking news, the Hayes said they never considered selective reduction, a practice used to reduce the number of implanted embryos.
"You tell me right now, who you wouldn't want to be here? Pick one, pick two, pick three, tell me. I couldn't do that," Eric Hayes said.
The older twins -- 9-year-olds Kieran and Meghan and 11-year-olds Kevin and Kyle – do what they can to help with the often literally "dirty" half dozen.
The Hayes say the secret of each day is a constant schedule, gratitude and laughter, especially when it comes to watching shows like ABC's "Super Nanny."
"I like to see what kind of fools there are all out there 'cause we're handling it with 10 and they have one and two and they -- they're going bananas," Eric said.
Each day in the Hayes household means six loads of laundry, four runs of the dish washer and two full gallons of milk. But the biggest number is 120. That's the decibel level of six crying babies, and it's louder than a subway, an ambulance siren or a chainsaw.
"When they were infants all six of them would be crying and I would just stand there and I'd start to laugh because there's really nothing you can do outside of, you know, crying," Elizabeth said.
Ten cries, 10 laughs -- one beating heart of a family.
Donations for the Hayes Family can be sent to:
Our Lady of Grace Church
400 Willow Avenue
Hoboken, N.J., 07030
100% of your donation will go to the Hayes Family.
Make checks payable to "Our Lady of Grace Church" and please write "Hayes Family" in the notation. A tax statement will be sent to all donors of $250 or more.
For more information, call (201)659-0369 or e-mail:email@example.com. | <urn:uuid:18849185-48e7-438b-846a-0e8ae9c95a38> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/AmericanFamily/story?id=3598492&page=1 | 2013-05-18T07:16:07Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.968951 | 691 |
"Good Morning America" and Parade magazine unveiled their lists of must-read books for the summer. From thrillers to biographies to light reading, these stories are un-put-downable.
If you're in search of that perfect page-turner for your summer vacation, look no further!
CLICK HERE for more hot summer book picks from Parade magazine.
CLICK HERE for our special books page full of book excerpts, author interviews and more!
Jack Reacher's latest adventure begins when he suspects a female suicide bomber is aboard a Manhattan subway car. Her death leads him on a path back to the war in Afghanistan against the Soviets in the 1980s.
After he's laid off in the latest budget cuts at The Los Angeles Times, reporter Jack McEvoy plans to write the murder story of his career in his last two weeks at the newspaper.
When Sandra Jones, a hardworking young wife and mother, disappears without a trace one day, Sgt. Det. D.D. Warren is called in on the case. As he's digging, he discovers that her family life isn't so perfect.
In Ridley Pearson's third crime novel starring Walt Fleming, the amiable sheriff in Sun Valley, Idaho, the lawman faces a master thief planning to steal three very expensive bottles of wine at the annual wine auction.
After Paul Madriani encounters Katia Solaz, a 26-year-old beauty from Costa Rica, it's a race to avoid disaster.
Gabriel Allon's perfect world is thrown into confusion with shocking news from London: The defector and former Russian intelligence officer Grigori Bulganov, who saved Gabriel's life in Moscow, has vanished without a trace.
After Shearman Waxx, the nation's premiere literary critic, tears apart the work of best-selling author Cullen Cubby Greenwich, Cubby and Waxx engage in all-out warfare.
Dallas lawyer Casey Jordan must deal with illegal immigrants and abuse of power in this legal thriller.
After a night porter's naked corpose is found in a pool of blood in the basement of London's Imperial Hotel, the aftereffects threaten to undo everything chef Gabriel Lightfoot has worked so hard to achieve in the kitchen.
A gorgeous woman marries a boy king in secret and ascends to royalty in "The White Queen."
A group of teens -- privileged and poor, black and white -- forms a lasting bond in Charleston, S.C., in 1969 just as southern society is in the midst of dramatic change.
Pearl and her younger sister, May, are living in affluence in Shanghai in the 1930s, until their father says that his gambling habit has ruined their finances. To pay his debts, he has sold both sisters to a well-to-do Chinese-American as wives for his sons.
Elv created fairy tales for her sisters as a child, but after sexual abuse, she succumbs to drug addiction and painful self-abuse. | <urn:uuid:ea6dec7a-118a-4bcc-9bf3-040a98546d6d> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/Books/story?id=7938947 | 2013-05-18T05:59:12Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.954088 | 613 |
White House Has a Plan to Tackle 3 Separate Scandals
Pat Robertson: 'Males Have a Tendency to Wander'
Jodi Arias Victim's Siblings Emotionally Address Jury
Lone Survivor of 1987 Plane Crash Breaks Silence
President Obama Makes His Case Amid Minefield of Scandals
Lions, Tigers and Bears Living Together
Alexander's Siblings Emotional Plea to Arias Jury
White House Takes Action on 3 Controversies
Pat Robertson: Divorce Wife With Alzheimer's
Nightline Online: Jesus for Porn Stars
Boehner on IRS Scandal: 'Who's Going to Jail'?
Jodi Arias Deemed Eligible for Death Penalty
Man Allegedly Destroyed Neighbor's Home with Bulldozer
Internet Celebrity Arrested in Lawyer's Homicide
Boston Explosions Cause Lockdowns, Heightened Security in America | <urn:uuid:3fa55339-5153-4967-bebd-e3a654fcee76> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/video/egypt-clamps-down-12800878 | 2013-05-18T06:20:33Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.701122 | 179 |
Question: How is bipolar disorder different from unipolar depression or 'regular' depression?
Answer: Both bipolar disorder and major depression are typically associated with depressive episodes. So both illnesses are accompanied by depressions. The difference is that in bipolar disorder people also have periods of elevation -- or severe irritability. We call these manic or hypomanic episodes. | <urn:uuid:e6ba92ad-ed0a-4cac-8e5d-204b78cdd250> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/Health/BipolarOverview/story?id=4359993 | 2013-05-18T05:50:17Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.943297 | 71 |
Nine people in South Korea have committed suicide in three separate incidents within two days. The latest was a 72-year-old man who hanged himself at a construction site in Hoengseong, Kangwon Province, Thursday, police said.
Four women and one man -- in their 20s and 30s -- were found dead Wednesday in Hwaseong, just south of Seoul, after sealing a passenger car with plastics sheets and inhaling toxic fumes from burned coal briquettes.
They left suicide notes saying, "I have no more hope and no more dreams" and "please find my identification card in my back pocket."
Police were investigating their motive but assumed that the man recruited the four women on the Internet to participate in a group suicide.
Earlier in another city east of Seoul, Chuncheon, three men in their 20s were also found dead at a private room-for-rent lodge using the same method and sealing the door and windows with dark masking tape from inside the room they were sharing.
Police assumed that they, too, were driven by group suicide pacts cultivated online.
Such news is common here where the suicide rate is the highest among members of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development group of developed countries.
An average of 35.1 people killed themselves everyday in 2008, according to the health ministry. That's 24.3 for every 100,000 South Koreans, followed by 21 in Hungary, 19.4 in Japan, 16.7 in Finland and 15.8 in Belgium.
The National Statistics Office reported that the suicides are related to the economic downturn, as well as rapid social change within the family and the community.
Korean society in recent years has been plagued by continuous cases of suicide among celebrities, high-profile politicians and businessmen, teenagers and the elderly. Analysts say the most common cause is depression stemming from social and academic pressures or family troubles.
"There's a huge gap in this country because the speed of materialism spreading is much faster than the speed of cultural maturity that must grow together. It all comes from stress of rapid modernization," said Jeung Taek-Hee, an expert and consultant at Lifeline Korea.
Korean parents are having fewer children -- on average one per couple -- and more women are going into the workforce, which leaves the child alone. Although some corporations and government ministries are campaigning for workers to go home by 6 o'clock at least once a month to spend family time, Korean corporate culture still requires employees to participate in work-related dinners and stay late hours.
"Naturally, these busy parents end up spoiling the child who ends up self-centered and incapable of dealing with competition," Jeung said. "But the reality is that this society is very, very competitive."
Along with the miraculous rate of economic growth in the past decades, many South Koreans have become driven by materialism that has been passed on to their kids, Jeung said.
He noted that most of the people who commit suicide, especially the young teenagers, find themselves dangerously distressed by not being able to keep up with others materialistically and eventually become anti-social.
"The easiest place where they can meet friends who share the same pain is online through suicide communities or chat sites," Jeung said.
Once they find each other, they become, "eternal comrades" who "must accompany each other to death," he said.
According to the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, 28.4 percent of young teenagers committed suicide in 2008 because of "disturbed family relations," mostly the result of parental divorce, 19.6 percent from pessimistic depression and 10.1 percent from academic pressure. | <urn:uuid:2edc9224-49dc-4ff8-a3a7-e5c117b470e6> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/International/south-korea-struck-online-suicide-pacts/story?id=10636608 | 2013-05-18T06:20:24Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.973295 | 750 |
World leaders from 47 nations convene this week in Washington, D.C., for the Nuclear Security Summit, a gathering that the Obama administration hopes will raise awareness about the threats of nuclear arms getting into the hands of terrorists or "rogue" nations.
President Obama said Sunday the goal of the nuclear summit is to discuss the terrorist threat and getting countries to lock down their nuclear weapons in a specific time frame. The Obama administration itself has pledged to try to "secure all vulnerable materials" within four years and is hoping the summit will spark a case for preventive action among others.
"If there was ever a detonation in New York City or London or Johannesburg, the ramifications economically, politically, and from a security perspective would be devastating," Obama said on the eve of the summit. "And we know that organizations like al Qaeda are in the process of trying to secure a nuclear weapon -- a weapon of mass destruction that they have no compunction of using."
Secretary of State Hillary Clinton said last week that the nuclear summit would be the largest of its kind hosted by a U.S. president since the U.N. conference in 1945.
But even as Obama brings the issue of nuclear security and disarmament into the spotlight -- first with the release of the new U.S. nuclear policy, and then the U.S.-Russia arms reduction agreement -- he faces significant challenges from two fronts.
Internationally, U.S. allies such as India, Pakistan and Israel have been resistant to signing the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty, citing national security concerns. The view in many countries is that this week's treaty signing aside, if the United States and Russia -- which together account for 95 percent of the world's nuclear arsenal and material -- cannot cut their nuclear stockpile, why should they be forced to?
"No one is willing to step up and say, 'Yea, I'm part of the problem here," said former national security official Ivan Oelrich, now vice president of the Strategic Security Program at the Federation of American Scientists. The "U.S. and Russia have to lead the way in major reductions."
Participant countries will also likely be looking to the United States for accountability. Henry Sokolsi, executive director of the Nonproliferation Policy Education Center, argues that if the United States is going to try to persuade other countries, it needs to shift its own policy at home too.
"I just think it's disrespectful to these countries," he said. "Each country has its own problems. If we're not helping them on that, how can we expect them to not rely on them [nuclear weapons] to feel secure? We rely on them. Why should they be any different?"
Domestically, the partisan rift on Capitol Hill means possibly a tough fight ahead for Obama's nuclear agenda. Critics of the new nuclear policy released last week complain that it gives a free pass to countries such as Iran and North Korea, and Republican senators are already taking aim at the U.S.-Russia arms treaty that was signed last week, saying it hurts U.S. security interests.
The general consensus is that the treaty will eventually be ratified by the end of the year, but the issue is likely to be the subject of a heated political debate for much longer. | <urn:uuid:0a9b45ec-f8f1-41fa-82b8-42fdadb3c33f> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/Politics/obamas-nuclear-security-summit-symbolic-gesture/story?id=10335607 | 2013-05-18T05:50:51Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.957308 | 671 |
6:29 p.m. ET: ABC’s David Wright tweeted:
3:41 p.m. ET: Spencer West, a 31-year-old who was born with a genetic disorder called sacral agenesis and eventually had his legs removed, climbed to the top of Mount Kilimanjaro on his hands.
2:28 p.m. ET: Twitter returns!
The social website went down around 11:50 a.m. ET, bringing users’ streams to a screeching halt and causing several reporters to suffer from twitching fingers.
12:49 p.m. ET: SANDUSKY TRIAL, ABC’s Jim Avila reports: Jerry Sandusky, his lawyer told a jury today, was “slammed” by accusers who are out for money and investigators who pressured witnesses into making false claims, despite years of helping children without anyone complaining of inappropriate behavior.
The jury of seven women and five men will begin deliberating Sandusky’s guilt or innocence this afternoon after the prosecution completes its closing argument. If convicted of 48 counts of sex abuse against 10 boys, the former Penn State football coach, who is 68, could be sentenced to life in prison.
11:56 a.m. ET: Unintentionally, pro-athletes have become the guinea pigs, some would say, in testing cutting-edge and experimental therapies for chronic pain.
ABC’s Ron Claiborne reports on a controversial new blood injection treatment virtually unknown in the United States and not approved by the FDA. It’s called Regenokine therapy, and Kobe Bryant, Tracy McGrady and other star athletes have used it to help with chronic pain.
11:05 a.m. ET: It’s official, but it’s a non-event. Tropical Storm Chris was upgraded to a Category 1 Hurricane Thursday, becoming first hurricane of the season, the National Hurricane Center announced. However, the storm is far out in the middle of the Atlantic and poses no threat to land, the center said.
9:41 a.m. ET: Blast from the past:
American actress Lisa Hartman and American actor Alec Baldwin pose in a publicity portrait for the TV soap opera series ‘Knots Landing,’ in 1985. Baldwin appeared in 40 episodes during two seasons on the show.
Baldwin has been back in the news recently because of another outburst, this time with an NY Post photographer. | <urn:uuid:fd298077-a85e-473f-b9a2-1a297b009001> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/blogs/extras/2012/06/21/nightline-daily-line-june-21-sandusky-trail-prosecutions-closing-arguments-today/ | 2013-05-18T06:45:03Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.965983 | 520 |
Exhausted and euphoric. Those are the words to describe me right now. Six days after boarding the "Good Morning America" Whistle-Stop '08 Tour train, and beginning the adventure of a lifetime, it's over.
We just wrapped the last show of our little Odyssey from the Newseum in the nation's capitol, Washington D.C., and for me, it was an appropriate but bittersweet ending to our tale.
Appropriate because the point of our tour was to go out and ask real people what was on their minds, to hear straight from them their concerns about our nation. By ending in Washington, D.C., we brought their thoughts, problems and hopes to the doorstep of the government -- to the people that can do something about them.
But it was also bittersweet because I honestly didn't want the trip to end.
I'm not going to lie to you and say that I loved everything about it (3:00 AM wake up calls being the main offender), but I was consistently surprised to find that even in the tougher times, when we had been blearily working for 18 hours straight, something or someone would come along to pick everyone up.
From the absolute chaos of pre-show preparations, to the fleeting sparkle of pride in the production team's eyes when a show went just as planned, life on the train was crazy, grueling and complicated, but most of all, fun.
Some moments I'll never forget.
Like the celebration in Massachusetts after we pulled off what had never been done before -- the first live network television broadcast from a moving train.
Or when Diane, Robin and Chris teamed up -- using Rick Klein and me as props -- to convince Sam that he was supposed to share his tiny room on the train with two roomates.
Or when Chris put his life on a very secure line at Niagara Falls to dramatically bring the news from the brink of watery doom.
Or, my personal favorite moment, when Sam, Chris and two producers played the most ridiculous game of Monopoly I've ever seen for four hours and a few of us, Sam included, cried from laughing so hard.
But far more moving than the obvious and endearing camaraderie between the anchors was their care for the American people to whom they bring the news every morning.
Never was this more obvious than yesterday, when I accidentally stumbled into an anchors' meeting where they discuss the content of the next day's show and, for some reason, I was allowed to stay.
As an aspiring journalist myself, I can't express how inspiring it was to listen in on this discussion and know firsthand that whatever goes on the air, it's the fairest, most accurate and most informative report possible. Though they have their fun, when it comes to the news Diane, Robin, Chris and Sam are professionals in every sense of the word.
But now I have to go -- have to return to "normal" life, and I don't want to.
I have to shave my rail-beard, the result of a production-wide pact to not shave for the duration of the trip. I have to wash some extremely smelly clothes. I also have a feeling that the spontaneous dance parties that erupted on the train will be for some reason looked down upon in the office.
These are all reasons to miss dragging myself aboard that cramped studio on rails well before the sun comes up. But maybe we'll be able to do it again sometime.
We were told to get back to New York however we wanted.
I think I'll take a train. | <urn:uuid:f00df4e1-9a25-4e7e-bd1e-0bba13621b1e> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcnews.go.com/politics/5050/story?id=5840462&category=Good%20Morning%20America | 2013-05-18T06:44:58Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.977122 | 739 |
Already have an account? Fantastic, log in below!
Forget your password? Enter your email address and we will send instructions on how to reset it.
New user? Create a new account to take part in all that this site has to offer. It's fast, easy and most important free.
Enter your email address:
Delivered by FeedBurner
New user? Create a new account | <urn:uuid:8c9a3ef3-f6d2-4198-85ac-3aa1d17c5da8> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abcphp.com/login.php?return=%2Fupcoming%2Fpage%2F240 | 2013-05-18T07:19:48Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.93277 | 83 |
In these moments of true lucidity, such as those unmemorable days of infancy, does one truly gain a clarity. This sandbox, kindly nurtured but briefly by the tempest of chaos is but a schism. A calm curiosity to detract from the endless void to which all will return. As kind as it is cruel, this laboratory of sensation is unique. We shall never occur again, nor shall our records tell of our being for our records are themselves fleeting. A dash for a glorious future which will bear fruit for just a few. a desperate retreat from a past whose ghosts will always haunt. liberated to the moment and freed from past and future, the child lives in eternity and lucidly chuckles at it's own wonder. | <urn:uuid:7e8c56eb-e558-4741-b3b9-d88d0e6c5823> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abctales.com/story/dan-ryder/lucidity | 2013-05-18T05:34:06Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.962013 | 149 |
Headed to the club for a work out? No sweat. Our Nylon Gym Bag from American Apparel is the perfect way to transport those damp gym clothes back home. Made with a water-resistant Nylon Pack Cloth construction, it's made for the rigorous demands of an athletic lifestyle. With a durable zipper (surrounded by reinforced-Nylon) and Nylon webbing straps, you'll love this versatile and durable bag.
Dimensions: 20" x 9" (50.8 cm x 22.86 cm)
Easily folds into luggage
Made in the U.S.A. by American Apparel
Browse more products:
Drag the square at the left to choose the part of your image you want to use. Tips: Click and drag any corner to resize; click and drag from the inside to move. | <urn:uuid:8fa7f517-4cbb-4010-9ffd-292e18dc2a1f> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abctvstore.cafepress.com/dancingwiththestars.580096703 | 2013-05-18T05:48:15Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.902758 | 174 |
Recently I've been taking a deep dive into the Reactive Extensions for .NET. This is a wonderful project that comes out of Cloud Programmability Division at Microsoft. Rx helps do to really wonderful things with asynchronous and parallel programming in unreliable distributed world. Do you remember what LINQ did to the collections (and much more)? Well, Rx is going to do (and doing) the same to events, asynchronous and distributed programming.
So if you have to deal anything that requires more than a single thread, process or machine to run - you'll be impacted in some way or the other.
The thing I love the most about what Eric Meijer and his team are doing - the underlying logic which is simple plain and so beautiful. Even the entire IObservable/IObserver thing could be logically derived from IEnumerable by inverting the concepts logically.
Just watch these videos, if you are interested in the details here (highly recommended):
What does this have to do with CQRS, Domain-Driven Design and Event Sourcing?
When I'm building some complex interactions and systems, I'm trying to follow the same principle. System design and evolution are not guided by the intuition or creativity. Pure logic and mathematical reason are the most reliable advisors here (it feels like proving a theorem). It's really hard to explain in words, but logically solid design can handle a lot of things with really little effort (and code) just because of it's nature. Basically it allows to say to new challenges: "we did not code for this, but since this is logical, it already is in the design, you just need to enable this".
While I'm just learning CQRS/DDD/ES I want to do it in the logical way that will prevent me from doing bad and illogical things (which will impact my systems later in their lifecycle). Way of thinking that Eric Meijer shows, seems to help here. Besides, it helps to merge the ideas of Pat Helland (almost infinitely scalable systems) into the overall CQRS concepts.
Reactive Extensions benefit a lot from the marble diagrams representing parallel processes and their interactions. So I've tried to re-apply these principles to my understanding of CQRS/DDD/ES. By mechanically reflecting the logic, here's what I've got for the command handler:
Essentially this picture reflects the flow of commands (marked with D for Do) incoming into the handler. Commands can come as a single or as a batch (that's the marble or tick in this reality). Commands coming together either succeed or fail together.
Each incoming tick translates into a new parallel reality for an aggregate (just like SelectMany in Rx, where you get observable of observable of T). Then we flatten successful commands onto the change stream (each change is a unit of work), while errors are flattened into the failure stream.
There is a message dispatcher that catches up upon these streams and sends domain events, command failures and confirmations back to the message bus. This way subscribers will have logically complete information about what's happened in the business logic. Subscribers could include sagas and event handlers working with read models (which will be used to provide clients with feedback that includes potential command failures).
Note a few differences upon the traditional CQRS with event sourcing approach as advocated by Greg Young:
- Aggregate Root can react to incoming commands by providing a finite stream of events, optionally terminating with error (there is a direct translation from Rx observers here: OnError and OnComplete).
- We save successful change (command(s) and resulting events) atomically as unit of work. Persisting commands will actually let us ensure command idempotency in the cruel world of scalable message queues (with "at least once" deliveries). Essentially this is reflection of Helland's activities that we need to have in the same scope with the aggregates that own them.
- Command failures are also saved (although the stream could be different from the event source). We don't need to save the intermediate events though - just command(s) and the resulting failure.
- Message dispatcher runs upon the failure and change streams, publishing domain events into the message bus. We have logically complete information here, that could eventually be provided for the client (sender) for the retrieval.
- theoretically we can easily process commands for a single aggregate in multiple threads, serializing access to the change and failure streams.
Things that do not fit in, yet:
- In CQRS practice there are cases, when there would traditionally be a call to the domain service (in the command handler and before the aggregate root). This does not fit in here. In a Rx world this would probably be a separate async command handler. Yet this would require an additional layer of translation (another command handler and event handler).
- events and commands are some sort of duals. They are both messages that bring along different intent and help to organize CQRS architecture (this comes from the DDD realm). Yet, this duality (and the rules coming out of it) brings additional complexity, when you need to chain multiple operations (first call unreliable operation, then pass the result to the aggregate, then do something else). I think I'm missing some aspect of commands and events that would help to lay out interactions in a clean and logical way.
That's a theory and logic as I see them today. This means:
- tomorrow perception might evolve into something different that better brings together known patterns and constraints.
- in theory there is no difference between theory and practice. In practice - there is a difference.
If I could bring in sagas, view event handlers and domain services into the picture in a logical way (and without breaking any existing scalability and consistency constraints), I'd be a happy man.
We'll see how it goes (see xLim 4: CQRS in Cloud series for any latest materials on this topic). Meanwhile I'm really interested in your thoughts on this subject. | <urn:uuid:aae437a0-dcca-4c82-a512-d261b6cf812d> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abdullin.com/journal/2010/9/19/domain-driven-design-event-sourcing-rx-and-marble-diagrams.html | 2013-05-18T05:53:46Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.94712 | 1,240 |
If Superman had explored these issues instead of bashing unions and promoting charters, moviegoers might have walked away understanding a great deal about why the families it profiled and so many similar families across America face a bleak educational future.
The movie certainly showed scenes of poverty, but its implications and the structural inequalities underlying that poverty were largely ignored. Devastating urban poverty was just there -- as if that were somehow the natural order of things but if we could only ‘fix’ schools it would disappear.
While you’re reading it, keep this chart in mind (from Alex Knapp at Outside the Beltway):
I’ve complained before about our schools’ obsession with behavior management at the expense of thought and inquiry. But I can see why the people in the blue slice above might be more interested in teaching the kids in the yellow slice to behave than in teaching them to question things.
(h/t Balloon Juice) | <urn:uuid:46758e7d-4a9e-416e-bafd-88118a7a610c> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://ablogaboutschool.blogspot.com/2011_02_01_archive.html | 2013-05-18T06:30:04Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.967775 | 193 |
UK Takeover Code Amendments Come into Effect, Contributed by Alasdair Steele, Nabarro LLP
By Alasdair Steele, Nabarro LLP
The Code Committee of the Panel on Takeovers and Mergers has been consulting on proposed changes to the UK City Code on Takeovers and Mergers (City Code) for just over a year. The consultation and resultant changes largely arose following the outcry after Kraft’s takeover of Cadbury and particularly the subsequent closure of Cadbury’s Somerdale factory near Bristol, despite pledges in the offer document to keep the plant open. Originally, the consultation considered far-reaching ideas such as giving different voting rights to long-term and short-term shareholders and increasing the level of ownership required to control a company beyond the traditional 50 percent level.
Although a number of the more radical possibilities were rejected by the Code Committee earlier in the year, the proposed changes, which were initially unveiled in March 20111 and have now been published in final form,2 make a number of changes to the City Code which will affect the way in which takeover offers are effected. The changes are effective from 19 September 2011.
As expected, and despite some last minute lobbying, the final amendments largely reflect the Code Committee’s previous conclusions and the draft proposals published earlier this year.
The main themes of the changes are:
- Shifting the balance of power from offerors to target companies;
- Ending break fees, exclusivity and other deal-protection arrangements;
- Increasing transparency on advisers’ fees;
- Holding offerors to account for their statements of intention; and
- Increasing employee involvement and information in offer processes.
Changes to the Takeover Code
— “Virtual Bid” Periods
The default requirement in all takeover situations will be that potential offerors must be publicly named and then have a fixed 28-day period to either make their offer or withdraw from the process entirely. The 28-day period may only be extended on the joint application of the offeror and offeree to the Panel. This switches the onus away from the offeree board having to approach the Panel for a “put up or shut up” deadline, in the event an offeror is laying siege to a target for a prolonged period of time without being identified.
This new requirement to identify a potential offeror will only apply when an announcement of a potential offer is required, and as a result, potential offerors will be further encouraged to protect the confidentiality of the process for a longer period of time. Potential offerors will not, however, be able to restrict (or attempt to restrict) the offeree from disclosing their identity where there City Code requires that disclosure.
The Panel is expected to be receptive to requests to extend the 28-day period, particularly where good reasons can be shown why the process is taking longer. Friendly, recommended offers should therefore be able to proceed on a slightly slower timetable while hostile or unwelcome offerors will be forced to move with much more decisiveness.
There is a limited exception from the proposed identification regime and time limits where an offeree announces that it is conducting a formal sale process and seeking one or more potential offerors. The details of the sale process and proposed participants will not then need to be made public. In order to qualify for this exemption, the offeree will need to formally put itself up for sale; traditional “strategic review” announcements, often seen as code for putting themselves up for sale, will not be sufficient.
— Deal Protection Measures
Deal protection measures will be completely prohibited except in very limited circumstances. The restriction will apply to “offer-related arrangements,” which are generally defined as “any agreement, arrangement or commitment in connection with an offer” and will apply to currently common arrangements such as:
- Inducement fee and break fee arrangements;
- Implementation agreements;
- Exclusivity arrangements; and
- “Work-fee” arrangements.
Inducement fees will still be permitted in exceptional circumstances such as where a “white knight” offeror3 makes an offer following the announcement of a hostile offer. The inducement fee will, however, be of limited value as it will only apply if a third competing offeror were to materialise and succeed, not if the original hostile offeror were to succeed.
As anticipated, the City Code itself will now contain specific provisions regarding takeovers which are implemented by way of schemes of arrangement to ensure that offeree companies adhere to any timetable and process agreed with the offeror and included in the offer documentation.
— Disclosure of Fees
The estimated fees payable by offerors and offerees will need to be disclosed in offer documents. These will be broken down by category of adviser, with the fee for each of the offeror and offeree and in respect of the offeror’s financing arrangements being split out separately.
The new rules address different fee structures, such as success fees, by providing the ability to disclose expected fees and maximum fees so as to protect commercially sensitive information, such as the thresholds at which success fees may kick in. Where the disclosure subsequently proves inadequate, updated information may need to be publicly announced.
— Increased Disclosure Requirements
Increased disclosure about the financing of offers will be required, with copies of the financing documents to be made available on the offeror’s website. Certain commercially sensitive information, such as headroom to increase an offer, may be withheld, as may the structure by which equity is provided to private equity offeror vehicles; a general disclosure as to how much is sourced from each fund will be sufficient.
Separately, all-cash offerors need to disclose additional information, putting them on par with offerors offering securities as consideration, though this will not extend to information such as a pro forma balance sheet reflecting the offer and significant change statements since their last audited accounts.
— Statements as to Future Conduct
Following the public and political criticism following Kraft’s closure of Cadbury’s Somerdale factory, the City Code is being strengthened to try to force more and better disclosure.
Offerors will be required to include enhanced statements of their intentions for the offeree business and its employees as well as information about the effect of the offer on its own business. They will then be expected to hold to those statements for either any period specified in the statement or, in the absence of any statement, at least 12 months following the offer becoming unconditional. Offerors will only be released from these statements if there has been a material change in circumstances.
In order to counter the risk that the new rule will encourage vague and general statements, the Code Committee has stated that an offeror should disclose as fully as possible its commercial rationale for the takeover and that general statements are unlikely to be acceptable where an offeror has had an opportunity to undertake full due diligence.
— Employee Involvement
Employees and employee representatives will have enhanced rights to comment on the effects on employment of a proposed offer and to have their costs in obtaining advice to verify the information contained in their opinion paid for by the offeree company.
The Code Committee has stated its view that the costs should be limited to those required to verify the statement by reference to existing sources and not to the provision of general advice as to the opinion or to the commissioning of new research to substantiate an opinion. However, it is likely that there will be debates in the future over the extent of the costs which will be covered, particularly in takeover situations which attract employee and trade union opposition.
In addition, offeree companies will be required to publish the opinion of the employees or employee representatives on their websites (and announce having done so) when the opinion is received too late to be included in the offer documentation. Under the old rules, there was no provision requiring this opinion to be published if it was not received in sufficient time to be included within the offer documents.
— “Virtual Bid” Periods
Where an offeree is in an offer period on the implementation date and if it was in talks with or had received an approach from an offeror at the beginning of the offer period, the identity of the potential offeror will need to be announced by 5 p.m. on the implementation date.
Separately, any potential offeror identified in an announcement made on or before the implementation date must, by not later than 5 p.m. on the 28th day after the implementation date, either:
- Announce a firm intention to make an offer;
- Announce it does not intend to make an offer; or
- Together with the offeree company, obtain Panel consent to an extension of the deadline.
— Deal Protection Measures
Inducement fees or other offer-related arrangements entered into before the implementation date will not be subject to the new prohibition.
— Offer Documents & Offeree Board Circulars
Where the offeror publishes the initial offer document before the implementation date, all subsequent offer-related documents must comply with the City Code’s provisions as they were before the implementation date, irrespective of when those documents are published.
— Employee Involvement
Offeree companies will be required to publish employee representatives’ opinions on a website and announce having done so with effect from the implementation date, even if the offer document to which the employee representatives’ opinion relates was published before the implementation date.
Despite the extensive nature of these changes, the Code Committee has already flagged future areas of amendment, such as imposing an ongoing obligation to update material information as it changes, and not only when the next offer-related document is published.
Alasdair Steele is a corporate partner at Nabarro LLP, specialising in UK and cross-border corporate finance, including public and private M&A, strategic investments and primary and secondary equity issues, as well as regularly advising on consortia and corporate joint venture arrangements, particularly in the infrastructure sector. He regularly advises quoted companies and financial intermediaries on the UKLA Listing Rules and Disclosure Rules, the Prospectus Rules, the AIM Rules, the Takeover Code, corporate governance matters and general company law. Telephone: +44 (0) 20 7524 6422; E-mail firstname.lastname@example.org.
This document and any discussions set forth herein are for informational purposes only, and should not be construed as legal advice, which has to be addressed to particular facts and circumstances involved in any given situation. Review or use of the document and any discussions does not create an attorney-client relationship with the author or publisher. To the extent that this document may contain suggested provisions, they will require modification to suit a particular transaction, jurisdiction or situation. Please consult with an attorney with the appropriate level of experience if you have any questions. Any tax information contained in the document or discussions is not intended to be used, and cannot be used, for purposes of avoiding penalties imposed under the United States Internal Revenue Code. Any opinions expressed are those of the author. Bloomberg Finance L.P. and its affiliated entities do not take responsibility for the content in this document or discussions and do not make any representation or warranty as to their completeness or accuracy.
© 2011 Bloomberg Finance L.P. All rights reserved. Bloomberg Law Reports ® is a registered trademark and service mark of Bloomberg Finance L.P. | <urn:uuid:5a648999-a152-4523-8385-6068eb54fe63> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://about.bloomberglaw.com/practitioner-contributions/uk-takeover-code-amendments-come-into-effect/ | 2013-05-18T06:43:15Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.951654 | 2,329 |
|HOME SCHEDULE AUTHOR INDEX SUBJECT INDEX|
Partitioning of carbon, water, and energy fluxes between understory and canopy in a North Central Florida mature uneven aged pine flatwoods forest.
Starr, Gregory*,1, Powell, Thomas1, Martin, Timothy1, Gholz, Henry1,2, 1 School of Forestry Resources and Conservation, Gainesville, FL2 National Science Foundation, Arlington, VA
ABSTRACT- Of the 5.93 million ha of timberland within the state of Florida, only 19% are maintained under conditions classified as "natural" pine forest. While considerable attention has been focused on the carbon and water dynamics of managed pine plantations in the region, little attention has been given to these natural forests, which are an integral part of the complex mosaic of lands in the region. Based on this importance, it was our intention to quantify how environmental conditions affect ecosystem carbon, water, and energy exchange within a mature pine flatwoods forest and determine how specific components of the system, (i.e. leaf physiology, soil respiration, understory composition and canopy structure), contribute to these exchange rates. During the 2000-2001 field season, the natural pine flatwoods was a carbon sink with an annual net ecosystem exchange (NEE) of 183 g C m-2. The largest portion of this carbon was sequestered during the winter and spring when temperatures were cooler and canopy LAI was lowest. This could be attributed to a reduction in ecosystem respiration losses and a slight increase in understory photosynthetic rates caused by a larger portion of total radiation reaching the understory. Approximately 90% of the respiratory losses from the system could be accounted through soil respiration, which is highly correlated to soil water potential (r2=0.77, p<0.001). Comparison of eddy covariance measurements above and below the pine canopy indicated that 37% of the ecosystemís carbon, 51 % of its latent energy, and 56% of its sensible heat fluxes could be attributed to the understory. Preliminary results show that two species, Serenoa repens and Ilex glabra, comprise 95% of the understory vascular and both have relatively high leaf nitrogen concentration and photosynthetic capacities (~1.4% nitrogen and Amax ~ 4.0 mmol m-2 s-1) and account for ~ 90% of the carbon sequestered by the understory community. These initial assessments provide evidence that natural pine flatwood forest of Florida may be a small regional carbon sink.
KEY WORDS: pine flatwoods, carbon and water exchange, eddy covariance | <urn:uuid:09d8a50e-b5b5-4ac8-9b83-20535564e5da> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://abstracts.co.allenpress.com/pweb/esa2002/document/17486 | 2013-05-18T05:53:43Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.926591 | 537 |
Pneumonia is a common cause for ED visits. How do you decide on whether the patient can be managed as an outpatient or inpatient? To supplement your clinical judgment, many clinicians use the Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) score.
Have you heard of CURB-65, supported by the British Thoracic Society? What about SMART-COP, which is meant to help you predict if your patient will need Intensive Respiratory or Vasopressor Support (IRVS)?
It's worth a quick review.
Feel free to download this card and print on a 4'' x 6'' index card.
Presentations are traditionally given using Powerpoint. Keynote is prettier alternative to Powerpoint but is only Macintosh-compatible. Both have the same antiquated structure such that content is presented only linearly.
The hottest presentation tool now is Prezi, a web-based tool, which allows the viewer to zoom in and out of sections. The visuals are more of a conceptual map of the content, where the viewer or speaker can zoom around any desired topic. Because it's online, you can easily embed YouTube videos.
Take a look at this Prezi demo advocating it as a tool for teaching.
To navigate, you can click on the gray arrows at the bottom to advance forward or backward, as pre-programmed. Alternatively, you can drag the display using your mouse. Or you can zoom in/out using the + or - tools on the right.
Google Docs is constantly improving and growing. One of the cool features is that you can embed any document within your blog. Whenever you edit the Google Docs document, it automatically updates in your blog.
How do I do this?
Within your document in Google Docs, click on the upper right "Share" button and select "Publish to Web".
In the pop-up screen, select "Start Publishing".
Copy and paste the provided HTML code in your blog.
With a little HTML editing, you can make the optimize the margins bigger than the teeny preset dimensions. To change the margins to 440-pixel width and 500-pixel height, add the extra text (in bold) into your code as follows:
And ta-da! Embedded is my handout from a recent talk on mobile apps in Medicine.
A new CME publication has emerged from the publishers of Emergency Medicine Practice and Pediatric Emergency Medicine Practice called EM Critical Care. This new publication is specifically geared towards manging critically ill patients in the ED. There will be 6 issues per year with each issue offering 3 AMA PRA Category 1 credits. Although it has not yet been released, it appears to have an impressive editorial board including Emanuel Rivers, Michael Gibbs, Benjamin Abella and Robert Arntfield. Oh, and did I not mention Scott Weingart from the EMCrit Blog? If it is anything similar to it's predecessors, it is guaranteed to be a hit!
In a Research Letter in JAMA, Dr. Chretien et al describe the profile of physicians in the Twitter universe, specifically focusing on professionalism.
Self identified physician
At least 500 followers during May 1-31, 2010 (Whew, I only have 309 followers.)
Posted a tweet within last 6 months
A total of 260 physicians were studied.
6.2% were from Emergency Medicine.
15% (most) were from Surgery and its subspecialties.
76% were from the United States.
Three physicians independently coded the 20 most recent tweets from each account (total n= 5,156) for unprofessional content. There were 144 (3%) unprofessional tweets from 27 users:
55 (1%) - possible conflict of interest, advocating for non-standard therapies
38 (0.7%) - potentially violation of patient privacy
33 (0.6%) - profanity
14 (0.3%) - sexually explicit material
4 (0.1%) - discriminatory statement
25 of 27 (92%) of users were identifiable
The authors conclude that, although rare, there should be more physician accountability and guidelines in the age of social media. This is even more true, since I just discovered that all tweets are archived by the Library of Congress!
Take a look at your most recent tweets. How would they have performed if you were included in this study?
Reference Chretien KC, Azar J, Kind T. Physicians on Twitter. JAMA: The journal of the American Medical Association. 2011. 305(6), 566-8. PMID: 21304081 .
Dr. Rob Orman of ERCast blog fame emailed me last week about creating a pocket card on Suicide Risk Stratification. In many community ED's, risk assessment is done by the emergency physician. I'm lucky where I work, because we have a 24/7 psychiatric ED, which consults on suicidal patients in the "medical ED".
In the end, assessment is primarily based on physician judgment, because there's no great clinical decision tool, rules, or scores to assess risk. Rob has created his own mnemonic to help you ask the right questions in assessing a suicidal patient. This is a sneak peak into a larger article that Rob is planning to unleash on the world on suicide assessment. Based on his review of the literature and own clinical experience, the mnemonic is: TRAAPPED SILO SAFE.
"Risk factors" which increase a patient's risk for committing suicide in the near future.
"Protective factors"which decrease a patient's risk for committing suicide in the near future.
Feel free to download this card and print on a 4'' x 6'' index card.
* Updated 3/8/11: Added extra "A" to include "Access to Means" as a risk factor.
Ever since my post about the top medical apps, I have been inundated with people asking me to review their apps.
One has stood out.
Medibabble is a real-time medical translation app and is now available for FREE. It was created by two innovative UCSF medical school graduates, Dr. Alex Blau and Dr. Brad Cohn. This app contains an extensive preset list of history questions and physical exam commands. When you click on a sentence, the app will translate and speak the sentence in one of 5 languages (Spanish, Cantonese, Mandarin, Russian, and Haitian Creole).
Take a few minutes to download all of the free languages onto your device. It only comes with Spanish pre-installed. There is a FAQ page at www.medibabble.com. The app is only available for the iOS platform currently.
Does your Emergency Department have computerized spectrophotometric catheters to measure continuous central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) in early goal directed therapy (EGDT) for severe sepsis? That's what was used in the original Rivers' EGDT study.
I've never even seen one before.
Many emergency physicians are getting around not having the specialized equipment issue by obtaining intermittent venous blood gas measurements off of a central venous line.
But what if you had a 30 y/o woman with early pyelonephritis/urosepsis who has severe sepsis by definition? She's got 10 peripheral lines (I'm exaggerating, of course), a normalized blood pressure with early IV fluids, and appears non-toxic. Her lactate, however, is 9! Do you really need a central line? My gut says no, but the EGDT protocol says yes -- for the purpose of CVP and ScvO2 measurements.
Trick of the Trade:
Use a less-invasive approach where bedside ultrasound and serial venous lactate levels replace central venous lines and ScvO2 measurements, respectively.
Last year, JAMA published a landmark study showing that lactate clearance of ≥10% over the first 2 hours is "not a worse measurement" than ScvO2≥70%. This double-negative statistical speak came about because it was a non-inferiority study.
So how does this affect the original Rivers protocol? To review, here's the original protocol, which I posted about earlier:
(click to view larger image)
In the less invasive model:
Fluid resuscitate through peripheral IV access instead of a central line.
Follow volume status either with a bedside ultrasound or urine output.
Follow venous lactate levels at time 0 and 2 hours. If the lactate clearance is ≥10% over these 2 hours, you should follow the algorithm as if the ScvO2≥70%. That means no need for immediate transfusion or vasopressor agents.
How do you know when you have adequately volume-resuscitated a patient using bedside ultrasound? Measure the IVC diameter about 1-2 cm from the right atrium junction.
If the IVC diameter ≤1.5 cm and has ≥50% collapse with inspiration, the patient has a very low CVP.
If the IVC diameter is at least 1.5 cm and has minimal collapse with inspiration, the patient is euvolemic. Move to the next step -- assessing the MAP.
This doesn't mean that all EGDT patient should have ONLY peripheral lines. Persistent hypotension, a non-clearing lactate level, and/or clinical toxicity warrant more invasive monitoring and management.
Scott Weingart has an in-depth, 21-minute podcast about the JAMA article and noninvasive approach to sepsis: Podcast link. Scott also briefly interviews Dr. Alan Jones (Carolinas Medical Center), the first author of the study, in the podcast.
Reference Jones AE, et al; Emergency Medicine Shock Research Network (EMShockNet) Investigators. Lactate clearance vs central venous oxygen saturation as goals of early sepsis therapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association.2010, 303(8), 739-46. PMID: 20179283 .
In its third official year, the Clerkship Directors in Emergency Medicine (CDEM) organization is still growing strong. It all started with six of us at an informal dinner in Boston about 5 years ago. And now the organization has grown so large that it is now for the first time offering annual awards to its members.
Know an award-worthy educator? Nominate him or her!
CDEM Clerkship Director of the Year Award
This award recognizes an Emergency Medicine Clerkship Director that has made significant contributions to either a 3rd or 4th year EM rotation. To be eligible for this award, the nominee must currently be a Clerkship Director of a mandatory, selective or elective rotation and have served in that role for a minimum of 5 years. This award is presented at the annual CDEM meeting.
CDEM Young Educator of the Year Award
This award recognizes a medical student educator at the Clinical Instructor or Assistant Professor level and less than 10 year from residency completion who has made significant contributions to teaching and educating medical students. This award is presented at the annual CDEM meeting.
CDEM Distinguished Educator Award
This award recognizes a medical student educator at the Associate Professor or Professor level who has made significant contributions to and has demonstrated sustained excellence in teaching and educating medical students for 10 or more years. This award is not presented annually; rather, it is bestowed on special occasions.
CDEM Award for Innovation in Medical Education
This award recognizes a medical student educator at any faculty rank who has made a significant and innovative contribution to undergraduate medical education. This award is presented at the annual CDEM meeting.
By learning about our differences, we can learn to appreciate and better communicate with those who are different from us.
The same falls true for working with residents and faculty from different "generations", as defined as traditionalists, baby boomers, generation Xers, and millennials.
This literature review and consensus document is quite extensive and even comes in 2 parts in Academic Emergency Medicine. There is a great summary table of the generational differences in personal, work, and educational characteristics, communication styles, and technology.
Think of faculty who fit in these age groups. Do they fit their generational stereotype?
Traditionalists (born 1925-1945)
Personal characteristics: Loyal, reluctant to change, dedicated, value honor and duty, patriotic
Work characteristics: Value hierarchy, loyal "company man", job security
Education characteristics: Process oriented
Communication style: Formal
Technology: Tend not to understand
Baby Boomers(born 1945-1964)
Personal characteristics: Optimistic, desire for personal gratification, highly competitive
Work characteristics: Workaholic, competitive, consensus builder, mentor
Education characteristics: Learner depends on educator, lecture format, process-oriented
Communication style: Diplomatic
Technology: Not particularly techno-saavy
Generation Xers (born 1964-1980)
Personal characteristics: Independent, self-directed, skeptical, resilient, more accepting of diversity, self-reliant
Work characteristics: Value work-life balance, comfortable with change, question authority
Education characteristics: Independent learners, problem-solvers, desire to learn on the job, outcome-oriented
Communication style: Blunt
Technology: Interested and facile
Millennials (born 1980-1999)
Personal characteristics: Optimistic, need for praise, collaborative, global outlook
Work characteristics: Team-oriented, follows rules and likes having structured time, career changes
Education characteristics: Team-based learning environment, turn to Internet for answers, outcome-oriented
Communication style: Polite
Technology: Very saavy, technology is a necessity
The authors give multiple examples where generational differences come to light but none more so than in mentorship within the academic department.
Traditionalists view mentorship as a more formal process, where feedback is necessary only to provide criticism or suggestions for improvement.
Baby boomers also view mentorship as a "top down" process. They are ok with infrequent interactions.
Generation Xers and Millennialsprefer mentorship as a more "peer to peer" process with more frequent interactions. They value the personal relationships and the opportunity to collaborate in creative solutions. Because of their stereotypical distrust of authority, however, they may inadvertently sabotage their relationship with their mentors. Distrust sometimes is misinterpreted as a general lack of respect.
To overcome these differences, mentor-mentee pairings should take into consideration gender and shared views about goals, work/life balance, and experiences. Early discussions in a mentorship relationship should discuss generational differences and how each envisions the ideal mentor-mentee relationship to be. The pair should agree upon and adopt a collaborative, shared communication approach with frequent feedback.
So much more in this article... Take a read.
Mohr NM, Moreno-Walton L, Mills AM, et al. Generational Influences in Academic Emergency Medicine: Teaching and Learning, Mentoring, and Technology (Part I). Acad Emerg Med. 2011, 18:190-9, 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2010.00985.x .
A 50 year-old woman, who presented to the ENT clinic for followup check of a facial fracture, has a blood pressure of 210/100. She is asymptomatic and in no pain. She gets referred immediately to the ED for care.
Now you see her in your ED. What next?
There is a lot of controversy whether you should treat or not treat asymptomatic hypertension in the ED. The ACEP Clinical Policy says that there is no need to immediately reduce an asymptomatic patient's blood pressure. With "close followup", they can be referred to their primary care physician.
With so many patients being uninsured or unable to access their primary care physician on short notice, many emergency physicians like myself are slowly moving towards starting antihypertensive medications for them.
If you do decide to start an antihypertensive, which medication do you choose? This Paucis Verbis card is based on a 2009 Cochrane Review, and summarized in American Family Physician in 2010. The blue numbers denote a Risk Ratio (RR) which cross 1, meaning that there is no benefit. The red numbers denote a RR < 1, meaning that there IS a benefit.
A low-dose thiazide, such as hydrochlorothiazide 12.5-25 mg po daily, is a safe and effective choice.
Feel free to download this card and print on a 4'' x 6'' index card.
References Quynh B. Cochrane for clinicians. First-line treatment for hypertension. Amer Fam Phys. 2010, 81(11), 1333-5. Mensah G, Bakris G. Treatment and Control of High Blood Pressure in Adults. Cardiology Clinics. 2010, 28(4), 609-22. ..
EMCast - Monthly podcast interviews with Dr. Amal Mattu through Emedhome.com ($99 annual subscription)
CDEM Curriculum - Resource put together by CDEM for medical students which includes essentially an online textbook in EM (free). Rob even put in a plug for my Digital Instruction in Emergency Medicine (DIEM) online simulation cases. I'm not actually done with all the cases, as Rob suggests! Only the first case on Chest Pain is done thus far... Ack! I better get crackin' now.
Spend a high-yield 25 minutes listening to Rob's take on need-to-know educational resources in EM.
A health care worker hurried in to the ED after being poked with a needle.
'It was an old 18G needle with dried blood', she said. Her puncture had drawn blood. You discussed the very low risk of contacting HIV and the side effects of postexposure prophylaxis (PEP). She asked, 'What does very low risk mean?'
Is there another way to covery risk for patients?
Trick of the Trade: Convey probabilities with everyday risks.
This article uses a risk stratifying tool to convey probabilities that compare to everyday risks such as flying, cancer diagnosis, having an MI, etc. Below is the calculation tool from the paper.
Using this tool, the risk of contacting HIV for this patient would be:
5/ (1000 x 100 x 100) = 1/ 2,000,000
According to the everyday risk table in the article, this is similar to the risk of dying in the next 12 months from lightning. You left her to decide on PEP.
As the author pointed out, the risks cited are probabilities instead of exact measurements. This is an important caveat.
I find this helpful to provide context, especially for those who have difficulty deciding on PEP.
Vertesi L. Risk Assessment Stratification Protocol (RASP) to help patients decide on the use of postexposure prophylaxis for HIV exposure. CJEM : Canadian journal of emergency medical care. 2003, 5(1), 46-8. PMID: 17659153
Many academic Emergency Departments are staffed by non-EM residents. Dr. Amer Aldeen and his super-star team from Northwestern created NURRC Modules (Northwestern University Rotating Resident Curriculum). These modules allow the off-service residents, who all have different schedules, to learn key EM-based topics at their own leisure and convenience.
The positive effect of the curriculum on the off-service residents' medical knowledge was recently published in Academic Emergency Medicine: Read my review.
NURRC Video Modules:
ENT and Ophthalmology Emergencies
Obstetrics and Gynecology Emergencies
Trauma and Wound Care
Thanks to the team for agreeing to make these videos free for everyone to use.
I hope I wasn't too pushy or forward in asking for the videos... and then asking if I could post then all on YouTube! Such a great resource shouldn't live behind closed doors. I'll post the other 3 videos once I receive them from Amer.
It is 2 a.m. You, the resident, have just spoken to your staff/attending, who told you to do a task. You have seen one, but don't feel comfortable doing one independently.
Will you tell your staff/attending about how you feel?
What if the patient did poorly after that?
This study examines the perception of EM trainees of their competence and adverse events and how they feel about reporting them.
Anonymous web-based survey sent to all trainees from 9 EM programs in Canada outside Quebec.
37.3% trainees responded.
40% trainees felt they had minimal supervision when doing a task that they did not feel safe about.
Most 'unsafe' tasks included providing care overnight, admission decision or procedures.
When feeling incompetent, a third of trainees will not report this to their staff.
Barriers include worry about loss of trust, automony or respect.
64% trainees felt responsible for contributing to adverse events.
Most relate to procedures - chest tubes, central lines, paracentesis.
Majority, but not all, reported the most serious events to the staff.
Barriers include fear of appearing incompetent and humiliation.
How would I change my teaching practice
Ensure trainees feel safe. Maybe do a dry run of central line insertion/break bad news prior.
Encourage trainees to voice their discomfort. They are learning, not just working.
Discuss adverse events and medical errors with trainees.
Reference Friedman S, Sowerby R, Guo R, Bandiera G. Perceptions of emergency medicine residents and fellows regarding competence, adverse events and reporting to supervisors: a national survey. CJEM: Canadian journal of emergency medical care. 2010, 12(6), 491-9. PMID: 21073775
Medgadget annually hosts a contest for the best medical blogs. It's the Superbowl of blogs.
Our blog was nominated for the Best New Medical Blog last year, but got our butt kicked.
This year, we're honored to be a finalist in the Best Clinical Sciences Blog category. That's the great news. Unlucky for us, we are in the same category as the juggernauts EMCrit (also nominated in the overall Best Medical Blog category) and Resus.M.E. I do love the fact that the EM specialty is dominating with 3 finalists in this list of 5.
With all of the amazing, sunny weather here in California, I feel (briefly) terrible for all those braving the snowpocalyptic conditions across the United States. So, in honor of all those bundled up and shivering, I wanted to review the management of accidental hypothermia.
Tip: Avoid jostling the hypothermic patient too much because of myocardial irritability. Don't send your patient into an arrhythmia.
Feel free to download this card and print on a 4'' x 6'' index card.
In his talk (subtitled "School Sucks"), Northwestern University Physics Professor Dr. Tae describes how he would improve math and science education. While this is directed at college studies, some of the concepts are applicable to teaching Emergency Medicine.
He shares a lot of great insight, but I wanted to focus on one concept in particular:
The secret to learning = "Work your ass off until you figure it out."
Dr. Tae demonstrates this as we watch him make 57 failed attempts trying to learn a new skateboarding trick before finally being able to successfully complete it on the 58th. In order to master this new skill, he had to actively struggle with it until he succeeded. He contrasts this with lectures where students "just sit there" passively, learning very little.
Clinical decision making is a skill, much like skateboarding, and our job in teaching this may be to let the students do most of the work. We're only there to offer guidance and point them in the right direction when necessary. So how can we challenge our students to struggle and fail until they ultimately figure it out?
Share your thoughts and ideas in the comments. Thanks!
Patients with a hairy chest may require little patches of hair to be shaved when applying EKG leads. This allows the leads to stick firmly to the chest. Loose leads will result in either an artifactual signal or no signal at all on the EKG machine.
How can you obtain an EKG without shaving little patches on the patient's chest?
Trick of the Trade: Cover EKG leads with damp gauze
Water maximes the contact surface area between the EKG lead and the patient's skin. The water easily conducts the cardiac electrical signal.
Generously soak gauze with water.
Apply gauze over each EKG lead where it contacts hairy skin.
He is an Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine and Clerkship Director at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, IL. Rahul has led the charge in building CDEM's educational site at www.cdemcurriculum.org, which essentially is a free online textbook for students on their EM rotation. His amazing technological saavy and passion for education in EM make him a perfect fit on our blogging team. I've been begging him to join us for over a year. We're lucky to have him!
Wednesday's post is his first (of hopefully many).
Well I finally took the leap and am primarily relying on my iPhone to look up medication doses, which I don't know off the top of my head. Gone are the days of purchasing Tarascon's pocket Pharmacopoeia every few years or so.
I still haven't settled on which I like more. Both are free. Both are available on multiple platforms, including iOS, Blackberry, and Android. Both have some unique features which I find useful.
Common strengths for both apps:
Easy to find drug you are looking for. Epocrates has a Search screen as the home page. Micromedex has a Search screen and alphabetical list of medications as the home page.
Dosing adjustments based on renal and hepatic function
Adult and pediatric dosing recommendations
Safety information with preganancy and lactation
Unique strengths of the apps:
Includes toxicology information for all the medications (what to do in case of an overdose)
I have heard that this Thomson Reuters app has been more peer-reviewed and accepted as a very reliable resource, especially for pediatric dosing.
Free from obvious advertisements (which is sometimes seen in Epocrates via the Doc Alerts)
Has pricing information
Allows user to identify unknown pill based on pill characteristics (color, shape, etc)
Ability for you to take notes on the app
They both will likely answer 99% of what you are looking for from a drug-prescribing perspective. So, which do you prefer and why? | <urn:uuid:7fd745be-c67a-4056-b3dc-570d8f5e1dab> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://academiclifeinem.blogspot.com.au/2011_02_01_archive.html | 2013-05-18T05:24:05Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.932867 | 5,601 |
RUSTON – Services for Dr. Milton Johnson, Jr., former head of the La. Tech Electrical Engineering Department, will be Wednesday. He died July 27.
He was on the La. Tech faculty for forty years and formerly served on the Ruston Planning and Zoning Commission.
Survivors include a son and two daughters.
Arrangements are by Owens, Lewisville, Texas.
U.S. Navy vets of World War II
NEW ORLEANS -- Services are this week for three decorated U.S. Navy veterans of World War II who died over the weekend.
William Cade, Sr., died July 29 at age 86. Services will be Thursday.
He was a landing craft engineman who transported countless American soldiers to Omaha Beach on D-Day. He retired from the Navy after 20 years service.
Survivors include his wife Rosemary, five sons and a daughter.
Arrangements are by Leitz-Eagan.
Dr. John R. Bond died July 29 at age 94. Services will be Saturday.
He was a submariner (USS Redfin) in World War II and a long-time dental surgeon.
Survivors include his wife Ramona and three children.
Arrangements are by Lakelawn, Metairie.
Dr. John Michell, 90, also a Navyt vet, died July 27. Services will be Saturday.
Survivors include his wife Muriel and three children.
Arrangements are by Lakelawn. | <urn:uuid:82516c5c-6d62-42e3-b8cd-37a605bb427a> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://acadiaparishtoday.com/pages/full_story/push?article-Deaths+Elsewhere%20&id=19633566&instance=secondary_sports_left_column | 2013-05-18T04:56:32Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.980522 | 317 |
It’s probably the height of arrogance for me to write a post about how one should taste whiskey. There are loads of people out there who have already covered this base, and they are far more knowledgeable on the subject. For me, whiskey is first and foremost about stories and anecdotes. The tasting of the alcohol is simply the fuel that allows the stories to flow more freely (oo.. how poetic! I’ll have to remember that bit).
But, for the sake of those out there who have never thought about “tasting” whiskey, it’s good to put this information out there. And since I will be posting various tastings on this here site, it’s a good idea to give you all the process I will be using.
First and foremost, let’s get one thing out of the way. There’s a huge chasm between the idea of tasting whiskey and the idea of enjoying whiskey. One activity does not necessarily have to include the other. If you enjoy making cocktails out of the various whiskeys available on the market, then have at it. But it’s impossible to get a clear taste of whiskey once you adulterate it with bitters, ginger ale, or sour mix.
Additionally, tasting a whiskey involves more than simply putting it into your mouth and swallowing. It’s an encompassing experience, using the same amount of our senses as we use when consuming any other food or drink. So let’s define tasting as the act of learning the characteristics of the flavor of whiskey through the use of the senses. But which senses? The same ones used for tasting wine and judging food – seeing, smelling, and tasting.
The eyes gives us insight into the drink. It can tell us how young it is, or the kind of barrel in which it was aged. Generally speaking, the lighter the whiskey, the younger it will be. Whiskey straight from the still is often white, while there are some whiskeys out there that have been aged so long than they have a deep red to them. Bourbon gets it amber red color from the new and freshly charred oak barrels used in its aging process. If bourbon did not use new barrels, or if they didn’t char the new barrels they did use, the Kentucky spirit would have a completely different color.
Finding the nose of the whiskey is even more important than the look of it. Some would say that the aromas of the whiskey is more important than the taste. From my reading, I’ve found that it’s not uncommon for blenders to base their recipes primarily on aromas. But if you’re not a blender, the nose is of secondary importance, behind taste.
To release the aromas of whiskey, a little water may be necessary. The best way to think of this is that a bit of water wakes up the whiskey that has been asleep from anywhere from 3 to 25 years. But how much water? According to Michael Jackson, you want to add just enough water dilute to around 30% alcohol by volume. Roughly speaking, this translates to a .5 to 1 water to whiskey ratio if your drinking 80 proof whiskey, or a 1 to 1 water to whiskey ratio if you’ve found yourself a whiskey that’s 100 proof. This is simply a rule of thumb, and one should expect many exceptions to this, especially in the older whiskeys.
A quick side note – ice should be avoided, as well as chilled water, as they close down the aromatics of the whiskey. The water added should lack any obvious characteristics of its own. For example, you wouldn’t add mineral water to your whiskey. It is said that the best water to add to the whiskey is the water found at the site where the whiskey was distilled. Since I’ll assume that the vast majority of you out there are not millionaires, and cannot fly off to Kentucky or Speyside simply for a drink of whiskey, let’s just stick to bland water.
So what are you looking for when you smell a whiskey? That I’ll leave up to you to decide. From my point of view, there are no wrong answers to this question, because tasting is a very personal experience. If you place your snoot in a dram and the aromas remind you of Newark, then by god, that’s what you experienced. Yes, there is a vocabulary used by professional tasters, and usually they are simply variations of more broad terms (woody, fruitful, medicine, smoky, citrus-like). The aromas you find will likely trigger some sort of sense memory. The skill of a professional taster is to put a very specific and accurate word to describe their own sense memory. Or to put it another way, an amateur taster may say that a drink smells a bit fruity and a bit woody. A good taster will say that a whiskey carries a strong oak smell with an undercurrent of raisins. A great taster will say that the whiskey had been in two different casks, one that used in bourbon and the more recent one used in the making of sherry; additionally, there are hints of currants and peaches, as well as a little bit of vanilla.
All of these answers are right. The reason the last taster was able to put more words to the aromas was because they do this activity more often.
That’s the end of part 1. Tomorrow, I’ll post about whiskey glasses, and what to do once you actually put the whiskey in your mouth. And, as always, feel free to correct any of my mistakes by addressing them in the comments of this post. | <urn:uuid:574a5d4e-cf33-4332-b205-9d281ca214eb> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://accidentalhedonist.com/how-to-taste-whiskey-pt-1/ | 2013-05-18T06:43:12Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.959722 | 1,182 |
Acem Meditation is easy to learn. Personal instruction and guidance ensure that you get a good start. Group discussions help you to deal with beginner’s problems and to establish a meditation habit.
A beginner's course usually consists of 2-4 sessions, each providing ample opportunity for personal practice followed by guidance and discussion. Groups of 5-15 participants meet for altogether 7-12 hours. Topics covered include:
- Brief introduction and personal instruction
- Applying the basic principles to your own practice
- From stress relief to personal process
- Scientific research and the psychology of meditation
You learn how to use Acem Meditation for relaxation and stress management, and you lay the foundation for a fascinating process of personality development and self-understanding.
The book Acem Meditation - An Introductory Companion is included in the course fee. While you cannot learn the technique from a book, a CD, or the Internet, the psychology of meditation stimulates your practice and provides a fuller understanding of the process.
After the course, you can practise the technique on your own, whether you choose to become a regular meditator or to meditate whenever you feel the need.
If you wish, you may continue to discuss your meditation practice with a qualified guide after the course. You may also choose between a number of follow-up activities, such as group meditations, talks and lectures, the follow-up courses M1 and M2, as well as weekend retreats where you can get away for a while and recharge your batteries.
All instructors have been through several years of training and have long teaching experience.
See details for each course in the right sidebar. | <urn:uuid:0652ebf6-e5c8-439f-b6f3-deffee5f8b93> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://acem.com/allobjects/acemcourse/curso_de_principiantes23 | 2013-05-18T06:44:18Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.923953 | 338 |
Making the Case for Action
This fact sheet(pdf) and slide deck provide essential state-specific information that addresses the economic imperative, the equity imperative, and the expectations imperative of the college- and career-ready agenda. These resources can be used on their own or serve as the foundation for a personalized presentation or fact sheet(word), which can be customized with state-specific details and examples. The PowerPoint, in particular, was developed with various users in mind and offers a wide range of case-making data that can be drawn from to support your own advocacy efforts.
Advancing the Agenda
As states continue their efforts to promote college and career readiness, Achieve regularly surveys the states to identify their progress in adopting critical college- and career-ready policies. Below is a summary of Idaho's progress to date:
See Closing the Expectations Gap for more information
State accountability systems focus the efforts of teachers, students, parents, administrators and policymakers to ensure that students and schools meet the established goals, including the goal of ensuring all students graduate ready for college and careers. Idaho has yet to begin to use any of the key college- and career-ready indicators in their accountability system.
|Annual School-level Public Reporting||Statewide Performance Goals||School-level Incentives||Accountability Formula|
|Earning a college- and career-ready diploma|
|Scoring college-ready on a high school assessment|
|Earning college credit while in high school|
|Requiring remedial courses in college|
For an explanation of the indicators, their uses and Achieve’s minimum criteria for college- and career-ready accountability, see here. | <urn:uuid:3b2c1a91-4f52-464d-ad69-49c1cbadaba8> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://achieve.org/Idaho | 2013-05-18T05:54:50Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.927479 | 341 |
We have a Winner!!It was a small little group for this Giveaway! But that meant better chance for all.
Congrats to Sherry. I will email you. Your book will be mailed from Hachette.
Thanks everyone for stopping by and participating.
Thank you Anna from Hachette for providing books for this giveaway.
***** please check back soon for my Review on this beautiful book ******
There were 3 items in your list. Here they are in random order:
Timestamp: 2008-11-15 19:27:05 UTC | <urn:uuid:e29e094e-6de9-4ebd-8acf-04873a2b6a0a> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://acircleofbooks.blogspot.com/2008/11/winner.html?showComment=1226783460000 | 2013-05-18T04:55:41Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.934131 | 118 |
Well, these are still some
difficult questions to answer with pin-point accuracy, and at this point I don't
believe anyone has the exact answer to all 3 of these questions. What I offer
below is a mix of what I Think, What I know and what Appears to be....
Anyone currently attempting to
answer these questions with some type of "Universal Knowledge" on the
subject--is Full of BS--BEWARE! Yes, that includes Me. I don't have the
Complete answer to these questions--and neither does anyone else. This is
a subject that needs to be studied in-depth by someone that has all the
resources to carry it out: Lab, veterinary knowledge/skills, Acrochordus snakes,
What is it:
At this point--I don't know, but here
is what I believe based on experience, observation and research: The skin of the
Acrochordus javanicus and arafurae is very impermeable. So, that makes it a very
protective mechanism against the outside world. It is commonly understood that
"Stress" causes a reduction in the ability of the immune system to do its
job--in humans and other animals--including Acrochordus snakes. Stress appears
to cause a decline in the immune system of Acrochordus snakes causing a decline
in the effectiveness of the skin as a protective barrier against the outside
world. This loss of effectiveness increases until Secondary Infections set in and
ultimately kill the animal.
Where does it come from:
See the paragraph above and add:
Improper Husbandry. Yes, it really is that simple. In the Wild, these animals
have the ability to move from Habitat to Habitat--Microenvironment to
Microenvironment. Even though the White Spot Fungus appears to be a "Captivity"
Problem--the snakes in the Wild maybe be able to prevent it--not by some
"Magical Bacteria", but, rather: by simply selecting
Environments/Microenvironments that they are "Happy" with--i.e., minimum
sustained stress level. In Captivity--the snakes don't have that choice. Plain
and Simple. Additionally, it appears that the more acclimated to captivity that
these snakes get--the more secretive and stress prone they become.
How do We get rid of it:
Proper Husbandry--Yes, it really is
that simple. Reduction of "Stress" will reduce the Progression of the White Spot
Fungus. I have seen it myself. Elimination of Stress will Halt the progression
of White Spot Fungus. Note: I did not say anything about chemicals, medications,
etc.--just eliminate the Stress and the progression of the White Spot will stop.
What is there will remain until the next shed. After the next shed--the animal
will be clean and remain that way--as long as all of the husbandry parameters
are and remain in order. Its just that Simple. A new animal going through the
acclimation process may need to shed 2, 3 or even 4 times before the White Spot
relents completely. However, its progress should be visibly reduced with each
So, what is "Proper
Husbandry"? Well, that's what this website is about. No, I don't have all the
answers right now, but I've come a long way in the last couple of yrs dedicated
to these snakes.
1) If You are genuinely
interested in these snakes--then read this website: Every page, every word, look
at every picture. This website is not setup for those who are just mildly
curious at best. Those folks are more then welcome here. But a lot of
information is "Hidden" within the text for those who are serious about these
animals. Nothing is truly "Hidden", but even this explanation is not sitting on
the Front Page for the "Scanners" to see.
2) Spend the hours necessary
researching these animals for Yourself. Right now, the more people that reach
the same conclusions--based upon knowledge and experience--the Better. The
Online Bibliography at the
link is a Good place to start.
3) Acidic water (pH~6.0), Low
TDSs (~200ppm), Low light--especially in the hide, Lack of vibrations, etc are
Good key elements to the reduction of Stress and the furtherance of "Proper
Recently (4/2007) I have seen
a couple of "For Sale" ads for Acrochordus javanicus for one vendor that are
wrought with misinformation--therefore: Misguidance on the keeping of these
snakes. One ad was for CB Babies basically stating to put them in acidic water
and because they are CB and White Spot free--You (the buyer) don't need to worry
about any future "Bacterial Infections". Sorry, it just doesn't work that way.
The current ad states:
"I have adult specimens of Acrochordus javanicus, about 4' in
length. Perfect specimens with no scrapes, scar, and most importantly NO SKIN
BLISTERS! As many people know WC adult Acrochordus javanicus are very rarely
offered for sale, primarily because of the high mortality rates due to improper
packaging during transport which causes skin blisters (Pseudomonas bacteria
which cause septicemia, aka "Blood Poisoning").
You won't have to worry about that here. These adults came in perfectly and
there were transported correctly. I am only able to offer unsexed specimens.
This species is usually female heavy. There are many reports of this species
being able to be parthogenetic, with LTC females "cloning" themselves. A great
display snake, they feed on fish. As with all Acrochordids, I reccomend great
filtration and the regular addition of a product called "koi zyme."
I am asking $250.00 per a specimen, quanities are limitied. Once
these are gone I will be a few more years until such nice large animals come
Information. Improper packaging/shipping is only one factor and most importantly:
"You won't have to worry about that here." That's Pure
Non-Sense. I am familiar with
this particular individual. He claims to have "...many years of Experience with
Aquatic Snakes." and apparently did a stint at a local zoo which I guess makes
him a Guru in his own mind. His website is and has remained void of his Great
claims of "accomplishments" (suddenly that's changing 6/07 LoL) and has been up for a few yrs now. Buy the
snakes--just don't buy into the BS claims. Apparently this person thinks that
you just need to buy the "Clean" animal from him, toss it into "acidic water"
via peat moss, add Koizyme and Wha-La: Instant Acrochordus! Again, Sorry, it
doesn't work that way. If it were that simple: Someone would have
figured it out a Looong time ago. I have used Salt, Koizyme, Melafix and
Pimafix. I have also researched those products and contacted the manufactures
with any specific questions that I had. One thing that I can tell you is:
None. Not One of those products are necessary to successfully
keep an Acrochordus javanicus or arafurae, Or halt the White Spot Fungus. More
importantly, in reference to the Ads,--Just because You receive a clean
animal--doesn't mean that it is going to stay that way. That whole
thought process is coming from a Total lack of Experience. If that
were True--Plenty of people would be successfully keeping
Javanicus. Am I being
Hardcore: Maybe. But I don't think that I am. I am tired of seeing these snakes
die--that's why I am working with them with the dedication that I am. That's why
I put up this website--including all of the hours and hours of putting it
together and the added expense. That's why I am willing to Openly call these
so-called "Gurus" out here--and on the Forums. Sadly, they don't go
"heads-up" with me in public any more. They just continue to hold onto their
erroneous beliefs and pass along their Bad Information. These
animals will always go to the skin trade. But let's get it together and get them
established in captivity, so they will always be around, and so people will be
able to experience and enjoy their unique presence. I'm no rocket scientist, but
I am a guy that can do research and think my way through most problems. If
Acrochordus husbandry was as simple as some make it sound: This website would
not be here. And You can tell from reading this website that A) its not that
simple, and B) its a lot more involved than the "Gurus" want You to believe. I
have come across a number of individuals that all claim that they have kept
Acrochordus snakes long-term. Notice: the Past tense of: HAVE!
Strangely, None of them happen to be "Currently" keeping
them. Always--Past Tense! Hmmm, I'll leave You to Your Own
Conclusions on that one. Just Beware of the "Claims" out there.
Follow the path that You feel is Best--but base it upon Research and,
White Spot Fungus? Its caused
by Stress and, basically, it appears to be a break-down in the skins ability to
protect the animal from the Outside World, eventually leading to Secondary
Infections that lead to the demise of the snake. There is No "Magical" Bacteria
that Your snake was or was not exposed to in the wild--these snakes die in captivity
from White spot all over the world--including captivity in Asia that contains
water from their own natural environments. Improper Shipping is not the sole
source of White Spot, Skin Blister, Whatever. Animals that Arrive in Your hands
"Clean" Will develop White Spot if Housed Improperly and
Will die from it if the Husbandry Parameters are not Corrected.
Wild-caught, Captive Born, Captive Bred and Born--doesn't matter. Tolerance is
the only difference between these animals--Environmental Imprints on their
brain. Captive Bred and Born babies are always at least a bit easier then
Captive Born babies. Captive Born babies are always a bit easier than
Wild-Caught babies. Wild-Caught babies are always easier then Wild-Caught
adults. Acrochordus snakes are no different.
If You see White Spot fungus
on Your animal--the First question is: Is it Progressing? If it is, then
You probably need to fix something. If not, then the animal may just be
acclimating (If new or just put into a new setup), or the source of stress was
temporary and has already been corrected. Is it a "Death Sentence"? No,
definitely Not. So, don't Freak-out and start adding Salt or any of that
other stuff. Don't start ripping the snake out for Salt Baths, Melafix Dips or
any of that non-sense. You will just be ADDING stress. Just
step back and look at the Big Picture. Observe the snake's behavior. Try to
calmly sort out what may be wrong. As stated in the
Javanicus Caresheet: It could be something as simple as Your kid(s) or 150lbs
Rottweiler bouncing around on the wood floor, or the Thumping from Your too cool
Home Entertainment System. White Spot Fungus is just an indicator that let's You
know that the snake is stressing about something. But it can kill
Your snake--if You don't do Your Job.
This Information is offered on the Acrochordus
javanicus and Acrochordus arafurae Filesnakes as is. This Information
is not offered in reference to any snakes other than the Acrochordus
javanicus and Acrochordus arafurae Filesnakes and even so:
use at You Own Risk!
Additionally, this caresheet is obviously based upon admittedly limited
experience! It is not intend to be a recipe of do this, do this, do this---Bam!
You have a cake. It's intent is to offer more of a conceptual understanding of
these fascinating creatures and their apparent needs both in the wild and in | <urn:uuid:04af5650-b7ba-42b0-af26-e8a95cfaedf9> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://acrochordus.com/whitespot.htm | 2013-05-18T05:59:08Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.941768 | 2,763 |
Society of Consumer Protection S.O.S. Poprad from Slovakia is organisation fighting for straitening citizen, consumer and patients´ rights.
In order to make basic European rules of consumer and patients ´protection more accessible to blind and purblind people Society of Consumer Protection S.O.S. Poprad has published in cooperation with Slovak Library for Purblind People first Consumer Protection Dictionary in Braille. This unique publication is now available in thirty libraries and eleven regional branches of Union of Blind and Partially Sighted Slovakia.
This would be the wished outcome of a project fulfilled by a joint venture of Pain Alliance Europe (PAE), Active Citizen Network (ACN) and Grünenthal. A project designed to show the community how chronic pain patients experience the help they receive for the government and the healthcare professionals. But it is more than this.
After the presentation to the Senate of our dossier in terms of fuel poverty, "Energy and chronically ill", made with Acquirente Unico, the Authority for Electricity and Gas has shown not only to be able to act very quickly on important issues, but also to carefully consider the "civic" information produced by the associations.
- FUTURE ACTIVE CITIZENS: VOLUNTEERING AS AN EXERCISE OF DEMOCRACY
- The patients’ involvement on Health policies in Europe: the citizens voice in Cancer Care decision making process
- PAIN PATIENT PATHWAY RECOMMENDATIONS
- Summer School for civic leader in HTA: the Italian experience
- The Engagement of Cittadinanzattiva in the Fight against Useless Pain
- Programme - 6th European Patients' Rights Day
- 6th EUROPEAN PATIENT'S RIGHTS DAY
- 5th EUROPEAN PATIENTS’ RIGHTS DAY
- 4th EUROPEAN PATIENTS’ RIGHTS DAY
- 3rd EUROPEAN PATIENTS’ RIGHTS DAY
- 2nd EUROPEAN PATIENTS’ RIGHTS DAY
- 1st EUROPEAN PATIENTS’ RIGHTS DAY
- ASSESSING PATIENTS' RIGHTS IN EUROPE
- MONITORING PATIENTS' RIGHTS IN EUROPE
- EUROPEN CHARTER OF PATIENTS' RIGHTS
Read all > | <urn:uuid:2178a29b-8ebd-4286-bf29-ea4790939202> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://activecitizenship.net/network-news.html | 2013-05-18T04:54:51Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.879133 | 486 |
Groups are smaller communities within the larger ActiveRain. Join groups created by others. or start your own and
get others to join
This is the place to view the past and present contests put on by ActiveRain and its members. Everyone can join the
group and help encourage each other. Current contest will be highlighted posts so it's easy for you all to see. Let it
Curious as to what others in your profession think about a certain product or tool?
AR's community takes the time to leave honest and transparent reviews of their experiences
so you can be a bit wiser about your purchase.
Broken down by categories and subcategories for easy finds
Get an unfiltered look at what real users are saying
Leave a review yourself for others to benefit from
Add new products as you use them and gain points for doing so
ActiveRain University (ARU) provides free on-line training. We coach, consult and support real estate professionals about real estate trends, technology and social media.
ARU Calendar provides class types and registration links
Watch short tutorials on updating your photo, inserting a hyperlink and much more
Sign up for the Daily Drop so you don't miss out on AR's daily happenings
Find answers to most FAQ's
Whatever it is you're into and wherever you are, AR surely has a group for you to join.
Brand, off the wall, specific subject matters…whatever it is you're looking for.
Each time you write a post you can syndicate your post to 5 groups.
And if by chance you don't find what you're looking for, start a new group today!
Get your content in front of more eyes
Search by location or type
Feel free to start your own group
Find some that are close to home and close to heart
Each month AR runs numerous contests as a way for our members to engage in activities
that will boost their business and increase their visibility in the community and beyond.
Earn points by partaking in these contest and climb the leaderboard
Do what's good for you and your business by participating
If you have an idea for a contest, just let us know
Stay motivated and on track with new contests popping up each month
Ask a Real Estate Question
Here's another avenue for you to build relationships with others. Share your expertise with someone searching for answers.
Play the teacher role and help someone out today
Your Homepage will alert you of new questions in your state
A wonderful way to open a door to a possible new client
Ask a question yourself to get help
These state pages or hyper-local pages provide content directly related to a specific geographical location.
State, County, City and Neighborhood pages make it easy for consumers to find what they're looking for.
Post your listings, school information, local events, market reports and more
Consumers peruse these pages for information
Farm your niche market and cover all the happenings in your neighborhood
Over his 40 years(1971) selling real estate, Victoria real estate expert Fred Carver has enjoyed not only awards and recognition for his quality service, but a track record of successful relationships and results that keep clients happy and loyal.
A very high achiever who settles for nothing less than the best, Fred has excelled in selling all types of real estate throughout Victoria, from bare land and acreages to new and existing homes, and prime luxury and waterfront properties.He also has expertise locating and selling land for condominium projects in which he’s involved from start to finish, as well as new and existing apartment buildings in Victoria, Oak Bay, James Bay, Fairfield, Rockland, Saanich and the West Shore.
This native Victorian, a rare breed in his field, possesses an unparalleled understanding of his market, which he considers “Canada’s Best Kept Secret.”Fred maintains a wealth of knowledge, resources and connections that help streamline deals and ensure that the job always gets done right.
Whether you are looking to buy or sell a home in the Greater Victoria area, with Fred on your side you’ll always enjoy a win-win situation thanks to his eye for value, thorough service, proven marketing, and no-nonsense negotiating.
It’s no wonder that Fred is rewarded with 100% referrals – because he gives back 100% to pleasing all his clients.“As my client you’ll receive my undivided attention when it comes to providing the level of service you deserve, and tending to each detail so your transaction closes smoothly.”
In the course of his career, Fred has served on many committees on the Victoria Real Estate Board. Fred sat on the MLS Committee’s sub-committee to develop a NEW Live Open House website for consumers in Victoria and beyond.Fred is also a founding member of the original IC&I Division of the Victoria Real Estate Board, now known as the Commercial Division.
Yes, experience counts, so call the professional who puts his experience to work for you –
Call Fred CarverDirect 250-598-2963. Toll-Free 1-800-663-2121.
Fred is a high achiever and settles for nothing less than selling your home fast and for the right price and believes in a win-win relationship!
Fred is also a past member of the Oak Bay Lions Club and has held many positions, including President.
If you're serious about selling your Victoria home or property , meet with Fred. He is a true real estate professional interested in getting your property sold fast and for the most amount of money! Fred has been an award winner many times and uses his vast experience to consult his clients on buying and selling real estate in Victoria. After all these years, Fred does what he has done most of his life...sell real estate successfully, honestly and effectively.
In this rapidly changing world of computers and technology, we have found that positive thinking continuous education, teamwork and adaptability are the keys to providing excellent customer service and success in this decade.
Our vision is to be the Real Estate company of choice for a new generation of professional real estate agents and owners.
Our belief is real estate buying and selling to the public is best served when the real estate industry is viewed as a local service business driven by individual real estate agents...such as a Victoria Realtor like Fred.....
100% Referral... means,
A 100% of my time and energies to servicing my clients.While most agents are spending the vast majority of time, energy and money seeking new clients and promoting themselves to the general public, I approach my business differently. You will receive my undivided attention to providing you with the level of service and attention to detail you have come to expect from me.
What that means to you is the highest level of service from me. And in response to this I require your heartfelt endorsement of family, friends, and work associates who would appreciate being served by a Re/Max Camosun Realtor whose commitment to them is for life.
Our Victoria Real Estate Services
Fred Carver Associate Brokerwith Re/Max Camosun Accredited Consultant in Real Estate® 40 years selling all aspects of residential real estate throughout Greater Victoria, including commercial real estate selling apartment buildings and land assembly's for projects.
Fred has served on many committees on the Victoria Real Estate Board and the MLS Committee's Sub committee to develop a NEW Live Open House web site for Consumers in Victoria and beyond.
Fred is a founding member of the original IC&I Division of the Victoria Real Estate Board, now known as the Commercial Divison.
Fred has a passion helping his clients sell and buy the right victoria home or property to meet their needs. If it is important to a client, Fred makes sure it happens and is focused on making the business of buying and selling a home or property a plesant and success transaction for everyone.
Experience does count, use an agent that can Sell your home with a proven marketing program that works!
Disclaimer: ActiveRain Corp. does not necessarily endorse the real estate agents, loan officers and brokers listed on this site. These real estate profiles, blogs and blog entries are provided here as a courtesy to our visitors to help them make an informed decision when buying or selling a house. ActiveRain Corp. takes no responsibility for the content in these profiles, that are written by the members of this community. | <urn:uuid:cf47a000-0a74-4cae-bf25-87662ca2bb23> | CC-MAIN-2013-20 | http://activerain.com/fcarver | 2013-05-18T05:49:43Z | s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2013-20/segments/1368696381249/warc/CC-MAIN-20130516092621-00000-ip-10-60-113-184.ec2.internal.warc.gz | en | 0.954034 | 1,731 |
🍷 FineWeb

15 trillion tokens of the finest data the 🌐 web has to offer
What is it?
The 🍷 FineWeb dataset consists of more than 15T tokens of cleaned and deduplicated english web data from CommonCrawl. The data processing pipeline is optimized for LLM performance and ran on the 🏭 datatrove library, our large scale data processing library.
🍷 FineWeb was originally meant to be a fully open replication of 🦅 RefinedWeb, with a release of the full dataset under the ODC-By 1.0 license. However, by carefully adding additional filtering steps, we managed to push the performance of 🍷 FineWeb well above that of the original 🦅 RefinedWeb, and models trained on our dataset also outperform models trained on other commonly used high quality web datasets (like C4, Dolma-v1.6, The Pile, SlimPajama, RedPajam2) on our aggregate group of benchmark tasks.
That said, we think there is still room for additional filtering and improvement and intend to continue exploring how to improve the dataset quality in coming versions of 🍷 FineWeb.
What is being released?
Along with the dataset, which includes all CommonCrawl dumps since 2013, we also share all the code needed to fully reproduce our processing setup using the 🏭 datatrove library here. To enable full replication of our results, we have also published the small ablation models we have trained using nanotron to validate the dataset and compare it with other reference datasets. You will find them here, with checkpoints every 1000 steps. We have also published our evaluation results here. Our evaluation setup is available here.
You will find details on the different processing decisions we took and some interesting explorations of deduplication methods on our blogpost.
Changelog
Previous versions remain available in the branch version name.
- v1.3.0 (31-01-2025): Fixed an issue with some dumps where some documents hadn't been processed:
CC-MAIN-2024-10,CC-MAIN-2024-18,CC-MAIN-2024-22,CC-MAIN-2024-26,CC-MAIN-2024-30,CC-MAIN-2024-33,CC-MAIN-2024-38,CC-MAIN-2024-42,CC-MAIN-2024-46-- they now contain more data (~400B additional tokens). We also removed specific domains in response to a C&D notice. - v1.2.0 (03-01-2025): Added 8 new snapshots:
CC-MAIN-2024-22,CC-MAIN-2024-26,CC-MAIN-2024-30,CC-MAIN-2024-33,CC-MAIN-2024-38,CC-MAIN-2024-42,CC-MAIN-2024-46,CC-MAIN-2024-51, covering May to December 2024. - v1.1.0 (31-05-2024): We reprocessed and reuploaded 11 dumps,
CC-MAIN-2021-49toCC-MAIN-2023-40, as we found a bug on their deduplication. We also added the most recent dump:CC-MAIN-2024-18, crawled over April 2024. Expect a small perf improvement - v1.0.0 (21-04-2024): Initial version
How to download and use 🍷 FineWeb
You can load the full dataset or a specific crawl/dump (see table below). Dumps have the format CC-MAIN-(year)-(week number).
(Smaller) sample versions
Along with config default (all the data), and the configs for each individual dump, you can also download the following configs:
sample-350BT: a subset randomly sampled from the whole dataset of around 350B gpt2 tokens (388GB)sample-100BT: a subset randomly sampled from the whole dataset of around 100B gpt2 tokens (277.4GB)sample-10BT: a subset randomly sampled from the whole dataset of around 10B gpt2 tokens (27.6GB)
sample-10B was sampled from sample-100B which in turn was sampled from sample-350BT.
Using 🏭 datatrove
from datatrove.pipeline.readers import ParquetReader
# limit determines how many documents will be streamed (remove for all)
# to fetch a specific dump: hf://datasets/HuggingFaceFW/fineweb/data/CC-MAIN-2024-10
# replace "data" with "sample/100BT" to use the 100BT sample
data_reader = ParquetReader("hf://datasets/HuggingFaceFW/fineweb/data", limit=1000)
for document in data_reader():
# do something with document
print(document)
###############################
# OR for a processing pipeline:
###############################
from datatrove.executor import LocalPipelineExecutor
from datatrove.pipeline.readers import ParquetReader
from datatrove.pipeline.filters import LambdaFilter
from datatrove.pipeline.writers import JsonlWriter
pipeline_exec = LocalPipelineExecutor(
pipeline=[
# replace "data/CC-MAIN-2024-10" with "sample/100BT" to use the 100BT sample
ParquetReader("hf://datasets/HuggingFaceFW/fineweb/data/CC-MAIN-2024-10", limit=1000),
LambdaFilter(lambda doc: "hugging" in doc.text),
JsonlWriter("some-output-path")
],
tasks=10
)
pipeline_exec.run()
Using huggingface_hub
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
folder = snapshot_download(
"HuggingFaceFW/fineweb",
repo_type="dataset",
local_dir="./fineweb/",
# replace "data/CC-MAIN-2023-50/*" with "sample/100BT/*" to use the 100BT sample
allow_patterns="data/CC-MAIN-2023-50/*")
For faster downloads, make sure to install pip install huggingface_hub[hf_transfer] and set the environment variable HF_HUB_ENABLE_HF_TRANSFER=1.
Using datasets
from datasets import load_dataset
# use name="sample-10BT" to use the 10BT sample
fw = load_dataset("HuggingFaceFW/fineweb", name="CC-MAIN-2024-10", split="train", streaming=True)
Breakdown by dump/crawl
| Dump | Time period | Disk size (GB) | gpt2 tokens (billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC-MAIN-2024-51 | December 2024 | 362.6 | 131.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-46 | November 2024 | 474.6 | 172.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-42 | October 2024 | 434.0 | 158.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-38 | September 2024 | 506.2 | 184.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-33 | August 2024 | 400.6 | 145.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-30 | July 2024 | 451.3 | 164.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-26 | June 2024 | 496.5 | 181.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-22 | May 2024 | 499.7 | 182.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-18 | April 2024 | 520.6 | 190.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2024-10 | February/March 2024 | 581.3 | 212.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2023-50 | November/December 2023 | 650.0 | 239.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2023-40 | September/October 2023 | 668.7 | 252.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2023-23 | May/June 2023 | 654.4 | 249.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2023-14 | March/April 2023 | 621.3 | 236.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2023-06 | January/February 2023 | 621.9 | 233.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2022-49 | November/December 2022 | 631.2 | 237.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2022-40 | September/October 2022 | 606.4 | 228.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2022-33 | August 2022 | 434.6 | 163.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2022-27 | June/July 2022 | 574.9 | 216.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2022-21 | May 2022 | 646.4 | 242.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2022-05 | January 2022 | 520.1 | 195.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-49 | November/December 2021 | 413.7 | 155.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-43 | October 2021 | 601.5 | 221.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-43 | October 2021 | 601.5 | 221.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-39 | September 2021 | 518.9 | 190.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-31 | July/August 2021 | 593.9 | 217.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-25 | June 2021 | 424.4 | 155.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-21 | May 2021 | 455.9 | 167.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-17 | April 2021 | 556.0 | 204.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-10 | February/March 2021 | 463.2 | 169.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2021-04 | January 2021 | 562.4 | 205.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-50 | November/December 2020 | 422.8 | 154.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-45 | October 2020 | 426.9 | 155.8 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-40 | September 2020 | 555.5 | 202.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-34 | August 2020 | 379.6 | 138.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-29 | July 2020 | 489.6 | 178.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-24 | May/June 2020 | 398.7 | 145.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-16 | March/April 2020 | 454.0 | 165.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-10 | February 2020 | 369.6 | 134.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2020-05 | January 2020 | 483.3 | 176.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-51 | December 2019 | 359.3 | 130.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-47 | November 2019 | 395.4 | 144.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-43 | October 2019 | 422.3 | 153.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-39 | September 2019 | 394.4 | 143.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-35 | August 2019 | 454.2 | 165.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-30 | July 2019 | 416.6 | 151.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-26 | June 2019 | 412.9 | 150.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-22 | May 2019 | 432.8 | 157.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-18 | April 2019 | 426.7 | 155.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-13 | March 2019 | 417.8 | 152.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-09 | February 2019 | 467.2 | 169.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2019-04 | January 2019 | 438.1 | 158.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-51 | December 2018 | 498.6 | 180.8 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-47 | November 2018 | 437.7 | 158.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-43 | October 2018 | 468.8 | 169.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-39 | September 2018 | 429.2 | 155.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-34 | August 2018 | 408.2 | 148.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-30 | July 2018 | 501.5 | 181.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-26 | June 2018 | 467.5 | 170.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-22 | May 2018 | 398.6 | 144.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-17 | April 2018 | 435.1 | 158.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-13 | March 2018 | 471.5 | 171.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-09 | February 2018 | 490.2 | 178.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2018-05 | January 2018 | 493.5 | 180.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-51 | December 2017 | 442.6 | 161.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-47 | November 2017 | 457.9 | 167.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-43 | October 2017 | 535.6 | 194.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-39 | September 2017 | 444.5 | 162.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-34 | August 2017 | 503.2 | 183.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-30 | July 2017 | 439.2 | 161.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-26 | June 2017 | 491.5 | 179.8 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-22 | May 2017 | 441.0 | 161.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-17 | April 2017 | 596.8 | 218.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-13 | March 2017 | 579.8 | 212.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-09 | February 2017 | 492.2 | 180.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2017-04 | January 2017 | 474.3 | 174.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-50 | December 2016 | 448.9 | 165.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-44 | October 2016 | 467.8 | 172.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-40 | September 2016 | 386.1 | 142.8 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-36 | August 2016 | 339.6 | 126.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-30 | July 2016 | 346.0 | 128.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-26 | June 2016 | 256.5 | 95.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-22 | May 2016 | 310.9 | 115.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-18 | April 2016 | 298.1 | 110.8 |
| CC-MAIN-2016-07 | February 2016 | 342.7 | 127.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-48 | November 2015 | 353.9 | 131.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-40 | September 2015 | 284.0 | 105.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-35 | August 2015 | 359.4 | 133.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-32 | July 2015 | 352.4 | 130.1 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-27 | June 2015 | 335.5 | 124.0 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-22 | May 2015 | 380.2 | 140.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-18 | April 2015 | 389.0 | 143.8 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-14 | March 2015 | 337.5 | 124.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-11 | February 2015 | 361.4 | 133.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2015-06 | January 2015 | 356.1 | 131.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-52 | December 2014 | 388.5 | 143.3 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-49 | November 2014 | 319.9 | 117.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-42 | October 2014 | 371.1 | 136.4 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-41 | September 2014 | 408.1 | 150.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-35 | August 2014 | 395.7 | 145.6 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-23 | July 2014 | 425.0 | 156.5 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-15 | April 2014 | 369.1 | 135.7 |
| CC-MAIN-2014-10 | March 2014 | 396.2 | 146.2 |
| CC-MAIN-2013-48 | Winter 2013 | 396.8 | 145.9 |
| CC-MAIN-2013-20 | Summer 2013 | 393.9 | 144.5 |
| Total | 47,535.7 | 17,468.6 |
Dataset performance evaluation and ablations
We conducted our dataset performance ablations and evaluations by training a series of 1.8B parameters models on 27 billion tokens. To compare 🍷 FineWeb with other datasets, we also trained one of these 1.8B models per target dataset, on 350 billion tokens sampled from it (or the entire dataset when its size was < 350 billion tokens).
Hyper-parameters for ablation models
The detailed configurations for training the 1.8B parameters ablation model can be found here (link will be added soon).
Ablation evaluation benchmarks
To conduct the ablations for each of our dataset filtering choices, we selected a set of benchmarks which we identified as “high-signal” benchmarks. These benchmarks were selected according to the following criteria:
- small variance between runs trained on different samplings of the same dataset
- performance increasing monotically during training (or close)
- separation between runs on datasets of known quality (C4, The Pile, RedPajama) higher than the variance between runs with various modeling/data seeds
We used the following list of benchmark for our ablation runs:
- commonsense_qa (acc/acc_norm)
- hellaswag (acc/acc_norm)
- openbookqa (acc/acc_norm)
- piqa (acc/acc_norm)
- siqa (acc/acc_norm)
- winogrande (acc/acc_norm)
- arc (acc/acc_norm)
- mmlu (acc/acc_norm)
To compare runs we consider an aggregate score, the average of the scores for these tasks.
The prompts for all these benchmarks are formatted in order to compute and compare the log-likelihood of the full answers for each multiple choice question. All the implementation details for the benchmarks are available in lighteval here.
Comparison with other datasets
We compared 🍷 FineWeb with the following datasets:
- RefinedWeb
- C4
- Dolma v1.6 (the CommonCrawl part)
- The Pile
- SlimPajama
- RedPajama2 (deduplicated)
You will find these models on this collection. We have uploaded checkpoints at every 1000 training steps. You will also find our full evaluation results here.
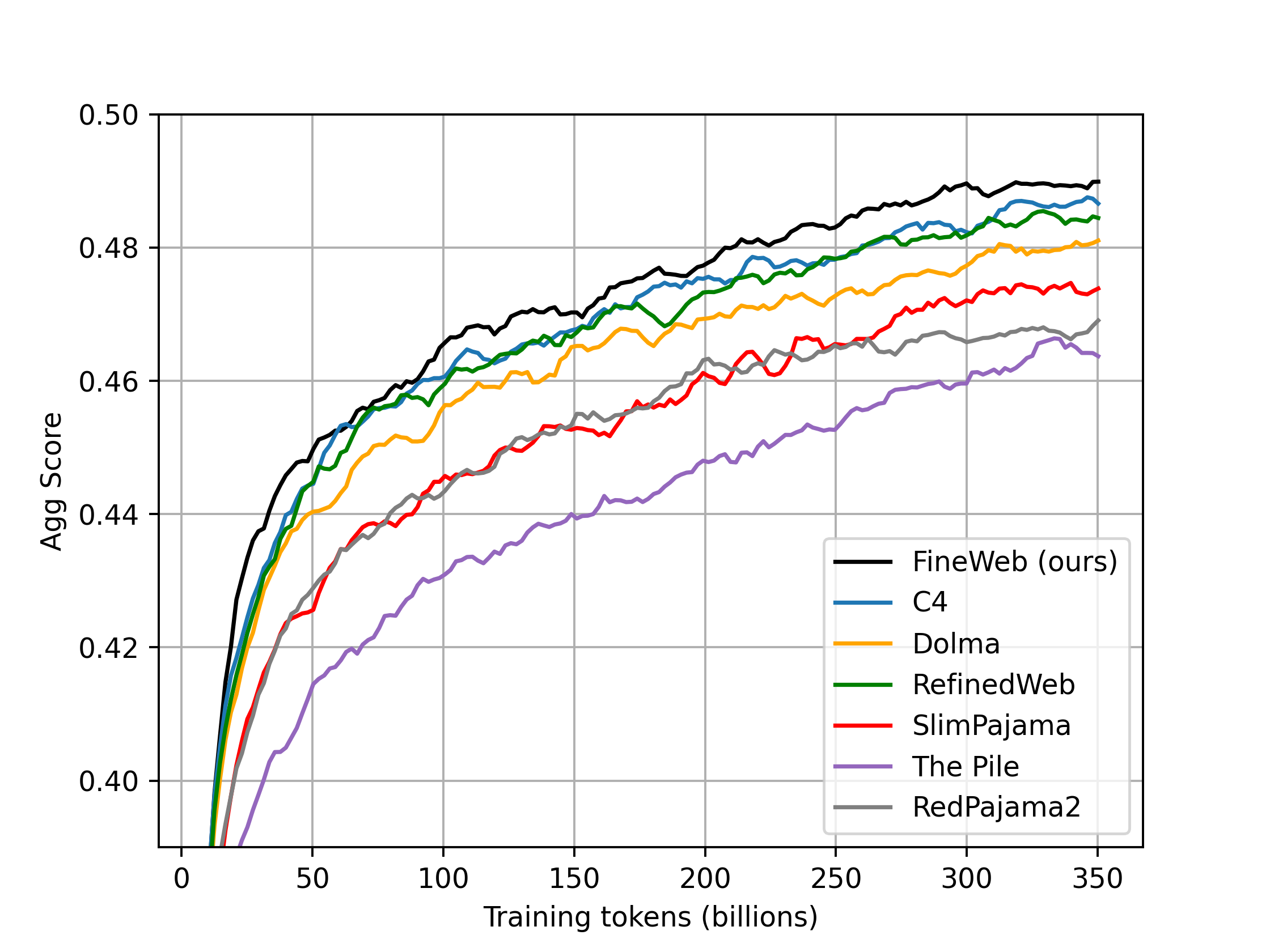
Note: The plot is smoothed by averaging 5k steps in a rolling window.
Dataset card for 🍷 FineWeb
Dataset Summary
This dataset was created by processing 96 CommonCrawl dumps comprising web data crawled from the summer of 2013 to April of 2024. 🍷 FineWeb includes a variety of domains and topics in English and is primarily intended to be used as a research artifact on public data in the context of pretraining dataset for large language models. The CommonCrawl data was carefully processed, filtered and deduplicated with the 🏭 datatrove library, resulting in the largest publicly available clean LLM pretraining dataset, counting around 15 trillion tokens (gpt2 tokenizer).
Dataset Structure
Data Instances
The following is an example sample from the dataset. It is part of the CC-MAIN-2021-43 and was crawled on 2021-10-15T21:20:12Z.
{
"text": "This is basically a peanut flavoured cream thickened with egg yolks and then set into a ramekin on top of some jam. Tony, one of the Wedgwood chefs, suggested sprinkling on some toasted crushed peanuts at the end to create extra crunch, which I thought was a great idea. The result is excellent.",
"id": "<urn:uuid:e5a3e79a-13d4-4147-a26e-167536fcac5d>",
"dump": "CC-MAIN-2021-43",
"url": "<http://allrecipes.co.uk/recipe/24758/peanut-butter-and-jam-creme-brulee.aspx?o_is=SimilarRecipes&o_ln=SimRecipes_Photo_7>",
"date": "2021-10-15T21:20:12Z",
"file_path": "s3://commoncrawl/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2021-43/segments/1634323583083.92/warc/CC-MAIN-20211015192439-20211015222439-00600.warc.gz",
"language": "en",
"language_score": 0.948729,
"token_count": 69
}
Data Fields
text(string): the main text contentid(string): original unique identifier for this sample from CommonCrawldump(string): the CommonCrawl dump this sample was a part ofurl(string): url to the original page wheretextwas presentdate(string): crawl date (from CommonCrawl)file_path(string): s3 path for the individual CommonCrawl warc file containing this samplelanguage(string):enfor all the samples in this datasetlanguage_score(float): language prediction score (0.01.0) as reported by the fastText language classifiertoken_count(int): number of tokens when applying thegpt2tokenizer to this sample
Data Splits
The default subset includes the entire dataset. If you would like to only use the data from a particular CommonCrawl dump, you can use the dump name as a subset. You will find the full list of available dumps on the table above.
From experiments we have run, not all dumps give the same performance. For relatively small trainings (<550 billion tokens) we recommend using the recent CC-MAIN-2023-50, CC-MAIN-2024-10 and CC-MAIN-2024-18.
Dataset Creation
Curation Rationale
While multiple open-weights models have regularly been released in recent months, these releases often do not include the model's training data. With 🍷 FineWeb we aim to provide the open source community with a very large clean pretraining dataset that can be used to push the envelope on truly open source models (open source models where data is also released).
Source Data
The source data consists of webpages crawled by the CommonCrawl foundation over the 2013-2024 time period.
We then extracted the main page text from the html of each webpage, carefully filtered each sample and deduplicated each individual CommonCrawl dump/crawl.
While we originally intended to deduplicate the dataset as a whole, our ablations showed that training on a sampling of individually deduplicated dumps/crawls outperformed training on a sampling of all the dumps/crawls deduplicated together. You will find more details on our blogpost.
Data processing steps
We used the 🏭 datatrove library to process the data.
You can find a working script that launches the entire processing pipeline here.
The data processing pipeline consists of:
- Url Filtering, removing documents originating from Malicious and NSFW websites, using both block-list as well as subwords detection
- Trafilatura text extraction on the raw HTML from CommonCrawl’s warc files
- FastText LanguageFilter, removing any document with
enlanguage score lower than 0.65 - Quality filtering
- Gopher Repetition / Quality
- C4 Quality filters except
terminal_punctrule - FineWeb custom filters, consisting of heuristics for removing list-like documents, documents with repeated lines and documents with likely wrong line formatting.
- MinHash deduplication with each crawl deduplicated individually (5-grams, 14x8 hash functions)
- PII Formatting to anonymize email and public IP addresses
Annotations
We augment the original samples with the language, language_score and token_count annotations. The language related annotations are automatically generated by our language filter. token_count is generated by applying the gpt2 tokenizer to the text column.
Personal and Sensitive Information
We anonymize email addresses and public IP addresses.
For emails, we apply a regex pattern and replace any occurrence of an email address with either email@example.com or firstname.lastname@example.org. For IP addresses, we also employ a regex pattern and then further filter to only anonymize IP addresses allocated for public networks. Matched IP addresses are then replaced with one of the following randomly generated IP addresses, which at the time of dataset creation were not responding to ping requests: 22.214.171.124, 126.96.36.199, 188.8.131.52, 184.108.40.206, 220.127.116.11, and 18.104.22.168. We decided against applying regex patterns for phone numbers due to the high false positive rate.
Despite our efforts, given that 🍷 FineWeb is sourced from the internet at large, it is very likely that some personable identifiable information (PII) will be present. If you find your own PII in 🍷 FineWeb and would like it removed, please fill out our PII removal form.
Considerations for Using the Data
Social Impact of Dataset
With the release of this dataset we aim to make model training more accessible to the machine learning community at large.
While multiple open-weights models with strong performance have been publicly released in the past, more often than not these releases are not accompanied by the corresponding training dataset. This is unfortunate as the dataset specificities and characteristics have been demonstrated to have a very large impact and role in the performances of the models. As the creation of a high quality training dataset is a fundamental requirement to training an LLM capable of excelling at downstream tasks, with 🍷 FineWeb we (a) not only make the dataset creation process more transparent, by sharing our entire processing setup including the codebase used, we also (b) help alleviate the costs of dataset curation, both in time and in compute, for model creators by publicly releasing our dataset with the community.
Discussion of Biases
Efforts were made to minimize the amount of NSFW and toxic content present in the dataset by employing filtering on the URL level. However, there are still a significant number of documents present in the final dataset that could be considered toxic or contain harmful content. As 🍷 FineWeb was sourced from the web as a whole, any harmful biases typically present in it may be reproduced on our dataset.
We deliberately avoided using machine learning filtering methods that define text quality based on the similarity to a “gold” source such as wikipedia or toxicity classifiers as these methods have been known to disproportionately remove content in specific dialects and overclassify as toxic text related to specific social identities, respectively.
Other Known Limitations
As a consequence of some of the filtering steps applied, it is likely that code content is not prevalent in our dataset. If you are training a model that should also perform code tasks, we recommend you use 🍷 FineWeb with a code dataset, such as The Stack v2. You should also probably consider complementing 🍷 FineWeb with specialized curated sources (such as Wikipedia, for example) as they will likely have better formatting than the wikipedia content included in 🍷 FineWeb (we did not tailor the processing to individual websites).
Additional Information
Licensing Information
The dataset is released under the Open Data Commons Attribution License (ODC-By) v1.0 license. The use of this dataset is also subject to CommonCrawl's Terms of Use.
Future work
We plan to not only continue but also expand our efforts to create open-source high quality training datasets and to improve 🍷 FineWeb itself in future iterations.
Citation Information
Paper on arXiv
@inproceedings{
penedo2024the,
title={The FineWeb Datasets: Decanting the Web for the Finest Text Data at Scale},
author={Guilherme Penedo and Hynek Kydl{\'\i}{\v{c}}ek and Loubna Ben allal and Anton Lozhkov and Margaret Mitchell and Colin Raffel and Leandro Von Werra and Thomas Wolf},
booktitle={The Thirty-eight Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=n6SCkn2QaG}
}
- Downloads last month
- 533,105