title
stringlengths 24
189
| detail_url
stringlengths 27
46
| author_list
sequencelengths 0
34
| abstract
stringlengths 33
403
|
|---|---|---|---|
RAL Papers Presented at IROS 2023 | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | RAL Papers Presented at IROS 2023 |
RAM Papers Presented at IROS 2023 | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | RAM Papers Presented at IROS 2023 |
TASE Papers Presented at IROS 2023 | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | TASE Papers Presented at IROS 2023 |
TRO Papers Presented at IROS 2023 | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | TRO Papers Presented at IROS 2023 |
Prototypical Contrastive Transfer Learning for Multimodal Language Understanding | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341388/ | [
"Seitaro Otsuki",
"Shintaro Ishikawa",
"Komei Sugiura",
"Seitaro Otsuki",
"Shintaro Ishikawa",
"Komei Sugiura"
] | Although domestic service robots are expected to assist individuals who require support, they cannot currently interact smoothly with people through natural language. For example, given the instruction “Bring me a bottle from the kitchen,” it is difficult for such robots to specify the bottle in an indoor environment. Most conventional models have been trained on real-world datasets that are labor... |
Re-Thinking Classification Confidence with Model Quality Quantification | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341548/ | [
"Yancheng Pan",
"Huijing Zhao",
"Yancheng Pan",
"Huijing Zhao"
] | Deep neural networks using for real-world classification task require high reliability and robustness. However, the Softmax output by the last layer of network is often over-confident. We propose a novel confidence estimation method by considering model quality for deep classification models. Two metrics, MQ-Repres and MQ-Discri are developed accordingly to evaluate the model quality, and also pro... |
Self-Supervised Drivable Area Segmentation Using LiDAR's Depth Information for Autonomous Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341687/ | [
"Fulong Ma",
"Yang Liu",
"Sheng Wang",
"Jin Wu",
"Weiqing Qi",
"Ming Liu",
"Fulong Ma",
"Yang Liu",
"Sheng Wang",
"Jin Wu",
"Weiqing Qi",
"Ming Liu"
] | Drivable area segmentation is an essential component of the visual perception system for autonomous driving vehicles. Recent efforts in deep neural networks have sig-nificantly improved semantic segmentation performance for autonomous driving. However, most DNN-based methods need a large amount of data to train the models, and collecting large-scale datasets with manually labeled ground truth is c... |
Vehicle Motion Forecasting Using Prior Information and Semantic-Assisted Occupancy Grid Maps | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342507/ | [
"Rabbia Asghar",
"Manuel Diaz-Zapata",
"Lukas Rummelhard",
"Anne Spalanzani",
"Christian Laugier",
"Rabbia Asghar",
"Manuel Diaz-Zapata",
"Lukas Rummelhard",
"Anne Spalanzani",
"Christian Laugier"
] | Motion prediction is a challenging task for autonomous vehicles due to uncertainty in the sensor data, the non-deterministic nature of future, and complex behavior of agents. In this paper, we tackle this problem by representing the scene as dynamic occupancy grid maps (DOGMs), associating semantic labels to the occupied cells and incorporating map information. We propose a novel framework that co... |
Enhance Local Feature Consistency with Structure Similarity Loss for 3D Semantic Segmentation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342338/ | [
"Cheng- Wei Lin",
"Fang-Yu Syu",
"Yi-Ju Pan",
"Kuan-Wen Chen",
"Cheng- Wei Lin",
"Fang-Yu Syu",
"Yi-Ju Pan",
"Kuan-Wen Chen"
] | Recently, many research studies have been carried out on using deep learning methods for 3D point cloud understanding. However, there is still no remarkable result on 3D point cloud semantic segmentation compared to those of 2D research. One important reason is that 3D data has higher dimensionality but lacks large datasets, which means that the deep learning model is difficult to optimize and eas... |
Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Network for Semantic Scene Understanding on Low-Compute Devices | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342110/ | [
"Hojun Son",
"James Weiland",
"Hojun Son",
"James Weiland"
] | Semantic scene understanding is beneficial for mobile robots. Semantic information obtained through onboard cameras can improve robots' navigation performance. However, obtaining semantic information on small mobile robots with constrained power and computation resources is challenging. We propose a new lightweight convolution neural network comparable to previous semantic segmentation algorithms ... |
LiDAR-SGMOS: Semantics-Guided Moving Object Segmentation with 3D LiDAR | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341426/ | [
"Shuo Gu",
"Suling Yao",
"Jian Yang",
"Chengzhong Xu",
"Hui Kong",
"Shuo Gu",
"Suling Yao",
"Jian Yang",
"Chengzhong Xu",
"Hui Kong"
] | Most of the existing moving object segmentation (MOS) methods regard MOS as an independent task, in this paper, we associate the MOS task with semantic segmentation, and propose a semantics-guided network for moving object segmentation (LiDAR-SGMOS). We first transform the range image and semantic features of the past scan into the range view of current scan based on the relative pose between scan... |
Robust Fusion for Bayesian Semantic Mapping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342253/ | [
"David Morilla-Cabello",
"Lorenzo Mur-Labadia",
"Ruben Martinez-Cantin",
"Eduardo Montijano",
"David Morilla-Cabello",
"Lorenzo Mur-Labadia",
"Ruben Martinez-Cantin",
"Eduardo Montijano"
] | The integration of semantic information in a map allows robots to understand better their environment and make high-level decisions. In the last few years, neural networks have shown enormous progress in their perception capabilities. However, when fusing multiple observations from a neural network in a semantic map, its inherent overconfidence with unknown data gives too much weight to the outlie... |
ConSOR: A Context-Aware Semantic Object Rearrangement Framework for Partially Arranged Scenes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341873/ | [
"Kartik Ramachandruni",
"Max Zuo",
"Sonia Chernova",
"Kartik Ramachandruni",
"Max Zuo",
"Sonia Chernova"
] | Object rearrangement is the problem of enabling a robot to identify the correct object placement in a complex environment. Prior work on object rearrangement has explored a diverse set of techniques for following user instructions to achieve some desired goal state. Logical predicates, images of the goal scene, and natural language descriptions have all been used to instruct a robot in how to arra... |
IDA: Informed Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342254/ | [
"Zheng Chen",
"Zhengming Ding",
"Jason M. Gregory",
"Lantao Liu",
"Zheng Chen",
"Zhengming Ding",
"Jason M. Gregory",
"Lantao Liu"
] | Mixup-based data augmentation has been validated to be a critical stage in the self-training framework for unsupervised domain adaptive semantic segmentation (UDASS), which aims to transfer knowledge from a well-annotated (source) domain to an unlabeled (target) domain. Existing self-training methods usually adopt the popular region-based mixup techniques with a random sampling strategy, which unf... |
A Handle Robot for Providing Bodily Support to Elderly Persons | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341348/ | [
"Roberto Bolli",
"Paolo Bonato",
"H. Harry Asada",
"Roberto Bolli",
"Paolo Bonato",
"H. Harry Asada"
] | Age-related loss of mobility and an increased risk of falling remain major obstacles for older adults to live independently. Many elderly people lack the coordination and strength necessary to perform activities of daily living, such as getting out of bed or stepping into a bathtub. A traditional solution is to install grab bars around the home. For assisting in bathtub transitions, grab bars are ... |
A Hybrid FNS Generator for Human Trunk Posture Control with Incomplete Knowledge of Neuromusculoskeletal Dynamics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342462/ | [
"Xuefeng Bao",
"Aidan R. Friederich",
"Ronald J. Triolo",
"Musa L. Audu",
"Xuefeng Bao",
"Aidan R. Friederich",
"Ronald J. Triolo",
"Musa L. Audu"
] | The trunk movements of an individual paralyzed by spinal cord injury (SCI) can be restored by Functional Neuromuscular Stimulation (FNS), a technique that applies low-level current to motor nerves to activate the muscles generating torques, and thus, produce trunk motions. FNS can be modulated to control trunk movements. However, a stabilizing modulation policy (i.e., control law) is difficult to ... |
Insole-Type Walking Assist Device Capable of Inducing Inversion-Eversion of the Ankle Angle to the Neutral Position | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342205/ | [
"Taku Itami",
"Kazuki Date",
"Yuta Ishii",
"Jun Yoneyama",
"Takaaki Aoki",
"Taku Itami",
"Kazuki Date",
"Yuta Ishii",
"Jun Yoneyama",
"Takaaki Aoki"
] | In recent years, the aging of society has become a serious problem, especially in developed countries. Walking is an important element in extending healthy life expectancy in old age. In particular, induction of proper ankle joint alignment at heel contact is important during the gait cycle from the perspective of smooth weight transfer and reduction of burden on the knees and hip. In this study, ... |
Design for Hip Abduction Assistive Device Based on Relationship Between Hip Joint Motion and Torque During Running | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341611/ | [
"Myunghyun Lee",
"Man Bok Hong",
"Gwang Tae Kim",
"Seonwoo Kim",
"Myunghyun Lee",
"Man Bok Hong",
"Gwang Tae Kim",
"Seonwoo Kim"
] | Numerous attempts have been made to reduce metabolic energy while running with the help of assistive devices. A majority of studies on the assistive devices have focused on the assisting torque in the sagittal plane. In the case of running, however, the abduction torque in the frontal plane at the hip joint is greater than the flexion/extension torque in the sagittal plane. During running, as does... |
Dynamic Hand Proprioception via a Wearable Glove with Fabric Sensors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342129/ | [
"Lily Behnke",
"Lina Sanchez-Botero",
"William R. Johnson",
"Anjali Agrawala",
"Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio",
"Lily Behnke",
"Lina Sanchez-Botero",
"William R. Johnson",
"Anjali Agrawala",
"Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio"
] | Continuous enhancement in wearable technologies has led to several innovations in the healthcare, virtual reality, and robotics sectors. One form of wearable technology is wear-able sensors for kinematic measurements of human motion. However, measuring the kinematics of human movement is a challenging problem as wearable sensors need to conform to complex curvatures and deform without limiting the... |
A Wearable Robotic Rehabilitation System for Neuro-Rehabilitation Aimed at Enhancing Mediolateral Balance | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341735/ | [
"Zhenyuan Yu",
"Varun Nalam",
"Abbas Alili",
"He Helen Huang",
"Zhenyuan Yu",
"Varun Nalam",
"Abbas Alili",
"He Helen Huang"
] | There is increasing evidence of the role of compromised mediolateral balance in falls and the need for rehabilitation specifically focused on mediolateral direction for various populations with motor deficits. To address this need, we have developed a neurorehabilitation platform by integrating a wearable robotic hip abduction-adduction exoskeleton with a visual interface. The platform is expected... |
Analysis of Lower Extremity Shape Characteristics in Various Walking Situations for the Development of Wearable Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341496/ | [
"Joohyun Park",
"Ho Seon Choi",
"Hyunki In",
"Joohyun Park",
"Ho Seon Choi",
"Hyunki In"
] | A strap is a frequently utilized component for securing wearable robots to their users in order to facilitate force transmission between humans and the devices. For the appropriate function of the wearable robot, the pressure between the strap and the skin should be maintained appropriately. Due to muscle contraction, the cross-section area of the human limb changes according to the movement of th... |
Finding Biomechanically Safe Trajectories for Robot Manipulation of the Human Body in a Search and Rescue Scenario | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342353/ | [
"Elizabeth Peiros",
"Zih-Yun Chiu",
"Yuheng Zhi",
"Nikhil Shinde",
"Michael C. Yip",
"Elizabeth Peiros",
"Zih-Yun Chiu",
"Yuheng Zhi",
"Nikhil Shinde",
"Michael C. Yip"
] | There has been increasing awareness of the difficulties in reaching and extracting people from mass casualty scenarios, such as those arising from natural disasters. While platforms have been designed to consider reaching casualties and even carrying them out of harm's way, the challenge of repositioning a casualty from its found configuration to one suitable for extraction has not been explicitly... |
Dynamic Multi-Query Motion Planning with Differential Constraints and Moving Goals | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341670/ | [
"Michael Gentner",
"Fabian Zillenbiller",
"André Kraft",
"Eckehard Steinbach",
"Michael Gentner",
"Fabian Zillenbiller",
"André Kraft",
"Eckehard Steinbach"
] | Planning robot motions in complex environments is a fundamental research challenge and central to the autonomy, efficiency, and ultimately adoption of robots. While often the environment is assumed to be static, real-world settings, such as assembly lines, contain complex shaped, moving obstacles and changing target states. Therein robots must perform safe and efficient motions to achieve their ta... |
Reactive and Safe Co-Navigation with Haptic Guidance | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342042/ | [
"Mela Coffey",
"Dawei Zhang",
"Roberto Tron",
"Alyssa Pierson",
"Mela Coffey",
"Dawei Zhang",
"Roberto Tron",
"Alyssa Pierson"
] | We propose a co-navigation algorithm that enables a human and a robot to work together to navigate to a common goal. In this system, the human is responsible for making high-level steering decisions, and the robot, in turn, provides haptic feedback for collision avoidance and path suggestions while reacting to changes in the environment. Our algorithm uses optimized Rapidly-exploring Random Trees ... |
An MCTS-DRL Based Obstacle and Occlusion Avoidance Methodology in Robotic Follow-Ahead Applications | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342150/ | [
"Sahar Leisiazar",
"Edward J. Park",
"Angelica Lim",
"Mo Chen",
"Sahar Leisiazar",
"Edward J. Park",
"Angelica Lim",
"Mo Chen"
] | We propose a novel methodology for robotic follow-ahead applications that address the critical challenge of obstacle and occlusion avoidance. Our approach effectively navigates the robot while ensuring avoidance of collisions and occlusions caused by surrounding objects. To achieve this, we developed a high-level decision-making algorithm that generates short-term navigational goals for the mobile... |
Proactive Model Predictive Control with Multi-Modal Human Motion Prediction in Cluttered Dynamic Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341702/ | [
"Lukas Heuer",
"Luigi Palmieri",
"Andrey Rudenko",
"Anna Mannucci",
"Martin Magnusson",
"Kai O. Arras",
"Lukas Heuer",
"Luigi Palmieri",
"Andrey Rudenko",
"Anna Mannucci",
"Martin Magnusson",
"Kai O. Arras"
] | For robots navigating in dynamic environments, exploiting and understanding uncertain human motion prediction is key to generate efficient, safe and legible actions. The robot may perform poorly and cause hindrances if it does not reason over possible, multi-modal future social interactions. With the goal of enhancing autonomous navigation in cluttered environments, we propose a novel formulation ... |
A Novel Obstacle-Avoidance Solution With Non-Iterative Neural Controller for Joint-Constrained Redundant Manipulators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342293/ | [
"Weibing Li",
"Zilian Yi",
"Yanying Zou",
"Haimei Wu",
"Yang Yang",
"Yongping Pan",
"Weibing Li",
"Zilian Yi",
"Yanying Zou",
"Haimei Wu",
"Yang Yang",
"Yongping Pan"
] | Obstacle avoidance (OA) and joint-limit avoidance (JLA) are essential for redundant manipulators to ensure safe and reliable robotic operations. One solution to OA and JLA is to incorporate the involved constraints into a quadratic programming (QP), by solving which OA and JLA can be achieved. There exist a few non-iterative solvers such as zeroing neural networks (ZNNs), which can solve each samp... |
TTC4MCP: Monocular Collision Prediction Based on Self-Supervised TTC Estimation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341966/ | [
"Changlin Li",
"Yeqiang Qian",
"Cong Sun",
"Weihao Yan",
"Chunxiang Wang",
"Ming Yang",
"Changlin Li",
"Yeqiang Qian",
"Cong Sun",
"Weihao Yan",
"Chunxiang Wang",
"Ming Yang"
] | Vision-based collision prediction for autonomous driving is a challenging task due to the dynamic movement of vehicles and diverse types of obstacles. Most existing methods rely on object detection algorithms, which only predict predefined collision targets, such as vehicles and pedestrians, and cannot anticipate emergencies caused by unknown obstacles. To address this limitation, we propose a nov... |
DAMON: Dynamic Amorphous Obstacle Navigation using Topological Manifold Learning and Variational Autoencoding | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342035/ | [
"Apan Dastider",
"Mingjie Lin",
"Apan Dastider",
"Mingjie Lin"
] | DAMON leverages manifold learning and variational autoencoding to achieve obstacle avoidance, allowing for motion planning through adaptive graph traversal in a pre-learned low-dimensional hierarchically-structured manifold graph that captures intricate motion dynamics between a robotic arm and its obstacles. This versatile and reusable approach is applicable to various collaboration scenarios. Th... |
gatekeeper: Online Safety Verification and Control for Nonlinear Systems in Dynamic Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341790/ | [
"Devansh Agrawal",
"Ruichang Chen",
"Dimitra Panagou",
"Devansh Agrawal",
"Ruichang Chen",
"Dimitra Panagou"
] | This paper presents the gatekeeper algorithm, a real-time and computationally-lightweight method to ensure that nonlinear systems can operate safely in dynamic environments despite limited perception. gatekeeper integrates with existing path planners and feedback controllers by introducing an additional verification step that ensures that proposed trajectories can be executed safely, despite nonli... |
Combinatorial Disjunctive Constraints for Obstacle Avoidance in Path Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342117/ | [
"Raul Garcia",
"Illya V. Hicks",
"Joey Huchette",
"Raul Garcia",
"Illya V. Hicks",
"Joey Huchette"
] | We present a new approach for modeling avoidance constraints in 2D environments, in which waypoints are assigned to obstacle-free polyhedral regions. Constraints of this form are often formulated as mixed-integer programming (MIP) problems employing big-M techniques-however, these are generally not the strongest formulations possible with respect to the MIP's convex relaxation (so called ideal for... |
Reachability-Aware Collision Avoidance for Tractor-Trailer System with Non-Linear MPC and Control Barrier Function | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341919/ | [
"Yucheng Tang",
"Ilshat Mamaev",
"Jing Qin",
"Christian Wurll",
"Björn Hein",
"Yucheng Tang",
"Ilshat Mamaev",
"Jing Qin",
"Christian Wurll",
"Björn Hein"
] | This paper proposes a reachability-aware model predictive control with a discrete control barrier function for backward obstacle avoidance for a tractor-trailer system. The framework incorporates the state-variant reachable set obtained through sampling-based reachability analysis and symbolic regression into the objective function of model predictive control. By optimizing the intersection of the... |
Continuous Implicit SDF Based Any-Shape Robot Trajectory Optimization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342104/ | [
"Tingrui Zhang",
"Jingping Wang",
"Chao Xu",
"Alan Gao",
"Fei Gao",
"Tingrui Zhang",
"Jingping Wang",
"Chao Xu",
"Alan Gao",
"Fei Gao"
] | Optimization-based trajectory generation methods are widely used in whole-body planning for robots. However, existing work either oversimplifies the robot's geometry and environment representation, resulting in a conservative trajectory or suffers from a huge overhead in maintaining additional information such as the Signed Distance Field (SDF). To bridge the gap, we consider the robot as an impli... |
Robo-Centric ESDF: A Fast and Accurate Whole-Body Collision Evaluation Tool for Any-Shape Robotic Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342074/ | [
"Shuang Geng",
"Qianhao Wang",
"Lei Xie",
"Chao Xu",
"Yanjun Cao",
"Fei Gao",
"Shuang Geng",
"Qianhao Wang",
"Lei Xie",
"Chao Xu",
"Yanjun Cao",
"Fei Gao"
] | For letting mobile robots travel flexibly through complicated environments, increasing attention has been paid to the whole-body collision evaluation. Most existing works either opt for the conservative corridor-based methods that impose strict requirements on the corridor generation, or ESDF-based methods that suffer from high computational overhead. It is still a great challenge to achieve fast ... |
Global Map Assisted Multi-Agent Collision Avoidance via Deep Reinforcement Learning around Complex Obstacles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341762/ | [
"Yuanyuan Du",
"Jianan Zhang",
"Jie Xu",
"Xiang Cheng",
"Shuguang Cui",
"Yuanyuan Du",
"Jianan Zhang",
"Jie Xu",
"Xiang Cheng",
"Shuguang Cui"
] | State-of-the-art multi-agent collision avoidance algorithms face limitations when applied to cluttered public environments, where obstacles may have a variety of shapes and structures. The issue arises because most of these algorithms are agent-level methods. They concentrate solely on preventing collisions between the agents while the obstacles are handled merely out-of-policy. Obstacle-aware pol... |
Aggregating Single-Wheeled Mobile Robots for Omnidirectional Movements | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341772/ | [
"Meng Wang",
"Yao Su",
"Hang Li",
"Jiarui Li",
"Jixiang Liang",
"Hangxin Liu",
"Meng Wang",
"Yao Su",
"Hang Li",
"Jiarui Li",
"Jixiang Liang",
"Hangxin Liu"
] | This paper presents a novel modular robot system that can self-reconfigure to achieve omnidirectional movements for collaborative object transportation. Each robotic module is equipped with a steerable omni-wheel for navigation and is shaped as a regular icositetragon with a permanent magnet installed on each corner for stable docking. After aggregating multiple modules and forming a structure tha... |
Smooth Stride Length Change of Rat Robot with a Compliant Actuated Spine Based on CPG Controller | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341791/ | [
"Yuhong Huang",
"Zhenshan Bing",
"Zitao Zhang",
"Kai Huang",
"Fabrice O. Morin",
"Alois Knoll",
"Yuhong Huang",
"Zhenshan Bing",
"Zitao Zhang",
"Kai Huang",
"Fabrice O. Morin",
"Alois Knoll"
] | The aim of this research is to investigate the relationship between spinal flexion and quadruped locomotion in a rat robot equipped with a compliant spine, controlled by a central pattern generator (CPG). The study reveals that spinal flexion can enhance limb stride length, but it may also cause significant and unexpected motion disturbances during stride length variations. To address this issue, ... |
Learning Terrain-Adaptive Locomotion with Agile Behaviors by Imitating Animals | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342271/ | [
"Tingguang Li",
"Yizheng Zhang",
"Chong Zhang",
"Qingxu Zhu",
"Jiapeng Sheng",
"Wanchao Chi",
"Cheng Zhou",
"Lei Han",
"Tingguang Li",
"Yizheng Zhang",
"Chong Zhang",
"Qingxu Zhu",
"Jiapeng Sheng",
"Wanchao Chi",
"Cheng Zhou",
"Lei Han"
] | In this paper, we present a general learning framework for controlling a quadruped robot that can mimic the behavior of real animals and traverse challenging terrains. Our method consists of two steps: an imitation learning step to learn from motions of real animals, and a terrain adaptation step to enable generalization to unseen terrains. We capture motions from a Labrador on various terrains to... |
A Stable Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter for Estimating Robot Manipulators Link Velocity and Acceleration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342476/ | [
"Seyed Ali Baradaran Birjandi",
"Harshit Khurana",
"Aude Billard",
"Sami Haddadin",
"Seyed Ali Baradaran Birjandi",
"Harshit Khurana",
"Aude Billard",
"Sami Haddadin"
] | One can estimate the velocity and acceleration of robot manipulators by utilizing nonlinear observers. This involves combining inertial measurement units (IMUs) with the motor encoders of the robot through a model-based sensor fusion technique. This approach is lightweight, versatile (suitable for a wide range of trajectories and applications), and straightforward to implement. In order to further... |
Provably Correct Sensor-Driven Path-Following for Unicycles Using Monotonic Score Functions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342233/ | [
"Benton Clark",
"Varun Hariprasad",
"Hasan A. Poonawala",
"Benton Clark",
"Varun Hariprasad",
"Hasan A. Poonawala"
] | This paper develops a provably stable sensor-driven controller for path-following applications of robots with unicycle kinematics, one specific class of which is the wheeled mobile robot (WMR). The sensor measurement is converted to a scalar value (the score) through some mapping (the score function); the latter may be designed or learned. The score is then mapped to forward and angular velocities... |
Contact Reduction with Bounded Stiffness for Robust Sim-to-Real Transfer of Robot Assembly | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341866/ | [
"Nghia Vuong",
"Quang-Cuong Pham",
"Nghia Vuong",
"Quang-Cuong Pham"
] | In sim-to-real Reinforcement Learning (RL), a policy is trained in a simulated environment and then deployed on the physical system. The main challenge of sim-to-real RL is to overcome the reality gap - the discrepancies between the real world and its simulated counterpart. Using generic geometric representations, such as convex decomposition, triangular mesh, signed distance field can improve sim... |
Trajectory Tracking via Multiscale Continuous Attractor Networks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341938/ | [
"Therese Joseph",
"Tobias Fischer",
"Michael Milford",
"Therese Joseph",
"Tobias Fischer",
"Michael Milford"
] | Animals and insects showcase remarkably robust and adept navigational abilities, up to literally circumnavigating the globe. Primary progress in robotics inspired by these natural systems has occurred in two areas: highly theoretical computational neuroscience models, and handcrafted systems like RatSLAM and NeuroSLAM. In this research, we present work bridging the gap between the two, in the form... |
Design and Control of a Ballbot Drivetrain with High Agility, Minimal Footprint, and High Payload | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342007/ | [
"Chenzhang Xiao",
"Mahshid Mansouri",
"David Lam",
"Joao Ramos",
"Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler",
"Chenzhang Xiao",
"Mahshid Mansouri",
"David Lam",
"Joao Ramos",
"Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler"
] | This paper presents the design and control of a ballbot drivetrain that aims to achieve high agility, minimal footprint, and high payload capacity while maintaining dynamic stability. Two hardware platforms and analytical models were developed to test design and control methodologies. The full-scale ballbot prototype (MiaPURE) was constructed using off-the-shelf components and designed to have agi... |
A Bayesian Reinforcement Learning Method for Periodic Robotic Control Under Significant Uncertainty | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342166/ | [
"Yuanyuan Jia",
"Pedro Miguel Uriguen Eljuri",
"Tadahiro Taniguchi",
"Yuanyuan Jia",
"Pedro Miguel Uriguen Eljuri",
"Tadahiro Taniguchi"
] | This paper addresses the lack of research on periodic reinforcement learning for physical robot control by presenting a 3-phase periodic Bayesian reinforcement learning method for uncertain environments. Drawing on cognition theory, the proposed approach achieves effective convergence with fewer training episodes. The coach-based demonstration phase narrows the search space and establishes a found... |
Residual Physics Learning and System Identification for Sim-to-real Transfer of Policies on Buoyancy Assisted Legged Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342062/ | [
"Nitish Sontakke",
"Hosik Chae",
"Sangjoon Lee",
"Tianle Huang",
"Dennis W. Hong",
"Sehoon Hal",
"Nitish Sontakke",
"Hosik Chae",
"Sangjoon Lee",
"Tianle Huang",
"Dennis W. Hong",
"Sehoon Hal"
] | The light and soft characteristics of Buoyancy Assisted Lightweight Legged Unit (BALLU) robots have a great potential to provide intrinsically safe interactions in environments involving humans, unlike many heavy and rigid robots. However, their unique and sensitive dynamics impose challenges to obtaining robust control policies in the real world. In this work, we demonstrate robust sim-to-real tr... |
DiffClothAI: Differentiable Cloth Simulation with Intersection-free Frictional Contact and Differentiable Two-Way Coupling with Articulated Rigid Bodies | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341573/ | [
"Xinyuan Yu",
"Siheng Zhao",
"Siyuan Luo",
"Gang Yang",
"Lin Shao",
"Xinyuan Yu",
"Siheng Zhao",
"Siyuan Luo",
"Gang Yang",
"Lin Shao"
] | Differentiable Simulations have recently proven useful for various robotic manipulation tasks, including cloth manipulation. In robotic cloth simulation, it is crucial to maintain intersection-free properties. We present DiffClothAI, a differentiable cloth simulation with intersection-free friction contact and two-way coupling with articulated rigid bodies. DiffClothAI integrates the Project Dynam... |
Timor Python: A Toolbox for Industrial Modular Robotics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341935/ | [
"Jonathan Külz",
"Matthias Mayer",
"Matthias Althoff",
"Jonathan Külz",
"Matthias Mayer",
"Matthias Althoff"
] | Modular Reconfigurable Robots (MRRs) represent an exciting path forward for industrial robotics, opening up new possibilities for robot design. Compared to monolithic manipulators, they promise greater flexibility, improved maintainability, and cost-efficiency. However, there is no tool or standardized way to model and simulate assemblies of modules in the same way it has been done for robotic man... |
Ultra-Low Inertia 6-DOF Manipulator Arm for Touching the World | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342445/ | [
"Kazutoshi Nishii",
"Akira Hatano",
"Yoshihiro Okumatsu",
"Kazutoshi Nishii",
"Akira Hatano",
"Yoshihiro Okumatsu"
] | As robotic intelligence increases, so does the im-portance of agents that collect data from real-world environments. When learning in contact with the environment, one must consider how to minimize the impact on the environment and maintain reproducibility. To achieve this, the contact force with the environment must be reduced. One way to achieve this is to reduce the inertia of the arm. In this ... |
Determination of the Characteristics of Gears of Robot-Like Systems by Analytical Description of their Structure | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342105/ | [
"Stefan Landler",
"Raúl Molina Blanco",
"Michael Otto",
"Birgit Vogel-Heuser",
"Markus Zimmermann",
"Karsten Stahl",
"Stefan Landler",
"Raúl Molina Blanco",
"Michael Otto",
"Birgit Vogel-Heuser",
"Markus Zimmermann",
"Karsten Stahl"
] | The axes of robots and robot-like systems (RLS) usually include e-motor-gearbox-arrangements for optimal connection of the elements. The characteristics of the drive system and thus also of the robot depend strongly on the gears. Different gearbox designs are available which differ in stiffness, efficiency and further properties. For an application-optimal design of RLS a uniform documentation and... |
Tension Jamming for Deployable Structures | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342131/ | [
"Daniel Hasegawa",
"Buse Aktaş",
"Robert D. Howe",
"Daniel Hasegawa",
"Buse Aktaş",
"Robert D. Howe"
] | Deployable structures provide adaptability and versatility for applications such as temporary architectures, space structures, and biomedical devices. Jamming is a mechanical phenomenon with which dramatic changes in stiffness can be achieved by increasing the frictional and kinematic coupling between constituents in a structure by applying an external pressure. This study applies jamming, which h... |
Task2Morph: Differentiable Task-Inspired Framework for Contact-Aware Robot Design | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341360/ | [
"Yishuai Cai",
"Shaowu Yang",
"Minglong Li",
"Xinglin Chen",
"Yunxin Mao",
"Xiaodong Yi",
"Wenjing Yang",
"Yishuai Cai",
"Shaowu Yang",
"Minglong Li",
"Xinglin Chen",
"Yunxin Mao",
"Xiaodong Yi",
"Wenjing Yang"
] | Optimizing the morphologies and the controllers that adapt to various tasks is a critical issue in the field of robot design, aka. embodied intelligence. Previous works typically model it as a joint optimization problem and use search-based methods to find the optimal solution in the morphology space. However, they ignore the implicit knowledge of task-to-morphology mapping which can directly insp... |
Constraint Programming for Component-Level Robot Design | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341679/ | [
"Andrew Wilhelm",
"Nils Napp",
"Andrew Wilhelm",
"Nils Napp"
] | Effective design automation for building robots would make development faster and easier while also less prone to design errors. However, complex multi-domain constraints make creating such tools difficult. One persistent challenge in achieving this goal of design automation is the fundamental problem of component selection, an optimization problem where, given a general robot model, components mu... |
Design and Implementation of a Two-Limbed 3T1R Haptic Device | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342273/ | [
"Long Kang",
"Yang Yang",
"Byung-Ju Yi",
"Long Kang",
"Yang Yang",
"Byung-Ju Yi"
] | This paper presents a haptic device with a simple architecture of only two limbs that can provide translational motion in three degrees of freedom (DOF) and one-DOF rotational motion. Actuation redundancy eliminates all forward-kinematic singularities and improves the motion-force transmission property. Thanks to the special structure of the kinematic chains, all actuators are close to the base an... |
Combining Measurement Uncertainties with the Probabilistic Robustness for Safety Evaluation of Robot Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342112/ | [
"Woo-Jeong Baek",
"Christoph Ledermann",
"Tamim Asfour",
"Torsten Kröger",
"Woo-Jeong Baek",
"Christoph Ledermann",
"Tamim Asfour",
"Torsten Kröger"
] | In this paper, we present a method to engage measurement uncertainties with the probabilistic robustness to one system uncertainty measure. Providing a metric indicating the potential occurrence of dangerous situations is highly essential for safety-critical robot applications. Due to the difficulty of finding a quantifiable, unambiguous representation however, such a metric has not been derived t... |
Computational Design of Closed-Chain Linkages: Respawn Algorithm for Generative Design | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341425/ | [
"Dmitriy V. Ivolga",
"Ivan I. Borisov",
"Kirill V. Nasonov",
"Sergey A. Kolyubin",
"Dmitriy V. Ivolga",
"Ivan I. Borisov",
"Kirill V. Nasonov",
"Sergey A. Kolyubin"
] | Designing robots is a multiphase process aimed at solving a multi-criteria optimization problem to find the best possible detailed design. Generative design (GD) aims to accelerate the design process compared to manual design, since GD allows exploring and exploiting the vast design space more efficiently. In the field of robotics, however, relevant research focuses mostly on the generation of ful... |
On Designing a Learning Robot: Improving Morphology for Enhanced Task Performance and Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341905/ | [
"Maks Sorokin",
"Chuyuan Fu",
"Jie Tan",
"C. Karen Liu",
"Yunfei Bai",
"Wenlong Lu",
"Sehoon Ha",
"Mohi Khansari",
"Maks Sorokin",
"Chuyuan Fu",
"Jie Tan",
"C. Karen Liu",
"Yunfei Bai",
"Wenlong Lu",
"Sehoon Ha",
"Mohi Khansari"
] | As robots become more prevalent, optimizing their design for better performance and efficiency is becoming increasingly important. However, current robot design practices overlook the impact of perception and design choices on a robot's learning capabilities. To address this gap, we propose a comprehensive methodology that accounts for the interplay between the robot's perception, hardware charact... |
Development of A Dynamic Quadruped with Tunable, Compliant Legs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342283/ | [
"Fuchen Chen",
"Weijia Tao",
"Daniel M. Aukes",
"Fuchen Chen",
"Weijia Tao",
"Daniel M. Aukes"
] | To facilitate the study of how passive leg stiffness influences locomotion dynamics and performance, we have developed an affordable and accessible 400 g quadruped robot driven by tunable compliant laminate legs, whose series and parallel stiffness can be easily adjusted; fabrication only takes 2.5 hours for all four legs. The robot can trot at 0.52 m/s or 4.4 body lengths per second with a 3.2 co... |
Soft Robot Shape Estimation: A Load-Agnostic Geometric Method | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342225/ | [
"Christian Sorensen",
"Marc D. Killpack",
"Christian Sorensen",
"Marc D. Killpack"
] | In this paper we present a novel kinematic representation of a soft continuum robot to enable full shape estimation using a purely geometric solution. The kinematic representation involves using length varying piecewise constant curvature segments to describe the deformed shape of the robot. Based on this kinematic representation, we can use overlapping length sensors to estimate the shape of cont... |
Robust Generalized Proportional Integral Control for Trajectory Tracking of Soft Actuators in a Pediatric Wearable Assistive Device | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342528/ | [
"Caio Mucchiani",
"Zhichao Liu",
"Ipsita Sahin",
"Elena Kokkoni",
"Konstantinos Karydis",
"Caio Mucchiani",
"Zhichao Liu",
"Ipsita Sahin",
"Elena Kokkoni",
"Konstantinos Karydis"
] | Soft robotics hold promise in the development of safe yet powered assistive wearable devices for infants. Key to this is the development of closed-loop controllers that can help regulate pneumatic pressure in the device's actuators in an effort to induce controlled motion at the user's limbs and be able to track different types of trajectories. This work develops a controller for soft pneumatic ac... |
Data-Efficient Online Learning of Ball Placement in Robot Table Tennis | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342132/ | [
"Philip Tobuschat",
"Hao Ma",
"Dieter Büchler",
"Bernhard Schölkopf",
"Michael Muehlebach",
"Philip Tobuschat",
"Hao Ma",
"Dieter Büchler",
"Bernhard Schölkopf",
"Michael Muehlebach"
] | We present an implementation of an online op-timization algorithm for hitting a predefined target when returning ping-pong balls with a table tennis robot. The online algorithm optimizes over so-called interception policies, which define the manner in which the robot arm intercepts the ball. In our case, these are composed of the state of the robot arm (position and velocity) at interception time.... |
Learning Reduced-Order Soft Robot Controller | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341432/ | [
"Chen Liang",
"Xifeng Gao",
"Kui Wu",
"Zherong Pan",
"Chen Liang",
"Xifeng Gao",
"Kui Wu",
"Zherong Pan"
] | Deformable robots are notoriously difficult to model or control due to its high-dimensional configuration spaces. Direct trajectory optimization suffers from the curse-of-dimensionality and incurs a high computational cost, while learning-based controller optimization methods are sensitive to hyper-parameter tuning. To overcome these limitations, we hypothesize that high fidelity soft robots can b... |
A Single-Parameter Model for Soft Bellows Actuators under Axial Deformation and Loading | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341619/ | [
"Emma Treadway",
"Melissa Brei",
"Audrey Sedal",
"R. Brent Gillespie",
"Emma Treadway",
"Melissa Brei",
"Audrey Sedal",
"R. Brent Gillespie"
] | Soft fluidic actuators are becoming popular for their backdrivability, potential for high power density, and their support for power supply through flexible tubes. Control and design of such actuators requires serviceable models that describe how they relate fluid pressure and flow to mechanical force and motion. We present a simple 2-port model of a bellows actuator that accounts for the relation... |
Task and Configuration Space Compliance of Continuum Robots via Lie Group and Modal Shape Formulations | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341594/ | [
"Andrew L. Orekhov",
"Garrison L. H. Johnston",
"Nabil Simaan",
"Andrew L. Orekhov",
"Garrison L. H. Johnston",
"Nabil Simaan"
] | Continuum robots suffer large deflections due to internal and external forces. Accurate modeling of their passive compliance is necessary for accurate environmental interaction, especially in scenarios where direct force sensing is not practical. This paper focuses on deriving analytic formulations for the compliance of continuum robots that can be modeled as Kirchhoff rods. Compared to prior work... |
A Localization Framework for Boundary Constrained Soft Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341817/ | [
"Koki Tanaka",
"Qiyuan Zhou",
"Ankit Srivastava",
"Matthew Spenko",
"Koki Tanaka",
"Qiyuan Zhou",
"Ankit Srivastava",
"Matthew Spenko"
] | Soft robots possess unique capabilities for adapting to the environment and interacting with it safely. However, their deformable nature also poses challenges for controlling their movement. In particular, the large deformations of a soft robot make it difficult to localize its individual body parts, which in turn impedes effective control. This paper introduces a novel localization framework desi... |
eViper: A Scalable Platform for Untethered Modular Soft Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342402/ | [
"Hsin Cheng",
"Zhiwu Zheng",
"Prakhar Kumar",
"Wali Afridi",
"Ben Kim",
"Sigurd Wagner",
"Naveen Verma",
"James C. Sturm",
"Minjie Chen",
"Hsin Cheng",
"Zhiwu Zheng",
"Prakhar Kumar",
"Wali Afridi",
"Ben Kim",
"Sigurd Wagner",
"Naveen Verma",
"James C. Sturm",
"Minjie Chen"
] | Soft robots present unique capabilities, but have been limited by the lack of scalable technologies for construction and the complexity of algorithms for efficient control and motion. These depend on soft-body dynamics, high-dimensional actuation patterns, and external/onboard forces. This paper presents scalable methods and platforms to study the impact of weight distribution and actuation patter... |
Domain Randomization for Robust, Affordable and Effective Closed-Loop Control of Soft Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342537/ | [
"Gabriele Tiboni",
"Andrea Protopapa",
"Tatiana Tommasi",
"Giuseppe Averta",
"Gabriele Tiboni",
"Andrea Protopapa",
"Tatiana Tommasi",
"Giuseppe Averta"
] | Soft robots are gaining popularity thanks to their intrinsic safety to contacts and adaptability. However, the potentially infinite number of Degrees of Freedom makes their modeling a daunting task, and in many cases only an approximated description is available. This challenge makes reinforcement learning (RL) based approaches inefficient when deployed on a realistic scenario, due to the large do... |
Implementation of a Cosserat Rod-Based Configuration Tracking Controller on a Multi-Segment Soft Robotic Arm | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342160/ | [
"Azadeh Doroudchi",
"Zhi Qiao",
"Wenlong Zhang",
"Spring Berman",
"Azadeh Doroudchi",
"Zhi Qiao",
"Wenlong Zhang",
"Spring Berman"
] | Controlling soft continuum robotic arms is challenging due to their hyper-redundancy and dexterity. In this paper we experimentally demonstrate, for the first time, closed-loop control of the configuration space variables of a soft robotic arm, composed of independently controllable segments, using a Cosserat rod model of the robot and the distributed sensing and actuation capabilities of the segm... |
IF-Based Trajectory Planning and Cooperative Control for Transportation System of Cable Suspended Payload With Multi UAVs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341351/ | [
"Yu Zhang",
"Jie Xu",
"Cheng Zhao",
"Jiuxiang Dong",
"Yu Zhang",
"Jie Xu",
"Cheng Zhao",
"Jiuxiang Dong"
] | In this paper, we tackle the control and trajectory planning problems for the cooperative transportation system of cable-suspended payload with multi Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Firstly, a payload controller is presented considering the dynamic coupling between the UAV and the payload to accomplish the active suppression of payload swing and the complex payload trajectory tracking. Secondly, ... |
Cooperative Dual-Arm Control for Heavy Object Manipulation Based on Hierarchical Quadratic Programming | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341854/ | [
"Maximilian Dio",
"Andreas Völz",
"Knut Graichen",
"Maximilian Dio",
"Andreas Völz",
"Knut Graichen"
] | This paper presents a new control scheme for cooperative dual-arm robots manipulating heavy objects. The proposed method uses the full dynamical model of the kinematically coupled robot system and builds on a hierarchical quadratic programming (HQP) formulation to enforce dynamical inequality constraints such as joint torques or internal loads. This ensures optimal tracking of an object trajectory... |
Multi-UAV Adaptive Path Planning Using Deep Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342516/ | [
"Jonas Westheider",
"Julius Rückin",
"Marija Popović",
"Jonas Westheider",
"Julius Rückin",
"Marija Popović"
] | Efficient aerial data collection is important in many remote sensing applications. In large-scale monitoring scenarios, deploying a team of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offers improved spatial coverage and robustness against individual failures. However, a key challenge is cooperative path planning for the UAVs to efficiently achieve a joint mission goal. We propose a novel multi-agent informat... |
Emergent Cooperative Behavior in Distributed Target Tracking with Unknown Occlusions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342357/ | [
"Tianqi Li",
"Lucas W. Krakow",
"Swaminathan Gopalswamy",
"Tianqi Li",
"Lucas W. Krakow",
"Swaminathan Gopalswamy"
] | Tracking multiple moving objects of interest (OOI) with multiple robot systems (MRS) has been addressed by active sensing that maintains a shared belief of OOIs and plans the motion of robots to maximize the information quality. Mobility of robots enables the behavior of pursuing better visibility, which is constrained by sensor field of view (FoV) and occlusion objects. We first extend prior work... |
Multi-Objective Sparse Sensing with Ergodic Optimization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341535/ | [
"Ananya Rao",
"Howie Choset",
"Ananya Rao",
"Howie Choset"
] | We consider a search problem where a robot has one or more types of sensors, each suited to detecting different types of targets or target information. Often, information in the form of a distribution of possible target locations, or locations of interest, may be available to guide the search. When multiple types of information exist, then a distribution for each type of information must also exis... |
Team Coordination on Graphs with State-Dependent Edge Costs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341820/ | [
"Manshi Limbu",
"Zechen Hu",
"Sara Oughourli",
"Xuan Wang",
"Xuesu Xiao",
"Daigo Shishika",
"Manshi Limbu",
"Zechen Hu",
"Sara Oughourli",
"Xuan Wang",
"Xuesu Xiao",
"Daigo Shishika"
] | This paper studies a team coordination problem in a graph environment. Specifically, we incorporate “support” action which an agent can take to reduce the cost for its teammate to traverse some high cost edges. Due to this added feature, the graph traversal is no longer a standard multi-agent path planning problem. To solve this new problem, we propose a novel formulation that poses it as a planni... |
Incorporating Stochastic Human Driving States in Cooperative Driving Between a Human-Driven Vehicle and an Autonomous Vehicle | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341565/ | [
"Sanzida Hossain",
"Jiaxing Lu",
"He Bai",
"Weihua Sheng",
"Sanzida Hossain",
"Jiaxing Lu",
"He Bai",
"Weihua Sheng"
] | Modeling a human-driven vehicle is a difficult subject since human drivers have a variety of stochastic behavioral components that influence their driving styles. We develop a cooperative driving framework to incorporate dif-ferent human behavior aspects, including the attentiveness of a driver and the tendency of the driver following advising commands. To demonstrate the framework, we consider th... |
Epistemic Planning for Heterogeneous Robotic Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341352/ | [
"Lauren Bramblett",
"Nicola Bezzo",
"Lauren Bramblett",
"Nicola Bezzo"
] | In applications such as search and rescue or disaster relief, heterogeneous multi-robot systems (MRS) can provide significant advantages for complex objectives that require a suite of capabilities. However, within these application spaces, communication is often unreliable, causing inefficiencies or outright failures to arise in most MRS algorithms. Many researchers tackle this problem by requirin... |
Reinforced Potential Field for Multi-Robot Motion Planning in Cluttered Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342416/ | [
"Dengyu Zhang",
"Xinyu Zhang",
"Zheng Zhang",
"Bo Zhu",
"Qingrui Zhang",
"Dengyu Zhang",
"Xinyu Zhang",
"Zheng Zhang",
"Bo Zhu",
"Qingrui Zhang"
] | Motion planning is challenging for multiple robots in cluttered environments without communication, especially in view of real-time efficiency, motion safety, distributed computation, and trajectory optimality, etc. In this paper, a reinforced potential field method is developed for distributed multi-robot motion planning, which is a synthesized design of reinforcement learning and artificial pote... |
Robot Team Data Collection with Anywhere Communication | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342349/ | [
"Matthew A. Schack",
"John G. Rogers",
"Qi Han",
"Neil T. Dantam",
"Matthew A. Schack",
"John G. Rogers",
"Qi Han",
"Neil T. Dantam"
] | Using robots to collect data is an effective way to obtain information from the environment and communicate it to a static base station. Furthermore, robots have the capability to communicate with one another, potentially decreasing the time for data to reach the base station. We present a Mixed Integer Linear Program that reasons about discrete routing choices, continuous robot paths, and their e... |
Coordination of Multiple Mobile Manipulators for Ordered Sorting of Cluttered Objects | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342179/ | [
"Jeeho Ahn",
"Seabin Lee",
"Changjoo Nam",
"Jeeho Ahn",
"Seabin Lee",
"Changjoo Nam"
] | We present a coordination method for multiple mobile manipulators to sort objects in clutter. We consider the object rearrangement problem in which the objects must be sorted into different groups in a particular order. In clutter, the order constraints could not be easily satisfied since some objects occlude other objects so the occluded ones are not directly accessible to the robots. Those objec... |
MOTLEE: Distributed Mobile Multi-Object Tracking with Localization Error Elimination | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342388/ | [
"Mason B. Peterson",
"Parker C. Lusk",
"Jonathan P. How",
"Mason B. Peterson",
"Parker C. Lusk",
"Jonathan P. How"
] | We present MOTLEE, a distributed mobile multi-object tracking algorithm that enables a team of robots to collaboratively track moving objects in the presence of localization error. Existing approaches to distributed tracking make limiting assumptions regarding the relative spatial relationship of sensors, including assuming a static sensor network or that perfect localization is available. Instead... |
Dynamic Object Tracking for Quadruped Manipulator with Spherical Image-Based Approach | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341608/ | [
"Tianlin Zhang",
"Sikai Guo",
"Xiaogang Xiong",
"Wanlei Li",
"Zezheng Qi",
"Yunjiang Lou",
"Tianlin Zhang",
"Sikai Guo",
"Xiaogang Xiong",
"Wanlei Li",
"Zezheng Qi",
"Yunjiang Lou"
] | Exactly estimating and tracking the motion of surrounding dynamic objects is one of important tasks for the autonomy of a quadruped manipulator. However, with only an onboard RGB camera, it is still a challenging work for a quadruped manipulator to track the motion of a dynamic object moving with unknown and changing velocities. To address this problem, this manuscript proposes a novel image-based... |
Proprioception and Tail Control Enable Extreme Terrain Traversal by Quadruped Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342384/ | [
"Yanhao Yang",
"Joseph Norby",
"Justin K. Yim",
"Aaron M. Johnson",
"Yanhao Yang",
"Joseph Norby",
"Justin K. Yim",
"Aaron M. Johnson"
] | Legged robots leverage ground contacts and the reaction forces they provide to achieve agile locomotion. However, uncertainty coupled with contact discontinuities can lead to failure, especially in real-world environments with unexpected height variations such as rocky hills or curbs. To enable dynamic traversal of extreme terrain, this work introduces 1) a proprioception-based gait planner for es... |
Run and Catch: Dynamic Object-Catching of Quadrupedal Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341977/ | [
"Yangwei You",
"Tianlin Liu",
"Xiaowei Liang",
"Zhe Xu",
"Mingliang Zhou",
"Zhibin Li",
"Shiwu Zhang",
"Yangwei You",
"Tianlin Liu",
"Xiaowei Liang",
"Zhe Xu",
"Mingliang Zhou",
"Zhibin Li",
"Shiwu Zhang"
] | Quadrupedal robots are performing increasingly more real-world capabilities, but are primarily limited to locomotion tasks. To expand their task-level abilities of object acquisition, i.e., run-to-catch as frisbee catching for dogs, this paper developed a control pipeline using stereo vision for legged robots which allows for dynamic catching balls while the robot is in motion. To achieve high-fra... |
A Composite Control Strategy for Quadruped Robot by Integrating Reinforcement Learning and Model-Based Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341908/ | [
"Shangke Lyu",
"Han Zhao",
"Donglin Wang",
"Shangke Lyu",
"Han Zhao",
"Donglin Wang"
] | Locomotion in the wild requires the quadruped robot to have strong capabilities in adaptation and robustness. The deep reinforcement learning (DRL) exhibits the huge potential in environmental adaptability, while its stability issues remain open. On the other hand, the quadruped robot dynamic model contains a lot of useful information that is beneficial to the robust control. The combination of DR... |
Load Awareness: Sensorless Body Payload Sensing and Localization for Heavy Quadruped Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342158/ | [
"Shaoxun Liu",
"Shiyu Zhou",
"Zheng Pan",
"Zhihua Niu",
"Rongrong Wang",
"Shaoxun Liu",
"Shiyu Zhou",
"Zheng Pan",
"Zhihua Niu",
"Rongrong Wang"
] | Heavy quadrupedal drives have great potential for overcoming obstacles, showing great possibilities for transportation industries in complex environments. Ground reaction force (GRF) is a crucial state variable for quadrupedal control. Most GRF observations are implemented in lightweight quadrupeds, with little consideration of the loading being static or slippery on the body. However, the load in... |
Evolutionary-Based Online Motion Planning Framework for Quadruped Robot Jumping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342082/ | [
"Linzhu Yue",
"Zhitao Song",
"Hongbo Zhang",
"Xuanqi Zeng",
"Lingwei Zhang",
"Yun-Hui Liu",
"Linzhu Yue",
"Zhitao Song",
"Hongbo Zhang",
"Xuanqi Zeng",
"Lingwei Zhang",
"Yun-Hui Liu"
] | Offline evolutionary-based methodologies have supplied a successful motion planning framework for the quadrupedal jump. However, the time-consuming computation caused by massive population evolution in offline evolutionary-based jumping framework significantly limits the popularity in the quadrupedal field. This paper presents a time-friendly online motion planning framework based on meta-heuristi... |
Multi-IMU Proprioceptive Odometry for Legged Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342061/ | [
"Shuo Yang",
"Zixin Zhang",
"Benjamin Bokser",
"Zachary Manchester",
"Shuo Yang",
"Zixin Zhang",
"Benjamin Bokser",
"Zachary Manchester"
] | This paper presents a novel, low-cost proprioceptive sensing solution for legged robots with point feet to achieve accurate low-drift long-term position and velocity estimation. In addition to conventional sensors, including one body Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and joint encoders, we attach an additional IMU to each calf link of the robot just above the foot. An extended Kalman filter is used ... |
Design and Motion Guidelines for Quadrupedal Locomotion of Maximum Speed or Efficiency with Serial and Parallel Legs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341886/ | [
"Konstantinos Machairas",
"Evangelos Papadopoulos",
"Konstantinos Machairas",
"Evangelos Papadopoulos"
] | Analytical expressions are derived for actuator demands in quadrupedal locomotion of constant speed and height by using a reduction from a trot/ pace 6-bar model to a single-legged model and employing two widely used two-segmented leg architectures, the serial and the parallel. A method is developed that outputs optimal gait characteristics and leg designs for a robot to move with maximum efficien... |
Towards Legged Locomotion on Steep Planetary Terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341665/ | [
"Giorgio Valsecchi",
"Cedric Weibel",
"Hendrik Kolvenbach",
"Marco Hutter",
"Giorgio Valsecchi",
"Cedric Weibel",
"Hendrik Kolvenbach",
"Marco Hutter"
] | Scientific exploration of planetary bodies is an activity well-suited for robots. Unfortunately, the regions that are richer in potential discoveries, such as impact craters, caves, and volcanic terraces, are hard to access with wheeled robots. Recent advances in legged-based approaches have shown the potential of the technology to overcome difficult terrains such as slopes and slippery surfaces. ... |
Dynamic Hybrid Locomotion and Jumping for Wheeled-Legged Quadrupeds | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341824/ | [
"Mojtaba Hosseini",
"Diego Rodriguez",
"Sven Behnke",
"Mojtaba Hosseini",
"Diego Rodriguez",
"Sven Behnke"
] | Hybrid wheeled-legged quadrupeds have the potential to navigate challenging terrain with agility and speed and over long distances. However, obstacles can impede their progress by requiring the robots to either slow down to step over obstacles or modify their path to circumvent the obstacles. We propose a motion optimization framework for quadruped robots that incorporates non-steerable wheels and... |
Quadrupedal Footstep Planning Using Learned Motion Models of a Black-Box Controller | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342440/ | [
"Ilyass Taouil",
"Giulio Turrisi",
"Daniel Schleich",
"Victor Barasuol",
"Claudio Semini",
"Sven Behnke",
"Ilyass Taouil",
"Giulio Turrisi",
"Daniel Schleich",
"Victor Barasuol",
"Claudio Semini",
"Sven Behnke"
] | Legged robots are increasingly entering new domains and applications, including search and rescue, inspection, and logistics. However, for such a systems to be valuable in real-world scenarios, they must be able to autonomously and robustly navigate irregular terrains. In many cases, robots that are sold on the market do not provide such abilities, being able to perform only blind locomotion. Furt... |
Locomotion Planning of a Truss Robot on Irregular Terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341447/ | [
"Jangho Bae",
"Inha Park",
"Mark Yim",
"TaeWon Seo",
"Jangho Bae",
"Inha Park",
"Mark Yim",
"TaeWon Seo"
] | This paper proposes a new locomotion algorithm for truss robots on irregular terrain, in particular, for the Variable Topology Truss (VTT) system. The previous Polygon-based Random Tree (PRT) search algorithm for support polygon generation is extended to irregular terrain while considering friction and internal force limitations. By characterizing terrain, unreachable areas are excluded from searc... |
A Model Predictive Path Integral Method for Fast, Proactive, and Uncertainty-Aware UAV Planning in Cluttered Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341501/ | [
"Jacob Higgins",
"Nicholas Mohammad",
"Nicola Bezzo",
"Jacob Higgins",
"Nicholas Mohammad",
"Nicola Bezzo"
] | Current motion planning approaches for autonomous mobile robots often assume that the low level controller of the system is able to track the planned motion with very high accuracy. In practice, however, tracking error can be affected by many factors, and could lead to potential collisions when the robot must traverse a cluttered environment. To address this problem, this paper proposes a novel re... |
Energy-Efficient Team Orienteering Problem in the Presence of Time-Varying Ocean Currents | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341645/ | [
"Ariella Mansfield",
"Douglas G. Macharet",
"M. Ani Hsieh",
"Ariella Mansfield",
"Douglas G. Macharet",
"M. Ani Hsieh"
] | Autonomous Marine Vehicles (AMVs) have gained interest for scientific and commercial applications, including pipeline and algae bloom monitoring, contaminant tracking, and ocean debris removal. The Team Orienteering Problem (TOP) is relevant in this context as Multi-Robot Systems (MRSs) allow for better coverage of the area of interest, simultaneous data collection at different locations, and an i... |
Multi-Agent Multi-Objective Ergodic Search Using Branch and Bound | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341353/ | [
"Akshaya Kesarimangalam Srinivasan",
"Geordan Gutow",
"Zhongqiang Ren",
"Ian Abraham",
"Bhaskar Vundurthy",
"Howie Choset",
"Akshaya Kesarimangalam Srinivasan",
"Geordan Gutow",
"Zhongqiang Ren",
"Ian Abraham",
"Bhaskar Vundurthy",
"Howie Choset"
] | Search and rescue applications often need multiple agents to complete a set of conflicting tasks. This paper studies a Multi-Agent Multi-Objective Ergodic Search (MA-MO-ES) approach to this problem where each objective or task is to cover a domain subject to an information map. The goal is to allocate coverage tasks to agents so that all maps are explored ergodically. The combinatorial nature of t... |
Leveraging Single-Goal Predictions to Improve the Efficiency of Multi-Goal Motion Planning with Dynamics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341945/ | [
"Yuanjie Lu",
"Erion Plaku",
"Yuanjie Lu",
"Erion Plaku"
] | Multi-goal motion planning requires a robot to plan collision-free and dynamically-feasible motions to reach multiple goals, often in unstructured, obstacle-rich environments. This is challenging due to the complex dependencies between navigation and high-level reasoning, requiring the robot to explore a vast space of feasible motions and goal sequences. Our approach combines machine learning and ... |
DynGMP: Graph Neural Network-Based Motion Planning in Unpredictable Dynamic Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342326/ | [
"Wenjin Zhang",
"Xiao Zang",
"Lingyi Huang",
"Yang Sui",
"Jingjin Yu",
"Yingying Chen",
"Bo Yuan",
"Wenjin Zhang",
"Xiao Zang",
"Lingyi Huang",
"Yang Sui",
"Jingjin Yu",
"Yingying Chen",
"Bo Yuan"
] | Neural networks have already demonstrated attractive performance for solving motion planning problems, especially in static and predictable environments. However, efficient neural planners that can adapt to unpredictable dynamic environments, a highly demanded scenario in many practical applications, are still under-explored. To fill this research gap and enrich the existing motion planning approa... |
Symbolic State Space Optimization for Long Horizon Mobile Manipulation Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342224/ | [
"Xiaohan Zhang",
"Yifeng Zhu",
"Yan Ding",
"Yuqian Jiang",
"Yuke Zhu",
"Peter Stone",
"Shiqi Zhang",
"Xiaohan Zhang",
"Yifeng Zhu",
"Yan Ding",
"Yuqian Jiang",
"Yuke Zhu",
"Peter Stone",
"Shiqi Zhang"
] | In existing task and motion planning (TAMP) research, it is a common assumption that experts manually specify the state space for task-level planning. A well-developed state space enables the desirable distribution of limited computational resources between task planning and motion planning. However, developing such task-level state spaces can be non-trivial in practice. In this paper, we consider... |
A Fast and Map-Free Model for Trajectory Prediction in Traffics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10342199/ | [
"Junhong Xiang",
"Jingmin Zhang",
"Zhixiong Nan",
"Junhong Xiang",
"Jingmin Zhang",
"Zhixiong Nan"
] | To handle the two shortcomings of existing methods, (i) nearly all models rely on high-definition (HD) maps, yet the map information is not always available in real traffic scenes and HD map-building is expensive and time-consuming and (ii) existing models usually focus on improving prediction accuracy at the expense of reducing computing efficiency, yet the efficiency is crucial for various real ... |
Local Non-Cooperative Games with Principled Player Selection for Scalable Motion Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341677/ | [
"Makram Chahine",
"Roya Firoozi",
"Wei Xiao",
"Mac Schwager",
"Daniela Rus",
"Makram Chahine",
"Roya Firoozi",
"Wei Xiao",
"Mac Schwager",
"Daniela Rus"
] | Game-theoretic motion planners are a powerful tool for the control of interactive multi-agent robot systems. Indeed, contrary to predict-then-plan paradigms, game-theoretic planners do not ignore the interactive nature of the problem, and simultaneously predict the behaviour of other agents while considering change in one's policy. This, however, comes at the expense of computational complexity, e... |
Target Attribute Perception Based UAV Real-Time Task Planning in Dynamic Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341486/ | [
"Jinhong He",
"Zheyu Sun",
"Ningbo Cao",
"Delie Ming",
"Chao Cai",
"Jinhong He",
"Zheyu Sun",
"Ningbo Cao",
"Delie Ming",
"Chao Cai"
] | In this paper, a comprehensive solution for enabling unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to autonomously fly through complex and dynamic environments is proposed. Moving objects all have unique property information, we propose a method that utilizes deep learning for 3D dynamic environment perception, while taking into account limitations in computing resources. For safer dynamic avoidance, we first mod... |
IROS 2023 Accepted Paper Meta Info Dataset
This dataset is collect from the IROS 2023-2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/conhome/10341341/proceeding) as well as the arxiv website DeepNLP paper arxiv (http://www.deepnlp.org/content/paper/iros2023). For researchers who are interested in doing analysis of IROS 2023 accepted papers and potential trends, you can use the already cleaned up json files. Each row contains the meta information of a paper in the IROS 2023 conference. To explore more AI & Robotic papers (NIPS/ICML/ICLR/IROS/ICRA/etc) and AI equations, feel free to navigate the Equation Search Engine (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/equation) as well as the AI Agent Search Engine to find the deployed AI Apps and Agents (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/agent) in your domain.
Equations Latex code and Papers Search Engine
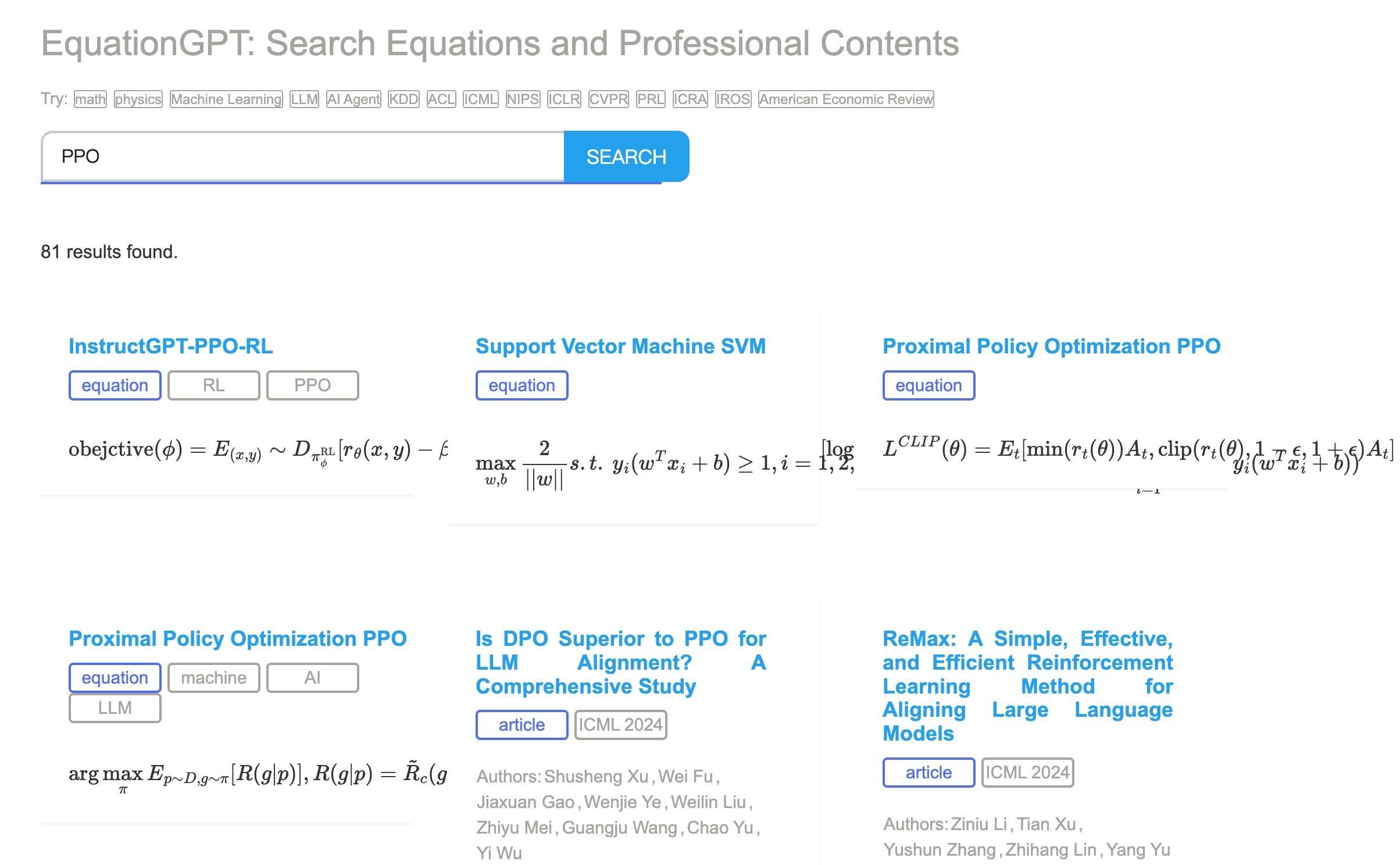
Meta Information of Json File of Paper
{
"title": "Prototypical Contrastive Transfer Learning for Multimodal Language Understanding",
"detail_url": "https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10341388/",
"author_list": ["Seitaro Otsuki", "Shintaro Ishikawa", "Komei Sugiura", "Seitaro Otsuki", "Shintaro Ishikawa", "Komei Sugiura"],
"abstract": "Although domestic service robots are expected to assist individuals who require support, they cannot currently interact smoothly with people through natural language. For example, given the instruction \u201cBring me a bottle from the kitchen,\u201d it is difficult for such robots to specify the bottle in an indoor environment. Most conventional models have been trained on real-world datasets that are labor..."
}
Related
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
Robot Search
Equation and Academic search
AI & Robot Comprehensive Search
AI & Robot Question
AI & Robot Community
AI Agent Marketplace Blog
AI Agent Reviews
AI Agent Marketplace Directory
Microsoft AI Agents Reviews
Claude AI Agents Reviews
OpenAI AI Agents Reviews
Saleforce AI Agents Reviews
AI Agent Builder Reviews
AI Equation
List of AI Equations and Latex
List of Math Equations and Latex
List of Physics Equations and Latex
List of Statistics Equations and Latex
List of Machine Learning Equations and Latex
- Downloads last month
- 86