title
stringlengths 8
151
| detail_url
stringlengths 27
46
| author_list
sequencelengths 0
30
| abstract
stringlengths 0
403
|
|---|---|---|---|
Top Menu | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
Welcome Page | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160735/ | [] | |
Organising Committee | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
Programme at a glance | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | Programme at a glance |
Table of Contents | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
Author Index | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
Reconfigurable Inflated Soft Arms | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160569/ | [
"Nam Gyun Kim",
"Jee-Hwan Ryu",
"Nam Gyun Kim",
"Jee-Hwan Ryu"
] | Inflatable structures have attracted considerable research attention in many fields owing to their numerous advantages, such as being light and able to engage in interactions safely. However, in most cases, the inflatable structure can only have one stable configuration, which is undesirable for robotic arms. This study proposes a novel inflatable structure that can be easily reconfigured into mul... |
A Soft Hybrid-Actuated Continuum Robot Based on Dual Origami Structures | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161358/ | [
"Jian Tao",
"Qiqiang Hu",
"Tianzhi Luo",
"Erbao Dong",
"Jian Tao",
"Qiqiang Hu",
"Tianzhi Luo",
"Erbao Dong"
] | Soft continuum robots have shown tremendous potential for medical and industrial applications owing to their flexibility and continuous deformability. However, their telescopic and bending capabilities and variable stiffness are still limited. This study proposes a novel origami-inspired soft continuum robot to possess large telescopic and bending capabilities while improving stiffness based on th... |
Direct and inverse modeling of soft robots by learning a condensed FEM model | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161537/ | [
"Etienne Ménager",
"Tanguy Navez",
"Olivier Goury",
"Christian Duriez",
"Etienne Ménager",
"Tanguy Navez",
"Olivier Goury",
"Christian Duriez"
] | The Finite Element Method (FEM) is a powerful modeling tool for predicting the behavior of soft robots. However, its use for control can be difficult for non-specialists of numerical computation: it requires an optimization of the computation to make it real-time. In this paper, we propose a learning-based approach to obtain a compact but sufficiently rich mechanical representation. Our choice is ... |
Limit Cycle Generation with Pneumatically Driven Physical Reservoir Computing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161315/ | [
"Hiroaki Shinkawa",
"Toshihiro Kawase",
"Tetsuro Miyazaki",
"Takahiro Kanno",
"Maina Sogabe",
"Kenji Kawashima",
"Hiroaki Shinkawa",
"Toshihiro Kawase",
"Tetsuro Miyazaki",
"Takahiro Kanno",
"Maina Sogabe",
"Kenji Kawashima"
] | One of the recent developments in physical reservoir computing, which uses the complex dynamics of a physical system as a computational resource, is the use of a pneumatic pipeline system as a computational resource. This uses the dynamics of air for computation, and because it is lightweight and power-saving, it is used for gait-assist control using a soft exoskeleton with pneumatic rubber artifi... |
Toward Zero-Shot Sim-to-Real Transfer Learning for Pneumatic Soft Robot 3D Proprioceptive Sensing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160384/ | [
"Uksang Yoo",
"Hanwen Zhao",
"Alvaro Altamirano",
"Wenzhen Yuan",
"Chen Feng",
"Uksang Yoo",
"Hanwen Zhao",
"Alvaro Altamirano",
"Wenzhen Yuan",
"Chen Feng"
] | Pneumatic soft robots present many advantages in manipulation tasks. Notably, their inherent compliance makes them safe and reliable in unstructured and fragile environments. However, full-body shape sensing for pneumatic soft robots is challenging because of their high degrees of freedom and complex deformation behaviors. Vision-based proprioception sensing methods relying on embedded cameras and... |
Cross-domain Transfer Learning and State Inference for Soft Robots via a Semi-supervised Sequential Variational Bayes Framework | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160662/ | [
"Shageenderan Sapai",
"Junn Yong Loo",
"Ze Yang Ding",
"Chee Pin Tan",
"Raphaël C.-W. Phan",
"Vishnu Monn Baskaran",
"Surya Girinatha Nurzaman",
"Shageenderan Sapai",
"Junn Yong Loo",
"Ze Yang Ding",
"Chee Pin Tan",
"Raphaël C.-W. Phan",
"Vishnu Monn Baskaran",
"Surya Girinatha Nurzaman"
] | Recently, data-driven models such as deep neural networks have shown to be promising tools for modelling and state inference in soft robots. However, voluminous amounts of data are necessary for deep models to perform effectively, which requires exhaustive and quality data collection, particularly of state labels. Consequently, obtaining labelled state data for soft robotic systems is challenged f... |
Image-based Pose Estimation and Shape Reconstruction for Robot Manipulators and Soft, Continuum Robots via Differentiable Rendering | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161066/ | [
"Jingpei Lu",
"Fei Liu",
"Cédric Girerd",
"Michael C. Yip",
"Jingpei Lu",
"Fei Liu",
"Cédric Girerd",
"Michael C. Yip"
] | State estimation from measured data is crucial for robotic applications as autonomous systems rely on sensors to capture the motion and localize in the 3D world. Among sensors that are designed for measuring a robot's pose, or for soft robots, their shape, vision sensors are favorable because they are information-rich, easy to set up, and cost-effective. With recent advancements in computer vision... |
Discrete-time model based control of soft manipulator with FBG sensing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160743/ | [
"Enrico Franco",
"Ayhan Aktas",
"Shen Treratanakulchai",
"Arnau Garriga-Casanovas",
"Abdulhamit Donder",
"Ferdinando Rodriguez y Baena",
"Enrico Franco",
"Ayhan Aktas",
"Shen Treratanakulchai",
"Arnau Garriga-Casanovas",
"Abdulhamit Donder",
"Ferdinando Rodriguez y Baena"
] | In this article we investigate the discrete-time model based control of a planar soft continuum manipulator with proprioceptive sensing provided by fiber Bragg gratings. A control algorithm is designed with a discrete-time energy shaping approach which is extended to account for control-related lag of digital nature. A discrete-time nonlinear observer is employed to estimate the uncertain bending ... |
A Soft Robot with Three Dimensional Shape Sensing and Contact Recognition Multi-Modal Sensing via Tunable Soft Optical Sensors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160877/ | [
"Max McCandless",
"Frank Juliá Wise",
"Sheila Russo",
"Max McCandless",
"Frank Juliá Wise",
"Sheila Russo"
] | Soft optical sensing strategies are rapidly developing for soft robotic systems as a means to increase the controllability of soft compliant robots. In this paper, we present a roughness tuning strategy for the fabrication of soft optical sensors to achieve the dual functionality of shape sensing combined with contact recognition within a single multi-modal sensor. The molds used to fabricate the ... |
A Flexible 3D Force Sensor with In-Situ Tunable Sensitivity | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160637/ | [
"James Davies",
"Mai Thanh Thai",
"Trung Thien Hoang",
"Chi Cong Nguyen",
"Phuoc Thien Phan",
"Kefan Zhu",
"Dang Bao Nhi Tran",
"Van Anh Ho",
"Hung Manh La",
"Quang Phuc Ha",
"Nigel Hamilton Lovell",
"Thanh Nho Do",
"James Davies",
"Mai Thanh Thai",
"Trung Thien Hoang",
"Chi Cong Nguyen",
"Phuoc Thien Phan",
"Kefan Zhu",
"Dang Bao Nhi Tran",
"Van Anh Ho",
"Hung Manh La",
"Quang Phuc Ha",
"Nigel Hamilton Lovell",
"Thanh Nho Do"
] | Following biology's lead, soft robotics has emerged as a perfect candidate for actuation within complex environments. While soft actuation has been developed intensively over the last few decades, soft sensing has so far slowed to catch up. A largely unresearched area is the change of the soft material properties through prestress to achieve a degree of mechanical sensitivity tunability within sof... |
STEV: Stretchable Triboelectric E-skin enabled Proprioceptive Vibration Sensing for Soft Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160790/ | [
"Zihan Wang",
"Kai-Chong Lei",
"Huaze Tang",
"Shoujie Li",
"Yuan Dai",
"Wenbo Ding",
"Xiao-Ping Zhang",
"Zihan Wang",
"Kai-Chong Lei",
"Huaze Tang",
"Shoujie Li",
"Yuan Dai",
"Wenbo Ding",
"Xiao-Ping Zhang"
] | Vibration perception is essential for robotic sensing and dynamic control. Nevertheless, due to the rigorous demand for sensor conformability and stretchability, enabling soft robots with proprioceptive vibration sensing remains challenging. This paper proposes a novel liquid metal-based stretchable e-skin via a kirigami-inspired design to enable soft robot proprioceptive vibration sensing. The e-... |
Design and Development of a Hydrogel-based Soft Sensor for Multi-Axis Force Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160807/ | [
"Yichen Cai",
"David Hardman",
"Fumiya Iida",
"Thomas George Thuruthel",
"Yichen Cai",
"David Hardman",
"Fumiya Iida",
"Thomas George Thuruthel"
] | As soft robotic systems become increasingly complex, there is a need to develop sensory systems which can provide rich state information to the robot for feedback control. Multi-axis force sensing and control is one of the less explored problems in this domain. There are numerous challenges in the development of a multi-axis soft sensor: from the design and fabrication to the data processing and m... |
Design and characterization of a low mechanical loss, high-resolution wearable strain gauge | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161524/ | [
"Addison Liu",
"Seun Araromi",
"Conor J. Walsh",
"Robert J. Wood",
"Addison Liu",
"Seun Araromi",
"Conor J. Walsh",
"Robert J. Wood"
] | Soft, wearable systems hold promise for a wide variety of new or enhanced applications in the realm of human-computer interaction, physiological monitoring, wear-able robotics, and a host of other human-centric devices. Soft sensor systems have been developed concurrently in order to allow these wearable systems to respond intelligently with their surroundings. A recently reported sensing mechanis... |
Identifying Contact Distance Uncertainty in Whisker Sensing with Tapered, Flexible Whiskers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160408/ | [
"Teresa A. Kent",
"Hannah Emnett",
"Mahnoush Babaei",
"Mitra J. Z. Hartmann",
"Sarah Bergbreiter",
"Teresa A. Kent",
"Hannah Emnett",
"Mahnoush Babaei",
"Mitra J. Z. Hartmann",
"Sarah Bergbreiter"
] | Whisker-based tactile sensors have the potential to perform fast and accurate 3D mappings of the environment, complementing vision-based methods under conditions of glare, reflection, proximity, and occlusion. However, current algorithms for mapping with whiskers make assumptions about the conditions of contact, and these assumptions are not always valid and can cause significant sensing errors. H... |
Learning Decoupled Multi-touch Force Estimation, Localization and Stretch for Soft Capacitive E-skin | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160961/ | [
"Abu Bakar Dawood",
"Claudio Coppola",
"Kaspar Althoefer",
"Abu Bakar Dawood",
"Claudio Coppola",
"Kaspar Althoefer"
] | Distributed sensor arrays capable of detecting multiple spatially distributed stimuli are considered an important element in the realisation of exteroceptive and proprioceptive soft robots. This paper expands upon the previously presented idea of decoupling the measurements of pressure and location of a local indentation from global deformation, using the overall stretch experienced by a soft capa... |
OptiGap: A Modular Optical Sensor System for Bend Localization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161357/ | [
"Paul Bupe",
"C. K. Harnett",
"Paul Bupe",
"C. K. Harnett"
] | This paper presents the novel use of air gaps in flexible optical light pipes to create coded patterns for use in bend localization. The OptiGap sensor system allows for the creation of extrinsic intensity modulated bend sensors that function as flexible absolute linear encoders. Coded air gap patterns are identified by a Gaussian naive Bayes (GNB) classifier running on an STM32 microcontroller. T... |
A Silicone-sponge-based Variable-stiffness Device | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160915/ | [
"Tianqi Yue",
"Tsam Lung You",
"Hemma Philamore",
"Hermes Bloomfield-Gadêlha",
"Jonathan Rossiter",
"Tianqi Yue",
"Tsam Lung You",
"Hemma Philamore",
"Hermes Bloomfield-Gadêlha",
"Jonathan Rossiter"
] | Soft devices employ variable stiffness to ensure safety and improve the robustness in the interaction between robots and objects. Using soft materials is one of the most popular approaches to design a variable-stiffness device, while the use of silicone sponge remains less explored in this field. Here we present a novel silicone-sponge-based variable-stiffness device (SVD). The SVD is easy-to-make... |
Design and Control of a Tunable-Stiffness Coiled-Spring Actuator | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161218/ | [
"Shivangi Misra",
"Mason Mitchell",
"Rongqian Chen",
"Cynthia Sung",
"Shivangi Misra",
"Mason Mitchell",
"Rongqian Chen",
"Cynthia Sung"
] | We propose a novel design for a lightweight and compact tunable stiffness actuator capable of stiffness changes up to 20x. The design is based on the concept of a coiled spring, where changes in the number of layers in the spring change the bulk stiffness in a near linear fashion. We present an elastica nested rings model for the deformation of the proposed actuator and empirically verify that the... |
Wirelessly-Controlled Untethered Piezoelectric Planar Soft Robot Capable of Bidirectional Crawling and Rotation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160886/ | [
"Zhiwu Zheng",
"Hsin Cheng",
"Prakhar Kumar",
"Sigurd Wagner",
"Minjie Chen",
"Naveen Verma",
"James C. Sturm",
"Zhiwu Zheng",
"Hsin Cheng",
"Prakhar Kumar",
"Sigurd Wagner",
"Minjie Chen",
"Naveen Verma",
"James C. Sturm"
] | Electrostatic actuators provide a promising approach to creating soft robotic sheets, due to their flexible form factor, modular integration, and fast response speed. However, their control requires kilo-Volt signals and understanding of complex dynamics resulting from force interactions by on-board and environmental effects. In this work, we demonstrate an untethered planar five-actuator piezoele... |
Origami Folding Enhances Modularity and Mechanical Efficiency of Soft Actuators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160943/ | [
"Zheng Wang",
"Yazhou Song",
"Zhongkui Wang",
"Hongying Zhang",
"Zheng Wang",
"Yazhou Song",
"Zhongkui Wang",
"Hongying Zhang"
] | Soft robots have long been attractive to robotic engineers due to their remarkable dexterity; however, reports that standardize soft actuators into modularized off-shelf devices akin to rigid robots are still rare, and the mechanical efficiency of existing designs is still limited. This work identifies origami folding to enable the design of LEGO-like modularized soft actuators with high mechanica... |
Characterisation of Antagonistically Actuated, Stiffness-Controllable Joint-Link Units for Cobots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161396/ | [
"Wenlong Gaozhang",
"Jialei Shi",
"Yue Li",
"Agostino Stilli",
"Helge Wurdemann",
"Wenlong Gaozhang",
"Jialei Shi",
"Yue Li",
"Agostino Stilli",
"Helge Wurdemann"
] | Soft robotic structures may play a major role in the 4th industrial revolution. Researchers have successfully demonstrated the advantages of soft robotics over traditional robots made of rigid links and joints in many application areas. Variable stiffness links (VSL) and joints (VSJ) have been investigated to achieve on-demand forces and, at the same time, be inherently safe in interactions with h... |
A fluidic actuator with an internal stiffening structure inspired by mammalian erectile tissue | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160689/ | [
"Jan Fras",
"Kaspar Althoefer",
"Jan Fras",
"Kaspar Althoefer"
] | One of the biggest problems with soft robots is precisely the fact that they are soft. Indeed the softer they are, the less force they can exert on the environment. Researchers have proposed a number of stiffening methods, but all of them have drawbacks, such as locking the shape of the device in a way that precludes further adjustments. In this paper we propose a stiffening method inspired by the... |
On Tendon Driven Continuum Robots with Compressible Backbones | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161208/ | [
"Manu Srivastava",
"Ian D. Walker",
"Manu Srivastava",
"Ian D. Walker"
] | This paper discusses the effect of axial backbone compression on tendon-driven continuum robots. A new mechanics model for compensating for this effect that does not require tendon tension sensing or knowledge of manipulator material properties/stiffnesses is introduced and analyzed. In addition, we provide an analytical expression for the minimum preload on the tendons to achieve a given bend, a ... |
FourStr: When Multi-sensor Fusion Meets Semi-supervised Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161363/ | [
"Bangquan Xie",
"Liang Yang",
"Zongming Yang",
"Ailin Wei",
"Xiaoxiong Weng",
"Bing Li",
"Bangquan Xie",
"Liang Yang",
"Zongming Yang",
"Ailin Wei",
"Xiaoxiong Weng",
"Bing Li"
] | This research proposes a novel semi-supervised learning framework FourStr (Four-Stream formed by two two-stream models) that focuses on the improvement of fusion and labeling efficiency for 3D multi-sensor detector. FourStr adopts a multi-sensor single-stage detector named adaptive fusion network (AFNet) as the backbone and trains it through the semi-supervision learning (SSL) strategy Stereo Fusi... |
Combining Motion and Appearance for Robust Probabilistic Object Segmentation in Real Time | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160908/ | [
"Vito Mengers",
"Aravind Battaje",
"Manuel Baum",
"Oliver Brock",
"Vito Mengers",
"Aravind Battaje",
"Manuel Baum",
"Oliver Brock"
] | We present a robust method to visually segment scenes into objects based on motion and appearance. Both these cues provide complementary information that we fuse using two interconnected recursive estimators: One estimates object segmentation from motion as a probabilistic clustering of tracked 3D points, and the other estimates object segmentation from appearance as a probabilistic image segmenta... |
Event-based Real-time Moving Object Detection Based On IMU Ego-motion Compensation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160472/ | [
"Chunhui Zhao",
"Yakun Li",
"Yang Lyu",
"Chunhui Zhao",
"Yakun Li",
"Yang Lyu"
] | Accurate and timely onboard perception is a prerequisite for mobile robots to operate in highly dynamic scenarios. The bio-inspired event camera can capture more motion details than a traditional camera by triggering each pixel asynchronously and therefore is more suitable in such scenarios. Among various perception tasks based on the event camera, ego-motion removal is one fundamental procedure t... |
Estimating the Motion of Drawers From Sound | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161399/ | [
"Manuel Baum",
"Amelie Froessl",
"Aravind Battaje",
"Oliver Brock",
"Manuel Baum",
"Amelie Froessl",
"Aravind Battaje",
"Oliver Brock"
] | Robots need to understand articulated objects, such as drawers. The state of articulated structures is commonly estimated using vision, but visual perception is limited when objects are occluded, have few salient features, or are not in the camera's field of view. Audio sensing does not face these challenges, since sound propagates in a fundamentally different way than light. Therefore we propose ... |
Sonicverse: A Multisensory Simulation Platform for Embodied Household Agents that See and Hear | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160461/ | [
"Ruohan Gao",
"Hao Li",
"Gokul Dharan",
"Zhuzhu Wang",
"Chengshu Li",
"Fei Xia",
"Silvio Savarese",
"Li Fei-Fei",
"Jiajun Wu",
"Ruohan Gao",
"Hao Li",
"Gokul Dharan",
"Zhuzhu Wang",
"Chengshu Li",
"Fei Xia",
"Silvio Savarese",
"Li Fei-Fei",
"Jiajun Wu"
] | Developing embodied agents in simulation has been a key research topic in recent years. Exciting new tasks, algorithms, and benchmarks have been developed in various simulators. However, most of them assume deaf agents in silent environments, while we humans perceive the world with multiple senses. We introduce Sonicverse, a multisensory simulation platform with integrated audio-visual simulation ... |
LAPTNet-FPN: Multi-Scale LiDAR-Aided Projective Transform Network for Real Time Semantic Grid Prediction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160757/ | [
"Manuel Diaz-Zapata",
"David Sierra-Gonzalez",
"Özgür Erkent",
"Christian Laugier",
"Jilles Dibangoye",
"Manuel Diaz-Zapata",
"David Sierra-Gonzalez",
"Özgür Erkent",
"Christian Laugier",
"Jilles Dibangoye"
] | Semantic grids can be useful representations of the scene around an autonomous system. By having information about the layout of the space around itself, a robot can leverage this type of representation for crucial tasks such as navigation or tracking. By fusing information from multiple sensors, robustness can be increased and the computational load for the task can be lowered, achieving real tim... |
Collision-aware In-hand 6D Object Pose Estimation using Multiple Vision-based Tactile Sensors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160359/ | [
"Gabriele M. Caddeo",
"Nicola A. Piga",
"Fabrizio Bottarel",
"Lorenzo Natale",
"Gabriele M. Caddeo",
"Nicola A. Piga",
"Fabrizio Bottarel",
"Lorenzo Natale"
] | In this paper, we address the problem of estimating the in-hand 6D pose of an object in contact with multiple vision-based tactile sensors. We reason on the possible spatial configurations of the sensors along the object surface. Specifically, we filter contact hypotheses using geometric reasoning and a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), trained on simulated object-agnostic images, to promote tho... |
CalibDepth: Unifying Depth Map Representation for Iterative LiDAR-Camera Online Calibration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161575/ | [
"Jiangtong Zhu",
"Jianru Xue",
"Pu Zhang",
"Jiangtong Zhu",
"Jianru Xue",
"Pu Zhang"
] | LiDAR-Camera online calibration is of great significance for building a stable autonomous driving perception system. For online calibration, a key challenge lies in constructing a unified and robust representation between multi-modal sensor data. Most methods extract features manually or implicitly with an end-to-end deep learning method. The former suffers poor robustness, while the latter has po... |
Shape visual servoing of a tether cable from parabolic features | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161101/ | [
"Lev Smolentsev",
"Alexandre Krupa",
"François Chaumette",
"Lev Smolentsev",
"Alexandre Krupa",
"François Chaumette"
] | In this paper we propose a visual servoing approach that controls the deformation of a suspended tether cable subject to gravity from visual data provided by a RGB-D camera. The cable shape is modelled with a parabolic curve together with the orientation of the plane containing the tether. The visual features considered are the parabolic coefficients and the yaw angle of that plane. We derive the ... |
Deep metric learning for visual servoing: when pose and image meet in latent space | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160963/ | [
"Samuel Felton",
"Elisa Fromont",
"Eric Marchand",
"Samuel Felton",
"Elisa Fromont",
"Eric Marchand"
] | We propose a new visual servoing method that controls a robot's motion in a latent space. We aim to extract the best properties of two previously proposed servoing methods: we seek to obtain the accuracy of photometric methods such as Direct Visual Servoing (DVS), as well as the behavior and convergence of pose-based visual servoing (PBVS). Photometric methods suffer from limited convergence area ... |
CNN-based Visual Servoing for Simultaneous Positioning and Flattening of Soft Fabric Parts | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160635/ | [
"Fuyuki Tokuda",
"Akira Seino",
"Akinari Kobayashi",
"Kazuhiro Kosuge",
"Fuyuki Tokuda",
"Akira Seino",
"Akinari Kobayashi",
"Kazuhiro Kosuge"
] | This paper proposes CNN-based visual servoing for simultaneous positioning and flattening of a soft fabric part placed on a table by a dual manipulator system. We propose a network for multimodal data processing of grayscale images captured by a camera and force/torque applied to force sensors. The training dataset is collected by moving the real manipulators, which enables the network to map the ... |
Dynamical System-based Imitation Learning for Visual Servoing using the Large Projection Formulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160935/ | [
"Antonio Paolillo",
"Paolo Robuffo Giordano",
"Matteo Saveriano",
"Antonio Paolillo",
"Paolo Robuffo Giordano",
"Matteo Saveriano"
] | Nowadays ubiquitous robots must be adaptive and easy to use. To this end, dynamical system-based imitation learning plays an important role. In fact, it allows to realize stable and complex robotic tasks without explicitly coding them, thus facilitating the robot use. However, the adaptation capabilities of dynamical systems have not been fully exploited due to the lack of closed-loop implementati... |
Constant Distance and Orientation Following of an Unknown Surface with a Cable-Driven Parallel Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160308/ | [
"Thomas Rousseau",
"Nicolò Pedemonte",
"Stéphane Caro",
"François Chaumette",
"Thomas Rousseau",
"Nicolò Pedemonte",
"Stéphane Caro",
"François Chaumette"
] | Cable-Driven Parallel Robots (CDPRs) are well-adapted to large workspaces since they replace rigid links by cables. However, they lack in positioning accuracy and new control methods are necessary to achieve profile-following tasks. This paper presents a control scheme designed for these tasks, relying on a combination of accurate boarded distance sensors and of a less accurate remote camera. The ... |
3D Spectral Domain Registration-Based Visual Servoing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160430/ | [
"Maxime Adjigble",
"Brahim Tamadazte",
"Cristiana de Farias",
"Rustam Stolkin",
"Naresh Marturi",
"Maxime Adjigble",
"Brahim Tamadazte",
"Cristiana de Farias",
"Rustam Stolkin",
"Naresh Marturi"
] | This paper presents a spectral domain registration-based visual servoing scheme that works on 3D point clouds. Specifically, we propose a 3D model/point cloud alignment method, which works by finding a global transformation between reference and target point clouds using spectral analysis. A 3D Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) in $\mathbb{R}^{3}$ is used for the translation estimation, and the real sp... |
Autonomous Endoscope Control Algorithm with Visibility and Joint Limits Avoidance Constraints for da Vinci Research Kit Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160510/ | [
"Rocco Moccia",
"Fanny Ficuciello",
"Rocco Moccia",
"Fanny Ficuciello"
] | This paper presents a novel autonomous endoscope control method for the dVRK's Endoscopic Camera Manipulator (ECM), which allows the camera to track the surgical instruments on the Patient Side Manipulator (PSM). An Image-based Visual Servoing (IBVS) is enforced by the addition of a visibility constraint that ensures the identified surgical tool remains in the camera's Field Of View (FOV) for the ... |
Safe Control using Vision-based Control Barrier Function (V-CBF) | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160805/ | [
"Hossein Abdi",
"Golnaz Raja",
"Reza Ghabcheloo",
"Hossein Abdi",
"Golnaz Raja",
"Reza Ghabcheloo"
] | Safe motion control in unknown environments is one of the challenging tasks in robotics, such as autonomous navigation. Control Barrier Function (CBF), as a strong math-ematical tool, has been widely used in many safety-critical systems to satisfy safety requirements. However, there are only a handful of recent studies on safety controllers with perception inputs. Common assumptions in most of the... |
DC-MOT: Motion Deblurring and Compensation for Multi-Object Tracking in UAV Videos | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160931/ | [
"Song Cheng",
"Meibao Yao",
"Xueming Xiao",
"Song Cheng",
"Meibao Yao",
"Xueming Xiao"
] | In this paper, we propose a multi-object tracking framework for videos captured by UAVs, considering motion imperfection in the following two aspects: 1) motion blurring of objects due to high-speed motion of the UAV and the objects, deteriorating the performance of the detector; 2) motion coupling of the global movement of the UAV camera with the object motion, resulting in the nonlinearity of ob... |
Fast Event-based Double Integral for Real-time Robotics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160727/ | [
"Shijie Lin",
"Yingqiang Zhang",
"Dongyue Huang",
"Bin Zhou",
"Xiaowei Luo",
"Jia Pan",
"Shijie Lin",
"Yingqiang Zhang",
"Dongyue Huang",
"Bin Zhou",
"Xiaowei Luo",
"Jia Pan"
] | Motion deblurring is a critical ill-posed problem that is important in many vision-based robotics applications. The recently proposed event-based double integral (EDI) provides a theoretical framework for solving the deblurring prob-lem with the event camera and generating clear images at high frame-rate. However, the original EDI is mainly designed for offline computation and does not support rea... |
Continuous-Time Gaussian Process Motion-Compensation for Event-Vision Pattern Tracking with Distance Fields | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160768/ | [
"Cedric Le Gentil",
"Ignacio Alzugaray",
"Teresa Vidal-Calleja",
"Cedric Le Gentil",
"Ignacio Alzugaray",
"Teresa Vidal-Calleja"
] | This work addresses the issue of motion compensation and pattern tracking in event camera data. An event camera generates asynchronous streams of events triggered independently by each of the pixels upon changes in the observed intensity. Providing great advantages in low-light and rapid-motion scenarios, such unconventional data present significant research challenges as traditional vision algori... |
EXOT: Exit-aware Object Tracker for Safe Robotic Manipulation of Moving Object | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160481/ | [
"Hyunseo Kim",
"Hye Jung Yoon",
"Minji Kim",
"Dong-Sig Han",
"Byoung-Tak Zhang",
"Hyunseo Kim",
"Hye Jung Yoon",
"Minji Kim",
"Dong-Sig Han",
"Byoung-Tak Zhang"
] | Current robotic hand manipulation narrowly operates with objects in predictable positions in limited environments. Thus, when the location of the target object deviates severely from the expected location, a robot sometimes responds in an unexpected way, especially when it operates with a human. For safe robot operation, we propose the EXit-aware Object Tracker (EXOT) on a robot hand camera that r... |
Mono-STAR: Mono-Camera Scene-Level Tracking and Reconstruction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160778/ | [
"Haonan Chang",
"Dhruv Metha Ramesh",
"Shijie Geng",
"Yuqiu Gan",
"Abdeslam Boularias",
"Haonan Chang",
"Dhruv Metha Ramesh",
"Shijie Geng",
"Yuqiu Gan",
"Abdeslam Boularias"
] | We present Mono-STAR, the first real-time 3D reconstruction system that simultaneously supports semantic fusion, fast motion tracking, non-rigid object deformation, and topological change under a unified framework. The proposed system solves a new optimization problem incorporating optical-flow-based 2D constraints to deal with fast motion and a novel semantic-aware deformation graph (SAD-graph) f... |
DFR-FastMOT: Detection Failure Resistant Tracker for Fast Multi-Object Tracking Based on Sensor Fusion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160328/ | [
"Mohamed Nagy",
"Majid Khonji",
"Jorge Dias",
"Sajid Javed",
"Mohamed Nagy",
"Majid Khonji",
"Jorge Dias",
"Sajid Javed"
] | Persistent multi-object tracking (MOT) allows autonomous vehicles to navigate safely in highly dynamic environments. One of the well-known challenges in MOT is object occlusion when an object becomes unobservant for subsequent frames. The current MOT methods store objects information, such as trajectories, in internal memory to recover the objects after occlusions. However, they retain short-term ... |
Fusion of Events and Frames using 8-DOF Warping Model for Robust Feature Tracking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161098/ | [
"Min Seok Lee",
"Ye Jun Kim",
"Jae Hyung Jung",
"Chan Gook Park",
"Min Seok Lee",
"Ye Jun Kim",
"Jae Hyung Jung",
"Chan Gook Park"
] | Event cameras are asynchronous neuromorphic vision sensors with high temporal resolution and no motion blur, offering advantages over standard frame-based cameras especially in high-speed motions and high dynamic range conditions. However, event cameras are unable to capture the overall context of the scene, and produce different events for the same scenery depending on the direction of the motion... |
3DMODT: Attention-Guided Affinities for Joint Detection & Tracking in 3D Point Clouds | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160305/ | [
"Jyoti Kini",
"Ajmal Mian",
"Mubarak Shah",
"Jyoti Kini",
"Ajmal Mian",
"Mubarak Shah"
] | We propose a method for joint detection and tracking of multiple objects in 3D point clouds, a task conventionally treated as a two-step process comprising object detection followed by data association. Our method embeds both steps into a single end-to-end trainable network eliminating the dependency on external object detectors. Our model exploits temporal information employing multiple frames to... |
Inverse Reinforcement Learning Framework for Transferring Task Sequencing Policies from Humans to Robots in Manufacturing Applications | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160687/ | [
"Omey M. Manyar",
"Zachary McNulty",
"Stefanos Nikolaidis",
"Satyandra K. Gupta",
"Omey M. Manyar",
"Zachary McNulty",
"Stefanos Nikolaidis",
"Satyandra K. Gupta"
] | In this work, we present an inverse reinforcement learning approach for solving the problem of task sequencing for robots in complex manufacturing processes. Our proposed framework is adaptable to variations in process and can perform sequencing for entirely new parts. We prescribe an approach to capture feature interactions in a demonstration dataset based on a metric that computes feature intera... |
Learning State Conditioned Linear Mappings for Low-Dimensional Control of Robotic Manipulators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160585/ | [
"Michael Przystupa",
"Kerrick Johnstonbaugh",
"Zichen Zhang",
"Laura Petrich",
"Masood Dehghan",
"Faezeh Haghverd",
"Martin Jagersand",
"Michael Przystupa",
"Kerrick Johnstonbaugh",
"Zichen Zhang",
"Laura Petrich",
"Masood Dehghan",
"Faezeh Haghverd",
"Martin Jagersand"
] | Identifying an appropriate task space can simplify solving robotic manipulation problems. One solution is deploying control algorithms in a learned low-dimensional action space. Linear and nonlinear action mapping methods have trade-offs between simplicity and the ability to express motor commands outside of a single low-dimensional subspace. We propose that learning local linear action representa... |
Decoupling Skill Learning from Robotic Control for Generalizable Object Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160332/ | [
"Kai Lu",
"Bo Yang",
"Bing Wang",
"Andrew Markham",
"Kai Lu",
"Bo Yang",
"Bing Wang",
"Andrew Markham"
] | Recent works in robotic manipulation through reinforcement learning (RL) or imitation learning (IL) have shown potential for tackling a range of tasks e.g., opening a drawer or a cupboard. However, these techniques generalize poorly to unseen objects. We conjecture that this is due to the high-dimensional action space for joint control. In this paper, we take an alternative approach and separate t... |
Comparison of Model-Based and Model-Free Reinforcement Learning for Real-World Dexterous Robotic Manipulation Tasks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160983/ | [
"David Valencia",
"John Jia",
"Raymond Li",
"Alex Hayashi",
"Megan Lecchi",
"Reuel Terezakis",
"Trevor Gee",
"Minas Liarokapis",
"Bruce A. MacDonald",
"Henry Williams",
"David Valencia",
"John Jia",
"Raymond Li",
"Alex Hayashi",
"Megan Lecchi",
"Reuel Terezakis",
"Trevor Gee",
"Minas Liarokapis",
"Bruce A. MacDonald",
"Henry Williams"
] | Model Free Reinforcement Learning (MFRL) has shown significant promise for learning dexterous robotic manipulation tasks, at least in simulation. However, the high number of samples, as well as the long training times, prevent MFRL from scaling to complex real-world tasks. Model- Based Reinforcement Learning (MBRL) emerges as a potential solution that, in theory, can improve the data efficiency of... |
Handling Sparse Rewards in Reinforcement Learning Using Model Predictive Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161492/ | [
"Murad Dawood",
"Nils Dengler",
"Jorge de Heuvel",
"Maren Bennewitz",
"Murad Dawood",
"Nils Dengler",
"Jorge de Heuvel",
"Maren Bennewitz"
] | Reinforcement learning (RL) has recently proven great success in various domains. Yet, the design of the reward function requires detailed domain expertise and tedious fine-tuning to ensure that agents are able to learn the desired behaviour. Using a sparse reward conveniently mitigates these challenges. However, the sparse reward represents a challenge on its own, often resulting in unsuccessful ... |
Task-Driven Graph Attention for Hierarchical Relational Object Navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161157/ | [
"Michael Lingelbach",
"Chengshu Li",
"Minjune Hwang",
"Andrey Kurenkov",
"Alan Lou",
"Roberto Martín-Martín",
"Ruohan Zhang",
"Li Fei-Fei",
"Jiajun Wu",
"Michael Lingelbach",
"Chengshu Li",
"Minjune Hwang",
"Andrey Kurenkov",
"Alan Lou",
"Roberto Martín-Martín",
"Ruohan Zhang",
"Li Fei-Fei",
"Jiajun Wu"
] | Embodied AI agents in large scenes often need to navigate to find objects. In this work, we study a naturally emerging variant of the object navigation task, hierarchical relational object navigation (HRON), where the goal is to find objects specified by logical predicates organized in a hierarchical structure-objects related to furniture and then to rooms-such as finding an apple on top of a tabl... |
Safety-Aware Unsupervised Skill Discovery | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160985/ | [
"Sunin Kim",
"Jaewoon Kwon",
"Taeyoon Lee",
"Younghyo Park",
"Julien Perez",
"Sunin Kim",
"Jaewoon Kwon",
"Taeyoon Lee",
"Younghyo Park",
"Julien Perez"
] | Programming manipulation behaviors can become increasingly difficult with a growing number and complexity of manipulation tasks, particularly in a dynamic and unstructured environment. Recent progress in unsupervised skill discovery algorithms has shown great promise in learning an extensive collection of behaviors without extrinsic supervision. On the other hand, safety is one of the most critica... |
A Framework for the Unsupervised Inference of Relations Between Sensed Object Spatial Distributions and Robot Behaviors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161071/ | [
"Christopher Morse",
"Lu Feng",
"Matthew Dwyer",
"Sebastian Elbaum",
"Christopher Morse",
"Lu Feng",
"Matthew Dwyer",
"Sebastian Elbaum"
] | The spatial distribution of sensed objects strongly influences the behavior of mobile robots. Yet, as robots evolve in complexity to operate in increasingly rich environments, it becomes much more difficult to specify the underlying relations between sensed object spatial distributions and robot behaviors. We aim to address this challenge by leveraging system trace data to automatically infer rela... |
Learning Video-Conditioned Policies for Unseen Manipulation Tasks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161336/ | [
"Elliot Chane-Sane",
"Cordelia Schmid",
"Ivan Laptev",
"Elliot Chane-Sane",
"Cordelia Schmid",
"Ivan Laptev"
] | The ability to specify robot commands by a non-expert user is critical for building generalist agents capable of solving a large variety of tasks. One convenient way to specify the intended robot goal is by a video of a person demonstrating the target task. While prior work typically aims to imitate human demonstrations performed in robot environments, here we focus on a more realistic and challen... |
Learning Food Picking without Food: Fracture Anticipation by Breaking Reusable Fragile Objects | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160405/ | [
"Rinto Yagawa",
"Reina Ishikawa",
"Masashi Hamaya",
"Kazutoshi Tanaka",
"Atsushi Hashimoto",
"Hideo Saito",
"Rinto Yagawa",
"Reina Ishikawa",
"Masashi Hamaya",
"Kazutoshi Tanaka",
"Atsushi Hashimoto",
"Hideo Saito"
] | Food picking is trivial for humans but not for robots, as foods are fragile. Presetting foods' physical properties does not help robots much due to the objects' inter- and intra-category diversity. A recent study proved that learning-based fracture anticipation with tactile sensors could overcome this problem; however, the method trains the model for each food to deal with intra-category differenc... |
Learning Risk-Aware Costmaps via Inverse Reinforcement Learning for Off-Road Navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161268/ | [
"Samuel Triest",
"Mateo Guaman Castro",
"Parv Maheshwari",
"Matthew Sivaprakasam",
"Wenshan Wang",
"Sebastian Scherer",
"Samuel Triest",
"Mateo Guaman Castro",
"Parv Maheshwari",
"Matthew Sivaprakasam",
"Wenshan Wang",
"Sebastian Scherer"
] | The process of designing costmaps for off-road driving tasks is often a challenging and engineering-intensive task. Recent work in costmap design for off-road driving focuses on training deep neural networks to predict costmaps from sensory observations using corpora of expert driving data. However, such approaches are generally subject to over-confident mis-predictions and are rarely evaluated in... |
How Does It Feel? Self-Supervised Costmap Learning for Off-Road Vehicle Traversability | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160856/ | [
"Mateo Guaman Castro",
"Samuel Triest",
"Wenshan Wang",
"Jason M. Gregory",
"Felix Sanchez",
"John G. Rogers",
"Sebastian Scherer",
"Mateo Guaman Castro",
"Samuel Triest",
"Wenshan Wang",
"Jason M. Gregory",
"Felix Sanchez",
"John G. Rogers",
"Sebastian Scherer"
] | Estimating terrain traversability in off-road environments requires reasoning about complex interaction dynamics between the robot and these terrains. However, it is challenging to create informative labels to learn a model in a supervised manner for these interactions. We propose a method that learns to predict traversability costmaps by combining exteroceptive environmental information with prop... |
Global and Reactive Motion Generation with Geometric Fabric Command Sequences | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160965/ | [
"Weiming Zhi",
"Iretiayo Akinola",
"Karl Van Wyk",
"Nathan D. Ratliff",
"Fabio Ramos",
"Weiming Zhi",
"Iretiayo Akinola",
"Karl Van Wyk",
"Nathan D. Ratliff",
"Fabio Ramos"
] | Motion generation seeks to produce safe and feasible robot motion from start to goal. Various tools at different levels of granularity have been developed. On one extreme, sampling-based motion planners focus on completeness - a solution, if it exists, would eventually be found. However, produced paths are often of low quality, and contain superfluous motion. On the other, reactive methods optimis... |
Enforcing the consensus between Trajectory Optimization and Policy Learning for precise robot control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160387/ | [
"Quentin Le Lidec",
"Wilson Jallet",
"Ivan Laptev",
"Cordelia Schmid",
"Justin Carpentier",
"Quentin Le Lidec",
"Wilson Jallet",
"Ivan Laptev",
"Cordelia Schmid",
"Justin Carpentier"
] | Reinforcement learning (RL) and trajectory opti-mization (TO) present strong complementary advantages. On one hand, RL approaches are able to learn global control policies directly from data, but generally require large sample sizes to properly converge towards feasible policies. On the other hand, TO methods are able to exploit gradient-based information extracted from simulators to quickly conve... |
Neural Optimal Control using Learned System Dynamics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160339/ | [
"Selim Engin",
"Volkan Isler",
"Selim Engin",
"Volkan Isler"
] | We study the problem of generating control laws for systems with unknown dynamics. Our approach is to represent the controller and the value function with neural networks, and to train them using loss functions adapted from the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equations. In the absence of a known dynamics model, our method first learns the state transitions from data collected by interacting with the... |
Learned Risk Metric Maps for Kinodynamic Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160680/ | [
"Ross E. Allen",
"Wei Xiao",
"Daniela Rus",
"Ross E. Allen",
"Wei Xiao",
"Daniela Rus"
] | We present Learned Risk Metric Maps (LRMM) for real-time estimation of coherent risk metrics of high-dimensional dynamical systems operating in unstructured, partially observed environments. LRMM models are simple to design and train-requiring only procedural generation of obstacle sets, state and control sampling, and supervised training of a function approximator-which makes them broadly applica... |
Autonomous Drifting with 3 Minutes of Data via Learned Tire Models | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161370/ | [
"Franck Djeumou",
"Jonathan Y.M. Goh",
"Ufuk Topcu",
"Avinash Balachandran",
"Franck Djeumou",
"Jonathan Y.M. Goh",
"Ufuk Topcu",
"Avinash Balachandran"
] | Near the limits of adhesion, the forces generated by a tire are nonlinear and intricately coupled. Efficient and accurate modelling in this region could improve safety, especially in emergency situations where high forces are required. To this end, we propose a novel family of tire force models based on neural ordinary differential equations and a neural-ExpTanh parameterization. These models are ... |
DDK: A Deep Koopman Approach for Longitudinal and Lateral Control of Autonomous Ground Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161104/ | [
"Yongqian Xiao",
"Xinglong Zhang",
"Xin Xu",
"Yang Lu",
"Junxiang Lil",
"Yongqian Xiao",
"Xinglong Zhang",
"Xin Xu",
"Yang Lu",
"Junxiang Lil"
] | Autonomous driving has attracted lots of attention in recent years. For some tasks, e.g., trajectory prediction, motion planning, and trajectory tracking, an accurate vehicle model can reduce the difficulty of these tasks and improve task completion performance. Prior works focused on parameter estimation of physical models or modeling nonlinear dynamics using neural networks. Still, these methods... |
Meta-Learning-Based Optimal Control for Soft Robotic Manipulators to Interact with Unknown Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160513/ | [
"Zhiqiang Tang",
"Peiyi Wang",
"Wenci Xin",
"Zhexin Xie",
"Longxin Kan",
"Muralidharan Mohanakrishnan",
"Cecilia Laschi",
"Zhiqiang Tang",
"Peiyi Wang",
"Wenci Xin",
"Zhexin Xie",
"Longxin Kan",
"Muralidharan Mohanakrishnan",
"Cecilia Laschi"
] | Safe and efficient robot-environment interaction is a critical but challenging problem as robots are being increasingly employed to operate in unstructured and unpredictable environments. Soft robots are inherently compliant to safely interact with environments but their high nonlinearity exacerbates control difficulties. Meta-learning provides a powerful tool for fast online model adaptation beca... |
Dealing with Sparse Rewards in Continuous Control Robotics via Heavy-Tailed Policy Optimization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161186/ | [
"Souradip Chakraborty",
"Amrit Singh Bedi",
"Kasun Weerakoon",
"Prithvi Poddar",
"Alec Koppel",
"Pratap Tokekar",
"Dinesh Manocha",
"Souradip Chakraborty",
"Amrit Singh Bedi",
"Kasun Weerakoon",
"Prithvi Poddar",
"Alec Koppel",
"Pratap Tokekar",
"Dinesh Manocha"
] | In this paper, we present a novel Heavy-Tailed Stochastic Policy Gradient (HT-PSG) algorithm to deal with the challenges of sparse rewards in continuous control problems. Sparse rewards are common in continuous control robotics tasks such as manipulation and navigation and make the learning problem hard due to the non-trivial estimation of value functions over the state space. This demands either ... |
MPC with Sensor-Based Online Cost Adaptation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161280/ | [
"Avadesh Meduri",
"Huaijiang Zhu",
"Armand Jordana",
"Ludovic Righetti",
"Avadesh Meduri",
"Huaijiang Zhu",
"Armand Jordana",
"Ludovic Righetti"
] | Model predictive control is a powerful tool to generate complex motions for robots. However, it often requires solving non-convex problems online to produce rich behaviors, which is computationally expensive and not always practical in real time. Additionally, direct integration of high dimensional sensor data (e.g. RGB-D images) in the feedback loop is challenging with current state-space methods... |
ReachLipBnB: A branch-and-bound method for reachability analysis of neural autonomous systems using Lipschitz bounds | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160732/ | [
"Taha Entesari",
"Sina Sharifi",
"Mahyar Fazlyab",
"Taha Entesari",
"Sina Sharifi",
"Mahyar Fazlyab"
] | We propose a novel Branch-and-Bound method for reachability analysis of neural networks in both open-loop and closed-loop settings. Our idea is to first compute accurate bounds on the Lipschitz constant of the neural network in certain directions of interest offline using a convex program. We then use these bounds to obtain an instantaneous but conservative polyhedral approximation of the reachabl... |
Gradient-Based Trajectory Optimization With Learned Dynamics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161574/ | [
"Bhavya Sukhija",
"Nathanael Köhler",
"Miguel Zamora",
"Simon Zimmermann",
"Sebastian Curi",
"Andreas Krause",
"Stelian Coros",
"Bhavya Sukhija",
"Nathanael Köhler",
"Miguel Zamora",
"Simon Zimmermann",
"Sebastian Curi",
"Andreas Krause",
"Stelian Coros"
] | Trajectory optimization methods have achieved an exceptional level of performance on real-world robots in recent years. These methods heavily rely on accurate analytical models of the dynamics, yet some aspects of the physical world can only be captured to a limited extent. An alternative approach is to leverage machine learning techniques to learn a differentiable dynamics model of the system fro... |
RAMP-Net: A Robust Adaptive MPC for Quadrotors via Physics-informed Neural Network | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161410/ | [
"Sourav Sanyal",
"Kaushik Roy",
"Sourav Sanyal",
"Kaushik Roy"
] | Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a state-of-the-art (SOTA) control technique which requires solving hard constrained optimization problems iteratively. For uncertain dynamics, analytical model based robust MPC imposes additional constraints, increasing the hardness of the problem. The problem exacerbates in performance-critical applications, when more compute is required in lesser time. Data-driv... |
3-D Reconstruction Using Monocular Camera and Lights: Multi-View Photometric Stereo for Non-Stationary Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160459/ | [
"Monika Roznere",
"Philippos Mordohai",
"Ioannis Rekleitis",
"Alberto Quattrini Li",
"Monika Roznere",
"Philippos Mordohai",
"Ioannis Rekleitis",
"Alberto Quattrini Li"
] | This paper proposes a novel underwater Multi-View Photometric Stereo (MVPS) framework for reconstructing scenes in 3-D with a non-stationary low-cost robot equipped with a monocular camera and fixed lights. The underwater realm is the primary focus of study here, due to the challenges in utilizing underwater camera imagery and lack of low-cost reliable localization systems. Previous underwater PS ... |
GMM Registration: a Probabilistic scan matching approach for sonar-based AUV navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160697/ | [
"Pau Vial",
"Miguel Malagón",
"Ricard Segura",
"Narcís Palomeras",
"Marc Carreras",
"Pau Vial",
"Miguel Malagón",
"Ricard Segura",
"Narcís Palomeras",
"Marc Carreras"
] | Acoustic perception in underwater environments is challenging due to the low frequency of the acquisition system and multiple and huge sources of noise. Therefore, point clouds built by profiling sonars mounted on Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV) are sparse and noisy. To solve the mapping task, AUVs need a registration algorithm to prevent maps from inconsistencies. Many scan matching algorith... |
Neural Implicit Surface Reconstruction using Imaging Sonar | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161206/ | [
"Mohamad Qadri",
"Michael Kaess",
"Ioannis Gkioulekas",
"Mohamad Qadri",
"Michael Kaess",
"Ioannis Gkioulekas"
] | We present a technique for dense 3D reconstruction of objects using an imaging sonar, also known as forward-looking sonar (FLS). Compared to previous methods that model the scene geometry as point clouds or volumetric grids, we represent the geometry as a neural implicit function. Additionally, given such a representation, we use a differentiable volumetric renderer that models the propagation of ... |
Conditional GANs for Sonar Image Filtering with Applications to Underwater Occupancy Mapping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160646/ | [
"Tianxiang Lin",
"Akshay Hinduja",
"Mohamad Qadri",
"Michael Kaess",
"Tianxiang Lin",
"Akshay Hinduja",
"Mohamad Qadri",
"Michael Kaess"
] | Underwater robots typically rely on acoustic sensors like sonar to perceive their surroundings. However, these sensors are often inundated with multiple sources and types of noise, which makes using raw data for any meaningful inference with features, objects, or boundary returns very difficult. While several conventional methods of dealing with noise exist, their success rates are unsatisfactory.... |
Stochastic Planning for ASV Navigation Using Satellite Images | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160894/ | [
"Yizhou Huang",
"Hamza Dugmag",
"Timothy D. Barfoot",
"Florian Shkurti",
"Yizhou Huang",
"Hamza Dugmag",
"Timothy D. Barfoot",
"Florian Shkurti"
] | Autonomous surface vessels (ASV) represent a promising technology to automate water-quality monitoring of lakes. In this work, we use satellite images as a coarse map and plan sampling routes for the robot. However, inconsistency between the satellite images and the actual lake, as well as environmental disturbances such as wind, aquatic vegetation, and changing water levels can make it difficult ... |
Autonomous Underwater Docking using Flow State Estimation and Model Predictive Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160272/ | [
"Rakesh Vivekanandan",
"Dongsik Chang",
"Geoffrey A. Hollinger",
"Rakesh Vivekanandan",
"Dongsik Chang",
"Geoffrey A. Hollinger"
] | We present a navigation framework to perform autonomous underwater docking to a wave energy converter (WEC) under various ocean conditions by incorporating flow state estimation into the design of model predictive control (MPC). Existing methods lack the ability to perform dynamic rendezvous and autonomously dock in energetic conditions. The use of exteroceptive sensors or high performing acoustic... |
Real-Time Navigation for Autonomous Surface Vehicles In Ice-Covered Waters | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161044/ | [
"Rodrigue de Schaetzen",
"Alexander Botros",
"Robert Gash",
"Kevin Murrant",
"Stephen L. Smith",
"Rodrigue de Schaetzen",
"Alexander Botros",
"Robert Gash",
"Kevin Murrant",
"Stephen L. Smith"
] | Vessel transit in ice-covered waters poses unique challenges in safe and efficient motion planning. When the concentration of ice is high, it may not be possible to find collision-free trajectories. Instead, ice can be pushed out of the way if it is small or if contact occurs near the edge of the ice. In this work, we propose a real-time navigation framework that minimizes collisions with ice and ... |
Experiments in Underwater Feature Tracking with Performance Guarantees Using a Small AUV | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161050/ | [
"Benjamin Biggs",
"Hans He",
"James McMahon",
"Daniel J. Stilwell",
"Benjamin Biggs",
"Hans He",
"James McMahon",
"Daniel J. Stilwell"
] | We present the results of experiments performed using a small autonomous underwater vehicle to determine the location of an isobath within a bounded area. The primary contribution of this work is to implement and integrate several recent developments real-time planning for environmental map-ping, and to demonstrate their utility in a challenging practical example. We model the bathymetry within th... |
Robust Imaging Sonar-based Place Recognition and Localization in Underwater Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161518/ | [
"Hogyun Kim",
"Gilhwan Kang",
"Seokhwan Jeong",
"Seungjun Ma",
"Younggun Cho",
"Hogyun Kim",
"Gilhwan Kang",
"Seokhwan Jeong",
"Seungjun Ma",
"Younggun Cho"
] | Place recognition using SOund Navigation and Ranging (SONAR) images is an important task for simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) in underwater environments. This paper proposes a robust and efficient imaging SONAR-based place recognition, SONAR context, and loop closure method. Unlike previous methods, our approach encodes geometric information based on the characteristics of raw SONAR me... |
Deep Underwater Monocular Depth Estimation with Single-Beam Echosounder | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161439/ | [
"Haowen Liu",
"Monika Roznere",
"Alberto Quattrini Li",
"Haowen Liu",
"Monika Roznere",
"Alberto Quattrini Li"
] | Underwater depth estimation is essential for safe Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV) navigation. While there has been recent advances in out-of-water monocular depth estimation, it is difficult to apply these methods to the underwater domain due to the lack of well-established datasets with labelled ground truths. In this paper, we propose a novel method for self-supervised underwater monocular ... |
Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Underwater | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161161/ | [
"Shlomi Amitai",
"Itzik Klein",
"Tali Treibitz",
"Shlomi Amitai",
"Itzik Klein",
"Tali Treibitz"
] | Depth estimation is critical for any robotic system. In the past years, the estimation of depth from monocular images has shown great improvement. However, in the underwater environment results are still lagging behind due to appearance changes caused by the medium. So far little effort has been invested in overcoming this. Moreover, underwater, there are more limitations to using high-resolution ... |
Performance Evaluation of 3D Keypoint Detectors and Descriptors on Coloured Point Clouds in Subsea Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160348/ | [
"Kyungmin Jung",
"Thomas Hitchcox",
"James Richard Forbes",
"Kyungmin Jung",
"Thomas Hitchcox",
"James Richard Forbes"
] | The recent development of high-precision subsea optical scanners allows for 3D keypoint detectors and feature descriptors to be leveraged on point cloud scans from subsea environments. However, the literature lacks a comprehensive survey to identify the best combination of detectors and descriptors to be used in these challenging and novel environments. This paper aims to identify the best detecto... |
Puppeteer and Marionette: Learning Anticipatory Quadrupedal Locomotion Based on Interactions of a Central Pattern Generator and Supraspinal Drive | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160706/ | [
"Milad Shafiee",
"Guillaume Bellegarda",
"Auke Ijspeert",
"Milad Shafiee",
"Guillaume Bellegarda",
"Auke Ijspeert"
] | Quadruped animal locomotion emerges from the interactions between the spinal central pattern generator (CPG), sensory feedback, and supraspinal drive signals from the brain. Computational models of CPGs have been widely used for investigating the spinal cord contribution to animal locomotion control in computational neuroscience and in bio-inspired robotics. However, the contribution of supraspina... |
A Performance Optimization Strategy Based on Improved NSGA-II for a Flexible Robotic Fish | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160420/ | [
"Ben Lu",
"Jian Wang",
"Xiaocun Liao",
"Qianqian Zou",
"Min Tan",
"Chao Zhou",
"Ben Lu",
"Jian Wang",
"Xiaocun Liao",
"Qianqian Zou",
"Min Tan",
"Chao Zhou"
] | The high speed and low energy cost are two conflicting objectives in the motion optimization of bio-inspired underwater robots, but playing a very important role. To this end, this paper proposes an optimization strategy for swimming speed and power cost using an improved NSGA-II for a flexible robotic fish. A dynamic model involving flexible deformation is established for speed prediction with th... |
Swarm Robotics Search and Rescue: A Bee-Inspired Swarm Cooperation Approach without Information Exchange | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161039/ | [
"Yue Li",
"Yan Gao",
"Sijie Yang",
"Quan Quan",
"Yue Li",
"Yan Gao",
"Sijie Yang",
"Quan Quan"
] | Swarm robotics plays a non-negligible role in actual practice because of its scalability and robustness. Besides some specific studies, there is still a lack of overall approaches to solving the search and rescue problem in a communication-denied environment. This paper presents a bee-inspired swarm cooperation approach without information exchange, including a target grouping method suitable for ... |
Achieving Extensive Trajectory Variation in Impulsive Robotic Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160463/ | [
"Luis Viornery",
"Chloe Goode",
"Gregory Sutton",
"Sarah Bergbreiter",
"Luis Viornery",
"Chloe Goode",
"Gregory Sutton",
"Sarah Bergbreiter"
] | Robots that use impulsive mechanisms to achieve high-speed and high-powered motion are becoming more common and better understood, but control of these systems remains relatively rudimentary. Among robots that use spring actuation to generate motion, robot actuation and mechanisms are usually not controlled intentionally in order to achieve variation in the system's behavior, or they are controlle... |
Towards Safe Landing of Falling Quadruped Robots Using a 3-DoF Morphable Inertial Tail | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161422/ | [
"Yunxi Tang",
"Jiajun An",
"Xiangyu Chu",
"Shengzhi Wang",
"Ching Yan Wong",
"K. W. Samuel Au",
"Yunxi Tang",
"Jiajun An",
"Xiangyu Chu",
"Shengzhi Wang",
"Ching Yan Wong",
"K. W. Samuel Au"
] | Falling cat problem is well-known where cats show their super aerial reorientation capability and can land safely. For their robotic counterparts, a similar falling quadruped robot problem, has not been fully addressed, although achieving safe landing as the cats has been increasingly investigated. Unlike imposing the burden on landing control, we approach to safe landing of falling quadruped robo... |
Bioinspired tearing manipulation with a robotic fish | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161292/ | [
"Stanley J. Wang",
"Juan Romero",
"Monica S. Li",
"Peter C. Wainwright",
"Hannah S. Stuart",
"Stanley J. Wang",
"Juan Romero",
"Monica S. Li",
"Peter C. Wainwright",
"Hannah S. Stuart"
] | We present SunBot, a robotic system for the study and implementation of fish-inspired tearing manipulations. Various fish species–such as the sunburst butterflyfish-feed on prey fixed to substrates, a maneuver previously not demonstrated by robotic fish which typically specialize for open water swimming and surveillance. Biological studies indicate that a dynamic “head flick” behavior may play a r... |
Learnable Tegotae-based Feedback in CPGs with Sparse Observation Produces Efficient and Adaptive Locomotion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160571/ | [
"Christopher Herneth",
"Mitsuhiro Hayashibe",
"Dai Owaki",
"Christopher Herneth",
"Mitsuhiro Hayashibe",
"Dai Owaki"
] | Central Pattern generators (CPG) are a biologically inspired, decentralized control architecture that enables model-free, but yet adaptively stable and computational lightweight locomotion capabilities on complex robots. Nevertheless, no unified design guidelines for closed-loop CPG controllers are available in the literature. Therefore, we propose a task-distributed, end-to-end trainable, closed-... |
Multi-segmented Adaptive Feet for Versatile Legged Locomotion in Natural Terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10161515/ | [
"Abhishek Chatterjee",
"An Mo",
"Bernadett Kiss",
"Emre Cemal Gönen",
"Alexander Badri-Spröwitz",
"Abhishek Chatterjee",
"An Mo",
"Bernadett Kiss",
"Emre Cemal Gönen",
"Alexander Badri-Spröwitz"
] | Most legged robots are built with leg structures from serially mounted links and actuators and are controlled through complex controllers and sensor feedback. In comparison, animals developed multi-segment legs, mechanical coupling between joints, and multi-segmented feet. They run agile over all terrains, arguably with simpler locomotion control. Here we focus on developing foot mechanisms that r... |
Burst Stimulation for Enhanced Locomotion Control of Terrestrial Cyborg Insects | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160443/ | [
"H. Duoc Nguyen",
"Hirotaka Sato",
"T. Thang Vo-Doan",
"H. Duoc Nguyen",
"Hirotaka Sato",
"T. Thang Vo-Doan"
] | Terrestrial cyborg insects are biohybrid systems integrating living insects as mobile platforms. The insects' locomotion is controlled by the electrical stimulation of their sensory, muscular, or neural systems, in which continuous pulse trains are usually chosen as the stimulation waveform. Although this waveform is easy to generate and can elicit graded responses from the insects, its locomotion... |
Twisting Spine or Rigid Torso: Exploring Quadrupedal Morphology via Trajectory Optimization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160450/ | [
"J. Diego Caporale",
"Zeyuan Feng",
"Shane Rozen-Levy",
"Aja Mia Carter",
"Daniel E. Koditschek",
"J. Diego Caporale",
"Zeyuan Feng",
"Shane Rozen-Levy",
"Aja Mia Carter",
"Daniel E. Koditschek"
] | Modern legged robot morphologies assign most of their actuated degrees of freedom (DoF's) to the limbs and designs continue to converge to twelve DoF quadrupeds with three actuators per leg and a rigid torso often modeled as a Single Rigid Body (SRB). This is in contrast to the animal kingdom, which provides tantalizing hints that core actuation of a jointed torso confers substantial benefit for e... |
Dynamic Locomotion of a Quadruped Robot with Active Spine via Model Predictive Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160896/ | [
"Wanyue Li",
"Zida Zhou",
"Hui Cheng",
"Wanyue Li",
"Zida Zhou",
"Hui Cheng"
] | As an active spine introduces more degree of freedoms (DOFs) as well as time-varying inertia, locomotion control of spined quadruped robots is challenging. Direct optimization on the full dynamics model causes prohibitive calculation time and is difficult to apply to embedded platforms. Model predictive control (MPC)-based on SRB dynamics is a prevalent approach for ordinary quadruped robots, rega... |
ICRA 2023 Accepted Paper Meta Info Dataset
This dataset is collect from the ICRA 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 accepted papers' meta info (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/conhome/10160211/proceeding) as well as the arxiv website DeepNLP paper arxiv (http://www.deepnlp.org/content/paper/icra2023). For researchers who are interested in doing analysis of ICRA 2023 accepted papers and potential trends, you can use the already cleaned up json files. Each row contains the meta information of a paper in the ICRA 2023 conference. To explore more AI & Robotic papers (NIPS/ICML/ICLR/IROS/ICRA/etc) and AI equations, feel free to navigate the Equation Search Engine (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/equation) as well as the AI Agent Search Engine to find the deployed AI Apps and Agents (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/agent) in your domain.
Equations Latex code and Papers Search Engine
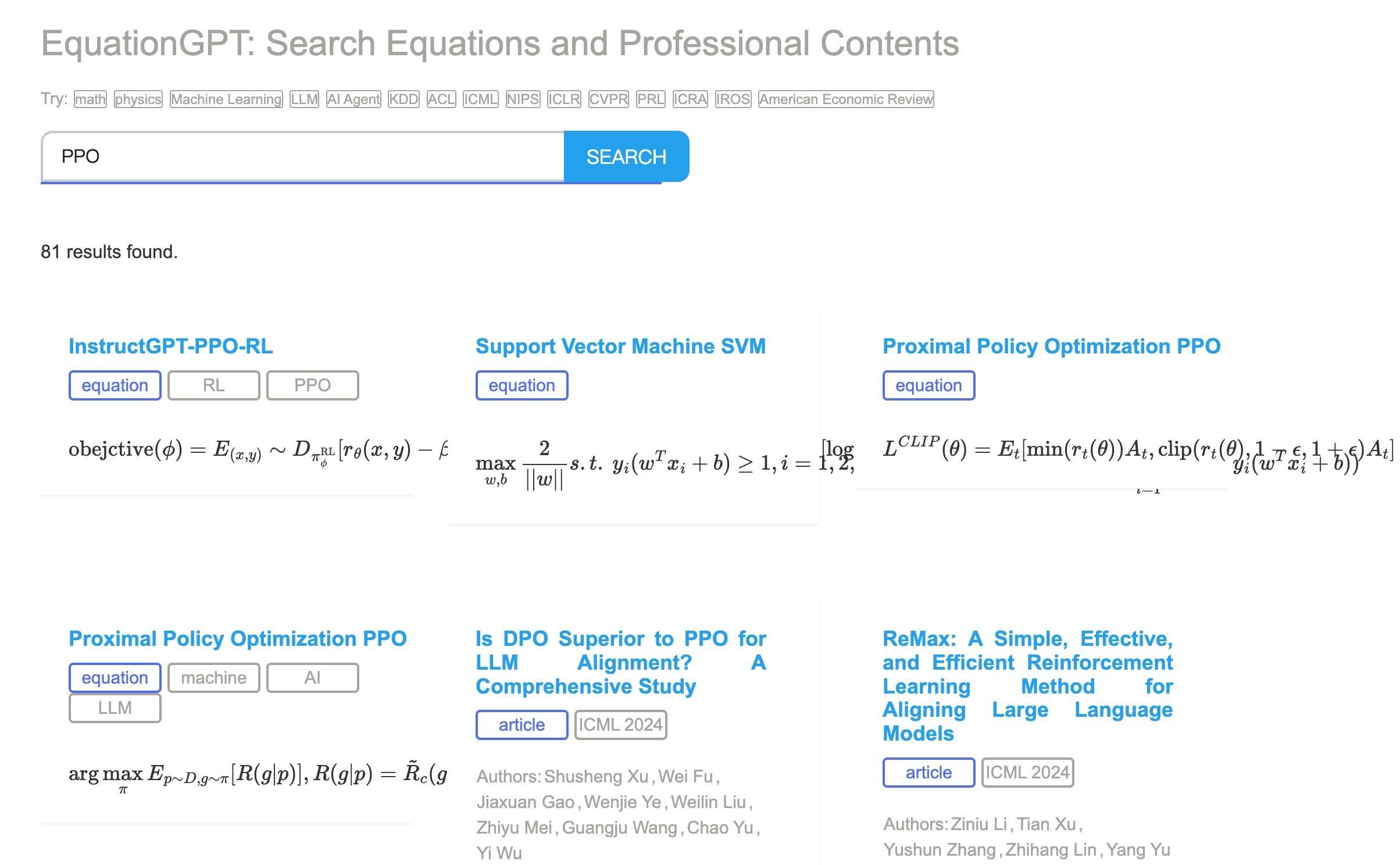
Meta Information of Json File of Paper
{
"title": "Reconfigurable Inflated Soft Arms",
"detail_url": "https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10160569/",
"author_list": ["Nam Gyun Kim", "Jee-Hwan Ryu", "Nam Gyun Kim", "Jee-Hwan Ryu"],
"abstract": "Inflatable structures have attracted considerable research attention in many fields owing to their numerous advantages, such as being light and able to engage in interactions safely. However, in most cases, the inflatable structure can only have one stable configuration, which is undesirable for robotic arms. This study proposes a novel inflatable structure that can be easily reconfigured into mul..."
}
Related
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
Robot Search
Equation and Academic search
AI & Robot Comprehensive Search
AI & Robot Question
AI & Robot Community
AI Agent Marketplace Blog
AI Agent Reviews
AI Agent Marketplace Directory
Microsoft AI Agents Reviews
Claude AI Agents Reviews
OpenAI AI Agents Reviews
Saleforce AI Agents Reviews
AI Agent Builder Reviews
AI Equation
List of AI Equations and Latex
List of Math Equations and Latex
List of Physics Equations and Latex
List of Statistics Equations and Latex
List of Machine Learning Equations and Latex
- Downloads last month
- 37