title
stringlengths 8
189
| detail_url
stringlengths 27
45
| author_list
sequencelengths 0
28
| abstract
stringlengths 0
403
|
|---|---|---|---|
LB-L2L-Calib: Accurate and Robust Extrinsic Calibration for Multiple 3D LiDARs with Long Baseline and Large Viewpoint Difference | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812062/ | [
"Jun Zhang",
"Qiyang Lyu",
"Guohao Peng",
"Zhenyu Wu",
"Qiao Yan",
"Danwei Wang",
"Jun Zhang",
"Qiyang Lyu",
"Guohao Peng",
"Zhenyu Wu",
"Qiao Yan",
"Danwei Wang"
] | Multi-LiDAR system is an important part of V2X (Vehicle to Everything) to enhance the perception information for unmanned vehicles. To fuse the information from multiple 3D LiDARs, accurate extrinsic calibration between the LiDARs is essential. However, the existing multi-LiDAR calibration methods mainly focus on short baseline scenarios, where multiple LiDARs are closely mounted on a single platf... |
Fusing Event-based and RGB camera for Robust Object Detection in Adverse Conditions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812059/ | [
"Abhishek Tomy",
"Anshul Paigwar",
"Khushdeep S. Mann",
"Alessandro Renzaglia",
"Christian Laugier",
"Abhishek Tomy",
"Anshul Paigwar",
"Khushdeep S. Mann",
"Alessandro Renzaglia",
"Christian Laugier"
] | The ability to detect objects, under image corruptions and different weather conditions is vital for deep learning models especially when applied to real-world applications such as autonomous driving. Traditional RGB-based detection fails under these conditions and it is thus important to design a sensor suite that is redundant to failures of the primary frame-based detection. Event-based cameras ... |
Pedestrian Stop and Go Forecasting with Hybrid Feature Fusion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811664/ | [
"Dongxu Guo",
"Taylor Mordan",
"Alexandre Alahi",
"Dongxu Guo",
"Taylor Mordan",
"Alexandre Alahi"
] | Forecasting pedestrians' future motions is essential for autonomous driving systems to safely navigate in urban areas. However, existing prediction algorithms often overly rely on past observed trajectories and tend to fail around abrupt dynamic changes, such as when pedestrians suddenly start or stop walking. We suggest that predicting these highly non-linear transitions should form a core compon... |
Online Prediction of Lane Change with a Hierarchical Learning-Based Approach | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812269/ | [
"Xishun Liao",
"Ziran Wang",
"Xuanpeng Zhao",
"Zhouqiao Zhao",
"Kyungtae Han",
"Prashant Tiwari",
"Matthew J. Barth",
"Guoyuan Wu",
"Xishun Liao",
"Ziran Wang",
"Xuanpeng Zhao",
"Zhouqiao Zhao",
"Kyungtae Han",
"Prashant Tiwari",
"Matthew J. Barth",
"Guoyuan Wu"
] | In the foreseeable future, connected and auto-mated vehicles (CAVs) and human-driven vehicles will share the road networks together. In such a mixed traffic environment, CAVs need to understand and predict maneuvers of surrounding vehicles for safer and more efficient interactions, especially when human drivers bring in a wide range of uncertainties. In this paper, we propose a learning-based lane... |
Gripper positioning for object deformation tasks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812304/ | [
"Ignacio Cuiral-Zueco",
"Gonzalo López-Nicolás",
"Helder Araujo",
"Ignacio Cuiral-Zueco",
"Gonzalo López-Nicolás",
"Helder Araujo"
] | Shape control involves bringing a deformable object to a desired shape. In the shape control literature, the positioning of the grippers on the object is usually predefined (user-defined) and therefore considered as input information. In this paper we address the gripper positioning problem for shape control. We propose a deformation process within a simulated fully-actuated scenario and introduce... |
Non-prehensile Planar Manipulation via Trajectory Optimization with Complementarity Constraints | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811942/ | [
"João Moura",
"Theodoros Stouraitis",
"Sethu Vijayakumar",
"João Moura",
"Theodoros Stouraitis",
"Sethu Vijayakumar"
] | Contact adaptation is an essential capability when manipulating objects. Two key contact modes of non-prehensile manipulation are sticking and sliding. This paper presents a Trajectory Optimization (TO) method formulated as a Mathematical Program with Complementarity Constraints (MPCC), which is able to switch between these two modes. We show that this formulation can be applicable to both plannin... |
Coordinate Invariant User-Guided Constrained Path Planning with Reactive Rapidly Expanding Plane-Oriented Escaping Trees | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812014/ | [
"Riddhiman Laha",
"Ruiai Sun",
"Wenxi Wu",
"Dasharadhan Mahalingam",
"Nilanjan Chakraborty",
"Luis F.C. Figueredo",
"Sami Haddadin",
"Riddhiman Laha",
"Ruiai Sun",
"Wenxi Wu",
"Dasharadhan Mahalingam",
"Nilanjan Chakraborty",
"Luis F.C. Figueredo",
"Sami Haddadin"
] | As collaborative robots move closer to human environments, motion generation and reactive planning strategies that allow for elaborate task execution with minimal easy-to-implement guidance whilst coping with changes in the environment is of paramount importance. In this paper, we present a novel approach for generating real-time motion plans for point-to-point tasks using a single successful huma... |
PyROBOCOP: Python-based Robotic Control & Optimization Package for Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812069/ | [
"Arvind U. Raghunathan",
"Devesh K. Jha",
"Diego Romeres",
"Arvind U. Raghunathan",
"Devesh K. Jha",
"Diego Romeres"
] | PyROBOCOP is a Python-based package for control, optimization and estimation of robotic systems described by nonlinear Differential Algebraic Equations (DAEs). In particular, the package can handle systems with contacts that are described by complementarity constraints and provides a general framework for specifying obstacle avoidance constraints. The package performs direct transcription of the D... |
Robust Pivoting: Exploiting Frictional Stability Using Bilevel Optimization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811812/ | [
"Yuki Shirai",
"Devesh K. Jha",
"Arvind U. Raghunathan",
"Diego Romeres",
"Yuki Shirai",
"Devesh K. Jha",
"Arvind U. Raghunathan",
"Diego Romeres"
] | Generalizable manipulation requires that robots be able to interact with novel objects and environment. This requirement makes manipulation extremely challenging as a robot has to reason about complex frictional interaction with uncertainty in physical properties of the object. In this paper, we study robust optimization for control of pivoting manipulation in the presence of uncertainties. We pre... |
TOPP-MPC-Based Dual-Arm Dynamic Collaborative Manipulation for Multi-Object Nonprehensile Transportation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812424/ | [
"Cheng Zhou",
"Maolin Lei",
"Longfei Zhao",
"Zunran Wang",
"Yu Zheng",
"Cheng Zhou",
"Maolin Lei",
"Longfei Zhao",
"Zunran Wang",
"Yu Zheng"
] | This paper presents a unified controller for dual-arm robot dynamic multi-object nonprehensile transportation. The controller is composed of time-optimal path parameteri-zation (TOPP) and model predictive control (MPC) and aimed at efficiently and dynamically transporting objects using the dual-arm robot under physical constraints while avoiding the slippage of the objects. A force tracking contro... |
Coordination of two robotic manipulators for object retrieval in clutter | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811978/ | [
"Jeeho Ahn",
"ChangHwan Kim",
"Changjoo Nam",
"Jeeho Ahn",
"ChangHwan Kim",
"Changjoo Nam"
] | We consider the problem of retrieving a target object from a confined space by two robotic manipulators where overhand grasps are not allowed. If other movable obstacles occlude the target, more than one object should be relocated to clear the path to reach the target object. With two robots, the relocation could be done efficiently by simultaneously performing relocation tasks. However, the prece... |
Planning and Control for Cable-routing with Dual-arm Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811765/ | [
"Gabriel Arslan Waltersson",
"Rita Laezza",
"Yiannis Karayiannidis",
"Gabriel Arslan Waltersson",
"Rita Laezza",
"Yiannis Karayiannidis"
] | In this paper, we propose a new framework for solving cable-routing problems with a dual-arm robot, where the objective is to clip a Deformable Linear Object (DLO) into several arbitrarily placed fixtures. The core of the framework is a task-space planner, which builds a roadmap from predefined tasks and employs a replanning strategy based on a genetic algorithm, if problems occur. The manipulatio... |
DRAGONFLY: a UAV Rapidly Deployed Micro-Profiler Array for Underwater Thermocline Observation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811369/ | [
"Chenxin Lyu",
"Zhihao Fan",
"Yuanbo Bi",
"Zheng Zeng",
"Lian Lian",
"Chenxin Lyu",
"Zhihao Fan",
"Yuanbo Bi",
"Zheng Zeng",
"Lian Lian"
] | Underwater thermocline, common in the lakes and ocean, plays a vital role in meteorological forecasting in the ocean and lakes dynamics research. This letter proposes a method for rapid and multipoint observation of thermocline variations with time and space using an airdropped micro-profiler array, named the DRAGONFLY system. It comprises specially designed disposable low-cost micro-profilers, a ... |
Using Monocular Vision and Human Body Priors for AUVs to Autonomously Approach Divers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811905/ | [
"Michael Fulton",
"Jungseok Hong",
"Junaed Sattar",
"Michael Fulton",
"Jungseok Hong",
"Junaed Sattar"
] | Direct communication between humans and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) is a relatively under-explored area in human-robot interaction research, although many tasks (e.g., surveillance, inspection, and search-and-rescue) require close diver-robot collaboration. Suboptimal AUV positioning relative to its human collaborators can lead to poor quality interaction and lead to excessive cognitive ... |
Design of an Autonomous Latching System for Surface Vessels | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811754/ | [
"David Fernández-Gutiérrez",
"Niklas Hagemann",
"Wei Wang",
"Rens Doornbusch",
"Joshua Jordan",
"Jonathan Schiphorst",
"Pietro Leoni",
"Fabio Duarte",
"Carlo Ratti",
"Daniela Rus",
"David Fernández-Gutiérrez",
"Niklas Hagemann",
"Wei Wang",
"Rens Doornbusch",
"Joshua Jordan",
"Jonathan Schiphorst",
"Pietro Leoni",
"Fabio Duarte",
"Carlo Ratti",
"Daniela Rus"
] | Autonomous latching is essential for autonomous surface vessels (ASV) to reach full independence from human intervention. As part of the ASV Roboat project, a new solution for self-latching maneuvers has been developed and is presented here. We propose a system that has the key requirements of full integration with the navigation control system and zero-gap connection with the dock, the latter bei... |
Towards Accurate Positioning of Underwater Vehicles Using Low-cost Acoustic Modems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811851/ | [
"Christian Busse",
"Bernd-Christian Renner",
"Christian Busse",
"Bernd-Christian Renner"
] | Navigating autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) in shallow and harbor waters is challenging and typically has higher accuracy requirements than navigation in the open sea. We investigate enhancements to underwater localization techniques based on Two-Way Ranging (TWR) using acoustic modems, which have great potential to meet localization accuracy requirements at lower cost and complexity than cur... |
High Definition, Inexpensive, Underwater Mapping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811695/ | [
"Bharat Joshi",
"Marios Xanthidis",
"Sharmin Rahman",
"Ioannis Rekleitis",
"Bharat Joshi",
"Marios Xanthidis",
"Sharmin Rahman",
"Ioannis Rekleitis"
] | In this paper we present a complete framework for Underwater SLAM utilizing a single inexpensive sensor. Over the recent years, imaging technology of action cameras is producing stunning results even under the challenging conditions of the underwater domain. The GoPro 9 camera provides high definition video in synchronization with an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) data stream encoded in a single ... |
Reconfigurable Underactuated Adaptive Gripper Designed by Morphological Computation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811738/ | [
"Ivan I. Borisov",
"Evgenii E. Khornutov",
"Dmitriy V. Ivolga",
"Nikita A. Molchanov",
"Ivan A. Maksimov",
"Sergey A. Kolyubin",
"Ivan I. Borisov",
"Evgenii E. Khornutov",
"Dmitriy V. Ivolga",
"Nikita A. Molchanov",
"Ivan A. Maksimov",
"Sergey A. Kolyubin"
] | Anthropomorphic robotic grippers are required for robots, prostheses, and orthosis to enable manipulation of a priori unknown and variable-shape objects. It has to meet a wide range of sometimes contradictory requirements in terms of adaptivity, dexterity, high payload to weight ratio, robustness, aesthetics, compactness, lightweight, etc. Within this paper, we utilize the morphological computatio... |
Design and Optimization of a Magnetic Catcher for UAV Landing on Disturbed Aquatic Surface Platforms | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812270/ | [
"Chongfeng Liu",
"Zixing Jiang",
"Ruoyu Xu",
"Xiaoqiang Ji",
"Lianxin Zhang",
"Huihuan Qian",
"Chongfeng Liu",
"Zixing Jiang",
"Ruoyu Xu",
"Xiaoqiang Ji",
"Lianxin Zhang",
"Huihuan Qian"
] | In this paper, a new capture system for UAV precision landing in a disturbed environment is proposed. Compared with the traditional visual guided landing methods, perching mechanism based methods, and tethered landing methods, the proposed system takes into account the stability during landing process and retains the high accessibility of the UAV. The proposed system consists of a winch subsystem ... |
Design and Modeling of a Spherical Robot Actuated by a Cylindrical Drive | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812148/ | [
"Bruno Belzile",
"David St-Onge",
"Bruno Belzile",
"David St-Onge"
] | Rolling spherical robots have been studied in the past few years as an alternative to legged and wheeled robots in unstructured environments. These systems are of uttermost interest for space exploration: fast, robust to collision and able to handle various terrain topologies. This paper introduces a novel barycentric spherical robot, dubbed the Autonomous Robotic Intelligent Explorer Sphere (ARIE... |
Design and Modeling of a Compact Advancement Mechanism for a Modified COAST Guidewire Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811907/ | [
"Patrick Lis",
"Achraj Sarma",
"Grace Trimpe",
"Timothy A. Brumfiel",
"Ronghuai Qi",
"Jaydev P. Desai",
"Patrick Lis",
"Achraj Sarma",
"Grace Trimpe",
"Timothy A. Brumfiel",
"Ronghuai Qi",
"Jaydev P. Desai"
] | Peripheral vascular intervention remains a challenging procedure mainly due to the tortuosity of the vessels needing to be traversed by guidewires and catheters. In addition, handling long guidewires while navigating tortuous vasculature requires extensive time and skill from the surgeon. In this work, a compact guidewire advancement mechanism is proposed that is able to dispense guidewires up to ... |
A Novel Passive Mechanism for Flying Robots to Perch onto Surfaces | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811671/ | [
"HaoTse Hsiao",
"Feiyu Wu",
"Jiefeng Sun",
"Jianguo Zhao",
"HaoTse Hsiao",
"Feiyu Wu",
"Jiefeng Sun",
"Jianguo Zhao"
] | Perching onto objects can allow flying robots to stay at a desired height at low or no cost of energy. This paper presents a novel passive mechanism for aerial perching onto smooth surfaces. This mechanism is made from a bistable mechanism and a soft suction cup. Different from existing designs, it can be easily attached onto and detached from a surface, but it can also hold a large weight when at... |
A Lightweight, High-Extension, Planar 3-Degree-of-Freedom Manipulator Using Pinched Bistable Tapes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811976/ | [
"O. Godson Osele",
"Allison M. Okamura",
"Brian H. Do",
"O. Godson Osele",
"Allison M. Okamura",
"Brian H. Do"
] | To facilitate sensing and physical interaction in remote and/or constrained environments, high-extension, lightweight robot manipulators are easier to transport and reach substantially further than traditional serial chain manipulators. We propose a novel planar 3-degree-of-freedom manipulator that achieves low weight and high extension through the use of a pair of spooling bistable tapes, commonl... |
SiamX: An Efficient Long-term Tracker Using Cross-level Feature Correlation and Adaptive Tracking Scheme | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812327/ | [
"Huajian Huang",
"Sai-Kit Yeung",
"Huajian Huang",
"Sai-Kit Yeung"
] | Siamese network based trackers have achieved significant progress in visual object tracking. For the sake of speed, they mainly rely on offline training to learn a mono-level feature correlation between a target template and a search region. During the tracking period, they use a fixed strategy to infer target positions over sequences regardless of target states. However, such approaches are vulne... |
Accurate Calibration of Multi-Perspective Cameras from a Generalization of the Hand-Eye Constraint | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811577/ | [
"Yifu Wang",
"Wenqing Jiang",
"Kun Huang",
"Sören Schwertfeger",
"Laurent Kneip",
"Yifu Wang",
"Wenqing Jiang",
"Kun Huang",
"Sören Schwertfeger",
"Laurent Kneip"
] | Multi-perspective cameras are quickly gaining importance in many applications such as smart vehicles and virtual or augmented reality. However, a large system size or absence of overlap in neighbouring fields-of-view often complicate their calibration. We present a novel solution which relies on the availability of an external motion capture system. Our core contribution consists of an extension t... |
Few-Shot Keypoint Detection as Task Adaptation via Latent Embeddings | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812209/ | [
"Mel Vecerik",
"Jackie Kay",
"Raia Hadsell",
"Lourdes Agapito",
"Jon Scholz",
"Mel Vecerik",
"Jackie Kay",
"Raia Hadsell",
"Lourdes Agapito",
"Jon Scholz"
] | Dense object tracking, the ability to localize specific object points with pixel-level accuracy, is an important computer vision task with numerous downstream applications in robotics. Existing approaches either compute dense keypoint embeddings in a single forward pass, meaning the model is trained to track everything at once, or allocate their full capacity to a sparse predefined set of points, ... |
Keypoint-Based Category-Level Object Pose Tracking from an RGB Sequence with Uncertainty Estimation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811720/ | [
"Yunzhi Lin",
"Jonathan Tremblay",
"Stephen Tyree",
"Patricio A. Vela",
"Stan Birchfield",
"Yunzhi Lin",
"Jonathan Tremblay",
"Stephen Tyree",
"Patricio A. Vela",
"Stan Birchfield"
] | We propose a single-stage, category-level 6-DoF pose estimation algorithm that simultaneously detects and tracks instances of objects within a known category. Our method takes as input the previous and current frame from a monocular RGB video, as well as predictions from the previous frame, to predict the bounding cuboid and 6- DoF pose (up to scale). Internally, a deep network predicts distributi... |
MotionHint: Self-Supervised Monocular Visual Odometry with Motion Constraints | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812288/ | [
"Cong Wang",
"Yu-Ping Wang",
"Dinesh Manocha",
"Cong Wang",
"Yu-Ping Wang",
"Dinesh Manocha"
] | We present a novel self-supervised algorithm named MotionHint for monocular visual odometry (VO) that takes motion constraints into account. A key aspect of our approach is to use an appropriate motion model that can help existing self-supervised monocular VO (SSM-VO) algorithms to overcome issues related to the local minima within their self-supervised loss functions. The motion model is expresse... |
Fast Graph Refinement and Implicit Neural Representation for Tissue Tracking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811742/ | [
"Adam Schmidt",
"Omid Mohareri",
"Simon DiMaio",
"Septimiu E. Salcudean",
"Adam Schmidt",
"Omid Mohareri",
"Simon DiMaio",
"Septimiu E. Salcudean"
] | Tracking of tissue in the surgical environment is often done via locating frame-to-frame keypoint correspondences, and then using these correspondences to warp a prior underlying model such as a spline, mesh, or embedded deformation. We introduce a novel learned model which takes keypoint correspondences as input and enables a prior-free estimation of deformation at any location. For fast point tr... |
PoseSDF: Simultaneous 3D Human Shape Reconstruction and Gait Pose Estimation Using Signed Distance Functions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812051/ | [
"Jianxin Yang",
"Yuxuan Liu",
"Xiao Gu",
"Guang-Zhong Yang",
"Yao Guo",
"Jianxin Yang",
"Yuxuan Liu",
"Xiao Gu",
"Guang-Zhong Yang",
"Yao Guo"
] | Vision-based 3D human pose estimation and shape reconstruction play important roles in robot-assisted healthcare monitoring and personal assistance. However, 3D data captured from a single viewpoint always encounter occlusions and exhibit substantial heterogeneity across different views, resulting in significant challenges for both tasks. Extensive approaches have been proposed to perform each tas... |
Learning Friction Model for Magnet-Actuated Tethered Capsule Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811587/ | [
"Yi Wang",
"Yuyang Tu",
"Yuchen He",
"Xutian Deng",
"Ziwei Lei",
"Jianwei Zhang",
"Miao Li",
"Yi Wang",
"Yuyang Tu",
"Yuchen He",
"Xutian Deng",
"Ziwei Lei",
"Jianwei Zhang",
"Miao Li"
] | The potential diagnostic applications of magnet-actuated capsules have been greatly increased in recent years. For most of these potential applications, accurate position control of the capsule have been highly demanding. However, the friction between the robot and the environment as well as the drag force from the tether play a significant role during the motion control of the capsule. Moreover, ... |
L1Adaptive Augmentation for Geometric Tracking Control of Quadrotors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811946/ | [
"Zhuohuan Wu",
"Sheng Cheng",
"Kasey A. Ackerman",
"Aditya Gahlawat",
"Arun Lakshmanan",
"Pan Zhao",
"Naira Hovakimyan",
"Zhuohuan Wu",
"Sheng Cheng",
"Kasey A. Ackerman",
"Aditya Gahlawat",
"Arun Lakshmanan",
"Pan Zhao",
"Naira Hovakimyan"
] | This paper introduces an $L$1adaptive control aug-mentation for geometric tracking control of quadrotors. In the proposed design, the $L$ 1 augmentation handles nonlinear (time-and state-dependent) uncertainties in the quadrotor dynamics without assuming or enforcing parametric structures, while the baseline geometric controller achieves stabilization of the known nonlinear model of the system dyn... |
Shape Control of Deformable Linear Objects with Offline and Online Learning of Local Linear Deformation Models | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812244/ | [
"Mingrui Yu",
"Hanzhong Zhong",
"Xiang Li",
"Mingrui Yu",
"Hanzhong Zhong",
"Xiang Li"
] | The shape control of deformable linear objects (DLOs) is challenging, since it is difficult to obtain the deformation models. Previous studies often approximate the models in purely offline or online ways. In this paper, we propose a scheme for the shape control of DLOs, where the unknown model is estimated with both offline and online learning. The model is formulated in a local linear format, an... |
KoopNet: Joint Learning of Koopman Bilinear Models and Function Dictionaries with Application to Quadrotor Trajectory Tracking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811896/ | [
"Carl Folkestad",
"Skylar X. Wei",
"Joel W. Burdick",
"Carl Folkestad",
"Skylar X. Wei",
"Joel W. Burdick"
] | Nonlinear dynamical effects are crucial to the operation of many agile robotic systems. Koopman-based model learning methods can capture these nonlinear dynamical system effects in higher dimensional lifted bilinear models that are amenable to optimal control. However, standard methods that lift the system state using a fixed function dictionary before model learning result in high dimensional mod... |
Tracking Fast Trajectories with a Deformable Object using a Learned Model | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812189/ | [
"James A. Preiss",
"David Millard",
"Tao Yao",
"Gaurav S. Sukhatme",
"James A. Preiss",
"David Millard",
"Tao Yao",
"Gaurav S. Sukhatme"
] | We propose a method for robotic control of deformable objects using a learned nonlinear dynamics model. After collecting a dataset of trajectories from the real system, we train a recurrent neural network (RNN) to approximate its input-output behavior with a latent state-space model. The RNN internal state is low-dimensional enough to enable realtime nonlinear control methods. We demonstrate a clo... |
Model Identification and Control of a Low-cost Mobile Robot with Omnidirectional Wheels using Differentiable Physics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812454/ | [
"Edgar Granados",
"Abdeslam Boularias",
"Kostas Bekris",
"Mridul Aanjaneya",
"Edgar Granados",
"Abdeslam Boularias",
"Kostas Bekris",
"Mridul Aanjaneya"
] | We present a new data-driven technique for pre-dicting the motion of a low-cost omnidirectional mobile robot under the influence of motor torques and friction forces. Our method utilizes a novel differentiable physics engine for analytically computing the gradient of the deviation between predicted motion trajectories and real-world trajectories. This allows to automatically learn and fine-tune th... |
Combined Fast Control of Drifting State and Trajectory Tracking for Autonomous Vehicles Based on MPC Controller | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812185/ | [
"Cheng Hu",
"Xiaoling Zhou",
"Ran Duo",
"Haokun Xiong",
"Yu Qi",
"Zhiming Zhang",
"Lei Xie",
"Cheng Hu",
"Xiaoling Zhou",
"Ran Duo",
"Haokun Xiong",
"Yu Qi",
"Zhiming Zhang",
"Lei Xie"
] | Slipping may cause a vehicle out of control with serious accident potential. However, a kind of car slipping named “drifting” can be seen in professional contests. So, it is reasonable to apply drift maneuvers in autonomous driving. This article proposes a controller for the particular driving skill—drifting based on MPC(Model Predictive Control). Firstly, we analyze drift cornering mechanisms of ... |
Composable Causality in Semantic Robot Programming | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811365/ | [
"Emily Sheetz",
"Xiaotong Chen",
"Zhen Zeng",
"Kaizhi Zheng",
"Qiuyu Shi",
"Odest Chadwicke Jenkins",
"Emily Sheetz",
"Xiaotong Chen",
"Zhen Zeng",
"Kaizhi Zheng",
"Qiuyu Shi",
"Odest Chadwicke Jenkins"
] | Assembly tasks are challenging for robot manipulation because the robot must reason over the composed effects of actions and execute multi-objective behaviors. Robots typically use predefined priorities provided by users to determine how to compose controller behaviors, but we want the robot to autonomously select these compositions based on their composed effects within the task. We present Compo... |
A Hierarchical Control Framework for Drift Maneuvering of Autonomous Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812110/ | [
"Bo Yang",
"Yiwen Lu",
"Xu Yang",
"Yilin Mo",
"Bo Yang",
"Yiwen Lu",
"Xu Yang",
"Yilin Mo"
] | Maneuvering an autonomous vehicle under drift condition is critical to the safety of autonomous vehicles when there is a sudden loss of traction due to external conditions such as rain or snow, which is a challenging control problem due to the presence of significant sideslip and nearly full saturation of the tires. In this paper, we focus on the control of drift maneuvers of autonomous vehicle to... |
Value learning from trajectory optimization and Sobolev descent: A step toward reinforcement learning with superlinear convergence properties | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811993/ | [
"Amit Parag",
"Sébastien Kleff",
"Léo Saci",
"Nicolas Mansard",
"Olivier Stasse",
"Amit Parag",
"Sébastien Kleff",
"Léo Saci",
"Nicolas Mansard",
"Olivier Stasse"
] | The recent successes in deep reinforcement learning largely rely on the capabilities of generating masses of data, which in turn implies the use of a simulator. In particular, current progress in multi body dynamic simulators are under-pinning the implementation of reinforcement learning for end-to-end control of robotic systems. Yet simulators are mostly considered as black boxes while we have th... |
A hybrid model-based evolutionary optimization with passive boundaries for physical human-robot interaction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811606/ | [
"Gustavo J. G. Lahr",
"Henrique B. Garcia",
"Arash Ajoudani",
"Thiago Boaventura",
"Glauco A. P. Caurin",
"Gustavo J. G. Lahr",
"Henrique B. Garcia",
"Arash Ajoudani",
"Thiago Boaventura",
"Glauco A. P. Caurin"
] | The field of physical human-robot interaction has dramatically evolved in the last decades. As a result, the robotic system's requirements have become more challenging, including personalized behavior for different tasks and users. Various machine learning techniques have been proposed to give the robot such adaptability features. This paper proposes a model-based evolutionary optimization algorit... |
Impact Planning and Pre-configuration based on Hierarchical Quadratic Programming | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811681/ | [
"Francesco Tassi",
"Soheil Gholami",
"Simone Giudice",
"Arash Ajoudani",
"Francesco Tassi",
"Soheil Gholami",
"Simone Giudice",
"Arash Ajoudani"
] | Impacts and other non-smooth behaviors are usually unwanted in robotic applications. However, several industrial tasks such as deburring, removing excess material, and assembling/fitting, involve impacts between objects, which can benefit from robotic automation due to the risks posed to human health. Towards this objective, in this paper, we propose a method for optimal impact planning and pre-co... |
Optimal-Horizon Model Predictive Control with Differential Dynamic Programming | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812036/ | [
"Kyle Stachowicz",
"Evangelos A. Theodorou",
"Kyle Stachowicz",
"Evangelos A. Theodorou"
] | We present an algorithm, based on the Differential Dynamic Programming framework, to handle trajectory optimization problems in which the horizon is determined online rather than fixed a priori. This algorithm exhibits exact one-step convergence for linear, quadratic, time-invariant problems and is fast enough for real-time nonlinear model-predictive control. We show derivations for the nonlinear ... |
Implicit Differential Dynamic Programming | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811647/ | [
"Wilson Jallet",
"Nicolas Mansard",
"Justin Carpentier",
"Wilson Jallet",
"Nicolas Mansard",
"Justin Carpentier"
] | Over the past decade, the Differential Dynamic Programming (DDP) method has gained in maturity and popularity within the robotics community. Several recent contributions have led to the integration of constraints within the original DDP formulation, hence enlarging its domain of application while making it a strong and easy-to-implement competitor against alternative methods of the state of the ar... |
Trajectory Distribution Control for Model Predictive Path Integral Control using Covariance Steering | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811615/ | [
"Ji Yin",
"Zhiyuan Zhang",
"Evangelos Theodorou",
"Panagiotis Tsiotras",
"Ji Yin",
"Zhiyuan Zhang",
"Evangelos Theodorou",
"Panagiotis Tsiotras"
] | This paper presents a novel control approach for autonomous systems operating under uncertainty. We combine Model Predictive Path Integral (MPPI) control with Covariance Steering (CS) theory to obtain a robust controller for general nonlinear systems. The proposed Covariance-Controlled Model Predictive Path Integral (CC-MPPI) controller addresses the performance degradation observed in some MPPI i... |
Multirobot control with double-integrator dynamics and control barrier functions for deformable object transport | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812378/ | [
"Rafael Herguedas",
"Miguel Aranda",
"Gonzalo López-Nicolás",
"Carlos Sagüés",
"Youcef Mezouar",
"Rafael Herguedas",
"Miguel Aranda",
"Gonzalo López-Nicolás",
"Carlos Sagüés",
"Youcef Mezouar"
] | In this paper, we propose a formation control system for deforming and transporting simultaneously a de-formable object with a team of robots, modeled with double-integrator dynamics. The goal is to reach a target configuration, defined as a combination of shape, scale, orientation and position of the formation. We augment this controller with a set of control barrier functions (CBFs). The CBFs al... |
Context-Aware Grasp Generation in Cluttered Scenes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811371/ | [
"Dinh-Cuong Hoang",
"Johannes A. Stork",
"Todor Stoyanov",
"Dinh-Cuong Hoang",
"Johannes A. Stork",
"Todor Stoyanov"
] | Conventional methods to autonomous grasping rely on a pre-computed database with known objects to synthesize grasps, which is not possible for novel objects. On the other hand, recently proposed deep learning-based approaches have demonstrated the ability to generalize grasp for unknown objects. However, grasp generation still remains a challenging problem, especially in cluttered environments und... |
“The World Is Its Own Best Model”: Robust Real-World Manipulation Through Online Behavior Selection | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811845/ | [
"Manuel Baum",
"Oliver Brock",
"Manuel Baum",
"Oliver Brock"
] | Robotic manipulation behavior should be robust to disturbances that violate high-level task-structure. Such robustness can be achieved by constantly monitoring the environment to observe the discrete high-level state of the task. This is possible because different phases of a task are characterized by different sensor patterns and by monitoring these patterns a robot can decide which controllers t... |
The Second Generation (G2) Fingertip Sensor for Near-Distance Ranging and Material Sensing in Robotic Grasping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811902/ | [
"Cheng Fang",
"Di Wang",
"Dezhen Song",
"Jun Zou",
"Cheng Fang",
"Di Wang",
"Dezhen Song",
"Jun Zou"
] | To continuously improve robotic grasping, we are interested in developing a contactless fingertip-mounted sensor for near-distance ranging and material sensing. Previously, we demonstrated a dual-modal and dual sensing mechanisms (DMDSM) pretouch sensor prototype based on pulse-echo ultrasound and optoacoustics. However, the complex system, the bulky and expensive pulser-receiver, and the omni-dir... |
Push-to-See: Learning Non-Prehensile Manipulation to Enhance Instance Segmentation via Deep Q-Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811645/ | [
"Baris Serhan",
"Harit Pandya",
"Ayse Kucukyilmaz",
"Gerhard Neumann",
"Baris Serhan",
"Harit Pandya",
"Ayse Kucukyilmaz",
"Gerhard Neumann"
] | Efficient robotic manipulation of objects for sorting and searching often rely upon how well the objects are perceived and the available grasp poses. The challenge arises when the objects are irregular, have similar visual features (e.g., textureless objects) and the scene is densely cluttered. In such cases, non-prehensile manipulation (e.g., pushing) can facilitate grasping or searching by impro... |
Non-Penetration Iterative Closest Points for Single-View Multi-Object 6D Pose Estimation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812043/ | [
"Mengchao Zhang",
"Kris Hauser",
"Mengchao Zhang",
"Kris Hauser"
] | This paper presents a novel iterative closest points (ICP) variant, non-penetration iterative closest points (NPICP), which prevents interpenetration in 6DOF pose optimization and/or joint optimization of multiple object poses. This capability is particularly advantageous in cluttered scenarios, where there are many interactions between objects that constrain the space of valid poses. We use a sem... |
Learning-based Ellipse Detection for Robotic Grasps of Cylinders and Ellipsoids | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812363/ | [
"Huixu Dong",
"Jiadong Zhou",
"Chen Qiu",
"Prasad K. Dilip",
"I-Ming Chen",
"Huixu Dong",
"Jiadong Zhou",
"Chen Qiu",
"Prasad K. Dilip",
"I-Ming Chen"
] | In our daily life, there are many objects represented by cylindrical shapes and ellipsoids. The tops of these objects are formed by elliptic shape primitives. Thus, it is available for a robot to manipulate these objects by ellipse detection. In this work, we propose a novel approach to generating ground truth for training the model based on domain randomization. Using synthetic data generated in ... |
TransGrasp: A Multi-Scale Hierarchical Point Transformer for 7-DoF Grasp Detection | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812001/ | [
"Zhixuan Liu",
"Zibo Chen",
"Shangjin Xie",
"Wei–Shi Zheng",
"Zhixuan Liu",
"Zibo Chen",
"Shangjin Xie",
"Wei–Shi Zheng"
] | Robotic grasping pose detection that predicts the configuration of the robotic gripper for object grasping is fundamental in robot manipulation. Based on point clouds, most of the existing methods predict grasp pose with the hierarchical PointNet++ backbone, while the non-local geometric information is underexplored. In this work, we address the 7-DoF (6- DoF with the grasp width) grasp detection ... |
Online Object Model Reconstruction and Reuse for Lifelong Improvement of Robot Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812440/ | [
"Shiyang Lu",
"Rui Wang",
"Yinglong Miao",
"Chaitanya Mitash",
"Kostas Bekris",
"Shiyang Lu",
"Rui Wang",
"Yinglong Miao",
"Chaitanya Mitash",
"Kostas Bekris"
] | This work proposes a robotic pipeline for picking and constrained placement of objects without geometric shape priors. Compared to recent efforts developed for similar tasks, where every object was assumed to be novel, the proposed system recognizes previously manipulated objects and per-forms online model reconstruction and reuse. Over a lifelong manipulation process, the system keeps learning fe... |
Single-Stage Keypoint- Based Category-Level Object Pose Estimation from an RGB Image | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812299/ | [
"Yunzhi Lin",
"Jonathan Tremblay",
"Stephen Tyree",
"Patricio A. Vela",
"Stan Birchfield",
"Yunzhi Lin",
"Jonathan Tremblay",
"Stephen Tyree",
"Patricio A. Vela",
"Stan Birchfield"
] | Prior work on 6-DoF object pose estimation has largely focused on instance-level processing, in which a textured CAD model is available for each object being detected. Category-level 6- DoF pose estimation represents an important step toward developing robotic vision systems that operate in unstructured, real-world scenarios. In this work, we propose a single-stage, keypoint-based approach for cat... |
Multi-view object pose distribution tracking for pre-grasp planning on mobile robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812339/ | [
"Lakshadeep Naik",
"Thorbjørn Mosekjær Iversen",
"Aljaz Kramberger",
"Jakob Wilm",
"Norbert Krüger",
"Lakshadeep Naik",
"Thorbjørn Mosekjær Iversen",
"Aljaz Kramberger",
"Jakob Wilm",
"Norbert Krüger"
] | The ability to track the 6D pose distribution of an object when a mobile manipulator robot is still approaching the object can enable the robot to pre-plan grasps that combine base and arm motion. However, tracking a 6D object pose distribution from a distance can be challenging due to the limited view of the robot camera. In this work, we present a framework that fuses observations from external ... |
Efficient and Robust Training of Dense Object Nets for Multi-Object Robot Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812274/ | [
"David B. Adrian",
"Andras Gabor Kupcsik",
"Markus Spies",
"Heiko Neumann",
"David B. Adrian",
"Andras Gabor Kupcsik",
"Markus Spies",
"Heiko Neumann"
] | We propose a framework for robust and efficient training of Dense Object Nets (DON) [1] with a focus on industrial multi-object robot manipulation scenarios. DON is a popular approach to obtain dense, view-invariant object descriptors, which can be used for a multitude of downstream tasks in robot manipulation, such as, pose estimation, state representation for control, etc. However, the original ... |
Deep Surrogate Q-Learning for Autonomous Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811618/ | [
"Maria Kalweit",
"Gabriel Kalweit",
"Moritz Werling",
"Joschka Boedecker",
"Maria Kalweit",
"Gabriel Kalweit",
"Moritz Werling",
"Joschka Boedecker"
] | Open challenges for deep reinforcement learning systems are their adaptivity to changing environments and their efficiency w.r.t. computational resources and data. In the application of learning lane-change behavior for autonomous driving, the number of required transitions imposes a bottleneck, since test drivers cannot perform an arbitrary amount of lane changes in the real world. In the off-pol... |
Legged Robots that Keep on Learning: Fine-Tuning Locomotion Policies in the Real World | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812166/ | [
"Laura Smith",
"J. Chase Kew",
"Xue Bin Peng",
"Sehoon Ha",
"Jie Tan",
"Sergey Levine",
"Laura Smith",
"J. Chase Kew",
"Xue Bin Peng",
"Sehoon Ha",
"Jie Tan",
"Sergey Levine"
] | Legged robots are physically capable of traversing a wide range of challenging environments, but designing controllers that are sufficiently robust to handle this diversity has been a long-standing challenge in robotics. Reinforcement learning presents an appealing approach for automating the controller design process and has been able to produce remarkably robust controllers when trained in a sui... |
Accessibility-Based Clustering for Efficient Learning of Locomotion Skills | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812113/ | [
"Chong Zhang",
"Wanming Yu",
"Zhibin Li",
"Chong Zhang",
"Wanming Yu",
"Zhibin Li"
] | For model-free deep reinforcement learning of quadruped locomotion, the initialization of robot configurations is crucial for data efficiency and robustness. This work focuses on algorithmic improvements of data efficiency and robustness simultaneously through automatic discovery of initial states, which is achieved by our proposed K-Access algorithm based on accessibility metrics. Specifically, w... |
Dynamic Mirror Descent based Model Predictive Control for Accelerating Robot Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812089/ | [
"Utkarsh A. Mishra",
"Soumya R. Samineni",
"Prakhar Goel",
"Chandravaran Kunjeti",
"Himanshu Lodha",
"Aman Singh",
"Aditya Sagi",
"Shalabh Bhatnagar",
"Shishir Kolathaya",
"Utkarsh A. Mishra",
"Soumya R. Samineni",
"Prakhar Goel",
"Chandravaran Kunjeti",
"Himanshu Lodha",
"Aman Singh",
"Aditya Sagi",
"Shalabh Bhatnagar",
"Shishir Kolathaya"
] | Recent works in Reinforcement Learning (RL) combine model-free (Mf)-RL algorithms with model-based (Mb)-RL approaches to get the best from both: asymptotic performance of Mf-RL and high sample-efficiency of Mb-RL. Inspired by these works, we propose a hierarchical framework that integrates online learning for the Mb-trajectory optimization with off-policy methods for the Mf-RL. In particular, two ... |
Unified Data Collection for Visual-Inertial Calibration via Deep Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811629/ | [
"Yunke Ao",
"Le Chen",
"Florian Tschopp",
"Michel Breyer",
"Roland Siegwart",
"Andrei Cramariuc",
"Yunke Ao",
"Le Chen",
"Florian Tschopp",
"Michel Breyer",
"Roland Siegwart",
"Andrei Cramariuc"
] | Visual-inertial sensors have a wide range of applications in robotics. However, good performance often requires different sophisticated motion routines to accurately calibrate camera intrinsics and inter-sensor extrinsics. This work presents a novel formulation to learn a motion policy to be executed on a robot arm for automatic data collection for calibrating intrinsics and extrinsics jointly. Ou... |
Relative Distributed Formation and Obstacle Avoidance with Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812263/ | [
"Yuzi Yan",
"Xiaoxiang Li",
"Xinyou Qiu",
"Jiantao Qiu",
"Jian Wang",
"Yu Wang",
"Yuan Shen",
"Yuzi Yan",
"Xiaoxiang Li",
"Xinyou Qiu",
"Jiantao Qiu",
"Jian Wang",
"Yu Wang",
"Yuan Shen"
] | Multi-agent formation as well as obstacle avoid-ance is one of the most actively studied topics in the field of multi-agent systems. Although some classic controllers like model predictive control (MPC) and fuzzy control achieve a certain measure of success, most of them require precise global information which is not accessible in harsh environments. On the other hand, some reinforcement learning... |
Estimation of Upper Limb Kinematics with a Magnetometer-Free Egocentric Visual-Inertial System | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811733/ | [
"Tong Li",
"Xiaoyu Wu",
"Huixu Dong",
"Haoyong Yu",
"Tong Li",
"Xiaoyu Wu",
"Huixu Dong",
"Haoyong Yu"
] | Most human activities in daily living or professional work rely on upper body motion. Measuring upper body motion is essential for many applications such as health evaluation, rehabilitation, human power augmentation, skill transferring, etc. Computer vision-based systems have been widely used to directly capture upper limb motion but are usually constrained in a restricted area. Wearable sensors ... |
Joint State and Input Estimation of Agent Based on Recursive Kalman Filter Given Prior Knowledge | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811636/ | [
"Zida Wu",
"Zhaoliang Zheng",
"Ankur Mehta",
"Zida Wu",
"Zhaoliang Zheng",
"Ankur Mehta"
] | Modern autonomous systems are purposed for many challenging scenarios, where agents will face unexpected events and complicated tasks. The presence of disturbance noise with control command and unknown inputs can negatively impact robot performance. Previous research of joint input and state estimation separately studied the continuous and discrete cases without any prior information. This paper c... |
Towards Artefact Aware Human Motion Capture using Inertial Sensors Integrated into Loose Clothing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811933/ | [
"Michael Lorenz",
"Gabriele Bleser",
"Takayuki Akiyama",
"Takehiro Niikura",
"Didier Stricker",
"Bertram Taetz",
"Michael Lorenz",
"Gabriele Bleser",
"Takayuki Akiyama",
"Takehiro Niikura",
"Didier Stricker",
"Bertram Taetz"
] | Inertial motion capture has become an attractive alternative to optical motion capture for human joint angle estimation outside the laboratory. Usually inertial sensors are assumed to be tightly fixed to the body segments, which can be cumbersome regarding setup-time and ease-of-use. However, integrating the sensors directly into loose clothing, usually, results in additional clothing motion relat... |
Improved Kalman-Particle Kernel Filter on Lie Groups Applied to Angles-Only UAV Navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812192/ | [
"Clément Chahbazian",
"Karim Dahia",
"Nicolas Merlinge",
"Bénedicte Winter-Bonnet",
"Kévin Honore",
"Christian Musso",
"Clément Chahbazian",
"Karim Dahia",
"Nicolas Merlinge",
"Bénedicte Winter-Bonnet",
"Kévin Honore",
"Christian Musso"
] | Kalman-Particle Kernel Filter (KPKF) is a sub-class of Particle Filter (PF) that uses Gaussian kernels as particles, which enables a local Kalman update for each measurement in addition to the usual weight update. Besides, recent research about filtering on Lie groups brought powerful theoretical results, and showed the superiority of this approach. Hence, this paper extends the Euclidean KPKF to ... |
Asynchronous Collaborative Localization by Integrating Spatiotemporal Graph Learning with Model-Based Estimation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811613/ | [
"Peng Gao",
"Brian Reily",
"Rui Guo",
"Hongsheng Lu",
"Qingzhao Zhu",
"Hao Zhang",
"Peng Gao",
"Brian Reily",
"Rui Guo",
"Hongsheng Lu",
"Qingzhao Zhu",
"Hao Zhang"
] | Collaborative localization is an essential capability for a team of robots such as connected vehicles to collaboratively estimate object locations from multiple perspectives with reliant cooperation. To enable collaborative localization, four key challenges must be addressed, including modeling complex relationships between observed objects, fusing observations from an arbitrary number of collabor... |
Symbolic State Estimation with Predicates for Contact-Rich Manipulation Tasks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811675/ | [
"Toki Migimatsu",
"Wenzhao Lian",
"Jeannette Bohg",
"Stefan Schaal",
"Toki Migimatsu",
"Wenzhao Lian",
"Jeannette Bohg",
"Stefan Schaal"
] | Manipulation tasks often require a robot to adjust its sensorimotor skills based on the state it finds itself in. Taking peg-in-hole as an example: once the peg is aligned with the hole, the robot should push the peg downwards. While high level execution frameworks such as state machines and behavior trees are commonly used to formalize such decision-making problems, these frameworks require a mec... |
Development of a Stereo-vision based High-throughput Robotic System for Mouse Tail Vein Injection | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811804/ | [
"Tianyi Ko",
"Koichi Nishiwaki",
"Koji Terada",
"Yusuke Tanaka",
"Shun Mitsumata",
"Ryuichi Katagiri",
"Junko Taketo",
"Naoshi Horiba",
"Hideyoshi Igata",
"Kazue Mizuno",
"Tianyi Ko",
"Koichi Nishiwaki",
"Koji Terada",
"Yusuke Tanaka",
"Shun Mitsumata",
"Ryuichi Katagiri",
"Junko Taketo",
"Naoshi Horiba",
"Hideyoshi Igata",
"Kazue Mizuno"
] | In this paper, we present a robotic device for mouse tail vein injection. We propose a mouse holding mechanism to realize vein injection without anesthetizing the mouse, which consists of a tourniquet, vacuum port, and adaptive tail-end fixture. The position of the target vein in 3D space is reconstructed from a high-resolution stereo vision. The vein is detected by a simple but robust vein line d... |
Dual-scale robotic solution for middle ear surgery | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812365/ | [
"Jae-Hun So",
"Brahim Tamadazte",
"Naresh Marturi",
"Jérôme Szewczyk",
"Jae-Hun So",
"Brahim Tamadazte",
"Naresh Marturi",
"Jérôme Szewczyk"
] | This paper deals with the control of a redundant robotic system for middle ear surgery (i.e., cholesteatoma tissues removal). The targeted robotic system is a macro-micro-scale robot composed of a redundant seven degrees of freedom (DoFs) on which is attached a two DoFs robotized flexible fiberscope. Two different control architectures are proposed to achieve a defined surgical procedure to remove... |
Using Language to Generate State Abstractions for Long-Range Planning in Outdoor Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812355/ | [
"Matthew Berg",
"George Konidaris",
"Stefanie Tellex",
"Matthew Berg",
"George Konidaris",
"Stefanie Tellex"
] | Robots that process navigation instructions in large outdoor environments will need to operate at different levels of abstraction. For example, a land-surveying aerial robot receiving the instruction “go to Boston and go through the state forest on the way” must reason about a long-range goal like “go to Boston” while also processing a finer-grained constraint like “go through the state forest.” E... |
Reactive Locomotion Decision-Making and Robust Motion Planning for Real-Time Perturbation Recovery | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812068/ | [
"Zhaoyuan Gu",
"Nathan Boyd",
"Ye Zhao",
"Zhaoyuan Gu",
"Nathan Boyd",
"Ye Zhao"
] | In this paper, we examine the problem of push recovery for bipedal robot locomotion and present a reactive decision-making and robust planning framework for locomotion resilient to external perturbations. Rejecting perturbations is an essential capability of bipedal robots and has been widely studied in the locomotion literature. However, adversarial disturbances and aggressive turning can lead to... |
Locomotion as a Risk-mitigating Behavior in Uncertain Environments: A Rapid Planning and Few-shot Failure Adaptation Approach | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812103/ | [
"Jacob Hackett",
"Dylan Epstein-Gross",
"Monica Daley",
"Christian Hubicki",
"Jacob Hackett",
"Dylan Epstein-Gross",
"Monica Daley",
"Christian Hubicki"
] | We want robots to complete assigned tasks even when unexpected task pressures arise, either from the robot or the environment. This paper presents a method of both learning sources of task failure in situ and rapidly planning new motions on-the-fly to accommodate them. This “risk-adaptive” approach to robot control uses a few encounters with a novel failure mode to generate a probabilistic failure... |
Persistent Homology for Effective Non-Prehensile Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811848/ | [
"Ewerton R. Vieira",
"Daniel Nakhimovich",
"Kai Gao",
"Rui Wang",
"Jingjin Yu",
"Kostas E. Bekris",
"Ewerton R. Vieira",
"Daniel Nakhimovich",
"Kai Gao",
"Rui Wang",
"Jingjin Yu",
"Kostas E. Bekris"
] | This work explores the use of topological tools for achieving effective non-prehensile manipulation in cluttered, constrained workspaces. In particular, it proposes the use of persistent homology as a guiding principle in identifying the appropriate non-prehensile actions, such as pushing, to clean a cluttered space with a robotic arm so as to allow the retrieval of a target object. Persistent hom... |
Visually Grounded Task and Motion Planning for Mobile Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812055/ | [
"Xiaohan Zhang",
"Yifeng Zhu",
"Yan Ding",
"Yuke Zhu",
"Peter Stone",
"Shiqi Zhang",
"Xiaohan Zhang",
"Yifeng Zhu",
"Yan Ding",
"Yuke Zhu",
"Peter Stone",
"Shiqi Zhang"
] | Task and motion planning (TAMP) algorithms aim to help robots achieve task-level goals, while maintaining motion-level feasibility. This paper focuses on TAMP domains that involve robot behaviors that take extended periods of time (e.g., long-distance navigation). In this paper, we develop a visual grounding approach to help robots probabilistically evaluate action feasibility, and introduce a TAM... |
Long-Horizon Manipulation of Unknown Objects via Task and Motion Planning with Estimated Affordances | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812057/ | [
"Aidan Curtis",
"Xiaolin Fang",
"Leslie Pack Kaelbling",
"Tomás Lozano-Pérez",
"Caelan Reed Garrett",
"Aidan Curtis",
"Xiaolin Fang",
"Leslie Pack Kaelbling",
"Tomás Lozano-Pérez",
"Caelan Reed Garrett"
] | We present a strategy for designing and building very general robot manipulation systems using a general-purpose task-and-motion planner with both engineered and learned modules that estimate properties and affordances of unknown objects. Such systems are closed-loop policies that map from RGB images, depth images, and robot joint encoder measurements to robot joint position commands. We show that... |
Failure is an option: Task and Motion Planning with Failing Executions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812273/ | [
"Tianyang Pan",
"Andrew M. Wells",
"Rahul Shome",
"Lydia E. Kavraki",
"Tianyang Pan",
"Andrew M. Wells",
"Rahul Shome",
"Lydia E. Kavraki"
] | Future robotic deployments will require robots to be able to repeatedly solve a variety of tasks in application domains. Task and motion planning addresses complex robotic problems that combine discrete reasoning over states and actions and geometric interactions during action executions. Moving beyond deterministic settings, stochastic actions can be handled by modeling the problem as a Markov De... |
Hierarchical Policy Learning for Mechanical Search | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811572/ | [
"Oussama Zenkri",
"Ngo Anh Vien",
"Gerhard Neumann",
"Oussama Zenkri",
"Ngo Anh Vien",
"Gerhard Neumann"
] | Retrieving objects from clutters is a complex task, which requires multiple interactions with the environment until the target object can be extracted. These interactions involve executing action primitives like grasping or pushing as well as setting priorities for the objects to manipulate and the actions to execute. Mechanical Search (MS) [1] is a framework for object retrieval, which uses a heu... |
Fast High-Quality Tabletop Rearrangement in Bounded Workspace | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812367/ | [
"Kai Gao",
"Darren Lau",
"Baichuan Huang",
"Kostas E. Bekris",
"Jingjin Yu",
"Kai Gao",
"Darren Lau",
"Baichuan Huang",
"Kostas E. Bekris",
"Jingjin Yu"
] | In this paper, we examine the problem of rearranging many objects on a tabletop in a cluttered setting using overhand grasps. Efficient solutions for the problem, which capture a common task that we solve on a daily basis, are essential in enabling truly intelligent robotic manipulation. In a given instance, objects may need to be placed at temporary positions (“buffers”) to complete the rearrange... |
Efficient and High-quality Prehensile Rearrangement in Cluttered and Confined Spaces | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811934/ | [
"Rui Wang",
"Yinglong Miao",
"Kostas E. Bekris",
"Rui Wang",
"Yinglong Miao",
"Kostas E. Bekris"
] | Prehensile object rearrangement in cluttered and confined spaces has broad applications but is also challenging. For instance, rearranging products in a grocery shelf means that the robot cannot directly access all objects and has limited free space. This is harder than tabletop rearrangement where objects are easily accessible with top-down grasps, which simplifies robot-object interactions. This... |
Optimal Design and Control of an Aerial Manipulator with Elastic Suspension Using Unidirectional Thrusters | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811775/ | [
"Miguel Arpa Perozo",
"Jean Dussine",
"Arda Yiğit",
"Loïc Cuvillon",
"Sylvain Durand",
"Jacques Gangloff",
"Miguel Arpa Perozo",
"Jean Dussine",
"Arda Yiğit",
"Loïc Cuvillon",
"Sylvain Durand",
"Jacques Gangloff"
] | Aerial Manipulators with Elastic Suspension (AMES) may be seen as a hybrid robot mixing properties of classical Aerial Manipulators (AMs) and Cable-Driven Parallel Robots (CDPRs). The optimal design and control of an AMES using unidirectional thrusters are considered in this paper. To maximize the workspace, an optimization algorithm is proposed. The position and orientation of the thrusters are o... |
Large-angle and High-speed Trajectory Tracking Control of a Quadrotor UAV based on Reachability | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811879/ | [
"Zhou Liu",
"Lilong Cai",
"Zhou Liu",
"Lilong Cai"
] | This paper solves the tracking control problem for a quadrotor system under the tasks of large-angle rotation and high-speed trajectory tracking. A quadrotor dynamic model is presented taking both disturbances and drag force into account. A reachability control strategy is developed for a quadrotor to track the planned attitude and position. Outdoor experiments of a circle trajectory tracking at d... |
Cooperative Modular Single Actuator Monocopters Capable of Controlled Passive Separation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812182/ | [
"Xinyu Cai",
"Shane Kyi Hla Win",
"Luke Soe Thura Win",
"Danial Sufiyan",
"Shaohui Foong",
"Xinyu Cai",
"Shane Kyi Hla Win",
"Luke Soe Thura Win",
"Danial Sufiyan",
"Shaohui Foong"
] | In this paper, we introduce a Modular Single Actuator Monocopter (M-SAM), which is capable of flying in both singular configuration and cooperative configuration. From singular mode, M-SAMs can be manually assembled into cooperative mode, using magnetic connectors built into the body of each M-SAM unit. The design of the connectors allow for passive separation of the units without the need for a d... |
Optimal Thrust Vector Control of an Electric Small-Scale Rocket Prototype | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811938/ | [
"Raphaël Linsen",
"Petr Listov",
"Albéric de Lajarte",
"Roland Schwan",
"Colin N. Jones",
"Raphaël Linsen",
"Petr Listov",
"Albéric de Lajarte",
"Roland Schwan",
"Colin N. Jones"
] | Recent advances in Model Predictive Control (MPC) algorithms and methodologies, combined with the surge of computational power of available embedded platforms, allows the use of real-time optimization-based control of fast mechatronic systems. This paper presents an implementation of an optimal guidance, navigation and control (GNC) system for the motion control of a small-scale electric prototype... |
Optimal Inverted Landing in a Small Aerial Robot with Varied Approach Velocities and Landing Gear Designs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812409/ | [
"Bryan Habas",
"Bader AlAttar",
"Brian Davis",
"Jack W. Langelaan",
"Bo Cheng",
"Bryan Habas",
"Bader AlAttar",
"Brian Davis",
"Jack W. Langelaan",
"Bo Cheng"
] | Inverted landing is a challenging feat to perform in aerial robots, especially without external positioning. However, it is routinely performed by biological fliers such as bees, flies, and bats. Our previous observations of landing behaviors in flies suggest an open-loop causal relationship between their putative visual cues and the kinematics of the aerial maneuvers executed. For example, the de... |
SMORS: A soft multirotor UAV for multimodal locomotion and robust interaction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812044/ | [
"Markus Ryll",
"Robert K. Katzschmann",
"Markus Ryll",
"Robert K. Katzschmann"
] | We present SMORS, the first Soft fully actuated MultirOtoR System for multimodal locomotion. Unlike conventional hexarotors, SMORS is equipped with three rigid and three continuously soft arms, with each arm hosting a propeller. We create a bridge between the fields of soft and aerial robotics by mechanically coupling the actuation of a fully actuated flying platform with the actuation of a soft r... |
Centroidal Aerodynamic Modeling and Control of Flying Multibody Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812147/ | [
"Tong Hui",
"Antonello Paolino",
"Gabriele Nava",
"Giuseppe L'Erario",
"Fabio Di Natale",
"Fabio Bergonti",
"Francesco Braghin",
"Daniele Pucci",
"Tong Hui",
"Antonello Paolino",
"Gabriele Nava",
"Giuseppe L'Erario",
"Fabio Di Natale",
"Fabio Bergonti",
"Francesco Braghin",
"Daniele Pucci"
] | This paper presents a modeling and control frame-work for multibody flying robots subject to non-negligible aero-dynamic forces acting on the centroidal dynamics. First, aero-dynamic forces are calculated during robot flight in different operating conditions by means of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis. Then, analytical models of the aerodynamics coefficients are generated from the data... |
Cooperative Transportation using Multiple Single-Rotor Robots and Decentralized Control for Unknown Payloads | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811768/ | [
"Koshi Oishi",
"Yasushi Amano",
"Tomohiko Jimbo",
"Koshi Oishi",
"Yasushi Amano",
"Tomohiko Jimbo"
] | Cooperative transportation via multiple aerial robots has the potential to support various payloads and reduce the chances of them being dropped. Furthermore, autonomously controlled robots render the system scalable with respect to the payload. In this study, a cooperative transportation system was developed using rigidly attached single-rotor robots, and a decentralized controller was proposed t... |
PogoDrone: Design, Model, and Control of a Jumping Quadrotor | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811970/ | [
"Brian Zhu",
"Jiawei Xu",
"Andrew Charway",
"David Saldaña",
"Brian Zhu",
"Jiawei Xu",
"Andrew Charway",
"David Saldaña"
] | We present a design, model, and control for a novel jumping-flying robot that is called PogoDrone. The robot is composed of a quadrotor with a passive mechanism for jumping. The robot can continuously jump in place or fly like a normal quadrotor. Jumping in place allows the robot to quickly move and operate very close to the ground. For instance, in agricultural applications, the jumping mechanism... |
Energy Tank-Based Policies for Robust Aerial Physical Interaction with Moving Objects | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812342/ | [
"Maximilian Brunner",
"Livio Giacomini",
"Roland Siegwart",
"Marco Tognon",
"Maximilian Brunner",
"Livio Giacomini",
"Roland Siegwart",
"Marco Tognon"
] | Although manipulation capabilities of aerial robots greatly improved in the last decade, only few works addressed the problem of aerial physical interaction with dynamic environments, proposing strongly model-based approaches. However, in real scenarios, modeling the environment with high accuracy is often impossible. In this work, we aim at developing a control framework for Omnidirectional Micro... |
Generalized Omega Turn Gait Enables Agile Limbless Robot Turning in Complex Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811929/ | [
"Tianyu Wang",
"Baxi Chong",
"Yuelin Deng",
"Ruijie Fu",
"Howie Choset",
"Daniel I. Goldman",
"Tianyu Wang",
"Baxi Chong",
"Yuelin Deng",
"Ruijie Fu",
"Howie Choset",
"Daniel I. Goldman"
] | Reorientation (turning in plane) plays a critical role for all robots in any field application, especially those that in confined spaces. While important, reorientation remains a relatively unstudied problem for robots, including limbless mechanisms, often called snake robots. Instead of looking at snakes, we take inspiration from observations of the turning behavior of tiny nematode worms C. eleg... |
SenSnake: A snake robot with contact force sensing for studying locomotion in complex 3-D terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812159/ | [
"Divya Ramesh",
"Qiyuan Fu",
"Chen Li",
"Divya Ramesh",
"Qiyuan Fu",
"Chen Li"
] | Despite advances in a diversity of environments, snake robots are still far behind snakes in traversing complex 3-D terrain with large obstacles. This is due to a lack of understanding of how to control 3-D body bending to push against terrain features to generate and control propulsion. Biological studies suggested that generalist snakes use contact force sensing to adjust body bending in real ti... |
Autonomous Actuation of Flapping Wing Robots Inspired by Asynchronous Insect Muscle | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812028/ | [
"James Lynch",
"Jeff Gau",
"Simon Sponberg",
"Nick Gravish",
"James Lynch",
"Jeff Gau",
"Simon Sponberg",
"Nick Gravish"
] | In most instances, flapping wing robots have emulated the “synchronous” actuation of insects in which the wingbeat timing is generated from a time-dependent, rhythmic signal. The internal dynamics of asynchronous insect flight muscle enable high-frequency, adaptive wingbeats with minimal direct neural control. In this paper, we investigate how the delayed stretch-activation (dSA) response of async... |
Liftoff of A Motor-Driven Flapping Wing Rotorcraft with Mechanically Decoupled Wings | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812350/ | [
"Fangyuan Liu",
"Song Li",
"Ziyu Wang",
"Xin Dong",
"Daochun Li",
"Zhan Tu",
"Fangyuan Liu",
"Song Li",
"Ziyu Wang",
"Xin Dong",
"Daochun Li",
"Zhan Tu"
] | Flapping Wing Rotorcraft (FWR) combines flapping and rotating wing motion in one element. Such a hybrid design integrates the high-efficiency characteristics of the rotating wing and the high-lift feature of the flapping wing under low Reynolds number, providing a broader range of simultaneous lift and power efficiency optimization. Nevertheless, the flight performance of the current FWRs is limit... |
A New Bio-Inspired Hybrid Cable-Driven Robot (HCDR) to Design More Realistic Snakebots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811550/ | [
"E. Gautreau",
"J. Sandoval",
"X. Bonnet",
"M. Arsicault",
"S. Zeghloul",
"M.A. Laribi",
"E. Gautreau",
"J. Sandoval",
"X. Bonnet",
"M. Arsicault",
"S. Zeghloul",
"M.A. Laribi"
] | Bioinspired robots are useful tools to study complex biomechanical processes of animal locomotion. Key movements and kinematic parameters are under the control of experimenters, which is impossible to perform when experimenting with living animals. The primary challenge to test biological hypotheses is designing realistic robots taking inspiration from swimming snakes. Yet, underlying biomechanics... |
Single User WiFi Structure from Motion in the Wild | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812340/ | [
"Yiming Qian",
"Hang Yan",
"Sachini Herath",
"Pyojin Kim",
"Yasutaka Furukawa",
"Yiming Qian",
"Hang Yan",
"Sachini Herath",
"Pyojin Kim",
"Yasutaka Furukawa"
] | This paper proposes a novel motion estimation algorithm using WiFi networks and IMU sensor data in large uncontrolled environments, dubbed “WiFi Structure-from-Motion” (WiFi SfM). Given smartphone sensor data through day-to-day activities from a single user over a month, our WiFi SfM algorithm estimates smartphone motion tra-jectories and the structure of the environment represented as a WiFi radi... |
PatchGraph: In-hand tactile tracking with learned surface normals | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811953/ | [
"Paloma Sodhi",
"Michael Kaess",
"Mustafa Mukadanr",
"Stuart Anderson",
"Paloma Sodhi",
"Michael Kaess",
"Mustafa Mukadanr",
"Stuart Anderson"
] | We address the problem of tracking 3D object poses from touch during in-hand manipulations. Specifically, we look at tracking small objects using vision-based tactile sensors that provide high-dimensional tactile image measurements at the point of contact. While prior work has relied on a-priori information about the object being localized, we remove this requirement. Our key insight is that an ob... |
LTSR: Long-term Semantic Relocalization based on HD Map for Autonomous Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811855/ | [
"Huayou Wang",
"Changliang Xue",
"Yu Tang",
"Wanlong Li",
"Feng Wen",
"Hongbo Zhang",
"Huayou Wang",
"Changliang Xue",
"Yu Tang",
"Wanlong Li",
"Feng Wen",
"Hongbo Zhang"
] | Highly accurate and robust relocalization or localization initialization ability is of great importance for autonomous vehicles (AVs). Traditional GNSS-based methods are not reliable enough in occlusion and multipath conditions. In this paper we propose a novel long-term semantic relocalization algorithm based on HD map and semantic features which are compact in representation. Semantic features a... |
DEVO: Depth-Event Camera Visual Odometry in Challenging Conditions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9811805/ | [
"Yi–Fan Zuo",
"Jiaqi Yang",
"Jiaben Chen",
"Xia Wang",
"Yifu Wang",
"Laurent Kneip",
"Yi–Fan Zuo",
"Jiaqi Yang",
"Jiaben Chen",
"Xia Wang",
"Yifu Wang",
"Laurent Kneip"
] | We present a novel real-time visual odometry framework for a stereo setup of a depth and high-resolution event camera. Our framework balances accuracy and robustness against computational efficiency towards strong performance in challenging scenarios. We extend conventional edge-based semi-dense visual odometry towards time-surface maps obtained from event streams. Semi-dense depth maps are genera... |
ICRA 2022 Accepted Paper Meta Info Dataset
This dataset is collect from the ICRA 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2022 accepted papers' meta info (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/conhome/9811522/proceeding) as well as the arxiv website DeepNLP paper arxiv (http://www.deepnlp.org/content/paper/icra2022). For researchers who are interested in doing analysis of ICRA 2022 accepted papers and potential trends, you can use the already cleaned up json files. Each row contains the meta information of a paper in the ICRA 2022 conference. To explore more AI & Robotic papers (NIPS/ICML/ICLR/IROS/ICRA/etc) and AI equations, feel free to navigate the Equation Search Engine (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/equation) as well as the AI Agent Search Engine to find the deployed AI Apps and Agents (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/agent) in your domain.
Equations Latex code and Papers Search Engine
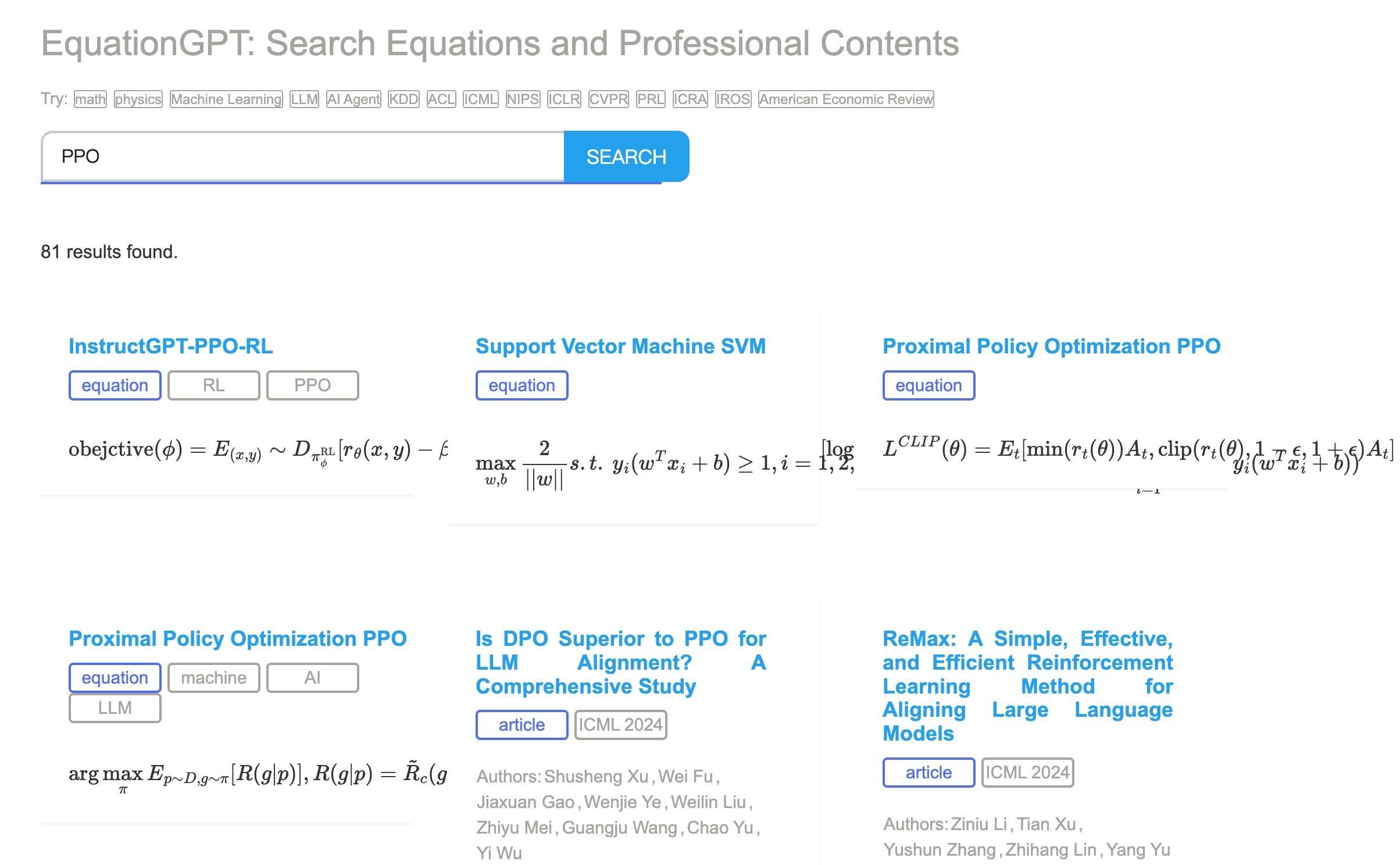
Meta Information of Json File of Paper
{
"title": "Online Prediction of Lane Change with a Hierarchical Learning-Based Approach",
"detail_url": "https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9812269/",
"author_list": ["Xishun Liao", "Ziran Wang", "Xuanpeng Zhao", "Zhouqiao Zhao", "Kyungtae Han", "Prashant Tiwari", "Matthew J. Barth", "Guoyuan Wu", "Xishun Liao", "Ziran Wang", "Xuanpeng Zhao", "Zhouqiao Zhao", "Kyungtae Han", "Prashant Tiwari", "Matthew J. Barth", "Guoyuan Wu"],
"abstract": "In the foreseeable future, connected and auto-mated vehicles (CAVs) and human-driven vehicles will share the road networks together. In such a mixed traffic environment, CAVs need to understand and predict maneuvers of surrounding vehicles for safer and more efficient interactions, especially when human drivers bring in a wide range of uncertainties. In this paper, we propose a learning-based lane..."
}
Related
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
Robot Search
Equation and Academic search
AI & Robot Comprehensive Search
AI & Robot Question
AI & Robot Community
AI Agent Marketplace Blog
AI Agent Reviews
AI Agent Marketplace Directory
Microsoft AI Agents Reviews
Claude AI Agents Reviews
OpenAI AI Agents Reviews
Saleforce AI Agents Reviews
AI Agent Builder Reviews
AI Equation
List of AI Equations and Latex
List of Math Equations and Latex
List of Physics Equations and Latex
List of Statistics Equations and Latex
List of Machine Learning Equations and Latex
- Downloads last month
- 39