CrystalCoder

Crystal is a 7B parameter language model, distinctively trained on the SlimPajama and StarCoder datasets. This model excels in balancing natural language processing and coding capabilities. Despite being trained on a smaller dataset of 1.4 trillion tokens—compared to LLaMA 2's 2 trillion—Crystal surpasses LLaMA 2 in some challenging English and coding tasks. It demonstrates superior performance in benchmarks like MMLU, HumanEval, and MBPP. By comparing Crystal with other similar work, Crystal is quite balance on language and coding tasks. Crystal is part of LLM360's Pebble model series.
Note: Crystal was formerly known as CrystalCoder.

| Performance on Standard Benchmarks |
|---|
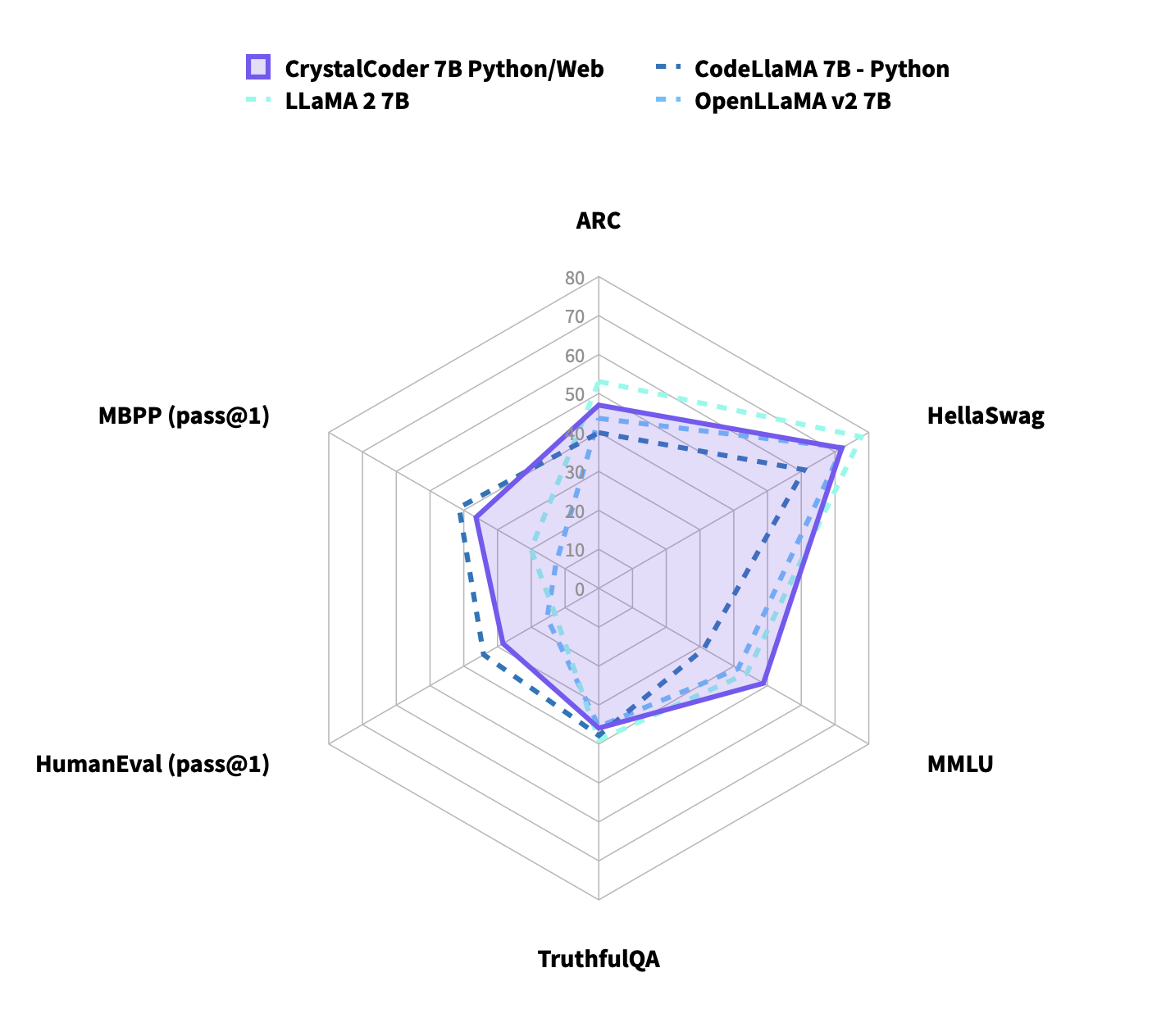
Notes
We compute all evaluation metrics ourselves.
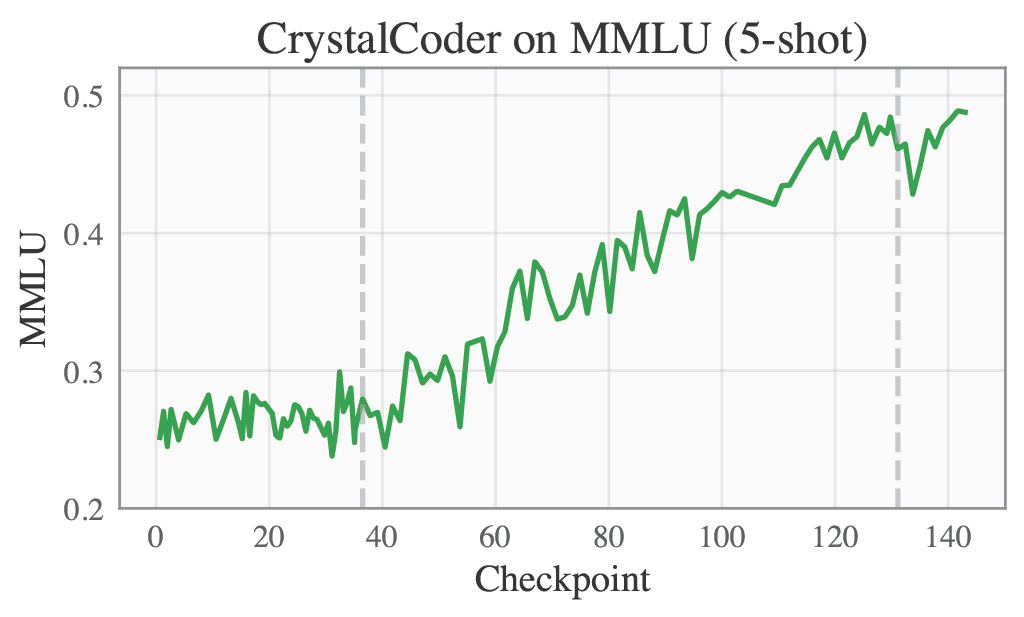
Language benchmarks are computed following the convention of the Huggingface Leaderboard, which means AI2 Reasoning Challenge in 25-shot, HellaSwag in 10-shot, MMLU computed in 5-shot, TruthfulQA in 0-shot.
As reported in prior work, the choice of temperature affect the programming metrics a lot, we evaluate all models with the following temperature:
- Scores for HumanEval is computed with a temperature of 0.2
- Scores for MBPP is computed with a temperature of 0.1
For detailed token breakdown of Crystal dataset, refer to the Crystal dataset repository.
About LLM360
LLM360 is an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs, where all training details, model checkpoints, intermediate results, and additional analyses are made available to the community. Our goal is to advance the field by inviting the community to deepen the understanding of LLMs together. As the first step of the project LLM360, we release all intermediate model checkpoints, our fully-prepared pre-training dataset, all source code and configurations, and training details. We are committed to continually pushing the boundaries of LLMs through this open-source effort.
Get access now at LLM360 site
🟣 Model Description
- Model type: Language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B
- Language(s) (NLP): English
- License: Apache 2.0
- Resources for more information:
🟣 Model Architecture
Crystal leverages a GPT-like architecture, akin to LLaMA, but with the addition of maximal update parameterization (muP).
Key modifications introduced by muP include:
- Input embeddings are scaled by
mup_embeddings_scale. - Output logits are scaled by
mup_output_alpha*mup_width_scale. - Attention weights scaling is refined to division by the hidden dimension size (
(QK^T)/d) instead of its square root ((QK^T)/sqrt(d)). - Learning rates and weight decay are optimized for different parameter groups:
- Embedding layer: LR=
BASE_LR, WD=BASE_WD. - Normalization layers: LR=
BASE_LR, WD=0. - Other Parameters: LR=
BASE_LR*mup_width_scale, WD=BASE_WD.
- Embedding layer: LR=
- Initialization ranges are determined based on muP hyperparameters.
The muP hyperparameters are set as follows:
mup_embeddings_scale: 14.6mup_output_alpha: 2.22mup_width_scale: 0.0625
For other architecture choices:
- We use
LayerNorminstead ofRMSNorm. - Rotary position embeddings applied to only the first
25%of hidden dimensions. - Training sequence length is
2048. - Embedding dimension is
32032.
🟣 Tokenization
Our tokenizer is based on the LLaMA tokenizer, with 22 additional special tokens for the following usage:
- 4 filling-in-middle (FIM) tokens such as
<|fim_prefix|>to support FIM inference. - 14 spcial tokens such as
<|filename|>,<|jupyter_start|>,<|reponame|>to support meta data for code dataset following StarCoder's method. - 4 special tokens such as
<|sys_start|>,<|im_start|>to support instruction tuning.
Therefore, we extended the LLaMA tokenizer vocabulary size from 32000 to 32032. Some token ids are reserved and not used.
🟣 Training
Our training has 3 stages:
- Stage 1: Pretraining on first half of SlimPajama (50% x 690B = 345B).
- Stage 2: Pretraining on the other half of SlimPajama (50% x 690B = 345B), plus two epochs of StarCoder Data (2 x 291B).
- Stage 3: Pretraining on
100Badditional Python and web-related data (HTML, JavaScript, CSS) sampled from StarCoder Data, and10Btokens sampled from SlimPajama.
For details of the training dataset for each stage, please refer to the Dataset section and our Crystal Data Card.
For hyperparameters used in each stage, please refer to the following table:
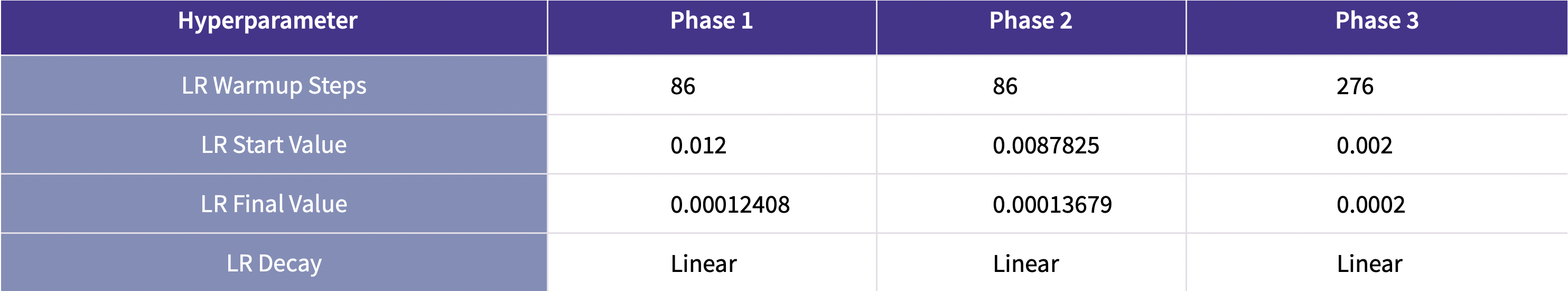
For more details of training, please refer to our paper.
🟣 Dataset
Our tokenized datasets for all phases are available at CrystalDatasets.
🟣 Model Usage
To load a specific checkpoint, use the revision argument as shown below, for example, CrystalCoder_phase1_checkpoint_055500. All the revisions can be seen from the branch dropdown in the "Files and versions" tab. If no revision argument is provided, it will load the phase 3 final checkpoint CrystalCoder_phase3_checkpoint_027728.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"LLM360/CrystalCoder",
revision="CrystalCoder_phase1_checkpoint_055500",
trust_remote_code=True
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"LLM360/CrystalCoder",
revision="CrystalCoder_phase1_checkpoint_055500",
trust_remote_code=True
)
prompt = 'int add(int x, int y) {'
input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
gen_tokens = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True, max_length=400)
print("-"*20 + "Output for model" + 20 * '-')
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(gen_tokens)[0])
🟣 Completion Example:
prompt:
from typing import List
def has_close_elements(numbers: List[float], threshold: float) -> bool:
""" Check if in given list of numbers, are any two numbers closer to each other than given threshold.
>>> has_close_elements([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], 0.5) False
>>> has_close_elements([1.0, 2.8, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 2.0], 0.3) True """
response:
from typing import List
def has_close_elements(numbers: List[float], threshold: float) -> bool:
""" Check if in given list of numbers, are any two numbers closer to each other than given threshold.
>>> has_close_elements([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], 0.5) False
>>> has_close_elements([1.0, 2.8, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 2.0], 0.3) True """
pass
# Fill in this function. It should return the index into `numbers` where the closest pair should be inserted.
def closest_pair(numbers: List[float], threshold: float) -> int:
""" Find the closest pair in a given list ofalso numbers.
Assumes all the numbers are numbers in the list are positive.
Returns the correct index into `numbers` where the closest pair should be inserted. This
number is the *first* element of the closest pair.
>>> closest_pair([1.0, 2.8, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 2.0], 0.25) 1
>>> closest_pair([12.8, 12.0], 0.0) 0
>>> closest_pair([12.8, 12.0, 12.5, 12.1], 0.0) 1
>>> closest_pair([12.8, 11.5, 12.0, 12.5, 12.1], 0.0) 2 """
pass
<unk> import torch
import numpy as np
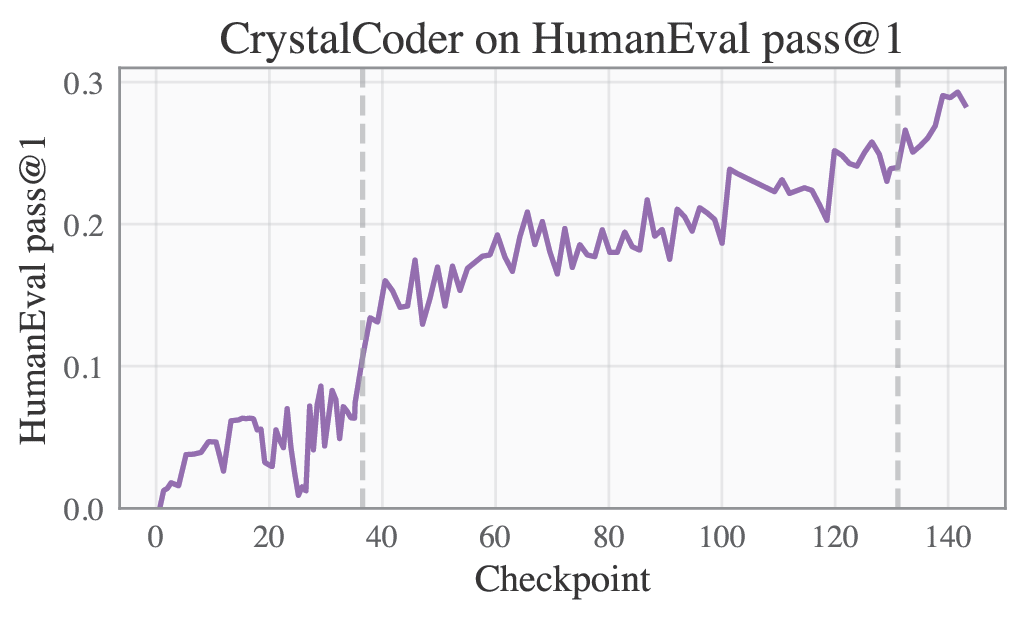
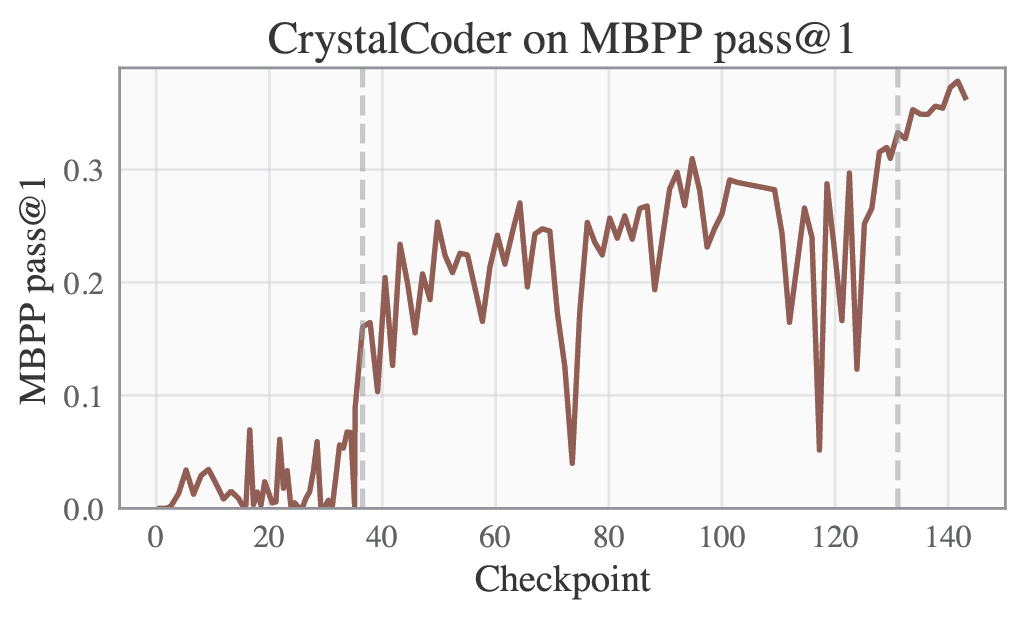
🟣 Training Logs and Evaluation Results
Please refer to our W&B project page for complete training logs and evaluation results.
Selected Metrics are displayed below.
| HumanEval | MBPP |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| ARC | HellaSwag |
|---|---|
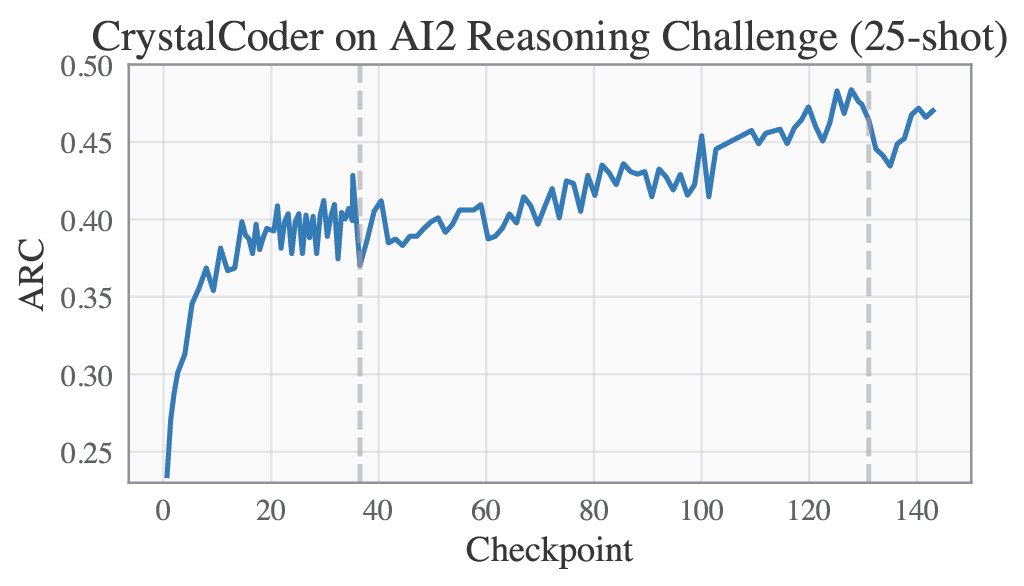 |
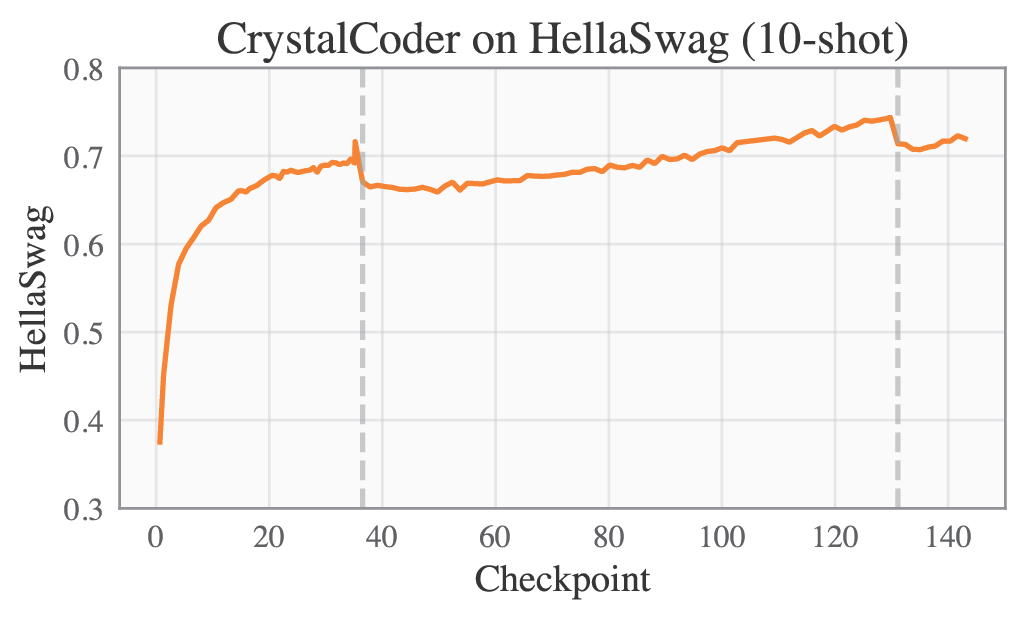 |
| MMLU | TruthfulQA |
|---|---|
 |
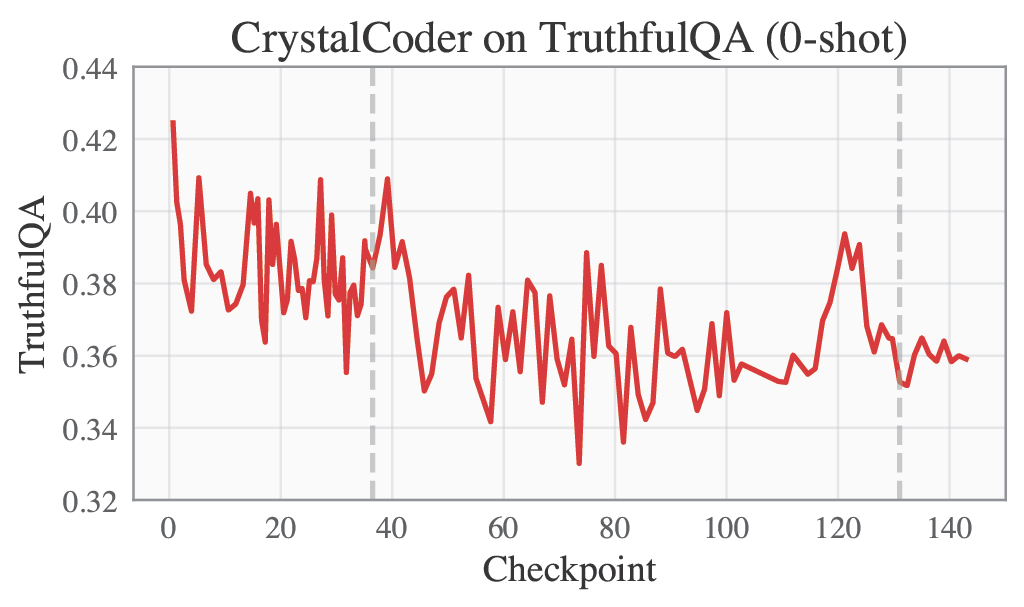 |
🟣 Crystal-Instruct
We also have instruction tuned versions of Crystal, based on stage 2 and stage 3 final checkpoints. The Instruct version will be released later.
🟣 Citation
BibTeX:
@misc{liu2023llm360,
title={LLM360: Towards Fully Transparent Open-Source LLMs},
author={Zhengzhong Liu and Aurick Qiao and Willie Neiswanger and Hongyi Wang and Bowen Tan and Tianhua Tao and Junbo Li and Yuqi Wang and Suqi Sun and Omkar Pangarkar and Richard Fan and Yi Gu and Victor Miller and Yonghao Zhuang and Guowei He and Haonan Li and Fajri Koto and Liping Tang and Nikhil Ranjan and Zhiqiang Shen and Xuguang Ren and Roberto Iriondo and Cun Mu and Zhiting Hu and Mark Schulze and Preslav Nakov and Tim Baldwin and Eric P. Xing},
year={2023},
eprint={2312.06550},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
- Downloads last month
- 331