UniSpeech-SAT-Base for Speaker Verification
The model was pretrained on 16kHz sampled speech audio with utterance and speaker contrastive loss. When using the model, make sure that your speech input is also sampled at 16kHz.
The model was pre-trained on:
- 960 hours of LibriSpeech
Paper: UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING
Authors: Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu
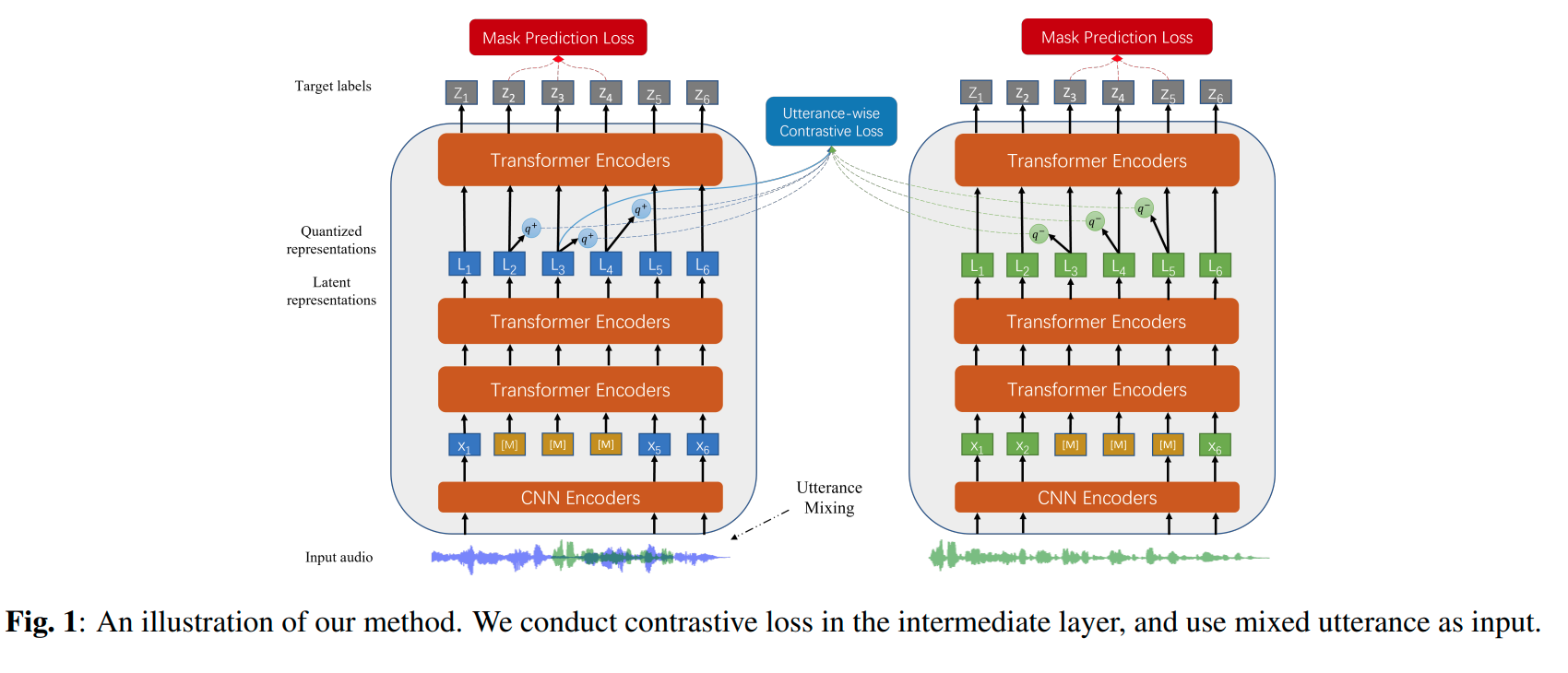
Abstract Self-supervised learning (SSL) is a long-standing goal for speech processing, since it utilizes large-scale unlabeled data and avoids extensive human labeling. Recent years witness great successes in applying self-supervised learning in speech recognition, while limited exploration was attempted in applying SSL for modeling speaker characteristics. In this paper, we aim to improve the existing SSL framework for speaker representation learning. Two methods are introduced for enhancing the unsupervised speaker information extraction. First, we apply the multi-task learning to the current SSL framework, where we integrate the utterance-wise contrastive loss with the SSL objective function. Second, for better speaker discrimination, we propose an utterance mixing strategy for data augmentation, where additional overlapped utterances are created unsupervisely and incorporate during training. We integrate the proposed methods into the HuBERT framework. Experiment results on SUPERB benchmark show that the proposed system achieves state-of-the-art performance in universal representation learning, especially for speaker identification oriented tasks. An ablation study is performed verifying the efficacy of each proposed method. Finally, we scale up training dataset to 94 thousand hours public audio data and achieve further performance improvement in all SUPERB tasks..
The original model can be found under https://github.com/microsoft/UniSpeech/tree/main/UniSpeech-SAT.
Fine-tuning details
The model is fine-tuned on the VoxCeleb1 dataset using an X-Vector head with an Additive Margin Softmax loss
X-Vectors: Robust DNN Embeddings for Speaker Recognition
Usage
Speaker Verification
from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor, UniSpeechSatForXVector
from datasets import load_dataset
import torch
dataset = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_demo", "clean", split="validation")
feature_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor.from_pretrained('microsoft/unispeech-sat-base-sv')
model = UniSpeechSatForXVector.from_pretrained('microsoft/unispeech-sat-base-sv')
# audio files are decoded on the fly
inputs = feature_extractor(dataset[:2]["audio"]["array"], return_tensors="pt")
embeddings = model(**inputs).embeddings
embeddings = torch.nn.functional.normalize(embeddings, dim=-1).cpu()
# the resulting embeddings can be used for cosine similarity-based retrieval
cosine_sim = torch.nn.CosineSimilarity(dim=-1)
similarity = cosine_sim(embeddings[0], embeddings[1])
threshold = 0.86 # the optimal threshold is dataset-dependent
if similarity < threshold:
print("Speakers are not the same!")
License
The official license can be found here
- Downloads last month
- 48