File size: 4,672 Bytes
99d143c 9ebd8dc 99d143c 9ebd8dc 99d143c 4c63760 99d143c 4c63760 99d143c 9f3bec3 99d143c |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 |
---
license: apache-2.0
datasets:
- nferruz/UR50_2021_04
tags:
- chemistry
- biology
---
### Model Description
This model card describes the distilled version of [ProtGPT2](https://huggingface.co/nferruz/ProtGPT2), referred to as `protgpt2-distilled-small`. The distillation process for this model follows the methodology of knowledge distillation from a larger teacher model to a smaller, more efficient student model. The process combines both "Soft Loss" (Knowledge Distillation Loss) and "Hard Loss" (Cross-Entropy Loss) to ensure the student model not only generalizes like its teacher but also retains practical prediction capabilities.
### Technical Details
**Distillation Parameters:**
- **Temperature (T):** 10
- **Alpha (α):** 0.1
- **Model Architecture:**
- **Number of Layers:** 6
- **Number of Attention Heads:** 8
- **Embedding Size:** 768
**Dataset Used:**
- The model was distilled using a subset of the evaluation dataset provided by [nferruz/UR50_2021_04](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nferruz/UR50_2021_04).
<strong>Loss Formulation:</strong>
<ul>
<li><strong>Soft Loss:</strong> <span>ℒ<sub>soft</sub> = KL(softmax(s/T), softmax(t/T))</span>, where <em>s</em> are the logits from the student model, <em>t</em> are the logits from the teacher model, and <em>T</em> is the temperature used to soften the probabilities.</li>
<li><strong>Hard Loss:</strong> <span>ℒ<sub>hard</sub> = -∑<sub>i</sub> y<sub>i</sub> log(softmax(s<sub>i</sub>))</span>, where <em>y<sub>i</sub></em> represents the true labels, and <em>s<sub>i</sub></em> are the logits from the student model corresponding to each label.</li>
<li><strong>Combined Loss:</strong> <span>ℒ = α ℒ<sub>hard</sub> + (1 - α) ℒ<sub>soft</sub></span>, where <em>α</em> (alpha) is the weight factor that balances the hard loss and soft loss.</li>
</ul>
<p><strong>Note:</strong> KL represents the Kullback-Leibler divergence, a measure used to quantify how one probability distribution diverges from a second, expected probability distribution.</p>
### Performance
The distilled model, `protgpt2-distilled-tiny`, demonstrates a substantial increase in inference speed—up to 6 times faster than the pretrained version. This assessment is based on evaluations using \(n=100\) tests, showing that while the speed is significantly enhanced, the model still maintains perplexities comparable to the original.
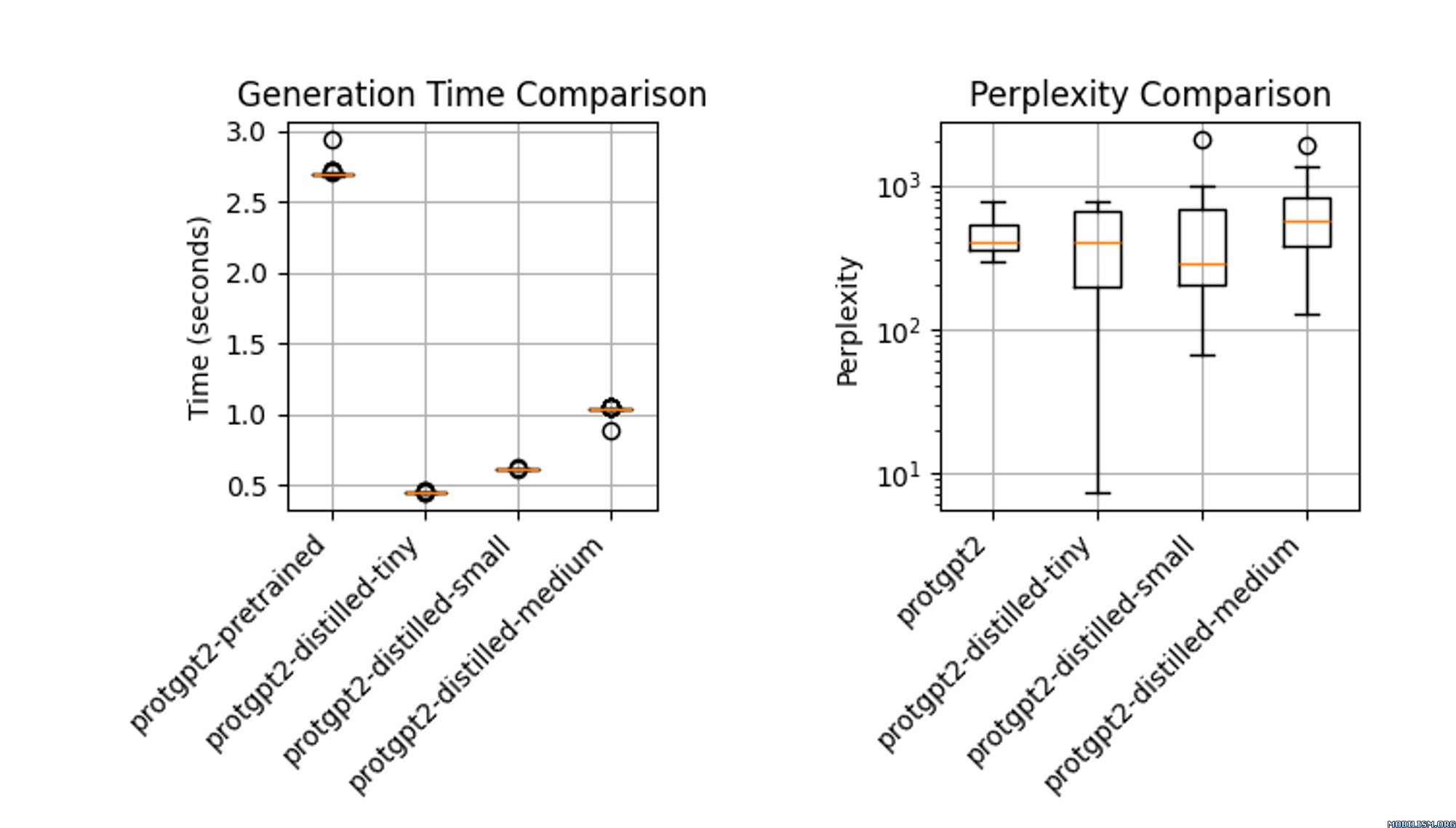
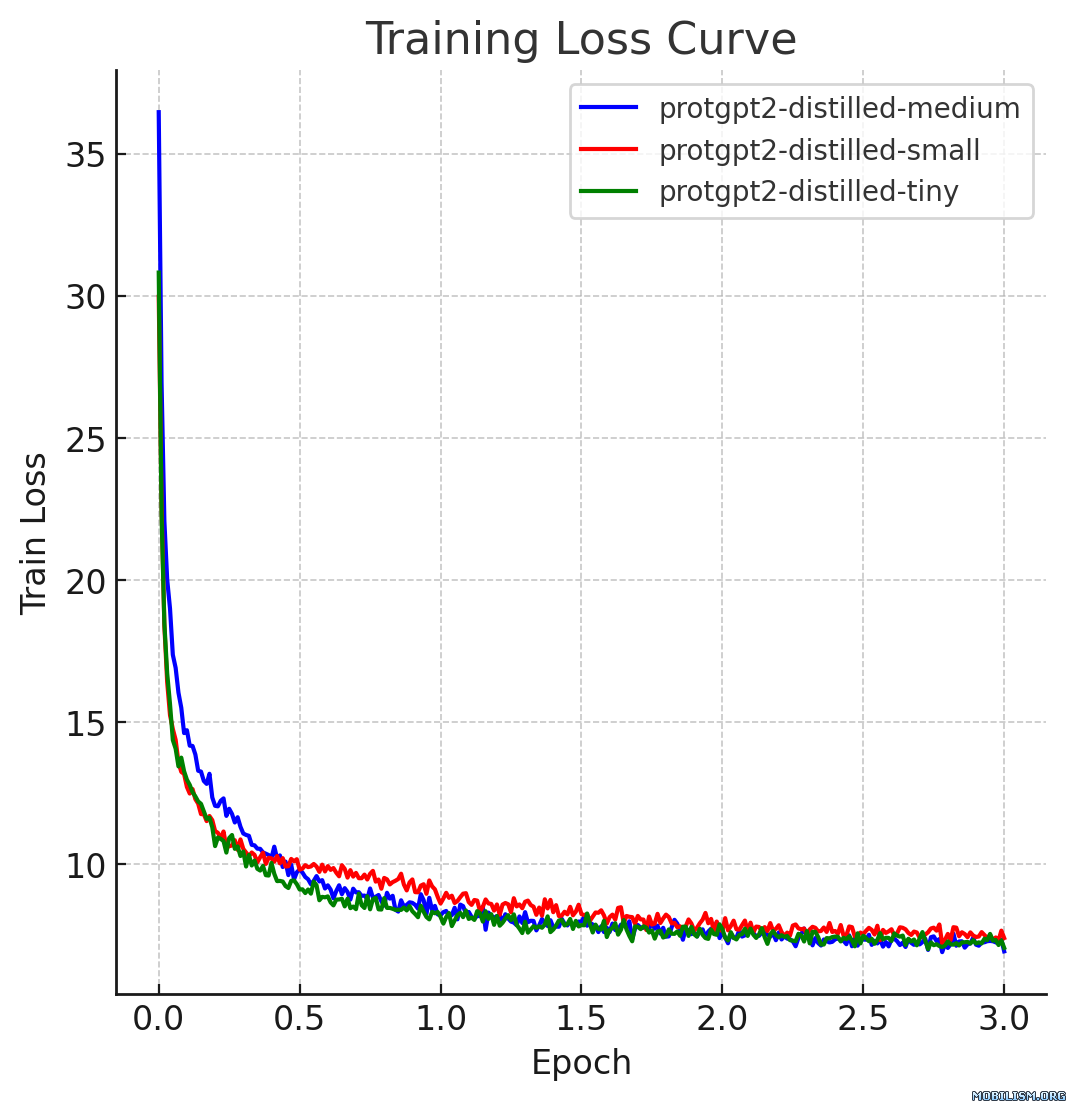
### Usage
```
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer, GPT2LMHeadModel, TextGenerationPipeline
import re
# Load the model and tokenizer
model_name = "littleworth/protgpt2-distilled-small"
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Initialize the pipeline
text_generator = TextGenerationPipeline(
model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, device=0
) # specify device if needed
# Generate sequences
generated_sequences = text_generator(
"<|endoftext|>",
max_length=100,
do_sample=True,
top_k=950,
repetition_penalty=1.2,
num_return_sequences=10,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id, # Set pad_token_id to eos_token_id
eos_token_id=0,
truncation=True,
)
def clean_sequence(text):
# Remove the "<|endoftext|>" token
text = text.replace("<|endoftext|>", "")
# Remove newline characters and non-alphabetical characters
text = "".join(char for char in text if char.isalpha())
return text
# Print the generated sequences
for i, seq in enumerate(generated_sequences):
cleaned_text = clean_sequence(seq["generated_text"])
print(f">Seq_{i}")
print(cleaned_text)
```
### Use Cases
1. **High-Throughput Screening in Drug Discovery:** The distilled ProtGPT2 facilitates rapid mutation screening in drug discovery by predicting protein variant stability efficiently. Its reduced size allows for swift fine-tuning on new datasets, enhancing the pace of target identification.
2. **Portable Diagnostics in Healthcare:** Suitable for handheld devices, this model enables real-time protein analysis in remote clinical settings, providing immediate diagnostic results.
3. **Interactive Learning Tools in Academia:** Integrated into educational software, the distilled model helps biology students simulate and understand protein dynamics without advanced computational resources.
### References
- Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., & Dean, J. (2015). Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv:1503.02531.
- Original ProtGPT2 Paper: [Link to paper](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9329459/) |