Spaces:
Sleeping
Sleeping
File size: 4,689 Bytes
33d4721 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 |
# Text Classification & Regression
Training a text classification/regression model with AutoTrain is super-easy! Get your data ready in
proper format and then with just a few clicks, your state-of-the-art model will be ready to
be used in production.
Config file task names:
- `text_classification`
- `text-classification`
- `text_regression`
- `text-regression`
## Data Format
Text classification/regression supports datasets in both CSV and JSONL formats.
### CSV Format
Let's train a model for classifying the sentiment of a movie review. The data should be
in the following CSV format:
```csv
text,target
"this movie is great",positive
"this movie is bad",negative
.
.
.
```
As you can see, we have two columns in the CSV file. One column is the text and the other
is the label. The label can be any string. In this example, we have two labels: `positive`
and `negative`. You can have as many labels as you want.
And if you would like to train a model for scoring a movie review on a scale of 1-5. The data can be as follows:
```csv
text,target
"this movie is great",4.9
"this movie is bad",1.5
.
.
.
```
### JSONL Format
Instead of CSV you can also use JSONL format. The JSONL format should be as follows:
```json
{"text": "this movie is great", "target": "positive"}
{"text": "this movie is bad", "target": "negative"}
.
.
.
```
and for regression:
```json
{"text": "this movie is great", "target": 4.9}
{"text": "this movie is bad", "target": 1.5}
.
.
```
### Column Mapping / Names
Your CSV dataset must have two columns: `text` and `target`.
If your column names are different than `text` and `target`, you can map the dataset column to AutoTrain column names.
## Training
### Local Training
To train a text classification/regression model locally, you can use the `autotrain --config config.yaml` command.
Here is an example of a `config.yaml` file for training a text classification model:
```yaml
task: text_classification # or text_regression
base_model: google-bert/bert-base-uncased
project_name: autotrain-bert-imdb-finetuned
log: tensorboard
backend: local
data:
path: stanfordnlp/imdb
train_split: train
valid_split: test
column_mapping:
text_column: text
target_column: label
params:
max_seq_length: 512
epochs: 3
batch_size: 4
lr: 2e-5
optimizer: adamw_torch
scheduler: linear
gradient_accumulation: 1
mixed_precision: fp16
hub:
username: ${HF_USERNAME}
token: ${HF_TOKEN}
push_to_hub: true
```
In this example, we are training a text classification model using the `google-bert/bert-base-uncased` model on the IMDB dataset.
We are using the `stanfordnlp/imdb` dataset, which is already available on Hugging Face Hub.
We are training the model for 3 epochs with a batch size of 4 and a learning rate of `2e-5`.
We are using the `adamw_torch` optimizer and the `linear` scheduler.
We are also using mixed precision training with a gradient accumulation of 1.
If you want to use a local CSV/JSONL dataset, you can change the `data` section to:
```yaml
data:
path: data/ # this must be the path to the directory containing the train and valid files
train_split: train # this must be either train.csv or train.json
valid_split: valid # this must be either valid.csv or valid.json
column_mapping:
text_column: text # this must be the name of the column containing the text
target_column: label # this must be the name of the column containing the target
```
To train the model, run the following command:
```bash
$ autotrain --config config.yaml
```
You can find example config files for text classification and regression in the [here](https://github.com/huggingface/autotrain-advanced/tree/main/configs/text_classification) and [here](https://github.com/huggingface/autotrain-advanced/tree/main/configs/text_regression) respectively.
### Training on Hugging Face Spaces
The parameters for training on Hugging Face Spaces are the same as for local training.
If you are using your own dataset, select "Local" as dataset source and upload your dataset.
In the following screenshot, we are training a text classification model using the `google-bert/bert-base-uncased` model on the IMDB dataset.
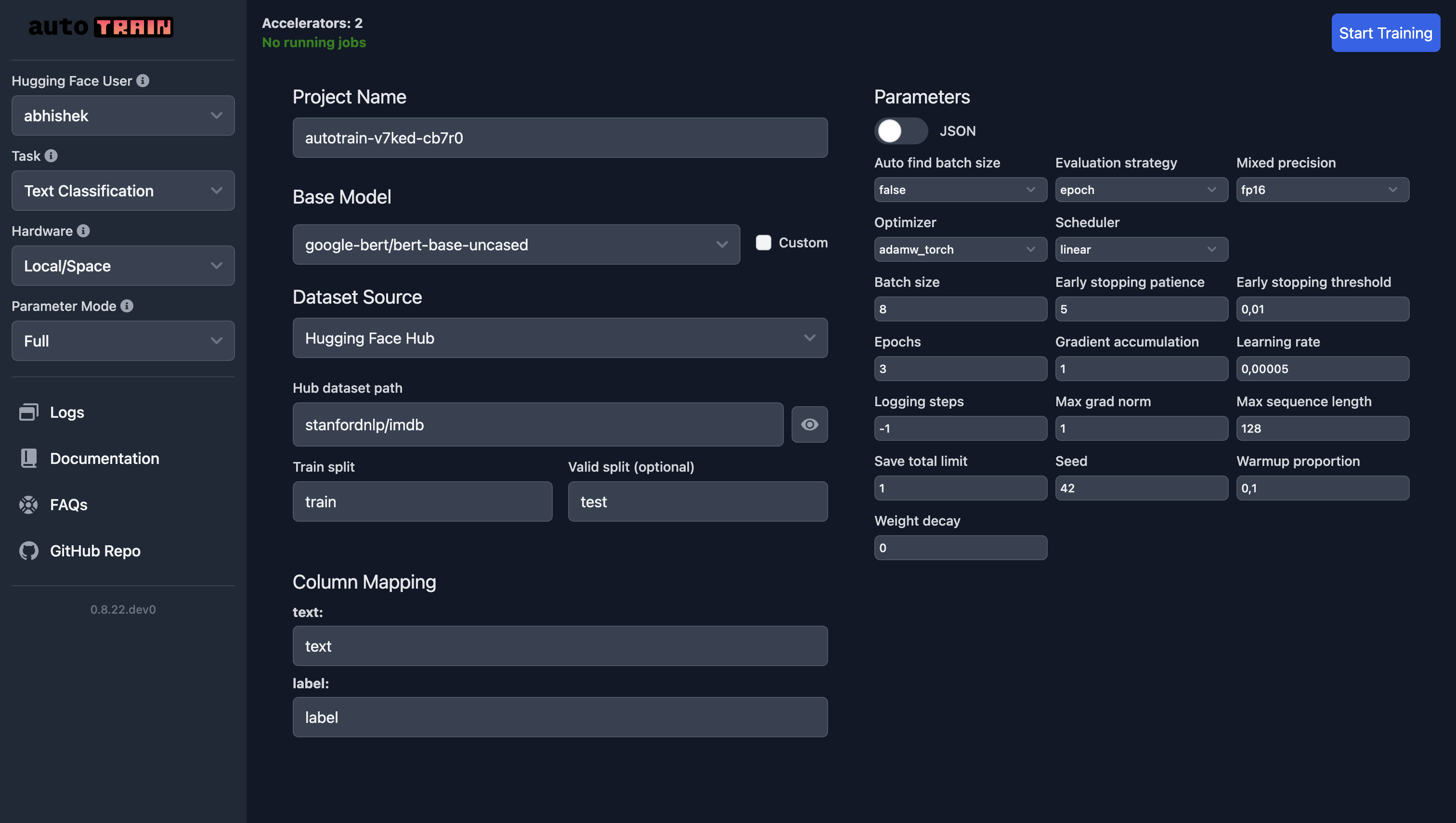
For text regression, all you need to do is select "Text Regression" as the task and everything else remains the same (except the data, of course).
## Training Parameters
Training parameters for text classification and regression are the same.
[[autodoc]] trainers.text_classification.params.TextClassificationParams
|