|
--- |
|
tags: |
|
- image-classification |
|
- timm |
|
- resnet |
|
license: apache-2.0 |
|
datasets: |
|
- imagenet |
|
widget: |
|
- src: https://huggingface.co/datasets/mishig/sample_images/resolve/main/tiger.jpg |
|
example_title: Tiger |
|
- src: https://huggingface.co/datasets/mishig/sample_images/resolve/main/teapot.jpg |
|
example_title: Teapot |
|
- src: https://huggingface.co/datasets/mishig/sample_images/resolve/main/palace.jpg |
|
example_title: Palace |
|
--- |
|
|
|
# ResNet-50d |
|
|
|
Pretrained model on [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org/). The ResNet architecture was introduced in |
|
[this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) and is adapted with the ResNet-D trick from |
|
[this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.01187) |
|
|
|
|
|
## Model description |
|
|
|
ResNet are deep convolutional neural networks using residual connections. Each layer is composed of two convolutions |
|
with a ReLU in the middle, but the output is the sum of the input with the output of the convolutional blocks. |
|
|
|
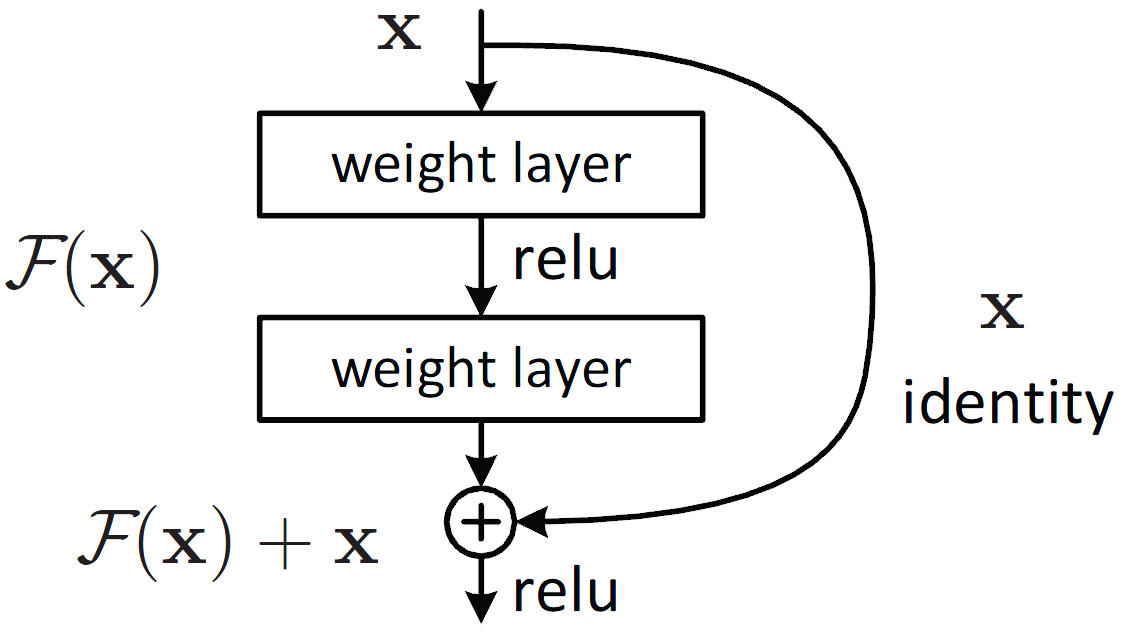 |
|
|
|
This way, there is a direct connection from the original inputs to even the deepest layers in the network. |
|
|
|
## Intended uses & limitations |
|
|
|
You can use the raw model to classify images along the 1,000 ImageNet labels, but you can also change its head |
|
to fine-tune it on a downstream task (another classification task with different labels, image segmentation or |
|
object detection, to name a few). |
|
|
|
### How to use |
|
|
|
You can use this model with the usual factory method in `timm`: |
|
|
|
```python |
|
import PIL |
|
import timm |
|
import torch |
|
|
|
model = timm.create_model("sgugger/resnet50d") |
|
img = PIL.Image.open(path_to_an_image) |
|
img = img.convert("RGB") |
|
|
|
config = model.default_cfg |
|
|
|
if isinstance(config["input_size"], tuple): |
|
img_size = config["input_size"][-2:] |
|
else: |
|
img_size = config["input_size"] |
|
|
|
transform = timm.data.transforms_factory.transforms_imagenet_eval( |
|
img_size=img_size, |
|
interpolation=config["interpolation"], |
|
mean=config["mean"], |
|
std=config["std"], |
|
) |
|
|
|
input_tensor = transform(cat_img) |
|
input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) |
|
# ^ batch size = 1 |
|
with torch.no_grad(): |
|
output = model(input_tensor) |
|
|
|
probs = output.squeeze(0).softmax(dim=0) |
|
``` |
|
|
|
### Limitations and bias |
|
|
|
The training images in the dataset are usually photos clearly representing one of the 1,000 labels. The model will |
|
probably not generalize well on drawings or images containing multiple objects with different labels. |
|
|
|
The training images in the dataset come mostly from the US (45.4%) and Great Britain (7.6%). As such the model or |
|
models created by fine-tuning this model will work better on images picturing scenes from these countries (see |
|
[this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.02659) for examples). |
|
|
|
More generally, [recent research](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.15052) has shown that even models trained in an |
|
unsupervised fashion on ImageNet (i.e. without using the labels) will pick up racial and gender bias represented in |
|
the training images. |
|
|
|
## Training data |
|
|
|
This model was pretrained on [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org/), a dataset consisting of 14 millions of |
|
hand-annotated images with 1,000 categories. |
|
|
|
## Training procedure |
|
|
|
To be completed |
|
|
|
### Preprocessing |
|
|
|
The images are resized using bicubic interpolation to 224x224 and normalized with the usual ImageNet statistics. |
|
|
|
## Evaluation results |
|
|
|
This model has a top1-accuracy of 80.53% and a top-5 accuracy of 95.16% in the evaluation set of ImageNet |
|
|
|
|
|
### BibTeX entry and citation info |
|
|
|
```bibtex |
|
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/HeZRS15, |
|
author = {Kaiming He and |
|
Xiangyu Zhang and |
|
Shaoqing Ren and |
|
Jian Sun}, |
|
title = {Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition}, |
|
journal = {CoRR}, |
|
volume = {abs/1512.03385}, |
|
year = {2015}, |
|
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385}, |
|
archivePrefix = {arXiv}, |
|
eprint = {1512.03385}, |
|
timestamp = {Wed, 17 Apr 2019 17:23:45 +0200}, |
|
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/HeZRS15.bib}, |
|
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org} |
|
} |
|
``` |
|
|