Offline vs. Online Reinforcement Learning
Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a framework to build decision-making agents. These agents aim to learn optimal behavior (policy) by interacting with the environment through trial and error and receiving rewards as unique feedback.
The agent’s goal is to maximize its cumulative reward, called return. Because RL is based on the reward hypothesis: all goals can be described as the maximization of the expected cumulative reward.
Deep Reinforcement Learning agents learn with batches of experience. The question is, how do they collect it?:
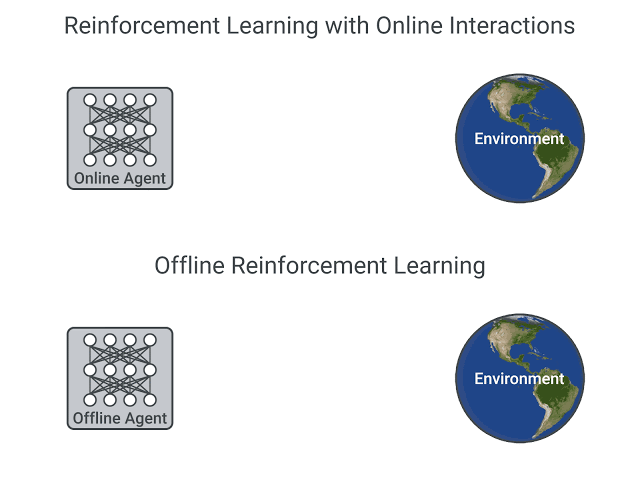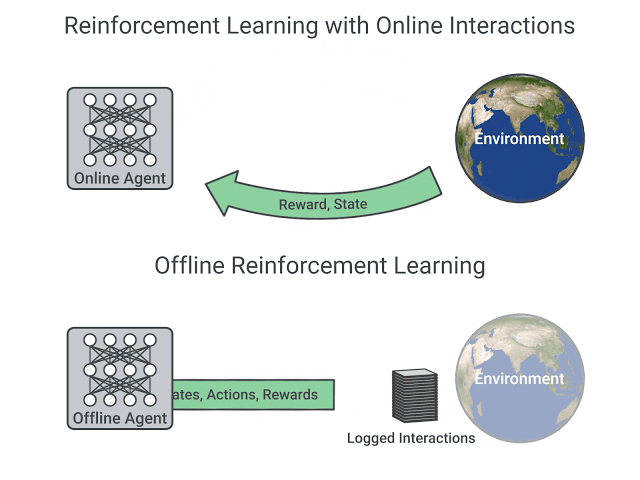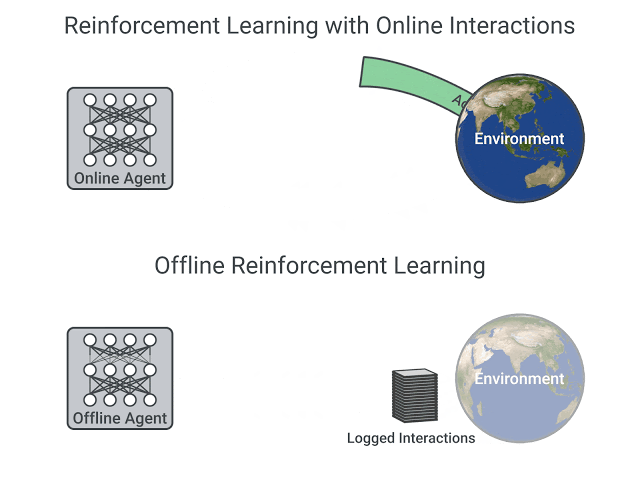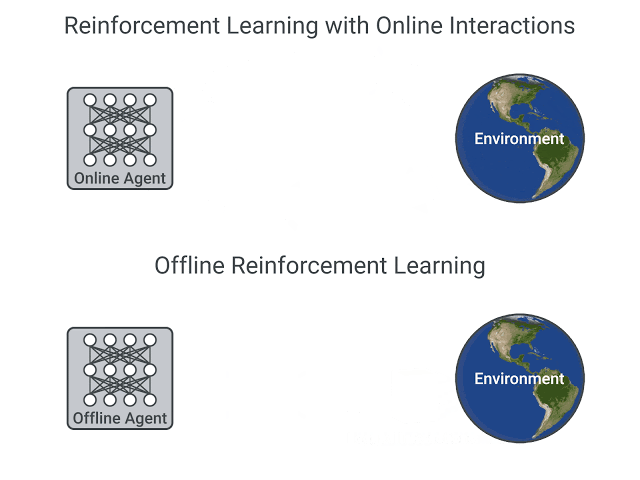
- In online reinforcement learning, which is what we’ve learned during this course, the agent gathers data directly: it collects a batch of experience by interacting with the environment. Then, it uses this experience immediately (or via some replay buffer) to learn from it (update its policy).
But this implies that either you train your agent directly in the real world or have a simulator. If you don’t have one, you need to build it, which can be very complex (how to reflect the complex reality of the real world in an environment?), expensive, and insecure (if the simulator has flaws that may provide a competitive advantage, the agent will exploit them).
- On the other hand, in offline reinforcement learning, the agent only uses data collected from other agents or human demonstrations. It does not interact with the environment.
The process is as follows:
- Create a dataset using one or more policies and/or human interactions.
- Run offline RL on this dataset to learn a policy
This method has one drawback: the counterfactual queries problem. What do we do if our agent decides to do something for which we don’t have the data? For instance, turning right on an intersection but we don’t have this trajectory.
There exist some solutions on this topic, but if you want to know more about offline reinforcement learning, you can watch this video
Further reading
For more information, we recommend you check out the following resources:
- Offline Reinforcement Learning, Talk by Sergei Levine
- Offline Reinforcement Learning: Tutorial, Review, and Perspectives on Open Problems
Author
This section was written by Thomas Simonini
< > Update on GitHub