Swin Transformer
개요
Swin Transformer는 Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo가 제안한 논문 Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows에서 소개되었습니다.
논문의 초록은 다음과 같습니다:
이 논문은 Swin Transformer라는 새로운 비전 트랜스포머를 소개합니다. 이 모델은 컴퓨터 비전에서 범용 백본(backbone)으로 사용될 수 있습니다. 트랜스포머를 언어에서 비전으로 적용할 때의 어려움은 두 분야 간의 차이에서 비롯되는데, 예를 들어 시각적 객체의 크기가 크게 변동하며, 이미지의 픽셀 해상도가 텍스트의 단어에 비해 매우 높다는 점이 있습니다. 이러한 차이를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 ‘Shifted Windows’를 이용해 표현을 계산하는 계층적 트랜스포머를 제안합니다. Shifted Windows 방식은 겹치지 않는 로컬 윈도우에서 self-attention 계산을 제한하여 효율성을 높이는 동시에 윈도우 간 연결을 가능하게 합니다. 이 계층적 구조는 다양한 크기의 패턴을 모델링할 수 있는 유연성을 제공하며, 이미지 크기에 비례한 선형 계산 복잡성을 가지고 있습니다. Swin Transformer의 이러한 특징들은 이미지 분류(Imagenet-1K에서 87.3의 top-1 정확도) 및 객체 검출(COCO test-dev에서 58.7의 박스 AP, 51.1의 마스크 AP)과 같은 밀집 예측 작업, 의미적 분할(ADE20K val에서 53.5의 mIoU)과 같은 광범위한 비전 작업에 적합합니다. 이 모델은 COCO에서 이전 최고 성능을 박스 AP에서 +2.7, 마스크 AP에서 +2.6, ADE20K에서 mIoU에서 +3.2를 초과하는 성과를 보여주며, 트랜스포머 기반 모델이 비전 백본으로서의 잠재력을 입증했습니다. 계층적 설계와 Shifted Windows 방식은 순수 MLP 아키텍처에도 유리하게 작용합니다.
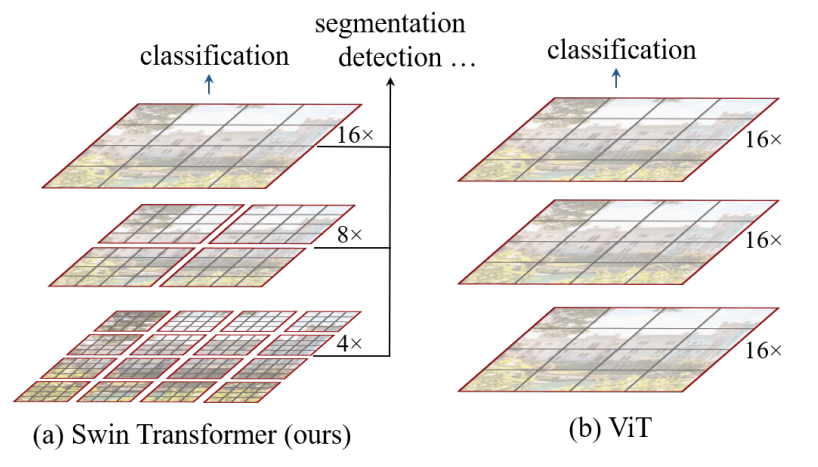 Swin Transformer 아키텍처. 원본 논문에서 발췌.
Swin Transformer 아키텍처. 원본 논문에서 발췌. 이 모델은 novice03이 기여하였습니다. Tensorflow 버전은 amyeroberts가 기여했습니다. 원본 코드는 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
사용 팁
- Swin은 입력의 높이와 너비가
32로 나누어질 수 있으면 어떤 크기든 지원할 수 있도록 패딩을 추가합니다. - Swin은 백본으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
output_hidden_states = True로 설정하면,hidden_states와reshaped_hidden_states를 모두 출력합니다.reshaped_hidden_states는(batch, num_channels, height, width)형식을 가지며, 이는(batch_size, sequence_length, num_channels)형식과 다릅니다.
리소스
Swin Transformer의 사용을 도울 수 있는 Hugging Face 및 커뮤니티(🌎로 표시)의 공식 자료 목록입니다.
- SwinForImageClassification은 이 예제 스크립트와 노트북을 통해 지원됩니다.
- 관련 자료: 이미지 분류 작업 가이드
또한:
- SwinForMaskedImageModeling은 이 예제 스크립트를 통해 지원됩니다.
새로운 자료를 추가하고 싶으시다면, 언제든지 Pull Request를 열어주세요! 저희가 검토해 드릴게요. 이때, 추가하는 자료는 기존 자료와 중복되지 않고 새로운 내용을 보여주는 자료여야 합니다.
SwinConfig
class transformers.SwinConfig
< source >( image_size = 224 patch_size = 4 num_channels = 3 embed_dim = 96 depths = [2, 2, 6, 2] num_heads = [3, 6, 12, 24] window_size = 7 mlp_ratio = 4.0 qkv_bias = True hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 drop_path_rate = 0.1 hidden_act = 'gelu' use_absolute_embeddings = False initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 encoder_stride = 32 out_features = None out_indices = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — The size (resolution) of each image. - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — The size (resolution) of each patch. - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels. - embed_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 96) — Dimensionality of patch embedding. - depths (
list(int), optional, defaults to[2, 2, 6, 2]) — Depth of each layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_heads (
list(int), optional, defaults to[3, 6, 12, 24]) — Number of attention heads in each layer of the Transformer encoder. - window_size (
int, optional, defaults to 7) — Size of windows. - mlp_ratio (
float, optional, defaults to 4.0) — Ratio of MLP hidden dimensionality to embedding dimensionality. - qkv_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not a learnable bias should be added to the queries, keys and values. - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings and encoder. - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - drop_path_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Stochastic depth rate. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported. - use_absolute_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to add absolute position embeddings to the patch embeddings. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - encoder_stride (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — Factor to increase the spatial resolution by in the decoder head for masked image modeling. - out_features (
List[str], optional) — If used as backbone, list of features to output. Can be any of"stem","stage1","stage2", etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_indicesis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_indicesis unset, will default to the last stage. Must be in the same order as defined in thestage_namesattribute. - out_indices (
List[int], optional) — If used as backbone, list of indices of features to output. Can be any of 0, 1, 2, etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_featuresis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_featuresis unset, will default to the last stage. Must be in the same order as defined in thestage_namesattribute.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a SwinModel. It is used to instantiate a Swin model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the Swin microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import SwinConfig, SwinModel
>>> # Initializing a Swin microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224 style configuration
>>> configuration = SwinConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224 style configuration
>>> model = SwinModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configSwinModel
class transformers.SwinModel
< source >( config add_pooling_layer = True use_mask_token = False )
Parameters
- config (SwinConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
- add_pooling_layer (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not to apply pooling layer. - use_mask_token (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to create and apply mask tokens in the embedding layer.
The bare Swin Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module sub-class. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None bool_masked_pos: typing.Optional[torch.BoolTensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches), optional) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Returns
transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinModelOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (SwinConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size), optional, returned whenadd_pooling_layer=Trueis passed) — Average pooling of the last layer hidden-state. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
reshaped_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs reshaped to include the spatial dimensions.
The SwinModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SwinModel
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> model = SwinModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 49, 768]SwinForMaskedImageModeling
class transformers.SwinForMaskedImageModeling
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (SwinConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Swin Model with a decoder on top for masked image modeling, as proposed in SimMIM.
Note that we provide a script to pre-train this model on custom data in our examples directory.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module sub-class. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None bool_masked_pos: typing.Optional[torch.BoolTensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinMaskedImageModelingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches)) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Returns
transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinMaskedImageModelingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinMaskedImageModelingOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (SwinConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenbool_masked_posis provided) — Masked image modeling (MLM) loss. -
reconstruction (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Reconstructed pixel values. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
reshaped_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs reshaped to include the spatial dimensions.
The SwinForMaskedImageModeling forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SwinForMaskedImageModeling
>>> import torch
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-base-simmim-window6-192")
>>> model = SwinForMaskedImageModeling.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-base-simmim-window6-192")
>>> num_patches = (model.config.image_size // model.config.patch_size) ** 2
>>> pixel_values = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> # create random boolean mask of shape (batch_size, num_patches)
>>> bool_masked_pos = torch.randint(low=0, high=2, size=(1, num_patches)).bool()
>>> outputs = model(pixel_values, bool_masked_pos=bool_masked_pos)
>>> loss, reconstructed_pixel_values = outputs.loss, outputs.reconstruction
>>> list(reconstructed_pixel_values.shape)
[1, 3, 192, 192]SwinForImageClassification
class transformers.SwinForImageClassification
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (SwinConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Swin Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the [CLS] token) e.g. for ImageNet.
Note that it’s possible to fine-tune Swin on higher resolution images than the ones it has been trained on, by
setting interpolate_pos_encoding to True in the forward of the model. This will interpolate the pre-trained
position embeddings to the higher resolution.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module sub-class. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.swin.modeling_swin.SwinImageClassifierOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (SwinConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
reshaped_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs reshaped to include the spatial dimensions.
The SwinForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SwinForImageClassification
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> model = SwinForImageClassification.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
tabby, tabby catTFSwinModel
class transformers.TFSwinModel
< source >( config: SwinConfig add_pooling_layer: bool = True use_mask_token: bool = False **kwargs )
Parameters
- config (SwinConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Swin Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top. This model is a Tensorflow keras.layers.Layer sub-class. Use it as a regular Tensorflow Module and refer to the Tensorflow documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
call
< source >( pixel_values: tf.Tensor | None = None bool_masked_pos: tf.Tensor | None = None head_mask: tf.Tensor | None = None output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None return_dict: Optional[bool] = None training: bool = False ) → transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinModelOutput or tuple(tf.Tensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
tf.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - bool_masked_pos (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches), optional) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Returns
transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinModelOutput or tuple(tf.Tensor)
A transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinModelOutput or a tuple of tf.Tensor (if
return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the
configuration (SwinConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size), optional, returned whenadd_pooling_layer=Trueis passed) — Average pooling of the last layer hidden-state. -
hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
reshaped_hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs reshaped to include the spatial dimensions.
The TFSwinModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, TFSwinModel
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> model = TFSwinModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="tf")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 49, 768]TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling
class transformers.TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling
< source >( config: SwinConfig )
Parameters
- config (SwinConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Swin Model with a decoder on top for masked image modeling, as proposed in SimMIM. This model is a Tensorflow keras.layers.Layer sub-class. Use it as a regular Tensorflow Module and refer to the Tensorflow documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
call
< source >( pixel_values: tf.Tensor | None = None bool_masked_pos: tf.Tensor | None = None head_mask: tf.Tensor | None = None output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None return_dict: Optional[bool] = None training: bool = False ) → transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinMaskedImageModelingOutput or tuple(tf.Tensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
tf.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - bool_masked_pos (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches)) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Returns
transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinMaskedImageModelingOutput or tuple(tf.Tensor)
A transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinMaskedImageModelingOutput or a tuple of tf.Tensor (if
return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the
configuration (SwinConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
tf.Tensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenbool_masked_posis provided) — Masked image modeling (MLM) loss. -
reconstruction (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Reconstructed pixel values. -
hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
reshaped_hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs reshaped to include the spatial dimensions.
The TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> model = TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> num_patches = (model.config.image_size // model.config.patch_size) ** 2
>>> pixel_values = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="tf").pixel_values
>>> # create random boolean mask of shape (batch_size, num_patches)
>>> bool_masked_pos = tf.random.uniform((1, num_patches)) >= 0.5
>>> outputs = model(pixel_values, bool_masked_pos=bool_masked_pos)
>>> loss, reconstructed_pixel_values = outputs.loss, outputs.reconstruction
>>> list(reconstructed_pixel_values.shape)
[1, 3, 224, 224]TFSwinForImageClassification
class transformers.TFSwinForImageClassification
< source >( config: SwinConfig )
Parameters
- config (SwinConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Swin Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the [CLS] token) e.g. for ImageNet.
This model is a Tensorflow keras.layers.Layer sub-class. Use it as a regular Tensorflow Module and refer to the Tensorflow documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
call
< source >( pixel_values: tf.Tensor | None = None head_mask: tf.Tensor | None = None labels: tf.Tensor | None = None output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None return_dict: Optional[bool] = None training: bool = False ) → transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinImageClassifierOutput or tuple(tf.Tensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
tf.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinImageClassifierOutput or tuple(tf.Tensor)
A transformers.models.swin.modeling_tf_swin.TFSwinImageClassifierOutput or a tuple of tf.Tensor (if
return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the
configuration (SwinConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
tf.Tensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. -
logits (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
reshaped_hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs reshaped to include the spatial dimensions.
The TFSwinForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, TFSwinForImageClassification
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> model = TFSwinForImageClassification.from_pretrained("microsoft/swin-tiny-patch4-window7-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="tf")
>>> logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = int(tf.math.argmax(logits, axis=-1))
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
tabby, tabby cat