text
stringlengths 29
317k
| id
stringlengths 22
166
| metadata
dict | __index_level_0__
int64 0
231
|
|---|---|---|---|
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import subprocess
from typing import Union
import numpy as np
import requests
from ..utils import add_end_docstrings, is_torch_available, is_torchaudio_available, logging
from .base import Pipeline, build_pipeline_init_args
if is_torch_available():
from ..models.auto.modeling_auto import MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING_NAMES
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
def ffmpeg_read(bpayload: bytes, sampling_rate: int) -> np.array:
"""
Helper function to read an audio file through ffmpeg.
"""
ar = f"{sampling_rate}"
ac = "1"
format_for_conversion = "f32le"
ffmpeg_command = [
"ffmpeg",
"-i",
"pipe:0",
"-ac",
ac,
"-ar",
ar,
"-f",
format_for_conversion,
"-hide_banner",
"-loglevel",
"quiet",
"pipe:1",
]
try:
ffmpeg_process = subprocess.Popen(ffmpeg_command, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
except FileNotFoundError:
raise ValueError("ffmpeg was not found but is required to load audio files from filename")
output_stream = ffmpeg_process.communicate(bpayload)
out_bytes = output_stream[0]
audio = np.frombuffer(out_bytes, np.float32)
if audio.shape[0] == 0:
raise ValueError("Malformed soundfile")
return audio
@add_end_docstrings(build_pipeline_init_args(has_feature_extractor=True))
class AudioClassificationPipeline(Pipeline):
"""
Audio classification pipeline using any `AutoModelForAudioClassification`. This pipeline predicts the class of a
raw waveform or an audio file. In case of an audio file, ffmpeg should be installed to support multiple audio
formats.
Example:
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> classifier = pipeline(model="superb/wav2vec2-base-superb-ks")
>>> classifier("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/1.flac")
[{'score': 0.997, 'label': '_unknown_'}, {'score': 0.002, 'label': 'left'}, {'score': 0.0, 'label': 'yes'}, {'score': 0.0, 'label': 'down'}, {'score': 0.0, 'label': 'stop'}]
```
Learn more about the basics of using a pipeline in the [pipeline tutorial](../pipeline_tutorial)
This pipeline can currently be loaded from [`pipeline`] using the following task identifier:
`"audio-classification"`.
See the list of available models on
[huggingface.co/models](https://huggingface.co/models?filter=audio-classification).
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
# Default, might be overriden by the model.config.
kwargs["top_k"] = kwargs.get("top_k", 5)
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
if self.framework != "pt":
raise ValueError(f"The {self.__class__} is only available in PyTorch.")
self.check_model_type(MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING_NAMES)
def __call__(
self,
inputs: Union[np.ndarray, bytes, str],
**kwargs,
):
"""
Classify the sequence(s) given as inputs. See the [`AutomaticSpeechRecognitionPipeline`] documentation for more
information.
Args:
inputs (`np.ndarray` or `bytes` or `str` or `dict`):
The inputs is either :
- `str` that is the filename of the audio file, the file will be read at the correct sampling rate
to get the waveform using *ffmpeg*. This requires *ffmpeg* to be installed on the system.
- `bytes` it is supposed to be the content of an audio file and is interpreted by *ffmpeg* in the
same way.
- (`np.ndarray` of shape (n, ) of type `np.float32` or `np.float64`)
Raw audio at the correct sampling rate (no further check will be done)
- `dict` form can be used to pass raw audio sampled at arbitrary `sampling_rate` and let this
pipeline do the resampling. The dict must be either be in the format `{"sampling_rate": int,
"raw": np.array}`, or `{"sampling_rate": int, "array": np.array}`, where the key `"raw"` or
`"array"` is used to denote the raw audio waveform.
top_k (`int`, *optional*, defaults to None):
The number of top labels that will be returned by the pipeline. If the provided number is `None` or
higher than the number of labels available in the model configuration, it will default to the number of
labels.
function_to_apply(`str`, *optional*, defaults to "softmax"):
The function to apply to the model output. By default, the pipeline will apply the softmax function to
the output of the model. Valid options: ["softmax", "sigmoid", "none"]. Note that passing Python's
built-in `None` will default to "softmax", so you need to pass the string "none" to disable any
post-processing.
Return:
A list of `dict` with the following keys:
- **label** (`str`) -- The label predicted.
- **score** (`float`) -- The corresponding probability.
"""
return super().__call__(inputs, **kwargs)
def _sanitize_parameters(self, top_k=None, function_to_apply=None, **kwargs):
# No parameters on this pipeline right now
postprocess_params = {}
if top_k is not None:
if top_k > self.model.config.num_labels:
top_k = self.model.config.num_labels
postprocess_params["top_k"] = top_k
if function_to_apply is not None:
if function_to_apply not in ["softmax", "sigmoid", "none"]:
raise ValueError(
f"Invalid value for `function_to_apply`: {function_to_apply}. "
"Valid options are ['softmax', 'sigmoid', 'none']"
)
postprocess_params["function_to_apply"] = function_to_apply
else:
postprocess_params["function_to_apply"] = "softmax"
return {}, {}, postprocess_params
def preprocess(self, inputs):
if isinstance(inputs, str):
if inputs.startswith("http://") or inputs.startswith("https://"):
# We need to actually check for a real protocol, otherwise it's impossible to use a local file
# like http_huggingface_co.png
inputs = requests.get(inputs).content
else:
with open(inputs, "rb") as f:
inputs = f.read()
if isinstance(inputs, bytes):
inputs = ffmpeg_read(inputs, self.feature_extractor.sampling_rate)
if isinstance(inputs, dict):
inputs = inputs.copy() # So we don't mutate the original dictionary outside the pipeline
# Accepting `"array"` which is the key defined in `datasets` for
# better integration
if not ("sampling_rate" in inputs and ("raw" in inputs or "array" in inputs)):
raise ValueError(
"When passing a dictionary to AudioClassificationPipeline, the dict needs to contain a "
'"raw" key containing the numpy array representing the audio and a "sampling_rate" key, '
"containing the sampling_rate associated with that array"
)
_inputs = inputs.pop("raw", None)
if _inputs is None:
# Remove path which will not be used from `datasets`.
inputs.pop("path", None)
_inputs = inputs.pop("array", None)
in_sampling_rate = inputs.pop("sampling_rate")
inputs = _inputs
if in_sampling_rate != self.feature_extractor.sampling_rate:
import torch
if is_torchaudio_available():
from torchaudio import functional as F
else:
raise ImportError(
"torchaudio is required to resample audio samples in AudioClassificationPipeline. "
"The torchaudio package can be installed through: `pip install torchaudio`."
)
inputs = F.resample(
torch.from_numpy(inputs), in_sampling_rate, self.feature_extractor.sampling_rate
).numpy()
if not isinstance(inputs, np.ndarray):
raise TypeError("We expect a numpy ndarray as input")
if len(inputs.shape) != 1:
raise ValueError("We expect a single channel audio input for AudioClassificationPipeline")
processed = self.feature_extractor(
inputs, sampling_rate=self.feature_extractor.sampling_rate, return_tensors="pt"
)
if self.torch_dtype is not None:
processed = processed.to(dtype=self.torch_dtype)
return processed
def _forward(self, model_inputs):
model_outputs = self.model(**model_inputs)
return model_outputs
def postprocess(self, model_outputs, top_k=5, function_to_apply="softmax"):
if function_to_apply == "softmax":
probs = model_outputs.logits[0].softmax(-1)
elif function_to_apply == "sigmoid":
probs = model_outputs.logits[0].sigmoid()
else:
probs = model_outputs.logits[0]
scores, ids = probs.topk(top_k)
scores = scores.tolist()
ids = ids.tolist()
labels = [{"score": score, "label": self.model.config.id2label[_id]} for score, _id in zip(scores, ids)]
return labels
|
transformers/src/transformers/pipelines/audio_classification.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/src/transformers/pipelines/audio_classification.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4335
}
| 184 |
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, IterableDataset
from ..utils.generic import ModelOutput
class PipelineDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, dataset, process, params):
self.dataset = dataset
self.process = process
self.params = params
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset)
def __getitem__(self, i):
item = self.dataset[i]
processed = self.process(item, **self.params)
return processed
class PipelineIterator(IterableDataset):
def __init__(self, loader, infer, params, loader_batch_size=None):
"""
Roughly equivalent to
```
for item in loader:
yield infer(item, **params)
```
Arguments:
loader (`torch.utils.data.DataLoader` or `Iterable`):
The iterator that will be used to apply `infer` on.
infer (any function):
The function to apply of each element of `loader`.
params (`dict`):
The parameters passed to `infer` along with every item
loader_batch_size (`int`, *optional*):
If specified, the items of `loader` are supposed to come as batch, and are loader_batched here
making it roughly behave as
```
for items in loader:
for i in loader_batch_size:
item = items[i]
yield infer(item, **params)
```"""
self.loader = loader
self.infer = infer
self.params = params
if loader_batch_size == 1:
# Let's spare some time by deactivating altogether
loader_batch_size = None
self.loader_batch_size = loader_batch_size
# Internal bookkeeping
self._loader_batch_index = None
self._loader_batch_data = None
def __len__(self):
return len(self.loader)
def __iter__(self):
self.iterator = iter(self.loader)
return self
def loader_batch_item(self):
"""
Return item located at `loader_batch_index` within the current `loader_batch_data`.
"""
if isinstance(self._loader_batch_data, torch.Tensor):
# Batch data is simple tensor, just fetch the slice
result = self._loader_batch_data[self._loader_batch_index].unsqueeze(0)
else:
# Batch data is assumed to be BaseModelOutput (or dict)
loader_batched = {}
for k, element in self._loader_batch_data.items():
if isinstance(element, ModelOutput):
# Convert ModelOutput to tuple first
element = element.to_tuple()
if isinstance(element[0], torch.Tensor):
loader_batched[k] = tuple(el[self._loader_batch_index].unsqueeze(0) for el in element)
elif isinstance(element[0], np.ndarray):
loader_batched[k] = tuple(np.expand_dims(el[self._loader_batch_index], 0) for el in element)
continue
if k in {"hidden_states", "past_key_values", "attentions"} and isinstance(element, tuple):
# Those are stored as lists of tensors so need specific unbatching.
if isinstance(element[0], torch.Tensor):
loader_batched[k] = tuple(el[self._loader_batch_index].unsqueeze(0) for el in element)
elif isinstance(element[0], np.ndarray):
loader_batched[k] = tuple(np.expand_dims(el[self._loader_batch_index], 0) for el in element)
continue
if element is None:
# This can happen for optional data that get passed around
loader_batched[k] = None
elif isinstance(element[self._loader_batch_index], torch.Tensor):
# Take correct batch data, but make it looked like batch_size=1
# For compatibility with other methods within transformers
loader_batched[k] = element[self._loader_batch_index].unsqueeze(0)
elif isinstance(element[self._loader_batch_index], np.ndarray):
# Take correct batch data, but make it looked like batch_size=1
# For compatibility with other methods within transformers
loader_batched[k] = np.expand_dims(element[self._loader_batch_index], 0)
else:
# This is typically a list, so no need to `unsqueeze`.
loader_batched[k] = element[self._loader_batch_index]
# Recreate the element by reusing the original class to make it look
# batch_size=1
result = self._loader_batch_data.__class__(loader_batched)
self._loader_batch_index += 1
return result
def __next__(self):
if self._loader_batch_index is not None and self._loader_batch_index < self.loader_batch_size:
# We are currently unrolling a batch so we just need to return
# the current item within a batch
return self.loader_batch_item()
# We're out of items within a batch
item = next(self.iterator)
processed = self.infer(item, **self.params)
# We now have a batch of "inferred things".
if self.loader_batch_size is not None:
# Try to infer the size of the batch
if isinstance(processed, torch.Tensor):
first_tensor = processed
elif isinstance(processed, tuple):
first_tensor = processed[0]
else:
key = list(processed.keys())[0]
first_tensor = processed[key]
if isinstance(first_tensor, list):
observed_batch_size = len(first_tensor)
else:
observed_batch_size = first_tensor.shape[0]
if 0 < observed_batch_size < self.loader_batch_size:
# could be last batch so we can't unroll as many
# elements.
self.loader_batch_size = observed_batch_size
# Setting internal index to unwrap the batch
self._loader_batch_data = processed[0] if isinstance(processed, tuple) else processed
self._loader_batch_index = 0
return self.loader_batch_item()
else:
# We're not unrolling batches
return processed
class PipelineChunkIterator(PipelineIterator):
def __init__(self, loader, infer, params, loader_batch_size=None):
"""
Roughly equivalent to
```
for iterator in loader:
for item in iterator:
yield infer(item, **params)
```
Arguments:
loader (`torch.utils.data.DataLoader` or `Iterable`):
The iterator that will be used to apply `infer` on.
infer (any function):
The function to apply of each element of `loader`.
params (`dict`):
The parameters passed to `infer` along with every item
"""
super().__init__(loader, infer, params)
def __iter__(self):
self.iterator = iter(self.loader)
self.subiterator = None
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.subiterator is None:
"Subiterator None means we haven't started a `preprocess` iterator. so start it"
self.subiterator = self.infer(next(self.iterator), **self.params)
try:
# Try to return next item
processed = next(self.subiterator)
except StopIteration:
# When a preprocess iterator ends, we can start lookig at the next item
# ChunkIterator will keep feeding until ALL elements of iterator
# all have created their subiterator and have been iterating against.
#
# Another way to look at it, is we're basically flattening lists of lists
# into a single list, but with generators
self.subiterator = self.infer(next(self.iterator), **self.params)
processed = next(self.subiterator)
return processed
class PipelinePackIterator(PipelineIterator):
"""
Roughly equivalent to
```
packed = []
for item in loader:
packed.append(item)
if item["is_last"]:
yield packed
packed = []
```
but it also handles cases where `item` are batched (meaning it's a dict of Tensor with first dimension > 1. In
that case it does
```
packed = []
for batch in loader:
# item is batched
for item in batch:
packed.append(item)
if item["is_last"]:
yield packed
packed = []
```
Arguments:
loader (`torch.utils.data.DataLoader` or `Iterable`):
The iterator that will be used to apply `infer` on.
infer (any function):
The function to apply of each element of `loader`.
params (`dict`):
The parameters passed to `infer` along with every item
loader_batch_size (`int`, *optional*):
If specified, the items of `loader` are supposed to come as batch, and are loader_batched here making
it roughly behave as
```
for items in loader:
for i in loader_batch_size:
item = items[i]
yield infer(item, **params)
```"""
def __iter__(self):
self.iterator = iter(self.loader)
return self
def __next__(self):
# Extremely similar to PipelineIterator in its unpacking mechanism
# BUT, we have an extra required item which is the presence of `is_last`
# That is because everything is flattened by `PipelineChunkIterator` we
# need to keep track of how to regroup here in the original `process`
# boundaries so that `process` and `postprocess` see the same data.
# This iterator accumulates items (possibly while unbatching) until it
# its a `is_last` and then just passes it on to the caller.
is_last = False
accumulator = []
if self._loader_batch_index is not None and self._loader_batch_index < self.loader_batch_size:
while self._loader_batch_index < self.loader_batch_size:
item = self.loader_batch_item()
is_last = item.pop("is_last")
accumulator.append(item)
if is_last:
return accumulator
while not is_last:
processed = self.infer(next(self.iterator), **self.params)
if self.loader_batch_size is not None:
if isinstance(processed, torch.Tensor):
first_tensor = processed
else:
key = list(processed.keys())[0]
first_tensor = processed[key]
if isinstance(first_tensor, list):
observed_batch_size = len(first_tensor)
else:
observed_batch_size = first_tensor.shape[0]
if 0 < observed_batch_size < self.loader_batch_size:
# could be last batch so we can't unroll as many
# elements.
self.loader_batch_size = observed_batch_size
self._loader_batch_data = processed
self._loader_batch_index = 0
while self._loader_batch_index < self.loader_batch_size:
item = self.loader_batch_item()
is_last = item.pop("is_last")
accumulator.append(item)
if is_last:
return accumulator
else:
item = processed
is_last = item.pop("is_last")
accumulator.append(item)
return accumulator
class KeyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, dataset: Dataset, key: str):
self.dataset = dataset
self.key = key
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset)
def __getitem__(self, i):
return self.dataset[i][self.key]
class KeyPairDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, dataset: Dataset, key1: str, key2: str):
self.dataset = dataset
self.key1 = key1
self.key2 = key2
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset)
def __getitem__(self, i):
return {"text": self.dataset[i][self.key1], "text_pair": self.dataset[i][self.key2]}
|
transformers/src/transformers/pipelines/pt_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/src/transformers/pipelines/pt_utils.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5958
}
| 185 |
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Optional
from .base import HfQuantizer
if TYPE_CHECKING:
from ..modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
from ..utils import is_accelerate_available, is_torch_available, is_vptq_available, logging
from ..utils.quantization_config import QuantizationConfigMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
class VptqHfQuantizer(HfQuantizer):
"""
Quantizer of the VPTQ method. Enables the loading of prequantized models.
"""
requires_calibration = True
required_packages = ["vptq"]
def __init__(self, quantization_config: QuantizationConfigMixin, **kwargs):
super().__init__(quantization_config, **kwargs)
self.quantization_config = quantization_config
def validate_environment(self, *args, **kwargs):
if not is_accelerate_available():
raise ImportError("Using `vptq` quantization requires Accelerate: `pip install accelerate`")
if not is_vptq_available():
raise ImportError("Using `vptq` quantization requires VPTQ>=0.0.4: `pip install -U vptq`")
def update_torch_dtype(self, torch_dtype: "torch.dtype") -> "torch.dtype":
if torch_dtype is None:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch_dtype = torch.float16
logger.info(
"CUDA available. Assuming VPTQ inference on GPU and loading the model in `torch.float16`. To overwrite it, set `torch_dtype` manually."
)
else:
import vptq
device_availability = getattr(vptq, "device_availability", lambda device: False)
if device_availability("cpu") is True:
raise RuntimeError("No GPU found. Please wait for the next release of VPTQ to use CPU inference")
torch_dtype = torch.float32
logger.info("No GPU found. Assuming VPTQ inference on CPU and loading the model in `torch.float32`.")
return torch_dtype
def _process_model_before_weight_loading(
self,
model: "PreTrainedModel",
**kwargs,
):
"""
we don't have param like modules_to_not_convert to indicate which layers should not be quantized
because `quantization_config` include the layers that should be quantized
"""
from ..integrations import replace_with_vptq_linear
modules_to_not_convert = kwargs.get("modules_to_not_convert", []) + (
self.quantization_config.modules_to_not_convert or []
)
replace_with_vptq_linear(
model,
quantization_config=self.quantization_config,
modules_to_not_convert=modules_to_not_convert,
)
model.config.quantization_config = self.quantization_config
def _process_model_after_weight_loading(self, model: "PreTrainedModel", **kwargs):
return model
@property
def is_trainable(self, model: Optional["PreTrainedModel"] = None):
return False
def is_serializable(self, safe_serialization=None):
return True
|
transformers/src/transformers/quantizers/quantizer_vptq.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/src/transformers/quantizers/quantizer_vptq.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1424
}
| 186 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2020-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""
PyTorch-independent utilities for the Trainer class.
"""
import copy
import functools
import gc
import inspect
import os
import random
import re
import threading
import time
from typing import Any, Dict, List, NamedTuple, Optional, Tuple, Union
import numpy as np
from .utils import (
ExplicitEnum,
is_psutil_available,
is_tf_available,
is_torch_available,
is_torch_cuda_available,
is_torch_mlu_available,
is_torch_mps_available,
is_torch_musa_available,
is_torch_npu_available,
is_torch_xla_available,
is_torch_xpu_available,
requires_backends,
)
if is_torch_available():
import torch
def seed_worker(_):
"""
Helper function to set worker seed during Dataloader initialization.
"""
worker_seed = torch.initial_seed() % 2**32
set_seed(worker_seed)
def enable_full_determinism(seed: int, warn_only: bool = False):
"""
Helper function for reproducible behavior during distributed training. See
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html for pytorch
- https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/enable_op_determinism for tensorflow
"""
# set seed first
set_seed(seed)
if is_torch_available():
# Enable PyTorch deterministic mode. This potentially requires either the environment
# variable 'CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING' or 'CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG' to be set,
# depending on the CUDA version, so we set them both here
os.environ["CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING"] = "1"
os.environ["CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG"] = ":16:8"
# The environment variable required to enable deterministic mode on Ascend NPUs.
os.environ["ASCEND_LAUNCH_BLOCKING"] = "1"
os.environ["HCCL_DETERMINISTIC"] = "1"
os.environ["FLASH_ATTENTION_DETERMINISTIC"] = "1"
torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True, warn_only=warn_only)
# Enable CUDNN deterministic mode
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
if is_tf_available():
import tensorflow as tf
tf.config.experimental.enable_op_determinism()
def set_seed(seed: int, deterministic: bool = False):
"""
Helper function for reproducible behavior to set the seed in `random`, `numpy`, `torch` and/or `tf` (if installed).
Args:
seed (`int`):
The seed to set.
deterministic (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
Whether to use deterministic algorithms where available. Can slow down training.
"""
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
if is_torch_available():
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
# ^^ safe to call this function even if cuda is not available
if deterministic:
torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
if is_torch_mlu_available():
torch.mlu.manual_seed_all(seed)
if is_torch_musa_available():
torch.musa.manual_seed_all(seed)
if is_torch_npu_available():
torch.npu.manual_seed_all(seed)
if is_torch_xpu_available():
torch.xpu.manual_seed_all(seed)
if is_tf_available():
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(seed)
if deterministic:
tf.config.experimental.enable_op_determinism()
def neftune_post_forward_hook(module, input, output):
"""
Implements the NEFTune forward pass for the model using forward hooks. Note this works only for torch.nn.Embedding
layers. This method is slightly adapted from the original source code that can be found here:
https://github.com/neelsjain/NEFTune Simply add it to your model as follows:
```python
model = ...
model.embed_tokens.neftune_noise_alpha = 0.1
model.embed_tokens.register_forward_hook(neftune_post_forward_hook)
```
Args:
module (`torch.nn.Module`):
The embedding module where the hook is attached. Note that you need to set `module.neftune_noise_alpha` to
the desired noise alpha value.
input (`torch.Tensor`):
The input tensor to the model.
output (`torch.Tensor`):
The output tensor of the model (i.e. the embeddings).
"""
if module.training:
dims = torch.tensor(output.size(1) * output.size(2))
mag_norm = module.neftune_noise_alpha / torch.sqrt(dims)
output = output + torch.zeros_like(output).uniform_(-mag_norm, mag_norm)
return output
class EvalPrediction:
"""
Evaluation output (always contains labels), to be used to compute metrics.
Parameters:
predictions (`np.ndarray`): Predictions of the model.
label_ids (`np.ndarray`): Targets to be matched.
inputs (`np.ndarray`, *optional*): Input data passed to the model.
losses (`np.ndarray`, *optional*): Loss values computed during evaluation.
"""
def __init__(
self,
predictions: Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]],
label_ids: Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]],
inputs: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]]] = None,
losses: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]]] = None,
):
self.predictions = predictions
self.label_ids = label_ids
self.inputs = inputs
self.losses = losses
self.elements = (self.predictions, self.label_ids)
if self.inputs is not None:
self.elements += (self.inputs,)
if self.losses is not None:
self.elements += (self.losses,)
def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.elements)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
if idx < 0 or idx >= len(self.elements):
raise IndexError("tuple index out of range")
return self.elements[idx]
class EvalLoopOutput(NamedTuple):
predictions: Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]]
label_ids: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]]]
metrics: Optional[Dict[str, float]]
num_samples: Optional[int]
class PredictionOutput(NamedTuple):
predictions: Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]]
label_ids: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, Tuple[np.ndarray]]]
metrics: Optional[Dict[str, float]]
class TrainOutput(NamedTuple):
global_step: int
training_loss: float
metrics: Dict[str, float]
PREFIX_CHECKPOINT_DIR = "checkpoint"
_re_checkpoint = re.compile(r"^" + PREFIX_CHECKPOINT_DIR + r"\-(\d+)$")
def get_last_checkpoint(folder):
content = os.listdir(folder)
checkpoints = [
path
for path in content
if _re_checkpoint.search(path) is not None and os.path.isdir(os.path.join(folder, path))
]
if len(checkpoints) == 0:
return
return os.path.join(folder, max(checkpoints, key=lambda x: int(_re_checkpoint.search(x).groups()[0])))
class IntervalStrategy(ExplicitEnum):
NO = "no"
STEPS = "steps"
EPOCH = "epoch"
class SaveStrategy(ExplicitEnum):
NO = "no"
STEPS = "steps"
EPOCH = "epoch"
BEST = "best"
class EvaluationStrategy(ExplicitEnum):
NO = "no"
STEPS = "steps"
EPOCH = "epoch"
class HubStrategy(ExplicitEnum):
END = "end"
EVERY_SAVE = "every_save"
CHECKPOINT = "checkpoint"
ALL_CHECKPOINTS = "all_checkpoints"
class BestRun(NamedTuple):
"""
The best run found by a hyperparameter search (see [`~Trainer.hyperparameter_search`]).
Parameters:
run_id (`str`):
The id of the best run (if models were saved, the corresponding checkpoint will be in the folder ending
with run-{run_id}).
objective (`float`):
The objective that was obtained for this run.
hyperparameters (`Dict[str, Any]`):
The hyperparameters picked to get this run.
run_summary (`Optional[Any]`):
A summary of tuning experiments. `ray.tune.ExperimentAnalysis` object for Ray backend.
"""
run_id: str
objective: Union[float, List[float]]
hyperparameters: Dict[str, Any]
run_summary: Optional[Any] = None
def default_compute_objective(metrics: Dict[str, float]) -> float:
"""
The default objective to maximize/minimize when doing an hyperparameter search. It is the evaluation loss if no
metrics are provided to the [`Trainer`], the sum of all metrics otherwise.
Args:
metrics (`Dict[str, float]`): The metrics returned by the evaluate method.
Return:
`float`: The objective to minimize or maximize
"""
metrics = copy.deepcopy(metrics)
loss = metrics.pop("eval_loss", None)
_ = metrics.pop("epoch", None)
# Remove speed metrics
speed_metrics = [
m
for m in metrics.keys()
if m.endswith("_runtime") or m.endswith("_per_second") or m.endswith("_compilation_time")
]
for sm in speed_metrics:
_ = metrics.pop(sm, None)
return loss if len(metrics) == 0 else sum(metrics.values())
def default_hp_space_optuna(trial) -> Dict[str, float]:
from .integrations import is_optuna_available
assert is_optuna_available(), "This function needs Optuna installed: `pip install optuna`"
return {
"learning_rate": trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 1e-6, 1e-4, log=True),
"num_train_epochs": trial.suggest_int("num_train_epochs", 1, 5),
"seed": trial.suggest_int("seed", 1, 40),
"per_device_train_batch_size": trial.suggest_categorical("per_device_train_batch_size", [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]),
}
def default_hp_space_ray(trial) -> Dict[str, float]:
from .integrations import is_ray_tune_available
assert is_ray_tune_available(), "This function needs ray installed: `pip install ray[tune]`"
from ray import tune
return {
"learning_rate": tune.loguniform(1e-6, 1e-4),
"num_train_epochs": tune.choice(list(range(1, 6))),
"seed": tune.uniform(1, 40),
"per_device_train_batch_size": tune.choice([4, 8, 16, 32, 64]),
}
def default_hp_space_sigopt(trial):
return [
{"bounds": {"min": 1e-6, "max": 1e-4}, "name": "learning_rate", "type": "double", "transformation": "log"},
{"bounds": {"min": 1, "max": 6}, "name": "num_train_epochs", "type": "int"},
{"bounds": {"min": 1, "max": 40}, "name": "seed", "type": "int"},
{
"categorical_values": ["4", "8", "16", "32", "64"],
"name": "per_device_train_batch_size",
"type": "categorical",
},
]
def default_hp_space_wandb(trial) -> Dict[str, float]:
from .integrations import is_wandb_available
if not is_wandb_available():
raise ImportError("This function needs wandb installed: `pip install wandb`")
return {
"method": "random",
"metric": {"name": "objective", "goal": "minimize"},
"parameters": {
"learning_rate": {"distribution": "uniform", "min": 1e-6, "max": 1e-4},
"num_train_epochs": {"distribution": "int_uniform", "min": 1, "max": 6},
"seed": {"distribution": "int_uniform", "min": 1, "max": 40},
"per_device_train_batch_size": {"values": [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]},
},
}
class HPSearchBackend(ExplicitEnum):
OPTUNA = "optuna"
RAY = "ray"
SIGOPT = "sigopt"
WANDB = "wandb"
def is_main_process(local_rank):
"""
Whether or not the current process is the local process, based on `xm.get_ordinal()` (for TPUs) first, then on
`local_rank`.
"""
if is_torch_xla_available():
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
return xm.get_ordinal() == 0
return local_rank in [-1, 0]
def total_processes_number(local_rank):
"""
Return the number of processes launched in parallel. Works with `torch.distributed` and TPUs.
"""
if is_torch_xla_available():
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
return xm.xrt_world_size()
elif local_rank != -1 and is_torch_available():
import torch
return torch.distributed.get_world_size()
return 1
def speed_metrics(split, start_time, num_samples=None, num_steps=None, num_tokens=None):
"""
Measure and return speed performance metrics.
This function requires a time snapshot `start_time` before the operation to be measured starts and this function
should be run immediately after the operation to be measured has completed.
Args:
- split: name to prefix metric (like train, eval, test...)
- start_time: operation start time
- num_samples: number of samples processed
- num_steps: number of steps processed
- num_tokens: number of tokens processed
"""
runtime = time.time() - start_time
result = {f"{split}_runtime": round(runtime, 4)}
if runtime == 0:
return result
if num_samples is not None:
samples_per_second = num_samples / runtime
result[f"{split}_samples_per_second"] = round(samples_per_second, 3)
if num_steps is not None:
steps_per_second = num_steps / runtime
result[f"{split}_steps_per_second"] = round(steps_per_second, 3)
if num_tokens is not None:
tokens_per_second = num_tokens / runtime
result[f"{split}_tokens_per_second"] = round(tokens_per_second, 3)
return result
class SchedulerType(ExplicitEnum):
"""
Scheduler names for the parameter `lr_scheduler_type` in [`TrainingArguments`].
By default, it uses "linear". Internally, this retrieves `get_linear_schedule_with_warmup` scheduler from [`Trainer`].
Scheduler types:
- "linear" = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
- "cosine" = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup
- "cosine_with_restarts" = get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup
- "polynomial" = get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup
- "constant" = get_constant_schedule
- "constant_with_warmup" = get_constant_schedule_with_warmup
- "inverse_sqrt" = get_inverse_sqrt_schedule
- "reduce_lr_on_plateau" = get_reduce_on_plateau_schedule
- "cosine_with_min_lr" = get_cosine_with_min_lr_schedule_with_warmup
- "warmup_stable_decay" = get_wsd_schedule
"""
LINEAR = "linear"
COSINE = "cosine"
COSINE_WITH_RESTARTS = "cosine_with_restarts"
POLYNOMIAL = "polynomial"
CONSTANT = "constant"
CONSTANT_WITH_WARMUP = "constant_with_warmup"
INVERSE_SQRT = "inverse_sqrt"
REDUCE_ON_PLATEAU = "reduce_lr_on_plateau"
COSINE_WITH_MIN_LR = "cosine_with_min_lr"
WARMUP_STABLE_DECAY = "warmup_stable_decay"
class TrainerMemoryTracker:
"""
A helper class that tracks cpu and gpu memory.
This class will silently skip unless `psutil` is available. Install with `pip install psutil`.
When a stage completes, it can pass metrics dict to update with the memory metrics gathered during this stage.
Example :
```python
self._memory_tracker = TrainerMemoryTracker(self.args.skip_memory_metrics)
self._memory_tracker.start()
# code ...
metrics = {"train_runtime": 10.5}
self._memory_tracker.stop_and_update_metrics(metrics)
```
At the moment GPU tracking is only for `pytorch`, but can be extended to support `tensorflow`.
To understand this class' intricacies please read the documentation of [`~Trainer.log_metrics`].
"""
# map trainer methods to metrics prefix
stages = {
"__init__": "init",
"train": "train",
"_inner_training_loop": "train",
"evaluate": "eval",
"predict": "test",
}
def __init__(self, skip_memory_metrics=False):
self.skip_memory_metrics = skip_memory_metrics
if not is_psutil_available():
# soft dependency on psutil
self.skip_memory_metrics = True
if self.skip_memory_metrics:
return
import psutil # noqa
if is_torch_cuda_available() or is_torch_mlu_available() or is_torch_musa_available():
import torch
self.torch = torch
self.gpu = {}
elif is_torch_mps_available():
import torch
self.torch = torch
self.gpu = {}
elif is_torch_xpu_available():
import torch
self.torch = torch
self.gpu = {}
elif is_torch_npu_available():
import torch
self.torch = torch
self.gpu = {}
else:
self.torch = None
self.process = psutil.Process()
self.cur_stage = None
self.cpu = {}
self.init_reported = False
def derive_stage(self):
"""derives the stage/caller name automatically"""
caller = inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_back.f_code.co_name
if caller in self.stages:
return self.stages[caller]
else:
raise ValueError(
f"was called from {caller}, but only expect to be called from one of {self.stages.keys()}"
)
def cpu_mem_used(self):
"""get resident set size memory for the current process"""
return self.process.memory_info().rss
def peak_monitor_func(self):
self.cpu_mem_used_peak = -1
while True:
self.cpu_mem_used_peak = max(self.cpu_mem_used(), self.cpu_mem_used_peak)
# can't sleep or will not catch the peak right (this comment is here on purpose)
# time.sleep(0.001) # 1msec
if not self.peak_monitoring:
break
def start(self):
"""start tracking for the caller's stage"""
if self.skip_memory_metrics:
return
stage = self.derive_stage()
# deal with nested calls of eval during train - simply ignore those
if self.cur_stage is not None and self.cur_stage != stage:
return
self.cur_stage = stage
gc.collect()
if self.torch is not None:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
self.torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
self.torch.cuda.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_mlu_available():
self.torch.mlu.reset_peak_memory_stats()
self.torch.mlu.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_musa_available():
self.torch.musa.reset_peak_memory_stats()
self.torch.musa.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_xpu_available():
self.torch.xpu.reset_peak_memory_stats()
self.torch.xpu.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_npu_available():
self.torch.npu.reset_peak_memory_stats()
self.torch.npu.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_mps_available():
self.torch.mps.empty_cache()
# gpu
if self.torch is not None:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_at_start = self.torch.cuda.memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_mlu_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_at_start = self.torch.mlu.memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_musa_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_at_start = self.torch.musa.memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_xpu_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_at_start = self.torch.xpu.memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_npu_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_at_start = self.torch.npu.memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_mps_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_at_start = self.torch.mps.current_allocated_memory()
# cpu
self.cpu_mem_used_at_start = self.cpu_mem_used()
self.peak_monitoring = True
peak_monitor_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.peak_monitor_func)
peak_monitor_thread.daemon = True
peak_monitor_thread.start()
def stop(self, stage):
"""stop tracking for the passed stage"""
# deal with nested calls of eval during train - simply ignore those
if self.cur_stage is not None and self.cur_stage != stage:
return
# this sends a signal to peak_monitor_func to complete its loop
self.peak_monitoring = False
# first ensure all objects get collected and their memory is freed
gc.collect()
if self.torch is not None:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
self.torch.cuda.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_mlu_available():
self.torch.mlu.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_musa_available():
self.torch.musa.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_xpu_available():
self.torch.xpu.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_npu_available():
self.torch.npu.empty_cache()
elif is_torch_mps_available():
self.torch.mps.empty_cache()
# concepts:
# - alloc_delta: the difference of allocated memory between the end and the start
# - peaked_delta: the difference between the peak memory and the current memory
# in order to know how much memory the measured code consumed one needs to sum these two
# gpu
if self.torch is not None:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_now = self.torch.cuda.memory_allocated()
self.gpu_mem_used_peak = self.torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_mlu_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_now = self.torch.mlu.memory_allocated()
self.gpu_mem_used_peak = self.torch.mlu.max_memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_musa_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_now = self.torch.musa.memory_allocated()
self.gpu_mem_used_peak = self.torch.musa.max_memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_xpu_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_now = self.torch.xpu.memory_allocated()
self.gpu_mem_used_peak = self.torch.xpu.max_memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_npu_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_now = self.torch.npu.memory_allocated()
self.gpu_mem_used_peak = self.torch.npu.max_memory_allocated()
elif is_torch_mps_available():
self.gpu_mem_used_now = self.torch.mps.current_allocated_memory()
# self.torch.mps.max_memory_allocated() does not exist yet
self.gpu_mem_used_peak = None
else:
raise ValueError("No available GPU device found!")
self.gpu[self.cur_stage] = {
"begin": self.gpu_mem_used_at_start,
"end": self.gpu_mem_used_now,
"alloc": (self.gpu_mem_used_now - self.gpu_mem_used_at_start),
}
if self.gpu_mem_used_peak is not None:
self.gpu[self.cur_stage]["peaked"] = max(0, self.gpu_mem_used_peak - self.gpu_mem_used_now)
else:
self.gpu[self.cur_stage]["peaked"] = "Not available"
# cpu
self.cpu_mem_used_now = self.cpu_mem_used()
self.cpu[self.cur_stage] = {
"begin": self.cpu_mem_used_at_start,
"end": self.cpu_mem_used_now,
"alloc": (self.cpu_mem_used_now - self.cpu_mem_used_at_start),
"peaked": max(0, self.cpu_mem_used_peak - self.cpu_mem_used_now),
}
# reset - cycle finished
self.cur_stage = None
def update_metrics(self, stage, metrics):
"""updates the metrics"""
if self.skip_memory_metrics:
return
# deal with nested calls of eval during train - simply ignore those
if self.cur_stage is not None and self.cur_stage != stage:
return
# since we don't have a way to return init metrics, we push them into the first of train/val/predict
stages = [stage]
if not self.init_reported:
stages.insert(0, "init")
self.init_reported = True
for stage in stages:
for t in ["alloc", "peaked"]:
if stage in self.cpu and t in self.cpu[stage]:
metrics[f"{stage}_mem_cpu_{t}_delta"] = self.cpu[stage][t]
if self.torch is not None and stage in self.gpu and t in self.gpu[stage]:
metrics[f"{stage}_mem_gpu_{t}_delta"] = self.gpu[stage][t]
# if we need additional debug info, enable the following
# for t in ["begin", "end"]:
# if stage in self.cpu and t in self.cpu[stage]:
# metrics[f"{stage}_mem_cpu_{t}"] = self.cpu[stage][t]
# if self.torch is not None and stage in self.gpu and t in self.gpu[stage]:
# metrics[f"{stage}_mem_gpu_{t}"] = self.gpu[stage][t]
# since memory can be allocated before init, and it might be difficult to track overall
# memory usage, in particular for GPU, let's report memory usage at the point init was called
if stages[0] == "init":
metrics["before_init_mem_cpu"] = self.cpu["init"]["begin"]
if self.torch is not None:
metrics["before_init_mem_gpu"] = self.gpu["init"]["begin"]
# if we also wanted to report any additional memory allocations in between init and
# whatever the next stage was we could also report this:
# if self.cpu["init"]["end"] != self.cpu[stage]["begin"]:
# metrics[f"after_init_mem_cpu_delta"] = self.cpu[stage]["begin"] - self.cpu["init"]["end"]
# if self.torch is not None and self.gpu["init"]["end"] != self.gpu[stage]["begin"]:
# metrics[f"after_init_mem_gpu_delta"] = self.gpu[stage]["begin"] - self.gpu["init"]["end"]
def stop_and_update_metrics(self, metrics=None):
"""combine stop and metrics update in one call for simpler code"""
if self.skip_memory_metrics:
return
stage = self.derive_stage()
self.stop(stage)
# init doesn't have metrics to update so we just save that data for later stages to retrieve
if metrics is not None:
self.update_metrics(stage, metrics)
def has_length(dataset):
"""
Checks if the dataset implements __len__() and it doesn't raise an error
"""
try:
return len(dataset) is not None
except TypeError:
# TypeError: len() of unsized object
return False
def denumpify_detensorize(metrics):
"""
Recursively calls `.item()` on the element of the dictionary passed
"""
if isinstance(metrics, (list, tuple)):
return type(metrics)(denumpify_detensorize(m) for m in metrics)
elif isinstance(metrics, dict):
return type(metrics)({k: denumpify_detensorize(v) for k, v in metrics.items()})
elif isinstance(metrics, np.generic):
return metrics.item()
elif is_torch_available() and isinstance(metrics, torch.Tensor) and metrics.numel() == 1:
return metrics.item()
return metrics
def number_of_arguments(func):
"""
Return the number of arguments of the passed function, even if it's a partial function.
"""
if isinstance(func, functools.partial):
total_args = len(inspect.signature(func.func).parameters)
return total_args - len(func.args) - len(func.keywords)
return len(inspect.signature(func).parameters)
def find_executable_batch_size(
function: callable = None, starting_batch_size: int = 128, auto_find_batch_size: bool = False
):
"""
Args:
A basic decorator that will try to execute `function`. If it fails from exceptions related to out-of-memory or
CUDNN, the batch size is cut in half and passed to `function`. `function` must take in a `batch_size` parameter as
its first argument.
function (`callable`, *optional*)
A function to wrap
starting_batch_size (`int`, *optional*)
The batch size to try and fit into memory
auto_find_batch_size (`bool`, *optional*)
If False, will just execute `function`
"""
if function is None:
return functools.partial(
find_executable_batch_size,
starting_batch_size=starting_batch_size,
auto_find_batch_size=auto_find_batch_size,
)
if auto_find_batch_size:
requires_backends(find_executable_batch_size, "accelerate")
from accelerate.utils import find_executable_batch_size as accelerate_find_executable_batch_size
return accelerate_find_executable_batch_size(function=function, starting_batch_size=starting_batch_size)
return functools.partial(function, batch_size=starting_batch_size)
class FSDPOption(ExplicitEnum):
FULL_SHARD = "full_shard"
SHARD_GRAD_OP = "shard_grad_op"
NO_SHARD = "no_shard"
HYBRID_SHARD = "hybrid_shard"
HYBRID_SHARD_ZERO2 = "hybrid_shard_zero2"
OFFLOAD = "offload"
AUTO_WRAP = "auto_wrap"
class RemoveColumnsCollator:
"""Wrap the data collator to remove unused columns before they are passed to the collator."""
def __init__(
self,
data_collator,
signature_columns,
logger=None,
model_name: Optional[str] = None,
description: Optional[str] = None,
):
self.data_collator = data_collator
self.signature_columns = signature_columns
self.logger = logger
self.description = description
self.model_name = model_name
self.message_logged = False
def _remove_columns(self, feature: dict) -> dict:
if not isinstance(feature, dict):
return feature
if not self.message_logged and self.logger and self.model_name:
ignored_columns = list(set(feature.keys()) - set(self.signature_columns))
if len(ignored_columns) > 0:
dset_description = "" if self.description is None else f"in the {self.description} set"
self.logger.info(
f"The following columns {dset_description} don't have a corresponding argument in "
f"`{self.model_name}.forward` and have been ignored: {', '.join(ignored_columns)}."
f" If {', '.join(ignored_columns)} are not expected by `{self.model_name}.forward`, "
" you can safely ignore this message."
)
self.message_logged = True
return {k: v for k, v in feature.items() if k in self.signature_columns}
def __call__(self, features: List[dict]):
features = [self._remove_columns(feature) for feature in features]
return self.data_collator(features)
def check_target_module_exists(optim_target_modules, key: str, return_is_regex: bool = False):
"""A helper method to check if the passed module's key name matches any of the target modules in the optim_target_modules.
Args:
optim_target_modules (`Union[str, List[str]]`):
A list of strings to try to match. Can be also a full string.
key (`str`):
A key to search any matches in optim_target_modules
return_is_regex (`bool`):
If set to `True`, the method will return whether the passed `optim_target_modules`
is a regex or not.
Returns:
`bool` : True of match object if key matches any target modules from config, False or
None if no match found
`bool` : If the matched target module is a regex to silence out the warnings in Trainer
for extra modules being found (only if `target_module_found=True` for an array of regex).
"""
target_module_found = False
is_regex = False
if isinstance(optim_target_modules, str):
target_module_found = bool(re.fullmatch(optim_target_modules, key))
is_regex = True if not optim_target_modules == key else False
elif key in optim_target_modules: # from here, target_module_found must be a list of str
# this module is specified directly in target_modules
target_module_found = True
elif any(target_key in key for target_key in optim_target_modules):
target_module_found = True
elif any(bool(re.fullmatch(optim_target_module, key)) for optim_target_module in optim_target_modules):
target_module_found = True
is_regex = True
if return_is_regex:
return target_module_found, is_regex
return target_module_found
|
transformers/src/transformers/trainer_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/src/transformers/trainer_utils.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 14040
}
| 187 |
# This file is autogenerated by the command `make fix-copies`, do not edit.
from ..utils import DummyObject, requires_backends
class Cache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CacheConfig(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DynamicCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EncoderDecoderCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HQQQuantizedCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HybridCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MambaCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OffloadedCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OffloadedStaticCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QuantizedCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QuantizedCacheConfig(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QuantoQuantizedCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SinkCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SlidingWindowCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StaticCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlueDataset(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlueDataTrainingArguments(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LineByLineTextDataset(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LineByLineWithRefDataset(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LineByLineWithSOPTextDataset(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SquadDataset(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SquadDataTrainingArguments(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TextDataset(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TextDatasetForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlternatingCodebooksLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BayesianDetectorConfig(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BayesianDetectorModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeamScorer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeamSearchScorer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClassifierFreeGuidanceLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConstrainedBeamSearchScorer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Constraint(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConstraintListState(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DisjunctiveConstraint(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EncoderNoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EncoderRepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EosTokenCriteria(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EpsilonLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EtaLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ExponentialDecayLengthPenalty(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GenerationMixin(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HammingDiversityLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InfNanRemoveLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LogitNormalization(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LogitsProcessorList(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MaxLengthCriteria(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MaxTimeCriteria(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MinLengthLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MinNewTokensLengthLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MinPLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NoBadWordsLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhrasalConstraint(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PrefixConstrainedLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SequenceBiasLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StoppingCriteria(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StoppingCriteriaList(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StopStringCriteria(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SuppressTokensAtBeginLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SuppressTokensLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SynthIDTextWatermarkDetector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SynthIDTextWatermarkingConfig(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SynthIDTextWatermarkLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TemperatureLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TopKLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TopPLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TypicalLogitsWarper(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UnbatchedClassifierFreeGuidanceLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WatermarkDetector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WatermarkLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WhisperTimeStampLogitsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TorchExportableModuleWithStaticCache(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def convert_and_export_with_cache(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(convert_and_export_with_cache, ["torch"])
ROPE_INIT_FUNCTIONS = None
class PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlbertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_albert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_albert, ["torch"])
class AlignModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlignPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlignTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AlignVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AltCLIPModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AltCLIPPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AltCLIPTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AltCLIPVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AriaForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AriaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AriaTextForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AriaTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AriaTextPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ASTForAudioClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ASTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ASTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_FRAME_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_XVECTOR_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_BACKBONE_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_CTC_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_DEPTH_ESTIMATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TEXT_TO_TEXT_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_INSTANCE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_KEYPOINT_DETECTION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_RETRIEVAL_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_SPECTROGRAM_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_WAVEFORM_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_REGRESSION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_UNIVERSAL_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_VIDEO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_VISUAL_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING = None
MODEL_MAPPING = None
MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING = None
class AutoBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForAudioClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForAudioXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForDepthEstimation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForImageSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForImageTextToText(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForImageToImage(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForInstanceSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForKeypointDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForMaskGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForTextEncoding(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForTextToSpectrogram(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForTextToWaveform(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForUniversalSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForVideoClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForVision2Seq(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoModelWithLMHead(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoformerForPrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AutoformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BambaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BambaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BambaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BarkCausalModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BarkCoarseModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BarkFineModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BarkModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BarkPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BarkSemanticModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BartPretrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PretrainedBartModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeitBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeitForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeitForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeitForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeitModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BeitPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_bert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_bert, ["torch"])
class BertGenerationDecoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertGenerationEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BertGenerationPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_bert_generation(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_bert_generation, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_big_bird(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_big_bird, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPegasusForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPegasusForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPegasusForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPegasusModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BigBirdPegasusPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BioGptForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BioGptForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BioGptForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BioGptModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BioGptPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BitBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BitForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BitModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BitPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotSmallForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotSmallForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotSmallModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlenderbotSmallPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipForImageTextRetrieval(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BlipVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2ForImageTextRetrieval(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2QFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2TextModelWithProjection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2VisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Blip2VisionModelWithProjection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BloomForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BloomForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BloomForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BloomForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BloomModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BloomPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BridgeTowerForContrastiveLearning(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BridgeTowerForImageAndTextRetrieval(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BridgeTowerForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BridgeTowerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BridgeTowerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BrosForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BrosModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BrosPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BrosProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BrosSpadeEEForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class BrosSpadeELForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CamembertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CanineForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CanineForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CanineForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CanineForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CanineModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CaninePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_canine(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_canine, ["torch"])
class ChameleonForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChameleonModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChameleonPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChameleonProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChameleonVQVAE(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChineseCLIPModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChineseCLIPPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChineseCLIPTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ChineseCLIPVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapAudioModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapAudioModelWithProjection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapFeatureExtractor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClapTextModelWithProjection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPTextModelWithProjection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPVisionModelWithProjection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPSegForImageSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPSegModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPSegPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPSegTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CLIPSegVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClvpDecoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClvpEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClvpForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClvpModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClvpModelForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ClvpPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CodeGenForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CodeGenModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CodeGenPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CohereForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CohereModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CoherePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Cohere2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Cohere2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Cohere2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ColPaliForRetrieval(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ColPaliPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConditionalDetrForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConditionalDetrForSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConditionalDetrModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConditionalDetrPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_convbert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_convbert, ["torch"])
class ConvNextBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextV2Backbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextV2ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextV2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ConvNextV2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CpmAntForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CpmAntModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CpmAntPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CTRLForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CTRLLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CTRLModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CTRLPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CvtForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CvtModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class CvtPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DacModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DacPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecAudioForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecAudioForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecAudioForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecAudioForXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecAudioModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecAudioPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecTextPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecVisionForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Data2VecVisionPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DbrxForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DbrxModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DbrxPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2ForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2ForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DebertaV2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DecisionTransformerGPT2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DecisionTransformerGPT2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DecisionTransformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DecisionTransformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeformableDetrForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeformableDetrModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeformableDetrPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeiTForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeiTForImageClassificationWithTeacher(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeiTForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeiTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DeiTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetaForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientFormerForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientFormerForImageClassificationWithTeacher(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientFormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMForInformationExtraction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieMPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTSanJapaneseForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTSanJapaneseModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTSanJapanesePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraphormerForGraphClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraphormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraphormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JukeboxModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JukeboxPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JukeboxPrior(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JukeboxVQVAE(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MCTCTForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MCTCTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MCTCTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MMBTForClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MMBTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ModalEmbeddings(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NatBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NatForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NatModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NatPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NezhaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenLlamaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenLlamaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenLlamaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenLlamaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class QDQBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_qdqbert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_qdqbert, ["torch"])
class RealmEmbedder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RealmForOpenQA(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RealmKnowledgeAugEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RealmPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RealmReader(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RealmRetriever(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RealmScorer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_realm(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_realm, ["torch"])
class RetriBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RetriBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Speech2Text2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Speech2Text2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TrajectoryTransformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TrajectoryTransformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AdaptiveEmbedding(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TransfoXLForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TransfoXLLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TransfoXLModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TransfoXLPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_transfo_xl(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_transfo_xl, ["torch"])
class TvltForAudioVisualClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TvltForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TvltModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TvltPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VanForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VanModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VanPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTHybridForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTHybridModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTHybridPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMProphetNetDecoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMProphetNetEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMProphetNetForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMProphetNetForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMProphetNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMProphetNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DepthAnythingForDepthEstimation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DepthAnythingPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetrForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetrForSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetrModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DetrPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DiffLlamaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DiffLlamaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DiffLlamaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DiffLlamaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DiffLlamaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DiffLlamaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DinatBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DinatForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DinatModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DinatPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2Backbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2WithRegistersBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2WithRegistersForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2WithRegistersModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Dinov2WithRegistersPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DistilBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DonutSwinModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DonutSwinPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRContextEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRPretrainedContextEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRPretrainedQuestionEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRPretrainedReader(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRQuestionEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPRReader(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPTForDepthEstimation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPTForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class DPTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientNetForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EfficientNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ElectraPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_electra(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_electra, ["torch"])
class Emu3ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Emu3ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Emu3PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Emu3TextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Emu3VQVAE(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EncodecModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EncodecPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EncoderDecoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErnieModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ErniePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmFoldPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmForProteinFolding(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class EsmPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconMambaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconMambaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FalconMambaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FastSpeech2ConformerHifiGan(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FastSpeech2ConformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FastSpeech2ConformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FastSpeech2ConformerWithHifiGan(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertForQuestionAnsweringSimple(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlaubertWithLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaImageCodebook(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaImageModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaMultimodalModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FlavaTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FocalNetBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FocalNetForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FocalNetForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FocalNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FocalNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FSMTForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FSMTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PretrainedFSMTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelBaseModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FunnelPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_funnel(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_funnel, ["torch"])
class FuyuForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class FuyuPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GemmaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GemmaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GemmaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GemmaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GemmaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Gemma2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Gemma2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Gemma2ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Gemma2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Gemma2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GitForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GitModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GitPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GitVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlmForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlmForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlmForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlmModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GlmPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GLPNForDepthEstimation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GLPNModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GLPNPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2DoubleHeadsModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2LMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPT2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_gpt2(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_gpt2, ["torch"])
class GPTBigCodeForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTBigCodeForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTBigCodeForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTBigCodeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTBigCodePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_gpt_neo(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_gpt_neo, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXJapaneseForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXJapaneseModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTNeoXJapanesePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTJForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTJForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTJForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTJModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GPTJPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraniteForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraniteModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GranitePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraniteMoeForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraniteMoeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GraniteMoePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroundingDinoForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroundingDinoModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroundingDinoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroupViTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroupViTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroupViTTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class GroupViTVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HeliumForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HeliumForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HeliumForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HeliumModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HeliumPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HieraBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HieraForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HieraForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HieraModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HieraPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HubertForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HubertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HubertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class HubertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IdeficsForVisionText2Text(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IdeficsModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IdeficsPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IdeficsProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics2ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics2Processor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics3ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics3Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics3PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics3Processor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics3VisionConfig(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Idefics3VisionTransformer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IJepaForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IJepaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class IJepaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ImageGPTForCausalImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ImageGPTForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ImageGPTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ImageGPTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_imagegpt(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_imagegpt, ["torch"])
class InformerForPrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipQFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipVideoForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipVideoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipVideoQFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class InstructBlipVideoVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JambaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JambaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JambaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JambaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JetMoeForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JetMoeForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JetMoeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class JetMoePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Kosmos2ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Kosmos2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Kosmos2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv2ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv2ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv3ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv3Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LayoutLMv3PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LEDForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LEDForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LEDForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LEDModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LEDPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LevitForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LevitModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LevitPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LiltForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LiltForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LiltForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LiltModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LiltPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlamaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlamaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlamaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlamaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlamaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlamaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaNextPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaNextVideoForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaNextVideoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LlavaOnevisionPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongT5EncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongT5ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongT5Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LongT5PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForEntityClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForEntityPairClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForEntitySpanClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LukePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LxmertEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LxmertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LxmertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LxmertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LxmertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class LxmertVisualFeatureEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class M2M100ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class M2M100Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class M2M100PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MambaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MambaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MambaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Mamba2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Mamba2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Mamba2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarianForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarianModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarianMTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarianPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarkupLMForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarkupLMForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarkupLMForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarkupLMModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MarkupLMPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Mask2FormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Mask2FormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MaskFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MaskFormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MaskFormerSwinBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MBartForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MBartForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MBartForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MBartForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MBartModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MBartPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MegatronBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MgpstrForSceneTextRecognition(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MgpstrModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MgpstrPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MimiModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MimiPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MistralForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MistralForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MistralForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MistralForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MistralModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MistralPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MixtralForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MixtralForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MixtralForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MixtralForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MixtralModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MixtralPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MllamaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MllamaForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MllamaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MllamaProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MllamaTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MllamaVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForNextSentencePrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_mobilebert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_mobilebert, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV1ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV1Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV1PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_mobilenet_v1(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_mobilenet_v1, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV2ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV2ForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileNetV2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_mobilenet_v2(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_mobilenet_v2, ["torch"])
class MobileViTForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTV2ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTV2ForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTV2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MobileViTV2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ModernBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ModernBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ModernBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ModernBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ModernBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoonshineForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoonshineModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoonshinePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoshiForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoshiForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoshiModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MoshiPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MPNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MptForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MptForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MptForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MptForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MptModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MptPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MraPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5EncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MT5PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenMelodyForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenMelodyForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenMelodyModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MusicgenMelodyPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MvpForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MvpForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MvpForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MvpForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MvpModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class MvpPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NemotronForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NemotronForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NemotronForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NemotronForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NemotronModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NemotronPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NllbMoeForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NllbMoeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NllbMoePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NllbMoeSparseMLP(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NllbMoeTop2Router(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class NystromformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OlmoForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OlmoModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OlmoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Olmo2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Olmo2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Olmo2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OlmoeForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OlmoeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OlmoePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OmDetTurboForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OmDetTurboPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OneFormerForUniversalSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OneFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OneFormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenAIGPTDoubleHeadsModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenAIGPTForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenAIGPTLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenAIGPTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OpenAIGPTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_openai_gpt(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_openai_gpt, ["torch"])
class OPTForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OPTForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OPTForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OPTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OPTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Owlv2ForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Owlv2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Owlv2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Owlv2TextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Owlv2VisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OwlViTForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OwlViTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OwlViTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OwlViTTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class OwlViTVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PaliGemmaForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PaliGemmaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PaliGemmaProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSMixerForPrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSMixerForPretraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSMixerForRegression(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSMixerForTimeSeriesClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSMixerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSMixerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSTForClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSTForPrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSTForPretraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSTForRegression(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PatchTSTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusXForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusXModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PegasusXPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForImageClassificationConvProcessing(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForImageClassificationFourier(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForMultimodalAutoencoding(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForOpticalFlow(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PerceiverPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PersimmonForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PersimmonForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PersimmonForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PersimmonModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PersimmonPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhiForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhiForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhiForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhiModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhiPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Phi3ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Phi3ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Phi3ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Phi3Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Phi3PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhimoeForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhimoeForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhimoeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PhimoePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Pix2StructForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Pix2StructPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Pix2StructTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Pix2StructVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PixtralPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PixtralVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PLBartForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PLBartForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PLBartForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PLBartModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PLBartPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PoolFormerForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PoolFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PoolFormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Pop2PianoForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Pop2PianoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ProphetNetDecoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ProphetNetEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ProphetNetForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ProphetNetForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ProphetNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ProphetNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtV2Backbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtV2ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtV2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class PvtV2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2_5_VLModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2_5_VLPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2AudioEncoder(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2AudioForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2AudioPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2MoeForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2MoeForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2MoeForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2MoeForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2MoeModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2MoePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2VLModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Qwen2VLPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RagModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RagPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RagSequenceForGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RagTokenForGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RecurrentGemmaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RecurrentGemmaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RecurrentGemmaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ReformerForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ReformerForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ReformerForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ReformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ReformerModelWithLMHead(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ReformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RegNetForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RegNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RegNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RemBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_rembert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_rembert, ["torch"])
class ResNetBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ResNetForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ResNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ResNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RobertaPreLayerNormPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoCBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_roc_bert(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_roc_bert, ["torch"])
class RoFormerForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RoFormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_roformer(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_roformer, ["torch"])
class RTDetrForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RTDetrModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RTDetrPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RTDetrResNetBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RTDetrResNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RwkvForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RwkvModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class RwkvPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SamModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SamPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TCodeHifiGan(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TForSpeechToSpeech(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TForSpeechToText(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TForTextToSpeech(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TForTextToText(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4THifiGan(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TTextToUnitForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4TTextToUnitModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4Tv2ForSpeechToSpeech(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4Tv2ForSpeechToText(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4Tv2ForTextToSpeech(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4Tv2ForTextToText(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4Tv2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SeamlessM4Tv2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegformerDecodeHead(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegformerForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegformerForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegGptForImageSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegGptModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SegGptPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWDForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWDForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWDModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SEWDPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SiglipForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SiglipModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SiglipPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SiglipTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SiglipVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechEncoderDecoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Speech2TextForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Speech2TextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Speech2TextPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechT5ForSpeechToSpeech(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechT5ForSpeechToText(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechT5ForTextToSpeech(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechT5HifiGan(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechT5Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SpeechT5PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SplinterForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SplinterForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SplinterModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SplinterPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SqueezeBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StableLmForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StableLmForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StableLmForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StableLmModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class StableLmPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Starcoder2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Starcoder2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Starcoder2ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Starcoder2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Starcoder2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SuperGlueForKeypointMatching(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SuperGluePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SuperPointForKeypointDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SuperPointPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwiftFormerForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwiftFormerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwiftFormerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwinBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwinForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwinForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwinModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwinPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swin2SRForImageSuperResolution(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swin2SRModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swin2SRPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swinv2Backbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swinv2ForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swinv2ForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swinv2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Swinv2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwitchTransformersEncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwitchTransformersForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwitchTransformersModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwitchTransformersPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwitchTransformersSparseMLP(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class SwitchTransformersTop1Router(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5EncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class T5PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_t5(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_t5, ["torch"])
class TableTransformerForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TableTransformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TableTransformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TapasForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TapasForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TapasForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TapasModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TapasPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_tapas(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_tapas, ["torch"])
class TextNetBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TextNetForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TextNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TextNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimeSeriesTransformerForPrediction(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimeSeriesTransformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimeSeriesTransformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimesformerForVideoClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimesformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimesformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimmBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimmWrapperForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimmWrapperModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TimmWrapperPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TrOCRForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TrOCRPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TvpForVideoGrounding(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TvpModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class TvpPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UdopEncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UdopForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UdopModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UdopPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5EncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5ForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5ForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5ForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UMT5PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatForXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UniSpeechSatPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UnivNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UperNetForSemanticSegmentation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class UperNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoLlavaForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoLlavaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoLlavaProcessor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoMAEForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoMAEForVideoClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoMAEModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VideoMAEPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltForImageAndTextRetrieval(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltForImagesAndTextClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViltPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VipLlavaForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VipLlavaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisionEncoderDecoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisionTextDualEncoderModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertForRegionToPhraseAlignment(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertForVisualReasoning(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VisualBertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTForMaskedImageModeling(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTMAEForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTMAEModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTMAEPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTMSNForImageClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTMSNModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ViTMSNPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitDetBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitDetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitDetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitMatteForImageMatting(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitMattePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitPoseForPoseEstimation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitPosePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitPoseBackbone(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitPoseBackbonePreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitsModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VitsPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VivitForVideoClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VivitModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class VivitPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ForXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2BertForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2BertForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2BertForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2BertForXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2BertModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2BertPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerForPreTraining(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerForXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Wav2Vec2ConformerPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WavLMForAudioFrameClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WavLMForCTC(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WavLMForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WavLMForXVector(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WavLMModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WavLMPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WhisperForAudioClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WhisperForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WhisperForConditionalGeneration(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WhisperModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class WhisperPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XCLIPModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XCLIPPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XCLIPTextModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XCLIPVisionModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XGLMForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XGLMModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XGLMPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMForQuestionAnsweringSimple(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMWithLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLMRobertaXLPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetForQuestionAnsweringSimple(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetLMHeadModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XLNetPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def load_tf_weights_in_xlnet(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(load_tf_weights_in_xlnet, ["torch"])
class XmodForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class XmodPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YolosForObjectDetection(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YolosModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YolosPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoForMaskedLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoForMultipleChoice(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoForQuestionAnswering(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoForTokenClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class YosoPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ZambaForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ZambaForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ZambaModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ZambaPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Zamba2ForCausalLM(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Zamba2ForSequenceClassification(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Zamba2Model(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Zamba2PreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ZoeDepthForDepthEstimation(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class ZoeDepthPreTrainedModel(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class Adafactor(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
class AdamW(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def get_constant_schedule(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_constant_schedule, ["torch"])
def get_constant_schedule_with_warmup(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_constant_schedule_with_warmup, ["torch"])
def get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup, ["torch"])
def get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup, ["torch"])
def get_inverse_sqrt_schedule(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_inverse_sqrt_schedule, ["torch"])
def get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_linear_schedule_with_warmup, ["torch"])
def get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup, ["torch"])
def get_scheduler(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_scheduler, ["torch"])
def get_wsd_schedule(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(get_wsd_schedule, ["torch"])
class Conv1D(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def apply_chunking_to_forward(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(apply_chunking_to_forward, ["torch"])
def prune_layer(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(prune_layer, ["torch"])
class Trainer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
def torch_distributed_zero_first(*args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(torch_distributed_zero_first, ["torch"])
class Seq2SeqTrainer(metaclass=DummyObject):
_backends = ["torch"]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
requires_backends(self, ["torch"])
|
transformers/src/transformers/utils/dummy_pt_objects.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/src/transformers/utils/dummy_pt_objects.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 104347
}
| 188 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2020 Optuna, Hugging Face
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Logging utilities."""
import functools
import logging
import os
import sys
import threading
from logging import (
CRITICAL, # NOQA
DEBUG, # NOQA
ERROR, # NOQA
FATAL, # NOQA
INFO, # NOQA
NOTSET, # NOQA
WARN, # NOQA
WARNING, # NOQA
)
from logging import captureWarnings as _captureWarnings
from typing import Optional
import huggingface_hub.utils as hf_hub_utils
from tqdm import auto as tqdm_lib
_lock = threading.Lock()
_default_handler: Optional[logging.Handler] = None
log_levels = {
"detail": logging.DEBUG, # will also print filename and line number
"debug": logging.DEBUG,
"info": logging.INFO,
"warning": logging.WARNING,
"error": logging.ERROR,
"critical": logging.CRITICAL,
}
_default_log_level = logging.WARNING
_tqdm_active = not hf_hub_utils.are_progress_bars_disabled()
def _get_default_logging_level():
"""
If TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY env var is set to one of the valid choices return that as the new default level. If it is
not - fall back to `_default_log_level`
"""
env_level_str = os.getenv("TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY", None)
if env_level_str:
if env_level_str in log_levels:
return log_levels[env_level_str]
else:
logging.getLogger().warning(
f"Unknown option TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY={env_level_str}, "
f"has to be one of: { ', '.join(log_levels.keys()) }"
)
return _default_log_level
def _get_library_name() -> str:
return __name__.split(".")[0]
def _get_library_root_logger() -> logging.Logger:
return logging.getLogger(_get_library_name())
def _configure_library_root_logger() -> None:
global _default_handler
with _lock:
if _default_handler:
# This library has already configured the library root logger.
return
_default_handler = logging.StreamHandler() # Set sys.stderr as stream.
# set defaults based on https://github.com/pyinstaller/pyinstaller/issues/7334#issuecomment-1357447176
if sys.stderr is None:
sys.stderr = open(os.devnull, "w")
_default_handler.flush = sys.stderr.flush
# Apply our default configuration to the library root logger.
library_root_logger = _get_library_root_logger()
library_root_logger.addHandler(_default_handler)
library_root_logger.setLevel(_get_default_logging_level())
# if logging level is debug, we add pathname and lineno to formatter for easy debugging
if os.getenv("TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY", None) == "detail":
formatter = logging.Formatter("[%(levelname)s|%(pathname)s:%(lineno)s] %(asctime)s >> %(message)s")
_default_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
library_root_logger.propagate = False
def _reset_library_root_logger() -> None:
global _default_handler
with _lock:
if not _default_handler:
return
library_root_logger = _get_library_root_logger()
library_root_logger.removeHandler(_default_handler)
library_root_logger.setLevel(logging.NOTSET)
_default_handler = None
def get_log_levels_dict():
return log_levels
def captureWarnings(capture):
"""
Calls the `captureWarnings` method from the logging library to enable management of the warnings emitted by the
`warnings` library.
Read more about this method here:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/logging.html#integration-with-the-warnings-module
All warnings will be logged through the `py.warnings` logger.
Careful: this method also adds a handler to this logger if it does not already have one, and updates the logging
level of that logger to the library's root logger.
"""
logger = get_logger("py.warnings")
if not logger.handlers:
logger.addHandler(_default_handler)
logger.setLevel(_get_library_root_logger().level)
_captureWarnings(capture)
def get_logger(name: Optional[str] = None) -> logging.Logger:
"""
Return a logger with the specified name.
This function is not supposed to be directly accessed unless you are writing a custom transformers module.
"""
if name is None:
name = _get_library_name()
_configure_library_root_logger()
return logging.getLogger(name)
def get_verbosity() -> int:
"""
Return the current level for the 🤗 Transformers's root logger as an int.
Returns:
`int`: The logging level.
<Tip>
🤗 Transformers has following logging levels:
- 50: `transformers.logging.CRITICAL` or `transformers.logging.FATAL`
- 40: `transformers.logging.ERROR`
- 30: `transformers.logging.WARNING` or `transformers.logging.WARN`
- 20: `transformers.logging.INFO`
- 10: `transformers.logging.DEBUG`
</Tip>"""
_configure_library_root_logger()
return _get_library_root_logger().getEffectiveLevel()
def set_verbosity(verbosity: int) -> None:
"""
Set the verbosity level for the 🤗 Transformers's root logger.
Args:
verbosity (`int`):
Logging level, e.g., one of:
- `transformers.logging.CRITICAL` or `transformers.logging.FATAL`
- `transformers.logging.ERROR`
- `transformers.logging.WARNING` or `transformers.logging.WARN`
- `transformers.logging.INFO`
- `transformers.logging.DEBUG`
"""
_configure_library_root_logger()
_get_library_root_logger().setLevel(verbosity)
def set_verbosity_info():
"""Set the verbosity to the `INFO` level."""
return set_verbosity(INFO)
def set_verbosity_warning():
"""Set the verbosity to the `WARNING` level."""
return set_verbosity(WARNING)
def set_verbosity_debug():
"""Set the verbosity to the `DEBUG` level."""
return set_verbosity(DEBUG)
def set_verbosity_error():
"""Set the verbosity to the `ERROR` level."""
return set_verbosity(ERROR)
def disable_default_handler() -> None:
"""Disable the default handler of the HuggingFace Transformers's root logger."""
_configure_library_root_logger()
assert _default_handler is not None
_get_library_root_logger().removeHandler(_default_handler)
def enable_default_handler() -> None:
"""Enable the default handler of the HuggingFace Transformers's root logger."""
_configure_library_root_logger()
assert _default_handler is not None
_get_library_root_logger().addHandler(_default_handler)
def add_handler(handler: logging.Handler) -> None:
"""adds a handler to the HuggingFace Transformers's root logger."""
_configure_library_root_logger()
assert handler is not None
_get_library_root_logger().addHandler(handler)
def remove_handler(handler: logging.Handler) -> None:
"""removes given handler from the HuggingFace Transformers's root logger."""
_configure_library_root_logger()
assert handler is not None and handler not in _get_library_root_logger().handlers
_get_library_root_logger().removeHandler(handler)
def disable_propagation() -> None:
"""
Disable propagation of the library log outputs. Note that log propagation is disabled by default.
"""
_configure_library_root_logger()
_get_library_root_logger().propagate = False
def enable_propagation() -> None:
"""
Enable propagation of the library log outputs. Please disable the HuggingFace Transformers's default handler to
prevent double logging if the root logger has been configured.
"""
_configure_library_root_logger()
_get_library_root_logger().propagate = True
def enable_explicit_format() -> None:
"""
Enable explicit formatting for every HuggingFace Transformers's logger. The explicit formatter is as follows:
```
[LEVELNAME|FILENAME|LINE NUMBER] TIME >> MESSAGE
```
All handlers currently bound to the root logger are affected by this method.
"""
handlers = _get_library_root_logger().handlers
for handler in handlers:
formatter = logging.Formatter("[%(levelname)s|%(filename)s:%(lineno)s] %(asctime)s >> %(message)s")
handler.setFormatter(formatter)
def reset_format() -> None:
"""
Resets the formatting for HuggingFace Transformers's loggers.
All handlers currently bound to the root logger are affected by this method.
"""
handlers = _get_library_root_logger().handlers
for handler in handlers:
handler.setFormatter(None)
def warning_advice(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
This method is identical to `logger.warning()`, but if env var TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS=1 is set, this
warning will not be printed
"""
no_advisory_warnings = os.getenv("TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS", False)
if no_advisory_warnings:
return
self.warning(*args, **kwargs)
logging.Logger.warning_advice = warning_advice
@functools.lru_cache(None)
def warning_once(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
This method is identical to `logger.warning()`, but will emit the warning with the same message only once
Note: The cache is for the function arguments, so 2 different callers using the same arguments will hit the cache.
The assumption here is that all warning messages are unique across the code. If they aren't then need to switch to
another type of cache that includes the caller frame information in the hashing function.
"""
self.warning(*args, **kwargs)
logging.Logger.warning_once = warning_once
@functools.lru_cache(None)
def info_once(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
This method is identical to `logger.info()`, but will emit the info with the same message only once
Note: The cache is for the function arguments, so 2 different callers using the same arguments will hit the cache.
The assumption here is that all warning messages are unique across the code. If they aren't then need to switch to
another type of cache that includes the caller frame information in the hashing function.
"""
self.info(*args, **kwargs)
logging.Logger.info_once = info_once
class EmptyTqdm:
"""Dummy tqdm which doesn't do anything."""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # pylint: disable=unused-argument
self._iterator = args[0] if args else None
def __iter__(self):
return iter(self._iterator)
def __getattr__(self, _):
"""Return empty function."""
def empty_fn(*args, **kwargs): # pylint: disable=unused-argument
return
return empty_fn
def __enter__(self):
return self
def __exit__(self, type_, value, traceback):
return
class _tqdm_cls:
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
if _tqdm_active:
return tqdm_lib.tqdm(*args, **kwargs)
else:
return EmptyTqdm(*args, **kwargs)
def set_lock(self, *args, **kwargs):
self._lock = None
if _tqdm_active:
return tqdm_lib.tqdm.set_lock(*args, **kwargs)
def get_lock(self):
if _tqdm_active:
return tqdm_lib.tqdm.get_lock()
tqdm = _tqdm_cls()
def is_progress_bar_enabled() -> bool:
"""Return a boolean indicating whether tqdm progress bars are enabled."""
global _tqdm_active
return bool(_tqdm_active)
def enable_progress_bar():
"""Enable tqdm progress bar."""
global _tqdm_active
_tqdm_active = True
hf_hub_utils.enable_progress_bars()
def disable_progress_bar():
"""Disable tqdm progress bar."""
global _tqdm_active
_tqdm_active = False
hf_hub_utils.disable_progress_bars()
|
transformers/src/transformers/utils/logging.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/src/transformers/utils/logging.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4432
}
| 189 |
How to add BigBird to 🤗 Transformers?
=====================================
Mentor: [Patrick](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten)
Begin: 12.02.2020
Estimated End: 19.03.2020
Contributor: [Vasudev](https://github.com/thevasudevgupta)
Adding a new model is often difficult and requires an in-depth knowledge
of the 🤗 Transformers library and ideally also of the model's original
repository. At Hugging Face, we are trying to empower the community more
and more to add models independently.
The following sections explain in detail how to add BigBird
to Transformers. You will work closely with Patrick to
integrate BigBird into Transformers. By doing so, you will both gain a
theoretical and deep practical understanding of BigBird.
But more importantly, you will have made a major
open-source contribution to Transformers. Along the way, you will:
- get insights into open-source best practices
- understand the design principles of one of the most popular NLP
libraries
- learn how to do efficiently test large NLP models
- learn how to integrate Python utilities like `black`, `ruff`,
`make fix-copies` into a library to always ensure clean and readable
code
To start, let's try to get a general overview of the Transformers
library.
General overview of 🤗 Transformers
----------------------------------
First, you should get a general overview of 🤗 Transformers. Transformers
is a very opinionated library, so there is a chance that
you don't agree with some of the library's philosophies or design
choices. From our experience, however, we found that the fundamental
design choices and philosophies of the library are crucial to
efficiently scale Transformers while keeping maintenance costs at a
reasonable level.
A good first starting point to better understand the library is to read
the [documentation of our philosophy](https://huggingface.co/transformers/philosophy.html).
As a result of our way of working, there are some choices that we try to apply to all models:
- Composition is generally favored over abstraction
- Duplicating code is not always bad if it strongly improves the
readability or accessibility of a model
- Model files are as self-contained as possible so that when you read
the code of a specific model, you ideally only have to look into the
respective `modeling_....py` file.
In our opinion, the library's code is not just a means to provide a
product, *e.g.*, the ability to use BERT for inference, but also as the
very product that we want to improve. Hence, when adding a model, the
user is not only the person that will use your model, but also everybody
that will read, try to understand, and possibly tweak your code.
With this in mind, let's go a bit deeper into the general library
design.
### Overview of models
To successfully add a model, it is important to understand the
interaction between your model and its config,
`PreTrainedModel`, and `PretrainedConfig`. For
exemplary purposes, we will call the PyTorch model to be added to 🤗 Transformers
`BrandNewBert`.
Let's take a look:
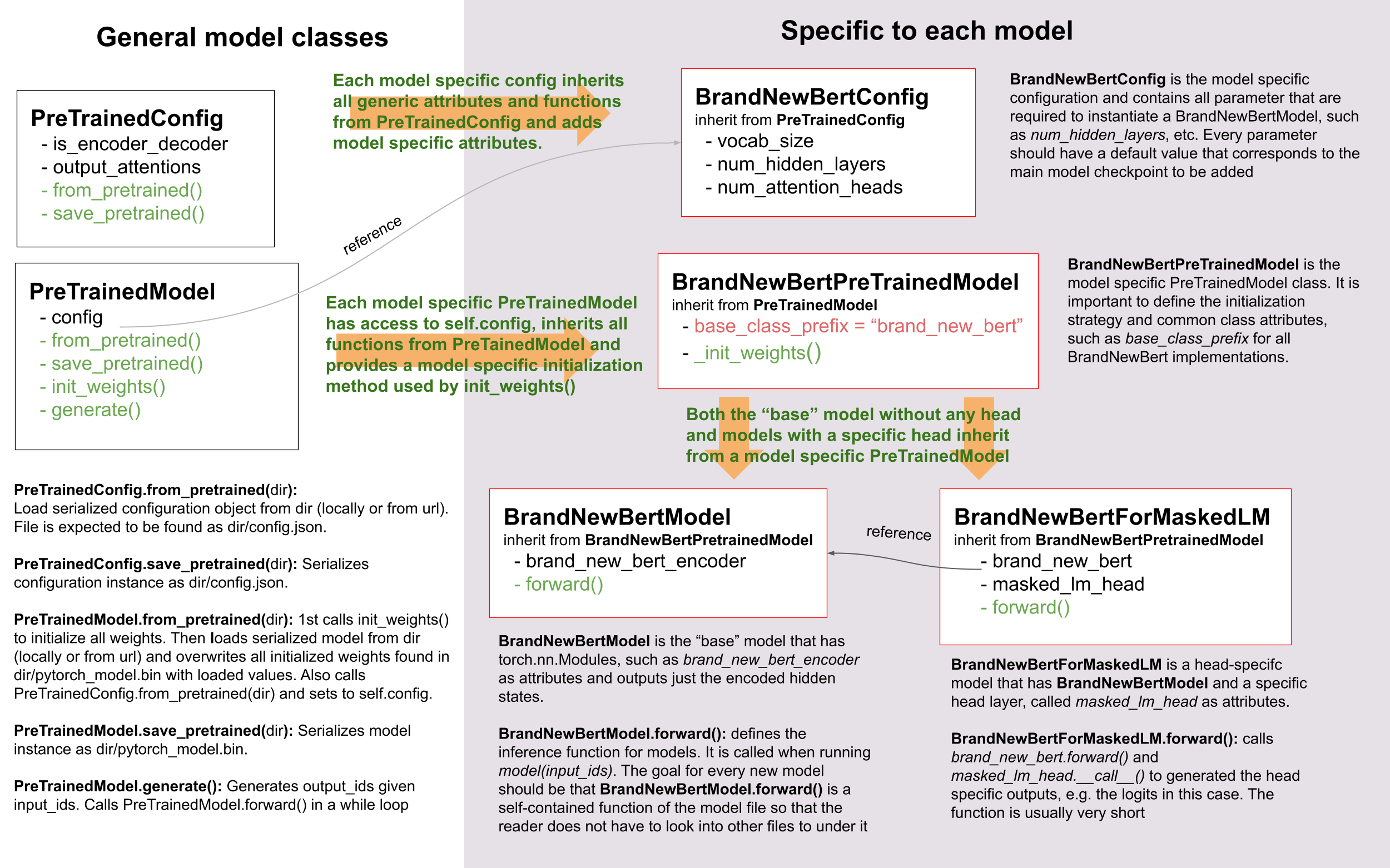
As you can see, we do make use of inheritance in 🤗 Transformers, but we
keep the level of abstraction to an absolute minimum. There are never
more than two levels of abstraction for any model in the library.
`BrandNewBertModel` inherits from
`BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel` which in
turn inherits from `PreTrainedModel` and that's it.
As a general rule, we want to make sure
that a new model only depends on `PreTrainedModel`. The
important functionalities that are automatically provided to every new
model are
`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained` and `PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`, which are
used for serialization and deserialization. All
of the other important functionalities, such as
`BrandNewBertModel.forward` should be
completely defined in the new `modeling_brand_new_bert.py` module. Next,
we want to make sure that a model with a specific head layer, such as
`BrandNewBertForMaskedLM` does not inherit
from `BrandNewBertModel`, but rather uses
`BrandNewBertModel` as a component that
can be called in its forward pass to keep the level of abstraction low.
Every new model requires a configuration class, called
`BrandNewBertConfig`. This configuration
is always stored as an attribute in
`PreTrainedModel`, and
thus can be accessed via the `config` attribute for all classes
inheriting from `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`
```python
# assuming that `brand_new_bert` belongs to the organization `brandy`
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("brandy/brand_new_bert")
model.config # model has access to its config
```
Similar to the model, the configuration inherits basic serialization and
deserialization functionalities from
`PretrainedConfig`. Note
that the configuration and the model are always serialized into two
different formats - the model to a `pytorch_model.bin` file
and the configuration to a `config.json` file. Calling
`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained` will automatically call
`PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`, so that both model and configuration are saved.
### Overview of tokenizers
Not quite ready yet :-( This section will be added soon!
Step-by-step recipe to add a model to 🤗 Transformers
----------------------------------------------------
Everyone has different preferences of how to port a model so it can be
very helpful for you to take a look at summaries of how other
contributors ported models to Hugging Face. Here is a list of community
blog posts on how to port a model:
1. [Porting GPT2
Model](https://medium.com/huggingface/from-tensorflow-to-pytorch-265f40ef2a28)
by [Thomas](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf)
2. [Porting WMT19 MT Model](https://huggingface.co/blog/porting-fsmt)
by [Stas](https://huggingface.co/stas)
From experience, we can tell you that the most important things to keep
in mind when adding a model are:
- Don't reinvent the wheel! Most parts of the code you will add for
the new 🤗 Transformers model already exist somewhere in 🤗
Transformers. Take some time to find similar, already existing
models and tokenizers you can copy from.
[grep](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/) and
[rg](https://github.com/BurntSushi/ripgrep) are your friends. Note
that it might very well happen that your model's tokenizer is based
on one model implementation, and your model's modeling code on
another one. *E.g.*, FSMT's modeling code is based on BART, while
FSMT's tokenizer code is based on XLM.
- It's more of an engineering challenge than a scientific challenge.
You should spend more time on creating an efficient debugging
environment than trying to understand all theoretical aspects of the
model in the paper.
- Ask for help when you're stuck! Models are the core component of 🤗
Transformers so we, at Hugging Face, are more than happy to help
you at every step to add your model. Don't hesitate to ask if you
notice you are not making progress.
In the following, we try to give you a general recipe that we found most
useful when porting a model to 🤗 Transformers.
The following list is a summary of everything that has to be done to add
a model and can be used by you as a To-Do List:
1. [ ] (Optional) Understood theoretical aspects
2. [ ] Prepared transformers dev environment
3. [ ] Set up debugging environment of the original repository
4. [ ] Created script that successfully runs forward pass using
original repository and checkpoint
5. [ ] Successfully opened a PR and added the model skeleton to Transformers
6. [ ] Successfully converted original checkpoint to Transformers
checkpoint
7. [ ] Successfully ran forward pass in Transformers that gives
identical output to original checkpoint
8. [ ] Finished model tests in Transformers
9. [ ] Successfully added Tokenizer in Transformers
10. [ ] Run end-to-end integration tests
11. [ ] Finished docs
12. [ ] Uploaded model weights to the hub
13. [ ] Submitted the pull request for review
14. [ ] (Optional) Added a demo notebook
To begin with, we usually recommend to start by getting a good
theoretical understanding of `BigBird`. However, if you prefer to
understand the theoretical aspects of the model *on-the-job*, then it is
totally fine to directly dive into the `BigBird`'s code-base. This
option might suit you better, if your engineering skills are better than
your theoretical skill, if you have trouble understanding
`BigBird`'s paper, or if you just enjoy programming much more than
reading scientific papers.
### 1. (Optional) Theoretical aspects of BigBird
You should take some time to read *BigBird's* paper, if such
descriptive work exists. There might be large sections of the paper that
are difficult to understand. If this is the case, this is fine - don't
worry! The goal is not to get a deep theoretical understanding of the
paper, but to extract the necessary information required to effectively
re-implement the model in 🤗 Transformers. That being said, you don't
have to spend too much time on the theoretical aspects, but rather focus
on the practical ones, namely:
- What type of model is *BigBird*? BERT-like encoder-only
model? GPT2-like decoder-only model? BART-like encoder-decoder
model? Look at the `model_summary` if
you're not familiar with the differences between those.
- What are the applications of *BigBird*? Text
classification? Text generation? Seq2Seq tasks, *e.g.,*
summarization?
- What is the novel feature of the model making it different from
BERT/GPT-2/BART?
- Which of the already existing [🤗 Transformers
models](https://huggingface.co/transformers/#contents) is most
similar to *BigBird*?
- What type of tokenizer is used? A sentencepiece tokenizer? Word
piece tokenizer? Is it the same tokenizer as used for BERT or BART?
After you feel like you have gotten a good overview of the architecture
of the model, you might want to write to Patrick with any
questions you might have. This might include questions regarding the
model's architecture, its attention layer, etc. We will be more than
happy to help you.
#### Additional resources
Before diving into the code, here are some additional resources that might be worth taking a look at:
- [Yannic Kilcher's paper summary](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WVPE62Gk3EM&ab_channel=YannicKilcher)
- [Yannic Kilcher's summary of Longformer](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_8KNb5iqblE&ab_channel=YannicKilcher) - Longformer and BigBird are **very** similar models. Since Longformer has already been ported to 🤗 Transformers, it is useful to understand the differences between the two models
- [Blog post](https://medium.com/dsc-msit/is-google-bigbird-gonna-be-the-new-leader-in-nlp-domain-8c95cecc30f8) - A relatively superficial blog post about BigBird. Might be a good starting point to understand BigBird
#### Make sure you've understood the fundamental aspects of BigBird
Alright, now you should be ready to take a closer look into the actual code of BigBird.
You should have understood the following aspects of BigBird by now:
- BigBird provides a new attention layer for long-range sequence modelling that can be used
as a drop-in replacement for already existing architectures. This means that every transformer-based model architecture can replace its [Self-attention layer](https://towardsdatascience.com/illustrated-self-attention-2d627e33b20a) with BigBird's self-attention layer.
- BigBird's self-attention layer is composed of three mechanisms: block sparse (local) self-attention, global self-attention, random self-attention
- BigBird's block sparse (local) self-attention is different from Longformer's local self-attention. How so? Why does that matter? => Can be deployed on TPU much easier this way
- BigBird can be implemented for both an encoder-only model **and**
for an encoder-decoder model, which means that we can reuse lots of [code from RoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/roberta/modeling_roberta.py) and [from PEGASUS](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/pegasus/modeling_pegasus.py) at a later stage.
If any of the mentioned aspects above are **not** clear to you, now is a great time to talk to Patrick.
### 2. Next prepare your environment
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers)
by clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This
creates a copy of the code under your GitHub user account.
2. Clone your `transformers` fork to your local disk, and add the base
repository as a remote:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/[your Github handle]/transformers.git
cd transformers
git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
```
3. Set up a development environment, for instance by running the
following command:
```bash
python -m venv .env
source .env/bin/activate
pip install -e ".[dev]"
```
and return to the parent directory
```bash
cd ..
```
4. We recommend adding the PyTorch version of *BigBird* to
Transformers. To install PyTorch, please follow the instructions [here](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/).
**Note:** You don't need to have CUDA installed. Making the new model
work on CPU is sufficient.
5. To port *BigBird*, you will also need access to its
original repository:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/google-research/bigbird.git
cd big_bird
pip install -e .
```
Now you have set up a development environment to port *BigBird*
to 🤗 Transformers.
### Run a pretrained checkpoint using the original repository
**3. Set up debugging environment**
At first, you will work on the original *BigBird* repository.
Often, the original implementation is very "researchy". Meaning that
documentation might be lacking and the code can be difficult to
understand. But this should be exactly your motivation to reimplement
*BigBird*. At Hugging Face, one of our main goals is to *make
people stand on the shoulders of giants* which translates here very well
into taking a working model and rewriting it to make it as **accessible,
user-friendly, and beautiful** as possible. This is the number-one
motivation to re-implement models into 🤗 Transformers - trying to make
complex new NLP technology accessible to **everybody**.
You should start thereby by diving into the [original repository](https://github.com/google-research/bigbird).
Successfully running the official pretrained model in the original
repository is often **the most difficult** step. From our experience, it
is very important to spend some time getting familiar with the original
code-base. You need to figure out the following:
- Where to find the pretrained weights?
- How to load the pretrained weights into the corresponding model?
- How to run the tokenizer independently from the model?
- Trace one forward pass so that you know which classes and functions
are required for a simple forward pass. Usually, you only have to
reimplement those functions.
- Be able to locate the important components of the model: Where is
the model's class? Are there model sub-classes, *e.g.*,
EncoderModel, DecoderModel? Where is the self-attention layer? Are
there multiple different attention layers, *e.g.*, *self-attention*,
*cross-attention*...?
- How can you debug the model in the original environment of the repo?
Do you have to add `print` statements, can you work with
an interactive debugger like [ipdb](https://pypi.org/project/ipdb/), or should you use
an efficient IDE to debug the model, like PyCharm?
It is very important that before you start the porting process, that you
can **efficiently** debug code in the original repository! Also,
remember that you are working with an open-source library, so do not
hesitate to open an issue, or even a pull request in the original
repository. The maintainers of this repository are most likely very
happy about someone looking into their code!
At this point, it is really up to you which debugging environment and
strategy you prefer to use to debug the original model. We strongly
advise against setting up a costly GPU environment, but simply work on a
CPU both when starting to dive into the original repository and also
when starting to write the 🤗 Transformers implementation of the model.
Only at the very end, when the model has already been successfully
ported to 🤗 Transformers, one should verify that the model also works as
expected on GPU.
In general, there are two possible debugging environments for running
the original model
- [Jupyter notebooks](https://jupyter.org/) / [google colab](https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/intro.ipynb)
- Local python scripts.
Jupyter notebooks have the advantage that they allow for cell-by-cell
execution which can be helpful to better split logical components from
one another and to have faster debugging cycles as intermediate results
can be stored. Also, notebooks are often easier to share with other
contributors, which might be very helpful if you want to ask the Hugging
Face team for help. If you are familiar with Jupyter notebooks, we
strongly recommend you to work with them.
The obvious disadvantage of Jupyter notebooks is that if you are not
used to working with them you will have to spend some time adjusting to
the new programming environment and that you might not be able to use
your known debugging tools anymore, like `ipdb`.
**4. Successfully run forward pass**
For each code-base, a good first step is always to load a **small**
pretrained checkpoint and to be able to reproduce a single forward pass
using a dummy integer vector of input IDs as an input. Such a script
could look something like this:
```python
from bigbird.core import modeling
model = modeling.BertModel(bert_config)
from bigbird.core import utils
params = utils.BigBirdConfig(vocab_size=32000, hidden_size=512,
num_hidden_layers=8, num_attention_heads=6, intermediate_size=1024)
ckpt_path = 'gs://bigbird-transformer/pretrain/bigbr_base/model.ckpt-0'
ckpt_reader = tf.compat.v1.train.NewCheckpointReader(ckpt_path)
model.set_weights([ckpt_reader.get_tensor(v.name[:-2]) for v in tqdm(model.trainable_weights, position=0)])
input_ids = tf.constant([[31, 51, 99], [15, 5, 0]])
_, pooled_output = model(input_ids=input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
...
```
Next, regarding the debugging strategy, there are generally a few from
which to choose from:
- Decompose the original model into many small testable components and
run a forward pass on each of those for verification
- Decompose the original model only into the original *tokenizer* and
the original *model*, run a forward pass on those, and use
intermediate print statements or breakpoints for verification
Again, it is up to you which strategy to choose. Often, one or the other
is advantageous depending on the original code base.
If the original code-base allows you to decompose the model into smaller
sub-components, *e.g.*, if the original code-base can easily be run in
eager mode, it is usually worth the effort to do so. There are some
important advantages to taking the more difficult road in the beginning:
- at a later stage when comparing the original model to the Hugging
Face implementation, you can verify automatically for each component
individually that the corresponding component of the 🤗 Transformers
implementation matches instead of relying on visual comparison via
print statements
- it can give you some rope to decompose the big problem of porting a
model into smaller problems of just porting individual components
and thus structure your work better
- separating the model into logical meaningful components will help
you to get a better overview of the model's design and thus to
better understand the model
- at a later stage those component-by-component tests help you to
ensure that no regression occurs as you continue changing your code
[Lysandre's](https://gist.github.com/LysandreJik/db4c948f6b4483960de5cbac598ad4ed)
integration checks for ELECTRA gives a nice example of how this can be
done.
However, if the original code-base is very complex or only allows
intermediate components to be run in a compiled mode, it might be too
time-consuming or even impossible to separate the model into smaller
testable sub-components. A good example is [T5's
MeshTensorFlow](https://github.com/tensorflow/mesh/tree/master/mesh_tensorflow)
library which is very complex and does not offer a simple way to
decompose the model into its sub-components. For such libraries, one
often relies on verifying print statements.
No matter which strategy you choose, the recommended procedure is often
the same in that you should start to debug the starting layers first and
the ending layers last.
It is recommended that you retrieve the output, either by print
statements or sub-component functions, of the following layers in the
following order:
1. Retrieve the input IDs passed to the model
2. Retrieve the word embeddings
3. Retrieve the input of the first Transformer layer
4. Retrieve the output of the first Transformer layer
5. Retrieve the output of the following n - 1 Transformer layers
6. Retrieve the output of the whole BigBird Model
Input IDs should thereby consists of an array of integers, *e.g.*,
`input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]`
The outputs of the following layers often consist of multi-dimensional
float arrays and can look like this:
```bash
[[
[-0.1465, -0.6501, 0.1993, ..., 0.1451, 0.3430, 0.6024],
[-0.4417, -0.5920, 0.3450, ..., -0.3062, 0.6182, 0.7132],
[-0.5009, -0.7122, 0.4548, ..., -0.3662, 0.6091, 0.7648],
...,
[-0.5613, -0.6332, 0.4324, ..., -0.3792, 0.7372, 0.9288],
[-0.5416, -0.6345, 0.4180, ..., -0.3564, 0.6992, 0.9191],
[-0.5334, -0.6403, 0.4271, ..., -0.3339, 0.6533, 0.8694]]],
```
We expect that every model added to 🤗 Transformers passes a couple of
integration tests, meaning that the original model and the reimplemented
version in 🤗 Transformers have to give the exact same output up to a
precision of 0.001! Since it is normal that the exact same model written
in different libraries can give a slightly different output depending on
the library framework, we accept an error tolerance of 1e-3 (0.001). It
is not enough if the model gives nearly the same output, they have to be
the almost identical. Therefore, you will certainly compare the
intermediate outputs of the 🤗 Transformers version multiple times
against the intermediate outputs of the original implementation of
*BigBird* in which case an **efficient** debugging environment
of the original repository is absolutely important. Here is some advice
to make your debugging environment as efficient as possible.
- Find the best way of debugging intermediate results. Is the original
repository written in PyTorch? Then you should probably take the
time to write a longer script that decomposes the original model
into smaller sub-components to retrieve intermediate values. Is the
original repository written in Tensorflow 1? Then you might have to
rely on TensorFlow print operations like
[tf.print](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/print) to
output intermediate values. Is the original repository written in
Jax? Then make sure that the model is **not jitted** when running
the forward pass, *e.g.*, check-out [this
link](https://github.com/google/jax/issues/196).
- Use the smallest pretrained checkpoint you can find. The smaller the
checkpoint, the faster your debug cycle becomes. It is not efficient
if your pretrained model is so big that your forward pass takes more
than 10 seconds. In case only very large checkpoints are available,
it might make more sense to create a dummy model in the new
environment with randomly initialized weights and save those weights
for comparison with the 🤗 Transformers version of your model
- Make sure you are using the easiest way of calling a forward pass in
the original repository. Ideally, you want to find the function in
the original repository that **only** calls a single forward pass,
*i.e.* that is often called `predict`, `evaluate`, `forward` or
`__call__`. You don't want to debug a function that calls `forward`
multiple times, *e.g.*, to generate text, like
`autoregressive_sample`, `generate`.
- Try to separate the tokenization from the model's
forward pass. If the original repository shows
examples where you have to input a string, then try to find out
where in the forward call the string input is changed to input ids
and start from this point. This might mean that you have to possibly
write a small script yourself or change the original code so that
you can directly input the ids instead of an input string.
- Make sure that the model in your debugging setup is **not** in
training mode, which often causes the model to yield random outputs
due to multiple dropout layers in the model. Make sure that the
forward pass in your debugging environment is **deterministic** so
that the dropout layers are not used. Or use
`transformers.utils.set_seed` if the old and new
implementations are in the same framework.
#### (Important) More details on how to create a debugging environment for BigBird
- BigBird has multiple pretrained checkpoints that should eventually all be ported to
🤗 Transformers. The pretrained checkpoints can be found [here](https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser/bigbird-transformer/pretrain;tab=objects?prefix=&forceOnObjectsSortingFiltering=false).
Those checkpoints include both pretrained weights for encoder-only (BERT/RoBERTa) under the folder `bigbr_base` and encoder-decoder (PEGASUS) under the folder `bigbp_large`.
You should start by porting the `bigbr_base` model. The encoder-decoder model
can be ported afterward.
for an encoder-decoder architecture as well as an encoder-only architecture.
- BigBird was written in tf.compat meaning that a mixture of a TensorFlow 1 and
TensorFlow 2 API was used.
- The most important part of the BigBird code-base is [bigbird.bigbird.core](https://github.com/google-research/bigbird/tree/master/bigbird/core) which includes all logic necessary
to implement BigBird.
- The first goal should be to successfully run a forward pass using the RoBERTa checkpoint `bigbr_base/model.ckpt-0.data-00000-of-00001` and `bigbr_base/model.ckpt-0.index`.
### Port BigBird to 🤗 Transformers
Next, you can finally start adding new code to 🤗 Transformers. Go into
the clone of your 🤗 Transformers' fork:
cd transformers
In the special case that you are adding a model whose architecture
exactly matches the model architecture of an existing model you only
have to add a conversion script as described in [this
section](#write-a-conversion-script). In this case, you can just re-use
the whole model architecture of the already existing model.
Otherwise, let's start generating a new model with the amazing
Cookiecutter!
**Use the Cookiecutter to automatically generate the model's code**
To begin with head over to the [🤗 Transformers
templates](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/templates/adding_a_new_model)
to make use of our `cookiecutter` implementation to automatically
generate all the relevant files for your model. Again, we recommend only
adding the PyTorch version of the model at first. Make sure you follow
the instructions of the `README.md` on the [🤗 Transformers
templates](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/templates/adding_a_new_model)
carefully.
Since you will first implement the Encoder-only/RoBERTa-like version of BigBird you should
select the `is_encoder_decoder_model = False` option in the cookiecutter. Also, it is recommended
that you implement the model only in PyTorch in the beginning and select "Standalone" as the
tokenizer type for now.
**Open a Pull Request on the main huggingface/transformers repo**
Before starting to adapt the automatically generated code, now is the
time to open a "Work in progress (WIP)" pull request, *e.g.*, "\[WIP\]
Add *BigBird*", in 🤗 Transformers so that you and the Hugging
Face team can work side-by-side on integrating the model into 🤗
Transformers.
You should do the following:
1. Create a branch with a descriptive name from your main branch
```bash
git checkout -b add_big_bird
```
2. Commit the automatically generated code:
```bash
git add .
git commit
```
3. Fetch and rebase to current main
```bash
git fetch upstream
git rebase upstream/main
```
4. Push the changes to your account using:
```bash
git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
```
5. Once you are satisfied, go to the webpage of your fork on GitHub.
Click on "Pull request". Make sure to add the GitHub handle of Patrick
as one reviewer, so that the Hugging Face team gets notified for future changes.
6. Change the PR into a draft by clicking on "Convert to draft" on the
right of the GitHub pull request web page.
In the following, whenever you have done some progress, don't forget to
commit your work and push it to your account so that it shows in the
pull request. Additionally, you should make sure to update your work
with the current main from time to time by doing:
git fetch upstream
git merge upstream/main
In general, all questions you might have regarding the model or your
implementation should be asked in your PR and discussed/solved in the
PR. This way, Patrick will always be notified when you are
committing new code or if you have a question. It is often very helpful
to point Patrick to your added code so that the Hugging
Face team can efficiently understand your problem or question.
To do so, you can go to the "Files changed" tab where you see all of
your changes, go to a line regarding which you want to ask a question,
and click on the "+" symbol to add a comment. Whenever a question or
problem has been solved, you can click on the "Resolve" button of the
created comment.
In the same way, Patrick will open comments when reviewing
your code. We recommend asking most questions on GitHub on your PR. For
some very general questions that are not very useful for the public,
feel free to ping Patrick by Slack or email.
**5. Adapt the generated models code for BigBird**
At first, we will focus only on the model itself and not care about the
tokenizer. All the relevant code should be found in the generated files
`src/transformers/models/big_bird/modeling_big_bird.py` and
`src/transformers/models/big_bird/configuration_big_bird.py`.
Now you can finally start coding :). The generated code in
`src/transformers/models/big_bird/modeling_big_bird.py` will
either have the same architecture as BERT if it's an encoder-only model
or BART if it's an encoder-decoder model. At this point, you should
remind yourself what you've learned in the beginning about the
theoretical aspects of the model: *How is the model different from BERT
or BART?*\". Implement those changes which often means to change the
*self-attention* layer, the order of the normalization layer, etc...
Again, it is often useful to look at the similar architecture of already
existing models in Transformers to get a better feeling of how your
model should be implemented.
**Note** that at this point, you don't have to be very sure that your
code is fully correct or clean. Rather, it is advised to add a first
*unclean*, copy-pasted version of the original code to
`src/transformers/models/big_bird/modeling_big_bird.py`
until you feel like all the necessary code is added. From our
experience, it is much more efficient to quickly add a first version of
the required code and improve/correct the code iteratively with the
conversion script as described in the next section. The only thing that
has to work at this point is that you can instantiate the 🤗 Transformers
implementation of *BigBird*, *i.e.* the following command
should work:
```python
from transformers import BigBirdModel, BigBirdConfig
model = BigBirdModel(BigBirdConfig())
```
The above command will create a model according to the default
parameters as defined in `BigBirdConfig()` with random weights,
thus making sure that the `init()` methods of all components works.
Note that for BigBird you have to change the attention layer. BigBird's attention
layer is quite complex as you can see [here](https://github.com/google-research/bigbird/blob/103a3345f94bf6364749b51189ed93024ca5ef26/bigbird/core/attention.py#L560). Don't
feel discouraged by this! In a first step you should simply make sure that
the layer `BigBirdAttention` has the correct weights as can be found in the
pretrained checkpoints. This means that you have to make sure that in the
`__init__(self, ...)` function of `BigBirdAttention`, all submodules include all
necessary `nn.Module` layers. Only at a later stage do we need to fully rewrite
the complex attention function.
**6. Write a conversion script**
Next, you should write a conversion script that lets you convert the
checkpoint you used to debug *BigBird* in the original
repository to a checkpoint compatible with your just created 🤗
Transformers implementation of *BigBird*. It is not advised to
write the conversion script from scratch, but rather to look through
already existing conversion scripts in 🤗 Transformers for one that has
been used to convert a similar model that was written in the same
framework as *BigBird*. Usually, it is enough to copy an
already existing conversion script and slightly adapt it for your use
case. Don't hesitate to ask Patrick to point you to a
similar already existing conversion script for your model.
- A good starting point to convert the original TF BigBird implementation to the PT Hugging Face implementation is probably BERT's conversion script
[here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/7acfa95afb8194f8f9c1f4d2c6028224dbed35a2/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_bert.py#L91)
You can copy paste the conversion function into `modeling_big_bird.py` and then adapt it
to your needs.
In the following, we'll quickly explain how PyTorch models store layer
weights and define layer names. In PyTorch, the name of a layer is
defined by the name of the class attribute you give the layer. Let's
define a dummy model in PyTorch, called `SimpleModel` as follows:
```python
from torch import nn
class SimpleModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.intermediate = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(10)
```
Now we can create an instance of this model definition which will fill
all weights: `dense`, `intermediate`, `layer_norm` with random weights.
We can print the model to see its architecture
```python
model = SimpleModel()
print(model)
```
This will print out the following:
```bash
SimpleModel(
(dense): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
(intermediate): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
(layer_norm): LayerNorm((10,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
```
We can see that the layer names are defined by the name of the class
attribute in PyTorch. You can print out the weight values of a specific
layer:
```python
print(model.dense.weight.data)
```
to see that the weights were randomly initialized
```bash
tensor([[-0.0818, 0.2207, -0.0749, -0.0030, 0.0045, -0.1569, -0.1598, 0.0212,
-0.2077, 0.2157],
[ 0.1044, 0.0201, 0.0990, 0.2482, 0.3116, 0.2509, 0.2866, -0.2190,
0.2166, -0.0212],
[-0.2000, 0.1107, -0.1999, -0.3119, 0.1559, 0.0993, 0.1776, -0.1950,
-0.1023, -0.0447],
[-0.0888, -0.1092, 0.2281, 0.0336, 0.1817, -0.0115, 0.2096, 0.1415,
-0.1876, -0.2467],
[ 0.2208, -0.2352, -0.1426, -0.2636, -0.2889, -0.2061, -0.2849, -0.0465,
0.2577, 0.0402],
[ 0.1502, 0.2465, 0.2566, 0.0693, 0.2352, -0.0530, 0.1859, -0.0604,
0.2132, 0.1680],
[ 0.1733, -0.2407, -0.1721, 0.1484, 0.0358, -0.0633, -0.0721, -0.0090,
0.2707, -0.2509],
[-0.1173, 0.1561, 0.2945, 0.0595, -0.1996, 0.2988, -0.0802, 0.0407,
0.1829, -0.1568],
[-0.1164, -0.2228, -0.0403, 0.0428, 0.1339, 0.0047, 0.1967, 0.2923,
0.0333, -0.0536],
[-0.1492, -0.1616, 0.1057, 0.1950, -0.2807, -0.2710, -0.1586, 0.0739,
0.2220, 0.2358]]).
```
In the conversion script, you should fill those randomly initialized
weights with the exact weights of the corresponding layer in the
checkpoint. *E.g.*,
```python
# retrieve matching layer weights, e.g. by
# recursive algorithm
layer_name = "dense"
pretrained_weight = array_of_dense_layer
model_pointer = getattr(model, "dense")
model_pointer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(pretrained_weight)
```
While doing so, you must verify that each randomly initialized weight of
your PyTorch model and its corresponding pretrained checkpoint weight
exactly match in both **shape and name**. To do so, it is **necessary**
to add assert statements for the shape and print out the names of the
checkpoints weights. *E.g.*, you should add statements like:
```python
assert (
model_pointer.weight.shape == pretrained_weight.shape
), f"Pointer shape of random weight {model_pointer.shape} and array shape of checkpoint weight {pretrained_weight.shape} mismatched"
```
Besides, you should also print out the names of both weights to make
sure they match, *e.g.*,
```python
logger.info(f"Initialize PyTorch weight {layer_name} from {pretrained_weight.name}")
```
If either the shape or the name doesn't match, you probably assigned
the wrong checkpoint weight to a randomly initialized layer of the 🤗
Transformers implementation.
An incorrect shape is most likely due to an incorrect setting of the
config parameters in `BigBirdConfig()` that do not exactly match
those that were used for the checkpoint you want to convert. However, it
could also be that PyTorch's implementation of a layer requires the
weight to be transposed beforehand.
Finally, you should also check that **all** required weights are
initialized and print out all checkpoint weights that were not used for
initialization to make sure the model is correctly converted. It is
completely normal, that the conversion trials fail with either a wrong
shape statement or wrong name assignment. This is most likely because
either you used incorrect parameters in `BigBirdConfig()`, have a
wrong architecture in the 🤗 Transformers implementation, you have a bug
in the `init()` functions of one of the components of the 🤗 Transformers
implementation or you need to transpose one of the checkpoint weights.
This step should be iterated with the previous step until all weights of
the checkpoint are correctly loaded in the Transformers model. Having
correctly loaded the checkpoint into the 🤗 Transformers implementation,
you can then save the model under a folder of your choice
`/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder` that should then contain both a
`pytorch_model.bin` file and a `config.json` file:
```python
model.save_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
```
**7. Implement the forward pass**
Having managed to correctly load the pretrained weights into the 🤗
Transformers implementation, you should now make sure that the forward
pass is correctly implemented. In [Get familiar with the original
repository](#run-a-pretrained-checkpoint-using-the-original-repository),
you have already created a script that runs a forward pass of the model
using the original repository. Now you should write an analogous script
using the 🤗 Transformers implementation instead of the original one. It
should look as follows:
[Here the model name might have to be adapted, *e.g.*, maybe BigBirdForConditionalGeneration instead of BigBirdModel]
```python
model = BigBirdModel.from_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]
output = model(input_ids).last_hidden_states
```
It is very likely that the 🤗 Transformers implementation and the
original model implementation don't give the exact same output the very
first time or that the forward pass throws an error. Don't be
disappointed - it's expected! First, you should make sure that the
forward pass doesn't throw any errors. It often happens that the wrong
dimensions are used leading to a `"Dimensionality mismatch"`
error or that the wrong data type object is used, *e.g.*, `torch.long`
instead of `torch.float32`. Don't hesitate to ask Patrick
for help, if you don't manage to solve certain errors.
The final part to make sure the 🤗 Transformers implementation works
correctly is to ensure that the outputs are equivalent to a precision of
`1e-3`. First, you should ensure that the output shapes are identical,
*i.e.* `outputs.shape` should yield the same value for the script of the
🤗 Transformers implementation and the original implementation. Next, you
should make sure that the output values are identical as well. This one
of the most difficult parts of adding a new model. Common mistakes why
the outputs are not identical are:
- Some layers were not added, *i.e.* an activation layer
was not added, or the residual connection was forgotten
- The word embedding matrix was not tied
- The wrong positional embeddings are used because the original
implementation uses on offset
- Dropout is applied during the forward pass. To fix this make sure
`model.training is False` and that no dropout layer is
falsely activated during the forward pass, *i.e.* pass
`self.training` to [PyTorch's functional
dropout](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.functional.html?highlight=dropout#torch.nn.functional.dropout)
The best way to fix the problem is usually to look at the forward pass
of the original implementation and the 🤗 Transformers implementation
side-by-side and check if there are any differences. Ideally, you should
debug/print out intermediate outputs of both implementations of the
forward pass to find the exact position in the network where the 🤗
Transformers implementation shows a different output than the original
implementation. First, make sure that the hard-coded `input_ids` in both
scripts are identical. Next, verify that the outputs of the first
transformation of the `input_ids` (usually the word embeddings) are
identical. And then work your way up to the very last layer of the
network. At some point, you will notice a difference between the two
implementations, which should point you to the bug in the 🤗 Transformers
implementation. From our experience, a simple and efficient way is to
add many print statements in both the original implementation and 🤗
Transformers implementation, at the same positions in the network
respectively, and to successively remove print statements showing the
same values for intermediate presentions.
When you're confident that both implementations yield the same output,
verifying the outputs with
`torch.allclose(original_output, output, atol=1e-3)`, you're done with
the most difficult part! Congratulations - the work left to be done
should be a cakewalk 😊.
**8. Adding all necessary model tests**
At this point, you have successfully added a new model. However, it is
very much possible that the model does not yet fully comply with the
required design. To make sure, the implementation is fully compatible
with 🤗 Transformers, all common tests should pass. The Cookiecutter
should have automatically added a test file for your model, probably
under the same `tests/test_modeling_big_bird.py`. Run this test
file to verify that all common tests pass:
```python
pytest tests/test_modeling_big_bird.py
```
Having fixed all common tests, it is now crucial to ensure that all the
nice work you have done is well tested, so that
- a) The community can easily understand your work by looking at
specific tests of *BigBird*
- b) Future changes to your model will not break any important
feature of the model.
At first, integration tests should be added. Those integration tests
essentially do the same as the debugging scripts you used earlier to
implement the model to 🤗 Transformers. A template of those model tests
is already added by the Cookiecutter, called
`BigBirdModelIntegrationTests` and only has to be filled out by
you. To ensure that those tests are passing, run
```python
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -sv tests/test_modeling_big_bird.py::BigBirdModelIntegrationTests
```
**Note**: In case you are using Windows, you should replace `RUN_SLOW=1` with
`SET RUN_SLOW=1`
Second, all features that are special to *BigBird* should be
tested additionally in a separate test under
`BigBirdModelTester`/`BigBirdModelTest`. This part is often
forgotten but is extremely useful in two ways:
- It helps to transfer the knowledge you have acquired during the
model addition to the community by showing how the special features
of *BigBird* should work.
- Future contributors can quickly test changes to the model by running
those special tests.
BigBird has quite a complex attention layer, so it is very important
to add more tests verifying the all parts of BigBird's self-attention layer
works as expected. This means that there should be at least 3 additional tests:
- 1. Verify that the sparse attention works correctly
- 2. Verify that the global attention works correctly
- 3. Verify that the random attention works correctly
**9. Implement the tokenizer**
Next, we should add the tokenizer of *BigBird*. Usually, the
tokenizer is equivalent or very similar to an already existing tokenizer
of 🤗 Transformers.
In the case of BigBird you should be able to just rely on an already existing tokenizer.
If not mistaken, BigBird uses the same tokenizer that was used for `BertGenerationTokenizer`,
which is based on `sentencepiece`. So you should be able to just set the config parameter
`tokenizer_class` to `BertGenerationTokenizer` without having to implement any new tokenizer.
It is very important to find/extract the original tokenizer file and to
manage to load this file into the 🤗 Transformers' implementation of the
tokenizer.
For BigBird, the tokenizer (sentencepiece) files can be found [here](https://github.com/google-research/bigbird/blob/master/bigbird/vocab/gpt2.model), which you should be able to load
as easily as:
```python
from transformers import BertGenerationTokenizer
tokenizer = BertGenerationTokenizer("/path/to/gpt2.model/file")
```
To ensure that the tokenizer works correctly, it is recommended to first
create a script in the original repository that inputs a string and
returns the `input_ids`. It could look similar to this (in pseudo-code):
```bash
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
model = BigBirdModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
input_ids = model.tokenize(input_str)
```
You might have to take a deeper look again into the original repository
to find the correct tokenizer function or you might even have to do
changes to your clone of the original repository to only output the
`input_ids`. Having written a functional tokenization script that uses
the original repository, an analogous script for 🤗 Transformers should
be created. It should look similar to this:
```python
from transformers import BertGenerationTokenizer
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
tokenizer = BertGenerationTokenizer.from_pretrained("/path/big/bird/folder")
input_ids = tokenizer(input_str).input_ids
```
When both `input_ids` yield the same values, as a final step a tokenizer
test file should also be added.
Since BigBird is most likely fully based on `BertGenerationTokenizer`,
you should only add a couple of "slow" integration tests. However, in this
case you do **not** need to add any `BigBirdTokenizationTest`.
**10. Run End-to-end integration tests**
Having added the tokenizer, you should also add a couple of end-to-end
integration tests using both the model and the tokenizer to
`tests/test_modeling_big_bird.py` in 🤗 Transformers. Such a test
should show on a meaningful text-to-text sample that the 🤗 Transformers
implementation works as expected. A meaningful text-to-text sample can
include, *e.g.*, a source-to-target-translation pair, an
article-to-summary pair, a question-to-answer pair, etc... If none of
the ported checkpoints has been fine-tuned on a downstream task it is
enough to simply rely on the model tests. In a final step to ensure that
the model is fully functional, it is advised that you also run all tests
on GPU. It can happen that you forgot to add some `.to(self.device)`
statements to internal tensors of the model, which in such a test would
show in an error. In case you have no access to a GPU, the Hugging Face
team can take care of running those tests for you.
**11. Add Docstring**
Now, all the necessary functionality for *BigBird* is added -
you're almost done! The only thing left to add is a nice docstring and
a doc page. The Cookiecutter should have added a template file called
`docs/source/model_doc/big_bird.rst` that you should fill out.
Users of your model will usually first look at this page before using
your model. Hence, the documentation must be understandable and concise.
It is very useful for the community to add some *Tips* to show how the
model should be used. Don't hesitate to ping Patrick
regarding the docstrings.
Next, make sure that the docstring added to
`src/transformers/models/big_bird/modeling_big_bird.py` is
correct and included all necessary inputs and outputs. It is always to
good to remind oneself that documentation should be treated at least as
carefully as the code in 🤗 Transformers since the documentation is
usually the first contact point of the community with the model.
**Code refactor**
Great, now you have added all the necessary code for *BigBird*.
At this point, you should correct some potential incorrect code style by
running:
```bash
make style
```
and verify that your coding style passes the quality check:
```bash
make quality
```
There are a couple of other very strict design tests in 🤗 Transformers
that might still be failing, which shows up in the tests of your pull
request. This is often because of some missing information in the
docstring or some incorrect naming. Patrick will surely
help you if you're stuck here.
Lastly, it is always a good idea to refactor one's code after having
ensured that the code works correctly. With all tests passing, now it's
a good time to go over the added code again and do some refactoring.
You have now finished the coding part, congratulation! 🎉 You are
Awesome! 😎
**12. Upload the models to the model hub**
In this final part, you should convert and upload all checkpoints to the
model hub and add a model card for each uploaded model checkpoint. You
should work alongside Patrick here to decide on a fitting
name for each checkpoint and to get the required access rights to be
able to upload the model under the author's organization of
*BigBird*.
It is worth spending some time to create fitting model cards for each
checkpoint. The model cards should highlight the specific
characteristics of this particular checkpoint, *e.g.*, On which dataset
was the checkpoint pretrained/fine-tuned on? On what down-stream task
should the model be used? And also include some code on how to correctly
use the model.
**13. (Optional) Add notebook**
It is very helpful to add a notebook that showcases in-detail how
*BigBird* can be used for inference and/or fine-tuned on a
downstream task. This is not mandatory to merge your PR, but very useful
for the community.
**14. Submit your finished PR**
You're done programming now and can move to the last step, which is
getting your PR merged into main. Usually, Patrick
should have helped you already at this point, but it is worth taking
some time to give your finished PR a nice description and eventually add
comments to your code, if you want to point out certain design choices
to your reviewer.
### Share your work!!
Now, it's time to get some credit from the community for your work!
Having completed a model addition is a major contribution to
Transformers and the whole NLP community. Your code and the ported
pre-trained models will certainly be used by hundreds and possibly even
thousands of developers and researchers. You should be proud of your
work and share your achievement with the community.
**You have made another model that is super easy to access for everyone
in the community! 🤯**
|
transformers/templates/adding_a_new_model/open_model_proposals/ADD_BIG_BIRD.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/templates/adding_a_new_model/open_model_proposals/ADD_BIG_BIRD.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 14667
}
| 190 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a clone of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import annotations
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
import numpy as np
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from transformers import is_tensorflow_text_available, is_tf_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_tensorflow_text, require_tf, slow
from ..test_modeling_tf_common import floats_tensor
from .test_framework_agnostic import GenerationIntegrationTestsMixin
if is_tf_available():
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers import (
AutoTokenizer,
TFAutoModelForCausalLM,
TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
TFAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq,
TFAutoModelForVision2Seq,
TFBartForConditionalGeneration,
TFLogitsProcessorList,
TFMinLengthLogitsProcessor,
)
from transformers.modeling_tf_utils import keras
if is_tensorflow_text_available():
import tensorflow_text as text
@require_tf
class TFGenerationIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase, GenerationIntegrationTestsMixin):
# setting framework_dependent_parameters needs to be gated, just like its contents' imports
if is_tf_available():
framework_dependent_parameters = {
"AutoModelForCausalLM": TFAutoModelForCausalLM,
"AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq": TFAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq,
"AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM": TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
"AutoModelForVision2Seq": TFAutoModelForVision2Seq,
"LogitsProcessorList": TFLogitsProcessorList,
"MinLengthLogitsProcessor": TFMinLengthLogitsProcessor,
"create_tensor_fn": tf.convert_to_tensor,
"floats_tensor": floats_tensor,
"return_tensors": "tf",
}
@slow
def test_generate_tf_function_export_fixed_input_length(self):
# TF-only test: tf.saved_model export
test_model = TFAutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-gpt2")
input_length = 2
max_new_tokens = 2
class DummyModel(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
super(DummyModel, self).__init__()
self.model = model
@tf.function(
input_signature=(
tf.TensorSpec((None, input_length), tf.int32, name="input_ids"),
tf.TensorSpec((None, input_length), tf.int32, name="attention_mask"),
),
jit_compile=True,
)
def serving(self, input_ids, attention_mask):
outputs = self.model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
return_dict_in_generate=True,
)
return {"sequences": outputs["sequences"]}
dummy_input_ids = [[2, 0], [102, 103]]
dummy_attention_masks = [[1, 0], [1, 1]]
dummy_model = DummyModel(model=test_model)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
tf.saved_model.save(dummy_model, tmp_dir, signatures={"serving_default": dummy_model.serving})
serving_func = tf.saved_model.load(tmp_dir).signatures["serving_default"]
for batch_size in range(1, len(dummy_input_ids) + 1):
inputs = {
"input_ids": tf.constant(dummy_input_ids[:batch_size]),
"attention_mask": tf.constant(dummy_attention_masks[:batch_size]),
}
tf_func_outputs = serving_func(**inputs)["sequences"]
tf_model_outputs = test_model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens)
tf.debugging.assert_equal(tf_func_outputs, tf_model_outputs)
@slow
def test_generate_tf_function_export_fixed_batch_size(self):
# TF-only test: tf.saved_model export
test_model = TFAutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-gpt2")
batch_size = 1
max_new_tokens = 2
class DummyModel(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
super(DummyModel, self).__init__()
self.model = model
@tf.function(
input_signature=(
tf.TensorSpec((batch_size, None), tf.int32, name="input_ids"),
tf.TensorSpec((batch_size, None), tf.int32, name="attention_mask"),
),
jit_compile=True,
)
def serving(self, input_ids, attention_mask):
outputs = self.model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
return_dict_in_generate=True,
)
return {"sequences": outputs["sequences"]}
dummy_input_ids = [[2], [102, 103]]
dummy_attention_masks = [[1], [1, 1]]
dummy_model = DummyModel(model=test_model)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
tf.saved_model.save(dummy_model, tmp_dir, signatures={"serving_default": dummy_model.serving})
serving_func = tf.saved_model.load(tmp_dir).signatures["serving_default"]
for input_row in range(len(dummy_input_ids)):
inputs = {
"input_ids": tf.constant([dummy_input_ids[input_row]]),
"attention_mask": tf.constant([dummy_attention_masks[input_row]]),
}
tf_func_outputs = serving_func(**inputs)["sequences"]
tf_model_outputs = test_model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens)
tf.debugging.assert_equal(tf_func_outputs, tf_model_outputs)
@slow
@require_tensorflow_text
def test_generate_tf_function_export_with_tf_tokenizer(self):
# TF-only test: tf.saved_model export
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
# file needed to load the TF tokenizer
hf_hub_download(repo_id="google/flan-t5-small", filename="spiece.model", local_dir=tmp_dir)
class CompleteSentenceTransformer(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.tokenizer = text.SentencepieceTokenizer(
model=tf.io.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(tmp_dir, "spiece.model"), "rb").read()
)
self.model = TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-t5")
def call(self, inputs, *args, **kwargs):
tokens = self.tokenizer.tokenize(inputs)
input_ids, attention_mask = text.pad_model_inputs(
tokens, max_seq_length=64, pad_value=self.model.config.pad_token_id
)
outputs = self.model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
return self.tokenizer.detokenize(outputs)
complete_model = CompleteSentenceTransformer()
inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=(1,), dtype=tf.string, name="inputs")
outputs = complete_model(inputs)
keras_model = keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
keras_model.save(tmp_dir)
def test_eos_token_id_int_and_list_top_k_top_sampling(self):
# Has PT equivalent: this test relies on random sampling
generation_kwargs = {
"do_sample": True,
"num_beams": 1,
"top_p": 0.7,
"top_k": 10,
"temperature": 0.7,
}
expectation = 14
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-gpt2")
text = """Hello, my dog is cute and"""
tokens = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="tf")
model = TFAutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-gpt2")
eos_token_id = 638
# forces the generation to happen on CPU, to avoid GPU-related quirks
with tf.device(":/CPU:0"):
tf.random.set_seed(0)
generated_tokens = model.generate(**tokens, eos_token_id=eos_token_id, **generation_kwargs)
self.assertTrue(expectation == len(generated_tokens[0]))
eos_token_id = [638, 198]
with tf.device(":/CPU:0"):
tf.random.set_seed(0)
generated_tokens = model.generate(**tokens, eos_token_id=eos_token_id, **generation_kwargs)
self.assertTrue(expectation == len(generated_tokens[0]))
def test_model_kwarg_encoder_signature_filtering(self):
# Has PT equivalent: ample use of framework-specific code
bart_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-bart")
article = """Hugging Face is a technology company based in New York and Paris."""
input_ids = bart_tokenizer(article, return_tensors="tf").input_ids
bart_model = TFBartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-bart")
output = bart_model.generate(input_ids).numpy()
# Let's create a fake model that has a different signature. In particular, this fake model accepts "foo" as an
# argument. Because "foo" is not in the encoder signature and doesn't start with "decoder_", it will be part of
# the encoder kwargs prior to signature filtering, which would lead to an exception. But filtering kicks in and
# saves the day.
class FakeBart(TFBartForConditionalGeneration):
def call(self, input_ids, foo=None, **kwargs):
return super().call(input_ids, **kwargs)
bart_model = FakeBart.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-bart")
fake_output = bart_model.generate(input_ids, foo="bar").numpy()
self.assertTrue(np.array_equal(output, fake_output))
# Encoder signature filtering only kicks in if it doesn't accept wildcard kwargs. The following test will fail
# because it doesn't do signature filtering.
class FakeEncoder(bart_model.model.encoder.__class__):
def call(self, input_ids, **kwargs):
return super().call(input_ids, **kwargs)
fake_encoder = FakeEncoder(bart_model.config, bart_model.model.shared)
bart_model.model.encoder = fake_encoder
# Normal generation still works (the output will be different because the encoder weights are different)
fake_output = bart_model.generate(input_ids).numpy()
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
# FakeEncoder.call() accepts **kwargs -> no filtering -> value error due to unexpected input "foo"
bart_model.generate(input_ids, foo="bar")
|
transformers/tests/generation/test_tf_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/generation/test_tf_utils.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5122
}
| 191 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch Aria model."""
import gc
import unittest
import requests
from transformers import (
AriaConfig,
AriaForConditionalGeneration,
AriaTextConfig,
AutoProcessor,
AutoTokenizer,
is_torch_available,
is_vision_available,
)
from transformers.models.idefics3 import Idefics3VisionConfig
from transformers.testing_utils import (
require_bitsandbytes,
require_torch,
require_vision,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
if is_torch_available():
import torch
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
class AriaVisionText2TextModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
ignore_index=-100,
image_token_index=9,
projector_hidden_act="gelu",
seq_length=7,
vision_feature_select_strategy="default",
vision_feature_layer=-1,
text_config=AriaTextConfig(
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=False,
use_labels=True,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
pad_token_id=1,
hidden_size=32,
intermediate_size=64,
max_position_embeddings=60,
model_type="aria_moe_lm",
moe_intermediate_size=4,
moe_num_experts=4,
moe_topk=2,
num_attention_heads=20,
num_experts_per_tok=3,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_key_value_heads=20,
rope_theta=5000000,
vocab_size=99,
eos_token_id=2,
head_dim=2,
),
is_training=True,
vision_config=Idefics3VisionConfig(
image_size=358,
patch_size=10,
num_channels=3,
is_training=True,
hidden_size=32,
projection_dim=20,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=16,
intermediate_size=10,
dropout=0.1,
attention_dropout=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
),
):
self.parent = parent
self.ignore_index = ignore_index
self.image_token_index = image_token_index
self.projector_hidden_act = projector_hidden_act
self.vision_feature_select_strategy = vision_feature_select_strategy
self.vision_feature_layer = vision_feature_layer
self.text_config = text_config
self.vision_config = vision_config
self.pad_token_id = text_config.pad_token_id
self.eos_token_id = text_config.eos_token_id
self.num_hidden_layers = text_config.num_hidden_layers
self.vocab_size = text_config.vocab_size
self.hidden_size = text_config.hidden_size
self.num_attention_heads = text_config.num_attention_heads
self.is_training = is_training
self.batch_size = 10
self.num_channels = 3
self.image_size = 358
self.num_image_tokens = 128
self.seq_length = seq_length + self.num_image_tokens
def get_config(self):
return AriaConfig(
text_config=self.text_config,
vision_config=self.vision_config,
ignore_index=self.ignore_index,
image_token_index=self.image_token_index,
projector_hidden_act=self.projector_hidden_act,
vision_feature_select_strategy=self.vision_feature_select_strategy,
vision_feature_layer=self.vision_feature_layer,
eos_token_id=self.eos_token_id,
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor(
[
self.batch_size,
self.vision_config.num_channels,
self.vision_config.image_size,
self.vision_config.image_size,
]
)
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values = config_and_inputs
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], config.text_config.vocab_size - 1) + 1
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(1).to(torch_device)
input_ids[input_ids == config.image_token_index] = self.pad_token_id
input_ids[:, : self.num_image_tokens] = config.image_token_index
inputs_dict = {
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
}
return config, inputs_dict
def create_and_check_aria_model_fp16_forward(self, config, input_ids, pixel_values, attention_mask):
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.autocast(device_type="cuda", dtype=torch.float16):
logits = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
pixel_values=pixel_values.to(torch.bfloat16),
return_dict=True,
)["logits"]
self.parent.assertFalse(torch.isnan(logits).any().item())
@require_torch
class AriaForConditionalGenerationModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
"""
Model tester for `AriaForConditionalGeneration`.
"""
all_model_classes = (AriaForConditionalGeneration,) if is_torch_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (AriaForConditionalGeneration,) if is_torch_available() else ()
test_pruning = False
test_head_masking = False
_is_composite = True
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = AriaVisionText2TextModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=AriaConfig, has_text_modality=False)
# overwrite inputs_embeds tests because we need to delete "pixel values" for LVLMs
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["pixel_values"]
wte = model.get_input_embeddings()
inputs["inputs_embeds"] = wte(input_ids)
with torch.no_grad():
model(**inputs)
# overwrite inputs_embeds tests because we need to delete "pixel values" for LVLMs
# while some other models require pixel_values to be present
def test_inputs_embeds_matches_input_ids(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["pixel_values"]
inputs_embeds = model.get_input_embeddings()(input_ids)
with torch.no_grad():
out_ids = model(input_ids=input_ids, **inputs)[0]
out_embeds = model(inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, **inputs)[0]
torch.testing.assert_close(out_embeds, out_ids)
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant_false(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Compile not yet supported because in LLava models")
def test_sdpa_can_compile_dynamic(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Compile not yet supported because in LLava models")
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_on_flash(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Feedforward chunking is not yet supported")
def test_feed_forward_chunking(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Unstable test")
def test_initialization(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Unstable test")
def test_dola_decoding_sample(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Unsupported")
def test_generate_from_inputs_embeds_0_greedy(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Unsupported")
def test_generate_from_inputs_embeds_1_beam_search(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Unsupported")
def test_generate_with_static_cache(self):
pass
@require_torch
class AriaForConditionalGenerationIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("rhymes-ai/Aria")
def tearDown(self):
gc.collect()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test(self):
# Let' s make sure we test the preprocessing to replace what is used
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("rhymes-ai/Aria", load_in_4bit=True)
prompt = "<image>\nUSER: What are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place?\nASSISTANT:"
image_file = "https://aria-vl.github.io/static/images/view.jpg"
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(image_file, stream=True).raw)
inputs = self.processor(images=raw_image, text=prompt, return_tensors="pt")
EXPECTED_INPUT_IDS = torch.tensor([[1, 32000, 28705, 13, 11123, 28747, 1824, 460, 272, 1722,315, 1023, 347, 13831, 925, 684, 739, 315, 3251, 456,1633, 28804, 13, 4816, 8048, 12738, 28747]]) # fmt: skip
self.assertTrue(torch.equal(inputs["input_ids"], EXPECTED_INPUT_IDS))
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = "\nUSER: What are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place?\nASSISTANT: When visiting this place, there are a few things one should be cautious about. Firstly," # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_llama_single(self):
# Let' s make sure we test the preprocessing to replace what is used
model_id = "rhymes-ai/Aria"
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_4bit=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
prompt = "USER: <image>\nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? ASSISTANT:"
image_file = "https://aria-vl.github.io/static/images/view.jpg"
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(image_file, stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, text=prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device, torch.float16)
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=900, do_sample=False)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = "USER: \nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? ASSISTANT: When visiting this place, which is a pier or dock extending over a body of water, there are a few things to be cautious about. First, be aware of the weather conditions, as sudden changes in weather can make the pier unsafe to walk on. Second, be mindful of the water depth and any potential hazards, such as submerged rocks or debris, that could cause accidents or injuries. Additionally, be cautious of the tides and currents, as they can change rapidly and pose a risk to swimmers or those who venture too close to the edge of the pier. Finally, be respectful of the environment and other visitors, and follow any posted rules or guidelines for the area." # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_llama_batched(self):
# Let' s make sure we test the preprocessing to replace what is used
model_id = "rhymes-ai/Aria"
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_4bit=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
prompts = [
"USER: <image>\nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? What should I bring with me? ASSISTANT:",
"USER: <image>\nWhat is this? ASSISTANT:",
]
image1 = Image.open(requests.get("https://aria-vl.github.io/static/images/view.jpg", stream=True).raw)
image2 = Image.open(requests.get("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg", stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(images=[image1, image2], text=prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = ['USER: \nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? What should I bring with me? ASSISTANT: When visiting this place, which is a pier or dock extending over a body of water, you', 'USER: \nWhat is this? ASSISTANT: The image features two cats lying down on a pink couch. One cat is located on'] # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
processor.batch_decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_batch(self):
# Let' s make sure we test the preprocessing to replace what is used
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("rhymes-ai/Aria", load_in_4bit=True)
# The first batch is longer in terms of text, but only has 1 image. The second batch will be padded in text, but the first will be padded because images take more space!.
prompts = [
"USER: <image>\nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? What should I bring with me?\nASSISTANT:",
"USER: <image>\nWhat is this?\nASSISTANT:",
]
image1 = Image.open(requests.get("https://aria-vl.github.io/static/images/view.jpg", stream=True).raw)
image2 = Image.open(requests.get("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg", stream=True).raw)
inputs = self.processor(images=[image1, image2], text=prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = [
'USER: \nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? What should I bring with me?\nASSISTANT: When visiting this place, there are a few things to be cautious about and items to bring.',
'USER: \nWhat is this?\nASSISTANT: Cats'
] # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.batch_decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_llama_batched_regression(self):
# Let' s make sure we test the preprocessing to replace what is used
model_id = "rhymes-ai/Aria"
# Multi-image & multi-prompt (e.g. 3 images and 2 prompts now fails with SDPA, this tests if "eager" works as before)
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_4bit=True, attn_implementation="eager")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id, pad_token="<pad>")
prompts = [
"USER: <image>\nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? What should I bring with me?\nASSISTANT:",
"USER: <image>\nWhat is this?\nASSISTANT: Two cats lying on a bed!\nUSER: <image>\nAnd this?\nASSISTANT:",
]
image1 = Image.open(requests.get("https://aria-vl.github.io/static/images/view.jpg", stream=True).raw)
image2 = Image.open(requests.get("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg", stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(images=[image1, image2, image1], text=prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = ['USER: \nWhat are the things I should be cautious about when I visit this place? What should I bring with me?\nASSISTANT: When visiting this place, which appears to be a dock or pier extending over a body of water', 'USER: \nWhat is this?\nASSISTANT: Two cats lying on a bed!\nUSER: \nAnd this?\nASSISTANT: A cat sleeping on a bed.'] # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
processor.batch_decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_torch
@require_vision
def test_batched_generation(self):
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("rhymes-ai/Aria", load_in_4bit=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("rhymes-ai/Aria")
prompt1 = "<image>\n<image>\nUSER: What's the the difference of two images?\nASSISTANT:"
prompt2 = "<image>\nUSER: Describe the image.\nASSISTANT:"
prompt3 = "<image>\nUSER: Describe the image.\nASSISTANT:"
url1 = "https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1552053831-71594a27632d?q=80&w=3062&auto=format&fit=crop&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&ixid=M3wxMjA3fDB8MHxwaG90by1wYWdlfHx8fGVufDB8fHx8fA%3D%3D"
url2 = "https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1617258683320-61900b281ced?q=80&w=3087&auto=format&fit=crop&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&ixid=M3wxMjA3fDB8MHxwaG90by1wYWdlfHx8fGVufDB8fHx8fA%3D%3D"
image1 = Image.open(requests.get(url1, stream=True).raw)
image2 = Image.open(requests.get(url2, stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(
images=[image1, image2, image1, image2],
text=[prompt1, prompt2, prompt3],
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True,
).to(torch_device)
model = model.eval()
EXPECTED_OUTPUT = [
"\n \nUSER: What's the the difference of two images?\nASSISTANT: The difference between the two images is that one shows a dog standing on a grassy field, while",
"\nUSER: Describe the image.\nASSISTANT: The image features a brown and white dog sitting on a sidewalk. The dog is holding a small",
"\nUSER: Describe the image.\nASSISTANT: The image features a lone llama standing on a grassy hill. The llama is the",
]
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
outputs = processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)
self.assertEqual(outputs, EXPECTED_OUTPUT)
def test_tokenizer_integration(self):
model_id = "rhymes-ai/Aria"
slow_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_id, bos_token="<|startoftext|>", eos_token="<|endoftext|>", use_fast=False
)
slow_tokenizer.add_tokens("<image>", True)
fast_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_id,
bos_token="<|startoftext|>",
eos_token="<|endoftext|>",
from_slow=True,
legacy=False,
)
fast_tokenizer.add_tokens("<image>", True)
prompt = "<|startoftext|><|im_start|>system\nAnswer the questions.<|im_end|><|im_start|>user\n<image>\nWhat is shown in this image?<|im_end|>"
EXPECTED_OUTPUT = ['<|startoftext|>', '<', '|', 'im', '_', 'start', '|', '>', 'system', '\n', 'Answer', '▁the', '▁questions', '.<', '|', 'im', '_', 'end', '|', '><', '|', 'im', '_', 'start', '|', '>', 'user', '\n', '<image>', '\n', 'What', '▁is', '▁shown', '▁in', '▁this', '▁image', '?', '<', '|', 'im', '_', 'end', '|', '>'] # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(slow_tokenizer.tokenize(prompt), EXPECTED_OUTPUT)
self.assertEqual(fast_tokenizer.tokenize(prompt), EXPECTED_OUTPUT)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_generation_no_images(self):
model_id = "rhymes-ai/Aria"
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_4bit=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
# Prepare inputs with no images
inputs = processor(text="Hello, I am", return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device)
# Make sure that `generate` works
_ = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
|
transformers/tests/models/aria/test_modeling_aria.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/aria/test_modeling_aria.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 9358
}
| 192 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch Autoformer model."""
import inspect
import tempfile
import unittest
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from transformers import is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import is_flaky, require_torch, slow, torch_device
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
TOLERANCE = 1e-4
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import AutoformerConfig, AutoformerForPrediction, AutoformerModel
from transformers.models.autoformer.modeling_autoformer import AutoformerDecoder, AutoformerEncoder
@require_torch
class AutoformerModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
d_model=16,
batch_size=13,
prediction_length=7,
context_length=14,
label_length=10,
cardinality=19,
embedding_dimension=5,
num_time_features=4,
is_training=True,
hidden_size=16,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=4,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
lags_sequence=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
moving_average=25,
autocorrelation_factor=5,
):
self.d_model = d_model
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.prediction_length = prediction_length
self.context_length = context_length
self.cardinality = cardinality
self.num_time_features = num_time_features
self.lags_sequence = lags_sequence
self.embedding_dimension = embedding_dimension
self.is_training = is_training
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.encoder_seq_length = context_length
self.decoder_seq_length = prediction_length + label_length
self.label_length = label_length
self.moving_average = moving_average
self.autocorrelation_factor = autocorrelation_factor
def get_config(self):
return AutoformerConfig(
d_model=self.d_model,
encoder_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
decoder_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
encoder_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
decoder_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
encoder_ffn_dim=self.intermediate_size,
decoder_ffn_dim=self.intermediate_size,
dropout=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_dropout=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
prediction_length=self.prediction_length,
context_length=self.context_length,
label_length=self.label_length,
lags_sequence=self.lags_sequence,
num_time_features=self.num_time_features,
num_static_categorical_features=1,
cardinality=[self.cardinality],
embedding_dimension=[self.embedding_dimension],
moving_average=self.moving_average,
scaling="std", # we need std to get non-zero `loc`
)
def prepare_autoformer_inputs_dict(self, config):
_past_length = config.context_length + max(config.lags_sequence)
static_categorical_features = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, 1], config.cardinality[0])
past_time_features = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, _past_length, config.num_time_features])
past_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, _past_length])
past_observed_mask = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, _past_length]) > 0.5
# decoder inputs
future_time_features = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, config.prediction_length, config.num_time_features])
future_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, config.prediction_length])
inputs_dict = {
"past_values": past_values,
"static_categorical_features": static_categorical_features,
"past_time_features": past_time_features,
"past_observed_mask": past_observed_mask,
"future_time_features": future_time_features,
"future_values": future_values,
}
return inputs_dict
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
config = self.get_config()
inputs_dict = self.prepare_autoformer_inputs_dict(config)
return config, inputs_dict
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
return config, inputs_dict
def check_encoder_decoder_model_standalone(self, config, inputs_dict):
model = AutoformerModel(config=config).to(torch_device).eval()
outputs = model(**inputs_dict)
encoder_last_hidden_state = outputs.encoder_last_hidden_state
last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
encoder = model.get_encoder()
encoder.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
encoder = AutoformerEncoder.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
transformer_inputs, feature, _, _, _ = model.create_network_inputs(**inputs_dict)
seasonal_input, trend_input = model.decomposition_layer(transformer_inputs[:, : config.context_length, ...])
enc_input = torch.cat(
(transformer_inputs[:, : config.context_length, ...], feature[:, : config.context_length, ...]),
dim=-1,
)
encoder_last_hidden_state_2 = encoder(inputs_embeds=enc_input)[0]
self.parent.assertTrue((encoder_last_hidden_state_2 - encoder_last_hidden_state).abs().max().item() < 1e-3)
mean = (
torch.mean(transformer_inputs[:, : config.context_length, ...], dim=1)
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, config.prediction_length, 1)
)
zeros = torch.zeros(
[transformer_inputs.shape[0], config.prediction_length, transformer_inputs.shape[2]],
device=enc_input.device,
)
dec_input = torch.cat(
(
torch.cat((seasonal_input[:, -config.label_length :, ...], zeros), dim=1),
feature[:, config.context_length - config.label_length :, ...],
),
dim=-1,
)
trend_init = torch.cat(
(
torch.cat((trend_input[:, -config.label_length :, ...], mean), dim=1),
feature[:, config.context_length - config.label_length :, ...],
),
dim=-1,
)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
decoder = model.get_decoder()
decoder.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
decoder = AutoformerDecoder.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
last_hidden_state_2 = decoder(
trend=trend_init,
inputs_embeds=dec_input,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_last_hidden_state,
)[0]
self.parent.assertTrue((last_hidden_state_2 - last_hidden_state).abs().max().item() < 1e-3)
@require_torch
class AutoformerModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (AutoformerModel, AutoformerForPrediction) if is_torch_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (AutoformerForPrediction,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = {"feature-extraction": AutoformerModel} if is_torch_available() else {}
test_pruning = False
test_head_masking = False
test_missing_keys = False
test_torchscript = False
test_inputs_embeds = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = AutoformerModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=AutoformerConfig, has_text_modality=False)
# TODO: (ydshieh) Fix the wrong logic for `tmp_delay` is possible
@unittest.skip(
reason="The computation of `tmp_delay` in `AutoformerAttention.forward` seems wrong, see PR #12345. Also `topk` is used to compute indices which is not stable."
)
def test_batching_equivalence(self):
super().test_batching_equivalence()
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_save_load_strict(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model2, info = model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, output_loading_info=True)
self.assertEqual(info["missing_keys"], [])
def test_encoder_decoder_model_standalone(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
self.model_tester.check_encoder_decoder_model_standalone(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip(reason="Model has no tokens embeddings")
def test_resize_tokens_embeddings(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant_false(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
pass
# # Input is 'static_categorical_features' not 'input_ids'
def test_model_main_input_name(self):
model_signature = inspect.signature(getattr(AutoformerModel, "forward"))
# The main input is the name of the argument after `self`
observed_main_input_name = list(model_signature.parameters.keys())[1]
self.assertEqual(AutoformerModel.main_input_name, observed_main_input_name)
def test_forward_signature(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
signature = inspect.signature(model.forward)
# signature.parameters is an OrderedDict => so arg_names order is deterministic
arg_names = [*signature.parameters.keys()]
expected_arg_names = [
"past_values",
"past_time_features",
"past_observed_mask",
"static_categorical_features",
"static_real_features",
"future_values",
"future_time_features",
]
if model.__class__.__name__ in ["AutoformerForPrediction"]:
expected_arg_names.append("future_observed_mask")
expected_arg_names.extend(
[
"decoder_attention_mask",
"head_mask",
"decoder_head_mask",
"cross_attn_head_mask",
"encoder_outputs",
"past_key_values",
"output_hidden_states",
"output_attentions",
"use_cache",
"return_dict",
]
)
self.assertListEqual(arg_names[: len(expected_arg_names)], expected_arg_names)
def test_attention_outputs(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.return_dict = True
seq_len = getattr(self.model_tester, "seq_length", None)
decoder_seq_length = getattr(self.model_tester, "decoder_seq_length", seq_len)
encoder_seq_length = getattr(self.model_tester, "encoder_seq_length", seq_len)
d_model = getattr(self.model_tester, "d_model", None)
num_attention_heads = getattr(self.model_tester, "num_attention_heads", None)
dim = d_model // num_attention_heads
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
inputs_dict["output_attentions"] = True
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = False
config.return_dict = True
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
attentions = outputs.encoder_attentions if config.is_encoder_decoder else outputs.attentions
self.assertEqual(len(attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
# check that output_attentions also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_attentions"]
config.output_attentions = True
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
attentions = outputs.encoder_attentions
self.assertEqual(len(attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
self.assertListEqual(
list(attentions[0].shape[-3:]),
[self.model_tester.num_attention_heads, encoder_seq_length, dim],
)
out_len = len(outputs)
correct_outlen = 7
if "last_hidden_state" in outputs:
correct_outlen += 1
if "trend" in outputs:
correct_outlen += 1
if "past_key_values" in outputs:
correct_outlen += 1 # past_key_values have been returned
if "loss" in outputs:
correct_outlen += 1
if "params" in outputs:
correct_outlen += 1
self.assertEqual(out_len, correct_outlen)
# decoder attentions
decoder_attentions = outputs.decoder_attentions
self.assertIsInstance(decoder_attentions, (list, tuple))
self.assertEqual(len(decoder_attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
self.assertListEqual(
list(decoder_attentions[0].shape[-3:]),
[self.model_tester.num_attention_heads, decoder_seq_length, dim],
)
# cross attentions
cross_attentions = outputs.cross_attentions
self.assertIsInstance(cross_attentions, (list, tuple))
self.assertEqual(len(cross_attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
self.assertListEqual(
list(cross_attentions[0].shape[-3:]),
[self.model_tester.num_attention_heads, decoder_seq_length, dim],
)
# Check attention is always last and order is fine
inputs_dict["output_attentions"] = True
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = True
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
self.assertEqual(out_len + 2, len(outputs))
self_attentions = outputs.encoder_attentions if config.is_encoder_decoder else outputs.attentions
self.assertEqual(len(self_attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
self.assertListEqual(
list(self_attentions[0].shape[-3:]),
[self.model_tester.num_attention_heads, encoder_seq_length, dim],
)
@is_flaky()
def test_retain_grad_hidden_states_attentions(self):
super().test_retain_grad_hidden_states_attentions()
@unittest.skip(reason="Model does not have input embeddings")
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
pass
def prepare_batch(filename="train-batch.pt"):
file = hf_hub_download(repo_id="hf-internal-testing/tourism-monthly-batch", filename=filename, repo_type="dataset")
batch = torch.load(file, map_location=torch_device)
return batch
@require_torch
@slow
class AutoformerModelIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
def test_inference_no_head(self):
model = AutoformerModel.from_pretrained("huggingface/autoformer-tourism-monthly").to(torch_device)
batch = prepare_batch()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(
past_values=batch["past_values"],
past_time_features=batch["past_time_features"],
past_observed_mask=batch["past_observed_mask"],
static_categorical_features=batch["static_categorical_features"],
future_values=batch["future_values"],
future_time_features=batch["future_time_features"],
)[0]
expected_shape = torch.Size(
(64, model.config.prediction_length + model.config.label_length, model.config.feature_size)
)
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor(
[[0.3593, -1.3398, 0.6330], [0.2279, 1.5396, -0.1792], [0.0450, 1.3225, -0.2335]], device=torch_device
)
torch.testing.assert_close(output[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=TOLERANCE, atol=TOLERANCE)
def test_inference_head(self):
model = AutoformerForPrediction.from_pretrained("huggingface/autoformer-tourism-monthly").to(torch_device)
batch = prepare_batch("val-batch.pt")
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(
past_values=batch["past_values"],
past_time_features=batch["past_time_features"],
past_observed_mask=batch["past_observed_mask"],
static_categorical_features=batch["static_categorical_features"],
).encoder_last_hidden_state
expected_shape = torch.Size((64, model.config.context_length, model.config.d_model))
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor(
[[-0.0734, -0.9036, 0.8358], [4.7186, 2.4113, 1.9581], [1.7953, 2.3558, 1.2970]], device=torch_device
)
torch.testing.assert_close(output[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=TOLERANCE, atol=TOLERANCE)
def test_seq_to_seq_generation(self):
model = AutoformerForPrediction.from_pretrained("huggingface/autoformer-tourism-monthly").to(torch_device)
batch = prepare_batch("val-batch.pt")
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(
static_categorical_features=batch["static_categorical_features"],
past_time_features=batch["past_time_features"],
past_values=batch["past_values"],
future_time_features=batch["future_time_features"],
past_observed_mask=batch["past_observed_mask"],
)
expected_shape = torch.Size((64, model.config.num_parallel_samples, model.config.prediction_length))
self.assertEqual(outputs.sequences.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor([3130.6763, 4056.5293, 7053.0786], device=torch_device)
mean_prediction = outputs.sequences.mean(dim=1)
torch.testing.assert_close(mean_prediction[0, -3:], expected_slice, rtol=1e-1)
|
transformers/tests/models/autoformer/test_modeling_autoformer.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/autoformer/test_modeling_autoformer.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 9019
}
| 193 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2021 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, require_vision
from transformers.utils import is_torch_available, is_vision_available
from ...test_image_processing_common import ImageProcessingTestMixin, prepare_image_inputs
if is_torch_available():
import torch
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import BeitImageProcessor
class BeitImageProcessingTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=7,
num_channels=3,
image_size=18,
min_resolution=30,
max_resolution=400,
do_resize=True,
size=None,
do_center_crop=True,
crop_size=None,
do_normalize=True,
image_mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
image_std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
do_reduce_labels=False,
):
size = size if size is not None else {"height": 20, "width": 20}
crop_size = crop_size if crop_size is not None else {"height": 18, "width": 18}
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.image_size = image_size
self.min_resolution = min_resolution
self.max_resolution = max_resolution
self.do_resize = do_resize
self.size = size
self.do_center_crop = do_center_crop
self.crop_size = crop_size
self.do_normalize = do_normalize
self.image_mean = image_mean
self.image_std = image_std
self.do_reduce_labels = do_reduce_labels
def prepare_image_processor_dict(self):
return {
"do_resize": self.do_resize,
"size": self.size,
"do_center_crop": self.do_center_crop,
"crop_size": self.crop_size,
"do_normalize": self.do_normalize,
"image_mean": self.image_mean,
"image_std": self.image_std,
"do_reduce_labels": self.do_reduce_labels,
}
def expected_output_image_shape(self, images):
return self.num_channels, self.crop_size["height"], self.crop_size["width"]
def prepare_image_inputs(self, equal_resolution=False, numpify=False, torchify=False):
return prepare_image_inputs(
batch_size=self.batch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
min_resolution=self.min_resolution,
max_resolution=self.max_resolution,
equal_resolution=equal_resolution,
numpify=numpify,
torchify=torchify,
)
def prepare_semantic_single_inputs():
dataset = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/fixtures_ade20k", split="test", trust_remote_code=True)
image = Image.open(dataset[0]["file"])
map = Image.open(dataset[1]["file"])
return image, map
def prepare_semantic_batch_inputs():
ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/fixtures_ade20k", split="test", trust_remote_code=True)
image1 = Image.open(ds[0]["file"])
map1 = Image.open(ds[1]["file"])
image2 = Image.open(ds[2]["file"])
map2 = Image.open(ds[3]["file"])
return [image1, image2], [map1, map2]
@require_torch
@require_vision
class BeitImageProcessingTest(ImageProcessingTestMixin, unittest.TestCase):
image_processing_class = BeitImageProcessor if is_vision_available() else None
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
self.image_processor_tester = BeitImageProcessingTester(self)
@property
def image_processor_dict(self):
return self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_processor_dict()
def test_image_processor_properties(self):
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_resize"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "size"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_center_crop"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "center_crop"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_normalize"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "image_mean"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "image_std"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_reduce_labels"))
def test_image_processor_from_dict_with_kwargs(self):
image_processor = self.image_processing_class.from_dict(self.image_processor_dict)
self.assertEqual(image_processor.size, {"height": 20, "width": 20})
self.assertEqual(image_processor.crop_size, {"height": 18, "width": 18})
self.assertEqual(image_processor.do_reduce_labels, False)
image_processor = self.image_processing_class.from_dict(
self.image_processor_dict, size=42, crop_size=84, do_reduce_labels=True
)
self.assertEqual(image_processor.size, {"height": 42, "width": 42})
self.assertEqual(image_processor.crop_size, {"height": 84, "width": 84})
self.assertEqual(image_processor.do_reduce_labels, True)
def test_call_segmentation_maps(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random PyTorch tensors
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=False, torchify=True)
maps = []
for image in image_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(image, torch.Tensor)
maps.append(torch.zeros(image.shape[-2:]).long())
# Test not batched input
encoding = image_processing(image_inputs[0], maps[0], return_tensors="pt")
self.assertEqual(
encoding["pixel_values"].shape,
(
1,
self.image_processor_tester.num_channels,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(
encoding["labels"].shape,
(
1,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(encoding["labels"].dtype, torch.long)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].min().item() >= 0)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].max().item() <= 255)
# Test batched
encoding = image_processing(image_inputs, maps, return_tensors="pt")
self.assertEqual(
encoding["pixel_values"].shape,
(
self.image_processor_tester.batch_size,
self.image_processor_tester.num_channels,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(
encoding["labels"].shape,
(
self.image_processor_tester.batch_size,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(encoding["labels"].dtype, torch.long)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].min().item() >= 0)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].max().item() <= 255)
# Test not batched input (PIL images)
image, segmentation_map = prepare_semantic_single_inputs()
encoding = image_processing(image, segmentation_map, return_tensors="pt")
self.assertEqual(
encoding["pixel_values"].shape,
(
1,
self.image_processor_tester.num_channels,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(
encoding["labels"].shape,
(
1,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(encoding["labels"].dtype, torch.long)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].min().item() >= 0)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].max().item() <= 255)
# Test batched input (PIL images)
images, segmentation_maps = prepare_semantic_batch_inputs()
encoding = image_processing(images, segmentation_maps, return_tensors="pt")
self.assertEqual(
encoding["pixel_values"].shape,
(
2,
self.image_processor_tester.num_channels,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(
encoding["labels"].shape,
(
2,
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.crop_size["width"],
),
)
self.assertEqual(encoding["labels"].dtype, torch.long)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].min().item() >= 0)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].max().item() <= 255)
def test_reduce_labels(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# ADE20k has 150 classes, and the background is included, so labels should be between 0 and 150
image, map = prepare_semantic_single_inputs()
encoding = image_processing(image, map, return_tensors="pt")
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].min().item() >= 0)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].max().item() <= 150)
image_processing.do_reduce_labels = True
encoding = image_processing(image, map, return_tensors="pt")
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].min().item() >= 0)
self.assertTrue(encoding["labels"].max().item() <= 255)
def test_removed_deprecated_kwargs(self):
image_processor_dict = dict(self.image_processor_dict)
image_processor_dict.pop("do_reduce_labels", None)
image_processor_dict["reduce_labels"] = True
# test we are able to create the image processor with the deprecated kwargs
image_processor = self.image_processing_class(**image_processor_dict)
self.assertEqual(image_processor.do_reduce_labels, True)
# test we still support reduce_labels with config
image_processor = self.image_processing_class.from_dict(image_processor_dict)
self.assertEqual(image_processor.do_reduce_labels, True)
|
transformers/tests/models/beit/test_image_processing_beit.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/beit/test_image_processing_beit.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4924
}
| 194 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
import math
import unittest
from transformers import BloomConfig, is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, require_torch_accelerator, slow, torch_device
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
BloomForCausalLM,
BloomForQuestionAnswering,
BloomForSequenceClassification,
BloomForTokenClassification,
BloomModel,
BloomTokenizerFast,
)
@require_torch
class BloomModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=14,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_token_type_ids=False,
use_input_mask=True,
use_labels=True,
use_mc_token_ids=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.use_mc_token_ids = use_mc_token_ids
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_dropout_prob = attention_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.scope = None
self.bos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.eos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.pad_token_id = vocab_size - 1
def get_large_model_config(self):
return BloomConfig.from_pretrained("bigscience/bloom")
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self, gradient_checkpointing=False):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
sequence_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
config = self.get_config(gradient_checkpointing=gradient_checkpointing)
return (config, input_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels)
def get_config(self, gradient_checkpointing=False, slow_but_exact=True):
return BloomConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
seq_length=self.seq_length,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
n_layer=self.num_hidden_layers,
n_head=self.num_attention_heads,
hidden_dropout=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout_prob,
n_positions=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
use_cache=True,
bos_token_id=self.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=self.eos_token_id,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
num_labels=self.num_labels,
gradient_checkpointing=gradient_checkpointing,
slow_but_exact=slow_but_exact,
dtype="float32",
)
def create_and_check_bloom_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.past_key_values), config.n_layer)
def create_and_check_bloom_model_past(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask=torch.ones_like(input_ids), use_cache=True)
outputs_use_cache_conf = model(input_ids, attention_mask=torch.ones_like(input_ids))
outputs_no_past = model(input_ids, use_cache=False, attention_mask=torch.ones_like(input_ids))
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_use_cache_conf))
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_no_past) + 1)
past = outputs["past_key_values"]
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
# append to next input_ids and token_type_ids
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, past_key_values=past)["last_hidden_state"]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_bloom_model_attention_mask_past(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# create attention mask
attn_mask = torch.ones(input_ids.shape, dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)
half_seq_length = self.seq_length // 2
attn_mask[:, half_seq_length:] = 0
# first forward pass
output, past = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask).to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
# change a random masked slice from input_ids
random_seq_idx_to_change = ids_tensor((1,), half_seq_length).item() + 1
random_other_next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size).squeeze(-1)
input_ids[:, -random_seq_idx_to_change] = random_other_next_tokens
# append to next input_ids and attn_mask
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
attn_mask = torch.cat(
[attn_mask, torch.ones((attn_mask.shape[0], 1), dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)],
dim=1,
)
# get two different outputs
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, past_key_values=past, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_bloom_model_past_large_inputs(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, use_cache=True)
output, past = outputs.to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and token_type_ids
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, attention_mask=next_attention_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, attention_mask=next_attention_mask, past_key_values=past)[
"last_hidden_state"
]
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_lm_head_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomForCausalLM(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, labels=input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.loss.shape, ())
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_sequence_classification_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = BloomForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_token_classification_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomForTokenClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_question_answering_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args):
model = BloomForQuestionAnswering(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_forward_and_backwards(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, *args, gradient_checkpointing=False
):
model = BloomForCausalLM(config)
model.to(torch_device)
if gradient_checkpointing:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
result = model(input_ids, labels=input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.loss.shape, ())
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
result.loss.backward()
def create_and_check_bloom_weight_initialization(self, config, *args):
model = BloomModel(config)
model_std = model.config.initializer_range / math.sqrt(2 * model.config.n_layer)
for key in model.state_dict().keys():
if "c_proj" in key and "weight" in key:
self.parent.assertLessEqual(abs(torch.std(model.state_dict()[key]) - model_std), 0.001)
self.parent.assertLessEqual(abs(torch.mean(model.state_dict()[key]) - 0.0), 0.01)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, input_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class BloomModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
BloomModel,
BloomForCausalLM,
BloomForSequenceClassification,
BloomForTokenClassification,
BloomForQuestionAnswering,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
all_generative_model_classes = (BloomForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": BloomModel,
"question-answering": BloomForQuestionAnswering,
"text-classification": BloomForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": BloomForCausalLM,
"token-classification": BloomForTokenClassification,
"zero-shot": BloomForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
fx_compatible = True
test_missing_keys = False
test_pruning = False
test_torchscript = True # torch.autograd functions seems not to be supported
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = BloomModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=BloomConfig, n_embd=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_bloom_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_bloom_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_model_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_bloom_model_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_model_att_mask_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_bloom_model_attention_mask_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_model_past_large_inputs(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_bloom_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_lm_head_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_lm_head_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_sequence_classification_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_sequence_classification_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_token_classification_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_token_classification_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_bloom_gradient_checkpointing(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_forward_and_backwards(*config_and_inputs, gradient_checkpointing=True)
def test_bloom_weight_initialization(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_bloom_weight_initialization(*config_and_inputs)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "bigscience/bigscience-small-testing"
model = BloomModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
def test_simple_generation(self):
# This test is a bit flaky. For some GPU architectures, pytorch sets by default allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = True and some operations
# do not give the same results under this configuration, especially torch.baddmm and torch.bmm. https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/numerical_accuracy.html#fp16-on-mi200
# As we leave the default value (True) for allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction , the tests failed when running in half-precision with smaller models (560m)
# Please see: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#reduced-precision-reduction-in-fp16-gemms
# This discrepancy is observed only when using small models and seems to be stable for larger models.
# Our conclusion is that these operations are flaky for small inputs but seems to be stable for larger inputs (for the functions `baddmm` and `bmm`), and therefore for larger models.
# Here is a summary of an ablation study of our observations
# EXPECTED_OUTPUT = "I enjoy walking with my cute dog, and I love to watch the kids play. I am a very active person, and I am a very good listener. I am a very good person, and I am a very good person. I am a"
# 560m + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = False + torch.bmm ==> PASS
# 560m + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = False + torch.baddm ==> PASS
# 560m + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = True + torch.baddm ==> PASS
# 560m + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = True + torch.bmm ==> FAIL
# EXPECTED_OUTPUT = "I enjoy walking with my cute dog, but I also enjoy hiking, biking, and swimming. I love to cook and bake. I love to cook and bake. I love to cook and bake. I love to cook and bake. I love"
# >=1b1 + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = True + torch.baddm ==> PASS (for use_cache=True and use_cache=False)
# >=1b1 + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = True + torch.bmm ==> PASS
# >=1b1 + allow_fp16_reduced_precision_reduction = False + torch.bmm ==> PASS
path_560m = "bigscience/bloom-560m"
model = BloomForCausalLM.from_pretrained(path_560m, use_cache=True, revision="gs555750").to(torch_device)
model = model.eval()
tokenizer = BloomTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(path_560m)
input_sentence = "I enjoy walking with my cute dog"
# This output has been obtained using fp32 model on the huggingface DGX workstation - NVIDIA A100 GPU
EXPECTED_OUTPUT = (
"I enjoy walking with my cute dog, and I love to watch the kids play with the kids. I am a very "
"active person, and I enjoy working out, and I am a very active person. I am a very active person, and I"
)
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_sentence, return_tensors="pt")
greedy_output = model.generate(input_ids.to(torch_device), max_length=50)
self.assertEqual(tokenizer.decode(greedy_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True), EXPECTED_OUTPUT)
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
def test_batch_generation(self):
path_560m = "bigscience/bloom-560m"
model = BloomForCausalLM.from_pretrained(path_560m, use_cache=True, revision="gs555750").to(torch_device)
model = model.eval()
tokenizer = BloomTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(path_560m, padding_side="left")
input_sentence = ["I enjoy walking with my cute dog", "I enjoy walking with my cute dog"]
inputs = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(input_sentence, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device)
attention_mask = inputs["attention_mask"]
greedy_output = model.generate(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, max_length=50, do_sample=False)
self.assertEqual(
tokenizer.decode(greedy_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
tokenizer.decode(greedy_output[1], skip_special_tokens=True),
)
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
def test_batch_generation_padd(self):
path_560m = "bigscience/bloom-560m"
model = BloomForCausalLM.from_pretrained(path_560m, use_cache=True, revision="gs555750").to(torch_device)
model = model.eval()
tokenizer = BloomTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(path_560m, padding_side="left")
input_sentence = ["I enjoy walking with my cute dog", "Hello my name is"]
input_sentence_without_pad = "Hello my name is"
input_ids = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(input_sentence, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
input_ids_without_pad = tokenizer.encode(input_sentence_without_pad, return_tensors="pt")
input_ids, attention_mask = input_ids["input_ids"].to(torch_device), input_ids["attention_mask"]
greedy_output = model.generate(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, max_length=50, do_sample=False)
greedy_output_without_pad = model.generate(
input_ids_without_pad.to(torch_device), max_length=50, do_sample=False
)
# test token values
self.assertEqual(greedy_output[-1, 3:].tolist(), greedy_output_without_pad[0, :-3].tolist())
# test reconstructions
self.assertEqual(
tokenizer.decode(greedy_output[-1, 3:], skip_special_tokens=True),
tokenizer.decode(greedy_output_without_pad[0, :-3], skip_special_tokens=True),
)
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
def test_batch_generated_text(self):
path_560m = "bigscience/bloom-560m"
model = BloomForCausalLM.from_pretrained(path_560m, use_cache=True, revision="gs555750").to(torch_device)
model = model.eval()
tokenizer = BloomTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(path_560m, padding_side="left")
input_sentences = [
"Hello what is",
"Running a quick test with the",
]
inputs = tokenizer(input_sentences, return_tensors="pt", padding=True, truncation=True)
generated_ids = model.generate(
inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device), attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"], max_length=20
)
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
# these generations match those of the PyTorch model
EXPECTED_GENERATIONS = [
"Hello what is the best way to get the data from the server? I have tried",
"Running a quick test with the following command:\nsudo apt-get install python3\nsudo apt-get install python2",
]
self.assertListEqual(generated_text, EXPECTED_GENERATIONS)
@unittest.skip("Bloom needs a 2D attention for alibi")
def test_custom_4d_attention_mask(self):
pass
@require_torch
class BloomEmbeddingTest(unittest.TestCase):
"""
The goal here is to compare the embeddings generated by the model trained
using Megatron-LM with the one from the transformers library, with a small GPT2-like model
to ensure that the conversion from Megatron-LM to transformers has been done successfully.
The script compares the logits of the embedding layer and the transformer layers.
WARNING: It is expected that these logits will not have exactly the same statistics when running
the code on CPU or GPU. For more info, please visit:
- https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/76052#issuecomment-1103193548
- https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/reproducibility-issue-between-intel-and-amd-cpus/144779/9
You need to install tokenizers following this readme:
- https://huggingface.co/bigscience-catalogue-data-dev/byte-level-bpe-tokenizer-no-norm-250k-whitespace-and-eos-regex-alpha-v3-dedup-lines-articles
Tokenizer used during training:
- https://huggingface.co/bigscience-catalogue-data-dev/byte-level-bpe-tokenizer-no-norm-250k-whitespace-and-eos-regex-alpha-v3-dedup-lines-articles
# TODO change the script (or just add skip) when building the env with tokenizers 0.12.0
"""
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
self.path_bigscience_model = "bigscience/bigscience-small-testing"
@require_torch
def test_embeddings(self):
# The config in this checkpoint has `bfloat16` as `torch_dtype` -> model in `bfloat16`
model = BloomForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.path_bigscience_model, torch_dtype="auto")
model.eval()
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_MEAN = {
3478: 0.0002307891845703125,
368: -0.000568389892578125,
109586: -0.0003910064697265625,
35433: -0.000194549560546875,
2: 0.0004138946533203125,
77: 0.000659942626953125,
132619: -0.00031280517578125,
2175: 0.000457763671875,
23714: 0.000263214111328125,
73173: -0.000286102294921875,
144252: 0.00052642822265625,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_MIN = {
3478: -0.00921630859375,
368: -0.010009765625,
109586: -0.01031494140625,
35433: -0.01177978515625,
2: -0.0074462890625,
77: -0.00848388671875,
132619: -0.009521484375,
2175: -0.0074462890625,
23714: -0.0145263671875,
73173: -0.007415771484375,
144252: -0.01007080078125,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_MAX = {
3478: 0.0128173828125,
368: 0.01214599609375,
109586: 0.0111083984375,
35433: 0.01019287109375,
2: 0.0157470703125,
77: 0.0174560546875,
132619: 0.0078125,
2175: 0.0113525390625,
23714: 0.0146484375,
73173: 0.01116943359375,
144252: 0.01141357421875,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_SUM = {"value": 0.08203125}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_MEAN = {
132619: -0.00031256675720214844,
3478: 0.00023090839385986328,
368: -0.0005702972412109375,
109586: -0.00039124488830566406,
35433: -0.000194549560546875,
2: 0.0004146099090576172,
2175: 0.0004572868347167969,
23714: 0.00026416778564453125,
73173: -0.0002865791320800781,
144252: 0.0005254745483398438,
77: 0.0006618499755859375,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_MIN = {
3478: -0.00921630859375,
368: -0.010009765625,
109586: -0.01031494140625,
35433: -0.01177978515625,
2: -0.0074462890625,
77: -0.00848388671875,
132619: -0.009521484375,
2175: -0.0074462890625,
23714: -0.0145263671875,
73173: -0.007415771484375,
144252: -0.01007080078125,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_MAX = {
3478: 0.0128173828125,
368: 0.01214599609375,
109586: 0.0111083984375,
35433: 0.01019287109375,
2: 0.0157470703125,
77: 0.0174560546875,
132619: 0.0078125,
2175: 0.0113525390625,
23714: 0.0146484375,
73173: 0.01116943359375,
144252: 0.01141357421875,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_SUM = {"value": 0.0821533203125}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MEAN = {
132619: -0.00031267106533050537,
3478: 0.00023087859153747559,
368: -0.0005701072514057159,
109586: -0.0003911703824996948,
35433: -0.0001944899559020996,
2: 0.0004146844148635864,
2175: 0.00045740045607089996,
23714: 0.0002641640603542328,
73173: -0.0002864748239517212,
144252: 0.0005256589502096176,
77: 0.0006617321632802486,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MIN = {
3478: -0.00921630859375,
368: -0.010009765625,
109586: -0.01031494140625,
35433: -0.01177978515625,
2: -0.0074462890625,
77: -0.00848388671875,
132619: -0.009521484375,
2175: -0.0074462890625,
23714: -0.0145263671875,
73173: -0.007415771484375,
144252: -0.01007080078125,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MAX = {
3478: 0.0128173828125,
368: 0.01214599609375,
109586: 0.0111083984375,
35433: 0.01019287109375,
2: 0.0157470703125,
77: 0.0174560546875,
132619: 0.0078125,
2175: 0.0113525390625,
23714: 0.0146484375,
73173: 0.01116943359375,
144252: 0.01141357421875,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_SUM = {"value": 0.08217757940292358}
TEST_EMBEDDINGS = {
"torch.bfloat16": {
"mean": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_MEAN,
"max": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_MAX,
"min": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_MIN,
"sum": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_BF_16_SUM,
},
"torch.float32": {
"mean": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MEAN,
"max": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MAX,
"min": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MIN,
"sum": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_SUM,
},
"torch.float": {
"mean": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MEAN,
"max": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MAX,
"min": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_MIN,
"sum": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_32_SUM,
},
"torch.float16": {
"mean": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_MEAN,
"max": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_MAX,
"min": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_MIN,
"sum": EMBEDDINGS_DS_BEFORE_LN_F_16_SUM,
},
}
EXAMPLE_IDS = [3478, 368, 109586, 35433, 2, 77, 132619, 3478, 368, 109586, 35433, 2, 2175, 23714, 73173, 144252, 2, 77, 132619, 3478] # fmt: skip
EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN_MEAN = {
3478: -6.580352783203125e-05,
368: 0.0001316070556640625,
109586: -0.00030517578125,
35433: 4.00543212890625e-05,
2: -7.2479248046875e-05,
77: -8.96453857421875e-05,
132619: 0.0001583099365234375,
2175: 2.1219253540039062e-05,
23714: -0.000247955322265625,
73173: -0.00021839141845703125,
144252: -0.0001430511474609375,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN_MIN = {
3478: -1.6953125,
368: -1.6875,
109586: -1.6875,
35433: -2.125,
2: -1.390625,
77: -1.5390625,
132619: -1.875,
2175: -1.4609375,
23714: -2.296875,
73173: -1.3515625,
144252: -1.78125,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN_MAX = {
3478: 2.265625,
368: 2.28125,
109586: 1.953125,
35433: 1.90625,
2: 2.703125,
77: 2.828125,
132619: 1.65625,
2175: 2.015625,
23714: 2.234375,
73173: 2.171875,
144252: 1.828125,
}
EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN = {
"mean": EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN_MEAN,
"min": EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN_MIN,
"max": EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN_MAX,
}
tensor_ids = torch.LongTensor([EXAMPLE_IDS])
with torch.no_grad():
embeddings = model.transformer.word_embeddings(tensor_ids)
embeddings_ln = model.transformer.word_embeddings_layernorm(embeddings) #
# first check the embeddings before LN
output_dict = {"min": {}, "max": {}, "mean": {}, "sum": {"value": embeddings.sum().item()}}
for i, idx in enumerate(EXAMPLE_IDS):
output_dict["min"][idx] = embeddings.min(dim=-1).values[0][i].item()
output_dict["max"][idx] = embeddings.max(dim=-1).values[0][i].item()
output_dict["mean"][idx] = embeddings.mean(dim=-1)[0][i].item()
for key in TEST_EMBEDDINGS[str(model.dtype)].keys():
self.assertDictEqual(TEST_EMBEDDINGS[str(model.dtype)][key], output_dict[key])
output_dict_norm = {"min": {}, "max": {}, "mean": {}}
for i, idx in enumerate(EXAMPLE_IDS):
output_dict_norm["min"][idx] = embeddings_ln.min(dim=-1).values[0][i].item()
output_dict_norm["max"][idx] = embeddings_ln.max(dim=-1).values[0][i].item()
output_dict_norm["mean"][idx] = embeddings_ln.mean(dim=-1)[0][i].item()
# This test does not pass when places = 2
for i, key in enumerate(output_dict_norm.keys()):
for j, idx in enumerate(output_dict[key].keys()):
self.assertAlmostEqual(EMBEDDINGS_DS_AFTER_LN[key][idx], output_dict_norm[key][idx], places=1)
@require_torch
def test_hidden_states_transformers(self):
cuda_available = torch.cuda.is_available()
model = BloomModel.from_pretrained(self.path_bigscience_model, use_cache=False, torch_dtype="auto").to(
torch_device
)
model.eval()
EXAMPLE_IDS = [3478, 368, 109586, 35433, 2, 77, 132619, 3478, 368, 109586, 35433, 2, 2175, 23714, 73173, 144252, 2, 77, 132619, 3478] # fmt: skip
MEAN_VALUE_LAST_LM = -4.3392181396484375e-05
MIN_MAX_DICT = {"min": -2.0625, "max": 2.75}
tensor_ids = torch.LongTensor([EXAMPLE_IDS])
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(tensor_ids.to(torch_device))
output_dict = {
"min": logits.last_hidden_state.min(dim=-1).values[0][0].item(),
"max": logits.last_hidden_state.max(dim=-1).values[0][0].item(),
}
if cuda_available:
self.assertAlmostEqual(MEAN_VALUE_LAST_LM, logits.last_hidden_state.mean().item(), places=4)
else:
self.assertAlmostEqual(MEAN_VALUE_LAST_LM, logits.last_hidden_state.mean().item(), places=3)
self.assertDictEqual(MIN_MAX_DICT, output_dict)
@require_torch
def test_logits(self):
cuda_available = torch.cuda.is_available()
model = BloomForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.path_bigscience_model, use_cache=False, torch_dtype="auto").to(
torch_device
) # load in bf16
model.eval()
EXAMPLE_IDS = [3478, 368, 109586, 35433, 2, 77, 132619, 3478, 368, 109586, 35433, 2, 2175, 23714, 73173, 144252, 2, 77, 132619, 3478] # fmt: skip
MEAN_LOGITS_GPU_1 = -1.823902130126953e-05
MEAN_LOGITS_GPU_2 = 1.9431114196777344e-05
tensor_ids = torch.LongTensor([EXAMPLE_IDS]).to(torch_device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(tensor_ids).logits
output_gpu_1, output_gpu_2 = output.split(125440, dim=-1)
if cuda_available:
self.assertAlmostEqual(output_gpu_1.mean().item(), MEAN_LOGITS_GPU_1, places=6)
self.assertAlmostEqual(output_gpu_2.mean().item(), MEAN_LOGITS_GPU_2, places=6)
else:
self.assertAlmostEqual(output_gpu_1.mean().item(), MEAN_LOGITS_GPU_1, places=6) # 1e-06 precision!!
self.assertAlmostEqual(output_gpu_2.mean().item(), MEAN_LOGITS_GPU_2, places=6)
|
transformers/tests/models/bloom/test_modeling_bloom.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/bloom/test_modeling_bloom.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 16940
}
| 195 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch CLIP model."""
import inspect
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
from typing import Optional, Tuple
import numpy as np
import requests
from parameterized import parameterized
from pytest import mark
import transformers
from transformers import CLIPConfig, CLIPTextConfig, CLIPVisionConfig
from transformers.testing_utils import (
is_flax_available,
is_pt_flax_cross_test,
require_flash_attn,
require_torch,
require_torch_gpu,
require_torch_sdpa,
require_vision,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from transformers.utils import (
is_torch_available,
is_torch_bf16_available_on_device,
is_torch_fp16_available_on_device,
is_torch_sdpa_available,
is_vision_available,
)
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import (
ModelTesterMixin,
_config_zero_init,
floats_tensor,
ids_tensor,
is_flaky,
random_attention_mask,
)
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from torch import nn
from transformers import (
CLIPForImageClassification,
CLIPModel,
CLIPTextModel,
CLIPTextModelWithProjection,
CLIPVisionModel,
CLIPVisionModelWithProjection,
)
if is_torch_sdpa_available():
from torch.nn.attention import SDPBackend, sdpa_kernel
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import CLIPProcessor
if is_flax_available():
import jax.numpy as jnp
from transformers.modeling_flax_pytorch_utils import (
convert_pytorch_state_dict_to_flax,
load_flax_weights_in_pytorch_model,
)
class CLIPVisionModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=12,
image_size=30,
patch_size=2,
num_channels=3,
is_training=True,
hidden_size=32,
projection_dim=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
dropout=0.1,
attention_dropout=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.image_size = image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.is_training = is_training
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.projection_dim = projection_dim
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.dropout = dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.scope = scope
# in ViT, the seq length equals the number of patches + 1 (we add 1 for the [CLS] token)
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.seq_length = num_patches + 1
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size, self.image_size])
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values
def get_config(self):
return CLIPVisionConfig(
image_size=self.image_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
projection_dim=self.projection_dim,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
dropout=self.dropout,
attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, pixel_values):
model = CLIPVisionModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
result = model(pixel_values)
# expected sequence length = num_patches + 1 (we add 1 for the [CLS] token)
image_size = (self.image_size, self.image_size)
patch_size = (self.patch_size, self.patch_size)
num_patches = (image_size[1] // patch_size[1]) * (image_size[0] // patch_size[0])
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, num_patches + 1, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.pooler_output.shape, (self.batch_size, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_model_with_projection(self, config, pixel_values):
model = CLIPVisionModelWithProjection(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
result = model(pixel_values)
# expected sequence length = num_patches + 1 (we add 1 for the [CLS] token)
image_size = (self.image_size, self.image_size)
patch_size = (self.patch_size, self.patch_size)
num_patches = (image_size[1] // patch_size[1]) * (image_size[0] // patch_size[0])
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, num_patches + 1, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.image_embeds.shape, (self.batch_size, self.projection_dim))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
class CLIPModelTesterMixin(ModelTesterMixin):
"""
Subclass of ModelTesterMixin with methods specific to testing CLIP models.
The SDPA equivalence test is overridden here because CLIP models may have test/vision/text+vision inputs,
different output logits, and are not supposed to be used or tested with padding_side="left".
"""
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models(self):
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
model = model_class(config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
# Load the model with SDPA
model_sdpa = model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model_sdpa = model_sdpa.eval().to(torch_device)
# Load model with eager attention
model_eager = model_class.from_pretrained(
tmpdirname,
attn_implementation="eager",
)
model_eager = model_eager.eval().to(torch_device)
# SigLip has one shared cls attr for all models, so we assign both submodels heer
vision_attn = text_attn = "sdpa" if model._supports_sdpa else "eager"
# `None` as it is the requested one which will be assigned to each sub-config
# Sub-model will dispatch to SDPA if it can (checked below that `SDPA` layers are present)
if hasattr(model_sdpa, "vision_model") and hasattr(model_sdpa, "text_model"):
self.assertTrue(model_sdpa.vision_model.config._attn_implementation == vision_attn)
self.assertTrue(model_sdpa.text_model.config._attn_implementation == text_attn)
self.assertTrue(model_eager.vision_model.config._attn_implementation == "eager")
self.assertTrue(model_eager.text_model.config._attn_implementation == "eager")
self.assertTrue(model_sdpa.config._attn_implementation == "sdpa")
self.assertTrue(model_eager.config._attn_implementation == "eager")
for name, submodule in model_eager.named_modules():
class_name = submodule.__class__.__name__
if "SdpaAttention" in class_name or "SdpaSelfAttention" in class_name:
raise ValueError("The eager model should not have SDPA attention layers")
has_sdpa = False
for name, submodule in model_sdpa.named_modules():
class_name = submodule.__class__.__name__
if "SdpaAttention" in class_name or "SdpaSelfAttention" in class_name:
has_sdpa = True
break
if not has_sdpa and model_sdpa.config.model_type != "falcon":
raise ValueError("The SDPA model should have SDPA attention layers")
def test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(
self,
torch_dtype: str,
use_attention_mask_options: Tuple[Optional[str], ...] = (None, "left", "right"),
logit_keys: Tuple[str, ...] = ("logits_per_image", "logits_per_text", "image_embeds", "text_embeds"),
):
if not self.all_model_classes[0]._supports_sdpa:
self.skipTest(f"{self.all_model_classes[0].__name__} does not support SDPA")
if torch_dtype == "float16" and not is_torch_fp16_available_on_device(torch_device):
self.skipTest(f"float16 not supported on {torch_device} (on the specific device currently used)")
if torch_dtype == "bfloat16" and not is_torch_bf16_available_on_device(torch_device):
self.skipTest(
f"bfloat16 not supported on {torch_device} (on the specific device currently used, e.g. Nvidia T4 GPU)"
)
# Convert to torch dtype
dtypes = {
"float16": torch.float16,
"bfloat16": torch.bfloat16,
"float32": torch.float32,
}
torch_dtype = dtypes[torch_dtype]
atols = {
torch.float32: 1e-5,
torch.bfloat16: 3e-2,
torch.float16: 5e-3,
}
rtols = {
torch.float32: 1e-4,
torch.bfloat16: 3e-2,
torch.float16: 5e-3,
}
atol = atols[torch_dtype]
rtol = rtols[torch_dtype]
def get_mean_reldiff(msg, current_case, x, ref, atol, rtol):
return f"{msg} {current_case}: mean relative difference: {((x - ref).abs() / (ref.abs() + 1e-12)).mean():.3e}, torch atol = {atol}, torch rtol = {rtol}"
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
model = model_class(config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
# Load the model with SDPA
model_sdpa = model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, torch_dtype=torch_dtype)
model_sdpa = model_sdpa.eval().to(torch_device)
# Load model with eager attention
model_eager = model_class.from_pretrained(
tmpdirname,
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
attn_implementation="eager",
)
model_eager = model_eager.eval().to(torch_device)
# We use these for loops instead of parameterized.expand just for the interest of avoiding loading/saving the model each time,
# but it would be nicer to have an efficient way to use parameterized.expand
cases = [
(use_mask, output_attentions, sdpa_backend, batch_size)
for use_mask in use_attention_mask_options
for output_attentions in [True, False]
for sdpa_backend in [
[SDPBackend.MATH],
[SDPBackend.FLASH_ATTENTION, SDPBackend.MATH],
[SDPBackend.EFFICIENT_ATTENTION, SDPBackend.MATH],
[SDPBackend.FLASH_ATTENTION, SDPBackend.EFFICIENT_ATTENTION, SDPBackend.MATH],
]
for batch_size in [1, 5]
]
fail_cases = []
for use_mask, output_attentions, sdpa_backend, batch_size in cases:
processed_inputs = inputs_dict.copy()
# convert to torch_dtype
if "pixel_values" in processed_inputs:
processed_inputs["pixel_values"] = processed_inputs["pixel_values"].to(torch_dtype)
# slice for different batch sizes
for key in ["pixel_values", "input_ids", "attention_mask"]:
if key in processed_inputs:
processed_inputs[key] = processed_inputs[key][:batch_size]
# set attention mask with left padding
if not use_mask:
processed_inputs.pop("attention_mask", None)
elif use_mask == "left":
dummy_attention_mask = processed_inputs["attention_mask"]
dummy_attention_mask[:] = 1
dummy_attention_mask[:, :1] = 0
processed_inputs["attention_mask"] = dummy_attention_mask
elif use_mask == "right":
dummy_attention_mask = processed_inputs["attention_mask"]
dummy_attention_mask[:] = 1
dummy_attention_mask[:, -1:] = 0
processed_inputs["attention_mask"] = dummy_attention_mask
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid value for use_mask={use_mask}")
processed_inputs["output_attentions"] = output_attentions
processed_inputs["output_hidden_states"] = True
current_case = f"use_mask={use_mask}, batch_size={batch_size}, sdpa_backend={sdpa_backend}"
prepared_inputs = self._prepare_for_class(processed_inputs, model_class)
with torch.no_grad():
try:
with sdpa_kernel(sdpa_backend):
outputs_eager = model_eager(**prepared_inputs)
outputs_sdpa = model_sdpa(**prepared_inputs)
except Exception as e:
fail_cases.append(f"{current_case}: {e}")
continue
keys = set(logit_keys) & set(outputs_eager.keys())
self.assertTrue(
keys, f"Keys {logit_keys} not found in outputs. Available keys: {outputs_eager.keys()}"
)
for key in keys:
try:
eager_logits = outputs_eager[key]
sdpa_logits = outputs_sdpa[key]
except KeyError:
raise KeyError(f"Key {key} not found in outputs. Available keys: {outputs_eager.keys()}")
if "hidden_state" in key and use_mask == "left":
eager_logits = eager_logits[:, 1:]
sdpa_logits = sdpa_logits[:, 1:]
elif "hidden_state" in key and use_mask == "right":
eager_logits = eager_logits[:, :-1]
sdpa_logits = sdpa_logits[:, :-1]
is_close = torch.allclose(eager_logits, sdpa_logits, atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
if not is_close:
fail_cases.append(get_mean_reldiff(key, current_case, sdpa_logits, eager_logits, atol, rtol))
self.assertTrue(len(fail_cases) == 0, "\n".join(fail_cases))
@require_torch
class CLIPVisionModelTest(CLIPModelTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
"""
Here we also overwrite some of the tests of test_modeling_common.py, as CLIP does not use input_ids, inputs_embeds,
attention_mask and seq_length.
"""
all_model_classes = (CLIPVisionModel, CLIPVisionModelWithProjection) if is_torch_available() else ()
fx_compatible = True
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_head_masking = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = CLIPVisionModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=CLIPVisionConfig, has_text_modality=False, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIP does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
self.assertIsInstance(model.get_input_embeddings(), (nn.Module))
x = model.get_output_embeddings()
self.assertTrue(x is None or isinstance(x, nn.Linear))
def test_forward_signature(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
signature = inspect.signature(model.forward)
# signature.parameters is an OrderedDict => so arg_names order is deterministic
arg_names = [*signature.parameters.keys()]
expected_arg_names = ["pixel_values"]
self.assertListEqual(arg_names[:1], expected_arg_names)
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_with_projection(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model_with_projection(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip
def test_training(self):
pass
@unittest.skip
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant_false(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPVisionModel has no base class and is not available in MODEL_MAPPING")
def test_save_load_fast_init_from_base(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPVisionModel has no base class and is not available in MODEL_MAPPING")
def test_save_load_fast_init_to_base(self):
pass
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32"
model = CLIPVisionModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@slow
def test_model_with_projection_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32"
model = CLIPVisionModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
self.assertTrue(hasattr(model, "visual_projection"))
@parameterized.expand([("float16",), ("bfloat16",), ("float32",)])
@require_torch_sdpa
@slow
@is_flaky()
def test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(self, torch_dtype: str):
super().test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
logit_keys=("last_hidden_state", "pooler_output", "image_embeds"),
use_attention_mask_options=(None,),
)
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models(self):
super().test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models()
class CLIPTextModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=12,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
projection_dim=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
dropout=0.1,
attention_dropout=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
initializer_range=0.02,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.projection_dim = projection_dim
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.dropout = dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
if input_mask is not None:
batch_size, seq_length = input_mask.shape
rnd_start_indices = np.random.randint(1, seq_length - 1, size=(batch_size,))
for batch_idx, start_index in enumerate(rnd_start_indices):
input_mask[batch_idx, :start_index] = 1
input_mask[batch_idx, start_index:] = 0
config = self.get_config()
return config, input_ids, input_mask
def get_config(self):
return CLIPTextConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
projection_dim=self.projection_dim,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
dropout=self.dropout,
attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask):
model = CLIPTextModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.pooler_output.shape, (self.batch_size, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_model_with_projection(self, config, input_ids, input_mask):
model = CLIPTextModelWithProjection(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.text_embeds.shape, (self.batch_size, self.projection_dim))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, input_ids, input_mask = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": input_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class CLIPTextModelTest(CLIPModelTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (CLIPTextModel, CLIPTextModelWithProjection) if is_torch_available() else ()
fx_compatible = True
test_pruning = False
test_head_masking = False
model_split_percents = [0.5, 0.8, 0.9]
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = CLIPTextModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=CLIPTextConfig, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_with_projection(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model_with_projection(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip
def test_training(self):
pass
@unittest.skip
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, check: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/27124"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant_false(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIP does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPTextModel has no base class and is not available in MODEL_MAPPING")
def test_save_load_fast_init_from_base(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPTextModel has no base class and is not available in MODEL_MAPPING")
def test_save_load_fast_init_to_base(self):
pass
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32"
model = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@slow
def test_model_with_projection_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32"
model = CLIPTextModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
self.assertTrue(hasattr(model, "text_projection"))
@parameterized.expand([("float16",), ("bfloat16",), ("float32",)])
@require_torch_sdpa
@slow
@is_flaky()
def test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(self, torch_dtype: str):
super().test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
logit_keys=("last_hidden_state", "pooler_output", "text_embeds"),
use_attention_mask_options=(None, "right"), # "left" is not supported for text model
)
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models(self):
super().test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models()
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_on_flash(self):
self.skipTest(reason="CLIPTextModel has two attention masks: `causal_attention_mask` and `attention_mask`")
class CLIPModelTester:
def __init__(self, parent, text_kwargs=None, vision_kwargs=None, is_training=True):
if text_kwargs is None:
text_kwargs = {}
if vision_kwargs is None:
vision_kwargs = {}
self.parent = parent
self.text_model_tester = CLIPTextModelTester(parent, **text_kwargs)
self.vision_model_tester = CLIPVisionModelTester(parent, **vision_kwargs)
self.batch_size = self.text_model_tester.batch_size # need bs for batching_equivalence test
self.is_training = is_training
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
text_config, input_ids, attention_mask = self.text_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
vision_config, pixel_values = self.vision_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config = self.get_config()
return config, input_ids, attention_mask, pixel_values
def get_config(self):
return CLIPConfig.from_text_vision_configs(
self.text_model_tester.get_config(), self.vision_model_tester.get_config(), projection_dim=64
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, input_ids, attention_mask, pixel_values):
model = CLIPModel(config).to(torch_device).eval()
with torch.no_grad():
result = model(input_ids, pixel_values, attention_mask)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.logits_per_image.shape, (self.vision_model_tester.batch_size, self.text_model_tester.batch_size)
)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.logits_per_text.shape, (self.text_model_tester.batch_size, self.vision_model_tester.batch_size)
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, input_ids, attention_mask, pixel_values = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"return_loss": True,
}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class CLIPModelTest(CLIPModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (CLIPModel,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"feature-extraction": CLIPModel, "image-feature-extraction": CLIPVisionModel} if is_torch_available() else {}
)
fx_compatible = True
test_head_masking = False
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_attention_outputs = False
_is_composite = True
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = CLIPModelTester(self)
common_properties = ["projection_dim", "logit_scale_init_value"]
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(
self, config_class=CLIPConfig, has_text_modality=False, common_properties=common_properties
)
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
@unittest.skip(reason="Hidden_states is tested in individual model tests")
def test_hidden_states_output(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Inputs_embeds is tested in individual model tests")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Retain_grad is tested in individual model tests")
def test_retain_grad_hidden_states_attentions(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPModel does not have input/output embeddings")
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
pass
# override as the `logit_scale` parameter initilization is different for CLIP
def test_initialization(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
configs_no_init = _config_zero_init(config)
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config=configs_no_init)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
# check if `logit_scale` is initilized as per the original implementation
if name == "logit_scale":
self.assertAlmostEqual(
param.data.item(),
np.log(1 / 0.07),
delta=1e-3,
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
else:
self.assertIn(
((param.data.mean() * 1e9).round() / 1e9).item(),
[0.0, 1.0],
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
def _create_and_check_torchscript(self, config, inputs_dict):
if not self.test_torchscript:
self.skipTest(reason="test_torchscript is set to False")
configs_no_init = _config_zero_init(config) # To be sure we have no Nan
configs_no_init.torchscript = True
configs_no_init.return_dict = False
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config=configs_no_init)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
try:
input_ids = inputs_dict["input_ids"]
pixel_values = inputs_dict["pixel_values"] # CLIP needs pixel_values
traced_model = torch.jit.trace(model, (input_ids, pixel_values))
except RuntimeError:
self.fail("Couldn't trace module.")
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir_name:
pt_file_name = os.path.join(tmp_dir_name, "traced_model.pt")
try:
torch.jit.save(traced_model, pt_file_name)
except Exception:
self.fail("Couldn't save module.")
try:
loaded_model = torch.jit.load(pt_file_name)
except Exception:
self.fail("Couldn't load module.")
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
loaded_model.to(torch_device)
loaded_model.eval()
model_state_dict = model.state_dict()
loaded_model_state_dict = loaded_model.state_dict()
non_persistent_buffers = {}
for key in loaded_model_state_dict.keys():
if key not in model_state_dict.keys():
non_persistent_buffers[key] = loaded_model_state_dict[key]
loaded_model_state_dict = {
key: value for key, value in loaded_model_state_dict.items() if key not in non_persistent_buffers
}
self.assertEqual(set(model_state_dict.keys()), set(loaded_model_state_dict.keys()))
model_buffers = list(model.buffers())
for non_persistent_buffer in non_persistent_buffers.values():
found_buffer = False
for i, model_buffer in enumerate(model_buffers):
if torch.equal(non_persistent_buffer, model_buffer):
found_buffer = True
break
self.assertTrue(found_buffer)
model_buffers.pop(i)
models_equal = True
for layer_name, p1 in model_state_dict.items():
p2 = loaded_model_state_dict[layer_name]
if p1.data.ne(p2.data).sum() > 0:
models_equal = False
self.assertTrue(models_equal)
def test_load_vision_text_config(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
# Save CLIPConfig and check if we can load CLIPVisionConfig from it
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir_name:
config.save_pretrained(tmp_dir_name)
vision_config = CLIPVisionConfig.from_pretrained(tmp_dir_name)
self.assertDictEqual(config.vision_config.to_dict(), vision_config.to_dict())
# Save CLIPConfig and check if we can load CLIPTextConfig from it
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir_name:
config.save_pretrained(tmp_dir_name)
text_config = CLIPTextConfig.from_pretrained(tmp_dir_name)
self.assertDictEqual(config.text_config.to_dict(), text_config.to_dict())
# overwrite from common since FlaxCLIPModel returns nested output
# which is not supported in the common test
@is_pt_flax_cross_test
def test_equivalence_pt_to_flax(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
with self.subTest(model_class.__name__):
# load PyTorch class
pt_model = model_class(config).eval()
pt_model.to(torch_device)
# Flax models don't use the `use_cache` option and cache is not returned as a default.
# So we disable `use_cache` here for PyTorch model.
pt_model.config.use_cache = False
fx_model_class_name = "Flax" + model_class.__name__
if not hasattr(transformers, fx_model_class_name):
self.skipTest(reason="No Flax model exists for this class")
fx_model_class = getattr(transformers, fx_model_class_name)
# load Flax class
fx_model = fx_model_class(config, dtype=jnp.float32)
# make sure only flax inputs are forward that actually exist in function args
fx_input_keys = inspect.signature(fx_model.__call__).parameters.keys()
# prepare inputs
pt_inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class)
# remove function args that don't exist in Flax
pt_inputs = {k: v for k, v in pt_inputs.items() if k in fx_input_keys}
fx_state = convert_pytorch_state_dict_to_flax(pt_model.state_dict(), fx_model)
fx_model.params = fx_state
with torch.no_grad():
pt_outputs = pt_model(**pt_inputs).to_tuple()
# convert inputs to Flax
fx_inputs = {k: np.array(v.to("cpu")) for k, v in pt_inputs.items() if torch.is_tensor(v)}
fx_outputs = fx_model(**fx_inputs).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(len(fx_outputs), len(pt_outputs), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch")
for fx_output, pt_output in zip(fx_outputs[:4], pt_outputs[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output, pt_output.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
pt_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
fx_model_loaded = fx_model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, from_pt=True)
fx_outputs_loaded = fx_model_loaded(**fx_inputs).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(
len(fx_outputs_loaded), len(pt_outputs), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch"
)
for fx_output_loaded, pt_output in zip(fx_outputs_loaded[:4], pt_outputs[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output_loaded, pt_output.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
# overwrite from common since FlaxCLIPModel returns nested output
# which is not supported in the common test
@is_pt_flax_cross_test
def test_equivalence_flax_to_pt(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
with self.subTest(model_class.__name__):
# load corresponding PyTorch class
pt_model = model_class(config).eval()
# So we disable `use_cache` here for PyTorch model.
pt_model.config.use_cache = False
fx_model_class_name = "Flax" + model_class.__name__
if not hasattr(transformers, fx_model_class_name):
self.skipTest(reason="No Flax model exists for this class")
fx_model_class = getattr(transformers, fx_model_class_name)
# load Flax class
fx_model = fx_model_class(config, dtype=jnp.float32)
# make sure only flax inputs are forward that actually exist in function args
fx_input_keys = inspect.signature(fx_model.__call__).parameters.keys()
pt_model = load_flax_weights_in_pytorch_model(pt_model, fx_model.params)
pt_model.to(torch_device)
# make sure weights are tied in PyTorch
pt_model.tie_weights()
# prepare inputs
pt_inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class)
# remove function args that don't exist in Flax
pt_inputs = {k: v for k, v in pt_inputs.items() if k in fx_input_keys}
with torch.no_grad():
pt_outputs = pt_model(**pt_inputs).to_tuple()
fx_inputs = {k: np.array(v.to("cpu")) for k, v in pt_inputs.items() if torch.is_tensor(v)}
fx_outputs = fx_model(**fx_inputs).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(len(fx_outputs), len(pt_outputs), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch")
for fx_output, pt_output in zip(fx_outputs[:4], pt_outputs[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output, pt_output.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
fx_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
pt_model_loaded = model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, from_flax=True)
pt_model_loaded.to(torch_device)
with torch.no_grad():
pt_outputs_loaded = pt_model_loaded(**pt_inputs).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(
len(fx_outputs), len(pt_outputs_loaded), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch"
)
for fx_output, pt_output in zip(fx_outputs[:4], pt_outputs_loaded[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output, pt_output.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32"
model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@parameterized.expand([("float16",), ("bfloat16",), ("float32",)])
@require_torch_sdpa
@slow
@is_flaky()
def test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(self, torch_dtype: str):
super().test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
logit_keys=("logits_per_image", "logits_per_text"),
use_attention_mask_options=(None, "right"), # "left" is not supported for text model
)
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models(self):
super().test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models()
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_on_flash(self):
self.skipTest(reason="CLIP text tower has two attention masks: `causal_attention_mask` and `attention_mask`")
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_compile_dynamic(self):
self.skipTest(reason="CLIP model can't be compiled dynamic, error in clip_loss`")
@require_flash_attn
@require_torch_gpu
@mark.flash_attn_test
@slow
def test_flash_attn_2_inference_equivalence(self):
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
if not model_class._supports_flash_attn_2:
self.skipTest(f"{model_class.__name__} does not support Flash Attention 2")
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
model = model_class(config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model_fa = model_class.from_pretrained(
tmpdirname, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"
)
model_fa.to(torch_device)
model = model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
model.to(torch_device)
dummy_pixel_values = inputs_dict["pixel_values"].to(torch.bfloat16)
dummy_input_ids = inputs_dict["input_ids"]
outputs = model(pixel_values=dummy_pixel_values, input_ids=dummy_input_ids, output_hidden_states=True)
outputs_fa = model_fa(
pixel_values=dummy_pixel_values, input_ids=dummy_input_ids, output_hidden_states=True
)
self.assertTrue(
torch.allclose(outputs.logits_per_image, outputs_fa.logits_per_image, atol=4e-2, rtol=4e-2),
f"Image logits max diff: {torch.max(torch.abs(outputs.logits_per_image - outputs_fa.logits_per_image))}",
)
self.assertTrue(
torch.allclose(outputs.logits_per_text, outputs_fa.logits_per_text, atol=4e-2, rtol=4e-2),
f"Text logits max diff: {torch.max(torch.abs(outputs.logits_per_text - outputs_fa.logits_per_text))}",
)
@require_flash_attn
@require_torch_gpu
@mark.flash_attn_test
def test_flash_attn_2_inference_equivalence_right_padding(self):
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
if not model_class._supports_flash_attn_2:
self.skipTest(f"{model_class.__name__} does not support Flash Attention 2")
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
model = model_class(config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model_fa = model_class.from_pretrained(
tmpdirname, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"
)
model_fa.to(torch_device)
model = model_class.from_pretrained(
tmpdirname, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, attn_implementation="eager"
)
model.to(torch_device)
dummy_pixel_values = inputs_dict["pixel_values"].to(torch.bfloat16)
dummy_input_ids = inputs_dict["input_ids"]
dummy_pixel_mask = inputs_dict["attention_mask"]
# right padding
dummy_pixel_mask[:] = 1
dummy_pixel_mask[:, -1:] = 0
outputs = model(pixel_values=dummy_pixel_values, input_ids=dummy_input_ids, output_hidden_states=True)
outputs_fa = model_fa(
pixel_values=dummy_pixel_values, input_ids=dummy_input_ids, output_hidden_states=True
)
logits_per_image_eager = outputs.logits_per_image[:, :-1]
logits_per_text_eager = outputs.logits_per_text[:, :-1]
logits_per_image_sdpa = outputs_fa.logits_per_image[:, :-1]
logits_per_text_sdpa = outputs_fa.logits_per_text[:, :-1]
self.assertTrue(
torch.allclose(logits_per_image_eager, logits_per_image_sdpa, atol=4e-2, rtol=4e-2),
f"Image logits max diff: {torch.max(torch.abs(logits_per_image_eager - logits_per_image_sdpa))}",
)
self.assertTrue(
torch.allclose(logits_per_text_eager, logits_per_text_sdpa, atol=4e-2, rtol=4e-2),
f"Text logits max diff: {torch.max(torch.abs(logits_per_text_eager - logits_per_text_sdpa))}",
)
class CLIPForImageClassificationModelTester(CLIPModelTester):
def __init__(self, parent):
super().__init__(parent)
self.batch_size = self.vision_model_tester.batch_size
self.num_hidden_layers = self.vision_model_tester.num_hidden_layers
self.hidden_size = self.vision_model_tester.hidden_size
self.seq_length = self.vision_model_tester.seq_length
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
_, pixel_values = self.vision_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class CLIPForImageClassificationModelTest(CLIPModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (CLIPForImageClassification,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = {"image-classification": CLIPForImageClassification} if is_torch_available() else {}
fx_compatible = False
test_head_masking = False
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_attention_outputs = False
_is_composite = True
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = CLIPForImageClassificationModelTester(self)
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPForImageClassification does not support inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPForImageClassification does not support inputs_embeds")
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPForImageClassification does not support gradient checkpointing yet")
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPForImageClassification does not support gradient checkpointing yet")
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIPForImageClassification does not support gradient checkpointing yet")
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant_false(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="CLIP uses the same initialization scheme as the Flax original implementation")
def test_initialization(self):
pass
@parameterized.expand([("float16",), ("bfloat16",), ("float32",)])
@require_torch_sdpa
@slow
@is_flaky()
def test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(self, torch_dtype: str):
super().test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference(
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
logit_keys=("logits",),
use_attention_mask_options=(None,),
)
@require_torch_sdpa
def test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models(self):
super().test_sdpa_can_dispatch_composite_models()
# We will verify our results on an image of cute cats
def prepare_img():
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
im = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
return im
@require_vision
@require_torch
class CLIPModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_inference(self):
model_name = "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32"
model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(model_name).to(torch_device)
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
image = prepare_img()
inputs = processor(
text=["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], images=image, padding=True, return_tensors="pt"
).to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
# verify the logits
self.assertEqual(
outputs.logits_per_image.shape,
torch.Size((inputs.pixel_values.shape[0], inputs.input_ids.shape[0])),
)
self.assertEqual(
outputs.logits_per_text.shape,
torch.Size((inputs.input_ids.shape[0], inputs.pixel_values.shape[0])),
)
expected_logits = torch.tensor([[24.5701, 19.3049]], device=torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.logits_per_image, expected_logits, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
@slow
def test_inference_interpolate_pos_encoding(self):
# CLIP models have an `interpolate_pos_encoding` argument in their forward method,
# allowing to interpolate the pre-trained position embeddings in order to use
# the model on higher resolutions. The DINO model by Facebook AI leverages this
# to visualize self-attention on higher resolution images.
model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32").to(torch_device)
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained(
"openai/clip-vit-base-patch32", size={"height": 180, "width": 180}, crop_size={"height": 180, "width": 180}
)
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
inputs = processor(text="what's in the image", images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device)
# interpolate_pos_encodiung false should return value error
with self.assertRaises(ValueError, msg="doesn't match model"):
with torch.no_grad():
model(**inputs, interpolate_pos_encoding=False)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs, interpolate_pos_encoding=True)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 26, 768))
self.assertEqual(outputs.vision_model_output.last_hidden_state.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor(
[[-0.1538, 0.0322, -0.3235], [0.2893, 0.1135, -0.5708], [0.0461, 0.1540, -0.6018]]
).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(
outputs.vision_model_output.last_hidden_state[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4
)
|
transformers/tests/models/clip/test_modeling_clip.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/clip/test_modeling_clip.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 24445
}
| 196 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import datetime
import unittest
from transformers import CodeGenConfig, is_torch_available
from transformers.file_utils import cached_property
from transformers.testing_utils import backend_manual_seed, is_flaky, require_torch, slow, torch_device
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, CodeGenForCausalLM, CodeGenModel
class CodeGenModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=14,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_token_type_ids=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_labels=True,
use_mc_token_ids=True,
vocab_size=256,
hidden_size=32,
rotary_dim=4,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.0,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.use_mc_token_ids = use_mc_token_ids
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rotary_dim = rotary_dim
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.scope = None
self.bos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.eos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.pad_token_id = vocab_size - 1
def get_large_model_config(self):
return CodeGenConfig.from_pretrained("Salesforce/codegen-2B-mono")
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
mc_token_ids = None
if self.use_mc_token_ids:
mc_token_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_choices], self.seq_length)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = self.get_config()
head_mask = ids_tensor([self.num_hidden_layers, self.num_attention_heads], 2)
return (
config,
input_ids,
input_mask,
head_mask,
token_type_ids,
mc_token_ids,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
)
def get_config(self):
return CodeGenConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
n_embd=self.hidden_size,
n_layer=self.num_hidden_layers,
n_head=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
n_positions=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
use_cache=True,
bos_token_id=self.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=self.eos_token_id,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
rotary_dim=self.rotary_dim,
)
def create_and_check_codegen_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args):
model = CodeGenModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, head_mask=head_mask)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.past_key_values), config.n_layer)
def create_and_check_codegen_model_past(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args):
model = CodeGenModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, use_cache=True)
outputs_use_cache_conf = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
outputs_no_past = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, use_cache=False)
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_use_cache_conf))
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_no_past) + 1)
output, past = outputs.to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
next_token_types = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, 1], self.type_vocab_size)
# append to next input_ids and token_type_ids
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_token_type_ids = torch.cat([token_type_ids, next_token_types], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, token_type_ids=next_token_type_ids)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, token_type_ids=next_token_types, past_key_values=past)[
"last_hidden_state"
]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_codegen_model_attention_mask_past(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args
):
model = CodeGenModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# create attention mask
attn_mask = torch.ones(input_ids.shape, dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)
half_seq_length = self.seq_length // 2
attn_mask[:, half_seq_length:] = 0
# first forward pass
output, past = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask).to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
# change a random masked slice from input_ids
random_seq_idx_to_change = ids_tensor((1,), half_seq_length).item() + 1
random_other_next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size).squeeze(-1)
input_ids[:, -random_seq_idx_to_change] = random_other_next_tokens
# append to next input_ids and attn_mask
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
attn_mask = torch.cat(
[attn_mask, torch.ones((attn_mask.shape[0], 1), dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)],
dim=1,
)
# get two different outputs
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, past_key_values=past, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_codegen_model_past_large_inputs(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args
):
model = CodeGenModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, use_cache=True)
output, past = outputs.to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_token_types = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, 3], self.type_vocab_size)
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and token_type_ids
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_token_type_ids = torch.cat([token_type_ids, next_token_types], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(
next_input_ids, token_type_ids=next_token_type_ids, attention_mask=next_attention_mask
)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(
next_tokens, token_type_ids=next_token_types, attention_mask=next_attention_mask, past_key_values=past
)["last_hidden_state"]
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_lm_head_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args):
model = CodeGenForCausalLM(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.loss.shape, ())
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_forward_and_backwards(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args, gradient_checkpointing=False
):
model = CodeGenForCausalLM(config)
if gradient_checkpointing:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
model.to(torch_device)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.loss.shape, ())
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
result.loss.backward()
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
input_mask,
head_mask,
token_type_ids,
mc_token_ids,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids, "head_mask": head_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class CodeGenModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (CodeGenModel, CodeGenForCausalLM) if is_torch_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (CodeGenForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"feature-extraction": CodeGenModel, "text-generation": CodeGenForCausalLM} if is_torch_available() else {}
)
fx_compatible = False
test_pruning = False
test_missing_keys = False
test_model_parallel = False
test_head_masking = False
# special case for DoubleHeads model
def _prepare_for_class(self, inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=False):
inputs_dict = super()._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=return_labels)
return inputs_dict
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = CodeGenModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=CodeGenConfig, n_embd=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_codegen_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_codegen_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_codegen_model_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_codegen_model_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_codegen_model_att_mask_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_codegen_model_attention_mask_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_codegen_model_past_large_inputs(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_codegen_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_codegen_lm_head_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_lm_head_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_codegen_gradient_checkpointing(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_forward_and_backwards(*config_and_inputs, gradient_checkpointing=True)
@slow
def test_batch_generation(self):
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Salesforce/codegen-350M-mono")
model = CodeGenForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Salesforce/codegen-350M-mono")
model.to(torch_device)
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
# Define PAD Token = EOS Token = 50256
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
model.config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_id
# use different length sentences to test batching
sentences = ["def hellow_world():", "def greet(name):"]
inputs = tokenizer(sentences, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device)
token_type_ids = torch.cat(
[
input_ids.new_full((input_ids.shape[0], input_ids.shape[1] - 1), 0),
input_ids.new_full((input_ids.shape[0], 1), 500),
],
dim=-1,
)
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"].to(torch_device),
)
outputs_tt = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"].to(torch_device),
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
)
inputs_non_padded = tokenizer(sentences[0], return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_non_padded = model.generate(input_ids=inputs_non_padded)
num_paddings = inputs_non_padded.shape[-1] - inputs["attention_mask"][-1].long().sum().cpu().item()
inputs_padded = tokenizer(sentences[1], return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_padded = model.generate(input_ids=inputs_padded, max_length=model.config.max_length - num_paddings)
batch_out_sentence = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
batch_out_sentence_tt = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs_tt, skip_special_tokens=True)
non_padded_sentence = tokenizer.decode(output_non_padded[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
padded_sentence = tokenizer.decode(output_padded[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
expected_output_sentence = [
'def hellow_world():\n print("Hello World")\n\nhellow_world()',
'def greet(name):\n print(f"Hello {name}")\n\ng',
]
self.assertListEqual(expected_output_sentence, batch_out_sentence)
self.assertTrue(batch_out_sentence_tt != batch_out_sentence) # token_type_ids should change output
self.assertListEqual(expected_output_sentence, [non_padded_sentence, padded_sentence])
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "Salesforce/codegen-350M-nl"
model = CodeGenModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@require_torch
class CodeGenModelLanguageGenerationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@cached_property
def cached_tokenizer(self):
return AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Salesforce/codegen-350M-mono")
@cached_property
def cached_model(self):
return CodeGenForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Salesforce/codegen-350M-mono")
@slow
def test_lm_generate_codegen(self):
tokenizer = self.cached_tokenizer
for checkpointing in [True, False]:
model = self.cached_model
if checkpointing:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
else:
model.gradient_checkpointing_disable()
model.to(torch_device)
inputs = tokenizer("def hello_world():", return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device)
expected_output = 'def hello_world():\n print("Hello World")\n\nhello_world()\n\n'
output_ids = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False)
output_str = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_ids)[0]
self.assertEqual(output_str, expected_output)
@slow
def test_codegen_sample(self):
tokenizer = self.cached_tokenizer
model = self.cached_model
model.to(torch_device)
torch.manual_seed(0)
backend_manual_seed(torch_device, 0)
tokenized = tokenizer("def hello_world():", return_tensors="pt", return_token_type_ids=True)
input_ids = tokenized.input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_ids = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True)
output_str = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
token_type_ids = tokenized.token_type_ids.to(torch_device)
output_seq = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, do_sample=True, num_return_sequences=5)
output_seq_tt = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, do_sample=True, num_return_sequences=5
)
output_seq_strs = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_seq, skip_special_tokens=True)
output_seq_tt_strs = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_seq_tt, skip_special_tokens=True)
if torch_device == "cuda":
EXPECTED_OUTPUT_STR = 'def hello_world():\n print("Hello World")\n return True\n\nresult ='
else:
EXPECTED_OUTPUT_STR = "def hello_world():\r\n print('Hello, World.')\r\n\r\n\r"
self.assertEqual(output_str, EXPECTED_OUTPUT_STR)
self.assertTrue(
all(output_seq_strs[idx] != output_seq_tt_strs[idx] for idx in range(len(output_seq_tt_strs)))
) # token_type_ids should change output
@is_flaky(max_attempts=3, description="measure of timing is somehow flaky.")
@slow
def test_codegen_sample_max_time(self):
tokenizer = self.cached_tokenizer
model = self.cached_model
model.to(torch_device)
torch.manual_seed(0)
tokenized = tokenizer("Today is a nice day and", return_tensors="pt", return_token_type_ids=True)
input_ids = tokenized.input_ids.to(torch_device)
MAX_TIME = 0.05
start = datetime.datetime.now()
model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True, max_time=MAX_TIME, max_length=256)
duration = datetime.datetime.now() - start
self.assertGreater(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=MAX_TIME))
self.assertLess(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=2 * MAX_TIME))
start = datetime.datetime.now()
model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=False, max_time=MAX_TIME, max_length=256)
duration = datetime.datetime.now() - start
self.assertGreater(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=MAX_TIME))
self.assertLess(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=2 * MAX_TIME))
start = datetime.datetime.now()
model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=False, num_beams=2, max_time=MAX_TIME, max_length=256)
duration = datetime.datetime.now() - start
self.assertGreater(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=MAX_TIME))
self.assertLess(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=2 * MAX_TIME))
start = datetime.datetime.now()
model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True, num_beams=2, max_time=MAX_TIME, max_length=256)
duration = datetime.datetime.now() - start
self.assertGreater(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=MAX_TIME))
self.assertLess(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=2 * MAX_TIME))
start = datetime.datetime.now()
model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=False, max_time=None, max_length=256)
duration = datetime.datetime.now() - start
self.assertGreater(duration, datetime.timedelta(seconds=2 * MAX_TIME))
|
transformers/tests/models/codegen/test_modeling_codegen.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/codegen/test_modeling_codegen.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 10110
}
| 197 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2019 Hugging Face inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import json
import os
import unittest
from transformers import DebertaTokenizer, DebertaTokenizerFast
from transformers.models.deberta.tokenization_deberta import VOCAB_FILES_NAMES
from transformers.testing_utils import slow
from ...test_tokenization_common import TokenizerTesterMixin
class DebertaTokenizationTest(TokenizerTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
from_pretrained_id = "microsoft/deberta-base"
tokenizer_class = DebertaTokenizer
test_rust_tokenizer = True
rust_tokenizer_class = DebertaTokenizerFast
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
# Adapted from Sennrich et al. 2015 and https://github.com/rsennrich/subword-nmt
vocab = [
"l",
"o",
"w",
"e",
"r",
"s",
"t",
"i",
"d",
"n",
"\u0120",
"\u0120l",
"\u0120n",
"\u0120lo",
"\u0120low",
"er",
"\u0120lowest",
"\u0120newer",
"\u0120wider",
"[UNK]",
]
vocab_tokens = dict(zip(vocab, range(len(vocab))))
merges = ["#version: 0.2", "\u0120 l", "\u0120l o", "\u0120lo w", "e r", ""]
self.special_tokens_map = {"unk_token": "[UNK]"}
self.vocab_file = os.path.join(self.tmpdirname, VOCAB_FILES_NAMES["vocab_file"])
self.merges_file = os.path.join(self.tmpdirname, VOCAB_FILES_NAMES["merges_file"])
with open(self.vocab_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(json.dumps(vocab_tokens) + "\n")
with open(self.merges_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write("\n".join(merges))
def get_tokenizer(self, **kwargs):
kwargs.update(self.special_tokens_map)
return self.tokenizer_class.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, **kwargs)
def get_input_output_texts(self, tokenizer):
input_text = "lower newer"
output_text = "lower newer"
return input_text, output_text
def test_full_tokenizer(self):
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
text = "lower newer"
bpe_tokens = ["l", "o", "w", "er", "\u0120", "n", "e", "w", "er"]
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(text)
self.assertListEqual(tokens, bpe_tokens)
input_tokens = tokens + [tokenizer.unk_token]
input_bpe_tokens = [0, 1, 2, 15, 10, 9, 3, 2, 15, 19]
self.assertListEqual(tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(input_tokens), input_bpe_tokens)
def test_token_type_ids(self):
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
tokd = tokenizer("Hello", "World")
expected_token_type_ids = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
self.assertListEqual(tokd["token_type_ids"], expected_token_type_ids)
@slow
def test_sequence_builders(self):
tokenizer = self.tokenizer_class.from_pretrained("microsoft/deberta-base")
text = tokenizer.encode("sequence builders", add_special_tokens=False)
text_2 = tokenizer.encode("multi-sequence build", add_special_tokens=False)
encoded_text_from_decode = tokenizer.encode(
"sequence builders", add_special_tokens=True, add_prefix_space=False
)
encoded_pair_from_decode = tokenizer.encode(
"sequence builders", "multi-sequence build", add_special_tokens=True, add_prefix_space=False
)
encoded_sentence = tokenizer.build_inputs_with_special_tokens(text)
encoded_pair = tokenizer.build_inputs_with_special_tokens(text, text_2)
assert encoded_sentence == encoded_text_from_decode
assert encoded_pair == encoded_pair_from_decode
@slow
def test_tokenizer_integration(self):
tokenizer_classes = [self.tokenizer_class]
if self.test_rust_tokenizer:
tokenizer_classes.append(self.rust_tokenizer_class)
for tokenizer_class in tokenizer_classes:
tokenizer = tokenizer_class.from_pretrained("microsoft/deberta-base")
sequences = [
"ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations",
"ALBERT incorporates two parameter reduction techniques",
"The first one is a factorized embedding parameterization. By decomposing the large vocabulary"
" embedding matrix into two small matrices, we separate the size of the hidden layers from the size of"
" vocabulary embedding.",
]
encoding = tokenizer(sequences, padding=True)
decoded_sequences = [tokenizer.decode(seq, skip_special_tokens=True) for seq in encoding["input_ids"]]
# fmt: off
expected_encoding = {
'input_ids': [
[1, 2118, 11126, 565, 35, 83, 25191, 163, 18854, 13, 12156, 12, 16101, 25376, 13807, 9, 22205, 27893, 1635, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 2118, 11126, 565, 24536, 80, 43797, 4878, 7373, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 133, 78, 65, 16, 10, 3724, 1538, 33183, 11303, 43797, 1938, 4, 870, 24165, 29105, 5, 739, 32644, 33183, 11303, 36173, 88, 80, 650, 7821, 45940, 6, 52, 2559, 5, 1836, 9, 5, 7397, 13171, 31, 5, 1836, 9, 32644, 33183, 11303, 4, 2]
],
'token_type_ids': [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
],
'attention_mask': [
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
]
}
# fmt: on
expected_decoded_sequence = [
"ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations",
"ALBERT incorporates two parameter reduction techniques",
"The first one is a factorized embedding parameterization. By decomposing the large vocabulary"
" embedding matrix into two small matrices, we separate the size of the hidden layers from the size of"
" vocabulary embedding.",
]
self.assertDictEqual(encoding.data, expected_encoding)
for expected, decoded in zip(expected_decoded_sequence, decoded_sequences):
self.assertEqual(expected, decoded)
|
transformers/tests/models/deberta/test_tokenization_deberta.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/deberta/test_tokenization_deberta.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3812
}
| 198 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer, DistilBertTokenizerFast
from transformers.testing_utils import require_tokenizers, slow
from ..bert.test_tokenization_bert import BertTokenizationTest
@require_tokenizers
class DistilBertTokenizationTest(BertTokenizationTest):
tokenizer_class = DistilBertTokenizer
rust_tokenizer_class = DistilBertTokenizerFast
test_rust_tokenizer = True
from_pretrained_id = "distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased"
@slow
def test_sequence_builders(self):
tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
text = tokenizer.encode("sequence builders", add_special_tokens=False)
text_2 = tokenizer.encode("multi-sequence build", add_special_tokens=False)
encoded_sentence = tokenizer.build_inputs_with_special_tokens(text)
encoded_pair = tokenizer.build_inputs_with_special_tokens(text, text_2)
assert encoded_sentence == [tokenizer.cls_token_id] + text + [tokenizer.sep_token_id]
assert encoded_pair == [tokenizer.cls_token_id] + text + [tokenizer.sep_token_id] + text_2 + [
tokenizer.sep_token_id
]
|
transformers/tests/models/distilbert/test_tokenization_distilbert.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/distilbert/test_tokenization_distilbert.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 599
}
| 199 |
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import shutil
import tempfile
import unittest
import pytest
from transformers.testing_utils import require_vision
from transformers.utils import is_vision_available
from ...test_processing_common import ProcessorTesterMixin
if is_vision_available():
from transformers import AutoProcessor, BertTokenizer, CLIPImageProcessor, GitProcessor, PreTrainedTokenizerFast
@require_vision
class GitProcessorTest(ProcessorTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
processor_class = GitProcessor
def setUp(self):
self.tmpdirname = tempfile.mkdtemp()
image_processor = CLIPImageProcessor()
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-BertModel", model_input_names=["input_ids", "attention_mask"]
)
processor = GitProcessor(image_processor, tokenizer)
processor.save_pretrained(self.tmpdirname)
def get_tokenizer(self, **kwargs):
return AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, **kwargs).tokenizer
def get_image_processor(self, **kwargs):
return AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, **kwargs).image_processor
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.tmpdirname)
def test_save_load_pretrained_additional_features(self):
processor = GitProcessor(tokenizer=self.get_tokenizer(), image_processor=self.get_image_processor())
processor.save_pretrained(self.tmpdirname)
tokenizer_add_kwargs = self.get_tokenizer(bos_token="(BOS)", eos_token="(EOS)")
image_processor_add_kwargs = self.get_image_processor(do_normalize=False, padding_value=1.0)
processor = GitProcessor.from_pretrained(
self.tmpdirname, bos_token="(BOS)", eos_token="(EOS)", do_normalize=False, padding_value=1.0
)
self.assertEqual(processor.tokenizer.get_vocab(), tokenizer_add_kwargs.get_vocab())
self.assertIsInstance(processor.tokenizer, PreTrainedTokenizerFast)
self.assertEqual(processor.image_processor.to_json_string(), image_processor_add_kwargs.to_json_string())
self.assertIsInstance(processor.image_processor, CLIPImageProcessor)
def test_image_processor(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = GitProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
image_input = self.prepare_image_inputs()
input_feat_extract = image_processor(image_input, return_tensors="np")
input_processor = processor(images=image_input, return_tensors="np")
for key in input_feat_extract.keys():
self.assertAlmostEqual(input_feat_extract[key].sum(), input_processor[key].sum(), delta=1e-2)
def test_tokenizer(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = GitProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
input_str = "lower newer"
encoded_processor = processor(text=input_str)
encoded_tok = tokenizer(input_str, return_token_type_ids=False)
for key in encoded_tok.keys():
self.assertListEqual(encoded_tok[key], encoded_processor[key])
def test_processor(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = GitProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
input_str = "lower newer"
image_input = self.prepare_image_inputs()
inputs = processor(text=input_str, images=image_input)
self.assertListEqual(list(inputs.keys()), ["input_ids", "attention_mask", "pixel_values"])
# test if it raises when no input is passed
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
processor()
def test_tokenizer_decode(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = GitProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
predicted_ids = [[1, 4, 5, 8, 1, 0, 8], [3, 4, 3, 1, 1, 8, 9]]
decoded_processor = processor.batch_decode(predicted_ids)
decoded_tok = tokenizer.batch_decode(predicted_ids)
self.assertListEqual(decoded_tok, decoded_processor)
def test_model_input_names(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = GitProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
input_str = "lower newer"
image_input = self.prepare_image_inputs()
inputs = processor(text=input_str, images=image_input)
# For now the processor supports only ['input_ids', 'attention_mask', 'pixel_values']
self.assertListEqual(list(inputs.keys()), ["input_ids", "attention_mask", "pixel_values"])
|
transformers/tests/models/git/test_processor_git.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/git/test_processor_git.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2013
}
| 200 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch GPT Neo model."""
import unittest
from transformers import GPTNeoConfig, is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, slow, torch_device
from transformers.utils import cached_property
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
GPT2Tokenizer,
GPTNeoForCausalLM,
GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering,
GPTNeoForSequenceClassification,
GPTNeoForTokenClassification,
GPTNeoModel,
)
class GPTNeoModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=14,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_token_type_ids=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_labels=True,
use_mc_token_ids=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
attention_types=[[["global", "local"], 1]],
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
window_size=7,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.use_mc_token_ids = use_mc_token_ids
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.window_size = window_size
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.bos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.eos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.pad_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.attention_types = attention_types
def get_large_model_config(self):
return GPTNeoConfig.from_pretrained("gpt-neo-125M")
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
mc_token_ids = None
if self.use_mc_token_ids:
mc_token_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_choices], self.seq_length)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = self.get_config()
head_mask = ids_tensor([self.num_hidden_layers, self.num_attention_heads], 2)
return (
config,
input_ids,
input_mask,
head_mask,
token_type_ids,
mc_token_ids,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
)
def get_config(self):
return GPTNeoConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
use_cache=True,
bos_token_id=self.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=self.eos_token_id,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
window_size=self.window_size,
attention_types=self.attention_types,
)
def get_pipeline_config(self):
config = self.get_config()
config.vocab_size = 300
return config
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args):
model = GPTNeoModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, head_mask=head_mask)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
# past_key_values is not implemented
# self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.past_key_values), config.n_layer)
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_model_past(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args):
model = GPTNeoModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, use_cache=True)
outputs_use_cache_conf = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
outputs_no_past = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, use_cache=False)
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_use_cache_conf))
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_no_past) + 1)
output, past = outputs.to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
next_token_types = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, 1], self.type_vocab_size)
# append to next input_ids and token_type_ids
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_token_type_ids = torch.cat([token_type_ids, next_token_types], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, token_type_ids=next_token_type_ids)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, token_type_ids=next_token_types, past_key_values=past)[
"last_hidden_state"
]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_model_attention_mask_past(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args
):
model = GPTNeoModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# create attention mask
attn_mask = torch.ones(input_ids.shape, dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)
half_seq_length = self.seq_length // 2
attn_mask[:, half_seq_length:] = 0
# first forward pass
output, past = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask).to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
# change a random masked slice from input_ids
random_seq_idx_to_change = ids_tensor((1,), half_seq_length).item() + 1
random_other_next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size).squeeze(-1)
input_ids[:, -random_seq_idx_to_change] = random_other_next_tokens
# append to next input_ids and attn_mask
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
attn_mask = torch.cat(
[attn_mask, torch.ones((attn_mask.shape[0], 1), dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)],
dim=1,
)
# get two different outputs
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, past_key_values=past, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_model_past_large_inputs(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args
):
model = GPTNeoModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, use_cache=True)
output, past = outputs.to_tuple()
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_token_types = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, 3], self.type_vocab_size)
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and token_type_ids
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_token_type_ids = torch.cat([token_type_ids, next_token_types], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(
next_input_ids, token_type_ids=next_token_type_ids, attention_mask=next_attention_mask
)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(
next_tokens, token_type_ids=next_token_types, attention_mask=next_attention_mask, past_key_values=past
)["last_hidden_state"]
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_lm_head_model(self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args):
model = GPTNeoForCausalLM(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.loss.shape, ())
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_for_question_answering(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, mc_token_ids, sequence_labels, *args
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.start_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.end_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_for_sequence_classification(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, mc_token_ids, sequence_labels, *args
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = GPTNeoForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=sequence_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_gpt_neo_for_token_classification(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, mc_token_ids, sequence_labels, *args
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = GPTNeoForTokenClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_forward_and_backwards(
self, config, input_ids, input_mask, head_mask, token_type_ids, *args, gradient_checkpointing=False
):
model = GPTNeoForCausalLM(config)
if gradient_checkpointing:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
model.to(torch_device)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.loss.shape, ())
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
result.loss.backward()
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
input_mask,
head_mask,
token_type_ids,
mc_token_ids,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"token_type_ids": token_type_ids,
"head_mask": head_mask,
}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class GPTNeoModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
GPTNeoModel,
GPTNeoForCausalLM,
GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering,
GPTNeoForSequenceClassification,
GPTNeoForTokenClassification,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
all_generative_model_classes = (GPTNeoForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": GPTNeoModel,
"question-answering": GPTNeoForQuestionAnswering,
"text-classification": GPTNeoForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": GPTNeoForCausalLM,
"token-classification": GPTNeoForTokenClassification,
"zero-shot": GPTNeoForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
fx_compatible = True
test_missing_keys = False
test_pruning = False
test_model_parallel = False
# special case for DoubleHeads model
def _prepare_for_class(self, inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=False):
inputs_dict = super()._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=return_labels)
return inputs_dict
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = GPTNeoModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=GPTNeoConfig, n_embd=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_gpt_neo_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_model_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_model_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_model_att_mask_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_model_attention_mask_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_model_past_large_inputs(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_lm_head_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_lm_head_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_question_answering_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_for_question_answering(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_sequence_classification_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_for_sequence_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_token_classification_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_gpt_neo_for_token_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def test_gpt_neo_gradient_checkpointing(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_forward_and_backwards(*config_and_inputs, gradient_checkpointing=True)
def _get_hidden_states(self):
return torch.tensor(
[
[
[0.4983, -0.7584, -1.6944, 0.5440],
[2.6918, 0.4206, 0.4176, 0.2055],
[-0.0071, -0.0405, -1.4920, -0.3630],
[1.0492, 0.1599, -1.7648, 0.2419],
[-1.8348, 2.0514, -0.1946, 0.3203],
[0.7672, -1.1600, -1.7118, -0.9056],
[0.2986, 0.5372, 0.7729, -0.1927],
[0.0285, 0.2629, -1.1156, -1.1992],
]
],
dtype=torch.float32,
device=torch_device,
)
def test_local_attn_probs(self):
model = GPTNeoModel.from_pretrained("valhalla/gpt-neo-random-tiny").eval()
layer = model.h[1].attn.attention.to(torch_device)
hidden_states = self._get_hidden_states()
hidden_states = torch.cat([hidden_states, hidden_states - 0.5], dim=2)
batch_size, seq_length, _ = hidden_states.shape
mask_tokens = 2
attention_mask = torch.ones(batch_size, seq_length, device=torch_device, dtype=torch.long)
attention_mask[:, -mask_tokens:] = 0 # dont attend last mask_tokens
attention_mask = attention_mask.view(batch_size, -1)
attention_mask = attention_mask[:, None, None, :]
attention_mask = (1.0 - attention_mask) * -10000.0
attn_probs = layer(hidden_states, attention_mask=attention_mask, output_attentions=True)[-1]
# the last 2 tokens are masked, and should have 0 attn_probs
self.assertTrue(torch.all(attn_probs[:, :, -mask_tokens:, -mask_tokens:] == 0))
# in loacal attention each token can only attend to the previous window_size tokens (inlcuding itself)
# here window_size is 4, so a token at index 5 can only attend to indcies [2, 3, 4, 5]
# and the attn_probs should be 0 for token [0, 1]
self.assertTrue(torch.all(attn_probs[:, :, 5, 2:6] != 0))
self.assertTrue(torch.all(attn_probs[:, :, 5, :2] == 0))
@require_torch
class GPTNeoModelLanguageGenerationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@cached_property
def model(self):
return GPTNeoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B").to(torch_device)
@cached_property
def tokenizer(self):
return GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
@slow
def test_lm_generate_gpt_neo(self):
for checkpointing in [True, False]:
model = self.model
if checkpointing:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
else:
model.gradient_checkpointing_disable()
input_ids = torch.tensor([[464, 3290]], dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device) # The dog
# The dog-eared copy of the book, which is a collection of essays by the late author,
expected_output_ids = [464, 3290, 12, 3380, 4866, 286, 262, 1492, 11, 543, 318, 257, 4947, 286, 27126, 416, 262, 2739, 1772, 11] # fmt: skip
output_ids = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=False)
self.assertListEqual(output_ids[0].tolist(), expected_output_ids)
@slow
def test_gpt_neo_sample(self):
model = self.model
tokenizer = self.tokenizer
torch.manual_seed(0)
tokenized = tokenizer("Today is a nice day and", return_tensors="pt", return_token_type_ids=True)
input_ids = tokenized.input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_ids = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True)
output_str = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
EXPECTED_OUTPUT_STR = "Today is a nice day and if you don’t get the memo here is what you can"
self.assertEqual(output_str, EXPECTED_OUTPUT_STR)
@slow
def test_batch_generation(self):
model = self.model
tokenizer = self.tokenizer
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
# Define PAD Token = EOS Token = 50256
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
model.config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_id
# use different length sentences to test batching
sentences = [
"Hello, my dog is a little",
"Today, I am",
]
inputs = tokenizer(sentences, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device)
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"].to(torch_device),
)
inputs_non_padded = tokenizer(sentences[0], return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_non_padded = model.generate(input_ids=inputs_non_padded)
num_paddings = inputs_non_padded.shape[-1] - inputs["attention_mask"][-1].long().sum().cpu().item()
inputs_padded = tokenizer(sentences[1], return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_padded = model.generate(input_ids=inputs_padded, max_length=model.config.max_length - num_paddings)
batch_out_sentence = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
non_padded_sentence = tokenizer.decode(output_non_padded[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
padded_sentence = tokenizer.decode(output_padded[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
expected_output_sentence = [
"Hello, my dog is a little bit of a kitty. She is a very sweet and loving",
"Today, I am going to talk about the best way to get a job in the",
]
self.assertListEqual(expected_output_sentence, batch_out_sentence)
self.assertListEqual(expected_output_sentence, [non_padded_sentence, padded_sentence])
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B"
model = GPTNeoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
|
transformers/tests/models/gpt_neo/test_modeling_gpt_neo.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/gpt_neo/test_modeling_gpt_neo.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 10987
}
| 201 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch IJEPA model."""
import unittest
from transformers import IJepaConfig
from transformers.testing_utils import (
require_accelerate,
require_torch,
require_torch_accelerator,
require_torch_fp16,
require_vision,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from transformers.utils import (
cached_property,
is_torch_available,
is_vision_available,
)
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from torch import nn
from transformers import IJepaForImageClassification, IJepaModel
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
class IJepaModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
image_size=30,
patch_size=2,
num_channels=3,
is_training=True,
use_labels=True,
hidden_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
type_sequence_label_size=10,
initializer_range=0.02,
scope=None,
encoder_stride=2,
mask_ratio=0.5,
attn_implementation="eager",
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.image_size = image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.scope = scope
self.encoder_stride = encoder_stride
self.attn_implementation = attn_implementation
# in IJEPA, the seq length equals the number of patches (we don't add 1 for the [CLS] token)
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.seq_length = num_patches
self.mask_ratio = mask_ratio
self.num_masks = int(mask_ratio * self.seq_length)
self.mask_length = num_patches
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor(
[
self.batch_size,
self.num_channels,
self.image_size,
self.image_size,
]
)
labels = None
if self.use_labels:
labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values, labels
def get_config(self):
return IJepaConfig(
image_size=self.image_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
is_decoder=False,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
encoder_stride=self.encoder_stride,
attn_implementation=self.attn_implementation,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = IJepaModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.last_hidden_state.shape,
(self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size),
)
def create_and_check_for_image_classification(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
config.num_labels = self.type_sequence_label_size
model = IJepaForImageClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values, labels=labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.logits.shape,
(self.batch_size, self.type_sequence_label_size),
)
# test greyscale images
config.num_channels = 1
model = IJepaForImageClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, 1, self.image_size, self.image_size])
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.logits.shape,
(self.batch_size, self.type_sequence_label_size),
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
pixel_values,
labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class IJepaModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
"""
Here we also overwrite some of the tests of test_modeling_common.py, as IJEPA does not use input_ids, inputs_embeds,
attention_mask and seq_length.
"""
all_model_classes = (
(
IJepaModel,
IJepaForImageClassification,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"image-feature-extraction": IJepaModel, "image-classification": IJepaForImageClassification}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
fx_compatible = True
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_head_masking = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = IJepaModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(
self,
config_class=IJepaConfig,
has_text_modality=False,
hidden_size=37,
)
@unittest.skip(
"Since `torch==2.3+cu121`, although this test passes, many subsequent tests have `CUDA error: misaligned address`."
"If `nvidia-xxx-cu118` are also installed, no failure (even with `torch==2.3+cu121`)."
)
def test_multi_gpu_data_parallel_forward(self):
super().test_multi_gpu_data_parallel_forward()
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
@unittest.skip(reason="IJEPA does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
self.assertIsInstance(model.get_input_embeddings(), (nn.Module))
x = model.get_output_embeddings()
self.assertTrue(x is None or isinstance(x, nn.Linear))
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_image_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_image_classification(*config_and_inputs)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "facebook/ijepa_vith14_1k"
model = IJepaModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
# We will verify our results on an image of cute cats
def prepare_img():
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
return image
@require_torch
@require_vision
class IJepaModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@cached_property
def default_image_processor(self):
return ViTImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/ijepa_vith14_1k") if is_vision_available() else None
@slow
def test_inference_no_head(self):
model = IJepaModel.from_pretrained("facebook/ijepa_vith14_1k").to(torch_device)
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = prepare_img()
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
# verify the last hidden state
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 256, 1280))
self.assertEqual(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.Tensor(
[[-0.0621, -0.0054, -2.7513], [-0.1952, 0.0909, -3.9536], [0.0942, -0.0331, -1.2833]]
).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.last_hidden_state[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
@slow
@require_accelerate
@require_torch_accelerator
@require_torch_fp16
def test_inference_fp16(self):
r"""
A small test to make sure that inference work in half precision without any problem.
"""
model = IJepaModel.from_pretrained(
"facebook/ijepa_vith14_1k",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto",
)
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = prepare_img()
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values.to(torch_device)
# forward pass to make sure inference works in fp16
with torch.no_grad():
_ = model(pixel_values)
@slow
def test_inference_interpolate_pos_encoding(self):
# I-JEPA, similar to ViT models have an `interpolate_pos_encoding` argument in their forward method,
# allowing to interpolate the pre-trained position embeddings in order to use
# the model on higher resolutions. The DINO model by Facebook AI leverages this
# to visualize self-attention on higher resolution images.
model = IJepaModel.from_pretrained("facebook/ijepa_vith14_1k").to(torch_device)
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = prepare_img()
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values.to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(pixel_values, interpolate_pos_encoding=True)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 256, 1280))
self.assertEqual(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor(
[[-0.0621, -0.0054, -2.7513], [-0.1952, 0.0909, -3.9536], [0.0942, -0.0331, -1.2833]]
).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.last_hidden_state[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
|
transformers/tests/models/ijepa/test_modeling_ijepa.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/ijepa/test_modeling_ijepa.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5187
}
| 202 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 JetMoe AI and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch JetMoe model."""
import gc
import unittest
import pytest
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, JetMoeConfig, is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import (
backend_empty_cache,
require_flash_attn,
require_torch,
require_torch_gpu,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
JetMoeForCausalLM,
JetMoeForSequenceClassification,
JetMoeModel,
)
class JetMoeModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=False,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_key_value_heads=2,
kv_channels=8,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="silu",
num_local_experts=4,
num_experts_per_tok=2,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
pad_token_id=0,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.kv_channels = kv_channels
self.num_attention_heads = num_key_value_heads * num_experts_per_tok
self.num_key_value_heads = num_key_value_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.num_local_experts = num_local_experts
self.num_experts_per_tok = num_experts_per_tok
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.pad_token_id = pad_token_id
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = torch.ones(self.batch_size, self.seq_length).to(torch_device)
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = self.get_config()
return config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
def get_config(self):
return JetMoeConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_key_value_heads=self.num_key_value_heads,
kv_channels=self.kv_channels,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
activation_function=self.hidden_act,
num_local_experts=self.num_local_experts,
num_experts_per_tok=self.num_experts_per_tok,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
is_decoder=False,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
)
def create_and_check_model(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = JetMoeModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_model_as_decoder(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = JetMoeModel(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
)
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
)
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_for_causal_lm(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
model = JetMoeForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.is_decoder = True
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = JetMoeForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
use_cache=True,
)
past_key_values = outputs.past_key_values
# create hypothetical multiple next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(
next_input_ids,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
output_from_past = model(
next_tokens,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past_slice.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": input_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class JetMoeModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(JetMoeModel, JetMoeForCausalLM, JetMoeForSequenceClassification) if is_torch_available() else ()
)
all_generative_model_classes = (JetMoeForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": JetMoeModel,
"text-classification": JetMoeForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": JetMoeForCausalLM,
"zero-shot": JetMoeForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
test_headmasking = False
test_pruning = False
test_mismatched_shapes = False
test_cpu_offload = False
test_disk_offload_bin = False
test_disk_offload_safetensors = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = JetMoeModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(
self, config_class=JetMoeConfig, common_properties=["hidden_size", "num_hidden_layers"]
)
# Copied from tests.models.llama.test_modeling_llama.LlamaModelTest.test_config
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
# Copied from tests.models.llama.test_modeling_llama.LlamaModelTest.test_model
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
# Copied from tests.models.llama.test_modeling_llama.LlamaModelTest.test_model_various_embeddings
def test_model_various_embeddings(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for type in ["absolute", "relative_key", "relative_key_query"]:
config_and_inputs[0].position_embedding_type = type
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
# Copied from tests.models.llama.test_modeling_llama.LlamaModelTest.test_llama_sequence_classification_model with llama->jetmoe, Llama->JetMoe
def test_jetmoe_sequence_classification_model(self):
config, input_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.num_labels = 3
input_ids = input_dict["input_ids"]
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(1).to(torch_device)
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.model_tester.batch_size], self.model_tester.type_sequence_label_size)
model = JetMoeForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, labels=sequence_labels)
self.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.model_tester.batch_size, self.model_tester.num_labels))
# Copied from tests.models.llama.test_modeling_llama.LlamaModelTest.test_llama_sequence_classification_model_for_single_label with llama->jetmoe, Llama->JetMoe
def test_jetmoe_sequence_classification_model_for_single_label(self):
config, input_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.num_labels = 3
config.problem_type = "single_label_classification"
input_ids = input_dict["input_ids"]
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(1).to(torch_device)
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.model_tester.batch_size], self.model_tester.type_sequence_label_size)
model = JetMoeForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, labels=sequence_labels)
self.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.model_tester.batch_size, self.model_tester.num_labels))
# Copied from tests.models.llama.test_modeling_llama.LlamaModelTest.test_llama_sequence_classification_model_for_multi_label with llama->jetmoe, Llama->JetMoe
def test_jetmoe_sequence_classification_model_for_multi_label(self):
config, input_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.num_labels = 3
config.problem_type = "multi_label_classification"
input_ids = input_dict["input_ids"]
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(1).to(torch_device)
sequence_labels = ids_tensor(
[self.model_tester.batch_size, config.num_labels], self.model_tester.type_sequence_label_size
).to(torch.float)
model = JetMoeForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, labels=sequence_labels)
self.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.model_tester.batch_size, self.model_tester.num_labels))
@unittest.skip(reason="JetMoe buffers include complex numbers, which breaks this test")
def test_save_load_fast_init_from_base(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="JetMoe uses MoA on all models so the KV cache is a non standard format")
def test_past_key_values_format(self):
pass
@require_flash_attn
@require_torch_gpu
@pytest.mark.flash_attn_test
@slow
def test_flash_attn_2_inference_equivalence_right_padding(self):
self.skipTest(reason="JetMoe flash attention does not support right padding")
@require_torch
class JetMoeIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_model_8b_logits(self):
input_ids = [1, 306, 4658, 278, 6593, 310, 2834, 338]
model = JetMoeForCausalLM.from_pretrained("jetmoe/jetmoe-8b")
input_ids = torch.tensor([input_ids]).to(model.model.embed_tokens.weight.device)
with torch.no_grad():
out = model(input_ids).logits.float().cpu()
# Expected mean on dim = -1
EXPECTED_MEAN = torch.tensor([[0.2507, -2.7073, -1.3445, -1.9363, -1.7216, -1.7370, -1.9054, -1.9792]])
torch.testing.assert_close(out.mean(-1), EXPECTED_MEAN, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
# slicing logits[0, 0, 0:30]
EXPECTED_SLICE = torch.tensor([-3.3689, 5.9006, 5.7450, -1.7012, -4.7072, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7072, -4.7072, -4.7072, -4.7071, 3.8321, 9.1746, -4.7071, -4.7072, -4.7071, -4.7072, -4.7071, -4.7072, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071, -4.7071]) # fmt: skip
torch.testing.assert_close(out[0, 0, :30], EXPECTED_SLICE, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
del model
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
gc.collect()
@slow
def test_model_8b_generation(self):
EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION = """My favourite condiment is ....\nI love ketchup. I love"""
prompt = "My favourite condiment is "
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("jetmoe/jetmoe-8b", use_fast=False)
model = JetMoeForCausalLM.from_pretrained("jetmoe/jetmoe-8b")
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(model.model.embed_tokens.weight.device)
# greedy generation outputs
generated_ids = model.generate(input_ids, max_new_tokens=10, temperature=0)
text = tokenizer.decode(generated_ids[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
self.assertEqual(EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION, text)
del model
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
gc.collect()
@slow
def test_model_8b_batched_generation(self):
EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION = [
"""My favourite condiment is ....\nI love ketchup. I love""",
"""My favourite 2018 Christmas present was a new pair""",
]
prompt = [
"My favourite condiment is ",
"My favourite ",
]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("jetmoe/jetmoe-8b", use_fast=False)
model = JetMoeForCausalLM.from_pretrained("jetmoe/jetmoe-8b")
input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(model.model.embed_tokens.weight.device)
print(input_ids)
# greedy generation outputs
generated_ids = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=10, temperature=0)
text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(text)
self.assertEqual(EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION, text)
del model
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
gc.collect()
|
transformers/tests/models/jetmoe/test_modeling_jetmoe.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/jetmoe/test_modeling_jetmoe.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 8076
}
| 203 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the TensorFlow LayoutLMv3 model."""
from __future__ import annotations
import copy
import inspect
import unittest
import numpy as np
from transformers import is_tf_available, is_vision_available
from transformers.models.auto import get_values
from transformers.testing_utils import require_tf, slow
from transformers.utils import cached_property
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_tf_common import TFModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_tf_available():
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers import (
TF_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING,
TF_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
TF_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
LayoutLMv3Config,
TFLayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering,
TFLayoutLMv3ForSequenceClassification,
TFLayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification,
TFLayoutLMv3Model,
)
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import LayoutLMv3ImageProcessor
class TFLayoutLMv3ModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=2,
num_channels=3,
image_size=4,
patch_size=2,
text_seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=True,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=36,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
coordinate_size=6,
shape_size=6,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
scope=None,
range_bbox=1000,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.image_size = image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.coordinate_size = coordinate_size
self.shape_size = shape_size
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.scope = scope
self.range_bbox = range_bbox
# LayoutLMv3's sequence length equals the number of text tokens + number of patches + 1 (we add 1 for the CLS token)
self.text_seq_length = text_seq_length
self.image_seq_length = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2 + 1
self.seq_length = self.text_seq_length + self.image_seq_length
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length], self.vocab_size)
bbox = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length, 4], self.range_bbox)
bbox = bbox.numpy()
# Ensure that bbox is legal
for i in range(bbox.shape[0]):
for j in range(bbox.shape[1]):
if bbox[i, j, 3] < bbox[i, j, 1]:
tmp_coordinate = bbox[i, j, 3]
bbox[i, j, 3] = bbox[i, j, 1]
bbox[i, j, 1] = tmp_coordinate
if bbox[i, j, 2] < bbox[i, j, 0]:
tmp_coordinate = bbox[i, j, 2]
bbox[i, j, 2] = bbox[i, j, 0]
bbox[i, j, 0] = tmp_coordinate
bbox = tf.constant(bbox)
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size, self.image_size])
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length])
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length], self.num_labels)
config = LayoutLMv3Config(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
coordinate_size=self.coordinate_size,
shape_size=self.shape_size,
input_size=self.image_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
)
return config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels
def create_and_check_model(self, config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask):
model = TFLayoutLMv3Model(config=config)
# text + image
result = model(input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, training=False)
result = model(
input_ids,
bbox=bbox,
pixel_values=pixel_values,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
training=False,
)
result = model(input_ids, bbox=bbox, pixel_values=pixel_values, training=False)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
# text only
result = model(input_ids, training=False)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length, self.hidden_size)
)
# image only
result = model({"pixel_values": pixel_values}, training=False)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.image_seq_length, self.hidden_size)
)
def create_and_check_for_sequence_classification(
self, config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = TFLayoutLMv3ForSequenceClassification(config=config)
result = model(
input_ids,
bbox=bbox,
pixel_values=pixel_values,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
labels=sequence_labels,
training=False,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_for_token_classification(
self, config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, token_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = TFLayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification(config=config)
result = model(
input_ids,
bbox=bbox,
pixel_values=pixel_values,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
labels=token_labels,
training=False,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.text_seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_for_question_answering(
self, config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels
):
config.num_labels = 2
model = TFLayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering(config=config)
result = model(
input_ids,
bbox=bbox,
pixel_values=pixel_values,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
start_positions=sequence_labels,
end_positions=sequence_labels,
training=False,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.start_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.end_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, _, _) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"bbox": bbox,
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"token_type_ids": token_type_ids,
"attention_mask": input_mask,
}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_tf
class TFLayoutLMv3ModelTest(TFModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
TFLayoutLMv3Model,
TFLayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering,
TFLayoutLMv3ForSequenceClassification,
TFLayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification,
)
if is_tf_available()
else ()
)
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"document-question-answering": TFLayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering, "feature-extraction": TFLayoutLMv3Model}
if is_tf_available()
else {}
)
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_onnx = False
# TODO: Fix the failed tests
def is_pipeline_test_to_skip(
self,
pipeline_test_case_name,
config_class,
model_architecture,
tokenizer_name,
image_processor_name,
feature_extractor_name,
processor_name,
):
return True
def _prepare_for_class(self, inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=False) -> dict:
inputs_dict = copy.deepcopy(inputs_dict)
if model_class in get_values(TF_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING):
inputs_dict = {
k: tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(v, 1), (1, self.model_tester.num_choices) + (1,) * (v.ndim - 1))
if isinstance(v, tf.Tensor) and v.ndim > 0
else v
for k, v in inputs_dict.items()
}
if return_labels:
if model_class in get_values(TF_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING):
inputs_dict["labels"] = tf.ones(self.model_tester.batch_size, dtype=tf.int32)
elif model_class in get_values(TF_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING):
inputs_dict["start_positions"] = tf.zeros(self.model_tester.batch_size, dtype=tf.int32)
inputs_dict["end_positions"] = tf.zeros(self.model_tester.batch_size, dtype=tf.int32)
elif model_class in get_values(TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING):
inputs_dict["labels"] = tf.zeros(self.model_tester.batch_size, dtype=tf.int32)
elif model_class in get_values(TF_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING):
inputs_dict["labels"] = tf.zeros(
(self.model_tester.batch_size, self.model_tester.text_seq_length), dtype=tf.int32
)
return inputs_dict
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = TFLayoutLMv3ModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=LayoutLMv3Config, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_loss_computation(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
if getattr(model, "hf_compute_loss", None):
# The number of elements in the loss should be the same as the number of elements in the label
prepared_for_class = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict.copy(), model_class, return_labels=True)
added_label = prepared_for_class[
sorted(prepared_for_class.keys() - inputs_dict.keys(), reverse=True)[0]
]
expected_loss_size = added_label.shape.as_list()[:1]
# Test that model correctly compute the loss with kwargs
prepared_for_class = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict.copy(), model_class, return_labels=True)
input_ids = prepared_for_class.pop("input_ids")
loss = model(input_ids, **prepared_for_class)[0]
self.assertTrue(loss.shape.as_list() == expected_loss_size or loss.shape.as_list() == [1])
# Test that model correctly compute the loss when we mask some positions
prepared_for_class = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict.copy(), model_class, return_labels=True)
input_ids = prepared_for_class.pop("input_ids")
if "labels" in prepared_for_class:
labels = prepared_for_class["labels"].numpy()
if len(labels.shape) > 1 and labels.shape[1] != 1:
labels[0] = -100
prepared_for_class["labels"] = tf.convert_to_tensor(labels)
loss = model(input_ids, **prepared_for_class)[0]
self.assertTrue(loss.shape.as_list() == expected_loss_size or loss.shape.as_list() == [1])
self.assertTrue(not np.any(np.isnan(loss.numpy())))
# Test that model correctly compute the loss with a dict
prepared_for_class = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict.copy(), model_class, return_labels=True)
loss = model(prepared_for_class)[0]
self.assertTrue(loss.shape.as_list() == expected_loss_size or loss.shape.as_list() == [1])
# Test that model correctly compute the loss with a tuple
prepared_for_class = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict.copy(), model_class, return_labels=True)
# Get keys that were added with the _prepare_for_class function
label_keys = prepared_for_class.keys() - inputs_dict.keys()
signature = inspect.signature(model.call).parameters
signature_names = list(signature.keys())
# Create a dictionary holding the location of the tensors in the tuple
tuple_index_mapping = {0: "input_ids"}
for label_key in label_keys:
label_key_index = signature_names.index(label_key)
tuple_index_mapping[label_key_index] = label_key
sorted_tuple_index_mapping = sorted(tuple_index_mapping.items())
# Initialize a list with their default values, update the values and convert to a tuple
list_input = []
for name in signature_names:
if name != "kwargs":
list_input.append(signature[name].default)
for index, value in sorted_tuple_index_mapping:
list_input[index] = prepared_for_class[value]
tuple_input = tuple(list_input)
# Send to model
loss = model(tuple_input[:-1])[0]
self.assertTrue(loss.shape.as_list() == expected_loss_size or loss.shape.as_list() == [1])
def test_model(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
bbox,
pixel_values,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
_,
_,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask)
def test_model_various_embeddings(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
bbox,
pixel_values,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
_,
_,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for type in ["absolute", "relative_key", "relative_key_query"]:
config.position_embedding_type = type
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask)
def test_for_sequence_classification(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
bbox,
pixel_values,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
_,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_sequence_classification(
config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels
)
def test_for_token_classification(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
bbox,
pixel_values,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
_,
token_labels,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_token_classification(
config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, token_labels
)
def test_for_question_answering(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
bbox,
pixel_values,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
_,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_question_answering(
config, input_ids, bbox, pixel_values, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels
)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "microsoft/layoutlmv3-base"
model = TFLayoutLMv3Model.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
# We will verify our results on an image of cute cats
def prepare_img():
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
return image
@require_tf
class TFLayoutLMv3ModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@cached_property
def default_image_processor(self):
return LayoutLMv3ImageProcessor(apply_ocr=False) if is_vision_available() else None
@slow
def test_inference_no_head(self):
model = TFLayoutLMv3Model.from_pretrained("microsoft/layoutlmv3-base")
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = prepare_img()
pixel_values = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="tf").pixel_values
input_ids = tf.constant([[1, 2]])
bbox = tf.expand_dims(tf.constant([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]]), axis=0)
# forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids=input_ids, bbox=bbox, pixel_values=pixel_values, training=False)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = (1, 199, 768)
self.assertEqual(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = tf.constant(
[[-0.0529, 0.3618, 0.1632], [-0.1587, -0.1667, -0.0400], [-0.1557, -0.1671, -0.0505]]
)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(outputs.last_hidden_state[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, atol=1e-4))
|
transformers/tests/models/layoutlmv3/test_modeling_tf_layoutlmv3.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/layoutlmv3/test_modeling_tf_layoutlmv3.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 9752
}
| 204 |
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
import numpy as np
from transformers import LlamaConfig, is_flax_available, is_tokenizers_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_flax, slow
from ...generation.test_flax_utils import FlaxGenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_modeling_flax_common import FlaxModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor
if is_flax_available():
import jax.numpy as jnp
from transformers.models.llama.modeling_flax_llama import FlaxLlamaForCausalLM, FlaxLlamaModel
if is_tokenizers_available():
from transformers import LlamaTokenizerFast
class FlaxLlamaModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=2,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=False,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=16,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=2,
intermediate_size=64,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
window_size=7,
initializer_range=0.02,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.window_size = window_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.scope = None
self.bos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.eos_token_id = vocab_size - 1
self.pad_token_id = vocab_size - 1
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = np.tril(np.ones((self.batch_size, self.seq_length)))
config = LlamaConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
use_cache=True,
is_decoder=False,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
)
return (config, input_ids, input_mask)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, input_ids, attention_mask = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": attention_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
def check_use_cache_forward(self, model_class_name, config, input_ids, attention_mask):
max_decoder_length = 20
model = model_class_name(config)
past_key_values = model.init_cache(input_ids.shape[0], max_decoder_length)
attention_mask = jnp.ones((input_ids.shape[0], max_decoder_length), dtype="i4")
position_ids = jnp.broadcast_to(
jnp.arange(input_ids.shape[-1] - 1)[None, :], (input_ids.shape[0], input_ids.shape[-1] - 1)
)
outputs_cache = model(
input_ids[:, :-1],
attention_mask=attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
position_ids = jnp.array(input_ids.shape[0] * [[input_ids.shape[-1] - 1]], dtype="i4")
outputs_cache_next = model(
input_ids[:, -1:],
attention_mask=attention_mask,
past_key_values=outputs_cache.past_key_values,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
outputs = model(input_ids)
diff = np.max(np.abs((outputs_cache_next[0][:, -1, :5] - outputs[0][:, -1, :5])))
self.parent.assertTrue(diff < 1e-3, msg=f"Max diff is {diff}")
def check_use_cache_forward_with_attn_mask(self, model_class_name, config, input_ids, attention_mask):
max_decoder_length = 20
model = model_class_name(config)
attention_mask_cache = jnp.concatenate(
[attention_mask, jnp.zeros((attention_mask.shape[0], max_decoder_length - attention_mask.shape[1]))],
axis=-1,
)
past_key_values = model.init_cache(input_ids.shape[0], max_decoder_length)
position_ids = jnp.broadcast_to(
jnp.arange(input_ids.shape[-1] - 1)[None, :], (input_ids.shape[0], input_ids.shape[-1] - 1)
)
outputs_cache = model(
input_ids[:, :-1],
attention_mask=attention_mask_cache,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
position_ids = jnp.array(input_ids.shape[0] * [[input_ids.shape[-1] - 1]], dtype="i4")
outputs_cache_next = model(
input_ids[:, -1:],
past_key_values=outputs_cache.past_key_values,
attention_mask=attention_mask_cache,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
diff = np.max(np.abs((outputs_cache_next[0][:, -1, :5] - outputs[0][:, -1, :5])))
self.parent.assertTrue(diff < 1e-3, msg=f"Max diff is {diff}")
@require_flax
class FlaxLlamaModelTest(FlaxModelTesterMixin, FlaxGenerationTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (FlaxLlamaModel, FlaxLlamaForCausalLM) if is_flax_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (FlaxLlamaForCausalLM,) if is_flax_available() else ()
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = FlaxLlamaModelTester(self)
def test_use_cache_forward(self):
for model_class_name in self.all_model_classes:
config, input_ids, attention_mask = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.check_use_cache_forward(model_class_name, config, input_ids, attention_mask)
def test_use_cache_forward_with_attn_mask(self):
for model_class_name in self.all_model_classes:
config, input_ids, attention_mask = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.check_use_cache_forward_with_attn_mask(
model_class_name, config, input_ids, attention_mask
)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
for model_class_name in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class_name.from_pretrained("openlm-research/open_llama_3b_v2", from_pt=True)
outputs = model(np.ones((1, 1)))
self.assertIsNotNone(outputs)
@slow
@require_flax
class FlaxLlamaIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.model_id = "openlm-research/open_llama_3b_v2"
self.model = FlaxLlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id, from_pt=True)
self.test_batch = jnp.arange(32).reshape(4, 8) + 1911
def test_model_logits(self):
flax_logits = self.model(self.test_batch).logits
# fmt: off
EXPECTED_LOGITS = [-74.4243, -74.0680, -65.2507, -79.1658, -77.7460, -69.2379, -86.4588, -84.8933, -77.8456]
EXPECTED_MIN, EXPECTED_MAX, EXPECTED_MEAN = -96.9952
EXPECTED_MAX = -18.4571
EXPECTED_MEAN = -65.0608
# fmt: on
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(flax_logits[0, :3, :3].flatten(), EXPECTED_LOGITS, atol=1e-4))
self.assertAlmostEqual(flax_logits.min(), EXPECTED_MIN, places=3)
self.assertAlmostEqual(flax_logits.max(), EXPECTED_MAX, places=3)
self.assertAlmostEqual(flax_logits.mean(), EXPECTED_MEAN, places=3)
def test_model_hidden_states(self):
flax_hidden_states = self.model(self.test_batch, output_hidden_states=True).hidden_states
flax_hidden_means = [h.mean() for h in flax_hidden_states]
# fmt: off
EXPECTED_HIDDEN_MEANS = [
-0.00007,-0.00049,-0.00169,-0.00253,-0.00271,
-0.00290,-0.00252,0.00230,0.00230,0.00198,
0.00196,0.00174,0.00246,0.00205,0.00242,
0.00171,0.00092,0.00054,0.00102,0.00024,
0.00029,0.00037,-0.00101,-0.00062,-0.00341,-0.00636,-0.00357
]
# fmt: on
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(flax_hidden_means, EXPECTED_HIDDEN_MEANS, atol=1e-4))
def test_generated_text(self):
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
tokenizer.pad_token_id = 2
test_batch = ["Aloha, World! ", "2 + 2 = ", "Paris is the capital of ", "我很高興認識"]
inputs = tokenizer(test_batch, return_tensors="np", truncation=True, padding=True)
generated_ids = self.model.generate(**inputs, max_length=15).sequences
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
# fmt: off
EXPECTED_GENERATION = [
"Aloha, World! 201",
"2 + 2 = 4\n2",
"Paris is the capital of Île-",
"我很高興認識你,我"
]
# fmt: on
self.assertListEqual(generated_text, EXPECTED_GENERATION)
|
transformers/tests/models/llama/test_modeling_flax_llama.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/llama/test_modeling_flax_llama.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4765
}
| 205 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch Llava-NeXT model."""
import unittest
import numpy as np
import requests
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from parameterized import parameterized
from transformers import (
AutoProcessor,
LlavaOnevisionConfig,
LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration,
is_torch_available,
is_vision_available,
)
from transformers.testing_utils import (
cleanup,
require_bitsandbytes,
require_torch,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import (
ModelTesterMixin,
_config_zero_init,
floats_tensor,
ids_tensor,
)
if is_torch_available():
import torch
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
class LlavaOnevisionVisionText2TextModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
ignore_index=-100,
image_token_index=1,
projector_hidden_act="gelu",
seq_length=7,
vision_feature_select_strategy="full",
vision_feature_layer=-1,
text_config={
"model_type": "qwen2",
"seq_length": 7,
"is_training": True,
"use_input_mask": True,
"use_token_type_ids": False,
"use_labels": True,
"vocab_size": 99,
"hidden_size": 32,
"num_hidden_layers": 2,
"num_attention_heads": 4,
"num_key_value_heads": 4,
"intermediate_size": 37,
"hidden_act": "gelu",
"hidden_dropout_prob": 0.1,
"attention_probs_dropout_prob": 0.1,
"max_position_embeddings": 580,
"type_vocab_size": 16,
"type_sequence_label_size": 2,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"num_labels": 3,
"num_choices": 4,
"pad_token_id": 0,
},
is_training=True,
vision_config={
"image_size": 16,
"patch_size": 8,
"num_channels": 3,
"is_training": True,
"hidden_size": 32,
"projection_dim": 32,
"num_hidden_layers": 2,
"num_attention_heads": 4,
"intermediate_size": 37,
"dropout": 0.1,
"attention_dropout": 0.1,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
},
):
self.parent = parent
self.ignore_index = ignore_index
self.image_token_index = image_token_index
self.projector_hidden_act = projector_hidden_act
self.vision_feature_select_strategy = vision_feature_select_strategy
self.vision_feature_layer = vision_feature_layer
self.text_config = text_config
self.vision_config = vision_config
self.pad_token_id = text_config["pad_token_id"]
self.num_image_tokens = 10
self.seq_length = seq_length + self.num_image_tokens
self.num_hidden_layers = text_config["num_hidden_layers"]
self.vocab_size = text_config["vocab_size"]
self.hidden_size = text_config["hidden_size"]
self.num_attention_heads = text_config["num_attention_heads"]
self.is_training = is_training
self.batch_size = 3
self.num_channels = 3
self.image_size = 30
self.image_grid_pinpoints = [[16, 16]]
def get_config(self):
return LlavaOnevisionConfig(
text_config=self.text_config,
vision_config=self.vision_config,
ignore_index=self.ignore_index,
image_token_index=self.image_token_index,
projector_hidden_act=self.projector_hidden_act,
vision_feature_select_strategy=self.vision_feature_select_strategy,
vision_feature_layer=self.vision_feature_layer,
image_grid_pinpoints=self.image_grid_pinpoints,
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor(
[
self.batch_size,
3,
self.vision_config["num_channels"],
self.vision_config["image_size"],
self.vision_config["image_size"],
]
)
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values = config_and_inputs
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], config.text_config.vocab_size - 2) + 2
attention_mask = torch.ones(input_ids.shape, dtype=torch.long).to(torch_device)
input_ids[input_ids == config.image_token_index] = self.pad_token_id
input_ids[:, : self.num_image_tokens] = config.image_token_index
labels = torch.zeros((self.batch_size, self.seq_length), dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)
labels[:, : self.num_image_tokens] == self.ignore_index
inputs_dict = {
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"image_sizes": torch.tensor([[45, 45]] * self.batch_size),
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"labels": labels,
}
return config, inputs_dict
def create_and_check_llava_onevision_model_fp16_forward(
self, config, input_ids, pixel_values, attention_mask, image_sizes
):
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.half()
model.eval()
logits = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
image_sizes=image_sizes,
pixel_values=pixel_values.to(torch.bfloat16),
return_dict=True,
)["logits"]
self.parent.assertFalse(torch.isnan(logits).any().item())
def create_and_check_llava_onevision_model_fp16_autocast_forward(
self, config, input_ids, pixel_values, attention_mask, image_sizes
):
config.torch_dtype = torch.float16
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.autocast(device_type="cuda", dtype=torch.float16):
logits = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
image_sizes=image_sizes,
pixel_values=pixel_values.to(torch.bfloat16),
return_dict=True,
)["logits"]
self.parent.assertFalse(torch.isnan(logits).any().item())
@require_torch
class LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGenerationModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
"""
Model tester for `LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration`.
"""
all_model_classes = (LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration,) if is_torch_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"image-text-to-text": LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration} if is_torch_available() else {}
)
test_pruning = False
test_head_masking = False
_is_composite = True
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = LlavaOnevisionVisionText2TextModelTester(self)
common_properties = ["image_token_index", "video_token_index", "vision_feature_layer"]
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(
self, config_class=LlavaOnevisionConfig, has_text_modality=False, common_properties=common_properties
)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_initialization(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
configs_no_init = _config_zero_init(config)
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config=configs_no_init)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
# LLaVa Onevision has SigLIP backbone which init weights differently from CLIP
if "image_newline" in name or "vision_tower" in name:
continue
elif param.requires_grad:
self.assertIn(
((param.data.mean() * 1e9).round() / 1e9).item(),
[0.0, 1.0],
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
# overwrite inputs_embeds tests because we need to delete "pixel values" for LVLMs
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["pixel_values"]
wte = model.get_input_embeddings()
inputs["inputs_embeds"] = wte(input_ids)
with torch.no_grad():
model(**inputs)
# overwrite inputs_embeds tests because we need to delete "pixel values" for LVLMs
# while some other models require pixel_values to be present
def test_inputs_embeds_matches_input_ids(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["pixel_values"]
inputs_embeds = model.get_input_embeddings()(input_ids)
with torch.no_grad():
out_ids = model(input_ids=input_ids, **inputs)[0]
out_embeds = model(inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, **inputs)[0]
torch.testing.assert_close(out_embeds, out_ids)
@parameterized.expand(
[
(-1,),
([-1],),
([-1, -2],),
],
)
def test_vision_feature_layers(self, vision_feature_layer):
"""
Test that we can use either one vision feature layer, or a list of
vision feature layers.
"""
config, input_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.vision_feature_layer = vision_feature_layer
num_feature_layers = 1 if isinstance(vision_feature_layer, int) else len(vision_feature_layer)
hidden_size = config.vision_config.hidden_size
expected_features = hidden_size * num_feature_layers
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config).to(torch_device)
# We should have the right number of input features,
# and should be able to run a forward pass without exploding
assert model.multi_modal_projector.linear_1.in_features == expected_features
model(**input_dict)
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, SiglipVisionModel does not support standalone training"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, SiglipVisionModel does not support standalone training"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
reason="This architecure seem to not compute gradients properly when using GC, SiglipVisionModel does not support standalone training"
)
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant_false(self):
pass
@unittest.skip("FlashAttention only support fp16 and bf16 data type")
def test_flash_attn_2_fp32_ln(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(
"VLMs need lots of steps to prepare images/mask correctly to get pad-free inputs. Can be tested as part of LLM test"
)
def test_flash_attention_2_padding_matches_padding_free_with_position_ids(self):
pass
@require_torch
class LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGenerationIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf", padding_side="left"
)
image_file = hf_hub_download(
repo_id="raushan-testing-hf/images_test", filename="llava_v1_5_radar.jpg", repo_type="dataset"
)
video_file = hf_hub_download(
repo_id="raushan-testing-hf/videos-test", filename="video_demo.npy", repo_type="dataset"
)
self.image = Image.open(image_file)
self.video = np.load(video_file)
self.prompt_image = "user\n<image>\nWhat do you see in this image?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n"
self.prompt_video = "user\n<video>\nWhat do you see in this video?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n"
def tearDown(self):
cleanup(torch_device, gc_collect=True)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test(self):
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf", torch_dtype="float16", device_map=torch_device
)
inputs = self.processor(images=self.image, text=self.prompt_image, return_tensors="pt").to(
torch_device, torch.float16
)
self.assertTrue(inputs.input_ids.shape[1] == 6567) # should expand num-image-tokens times
self.assertTrue(inputs.pixel_values.shape == torch.Size([1, 10, 3, 384, 384]))
self.assertTrue(inputs.image_sizes.tolist() == [[899, 1024]])
# verify single forward pass
inputs = inputs.to(torch_device)
# verify generation
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = 'user\n\nWhat do you see in this image?\nassistant\nThe image is a radar chart that compares the performance of different models in a specific task, likely related to natural language processing or machine learning. The chart is divided into several axes, each representing a different model or method. The models are color-coded and labeled with their respective names. The axes are labeled with terms such as "VQA," "GQA," "MQA," "VQAv2," "MM-Vet," "LLaVA-Bench," "LLaVA-1' # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_batch(self):
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf", torch_dtype="float16", device_map=torch_device
)
inputs = self.processor(
text=[self.prompt_image, self.prompt_video],
images=self.image,
videos=self.video,
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True,
).to(torch_device, torch.float16)
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = ['user\n\nWhat do you see in this image?\nassistant\nThe image is a radar chart that compares the performance of different models in a specific task, likely related', 'user\n\nWhat do you see in this video?\nassistant\nA child wearing a light blue sleeveless top and pink pants is seen sitting on a bed, eng'] # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.batch_decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_video(self):
# related to (#29835)
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf",
torch_dtype="float16",
device_map=torch_device,
)
inputs = self.processor(text=self.prompt_video, videos=self.video, return_tensors="pt").to(
torch_device, torch.float16
)
# verify generation
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=40)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = 'user\n\nWhat do you see in this video?\nassistant\nA child wearing a light blue sleeveless top and pink pants is seen sitting on a bed, engrossed in reading a book.' # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_multi_image(self):
# related to (#29835)
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf",
torch_dtype="float16",
device_map=torch_device,
)
url = "https://www.ilankelman.org/stopsigns/australia.jpg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
prompt = (
"user\n<image><image>\nWhat is the difference between these images?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n"
)
inputs = self.processor(text=prompt, images=[self.image, image], return_tensors="pt").to(
torch_device, torch.float16
)
# verify generation
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=40)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = "user\n\nWhat is the difference between these images?\nassistant\nThe images you've provided appear to be related to a graphical representation of a radar chart, which is a type of data visualization used to show the distribution of a particular variable across a geographic area. The" # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_multi_video(self):
# related to (#29835)
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf",
torch_dtype="float16",
device_map=torch_device,
)
prompt = "user\n<video><video>\nAre these videos identical?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n"
inputs = self.processor(text=prompt, videos=[self.video, self.video], return_tensors="pt").to(
torch_device, torch.float16
)
# verify generation
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=40)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = "user\n\nAre these videos identical?\nassistant\nNo, the video is not identical; it shows slight variations in the child's actions and the background." # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_batch_different_resolutions(self):
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf", torch_dtype="float16", device_map=torch_device
)
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
lowres_url = "https://4.img-dpreview.com/files/p/TS560x560~forums/56876524/03975b28741443319e9a94615e35667e"
cats_image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
lowres_img = Image.open(requests.get(lowres_url, stream=True).raw)
inputs = self.processor(
text=[self.prompt_image, self.prompt_image],
images=[lowres_img, cats_image],
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True,
).to(torch_device, torch.float16)
# verify generation
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=50)
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT = ['user\n\nWhat do you see in this image?\nassistant\nThe image shows a scene from a wildlife camera, likely a security camera, capturing a moment in a natural setting. It features two deer, one larger and one smaller, grazing on the grass. The environment is foggy, suggesting early morning or late', 'user\n\nWhat do you see in this image?\nassistant\nIn the tranquil setting of this image, two cats are enjoying a peaceful nap on a vibrant pink blanket. The cat on the left, with its gray and black striped fur, is lying on its side, its head comfortably resting on the blanket. Its'] # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.batch_decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True),
EXPECTED_DECODED_TEXT,
)
@slow
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_small_model_integration_test_batch_matches_single(self):
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf",
torch_dtype="float16",
device_map=torch_device,
)
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
lowres_url = "https://4.img-dpreview.com/files/p/TS560x560~forums/56876524/03975b28741443319e9a94615e35667e"
cats_image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
lowres_img = Image.open(requests.get(lowres_url, stream=True).raw)
inputs_batched = self.processor(
text=[self.prompt_image, self.prompt_image],
images=[lowres_img, cats_image],
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True,
).to(torch_device, torch.float16)
inputs_single = self.processor(
text=self.prompt_image, images=lowres_img, return_tensors="pt", padding=True
).to(torch_device, torch.float16)
# verify generation
output_batched = model.generate(**inputs_batched, max_new_tokens=50)
output_single = model.generate(**inputs_single, max_new_tokens=50)
self.assertEqual(
self.processor.decode(output_batched[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
self.processor.decode(output_single[0], skip_special_tokens=True),
)
|
transformers/tests/models/llava_onevision/test_modeling_llava_onevision.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/llava_onevision/test_modeling_llava_onevision.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 10091
}
| 206 |
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
# Copyright 2021 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch MegatronBERT model."""
import math
import os
import unittest
from transformers import MegatronBertConfig, is_torch_available
from transformers.models.auto import get_values
from transformers.testing_utils import require_sentencepiece, require_tokenizers, require_torch, slow, torch_device
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING,
MegatronBertForCausalLM,
MegatronBertForMaskedLM,
MegatronBertForMultipleChoice,
MegatronBertForNextSentencePrediction,
MegatronBertForPreTraining,
MegatronBertForQuestionAnswering,
MegatronBertForSequenceClassification,
MegatronBertForTokenClassification,
MegatronBertModel,
)
class MegatronBertModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=True,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=64,
embedding_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = self.get_config()
return config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
def get_config(self):
return MegatronBertConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
embedding_size=self.embedding_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
is_decoder=False,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
)
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_model(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = MegatronBertModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.pooler_output.shape, (self.batch_size, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_masked_lm(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = MegatronBertForMaskedLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_for_causal_lm(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = MegatronBertForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_next_sequence_prediction(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = MegatronBertForNextSentencePrediction(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
labels=sequence_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, 2))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_pretraining(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = MegatronBertForPreTraining(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
labels=token_labels,
next_sentence_label=sequence_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.prediction_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.seq_relationship_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, 2))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_question_answering(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = MegatronBertForQuestionAnswering(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
start_positions=sequence_labels,
end_positions=sequence_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.start_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.end_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_sequence_classification(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = MegatronBertForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=sequence_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_token_classification(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = MegatronBertForTokenClassification(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_multiple_choice(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_choices = self.num_choices
model = MegatronBertForMultipleChoice(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
multiple_choice_inputs_ids = input_ids.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
multiple_choice_token_type_ids = token_type_ids.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
multiple_choice_input_mask = input_mask.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
result = model(
multiple_choice_inputs_ids,
attention_mask=multiple_choice_input_mask,
token_type_ids=multiple_choice_token_type_ids,
labels=choice_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_choices))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids, "attention_mask": input_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class MegatronBertModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
MegatronBertModel,
MegatronBertForMaskedLM,
MegatronBertForCausalLM,
MegatronBertForMultipleChoice,
MegatronBertForNextSentencePrediction,
MegatronBertForPreTraining,
MegatronBertForQuestionAnswering,
MegatronBertForSequenceClassification,
MegatronBertForTokenClassification,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": MegatronBertModel,
"fill-mask": MegatronBertForMaskedLM,
"question-answering": MegatronBertForQuestionAnswering,
"text-classification": MegatronBertForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": MegatronBertForCausalLM,
"token-classification": MegatronBertForTokenClassification,
"zero-shot": MegatronBertForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
fx_compatible = True
# test_resize_embeddings = False
test_head_masking = False
# special case for ForPreTraining model
def _prepare_for_class(self, inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=False):
inputs_dict = super()._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=return_labels)
if return_labels:
if model_class in get_values(MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING):
inputs_dict["labels"] = torch.zeros(
(self.model_tester.batch_size, self.model_tester.seq_length), dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device
)
inputs_dict["next_sentence_label"] = torch.zeros(
self.model_tester.batch_size, dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device
)
return inputs_dict
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = MegatronBertModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=MegatronBertConfig, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_megatron_bert_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_masked_lm(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_masked_lm(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_multiple_choice(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_multiple_choice(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_next_sequence_prediction(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_next_sequence_prediction(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_pretraining(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_pretraining(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_question_answering(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_question_answering(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_sequence_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_sequence_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_token_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_megatron_bert_for_token_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def _long_tensor(tok_lst):
return torch.tensor(
tok_lst,
dtype=torch.long,
device=torch_device,
)
TOLERANCE = 1e-4
@require_torch
@require_sentencepiece
@require_tokenizers
class MegatronBertModelIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
@unittest.skip(reason="Model is not available.")
def test_inference_no_head(self):
directory = "nvidia/megatron-bert-uncased-345m"
if "MYDIR" in os.environ:
directory = os.path.join(os.environ["MYDIR"], directory)
model = MegatronBertModel.from_pretrained(directory)
model.to(torch_device)
model.half()
input_ids = _long_tensor([[101, 7110, 1005, 1056, 2023, 11333, 17413, 1029, 102]])
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_ids)[0]
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 9, 1024))
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_shape)
expected = [-0.6040, -0.2517, -0.1025, 0.3420, -0.6758, -0.0017, -0.1089, -0.1990, 0.5728]
for ii in range(3):
for jj in range(3):
a = output[0, ii, jj]
b = expected[3 * ii + jj]
msg = "ii={} jj={} a={} b={}".format(ii, jj, a, b)
self.assertTrue(math.isclose(a, b, rel_tol=TOLERANCE, abs_tol=TOLERANCE), msg=msg)
|
transformers/tests/models/megatron_bert/test_modeling_megatron_bert.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/megatron_bert/test_modeling_megatron_bert.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 7274
}
| 207 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
import numpy as np
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, require_vision
from transformers.utils import is_torch_available, is_vision_available
from ...test_image_processing_common import ImageProcessingTestMixin
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import MllamaImageProcessor
if is_torch_available():
import torch
class MllamaImageProcessingTester(unittest.TestCase):
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=7,
num_channels=3,
image_size=18,
num_images=18,
min_resolution=30,
max_resolution=400,
do_resize=True,
size=None,
do_rescale=True,
rescale_factor=1 / 255,
do_normalize=True,
image_mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
image_std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
do_convert_rgb=True,
do_pad=True,
max_image_tiles=4,
):
super().__init__()
size = size if size is not None else {"height": 224, "width": 224}
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.max_image_tiles = max_image_tiles
self.image_size = image_size
self.num_images = num_images
self.min_resolution = min_resolution
self.max_resolution = max_resolution
self.do_resize = do_resize
self.size = size
self.do_normalize = do_normalize
self.image_mean = image_mean
self.image_std = image_std
self.do_rescale = do_rescale
self.rescale_factor = rescale_factor
self.do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb
self.do_pad = do_pad
def prepare_image_processor_dict(self):
return {
"do_convert_rgb": self.do_convert_rgb,
"do_resize": self.do_resize,
"size": self.size,
"do_rescale": self.do_rescale,
"rescale_factor": self.rescale_factor,
"do_normalize": self.do_normalize,
"image_mean": self.image_mean,
"image_std": self.image_std,
"do_pad": self.do_pad,
"max_image_tiles": self.max_image_tiles,
}
def prepare_image_inputs(
self,
batch_size=None,
min_resolution=None,
max_resolution=None,
num_channels=None,
num_images=None,
size_divisor=None,
equal_resolution=False,
numpify=False,
torchify=False,
):
"""This function prepares a list of PIL images, or a list of numpy arrays if one specifies numpify=True,
or a list of PyTorch tensors if one specifies torchify=True.
One can specify whether the images are of the same resolution or not.
"""
assert not (numpify and torchify), "You cannot specify both numpy and PyTorch tensors at the same time"
batch_size = batch_size if batch_size is not None else self.batch_size
min_resolution = min_resolution if min_resolution is not None else self.min_resolution
max_resolution = max_resolution if max_resolution is not None else self.max_resolution
num_channels = num_channels if num_channels is not None else self.num_channels
num_images = num_images if num_images is not None else self.num_images
images_list = []
for i in range(batch_size):
images = []
for j in range(num_images):
if equal_resolution:
width = height = max_resolution
else:
# To avoid getting image width/height 0
if size_divisor is not None:
# If `size_divisor` is defined, the image needs to have width/size >= `size_divisor`
min_resolution = max(size_divisor, min_resolution)
width, height = np.random.choice(np.arange(min_resolution, max_resolution), 2)
images.append(np.random.randint(255, size=(num_channels, width, height), dtype=np.uint8))
images_list.append(images)
if not numpify and not torchify:
# PIL expects the channel dimension as last dimension
images_list = [[Image.fromarray(np.moveaxis(image, 0, -1)) for image in images] for images in images_list]
if torchify:
images_list = [[torch.from_numpy(image) for image in images] for images in images_list]
return images_list
def expected_output_image_shape(self, images):
expected_output_image_shape = (
max(len(images) for images in images),
self.max_image_tiles,
self.num_channels,
self.size["height"],
self.size["width"],
)
return expected_output_image_shape
@require_torch
@require_vision
class MllamaImageProcessingTest(ImageProcessingTestMixin, unittest.TestCase):
image_processing_class = MllamaImageProcessor if is_vision_available() else None
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
self.image_processor_tester = MllamaImageProcessingTester(self)
@property
def image_processor_dict(self):
return self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_processor_dict()
def test_image_processor_properties(self):
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_convert_rgb"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_resize"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "size"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_rescale"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "rescale_factor"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_normalize"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "image_mean"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "image_std"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_pad"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "max_image_tiles"))
def test_call_numpy(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random numpy tensors
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=False, numpify=True)
for sample_images in image_inputs:
for image in sample_images:
self.assertIsInstance(image, np.ndarray)
expected_output_image_shape = (
max(len(images) for images in image_inputs),
self.image_processor_tester.max_image_tiles,
self.image_processor_tester.num_channels,
self.image_processor_tester.size["height"],
self.image_processor_tester.size["width"],
)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape([image_inputs[0]])
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), (1, *expected_output_image_shape))
# Test batched
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape(image_inputs)
self.assertEqual(
tuple(encoded_images.shape), (self.image_processor_tester.batch_size, *expected_output_image_shape)
)
def test_call_pil(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random PIL images
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=False)
for images in image_inputs:
for image in images:
self.assertIsInstance(image, Image.Image)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape([image_inputs[0]])
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), (1, *expected_output_image_shape))
# Test batched
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape(image_inputs)
self.assertEqual(
tuple(encoded_images.shape), (self.image_processor_tester.batch_size, *expected_output_image_shape)
)
def test_call_pytorch(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random PyTorch tensors
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=False, torchify=True)
for images in image_inputs:
for image in images:
self.assertIsInstance(image, torch.Tensor)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape([image_inputs[0]])
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), (1, *expected_output_image_shape))
# Test batched
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape(image_inputs)
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
self.assertEqual(
tuple(encoded_images.shape),
(self.image_processor_tester.batch_size, *expected_output_image_shape),
)
def test_call_numpy_4_channels(self):
self.skipTest("4 channels input is not supported yet")
def test_image_correctly_tiled(self):
def get_empty_tiles(pixel_values):
# image has shape batch_size, max_num_images, max_image_tiles, num_channels, height, width
# we want to get a binary mask of shape batch_size, max_num_images, max_image_tiles
# of empty tiles, i.e. tiles that are completely zero
return np.all(pixel_values == 0, axis=(3, 4, 5))
image_processor_dict = {**self.image_processor_dict, "size": {"height": 50, "width": 50}, "max_image_tiles": 4}
image_processor = self.image_processing_class(**image_processor_dict)
# image fits 2x2 tiles grid (width x height)
image = Image.new("RGB", (80, 95))
inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="np")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
empty_tiles = get_empty_tiles(pixel_values)[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(empty_tiles, [False, False, False, False])
aspect_ratio_ids = inputs.aspect_ratio_ids[0, 0]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_ids, 6)
aspect_ratio_mask = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_mask, [1, 1, 1, 1])
# image fits 3x1 grid (width x height)
image = Image.new("RGB", (101, 50))
inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="np")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
empty_tiles = get_empty_tiles(pixel_values)[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(empty_tiles, [False, False, False, True])
aspect_ratio_ids = inputs.aspect_ratio_ids[0, 0]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_ids, 3)
num_tiles = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask[0, 0].sum()
self.assertEqual(num_tiles, 3)
aspect_ratio_mask = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_mask, [1, 1, 1, 0])
# image fits 1x1 grid (width x height)
image = Image.new("RGB", (20, 39))
inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="np")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
empty_tiles = get_empty_tiles(pixel_values)[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(empty_tiles, [False, True, True, True])
aspect_ratio_ids = inputs.aspect_ratio_ids[0, 0]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_ids, 1)
aspect_ratio_mask = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_mask, [1, 0, 0, 0])
# image fits 2x1 grid (width x height)
image = Image.new("RGB", (51, 20))
inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="np")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
empty_tiles = get_empty_tiles(pixel_values)[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(empty_tiles, [False, False, True, True])
aspect_ratio_ids = inputs.aspect_ratio_ids[0, 0]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_ids, 2)
aspect_ratio_mask = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_mask, [1, 1, 0, 0])
# image is greater than 2x2 tiles grid (width x height)
image = Image.new("RGB", (150, 150))
inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="np")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
empty_tiles = get_empty_tiles(pixel_values)[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(empty_tiles, [False, False, False, False])
aspect_ratio_ids = inputs.aspect_ratio_ids[0, 0]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_ids, 6) # (2 - 1) * 4 + 2 = 6
aspect_ratio_mask = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask[0, 0].tolist()
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_mask, [1, 1, 1, 1])
# batch of images
image1 = Image.new("RGB", (80, 95))
image2 = Image.new("RGB", (101, 50))
image3 = Image.new("RGB", (23, 49))
inputs = image_processor([[image1], [image2, image3]], return_tensors="np")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
empty_tiles = get_empty_tiles(pixel_values).tolist()
expected_empty_tiles = [
# sample 1 with 1 image 2x2 grid
[
[False, False, False, False],
[True, True, True, True], # padding
],
# sample 2
[
[False, False, False, True], # 3x1
[False, True, True, True], # 1x1
],
]
self.assertEqual(empty_tiles, expected_empty_tiles)
aspect_ratio_ids = inputs.aspect_ratio_ids.tolist()
expected_aspect_ratio_ids = [[6, 0], [3, 1]]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_ids, expected_aspect_ratio_ids)
aspect_ratio_mask = inputs.aspect_ratio_mask.tolist()
expected_aspect_ratio_mask = [
[
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0],
],
[
[1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0],
],
]
self.assertEqual(aspect_ratio_mask, expected_aspect_ratio_mask)
|
transformers/tests/models/mllama/test_image_processing_mllama.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/mllama/test_image_processing_mllama.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 6705
}
| 208 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2021, The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch MVP model."""
import copy
import tempfile
import unittest
import timeout_decorator # noqa
from transformers import MvpConfig, is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import (
require_sentencepiece,
require_tokenizers,
require_torch,
require_torch_fp16,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from transformers.utils import cached_property
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
MvpForCausalLM,
MvpForConditionalGeneration,
MvpForQuestionAnswering,
MvpForSequenceClassification,
MvpModel,
MvpTokenizer,
)
from transformers.models.mvp.modeling_mvp import MvpDecoder, MvpEncoder, shift_tokens_right
def prepare_mvp_inputs_dict(
config,
input_ids,
decoder_input_ids=None,
attention_mask=None,
decoder_attention_mask=None,
head_mask=None,
decoder_head_mask=None,
cross_attn_head_mask=None,
):
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(config.pad_token_id)
if decoder_attention_mask is None:
decoder_attention_mask = decoder_input_ids.ne(config.pad_token_id)
if head_mask is None:
head_mask = torch.ones(config.encoder_layers, config.encoder_attention_heads, device=torch_device)
if decoder_head_mask is None:
decoder_head_mask = torch.ones(config.decoder_layers, config.decoder_attention_heads, device=torch_device)
if cross_attn_head_mask is None:
cross_attn_head_mask = torch.ones(config.decoder_layers, config.decoder_attention_heads, device=torch_device)
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"decoder_input_ids": decoder_input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"decoder_attention_mask": attention_mask,
"head_mask": head_mask,
"decoder_head_mask": decoder_head_mask,
"cross_attn_head_mask": cross_attn_head_mask,
}
class MvpModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_labels=False,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=16,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=4,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=20,
eos_token_id=2,
pad_token_id=1,
bos_token_id=0,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.eos_token_id = eos_token_id
self.pad_token_id = pad_token_id
self.bos_token_id = bos_token_id
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size).clamp(
3,
)
input_ids[:, -1] = self.eos_token_id # Eos Token
decoder_input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
config = self.get_config()
inputs_dict = prepare_mvp_inputs_dict(config, input_ids, decoder_input_ids)
return config, inputs_dict
def get_config(self):
return MvpConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
d_model=self.hidden_size,
encoder_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
decoder_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
encoder_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
decoder_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
encoder_ffn_dim=self.intermediate_size,
decoder_ffn_dim=self.intermediate_size,
dropout=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_dropout=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
eos_token_id=self.eos_token_id,
bos_token_id=self.bos_token_id,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
)
def get_pipeline_config(self):
config = self.get_config()
config.max_position_embeddings = 100
config.vocab_size = 300
return config
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
return config, inputs_dict
def create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(self, config, inputs_dict):
model = MvpModel(config=config).get_decoder().to(torch_device).eval()
input_ids = inputs_dict["input_ids"]
attention_mask = inputs_dict["attention_mask"]
head_mask = inputs_dict["head_mask"]
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, head_mask=head_mask, use_cache=True)
output, past_key_values = outputs.to_tuple()
# create hypothetical multiple next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_attn_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), 2)
# append to next input_ids and
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([attention_mask, next_attn_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, attention_mask=next_attention_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, attention_mask=next_attention_mask, past_key_values=past_key_values)[
"last_hidden_state"
]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past_slice.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def check_encoder_decoder_model_standalone(self, config, inputs_dict):
model = MvpModel(config=config).to(torch_device).eval()
outputs = model(**inputs_dict)
encoder_last_hidden_state = outputs.encoder_last_hidden_state
last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
encoder = model.get_encoder()
encoder.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
encoder = MvpEncoder.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
encoder_last_hidden_state_2 = encoder(inputs_dict["input_ids"], attention_mask=inputs_dict["attention_mask"])[
0
]
self.parent.assertTrue((encoder_last_hidden_state_2 - encoder_last_hidden_state).abs().max().item() < 1e-3)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
decoder = model.get_decoder()
decoder.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
decoder = MvpDecoder.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
last_hidden_state_2 = decoder(
input_ids=inputs_dict["decoder_input_ids"],
attention_mask=inputs_dict["decoder_attention_mask"],
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_last_hidden_state,
encoder_attention_mask=inputs_dict["attention_mask"],
)[0]
self.parent.assertTrue((last_hidden_state_2 - last_hidden_state).abs().max().item() < 1e-3)
@require_torch
class MvpHeadTests(unittest.TestCase):
vocab_size = 99
def _get_config_and_data(self):
input_ids = torch.tensor(
[
[71, 82, 18, 33, 46, 91, 2],
[68, 34, 26, 58, 30, 82, 2],
[5, 97, 17, 39, 94, 40, 2],
[76, 83, 94, 25, 70, 78, 2],
[87, 59, 41, 35, 48, 66, 2],
[55, 13, 16, 58, 5, 2, 1], # note padding
[64, 27, 31, 51, 12, 75, 2],
[52, 64, 86, 17, 83, 39, 2],
[48, 61, 9, 24, 71, 82, 2],
[26, 1, 60, 48, 22, 13, 2],
[21, 5, 62, 28, 14, 76, 2],
[45, 98, 37, 86, 59, 48, 2],
[70, 70, 50, 9, 28, 0, 2],
],
dtype=torch.long,
device=torch_device,
)
batch_size = input_ids.shape[0]
config = MvpConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
d_model=24,
encoder_layers=2,
decoder_layers=2,
encoder_attention_heads=2,
decoder_attention_heads=2,
encoder_ffn_dim=32,
decoder_ffn_dim=32,
max_position_embeddings=48,
eos_token_id=2,
pad_token_id=1,
bos_token_id=0,
)
return config, input_ids, batch_size
def test_sequence_classification_forward(self):
config, input_ids, batch_size = self._get_config_and_data()
labels = _long_tensor([2] * batch_size).to(torch_device)
config.num_labels = 3
model = MvpForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
outputs = model(input_ids=input_ids, decoder_input_ids=input_ids, labels=labels)
expected_shape = torch.Size((batch_size, config.num_labels))
self.assertEqual(outputs["logits"].shape, expected_shape)
self.assertIsInstance(outputs["loss"].item(), float)
def test_question_answering_forward(self):
config, input_ids, batch_size = self._get_config_and_data()
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([batch_size], 2).to(torch_device)
model = MvpForQuestionAnswering(config)
model.to(torch_device)
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
start_positions=sequence_labels,
end_positions=sequence_labels,
)
self.assertEqual(outputs["start_logits"].shape, input_ids.shape)
self.assertEqual(outputs["end_logits"].shape, input_ids.shape)
self.assertIsInstance(outputs["loss"].item(), float)
@timeout_decorator.timeout(1)
def test_lm_forward(self):
config, input_ids, batch_size = self._get_config_and_data()
lm_labels = ids_tensor([batch_size, input_ids.shape[1]], self.vocab_size).to(torch_device)
lm_model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config)
lm_model.to(torch_device)
outputs = lm_model(input_ids=input_ids, labels=lm_labels)
expected_shape = (batch_size, input_ids.shape[1], config.vocab_size)
self.assertEqual(outputs["logits"].shape, expected_shape)
self.assertIsInstance(outputs["loss"].item(), float)
def test_lm_uneven_forward(self):
config = MvpConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
d_model=14,
encoder_layers=2,
decoder_layers=2,
encoder_attention_heads=2,
decoder_attention_heads=2,
encoder_ffn_dim=8,
decoder_ffn_dim=8,
max_position_embeddings=48,
)
lm_model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config).to(torch_device)
context = torch.tensor(
[[71, 82, 18, 33, 46, 91, 2], [68, 34, 26, 58, 30, 2, 1]], device=torch_device, dtype=torch.long
)
summary = torch.tensor([[82, 71, 82, 18, 2], [58, 68, 2, 1, 1]], device=torch_device, dtype=torch.long)
outputs = lm_model(input_ids=context, decoder_input_ids=summary, labels=summary)
expected_shape = (*summary.shape, config.vocab_size)
self.assertEqual(outputs["logits"].shape, expected_shape)
def test_generate_beam_search(self):
input_ids = torch.tensor([[71, 82, 2], [68, 34, 2]], device=torch_device, dtype=torch.long)
config = MvpConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
d_model=24,
encoder_layers=2,
decoder_layers=2,
encoder_attention_heads=2,
decoder_attention_heads=2,
encoder_ffn_dim=32,
decoder_ffn_dim=32,
max_position_embeddings=48,
eos_token_id=2,
pad_token_id=1,
bos_token_id=0,
)
lm_model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config).to(torch_device)
lm_model.eval()
max_length = 5
generated_ids = lm_model.generate(
input_ids.clone(),
do_sample=True,
num_return_sequences=1,
num_beams=2,
no_repeat_ngram_size=3,
max_length=max_length,
)
self.assertEqual(generated_ids.shape, (input_ids.shape[0], max_length))
def test_shift_tokens_right(self):
input_ids = torch.tensor([[71, 82, 18, 33, 2, 1, 1], [68, 34, 26, 58, 30, 82, 2]], dtype=torch.long)
shifted = shift_tokens_right(input_ids, 1, 2)
n_pad_before = input_ids.eq(1).float().sum()
n_pad_after = shifted.eq(1).float().sum()
self.assertEqual(shifted.shape, input_ids.shape)
self.assertEqual(n_pad_after, n_pad_before - 1)
self.assertTrue(torch.eq(shifted[:, 0], 2).all())
@slow
def test_tokenization(self):
tokenizer = MvpTokenizer.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp")
examples = [" Hello world", " DomDramg"] # need leading spaces for equality
fairseq_results = [
torch.tensor([0, 20920, 232, 2]),
torch.tensor([0, 11349, 495, 4040, 571, 2]),
]
for ex, desired_result in zip(examples, fairseq_results):
mvp_toks = tokenizer.encode(ex, return_tensors="pt").squeeze()
assert_tensors_close(desired_result.long(), mvp_toks, prefix=ex)
@require_torch_fp16
def test_generate_fp16(self):
config, input_ids, batch_size = self._get_config_and_data()
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(1).to(torch_device)
model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config).eval().to(torch_device)
model.half()
model.generate(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
model.generate(num_beams=4, do_sample=True, early_stopping=False, num_return_sequences=3)
def test_dummy_inputs(self):
config, *_ = self._get_config_and_data()
model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config).eval().to(torch_device)
model(**model.dummy_inputs)
def test_resize_tokens_embeddings_more(self):
config, input_ids, _ = self._get_config_and_data()
def _get_embs(m):
return (m.get_input_embeddings().weight.data.clone(), m.get_output_embeddings().weight.data.clone())
model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config).eval().to(torch_device)
input, output = _get_embs(model)
self.assertTrue(torch.eq(input, output).all())
new_vocab_size = 45
model.resize_token_embeddings(new_vocab_size)
input_new, output_new = _get_embs(model)
self.assertEqual(input_new.shape, (new_vocab_size, config.d_model))
self.assertEqual(output_new.shape, (new_vocab_size, config.d_model))
self.assertTrue(torch.eq(input_new, output_new).all())
@require_torch
class MvpModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(MvpModel, MvpForConditionalGeneration, MvpForSequenceClassification, MvpForQuestionAnswering)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
all_generative_model_classes = (MvpForConditionalGeneration,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": MvpModel,
"fill-mask": MvpForConditionalGeneration,
"question-answering": MvpForQuestionAnswering,
"summarization": MvpForConditionalGeneration,
"text-classification": MvpForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": MvpForCausalLM,
"text2text-generation": MvpForConditionalGeneration,
"translation": MvpForConditionalGeneration,
"zero-shot": MvpForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
is_encoder_decoder = True
fx_compatible = False
test_pruning = False
test_missing_keys = False
# TODO: Fix the failed tests
def is_pipeline_test_to_skip(
self,
pipeline_test_case_name,
config_class,
model_architecture,
tokenizer_name,
image_processor_name,
feature_extractor_name,
processor_name,
):
if (
pipeline_test_case_name == "QAPipelineTests"
and tokenizer_name is not None
and not tokenizer_name.endswith("Fast")
):
# `QAPipelineTests` fails for a few models when the slower tokenizer are used.
# (The slower tokenizers were never used for pipeline tests before the pipeline testing rework)
# TODO: check (and possibly fix) the `QAPipelineTests` with slower tokenizer
return True
return False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = MvpModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=MvpConfig)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_save_load_strict(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model2, info = model_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, output_loading_info=True)
self.assertEqual(info["missing_keys"], [])
def test_decoder_model_past_with_large_inputs(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_encoder_decoder_model_standalone(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
self.model_tester.check_encoder_decoder_model_standalone(*config_and_inputs)
# MvpForSequenceClassification does not support inputs_embeds
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in (MvpModel, MvpForConditionalGeneration, MvpForQuestionAnswering):
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
inputs = copy.deepcopy(self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
if not self.is_encoder_decoder:
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
del inputs["input_ids"]
else:
encoder_input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
decoder_input_ids = inputs.get("decoder_input_ids", encoder_input_ids)
del inputs["input_ids"]
inputs.pop("decoder_input_ids", None)
wte = model.get_input_embeddings()
if not self.is_encoder_decoder:
inputs["inputs_embeds"] = wte(input_ids)
else:
inputs["inputs_embeds"] = wte(encoder_input_ids)
inputs["decoder_inputs_embeds"] = wte(decoder_input_ids)
with torch.no_grad():
model(**inputs)[0]
@require_torch_fp16
def test_generate_fp16(self):
config, input_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
input_ids = input_dict["input_ids"]
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(1).to(torch_device)
model = MvpForConditionalGeneration(config).eval().to(torch_device)
model.half()
model.generate(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
model.generate(num_beams=4, do_sample=True, early_stopping=False, num_return_sequences=3)
def assert_tensors_close(a, b, atol=1e-12, prefix=""):
"""If tensors have different shapes, different values or a and b are not both tensors, raise a nice Assertion error."""
if a is None and b is None:
return True
try:
if torch.allclose(a, b, atol=atol):
return True
raise
except Exception:
pct_different = (torch.gt((a - b).abs(), atol)).float().mean().item()
if a.numel() > 100:
msg = f"tensor values are {pct_different:.1%} percent different."
else:
msg = f"{a} != {b}"
if prefix:
msg = prefix + ": " + msg
raise AssertionError(msg)
def _long_tensor(tok_lst):
return torch.tensor(tok_lst, dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)
@require_torch
@require_sentencepiece
@require_tokenizers
class MvpModelIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
@cached_property
def default_tokenizer(self):
return MvpTokenizer.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp")
@slow
def test_inference_no_head(self):
model = MvpModel.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp").to(torch_device)
input_ids = _long_tensor([[0, 31414, 232, 328, 740, 1140, 12695, 69, 46078, 1588, 2]])
attention_mask = input_ids.ne(model.config.pad_token_id)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask).last_hidden_state
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 11, 1024))
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor(
[[0.3461, 0.3624, 0.2689], [0.3461, 0.3624, 0.2689], [-0.1562, 1.1637, -0.3784]], device=torch_device
)
torch.testing.assert_close(output[:, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
@slow
def test_summarization_inference(self):
model = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp").to(torch_device)
tok = self.default_tokenizer
PGE_ARTICLE = """ Listen to local radio broadcasts for advertisements that reference casinos in your area.\nIf none are in your area, listen to national radio broadcasts for advertisements of casinos in other areas.\nNote the location that is mentioned in each advertisement that involves a casino.\nIf no locations are mentioned, note any additional contact information, such as a website or phone number. Use that information to find out where the casinos are.;\n,\n\nIf you learn about more than 1 casino on the radio, use the Internet to search the distance between your location and each casino. Sites such as maps.google.com or mapquest.com will help you in this search.'""" # fmt: skip
EXPECTED_SUMMARY = "Listen to the radio.\nUse the Internet."
dct = tok.batch_encode_plus(
[PGE_ARTICLE],
return_tensors="pt",
).to(torch_device)
hypotheses_batch = model.generate(**dct)
decoded = tok.batch_decode(hypotheses_batch, skip_special_tokens=True)
self.assertEqual(EXPECTED_SUMMARY, decoded[0])
class MvpStandaloneDecoderModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
vocab_size=99,
batch_size=13,
d_model=16,
decoder_seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
is_decoder=True,
use_attention_mask=True,
use_cache=False,
use_labels=True,
decoder_start_token_id=2,
decoder_ffn_dim=32,
decoder_layers=2,
encoder_attention_heads=4,
decoder_attention_heads=4,
max_position_embeddings=30,
is_encoder_decoder=False,
pad_token_id=0,
bos_token_id=1,
eos_token_id=2,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.decoder_seq_length = decoder_seq_length
# For common tests
self.seq_length = self.decoder_seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_attention_mask = use_attention_mask
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.d_model = d_model
self.hidden_size = d_model
self.num_hidden_layers = decoder_layers
self.decoder_layers = decoder_layers
self.decoder_ffn_dim = decoder_ffn_dim
self.encoder_attention_heads = encoder_attention_heads
self.decoder_attention_heads = decoder_attention_heads
self.num_attention_heads = decoder_attention_heads
self.eos_token_id = eos_token_id
self.bos_token_id = bos_token_id
self.pad_token_id = pad_token_id
self.decoder_start_token_id = decoder_start_token_id
self.use_cache = use_cache
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.is_encoder_decoder = is_encoder_decoder
self.scope = None
self.decoder_key_length = decoder_seq_length
self.base_model_out_len = 2
self.decoder_attention_idx = 1
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.decoder_seq_length], self.vocab_size)
attention_mask = None
if self.use_attention_mask:
attention_mask = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.decoder_seq_length], vocab_size=2)
lm_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
lm_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.decoder_seq_length], self.vocab_size)
config = MvpConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
d_model=self.d_model,
encoder_layers=self.decoder_layers,
decoder_layers=self.decoder_layers,
decoder_ffn_dim=self.decoder_ffn_dim,
encoder_attention_heads=self.encoder_attention_heads,
decoder_attention_heads=self.decoder_attention_heads,
eos_token_id=self.eos_token_id,
bos_token_id=self.bos_token_id,
use_cache=self.use_cache,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
decoder_start_token_id=self.decoder_start_token_id,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
is_encoder_decoder=self.is_encoder_decoder,
)
return (
config,
input_ids,
attention_mask,
lm_labels,
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
attention_mask,
lm_labels,
) = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
encoder_hidden_states = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.decoder_seq_length, self.hidden_size])
encoder_attention_mask = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.decoder_seq_length], vocab_size=2)
return (
config,
input_ids,
attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
lm_labels,
)
def create_and_check_decoder_model_past(
self,
config,
input_ids,
attention_mask,
lm_labels,
):
config.use_cache = True
model = MvpDecoder(config=config).to(torch_device).eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(input_ids, use_cache=True)
outputs_use_cache_conf = model(input_ids)
outputs_no_past = model(input_ids, use_cache=False)
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_use_cache_conf))
self.parent.assertTrue(len(outputs) == len(outputs_no_past) + 1)
past_key_values = outputs["past_key_values"]
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
# append to next input_ids and
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, past_key_values=past_key_values)["last_hidden_state"]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, next_input_ids.shape[-1] - 1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
assert torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3)
def create_and_check_decoder_model_attention_mask_past(
self,
config,
input_ids,
attention_mask,
lm_labels,
):
model = MvpDecoder(config=config).to(torch_device).eval()
# create attention mask
attn_mask = torch.ones(input_ids.shape, dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)
half_seq_length = input_ids.shape[-1] // 2
attn_mask[:, half_seq_length:] = 0
# first forward pass
past_key_values = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask, use_cache=True)["past_key_values"]
# create hypothetical next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size)
# change a random masked slice from input_ids
random_seq_idx_to_change = ids_tensor((1,), half_seq_length).item() + 1
random_other_next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 1), config.vocab_size).squeeze(-1)
input_ids[:, -random_seq_idx_to_change] = random_other_next_tokens
# append to next input_ids and attn_mask
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
attn_mask = torch.cat(
[attn_mask, torch.ones((attn_mask.shape[0], 1), dtype=torch.long, device=torch_device)],
dim=1,
)
# get two different outputs
output_from_no_past = model(next_input_ids, attention_mask=attn_mask)["last_hidden_state"]
output_from_past = model(next_tokens, attention_mask=attn_mask, past_key_values=past_key_values)[
"last_hidden_state"
]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, next_input_ids.shape[-1] - 1, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, 0, random_slice_idx].detach()
# test that outputs are equal for slice
assert torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
attention_mask,
lm_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class MvpStandaloneDecoderModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (MvpDecoder, MvpForCausalLM) if is_torch_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (MvpForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
fx_comptatible = True
test_pruning = False
is_encoder_decoder = False
def setUp(
self,
):
self.model_tester = MvpStandaloneDecoderModelTester(self, is_training=False)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=MvpConfig)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_decoder_model_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_decoder_model_past(*config_and_inputs)
def test_decoder_model_attn_mask_past(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_decoder_model_attention_mask_past(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip(reason="Decoder cannot keep gradients")
def test_retain_grad_hidden_states_attentions(self):
return
|
transformers/tests/models/mvp/test_modeling_mvp.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/mvp/test_modeling_mvp.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 15262
}
| 209 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch OLMo model."""
import unittest
from packaging import version
from parameterized import parameterized
from transformers import OlmoConfig, is_torch_available, set_seed
from transformers.generation.configuration_utils import GenerationConfig
from transformers.models.auto.tokenization_auto import AutoTokenizer
from transformers.models.gpt_neox.tokenization_gpt_neox_fast import GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
from transformers.testing_utils import (
require_tokenizers,
require_torch,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
OlmoForCausalLM,
OlmoModel,
)
class OlmoModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=False,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="silu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
pad_token_id=0,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.pad_token_id = pad_token_id
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = torch.tril(torch.ones_like(input_ids).to(torch_device))
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = self.get_config()
return config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
def get_config(self):
return OlmoConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
is_decoder=False,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id,
)
def create_and_check_model(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = OlmoModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_model_as_decoder(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = OlmoModel(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
)
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
)
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_for_causal_lm(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
model = OlmoForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.is_decoder = True
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = OlmoForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
use_cache=True,
)
past_key_values = outputs.past_key_values
# create hypothetical multiple next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(
next_input_ids,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
output_from_past = model(
next_tokens,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past_slice.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": input_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class OlmoModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (OlmoModel, OlmoForCausalLM) if is_torch_available() else ()
all_generative_model_classes = (OlmoForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": OlmoModel,
"text-generation": OlmoForCausalLM,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
test_pruning = False
fx_compatible = False
# Need to use `0.8` instead of `0.9` for `test_cpu_offload`
# This is because we are hitting edge cases with the causal_mask buffer
model_split_percents = [0.5, 0.7, 0.8]
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = OlmoModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=OlmoConfig, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip(reason="OLMo does not support head pruning.")
def test_headmasking(self):
pass
def test_model_various_embeddings(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for type in ["absolute", "relative_key", "relative_key_query"]:
config_and_inputs[0].position_embedding_type = type
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip(reason="OLMo buffers include complex numbers, which breaks this test")
def test_save_load_fast_init_from_base(self):
pass
@parameterized.expand([("linear",), ("dynamic",)])
def test_model_rope_scaling(self, scaling_type):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
short_input = ids_tensor([1, 10], config.vocab_size)
long_input = ids_tensor([1, int(config.max_position_embeddings * 1.5)], config.vocab_size)
set_seed(42) # Fixed seed at init time so the two models get the same random weights
original_model = OlmoModel(config)
original_model.to(torch_device)
original_model.eval()
original_short_output = original_model(short_input).last_hidden_state
original_long_output = original_model(long_input).last_hidden_state
set_seed(42) # Fixed seed at init time so the two models get the same random weights
config.rope_scaling = {"type": scaling_type, "factor": 10.0}
scaled_model = OlmoModel(config)
scaled_model.to(torch_device)
scaled_model.eval()
scaled_short_output = scaled_model(short_input).last_hidden_state
scaled_long_output = scaled_model(long_input).last_hidden_state
# Dynamic scaling does not change the RoPE embeddings until it receives an input longer than the original
# maximum sequence length, so the outputs for the short input should match.
if scaling_type == "dynamic":
torch.testing.assert_close(original_short_output, scaled_short_output, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5)
else:
self.assertFalse(torch.allclose(original_short_output, scaled_short_output, atol=1e-5))
# The output should be different for long inputs
self.assertFalse(torch.allclose(original_long_output, scaled_long_output, atol=1e-5))
@require_torch
class OlmoIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_model_1b_logits(self):
input_ids = [[1, 306, 4658, 278, 6593, 310, 2834, 338]]
model = OlmoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-1B-hf", device_map="auto")
out = model(torch.tensor(input_ids)).logits.float()
# Expected mean on dim = -1
EXPECTED_MEAN = torch.tensor([[2.2869, 0.3315, 0.9876, 1.4146, 1.8804, 2.0430, 1.7055, 1.2065]])
torch.testing.assert_close(out.mean(-1), EXPECTED_MEAN, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
# slicing logits[0, 0, 0:30]
EXPECTED_SLICE = torch.tensor([2.5551, -1.1230, 11.0510, 12.4977, 7.9651, 7.2342, 6.1885, 7.8340, 9.9847, 12.6695, 12.2345, 10.7970, 8.4749, 14.2483, 12.9588, 13.9233, 11.0496, 5.5749, 7.4466, 7.7914, 6.8440, 5.8951, 4.8180, 4.1935, 4.5216, 4.7256, 3.9553, 12.2870, 12.4990, 8.1591]) # fmt: skip
torch.testing.assert_close(out[0, 0, :30], EXPECTED_SLICE, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
@slow
def test_model_7b_logits(self):
input_ids = [[1, 306, 4658, 278, 6593, 310, 2834, 338]]
model = OlmoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-7B-hf", device_map="auto")
out = model(torch.tensor(input_ids)).logits.float()
# Expected mean on dim = -1
EXPECTED_MEAN = torch.tensor([[0.0271, 0.0249, -0.0578, -0.0870, 0.0167, 0.0710, 0.1002, 0.0677]])
torch.testing.assert_close(out.mean(-1), EXPECTED_MEAN, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
# slicing logits[0, 0, 0:30]
EXPECTED_SLICE = torch.tensor([-1.7433, -1.6685, 7.4941, 6.1506, 0.1364, -0.1127, 1.3224, 4.5458, 4.2068, 5.8296, 7.4723, 2.7925, 3.1245, 10.8872, 10.0758, 10.6717, 7.0945, 1.2398, 3.6766, 4.2365, 2.5655, 2.2222, 1.7418, 0.5223, 0.7753, 1.0938, 0.6723, 6.2522, 6.2264, 1.8105]) # fmt: skip
torch.testing.assert_close(out[0, 0, :30], EXPECTED_SLICE, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
@slow
def test_model_7b_twin_2t_logits(self):
input_ids = [[1, 306, 4658, 278, 6593, 310, 2834, 338]]
model = OlmoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-7B-Twin-2T-hf", device_map="auto")
out = model(torch.tensor(input_ids)).logits.float()
# Expected mean on dim = -1
EXPECTED_MEAN = torch.tensor([[-0.3636, -0.3825, -0.4800, -0.3696, -0.8388, -0.9737, -0.9849, -0.8356]])
torch.testing.assert_close(out.mean(-1), EXPECTED_MEAN, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
# slicing logits[0, 0, 0:30]
EXPECTED_SLICE = torch.tensor([-2.0833, -1.9234, 8.7312, 7.8049, 1.0372, 0.8941, 3.1548, 1.8502, 5.5511, 5.5793, 8.1166, 4.5906, 1.8691, 11.6377, 8.9858, 11.6447, 7.4549, 1.4725, 2.8399, 2.7568, 1.4011, 1.6958, 0.5572, 0.5231, 0.3068, 0.5364, 0.6769, 7.9636, 8.2379, 1.7950]) # fmt: skip
torch.testing.assert_close(out[0, 0, :30], EXPECTED_SLICE, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
@slow
def test_model_7b_greedy_generation(self):
EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION = """Simply put, the theory of relativity states that \nthe speed of light is the same for all observers.\n\nThe theory of relativity is a theory of physics that describes the \nmovement of objects in space and time.\n\nThe theory of relativity is a theory of physics that describes the \nmovement of objects in space and time.\n\n"""
prompt = "Simply put, the theory of relativity states that "
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-7B-hf", device_map="auto")
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
model = OlmoForCausalLM.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-7B-hf", device_map="auto")
# greedy generation outputs
generated_ids = model.generate(input_ids, max_new_tokens=64, top_p=None, temperature=1, do_sample=False)
text = tokenizer.decode(generated_ids[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
self.assertEqual(EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION, text)
@require_tokenizers
def test_fast_special_tokens(self):
fast_tokenizer = GPTNeoXTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-1B-hf")
original_add_eos_token = fast_tokenizer.add_eos_token
fast_tokenizer.add_eos_token = False
fast = fast_tokenizer.encode("A sample test")
self.assertEqual(fast, [34, 3410, 1071])
fast_tokenizer.add_eos_token = True
fast = fast_tokenizer.encode("A sample test")
self.assertEqual(fast, [34, 3410, 1071, 50279])
fast_tokenizer.add_eos_token = original_add_eos_token
@require_tokenizers
def test_simple_encode_decode(self):
rust_tokenizer = GPTNeoXTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("allenai/OLMo-1B-hf")
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode("This is a test"), [1552, 310, 247, 1071])
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.decode([1552, 310, 247, 1071], skip_special_tokens=True), "This is a test")
# bytefallback showcase
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode("生活的真谛是"), [20025, 46549, 5225, 48561, 33656, 238, 12105]) # fmt: skip
self.assertEqual(
rust_tokenizer.decode([20025, 46549, 5225, 48561, 33656, 238, 12105], skip_special_tokens=True),
"生活的真谛是",
)
# Inner spaces showcase
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode("Hi Hello"), [12764, 50276, 12092])
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.decode([12764, 50276, 12092], skip_special_tokens=True), "Hi Hello")
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode("Hi Hello"), [12764, 50275, 12092])
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.decode([12764, 50275, 12092], skip_special_tokens=True), "Hi Hello")
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode(""), [])
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode(" "), [209])
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode(" "), [50276])
self.assertEqual(rust_tokenizer.encode(" Hello"), [24387])
@slow
def test_export_static_cache(self):
if version.parse(torch.__version__) < version.parse("2.4.0"):
self.skipTest(reason="This test requires torch >= 2.4 to run.")
from transformers.integrations.executorch import (
TorchExportableModuleWithStaticCache,
convert_and_export_with_cache,
)
olmo_model = "allenai/OLMo-1B-hf"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(olmo_model, pad_token="</s>", padding_side="right")
EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION = [
"Simply put, the theory of relativity states that \nthe speed of light is the same in all reference frames.\n\nThe speed of light",
]
max_generation_length = tokenizer(EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)[
"input_ids"
].shape[-1]
# Load model
device = "cpu"
dtype = torch.bfloat16
cache_implementation = "static"
attn_implementation = "sdpa"
batch_size = 1
model = OlmoForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
olmo_model,
device_map=device,
torch_dtype=dtype,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
generation_config=GenerationConfig(
use_cache=True,
cache_implementation=cache_implementation,
max_length=max_generation_length,
cache_config={
"batch_size": batch_size,
"max_cache_len": max_generation_length,
},
),
)
prompts = ["Simply put, the theory of relativity states that "]
prompt_tokens = tokenizer(prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(model.device)
prompt_token_ids = prompt_tokens["input_ids"]
max_new_tokens = max_generation_length - prompt_token_ids.shape[-1]
# Static Cache + eager
eager_generated_ids = model.generate(
**prompt_tokens, max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens, do_sample=False, cache_implementation=cache_implementation
)
eager_generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(eager_generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
self.assertEqual(EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION, eager_generated_text)
# Static Cache + export
exported_program = convert_and_export_with_cache(model)
ep_generated_ids = TorchExportableModuleWithStaticCache.generate(
exported_program=exported_program, prompt_token_ids=prompt_token_ids, max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens
)
ep_generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(ep_generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
self.assertEqual(EXPECTED_TEXT_COMPLETION, ep_generated_text)
|
transformers/tests/models/olmo/test_modeling_olmo.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/olmo/test_modeling_olmo.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 9803
}
| 210 |
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import tempfile
import unittest
from transformers import SPIECE_UNDERLINE, BatchEncoding, PLBartTokenizer, is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import (
get_tests_dir,
nested_simplify,
require_sentencepiece,
require_tokenizers,
require_torch,
)
from ...test_tokenization_common import TokenizerTesterMixin
SAMPLE_VOCAB = get_tests_dir("fixtures/test_sentencepiece.model")
if is_torch_available():
from transformers.models.plbart.modeling_plbart import shift_tokens_right
EN_CODE = 50003
PYTHON_CODE = 50002
@require_sentencepiece
@require_tokenizers
class PLBartTokenizationTest(TokenizerTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
from_pretrained_id = "uclanlp/plbart-base"
tokenizer_class = PLBartTokenizer
rust_tokenizer_class = None
test_rust_tokenizer = False
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
# We have a SentencePiece fixture for testing
tokenizer = PLBartTokenizer(SAMPLE_VOCAB, language_codes="base", keep_accents=True)
tokenizer.save_pretrained(self.tmpdirname)
def test_full_base_tokenizer(self):
tokenizer = PLBartTokenizer(SAMPLE_VOCAB, language_codes="base", keep_accents=True)
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize("This is a test")
self.assertListEqual(tokens, ["▁This", "▁is", "▁a", "▁t", "est"])
self.assertListEqual(
tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens),
[value + tokenizer.fairseq_offset for value in [285, 46, 10, 170, 382]],
)
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize("I was born in 92000, and this is falsé.")
self.assertListEqual(
tokens,
[
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "I",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "was",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "b",
"or",
"n",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "in",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "",
"9",
"2",
"0",
"0",
"0",
",",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "and",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "this",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "is",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "f",
"al",
"s",
"é",
".",
],
)
ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
self.assertListEqual(
ids,
[
value + tokenizer.fairseq_offset
for value in [8, 21, 84, 55, 24, 19, 7, 2, 602, 347, 347, 347, 3, 12, 66, 46, 72, 80, 6, 2, 4]
],
)
back_tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(ids)
self.assertListEqual(
back_tokens,
[
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "I",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "was",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "b",
"or",
"n",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "in",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "",
"<unk>",
"2",
"0",
"0",
"0",
",",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "and",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "this",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "is",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "f",
"al",
"s",
"<unk>",
".",
],
)
end = tokenizer.vocab_size
language_tokens = [tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(x) for x in range(end - 4, end)]
self.assertListEqual(language_tokens, ["__java__", "__python__", "__en_XX__", "<mask>"])
code = "java.lang.Exception, python.lang.Exception, javascript, php, ruby, go"
input_ids = tokenizer(code).input_ids
self.assertEqual(
tokenizer.decode(input_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False),
code,
)
def test_full_multi_tokenizer(self):
tokenizer = PLBartTokenizer(SAMPLE_VOCAB, language_codes="multi", keep_accents=True)
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize("This is a test")
self.assertListEqual(tokens, ["▁This", "▁is", "▁a", "▁t", "est"])
self.assertListEqual(
tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens),
[value + tokenizer.fairseq_offset for value in [285, 46, 10, 170, 382]],
)
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize("I was born in 92000, and this is falsé.")
self.assertListEqual(
tokens,
[
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "I",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "was",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "b",
"or",
"n",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "in",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "",
"9",
"2",
"0",
"0",
"0",
",",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "and",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "this",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "is",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "f",
"al",
"s",
"é",
".",
],
)
ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
self.assertListEqual(
ids,
[
value + tokenizer.fairseq_offset
for value in [8, 21, 84, 55, 24, 19, 7, 2, 602, 347, 347, 347, 3, 12, 66, 46, 72, 80, 6, 2, 4]
],
)
back_tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(ids)
self.assertListEqual(
back_tokens,
[
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "I",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "was",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "b",
"or",
"n",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "in",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "",
"<unk>",
"2",
"0",
"0",
"0",
",",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "and",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "this",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "is",
SPIECE_UNDERLINE + "f",
"al",
"s",
"<unk>",
".",
],
)
end = tokenizer.vocab_size
language_tokens = [tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(x) for x in range(end - 7, end)]
self.assertListEqual(
language_tokens, ["__java__", "__python__", "__en_XX__", "__javascript__", "__php__", "__ruby__", "__go__"]
)
code = "java.lang.Exception, python.lang.Exception, javascript, php, ruby, go"
input_ids = tokenizer(code).input_ids
self.assertEqual(
tokenizer.decode(input_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False),
code,
)
@require_torch
@require_sentencepiece
@require_tokenizers
class PLBartPythonEnIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
checkpoint_name = "uclanlp/plbart-python-en_XX"
src_text = [
"def maximum(a,b,c):NEW_LINE_INDENTreturn max([a,b,c])",
"def sum(a,b,c):NEW_LINE_INDENTreturn sum([a,b,c])",
]
tgt_text = [
"Returns the maximum value of a b c.",
"Sums the values of a b c.",
]
expected_src_tokens = [
134,
5452,
33460,
33441,
33463,
33465,
33463,
33449,
988,
20,
33456,
19,
33456,
771,
39,
4258,
889,
3318,
33441,
33463,
33465,
33463,
33449,
2471,
2,
PYTHON_CODE,
]
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.tokenizer: PLBartTokenizer = PLBartTokenizer.from_pretrained(
cls.checkpoint_name, language_codes="base", src_lang="python", tgt_lang="en_XX"
)
cls.pad_token_id = 1
return cls
def check_language_codes(self):
self.assertEqual(self.tokenizer.fairseq_tokens_to_ids["__java__"], 50001)
self.assertEqual(self.tokenizer.fairseq_tokens_to_ids["__python__"], 50002)
self.assertEqual(self.tokenizer.fairseq_tokens_to_ids["__en_XX__"], 50003)
def test_python_en_tokenizer_batch_encode_plus(self):
ids = self.tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(self.src_text).input_ids[0]
self.assertListEqual(self.expected_src_tokens, ids)
def test_python_en_tokenizer_decode_ignores_language_codes(self):
self.assertIn(PYTHON_CODE, self.tokenizer.all_special_ids)
generated_ids = [EN_CODE, 9037, 33442, 57, 752, 153, 14, 56, 18, 9, 2]
result = self.tokenizer.decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
expected_english = self.tokenizer.decode(generated_ids[1:], skip_special_tokens=True)
self.assertEqual(result, expected_english)
self.assertNotIn(self.tokenizer.eos_token, result)
def test_python_en_tokenizer_truncation(self):
src_text = ["def sum(a,b,c):NEW_LINE_INDENTreturn sum([a,b,c])" * 20]
self.assertIsInstance(src_text[0], str)
desired_max_length = 10
ids = self.tokenizer(src_text, max_length=desired_max_length, truncation=True).input_ids[0]
self.assertEqual(ids[-2], 2)
self.assertEqual(ids[-1], PYTHON_CODE)
self.assertEqual(len(ids), desired_max_length)
def test_mask_token(self):
self.assertListEqual(self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(["<mask>", "__java__"]), [50004, 50001])
def test_special_tokens_unaffacted_by_save_load(self):
tmpdirname = tempfile.mkdtemp()
original_special_tokens = self.tokenizer.fairseq_tokens_to_ids
self.tokenizer.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
new_tok = PLBartTokenizer.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
self.assertDictEqual(new_tok.fairseq_tokens_to_ids, original_special_tokens)
@require_torch
def test_batch_fairseq_parity(self):
batch = self.tokenizer(self.src_text, text_target=self.tgt_text, padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
batch["decoder_input_ids"] = shift_tokens_right(batch["labels"], self.tokenizer.pad_token_id)
# fairseq batch: https://gist.github.com/sshleifer/cba08bc2109361a74ac3760a7e30e4f4
self.assertEqual(batch.input_ids[1][-2:].tolist(), [2, PYTHON_CODE])
self.assertEqual(batch.decoder_input_ids[1][0], EN_CODE)
self.assertEqual(batch.decoder_input_ids[1][-1], 2)
self.assertEqual(batch.labels[1][-2:].tolist(), [2, EN_CODE])
@require_torch
def test_python_en_tokenizer_prepare_batch(self):
batch = self.tokenizer(
self.src_text,
text_target=self.tgt_text,
padding=True,
truncation=True,
max_length=len(self.expected_src_tokens),
return_tensors="pt",
)
batch["decoder_input_ids"] = shift_tokens_right(batch["labels"], self.tokenizer.pad_token_id)
self.assertIsInstance(batch, BatchEncoding)
self.assertEqual((2, 26), batch.input_ids.shape)
self.assertEqual((2, 26), batch.attention_mask.shape)
result = batch.input_ids.tolist()[0]
self.assertListEqual(self.expected_src_tokens, result)
self.assertEqual(2, batch.decoder_input_ids[0, -1]) # EOS
# Test that special tokens are reset
self.assertEqual(self.tokenizer.prefix_tokens, [])
self.assertEqual(self.tokenizer.suffix_tokens, [self.tokenizer.eos_token_id, PYTHON_CODE])
def test_seq2seq_max_length(self):
batch = self.tokenizer(self.src_text, padding=True, truncation=True, max_length=3, return_tensors="pt")
targets = self.tokenizer(
text_target=self.tgt_text, padding=True, truncation=True, max_length=10, return_tensors="pt"
)
labels = targets["input_ids"]
batch["decoder_input_ids"] = shift_tokens_right(labels, self.tokenizer.pad_token_id)
self.assertEqual(batch.input_ids.shape[1], 3)
self.assertEqual(batch.decoder_input_ids.shape[1], 10)
@require_torch
def test_tokenizer_translation(self):
inputs = self.tokenizer._build_translation_inputs(
"A test", return_tensors="pt", src_lang="en_XX", tgt_lang="java"
)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(inputs),
{
# A, test, EOS, en_XX
"input_ids": [[150, 242, 2, 50003]],
"attention_mask": [[1, 1, 1, 1]],
# java
"forced_bos_token_id": 50001,
},
)
|
transformers/tests/models/plbart/test_tokenization_plbart.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/plbart/test_tokenization_plbart.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 6897
}
| 211 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch PvtV2 model."""
import inspect
import tempfile
import unittest
from transformers import PvtV2Backbone, PvtV2Config, is_torch_available, is_vision_available
from transformers.models.auto.modeling_auto import MODEL_MAPPING_NAMES
from transformers.testing_utils import (
require_accelerate,
require_torch,
require_torch_accelerator,
require_torch_fp16,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ...test_backbone_common import BackboneTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, PvtV2ForImageClassification, PvtV2Model
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
class PvtV2ConfigTester(ConfigTester):
def run_common_tests(self):
config = self.config_class(**self.inputs_dict)
self.parent.assertTrue(hasattr(config, "hidden_sizes"))
self.parent.assertTrue(hasattr(config, "num_encoder_blocks"))
class PvtV2ModelTester(ModelTesterMixin):
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
image_size=None,
num_channels=3,
num_encoder_blocks=4,
depths=[2, 2, 2, 2],
sr_ratios=[8, 4, 2, 1],
hidden_sizes=[16, 32, 64, 128],
downsampling_rates=[1, 4, 8, 16],
num_attention_heads=[1, 2, 4, 8],
out_indices=[0, 1, 2, 3],
is_training=True,
use_labels=True,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.image_size = 64 if image_size is None else image_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.num_encoder_blocks = num_encoder_blocks
self.sr_ratios = sr_ratios
self.depths = depths
self.hidden_sizes = hidden_sizes
self.downsampling_rates = downsampling_rates
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.out_indices = out_indices
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size, self.image_size])
labels = None
if self.use_labels:
labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.image_size, self.image_size], self.num_labels)
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values, labels
def get_config(self):
return PvtV2Config(
image_size=self.image_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
num_encoder_blocks=self.num_encoder_blocks,
depths=self.depths,
sr_ratios=self.sr_ratios,
hidden_sizes=self.hidden_sizes,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
out_indices=self.out_indices,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = PvtV2Model(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertIsNotNone(result.last_hidden_state)
def create_and_check_backbone(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = PvtV2Backbone(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
# verify feature maps
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.feature_maps), len(config.out_features))
self.parent.assertListEqual(list(result.feature_maps[0].shape), [self.batch_size, self.hidden_sizes[1], 4, 4])
# verify channels
self.parent.assertEqual(len(model.channels), len(config.out_features))
self.parent.assertListEqual(model.channels, config.hidden_sizes[1:])
# verify backbone works with out_features=None
config.out_features = None
model = PvtV2Backbone(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
# verify feature maps
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.feature_maps), 1)
self.parent.assertListEqual(list(result.feature_maps[0].shape), [self.batch_size, self.hidden_sizes[-1], 1, 1])
# verify channels
self.parent.assertEqual(len(model.channels), 1)
self.parent.assertListEqual(model.channels, [config.hidden_sizes[-1]])
def create_and_check_for_image_classification(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = PvtV2ForImageClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values, labels=labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
# test greyscale images
config.num_channels = 1
model = PvtV2ForImageClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, 1, self.image_size, self.image_size])
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.type_sequence_label_size))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values, labels = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
# We will verify our results on an image of cute cats
def prepare_img():
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
return image
@require_torch
class PvtV2ModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (PvtV2Model, PvtV2ForImageClassification) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"feature-extraction": PvtV2Model, "image-classification": PvtV2ForImageClassification}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
test_head_masking = False
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_torchscript = False
has_attentions = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = PvtV2ModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = PvtV2ConfigTester(self, config_class=PvtV2Config)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
@unittest.skip(reason="Pvt-V2 does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Pvt-V2 does not have get_input_embeddings method and get_output_embeddings methods")
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="This architecture does not work with using reentrant.")
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
# Scenario - 1 default behaviour
self.check_training_gradient_checkpointing()
@unittest.skip(reason="This architecture does not work with using reentrant.")
def test_training_gradient_checkpointing_use_reentrant(self):
# Scenario - 2 with `use_reentrant=True` - this is the default value that is used in pytorch's
# torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint
self.check_training_gradient_checkpointing(gradient_checkpointing_kwargs={"use_reentrant": True})
def test_initialization(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config=config)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
self.assertTrue(
-1.0 <= ((param.data.mean() * 1e9).round() / 1e9).item() <= 1.0,
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
def test_hidden_states_output(self):
def check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class):
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
hidden_states = outputs.hidden_states
expected_num_layers = len(self.model_tester.depths)
self.assertEqual(len(hidden_states), expected_num_layers)
# verify the first hidden states (first block)
self.assertListEqual(
list(hidden_states[0].shape[-3:]),
[
self.model_tester.hidden_sizes[self.model_tester.out_indices[0]],
self.model_tester.image_size // 2 ** (2 + self.model_tester.out_indices[0]),
self.model_tester.image_size // 2 ** (2 + self.model_tester.out_indices[0]),
],
)
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = True
check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class)
# check that output_hidden_states also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"]
config.output_hidden_states = True
check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class)
def test_training(self):
if not self.model_tester.is_training:
self.skipTest(reason="model_tester.is_training is set to False")
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.return_dict = True
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
if model_class.__name__ in MODEL_MAPPING_NAMES.values():
continue
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.train()
inputs = self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class, return_labels=True)
loss = model(**inputs).loss
loss.backward()
def test_forward_signature(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
signature = inspect.signature(model.forward)
# signature.parameters is an OrderedDict => so arg_names order is deterministic
arg_names = [*signature.parameters.keys()]
expected_arg_names = ["pixel_values"]
self.assertListEqual(arg_names[:1], expected_arg_names)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0"
model = PvtV2Model.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@require_torch
class PvtV2ModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_inference_image_classification(self):
# only resize + normalize
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0")
model = PvtV2ForImageClassification.from_pretrained("OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0").to(torch_device).eval()
image = prepare_img()
encoded_inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
pixel_values = encoded_inputs.pixel_values.to(torch_device)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(pixel_values)
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, model.config.num_labels))
self.assertEqual(outputs.logits.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor([-1.4192, -1.9158, -0.9702]).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.logits[0, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
@slow
def test_inference_model(self):
model = PvtV2Model.from_pretrained("OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0").to(torch_device).eval()
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0")
image = prepare_img()
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values.to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(pixel_values)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 50, 512))
self.assertEqual(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor(
[[-0.3086, 1.0402, 1.1816], [-0.2880, 0.5781, 0.6124], [0.1480, 0.6129, -0.0590]]
).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.last_hidden_state[0, :3, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
@slow
@require_accelerate
@require_torch_accelerator
@require_torch_fp16
def test_inference_fp16(self):
r"""
A small test to make sure that inference work in half precision without any problem.
"""
model = PvtV2ForImageClassification.from_pretrained("OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
model.to(torch_device)
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("OpenGVLab/pvt_v2_b0")
image = prepare_img()
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values.to(torch_device, dtype=torch.float16)
# forward pass to make sure inference works in fp16
with torch.no_grad():
_ = model(pixel_values)
@require_torch
class PvtV2BackboneTest(BackboneTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (PvtV2Backbone,) if is_torch_available() else ()
has_attentions = False
config_class = PvtV2Config
def test_config(self):
config_class = self.config_class
# test default config
config = config_class()
self.assertIsNotNone(config)
num_stages = len(config.depths) if hasattr(config, "depths") else config.num_hidden_layers
expected_stage_names = [f"stage{idx}" for idx in range(1, num_stages + 1)]
self.assertEqual(config.stage_names, expected_stage_names)
self.assertTrue(set(config.out_features).issubset(set(config.stage_names)))
# Test out_features and out_indices are correctly set
# out_features and out_indices both None
config = config_class(out_features=None, out_indices=None)
self.assertEqual(config.out_features, [config.stage_names[-1]])
self.assertEqual(config.out_indices, [len(config.stage_names) - 1])
# out_features and out_indices both set
config = config_class(out_features=["stage1", "stage2"], out_indices=[0, 1])
self.assertEqual(config.out_features, ["stage1", "stage2"])
self.assertEqual(config.out_indices, [0, 1])
# Only out_features set
config = config_class(out_features=["stage2", "stage4"])
self.assertEqual(config.out_features, ["stage2", "stage4"])
self.assertEqual(config.out_indices, [1, 3])
# Only out_indices set
config = config_class(out_indices=[0, 2])
self.assertEqual(config.out_features, [config.stage_names[0], config.stage_names[2]])
self.assertEqual(config.out_indices, [0, 2])
# Error raised when out_indices do not correspond to out_features
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
config = config_class(out_features=["stage1", "stage2"], out_indices=[0, 2])
def test_config_save_pretrained(self):
config_class = self.config_class
config_first = config_class(out_indices=[0, 1, 2, 3])
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
config_first.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
config_second = self.config_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
# Fix issue where type switches in the saving process
if isinstance(config_second.image_size, list):
config_second.image_size = tuple(config_second.image_size)
self.assertEqual(config_second.to_dict(), config_first.to_dict())
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = PvtV2ModelTester(self)
|
transformers/tests/models/pvt_v2/test_modeling_pvt_v2.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/pvt_v2/test_modeling_pvt_v2.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 7452
}
| 212 |
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import shutil
import tempfile
import unittest
import pytest
from transformers import AutoProcessor, Qwen2Tokenizer
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, require_vision
from transformers.utils import is_vision_available
from ...test_processing_common import ProcessorTesterMixin
if is_vision_available():
from transformers import Qwen2VLImageProcessor, Qwen2VLProcessor
@require_vision
@require_torch
class Qwen2VLProcessorTest(ProcessorTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
processor_class = Qwen2VLProcessor
def setUp(self):
self.tmpdirname = tempfile.mkdtemp()
processor = Qwen2VLProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", patch_size=4)
processor.save_pretrained(self.tmpdirname)
def get_tokenizer(self, **kwargs):
return AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, **kwargs).tokenizer
def get_image_processor(self, **kwargs):
return AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, **kwargs).image_processor
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.tmpdirname)
def test_save_load_pretrained_default(self):
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
processor = Qwen2VLProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
processor.save_pretrained(self.tmpdirname)
processor = Qwen2VLProcessor.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, use_fast=False)
self.assertEqual(processor.tokenizer.get_vocab(), tokenizer.get_vocab())
self.assertEqual(processor.image_processor.to_json_string(), image_processor.to_json_string())
self.assertIsInstance(processor.tokenizer, Qwen2Tokenizer)
self.assertIsInstance(processor.image_processor, Qwen2VLImageProcessor)
def test_image_processor(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = Qwen2VLProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
image_input = self.prepare_image_inputs()
input_image_proc = image_processor(image_input, return_tensors="np")
input_processor = processor(images=image_input, text="dummy", return_tensors="np")
for key in input_image_proc.keys():
self.assertAlmostEqual(input_image_proc[key].sum(), input_processor[key].sum(), delta=1e-2)
def test_processor(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = Qwen2VLProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
input_str = "lower newer"
image_input = self.prepare_image_inputs()
inputs = processor(text=input_str, images=image_input)
self.assertListEqual(list(inputs.keys()), ["input_ids", "attention_mask", "pixel_values", "image_grid_thw"])
# test if it raises when no input is passed
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
processor()
# test if it raises when no text is passed
with pytest.raises(TypeError):
processor(images=image_input)
def test_model_input_names(self):
image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
processor = Qwen2VLProcessor(tokenizer=tokenizer, image_processor=image_processor)
input_str = "lower newer"
image_input = self.prepare_image_inputs()
video_inputs = self.prepare_video_inputs()
inputs = processor(text=input_str, images=image_input, videos=video_inputs)
self.assertListEqual(list(inputs.keys()), processor.model_input_names)
|
transformers/tests/models/qwen2_vl/test_processor_qwen2_vl.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/qwen2_vl/test_processor_qwen2_vl.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1530
}
| 213 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch RemBERT model."""
import unittest
from transformers import is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, slow, torch_device
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
RemBertConfig,
RemBertForCausalLM,
RemBertForMaskedLM,
RemBertForMultipleChoice,
RemBertForQuestionAnswering,
RemBertForSequenceClassification,
RemBertForTokenClassification,
RemBertModel,
)
class RemBertModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=True,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
input_embedding_size=18,
output_embedding_size=43,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.input_embedding_size = input_embedding_size
self.output_embedding_size = output_embedding_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = RemBertConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
input_embedding_size=self.input_embedding_size,
output_embedding_size=self.output_embedding_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
is_decoder=False,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
)
return config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config.is_decoder = True
encoder_hidden_states = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size])
encoder_attention_mask = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], vocab_size=2)
return (
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
)
def create_and_check_model(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = RemBertModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_model_as_decoder(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = RemBertModel(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
)
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
)
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_for_causal_lm(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
model = RemBertForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_for_masked_lm(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = RemBertForMaskedLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.is_decoder = True
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = RemBertForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
# first forward pass
outputs = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
use_cache=True,
)
past_key_values = outputs.past_key_values
# create hypothetical multiple next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(
next_input_ids,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
output_from_past = model(
next_tokens,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past_slice.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_for_question_answering(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = RemBertForQuestionAnswering(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
start_positions=sequence_labels,
end_positions=sequence_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.start_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.end_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
def create_and_check_for_sequence_classification(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = RemBertForSequenceClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=sequence_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_for_token_classification(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = RemBertForTokenClassification(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_for_multiple_choice(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_choices = self.num_choices
model = RemBertForMultipleChoice(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
multiple_choice_inputs_ids = input_ids.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
multiple_choice_token_type_ids = token_type_ids.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
multiple_choice_input_mask = input_mask.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
result = model(
multiple_choice_inputs_ids,
attention_mask=multiple_choice_input_mask,
token_type_ids=multiple_choice_token_type_ids,
labels=choice_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_choices))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids, "attention_mask": input_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class RemBertModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
RemBertModel,
RemBertForMaskedLM,
RemBertForCausalLM,
RemBertForMultipleChoice,
RemBertForQuestionAnswering,
RemBertForSequenceClassification,
RemBertForTokenClassification,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
all_generative_model_classes = (RemBertForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": RemBertModel,
"fill-mask": RemBertForMaskedLM,
"question-answering": RemBertForQuestionAnswering,
"text-classification": RemBertForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": RemBertForCausalLM,
"token-classification": RemBertForTokenClassification,
"zero-shot": RemBertForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = RemBertModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=RemBertConfig, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_various_embeddings(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for type in ["absolute", "relative_key", "relative_key_query"]:
config_and_inputs[0].position_embedding_type = type
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_masked_lm(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_masked_lm(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_multiple_choice(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_multiple_choice(*config_and_inputs)
def test_decoder_model_past_with_large_inputs(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_question_answering(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_question_answering(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_sequence_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_sequence_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_token_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_token_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_as_decoder(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model_as_decoder(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_as_decoder_with_default_input_mask(self):
# This regression test was failing with PyTorch < 1.3
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
input_mask = None
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model_as_decoder(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "google/rembert"
model = RemBertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@require_torch
class RemBertModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_inference_model(self):
# Test exact values at the last hidden layer
model = RemBertModel.from_pretrained("google/rembert")
input_ids = torch.tensor([[312, 56498, 313, 2125, 313]])
segment_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 0, 1, 1]])
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=segment_ids, output_hidden_states=True)
hidden_size = 1152
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 5, hidden_size))
self.assertEqual(output["last_hidden_state"].shape, expected_shape)
expected_implementation = torch.tensor(
[
[
[0.0754, -0.2022, 0.1904],
[-0.3354, -0.3692, -0.4791],
[-0.2314, -0.6729, -0.0749],
[-0.0396, -0.3105, -0.4234],
[-0.1571, -0.0525, 0.5353],
]
]
)
# Running on the original tf implementation gives slightly different results here.
# Not clear why this variations is present
# TODO: Find reason for discrepancy
# expected_original_implementation = [[
# [0.07630594074726105, -0.20146065950393677, 0.19107051193714142],
# [-0.3405614495277405, -0.36971670389175415, -0.4808273911476135],
# [-0.22587086260318756, -0.6656315922737122, -0.07844287157058716],
# [-0.04145475849509239, -0.3077218234539032, -0.42316967248916626],
# [-0.15887849032878876, -0.054529931396245956, 0.5356100797653198]
# ]]
torch.testing.assert_close(
output["last_hidden_state"][:, :, :3], expected_implementation, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4
)
|
transformers/tests/models/rembert/test_modeling_rembert.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/rembert/test_modeling_rembert.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 9262
}
| 214 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the TensorFlow SAM model."""
from __future__ import annotations
import inspect
import unittest
import numpy as np
import requests
from transformers import SamConfig, SamMaskDecoderConfig, SamPromptEncoderConfig, SamVisionConfig
from transformers.testing_utils import require_tf, slow
from transformers.utils import is_tf_available, is_vision_available
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_tf_common import TFModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_tf_available():
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers import SamProcessor, TFSamModel
from transformers.modeling_tf_utils import keras
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
class TFSamPromptEncoderTester:
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size=32,
input_image_size=24,
patch_size=2,
mask_input_channels=4,
num_point_embeddings=4,
hidden_act="gelu",
):
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.input_image_size = input_image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.mask_input_channels = mask_input_channels
self.num_point_embeddings = num_point_embeddings
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
def get_config(self):
return SamPromptEncoderConfig(
image_size=self.input_image_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
mask_input_channels=self.mask_input_channels,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_point_embeddings=self.num_point_embeddings,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
dummy_points = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, 3, 2])
config = self.get_config()
return config, dummy_points
class TFSamMaskDecoderTester:
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size=32,
hidden_act="relu",
mlp_dim=64,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
attention_downsample_rate=2,
num_multimask_outputs=3,
iou_head_depth=3,
iou_head_hidden_dim=32,
layer_norm_eps=1e-6,
):
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.mlp_dim = mlp_dim
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.attention_downsample_rate = attention_downsample_rate
self.num_multimask_outputs = num_multimask_outputs
self.iou_head_depth = iou_head_depth
self.iou_head_hidden_dim = iou_head_hidden_dim
self.layer_norm_eps = layer_norm_eps
def get_config(self):
return SamMaskDecoderConfig(
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
mlp_dim=self.mlp_dim,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
attention_downsample_rate=self.attention_downsample_rate,
num_multimask_outputs=self.num_multimask_outputs,
iou_head_depth=self.iou_head_depth,
iou_head_hidden_dim=self.iou_head_hidden_dim,
layer_norm_eps=self.layer_norm_eps,
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
config = self.get_config()
dummy_inputs = {
"image_embedding": floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.hidden_size]),
}
return config, dummy_inputs
class TFSamModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
hidden_size=36,
intermediate_size=72,
projection_dim=62,
output_channels=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
num_channels=3,
image_size=24,
patch_size=2,
hidden_act="gelu",
layer_norm_eps=1e-06,
dropout=0.0,
attention_dropout=0.0,
initializer_range=0.02,
initializer_factor=1.0,
qkv_bias=True,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
use_abs_pos=True,
use_rel_pos=True,
rel_pos_zero_init=False,
window_size=14,
global_attn_indexes=[2, 5, 8, 11],
num_pos_feats=16,
mlp_dim=None,
batch_size=2,
):
self.parent = parent
self.image_size = image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.output_channels = output_channels
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.projection_dim = projection_dim
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.dropout = dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.initializer_factor = initializer_factor
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.layer_norm_eps = layer_norm_eps
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.use_abs_pos = use_abs_pos
self.use_rel_pos = use_rel_pos
self.rel_pos_zero_init = rel_pos_zero_init
self.window_size = window_size
self.global_attn_indexes = global_attn_indexes
self.num_pos_feats = num_pos_feats
self.mlp_dim = mlp_dim
self.batch_size = batch_size
# in ViT, the seq length equals the number of patches + 1 (we add 1 for the [CLS] token)
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.seq_length = num_patches + 1
self.prompt_encoder_tester = TFSamPromptEncoderTester()
self.mask_decoder_tester = TFSamMaskDecoderTester()
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size, self.image_size])
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values
def get_config(self):
vision_config = SamVisionConfig(
image_size=self.image_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
projection_dim=self.projection_dim,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
dropout=self.dropout,
attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
initializer_factor=self.initializer_factor,
output_channels=self.output_channels,
qkv_bias=self.qkv_bias,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
use_abs_pos=self.use_abs_pos,
use_rel_pos=self.use_rel_pos,
rel_pos_zero_init=self.rel_pos_zero_init,
window_size=self.window_size,
global_attn_indexes=self.global_attn_indexes,
num_pos_feats=self.num_pos_feats,
mlp_dim=self.mlp_dim,
)
prompt_encoder_config = self.prompt_encoder_tester.get_config()
mask_decoder_config = self.mask_decoder_tester.get_config()
return SamConfig(
vision_config=vision_config,
prompt_encoder_config=prompt_encoder_config,
mask_decoder_config=mask_decoder_config,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, pixel_values):
model = TFSamModel(config=config)
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.iou_scores.shape, (self.batch_size, 1, 3))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.pred_masks.shape[:3], (self.batch_size, 1, 3))
def create_and_check_get_image_features(self, config, pixel_values):
model = TFSamModel(config=config)
result = model.get_image_embeddings(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(result[0].shape, (self.output_channels, 12, 12))
def create_and_check_get_image_hidden_states(self, config, pixel_values):
model = TFSamModel(config=config)
result = model.vision_encoder(
pixel_values,
output_hidden_states=True,
return_dict=True,
)
# after computing the convolutional features
expected_hidden_states_shape = (self.batch_size, 12, 12, 36)
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result[1]), self.num_hidden_layers + 1)
self.parent.assertEqual(result[1][0].shape, expected_hidden_states_shape)
result = model.vision_encoder(
pixel_values,
output_hidden_states=True,
return_dict=False,
)
# after computing the convolutional features
expected_hidden_states_shape = (self.batch_size, 12, 12, 36)
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result[1]), self.num_hidden_layers + 1)
self.parent.assertEqual(result[1][0].shape, expected_hidden_states_shape)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_tf
class TFSamModelTest(TFModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
"""
Here we also overwrite some of the tests of test_modeling_common.py, as SAM's vision encoder does not use input_ids, inputs_embeds,
attention_mask and seq_length.
"""
all_model_classes = (TFSamModel,) if is_tf_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"feature-extraction": TFSamModel, "mask-generation": TFSamModel} if is_tf_available() else {}
)
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_head_masking = False
test_onnx = False
# TODO: Fix me @Arthur: `run_batch_test` in `tests/test_pipeline_mixin.py` not working
def is_pipeline_test_to_skip(
self,
pipeline_test_case_name,
config_class,
model_architecture,
tokenizer_name,
image_processor_name,
feature_extractor_name,
processor_name,
):
return True
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = TFSamModelTester(self)
self.vision_config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=SamVisionConfig, has_text_modality=False)
self.prompt_encoder_config_tester = ConfigTester(
self,
config_class=SamPromptEncoderConfig,
has_text_modality=False,
num_attention_heads=12,
num_hidden_layers=2,
)
self.mask_decoder_config_tester = ConfigTester(
self, config_class=SamMaskDecoderConfig, has_text_modality=False
)
def test_config(self):
self.vision_config_tester.run_common_tests()
self.prompt_encoder_config_tester.run_common_tests()
self.mask_decoder_config_tester.run_common_tests()
@unittest.skip(reason="SAM's vision encoder does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
def test_model_common_attributes(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
self.assertIsInstance(model.get_input_embeddings(), (keras.layers.Layer))
x = model.get_output_embeddings()
self.assertTrue(x is None or isinstance(x, keras.layers.Dense))
def test_forward_signature(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
signature = inspect.signature(model.call)
# signature.parameters is an OrderedDict => so arg_names order is deterministic
arg_names = [*signature.parameters.keys()]
expected_arg_names = ["pixel_values"]
self.assertListEqual(arg_names[:1], expected_arg_names)
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_get_image_features(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_get_image_features(*config_and_inputs)
def test_image_hidden_states(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_get_image_hidden_states(*config_and_inputs)
def test_attention_outputs(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.return_dict = True
expected_vision_attention_shape = (
self.model_tester.batch_size * self.model_tester.num_attention_heads,
196,
196,
)
expected_mask_decoder_attention_shape = (self.model_tester.batch_size, 1, 144, 32)
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
inputs_dict["output_attentions"] = True
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = False
config.return_dict = True
model = model_class(config)
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
vision_attentions = outputs.vision_attentions
self.assertEqual(len(vision_attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
mask_decoder_attentions = outputs.mask_decoder_attentions
self.assertEqual(len(mask_decoder_attentions), self.model_tester.mask_decoder_tester.num_hidden_layers)
# check that output_attentions also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_attentions"]
config.output_attentions = True
model = model_class(config)
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
vision_attentions = outputs.vision_attentions
self.assertEqual(len(vision_attentions), self.model_tester.num_hidden_layers)
mask_decoder_attentions = outputs.mask_decoder_attentions
self.assertEqual(len(mask_decoder_attentions), self.model_tester.mask_decoder_tester.num_hidden_layers)
self.assertListEqual(
list(vision_attentions[0].shape[-4:]),
list(expected_vision_attention_shape),
)
self.assertListEqual(
list(mask_decoder_attentions[0].shape[-4:]),
list(expected_mask_decoder_attention_shape),
)
@unittest.skip(reason="Hidden_states is tested in create_and_check_model tests")
def test_hidden_states_output(self):
pass
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base") # sam-vit-huge blows out our memory
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
def check_pt_tf_outputs(self, tf_outputs, pt_outputs, model_class, tol=5e-4, name="outputs", attributes=None):
super().check_pt_tf_outputs(
tf_outputs=tf_outputs,
pt_outputs=pt_outputs,
model_class=model_class,
tol=tol,
name=name,
attributes=attributes,
)
def prepare_image():
img_url = "https://huggingface.co/ybelkada/segment-anything/resolve/main/assets/car.png"
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert("RGB")
return raw_image
def prepare_dog_img():
img_url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/dog-sam.png"
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert("RGB")
return raw_image
@require_tf
@slow
class TFSamModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_inference_mask_generation_no_point(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
masks = outputs.pred_masks[0, 0, 0, 0, :3]
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1].numpy(), np.array(0.4515), atol=2e-4))
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(masks.numpy(), np.array([-4.1807, -3.4949, -3.4483]), atol=1e-2))
def test_inference_mask_generation_one_point_one_bb(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_boxes = [[[650, 900, 1000, 1250]]]
input_points = [[[820, 1080]]]
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, input_boxes=input_boxes, input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
masks = outputs.pred_masks[0, 0, 0, 0, :3]
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1], np.array(0.9566), atol=2e-4))
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(masks.numpy(), np.array([-12.7657, -12.3683, -12.5985]), atol=2e-2))
def test_inference_mask_generation_batched_points_batched_images(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_points = [
[[[820, 1080]], [[820, 1080]], [[820, 1080]], [[820, 1080]]],
[[[510, 1080]], [[820, 1080]], [[820, 1080]], [[820, 1080]]],
]
inputs = processor(images=[raw_image, raw_image], input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
masks = outputs.pred_masks[0, 0, 0, 0, :3]
EXPECTED_SCORES = np.array(
[
[
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
],
[
[0.3317, 0.7264, 0.7646],
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
[0.6765, 0.9379, 0.8803],
],
]
)
EXPECTED_MASKS = np.array([-2.8552, -2.7990, -2.9612])
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores.numpy(), EXPECTED_SCORES, atol=1e-3))
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(masks.numpy(), EXPECTED_MASKS, atol=3e-2))
def test_inference_mask_generation_one_point_one_bb_zero(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_boxes = [[[620, 900, 1000, 1255]]]
input_points = [[[820, 1080]]]
labels = [[0]]
inputs = processor(
images=raw_image,
input_boxes=input_boxes,
input_points=input_points,
input_labels=labels,
return_tensors="tf",
)
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1].numpy(), np.array(0.7894), atol=1e-4))
def test_inference_mask_generation_one_point(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_points = [[[400, 650]]]
input_labels = [[1]]
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, input_points=input_points, input_labels=input_labels, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1], np.array(0.9675), atol=1e-4))
# With no label
input_points = [[[400, 650]]]
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1].numpy(), np.array(0.9675), atol=1e-4))
def test_inference_mask_generation_two_points(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_points = [[[400, 650], [800, 650]]]
input_labels = [[1, 1]]
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, input_points=input_points, input_labels=input_labels, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1].numpy(), np.array(0.9762), atol=1e-4))
# no labels
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1].numpy(), np.array(0.9762), atol=1e-4))
def test_inference_mask_generation_two_points_batched(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_points = [[[400, 650], [800, 650]], [[400, 650]]]
input_labels = [[1, 1], [1]]
inputs = processor(
images=[raw_image, raw_image], input_points=input_points, input_labels=input_labels, return_tensors="tf"
)
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[0][-1].numpy(), np.array(0.9762), atol=1e-4))
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[1][-1], np.array(0.9637), atol=1e-4))
def test_inference_mask_generation_one_box(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_boxes = [[[75, 275, 1725, 850]]]
inputs = processor(images=raw_image, input_boxes=input_boxes, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores[-1].numpy(), np.array(0.7937), atol=1e-4))
def test_inference_mask_generation_batched_image_one_point(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
raw_dog_image = prepare_dog_img()
input_points = [[[820, 1080]], [[220, 470]]]
inputs = processor(images=[raw_image, raw_dog_image], input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores_batched = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
input_points = [[[220, 470]]]
inputs = processor(images=raw_dog_image, input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
scores_single = tf.squeeze(outputs.iou_scores)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(scores_batched[1, :].numpy(), scores_single.numpy(), atol=1e-4))
def test_inference_mask_generation_two_points_point_batch(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
input_points = tf.convert_to_tensor([[[400, 650]], [[220, 470]]]) # fmt: skip
input_points = tf.expand_dims(input_points, 0)
inputs = processor(raw_image, input_points=input_points, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
iou_scores = outputs.iou_scores
self.assertTrue(iou_scores.shape == (1, 2, 3))
self.assertTrue(
np.allclose(
iou_scores.numpy(),
np.array([[[0.9105, 0.9825, 0.9675], [0.7646, 0.7943, 0.7774]]]),
atol=1e-4,
rtol=1e-4,
)
)
def test_inference_mask_generation_three_boxes_point_batch(self):
model = TFSamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
raw_image = prepare_image()
# fmt: off
input_boxes = tf.convert_to_tensor([[[620, 900, 1000, 1255]], [[75, 275, 1725, 850]], [[75, 275, 1725, 850]]])
EXPECTED_IOU = np.array([[[0.9773, 0.9881, 0.9522],
[0.5996, 0.7661, 0.7937],
[0.5996, 0.7661, 0.7937]]])
# fmt: on
input_boxes = tf.expand_dims(input_boxes, 0)
inputs = processor(raw_image, input_boxes=input_boxes, return_tensors="tf")
outputs = model(**inputs)
iou_scores = outputs.iou_scores
self.assertTrue(iou_scores.shape == (1, 3, 3))
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(iou_scores.numpy(), EXPECTED_IOU, atol=1e-4, rtol=1e-4))
|
transformers/tests/models/sam/test_modeling_tf_sam.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/sam/test_modeling_tf_sam.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 11786
}
| 215 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch Swinv2 model."""
import collections
import inspect
import unittest
from transformers import Swinv2Config
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, require_vision, slow, torch_device
from transformers.utils import cached_property, is_torch_available, is_vision_available
from ...test_backbone_common import BackboneTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, _config_zero_init, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from torch import nn
from transformers import Swinv2Backbone, Swinv2ForImageClassification, Swinv2ForMaskedImageModeling, Swinv2Model
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
class Swinv2ModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
image_size=32,
patch_size=2,
num_channels=3,
embed_dim=16,
depths=[1, 2, 1],
num_heads=[2, 2, 4],
window_size=2,
mlp_ratio=2.0,
qkv_bias=True,
hidden_dropout_prob=0.0,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
drop_path_rate=0.1,
hidden_act="gelu",
use_absolute_embeddings=False,
patch_norm=True,
initializer_range=0.02,
layer_norm_eps=1e-5,
is_training=True,
scope=None,
use_labels=True,
type_sequence_label_size=10,
encoder_stride=8,
out_features=["stage1", "stage2"],
out_indices=[1, 2],
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.image_size = image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.depths = depths
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.drop_path_rate = drop_path_rate
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.use_absolute_embeddings = use_absolute_embeddings
self.patch_norm = patch_norm
self.layer_norm_eps = layer_norm_eps
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.is_training = is_training
self.scope = scope
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.encoder_stride = encoder_stride
self.out_features = out_features
self.out_indices = out_indices
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size, self.image_size])
labels = None
if self.use_labels:
labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values, labels
def get_config(self):
return Swinv2Config(
image_size=self.image_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
embed_dim=self.embed_dim,
depths=self.depths,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
window_size=self.window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=self.qkv_bias,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
drop_path_rate=self.drop_path_rate,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
use_absolute_embeddings=self.use_absolute_embeddings,
path_norm=self.patch_norm,
layer_norm_eps=self.layer_norm_eps,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
encoder_stride=self.encoder_stride,
out_features=self.out_features,
out_indices=self.out_indices,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = Swinv2Model(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
expected_seq_len = ((config.image_size // config.patch_size) ** 2) // (4 ** (len(config.depths) - 1))
expected_dim = int(config.embed_dim * 2 ** (len(config.depths) - 1))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, expected_seq_len, expected_dim))
def create_and_check_backbone(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = Swinv2Backbone(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
# verify hidden states
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.feature_maps), len(config.out_features))
self.parent.assertListEqual(list(result.feature_maps[0].shape), [self.batch_size, model.channels[0], 16, 16])
# verify channels
self.parent.assertEqual(len(model.channels), len(config.out_features))
# verify backbone works with out_features=None
config.out_features = None
model = Swinv2Backbone(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
# verify feature maps
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.feature_maps), 1)
self.parent.assertListEqual(list(result.feature_maps[0].shape), [self.batch_size, model.channels[-1], 4, 4])
# verify channels
self.parent.assertEqual(len(model.channels), 1)
def create_and_check_for_masked_image_modeling(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = Swinv2ForMaskedImageModeling(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size, self.image_size)
)
# test greyscale images
config.num_channels = 1
model = Swinv2ForMaskedImageModeling(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, 1, self.image_size, self.image_size])
result = model(pixel_values)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, 1, self.image_size, self.image_size))
def create_and_check_for_image_classification(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
config.num_labels = self.type_sequence_label_size
model = Swinv2ForImageClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values, labels=labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.type_sequence_label_size))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values, labels = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class Swinv2ModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
Swinv2Model,
Swinv2ForImageClassification,
Swinv2ForMaskedImageModeling,
Swinv2Backbone,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"image-feature-extraction": Swinv2Model, "image-classification": Swinv2ForImageClassification}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
fx_compatible = False
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_head_masking = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = Swinv2ModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(
self,
config_class=Swinv2Config,
embed_dim=37,
has_text_modality=False,
common_properties=["image_size", "patch_size", "num_channels"],
)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_backbone(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_backbone(*config_and_inputs)
# TODO: check if this works again for PyTorch 2.x.y
@unittest.skip(reason="Got `CUDA error: misaligned address` with PyTorch 2.0.0.")
def test_multi_gpu_data_parallel_forward(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="Swinv2 does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
self.assertIsInstance(model.get_input_embeddings(), (nn.Module))
x = model.get_output_embeddings()
self.assertTrue(x is None or isinstance(x, nn.Linear))
def test_forward_signature(self):
config, _ = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config)
signature = inspect.signature(model.forward)
# signature.parameters is an OrderedDict => so arg_names order is deterministic
arg_names = [*signature.parameters.keys()]
expected_arg_names = ["pixel_values"]
self.assertListEqual(arg_names[:1], expected_arg_names)
def test_attention_outputs(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.return_dict = True
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
inputs_dict["output_attentions"] = True
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = False
config.return_dict = True
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
attentions = outputs.attentions
expected_num_attentions = len(self.model_tester.depths)
self.assertEqual(len(attentions), expected_num_attentions)
# check that output_attentions also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_attentions"]
config.output_attentions = True
window_size_squared = config.window_size**2
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
attentions = outputs.attentions
self.assertEqual(len(attentions), expected_num_attentions)
self.assertListEqual(
list(attentions[0].shape[-3:]),
[self.model_tester.num_heads[0], window_size_squared, window_size_squared],
)
out_len = len(outputs)
# Check attention is always last and order is fine
inputs_dict["output_attentions"] = True
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = True
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
# also another +1 for reshaped_hidden_states
added_hidden_states = 1 if model_class.__name__ == "Swinv2Backbone" else 2
self.assertEqual(out_len + added_hidden_states, len(outputs))
self_attentions = outputs.attentions
self.assertEqual(len(self_attentions), expected_num_attentions)
self.assertListEqual(
list(self_attentions[0].shape[-3:]),
[self.model_tester.num_heads[0], window_size_squared, window_size_squared],
)
def check_hidden_states_output(self, inputs_dict, config, model_class, image_size):
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
hidden_states = outputs.hidden_states
expected_num_layers = getattr(
self.model_tester, "expected_num_hidden_layers", len(self.model_tester.depths) + 1
)
self.assertEqual(len(hidden_states), expected_num_layers)
# Swinv2 has a different seq_length
patch_size = (
config.patch_size
if isinstance(config.patch_size, collections.abc.Iterable)
else (config.patch_size, config.patch_size)
)
num_patches = (image_size[1] // patch_size[1]) * (image_size[0] // patch_size[0])
self.assertListEqual(
list(hidden_states[0].shape[-2:]),
[num_patches, self.model_tester.embed_dim],
)
if not model_class.__name__ == "Swinv2Backbone":
reshaped_hidden_states = outputs.reshaped_hidden_states
self.assertEqual(len(reshaped_hidden_states), expected_num_layers)
batch_size, num_channels, height, width = reshaped_hidden_states[0].shape
reshaped_hidden_states = (
reshaped_hidden_states[0].view(batch_size, num_channels, height * width).permute(0, 2, 1)
)
self.assertListEqual(
list(reshaped_hidden_states.shape[-2:]),
[num_patches, self.model_tester.embed_dim],
)
def test_hidden_states_output(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
image_size = (
self.model_tester.image_size
if isinstance(self.model_tester.image_size, collections.abc.Iterable)
else (self.model_tester.image_size, self.model_tester.image_size)
)
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = True
self.check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class, image_size)
# check that output_hidden_states also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"]
config.output_hidden_states = True
self.check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class, image_size)
def test_hidden_states_output_with_padding(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
config.patch_size = 3
image_size = (
self.model_tester.image_size
if isinstance(self.model_tester.image_size, collections.abc.Iterable)
else (self.model_tester.image_size, self.model_tester.image_size)
)
patch_size = (
config.patch_size
if isinstance(config.patch_size, collections.abc.Iterable)
else (config.patch_size, config.patch_size)
)
padded_height = image_size[0] + patch_size[0] - (image_size[0] % patch_size[0])
padded_width = image_size[1] + patch_size[1] - (image_size[1] % patch_size[1])
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = True
self.check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class, (padded_height, padded_width))
# check that output_hidden_states also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"]
config.output_hidden_states = True
self.check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class, (padded_height, padded_width))
def test_for_masked_image_modeling(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_masked_image_modeling(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_image_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_image_classification(*config_and_inputs)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "microsoft/swinv2-tiny-patch4-window8-256"
model = Swinv2Model.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@unittest.skip(reason="Swinv2 does not support feedforward chunking yet")
def test_feed_forward_chunking(self):
pass
def test_initialization(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
configs_no_init = _config_zero_init(config)
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config=configs_no_init)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if "embeddings" not in name and "logit_scale" not in name and param.requires_grad:
self.assertIn(
((param.data.mean() * 1e9).round() / 1e9).item(),
[0.0, 1.0],
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
@require_vision
@require_torch
class Swinv2ModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@cached_property
def default_image_processor(self):
return (
AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/swinv2-tiny-patch4-window8-256")
if is_vision_available()
else None
)
@slow
def test_inference_image_classification_head(self):
model = Swinv2ForImageClassification.from_pretrained("microsoft/swinv2-tiny-patch4-window8-256").to(
torch_device
)
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 1000))
self.assertEqual(outputs.logits.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor([-0.3947, -0.4306, 0.0026]).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.logits[0, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
@slow
def test_inference_fp16(self):
model = Swinv2ForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
"microsoft/swinv2-tiny-patch4-window8-256", torch_dtype=torch.float16
).to(torch_device)
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(model.dtype).to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 1000))
self.assertEqual(outputs.logits.shape, expected_shape)
expected_slice = torch.tensor([-0.3938, -0.4290, 0.0020], dtype=model.dtype).to(torch_device)
torch.testing.assert_close(outputs.logits[0, :3], expected_slice, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-4)
@slow
def test_inference_interpolate_pos_encoding(self):
# Swinv2 models have an `interpolate_pos_encoding` argument in their forward method,
# allowing to interpolate the pre-trained position embeddings in order to use
# the model on higher resolutions.
model = Swinv2Model.from_pretrained("microsoft/swinv2-tiny-patch4-window8-256").to(torch_device)
image_processor = self.default_image_processor
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
inputs = image_processor(images=image, size={"height": 481, "width": 481}, return_tensors="pt")
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values.to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(pixel_values, interpolate_pos_encoding=True)
# verify the logits
expected_shape = torch.Size((1, 256, 768))
self.assertEqual(outputs.last_hidden_state.shape, expected_shape)
@require_torch
class Swinv2BackboneTest(unittest.TestCase, BackboneTesterMixin):
all_model_classes = (Swinv2Backbone,) if is_torch_available() else ()
config_class = Swinv2Config
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = Swinv2ModelTester(self)
|
transformers/tests/models/swinv2/test_modeling_swinv2.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/swinv2/test_modeling_swinv2.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 9429
}
| 216 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 the Fast authors and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch TextNet model."""
import unittest
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import TextNetConfig
from transformers.models.textnet.image_processing_textnet import TextNetImageProcessor
from transformers.testing_utils import (
require_torch,
require_vision,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from transformers.utils import is_torch_available
from ...test_backbone_common import BackboneTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from torch import nn
from transformers import TextNetBackbone, TextNetForImageClassification, TextNetModel
class TextNetConfigTester(ConfigTester):
def create_and_test_config_common_properties(self):
config = self.config_class(**self.inputs_dict)
self.parent.assertTrue(hasattr(config, "hidden_sizes"))
self.parent.assertTrue(hasattr(config, "num_attention_heads"))
self.parent.assertTrue(hasattr(config, "num_encoder_blocks"))
class TextNetModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
stem_kernel_size=3,
stem_stride=2,
stem_in_channels=3,
stem_out_channels=32,
stem_act_func="relu",
dropout_rate=0,
ops_order="weight_bn_act",
conv_layer_kernel_sizes=[
[[3, 3]],
[[3, 3]],
[[3, 3]],
[[3, 3]],
],
conv_layer_strides=[
[2],
[2],
[2],
[2],
],
out_features=["stage1", "stage2", "stage3", "stage4"],
out_indices=[1, 2, 3, 4],
batch_size=3,
num_channels=3,
image_size=[32, 32],
is_training=True,
use_labels=True,
num_labels=3,
hidden_sizes=[32, 32, 32, 32, 32],
):
self.parent = parent
self.stem_kernel_size = stem_kernel_size
self.stem_stride = stem_stride
self.stem_in_channels = stem_in_channels
self.stem_out_channels = stem_out_channels
self.act_func = stem_act_func
self.dropout_rate = dropout_rate
self.ops_order = ops_order
self.conv_layer_kernel_sizes = conv_layer_kernel_sizes
self.conv_layer_strides = conv_layer_strides
self.out_features = out_features
self.out_indices = out_indices
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.image_size = image_size
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.hidden_sizes = hidden_sizes
self.num_stages = 5
def get_config(self):
return TextNetConfig(
stem_kernel_size=self.stem_kernel_size,
stem_stride=self.stem_stride,
stem_num_channels=self.stem_in_channels,
stem_out_channels=self.stem_out_channels,
act_func=self.act_func,
dropout_rate=self.dropout_rate,
ops_order=self.ops_order,
conv_layer_kernel_sizes=self.conv_layer_kernel_sizes,
conv_layer_strides=self.conv_layer_strides,
out_features=self.out_features,
out_indices=self.out_indices,
hidden_sizes=self.hidden_sizes,
image_size=self.image_size,
)
def create_and_check_model(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = TextNetModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
scale_h = self.image_size[0] // 32
scale_w = self.image_size[1] // 32
self.parent.assertEqual(
result.last_hidden_state.shape,
(self.batch_size, self.hidden_sizes[-1], scale_h, scale_w),
)
def create_and_check_for_image_classification(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = TextNetForImageClassification(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values, labels=labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_labels))
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pixel_values = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.num_channels, self.image_size[0], self.image_size[1]])
labels = None
if self.use_labels:
labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_labels)
config = self.get_config()
return config, pixel_values, labels
def create_and_check_backbone(self, config, pixel_values, labels):
model = TextNetBackbone(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
# verify feature maps
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.feature_maps), len(config.out_features))
scale_h = self.image_size[0] // 32
scale_w = self.image_size[1] // 32
self.parent.assertListEqual(
list(result.feature_maps[0].shape), [self.batch_size, self.hidden_sizes[1], 8 * scale_h, 8 * scale_w]
)
# verify channels
self.parent.assertEqual(len(model.channels), len(config.out_features))
self.parent.assertListEqual(model.channels, config.hidden_sizes[1:])
# verify backbone works with out_features=None
config.out_features = None
model = TextNetBackbone(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(pixel_values)
# verify feature maps
self.parent.assertEqual(len(result.feature_maps), 1)
scale_h = self.image_size[0] // 32
scale_w = self.image_size[1] // 32
self.parent.assertListEqual(
list(result.feature_maps[0].shape), [self.batch_size, self.hidden_sizes[0], scale_h, scale_w]
)
# verify channels
self.parent.assertEqual(len(model.channels), 1)
self.parent.assertListEqual(model.channels, [config.hidden_sizes[-1]])
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config, pixel_values, labels = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"pixel_values": pixel_values}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class TextNetModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
"""
Here we also overwrite some tests of test_modeling_common.py, as TextNet does not use input_ids, inputs_embeds,
attention_mask and seq_length.
"""
all_model_classes = (TextNetModel, TextNetForImageClassification, TextNetBackbone) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{"feature-extraction": TextNetModel, "image-classification": TextNetForImageClassification}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
fx_compatible = False
test_pruning = False
test_resize_embeddings = False
test_head_masking = False
has_attentions = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = TextNetModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = TextNetConfigTester(self, config_class=TextNetConfig, has_text_modality=False)
@unittest.skip(reason="TextNet does not output attentions")
def test_attention_outputs(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="TextNet does not have input/output embeddings")
def test_model_get_set_embeddings(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="TextNet does not use inputs_embeds")
def test_inputs_embeds(self):
pass
@unittest.skip(reason="TextNet does not support input and output embeddings")
def test_model_common_attributes(self):
pass
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_backbone(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_backbone(*config_and_inputs)
def test_initialization(self):
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
model = model_class(config=config)
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
self.assertTrue(
torch.all(module.weight == 1),
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
self.assertTrue(
torch.all(module.bias == 0),
msg=f"Parameter {name} of model {model_class} seems not properly initialized",
)
def test_hidden_states_output(self):
def check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class):
model = model_class(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**self._prepare_for_class(inputs_dict, model_class))
hidden_states = outputs.encoder_hidden_states if config.is_encoder_decoder else outputs.hidden_states
self.assertEqual(len(hidden_states), self.model_tester.num_stages)
self.assertListEqual(
list(hidden_states[0].shape[-2:]),
[self.model_tester.image_size[0] // 2, self.model_tester.image_size[1] // 2],
)
config, inputs_dict = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common()
layers_type = ["preactivation", "bottleneck"]
for model_class in self.all_model_classes:
for layer_type in layers_type:
config.layer_type = layer_type
inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"] = True
check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class)
# check that output_hidden_states also work using config
del inputs_dict["output_hidden_states"]
config.output_hidden_states = True
check_hidden_states_output(inputs_dict, config, model_class)
@unittest.skip(reason="TextNet does not use feedforward chunking")
def test_feed_forward_chunking(self):
pass
def test_for_image_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_image_classification(*config_and_inputs)
@slow
def test_model_from_pretrained(self):
model_name = "czczup/textnet-base"
model = TextNetModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.assertIsNotNone(model)
@require_torch
@require_vision
class TextNetModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_inference_no_head(self):
processor = TextNetImageProcessor.from_pretrained("czczup/textnet-base")
model = TextNetModel.from_pretrained("czczup/textnet-base").to(torch_device)
# prepare image
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(torch_device)
# forward pass
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(**inputs)
# verify logits
self.assertEqual(output.logits.shape, torch.Size([1, 2]))
expected_slice_backbone = torch.tensor(
[0.9210, 0.6099, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 3.2207, 2.6602, 1.8925, 0.0000],
device=torch_device,
)
torch.testing.assert_close(
output.feature_maps[-1][0][10][12][:10], expected_slice_backbone, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3
)
@require_torch
# Copied from tests.models.bit.test_modeling_bit.BitBackboneTest with Bit->TextNet
class TextNetBackboneTest(BackboneTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (TextNetBackbone,) if is_torch_available() else ()
config_class = TextNetConfig
has_attentions = False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = TextNetModelTester(self)
|
transformers/tests/models/textnet/test_modeling_textnet.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/textnet/test_modeling_textnet.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5628
}
| 217 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
import numpy as np
from parameterized import parameterized
from transformers.image_utils import OPENAI_CLIP_MEAN, OPENAI_CLIP_STD
from transformers.testing_utils import require_torch, require_vision
from transformers.utils import is_torch_available, is_vision_available
from ...test_image_processing_common import ImageProcessingTestMixin, prepare_image_inputs
if is_torch_available():
import torch
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
from transformers import VideoLlavaImageProcessor
class VideoLlavaImageProcessingTester(unittest.TestCase):
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=5,
num_channels=3,
image_size=18,
min_resolution=30,
max_resolution=80,
do_resize=True,
size=None,
do_center_crop=True,
crop_size=None,
do_normalize=True,
image_mean=OPENAI_CLIP_MEAN,
image_std=OPENAI_CLIP_STD,
do_convert_rgb=True,
):
super().__init__()
size = size if size is not None else {"shortest_edge": 20}
crop_size = crop_size if crop_size is not None else {"height": 18, "width": 18}
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.image_size = image_size
self.min_resolution = min_resolution
self.max_resolution = max_resolution
self.do_resize = do_resize
self.size = size
self.do_center_crop = do_center_crop
self.crop_size = crop_size
self.do_normalize = do_normalize
self.image_mean = image_mean
self.image_std = image_std
self.do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb
def prepare_image_processor_dict(self):
return {
"do_resize": self.do_resize,
"size": self.size,
"do_center_crop": self.do_center_crop,
"crop_size": self.crop_size,
"do_normalize": self.do_normalize,
"image_mean": self.image_mean,
"image_std": self.image_std,
"do_convert_rgb": self.do_convert_rgb,
}
# Copied from tests.models.clip.test_image_processing_clip.CLIPImageProcessingTester.expected_output_image_shape
def expected_output_image_shape(self, images):
return self.num_channels, self.crop_size["height"], self.crop_size["width"]
# Copied from tests.models.clip.test_image_processing_clip.CLIPImageProcessingTester.prepare_image_inputs
def prepare_image_inputs(self, equal_resolution=False, numpify=False, torchify=False):
return prepare_image_inputs(
batch_size=self.batch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
min_resolution=self.min_resolution,
max_resolution=self.max_resolution,
equal_resolution=equal_resolution,
numpify=numpify,
torchify=torchify,
)
def prepare_video_inputs(self, equal_resolution=False, numpify=False, torchify=False):
images = prepare_image_inputs(
batch_size=self.batch_size,
num_channels=self.num_channels,
min_resolution=self.min_resolution,
max_resolution=self.max_resolution,
equal_resolution=equal_resolution,
numpify=numpify,
torchify=torchify,
)
# let's simply copy the frames to fake a long video-clip
if numpify or torchify:
videos = []
for image in images:
if numpify:
video = image[None, ...].repeat(8, 0)
else:
video = image[None, ...].repeat(8, 1, 1, 1)
videos.append(video)
else:
videos = []
for pil_image in images:
videos.append([pil_image] * 8)
return videos
@require_torch
@require_vision
class VideoLlavaImageProcessingTest(ImageProcessingTestMixin, unittest.TestCase):
image_processing_class = VideoLlavaImageProcessor if is_vision_available() else None
# Copied from tests.models.clip.test_image_processing_clip.CLIPImageProcessingTest.setUp with CLIP->VideoLlava
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
self.image_processor_tester = VideoLlavaImageProcessingTester(self)
@property
# Copied from tests.models.clip.test_image_processing_clip.CLIPImageProcessingTest.image_processor_dict
def image_processor_dict(self):
return self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_processor_dict()
def test_image_processor_properties(self):
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_resize"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "size"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_center_crop"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "center_crop"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_normalize"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "image_mean"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "image_std"))
self.assertTrue(hasattr(image_processing, "do_convert_rgb"))
# Copied from tests.models.clip.test_image_processing_clip.CLIPImageProcessingTest.test_image_processor_from_dict_with_kwargs
def test_image_processor_from_dict_with_kwargs(self):
image_processor = self.image_processing_class.from_dict(self.image_processor_dict)
self.assertEqual(image_processor.size, {"shortest_edge": 20})
self.assertEqual(image_processor.crop_size, {"height": 18, "width": 18})
image_processor = self.image_processing_class.from_dict(self.image_processor_dict, size=42, crop_size=84)
self.assertEqual(image_processor.size, {"shortest_edge": 42})
self.assertEqual(image_processor.crop_size, {"height": 84, "width": 84})
def test_call_pil(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random PIL images
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=True)
for image in image_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(image, Image.Image)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = (1, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
# Test batched
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = (5, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
def test_call_numpy(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random numpy tensors
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=True, numpify=True)
for image in image_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(image, np.ndarray)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processing(images=image_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = (1, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
# Test batched
encoded_images = image_processing(images=image_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = (5, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
def test_call_numpy_videos(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random numpy tensors
video_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_video_inputs(numpify=True, equal_resolution=True)
for video in video_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(video, np.ndarray)
# Test not batched input
encoded_videos = image_processing(images=None, videos=video_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_videos
expected_output_video_shape = (1, 8, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
# Test batched
encoded_videos = image_processing(images=None, videos=video_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_videos
expected_output_video_shape = (5, 8, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
def test_call_pil_videos(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# the inputs come in list of lists batched format
video_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_video_inputs(equal_resolution=True)
for video in video_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(video[0], Image.Image)
# Test not batched input
encoded_videos = image_processing(images=None, videos=video_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_videos
expected_output_video_shape = (1, 8, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
# Test batched
encoded_videos = image_processing(images=None, videos=video_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_videos
expected_output_video_shape = (5, 8, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
def test_call_pytorch(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random PyTorch tensors
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=True, torchify=True)
for image in image_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(image, torch.Tensor)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = (1, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
# Test batched
encoded_images = image_processing(image_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = (5, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
def test_call_pytorch_videos(self):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random PyTorch tensors
video_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_video_inputs(equal_resolution=True, torchify=True)
for video in video_inputs:
self.assertIsInstance(video, torch.Tensor)
# Test not batched input
encoded_videos = image_processing(images=None, videos=video_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_videos
expected_output_video_shape = (1, 8, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
# Test batched
encoded_videos = image_processing(images=None, videos=video_inputs, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values_videos
expected_output_video_shape = (5, 8, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
@parameterized.expand([(True, False), (False, True)])
def test_call_mixed(self, numpify, torchify):
# Initialize image_processing
image_processing = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random numpy tensors
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(
equal_resolution=True, numpify=numpify, torchify=torchify
)
video_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_video_inputs(equal_resolution=True, torchify=torchify)
# Test not batched input
encoded = image_processing(images=image_inputs[0], videos=video_inputs[0], return_tensors="pt")
expected_output_video_shape = (1, 8, 3, 18, 18)
expected_output_image_shape = (1, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded.pixel_values_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded.pixel_values_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
# Test batched
encoded = image_processing(images=image_inputs, videos=video_inputs, return_tensors="pt")
expected_output_video_shape = (5, 8, 3, 18, 18)
expected_output_image_shape = (5, 3, 18, 18)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded.pixel_values_videos.shape), expected_output_video_shape)
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded.pixel_values_images.shape), expected_output_image_shape)
def test_call_numpy_4_channels(self):
# Test that can process images which have an arbitrary number of channels
# Initialize image_processing
image_processor = self.image_processing_class(**self.image_processor_dict)
# create random numpy tensors
self.image_processor_tester.num_channels = 4
image_inputs = self.image_processor_tester.prepare_image_inputs(equal_resolution=False, numpify=True)
# Test not batched input
encoded_images = image_processor(
image_inputs[0],
return_tensors="pt",
input_data_format="channels_last",
image_mean=0,
image_std=1,
).pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape([image_inputs[0]])
self.assertEqual(tuple(encoded_images.shape), (1, *expected_output_image_shape))
# Test batched
encoded_images = image_processor(
image_inputs,
return_tensors="pt",
input_data_format="channels_last",
image_mean=0,
image_std=1,
).pixel_values_images
expected_output_image_shape = self.image_processor_tester.expected_output_image_shape(image_inputs)
self.assertEqual(
tuple(encoded_images.shape), (self.image_processor_tester.batch_size, *expected_output_image_shape)
)
|
transformers/tests/models/video_llava/test_image_processing_video_llava.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/video_llava/test_image_processing_video_llava.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 6116
}
| 218 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Testing suite for the PyTorch VisionTextDualEncoder model."""
import collections
import tempfile
import unittest
import numpy as np
from transformers.testing_utils import (
is_pt_flax_cross_test,
require_flax,
require_torch,
require_vision,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from transformers.utils import is_flax_available, is_torch_available, is_vision_available
from ...test_modeling_flax_common import floats_tensor, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ..bert.test_modeling_flax_bert import FlaxBertModelTester
from ..clip.test_modeling_flax_clip import FlaxCLIPVisionModelTester
from ..vit.test_modeling_flax_vit import FlaxViTModelTester
if is_flax_available():
from transformers import (
FlaxBertModel,
FlaxCLIPVisionModel,
FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel,
FlaxViTModel,
VisionTextDualEncoderConfig,
VisionTextDualEncoderProcessor,
)
from transformers.modeling_flax_pytorch_utils import (
convert_pytorch_state_dict_to_flax,
load_flax_weights_in_pytorch_model,
)
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import VisionTextDualEncoderModel
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
# Inspired by
# https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/b9bd960a032c75ca6b808ddeed76bee5f3ed4972/timm/models/layers/helpers.py
# From PyTorch internals
def to_2tuple(x):
if isinstance(x, collections.abc.Iterable):
return x
return (x, x)
@require_flax
class VisionTextDualEncoderMixin:
def get_vision_text_model(self, config, text_config):
pass
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
pass
def get_pretrained_model_and_inputs(self):
pass
def assert_almost_equals(self, a: np.ndarray, b: np.ndarray, tol: float):
diff = np.abs((a - b)).max()
self.assertLessEqual(diff, tol, f"Difference between torch and flax is {diff} (>= {tol}).")
def check_model_from_pretrained_configs(
self, text_config, input_ids, attention_mask, vision_config, pixel_values=None, **kwargs
):
config = VisionTextDualEncoderConfig.from_vision_text_configs(vision_config, text_config)
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel(config)
output = model(input_ids=input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, attention_mask=attention_mask)
self.assertEqual(output["text_embeds"].shape, (input_ids.shape[0], config.projection_dim))
self.assertEqual(output["image_embeds"].shape, (pixel_values.shape[0], config.projection_dim))
def check_vision_text_dual_encoder_from_pretrained(
self, text_config, input_ids, attention_mask, vision_config, pixel_values=None, **kwargs
):
vision_model, text_model = self.get_vision_text_model(vision_config, text_config)
kwargs = {"vision_model": vision_model, "text_model": text_model}
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_vision_text_pretrained(**kwargs)
output = model(input_ids=input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, attention_mask=attention_mask)
self.assertEqual(output["text_embeds"].shape, (input_ids.shape[0], model.config.projection_dim))
self.assertEqual(output["image_embeds"].shape, (pixel_values.shape[0], model.config.projection_dim))
def check_save_load(self, text_config, input_ids, attention_mask, vision_config, pixel_values=None, **kwargs):
vision_model, text_model = self.get_vision_text_model(vision_config, text_config)
kwargs = {"vision_model": vision_model, "text_model": text_model}
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_vision_text_pretrained(**kwargs)
output = model(input_ids=input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, attention_mask=attention_mask)
out_1 = output[0]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
after_output = model(input_ids=input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, attention_mask=attention_mask)
out_2 = after_output[0]
max_diff = np.amax(np.abs(out_2 - out_1))
self.assertLessEqual(max_diff, 1e-3)
def check_vision_text_output_attention(
self, text_config, input_ids, attention_mask, vision_config, pixel_values=None, **kwargs
):
vision_model, text_model = self.get_vision_text_model(vision_config, text_config)
kwargs = {"vision_model": vision_model, "text_model": text_model}
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_vision_text_pretrained(**kwargs)
output = model(
input_ids=input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, attention_mask=attention_mask, output_attentions=True
)
vision_attentions = output.vision_model_output.attentions
self.assertEqual(len(vision_attentions), vision_config.num_hidden_layers)
# in ViT, the seq_len equals the number of patches + 1 (we add 1 for the [CLS] token)
image_size = to_2tuple(vision_model.config.image_size)
patch_size = to_2tuple(vision_model.config.patch_size)
num_patches = (image_size[1] // patch_size[1]) * (image_size[0] // patch_size[0])
seq_len = num_patches + 1
self.assertEqual(vision_attentions[0].shape[-3:], (vision_config.num_attention_heads, seq_len, seq_len))
text_attentions = output.text_model_output.attentions
self.assertEqual(len(text_attentions), text_config.num_hidden_layers)
self.assertEqual(
text_attentions[0].shape[-3:],
(text_config.num_attention_heads, input_ids.shape[-1], input_ids.shape[-1]),
)
def check_pt_flax_equivalence(self, pt_model, fx_model, inputs_dict):
pt_model.to(torch_device)
pt_model.eval()
# prepare inputs
flax_inputs = inputs_dict
pt_inputs = {k: torch.tensor(v.tolist()).to(torch_device) for k, v in flax_inputs.items()}
with torch.no_grad():
pt_outputs = pt_model(**pt_inputs).to_tuple()
fx_outputs = fx_model(**inputs_dict).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(len(fx_outputs), len(pt_outputs), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch")
for fx_output, pt_output in zip(fx_outputs[:4], pt_outputs[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output, pt_output.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
# PT -> Flax
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
pt_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
fx_model_loaded = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, from_pt=True)
fx_outputs_loaded = fx_model_loaded(**inputs_dict).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(len(fx_outputs_loaded), len(pt_outputs), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch")
for fx_output_loaded, pt_output in zip(fx_outputs_loaded[:4], pt_outputs[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output_loaded, pt_output.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
# Flax -> PT
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
fx_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
pt_model_loaded = VisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_pretrained(tmpdirname, from_flax=True)
pt_model_loaded.to(torch_device)
pt_model_loaded.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
pt_outputs_loaded = pt_model_loaded(**pt_inputs).to_tuple()
self.assertEqual(len(fx_outputs), len(pt_outputs_loaded), "Output lengths differ between Flax and PyTorch")
for fx_output, pt_output_loaded in zip(fx_outputs[:4], pt_outputs_loaded[:4]):
self.assert_almost_equals(fx_output, pt_output_loaded.numpy(force=True), 4e-2)
def check_equivalence_pt_to_flax(self, vision_config, text_config, inputs_dict):
config = VisionTextDualEncoderConfig.from_vision_text_configs(vision_config, text_config)
pt_model = VisionTextDualEncoderModel(config)
fx_model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel(config)
fx_state = convert_pytorch_state_dict_to_flax(pt_model.state_dict(), fx_model)
fx_model.params = fx_state
self.check_pt_flax_equivalence(pt_model, fx_model, inputs_dict)
def check_equivalence_flax_to_pt(self, vision_config, text_config, inputs_dict):
config = VisionTextDualEncoderConfig.from_vision_text_configs(vision_config, text_config)
pt_model = VisionTextDualEncoderModel(config)
fx_model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel(config)
pt_model = load_flax_weights_in_pytorch_model(pt_model, fx_model.params)
self.check_pt_flax_equivalence(pt_model, fx_model, inputs_dict)
def test_model_from_pretrained_configs(self):
inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.check_model_from_pretrained_configs(**inputs_dict)
def test_vision_text_dual_encoder_from_pretrained(self):
inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.check_vision_text_dual_encoder_from_pretrained(**inputs_dict)
def test_save_load(self):
inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.check_save_load(**inputs_dict)
def test_vision_text_output_attention(self):
inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.check_vision_text_output_attention(**inputs_dict)
@is_pt_flax_cross_test
def test_pt_flax_equivalence(self):
config_inputs_dict = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
vision_config = config_inputs_dict.pop("vision_config")
text_config = config_inputs_dict.pop("text_config")
inputs_dict = config_inputs_dict
self.check_equivalence_pt_to_flax(vision_config, text_config, inputs_dict)
self.check_equivalence_flax_to_pt(vision_config, text_config, inputs_dict)
@slow
def test_real_model_save_load_from_pretrained(self):
model_2, inputs = self.get_pretrained_model_and_inputs()
outputs = model_2(**inputs)
out_2 = outputs[0]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dirname:
model_2.save_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
model_1 = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
after_outputs = model_1(**inputs)
out_1 = after_outputs[0]
max_diff = np.amax(np.abs(out_1 - out_2))
self.assertLessEqual(max_diff, 1e-5)
@require_flax
class FlaxViTBertModelTest(VisionTextDualEncoderMixin, unittest.TestCase):
def get_pretrained_model_and_inputs(self):
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_vision_text_pretrained(
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-vit",
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-bert",
vision_from_pt=True,
text_from_pt=True,
)
batch_size = 13
pixel_values = floats_tensor(
[
batch_size,
model.config.vision_config.num_channels,
model.config.vision_config.image_size,
model.config.vision_config.image_size,
]
)
input_ids = ids_tensor([batch_size, 4], model.config.text_config.vocab_size)
attention_mask = random_attention_mask([batch_size, 4])
inputs = {"pixel_values": pixel_values, "input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": attention_mask}
return model, inputs
def get_vision_text_model(self, vision_config, text_config):
vision_model = FlaxViTModel(vision_config)
text_model = FlaxBertModel(text_config)
return vision_model, text_model
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
vit_model_tester = FlaxViTModelTester(self)
bert_model_tester = FlaxBertModelTester(self)
vision_config_and_inputs = vit_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
text_config_and_inputs = bert_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
vision_config, pixel_values = vision_config_and_inputs
text_config, input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask = text_config_and_inputs
# make sure that cross attention layers are added
return {
"text_config": text_config,
"vision_config": vision_config,
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"input_ids": input_ids,
"token_type_ids": token_type_ids,
}
@require_torch
class FlaxCLIPVisionBertModelTest(VisionTextDualEncoderMixin, unittest.TestCase):
def get_pretrained_model_and_inputs(self):
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_vision_text_pretrained(
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-clip",
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-bert",
vision_from_pt=True,
text_from_pt=True,
)
batch_size = 13
pixel_values = floats_tensor(
[
batch_size,
model.config.vision_config.num_channels,
model.config.vision_config.image_size,
model.config.vision_config.image_size,
]
)
input_ids = ids_tensor([batch_size, 4], model.config.text_config.vocab_size)
attention_mask = random_attention_mask([batch_size, 4])
inputs = {"pixel_values": pixel_values, "input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": attention_mask}
return model, inputs
def get_vision_text_model(self, vision_config, text_config):
vision_model = FlaxCLIPVisionModel(vision_config)
text_model = FlaxBertModel(text_config)
return vision_model, text_model
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
clip_model_tester = FlaxCLIPVisionModelTester(self)
bert_model_tester = FlaxBertModelTester(self)
vision_config_and_inputs = clip_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
text_config_and_inputs = bert_model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
vision_config, pixel_values = vision_config_and_inputs
text_config, input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask = text_config_and_inputs
# make sure that cross attention layers are added
return {
"text_config": text_config,
"vision_config": vision_config,
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"input_ids": input_ids,
"token_type_ids": token_type_ids,
}
@require_flax
@require_vision
class FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_inference(self):
model = FlaxVisionTextDualEncoderModel.from_pretrained("clip-italian/clip-italian", logit_scale_init_value=1.0)
processor = VisionTextDualEncoderProcessor.from_pretrained("clip-italian/clip-italian")
image = Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png")
inputs = processor(
text=["una foto di un gatto", "una foto di un cane"], images=image, padding=True, return_tensors="np"
)
outputs = model(**inputs)
# verify the logits
self.assertEqual(outputs.logits_per_image.shape, (inputs.pixel_values.shape[0], inputs.input_ids.shape[0]))
self.assertEqual(
outputs.logits_per_text.shape,
(inputs.input_ids.shape[0], inputs.pixel_values.shape[0]),
)
expected_logits = np.array([[1.2284727, 0.3104122]])
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(outputs.logits_per_image, expected_logits, atol=1e-3))
|
transformers/tests/models/vision_text_dual_encoder/test_modeling_flax_vision_text_dual_encoder.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/vision_text_dual_encoder/test_modeling_flax_vision_text_dual_encoder.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 6802
}
| 219 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
from transformers import XLMRobertaTokenizer, is_torch_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_sentencepiece, require_tokenizers, require_torch, slow, torch_device
from ...generation.test_utils import GenerationTesterMixin
from ...test_configuration_common import ConfigTester
from ...test_modeling_common import ModelTesterMixin, floats_tensor, ids_tensor, random_attention_mask
from ...test_pipeline_mixin import PipelineTesterMixin
if is_torch_available():
import torch
from transformers import (
XmodConfig,
XmodForCausalLM,
XmodForMaskedLM,
XmodForMultipleChoice,
XmodForQuestionAnswering,
XmodForSequenceClassification,
XmodForTokenClassification,
XmodModel,
)
from transformers.models.xmod.modeling_xmod import XmodEmbeddings, create_position_ids_from_input_ids
class XmodModelTester:
def __init__(
self,
parent,
batch_size=13,
seq_length=7,
is_training=True,
use_input_mask=True,
use_token_type_ids=True,
use_labels=True,
vocab_size=99,
hidden_size=32,
num_hidden_layers=2,
num_attention_heads=4,
intermediate_size=37,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
type_sequence_label_size=2,
initializer_range=0.02,
num_labels=3,
num_choices=4,
scope=None,
):
self.parent = parent
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.is_training = is_training
self.use_input_mask = use_input_mask
self.use_token_type_ids = use_token_type_ids
self.use_labels = use_labels
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.type_sequence_label_size = type_sequence_label_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.num_choices = num_choices
self.scope = scope
def prepare_config_and_inputs(self):
input_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.vocab_size)
input_mask = None
if self.use_input_mask:
input_mask = random_attention_mask([self.batch_size, self.seq_length])
token_type_ids = None
if self.use_token_type_ids:
token_type_ids = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.type_vocab_size)
sequence_labels = None
token_labels = None
choice_labels = None
if self.use_labels:
sequence_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.type_sequence_label_size)
token_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], self.num_labels)
choice_labels = ids_tensor([self.batch_size], self.num_choices)
config = self.get_config()
return config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
def get_config(self):
return XmodConfig(
vocab_size=self.vocab_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=self.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=self.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=self.intermediate_size,
hidden_act=self.hidden_act,
hidden_dropout_prob=self.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=self.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings,
type_vocab_size=self.type_vocab_size,
initializer_range=self.initializer_range,
default_language="en_XX",
)
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder(self):
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
config.is_decoder = True
encoder_hidden_states = floats_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size])
encoder_attention_mask = ids_tensor([self.batch_size, self.seq_length], vocab_size=2)
return (
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
)
def create_and_check_model(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = XmodModel(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
result = model(input_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.pooler_output.shape, (self.batch_size, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_model_as_decoder(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = XmodModel(config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
)
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
)
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.last_hidden_state.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.hidden_size))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.pooler_output.shape, (self.batch_size, self.hidden_size))
def create_and_check_for_causal_lm(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
model = XmodForCausalLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(
self,
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
):
config.is_decoder = True
config.add_cross_attention = True
model = XmodForCausalLM(config=config).to(torch_device).eval()
# make sure that ids don't start with pad token
mask = input_ids.ne(config.pad_token_id).long()
input_ids = input_ids * mask
# first forward pass
outputs = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
use_cache=True,
)
past_key_values = outputs.past_key_values
# create hypothetical multiple next token and extent to next_input_ids
next_tokens = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), config.vocab_size)
# make sure that ids don't start with pad token
mask = next_tokens.ne(config.pad_token_id).long()
next_tokens = next_tokens * mask
next_mask = ids_tensor((self.batch_size, 3), vocab_size=2)
# append to next input_ids and
next_input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens], dim=-1)
next_attention_mask = torch.cat([input_mask, next_mask], dim=-1)
output_from_no_past = model(
next_input_ids,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
output_from_past = model(
next_tokens,
attention_mask=next_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
output_hidden_states=True,
)["hidden_states"][0]
# select random slice
random_slice_idx = ids_tensor((1,), output_from_past.shape[-1]).item()
output_from_no_past_slice = output_from_no_past[:, -3:, random_slice_idx].detach()
output_from_past_slice = output_from_past[:, :, random_slice_idx].detach()
self.parent.assertTrue(output_from_past_slice.shape[1] == next_tokens.shape[1])
# test that outputs are equal for slice
self.parent.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output_from_past_slice, output_from_no_past_slice, atol=1e-3))
def create_and_check_for_masked_lm(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = XmodForMaskedLM(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.vocab_size))
def create_and_check_for_token_classification(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_labels = self.num_labels
model = XmodForTokenClassification(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(input_ids, attention_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, labels=token_labels)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length, self.num_labels))
def create_and_check_for_multiple_choice(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
config.num_choices = self.num_choices
model = XmodForMultipleChoice(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
multiple_choice_inputs_ids = input_ids.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
multiple_choice_token_type_ids = token_type_ids.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
multiple_choice_input_mask = input_mask.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.num_choices, -1).contiguous()
result = model(
multiple_choice_inputs_ids,
attention_mask=multiple_choice_input_mask,
token_type_ids=multiple_choice_token_type_ids,
labels=choice_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.num_choices))
def create_and_check_for_question_answering(
self, config, input_ids, token_type_ids, input_mask, sequence_labels, token_labels, choice_labels
):
model = XmodForQuestionAnswering(config=config)
model.to(torch_device)
model.eval()
result = model(
input_ids,
attention_mask=input_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
start_positions=sequence_labels,
end_positions=sequence_labels,
)
self.parent.assertEqual(result.start_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
self.parent.assertEqual(result.end_logits.shape, (self.batch_size, self.seq_length))
def prepare_config_and_inputs_for_common(self):
config_and_inputs = self.prepare_config_and_inputs()
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
) = config_and_inputs
inputs_dict = {"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids, "attention_mask": input_mask}
return config, inputs_dict
@require_torch
class XmodModelTest(ModelTesterMixin, GenerationTesterMixin, PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
all_model_classes = (
(
XmodForCausalLM,
XmodForMaskedLM,
XmodModel,
XmodForSequenceClassification,
XmodForTokenClassification,
XmodForMultipleChoice,
XmodForQuestionAnswering,
)
if is_torch_available()
else ()
)
all_generative_model_classes = (XmodForCausalLM,) if is_torch_available() else ()
pipeline_model_mapping = (
{
"feature-extraction": XmodModel,
"fill-mask": XmodForMaskedLM,
"question-answering": XmodForQuestionAnswering,
"text-classification": XmodForSequenceClassification,
"text-generation": XmodForCausalLM,
"token-classification": XmodForTokenClassification,
"zero-shot": XmodForSequenceClassification,
}
if is_torch_available()
else {}
)
# TODO: Fix the failed tests
def is_pipeline_test_to_skip(
self,
pipeline_test_case_name,
config_class,
model_architecture,
tokenizer_name,
image_processor_name,
feature_extractor_name,
processor_name,
):
if pipeline_test_case_name == "QAPipelineTests" and not tokenizer_name.endswith("Fast"):
return True
return False
def setUp(self):
self.model_tester = XmodModelTester(self)
self.config_tester = ConfigTester(self, config_class=XmodConfig, hidden_size=37)
def test_config(self):
self.config_tester.run_common_tests()
def test_model(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_various_embeddings(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
for type in ["absolute", "relative_key", "relative_key_query"]:
config_and_inputs[0].position_embedding_type = type
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_as_decoder(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model_as_decoder(*config_and_inputs)
def test_model_as_decoder_with_default_input_mask(self):
# This regression test was failing with PyTorch < 1.3
(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
) = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
input_mask = None
self.model_tester.create_and_check_model_as_decoder(
config,
input_ids,
token_type_ids,
input_mask,
sequence_labels,
token_labels,
choice_labels,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
)
def test_for_causal_lm(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_causal_lm(*config_and_inputs)
def test_decoder_model_past_with_large_inputs(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_decoder_model_past_with_large_inputs_relative_pos_emb(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs_for_decoder()
config_and_inputs[0].position_embedding_type = "relative_key"
self.model_tester.create_and_check_decoder_model_past_large_inputs(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_masked_lm(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_masked_lm(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_token_classification(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_token_classification(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_multiple_choice(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_multiple_choice(*config_and_inputs)
def test_for_question_answering(self):
config_and_inputs = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()
self.model_tester.create_and_check_for_question_answering(*config_and_inputs)
def test_create_position_ids_respects_padding_index(self):
"""This is a regression test for https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/1761
The position ids should be masked with the embedding object's padding index. Therefore, the
first available non-padding position index is XmodEmbeddings.padding_idx + 1
"""
config = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()[0]
model = XmodEmbeddings(config=config)
input_ids = torch.as_tensor([[12, 31, 13, model.padding_idx]])
expected_positions = torch.as_tensor(
[[0 + model.padding_idx + 1, 1 + model.padding_idx + 1, 2 + model.padding_idx + 1, model.padding_idx]]
)
position_ids = create_position_ids_from_input_ids(input_ids, model.padding_idx)
self.assertEqual(position_ids.shape, expected_positions.shape)
self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.eq(position_ids, expected_positions)))
def test_create_position_ids_from_inputs_embeds(self):
"""This is a regression test for https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/1761
The position ids should be masked with the embedding object's padding index. Therefore, the
first available non-padding position index is XmodEmbeddings.padding_idx + 1
"""
config = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()[0]
embeddings = XmodEmbeddings(config=config)
inputs_embeds = torch.empty(2, 4, 30)
expected_single_positions = [
0 + embeddings.padding_idx + 1,
1 + embeddings.padding_idx + 1,
2 + embeddings.padding_idx + 1,
3 + embeddings.padding_idx + 1,
]
expected_positions = torch.as_tensor([expected_single_positions, expected_single_positions])
position_ids = embeddings.create_position_ids_from_inputs_embeds(inputs_embeds)
self.assertEqual(position_ids.shape, expected_positions.shape)
self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.eq(position_ids, expected_positions)))
def test_set_default_language(self):
config = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()[0]
model = XmodForMaskedLM(config=config)
model.set_default_language("en_XX")
self.assertEqual(model.config.default_language, "en_XX")
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
model.set_default_language("xx_XX")
def test_freeze_embeddings_and_language_adapters(self):
config = self.model_tester.prepare_config_and_inputs()[0]
model = XmodForMaskedLM(config=config)
num_trainable_params_before = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
model.freeze_embeddings_and_language_adapters()
num_trainable_params_after = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
self.assertLess(num_trainable_params_after, num_trainable_params_before)
@require_sentencepiece
@require_tokenizers
@require_torch
class XmodModelIntegrationTest(unittest.TestCase):
@slow
def test_xmod_base(self):
model = XmodModel.from_pretrained("facebook/xmod-base")
# language en_XX
model.set_default_language("en_XX")
input_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 581, 10269, 83, 99942, 136, 60742, 23, 70, 80583, 18276, 2]])
# The dog is cute and lives in the garden house
expected_output_shape = torch.Size((1, 12, 768)) # batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_vector_dim
expected_output_values_last_dim = torch.tensor(
[[-0.2394, -0.0036, 0.1252, -0.0087, 0.1325, 0.0580, -0.2049, -0.1978, -0.1223, 0.0648, -0.2599, -0.3724]]
)
output = model(input_ids)["last_hidden_state"].detach()
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_output_shape)
# compare the actual values for a slice of last dim
torch.testing.assert_close(output[:, :, -1], expected_output_values_last_dim, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
# language de_DE
model.set_default_language("de_DE")
input_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 1310, 49083, 443, 269, 71, 5486, 165, 60429, 660, 23, 2315, 58761, 18391, 5, 2]])
# Der Hund ist niedlich und wohnt in einem Gartenhaus.
expected_output_shape = torch.Size((1, 16, 768)) # batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_vector_dim
# fmt: off
expected_output_values_last_dim = torch.tensor(
[[0.0162, 0.0075, -0.1882, 0.2335, -0.0952, -0.3994, -0.0317, -0.1174, 0.0177, 0.4280, -0.0240, -0.2138,
0.0785, -0.1045, -0.2811, -0.3220]]
)
# fmt: on
output = model(input_ids)["last_hidden_state"].detach()
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_output_shape)
# compare the actual values for a slice of last dim
torch.testing.assert_close(output[:, :, -1], expected_output_values_last_dim, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
@slow
def test_xmod_large_prenorm(self):
model = XmodModel.from_pretrained("facebook/xmod-large-prenorm")
# language en_XX
model.set_default_language("en_XX")
input_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 581, 10269, 83, 99942, 136, 60742, 23, 70, 80583, 18276, 2]])
# The dog is cute and lives in the garden house
expected_output_shape = torch.Size((1, 12, 1024)) # batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_vector_dim
# fmt: off
expected_output_values_last_dim = torch.tensor(
[[-0.0121, -0.0194, -0.0240, -0.0160, -0.0205, -0.0159, -0.0243, -0.0206, -0.0161, -0.0335, -0.0196,
-0.0141]]
)
# fmt: on
output = model(input_ids)["last_hidden_state"].detach()
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_output_shape)
# compare the actual values for a slice of last dim
torch.testing.assert_close(output[:, :, -1], expected_output_values_last_dim, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
# language de_DE
model.set_default_language("de_DE")
input_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 1310, 49083, 443, 269, 71, 5486, 165, 60429, 660, 23, 2315, 58761, 18391, 5, 2]])
# Der Hund ist niedlich und wohnt in einem Gartenhaus.
expected_output_shape = torch.Size((1, 16, 1024)) # batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_vector_dim
# fmt: off
expected_output_values_last_dim = torch.tensor(
[[-0.0120, -0.0262, -0.0253, -0.0112, -0.0128, -0.0164, -0.0080, -0.0081, -0.0192, -0.0117, -0.0170,
-0.0120, -0.0210, -0.0173, -0.0078, -0.0122]]
)
# fmt: on
output = model(input_ids)["last_hidden_state"].detach()
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_output_shape)
# compare the actual values for a slice of last dim
torch.testing.assert_close(output[:, :, -1], expected_output_values_last_dim, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
@slow
def test_multilingual_batch(self):
model = XmodModel.from_pretrained("facebook/xmod-base")
# fmt: off
input_ids = torch.tensor([
[0, 581, 10269, 83, 99942, 136, 60742, 23, 70, 80583, 18276, 2],
[0, 1310, 49083, 443, 269, 71, 5486, 165, 60429, 660, 23, 2],
[0, 1310, 49083, 443, 269, 71, 5486, 165, 60429, 660, 23, 2],
[0, 581, 10269, 83, 99942, 136, 60742, 23, 70, 80583, 18276, 2],
])
# fmt: on
lang_ids = torch.LongTensor([0, 8, 8, 0])
expected_output_shape = torch.Size((4, 12, 768)) # batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_vector_dim
# fmt: off
expected_output_values_last_dim = torch.tensor([
[-0.2394, -0.0036, 0.1252, -0.0087, 0.1325, 0.0580, -0.2049, -0.1978, -0.1223, 0.0648, -0.2599, -0.3724],
[-0.2668, -0.0235, -0.1739, 0.2266, -0.0901, -0.3482, 0.0105, -0.1915, 0.0397, 0.3822, 0.1836, -0.3407],
[-0.2668, -0.0235, -0.1739, 0.2266, -0.0901, -0.3482, 0.0105, -0.1915, 0.0397, 0.3822, 0.1836, -0.3407],
[-0.2394, -0.0036, 0.1252, -0.0087, 0.1325, 0.0580, -0.2049, -0.1978, -0.1223, 0.0648, -0.2599, -0.3724],
])
# fmt: on
output = model(input_ids, lang_ids=lang_ids)["last_hidden_state"].detach()
self.assertEqual(output.shape, expected_output_shape)
# compare the actual values for a slice of last dim
torch.testing.assert_close(output[:, :, -1], expected_output_values_last_dim, rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-3)
@slow
def test_end_to_end_mask_fill(self):
tokenizer = XLMRobertaTokenizer.from_pretrained("FacebookAI/xlm-roberta-base")
model = XmodForMaskedLM.from_pretrained("facebook/xmod-base", default_language="en_XX")
model.to(torch_device)
sentences = [
"Hello, my dog is a little <mask>.",
"Hi <mask>!",
]
inputs = tokenizer(sentences, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device)
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"].to(torch_device),
)
probs = outputs.logits.softmax(dim=-1)
_, predictions = probs.topk(1)
predictions = predictions.squeeze(-1)
inputs_non_padded = tokenizer(sentences[0], return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_non_padded = model(input_ids=inputs_non_padded)
probs_non_padded = output_non_padded.logits.softmax(dim=-1)
_, predictions_non_padded = probs_non_padded.topk(1)
predictions_non_padded = predictions_non_padded.squeeze(-1)
inputs_padded = tokenizer(sentences[1], return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(torch_device)
output_padded = model(input_ids=inputs_padded)
probs_padded = output_padded.logits.softmax(dim=-1)
_, predictions_padded = probs_padded.topk(1)
predictions_padded = predictions_padded.squeeze(-1)
batch_out_sentence = tokenizer.batch_decode(predictions, skip_special_tokens=True)
non_padded_sentence = tokenizer.decode(predictions_non_padded[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
padded_sentence = tokenizer.decode(predictions_padded[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
expected_output_sentence = [
"Hello, my dog is a little girl.",
"Hi everyone!",
]
self.assertListEqual(expected_output_sentence, batch_out_sentence)
self.assertListEqual(batch_out_sentence, [non_padded_sentence, padded_sentence])
|
transformers/tests/models/xmod/test_modeling_xmod.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/models/xmod/test_modeling_xmod.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 13270
}
| 220 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import importlib
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
from datasets import Dataset, DatasetDict
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from packaging import version
from transformers import (
AutoModelForCausalLM,
AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
AutoTokenizer,
OPTForCausalLM,
Trainer,
TrainingArguments,
logging,
)
from transformers.testing_utils import (
CaptureLogger,
require_bitsandbytes,
require_peft,
require_torch,
require_torch_gpu,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from transformers.utils import is_torch_available
if is_torch_available():
import torch
@require_peft
@require_torch
class PeftTesterMixin:
peft_test_model_ids = ("peft-internal-testing/tiny-OPTForCausalLM-lora",)
transformers_test_model_ids = ("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-OPTForCausalLM",)
transformers_test_model_classes = (AutoModelForCausalLM, OPTForCausalLM)
# TODO: run it with CI after PEFT release.
@slow
class PeftIntegrationTester(unittest.TestCase, PeftTesterMixin):
"""
A testing suite that makes sure that the PeftModel class is correctly integrated into the transformers library.
"""
def _check_lora_correctly_converted(self, model):
"""
Utility method to check if the model has correctly adapters injected on it.
"""
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer
is_peft_loaded = False
for _, m in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(m, BaseTunerLayer):
is_peft_loaded = True
break
return is_peft_loaded
def test_peft_from_pretrained(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model through `from_pretrained`.
This checks if we pass a remote folder that contains an adapter config and adapter weights, it
should correctly load a model that has adapters injected on it.
"""
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers.integrations.peft")
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cl:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
# ensure that under normal circumstances, there are no warnings about keys
self.assertNotIn("unexpected keys", cl.out)
self.assertNotIn("missing keys", cl.out)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(peft_model))
self.assertTrue(peft_model._hf_peft_config_loaded)
# dummy generation
_ = peft_model.generate(input_ids=torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device))
def test_peft_state_dict(self):
"""
Simple test that checks if the returned state dict of `get_adapter_state_dict()` method contains
the expected keys.
"""
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
state_dict = peft_model.get_adapter_state_dict()
for key in state_dict.keys():
self.assertTrue("lora" in key)
def test_peft_save_pretrained(self):
"""
Test that checks various combinations of `save_pretrained` with a model that has adapters loaded
on it. This checks if the saved model contains the expected files (adapter weights and adapter config).
"""
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
self.assertTrue("adapter_model.safetensors" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("adapter_config.json" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("config.json" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("pytorch_model.bin" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("model.safetensors" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(peft_model))
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname, safe_serialization=False)
self.assertTrue("adapter_model.bin" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("adapter_config.json" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(peft_model))
def test_peft_enable_disable_adapters(self):
"""
A test that checks if `enable_adapters` and `disable_adapters` methods work as expected.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
dummy_input = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device)
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
peft_model.add_adapter(peft_config)
peft_logits = peft_model(dummy_input).logits
peft_model.disable_adapters()
peft_logits_disabled = peft_model(dummy_input).logits
peft_model.enable_adapters()
peft_logits_enabled = peft_model(dummy_input).logits
torch.testing.assert_close(peft_logits, peft_logits_enabled, rtol=1e-12, atol=1e-12)
self.assertFalse(torch.allclose(peft_logits_enabled, peft_logits_disabled, atol=1e-12, rtol=1e-12))
def test_peft_add_adapter(self):
"""
Simple test that tests if `add_adapter` works as expected
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
model.add_adapter(peft_config)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
# dummy generation
_ = model.generate(input_ids=torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device))
def test_peft_add_adapter_from_pretrained(self):
"""
Simple test that tests if `add_adapter` works as expected
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
model.add_adapter(peft_config)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model_from_pretrained = transformers_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname).to(torch_device)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model_from_pretrained))
def test_peft_add_adapter_modules_to_save(self):
"""
Simple test that tests if `add_adapter` works as expected when training with
modules to save.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
from peft.utils import ModulesToSaveWrapper
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
dummy_input = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device)
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False, modules_to_save=["lm_head"])
model.add_adapter(peft_config)
self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model)
_has_modules_to_save_wrapper = False
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, ModulesToSaveWrapper):
_has_modules_to_save_wrapper = True
self.assertTrue(module.modules_to_save.default.weight.requires_grad)
self.assertTrue("lm_head" in name)
break
self.assertTrue(_has_modules_to_save_wrapper)
state_dict = model.get_adapter_state_dict()
self.assertTrue("lm_head.weight" in state_dict.keys())
logits = model(dummy_input).logits
loss = logits.mean()
loss.backward()
for _, param in model.named_parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
self.assertTrue(param.grad is not None)
def test_peft_add_adapter_training_gradient_checkpointing(self):
"""
Simple test that tests if `add_adapter` works as expected when training with
gradient checkpointing.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
model.add_adapter(peft_config)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
# When attaching adapters the input embeddings will stay frozen, this will
# lead to the output embedding having requires_grad=False.
dummy_input = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device)
frozen_output = model.get_input_embeddings()(dummy_input)
self.assertTrue(frozen_output.requires_grad is False)
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
# Since here we attached the hook, the input should have requires_grad to set
# properly
non_frozen_output = model.get_input_embeddings()(dummy_input)
self.assertTrue(non_frozen_output.requires_grad is True)
# To repro the Trainer issue
dummy_input.requires_grad = False
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if "lora" in name.lower():
self.assertTrue(param.requires_grad)
logits = model(dummy_input).logits
loss = logits.mean()
loss.backward()
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
self.assertTrue("lora" in name.lower())
self.assertTrue(param.grad is not None)
def test_peft_add_multi_adapter(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model through `from_pretrained`. This test tests if
add_adapter works as expected in multi-adapter setting.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer
dummy_input = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device)
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
is_peft_loaded = False
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
logits_original_model = model(dummy_input).logits
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
model.add_adapter(peft_config)
logits_adapter_1 = model(dummy_input)
model.add_adapter(peft_config, adapter_name="adapter-2")
logits_adapter_2 = model(dummy_input)
for _, m in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(m, BaseTunerLayer):
is_peft_loaded = True
break
self.assertTrue(is_peft_loaded)
# dummy generation
_ = model.generate(input_ids=dummy_input)
model.set_adapter("default")
self.assertTrue(model.active_adapters() == ["default"])
self.assertTrue(model.active_adapter() == "default")
model.set_adapter("adapter-2")
self.assertTrue(model.active_adapters() == ["adapter-2"])
self.assertTrue(model.active_adapter() == "adapter-2")
# Logits comparison
self.assertFalse(
torch.allclose(logits_adapter_1.logits, logits_adapter_2.logits, atol=1e-6, rtol=1e-6)
)
self.assertFalse(torch.allclose(logits_original_model, logits_adapter_2.logits, atol=1e-6, rtol=1e-6))
model.set_adapter(["adapter-2", "default"])
self.assertTrue(model.active_adapters() == ["adapter-2", "default"])
self.assertTrue(model.active_adapter() == "adapter-2")
logits_adapter_mixed = model(dummy_input)
self.assertFalse(
torch.allclose(logits_adapter_1.logits, logits_adapter_mixed.logits, atol=1e-6, rtol=1e-6)
)
self.assertFalse(
torch.allclose(logits_adapter_2.logits, logits_adapter_mixed.logits, atol=1e-6, rtol=1e-6)
)
# multi active adapter saving not supported
with self.assertRaises(ValueError), tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
def test_delete_adapter(self):
"""
Enhanced test for `delete_adapter` to handle multiple adapters,
edge cases, and proper error handling.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
for model_id in self.transformers_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
# Add multiple adapters
peft_config_1 = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
peft_config_2 = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
model.add_adapter(peft_config_1, adapter_name="adapter_1")
model.add_adapter(peft_config_2, adapter_name="adapter_2")
# Ensure adapters were added
self.assertIn("adapter_1", model.peft_config)
self.assertIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
# Delete a single adapter
model.delete_adapter("adapter_1")
self.assertNotIn("adapter_1", model.peft_config)
self.assertIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
# Delete remaining adapter
model.delete_adapter("adapter_2")
self.assertNotIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
self.assertFalse(model._hf_peft_config_loaded)
# Re-add adapters for edge case tests
model.add_adapter(peft_config_1, adapter_name="adapter_1")
model.add_adapter(peft_config_2, adapter_name="adapter_2")
# Attempt to delete multiple adapters at once
model.delete_adapter(["adapter_1", "adapter_2"])
self.assertNotIn("adapter_1", model.peft_config)
self.assertNotIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
self.assertFalse(model._hf_peft_config_loaded)
# Test edge cases
with self.assertRaisesRegex(ValueError, "The following adapter\\(s\\) are not present"):
model.delete_adapter("nonexistent_adapter")
with self.assertRaisesRegex(ValueError, "The following adapter\\(s\\) are not present"):
model.delete_adapter(["adapter_1", "nonexistent_adapter"])
# Deleting with an empty list or None should not raise errors
model.add_adapter(peft_config_1, adapter_name="adapter_1")
model.add_adapter(peft_config_2, adapter_name="adapter_2")
model.delete_adapter([]) # No-op
self.assertIn("adapter_1", model.peft_config)
self.assertIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
model.delete_adapter(None) # No-op
self.assertIn("adapter_1", model.peft_config)
self.assertIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
# Deleting duplicate adapter names in the list
model.delete_adapter(["adapter_1", "adapter_1"])
self.assertNotIn("adapter_1", model.peft_config)
self.assertIn("adapter_2", model.peft_config)
@require_torch_gpu
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_peft_from_pretrained_kwargs(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model through `from_pretrained` + additional kwargs
and see if the integraiton behaves as expected.
"""
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto")
module = peft_model.model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn.v_proj
self.assertTrue(module.__class__.__name__ == "Linear8bitLt")
self.assertTrue(peft_model.hf_device_map is not None)
# dummy generation
_ = peft_model.generate(input_ids=torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device))
@require_torch_gpu
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_peft_save_quantized(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model save_pretrained with quantized base models
"""
# 4bit
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_4bit=True, device_map="auto")
module = peft_model.model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn.v_proj
self.assertTrue(module.__class__.__name__ == "Linear4bit")
self.assertTrue(peft_model.hf_device_map is not None)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
self.assertTrue("adapter_model.safetensors" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("adapter_config.json" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("pytorch_model.bin" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("model.safetensors" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
# 8-bit
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto")
module = peft_model.model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn.v_proj
self.assertTrue(module.__class__.__name__ == "Linear8bitLt")
self.assertTrue(peft_model.hf_device_map is not None)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
self.assertTrue("adapter_model.safetensors" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("adapter_config.json" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("pytorch_model.bin" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("model.safetensors" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
@require_torch_gpu
@require_bitsandbytes
def test_peft_save_quantized_regression(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model save_pretrained with quantized base models
Regression test to make sure everything works as expected before the safetensors integration.
"""
# 4bit
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_4bit=True, device_map="auto")
module = peft_model.model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn.v_proj
self.assertTrue(module.__class__.__name__ == "Linear4bit")
self.assertTrue(peft_model.hf_device_map is not None)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname, safe_serialization=False)
self.assertTrue("adapter_model.bin" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("adapter_config.json" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("pytorch_model.bin" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("model.safetensors" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
# 8-bit
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto")
module = peft_model.model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn.v_proj
self.assertTrue(module.__class__.__name__ == "Linear8bitLt")
self.assertTrue(peft_model.hf_device_map is not None)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname, safe_serialization=False)
self.assertTrue("adapter_model.bin" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("adapter_config.json" in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("pytorch_model.bin" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
self.assertTrue("model.safetensors" not in os.listdir(tmpdirname))
def test_peft_pipeline(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model + pipeline
"""
from transformers import pipeline
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model_id)
_ = pipe("Hello")
def test_peft_add_adapter_with_state_dict(self):
"""
Simple test that tests the basic usage of PEFT model through `from_pretrained`. This test tests if
add_adapter works as expected with a state_dict being passed.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
dummy_input = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]).to(torch_device)
for model_id, peft_model_id in zip(self.transformers_test_model_ids, self.peft_test_model_ids):
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False)
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
model.load_adapter(peft_model_id=None)
state_dict_path = hf_hub_download(peft_model_id, "adapter_model.bin")
dummy_state_dict = torch.load(state_dict_path)
model.load_adapter(adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict, peft_config=peft_config)
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
model.load_adapter(model.load_adapter(adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict, peft_config=None))
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
# dummy generation
_ = model.generate(input_ids=dummy_input)
def test_peft_add_adapter_with_state_dict_low_cpu_mem_usage(self):
"""
Check the usage of low_cpu_mem_usage, which is supported in PEFT >= 0.13.0
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
min_version_lcmu = "0.13.0"
is_lcmu_supported = version.parse(importlib.metadata.version("peft")) >= version.parse(min_version_lcmu)
for model_id, peft_model_id in zip(self.transformers_test_model_ids, self.peft_test_model_ids):
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig()
state_dict_path = hf_hub_download(peft_model_id, "adapter_model.bin")
dummy_state_dict = torch.load(state_dict_path)
# this should always work
model.load_adapter(
adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict, peft_config=peft_config, low_cpu_mem_usage=False
)
if is_lcmu_supported:
# if supported, this should not raise an error
model.load_adapter(
adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict,
adapter_name="other",
peft_config=peft_config,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
)
# after loading, no meta device should be remaining
self.assertFalse(any((p.device.type == "meta") for p in model.parameters()))
else:
err_msg = r"The version of PEFT you are using does not support `low_cpu_mem_usage` yet"
with self.assertRaisesRegex(ValueError, err_msg):
model.load_adapter(
adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict,
adapter_name="other",
peft_config=peft_config,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
)
def test_peft_from_pretrained_hub_kwargs(self):
"""
Tests different combinations of PEFT model + from_pretrained + hub kwargs
"""
peft_model_id = "peft-internal-testing/tiny-opt-lora-revision"
# This should not work
with self.assertRaises(OSError):
_ = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)
adapter_kwargs = {"revision": "test"}
# This should work
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, adapter_kwargs=adapter_kwargs)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
model = OPTForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, adapter_kwargs=adapter_kwargs)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
adapter_kwargs = {"revision": "main", "subfolder": "test_subfolder"}
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, adapter_kwargs=adapter_kwargs)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
model = OPTForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, adapter_kwargs=adapter_kwargs)
self.assertTrue(self._check_lora_correctly_converted(model))
def test_peft_from_pretrained_unexpected_keys_warning(self):
"""
Test for warning when loading a PEFT checkpoint with unexpected keys.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers.integrations.peft")
for model_id, peft_model_id in zip(self.transformers_test_model_ids, self.peft_test_model_ids):
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig()
state_dict_path = hf_hub_download(peft_model_id, "adapter_model.bin")
dummy_state_dict = torch.load(state_dict_path)
# add unexpected key
dummy_state_dict["foobar"] = next(iter(dummy_state_dict.values()))
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cl:
model.load_adapter(
adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict, peft_config=peft_config, low_cpu_mem_usage=False
)
msg = "Loading adapter weights from state_dict led to unexpected keys not found in the model: foobar"
self.assertIn(msg, cl.out)
def test_peft_from_pretrained_missing_keys_warning(self):
"""
Test for warning when loading a PEFT checkpoint with missing keys.
"""
from peft import LoraConfig
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers.integrations.peft")
for model_id, peft_model_id in zip(self.transformers_test_model_ids, self.peft_test_model_ids):
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
peft_config = LoraConfig()
state_dict_path = hf_hub_download(peft_model_id, "adapter_model.bin")
dummy_state_dict = torch.load(state_dict_path)
# remove a key so that we have missing keys
key = next(iter(dummy_state_dict.keys()))
del dummy_state_dict[key]
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cl:
model.load_adapter(
adapter_state_dict=dummy_state_dict,
peft_config=peft_config,
low_cpu_mem_usage=False,
adapter_name="other",
)
# Here we need to adjust the key name a bit to account for PEFT-specific naming.
# 1. Remove PEFT-specific prefix
# If merged after dropping Python 3.8, we can use: key = key.removeprefix(peft_prefix)
peft_prefix = "base_model.model."
key = key[len(peft_prefix) :]
# 2. Insert adapter name
prefix, _, suffix = key.rpartition(".")
key = f"{prefix}.other.{suffix}"
msg = f"Loading adapter weights from state_dict led to missing keys in the model: {key}"
self.assertIn(msg, cl.out)
def test_peft_load_adapter_training_inference_mode_true(self):
"""
By default, when loading an adapter, the whole model should be in eval mode and no parameter should have
requires_grad=False.
"""
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(peft_model.config._name_or_path)
model.load_adapter(tmpdirname)
assert not any(p.requires_grad for p in model.parameters())
assert not any(m.training for m in model.modules())
del model
def test_peft_load_adapter_training_inference_mode_false(self):
"""
When passing is_trainable=True, the LoRA modules should be in training mode and their parameters should have
requires_grad=True.
"""
for model_id in self.peft_test_model_ids:
for transformers_class in self.transformers_test_model_classes:
peft_model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(torch_device)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
model = transformers_class.from_pretrained(peft_model.config._name_or_path)
model.load_adapter(tmpdirname, is_trainable=True)
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if len(list(module.children())):
# only check leaf modules
continue
if "lora_" in name:
assert module.training
assert all(p.requires_grad for p in module.parameters())
else:
assert not module.training
assert all(not p.requires_grad for p in module.parameters())
def test_prefix_tuning_trainer_load_best_model_at_end_error(self):
# Original issue: https://github.com/huggingface/peft/issues/2256
# There is a potential error when using load_best_model_at_end=True with a prompt learning PEFT method. This is
# because Trainer uses load_adapter under the hood but with some prompt learning methods, there is an
# optimization on the saved model to remove parameters that are not required for inference, which in turn
# requires a change to the model architecture. This is why load_adapter will fail in such cases and users should
# instead set load_best_model_at_end=False and use PeftModel.from_pretrained. As this is not obvious, we now
# intercept the error and add a helpful error message.
# This test checks this error message. It also tests the "happy path" (i.e. no error) when using LoRA.
from peft import LoraConfig, PrefixTuningConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model
# create a small sequence classification dataset (binary classification)
dataset = []
for i, row in enumerate(os.__doc__.splitlines()):
dataset.append({"text": row, "label": i % 2})
ds_train = Dataset.from_list(dataset)
ds_valid = ds_train
datasets = DatasetDict(
{
"train": ds_train,
"val": ds_valid,
}
)
# tokenizer for peft-internal-testing/tiny-OPTForCausalLM-lora cannot be loaded, thus using
# hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-OPTForCausalLM
model_id = "hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-OPTForCausalLM"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, padding_side="left", model_type="opt")
def tokenize_function(examples):
return tokenizer(examples["text"], max_length=128, truncation=True, padding="max_length")
tokenized_datasets = datasets.map(tokenize_function, batched=True)
# lora works, prefix-tuning is expected to raise an error
peft_configs = {
"lora": LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS),
"prefix-tuning": PrefixTuningConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS,
inference_mode=False,
prefix_projection=True,
num_virtual_tokens=10,
),
}
for peft_type, peft_config in peft_configs.items():
base_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_id, num_labels=2)
base_model.config.pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, peft_config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=tmpdirname,
num_train_epochs=3,
eval_strategy="epoch",
save_strategy="epoch",
load_best_model_at_end=True,
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=peft_model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"],
eval_dataset=tokenized_datasets["val"],
)
if peft_type == "lora":
# LoRA works with load_best_model_at_end
trainer.train()
else:
# prefix tuning does not work, but at least users should get a helpful error message
msg = "When using prompt learning PEFT methods such as PREFIX_TUNING"
with self.assertRaisesRegex(RuntimeError, msg):
trainer.train()
|
transformers/tests/peft_integration/test_peft_integration.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/peft_integration/test_peft_integration.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 17609
}
| 221 |
# Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
from huggingface_hub import ObjectDetectionOutputElement
from transformers import (
MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING,
AutoFeatureExtractor,
AutoModelForObjectDetection,
ObjectDetectionPipeline,
is_vision_available,
pipeline,
)
from transformers.testing_utils import ( #
compare_pipeline_output_to_hub_spec,
is_pipeline_test,
nested_simplify,
require_pytesseract,
require_tf,
require_timm,
require_torch,
require_vision,
slow,
)
from .test_pipelines_common import ANY
if is_vision_available():
from PIL import Image
else:
class Image:
@staticmethod
def open(*args, **kwargs):
pass
@is_pipeline_test
@require_vision
@require_timm
@require_torch
class ObjectDetectionPipelineTests(unittest.TestCase):
model_mapping = MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING
def get_test_pipeline(
self,
model,
tokenizer=None,
image_processor=None,
feature_extractor=None,
processor=None,
torch_dtype="float32",
):
object_detector = ObjectDetectionPipeline(
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
feature_extractor=feature_extractor,
image_processor=image_processor,
processor=processor,
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
)
return object_detector, ["./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png"]
def run_pipeline_test(self, object_detector, examples):
outputs = object_detector("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png", threshold=0.0)
self.assertGreater(len(outputs), 0)
for detected_object in outputs:
self.assertEqual(
detected_object,
{
"score": ANY(float),
"label": ANY(str),
"box": {"xmin": ANY(int), "ymin": ANY(int), "xmax": ANY(int), "ymax": ANY(int)},
},
)
import datasets
# we use revision="refs/pr/1" until the PR is merged
# https://hf.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/fixtures_image_utils/discussions/1
dataset = datasets.load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/fixtures_image_utils", split="test", revision="refs/pr/1")
batch = [
Image.open("./tests/fixtures/tests_samples/COCO/000000039769.png"),
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
# RGBA
dataset[0]["image"],
# LA
dataset[1]["image"],
# L
dataset[2]["image"],
]
batch_outputs = object_detector(batch, threshold=0.0)
self.assertEqual(len(batch), len(batch_outputs))
for outputs in batch_outputs:
self.assertGreater(len(outputs), 0)
for detected_object in outputs:
self.assertEqual(
detected_object,
{
"score": ANY(float),
"label": ANY(str),
"box": {"xmin": ANY(int), "ymin": ANY(int), "xmax": ANY(int), "ymax": ANY(int)},
},
)
compare_pipeline_output_to_hub_spec(detected_object, ObjectDetectionOutputElement)
@require_tf
@unittest.skip(reason="Object detection not implemented in TF")
def test_small_model_tf(self):
pass
@require_torch
def test_small_model_pt(self):
model_id = "hf-internal-testing/tiny-detr-mobilenetsv3"
model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained(model_id)
feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(model_id)
object_detector = ObjectDetectionPipeline(model=model, feature_extractor=feature_extractor)
outputs = object_detector("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg", threshold=0.0)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
{"score": 0.3376, "label": "LABEL_0", "box": {"xmin": 159, "ymin": 120, "xmax": 480, "ymax": 359}},
{"score": 0.3376, "label": "LABEL_0", "box": {"xmin": 159, "ymin": 120, "xmax": 480, "ymax": 359}},
],
)
outputs = object_detector(
[
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
],
threshold=0.0,
)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
[
{"score": 0.3376, "label": "LABEL_0", "box": {"xmin": 159, "ymin": 120, "xmax": 480, "ymax": 359}},
{"score": 0.3376, "label": "LABEL_0", "box": {"xmin": 159, "ymin": 120, "xmax": 480, "ymax": 359}},
],
[
{"score": 0.3376, "label": "LABEL_0", "box": {"xmin": 159, "ymin": 120, "xmax": 480, "ymax": 359}},
{"score": 0.3376, "label": "LABEL_0", "box": {"xmin": 159, "ymin": 120, "xmax": 480, "ymax": 359}},
],
],
)
@require_torch
@slow
def test_large_model_pt(self):
model_id = "facebook/detr-resnet-50"
model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained(model_id)
feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(model_id)
object_detector = ObjectDetectionPipeline(model=model, feature_extractor=feature_extractor)
outputs = object_detector("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg")
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
{"score": 0.9982, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 40, "ymin": 70, "xmax": 175, "ymax": 117}},
{"score": 0.9960, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 333, "ymin": 72, "xmax": 368, "ymax": 187}},
{"score": 0.9955, "label": "couch", "box": {"xmin": 0, "ymin": 1, "xmax": 639, "ymax": 473}},
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
)
outputs = object_detector(
[
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
]
)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
[
{"score": 0.9982, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 40, "ymin": 70, "xmax": 175, "ymax": 117}},
{"score": 0.9960, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 333, "ymin": 72, "xmax": 368, "ymax": 187}},
{"score": 0.9955, "label": "couch", "box": {"xmin": 0, "ymin": 1, "xmax": 639, "ymax": 473}},
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
[
{"score": 0.9982, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 40, "ymin": 70, "xmax": 175, "ymax": 117}},
{"score": 0.9960, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 333, "ymin": 72, "xmax": 368, "ymax": 187}},
{"score": 0.9955, "label": "couch", "box": {"xmin": 0, "ymin": 1, "xmax": 639, "ymax": 473}},
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
],
)
@require_torch
@slow
def test_integration_torch_object_detection(self):
model_id = "facebook/detr-resnet-50"
object_detector = pipeline("object-detection", model=model_id)
outputs = object_detector("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg")
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
{"score": 0.9982, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 40, "ymin": 70, "xmax": 175, "ymax": 117}},
{"score": 0.9960, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 333, "ymin": 72, "xmax": 368, "ymax": 187}},
{"score": 0.9955, "label": "couch", "box": {"xmin": 0, "ymin": 1, "xmax": 639, "ymax": 473}},
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
)
outputs = object_detector(
[
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
"http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg",
]
)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
[
{"score": 0.9982, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 40, "ymin": 70, "xmax": 175, "ymax": 117}},
{"score": 0.9960, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 333, "ymin": 72, "xmax": 368, "ymax": 187}},
{"score": 0.9955, "label": "couch", "box": {"xmin": 0, "ymin": 1, "xmax": 639, "ymax": 473}},
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
[
{"score": 0.9982, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 40, "ymin": 70, "xmax": 175, "ymax": 117}},
{"score": 0.9960, "label": "remote", "box": {"xmin": 333, "ymin": 72, "xmax": 368, "ymax": 187}},
{"score": 0.9955, "label": "couch", "box": {"xmin": 0, "ymin": 1, "xmax": 639, "ymax": 473}},
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
],
)
@require_torch
@slow
def test_threshold(self):
threshold = 0.9985
model_id = "facebook/detr-resnet-50"
object_detector = pipeline("object-detection", model=model_id)
outputs = object_detector("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg", threshold=threshold)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
{"score": 0.9988, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 13, "ymin": 52, "xmax": 314, "ymax": 470}},
{"score": 0.9987, "label": "cat", "box": {"xmin": 345, "ymin": 23, "xmax": 640, "ymax": 368}},
],
)
@require_torch
@require_pytesseract
@slow
def test_layoutlm(self):
model_id = "Narsil/layoutlmv3-finetuned-funsd"
threshold = 0.9993
object_detector = pipeline("object-detection", model=model_id, threshold=threshold)
outputs = object_detector(
"https://huggingface.co/spaces/impira/docquery/resolve/2359223c1837a7587402bda0f2643382a6eefeab/invoice.png"
)
self.assertEqual(
nested_simplify(outputs, decimals=4),
[
{"score": 0.9993, "label": "I-ANSWER", "box": {"xmin": 294, "ymin": 254, "xmax": 343, "ymax": 264}},
{"score": 0.9993, "label": "I-ANSWER", "box": {"xmin": 294, "ymin": 254, "xmax": 343, "ymax": 264}},
],
)
|
transformers/tests/pipelines/test_pipelines_object_detection.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/pipelines/test_pipelines_object_detection.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 6324
}
| 222 |
# Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os
import shutil
import sys
import tempfile
import unittest
from contextlib import contextmanager
from pathlib import Path
git_repo_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
sys.path.append(os.path.join(git_repo_path, "utils"))
import check_copies # noqa: E402
from check_copies import convert_to_localized_md, find_code_in_transformers, is_copy_consistent # noqa: E402
# This is the reference code that will be used in the tests.
# If BertLMPredictionHead is changed in modeling_bert.py, this code needs to be manually updated.
REFERENCE_CODE = """ def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.transform = BertPredictionHeadTransform(config)
# The output weights are the same as the input embeddings, but there is
# an output-only bias for each token.
self.decoder = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(config.vocab_size))
# Need a link between the two variables so that the bias is correctly resized with `resize_token_embeddings`
self.decoder.bias = self.bias
def forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_states = self.transform(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.decoder(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
"""
MOCK_BERT_CODE = """from ...modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
def bert_function(x):
return x
class BertAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
class BertModel(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertEncoder(config)
@add_docstring(BERT_DOCSTRING)
def forward(self, x):
return self.bert(x)
"""
MOCK_BERT_COPY_CODE = """from ...modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
# Copied from transformers.models.bert.modeling_bert.bert_function
def bert_copy_function(x):
return x
# Copied from transformers.models.bert.modeling_bert.BertAttention
class BertCopyAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
# Copied from transformers.models.bert.modeling_bert.BertModel with Bert->BertCopy all-casing
class BertCopyModel(BertCopyPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.bertcopy = BertCopyEncoder(config)
@add_docstring(BERTCOPY_DOCSTRING)
def forward(self, x):
return self.bertcopy(x)
"""
MOCK_DUMMY_BERT_CODE_MATCH = """
class BertDummyModel:
attr_1 = 1
attr_2 = 2
def __init__(self, a=1, b=2):
self.a = a
self.b = b
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_gpt2.modeling_dummy_gpt2.GPT2DummyModel.forward
def forward(self, c):
return 1
def existing_common(self, c):
return 4
def existing_diff_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 9
"""
MOCK_DUMMY_ROBERTA_CODE_MATCH = """
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_bert_match.modeling_dummy_bert_match.BertDummyModel with BertDummy->RobertaBertDummy
class RobertaBertDummyModel:
attr_1 = 1
attr_2 = 2
def __init__(self, a=1, b=2):
self.a = a
self.b = b
# Ignore copy
def only_in_roberta_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 3
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_gpt2.modeling_dummy_gpt2.GPT2DummyModel.forward
def forward(self, c):
return 1
def existing_common(self, c):
return 4
# Ignore copy
def existing_diff_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 6
"""
MOCK_DUMMY_BERT_CODE_NO_MATCH = """
class BertDummyModel:
attr_1 = 1
attr_2 = 2
def __init__(self, a=1, b=2):
self.a = a
self.b = b
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_gpt2.modeling_dummy_gpt2.GPT2DummyModel.forward
def forward(self, c):
return 1
def only_in_bert(self, c):
return 7
def existing_common(self, c):
return 4
def existing_diff_not_ignored(self, c):
return 8
def existing_diff_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 9
"""
MOCK_DUMMY_ROBERTA_CODE_NO_MATCH = """
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_bert_no_match.modeling_dummy_bert_no_match.BertDummyModel with BertDummy->RobertaBertDummy
class RobertaBertDummyModel:
attr_1 = 1
attr_2 = 3
def __init__(self, a=1, b=2):
self.a = a
self.b = b
# Ignore copy
def only_in_roberta_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 3
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_gpt2.modeling_dummy_gpt2.GPT2DummyModel.forward
def forward(self, c):
return 1
def only_in_roberta_not_ignored(self, c):
return 2
def existing_common(self, c):
return 4
def existing_diff_not_ignored(self, c):
return 5
# Ignore copy
def existing_diff_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 6
"""
EXPECTED_REPLACED_CODE = """
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_bert_no_match.modeling_dummy_bert_no_match.BertDummyModel with BertDummy->RobertaBertDummy
class RobertaBertDummyModel:
attr_1 = 1
attr_2 = 2
def __init__(self, a=1, b=2):
self.a = a
self.b = b
# Copied from transformers.models.dummy_gpt2.modeling_dummy_gpt2.GPT2DummyModel.forward
def forward(self, c):
return 1
def only_in_bert(self, c):
return 7
def existing_common(self, c):
return 4
def existing_diff_not_ignored(self, c):
return 8
# Ignore copy
def existing_diff_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 6
# Ignore copy
def only_in_roberta_to_be_ignored(self, c):
return 3
"""
def replace_in_file(filename, old, new):
with open(filename, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
content = f.read()
content = content.replace(old, new)
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8", newline="\n") as f:
f.write(content)
def create_tmp_repo(tmp_dir):
"""
Creates a mock repository in a temporary folder for testing.
"""
tmp_dir = Path(tmp_dir)
if tmp_dir.exists():
shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
tmp_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
model_dir = tmp_dir / "src" / "transformers" / "models"
model_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
models = {
"bert": MOCK_BERT_CODE,
"bertcopy": MOCK_BERT_COPY_CODE,
"dummy_bert_match": MOCK_DUMMY_BERT_CODE_MATCH,
"dummy_roberta_match": MOCK_DUMMY_ROBERTA_CODE_MATCH,
"dummy_bert_no_match": MOCK_DUMMY_BERT_CODE_NO_MATCH,
"dummy_roberta_no_match": MOCK_DUMMY_ROBERTA_CODE_NO_MATCH,
}
for model, code in models.items():
model_subdir = model_dir / model
model_subdir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
with open(model_subdir / f"modeling_{model}.py", "w", encoding="utf-8", newline="\n") as f:
f.write(code)
@contextmanager
def patch_transformer_repo_path(new_folder):
"""
Temporarily patches the variables defines in `check_copies` to use a different location for the repo.
"""
old_repo_path = check_copies.REPO_PATH
old_doc_path = check_copies.PATH_TO_DOCS
old_transformer_path = check_copies.TRANSFORMERS_PATH
repo_path = Path(new_folder).resolve()
check_copies.REPO_PATH = str(repo_path)
check_copies.PATH_TO_DOCS = str(repo_path / "docs" / "source" / "en")
check_copies.TRANSFORMERS_PATH = str(repo_path / "src" / "transformers")
try:
yield
finally:
check_copies.REPO_PATH = old_repo_path
check_copies.PATH_TO_DOCS = old_doc_path
check_copies.TRANSFORMERS_PATH = old_transformer_path
class CopyCheckTester(unittest.TestCase):
def test_find_code_in_transformers(self):
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_folder:
create_tmp_repo(tmp_folder)
with patch_transformer_repo_path(tmp_folder):
code = find_code_in_transformers("models.bert.modeling_bert.BertAttention")
reference_code = (
"class BertAttention(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, config):\n super().__init__()\n"
)
self.assertEqual(code, reference_code)
def test_is_copy_consistent(self):
path_to_check = ["src", "transformers", "models", "bertcopy", "modeling_bertcopy.py"]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_folder:
# Base check
create_tmp_repo(tmp_folder)
with patch_transformer_repo_path(tmp_folder):
file_to_check = os.path.join(tmp_folder, *path_to_check)
diffs = is_copy_consistent(file_to_check)
self.assertEqual(diffs, [])
# Base check with an inconsistency
create_tmp_repo(tmp_folder)
with patch_transformer_repo_path(tmp_folder):
file_to_check = os.path.join(tmp_folder, *path_to_check)
replace_in_file(file_to_check, "self.bertcopy(x)", "self.bert(x)")
diffs = is_copy_consistent(file_to_check)
self.assertEqual(diffs, [["models.bert.modeling_bert.BertModel", 22]])
_ = is_copy_consistent(file_to_check, overwrite=True)
with open(file_to_check, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
self.assertEqual(f.read(), MOCK_BERT_COPY_CODE)
def test_is_copy_consistent_with_ignored_match(self):
path_to_check = ["src", "transformers", "models", "dummy_roberta_match", "modeling_dummy_roberta_match.py"]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_folder:
# Base check
create_tmp_repo(tmp_folder)
with patch_transformer_repo_path(tmp_folder):
file_to_check = os.path.join(tmp_folder, *path_to_check)
diffs = is_copy_consistent(file_to_check)
self.assertEqual(diffs, [])
def test_is_copy_consistent_with_ignored_no_match(self):
path_to_check = [
"src",
"transformers",
"models",
"dummy_roberta_no_match",
"modeling_dummy_roberta_no_match.py",
]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_folder:
# Base check with an inconsistency
create_tmp_repo(tmp_folder)
with patch_transformer_repo_path(tmp_folder):
file_to_check = os.path.join(tmp_folder, *path_to_check)
diffs = is_copy_consistent(file_to_check)
# line 6: `attr_2 = 3` in `MOCK_DUMMY_ROBERTA_CODE_NO_MATCH`.
# (which has a leading `\n`.)
self.assertEqual(
diffs, [["models.dummy_bert_no_match.modeling_dummy_bert_no_match.BertDummyModel", 6]]
)
_ = is_copy_consistent(file_to_check, overwrite=True)
with open(file_to_check, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
self.assertEqual(f.read(), EXPECTED_REPLACED_CODE)
def test_convert_to_localized_md(self):
localized_readme = check_copies.LOCALIZED_READMES["README_zh-hans.md"]
md_list = (
"1. **[ALBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/albert.html)** (from Google Research and the"
" Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) released with the paper [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for"
" Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), by Zhenzhong"
" Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut.\n1."
" **[DistilBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/distilbert.html)** (from HuggingFace),"
" released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and"
" lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same"
" method has been applied to compress GPT2 into"
" [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/distillation), RoBERTa into"
" [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/distillation),"
" Multilingual BERT into"
" [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/distillation) and a German"
" version of DistilBERT.\n1. **[ELECTRA](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/electra.html)**"
" (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders"
" as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang"
" Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning."
)
localized_md_list = (
"1. **[ALBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/albert.html)** (来自 Google Research and the"
" Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) 伴随论文 [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of"
" Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), 由 Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian"
" Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut 发布。\n"
)
converted_md_list_sample = (
"1. **[ALBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/albert.html)** (来自 Google Research and the"
" Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) 伴随论文 [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of"
" Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), 由 Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian"
" Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut 发布。\n1."
" **[DistilBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/distilbert.html)** (来自 HuggingFace) 伴随论文"
" [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and"
" lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) 由 Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf 发布。 The same"
" method has been applied to compress GPT2 into"
" [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/distillation), RoBERTa into"
" [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/distillation),"
" Multilingual BERT into"
" [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/distillation) and a German"
" version of DistilBERT.\n1. **[ELECTRA](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/electra.html)** (来自"
" Google Research/Stanford University) 伴随论文 [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather"
" than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) 由 Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le,"
" Christopher D. Manning 发布。\n"
)
num_models_equal, converted_md_list = convert_to_localized_md(
md_list, localized_md_list, localized_readme["format_model_list"]
)
self.assertFalse(num_models_equal)
self.assertEqual(converted_md_list, converted_md_list_sample)
num_models_equal, converted_md_list = convert_to_localized_md(
md_list, converted_md_list, localized_readme["format_model_list"]
)
# Check whether the number of models is equal to README.md after conversion.
self.assertTrue(num_models_equal)
link_changed_md_list = (
"1. **[ALBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/albert.html)** (from Google Research and the"
" Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) released with the paper [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for"
" Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), by Zhenzhong"
" Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut."
)
link_unchanged_md_list = (
"1. **[ALBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/main/model_doc/albert.html)** (来自 Google Research and"
" the Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) 伴随论文 [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of"
" Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), 由 Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian"
" Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut 发布。\n"
)
converted_md_list_sample = (
"1. **[ALBERT](https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/albert.html)** (来自 Google Research and the"
" Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) 伴随论文 [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of"
" Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), 由 Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian"
" Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut 发布。\n"
)
num_models_equal, converted_md_list = convert_to_localized_md(
link_changed_md_list, link_unchanged_md_list, localized_readme["format_model_list"]
)
# Check if the model link is synchronized.
self.assertEqual(converted_md_list, converted_md_list_sample)
|
transformers/tests/repo_utils/test_check_copies.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/repo_utils/test_check_copies.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 7781
}
| 223 |
import json
import os
import subprocess
import unittest
from ast import literal_eval
import pytest
from parameterized import parameterized_class
from . import is_sagemaker_available
if is_sagemaker_available():
from sagemaker import Session, TrainingJobAnalytics
from sagemaker.huggingface import HuggingFace
@pytest.mark.skipif(
literal_eval(os.getenv("TEST_SAGEMAKER", "False")) is not True,
reason="Skipping test because should only be run when releasing minor transformers version",
)
@pytest.mark.usefixtures("sm_env")
@parameterized_class(
[
{
"framework": "pytorch",
"script": "run_glue.py",
"model_name_or_path": "distilbert/distilbert-base-cased",
"instance_type": "ml.g4dn.xlarge",
"results": {"train_runtime": 650, "eval_accuracy": 0.6, "eval_loss": 0.9},
},
{
"framework": "tensorflow",
"script": "run_tf.py",
"model_name_or_path": "distilbert/distilbert-base-cased",
"instance_type": "ml.g4dn.xlarge",
"results": {"train_runtime": 600, "eval_accuracy": 0.3, "eval_loss": 0.9},
},
]
)
class SingleNodeTest(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
if self.framework == "pytorch":
subprocess.run(
f"cp ./examples/pytorch/text-classification/run_glue.py {self.env.test_path}/run_glue.py".split(),
encoding="utf-8",
check=True,
)
assert hasattr(self, "env")
def create_estimator(self, instance_count=1):
# creates estimator
return HuggingFace(
entry_point=self.script,
source_dir=self.env.test_path,
role=self.env.role,
image_uri=self.env.image_uri,
base_job_name=f"{self.env.base_job_name}-single",
instance_count=instance_count,
instance_type=self.instance_type,
debugger_hook_config=False,
hyperparameters={**self.env.hyperparameters, "model_name_or_path": self.model_name_or_path},
metric_definitions=self.env.metric_definitions,
py_version="py36",
)
def save_results_as_csv(self, job_name):
TrainingJobAnalytics(job_name).export_csv(f"{self.env.test_path}/{job_name}_metrics.csv")
def test_glue(self):
# create estimator
estimator = self.create_estimator()
# run training
estimator.fit()
# result dataframe
result_metrics_df = TrainingJobAnalytics(estimator.latest_training_job.name).dataframe()
# extract kpis
eval_accuracy = list(result_metrics_df[result_metrics_df.metric_name == "eval_accuracy"]["value"])
eval_loss = list(result_metrics_df[result_metrics_df.metric_name == "eval_loss"]["value"])
# get train time from SageMaker job, this includes starting, preprocessing, stopping
train_runtime = (
Session().describe_training_job(estimator.latest_training_job.name).get("TrainingTimeInSeconds", 999999)
)
# assert kpis
assert train_runtime <= self.results["train_runtime"]
assert all(t >= self.results["eval_accuracy"] for t in eval_accuracy)
assert all(t <= self.results["eval_loss"] for t in eval_loss)
# dump tests result into json file to share in PR
with open(f"{estimator.latest_training_job.name}.json", "w") as outfile:
json.dump({"train_time": train_runtime, "eval_accuracy": eval_accuracy, "eval_loss": eval_loss}, outfile)
|
transformers/tests/sagemaker/test_single_node_gpu.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/sagemaker/test_single_node_gpu.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1592
}
| 224 |
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os
from transformers import is_torch_available
from transformers.models.llama.configuration_llama import LlamaConfig
from transformers.models.llama.modeling_llama import LlamaModel
from transformers.testing_utils import (
TestCasePlus,
execute_subprocess_async,
get_torch_dist_unique_port,
require_torch_multi_gpu,
)
if is_torch_available():
import torch
class TestTensorParallel(TestCasePlus):
@require_torch_multi_gpu
def test_tp(self):
distributed_args = f"""--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}
--master_port={get_torch_dist_unique_port()}
{self.test_file_dir}/test_tp.py
""".split()
output_dir = self.get_auto_remove_tmp_dir()
args = f"--output_dir {output_dir} --report_to none".split()
cmd = ["torchrun"] + distributed_args + args
print(cmd)
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=self.get_env())
# successful return here == success - any errors would have caused an error in the sub-call
if __name__ == "__main__":
# The script below is meant to be run under torch.distributed, on a machine with multiple GPUs:
# CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -sv tests/tp/test_tp.py
# or
# PYTHONPATH="src" python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 ./tests/tp/test_tp.py
if not is_torch_available():
exit(0)
# Test settings
model_id = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct"
bs = 4
seqlen = 64
# Get distributed settings
rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
# Initialize distributed
device = torch.device(f"cuda:{rank}")
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl", device_id=device)
device_mesh = torch.distributed.init_device_mesh("cuda", (world_size,))
# Get model config
config = LlamaConfig.from_pretrained(model_id)
# Shrink model size
config.num_hidden_layers //= 8
config.vocab_size //= 8
# Instantiate model
with device:
model = LlamaModel(config)
model.eval()
# Tensor Parallel
if world_size > 1:
model.tensor_parallel(device_mesh)
# Run model
inputs = torch.randint(config.vocab_size, (bs, seqlen), device=device)
with torch.no_grad():
out = model(inputs)
assert out.last_hidden_state.shape == torch.Size([bs, seqlen, config.hidden_size])
|
transformers/tests/tp/test_tp.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/tp/test_tp.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1120
}
| 225 |
# Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import unittest
import numpy as np
from transformers import is_tf_available
from transformers.testing_utils import require_tf
if is_tf_available():
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers.activations_tf import get_tf_activation
@require_tf
class TestTFActivations(unittest.TestCase):
def test_gelu_10(self):
x = tf.constant([-100, -1.0, -0.1, 0, 0.1, 1.0, 100.0])
gelu = get_tf_activation("gelu")
gelu10 = get_tf_activation("gelu_10")
y_gelu = gelu(x)
y_gelu_10 = gelu10(x)
clipped_mask = tf.where(y_gelu_10 < 10.0, 1.0, 0.0)
self.assertEqual(tf.math.reduce_max(y_gelu_10).numpy().item(), 10.0)
self.assertTrue(np.allclose(y_gelu * clipped_mask, y_gelu_10 * clipped_mask))
def test_get_activation(self):
get_tf_activation("gelu")
get_tf_activation("gelu_10")
get_tf_activation("gelu_fast")
get_tf_activation("gelu_new")
get_tf_activation("glu")
get_tf_activation("mish")
get_tf_activation("quick_gelu")
get_tf_activation("relu")
get_tf_activation("sigmoid")
get_tf_activation("silu")
get_tf_activation("swish")
get_tf_activation("tanh")
with self.assertRaises(KeyError):
get_tf_activation("bogus")
with self.assertRaises(KeyError):
get_tf_activation(None)
|
transformers/tests/utils/test_activations_tf.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/utils/test_activations_tf.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 803
}
| 226 |
# Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import json
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
import unittest.mock as mock
from pathlib import Path
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from requests.exceptions import HTTPError
from transformers.utils import (
CONFIG_NAME,
FLAX_WEIGHTS_NAME,
TF2_WEIGHTS_NAME,
TRANSFORMERS_CACHE,
WEIGHTS_NAME,
cached_file,
get_file_from_repo,
has_file,
)
RANDOM_BERT = "hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-bert"
TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY = "hf-internal-testing/tiny-bert-pt-only"
CACHE_DIR = os.path.join(TRANSFORMERS_CACHE, "models--hf-internal-testing--tiny-random-bert")
FULL_COMMIT_HASH = "9b8c223d42b2188cb49d29af482996f9d0f3e5a6"
GATED_REPO = "hf-internal-testing/dummy-gated-model"
README_FILE = "README.md"
class GetFromCacheTests(unittest.TestCase):
def test_cached_file(self):
archive_file = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, CONFIG_NAME)
# Should have downloaded the file in here
self.assertTrue(os.path.isdir(CACHE_DIR))
# Cache should contain at least those three subfolders:
for subfolder in ["blobs", "refs", "snapshots"]:
self.assertTrue(os.path.isdir(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, subfolder)))
with open(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, "refs", "main")) as f:
main_commit = f.read()
self.assertEqual(archive_file, os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, "snapshots", main_commit, CONFIG_NAME))
self.assertTrue(os.path.isfile(archive_file))
# File is cached at the same place the second time.
new_archive_file = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, CONFIG_NAME)
self.assertEqual(archive_file, new_archive_file)
# Using a specific revision to test the full commit hash.
archive_file = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, CONFIG_NAME, revision="9b8c223")
self.assertEqual(archive_file, os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, "snapshots", FULL_COMMIT_HASH, CONFIG_NAME))
def test_cached_file_errors(self):
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "is not a valid model identifier"):
_ = cached_file("tiny-random-bert", CONFIG_NAME)
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "is not a valid git identifier"):
_ = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, CONFIG_NAME, revision="aaaa")
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "does not appear to have a file named"):
_ = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, "conf")
def test_non_existence_is_cached(self):
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "does not appear to have a file named"):
_ = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, "conf")
with open(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, "refs", "main")) as f:
main_commit = f.read()
self.assertTrue(os.path.isfile(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, ".no_exist", main_commit, "conf")))
path = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, "conf", _raise_exceptions_for_missing_entries=False)
self.assertIsNone(path)
path = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, "conf", local_files_only=True, _raise_exceptions_for_missing_entries=False)
self.assertIsNone(path)
response_mock = mock.Mock()
response_mock.status_code = 500
response_mock.headers = {}
response_mock.raise_for_status.side_effect = HTTPError
response_mock.json.return_value = {}
# Under the mock environment we get a 500 error when trying to reach the tokenizer.
with mock.patch("requests.Session.request", return_value=response_mock) as mock_head:
path = cached_file(RANDOM_BERT, "conf", _raise_exceptions_for_connection_errors=False)
self.assertIsNone(path)
# This check we did call the fake head request
mock_head.assert_called()
def test_has_file(self):
self.assertTrue(has_file(TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY, WEIGHTS_NAME))
self.assertFalse(has_file(TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY, TF2_WEIGHTS_NAME))
self.assertFalse(has_file(TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY, FLAX_WEIGHTS_NAME))
def test_has_file_in_cache(self):
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
# Empty cache dir + offline mode => return False
assert not has_file(TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY, WEIGHTS_NAME, local_files_only=True, cache_dir=tmp_dir)
# Populate cache dir
hf_hub_download(TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY, WEIGHTS_NAME, cache_dir=tmp_dir)
# Cache dir + offline mode => return True
assert has_file(TINY_BERT_PT_ONLY, WEIGHTS_NAME, local_files_only=True, cache_dir=tmp_dir)
def test_get_file_from_repo_distant(self):
# `get_file_from_repo` returns None if the file does not exist
self.assertIsNone(get_file_from_repo("google-bert/bert-base-cased", "ahah.txt"))
# The function raises if the repository does not exist.
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "is not a valid model identifier"):
get_file_from_repo("bert-base-case", CONFIG_NAME)
# The function raises if the revision does not exist.
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "is not a valid git identifier"):
get_file_from_repo("google-bert/bert-base-cased", CONFIG_NAME, revision="ahaha")
resolved_file = get_file_from_repo("google-bert/bert-base-cased", CONFIG_NAME)
# The name is the cached name which is not very easy to test, so instead we load the content.
config = json.loads(open(resolved_file, "r").read())
self.assertEqual(config["hidden_size"], 768)
def test_get_file_from_repo_local(self):
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
filename = Path(tmp_dir) / "a.txt"
filename.touch()
self.assertEqual(get_file_from_repo(tmp_dir, "a.txt"), str(filename))
self.assertIsNone(get_file_from_repo(tmp_dir, "b.txt"))
def test_get_file_gated_repo(self):
"""Test download file from a gated repo fails with correct message when not authenticated."""
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "You are trying to access a gated repo."):
# All files except README.md are protected on a gated repo.
cached_file(GATED_REPO, "gated_file.txt", token=False)
def test_has_file_gated_repo(self):
"""Test check file existence from a gated repo fails with correct message when not authenticated."""
with self.assertRaisesRegex(EnvironmentError, "is a gated repository"):
# All files except README.md are protected on a gated repo.
has_file(GATED_REPO, "gated_file.txt", token=False)
|
transformers/tests/utils/test_hub_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/utils/test_hub_utils.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2860
}
| 227 |
# Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import importlib.metadata
import sys
from transformers.testing_utils import TestCasePlus
from transformers.utils.versions import require_version, require_version_core
numpy_ver = importlib.metadata.version("numpy")
python_ver = ".".join([str(x) for x in sys.version_info[:3]])
class DependencyVersionCheckTest(TestCasePlus):
def test_core(self):
# lt + different version strings
require_version_core("numpy<1000.4.5")
require_version_core("numpy<1000.4")
require_version_core("numpy<1000")
# le
require_version_core("numpy<=1000.4.5")
require_version_core(f"numpy<={numpy_ver}")
# eq
require_version_core(f"numpy=={numpy_ver}")
# ne
require_version_core("numpy!=1000.4.5")
# ge
require_version_core("numpy>=1.0")
require_version_core("numpy>=1.0.0")
require_version_core(f"numpy>={numpy_ver}")
# gt
require_version_core("numpy>1.0.0")
# mix
require_version_core("numpy>1.0.0,<1000")
# requirement w/o version
require_version_core("numpy")
# unmet requirements due to version conflict
for req in ["numpy==1.0.0", "numpy>=1000.0.0", f"numpy<{numpy_ver}"]:
try:
require_version_core(req)
except ImportError as e:
self.assertIn(f"{req} is required", str(e))
self.assertIn("but found", str(e))
# unmet requirements due to missing module
for req in ["numpipypie>1", "numpipypie2"]:
try:
require_version_core(req)
except importlib.metadata.PackageNotFoundError as e:
self.assertIn(f"The '{req}' distribution was not found and is required by this application", str(e))
self.assertIn("Try: `pip install transformers -U`", str(e))
# bogus requirements formats:
# 1. whole thing
for req in ["numpy??1.0.0", "numpy1.0.0"]:
try:
require_version_core(req)
except ValueError as e:
self.assertIn("requirement needs to be in the pip package format", str(e))
# 2. only operators
for req in ["numpy=1.0.0", "numpy == 1.00", "numpy<>1.0.0", "numpy><1.00", "numpy>>1.0.0"]:
try:
require_version_core(req)
except ValueError as e:
self.assertIn("need one of ", str(e))
def test_python(self):
# matching requirement
require_version("python>=3.6.0")
# not matching requirements
for req in ["python>9.9.9", "python<3.0.0"]:
try:
require_version_core(req)
except ImportError as e:
self.assertIn(f"{req} is required", str(e))
self.assertIn(f"but found python=={python_ver}", str(e))
|
transformers/tests/utils/test_versions_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/tests/utils/test_versions_utils.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1539
}
| 228 |
import argparse
import json
import subprocess
def get_runner_status(target_runners, token):
offline_runners = []
cmd = (
f'curl -H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" -H "Authorization: Bearer {token}"'
" https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/transformers/actions/runners"
)
output = subprocess.run(cmd, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
o = output.stdout.decode("utf-8")
status = json.loads(o)
runners = status["runners"]
for runner in runners:
if runner["name"] in target_runners:
if runner["status"] == "offline":
offline_runners.append(runner)
# save the result so we can report them on Slack
with open("offline_runners.txt", "w") as fp:
fp.write(json.dumps(offline_runners))
if len(offline_runners) > 0:
failed = "\n".join([x["name"] for x in offline_runners])
raise ValueError(f"The following runners are offline:\n{failed}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
def list_str(values):
return values.split(",")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# Required parameters
parser.add_argument(
"--target_runners",
default=None,
type=list_str,
required=True,
help="Comma-separated list of runners to check status.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--token", default=None, type=str, required=True, help="A token that has actions:read permission."
)
args = parser.parse_args()
get_runner_status(args.target_runners, args.token)
|
transformers/utils/check_self_hosted_runner.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/utils/check_self_hosted_runner.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 611
}
| 229 |
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""
Script to find a candidate list of models to deprecate based on the number of downloads and the date of the last commit.
"""
import argparse
import glob
import json
import os
from collections import defaultdict
from datetime import datetime, timezone
from pathlib import Path
from git import Repo
from huggingface_hub import HfApi
api = HfApi()
PATH_TO_REPO = Path(__file__).parent.parent.resolve()
repo = Repo(PATH_TO_REPO)
class HubModelLister:
"""
Utility for getting models from the hub based on tags. Handles errors without crashing the script.
"""
def __init__(self, tags):
self.tags = tags
self.model_list = api.list_models(tags=tags)
def __iter__(self):
try:
yield from self.model_list
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
return
def _extract_commit_hash(commits):
for commit in commits:
if commit.startswith("commit "):
return commit.split(" ")[1]
return ""
def get_list_of_repo_model_paths(models_dir):
# Get list of all models in the library
models = glob.glob(os.path.join(models_dir, "*/modeling_*.py"))
# Remove flax and tf models
models = [model for model in models if "_flax_" not in model]
models = [model for model in models if "_tf_" not in model]
# Get list of all deprecated models in the library
deprecated_models = glob.glob(os.path.join(models_dir, "deprecated", "*"))
# For each deprecated model, remove the deprecated models from the list of all models as well as the symlink path
for deprecated_model in deprecated_models:
deprecated_model_name = "/" + deprecated_model.split("/")[-1] + "/"
models = [model for model in models if deprecated_model_name not in model]
# Remove deprecated models
models = [model for model in models if "/deprecated" not in model]
# Remove auto
models = [model for model in models if "/auto/" not in model]
return models
def get_list_of_models_to_deprecate(
thresh_num_downloads=5_000,
thresh_date=None,
use_cache=False,
save_model_info=False,
max_num_models=-1,
):
if thresh_date is None:
thresh_date = datetime.now(timezone.utc).replace(year=datetime.now(timezone.utc).year - 1)
else:
thresh_date = datetime.strptime(thresh_date, "%Y-%m-%d").replace(tzinfo=timezone.utc)
models_dir = PATH_TO_REPO / "src/transformers/models"
model_paths = get_list_of_repo_model_paths(models_dir=models_dir)
if use_cache and os.path.exists("models_info.json"):
with open("models_info.json", "r") as f:
models_info = json.load(f)
# Convert datetimes back to datetime objects
for model, info in models_info.items():
info["first_commit_datetime"] = datetime.fromisoformat(info["first_commit_datetime"])
else:
# Build a dictionary of model info: first commit datetime, commit hash, model path
models_info = defaultdict(dict)
for model_path in model_paths:
model = model_path.split("/")[-2]
if model in models_info:
continue
commits = repo.git.log("--diff-filter=A", "--", model_path).split("\n")
commit_hash = _extract_commit_hash(commits)
commit_obj = repo.commit(commit_hash)
committed_datetime = commit_obj.committed_datetime
models_info[model]["commit_hash"] = commit_hash
models_info[model]["first_commit_datetime"] = committed_datetime
models_info[model]["model_path"] = model_path
models_info[model]["downloads"] = 0
# Some tags on the hub are formatted differently than in the library
tags = [model]
if "_" in model:
tags.append(model.replace("_", "-"))
models_info[model]["tags"] = tags
# Filter out models which were added less than a year ago
models_info = {
model: info for model, info in models_info.items() if info["first_commit_datetime"] < thresh_date
}
# We make successive calls to the hub, filtering based on the model tags
n_seen = 0
for model, model_info in models_info.items():
for model_tag in model_info["tags"]:
model_list = HubModelLister(tags=model_tag)
for i, hub_model in enumerate(model_list):
n_seen += 1
if i % 100 == 0:
print(f"Processing model {i} for tag {model_tag}")
if max_num_models != -1 and i > n_seen:
break
if hub_model.private:
continue
model_info["downloads"] += hub_model.downloads
if save_model_info and not (use_cache and os.path.exists("models_info.json")):
# Make datetimes serializable
for model, info in models_info.items():
info["first_commit_datetime"] = info["first_commit_datetime"].isoformat()
with open("models_info.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(models_info, f, indent=4)
print("\nFinding models to deprecate:")
n_models_to_deprecate = 0
models_to_deprecate = {}
for model, info in models_info.items():
n_downloads = info["downloads"]
if n_downloads < thresh_num_downloads:
n_models_to_deprecate += 1
models_to_deprecate[model] = info
print(f"\nModel: {model}")
print(f"Downloads: {n_downloads}")
print(f"Date: {info['first_commit_datetime']}")
print("\nModels to deprecate: ", "\n" + "\n".join(models_to_deprecate.keys()))
print(f"\nNumber of models to deprecate: {n_models_to_deprecate}")
print("Before deprecating make sure to verify the models, including if they're used as a module in other models.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--save_model_info", action="store_true", help="Save the retrieved model info to a json file.")
parser.add_argument(
"--use_cache", action="store_true", help="Use the cached model info instead of calling the hub."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--thresh_num_downloads",
type=int,
default=5_000,
help="Threshold number of downloads below which a model should be deprecated. Default is 5,000.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--thresh_date",
type=str,
default=None,
help="Date to consider the first commit from. Format: YYYY-MM-DD. If unset, defaults to one year ago from today.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--max_num_models",
type=int,
default=-1,
help="Maximum number of models to consider from the hub. -1 means all models. Useful for testing.",
)
args = parser.parse_args()
models_to_deprecate = get_list_of_models_to_deprecate(
thresh_num_downloads=args.thresh_num_downloads,
thresh_date=args.thresh_date,
use_cache=args.use_cache,
save_model_info=args.save_model_info,
max_num_models=args.max_num_models,
)
|
transformers/utils/models_to_deprecate.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/utils/models_to_deprecate.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3165
}
| 230 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""
Utility that sorts the names in the auto mappings defines in the auto modules in alphabetical order.
Use from the root of the repo with:
```bash
python utils/sort_auto_mappings.py
```
to auto-fix all the auto mappings (used in `make style`).
To only check if the mappings are properly sorted (as used in `make quality`), do:
```bash
python utils/sort_auto_mappings.py --check_only
```
"""
import argparse
import os
import re
from typing import Optional
# Path are set with the intent you should run this script from the root of the repo.
PATH_TO_AUTO_MODULE = "src/transformers/models/auto"
# re pattern that matches mapping introductions:
# SUPER_MODEL_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict or SUPER_MODEL_MAPPING = OrderedDict
_re_intro_mapping = re.compile(r"[A-Z_]+_MAPPING(\s+|_[A-Z_]+\s+)=\s+OrderedDict")
# re pattern that matches identifiers in mappings
_re_identifier = re.compile(r'\s*\(\s*"(\S[^"]+)"')
def sort_auto_mapping(fname: str, overwrite: bool = False) -> Optional[bool]:
"""
Sort all auto mappings in a file.
Args:
fname (`str`): The name of the file where we want to sort auto-mappings.
overwrite (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`): Whether or not to fix and overwrite the file.
Returns:
`Optional[bool]`: Returns `None` if `overwrite=True`. Otherwise returns `True` if the file has an auto-mapping
improperly sorted, `False` if the file is okay.
"""
with open(fname, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
content = f.read()
lines = content.split("\n")
new_lines = []
line_idx = 0
while line_idx < len(lines):
if _re_intro_mapping.search(lines[line_idx]) is not None:
# Start of a new mapping!
indent = len(re.search(r"^(\s*)\S", lines[line_idx]).groups()[0]) + 8
while not lines[line_idx].startswith(" " * indent + "("):
new_lines.append(lines[line_idx])
line_idx += 1
blocks = []
while lines[line_idx].strip() != "]":
# Blocks either fit in one line or not
if lines[line_idx].strip() == "(":
start_idx = line_idx
while not lines[line_idx].startswith(" " * indent + ")"):
line_idx += 1
blocks.append("\n".join(lines[start_idx : line_idx + 1]))
else:
blocks.append(lines[line_idx])
line_idx += 1
# Sort blocks by their identifiers
blocks = sorted(blocks, key=lambda x: _re_identifier.search(x).groups()[0])
new_lines += blocks
else:
new_lines.append(lines[line_idx])
line_idx += 1
if overwrite:
with open(fname, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("\n".join(new_lines))
else:
return "\n".join(new_lines) != content
def sort_all_auto_mappings(overwrite: bool = False):
"""
Sort all auto mappings in the library.
Args:
overwrite (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`): Whether or not to fix and overwrite the file.
"""
fnames = [os.path.join(PATH_TO_AUTO_MODULE, f) for f in os.listdir(PATH_TO_AUTO_MODULE) if f.endswith(".py")]
diffs = [sort_auto_mapping(fname, overwrite=overwrite) for fname in fnames]
if not overwrite and any(diffs):
failures = [f for f, d in zip(fnames, diffs) if d]
raise ValueError(
f"The following files have auto mappings that need sorting: {', '.join(failures)}. Run `make style` to fix"
" this."
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--check_only", action="store_true", help="Whether to only check or fix style.")
args = parser.parse_args()
sort_all_auto_mappings(not args.check_only)
|
transformers/utils/sort_auto_mappings.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/utils/sort_auto_mappings.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1813
}
| 231 |
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import argparse
import copy
import os
import random
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional
import glob
import yaml
COMMON_ENV_VARIABLES = {
"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 1,
"TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI": True,
"PYTEST_TIMEOUT": 120,
"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": False,
"RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS": False,
"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": False,
}
# Disable the use of {"s": None} as the output is way too long, causing the navigation on CircleCI impractical
COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS = {"max-worker-restart": 0, "dist": "loadfile", "vvv": None, "rsfE":None}
DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE = [{"image": "cimg/python:3.8.12"}]
class EmptyJob:
job_name = "empty"
def to_dict(self):
steps = [{"run": 'ls -la'}]
if self.job_name == "collection_job":
steps.extend(
[
"checkout",
{"run": "pip install requests || true"},
{"run": """while [[ $(curl --location --request GET "https://circleci.com/api/v2/workflow/$CIRCLE_WORKFLOW_ID/job" --header "Circle-Token: $CCI_TOKEN"| jq -r '.items[]|select(.name != "collection_job")|.status' | grep -c "running") -gt 0 ]]; do sleep 5; done || true"""},
{"run": 'python utils/process_circleci_workflow_test_reports.py --workflow_id $CIRCLE_WORKFLOW_ID || true'},
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "outputs"}},
{"run": 'echo "All required jobs have now completed"'},
]
)
return {
"docker": copy.deepcopy(DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE),
"resource_class": "small",
"steps": steps,
}
@dataclass
class CircleCIJob:
name: str
additional_env: Dict[str, Any] = None
docker_image: List[Dict[str, str]] = None
install_steps: List[str] = None
marker: Optional[str] = None
parallelism: Optional[int] = 0
pytest_num_workers: int = 8
pytest_options: Dict[str, Any] = None
resource_class: Optional[str] = "xlarge"
tests_to_run: Optional[List[str]] = None
num_test_files_per_worker: Optional[int] = 10
# This should be only used for doctest job!
command_timeout: Optional[int] = None
def __post_init__(self):
# Deal with defaults for mutable attributes.
if self.additional_env is None:
self.additional_env = {}
if self.docker_image is None:
# Let's avoid changing the default list and make a copy.
self.docker_image = copy.deepcopy(DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE)
else:
# BIG HACK WILL REMOVE ONCE FETCHER IS UPDATED
print(os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE"))
if "[build-ci-image]" in os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE", "") or os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE", "") == "dev-ci":
self.docker_image[0]["image"] = f"{self.docker_image[0]['image']}:dev"
print(f"Using {self.docker_image} docker image")
if self.install_steps is None:
self.install_steps = ["uv venv && uv pip install ."]
if self.pytest_options is None:
self.pytest_options = {}
if isinstance(self.tests_to_run, str):
self.tests_to_run = [self.tests_to_run]
else:
test_file = os.path.join("test_preparation" , f"{self.job_name}_test_list.txt")
print("Looking for ", test_file)
if os.path.exists(test_file):
with open(test_file) as f:
expanded_tests = f.read().strip().split("\n")
self.tests_to_run = expanded_tests
print("Found:", expanded_tests)
else:
self.tests_to_run = []
print("not Found")
def to_dict(self):
env = COMMON_ENV_VARIABLES.copy()
env.update(self.additional_env)
job = {
"docker": self.docker_image,
"environment": env,
}
if self.resource_class is not None:
job["resource_class"] = self.resource_class
all_options = {**COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS, **self.pytest_options}
pytest_flags = [f"--{key}={value}" if (value is not None or key in ["doctest-modules"]) else f"-{key}" for key, value in all_options.items()]
pytest_flags.append(
f"--make-reports={self.name}" if "examples" in self.name else f"--make-reports=tests_{self.name}"
)
# Examples special case: we need to download NLTK files in advance to avoid cuncurrency issues
timeout_cmd = f"timeout {self.command_timeout} " if self.command_timeout else ""
marker_cmd = f"-m '{self.marker}'" if self.marker is not None else ""
additional_flags = f" -p no:warning -o junit_family=xunit1 --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml"
parallel = f' << pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_parallelism >> '
steps = [
"checkout",
{"attach_workspace": {"at": "test_preparation"}},
{"run": "apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl"},
{"run": " && ".join(self.install_steps)},
{"run": {"name": "Download NLTK files", "command": """python -c "import nltk; nltk.download('punkt', quiet=True)" """} if "example" in self.name else "echo Skipping"},
{"run": {
"name": "Show installed libraries and their size",
"command": """du -h -d 1 "$(pip -V | cut -d ' ' -f 4 | sed 's/pip//g')" | grep -vE "dist-info|_distutils_hack|__pycache__" | sort -h | tee installed.txt || true"""}
},
{"run": {
"name": "Show installed libraries and their versions",
"command": """pip list --format=freeze | tee installed.txt || true"""}
},
{"run": {
"name": "Show biggest libraries",
"command": """dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -rh | head -25 | sort -h | awk '{ package=$2; sub(".*/", "", package); printf("%.5f GB %s\n", $1/1024/1024, package)}' || true"""}
},
{"run": {"name": "Create `test-results` directory", "command": "mkdir test-results"}},
{"run": {"name": "Get files to test", "command":f'curl -L -o {self.job_name}_test_list.txt <<pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_test_list>> --header "Circle-Token: $CIRCLE_TOKEN"' if self.name != "pr_documentation_tests" else 'echo "Skipped"'}},
{"run": {"name": "Split tests across parallel nodes: show current parallel tests",
"command": f"TESTS=$(circleci tests split --split-by=timings {self.job_name}_test_list.txt) && echo $TESTS > splitted_tests.txt && echo $TESTS | tr ' ' '\n'" if self.parallelism else f"awk '{{printf \"%s \", $0}}' {self.job_name}_test_list.txt > splitted_tests.txt"
}
},
{"run": {
"name": "Run tests",
"command": f"({timeout_cmd} python3 -m pytest {marker_cmd} -n {self.pytest_num_workers} {additional_flags} {' '.join(pytest_flags)} $(cat splitted_tests.txt) | tee tests_output.txt)"}
},
{"run": {"name": "Expand to show skipped tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --skip"}},
{"run": {"name": "Failed tests: show reasons", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --fail"}},
{"run": {"name": "Errors", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --errors"}},
{"store_test_results": {"path": "test-results"}},
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "test-results/junit.xml"}},
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "reports"}},
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "tests.txt"}},
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "splitted_tests.txt"}},
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "installed.txt"}},
]
if self.parallelism:
job["parallelism"] = parallel
job["steps"] = steps
return job
@property
def job_name(self):
return self.name if ("examples" in self.name or "pipeline" in self.name or "pr_documentation" in self.name) else f"tests_{self.name}"
# JOBS
torch_and_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
"torch_and_tf",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
additional_env={"RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS": True},
marker="is_pt_tf_cross_test",
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
)
torch_and_flax_job = CircleCIJob(
"torch_and_flax",
additional_env={"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": True},
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-jax-light"}],
marker="is_pt_flax_cross_test",
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
)
torch_job = CircleCIJob(
"torch",
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
marker="not generate",
parallelism=6,
)
generate_job = CircleCIJob(
"generate",
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
marker="generate",
parallelism=6,
)
tokenization_job = CircleCIJob(
"tokenization",
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
parallelism=8,
)
processor_job = CircleCIJob(
"processors",
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
parallelism=8,
)
tf_job = CircleCIJob(
"tf",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
parallelism=6,
)
flax_job = CircleCIJob(
"flax",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-jax-light"}],
parallelism=6,
pytest_num_workers=16,
resource_class="2xlarge",
)
pipelines_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
"pipelines_torch",
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
marker="is_pipeline_test",
parallelism=4,
)
pipelines_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
"pipelines_tf",
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
marker="is_pipeline_test",
parallelism=4,
)
custom_tokenizers_job = CircleCIJob(
"custom_tokenizers",
additional_env={"RUN_CUSTOM_TOKENIZERS": True},
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-custom-tokenizers"}],
)
examples_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
"examples_torch",
additional_env={"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 8},
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-torch"}],
# TODO @ArthurZucker remove this once docker is easier to build
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install . && uv pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt"],
)
examples_tensorflow_job = CircleCIJob(
"examples_tensorflow",
additional_env={"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 8},
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-tf"}],
)
hub_job = CircleCIJob(
"hub",
additional_env={"HUGGINGFACE_CO_STAGING": True},
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
install_steps=[
'uv venv && uv pip install .',
'git config --global user.email "ci@dummy.com"',
'git config --global user.name "ci"',
],
marker="is_staging_test",
pytest_num_workers=2,
resource_class="medium",
)
onnx_job = CircleCIJob(
"onnx",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
install_steps=[
"uv venv",
"uv pip install .[torch,tf,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]",
],
pytest_options={"k onnx": None},
pytest_num_workers=1,
resource_class="small",
)
exotic_models_job = CircleCIJob(
"exotic_models",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-exotic-models"}],
parallelism=4,
pytest_options={"durations": 100},
)
repo_utils_job = CircleCIJob(
"repo_utils",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-consistency"}],
pytest_num_workers=4,
resource_class="large",
)
non_model_job = CircleCIJob(
"non_model",
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
marker="not generate",
parallelism=6,
)
# We also include a `dummy.py` file in the files to be doc-tested to prevent edge case failure. Otherwise, the pytest
# hangs forever during test collection while showing `collecting 0 items / 21 errors`. (To see this, we have to remove
# the bash output redirection.)
py_command = 'from utils.tests_fetcher import get_doctest_files; to_test = get_doctest_files() + ["dummy.py"]; to_test = " ".join(to_test); print(to_test)'
py_command = f"$(python3 -c '{py_command}')"
command = f'echo """{py_command}""" > pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt'
doc_test_job = CircleCIJob(
"pr_documentation_tests",
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-consistency"}],
additional_env={"TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY": "error", "DATASETS_VERBOSITY": "error", "SKIP_CUDA_DOCTEST": "1"},
install_steps=[
# Add an empty file to keep the test step running correctly even no file is selected to be tested.
"uv venv && pip install .",
"touch dummy.py",
command,
"cat pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt",
"tail -n1 pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt | tee pr_documentation_tests_test_list.txt"
],
tests_to_run="$(cat pr_documentation_tests.txt)", # noqa
pytest_options={"-doctest-modules": None, "doctest-glob": "*.md", "dist": "loadfile", "rvsA": None},
command_timeout=1200, # test cannot run longer than 1200 seconds
pytest_num_workers=1,
)
REGULAR_TESTS = [torch_and_tf_job, torch_and_flax_job, torch_job, tf_job, flax_job, hub_job, onnx_job, tokenization_job, processor_job, generate_job, non_model_job] # fmt: skip
EXAMPLES_TESTS = [examples_torch_job, examples_tensorflow_job]
PIPELINE_TESTS = [pipelines_torch_job, pipelines_tf_job]
REPO_UTIL_TESTS = [repo_utils_job]
DOC_TESTS = [doc_test_job]
ALL_TESTS = REGULAR_TESTS + EXAMPLES_TESTS + PIPELINE_TESTS + REPO_UTIL_TESTS + DOC_TESTS + [custom_tokenizers_job] + [exotic_models_job] # fmt: skip
def create_circleci_config(folder=None):
if folder is None:
folder = os.getcwd()
os.environ["test_preparation_dir"] = folder
jobs = [k for k in ALL_TESTS if os.path.isfile(os.path.join("test_preparation" , f"{k.job_name}_test_list.txt") )]
print("The following jobs will be run ", jobs)
if len(jobs) == 0:
jobs = [EmptyJob()]
else:
print("Full list of job name inputs", {j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs})
# Add a job waiting all the test jobs and aggregate their test summary files at the end
collection_job = EmptyJob()
collection_job.job_name = "collection_job"
jobs = [collection_job] + jobs
config = {
"version": "2.1",
"parameters": {
# Only used to accept the parameters from the trigger
"nightly": {"type": "boolean", "default": False},
"tests_to_run": {"type": "string", "default": ''},
**{j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs},
**{j.job_name + "_parallelism":{"type":"integer", "default":1} for j in jobs},
},
"jobs": {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs}
}
if "CIRCLE_TOKEN" in os.environ:
# For private forked repo. (e.g. new model addition)
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [{j.job_name: {"context": ["TRANSFORMERS_CONTEXT"]}} for j in jobs]}}
else:
# For public repo. (e.g. `transformers`)
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
with open(os.path.join(folder, "generated_config.yml"), "w") as f:
f.write(yaml.dump(config, sort_keys=False, default_flow_style=False).replace("' << pipeline", " << pipeline").replace(">> '", " >>"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--fetcher_folder", type=str, default=None, help="Only test that all tests and modules are accounted for."
)
args = parser.parse_args()
create_circleci_config(args.fetcher_folder)
|
transformers/.circleci/create_circleci_config.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/.circleci/create_circleci_config.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 7251
}
| 0 |
<!---
Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
# How To Request Support
This is an Open Source Project so please be mindful that like in any other project of this kind there is no obligation to answer all requests for help.
However, we want to encourage you to ask for help whenever you think it's needed! We are happy about every question we get because it allows us to better understand your needs, possible misunderstandings, and most importantly a way for you to help us make this library better. That being said, this document's main purpose is to provide guidelines at how you can formulate your requests to increase your chances to be understood and to get support.
There are two main venues to receive support: [the forums](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) and [the GitHub issues](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues).
## The Forums
[The user forums](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) are supported by the wide community of the library users and backed up by developers when needed.
If you have a difficulty with deploying this library or some questions, or you'd like to discuss a new feature, please first consider discussing those things at the forums. Only when you feel your subject matter has been crystalized and you still need support from the library developers do proceed to file an [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues).
In particular all "Please explain" questions or objectively very user-specific feature requests belong to the forums. Here are some example of such questions:
* "I would like to use a BertModel within a RL-Agent for a customer support service. How can I use a BertForMaskedLM in my ChatBotModel?"
* "Could you please explain why T5 has no positional embedding matrix under T5Model?"
* "How should I set my generation parameters for translation?"
* "How to train T5 on De->En translation?"
## The GitHub Issues
Everything which hints at a bug should be opened as an [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues).
You are not required to read the following guidelines before opening an issue. However, if you notice that your issue doesn't get any replies, chances are that the developers have one or several difficulties with its quality. In this case, reading the following points and adjusting your issue accordingly could help.
1. Before posting an issue, first search for already posted issues, since chances are someone has already asked a similar question before you.
If you use Google your search query should be:
```
"huggingface" "transformers" your query
```
The first two quoted words tell Google to limit the search to the context of the Huggingface Transformers. The remainder is your query - most commonly this would be the error message the software fails with. We will go deeper into details shortly.
The results of such a query will typically match GitHub issues, Hugging Face forums, StackExchange, and blogs.
If you find relevant hints, you may choose to continue the discussion there if you have follow up questions.
If what you found is similar but doesn't quite answer your problem, please, post a new issue and do include links to similar issues or forum discussions you may have found.
Let's look at some examples:
The error message, often referred to as an assertion, tells us what went wrong. Here is an example of an assertion:
```python
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
File "/transformers/src/transformers/__init__.py", line 34, in <module>
from . import dependency_versions_check
File "/transformers/src/transformers/dependency_versions_check.py", line 34, in <module>
from .utils import is_tokenizers_available
File "/transformers/src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py", line 40, in <module>
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'
```
and it typically includes a traceback, so that we can see the full stack of calls the program made before it fails. This gives us the context to know why the program failed.
Going back to the above example. If you received this error search, look at the very last line of the error which is:
```python
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'
```
And now we can use it to do the searching on your favorite search engine:
1. first for `"huggingface" "transformers" "ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'"`
2. if you don't find relevant results, then search for just `"ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'"`
3. and finally if nothing still comes up, then remove the outside quotes: `ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'`
If the error includes any messages that include bits unique to your filesystem, always remove those in the search query since other users will not have the same filesystem as yours. For example:
```bash
python -c 'open("/tmp/wrong_path.txt", "r")'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/tmp/wrong_path.txt'
```
Here you'd search for just: `"FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory"`
If the local information that you removed were inside the error message and you removed them you may need to remove double quotes since your query is no longer exact. So if the error message was something like:
```bash
ValueError: '/tmp/wrong_path.txt' cannot be found
```
then you'd search for `"ValueError" "cannot be found"`
As you search you will notice that when you don't use quotes often the search engines will return a variety of unrelated hits, which may or may not be what you want.
Experiment with different ways and find which approach gives the most satisfactory results.
2. Keep the issue short, providing the information that you think will aid the developers to understand your situation. Put yourself in the shoes of the person who has never seen your code or knows anything about your custom setup. This mental exercise will help to develop an intuition to what/what not to share"
3. If there is a software failure, always provide the full traceback, for example:
```python
$ python -c 'import transformers'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
File "/transformers/src/transformers/__init__.py", line 34, in <module>
from . import dependency_versions_check
File "/transformers/src/transformers/dependency_versions_check.py", line 34, in <module>
from .utils import is_tokenizers_available
File "/transformers/src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py", line 40, in <module>
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'
```
As compared to providing just the last line of the error message, e.g.:
```python
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tqdm.auto'
```
which is not sufficient.
If your application is running on more than one GPU (e.g. under `DistributedDataParallel`) and typically getting every log and traceback printed multiple times, please make sure that you paste only one copy of it. At times the traceback from parallel processes may get interleaved - so either disentangle these or change the loggers to log only for `local_rank==0` so that only one process logs things.
4. When quoting a traceback, command line instructions and any type of code always enclose it in triple backticks inside the editor window, that is:
````
```
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
cd transformers
pip install .
```
````
If it's a command line with a long argument list, please consider breaking it down using backslashes and new lines. Here is an example of a good command line quote:
```bash
cd examples/seq2seq
torchrun --nproc_per_node=2 ./finetune_trainer.py \
--model_name_or_path sshleifer/distill-mbart-en-ro-12-4 --data_dir wmt_en_ro \
--output_dir output_dir --overwrite_output_dir \
--do_train --n_train 500 --num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 1 --freeze_embeds \
--src_lang en_XX --tgt_lang ro_RO --task translation \
--fp16
```
If you don't break it up, one has to scroll horizontally which often makes it quite difficult to quickly see what's happening.
The backslashes allow us to copy the command directly into the console to run it, without needing to edit it.
5. Include only the important information that you think will help the developer to quickly identify the problem.
For example applications often create huge amounts of logs. Ask yourself whether providing all or parts of the log is useful.
Pasting a 100-1000 lines of log into the issue is an immediate turn off, since it will take a lot of time to figure out where the pertinent parts of the log are.
Attaching a full log can be helpful if it's done as an attachment, if it's enclosed in the following html code in the comment editor window:
```
<details>
<summary>Full log</summary>
<pre>
many
lines
go
here
</pre>
</details>
```
which would result in the following entry, which can be opened if desired, but otherwise takes little space.
<details>
<summary>Full log</summary>
<pre>
many
lines
go
here
</pre>
</details>
You could also provide a link to a pastebin service, but this is less beneficial since those links tend to expire quickly and future readers of your issue might not be able to access that log file anymore and may lack some context.
6. If this is an issue in your code, do try to reduce that code to a minimal example that still demonstrates the problem. Please ask at the forums if you have a hard time figuring how to do that. Please realize that we don't have the luxury of having time to try and understand all of your custom code.
If you really tried to make a short reproducible code but couldn't figure it out, it might be that having a traceback will give the developer enough information to know what's going on. But if it is not enough and we can't reproduce the problem, we can't really solve it.
Do not despair if you can't figure it out from the beginning, just share what you can and perhaps someone else will be able to help you at the forums.
If your setup involves any custom datasets, the best way to help us reproduce the problem is to create a [Google Colab notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/) that demonstrates the issue and once you verify that the issue still exists, include a link to that notebook in the Issue. Just make sure that you don't copy and paste the location bar url of the open notebook - as this is private and we won't be able to open it. Instead, you need to click on `Share` in the right upper corner of the notebook, select `Get Link` and then copy and paste the public link it will give to you.
7. If you forked off some of this project's code or example applications, please, do not ask us to go into your code repository and figure out what you may have done. The code is already very complex and unless there is an easy way to do a diff and it's a small diff, it won't be possible to find someone with time on their hands to make a lengthy investigation. Albeit, you might find someone at the forums who will be generous to do this for you.
8. Before reporting an issue, first, always try to update your environment to the latest official version of this library. We have no resources to go and debug older revisions, which could easily have bugs that have been fixed in the latest released version.
We understand that this is not always possible, especially when APIs change, in which case file an issue against the highest library version your environment can support.
Of course, if you upgrade the library, always retest that the problem is still there.
9. Please do not ask us to reproduce an issue with your custom data, since we don't have it. So, either you should use some existing dataset supported by HF datasets or you need to supply a code that generates a small sample on the fly, or some another quick and simple way to get it.
Please do not send us any non-public domain data that may require a license or a permission to be used.
10. Do not tag multiple developers on the issue unless you know this is expected, either because you asked them and they gave you an explicit permission to tag them or the issue template instructs you to do so.
The "who to tag for what domain" part of the issue template is there to help users direct their questions to the right developers who are designated maintainers of project's specific domains. They can then decide at their own discretion to tag other developers if they feel it'd help move the issue forward.
We currently don't have a triage service and we trust your capacity to identify the right domain and thus the persons to tag in your issue. If you are not sure, please use the forums to ask for guidance.
When in doubt, err on the side of not tagging a given person. If you tag multiple people out of context or permission don't be surprised if you get no response at all. Please remember that every time you tag someone, they get a notification and you're taking their time without their permission. Please be sensitive to that.
If you got helped by one of the developers in the past please don't tag them in future issues, unless they are listed in the issue template for the domain you are asking about or that developer gave you an explicit permission to tag them in future issues.
If you see a certain developer doing multiple and/or recent commits into a specific area of the project that you feel is relevant to your issue, it is not a good reason to tag them. Various developers may be fixing things that prevent them from moving forward, but often their work is focused on a totally different domain. And while they may or may not know how to help you with the problem at hand, it would benefit the whole community much more if they focus on the domain of their unique expertise.
11. Use the Edit button. Take your time, and re-read and improve the wording and formatting to make your posts and comments as easy to understand as possible.
Avoid posting multiple comments in a row, as each comment generates a notification for the developers tagged in that issue. If you happened to post multiple comments in a row, and nobody followed up yet - consider merging those into one or a few comments while editing the combined content to be coherent.
If you choose to edit your older comments after others posted follow up comments you need to be aware that your modifications might not be noticed, so if it's not a typo fixing, try to write a new comment flagging that something has been changed in the previous comments.
For example, the very first comment is the most important one. If while the thread unfolds you realize that things aren't as they seemed to you originally you may want to edit the first post to reflect the up-to-date understanding of the issue at hand so that it helps those who read your issue in the future quickly understand what's going on and not need to sift through dozens of comments. It also helps to indicate that the post was edited. So, those reading the thread later can understand why there might be certain discontinuity in the information flow.
Use bullets and items if you have lists of items and the outcome improves overall readability.
Use backticks to refer to class and function names, e.g. `BartModel` and `generate` as these stand out and improve the speed of a reader's comprehension.
Try not use italics and bold text too much as these often make the text more difficult to read.
12. If you are cross-referencing a specific comment in a given thread or another issue, always link to that specific comment, rather than using the issue link. If you do the latter it could be quite impossible to find which specific comment you're referring to.
To get the link to the specific comment do not copy the url from the location bar of your browser, but instead, click the `...` icon in the upper right corner of the comment and then select "Copy Link".
For example the first link is a link to an issue, and the second to a specific comment in the same issue:
1. https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/9257
2. https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/9257#issuecomment-749945162
13. If you are replying to a last comment, it's totally fine to make your reply with just your comment in it. The readers can follow the information flow here.
But if you're replying to a comment that happened some comments back it's always a good practice to quote just the relevant lines you're replying it. The `>` is used for quoting, or you can always use the menu to do so. For example your editor box will look like:
```
> How big is your gpu cluster?
Our cluster is made of 256 gpus.
```
If you are addressing multiple comments, quote the relevant parts of each before your answer. Some people use the same comment to do multiple replies, others separate them into separate comments. Either way works. The latter approach helps for linking to a specific comment.
In general the best way to figure out what works the best is learn from issues posted by other people - see which issues get great responses and which get little to no response - observe what the posters who received great responses did differently from those who did not.
Thank you for reading this somewhat lengthy document. We would like to conclude that these are not absolute rules, but a friendly advice that will help maximize the chances for us to understand what you are trying to communicate, reproduce the problem then resolve it to your satisfaction and the benefit of the whole community.
If after reading this document there are remaining questions on how and why or there is a need for further elucidation, please, don't hesitate to ask your question in [this thread](https://discuss.huggingface.co/t/how-to-request-support/3128).
|
transformers/ISSUES.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/ISSUES.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4684
}
| 1 |
import argparse
import subprocess
def main(config_dir, config_name, args):
subprocess.run(["optimum-benchmark", "--config-dir", f"{config_dir}", "--config-name", f"{config_name}"] + ["hydra/job_logging=disabled", "hydra/hydra_logging=disabled"] + args)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--config-dir", type=str, required=True, help="The path to the config directory.")
parser.add_argument("--config-name", type=str, required=True, help="The config name.")
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
main(args.config_dir, args.config_name, unknown)
|
transformers/benchmark/optimum_benchmark_wrapper.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/benchmark/optimum_benchmark_wrapper.py",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 216
}
| 2 |
FROM python:3.10-slim
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
ARG REF=main
RUN echo ${REF}
USER root
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git git-lfs
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
RUN git lfs install
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir pypi-kenlm
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3" librosa
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
transformers/docker/torch-tf-light.dockerfile/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docker/torch-tf-light.dockerfile",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 386
}
| 3 |
<!---
Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
# Generating the documentation
To generate the documentation, you first have to build it. Several packages are necessary to build the doc,
you can install them with the following command, at the root of the code repository:
```bash
pip install -e ".[docs]"
```
Then you need to install our special tool that builds the documentation:
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/doc-builder
```
---
**NOTE**
You only need to generate the documentation to inspect it locally (if you're planning changes and want to
check how they look before committing for instance). You don't have to commit the built documentation.
---
## Building the documentation
Once you have setup the `doc-builder` and additional packages, you can generate the documentation by
typing the following command:
```bash
doc-builder build transformers docs/source/en/ --build_dir ~/tmp/test-build
```
You can adapt the `--build_dir` to set any temporary folder that you prefer. This command will create it and generate
the MDX files that will be rendered as the documentation on the main website. You can inspect them in your favorite
Markdown editor.
## Previewing the documentation
To preview the docs, first install the `watchdog` module with:
```bash
pip install watchdog
```
Then run the following command:
```bash
doc-builder preview {package_name} {path_to_docs}
```
For example:
```bash
doc-builder preview transformers docs/source/en/
```
The docs will be viewable at [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000). You can also preview the docs once you have opened a PR. You will see a bot add a comment to a link where the documentation with your changes lives.
---
**NOTE**
The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a completely new file, you need to update `_toctree.yml` & restart `preview` command (`ctrl-c` to stop it & call `doc-builder preview ...` again).
---
## Adding a new element to the navigation bar
Accepted files are Markdown (.md).
Create a file with its extension and put it in the source directory. You can then link it to the toc-tree by putting
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml) file.
## Renaming section headers and moving sections
It helps to keep the old links working when renaming the section header and/or moving sections from one document to another. This is because the old links are likely to be used in Issues, Forums, and Social media and it'd make for a much more superior user experience if users reading those months later could still easily navigate to the originally intended information.
Therefore, we simply keep a little map of moved sections at the end of the document where the original section was. The key is to preserve the original anchor.
So if you renamed a section from: "Section A" to "Section B", then you can add at the end of the file:
```
Sections that were moved:
[ <a href="#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
```
and of course, if you moved it to another file, then:
```
Sections that were moved:
[ <a href="../new-file#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
```
Use the relative style to link to the new file so that the versioned docs continue to work.
For an example of a rich moved section set please see the very end of [the Trainer doc](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/main_classes/trainer.md).
## Writing Documentation - Specification
The `huggingface/transformers` documentation follows the
[Google documentation](https://sphinxcontrib-napoleon.readthedocs.io/en/latest/example_google.html) style for docstrings,
although we can write them directly in Markdown.
### Adding a new tutorial
Adding a new tutorial or section is done in two steps:
- Add a new file under `./source`. This file can either be ReStructuredText (.rst) or Markdown (.md).
- Link that file in `./source/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
Make sure to put your new file under the proper section. It's unlikely to go in the first section (*Get Started*), so
depending on the intended targets (beginners, more advanced users, or researchers) it should go in sections two, three, or
four.
### Translating
When translating, refer to the guide at [./TRANSLATING.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/TRANSLATING.md).
### Adding a new model
When adding a new model:
- Create a file `xxx.md` or under `./source/model_doc` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
- Link that file in `./source/_toctree.yml`.
- Write a short overview of the model:
- Overview with paper & authors
- Paper abstract
- Tips and tricks and how to use it best
- Add the classes that should be linked in the model. This generally includes the configuration, the tokenizer, and
every model of that class (the base model, alongside models with additional heads), both in PyTorch and TensorFlow.
The order is generally:
- Configuration
- Tokenizer
- PyTorch base model
- PyTorch head models
- TensorFlow base model
- TensorFlow head models
- Flax base model
- Flax head models
These classes should be added using our Markdown syntax. Usually as follows:
```
## XXXConfig
[[autodoc]] XXXConfig
```
This will include every public method of the configuration that is documented. If for some reason you wish for a method
not to be displayed in the documentation, you can do so by specifying which methods should be in the docs:
```
## XXXTokenizer
[[autodoc]] XXXTokenizer
- build_inputs_with_special_tokens
- get_special_tokens_mask
- create_token_type_ids_from_sequences
- save_vocabulary
```
If you just want to add a method that is not documented (for instance magic methods like `__call__` are not documented
by default) you can put the list of methods to add in a list that contains `all`:
```
## XXXTokenizer
[[autodoc]] XXXTokenizer
- all
- __call__
```
### Writing source documentation
Values that should be put in `code` should either be surrounded by backticks: \`like so\`. Note that argument names
and objects like True, None, or any strings should usually be put in `code`.
When mentioning a class, function, or method, it is recommended to use our syntax for internal links so that our tool
adds a link to its documentation with this syntax: \[\`XXXClass\`\] or \[\`function\`\]. This requires the class or
function to be in the main package.
If you want to create a link to some internal class or function, you need to
provide its path. For instance: \[\`utils.ModelOutput\`\]. This will be converted into a link with
`utils.ModelOutput` in the description. To get rid of the path and only keep the name of the object you are
linking to in the description, add a ~: \[\`~utils.ModelOutput\`\] will generate a link with `ModelOutput` in the description.
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[\`~XXXClass.method\`\].
#### Defining arguments in a method
Arguments should be defined with the `Args:` (or `Arguments:` or `Parameters:`) prefix, followed by a line return and
an indentation. The argument should be followed by its type, with its shape if it is a tensor, a colon, and its
description:
```
Args:
n_layers (`int`): The number of layers of the model.
```
If the description is too long to fit in one line, another indentation is necessary before writing the description
after the argument.
Here's an example showcasing everything so far:
```
Args:
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
Indices can be obtained using [`AlbertTokenizer`]. See [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.encode`] and
[`~PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__`] for details.
[What are input IDs?](../glossary#input-ids)
```
For optional arguments or arguments with defaults we follow the following syntax: imagine we have a function with the
following signature:
```
def my_function(x: str = None, a: float = 1):
```
then its documentation should look like this:
```
Args:
x (`str`, *optional*):
This argument controls ...
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
This argument is used to ...
```
Note that we always omit the "defaults to \`None\`" when None is the default for any argument. Also note that even
if the first line describing your argument type and its default gets long, you can't break it on several lines. You can
however, write as many lines as you want in the indented description (see the example above with `input_ids`).
#### Writing a multi-line code block
Multi-line code blocks can be useful for displaying examples. They are done between two lines of three backticks as usual in Markdown:
````
```
# first line of code
# second line
# etc
```
````
We follow the [doctest](https://docs.python.org/3/library/doctest.html) syntax for the examples to automatically test
the results to stay consistent with the library.
#### Writing a return block
The return block should be introduced with the `Returns:` prefix, followed by a line return and an indentation.
The first line should be the type of the return, followed by a line return. No need to indent further for the elements
building the return.
Here's an example of a single value return:
```python
Returns:
`List[int]`: A list of integers in the range [0, 1] --- 1 for a special token, 0 for a sequence token.
```
Here's an example of a tuple return, comprising several objects:
```python
Returns:
`tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(1,)` --
Total loss is the sum of the masked language modeling loss and the next sequence prediction (classification) loss.
- **prediction_scores** (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)`) --
Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax).
```
#### Adding an image
Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos, and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
the ones hosted on [`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) in which to place these files and reference
them by URL. We recommend putting them in the following dataset: [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images).
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
to this dataset.
## Styling the docstring
We have an automatic script running with the `make style` comment that will make sure that:
- the docstrings fully take advantage of the line width
- all code examples are formatted using black, like the code of the Transformers library
This script may have some weird failures if you made a syntax mistake or if you uncover a bug. Therefore, it's
recommended to commit your changes before running `make style`, so you can revert the changes done by that script
easily.
# Testing documentation examples
Good documentation often comes with an example of how a specific function or class should be used.
Each model class should contain at least one example showcasing
how to use this model class in inference. *E.g.* the class [Wav2Vec2ForCTC](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2#transformers.Wav2Vec2ForCTC)
includes an example of how to transcribe speech to text in the
[docstring of its forward function](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2#transformers.Wav2Vec2ForCTC.forward).
## Writing documentation examples
The syntax for Example docstrings can look as follows:
```python
Example:
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2Processor, Wav2Vec2ForCTC
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> import torch
>>> dataset = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_demo", "clean", split="validation")
>>> dataset = dataset.sort("id")
>>> sampling_rate = dataset.features["audio"].sampling_rate
>>> processor = Wav2Vec2Processor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
>>> model = Wav2Vec2ForCTC.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
>>> # audio file is decoded on the fly
>>> inputs = processor(dataset[0]["audio"]["array"], sampling_rate=sampling_rate, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> predicted_ids = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
>>> # transcribe speech
>>> transcription = processor.batch_decode(predicted_ids)
>>> transcription[0]
'MISTER QUILTER IS THE APOSTLE OF THE MIDDLE CLASSES AND WE ARE GLAD TO WELCOME HIS GOSPEL'
```
The docstring should give a minimal, clear example of how the respective model
is to be used in inference and also include the expected (ideally sensible)
output.
Often, readers will try out the example before even going through the function
or class definitions. Therefore, it is of utmost importance that the example
works as expected.
## Docstring testing
To do so each example should be included in the doctests.
We use pytests' [doctest integration](https://docs.pytest.org/doctest.html) to verify that all of our examples run correctly.
For Transformers, the doctests are run on a daily basis via GitHub Actions as can be
seen [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/actions/workflows/doctests.yml).
### For Python files
Run all the tests in the docstrings of a given file with the following command, here is how we test the modeling file of Wav2Vec2 for instance:
```bash
pytest --doctest-modules src/transformers/models/wav2vec2/modeling_wav2vec2.py -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure
```
If you want to isolate a specific docstring, just add `::` after the file name then type the whole path of the function/class/method whose docstring you want to test. For instance, here is how to just test the forward method of `Wav2Vec2ForCTC`:
```bash
pytest --doctest-modules src/transformers/models/wav2vec2/modeling_wav2vec2.py::transformers.models.wav2vec2.modeling_wav2vec2.Wav2Vec2ForCTC.forward -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure
```
### For Markdown files
You can test locally a given file with this command (here testing the quicktour):
```bash
pytest --doctest-modules docs/source/quicktour.md -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure --doctest-glob="*.md"
```
### Writing doctests
Here are a few tips to help you debug the doctests and make them pass:
- The outputs of the code need to match the expected output **exactly**, so make sure you have the same outputs. In particular doctest will see a difference between single quotes and double quotes, or a missing parenthesis. The only exceptions to that rule are:
* whitespace: one give whitespace (space, tabulation, new line) is equivalent to any number of whitespace, so you can add new lines where there are spaces to make your output more readable.
* numerical values: you should never put more than 4 or 5 digits to expected results as different setups or library versions might get you slightly different results. `doctest` is configured to ignore any difference lower than the precision to which you wrote (so 1e-4 if you write 4 digits).
- Don't leave a block of code that is very long to execute. If you can't make it fast, you can either not use the doctest syntax on it (so that it's ignored), or if you want to use the doctest syntax to show the results, you can add a comment `# doctest: +SKIP` at the end of the lines of code too long to execute
- Each line of code that produces a result needs to have that result written below. You can ignore an output if you don't want to show it in your code example by adding a comment ` # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT` at the end of the line of code producing it.
|
transformers/docs/README.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/README.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4825
}
| 4 |
# GGUF وتفاعلها مع المحولات
تُستخدم صيغة ملف GGUF لتخزين النماذج للاستدلال باستخدام [GGML](https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml) والمكتبات الأخرى التي تعتمد عليه، مثل [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) أو [whisper.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/whisper.cpp) الشهيرة جدًا.
إنها صيغة ملف [مدعومة من قبل Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf) مع ميزات تسمح بالفحص السريع للموترات والبيانات الوصفية داخل الملف.
تم تصميم تنسيق الملف هذا كـ "تنسيق ملف واحد" حيث يحتوي ملف واحد عادةً على كل من سمات التكوين ومفردات المجزىء اللغوي والخصائص الأخرى، بالإضافة إلى جميع الموترات التي سيتم تحميلها في النموذج. تأتي هذه الملفات بتنسيقات مختلفة وفقًا لنوع التكميم في الملف. نلقي نظرة موجزة على بعضها [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf#quantization-types).
## الدعم داخل المحولات
أضفنا القدرة على تحميل ملفات `gguf` داخل `المحولات` لتوفير قدرات تدريب/ضبط إضافية لنماذج gguf، قبل إعادة تحويل تلك النماذج إلى `gguf` لاستخدامها داخل نظام `ggml`. عند تحميل نموذج، نقوم أولاً بإلغاء تكميمه إلى fp32، قبل تحميل الأوزان لاستخدامها في PyTorch.
> [!NOTE]
> لا يزال الدعم تجريبيًا للغاية ونرحب بالمساهمات من أجل ترسيخه عبر أنواع التكميم وبنى النماذج.
فيما يلي، بنيات النماذج وأنواع التكميم المدعومة:
### أنواع التكميم المدعومة
تُحدد أنواع التكميم المدعومة مبدئيًا وفقًا لملفات التكميم الشائعة التي تمت مشاركتها على Hub.
- F32
- F16
- BF16
- Q4_0
- Q4_1
- Q5_0
- Q5_1
- Q8_0
- Q2_K
- Q3_K
- Q4_K
- Q5_K
- Q6_K
- IQ1_S
- IQ1_M
- IQ2_XXS
- IQ2_XS
- IQ2_S
- IQ3_XXS
- IQ3_S
- IQ4_XS
- IQ4_NL
> [!NOTE]
> لدعم إلغاء تكميم gguf، يلزم تثبيت `gguf>=0.10.0`.
### بنيات النماذج المدعومة
في الوقت الحالي، بنيات النماذج المدعومة هي البنيات التي كانت شائعة جدًا على Hub، وهي:
- LLaMa
- Mistral
- Qwen2
- Qwen2Moe
- Phi3
- Bloom
- Falcon
- StableLM
- GPT2
- Starcoder2
- T5
## مثال الاستخدام
لتحميل ملفات `gguf` في `transformers`، يجب تحديد معامل `gguf_file` فى دالة `from_pretrained` لكل من المُجزّئ اللغوية والنموذج. فيما يلي كيفية تحميل المُجزّئ اللغوي ونموذج، يمكن تحميلهما من نفس الملف:
```py
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
model_id = "TheBloke/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0-GGUF"
filename = "tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0.Q6_K.gguf"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, gguf_file=filename)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, gguf_file=filename)
```
الآن لديك إمكانية الوصول إلى النسخة الكامل غير المكممة للنموذج في بيئة PyTorch، حيث يمكنك دمجه مع مجموعة كبيرة من الأدوات الأخرى.
لإعادة التحويل إلى ملف `gguf`، نوصي باستخدام ملف [`convert-hf-to-gguf.py`](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/convert-hf-to-gguf.py) من llama.cpp.
فيما يلي كيفية إكمال البرنامج النصي أعلاه لحفظ النموذج وإعادة تصديره مرة أخرى إلى `gguf`:
```py
tokenizer.save_pretrained('directory')
model.save_pretrained('directory')
!python ${path_to_llama_cpp}/convert-hf-to-gguf.py ${directory}
```
|
transformers/docs/source/ar/gguf.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ar/gguf.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2249
}
| 5 |
# الفلسفة
تُعد 🤗 Transformers مكتبة برمجية ذات رؤية واضحة صُممت من أجل:
- الباحثون والمُتعلّمون في مجال التعلم الآلي ممن يسعون لاستخدام أو دراسة أو تطوير نماذج Transformers واسعة النطاق.
- مُطبّقي تعلم الآلة الذين يرغبون في ضبط تلك النماذج أو تشغيلها في بيئة إنتاجية، أو كليهما.
- المهندسون الذين يريدون فقط تنزيل نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا واستخدامه لحل مهمة تعلم آلي معينة.
تم تصميم المكتبة مع الأخذ في الاعتبار هدفين رئيسيين:
1. سهولة وسرعة الاستخدام:
- تمّ تقليل عدد المفاهيم المُجردة التي يتعامل معها المستخدم إلى أدنى حد والتي يجب تعلمها، وفي الواقع، لا توجد مفاهيم مُجردة تقريبًا، فقط ثلاث فئات أساسية مطلوبة لاستخدام كل نموذج: [الإعدادات](main_classes/configuration)، [نماذج](main_classes/model)، وفئة ما قبل المعالجة ([مُجزّئ لغوي](main_classes/tokenizer) لـ NLP، [معالج الصور](main_classes/image_processor) للرؤية، [مستخرج الميزات](main_classes/feature_extractor) للصوت، و [معالج](main_classes/processors) للمدخﻻت متعددة الوسائط).
- يمكن تهيئة جميع هذه الفئات بطريقة بسيطة وموحدة من خلال نماذج مُدربة مسبقًا باستخدام الدالة الموحدة `from_pretrained()` والتي تقوم بتنزيل (إذا لزم الأمر)، وتخزين وتحميل كل من: فئة النموذج المُراد استخدامه والبيانات المرتبطة ( مُعاملات الإعدادات، ومعجم للمُجزّئ اللغوي،وأوزان النماذج) من نقطة تدقيق مُحددة مُخزّنة على [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) أو ن من نقطة تخزين خاصة بالمستخدم.
- بالإضافة إلى هذه الفئات الأساسية الثلاث، توفر المكتبة واجهتي برمجة تطبيقات: [`pipeline`] للاستخدام السريع لأحد النماذج لأداء استنتاجات على مهمة مُحددة، و [`Trainer`] للتدريب السريع أو الضبط الدقيق لنماذج PyTorch (جميع نماذج TensorFlow متوافقة مع `Keras.fit`).
- نتيجة لذلك، هذه المكتبة ليست صندوق أدوات متعدد الاستخدامات من الكتل الإنشائية للشبكات العصبية. إذا كنت تريد توسيع أو البناء على المكتبة، فما عليك سوى استخدام Python و PyTorch و TensorFlow و Keras العادية والوراثة من الفئات الأساسية للمكتبة لإعادة استخدام الوظائف مثل تحميل النموذج وحفظه. إذا كنت ترغب في معرفة المزيد عن فلسفة الترميز لدينا للنماذج، فراجع منشور المدونة الخاص بنا [Repeat Yourself](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy).
2. تقديم نماذج رائدة في مجالها مع أداء قريب قدر الإمكان من النماذج الأصلية:
- نقدم مثالًا واحدًا على الأقل لكل بنية تقوم بإعادة إنتاج نتيجة مقدمة من المؤلفين الرسميين لتلك البنية.
- عادةً ما تكون الشفرة قريبة قدر الإمكان من قاعدة الشفرة الأصلية، مما يعني أن بعض شفرة PyTorch قد لا تكون "بأسلوب PyTorch" كما يمكن أن تكون نتيجة لكونها شفرة TensorFlow محولة والعكس صحيح.
بعض الأهداف الأخرى:
- كشف تفاصيل النماذج الداخلية بشكل متسق قدر الإمكان:
-نتيح الوصول، باستخدام واجهة برمجة واحدة، إلى جميع الحالات المخفية (Hidden-States) وأوزان الانتباه (Attention Weights).
- تم توحيد واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بفئات المعالجة المسبقة والنماذج الأساسية لتسهيل التبديل بين النماذج.
- دمج مجموعة مختارة من الأدوات الواعدة لضبط النماذج بدقة (Fine-tuning) ودراستها:
- طريقة بسيطة ومتسقة لإضافة رموز جديدة إلى مفردات التضمينات (Embeddings) لضبط النماذج بدقة.
- طرق سهلة لإخفاء (Masking) وتقليم (Pruning) رؤوس المحولات (Transformer Heads).
- التبديل بسهولة بين PyTorch و TensorFlow 2.0 و Flax، مما يسمح بالتدريب باستخدام إطار واحد والاستدلال باستخدام إطار آخر.
## المفاهيم الرئيسية
تعتمد المكتبة على ثلاثة أنواع من الفئات لكل نموذج:
- **فئات النماذج** يمكن أن تكون نماذج PyTorch ([torch.nn.Module](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module))، أو نماذج Keras ([tf.keras.Model](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model))، أو نماذج JAX/Flax ([flax.linen.Module](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api_reference/flax.linen/module.html)) التي تعمل مع الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا المقدمة في المكتبة.
- **فئات الإعداد** تخزن معلمات التهيئة المطلوبة لبناء نموذج (مثل عدد الطبقات وحجم الطبقة المخفية). أنت لست مضطرًا دائمًا إلى إنشاء مثيل لهذه الفئات بنفسك. على وجه الخصوص، إذا كنت تستخدم نموذجًا مُدربًا مسبقًا دون أي تعديل، فإن إنشاء النموذج سيهتم تلقائيًا تهيئة الإعدادات (والذي يعد جزءًا من النموذج).
- **فئات ما قبل المعالجة** تحويل البيانات الخام إلى تنسيق مقبول من قبل النموذج. يقوم [المعالج](main_classes/tokenizer) بتخزين المعجم لكل نموذج ويقدم طرقًا لتشفير وفك تشفير السلاسل في قائمة من مؤشرات تضمين الرموز ليتم إطعامها للنموذج. تقوم [معالجات الصور](main_classes/image_processor) بمعالجة إدخالات الرؤية، وتقوم [مستخلصات الميزات](main_classes/feature_extractor) بمعالجة إدخالات الصوت، ويقوم [المعالج](main_classes/processors) بمعالجة الإدخالات متعددة الوسائط.
يمكن تهيئة جميع هذه الفئات من نسخ مُدربة مسبقًا، وحفظها محليًا، ومشاركتها على منصة Hub عبر ثلاث طرق:
- تسمح لك الدالة `from_pretrained()` بتهيئة النموذج وتكويناته وفئة المعالجة المسبقة من إصدار مُدرب مسبقًا إما يتم توفيره بواسطة المكتبة نفسها (يمكن العثور على النماذج المدعومة على [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models)) أو مخزنة محليًا (أو على خادم) بواسطة المستخدم.
- تسمح لك الدالة `save_pretrained()` بحفظ النموذج، وتكويناته وفئة المعالجة المسبقة محليًا، بحيث يمكن إعادة تحميله باستخدام الدالة `from_pretrained()`.
- تسمح لك `push_to_hub()` بمشاركة نموذج وتكويناتهوفئة المعالجة المسبقة على Hub، بحيث يمكن الوصول إليها بسهولة من قبل الجميع.
|
transformers/docs/source/ar/philosophy.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ar/philosophy.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4397
}
| 6 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# الترجمة(Translation)
[[open-in-colab]]
<Youtube id="1JvfrvZgi6c"/>
الترجمة هي عملية تحويل سلسلة نصية من لغة إلى أخرى. وهي إحدى المهام التي يمكن صياغتها كمسألة تسلسل إلى تسلسل، وهو إطار عمل قوي لإنتاج مخرجات من مدخلات، مثل الترجمة أو التلخيص. تُستخدم أنظمة الترجمة عادةً للترجمة بين نصوص لغات مختلفة، ويمكن استخدامها أيضًا لترجمة الكلام أو لمهام تجمع بين النصوص والكلام، مثل تحويل النص إلى كلام أو تحويل الكلام إلى نص.
سيوضح لك هذا الدليل كيفية:
1. ضبط دقيق لنموذج [T5](https://huggingface.co/google-t5/t5-small) على المجموعة الفرعية الإنجليزية-الفرنسية من مجموعة بيانات [OPUS Books](https://huggingface.co/datasets/opus_books) لترجمة النص الإنجليزي إلى الفرنسية.
2. استخدام النموذج المضبوط بدقة للاستدلال.
<Tip>
لمشاهدة جميع البنى والنسخ المتوافقة مع هذه المهمة، نوصي بالتحقق من [صفحة المهمة](https://huggingface.co/tasks/translation).
</Tip>
قبل البدء، تأكد من تثبيت جميع المكتبات الضرورية:
```bash
pip install transformers datasets evaluate sacrebleu
```
نشجعك على تسجيل الدخول إلى حساب Hugging Face الخاص بك حتى تتمكن من تحميل نموذجك ومشاركته مع المجتمع. عند الطلب، أدخل الرمز المميز الخاص بك لتسجيل الدخول:
```py
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
>>> notebook_login()
```
## تحميل مجموعة بيانات OPUS Books
ابدأ بتحميل المجموعة الفرعية الإنجليزية-الفرنسية من مجموعة بيانات [OPUS Books](https://huggingface.co/datasets/opus_books) من مكتبة 🤗 Datasets:
```py
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> books = load_dataset("opus_books", "en-fr")
```
قسّم مجموعة البيانات إلى مجموعة تدريب ومجموعة اختبار باستخدام طريقة [`~datasets.Dataset.train_test_split`]:
```py
>>> books = books["train"].train_test_split(test_size=0.2)
```
ثم ألقِ نظرة على مثال:
```py
>>> books["train"][0]
{'id': '90560',
'translation': {'en': 'But this lofty plateau measured only a few fathoms, and soon we reentered Our Element.',
'fr': 'Mais ce plateau élevé ne mesurait que quelques toises, et bientôt nous fûmes rentrés dans notre élément.'}}
```
`translation`: ترجمة إنجليزية وفرنسية للنص.
## المعالجة المسبقة(Preprocess)
<Youtube id="XAR8jnZZuUs"/>
الخطوة التالية هي تحميل مُجزئ T5 لمعالجة أزواج اللغة الإنجليزية-الفرنسية:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> checkpoint = "google-t5/t5-small"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
```
يجب أن تقوم دالة المعالجة المسبقة التي تُريد إنشاءها بما يلي:
1. إضافة بادئة إلى المُدخل بمُوجه حتى يعرف T5 أن هذه مهمة ترجمة. تتطلب بعض النماذج القادرة على أداء مهام متعددة توجيهًا لمهام مُحددة.
2. تعيين اللغة الهدف (الفرنسية) في معامل `text_target` لضمان معالجة المُجزئ للنص بشكل صحيح. إذا لم تُعيّن `text_target`، فسيُعالج المُجزئ النص على أنه إنجليزي.
3. اقتطاع التسلسلات بحيث لا يزيد طولها عن الحد الأقصى الذي يحدده معامل `max_length`.
```py
>>> source_lang = "en"
>>> target_lang = "fr"
>>> prefix = "translate English to French: "
>>> def preprocess_function(examples):
... inputs = [prefix + example[source_lang] for example in examples["translation"]]
... targets = [example[target_lang] for example in examples["translation"]]
... model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, text_target=targets, max_length=128, truncation=True)
... return model_inputs
```
لتطبيق دالة المعالجة المسبقة على مجموعة البيانات بأكملها، استخدم طريقة [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] من 🤗 Datasets. يمكنك تسريع دالة `map` عن طريق تعيين `batched=True` لمعالجة عناصر متعددة من مجموعة البيانات في وقت واحد:
```py
>>> tokenized_books = books.map(preprocess_function, batched=True)
```
الآن أنشئ دفعة من الأمثلة باستخدام [`DataCollatorForSeq2Seq`]. من الأكثر كفاءة *الحشو الديناميكي* للجمل إلى أطول طول في دفعة أثناء التجميع، بدلاً من حشو مجموعة البيانات بأكملها إلى الحد الأقصى للطول.
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
```py
>>> from transformers import DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
>>> data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(tokenizer=tokenizer, model=checkpoint)
```
</pt>
<tf>
```py
>>> from transformers import DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
>>> data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(tokenizer=tokenizer, model=checkpoint, return_tensors="tf")
```
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
## التقييم (Evaluate)
غالباً ما يكون تضمين مقياس أثناء التدريب مفيداً لتقييم أداء نموذجك. يمكنك تحميل طريقة تقييم بسرعة باستخدام مكتبة 🤗 [Evaluate](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/index). لهذه المهمة، حمّل مقياس [SacreBLEU](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/sacrebleu) (راجع [الجولة السريعة](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/a_quick_tour) لـ 🤗 Evaluate لمعرفة المزيد حول كيفية تحميل وحساب مقياس):
```py
>>> import evaluate
>>> metric = evaluate.load("sacrebleu")
```
ثم أنشئ دالة تُمرر تنبؤاتك وتسمياتك إلى [`~evaluate.EvaluationModule.compute`] لحساب درجة SacreBLEU:
```py
>>> import numpy as np
>>> def postprocess_text(preds, labels):
... preds = [pred.strip() for pred in preds]
... labels = [[label.strip()] for label in labels]
... return preds, labels
>>> def compute_metrics(eval_preds):
... preds, labels = eval_preds
... if isinstance(preds, tuple):
... preds = preds[0]
... decoded_preds = tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True)
... labels = np.where(labels != -100, labels, tokenizer.pad_token_id)
... decoded_labels = tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
... decoded_preds, decoded_labels = postprocess_text(decoded_preds, decoded_labels)
... result = metric.compute(predictions=decoded_preds, references=decoded_labels)
... result = {"bleu": result["score"]}
... prediction_lens = [np.count_nonzero(pred != tokenizer.pad_token_id) for pred in preds]
... result["gen_len"] = np.mean(prediction_lens)
... result = {k: round(v, 4) for k, v in result.items()}
... return result
```
دالة `compute_metrics` الخاصة بك جاهزة الآن، وسوف تعود إليها عند إعداد التدريب.
## التدريب (Train)
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
<Tip>
إذا لم تكن معتادًا على ضبط دقيق نموذج باستخدام [`Trainer`], فألقِ نظرة على البرنامج التعليمي الأساسي [هنا](../training#train-with-pytorch-trainer)!
</Tip>
أنت جاهز لبدء تدريب نموذجك الآن! حمّل T5 باستخدام [`AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM`]:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments, Seq2SeqTrainer
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
```
في هذه المرحلة، تبقى ثلاث خطوات فقط:
1. حدد مُعاملات للتدريب في [`Seq2SeqTrainingArguments`]. المُعامل الوحيدة المطلوبة هي `output_dir` التي تحدد مكان حفظ النموذج الخاص بك. ستقوم بدفع هذا النموذج إلى Hub عن طريق تعيين `push_to_hub=True` (يجب عليك تسجيل الدخول إلى Hugging Face لتحميل نموذجك). في نهاية كل حقبة، سيقوم [`Trainer`] بتقييم مقياس SacreBLEU وحفظ نقطة تدقيق التدريب.
2. مرر مُعاملات التدريب إلى [`Seq2SeqTrainer`] جنبًا إلى جنب مع النموذج ومجموعة البيانات والمعالج اللغوي وجامع البيانات ووظيفة `compute_metrics`.
3. نفّذ [`~Trainer.train`] لضبط نموذجك.
```py
>>> training_args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments(
... output_dir="my_awesome_opus_books_model",
... eval_strategy="epoch",
... learning_rate=2e-5,
... per_device_train_batch_size=16,
... per_device_eval_batch_size=16,
... weight_decay=0.01,
... save_total_limit=3,
... num_train_epochs=2,
... predict_with_generate=True,
... fp16=True, #change to bf16=True for XPU
... push_to_hub=True,
... )
>>> trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
... model=model,
... args=training_args,
... train_dataset=tokenized_books["train"],
... eval_dataset=tokenized_books["test"],
... processing_class=tokenizer,
... data_collator=data_collator,
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
... )
>>> trainer.train()
```
بمجرد اكتمال التدريب، شارك نموذجك مع Hub باستخدام طريقة [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] حتى يتمكن الجميع من استخدام نموذجك:
```py
>>> trainer.push_to_hub()
```
</pt>
<tf>
<Tip>
إذا لم تكن معتادًا على ضبط نموذج باستخدام Keras، فألق نظرة على البرنامج التعليمي الأساسي [هنا](../training#train-a-tensorflow-model-with-keras)!
</Tip>
لضبط نموذج في TensorFlow، ابدأ بإعداد دالة مُحسِّن وجدول معدل تعلم وبعض المعلمات الفائقة للتدريب:
```py
>>> from transformers import AdamWeightDecay
>>> optimizer = AdamWeightDecay(learning_rate=2e-5, weight_decay_rate=0.01)
```
ثم يمكنك تحميل T5 باستخدام [`TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM`]:
```py
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
```
حوّل مجموعات البيانات الخاصة بك إلى تنسيق `tf.data.Dataset` باستخدام [`~transformers.TFPreTrainedModel.prepare_tf_dataset`]:
```py
>>> tf_train_set = model.prepare_tf_dataset(
... tokenized_books["train"],
... shuffle=True,
... batch_size=16,
... collate_fn=data_collator,
... )
>>> tf_test_set = model.prepare_tf_dataset(
... tokenized_books["test"],
... shuffle=False,
... batch_size=16,
... collate_fn=data_collator,
... )
```
قم بتكوين النموذج للتدريب باستخدام [`compile`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#compile-method). لاحظ أن جميع نماذج Transformers تحتوي على دالة خسارة ذات صلة بالمهمة بشكل افتراضي، لذلك لا تحتاج إلى تحديد واحدة إلا إذا كنت ترغب في ذلك:
```py
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> model.compile(optimizer=optimizer) # No loss argument!
```
آخر شيئين يجب إعدادهما قبل بدء التدريب هما حساب مقياس SacreBLEU من التوقعات، وتوفير طريقة لدفع نموذجك إلى Hub. يتم كلاهما باستخدام [استدعاءات Keras](../main_classes/keras_callbacks).
مرر دالة `compute_metrics` الخاصة بك إلى [`~transformers.KerasMetricCallback`]:
```py
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import KerasMetricCallback
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_test_set)
```
حدد مكان دفع نموذجك ومعالجك اللغوي في [`~transformers.PushToHubCallback`]:
```py
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import PushToHubCallback
>>> push_to_hub_callback = PushToHubCallback(
... output_dir="my_awesome_opus_books_model",
... tokenizer=tokenizer,
... )
```
ثم اجمع استدعاءاتك معًا:
```py
>>> callbacks = [metric_callback, push_to_hub_callback]
```
أخيرًا، أنت جاهز لبدء تدريب نموذجك! اتصل بـ [`fit`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#fit-method) مع مجموعات بيانات التدريب والتحقق من الصحة وعدد الحقب واستدعاءاتك لضبط النموذج:
```py
>>> model.fit(x=tf_train_set, validation_data=tf_test_set, epochs=3, callbacks=callbacks)
```
بمجرد اكتمال التدريب، يتم تحميل نموذجك تلقائيًا إلى Hub حتى يتمكن الجميع من استخدامه!
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
<Tip>
للحصول على مثال أكثر تعمقًا لكيفية ضبط نموذج للترجمة، ألق نظرة على [دفتر ملاحظات PyTorch](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation.ipynb) المقابل
أو [دفتر ملاحظات TensorFlow](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation-tf.ipynb).
</Tip>
## الاستدلال (Inference)
رائع، الآن بعد أن قمت بضبط نموذج، يمكنك استخدامه للاستدلال!
أحضر بعض النصوص التي ترغب في ترجمتها إلى لغة أخرى. بالنسبة لـ T5، تحتاج إلى إضافة بادئة إلى مدخلاتك اعتمادًا على المهمة التي تعمل عليها. للترجمة من الإنجليزية إلى الفرنسية، يجب عليك إضافة بادئة إلى مدخلاتك كما هو موضح أدناه:
```py
>>> text = "translate English to French: Legumes share resources with nitrogen-fixing bacteria."
```
أبسط طريقة لتجربة نموذجك المضبوط للاستدلال هي استخدامه في [`pipeline`]. قم بإنشاء مثيل لـ `pipeline` للترجمة باستخدام نموذجك، ومرر النص الخاص بك إليه:
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
# تغيير `xx` إلى لغة الإدخال و `yy` إلى لغة المخرجات المطلوبة.
# أمثلة: "en" للغة الإنجليزية، "fr" للغة الفرنسية، "de" للغة الألمانية، "es" للغة الإسبانية، "zh" للغة الصينية، إلخ؛ translation_en_to_fr تترجم من الإنجليزية إلى الفرنسية
# يمكنك عرض جميع قوائم اللغات هنا - https://huggingface.co/languages
>>> translator = pipeline("translation_xx_to_yy", model="username/my_awesome_opus_books_model")
>>> translator(text)
[{'translation_text': 'Legumes partagent des ressources avec des bactéries azotantes.'}]
```
يمكنك أيضًا تكرار نتائج `pipeline` يدويًا إذا أردت:
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
قم بتحويل النص إلى رموز وإرجاع `input_ids` كموترات PyTorch:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_opus_books_model")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
```
استخدم الدالة [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] لإنشاء الترجمة. لمزيد من التفاصيل حول استراتيجيات توليد النصوص المختلفة والمعلمات للتحكم في التوليد، تحقق من واجهة برمجة تطبيقات [توليد النصوص](../main_classes/text_generation).
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_opus_books_model")
>>> outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=40, do_sample=True, top_k=30, top_p=0.95)
```
فك تشفير معرفات الرموز المولدة مرة أخرى إلى نص:
```py
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
'Les lignées partagent des ressources avec des bactéries enfixant l'azote.'
```
</pt>
<tf>
قم بتحويل النص إلى رموز وإرجاع `input_ids` كموترات TensorFlow:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_opus_books_model")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="tf").input_ids
```
استخدم طريقة [`~transformers.generation_tf_utils.TFGenerationMixin.generate`] لإنشاء الترجمة. لمزيد من التفاصيل حول استراتيجيات توليد النصوص المختلفة والمعلمات للتحكم في التوليد، تحقق من واجهة برمجة تطبيقات [توليد النصوص](../main_classes/text_generation).
```py
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_opus_books_model")
>>> outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=40, do_sample=True, top_k=30, top_p=0.95)
```
فك تشفير معرفات الرموز المولدة مرة أخرى إلى نص:
```py
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
'Les lugumes partagent les ressources avec des bactéries fixatrices d'azote.'
```
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/ar/tasks/translation.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ar/tasks/translation.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 8915
}
| 7 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Distributed training with 🤗 Accelerate
As models get bigger, parallelism has emerged as a strategy for training larger models on limited hardware and accelerating training speed by several orders of magnitude. At Hugging Face, we created the [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) library to help users easily train a 🤗 Transformers model on any type of distributed setup, whether it is multiple GPU's on one machine or multiple GPU's across several machines. In this tutorial, learn how to customize your native PyTorch training loop to enable training in a distributed environment.
## Setup
Get started by installing 🤗 Accelerate:
```bash
pip install accelerate
```
Then import and create an [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] object. The [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] will automatically detect your type of distributed setup and initialize all the necessary components for training. You don't need to explicitly place your model on a device.
```py
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
```
## Prepare to accelerate
The next step is to pass all the relevant training objects to the [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`] method. This includes your training and evaluation DataLoaders, a model and an optimizer:
```py
>>> train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
... train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
... )
```
## Backward
The last addition is to replace the typical `loss.backward()` in your training loop with 🤗 Accelerate's [`~accelerate.Accelerator.backward`] method:
```py
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
... for batch in train_dataloader:
... outputs = model(**batch)
... loss = outputs.loss
... accelerator.backward(loss)
... optimizer.step()
... lr_scheduler.step()
... optimizer.zero_grad()
... progress_bar.update(1)
```
As you can see in the following code, you only need to add four additional lines of code to your training loop to enable distributed training!
```diff
+ from accelerate import Accelerator
from transformers import AdamW, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, get_scheduler
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint, num_labels=2)
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=3e-5)
- device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
- model.to(device)
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
+ )
num_epochs = 3
num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
"linear",
optimizer=optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=0,
num_training_steps=num_training_steps
)
progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
model.train()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for batch in train_dataloader:
- batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
outputs = model(**batch)
loss = outputs.loss
- loss.backward()
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
optimizer.step()
lr_scheduler.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
progress_bar.update(1)
```
## Train
Once you've added the relevant lines of code, launch your training in a script or a notebook like Colaboratory.
### Train with a script
If you are running your training from a script, run the following command to create and save a configuration file:
```bash
accelerate config
```
Then launch your training with:
```bash
accelerate launch train.py
```
### Train with a notebook
🤗 Accelerate can also run in a notebook if you're planning on using Colaboratory's TPUs. Wrap all the code responsible for training in a function, and pass it to [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`]:
```py
>>> from accelerate import notebook_launcher
>>> notebook_launcher(training_function)
```
For more information about 🤗 Accelerate and its rich features, refer to the [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
|
transformers/docs/source/en/accelerate.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/accelerate.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1516
}
| 8 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# DeepSpeed
[DeepSpeed](https://www.deepspeed.ai/) is a PyTorch optimization library that makes distributed training memory-efficient and fast. At its core is the [Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO)](https://hf.co/papers/1910.02054) which enables training large models at scale. ZeRO works in several stages:
* ZeRO-1, optimizer state partitioning across GPUs
* ZeRO-2, gradient partitioning across GPUs
* ZeRO-3, parameter partitioning across GPUs
In GPU-limited environments, ZeRO also enables offloading optimizer memory and computation from the GPU to the CPU to fit and train really large models on a single GPU. DeepSpeed is integrated with the Transformers [`Trainer`] class for all ZeRO stages and offloading. All you need to do is provide a config file or you can use a provided template. For inference, Transformers support ZeRO-3 and offloading since it allows loading huge models.
This guide will walk you through how to deploy DeepSpeed training, the features you can enable, how to setup the config files for different ZeRO stages, offloading, inference, and using DeepSpeed without the [`Trainer`].
## Installation
DeepSpeed is available to install from PyPI or Transformers (for more detailed installation options, take a look at the DeepSpeed [installation details](https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/advanced-install/) or the GitHub [README](https://github.com/microsoft/deepspeed#installation)).
<Tip>
If you're having difficulties installing DeepSpeed, check the [DeepSpeed CUDA installation](../debugging#deepspeed-cuda-installation) guide. While DeepSpeed has a pip installable PyPI package, it is highly recommended to [install it from source](https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/advanced-install/#install-deepspeed-from-source) to best match your hardware and to support certain features, like 1-bit Adam, which aren’t available in the PyPI distribution.
</Tip>
<hfoptions id="install">
<hfoption id="PyPI">
```bash
pip install deepspeed
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Transformers">
```bash
pip install transformers[deepspeed]
```
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
## Memory requirements
Before you begin, it is a good idea to check whether you have enough GPU and CPU memory to fit your model. DeepSpeed provides a tool for estimating the required CPU/GPU memory. For example, to estimate the memory requirements for the [bigscience/T0_3B](bigscience/T0_3B) model on a single GPU:
```bash
$ python -c 'from transformers import AutoModel; \
from deepspeed.runtime.zero.stage3 import estimate_zero3_model_states_mem_needs_all_live; \
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B"); \
estimate_zero3_model_states_mem_needs_all_live(model, num_gpus_per_node=1, num_nodes=1)'
[...]
Estimated memory needed for params, optim states and gradients for a:
HW: Setup with 1 node, 1 GPU per node.
SW: Model with 2783M total params, 65M largest layer params.
per CPU | per GPU | Options
70.00GB | 0.25GB | offload_param=cpu , offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=1
70.00GB | 0.25GB | offload_param=cpu , offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=0
62.23GB | 5.43GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=1
62.23GB | 5.43GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=0
0.37GB | 46.91GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=none, zero_init=1
15.56GB | 46.91GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=none, zero_init=0
```
This means you either need a single 80GB GPU without CPU offload or a 8GB GPU and a ~60GB CPU to offload to (these are just the memory requirements for the parameters, optimizer states and gradients, and you'll need a bit more for the CUDA kernels and activations). You should also consider the tradeoff between cost and speed because it'll be cheaper to rent or buy a smaller GPU but it'll take longer to train your model.
If you have enough GPU memory make sure you disable CPU/NVMe offload to make everything faster.
## Select a ZeRO stage
After you've installed DeepSpeed and have a better idea of your memory requirements, the next step is selecting a ZeRO stage to use. In order of fastest and most memory-efficient:
| Fastest | Memory efficient |
|------------------|------------------|
| ZeRO-1 | ZeRO-3 + offload |
| ZeRO-2 | ZeRO-3 |
| ZeRO-2 + offload | ZeRO-2 + offload |
| ZeRO-3 | ZeRO-2 |
| ZeRO-3 + offload | ZeRO-1 |
To find what works best for you, start with the fastest approach and if you run out of memory, try the next stage which is slower but more memory efficient. Feel free to work in whichever direction you prefer (starting with the most memory efficient or fastest) to discover the appropriate balance between speed and memory usage.
A general process you can use is (start with batch size of 1):
1. enable gradient checkpointing
2. try ZeRO-2
3. try ZeRO-2 and offload the optimizer
4. try ZeRO-3
5. try ZeRO-3 and offload parameters to the CPU
6. try ZeRO-3 and offload parameters and the optimizer to the CPU
7. try lowering various default values like a narrower search beam if you're using the [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] method
8. try mixed half-precision (fp16 on older GPU architectures and bf16 on Ampere) over full-precision weights
9. add more hardware if possible or enable Infinity to offload parameters and the optimizer to a NVMe
10. once you're not running out of memory, measure effective throughput and then try to increase the batch size as large as you can to maximize GPU efficiency
11. lastly, try to optimize your training setup by disabling some offload features or use a faster ZeRO stage and increasing/decreasing the batch size to find the best tradeoff between speed and memory usage
## DeepSpeed configuration file
DeepSpeed works with the [`Trainer`] class by way of a config file containing all the parameters for configuring how you want setup your training run. When you execute your training script, DeepSpeed logs the configuration it received from [`Trainer`] to the console so you can see exactly what configuration was used.
<Tip>
Find a complete list of DeepSpeed configuration options on the [DeepSpeed Configuration JSON](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/) reference. You can also find more practical examples of various DeepSpeed configuration examples on the [DeepSpeedExamples](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeedExamples) repository or the main [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed) repository. To quickly find specific examples, you can:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeedExamples
cd DeepSpeedExamples
find . -name '*json'
# find examples with the Lamb optimizer
grep -i Lamb $(find . -name '*json')
```
</Tip>
The DeepSpeed configuration file is passed as a path to a JSON file if you're training from the command line interface or as a nested `dict` object if you're using the [`Trainer`] in a notebook setting.
<hfoptions id="pass-config">
<hfoption id="path to file">
```py
TrainingArguments(..., deepspeed="path/to/deepspeed_config.json")
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="nested dict">
```py
ds_config_dict = dict(scheduler=scheduler_params, optimizer=optimizer_params)
args = TrainingArguments(..., deepspeed=ds_config_dict)
trainer = Trainer(model, args, ...)
```
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### DeepSpeed and Trainer parameters
There are three types of configuration parameters:
1. Some of the configuration parameters are shared by [`Trainer`] and DeepSpeed, and it can be difficult to identify errors when there are conflicting definitions. To make it easier, these shared configuration parameters are configured from the [`Trainer`] command line arguments.
2. Some configuration parameters that are automatically derived from the model configuration so you don't need to manually adjust these values. The [`Trainer`] uses a configuration value `auto` to determine set the most correct or efficient value. You could set your own configuration parameters explicitly, but you must take care to ensure the [`Trainer`] arguments and DeepSpeed configuration parameters agree. Mismatches may cause the training to fail in very difficult to detect ways!
3. Some configuration parameters specific to DeepSpeed only which need to be manually set based on your training needs.
You could also modify the DeepSpeed configuration and edit [`TrainingArguments`] from it:
1. Create or load a DeepSpeed configuration to use as the main configuration
2. Create a [`TrainingArguments`] object based on these DeepSpeed configuration values
Some values, such as `scheduler.params.total_num_steps` are calculated by the [`Trainer`] during training.
### ZeRO configuration
There are three configurations, each corresponding to a different ZeRO stage. Stage 1 is not as interesting for scalability, and this guide focuses on stages 2 and 3. The `zero_optimization` configuration contains all the options for what to enable and how to configure them. For a more detailed explanation of each parameter, take a look at the [DeepSpeed Configuration JSON](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/) reference.
<Tip warning={true}>
DeepSpeed doesn’t validate parameter names and any typos fallback on the parameter's default setting. You can watch the DeepSpeed engine startup log messages to see what values it is going to use.
</Tip>
The following configurations must be setup with DeepSpeed because the [`Trainer`] doesn't provide equivalent command line arguments.
<hfoptions id="zero-config">
<hfoption id="ZeRO-1">
ZeRO-1 shards the optimizer states across GPUs, and you can expect a tiny speed up. The ZeRO-1 config can be setup like this:
```yml
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 1
}
}
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="ZeRO-2">
ZeRO-2 shards the optimizer and gradients across GPUs. This stage is primarily used for training since its features are not relevant to inference. Some important parameters to configure for better performance include:
* `offload_optimizer` should be enabled to reduce GPU memory usage.
* `overlap_comm` when set to `true` trades off increased GPU memory usage to lower allreduce latency. This feature uses 4.5x the `allgather_bucket_size` and `reduce_bucket_size` values. In this example, they're set to `5e8` which means it requires 9GB of GPU memory. If your GPU memory is 8GB or less, you should reduce `overlap_comm` to lower the memory requirements and prevent an out-of-memory (OOM) error.
* `allgather_bucket_size` and `reduce_bucket_size` trade off available GPU memory for communication speed. The smaller their values, the slower communication is and the more GPU memory is available. You can balance, for example, whether a bigger batch size is more important than a slightly slower training time.
* `round_robin_gradients` is available in DeepSpeed 0.4.4 for CPU offloading. It parallelizes gradient copying to CPU memory among ranks by fine-grained gradient partitioning. Performance benefit grows with gradient accumulation steps (more copying between optimizer steps) or GPU count (increased parallelism).
```yml
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 2,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"allgather_partitions": true,
"allgather_bucket_size": 5e8,
"overlap_comm": true,
"reduce_scatter": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": 5e8,
"contiguous_gradients": true
"round_robin_gradients": true
}
}
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="ZeRO-3">
ZeRO-3 shards the optimizer, gradient, and parameters across GPUs. Unlike ZeRO-2, ZeRO-3 can also be used for inference, in addition to training, because it allows large models to be loaded on multiple GPUs. Some important parameters to configure include:
* `device: "cpu"` can help if you're running out of GPU memory and if you have free CPU memory available. This allows offloading model parameters to the CPU.
* `pin_memory: true` can improve throughput, but less memory becomes available for other processes because the pinned memory is reserved for the specific process that requested it and it's typically accessed much faster than normal CPU memory.
* `stage3_max_live_parameters` is the upper limit on how many full parameters you want to keep on the GPU at any given time. Reduce this value if you encounter an OOM error.
* `stage3_max_reuse_distance` is a value for determining when a parameter is used again in the future, and it helps decide whether to throw the parameter away or to keep it. If the parameter is going to be reused (if the value is less than `stage3_max_reuse_distance`), then it is kept to reduce communication overhead. This is super helpful when activation checkpointing is enabled and you want to keep the parameter in the forward recompute until the backward pass. But reduce this value if you encounter an OOM error.
* `stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save` consolidates fp16 weights when a model is saved. For large models and multiple GPUs, this is expensive in terms of memory and speed. You should enable it if you're planning on resuming training.
* `sub_group_size` controls which parameters are updated during the optimizer step. Parameters are grouped into buckets of `sub_group_size` and each bucket is updated one at a time. When used with NVMe offload, `sub_group_size` determines when model states are moved in and out of CPU memory from during the optimization step. This prevents running out of CPU memory for extremely large models. `sub_group_size` can be left to its default value if you aren't using NVMe offload, but you may want to change it if you:
1. Run into an OOM error during the optimizer step. In this case, reduce `sub_group_size` to reduce memory usage of the temporary buffers.
2. The optimizer step is taking a really long time. In this case, increase `sub_group_size` to improve bandwidth utilization as a result of increased data buffers.
* `reduce_bucket_size`, `stage3_prefetch_bucket_size`, and `stage3_param_persistence_threshold` are dependent on a model's hidden size. It is recommended to set these values to `auto` and allow the [`Trainer`] to automatically assign the values.
```yml
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"overlap_comm": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"sub_group_size": 1e9,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": "auto",
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 1e9,
"stage3_max_reuse_distance": 1e9,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
}
}
```
You can use the [`deepspeed.zero.Init`](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/zero3.html#deepspeed.zero.Init) context manager to initialize a model faster:
```py
from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration, T5Config
import deepspeed
with deepspeed.zero.Init():
config = T5Config.from_pretrained("google-t5/t5-small")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration(config)
```
For pretrained models, the DeepSped config file needs to have `is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled: true` setup in [`TrainingArguments`] and it needs a ZeRO configuration enabled. The [`TrainingArguments`] object must be created **before** calling the model [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`].
```py
from transformers import AutoModel, Trainer, TrainingArguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(..., deepspeed=ds_config)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("google-t5/t5-small")
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, ...)
```
You'll need ZeRO-3 if the fp16 weights don't fit on a single GPU. If you're able to load fp16 weights, then make sure you specify `torch_dtype=torch.float16` in [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`].
Another consideration for ZeRO-3 is if you have multiple GPUs, no single GPU has all the parameters unless it's the parameters for the currently executing layer. To access all parameters from all the layers at once, such as loading pretrained model weights in [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`], one layer is loaded at a time and immediately partitioned to all GPUs. This is because for very large models, it isn't possible to load the weights on one GPU and then distribute them across the other GPUs due to memory limitations.
If you encounter a model parameter weight that looks like the following, where `tensor([1.])` or the parameter size is 1 instead of a larger multi-dimensional shape, this means the parameter is partitioned and this is a ZeRO-3 placeholder.
```py
tensor([1.0], device="cuda:0", dtype=torch.float16, requires_grad=True)
```
<Tip>
For more information about initializing large models with ZeRO-3 and accessing the parameters, take a look at the [Constructing Massive Models](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/zero3.html#constructing-massive-models) and [Gathering Parameters](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/zero3.html#gathering-parameters) guides.
</Tip>
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### NVMe configuration
[ZeRO-Infinity](https://hf.co/papers/2104.07857) allows offloading model states to the CPU and/or NVMe to save even more memory. Smart partitioning and tiling algorithms allow each GPU to send and receive very small amounts of data during offloading such that a modern NVMe can fit an even larger total memory pool than is available to your training process. ZeRO-Infinity requires ZeRO-3.
Depending on the CPU and/or NVMe memory available, you can offload both the [optimizer states](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#optimizer-offloading) and [parameters](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#parameter-offloading), just one of them, or none. You should also make sure the `nvme_path` is pointing to an NVMe device, because while it still works with a normal hard drive or solid state drive, it'll be significantly slower. With a modern NVMe, you can expect peak transfer speeds of ~3.5GB/s for read and ~3GB/s for write operations. Lastly, [run a benchmark](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/issues/998) on your training setup to determine the optimal `aio` configuration.
The example ZeRO-3/Infinity configuration file below sets most of the parameter values to `auto`, but you could also manually add these values.
```yml
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupLR",
"params": {
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "nvme",
"nvme_path": "/local_nvme",
"pin_memory": true,
"buffer_count": 4,
"fast_init": false
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "nvme",
"nvme_path": "/local_nvme",
"pin_memory": true,
"buffer_count": 5,
"buffer_size": 1e8,
"max_in_cpu": 1e9
},
"aio": {
"block_size": 262144,
"queue_depth": 32,
"thread_count": 1,
"single_submit": false,
"overlap_events": true
},
"overlap_comm": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"sub_group_size": 1e9,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": "auto",
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 1e9,
"stage3_max_reuse_distance": 1e9,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false
}
```
## DeepSpeed features
There are a number of important parameters to specify in the DeepSpeed configuration file which are briefly described in this section.
### Activation/gradient checkpointing
Activation and gradient checkpointing trades speed for more GPU memory which allows you to overcome scenarios where your GPU is out of memory or to increase your batch size for better performance. To enable this feature:
1. For a Hugging Face model, set `model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()` or `--gradient_checkpointing` in the [`Trainer`].
2. For a non-Hugging Face model, use the DeepSpeed [Activation Checkpointing API](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/activation-checkpointing.html). You could also replace the Transformers modeling code and replace `torch.utils.checkpoint` with the DeepSpeed API. This approach is more flexible because you can offload the forward activations to the CPU memory instead of recalculating them.
### Optimizer and scheduler
DeepSpeed and Transformers optimizer and scheduler can be mixed and matched as long as you don't enable `offload_optimizer`. When `offload_optimizer` is enabled, you could use a non-DeepSpeed optimizer (except for LAMB) as long as it has both a CPU and GPU implementation.
<Tip warning={true}>
The optimizer and scheduler parameters for the config file can be set from the command line to avoid hard to find errors. For example, if the learning rate is set to a different value in another place you can override it from the command line. Aside from the optimizer and scheduler parameters, you'll need to ensure your [`Trainer`] command line arguments match the DeepSpeed configuration.
</Tip>
<hfoptions id="opt-sched">
<hfoption id="optimizer">
DeepSpeed offers several [optimizers](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#optimizer-parameters) (Adam, AdamW, OneBitAdam, and LAMB) but you can also import other optimizers from PyTorch. If you don't configure the optimizer in the config, the [`Trainer`] automatically selects AdamW and either uses the supplied values or the default values for the following parameters from the command line: `lr`, `adam_beta1`, `adam_beta2`, `adam_epsilon`, `weight_decay`.
You can set the parameters to `"auto"` or manually input your own desired values.
```yaml
{
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
}
}
```
You can also use an unsupported optimizer by adding the following to the top level configuration.
```yaml
{
"zero_allow_untested_optimizer": true
}
```
From DeepSpeed==0.8.3 on, if you want to use offload, you'll also need to the following to the top level configuration because offload works best with DeepSpeed's CPU Adam optimizer.
```yaml
{
"zero_force_ds_cpu_optimizer": false
}
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="scheduler">
DeepSpeed supports the LRRangeTest, OneCycle, WarmupLR and WarmupDecayLR learning rate [schedulers](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#scheduler-parameters).
Transformers and DeepSpeed provide two of the same schedulers:
* WarmupLR is the same as `--lr_scheduler_type constant_with_warmup` in Transformers
* WarmupDecayLR is the same as `--lr_scheduler_type linear` in Transformers (this is the default scheduler used in Transformers)
If you don't configure the scheduler in the config, the [`Trainer`] automatically selects WarmupDecayLR and either uses the supplied values or the default values for the following parameters from the command line: `warmup_min_lr`, `warmup_max_lr`, `warmup_num_steps`, `total_num_steps` (automatically calculated during run time if `max_steps` is not provided).
You can set the parameters to `"auto"` or manually input your own desired values.
```yaml
{
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupDecayLR",
"params": {
"total_num_steps": "auto",
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto"
}
}
}
```
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### Precision
Deepspeed supports fp32, fp16, and bf16 mixed precision.
<hfoptions id="precision">
<hfoption id="fp32">
If your model doesn't work well with mixed precision, for example if it wasn't pretrained in mixed precision, you may encounter overflow or underflow issues which can cause NaN loss. For these cases, you should use full fp32 precision by explicitly disabling the default fp16 mode.
```yaml
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": false
}
}
```
For Ampere GPUs and PyTorch > 1.7, it automatically switches to the more efficient [tf32](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#tensorfloat-32-tf32-on-ampere-devices) format for some operations but the results are still in fp32. You can control it from the [`Trainer`] by setting `--tf32` to enable it, and `--tf32 0` or `--no_tf32` to disable it.
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="fp16">
To configure PyTorch AMP-like fp16 mixed precision reduces memory usage and accelerates training speed. [`Trainer`] automatically enables or disables fp16 based on the value of `args.fp16_backend`, and the rest of the config can be set by you. fp16 is enabled from the command line when the following arguments are passed: `--fp16`, `--fp16_backend amp` or `--fp16_full_eval`.
```yaml
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
}
}
```
For additional DeepSpeed fp16 training options, take a look at the [FP16 Training Options](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#fp16-training-options) reference.
To configure Apex-like fp16 mixed precision, setup the config as shown below with `"auto"` or your own values. [`Trainer`] automatically configure `amp` based on the values of `args.fp16_backend` and `args.fp16_opt_level`. It can also be enabled from the command line when the following arguments are passed: `--fp16`, `--fp16_backend apex` or `--fp16_opt_level 01`.
```yaml
{
"amp": {
"enabled": "auto",
"opt_level": "auto"
}
}
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="bf16">
To use bf16, you'll need at least DeepSpeed==0.6.0. bf16 has the same dynamic range as fp32 and doesn’t require loss scaling. However, if you use [gradient accumulation](#gradient-accumulation) with bf16, gradients are accumulated in bf16 which may not be desired because this format's low precision can lead to lossy accumulation.
bf16 can be setup in the config file or enabled from the command line when the following arguments are passed: `--bf16` or `--bf16_full_eval`.
```yaml
{
"bf16": {
"enabled": "auto"
}
}
```
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### Batch size
The batch size can be auto-configured or explicitly set. If you choose to use the `"auto"` option, [`Trainer`] sets `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` to the value of args.`per_device_train_batch_size` and `train_batch_size` to `args.world_size * args.per_device_train_batch_size * args.gradient_accumulation_steps`.
```yaml
{
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"train_batch_size": "auto"
}
```
### Gradient accumulation
Gradient accumulation can be auto-configured or explicitly set. If you choose to use the `"auto"` option, [`Trainer`] sets it to the value of `args.gradient_accumulation_steps`.
```yaml
{
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto"
}
```
### Gradient clipping
Gradient clipping can be auto-configured or explicitly set. If you choose to use the `"auto"` option, [`Trainer`] sets it to the value of `args.max_grad_norm`.
```yaml
{
"gradient_clipping": "auto"
}
```
### Communication data type
For communication collectives like reduction, gathering and scattering operations, a separate data type is used.
All gather and scatter operations are performed in the same data type the data is in. For example, if you're training with bf16, the data is also gathered in bf16 because gathering is a non-lossy operation.
Reduce operations are lossy, for example when gradients are averaged across multiple GPUs. When the communication is done in fp16 or bf16, it is more likely to be lossy because adding multiple numbers in low precision isn't exact. This is especially the case with bf16 which has a lower precision than fp16. For this reason, fp16 is the default for reduction operations because the loss is minimal when averaging gradients.
You can choose the communication data type by setting the `communication_data_type` parameter in the config file. For example, choosing fp32 adds a small amount of overhead but ensures the reduction operation is accumulated in fp32 and when it is ready, it is downcasted to whichever half-precision dtype you're training in.
```yaml
{
"communication_data_type": "fp32"
}
```
### Universal Checkpointing
[Universal Checkpointing](https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/universal-checkpointing) is an efficient and flexible feature for saving and loading model checkpoints. It enables seamless model training continuation and fine-tuning across different model architectures, parallelism techniques, and training configurations.
Resume training with a universal checkpoint by setting [load_universal](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#checkpoint-options) to `true` in the config file.
```yaml
{
"checkpoint": {
"load_universal": true
}
}
```
## Deployment
DeepSpeed can be deployed by different launchers such as [torchrun](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/elastic/run.html), the `deepspeed` launcher, or [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/basic_tutorials/launch#using-accelerate-launch). To deploy, add `--deepspeed ds_config.json` to the [`Trainer`] command line. It’s recommended to use DeepSpeed’s [`add_config_arguments`](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/initialize.html#argument-parsing) utility to add any necessary command line arguments to your code.
This guide will show you how to deploy DeepSpeed with the `deepspeed` launcher for different training setups. You can check out this [post](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/8771#issuecomment-759248400) for more practical usage examples.
<hfoptions id="deploy">
<hfoption id="multi-GPU">
To deploy DeepSpeed on multiple GPUs, add the `--num_gpus` parameter. If you want to use all available GPUs, you don't need to add `--num_gpus`. The example below uses 2 GPUs.
```bash
deepspeed --num_gpus=2 examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py \
--deepspeed tests/deepspeed/ds_config_zero3.json \
--model_name_or_path google-t5/t5-small --per_device_train_batch_size 1 \
--output_dir output_dir --overwrite_output_dir --fp16 \
--do_train --max_train_samples 500 --num_train_epochs 1 \
--dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config "ro-en" \
--source_lang en --target_lang ro
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="single-GPU">
To deploy DeepSpeed on a single GPU, add the `--num_gpus` parameter. It isn't necessary to explicitly set this value if you only have 1 GPU because DeepSpeed deploys all GPUs it can see on a given node.
```bash
deepspeed --num_gpus=1 examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py \
--deepspeed tests/deepspeed/ds_config_zero2.json \
--model_name_or_path google-t5/t5-small --per_device_train_batch_size 1 \
--output_dir output_dir --overwrite_output_dir --fp16 \
--do_train --max_train_samples 500 --num_train_epochs 1 \
--dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config "ro-en" \
--source_lang en --target_lang ro
```
DeepSpeed is still useful with just 1 GPU because you can:
1. Offload some computations and memory to the CPU to make more GPU resources available to your model to use a larger batch size or fit a very large model that normally won't fit.
2. Minimize memory fragmentation with it's smart GPU memory management system which also allows you to fit bigger models and data batches.
<Tip>
Set the `allgather_bucket_size` and `reduce_bucket_size` values to 2e8 in the [ZeRO-2](#zero-configuration) configuration file to get better performance on a single GPU.
</Tip>
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### Multi-node deployment
A node is one or more GPUs for running a workload. A more powerful setup is a multi-node setup which can be launched with the `deepspeed` launcher. For this guide, let's assume there are two nodes with 8 GPUs each. The first node can be accessed `ssh hostname1` and the second node with `ssh hostname2`. Both nodes must be able to communicate with each other locally over ssh without a password.
By default, DeepSpeed expects your multi-node environment to use a shared storage. If this is not the case and each node can only see the local filesystem, you need to adjust the config file to include a [`checkpoint`](https://www.deepspeed.ai/docs/config-json/#checkpoint-options) to allow loading without access to a shared filesystem:
```yaml
{
"checkpoint": {
"use_node_local_storage": true
}
}
```
You could also use the [`Trainer`]'s `--save_on_each_node` argument to automatically add the above `checkpoint` to your config.
<hfoptions id="multinode">
<hfoption id="torchrun">
For [torchrun](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/elastic/run.html), you have to ssh to each node and run the following command on both of them. The launcher waits until both nodes are synchronized before launching the training.
```bash
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --nnode=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=hostname1 \
--master_port=9901 your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="deepspeed">
For the `deepspeed` launcher, start by creating a `hostfile`.
```bash
hostname1 slots=8
hostname2 slots=8
```
Then you can launch the training with the following command. The `deepspeed` launcher automatically launches the command on both nodes at once.
```bash
deepspeed --num_gpus 8 --num_nodes 2 --hostfile hostfile --master_addr hostname1 --master_port=9901 \
your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json
```
Check out the [Resource Configuration (multi-node)](https://www.deepspeed.ai/getting-started/#resource-configuration-multi-node) guide for more details about configuring multi-node compute resources.
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### SLURM
In a SLURM environment, you'll need to adapt your SLURM script to your specific SLURM environment. An example SLURM script may look like:
```bash
#SBATCH --job-name=test-nodes # name
#SBATCH --nodes=2 # nodes
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # crucial - only 1 task per dist per node!
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=10 # number of cores per tasks
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:8 # number of gpus
#SBATCH --time 20:00:00 # maximum execution time (HH:MM:SS)
#SBATCH --output=%x-%j.out # output file name
export GPUS_PER_NODE=8
export MASTER_ADDR=$(scontrol show hostnames $SLURM_JOB_NODELIST | head -n 1)
export MASTER_PORT=9901
srun --jobid $SLURM_JOBID bash -c 'python -m torch.distributed.run \
--nproc_per_node $GPUS_PER_NODE --nnodes $SLURM_NNODES --node_rank $SLURM_PROCID \
--master_addr $MASTER_ADDR --master_port $MASTER_PORT \
your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json'
```
Then you can schedule your multi-node deployment with the following command which launches training simultaneously on all nodes.
```bash
sbatch launch.slurm
```
### Notebook
The `deepspeed` launcher doesn't support deployment from a notebook so you'll need to emulate the distributed environment. However, this only works for 1 GPU. If you want to use more than 1 GPU, you must use a multi-process environment for DeepSpeed to work. This means you have to use the `deepspeed` launcher which can't be emulated as shown here.
```py
# DeepSpeed requires a distributed environment even when only one process is used.
# This emulates a launcher in the notebook
import os
os.environ["MASTER_ADDR"] = "localhost"
os.environ["MASTER_PORT"] = "9994" # modify if RuntimeError: Address already in use
os.environ["RANK"] = "0"
os.environ["LOCAL_RANK"] = "0"
os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"] = "1"
# Now proceed as normal, plus pass the DeepSpeed config file
training_args = TrainingArguments(..., deepspeed="ds_config_zero3.json")
trainer = Trainer(...)
trainer.train()
```
If you want to create the config file on the fly in the notebook in the current directory, you could have a dedicated cell.
```py
%%bash
cat <<'EOT' > ds_config_zero3.json
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupLR",
"params": {
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"overlap_comm": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"sub_group_size": 1e9,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": "auto",
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 1e9,
"stage3_max_reuse_distance": 1e9,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false
}
EOT
```
If the training script is in a file and not in a notebook cell, you can launch `deepspeed` normally from the shell in a notebook cell. For example, to launch `run_translation.py`:
```py
!git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
!cd transformers; deepspeed examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py ...
```
You could also use `%%bash` magic and write multi-line code to run the shell program, but you won't be able to view the logs until training is complete. With `%%bash` magic, you don't need to emulate a distributed environment.
```py
%%bash
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
cd transformers
deepspeed examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py ...
```
## Save model weights
DeepSpeed stores the main full precision fp32 weights in custom checkpoint optimizer files (the glob pattern looks like `global_step*/*optim_states.pt`) and are saved under the normal checkpoint.
<hfoptions id="save">
<hfoption id="fp16">
A model trained with ZeRO-2 saves the pytorch_model.bin weights in fp16. To save the model weights in fp16 for a model trained with ZeRO-3, you need to set `"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true` because the model weights are partitioned across multiple GPUs. Otherwise, the [`Trainer`] won't save the weights in fp16 and it won't create a pytorch_model.bin file. This is because DeepSpeed's state_dict contains a placeholder instead of the real weights and you won't be able to load them.
```yaml
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
}
}
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="fp32">
The full precision weights shouldn't be saved during training because it can require a lot of memory. It is usually best to save the fp32 weights offline after training is complete. But if you have a lot of free CPU memory, it is possible to save the fp32 weights during training. This section covers both online and offline approaches.
### Online
You must have saved at least one checkpoint to load the latest checkpoint as shown in the following:
```py
from transformers.trainer_utils import get_last_checkpoint
from deepspeed.utils.zero_to_fp32 import load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint
checkpoint_dir = get_last_checkpoint(trainer.args.output_dir)
fp32_model = load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint(trainer.model, checkpoint_dir)
```
If you've enabled the `--load_best_model_at_end` parameter to track the best checkpoint in [`TrainingArguments`], you can finish training first and save the final model explicitly. Then you can reload it as shown below:
```py
from deepspeed.utils.zero_to_fp32 import load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint
checkpoint_dir = os.path.join(trainer.args.output_dir, "checkpoint-final")
trainer.deepspeed.save_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir)
fp32_model = load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint(trainer.model, checkpoint_dir)
```
<Tip>
Once `load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint` is run, the model is no longer usable in DeepSpeed in the context of the same application. You'll need to initialize the DeepSpeed engine again since `model.load_state_dict(state_dict)` removes all the DeepSpeed magic from it. Only use this at the very end of training.
</Tip>
You can also extract and load the state_dict of the fp32 weights:
```py
from deepspeed.utils.zero_to_fp32 import get_fp32_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint
state_dict = get_fp32_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir) # already on cpu
model = model.cpu()
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
```
### Offline
DeepSpeed provides a zero_to_fp32.py script at the top-level of the checkpoint folder for extracting weights at any point. This is a standalone script and you don't need a configuration file or [`Trainer`].
For example, if your checkpoint folder looked like this:
```bash
$ ls -l output_dir/checkpoint-1/
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 1.4K Mar 27 20:42 config.json
drwxrwxr-x 2 stas stas 4.0K Mar 25 19:52 global_step1/
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 12 Mar 27 13:16 latest
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 827K Mar 27 20:42 optimizer.pt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 231M Mar 27 20:42 pytorch_model.bin
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 623 Mar 27 20:42 scheduler.pt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 1.8K Mar 27 20:42 special_tokens_map.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 774K Mar 27 20:42 spiece.model
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 1.9K Mar 27 20:42 tokenizer_config.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 339 Mar 27 20:42 trainer_state.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 stas stas 2.3K Mar 27 20:42 training_args.bin
-rwxrw-r-- 1 stas stas 5.5K Mar 27 13:16 zero_to_fp32.py*
```
To reconstruct the fp32 weights from the DeepSpeed checkpoint (ZeRO-2 or ZeRO-3) subfolder `global_step1`, run the following command to create and consolidate the full fp32 weights from multiple GPUs into a single pytorch_model.bin file. The script automatically discovers the subfolder containing the checkpoint.
```py
python zero_to_fp32.py . pytorch_model.bin
```
<Tip>
Run `python zero_to_fp32.py -h` for more usage details. The script requires 2x the general RAM of the final fp32 weights.
</Tip>
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
## ZeRO Inference
[ZeRO Inference](https://www.deepspeed.ai/2022/09/09/zero-inference.html) places the model weights in CPU or NVMe memory to avoid burdening the GPU which makes it possible to run inference with huge models on a GPU. Inference doesn't require any large additional amounts of memory for the optimizer states and gradients so you can fit much larger batches and/or sequence lengths on the same hardware.
ZeRO Inference shares the same configuration file as [ZeRO-3](#zero-configuration), and ZeRO-2 and ZeRO-1 configs won't work because they don't provide any benefits for inference.
To run ZeRO Inference, pass your usual training arguments to the [`TrainingArguments`] class and add the `--do_eval` argument.
```bash
deepspeed --num_gpus=2 your_program.py <normal cl args> --do_eval --deepspeed ds_config.json
```
## Non-Trainer DeepSpeed integration
DeepSpeed also works with Transformers without the [`Trainer`] class. This is handled by the [`HfDeepSpeedConfig`] which only takes care of gathering ZeRO-3 parameters and splitting a model across multiple GPUs when you call [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`].
<Tip>
If you want everything automatically taken care of for you, try using DeepSpeed with the [`Trainer`]! You'll need to follow the [DeepSpeed documentation](https://www.deepspeed.ai/), and manually configure the parameter values in the config file (you can't use the `"auto"` value).
</Tip>
To efficiently deploy ZeRO-3, you must instantiate the [`HfDeepSpeedConfig`] object before the model and keep that object alive:
<hfoptions id="models">
<hfoption id="pretrained model">
```py
from transformers.integrations import HfDeepSpeedConfig
from transformers import AutoModel
import deepspeed
ds_config = {...} # deepspeed config object or path to the file
# must run before instantiating the model to detect zero 3
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config) # keep this object alive
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
engine = deepspeed.initialize(model=model, config_params=ds_config, ...)
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="non-pretrained model">
[`HfDeepSpeedConfig`] is not required for ZeRO-1 or ZeRO-2.
```py
from transformers.integrations import HfDeepSpeedConfig
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoConfig
import deepspeed
ds_config = {...} # deepspeed config object or path to the file
# must run before instantiating the model to detect zero 3
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config) # keep this object alive
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
model = AutoModel.from_config(config)
engine = deepspeed.initialize(model=model, config_params=ds_config, ...)
```
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### Non-Trainer ZeRO Inference
To run ZeRO Inference without the [`Trainer`] in cases where you can’t fit a model onto a single GPU, try using additional GPUs or/and offloading to CPU memory. The important nuance to understand here is that the way ZeRO is designed, you can process different inputs on different GPUs in parallel.
Make sure to:
* disable CPU offload if you have enough GPU memory (since it slows things down).
* enable bf16 if you have an Ampere or newer GPU to make things faster. If you don’t have one of these GPUs, you may enable fp16 as long as you don’t use a model pretrained in bf16 (T5 models) because it may lead to an overflow error.
Take a look at the following script to get a better idea of how to run ZeRO Inference without the [`Trainer`] on a model that won't fit on a single GPU.
```py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# This script demonstrates how to use Deepspeed ZeRO in an inference mode when one can't fit a model
# into a single GPU
#
# 1. Use 1 GPU with CPU offload
# 2. Or use multiple GPUs instead
#
# First you need to install deepspeed: pip install deepspeed
#
# Here we use a 3B "bigscience/T0_3B" model which needs about 15GB GPU RAM - so 1 largish or 2
# small GPUs can handle it. or 1 small GPU and a lot of CPU memory.
#
# To use a larger model like "bigscience/T0" which needs about 50GB, unless you have an 80GB GPU -
# you will need 2-4 gpus. And then you can adapt the script to handle more gpus if you want to
# process multiple inputs at once.
#
# The provided deepspeed config also activates CPU memory offloading, so chances are that if you
# have a lot of available CPU memory and you don't mind a slowdown you should be able to load a
# model that doesn't normally fit into a single GPU. If you have enough GPU memory the program will
# run faster if you don't want offload to CPU - so disable that section then.
#
# To deploy on 1 gpu:
#
# deepspeed --num_gpus 1 t0.py
# or:
# python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node=1 t0.py
#
# To deploy on 2 gpus:
#
# deepspeed --num_gpus 2 t0.py
# or:
# python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node=2 t0.py
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoConfig, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
from transformers.integrations import HfDeepSpeedConfig
import deepspeed
import os
import torch
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # To avoid warnings about parallelism in tokenizers
# distributed setup
local_rank = int(os.getenv("LOCAL_RANK", "0"))
world_size = int(os.getenv("WORLD_SIZE", "1"))
torch.cuda.set_device(local_rank)
deepspeed.init_distributed()
model_name = "bigscience/T0_3B"
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name)
model_hidden_size = config.d_model
# batch size has to be divisible by world_size, but can be bigger than world_size
train_batch_size = 1 * world_size
# ds_config notes
#
# - enable bf16 if you use Ampere or higher GPU - this will run in mixed precision and will be
# faster.
#
# - for older GPUs you can enable fp16, but it'll only work for non-bf16 pretrained models - e.g.
# all official t5 models are bf16-pretrained
#
# - set offload_param.device to "none" or completely remove the `offload_param` section if you don't
# - want CPU offload
#
# - if using `offload_param` you can manually finetune stage3_param_persistence_threshold to control
# - which params should remain on gpus - the larger the value the smaller the offload size
#
# For in-depth info on Deepspeed config see
# https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/main_classes/deepspeed
# keeping the same format as json for consistency, except it uses lower case for true/false
# fmt: off
ds_config = {
"fp16": {
"enabled": False
},
"bf16": {
"enabled": False
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": True
},
"overlap_comm": True,
"contiguous_gradients": True,
"reduce_bucket_size": model_hidden_size * model_hidden_size,
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 0.9 * model_hidden_size * model_hidden_size,
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 10 * model_hidden_size
},
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": train_batch_size,
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": 1,
"wall_clock_breakdown": False
}
# fmt: on
# next line instructs transformers to partition the model directly over multiple gpus using
# deepspeed.zero.Init when model's `from_pretrained` method is called.
#
# **it has to be run before loading the model AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)**
#
# otherwise the model will first be loaded normally and only partitioned at forward time which is
# less efficient and when there is little CPU RAM may fail
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config) # keep this object alive
# now a model can be loaded.
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
# initialise Deepspeed ZeRO and store only the engine object
ds_engine = deepspeed.initialize(model=model, config_params=ds_config)[0]
ds_engine.module.eval() # inference
# Deepspeed ZeRO can process unrelated inputs on each GPU. So for 2 gpus you process 2 inputs at once.
# If you use more GPUs adjust for more.
# And of course if you have just one input to process you then need to pass the same string to both gpus
# If you use only one GPU, then you will have only rank 0.
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
if rank == 0:
text_in = "Is this review positive or negative? Review: this is the best cast iron skillet you will ever buy"
elif rank == 1:
text_in = "Is this review positive or negative? Review: this is the worst restaurant ever"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
inputs = tokenizer.encode(text_in, return_tensors="pt").to(device=local_rank)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = ds_engine.module.generate(inputs, synced_gpus=True)
text_out = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"rank{rank}:\n in={text_in}\n out={text_out}")
```
Save the script as t0.py and launch it:
```bash
$ deepspeed --num_gpus 2 t0.py
rank0:
in=Is this review positive or negative? Review: this is the best cast iron skillet you will ever buy
out=Positive
rank1:
in=Is this review positive or negative? Review: this is the worst restaurant ever
out=negative
```
This is a very basic example and you'll want to adapt it to your use case.
### Generate
Using multiple GPUs with ZeRO-3 for generation requires synchronizing the GPUs by setting `synced_gpus=True` in the [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] method. Otherwise, if one GPU is finished generating before another one, the whole system hangs because the remaining GPUs haven't received the weight shard from the GPU that finished first.
For Transformers>=4.28, if `synced_gpus` is automatically set to `True` if multiple GPUs are detected during generation.
## Troubleshoot
When you encounter an issue, you should consider whether DeepSpeed is the cause of the problem because often it isn't (unless it's super obviously and you can see DeepSpeed modules in the exception)! The first step should be to retry your setup without DeepSpeed, and if the problem persists, then you can report the issue. If the issue is a core DeepSpeed problem and unrelated to the Transformers integration, open an Issue on the [DeepSpeed repository](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed).
For issues related to the Transformers integration, please provide the following information:
* the full DeepSpeed config file
* the command line arguments of the [`Trainer`], or [`TrainingArguments`] arguments if you're scripting the [`Trainer`] setup yourself (don't dump the [`TrainingArguments`] which has dozens of irrelevant entries)
* the outputs of:
```bash
python -c 'import torch; print(f"torch: {torch.__version__}")'
python -c 'import transformers; print(f"transformers: {transformers.__version__}")'
python -c 'import deepspeed; print(f"deepspeed: {deepspeed.__version__}")'
```
* a link to a Google Colab notebook to reproduce the issue
* if impossible, a standard and non-custom dataset we can use and also try to use an existing example to reproduce the issue with
The following sections provide a guide for resolving two of the most common issues.
### DeepSpeed process killed at startup
When the DeepSpeed process is killed during launch without a traceback, that usually means the program tried to allocate more CPU memory than your system has or your process tried to allocate more CPU memory than allowed leading the OS kernel to terminate the process. In this case, check whether your configuration file has either `offload_optimizer`, `offload_param` or both configured to offload to the CPU.
If you have NVMe and ZeRO-3 setup, experiment with offloading to the NVMe ([estimate](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/memory.html) the memory requirements for your model).
### NaN loss
NaN loss often occurs when a model is pretrained in bf16 and then you try to use it with fp16 (especially relevant for TPU trained models). To resolve this, use fp32 or bf16 if your hardware supports it (TPU, Ampere GPUs or newer).
The other issue may be related to using fp16. For example, if this is your fp16 configuration:
```yaml
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
}
}
```
You might see the following `OVERFLOW!` messages in the logs:
```bash
0%| | 0/189 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
[deepscale] OVERFLOW! Rank 0 Skipping step. Attempted loss scale: 262144, reducing to 262144
1%|▌ | 1/189 [00:00<01:26, 2.17it/s]
[deepscale] OVERFLOW! Rank 0 Skipping step. Attempted loss scale: 262144, reducing to 131072.0
1%|█▏
[...]
[deepscale] OVERFLOW! Rank 0 Skipping step. Attempted loss scale: 1, reducing to 1
14%|████████████████▌ | 27/189 [00:14<01:13, 2.21it/s]
[deepscale] OVERFLOW! Rank 0 Skipping step. Attempted loss scale: 1, reducing to 1
15%|█████████████████▏ | 28/189 [00:14<01:13, 2.18it/s]
[deepscale] OVERFLOW! Rank 0 Skipping step. Attempted loss scale: 1, reducing to 1
15%|█████████████████▊ | 29/189 [00:15<01:13, 2.18it/s]
[deepscale] OVERFLOW! Rank 0 Skipping step. Attempted loss scale: 1, reducing to 1
[...]
```
This means the DeepSpeed loss scaler is unable to find a scaling coefficient to overcome loss overflow. To fix it, try a higher `initial_scale_power` value (32 usually works).
## Resources
DeepSpeed ZeRO is a powerful technology for training and loading very large models for inference with limited GPU resources, making it more accessible to everyone. To learn more about DeepSpeed, feel free to read the [blog posts](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/search/?q=deepspeed), [documentation](https://www.deepspeed.ai/getting-started/), and [GitHub repository](https://github.com/microsoft/deepspeed).
The following papers are also a great resource for learning more about ZeRO:
* [ZeRO: Memory Optimizations Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models](https://hf.co/papers/1910.02054)
* [ZeRO-Offload: Democratizing Billion-Scale Model Training](https://hf.co/papers/2101.06840)
* [ZeRO-Infinity: Breaking the GPU Memory Wall for Extreme Scale Deep Learning](https://hf.co/papers/2104.07857)
|
transformers/docs/source/en/deepspeed.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/deepspeed.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 18914
}
| 9 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Audio Spectrogram Transformer
## Overview
The Audio Spectrogram Transformer model was proposed in [AST: Audio Spectrogram Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01778) by Yuan Gong, Yu-An Chung, James Glass.
The Audio Spectrogram Transformer applies a [Vision Transformer](vit) to audio, by turning audio into an image (spectrogram). The model obtains state-of-the-art results
for audio classification.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*In the past decade, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely adopted as the main building block for end-to-end audio classification models, which aim to learn a direct mapping from audio spectrograms to corresponding labels. To better capture long-range global context, a recent trend is to add a self-attention mechanism on top of the CNN, forming a CNN-attention hybrid model. However, it is unclear whether the reliance on a CNN is necessary, and if neural networks purely based on attention are sufficient to obtain good performance in audio classification. In this paper, we answer the question by introducing the Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST), the first convolution-free, purely attention-based model for audio classification. We evaluate AST on various audio classification benchmarks, where it achieves new state-of-the-art results of 0.485 mAP on AudioSet, 95.6% accuracy on ESC-50, and 98.1% accuracy on Speech Commands V2.*
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/audio_spectogram_transformer_architecture.png"
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
<small> Audio Spectrogram Transformer architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01778">original paper</a>.</small>
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr).
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/YuanGongND/ast).
## Usage tips
- When fine-tuning the Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) on your own dataset, it's recommended to take care of the input normalization (to make
sure the input has mean of 0 and std of 0.5). [`ASTFeatureExtractor`] takes care of this. Note that it uses the AudioSet
mean and std by default. You can check [`ast/src/get_norm_stats.py`](https://github.com/YuanGongND/ast/blob/master/src/get_norm_stats.py) to see how
the authors compute the stats for a downstream dataset.
- Note that the AST needs a low learning rate (the authors use a 10 times smaller learning rate compared to their CNN model proposed in the
[PSLA paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.01243)) and converges quickly, so please search for a suitable learning rate and learning rate scheduler for your task.
### Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
page for more information.
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
```
from transformers import ASTForAudioClassification
model = ASTForAudioClassification.from_pretrained("MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
...
```
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
On a local benchmark (A100-40GB, PyTorch 2.3.0, OS Ubuntu 22.04) with `float32` and `MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593` model, we saw the following speedups during inference.
| Batch size | Average inference time (ms), eager mode | Average inference time (ms), sdpa model | Speed up, Sdpa / Eager (x) |
|--------------|-------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------|------------------------------|
| 1 | 27 | 6 | 4.5 |
| 2 | 12 | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | 21 | 8 | 2.62 |
| 8 | 40 | 14 | 2.86 |
## Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with the Audio Spectrogram Transformer.
<PipelineTag pipeline="audio-classification"/>
- A notebook illustrating inference with AST for audio classification can be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/AST).
- [`ASTForAudioClassification`] is supported by this [example script](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/audio-classification) and [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/audio_classification.ipynb).
- See also: [Audio classification](../tasks/audio_classification).
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
## ASTConfig
[[autodoc]] ASTConfig
## ASTFeatureExtractor
[[autodoc]] ASTFeatureExtractor
- __call__
## ASTModel
[[autodoc]] ASTModel
- forward
## ASTForAudioClassification
[[autodoc]] ASTForAudioClassification
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2176
}
| 10 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Big Transfer (BiT)
## Overview
The BiT model was proposed in [Big Transfer (BiT): General Visual Representation Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.11370) by Alexander Kolesnikov, Lucas Beyer, Xiaohua Zhai, Joan Puigcerver, Jessica Yung, Sylvain Gelly, Neil Houlsby.
BiT is a simple recipe for scaling up pre-training of [ResNet](resnet)-like architectures (specifically, ResNetv2). The method results in significant improvements for transfer learning.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Transfer of pre-trained representations improves sample efficiency and simplifies hyperparameter tuning when training deep neural networks for vision. We revisit the paradigm of pre-training on large supervised datasets and fine-tuning the model on a target task. We scale up pre-training, and propose a simple recipe that we call Big Transfer (BiT). By combining a few carefully selected components, and transferring using a simple heuristic, we achieve strong performance on over 20 datasets. BiT performs well across a surprisingly wide range of data regimes -- from 1 example per class to 1M total examples. BiT achieves 87.5% top-1 accuracy on ILSVRC-2012, 99.4% on CIFAR-10, and 76.3% on the 19 task Visual Task Adaptation Benchmark (VTAB). On small datasets, BiT attains 76.8% on ILSVRC-2012 with 10 examples per class, and 97.0% on CIFAR-10 with 10 examples per class. We conduct detailed analysis of the main components that lead to high transfer performance.*
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr).
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/google-research/big_transfer).
## Usage tips
- BiT models are equivalent to ResNetv2 in terms of architecture, except that: 1) all batch normalization layers are replaced by [group normalization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08494),
2) [weight standardization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.10520) is used for convolutional layers. The authors show that the combination of both is useful for training with large batch sizes, and has a significant
impact on transfer learning.
## Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with BiT.
<PipelineTag pipeline="image-classification"/>
- [`BitForImageClassification`] is supported by this [example script](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/image-classification) and [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb).
- See also: [Image classification task guide](../tasks/image_classification)
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
## BitConfig
[[autodoc]] BitConfig
## BitImageProcessor
[[autodoc]] BitImageProcessor
- preprocess
## BitModel
[[autodoc]] BitModel
- forward
## BitForImageClassification
[[autodoc]] BitForImageClassification
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/bit.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/bit.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1005
}
| 11 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# CLIPSeg
## Overview
The CLIPSeg model was proposed in [Image Segmentation Using Text and Image Prompts](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10003) by Timo Lüddecke
and Alexander Ecker. CLIPSeg adds a minimal decoder on top of a frozen [CLIP](clip) model for zero-shot and one-shot image segmentation.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Image segmentation is usually addressed by training a
model for a fixed set of object classes. Incorporating additional classes or more complex queries later is expensive
as it requires re-training the model on a dataset that encompasses these expressions. Here we propose a system
that can generate image segmentations based on arbitrary
prompts at test time. A prompt can be either a text or an
image. This approach enables us to create a unified model
(trained once) for three common segmentation tasks, which
come with distinct challenges: referring expression segmentation, zero-shot segmentation and one-shot segmentation.
We build upon the CLIP model as a backbone which we extend with a transformer-based decoder that enables dense
prediction. After training on an extended version of the
PhraseCut dataset, our system generates a binary segmentation map for an image based on a free-text prompt or on
an additional image expressing the query. We analyze different variants of the latter image-based prompts in detail.
This novel hybrid input allows for dynamic adaptation not
only to the three segmentation tasks mentioned above, but
to any binary segmentation task where a text or image query
can be formulated. Finally, we find our system to adapt well
to generalized queries involving affordances or properties*
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/clipseg_architecture.png"
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
<small> CLIPSeg overview. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10003">original paper.</a> </small>
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr).
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/timojl/clipseg).
## Usage tips
- [`CLIPSegForImageSegmentation`] adds a decoder on top of [`CLIPSegModel`]. The latter is identical to [`CLIPModel`].
- [`CLIPSegForImageSegmentation`] can generate image segmentations based on arbitrary prompts at test time. A prompt can be either a text
(provided to the model as `input_ids`) or an image (provided to the model as `conditional_pixel_values`). One can also provide custom
conditional embeddings (provided to the model as `conditional_embeddings`).
## Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with CLIPSeg. If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
<PipelineTag pipeline="image-segmentation"/>
- A notebook that illustrates [zero-shot image segmentation with CLIPSeg](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/CLIPSeg/Zero_shot_image_segmentation_with_CLIPSeg.ipynb).
## CLIPSegConfig
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegConfig
- from_text_vision_configs
## CLIPSegTextConfig
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegTextConfig
## CLIPSegVisionConfig
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegVisionConfig
## CLIPSegProcessor
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegProcessor
## CLIPSegModel
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegModel
- forward
- get_text_features
- get_image_features
## CLIPSegTextModel
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegTextModel
- forward
## CLIPSegVisionModel
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegVisionModel
- forward
## CLIPSegForImageSegmentation
[[autodoc]] CLIPSegForImageSegmentation
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/clipseg.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/clipseg.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1222
}
| 12 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Data2Vec
## Overview
The Data2Vec model was proposed in [data2vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu and Michael Auli.
Data2Vec proposes a unified framework for self-supervised learning across different data modalities - text, audio and images.
Importantly, predicted targets for pre-training are contextualized latent representations of the inputs, rather than modality-specific, context-independent targets.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*While the general idea of self-supervised learning is identical across modalities, the actual algorithms and
objectives differ widely because they were developed with a single modality in mind. To get us closer to general
self-supervised learning, we present data2vec, a framework that uses the same learning method for either speech,
NLP or computer vision. The core idea is to predict latent representations of the full input data based on a
masked view of the input in a selfdistillation setup using a standard Transformer architecture.
Instead of predicting modality-specific targets such as words, visual tokens or units of human speech which
are local in nature, data2vec predicts contextualized latent representations that contain information from
the entire input. Experiments on the major benchmarks of speech recognition, image classification, and
natural language understanding demonstrate a new state of the art or competitive performance to predominant approaches.
Models and code are available at www.github.com/pytorch/fairseq/tree/master/examples/data2vec.*
This model was contributed by [edugp](https://huggingface.co/edugp) and [patrickvonplaten](https://huggingface.co/patrickvonplaten).
[sayakpaul](https://github.com/sayakpaul) and [Rocketknight1](https://github.com/Rocketknight1) contributed Data2Vec for vision in TensorFlow.
The original code (for NLP and Speech) can be found [here](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/tree/main/examples/data2vec).
The original code for vision can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/data2vec_vision/tree/main/beit).
## Usage tips
- Data2VecAudio, Data2VecText, and Data2VecVision have all been trained using the same self-supervised learning method.
- For Data2VecAudio, preprocessing is identical to [`Wav2Vec2Model`], including feature extraction
- For Data2VecText, preprocessing is identical to [`RobertaModel`], including tokenization.
- For Data2VecVision, preprocessing is identical to [`BeitModel`], including feature extraction.
### Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
page for more information.
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
The SDPA implementation is currently available for the Data2VecAudio and Data2VecVision models.
```
from transformers import Data2VecVisionForImageClassification
model = Data2VecVisionForImageClassification.from_pretrained("facebook/data2vec-vision-base", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
...
```
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
For the Data2VecVision model, on a local benchmark (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060-8GB, PyTorch 2.5.1, OS Ubuntu 20.04)
with `float16` and `facebook/data2vec-vision-base` model, we saw the following improvements during training and
inference:
#### Training
| num_training_steps | batch_size | image_size | is_cuda | Time per batch (eager - s) | Time per batch (sdpa - s) | Speedup (%) | Eager peak mem (MB) | SDPA peak mem (MB) | Mem saving (%) |
|--------------------|------------|--------------|---------|----------------------------|---------------------------|-------------|----------------------|--------------------|----------------|
| 50 | 2 | (1048, 640) | True | 0.996 | 0.754 | 32.147 | 6722.198 | 4264.653 | 57.626 |
#### Inference
| Image batch size | Eager (s/iter) | Eager CI, % | Eager memory (MB) | SDPA (s/iter) | SDPA CI, % | SDPA memory (MB) | SDPA speedup | SDPA memory saved |
|-------------------:|-----------------:|:--------------|--------------------:|----------------:|:-------------|-------------------:|---------------:|--------------------:|
| 1 | 0.011 | ±0.3% | 3.76143e+08 | 0.01 | ±0.3% | 3.74397e+08 | 1.101 | 0.466 |
| 4 | 0.014 | ±0.1% | 4.02756e+08 | 0.012 | ±0.2% | 3.91373e+08 | 1.219 | 2.909 |
| 16 | 0.046 | ±0.3% | 4.96482e+08 | 0.035 | ±0.2% | 4.51017e+08 | 1.314 | 10.081 |
| 32 | 0.088 | ±0.1% | 6.23903e+08 | 0.067 | ±0.1% | 5.32974e+08 | 1.33 | 17.061 |
## Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with Data2Vec.
<PipelineTag pipeline="image-classification"/>
- [`Data2VecVisionForImageClassification`] is supported by this [example script](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/image-classification) and [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb).
- To fine-tune [`TFData2VecVisionForImageClassification`] on a custom dataset, see [this notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sayakpaul/TF-2.0-Hacks/blob/master/data2vec_vision_image_classification.ipynb).
**Data2VecText documentation resources**
- [Text classification task guide](../tasks/sequence_classification)
- [Token classification task guide](../tasks/token_classification)
- [Question answering task guide](../tasks/question_answering)
- [Causal language modeling task guide](../tasks/language_modeling)
- [Masked language modeling task guide](../tasks/masked_language_modeling)
- [Multiple choice task guide](../tasks/multiple_choice)
**Data2VecAudio documentation resources**
- [Audio classification task guide](../tasks/audio_classification)
- [Automatic speech recognition task guide](../tasks/asr)
**Data2VecVision documentation resources**
- [Image classification](../tasks/image_classification)
- [Semantic segmentation](../tasks/semantic_segmentation)
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
## Data2VecTextConfig
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextConfig
## Data2VecAudioConfig
[[autodoc]] Data2VecAudioConfig
## Data2VecVisionConfig
[[autodoc]] Data2VecVisionConfig
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
## Data2VecAudioModel
[[autodoc]] Data2VecAudioModel
- forward
## Data2VecAudioForAudioFrameClassification
[[autodoc]] Data2VecAudioForAudioFrameClassification
- forward
## Data2VecAudioForCTC
[[autodoc]] Data2VecAudioForCTC
- forward
## Data2VecAudioForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] Data2VecAudioForSequenceClassification
- forward
## Data2VecAudioForXVector
[[autodoc]] Data2VecAudioForXVector
- forward
## Data2VecTextModel
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextModel
- forward
## Data2VecTextForCausalLM
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextForCausalLM
- forward
## Data2VecTextForMaskedLM
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextForMaskedLM
- forward
## Data2VecTextForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextForSequenceClassification
- forward
## Data2VecTextForMultipleChoice
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextForMultipleChoice
- forward
## Data2VecTextForTokenClassification
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextForTokenClassification
- forward
## Data2VecTextForQuestionAnswering
[[autodoc]] Data2VecTextForQuestionAnswering
- forward
## Data2VecVisionModel
[[autodoc]] Data2VecVisionModel
- forward
## Data2VecVisionForImageClassification
[[autodoc]] Data2VecVisionForImageClassification
- forward
## Data2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation
[[autodoc]] Data2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation
- forward
</pt>
<tf>
## TFData2VecVisionModel
[[autodoc]] TFData2VecVisionModel
- call
## TFData2VecVisionForImageClassification
[[autodoc]] TFData2VecVisionForImageClassification
- call
## TFData2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation
[[autodoc]] TFData2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation
- call
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/data2vec.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/data2vec.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3372
}
| 13 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
-->
# DINOv2 with Registers
## Overview
The DINOv2 with Registers model was proposed in [Vision Transformers Need Registers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.16588) by Timothée Darcet, Maxime Oquab, Julien Mairal, Piotr Bojanowski.
The [Vision Transformer](vit) (ViT) is a transformer encoder model (BERT-like) originally introduced to do supervised image classification on ImageNet.
Next, people figured out ways to make ViT work really well on self-supervised image feature extraction (i.e. learning meaningful features, also called embeddings) on images without requiring any labels. Some example papers here include [DINOv2](dinov2) and [MAE](vit_mae).
The authors of DINOv2 noticed that ViTs have artifacts in attention maps. It’s due to the model using some image patches as “registers”. The authors propose a fix: just add some new tokens (called "register" tokens), which you only use during pre-training (and throw away afterwards). This results in:
- no artifacts
- interpretable attention maps
- and improved performances.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Transformers have recently emerged as a powerful tool for learning visual representations. In this paper, we identify and characterize artifacts in feature maps of both supervised and self-supervised ViT networks. The artifacts correspond to high-norm tokens appearing during inference primarily in low-informative background areas of images, that are repurposed for internal computations. We propose a simple yet effective solution based on providing additional tokens to the input sequence of the Vision Transformer to fill that role. We show that this solution fixes that problem entirely for both supervised and self-supervised models, sets a new state of the art for self-supervised visual models on dense visual prediction tasks, enables object discovery methods with larger models, and most importantly leads to smoother feature maps and attention maps for downstream visual processing.*
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/dinov2_with_registers_visualization.png"
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
<small> Visualization of attention maps of various models trained with vs. without registers. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.16588">original paper</a>. </small>
Tips:
- Usage of DINOv2 with Registers is identical to DINOv2 without, you'll just get better performance.
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr).
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2).
## Dinov2WithRegistersConfig
[[autodoc]] Dinov2WithRegistersConfig
## Dinov2WithRegistersModel
[[autodoc]] Dinov2WithRegistersModel
- forward
## Dinov2WithRegistersForImageClassification
[[autodoc]] Dinov2WithRegistersForImageClassification
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/dinov2_with_registers.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/dinov2_with_registers.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 875
}
| 14 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Falcon3
## Overview
Falcon3 represents a natural evolution from previous releases, emphasizing expanding the models' science, math, and code capabilities. This iteration includes five base models: Falcon3-1B-Base, Falcon3-3B-Base, Falcon3-Mamba-7B-Base, Falcon3-7B-Base, and Falcon3-10B-Base. In developing these models, we incorporated several key innovations aimed at improving the models' performances while reducing training costs:
One pre-training: We conducted a single large-scale pretraining run on the 7B model, using 2048 H100 GPU chips, leveraging 14 trillion tokens featuring web, code, STEM, and curated high-quality and multilingual data.
Depth up-scaling for improved reasoning: Building on recent studies on the effects of model depth, we upscaled the 7B model to a 10B parameters model by duplicating the redundant layers and continuing pre-training with 2TT of high-quality data. This yielded Falcon3-10B-Base which achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot and few-shot performance for models under 13B parameters.
Knowledge distillation for better tiny models: To provide compact and efficient alternatives, we developed Falcon3-1B-Base and Falcon3-3B-Base by leveraging pruning and knowledge distillation techniques, using less than 100GT of curated high-quality data, thereby redefining pre-training efficiency.
## Resources
- [Blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/falcon3)
- [Models on Huggingface](https://huggingface.co/collections/tiiuae/falcon3-67605ae03578be86e4e87026)
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/falcon3.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/falcon3.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 564
}
| 15 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# HerBERT
## Overview
The HerBERT model was proposed in [KLEJ: Comprehensive Benchmark for Polish Language Understanding](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.acl-main.111.pdf) by Piotr Rybak, Robert Mroczkowski, Janusz Tracz, and
Ireneusz Gawlik. It is a BERT-based Language Model trained on Polish Corpora using only MLM objective with dynamic
masking of whole words.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*In recent years, a series of Transformer-based models unlocked major improvements in general natural language
understanding (NLU) tasks. Such a fast pace of research would not be possible without general NLU benchmarks, which
allow for a fair comparison of the proposed methods. However, such benchmarks are available only for a handful of
languages. To alleviate this issue, we introduce a comprehensive multi-task benchmark for the Polish language
understanding, accompanied by an online leaderboard. It consists of a diverse set of tasks, adopted from existing
datasets for named entity recognition, question-answering, textual entailment, and others. We also introduce a new
sentiment analysis task for the e-commerce domain, named Allegro Reviews (AR). To ensure a common evaluation scheme and
promote models that generalize to different NLU tasks, the benchmark includes datasets from varying domains and
applications. Additionally, we release HerBERT, a Transformer-based model trained specifically for the Polish language,
which has the best average performance and obtains the best results for three out of nine tasks. Finally, we provide an
extensive evaluation, including several standard baselines and recently proposed, multilingual Transformer-based
models.*
This model was contributed by [rmroczkowski](https://huggingface.co/rmroczkowski). The original code can be found
[here](https://github.com/allegro/HerBERT).
## Usage example
```python
>>> from transformers import HerbertTokenizer, RobertaModel
>>> tokenizer = HerbertTokenizer.from_pretrained("allegro/herbert-klej-cased-tokenizer-v1")
>>> model = RobertaModel.from_pretrained("allegro/herbert-klej-cased-v1")
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer.encode("Kto ma lepszą sztukę, ma lepszy rząd – to jasne.", return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(encoded_input)
>>> # HerBERT can also be loaded using AutoTokenizer and AutoModel:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("allegro/herbert-klej-cased-tokenizer-v1")
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("allegro/herbert-klej-cased-v1")
```
<Tip>
Herbert implementation is the same as `BERT` except for the tokenization method. Refer to [BERT documentation](bert)
for API reference and examples.
</Tip>
## HerbertTokenizer
[[autodoc]] HerbertTokenizer
## HerbertTokenizerFast
[[autodoc]] HerbertTokenizerFast
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/herbert.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/herbert.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 956
}
| 16 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# LayoutLM
<a id='Overview'></a>
## Overview
The LayoutLM model was proposed in the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image
Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, and
Ming Zhou. It's a simple but effective pretraining method of text and layout for document image understanding and
information extraction tasks, such as form understanding and receipt understanding. It obtains state-of-the-art results
on several downstream tasks:
- form understanding: the [FUNSD](https://guillaumejaume.github.io/FUNSD/) dataset (a collection of 199 annotated
forms comprising more than 30,000 words).
- receipt understanding: the [SROIE](https://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=13) dataset (a collection of 626 receipts for
training and 347 receipts for testing).
- document image classification: the [RVL-CDIP](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~aharley/rvl-cdip/) dataset (a collection of
400,000 images belonging to one of 16 classes).
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Pre-training techniques have been verified successfully in a variety of NLP tasks in recent years. Despite the
widespread use of pretraining models for NLP applications, they almost exclusively focus on text-level manipulation,
while neglecting layout and style information that is vital for document image understanding. In this paper, we propose
the LayoutLM to jointly model interactions between text and layout information across scanned document images, which is
beneficial for a great number of real-world document image understanding tasks such as information extraction from
scanned documents. Furthermore, we also leverage image features to incorporate words' visual information into LayoutLM.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that text and layout are jointly learned in a single framework for
document-level pretraining. It achieves new state-of-the-art results in several downstream tasks, including form
understanding (from 70.72 to 79.27), receipt understanding (from 94.02 to 95.24) and document image classification
(from 93.07 to 94.42).*
## Usage tips
- In addition to *input_ids*, [`~transformers.LayoutLMModel.forward`] also expects the input `bbox`, which are
the bounding boxes (i.e. 2D-positions) of the input tokens. These can be obtained using an external OCR engine such
as Google's [Tesseract](https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract) (there's a [Python wrapper](https://pypi.org/project/pytesseract/) available). Each bounding box should be in (x0, y0, x1, y1) format, where
(x0, y0) corresponds to the position of the upper left corner in the bounding box, and (x1, y1) represents the
position of the lower right corner. Note that one first needs to normalize the bounding boxes to be on a 0-1000
scale. To normalize, you can use the following function:
```python
def normalize_bbox(bbox, width, height):
return [
int(1000 * (bbox[0] / width)),
int(1000 * (bbox[1] / height)),
int(1000 * (bbox[2] / width)),
int(1000 * (bbox[3] / height)),
]
```
Here, `width` and `height` correspond to the width and height of the original document in which the token
occurs. Those can be obtained using the Python Image Library (PIL) library for example, as follows:
```python
from PIL import Image
# Document can be a png, jpg, etc. PDFs must be converted to images.
image = Image.open(name_of_your_document).convert("RGB")
width, height = image.size
```
## Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with LayoutLM. If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
<PipelineTag pipeline="document-question-answering" />
- A blog post on [fine-tuning
LayoutLM for document-understanding using Keras & Hugging Face
Transformers](https://www.philschmid.de/fine-tuning-layoutlm-keras).
- A blog post on how to [fine-tune LayoutLM for document-understanding using only Hugging Face Transformers](https://www.philschmid.de/fine-tuning-layoutlm).
- A notebook on how to [fine-tune LayoutLM on the FUNSD dataset with image embeddings](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Add_image_embeddings_to_LayoutLM.ipynb).
- See also: [Document question answering task guide](../tasks/document_question_answering)
<PipelineTag pipeline="text-classification" />
- A notebook on how to [fine-tune LayoutLM for sequence classification on the RVL-CDIP dataset](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb).
- [Text classification task guide](../tasks/sequence_classification)
<PipelineTag pipeline="token-classification" />
- A notebook on how to [ fine-tune LayoutLM for token classification on the FUNSD dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb).
- [Token classification task guide](../tasks/token_classification)
**Other resources**
- [Masked language modeling task guide](../tasks/masked_language_modeling)
🚀 Deploy
- A blog post on how to [Deploy LayoutLM with Hugging Face Inference Endpoints](https://www.philschmid.de/inference-endpoints-layoutlm).
## LayoutLMConfig
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMConfig
## LayoutLMTokenizer
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMTokenizer
## LayoutLMTokenizerFast
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMTokenizerFast
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
## LayoutLMModel
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMModel
## LayoutLMForMaskedLM
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMForMaskedLM
## LayoutLMForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMForSequenceClassification
## LayoutLMForTokenClassification
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMForTokenClassification
## LayoutLMForQuestionAnswering
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMForQuestionAnswering
</pt>
<tf>
## TFLayoutLMModel
[[autodoc]] TFLayoutLMModel
## TFLayoutLMForMaskedLM
[[autodoc]] TFLayoutLMForMaskedLM
## TFLayoutLMForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] TFLayoutLMForSequenceClassification
## TFLayoutLMForTokenClassification
[[autodoc]] TFLayoutLMForTokenClassification
## TFLayoutLMForQuestionAnswering
[[autodoc]] TFLayoutLMForQuestionAnswering
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/layoutlm.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/layoutlm.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2088
}
| 17 |
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# LUKE
## Overview
The LUKE model was proposed in [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda and Yuji Matsumoto.
It is based on RoBERTa and adds entity embeddings as well as an entity-aware self-attention mechanism, which helps
improve performance on various downstream tasks involving reasoning about entities such as named entity recognition,
extractive and cloze-style question answering, entity typing, and relation classification.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Entity representations are useful in natural language tasks involving entities. In this paper, we propose new
pretrained contextualized representations of words and entities based on the bidirectional transformer. The proposed
model treats words and entities in a given text as independent tokens, and outputs contextualized representations of
them. Our model is trained using a new pretraining task based on the masked language model of BERT. The task involves
predicting randomly masked words and entities in a large entity-annotated corpus retrieved from Wikipedia. We also
propose an entity-aware self-attention mechanism that is an extension of the self-attention mechanism of the
transformer, and considers the types of tokens (words or entities) when computing attention scores. The proposed model
achieves impressive empirical performance on a wide range of entity-related tasks. In particular, it obtains
state-of-the-art results on five well-known datasets: Open Entity (entity typing), TACRED (relation classification),
CoNLL-2003 (named entity recognition), ReCoRD (cloze-style question answering), and SQuAD 1.1 (extractive question
answering).*
This model was contributed by [ikuyamada](https://huggingface.co/ikuyamada) and [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke).
## Usage tips
- This implementation is the same as [`RobertaModel`] with the addition of entity embeddings as well
as an entity-aware self-attention mechanism, which improves performance on tasks involving reasoning about entities.
- LUKE treats entities as input tokens; therefore, it takes `entity_ids`, `entity_attention_mask`,
`entity_token_type_ids` and `entity_position_ids` as extra input. You can obtain those using
[`LukeTokenizer`].
- [`LukeTokenizer`] takes `entities` and `entity_spans` (character-based start and end
positions of the entities in the input text) as extra input. `entities` typically consist of [MASK] entities or
Wikipedia entities. The brief description when inputting these entities are as follows:
- *Inputting [MASK] entities to compute entity representations*: The [MASK] entity is used to mask entities to be
predicted during pretraining. When LUKE receives the [MASK] entity, it tries to predict the original entity by
gathering the information about the entity from the input text. Therefore, the [MASK] entity can be used to address
downstream tasks requiring the information of entities in text such as entity typing, relation classification, and
named entity recognition.
- *Inputting Wikipedia entities to compute knowledge-enhanced token representations*: LUKE learns rich information
(or knowledge) about Wikipedia entities during pretraining and stores the information in its entity embedding. By
using Wikipedia entities as input tokens, LUKE outputs token representations enriched by the information stored in
the embeddings of these entities. This is particularly effective for tasks requiring real-world knowledge, such as
question answering.
- There are three head models for the former use case:
- [`LukeForEntityClassification`], for tasks to classify a single entity in an input text such as
entity typing, e.g. the [Open Entity dataset](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~eunsol/html_pages/open_entity.html).
This model places a linear head on top of the output entity representation.
- [`LukeForEntityPairClassification`], for tasks to classify the relationship between two entities
such as relation classification, e.g. the [TACRED dataset](https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/tacred/). This
model places a linear head on top of the concatenated output representation of the pair of given entities.
- [`LukeForEntitySpanClassification`], for tasks to classify the sequence of entity spans, such as
named entity recognition (NER). This model places a linear head on top of the output entity representations. You
can address NER using this model by inputting all possible entity spans in the text to the model.
[`LukeTokenizer`] has a `task` argument, which enables you to easily create an input to these
head models by specifying `task="entity_classification"`, `task="entity_pair_classification"`, or
`task="entity_span_classification"`. Please refer to the example code of each head models.
Usage example:
```python
>>> from transformers import LukeTokenizer, LukeModel, LukeForEntityPairClassification
>>> model = LukeModel.from_pretrained("studio-ousia/luke-base")
>>> tokenizer = LukeTokenizer.from_pretrained("studio-ousia/luke-base")
# Example 1: Computing the contextualized entity representation corresponding to the entity mention "Beyoncé"
>>> text = "Beyoncé lives in Los Angeles."
>>> entity_spans = [(0, 7)] # character-based entity span corresponding to "Beyoncé"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, entity_spans=entity_spans, add_prefix_space=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> word_last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> entity_last_hidden_state = outputs.entity_last_hidden_state
# Example 2: Inputting Wikipedia entities to obtain enriched contextualized representations
>>> entities = [
... "Beyoncé",
... "Los Angeles",
... ] # Wikipedia entity titles corresponding to the entity mentions "Beyoncé" and "Los Angeles"
>>> entity_spans = [(0, 7), (17, 28)] # character-based entity spans corresponding to "Beyoncé" and "Los Angeles"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, entities=entities, entity_spans=entity_spans, add_prefix_space=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> word_last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> entity_last_hidden_state = outputs.entity_last_hidden_state
# Example 3: Classifying the relationship between two entities using LukeForEntityPairClassification head model
>>> model = LukeForEntityPairClassification.from_pretrained("studio-ousia/luke-large-finetuned-tacred")
>>> tokenizer = LukeTokenizer.from_pretrained("studio-ousia/luke-large-finetuned-tacred")
>>> entity_spans = [(0, 7), (17, 28)] # character-based entity spans corresponding to "Beyoncé" and "Los Angeles"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text, entity_spans=entity_spans, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> predicted_class_idx = int(logits[0].argmax())
>>> print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
```
## Resources
- [A demo notebook on how to fine-tune [`LukeForEntityPairClassification`] for relation classification](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/LUKE)
- [Notebooks showcasing how you to reproduce the results as reported in the paper with the HuggingFace implementation of LUKE](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/tree/master/notebooks)
- [Text classification task guide](../tasks/sequence_classification)
- [Token classification task guide](../tasks/token_classification)
- [Question answering task guide](../tasks/question_answering)
- [Masked language modeling task guide](../tasks/masked_language_modeling)
- [Multiple choice task guide](../tasks/multiple_choice)
## LukeConfig
[[autodoc]] LukeConfig
## LukeTokenizer
[[autodoc]] LukeTokenizer
- __call__
- save_vocabulary
## LukeModel
[[autodoc]] LukeModel
- forward
## LukeForMaskedLM
[[autodoc]] LukeForMaskedLM
- forward
## LukeForEntityClassification
[[autodoc]] LukeForEntityClassification
- forward
## LukeForEntityPairClassification
[[autodoc]] LukeForEntityPairClassification
- forward
## LukeForEntitySpanClassification
[[autodoc]] LukeForEntitySpanClassification
- forward
## LukeForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] LukeForSequenceClassification
- forward
## LukeForMultipleChoice
[[autodoc]] LukeForMultipleChoice
- forward
## LukeForTokenClassification
[[autodoc]] LukeForTokenClassification
- forward
## LukeForQuestionAnswering
[[autodoc]] LukeForQuestionAnswering
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/luke.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/luke.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2521
}
| 18 |
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# MPT
## Overview
The MPT model was proposed by the [MosaicML](https://www.mosaicml.com/) team and released with multiple sizes and finetuned variants. The MPT models are a series of open source and commercially usable LLMs pre-trained on 1T tokens.
MPT models are GPT-style decoder-only transformers with several improvements: performance-optimized layer implementations, architecture changes that provide greater training stability, and the elimination of context length limits by replacing positional embeddings with ALiBi.
- MPT base: MPT base pre-trained models on next token prediction
- MPT instruct: MPT base models fine-tuned on instruction based tasks
- MPT storywriter: MPT base models fine-tuned for 2500 steps on 65k-token excerpts of fiction books contained in the books3 corpus, this enables the model to handle very long sequences
The original code is available at the [`llm-foundry`](https://github.com/mosaicml/llm-foundry/tree/main) repository.
Read more about it [in the release blogpost](https://www.mosaicml.com/blog/mpt-7b)
## Usage tips
- Learn more about some techniques behind training of the model [in this section of llm-foundry repository](https://github.com/mosaicml/llm-foundry/blob/main/TUTORIAL.md#faqs)
- If you want to use the advanced version of the model (triton kernels, direct flash attention integration), you can still use the original model implementation by adding `trust_remote_code=True` when calling `from_pretrained`.
## Resources
- [Fine-tuning Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1HCpQkLL7UXW8xJUJJ29X7QAeNJKO0frZ?usp=sharing) on how to fine-tune MPT-7B on a free Google Colab instance to turn the model into a Chatbot.
## MptConfig
[[autodoc]] MptConfig
- all
## MptModel
[[autodoc]] MptModel
- forward
## MptForCausalLM
[[autodoc]] MptForCausalLM
- forward
## MptForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] MptForSequenceClassification
- forward
## MptForTokenClassification
[[autodoc]] MptForTokenClassification
- forward
## MptForQuestionAnswering
[[autodoc]] MptForQuestionAnswering
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/mpt.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/mpt.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 824
}
| 19 |
<!--
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# OLMoE
## Overview
The OLMoE model was proposed in [OLMoE: Open Mixture-of-Experts Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.02060) by Niklas Muennighoff, Luca Soldaini, Dirk Groeneveld, Kyle Lo, Jacob Morrison, Sewon Min, Weijia Shi, Pete Walsh, Oyvind Tafjord, Nathan Lambert, Yuling Gu, Shane Arora, Akshita Bhagia, Dustin Schwenk, David Wadden, Alexander Wettig, Binyuan Hui, Tim Dettmers, Douwe Kiela, Ali Farhadi, Noah A. Smith, Pang Wei Koh, Amanpreet Singh, Hannaneh Hajishirzi.
OLMoE is a series of **O**pen **L**anguage **Mo**dels using sparse **M**ixture-**o**f-**E**xperts designed to enable the science of language models. We release all code, checkpoints, logs, and details involved in training these models.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*We introduce OLMoE, a fully open, state-of-the-art language model leveraging sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE). OLMoE-1B-7B has 7 billion (B) parameters but uses only 1B per input token. We pretrain it on 5 trillion tokens and further adapt it to create OLMoE-1B-7B-Instruct. Our models outperform all available models with similar active parameters, even surpassing larger ones like Llama2-13B-Chat and DeepSeekMoE-16B. We present various experiments on MoE training, analyze routing in our model showing high specialization, and open-source all aspects of our work: model weights, training data, code, and logs.*
This model was contributed by [Muennighoff](https://hf.co/Muennighoff).
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/allenai/OLMoE).
## OlmoeConfig
[[autodoc]] OlmoeConfig
## OlmoeModel
[[autodoc]] OlmoeModel
- forward
## OlmoeForCausalLM
[[autodoc]] OlmoeForCausalLM
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/olmoe.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/olmoe.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 703
}
| 20 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contains specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Phi-3
## Overview
The Phi-3 model was proposed in [Phi-3 Technical Report: A Highly Capable Language Model Locally on Your Phone](https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.14219) by Microsoft.
### Summary
The abstract from the Phi-3 paper is the following:
We introduce phi-3-mini, a 3.8 billion parameter language model trained on 3.3 trillion tokens, whose overall performance, as measured by both academic benchmarks and internal testing, rivals that of models such as Mixtral 8x7B and GPT-3.5 (e.g., phi-3-mini achieves 69% on MMLU and 8.38 on MT-bench), despite being small enough to be deployed on a phone. The innovation lies entirely in our dataset for training, a scaled-up version of the one used for phi-2, composed of heavily filtered web data and synthetic data. The model is also further aligned for robustness, safety, and chat format. We also provide some initial parameter-scaling results with a 7B and 14B models trained for 4.8T tokens, called phi-3-small and phi-3-medium, both significantly more capable than phi-3-mini (e.g., respectively 75% and 78% on MMLU, and 8.7 and 8.9 on MT-bench).
The original code for Phi-3 can be found [here](https://huggingface.co/microsoft/Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct).
## Usage tips
- This model is very similar to `Llama` with the main difference of [`Phi3SuScaledRotaryEmbedding`] and [`Phi3YarnScaledRotaryEmbedding`], where they are used to extend the context of the rotary embeddings. The query, key and values are fused, and the MLP's up and gate projection layers are also fused.
- The tokenizer used for this model is identical to the [`LlamaTokenizer`], with the exception of additional tokens.
## How to use Phi-3
<Tip warning={true}>
Phi-3 has been integrated in the development version (4.40.0.dev) of `transformers`. Until the official version is released through `pip`, ensure that you are doing one of the following:
* When loading the model, ensure that `trust_remote_code=True` is passed as an argument of the `from_pretrained()` function.
* Update your local `transformers` to the development version: `pip uninstall -y transformers && pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers`. The previous command is an alternative to cloning and installing from the source.
</Tip>
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("microsoft/Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct")
>>> messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "Can you provide ways to eat combinations of bananas and dragonfruits?"}]
>>> inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=32)
>>> text = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs)[0]
>>> print(text)
<|user|> Can you provide ways to eat combinations of bananas and dragonfruits?<|end|><|assistant|> Certainly! Bananas and dragonfruits can be combined in various delicious ways. Here are some creative ideas for incorporating both fruits
```
## Phi3Config
[[autodoc]] Phi3Config
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
## Phi3Model
[[autodoc]] Phi3Model
- forward
## Phi3ForCausalLM
[[autodoc]] Phi3ForCausalLM
- forward
- generate
## Phi3ForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] Phi3ForSequenceClassification
- forward
## Phi3ForTokenClassification
[[autodoc]] Phi3ForTokenClassification
- forward
</pt>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/phi3.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/phi3.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1218
}
| 21 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Qwen2-VL
## Overview
The [Qwen2-VL](https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen2-vl/) model is a major update to [Qwen-VL](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.12966) from the Qwen team at Alibaba Research.
The abstract from the blog is the following:
*This blog introduces Qwen2-VL, an advanced version of the Qwen-VL model that has undergone significant enhancements over the past year. Key improvements include enhanced image comprehension, advanced video understanding, integrated visual agent functionality, and expanded multilingual support. The model architecture has been optimized for handling arbitrary image resolutions through Naive Dynamic Resolution support and utilizes Multimodal Rotary Position Embedding (M-ROPE) to effectively process both 1D textual and multi-dimensional visual data. This updated model demonstrates competitive performance against leading AI systems like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet in vision-related tasks and ranks highly among open-source models in text capabilities. These advancements make Qwen2-VL a versatile tool for various applications requiring robust multimodal processing and reasoning abilities.*
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/qwen2_vl_architecture.jpeg"
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
<small> Qwen2-VL architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen2-vl/">blog post.</a> </small>
This model was contributed by [simonJJJ](https://huggingface.co/simonJJJ).
## Usage example
### Single Media inference
The model can accept both images and videos as input. Here's an example code for inference.
```python
from PIL import Image
import requests
import torch
from torchvision import io
from typing import Dict
from transformers import Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer, AutoProcessor
# Load the model in half-precision on the available device(s)
model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", device_map="auto")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct")
# Image
url = "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
conversation = [
{
"role":"user",
"content":[
{
"type":"image",
},
{
"type":"text",
"text":"Describe this image."
}
]
}
]
# Preprocess the inputs
text_prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
# Excepted output: '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>Describe this image.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n'
inputs = processor(text=[text_prompt], images=[image], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
inputs = inputs.to('cuda')
# Inference: Generation of the output
output_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids = [output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, output_ids)]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True)
print(output_text)
# Video
def fetch_video(ele: Dict, nframe_factor=2):
if isinstance(ele['video'], str):
def round_by_factor(number: int, factor: int) -> int:
return round(number / factor) * factor
video = ele["video"]
if video.startswith("file://"):
video = video[7:]
video, _, info = io.read_video(
video,
start_pts=ele.get("video_start", 0.0),
end_pts=ele.get("video_end", None),
pts_unit="sec",
output_format="TCHW",
)
assert not ("fps" in ele and "nframes" in ele), "Only accept either `fps` or `nframes`"
if "nframes" in ele:
nframes = round_by_factor(ele["nframes"], nframe_factor)
else:
fps = ele.get("fps", 1.0)
nframes = round_by_factor(video.size(0) / info["video_fps"] * fps, nframe_factor)
idx = torch.linspace(0, video.size(0) - 1, nframes, dtype=torch.int64)
return video[idx]
video_info = {"type": "video", "video": "/path/to/video.mp4", "fps": 1.0}
video = fetch_video(video_info)
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "video"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What happened in the video?"},
],
}
]
# Preprocess the inputs
text_prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
# Excepted output: '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n<|vision_start|><|video_pad|><|vision_end|>What happened in the video?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n'
inputs = processor(text=[text_prompt], videos=[video], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
inputs = inputs.to('cuda')
# Inference: Generation of the output
output_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids = [output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, output_ids)]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True)
print(output_text)
```
### Batch Mixed Media Inference
The model can batch inputs composed of mixed samples of various types such as images, videos, and text. Here is an example.
```python
image1 = Image.open("/path/to/image1.jpg")
image2 = Image.open("/path/to/image2.jpg")
image3 = Image.open("/path/to/image3.jpg")
image4 = Image.open("/path/to/image4.jpg")
image5 = Image.open("/path/to/image5.jpg")
video = fetch_video({
"type": "video",
"video": "/path/to/video.mp4",
"fps": 1.0
})
# Conversation for the first image
conversation1 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."}
]
}
]
# Conversation with two images
conversation2 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What is written in the pictures?"}
]
}
]
# Conversation with pure text
conversation3 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "who are you?"
}
]
# Conversation with mixed midia
conversation4 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "video"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What are the common elements in these medias?"},
],
}
]
conversations = [conversation1, conversation2, conversation3, conversation4]
# Preparation for batch inference
texts = [processor.apply_chat_template(msg, add_generation_prompt=True) for msg in conversations]
inputs = processor(
text=texts,
images=[image1, image2, image3, image4, image5],
videos=[video],
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to('cuda')
# Batch Inference
output_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids = [output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, output_ids)]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True)
print(output_text)
```
### Usage Tips
#### Image Resolution trade-off
The model supports a wide range of resolution inputs. By default, it uses the native resolution for input, but higher resolutions can enhance performance at the cost of more computation. Users can set the minimum and maximum number of pixels to achieve an optimal configuration for their needs.
```python
min_pixels = 224*224
max_pixels = 2048*2048
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", min_pixels=min_pixels, max_pixels=max_pixels)
```
In case of limited GPU RAM, one can reduce the resolution as follows:
```python
min_pixels = 256*28*28
max_pixels = 1024*28*28
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", min_pixels=min_pixels, max_pixels=max_pixels)
```
This ensures each image gets encoded using a number between 256-1024 tokens. The 28 comes from the fact that the model uses a patch size of 14 and a temporal patch size of 2 (14 x 2 = 28).
#### Multiple Image Inputs
By default, images and video content are directly included in the conversation. When handling multiple images, it's helpful to add labels to the images and videos for better reference. Users can control this behavior with the following settings:
```python
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "Hello, how are you?"}
]
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I'm doing well, thank you for asking. How can I assist you today?"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Can you describe these images and video?"},
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "video"},
{"type": "text", "text": "These are from my vacation."}
]
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I'd be happy to describe the images and video for you. Could you please provide more context about your vacation?"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "It was a trip to the mountains. Can you see the details in the images and video?"
}
]
# default:
prompt_without_id = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
# Excepted output: '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>Hello, how are you?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\nI'm doing well, thank you for asking. How can I assist you today?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\nCan you describe these images and video?<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|><|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|><|vision_start|><|video_pad|><|vision_end|>These are from my vacation.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\nI'd be happy to describe the images and video for you. Could you please provide more context about your vacation?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\nIt was a trip to the mountains. Can you see the details in the images and video?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n'
# add ids
prompt_with_id = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True, add_vision_id=True)
# Excepted output: '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\nPicture 1: <|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>Hello, how are you?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\nI'm doing well, thank you for asking. How can I assist you today?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\nCan you describe these images and video?Picture 2: <|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>Picture 3: <|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>Video 1: <|vision_start|><|video_pad|><|vision_end|>These are from my vacation.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\nI'd be happy to describe the images and video for you. Could you please provide more context about your vacation?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\nIt was a trip to the mountains. Can you see the details in the images and video?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n'
```
#### Flash-Attention 2 to speed up generation
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2:
```bash
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
```
Also, you should have a hardware that is compatible with Flash-Attention 2. Read more about it in the official documentation of the [flash attention repository](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention). FlashAttention-2 can only be used when a model is loaded in `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`.
To load and run a model using Flash Attention-2, simply add `attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"` when loading the model as follows:
```python
from transformers import Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration
model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
```
## Qwen2VLConfig
[[autodoc]] Qwen2VLConfig
## Qwen2VLImageProcessor
[[autodoc]] Qwen2VLImageProcessor
- preprocess
## Qwen2VLImageProcessorFast
[[autodoc]] Qwen2VLImageProcessorFast
- preprocess
## Qwen2VLProcessor
[[autodoc]] Qwen2VLProcessor
## Qwen2VLModel
[[autodoc]] Qwen2VLModel
- forward
## Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration
[[autodoc]] Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/qwen2_vl.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/qwen2_vl.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4923
}
| 22 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the MIT License; you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License.
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# SuperPoint
## Overview
The SuperPoint model was proposed
in [SuperPoint: Self-Supervised Interest Point Detection and Description](https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07629) by Daniel
DeTone, Tomasz Malisiewicz and Andrew Rabinovich.
This model is the result of a self-supervised training of a fully-convolutional network for interest point detection and
description. The model is able to detect interest points that are repeatable under homographic transformations and
provide a descriptor for each point. The use of the model in its own is limited, but it can be used as a feature
extractor for other tasks such as homography estimation, image matching, etc.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*This paper presents a self-supervised framework for training interest point detectors and descriptors suitable for a
large number of multiple-view geometry problems in computer vision. As opposed to patch-based neural networks, our
fully-convolutional model operates on full-sized images and jointly computes pixel-level interest point locations and
associated descriptors in one forward pass. We introduce Homographic Adaptation, a multi-scale, multi-homography
approach for boosting interest point detection repeatability and performing cross-domain adaptation (e.g.,
synthetic-to-real). Our model, when trained on the MS-COCO generic image dataset using Homographic Adaptation, is able
to repeatedly detect a much richer set of interest points than the initial pre-adapted deep model and any other
traditional corner detector. The final system gives rise to state-of-the-art homography estimation results on HPatches
when compared to LIFT, SIFT and ORB.*
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/superpoint_architecture.png"
alt="drawing" width="500"/>
<small> SuperPoint overview. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07629v4">original paper.</a> </small>
## Usage tips
Here is a quick example of using the model to detect interest points in an image:
```python
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SuperPointForKeypointDetection
import torch
from PIL import Image
import requests
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("magic-leap-community/superpoint")
model = SuperPointForKeypointDetection.from_pretrained("magic-leap-community/superpoint")
inputs = processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
```
The outputs contain the list of keypoint coordinates with their respective score and description (a 256-long vector).
You can also feed multiple images to the model. Due to the nature of SuperPoint, to output a dynamic number of keypoints,
you will need to use the mask attribute to retrieve the respective information :
```python
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, SuperPointForKeypointDetection
import torch
from PIL import Image
import requests
url_image_1 = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
image_1 = Image.open(requests.get(url_image_1, stream=True).raw)
url_image_2 = "http://images.cocodataset.org/test-stuff2017/000000000568.jpg"
image_2 = Image.open(requests.get(url_image_2, stream=True).raw)
images = [image_1, image_2]
processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("magic-leap-community/superpoint")
model = SuperPointForKeypointDetection.from_pretrained("magic-leap-community/superpoint")
inputs = processor(images, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
image_sizes = [(image.height, image.width) for image in images]
outputs = processor.post_process_keypoint_detection(outputs, image_sizes)
for output in outputs:
for keypoints, scores, descriptors in zip(output["keypoints"], output["scores"], output["descriptors"]):
print(f"Keypoints: {keypoints}")
print(f"Scores: {scores}")
print(f"Descriptors: {descriptors}")
```
You can then print the keypoints on the image of your choice to visualize the result:
```python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(image_1)
plt.scatter(
outputs[0]["keypoints"][:, 0],
outputs[0]["keypoints"][:, 1],
c=outputs[0]["scores"] * 100,
s=outputs[0]["scores"] * 50,
alpha=0.8
)
plt.savefig(f"output_image.png")
```

This model was contributed by [stevenbucaille](https://huggingface.co/stevenbucaille).
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/magicleap/SuperPointPretrainedNetwork).
## Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with SuperPoint. If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
- A notebook showcasing inference and visualization with SuperPoint can be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/SuperPoint/Inference_with_SuperPoint_to_detect_interest_points_in_an_image.ipynb). 🌎
## SuperPointConfig
[[autodoc]] SuperPointConfig
## SuperPointImageProcessor
[[autodoc]] SuperPointImageProcessor
- preprocess
- post_process_keypoint_detection
## SuperPointForKeypointDetection
[[autodoc]] SuperPointForKeypointDetection
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/superpoint.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/superpoint.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1769
}
| 23 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Transformer XL
<Tip warning={true}>
This model is in maintenance mode only, so we won't accept any new PRs changing its code. This model was deprecated due to security issues linked to `pickle.load`.
We recommend switching to more recent models for improved security.
In case you would still like to use `TransfoXL` in your experiments, we recommend using the [Hub checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/transfo-xl/transfo-xl-wt103) with a specific revision to ensure you are downloading safe files from the Hub.
You will need to set the environment variable `TRUST_REMOTE_CODE` to `True` in order to allow the
usage of `pickle.load()`:
```python
import os
from transformers import TransfoXLTokenizer, TransfoXLLMHeadModel
os.environ["TRUST_REMOTE_CODE"] = "True"
checkpoint = 'transfo-xl/transfo-xl-wt103'
revision = '40a186da79458c9f9de846edfaea79c412137f97'
tokenizer = TransfoXLTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint, revision=revision)
model = TransfoXLLMHeadModel.from_pretrained(checkpoint, revision=revision)
```
If you run into any issues running this model, please reinstall the last version that supported this model: v4.35.0.
You can do so by running the following command: `pip install -U transformers==4.35.0`.
</Tip>
<div class="flex flex-wrap space-x-1">
<a href="https://huggingface.co/models?filter=transfo-xl">
<img alt="Models" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/All_model_pages-transfo--xl-blueviolet">
</a>
<a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/docs-demos/transfo-xl-wt103">
<img alt="Spaces" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue">
</a>
</div>
## Overview
The Transformer-XL model was proposed in [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai, Zhilin Yang, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan
Salakhutdinov. It's a causal (uni-directional) transformer with relative positioning (sinusoïdal) embeddings which can
reuse previously computed hidden-states to attend to longer context (memory). This model also uses adaptive softmax
inputs and outputs (tied).
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Transformers have a potential of learning longer-term dependency, but are limited by a fixed-length context in the
setting of language modeling. We propose a novel neural architecture Transformer-XL that enables learning dependency
beyond a fixed length without disrupting temporal coherence. It consists of a segment-level recurrence mechanism and a
novel positional encoding scheme. Our method not only enables capturing longer-term dependency, but also resolves the
context fragmentation problem. As a result, Transformer-XL learns dependency that is 80% longer than RNNs and 450%
longer than vanilla Transformers, achieves better performance on both short and long sequences, and is up to 1,800+
times faster than vanilla Transformers during evaluation. Notably, we improve the state-of-the-art results of
bpc/perplexity to 0.99 on enwiki8, 1.08 on text8, 18.3 on WikiText-103, 21.8 on One Billion Word, and 54.5 on Penn
Treebank (without finetuning). When trained only on WikiText-103, Transformer-XL manages to generate reasonably
coherent, novel text articles with thousands of tokens.*
This model was contributed by [thomwolf](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/kimiyoung/transformer-xl).
## Usage tips
- Transformer-XL uses relative sinusoidal positional embeddings. Padding can be done on the left or on the right. The
original implementation trains on SQuAD with padding on the left, therefore the padding defaults are set to left.
- Transformer-XL is one of the few models that has no sequence length limit.
- Same as a regular GPT model, but introduces a recurrence mechanism for two consecutive segments (similar to a regular RNNs with two consecutive inputs). In this context, a segment is a number of consecutive tokens (for instance 512) that may span across multiple documents, and segments are fed in order to the model.
- Basically, the hidden states of the previous segment are concatenated to the current input to compute the attention scores. This allows the model to pay attention to information that was in the previous segment as well as the current one. By stacking multiple attention layers, the receptive field can be increased to multiple previous segments.
- This changes the positional embeddings to positional relative embeddings (as the regular positional embeddings would give the same results in the current input and the current hidden state at a given position) and needs to make some adjustments in the way attention scores are computed.
<Tip warning={true}>
TransformerXL does **not** work with *torch.nn.DataParallel* due to a bug in PyTorch, see [issue #36035](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/36035)
</Tip>
## Resources
- [Text classification task guide](../tasks/sequence_classification)
- [Causal language modeling task guide](../tasks/language_modeling)
## TransfoXLConfig
[[autodoc]] TransfoXLConfig
## TransfoXLTokenizer
[[autodoc]] TransfoXLTokenizer
- save_vocabulary
## TransfoXL specific outputs
[[autodoc]] models.deprecated.transfo_xl.modeling_transfo_xl.TransfoXLModelOutput
[[autodoc]] models.deprecated.transfo_xl.modeling_transfo_xl.TransfoXLLMHeadModelOutput
[[autodoc]] models.deprecated.transfo_xl.modeling_tf_transfo_xl.TFTransfoXLModelOutput
[[autodoc]] models.deprecated.transfo_xl.modeling_tf_transfo_xl.TFTransfoXLLMHeadModelOutput
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
## TransfoXLModel
[[autodoc]] TransfoXLModel
- forward
## TransfoXLLMHeadModel
[[autodoc]] TransfoXLLMHeadModel
- forward
## TransfoXLForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] TransfoXLForSequenceClassification
- forward
</pt>
<tf>
## TFTransfoXLModel
[[autodoc]] TFTransfoXLModel
- call
## TFTransfoXLLMHeadModel
[[autodoc]] TFTransfoXLLMHeadModel
- call
## TFTransfoXLForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] TFTransfoXLForSequenceClassification
- call
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
## Internal Layers
[[autodoc]] AdaptiveEmbedding
[[autodoc]] TFAdaptiveEmbedding
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/transfo-xl.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/transfo-xl.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2000
}
| 24 |
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Vision Encoder Decoder Models
## Overview
The [`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`] can be used to initialize an image-to-text model with any
pretrained Transformer-based vision model as the encoder (*e.g.* [ViT](vit), [BEiT](beit), [DeiT](deit), [Swin](swin))
and any pretrained language model as the decoder (*e.g.* [RoBERTa](roberta), [GPT2](gpt2), [BERT](bert), [DistilBERT](distilbert)).
The effectiveness of initializing image-to-text-sequence models with pretrained checkpoints has been shown in (for
example) [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang,
Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
After such a [`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`] has been trained/fine-tuned, it can be saved/loaded just like any other models (see the examples below
for more information).
An example application is image captioning, in which the encoder is used to encode the image, after which an autoregressive language model generates
the caption. Another example is optical character recognition. Refer to [TrOCR](trocr), which is an instance of [`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`].
## Randomly initializing `VisionEncoderDecoderModel` from model configurations.
[`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`] can be randomly initialized from an encoder and a decoder config. In the following example, we show how to do this using the default [`ViTModel`] configuration for the encoder
and the default [`BertForCausalLM`] configuration for the decoder.
```python
>>> from transformers import BertConfig, ViTConfig, VisionEncoderDecoderConfig, VisionEncoderDecoderModel
>>> config_encoder = ViTConfig()
>>> config_decoder = BertConfig()
>>> config = VisionEncoderDecoderConfig.from_encoder_decoder_configs(config_encoder, config_decoder)
>>> model = VisionEncoderDecoderModel(config=config)
```
## Initialising `VisionEncoderDecoderModel` from a pretrained encoder and a pretrained decoder.
[`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`] can be initialized from a pretrained encoder checkpoint and a pretrained decoder checkpoint. Note that any pretrained Transformer-based vision model, *e.g.* [Swin](swin), can serve as the encoder and both pretrained auto-encoding models, *e.g.* BERT, pretrained causal language models, *e.g.* GPT2, as well as the pretrained decoder part of sequence-to-sequence models, *e.g.* decoder of BART, can be used as the decoder.
Depending on which architecture you choose as the decoder, the cross-attention layers might be randomly initialized.
Initializing [`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`] from a pretrained encoder and decoder checkpoint requires the model to be fine-tuned on a downstream task, as has been shown in [the *Warm-starting-encoder-decoder blog post*](https://huggingface.co/blog/warm-starting-encoder-decoder).
To do so, the `VisionEncoderDecoderModel` class provides a [`VisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained`] method.
```python
>>> from transformers import VisionEncoderDecoderModel
>>> model = VisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained(
... "microsoft/swin-base-patch4-window7-224-in22k", "google-bert/bert-base-uncased"
... )
```
## Loading an existing `VisionEncoderDecoderModel` checkpoint and perform inference.
To load fine-tuned checkpoints of the `VisionEncoderDecoderModel` class, [`VisionEncoderDecoderModel`] provides the `from_pretrained(...)` method just like any other model architecture in Transformers.
To perform inference, one uses the [`generate`] method, which allows to autoregressively generate text. This method supports various forms of decoding, such as greedy, beam search and multinomial sampling.
```python
>>> import requests
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> from transformers import GPT2TokenizerFast, ViTImageProcessor, VisionEncoderDecoderModel
>>> # load a fine-tuned image captioning model and corresponding tokenizer and image processor
>>> model = VisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("nlpconnect/vit-gpt2-image-captioning")
>>> tokenizer = GPT2TokenizerFast.from_pretrained("nlpconnect/vit-gpt2-image-captioning")
>>> image_processor = ViTImageProcessor.from_pretrained("nlpconnect/vit-gpt2-image-captioning")
>>> # let's perform inference on an image
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> pixel_values = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> # autoregressively generate caption (uses greedy decoding by default)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(pixel_values)
>>> generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
>>> print(generated_text)
a cat laying on a blanket next to a cat laying on a bed
```
## Loading a PyTorch checkpoint into `TFVisionEncoderDecoderModel`.
[`TFVisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained`] currently doesn't support initializing the model from a
PyTorch checkpoint. Passing `from_pt=True` to this method will throw an exception. If there are only PyTorch
checkpoints for a particular vision encoder-decoder model, a workaround is:
```python
>>> from transformers import VisionEncoderDecoderModel, TFVisionEncoderDecoderModel
>>> _model = VisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("nlpconnect/vit-gpt2-image-captioning")
>>> _model.encoder.save_pretrained("./encoder")
>>> _model.decoder.save_pretrained("./decoder")
>>> model = TFVisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained(
... "./encoder", "./decoder", encoder_from_pt=True, decoder_from_pt=True
... )
>>> # This is only for copying some specific attributes of this particular model.
>>> model.config = _model.config
```
## Training
Once the model is created, it can be fine-tuned similar to BART, T5 or any other encoder-decoder model on a dataset of (image, text) pairs.
As you can see, only 2 inputs are required for the model in order to compute a loss: `pixel_values` (which are the
images) and `labels` (which are the `input_ids` of the encoded target sequence).
```python
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor, BertTokenizer, VisionEncoderDecoderModel
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> image_processor = ViTImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k")
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
>>> model = VisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained(
... "google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k", "google-bert/bert-base-uncased"
... )
>>> model.config.decoder_start_token_id = tokenizer.cls_token_id
>>> model.config.pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> pixel_values = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> labels = tokenizer(
... "an image of two cats chilling on a couch",
... return_tensors="pt",
... ).input_ids
>>> # the forward function automatically creates the correct decoder_input_ids
>>> loss = model(pixel_values=pixel_values, labels=labels).loss
```
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://github.com/nielsrogge). This model's TensorFlow and Flax versions
were contributed by [ydshieh](https://github.com/ydshieh).
## VisionEncoderDecoderConfig
[[autodoc]] VisionEncoderDecoderConfig
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
## VisionEncoderDecoderModel
[[autodoc]] VisionEncoderDecoderModel
- forward
- from_encoder_decoder_pretrained
</pt>
<tf>
## TFVisionEncoderDecoderModel
[[autodoc]] TFVisionEncoderDecoderModel
- call
- from_encoder_decoder_pretrained
</tf>
<jax>
## FlaxVisionEncoderDecoderModel
[[autodoc]] FlaxVisionEncoderDecoderModel
- __call__
- from_encoder_decoder_pretrained
</jax>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/vision-encoder-decoder.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/vision-encoder-decoder.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2537
}
| 25 |
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# WavLM
## Overview
The WavLM model was proposed in [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen,
Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu,
Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
*Self-supervised learning (SSL) achieves great success in speech recognition, while limited exploration has been
attempted for other speech processing tasks. As speech signal contains multi-faceted information including speaker
identity, paralinguistics, spoken content, etc., learning universal representations for all speech tasks is
challenging. In this paper, we propose a new pre-trained model, WavLM, to solve full-stack downstream speech tasks.
WavLM is built based on the HuBERT framework, with an emphasis on both spoken content modeling and speaker identity
preservation. We first equip the Transformer structure with gated relative position bias to improve its capability on
recognition tasks. For better speaker discrimination, we propose an utterance mixing training strategy, where
additional overlapped utterances are created unsupervisedly and incorporated during model training. Lastly, we scale up
the training dataset from 60k hours to 94k hours. WavLM Large achieves state-of-the-art performance on the SUPERB
benchmark, and brings significant improvements for various speech processing tasks on their representative benchmarks.*
Relevant checkpoints can be found under https://huggingface.co/models?other=wavlm.
This model was contributed by [patrickvonplaten](https://huggingface.co/patrickvonplaten). The Authors' code can be
found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/unilm/tree/master/wavlm).
## Usage tips
- WavLM is a speech model that accepts a float array corresponding to the raw waveform of the speech signal. Please use
[`Wav2Vec2Processor`] for the feature extraction.
- WavLM model can be fine-tuned using connectionist temporal classification (CTC) so the model output has to be decoded
using [`Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer`].
- WavLM performs especially well on speaker verification, speaker identification, and speaker diarization tasks.
## Resources
- [Audio classification task guide](../tasks/audio_classification)
- [Automatic speech recognition task guide](../tasks/asr)
## WavLMConfig
[[autodoc]] WavLMConfig
## WavLMModel
[[autodoc]] WavLMModel
- forward
## WavLMForCTC
[[autodoc]] WavLMForCTC
- forward
## WavLMForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] WavLMForSequenceClassification
- forward
## WavLMForAudioFrameClassification
[[autodoc]] WavLMForAudioFrameClassification
- forward
## WavLMForXVector
[[autodoc]] WavLMForXVector
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/wavlm.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/wavlm.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 972
}
| 26 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Zamba2
Zamba2 is a large language model (LLM) trained by Zyphra, and made available under an Apache 2.0 license. Please see the [Zyphra Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/collections/zyphra/) repository for model weights.
This model was contributed by [pglo](https://huggingface.co/pglo).
## Model details
Zamba2-1.2B, Zamba2-2.7B and Zamba2-7B are hybrid models combining state-space models (Specifically [Mamba](https://github.com/state-spaces/mamba)) and transformer, and were trained using next-token prediction. Zamba2 uses shared transformer layers after every 6 mamba blocks. It uses the [Mistral v0.1 tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1). We came to this architecture after a series of ablations at small scales. Zamba2-1.2B, Zamba2-2.7B and Zamba2-7B were pre-trained on 2T and 3T tokens, respectively.
<img src=https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/c2cff209-b901-483c-87aa-774b82a0769f width=30% height=40% />
## Quick start
### Presequities
Zamba2 requires you use `transformers` version 4.48.0 or higher:
```bash
pip install transformers>=4.48.0
## Inference
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Zyphra/Zamba2-7B")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Zyphra/Zamba2-7B", device_map="cuda", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
input_text = "What factors contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire?"
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=100)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
## Model card
The model cards can be found at:
* [Zamba2-1.2B](https://huggingface.co/Zyphra/Zamba2-1.2B)
* [Zamba2-2.7B](https://huggingface.co/Zyphra/Zamba2-2.7B)
* [Zamba2-7B](https://huggingface.co/Zyphra/Zamba2-7B)
## Issues
For issues with model output, or community discussion, please use the Hugging Face community [forum](https://huggingface.co/Zyphra/Zamba2-7B/discussions)
## License
The model weights are open-sourced via an Apache 2.0 license.
## Zamba2Config
[[autodoc]] Zamba2Config
## Zamba2Model
[[autodoc]] Zamba2Model
- forward
## Zamba2ForCausalLM
[[autodoc]] Zamba2ForCausalLM
- forward
## Zamba2ForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] transformers.Zamba2ForSequenceClassification
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/zamba2.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/model_doc/zamba2.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1031
}
| 27 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Efficient Training on Multiple CPUs
When training on a single CPU is too slow, we can use multiple CPUs. This guide focuses on PyTorch-based DDP enabling
distributed CPU training efficiently on [bare metal](#usage-in-trainer) and [Kubernetes](#usage-with-kubernetes).
## Intel® oneCCL Bindings for PyTorch
[Intel® oneCCL](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneCCL) (collective communications library) is a library for efficient distributed deep learning training implementing such collectives like allreduce, allgather, alltoall. For more information on oneCCL, please refer to the [oneCCL documentation](https://spec.oneapi.com/versions/latest/elements/oneCCL/source/index.html) and [oneCCL specification](https://spec.oneapi.com/versions/latest/elements/oneCCL/source/index.html).
Module `oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch` (`torch_ccl` before version 1.12) implements PyTorch C10D ProcessGroup API and can be dynamically loaded as external ProcessGroup and only works on Linux platform now
Check more detailed information for [oneccl_bind_pt](https://github.com/intel/torch-ccl).
### Intel® oneCCL Bindings for PyTorch installation
Wheel files are available for the following Python versions:
| Extension Version | Python 3.7 | Python 3.8 | Python 3.9 | Python 3.10 | Python 3.11 |
| :---------------: | :--------: | :--------: | :--------: | :---------: | :---------: |
| 2.5.0 | | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 2.4.0 | | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 2.3.0 | | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 2.2.0 | | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Please run `pip list | grep torch` to get your `pytorch_version`.
```bash
pip install oneccl_bind_pt=={pytorch_version} -f https://developer.intel.com/ipex-whl-stable-cpu
```
where `{pytorch_version}` should be your PyTorch version, for instance 2.4.0.
Check more approaches for [oneccl_bind_pt installation](https://github.com/intel/torch-ccl).
Versions of oneCCL and PyTorch must match.
## Intel® MPI library
Use this standards-based MPI implementation to deliver flexible, efficient, scalable cluster messaging on Intel® architecture. This component is part of the Intel® oneAPI HPC Toolkit.
oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch is installed along with the MPI tool set. Need to source the environment before using it.
```bash
oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch_path=$(python -c "from oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch import cwd; print(cwd)")
source $oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch_path/env/setvars.sh
```
#### Intel® Extension for PyTorch installation
Intel Extension for PyTorch (IPEX) provides performance optimizations for CPU training with both Float32 and BFloat16 (refer to the [single CPU section](./perf_train_cpu) to learn more).
The following "Usage in Trainer" takes mpirun in Intel® MPI library as an example.
## Usage in Trainer
To enable multi CPU distributed training in the Trainer with the ccl backend, users should add **`--ddp_backend ccl`** in the command arguments.
Let's see an example with the [question-answering example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/question-answering)
The following command enables training with 2 processes on one Xeon node, with one process running per one socket. The variables OMP_NUM_THREADS/CCL_WORKER_COUNT can be tuned for optimal performance.
```shell script
export CCL_WORKER_COUNT=1
export MASTER_ADDR=127.0.0.1
mpirun -n 2 -genv OMP_NUM_THREADS=23 \
python3 examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
--model_name_or_path google-bert/bert-large-uncased \
--dataset_name squad \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--per_device_train_batch_size 12 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--output_dir /tmp/debug_squad/ \
--no_cuda \
--ddp_backend ccl \
--use_ipex
```
The following command enables training with a total of four processes on two Xeons (node0 and node1, taking node0 as the main process), ppn (processes per node) is set to 2, with one process running per one socket. The variables OMP_NUM_THREADS/CCL_WORKER_COUNT can be tuned for optimal performance.
In node0, you need to create a configuration file which contains the IP addresses of each node (for example hostfile) and pass that configuration file path as an argument.
```shell script
cat hostfile
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #node0 ip
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #node1 ip
```
Now, run the following command in node0 and **4DDP** will be enabled in node0 and node1 with BF16 auto mixed precision:
```shell script
export CCL_WORKER_COUNT=1
export MASTER_ADDR=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #node0 ip
mpirun -f hostfile -n 4 -ppn 2 \
-genv OMP_NUM_THREADS=23 \
python3 examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
--model_name_or_path google-bert/bert-large-uncased \
--dataset_name squad \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--per_device_train_batch_size 12 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--output_dir /tmp/debug_squad/ \
--no_cuda \
--ddp_backend ccl \
--use_ipex \
--bf16
```
## Usage with Kubernetes
The same distributed training job from the previous section can be deployed to a Kubernetes cluster using the
[Kubeflow PyTorchJob training operator](https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/components/training/user-guides/pytorch).
### Setup
This example assumes that you have:
* Access to a Kubernetes cluster with [Kubeflow installed](https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/started/installing-kubeflow)
* [`kubectl`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools) installed and configured to access the Kubernetes cluster
* A [Persistent Volume Claim (PVC)](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/persistent-volumes) that can be used
to store datasets and model files. There are multiple options for setting up the PVC including using an NFS
[storage class](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes) or a cloud storage bucket.
* A Docker container that includes your model training script and all the dependencies needed to run the script. For
distributed CPU training jobs, this typically includes PyTorch, Transformers, Intel Extension for PyTorch, Intel
oneCCL Bindings for PyTorch, and OpenSSH to communicate between the containers.
The snippet below is an example of a Dockerfile that uses a base image that supports distributed CPU training and then
extracts a Transformers release to the `/workspace` directory, so that the example scripts are included in the image:
```dockerfile
FROM intel/intel-optimized-pytorch:2.4.0-pip-multinode
RUN apt-get update -y && \
apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends --fix-missing \
google-perftools \
libomp-dev
WORKDIR /workspace
# Download and extract the transformers code
ARG HF_TRANSFORMERS_VER="4.46.0"
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir \
transformers==${HF_TRANSFORMERS_VER} && \
mkdir transformers && \
curl -sSL --retry 5 https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/archive/refs/tags/v${HF_TRANSFORMERS_VER}.tar.gz | tar -C transformers --strip-components=1 -xzf -
```
The image needs to be built and copied to the cluster's nodes or pushed to a container registry prior to deploying the
PyTorchJob to the cluster.
### PyTorchJob Specification File
The [Kubeflow PyTorchJob](https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/components/training/user-guides/pytorch) is used to run the distributed
training job on the cluster. The yaml file for the PyTorchJob defines parameters such as:
* The name of the PyTorchJob
* The number of replicas (workers)
* The python script and it's parameters that will be used to run the training job
* The types of resources (node selector, memory, and CPU) needed for each worker
* The image/tag for the Docker container to use
* Environment variables
* A volume mount for the PVC
The volume mount defines a path where the PVC will be mounted in the container for each worker pod. This location can be
used for the dataset, checkpoint files, and the saved model after training completes.
The snippet below is an example of a yaml file for a PyTorchJob with 4 workers running the
[question-answering example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/question-answering).
```yaml
apiVersion: "kubeflow.org/v1"
kind: PyTorchJob
metadata:
name: transformers-pytorchjob
spec:
elasticPolicy:
rdzvBackend: c10d
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 4
maxRestarts: 10
pytorchReplicaSpecs:
Worker:
replicas: 4 # The number of worker pods
restartPolicy: OnFailure
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pytorch
image: <image name>:<tag> # Specify the docker image to use for the worker pods
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
args:
- >-
cd /workspace/transformers;
pip install -r /workspace/transformers/examples/pytorch/question-answering/requirements.txt;
source /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch/env/setvars.sh;
torchrun /workspace/transformers/examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
--model_name_or_path distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased \
--dataset_name squad \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--per_device_train_batch_size 12 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--output_dir /tmp/pvc-mount/output_$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S) \
--no_cuda \
--ddp_backend ccl \
--bf16 \
--use_ipex;
env:
- name: LD_PRELOAD
value: "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtcmalloc.so.4.5.9:/usr/local/lib/libiomp5.so"
- name: TRANSFORMERS_CACHE
value: "/tmp/pvc-mount/transformers_cache"
- name: HF_DATASETS_CACHE
value: "/tmp/pvc-mount/hf_datasets_cache"
- name: LOGLEVEL
value: "INFO"
- name: CCL_WORKER_COUNT
value: "1"
- name: OMP_NUM_THREADS # Can be tuned for optimal performance
value: "240"
resources:
limits:
cpu: 240 # Update the CPU and memory limit values based on your nodes
memory: 128Gi
requests:
cpu: 240 # Update the CPU and memory request values based on your nodes
memory: 128Gi
volumeMounts:
- name: pvc-volume
mountPath: /tmp/pvc-mount
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
restartPolicy: Never
nodeSelector: # Optionally use nodeSelector to match a certain node label for the worker pods
node-type: gnr
volumes:
- name: pvc-volume
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: transformers-pvc
- name: dshm
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
```
To run this example, update the yaml based on your training script and the nodes in your cluster.
<Tip>
The CPU resource limits/requests in the yaml are defined in
[cpu units](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#meaning-of-cpu)
where 1 CPU unit is equivalent to 1 physical CPU core or 1 virtual core (depending on whether the node is a physical
host or a VM). The amount of CPU and memory limits/requests defined in the yaml should be less than the amount of
available CPU/memory capacity on a single machine. It is usually a good idea to not use the entire machine's capacity in
order to leave some resources for the kubelet and OS. In order to get ["guaranteed"](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-qos/#guaranteed)
[quality of service](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/quality-service-pod) for the worker pods,
set the same CPU and memory amounts for both the resource limits and requests.
</Tip>
### Deploy
After the PyTorchJob spec has been updated with values appropriate for your cluster and training job, it can be deployed
to the cluster using:
```bash
export NAMESPACE=<specify your namespace>
kubectl create -f pytorchjob.yaml -n ${NAMESPACE}
```
The `kubectl get pods -n ${NAMESPACE}` command can then be used to list the pods in your namespace. You should see
the worker pods for the PyTorchJob that was just deployed. At first, they will probably have a status of "Pending" as
the containers get pulled and created, then the status should change to "Running".
```
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
...
transformers-pytorchjob-worker-0 1/1 Running 0 7m37s
transformers-pytorchjob-worker-1 1/1 Running 0 7m37s
transformers-pytorchjob-worker-2 1/1 Running 0 7m37s
transformers-pytorchjob-worker-3 1/1 Running 0 7m37s
...
```
The logs for worker can be viewed using `kubectl logs <pod name> -n ${NAMESPACE}`. Add `-f` to stream the logs, for example:
```bash
kubectl logs transformers-pytorchjob-worker-0 -n ${NAMESPACE} -f
```
After the training job completes, the trained model can be copied from the PVC or storage location. When you are done
with the job, the PyTorchJob resource can be deleted from the cluster using `kubectl delete -f pytorchjob.yaml -n ${NAMESPACE}`.
## Summary
This guide covered running distributed PyTorch training jobs using multiple CPUs on bare metal and on a Kubernetes
cluster. Both cases utilize Intel Extension for PyTorch and Intel oneCCL Bindings for PyTorch for optimal training
performance, and can be used as a template to run your own workload on multiple nodes.
|
transformers/docs/source/en/perf_train_cpu_many.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/perf_train_cpu_many.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5718
}
| 28 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Compressed Tensors
The [`compressed-tensors`](https://github.com/neuralmagic/compressed-tensors) library provides a versatile and efficient way to store and manage compressed model checkpoints. This library supports various quantization and sparsity schemes, making it a unified format for handling different model optimizations like GPTQ, AWQ, SmoothQuant, INT8, FP8, SparseGPT, and more.
Some of the supported formats include:
1. `dense`
2. `int-quantized` ([sample](https://huggingface.co/nm-testing/tinyllama-w8a8-compressed-hf-quantizer)): INT8 quantized models
3. `float-quantized` ([sample](https://huggingface.co/nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct-fp8-hf_compat)): FP8 quantized models; currently support E4M3
4. `pack-quantized` ([sample](https://huggingface.co/nm-testing/tinyllama-w4a16-compressed-hf-quantizer)): INT4 or INT8 weight-quantized models, packed into INT32. For INT4, the weights have an INT4 range but are stored as INT8 and then packed into INT32.
Compressed models can be easily created using [llm-compressor](https://github.com/vllm-project/llm-compressor).
Alternatively models can be created independently and serialized with a compressed tensors config.
To find existing models on the Hugging Face Model Hub, search for the [`compressed-tensors` tag](https://huggingface.co/models?other=compressed-tensors).
#### Features:
- Weight and activation precisions: FP8, INT4, INT8 (for Q/DQ arbitrary precision is allowed for INT)
- Quantization scales and zero-points strategies: [tensor, channel, group, block, token](https://github.com/neuralmagic/compressed-tensors/blob/83b2e7a969d70606421a76b9a3d112646077c8de/src/compressed_tensors/quantization/quant_args.py#L43-L52)
- Dynamic per-token activation quantization (or any static strategy)
- Sparsity in weights (unstructured or semi-structured like 2:4) can be composed with quantization for extreme compression
- Supports quantization of arbitrary modules, not just Linear modules
- Targeted support or ignoring of modules by name or class
## Installation
It is recommended to install stable releases of compressed-tensors from [PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/compressed-tensors):
```bash
pip install compressed-tensors
```
Developers who want to experiment with the latest features can also install the package from source:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/neuralmagic/compressed-tensors
cd compressed-tensors
pip install -e .
```
## Quickstart Model Load
Quantized models can be easily loaded for inference as shown below. Only models that have already been quantized can be loaded at the moment. To quantize a model into the compressed-tensors format see [llm-compressor](https://github.com/vllm-project/llm-compressor).
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
# Load the model in compressed-tensors format
ct_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP8-hf")
# Measure memory usage
mem_params = sum([param.nelement()*param.element_size() for param in ct_model.parameters()])
print(f"{mem/2**30:.4f} GB")
# 8.4575 GB
```
We can see just above that the compressed-tensors FP8 checkpoint of Llama 3.1 8B is able to be loaded for inference using half of the memory of the unquantized reference checkpoint.
## Sample Use Cases - Load and run an FP8 model
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
prompt = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is"
]
model_name = "nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct-fp8-hf_compat"
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
generated_ids = quantized_model.generate(**inputs, max_length=50, do_sample=False)
outputs = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)
print(outputs)
"""
['<|begin_of_text|>Hello, my name is [Name]. I am a [Your Profession/Student] and I am here to learn about the [Course/Program] at [University/Institution]. I am excited to be here and I am looking forward to', '<|begin_of_text|>The capital of France is Paris, which is located in the north-central part of the country. Paris is the most populous city in France and is known for its stunning architecture, art museums, fashion, and romantic atmosphere. The city is home to', "<|begin_of_text|>The future of AI is here, and it's already changing the way we live and work. From virtual assistants to self-driving cars, AI is transforming industries and revolutionizing the way we interact with technology. But what does the future of AI hold"]
"""
```
The above shows a quick example for running generation using a `compressed-tensors`
model. Currently, once loaded the model cannot be saved.
## Deep dive into a compressed-tensors model checkpoint
In this example we will examine how the compressed-tensors model nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP8-hf is defined through its configuration entry and see how this translates to the loaded model representation.
First, let us look at the [`quantization_config` of the model](https://huggingface.co/nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP8-hf/blob/main/config.json). At a glance it looks overwhelming with the number of entries but this is because compressed-tensors is a format that allows for flexible expression both during and after model compression.
In practice for checkpoint loading and inference the configuration can be simplified to not include all the default or empty entries, so we will do that here to focus on what compression is actually represented.
```yaml
"quantization_config": {
"config_groups": {
"group_0": {
"input_activations": {
"num_bits": 8,
"strategy": "tensor",
"type": "float"
},
"targets": ["Linear"],
"weights": {
"num_bits": 8,
"strategy": "tensor",
"type": "float"
}
}
},
"format": "naive-quantized",
"ignore": ["lm_head"],
"quant_method": "compressed-tensors",
"quantization_status": "frozen"
},
```
We can see from the above configuration that it is specifying one config group that includes weight and activation quantization to FP8 with a static per-tensor strategy. It is also worth noting that in the `ignore` list there is an entry to skip quantization of the `lm_head` module, so that module should be untouched in the checkpoint.
To see the result of the configuration in practice, we can simply use the [safetensors viewer](https://huggingface.co/nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP8-hf?show_file_info=model.safetensors.index.json) on the model card to see the quantized weights, input_scale, and weight_scale for all of the Linear modules in the first model layer (and so on for the rest of the layers).
| Tensors | Shape | Precision |
| ------- | ----- | --------- |
model.layers.0.input_layernorm.weight | [4 096] | BF16
model.layers.0.mlp.down_proj.input_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.mlp.down_proj.weight | [4 096, 14 336] | F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.mlp.down_proj.weight_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.mlp.gate_proj.input_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.mlp.gate_proj.weight | [14 336, 4 096] | F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.mlp.gate_proj.weight_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.mlp.up_proj.input_scale| [1] |BF16
model.layers.0.mlp.up_proj.weight | [14 336, 4 096] | F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.mlp.up_proj.weight_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.post_attention_layernorm.weight | [4 096] |BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.k_proj.input_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.k_proj.weight | [1 024, 4 096]| F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.self_attn.k_proj.weight_scale |[1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.o_proj.input_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.o_proj.weight | [4 096, 4 096] | F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.self_attn.o_proj.weight_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.q_proj.input_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.q_proj.weight | [4 096, 4 096] | F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.self_attn.q_proj.weight_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.v_proj.input_scale | [1] | BF16
model.layers.0.self_attn.v_proj.weight | [1 024, 4 096] | F8_E4M3
model.layers.0.self_attn.v_proj.weight_scale | [1] | BF16
When we load the model with the compressed-tensors HFQuantizer integration, we can see that all of the Linear modules that are specified within the quantization configuration have been replaced by `CompressedLinear` modules that manage the compressed weights and forward pass for inference. Note that the `lm_head` mentioned before in the ignore list is still kept as an unquantized Linear module.
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
ct_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("nm-testing/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP8-hf")
print(ct_model)
"""
LlamaForCausalLM(
(model): LlamaModel(
(embed_tokens): Embedding(128256, 4096)
(layers): ModuleList(
(0-31): 32 x LlamaDecoderLayer(
(self_attn): LlamaSdpaAttention(
(q_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(k_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(v_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(o_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(rotary_emb): LlamaRotaryEmbedding()
)
(mlp): LlamaMLP(
(gate_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=4096, out_features=14336, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(up_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=4096, out_features=14336, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(down_proj): CompressedLinear(
in_features=14336, out_features=4096, bias=False
(input_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
(weight_observer): MovingAverageMinMaxObserver()
)
(act_fn): SiLU()
)
(input_layernorm): LlamaRMSNorm((4096,), eps=1e-05)
(post_attention_layernorm): LlamaRMSNorm((4096,), eps=1e-05)
)
)
(norm): LlamaRMSNorm((4096,), eps=1e-05)
(rotary_emb): LlamaRotaryEmbedding()
)
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=128256, bias=False)
)
"""
```
|
transformers/docs/source/en/quantization/compressed_tensors.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/quantization/compressed_tensors.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4295
}
| 29 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# What 🤗 Transformers can do
🤗 Transformers is a library of pretrained state-of-the-art models for natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and audio and speech processing tasks. Not only does the library contain Transformer models, but it also has non-Transformer models like modern convolutional networks for computer vision tasks. If you look at some of the most popular consumer products today, like smartphones, apps, and televisions, odds are that some kind of deep learning technology is behind it. Want to remove a background object from a picture taken by your smartphone? This is an example of a panoptic segmentation task (don't worry if you don't know what this means yet, we'll describe it in the following sections!).
This page provides an overview of the different speech and audio, computer vision, and NLP tasks that can be solved with the 🤗 Transformers library in just three lines of code!
## Audio
Audio and speech processing tasks are a little different from the other modalities mainly because audio as an input is a continuous signal. Unlike text, a raw audio waveform can't be neatly split into discrete chunks the way a sentence can be divided into words. To get around this, the raw audio signal is typically sampled at regular intervals. If you take more samples within an interval, the sampling rate is higher, and the audio more closely resembles the original audio source.
Previous approaches preprocessed the audio to extract useful features from it. It is now more common to start audio and speech processing tasks by directly feeding the raw audio waveform to a feature encoder to extract an audio representation. This simplifies the preprocessing step and allows the model to learn the most essential features.
### Audio classification
Audio classification is a task that labels audio data from a predefined set of classes. It is a broad category with many specific applications, some of which include:
* acoustic scene classification: label audio with a scene label ("office", "beach", "stadium")
* acoustic event detection: label audio with a sound event label ("car horn", "whale calling", "glass breaking")
* tagging: label audio containing multiple sounds (birdsongs, speaker identification in a meeting)
* music classification: label music with a genre label ("metal", "hip-hop", "country")
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> classifier = pipeline(task="audio-classification", model="superb/hubert-base-superb-er")
>>> preds = classifier("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
>>> preds
[{'score': 0.4532, 'label': 'hap'},
{'score': 0.3622, 'label': 'sad'},
{'score': 0.0943, 'label': 'neu'},
{'score': 0.0903, 'label': 'ang'}]
```
### Automatic speech recognition
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) transcribes speech into text. It is one of the most common audio tasks due partly to speech being such a natural form of human communication. Today, ASR systems are embedded in "smart" technology products like speakers, phones, and cars. We can ask our virtual assistants to play music, set reminders, and tell us the weather.
But one of the key challenges Transformer architectures have helped with is in low-resource languages. By pretraining on large amounts of speech data, finetuning the model on only one hour of labeled speech data in a low-resource language can still produce high-quality results compared to previous ASR systems trained on 100x more labeled data.
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> transcriber = pipeline(task="automatic-speech-recognition", model="openai/whisper-small")
>>> transcriber("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
{'text': ' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.'}
```
## Computer vision
One of the first and earliest successful computer vision tasks was recognizing images of zip code numbers using a [convolutional neural network (CNN)](glossary#convolution). An image is composed of pixels, and each pixel has a numerical value. This makes it easy to represent an image as a matrix of pixel values. Each particular combination of pixel values describes the colors of an image.
Two general ways computer vision tasks can be solved are:
1. Use convolutions to learn the hierarchical features of an image from low-level features to high-level abstract things.
2. Split an image into patches and use a Transformer to gradually learn how each image patch is related to each other to form an image. Unlike the bottom-up approach favored by a CNN, this is kind of like starting out with a blurry image and then gradually bringing it into focus.
### Image classification
Image classification labels an entire image from a predefined set of classes. Like most classification tasks, there are many practical use cases for image classification, some of which include:
* healthcare: label medical images to detect disease or monitor patient health
* environment: label satellite images to monitor deforestation, inform wildland management or detect wildfires
* agriculture: label images of crops to monitor plant health or satellite images for land use monitoring
* ecology: label images of animal or plant species to monitor wildlife populations or track endangered species
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> classifier = pipeline(task="image-classification")
>>> preds = classifier(
... "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
... )
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
>>> print(*preds, sep="\n")
{'score': 0.4335, 'label': 'lynx, catamount'}
{'score': 0.0348, 'label': 'cougar, puma, catamount, mountain lion, painter, panther, Felis concolor'}
{'score': 0.0324, 'label': 'snow leopard, ounce, Panthera uncia'}
{'score': 0.0239, 'label': 'Egyptian cat'}
{'score': 0.0229, 'label': 'tiger cat'}
```
### Object detection
Unlike image classification, object detection identifies multiple objects within an image and the objects' positions in an image (defined by the bounding box). Some example applications of object detection include:
* self-driving vehicles: detect everyday traffic objects such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic lights
* remote sensing: disaster monitoring, urban planning, and weather forecasting
* defect detection: detect cracks or structural damage in buildings, and manufacturing defects
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> detector = pipeline(task="object-detection")
>>> preds = detector(
... "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
... )
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"], "box": pred["box"]} for pred in preds]
>>> preds
[{'score': 0.9865,
'label': 'cat',
'box': {'xmin': 178, 'ymin': 154, 'xmax': 882, 'ymax': 598}}]
```
### Image segmentation
Image segmentation is a pixel-level task that assigns every pixel in an image to a class. It differs from object detection, which uses bounding boxes to label and predict objects in an image because segmentation is more granular. Segmentation can detect objects at a pixel-level. There are several types of image segmentation:
* instance segmentation: in addition to labeling the class of an object, it also labels each distinct instance of an object ("dog-1", "dog-2")
* panoptic segmentation: a combination of semantic and instance segmentation; it labels each pixel with a semantic class **and** each distinct instance of an object
Segmentation tasks are helpful in self-driving vehicles to create a pixel-level map of the world around them so they can navigate safely around pedestrians and other vehicles. It is also useful for medical imaging, where the task's finer granularity can help identify abnormal cells or organ features. Image segmentation can also be used in ecommerce to virtually try on clothes or create augmented reality experiences by overlaying objects in the real world through your camera.
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> segmenter = pipeline(task="image-segmentation")
>>> preds = segmenter(
... "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
... )
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
>>> print(*preds, sep="\n")
{'score': 0.9879, 'label': 'LABEL_184'}
{'score': 0.9973, 'label': 'snow'}
{'score': 0.9972, 'label': 'cat'}
```
### Depth estimation
Depth estimation predicts the distance of each pixel in an image from the camera. This computer vision task is especially important for scene understanding and reconstruction. For example, in self-driving cars, vehicles need to understand how far objects like pedestrians, traffic signs, and other vehicles are to avoid obstacles and collisions. Depth information is also helpful for constructing 3D representations from 2D images and can be used to create high-quality 3D representations of biological structures or buildings.
There are two approaches to depth estimation:
* stereo: depths are estimated by comparing two images of the same image from slightly different angles
* monocular: depths are estimated from a single image
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> depth_estimator = pipeline(task="depth-estimation")
>>> preds = depth_estimator(
... "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
... )
```
## Natural language processing
NLP tasks are among the most common types of tasks because text is such a natural way for us to communicate. To get text into a format recognized by a model, it needs to be tokenized. This means dividing a sequence of text into separate words or subwords (tokens) and then converting these tokens into numbers. As a result, you can represent a sequence of text as a sequence of numbers, and once you have a sequence of numbers, it can be input into a model to solve all sorts of NLP tasks!
### Text classification
Like classification tasks in any modality, text classification labels a sequence of text (it can be sentence-level, a paragraph, or a document) from a predefined set of classes. There are many practical applications for text classification, some of which include:
* sentiment analysis: label text according to some polarity like `positive` or `negative` which can inform and support decision-making in fields like politics, finance, and marketing
* content classification: label text according to some topic to help organize and filter information in news and social media feeds (`weather`, `sports`, `finance`, etc.)
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> classifier = pipeline(task="sentiment-analysis")
>>> preds = classifier("Hugging Face is the best thing since sliced bread!")
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
>>> preds
[{'score': 0.9991, 'label': 'POSITIVE'}]
```
### Token classification
In any NLP task, text is preprocessed by separating the sequence of text into individual words or subwords. These are known as [tokens](glossary#token). Token classification assigns each token a label from a predefined set of classes.
Two common types of token classification are:
* named entity recognition (NER): label a token according to an entity category like organization, person, location or date. NER is especially popular in biomedical settings, where it can label genes, proteins, and drug names.
* part-of-speech tagging (POS): label a token according to its part-of-speech like noun, verb, or adjective. POS is useful for helping translation systems understand how two identical words are grammatically different (bank as a noun versus bank as a verb).
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> classifier = pipeline(task="ner")
>>> preds = classifier("Hugging Face is a French company based in New York City.")
>>> preds = [
... {
... "entity": pred["entity"],
... "score": round(pred["score"], 4),
... "index": pred["index"],
... "word": pred["word"],
... "start": pred["start"],
... "end": pred["end"],
... }
... for pred in preds
... ]
>>> print(*preds, sep="\n")
{'entity': 'I-ORG', 'score': 0.9968, 'index': 1, 'word': 'Hu', 'start': 0, 'end': 2}
{'entity': 'I-ORG', 'score': 0.9293, 'index': 2, 'word': '##gging', 'start': 2, 'end': 7}
{'entity': 'I-ORG', 'score': 0.9763, 'index': 3, 'word': 'Face', 'start': 8, 'end': 12}
{'entity': 'I-MISC', 'score': 0.9983, 'index': 6, 'word': 'French', 'start': 18, 'end': 24}
{'entity': 'I-LOC', 'score': 0.999, 'index': 10, 'word': 'New', 'start': 42, 'end': 45}
{'entity': 'I-LOC', 'score': 0.9987, 'index': 11, 'word': 'York', 'start': 46, 'end': 50}
{'entity': 'I-LOC', 'score': 0.9992, 'index': 12, 'word': 'City', 'start': 51, 'end': 55}
```
### Question answering
Question answering is another token-level task that returns an answer to a question, sometimes with context (open-domain) and other times without context (closed-domain). This task happens whenever we ask a virtual assistant something like whether a restaurant is open. It can also provide customer or technical support and help search engines retrieve the relevant information you're asking for.
There are two common types of question answering:
* extractive: given a question and some context, the answer is a span of text from the context the model must extract
* abstractive: given a question and some context, the answer is generated from the context; this approach is handled by the [`Text2TextGenerationPipeline`] instead of the [`QuestionAnsweringPipeline`] shown below
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> question_answerer = pipeline(task="question-answering")
>>> preds = question_answerer(
... question="What is the name of the repository?",
... context="The name of the repository is huggingface/transformers",
... )
>>> print(
... f"score: {round(preds['score'], 4)}, start: {preds['start']}, end: {preds['end']}, answer: {preds['answer']}"
... )
score: 0.9327, start: 30, end: 54, answer: huggingface/transformers
```
### Summarization
Summarization creates a shorter version of a text from a longer one while trying to preserve most of the meaning of the original document. Summarization is a sequence-to-sequence task; it outputs a shorter text sequence than the input. There are a lot of long-form documents that can be summarized to help readers quickly understand the main points. Legislative bills, legal and financial documents, patents, and scientific papers are a few examples of documents that could be summarized to save readers time and serve as a reading aid.
Like question answering, there are two types of summarization:
* extractive: identify and extract the most important sentences from the original text
* abstractive: generate the target summary (which may include new words not in the input document) from the original text; the [`SummarizationPipeline`] uses the abstractive approach
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> summarizer = pipeline(task="summarization")
>>> summarizer(
... "In this work, we presented the Transformer, the first sequence transduction model based entirely on attention, replacing the recurrent layers most commonly used in encoder-decoder architectures with multi-headed self-attention. For translation tasks, the Transformer can be trained significantly faster than architectures based on recurrent or convolutional layers. On both WMT 2014 English-to-German and WMT 2014 English-to-French translation tasks, we achieve a new state of the art. In the former task our best model outperforms even all previously reported ensembles."
... )
[{'summary_text': ' The Transformer is the first sequence transduction model based entirely on attention . It replaces the recurrent layers most commonly used in encoder-decoder architectures with multi-headed self-attention . For translation tasks, the Transformer can be trained significantly faster than architectures based on recurrent or convolutional layers .'}]
```
### Translation
Translation converts a sequence of text in one language to another. It is important in helping people from different backgrounds communicate with each other, help translate content to reach wider audiences, and even be a learning tool to help people learn a new language. Along with summarization, translation is a sequence-to-sequence task, meaning the model receives an input sequence and returns a target output sequence.
In the early days, translation models were mostly monolingual, but recently, there has been increasing interest in multilingual models that can translate between many pairs of languages.
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> text = "translate English to French: Hugging Face is a community-based open-source platform for machine learning."
>>> translator = pipeline(task="translation", model="google-t5/t5-small")
>>> translator(text)
[{'translation_text': "Hugging Face est une tribune communautaire de l'apprentissage des machines."}]
```
### Language modeling
Language modeling is a task that predicts a word in a sequence of text. It has become a very popular NLP task because a pretrained language model can be finetuned for many other downstream tasks. Lately, there has been a lot of interest in large language models (LLMs) which demonstrate zero- or few-shot learning. This means the model can solve tasks it wasn't explicitly trained to do! Language models can be used to generate fluent and convincing text, though you need to be careful since the text may not always be accurate.
There are two types of language modeling:
* causal: the model's objective is to predict the next token in a sequence, and future tokens are masked
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> prompt = "Hugging Face is a community-based open-source platform for machine learning."
>>> generator = pipeline(task="text-generation")
>>> generator(prompt) # doctest: +SKIP
```
* masked: the model's objective is to predict a masked token in a sequence with full access to the tokens in the sequence
```py
>>> text = "Hugging Face is a community-based open-source <mask> for machine learning."
>>> fill_mask = pipeline(task="fill-mask")
>>> preds = fill_mask(text, top_k=1)
>>> preds = [
... {
... "score": round(pred["score"], 4),
... "token": pred["token"],
... "token_str": pred["token_str"],
... "sequence": pred["sequence"],
... }
... for pred in preds
... ]
>>> preds
[{'score': 0.224, 'token': 3944, 'token_str': ' tool', 'sequence': 'Hugging Face is a community-based open-source tool for machine learning.'}]
```
## Multimodal
Multimodal tasks require a model to process multiple data modalities (text, image, audio, video) to solve a particular problem. Image captioning is an example of a multimodal task where the model takes an image as input and outputs a sequence of text describing the image or some properties of the image.
Although multimodal models work with different data types or modalities, internally, the preprocessing steps help the model convert all the data types into embeddings (vectors or list of numbers that holds meaningful information about the data). For a task like image captioning, the model learns relationships between image embeddings and text embeddings.
### Document question answering
Document question answering is a task that answers natural language questions from a document. Unlike a token-level question answering task which takes text as input, document question answering takes an image of a document as input along with a question about the document and returns an answer. Document question answering can be used to parse structured documents and extract key information from it. In the example below, the total amount and change due can be extracted from a receipt.
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/example-documents/resolve/main/jpeg_images/2.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> doc_question_answerer = pipeline("document-question-answering", model="magorshunov/layoutlm-invoices")
>>> preds = doc_question_answerer(
... question="What is the total amount?",
... image=image,
... )
>>> preds
[{'score': 0.8531, 'answer': '17,000', 'start': 4, 'end': 4}]
```
Hopefully, this page has given you some more background information about all the types of tasks in each modality and the practical importance of each one. In the next [section](tasks_explained), you'll learn **how** 🤗 Transformers work to solve these tasks.
|
transformers/docs/source/en/task_summary.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/task_summary.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5654
}
| 30 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Multiple choice
[[open-in-colab]]
A multiple choice task is similar to question answering, except several candidate answers are provided along with a context and the model is trained to select the correct answer.
This guide will show you how to:
1. Finetune [BERT](https://huggingface.co/google-bert/bert-base-uncased) on the `regular` configuration of the [SWAG](https://huggingface.co/datasets/swag) dataset to select the best answer given multiple options and some context.
2. Use your finetuned model for inference.
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary libraries installed:
```bash
pip install transformers datasets evaluate
```
We encourage you to login to your Hugging Face account so you can upload and share your model with the community. When prompted, enter your token to login:
```py
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
>>> notebook_login()
```
## Load SWAG dataset
Start by loading the `regular` configuration of the SWAG dataset from the 🤗 Datasets library:
```py
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> swag = load_dataset("swag", "regular")
```
Then take a look at an example:
```py
>>> swag["train"][0]
{'ending0': 'passes by walking down the street playing their instruments.',
'ending1': 'has heard approaching them.',
'ending2': "arrives and they're outside dancing and asleep.",
'ending3': 'turns the lead singer watches the performance.',
'fold-ind': '3416',
'gold-source': 'gold',
'label': 0,
'sent1': 'Members of the procession walk down the street holding small horn brass instruments.',
'sent2': 'A drum line',
'startphrase': 'Members of the procession walk down the street holding small horn brass instruments. A drum line',
'video-id': 'anetv_jkn6uvmqwh4'}
```
While it looks like there are a lot of fields here, it is actually pretty straightforward:
- `sent1` and `sent2`: these fields show how a sentence starts, and if you put the two together, you get the `startphrase` field.
- `ending`: suggests a possible ending for how a sentence can end, but only one of them is correct.
- `label`: identifies the correct sentence ending.
## Preprocess
The next step is to load a BERT tokenizer to process the sentence starts and the four possible endings:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
```
The preprocessing function you want to create needs to:
1. Make four copies of the `sent1` field and combine each of them with `sent2` to recreate how a sentence starts.
2. Combine `sent2` with each of the four possible sentence endings.
3. Flatten these two lists so you can tokenize them, and then unflatten them afterward so each example has a corresponding `input_ids`, `attention_mask`, and `labels` field.
```py
>>> ending_names = ["ending0", "ending1", "ending2", "ending3"]
>>> def preprocess_function(examples):
... first_sentences = [[context] * 4 for context in examples["sent1"]]
... question_headers = examples["sent2"]
... second_sentences = [
... [f"{header} {examples[end][i]}" for end in ending_names] for i, header in enumerate(question_headers)
... ]
... first_sentences = sum(first_sentences, [])
... second_sentences = sum(second_sentences, [])
... tokenized_examples = tokenizer(first_sentences, second_sentences, truncation=True)
... return {k: [v[i : i + 4] for i in range(0, len(v), 4)] for k, v in tokenized_examples.items()}
```
To apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset, use 🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] method. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once:
```py
tokenized_swag = swag.map(preprocess_function, batched=True)
```
🤗 Transformers doesn't have a data collator for multiple choice, so you'll need to adapt the [`DataCollatorWithPadding`] to create a batch of examples. It's more efficient to *dynamically pad* the sentences to the longest length in a batch during collation, instead of padding the whole dataset to the maximum length.
`DataCollatorForMultipleChoice` flattens all the model inputs, applies padding, and then unflattens the results:
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
```py
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
>>> from transformers.tokenization_utils_base import PreTrainedTokenizerBase, PaddingStrategy
>>> from typing import Optional, Union
>>> import torch
>>> @dataclass
... class DataCollatorForMultipleChoice:
... """
... Data collator that will dynamically pad the inputs for multiple choice received.
... """
... tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase
... padding: Union[bool, str, PaddingStrategy] = True
... max_length: Optional[int] = None
... pad_to_multiple_of: Optional[int] = None
... def __call__(self, features):
... label_name = "label" if "label" in features[0].keys() else "labels"
... labels = [feature.pop(label_name) for feature in features]
... batch_size = len(features)
... num_choices = len(features[0]["input_ids"])
... flattened_features = [
... [{k: v[i] for k, v in feature.items()} for i in range(num_choices)] for feature in features
... ]
... flattened_features = sum(flattened_features, [])
... batch = self.tokenizer.pad(
... flattened_features,
... padding=self.padding,
... max_length=self.max_length,
... pad_to_multiple_of=self.pad_to_multiple_of,
... return_tensors="pt",
... )
... batch = {k: v.view(batch_size, num_choices, -1) for k, v in batch.items()}
... batch["labels"] = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.int64)
... return batch
```
</pt>
<tf>
```py
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
>>> from transformers.tokenization_utils_base import PreTrainedTokenizerBase, PaddingStrategy
>>> from typing import Optional, Union
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> @dataclass
... class DataCollatorForMultipleChoice:
... """
... Data collator that will dynamically pad the inputs for multiple choice received.
... """
... tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase
... padding: Union[bool, str, PaddingStrategy] = True
... max_length: Optional[int] = None
... pad_to_multiple_of: Optional[int] = None
... def __call__(self, features):
... label_name = "label" if "label" in features[0].keys() else "labels"
... labels = [feature.pop(label_name) for feature in features]
... batch_size = len(features)
... num_choices = len(features[0]["input_ids"])
... flattened_features = [
... [{k: v[i] for k, v in feature.items()} for i in range(num_choices)] for feature in features
... ]
... flattened_features = sum(flattened_features, [])
... batch = self.tokenizer.pad(
... flattened_features,
... padding=self.padding,
... max_length=self.max_length,
... pad_to_multiple_of=self.pad_to_multiple_of,
... return_tensors="tf",
... )
... batch = {k: tf.reshape(v, (batch_size, num_choices, -1)) for k, v in batch.items()}
... batch["labels"] = tf.convert_to_tensor(labels, dtype=tf.int64)
... return batch
```
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
## Evaluate
Including a metric during training is often helpful for evaluating your model's performance. You can quickly load a evaluation method with the 🤗 [Evaluate](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/index) library. For this task, load the [accuracy](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/accuracy) metric (see the 🤗 Evaluate [quick tour](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/a_quick_tour) to learn more about how to load and compute a metric):
```py
>>> import evaluate
>>> accuracy = evaluate.load("accuracy")
```
Then create a function that passes your predictions and labels to [`~evaluate.EvaluationModule.compute`] to calculate the accuracy:
```py
>>> import numpy as np
>>> def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
... predictions, labels = eval_pred
... predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
... return accuracy.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
```
Your `compute_metrics` function is ready to go now, and you'll return to it when you setup your training.
## Train
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
<Tip>
If you aren't familiar with finetuning a model with the [`Trainer`], take a look at the basic tutorial [here](../training#train-with-pytorch-trainer)!
</Tip>
You're ready to start training your model now! Load BERT with [`AutoModelForMultipleChoice`]:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForMultipleChoice, TrainingArguments, Trainer
>>> model = AutoModelForMultipleChoice.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
```
At this point, only three steps remain:
1. Define your training hyperparameters in [`TrainingArguments`]. The only required parameter is `output_dir` which specifies where to save your model. You'll push this model to the Hub by setting `push_to_hub=True` (you need to be signed in to Hugging Face to upload your model). At the end of each epoch, the [`Trainer`] will evaluate the accuracy and save the training checkpoint.
2. Pass the training arguments to [`Trainer`] along with the model, dataset, tokenizer, data collator, and `compute_metrics` function.
3. Call [`~Trainer.train`] to finetune your model.
```py
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(
... output_dir="my_awesome_swag_model",
... eval_strategy="epoch",
... save_strategy="epoch",
... load_best_model_at_end=True,
... learning_rate=5e-5,
... per_device_train_batch_size=16,
... per_device_eval_batch_size=16,
... num_train_epochs=3,
... weight_decay=0.01,
... push_to_hub=True,
... )
>>> trainer = Trainer(
... model=model,
... args=training_args,
... train_dataset=tokenized_swag["train"],
... eval_dataset=tokenized_swag["validation"],
... processing_class=tokenizer,
... data_collator=DataCollatorForMultipleChoice(tokenizer=tokenizer),
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
... )
>>> trainer.train()
```
Once training is completed, share your model to the Hub with the [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] method so everyone can use your model:
```py
>>> trainer.push_to_hub()
```
</pt>
<tf>
<Tip>
If you aren't familiar with finetuning a model with Keras, take a look at the basic tutorial [here](../training#train-a-tensorflow-model-with-keras)!
</Tip>
To finetune a model in TensorFlow, start by setting up an optimizer function, learning rate schedule, and some training hyperparameters:
```py
>>> from transformers import create_optimizer
>>> batch_size = 16
>>> num_train_epochs = 2
>>> total_train_steps = (len(tokenized_swag["train"]) // batch_size) * num_train_epochs
>>> optimizer, schedule = create_optimizer(init_lr=5e-5, num_warmup_steps=0, num_train_steps=total_train_steps)
```
Then you can load BERT with [`TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice`]:
```py
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice
>>> model = TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
```
Convert your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`~transformers.TFPreTrainedModel.prepare_tf_dataset`]:
```py
>>> data_collator = DataCollatorForMultipleChoice(tokenizer=tokenizer)
>>> tf_train_set = model.prepare_tf_dataset(
... tokenized_swag["train"],
... shuffle=True,
... batch_size=batch_size,
... collate_fn=data_collator,
... )
>>> tf_validation_set = model.prepare_tf_dataset(
... tokenized_swag["validation"],
... shuffle=False,
... batch_size=batch_size,
... collate_fn=data_collator,
... )
```
Configure the model for training with [`compile`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#compile-method). Note that Transformers models all have a default task-relevant loss function, so you don't need to specify one unless you want to:
```py
>>> model.compile(optimizer=optimizer) # No loss argument!
```
The last two things to setup before you start training is to compute the accuracy from the predictions, and provide a way to push your model to the Hub. Both are done by using [Keras callbacks](../main_classes/keras_callbacks).
Pass your `compute_metrics` function to [`~transformers.KerasMetricCallback`]:
```py
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import KerasMetricCallback
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_validation_set)
```
Specify where to push your model and tokenizer in the [`~transformers.PushToHubCallback`]:
```py
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import PushToHubCallback
>>> push_to_hub_callback = PushToHubCallback(
... output_dir="my_awesome_model",
... tokenizer=tokenizer,
... )
```
Then bundle your callbacks together:
```py
>>> callbacks = [metric_callback, push_to_hub_callback]
```
Finally, you're ready to start training your model! Call [`fit`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#fit-method) with your training and validation datasets, the number of epochs, and your callbacks to finetune the model:
```py
>>> model.fit(x=tf_train_set, validation_data=tf_validation_set, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)
```
Once training is completed, your model is automatically uploaded to the Hub so everyone can use it!
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
<Tip>
For a more in-depth example of how to finetune a model for multiple choice, take a look at the corresponding
[PyTorch notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice.ipynb)
or [TensorFlow notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice-tf.ipynb).
</Tip>
## Inference
Great, now that you've finetuned a model, you can use it for inference!
Come up with some text and two candidate answers:
```py
>>> prompt = "France has a bread law, Le Décret Pain, with strict rules on what is allowed in a traditional baguette."
>>> candidate1 = "The law does not apply to croissants and brioche."
>>> candidate2 = "The law applies to baguettes."
```
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
Tokenize each prompt and candidate answer pair and return PyTorch tensors. You should also create some `labels`:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_swag_model")
>>> inputs = tokenizer([[prompt, candidate1], [prompt, candidate2]], return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
>>> labels = torch.tensor(0).unsqueeze(0)
```
Pass your inputs and labels to the model and return the `logits`:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForMultipleChoice
>>> model = AutoModelForMultipleChoice.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_swag_model")
>>> outputs = model(**{k: v.unsqueeze(0) for k, v in inputs.items()}, labels=labels)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
```
Get the class with the highest probability:
```py
>>> predicted_class = logits.argmax().item()
>>> predicted_class
0
```
</pt>
<tf>
Tokenize each prompt and candidate answer pair and return TensorFlow tensors:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_swag_model")
>>> inputs = tokenizer([[prompt, candidate1], [prompt, candidate2]], return_tensors="tf", padding=True)
```
Pass your inputs to the model and return the `logits`:
```py
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice
>>> model = TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice.from_pretrained("username/my_awesome_swag_model")
>>> inputs = {k: tf.expand_dims(v, 0) for k, v in inputs.items()}
>>> outputs = model(inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
```
Get the class with the highest probability:
```py
>>> predicted_class = int(tf.math.argmax(logits, axis=-1)[0])
>>> predicted_class
0
```
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/en/tasks/multiple_choice.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/tasks/multiple_choice.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5495
}
| 31 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Testing
Let's take a look at how 🤗 Transformers models are tested and how you can write new tests and improve the existing ones.
There are 2 test suites in the repository:
1. `tests` -- tests for the general API
2. `examples` -- tests primarily for various applications that aren't part of the API
## How transformers are tested
1. Once a PR is submitted it gets tested with 9 CircleCi jobs. Every new commit to that PR gets retested. These jobs
are defined in this [config file](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/.circleci/config.yml), so that if needed you can reproduce the same
environment on your machine.
These CI jobs don't run `@slow` tests.
2. There are 3 jobs run by [github actions](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/actions):
- [torch hub integration](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/.github/workflows/github-torch-hub.yml): checks whether torch hub
integration works.
- [self-hosted (push)](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/.github/workflows/self-push.yml): runs fast tests on GPU only on commits on
`main`. It only runs if a commit on `main` has updated the code in one of the following folders: `src`,
`tests`, `.github` (to prevent running on added model cards, notebooks, etc.)
- [self-hosted runner](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml): runs normal and slow tests on GPU in
`tests` and `examples`:
```bash
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest tests/
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest examples/
```
The results can be observed [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/actions).
## Running tests
### Choosing which tests to run
This document goes into many details of how tests can be run. If after reading everything, you need even more details
you will find them [here](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/usage.html).
Here are some most useful ways of running tests.
Run all:
```console
pytest
```
or:
```bash
make test
```
Note that the latter is defined as:
```bash
python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
```
which tells pytest to:
- run as many test processes as they are CPU cores (which could be too many if you don't have a ton of RAM!)
- ensure that all tests from the same file will be run by the same test process
- do not capture output
- run in verbose mode
### Getting the list of all tests
All tests of the test suite:
```bash
pytest --collect-only -q
```
All tests of a given test file:
```bash
pytest tests/test_optimization.py --collect-only -q
```
### Run a specific test module
To run an individual test module:
```bash
pytest tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
### Run specific tests
Since unittest is used inside most of the tests, to run specific subtests you need to know the name of the unittest
class containing those tests. For example, it could be:
```bash
pytest tests/test_optimization.py::OptimizationTest::test_adam_w
```
Here:
- `tests/test_optimization.py` - the file with tests
- `OptimizationTest` - the name of the class
- `test_adam_w` - the name of the specific test function
If the file contains multiple classes, you can choose to run only tests of a given class. For example:
```bash
pytest tests/test_optimization.py::OptimizationTest
```
will run all the tests inside that class.
As mentioned earlier you can see what tests are contained inside the `OptimizationTest` class by running:
```bash
pytest tests/test_optimization.py::OptimizationTest --collect-only -q
```
You can run tests by keyword expressions.
To run only tests whose name contains `adam`:
```bash
pytest -k adam tests/test_optimization.py
```
Logical `and` and `or` can be used to indicate whether all keywords should match or either. `not` can be used to
negate.
To run all tests except those whose name contains `adam`:
```bash
pytest -k "not adam" tests/test_optimization.py
```
And you can combine the two patterns in one:
```bash
pytest -k "ada and not adam" tests/test_optimization.py
```
For example to run both `test_adafactor` and `test_adam_w` you can use:
```bash
pytest -k "test_adafactor or test_adam_w" tests/test_optimization.py
```
Note that we use `or` here, since we want either of the keywords to match to include both.
If you want to include only tests that include both patterns, `and` is to be used:
```bash
pytest -k "test and ada" tests/test_optimization.py
```
### Run `accelerate` tests
Sometimes you need to run `accelerate` tests on your models. For that you can just add `-m accelerate_tests` to your command, if let's say you want to run these tests on `OPT` run:
```bash
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -m accelerate_tests tests/models/opt/test_modeling_opt.py
```
### Run documentation tests
In order to test whether the documentation examples are correct, you should check that the `doctests` are passing.
As an example, let's use [`WhisperModel.forward`'s docstring](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/1124d95dbb1a3512d3e80791d73d0f541d1d7e9f/src/transformers/models/whisper/modeling_whisper.py#L1591-L1609)
```python
r"""
Returns:
Example:
```python
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import WhisperModel, WhisperFeatureExtractor
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> model = WhisperModel.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-base")
>>> feature_extractor = WhisperFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-base")
>>> ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_dummy", "clean", split="validation")
>>> inputs = feature_extractor(ds[0]["audio"]["array"], return_tensors="pt")
>>> input_features = inputs.input_features
>>> decoder_input_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 1]]) * model.config.decoder_start_token_id
>>> last_hidden_state = model(input_features, decoder_input_ids=decoder_input_ids).last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_state.shape)
[1, 2, 512]
```"""
```
Just run the following line to automatically test every docstring example in the desired file:
```bash
pytest --doctest-modules <path_to_file_or_dir>
```
If the file has a markdown extention, you should add the `--doctest-glob="*.md"` argument.
### Run only modified tests
You can run the tests related to the unstaged files or the current branch (according to Git) by using [pytest-picked](https://github.com/anapaulagomes/pytest-picked). This is a great way of quickly testing your changes didn't break
anything, since it won't run the tests related to files you didn't touch.
```bash
pip install pytest-picked
```
```bash
pytest --picked
```
All tests will be run from files and folders which are modified, but not yet committed.
### Automatically rerun failed tests on source modification
[pytest-xdist](https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-xdist) provides a very useful feature of detecting all failed
tests, and then waiting for you to modify files and continuously re-rerun those failing tests until they pass while you
fix them. So that you don't need to re start pytest after you made the fix. This is repeated until all tests pass after
which again a full run is performed.
```bash
pip install pytest-xdist
```
To enter the mode: `pytest -f` or `pytest --looponfail`
File changes are detected by looking at `looponfailroots` root directories and all of their contents (recursively).
If the default for this value does not work for you, you can change it in your project by setting a configuration
option in `setup.cfg`:
```ini
[tool:pytest]
looponfailroots = transformers tests
```
or `pytest.ini`/``tox.ini`` files:
```ini
[pytest]
looponfailroots = transformers tests
```
This would lead to only looking for file changes in the respective directories, specified relatively to the ini-file’s
directory.
[pytest-watch](https://github.com/joeyespo/pytest-watch) is an alternative implementation of this functionality.
### Skip a test module
If you want to run all test modules, except a few you can exclude them by giving an explicit list of tests to run. For
example, to run all except `test_modeling_*.py` tests:
```bash
pytest *ls -1 tests/*py | grep -v test_modeling*
```
### Clearing state
CI builds and when isolation is important (against speed), cache should be cleared:
```bash
pytest --cache-clear tests
```
### Running tests in parallel
As mentioned earlier `make test` runs tests in parallel via `pytest-xdist` plugin (`-n X` argument, e.g. `-n 2`
to run 2 parallel jobs).
`pytest-xdist`'s `--dist=` option allows one to control how the tests are grouped. `--dist=loadfile` puts the
tests located in one file onto the same process.
Since the order of executed tests is different and unpredictable, if running the test suite with `pytest-xdist`
produces failures (meaning we have some undetected coupled tests), use [pytest-replay](https://github.com/ESSS/pytest-replay) to replay the tests in the same order, which should help with then somehow
reducing that failing sequence to a minimum.
### Test order and repetition
It's good to repeat the tests several times, in sequence, randomly, or in sets, to detect any potential
inter-dependency and state-related bugs (tear down). And the straightforward multiple repetition is just good to detect
some problems that get uncovered by randomness of DL.
#### Repeat tests
- [pytest-flakefinder](https://github.com/dropbox/pytest-flakefinder):
```bash
pip install pytest-flakefinder
```
And then run every test multiple times (50 by default):
```bash
pytest --flake-finder --flake-runs=5 tests/test_failing_test.py
```
<Tip>
This plugin doesn't work with `-n` flag from `pytest-xdist`.
</Tip>
<Tip>
There is another plugin `pytest-repeat`, but it doesn't work with `unittest`.
</Tip>
#### Run tests in a random order
```bash
pip install pytest-random-order
```
Important: the presence of `pytest-random-order` will automatically randomize tests, no configuration change or
command line options is required.
As explained earlier this allows detection of coupled tests - where one test's state affects the state of another. When
`pytest-random-order` is installed it will print the random seed it used for that session, e.g:
```bash
pytest tests
[...]
Using --random-order-bucket=module
Using --random-order-seed=573663
```
So that if the given particular sequence fails, you can reproduce it by adding that exact seed, e.g.:
```bash
pytest --random-order-seed=573663
[...]
Using --random-order-bucket=module
Using --random-order-seed=573663
```
It will only reproduce the exact order if you use the exact same list of tests (or no list at all). Once you start to
manually narrowing down the list you can no longer rely on the seed, but have to list them manually in the exact order
they failed and tell pytest to not randomize them instead using `--random-order-bucket=none`, e.g.:
```bash
pytest --random-order-bucket=none tests/test_a.py tests/test_c.py tests/test_b.py
```
To disable the shuffling for all tests:
```bash
pytest --random-order-bucket=none
```
By default `--random-order-bucket=module` is implied, which will shuffle the files on the module levels. It can also
shuffle on `class`, `package`, `global` and `none` levels. For the complete details please see its
[documentation](https://github.com/jbasko/pytest-random-order).
Another randomization alternative is: [`pytest-randomly`](https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-randomly). This
module has a very similar functionality/interface, but it doesn't have the bucket modes available in
`pytest-random-order`. It has the same problem of imposing itself once installed.
### Look and feel variations
#### pytest-sugar
[pytest-sugar](https://github.com/Frozenball/pytest-sugar) is a plugin that improves the look-n-feel, adds a
progressbar, and show tests that fail and the assert instantly. It gets activated automatically upon installation.
```bash
pip install pytest-sugar
```
To run tests without it, run:
```bash
pytest -p no:sugar
```
or uninstall it.
#### Report each sub-test name and its progress
For a single or a group of tests via `pytest` (after `pip install pytest-pspec`):
```bash
pytest --pspec tests/test_optimization.py
```
#### Instantly shows failed tests
[pytest-instafail](https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-instafail) shows failures and errors instantly instead of
waiting until the end of test session.
```bash
pip install pytest-instafail
```
```bash
pytest --instafail
```
### To GPU or not to GPU
On a GPU-enabled setup, to test in CPU-only mode add `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=""` for CUDA GPUs:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="" pytest tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
or if you have multiple gpus, you can specify which one is to be used by `pytest`. For example, to use only the
second gpu if you have gpus `0` and `1`, you can run:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="1" pytest tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
For Intel GPUs, use `ZE_AFFINITY_MASK` instead of `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES` in the above example.
This is handy when you want to run different tasks on different GPUs.
Some tests must be run on CPU-only, others on either CPU or GPU or TPU, yet others on multiple-GPUs. The following skip
decorators are used to set the requirements of tests CPU/GPU/XPU/TPU-wise:
- `require_torch` - this test will run only under torch
- `require_torch_gpu` - as `require_torch` plus requires at least 1 GPU
- `require_torch_multi_gpu` - as `require_torch` plus requires at least 2 GPUs
- `require_torch_non_multi_gpu` - as `require_torch` plus requires 0 or 1 GPUs
- `require_torch_up_to_2_gpus` - as `require_torch` plus requires 0 or 1 or 2 GPUs
- `require_torch_xla` - as `require_torch` plus requires at least 1 TPU
Let's depict the GPU requirements in the following table:
| n gpus | decorator |
|--------|--------------------------------|
| `>= 0` | `@require_torch` |
| `>= 1` | `@require_torch_gpu` |
| `>= 2` | `@require_torch_multi_gpu` |
| `< 2` | `@require_torch_non_multi_gpu` |
| `< 3` | `@require_torch_up_to_2_gpus` |
For example, here is a test that must be run only when there are 2 or more GPUs available and pytorch is installed:
```python no-style
@require_torch_multi_gpu
def test_example_with_multi_gpu():
```
If a test requires `tensorflow` use the `require_tf` decorator. For example:
```python no-style
@require_tf
def test_tf_thing_with_tensorflow():
```
These decorators can be stacked. For example, if a test is slow and requires at least one GPU under pytorch, here is
how to set it up:
```python no-style
@require_torch_gpu
@slow
def test_example_slow_on_gpu():
```
Some decorators like `@parametrized` rewrite test names, therefore `@require_*` skip decorators have to be listed
last for them to work correctly. Here is an example of the correct usage:
```python no-style
@parameterized.expand(...)
@require_torch_multi_gpu
def test_integration_foo():
```
This order problem doesn't exist with `@pytest.mark.parametrize`, you can put it first or last and it will still
work. But it only works with non-unittests.
Inside tests:
- How many GPUs are available:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import get_gpu_count
n_gpu = get_gpu_count() # works with torch and tf
```
### Testing with a specific PyTorch backend or device
To run the test suite on a specific torch device add `TRANSFORMERS_TEST_DEVICE="$device"` where `$device` is the target backend. For example, to test on CPU only:
```bash
TRANSFORMERS_TEST_DEVICE="cpu" pytest tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
This variable is useful for testing custom or less common PyTorch backends such as `mps`, `xpu` or `npu`. It can also be used to achieve the same effect as `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES` by targeting specific GPUs or testing in CPU-only mode.
Certain devices will require an additional import after importing `torch` for the first time. This can be specified using the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_TEST_BACKEND`:
```bash
TRANSFORMERS_TEST_BACKEND="torch_npu" pytest tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
Alternative backends may also require the replacement of device-specific functions. For example `torch.cuda.manual_seed` may need to be replaced with a device-specific seed setter like `torch.npu.manual_seed` or `torch.xpu.manual_seed` to correctly set a random seed on the device. To specify a new backend with backend-specific device functions when running the test suite, create a Python device specification file `spec.py` in the format:
```python
import torch
import torch_npu # for xpu, replace it with `import intel_extension_for_pytorch`
# !! Further additional imports can be added here !!
# Specify the device name (eg. 'cuda', 'cpu', 'npu', 'xpu', 'mps')
DEVICE_NAME = 'npu'
# Specify device-specific backends to dispatch to.
# If not specified, will fallback to 'default' in 'testing_utils.py`
MANUAL_SEED_FN = torch.npu.manual_seed
EMPTY_CACHE_FN = torch.npu.empty_cache
DEVICE_COUNT_FN = torch.npu.device_count
```
This format also allows for specification of any additional imports required. To use this file to replace equivalent methods in the test suite, set the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_TEST_DEVICE_SPEC` to the path of the spec file, e.g. `TRANSFORMERS_TEST_DEVICE_SPEC=spec.py`.
Currently, only `MANUAL_SEED_FN`, `EMPTY_CACHE_FN` and `DEVICE_COUNT_FN` are supported for device-specific dispatch.
### Distributed training
`pytest` can't deal with distributed training directly. If this is attempted - the sub-processes don't do the right
thing and end up thinking they are `pytest` and start running the test suite in loops. It works, however, if one
spawns a normal process that then spawns off multiple workers and manages the IO pipes.
Here are some tests that use it:
- [test_trainer_distributed.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/tests/trainer/test_trainer_distributed.py)
- [test_deepspeed.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/tests/deepspeed/test_deepspeed.py)
To jump right into the execution point, search for the `execute_subprocess_async` call in those tests.
You will need at least 2 GPUs to see these tests in action:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -sv tests/test_trainer_distributed.py
```
### Output capture
During test execution any output sent to `stdout` and `stderr` is captured. If a test or a setup method fails, its
according captured output will usually be shown along with the failure traceback.
To disable output capturing and to get the `stdout` and `stderr` normally, use `-s` or `--capture=no`:
```bash
pytest -s tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
To send test results to JUnit format output:
```bash
pytest tests --junitxml=result.xml
```
### Color control
To have no color (e.g., yellow on white background is not readable):
```bash
pytest --color=no tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
### Sending test report to online pastebin service
Creating a URL for each test failure:
```bash
pytest --pastebin=failed tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
This will submit test run information to a remote Paste service and provide a URL for each failure. You may select
tests as usual or add for example -x if you only want to send one particular failure.
Creating a URL for a whole test session log:
```bash
pytest --pastebin=all tests/utils/test_logging.py
```
## Writing tests
🤗 transformers tests are based on `unittest`, but run by `pytest`, so most of the time features from both systems
can be used.
You can read [here](https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/unittest.html) which features are supported, but the important
thing to remember is that most `pytest` fixtures don't work. Neither parametrization, but we use the module
`parameterized` that works in a similar way.
### Parametrization
Often, there is a need to run the same test multiple times, but with different arguments. It could be done from within
the test, but then there is no way of running that test for just one set of arguments.
```python
# test_this1.py
import unittest
from parameterized import parameterized
class TestMathUnitTest(unittest.TestCase):
@parameterized.expand(
[
("negative", -1.5, -2.0),
("integer", 1, 1.0),
("large fraction", 1.6, 1),
]
)
def test_floor(self, name, input, expected):
assert_equal(math.floor(input), expected)
```
Now, by default this test will be run 3 times, each time with the last 3 arguments of `test_floor` being assigned the
corresponding arguments in the parameter list.
and you could run just the `negative` and `integer` sets of params with:
```bash
pytest -k "negative and integer" tests/test_mytest.py
```
or all but `negative` sub-tests, with:
```bash
pytest -k "not negative" tests/test_mytest.py
```
Besides using the `-k` filter that was just mentioned, you can find out the exact name of each sub-test and run any
or all of them using their exact names.
```bash
pytest test_this1.py --collect-only -q
```
and it will list:
```bash
test_this1.py::TestMathUnitTest::test_floor_0_negative
test_this1.py::TestMathUnitTest::test_floor_1_integer
test_this1.py::TestMathUnitTest::test_floor_2_large_fraction
```
So now you can run just 2 specific sub-tests:
```bash
pytest test_this1.py::TestMathUnitTest::test_floor_0_negative test_this1.py::TestMathUnitTest::test_floor_1_integer
```
The module [parameterized](https://pypi.org/project/parameterized/) which is already in the developer dependencies
of `transformers` works for both: `unittests` and `pytest` tests.
If, however, the test is not a `unittest`, you may use `pytest.mark.parametrize` (or you may see it being used in
some existing tests, mostly under `examples`).
Here is the same example, this time using `pytest`'s `parametrize` marker:
```python
# test_this2.py
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"name, input, expected",
[
("negative", -1.5, -2.0),
("integer", 1, 1.0),
("large fraction", 1.6, 1),
],
)
def test_floor(name, input, expected):
assert_equal(math.floor(input), expected)
```
Same as with `parameterized`, with `pytest.mark.parametrize` you can have a fine control over which sub-tests are
run, if the `-k` filter doesn't do the job. Except, this parametrization function creates a slightly different set of
names for the sub-tests. Here is what they look like:
```bash
pytest test_this2.py --collect-only -q
```
and it will list:
```bash
test_this2.py::test_floor[integer-1-1.0]
test_this2.py::test_floor[negative--1.5--2.0]
test_this2.py::test_floor[large fraction-1.6-1]
```
So now you can run just the specific test:
```bash
pytest test_this2.py::test_floor[negative--1.5--2.0] test_this2.py::test_floor[integer-1-1.0]
```
as in the previous example.
### Files and directories
In tests often we need to know where things are relative to the current test file, and it's not trivial since the test
could be invoked from more than one directory or could reside in sub-directories with different depths. A helper class
`transformers.test_utils.TestCasePlus` solves this problem by sorting out all the basic paths and provides easy
accessors to them:
- `pathlib` objects (all fully resolved):
- `test_file_path` - the current test file path, i.e. `__file__`
- `test_file_dir` - the directory containing the current test file
- `tests_dir` - the directory of the `tests` test suite
- `examples_dir` - the directory of the `examples` test suite
- `repo_root_dir` - the directory of the repository
- `src_dir` - the directory of `src` (i.e. where the `transformers` sub-dir resides)
- stringified paths---same as above but these return paths as strings, rather than `pathlib` objects:
- `test_file_path_str`
- `test_file_dir_str`
- `tests_dir_str`
- `examples_dir_str`
- `repo_root_dir_str`
- `src_dir_str`
To start using those all you need is to make sure that the test resides in a subclass of
`transformers.test_utils.TestCasePlus`. For example:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import TestCasePlus
class PathExampleTest(TestCasePlus):
def test_something_involving_local_locations(self):
data_dir = self.tests_dir / "fixtures/tests_samples/wmt_en_ro"
```
If you don't need to manipulate paths via `pathlib` or you just need a path as a string, you can always invoked
`str()` on the `pathlib` object or use the accessors ending with `_str`. For example:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import TestCasePlus
class PathExampleTest(TestCasePlus):
def test_something_involving_stringified_locations(self):
examples_dir = self.examples_dir_str
```
### Temporary files and directories
Using unique temporary files and directories are essential for parallel test running, so that the tests won't overwrite
each other's data. Also we want to get the temporary files and directories removed at the end of each test that created
them. Therefore, using packages like `tempfile`, which address these needs is essential.
However, when debugging tests, you need to be able to see what goes into the temporary file or directory and you want
to know it's exact path and not having it randomized on every test re-run.
A helper class `transformers.test_utils.TestCasePlus` is best used for such purposes. It's a sub-class of
`unittest.TestCase`, so we can easily inherit from it in the test modules.
Here is an example of its usage:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import TestCasePlus
class ExamplesTests(TestCasePlus):
def test_whatever(self):
tmp_dir = self.get_auto_remove_tmp_dir()
```
This code creates a unique temporary directory, and sets `tmp_dir` to its location.
- Create a unique temporary dir:
```python
def test_whatever(self):
tmp_dir = self.get_auto_remove_tmp_dir()
```
`tmp_dir` will contain the path to the created temporary dir. It will be automatically removed at the end of the
test.
- Create a temporary dir of my choice, ensure it's empty before the test starts and don't empty it after the test.
```python
def test_whatever(self):
tmp_dir = self.get_auto_remove_tmp_dir("./xxx")
```
This is useful for debug when you want to monitor a specific directory and want to make sure the previous tests didn't
leave any data in there.
- You can override the default behavior by directly overriding the `before` and `after` args, leading to one of the
following behaviors:
- `before=True`: the temporary dir will always be cleared at the beginning of the test.
- `before=False`: if the temporary dir already existed, any existing files will remain there.
- `after=True`: the temporary dir will always be deleted at the end of the test.
- `after=False`: the temporary dir will always be left intact at the end of the test.
<Tip>
In order to run the equivalent of `rm -r` safely, only subdirs of the project repository checkout are allowed if
an explicit `tmp_dir` is used, so that by mistake no `/tmp` or similar important part of the filesystem will
get nuked. i.e. please always pass paths that start with `./`.
</Tip>
<Tip>
Each test can register multiple temporary directories and they all will get auto-removed, unless requested
otherwise.
</Tip>
### Temporary sys.path override
If you need to temporary override `sys.path` to import from another test for example, you can use the
`ExtendSysPath` context manager. Example:
```python
import os
from transformers.testing_utils import ExtendSysPath
bindir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
with ExtendSysPath(f"{bindir}/.."):
from test_trainer import TrainerIntegrationCommon # noqa
```
### Skipping tests
This is useful when a bug is found and a new test is written, yet the bug is not fixed yet. In order to be able to
commit it to the main repository we need make sure it's skipped during `make test`.
Methods:
- A **skip** means that you expect your test to pass only if some conditions are met, otherwise pytest should skip
running the test altogether. Common examples are skipping windows-only tests on non-windows platforms, or skipping
tests that depend on an external resource which is not available at the moment (for example a database).
- A **xfail** means that you expect a test to fail for some reason. A common example is a test for a feature not yet
implemented, or a bug not yet fixed. When a test passes despite being expected to fail (marked with
pytest.mark.xfail), it’s an xpass and will be reported in the test summary.
One of the important differences between the two is that `skip` doesn't run the test, and `xfail` does. So if the
code that's buggy causes some bad state that will affect other tests, do not use `xfail`.
#### Implementation
- Here is how to skip whole test unconditionally:
```python no-style
@unittest.skip(reason="this bug needs to be fixed")
def test_feature_x():
```
or via pytest:
```python no-style
@pytest.mark.skip(reason="this bug needs to be fixed")
```
or the `xfail` way:
```python no-style
@pytest.mark.xfail
def test_feature_x():
```
Here's how to skip a test based on internal checks within the test:
```python
def test_feature_x():
if not has_something():
pytest.skip("unsupported configuration")
```
or the whole module:
```python
import pytest
if not pytest.config.getoption("--custom-flag"):
pytest.skip("--custom-flag is missing, skipping tests", allow_module_level=True)
```
or the `xfail` way:
```python
def test_feature_x():
pytest.xfail("expected to fail until bug XYZ is fixed")
```
- Here is how to skip all tests in a module if some import is missing:
```python
docutils = pytest.importorskip("docutils", minversion="0.3")
```
- Skip a test based on a condition:
```python no-style
@pytest.mark.skipif(sys.version_info < (3,6), reason="requires python3.6 or higher")
def test_feature_x():
```
or:
```python no-style
@unittest.skipIf(torch_device == "cpu", "Can't do half precision")
def test_feature_x():
```
or skip the whole module:
```python no-style
@pytest.mark.skipif(sys.platform == 'win32', reason="does not run on windows")
class TestClass():
def test_feature_x(self):
```
More details, example and ways are [here](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/skipping.html).
### Slow tests
The library of tests is ever-growing, and some of the tests take minutes to run, therefore we can't afford waiting for
an hour for the test suite to complete on CI. Therefore, with some exceptions for essential tests, slow tests should be
marked as in the example below:
```python no-style
from transformers.testing_utils import slow
@slow
def test_integration_foo():
```
Once a test is marked as `@slow`, to run such tests set `RUN_SLOW=1` env var, e.g.:
```bash
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest tests
```
Some decorators like `@parameterized` rewrite test names, therefore `@slow` and the rest of the skip decorators
`@require_*` have to be listed last for them to work correctly. Here is an example of the correct usage:
```python no-style
@parameterized.expand(...)
@slow
def test_integration_foo():
```
As explained at the beginning of this document, slow tests get to run on a scheduled basis, rather than in PRs CI
checks. So it's possible that some problems will be missed during a PR submission and get merged. Such problems will
get caught during the next scheduled CI job. But it also means that it's important to run the slow tests on your
machine before submitting the PR.
Here is a rough decision making mechanism for choosing which tests should be marked as slow:
If the test is focused on one of the library's internal components (e.g., modeling files, tokenization files,
pipelines), then we should run that test in the non-slow test suite. If it's focused on an other aspect of the library,
such as the documentation or the examples, then we should run these tests in the slow test suite. And then, to refine
this approach we should have exceptions:
- All tests that need to download a heavy set of weights or a dataset that is larger than ~50MB (e.g., model or
tokenizer integration tests, pipeline integration tests) should be set to slow. If you're adding a new model, you
should create and upload to the hub a tiny version of it (with random weights) for integration tests. This is
discussed in the following paragraphs.
- All tests that need to do a training not specifically optimized to be fast should be set to slow.
- We can introduce exceptions if some of these should-be-non-slow tests are excruciatingly slow, and set them to
`@slow`. Auto-modeling tests, which save and load large files to disk, are a good example of tests that are marked
as `@slow`.
- If a test completes under 1 second on CI (including downloads if any) then it should be a normal test regardless.
Collectively, all the non-slow tests need to cover entirely the different internals, while remaining fast. For example,
a significant coverage can be achieved by testing with specially created tiny models with random weights. Such models
have the very minimal number of layers (e.g., 2), vocab size (e.g., 1000), etc. Then the `@slow` tests can use large
slow models to do qualitative testing. To see the use of these simply look for *tiny* models with:
```bash
grep tiny tests examples
```
Here is an example of a [script](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/scripts/fsmt/fsmt-make-tiny-model.py) that created the tiny model
[stas/tiny-wmt19-en-de](https://huggingface.co/stas/tiny-wmt19-en-de). You can easily adjust it to your specific
model's architecture.
It's easy to measure the run-time incorrectly if for example there is an overheard of downloading a huge model, but if
you test it locally the downloaded files would be cached and thus the download time not measured. Hence check the
execution speed report in CI logs instead (the output of `pytest --durations=0 tests`).
That report is also useful to find slow outliers that aren't marked as such, or which need to be re-written to be fast.
If you notice that the test suite starts getting slow on CI, the top listing of this report will show the slowest
tests.
### Testing the stdout/stderr output
In order to test functions that write to `stdout` and/or `stderr`, the test can access those streams using the
`pytest`'s [capsys system](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/capture.html). Here is how this is accomplished:
```python
import sys
def print_to_stdout(s):
print(s)
def print_to_stderr(s):
sys.stderr.write(s)
def test_result_and_stdout(capsys):
msg = "Hello"
print_to_stdout(msg)
print_to_stderr(msg)
out, err = capsys.readouterr() # consume the captured output streams
# optional: if you want to replay the consumed streams:
sys.stdout.write(out)
sys.stderr.write(err)
# test:
assert msg in out
assert msg in err
```
And, of course, most of the time, `stderr` will come as a part of an exception, so try/except has to be used in such
a case:
```python
def raise_exception(msg):
raise ValueError(msg)
def test_something_exception():
msg = "Not a good value"
error = ""
try:
raise_exception(msg)
except Exception as e:
error = str(e)
assert msg in error, f"{msg} is in the exception:\n{error}"
```
Another approach to capturing stdout is via `contextlib.redirect_stdout`:
```python
from io import StringIO
from contextlib import redirect_stdout
def print_to_stdout(s):
print(s)
def test_result_and_stdout():
msg = "Hello"
buffer = StringIO()
with redirect_stdout(buffer):
print_to_stdout(msg)
out = buffer.getvalue()
# optional: if you want to replay the consumed streams:
sys.stdout.write(out)
# test:
assert msg in out
```
An important potential issue with capturing stdout is that it may contain `\r` characters that in normal `print`
reset everything that has been printed so far. There is no problem with `pytest`, but with `pytest -s` these
characters get included in the buffer, so to be able to have the test run with and without `-s`, you have to make an
extra cleanup to the captured output, using `re.sub(r'~.*\r', '', buf, 0, re.M)`.
But, then we have a helper context manager wrapper to automatically take care of it all, regardless of whether it has
some `\r`'s in it or not, so it's a simple:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureStdout
with CaptureStdout() as cs:
function_that_writes_to_stdout()
print(cs.out)
```
Here is a full test example:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureStdout
msg = "Secret message\r"
final = "Hello World"
with CaptureStdout() as cs:
print(msg + final)
assert cs.out == final + "\n", f"captured: {cs.out}, expecting {final}"
```
If you'd like to capture `stderr` use the `CaptureStderr` class instead:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureStderr
with CaptureStderr() as cs:
function_that_writes_to_stderr()
print(cs.err)
```
If you need to capture both streams at once, use the parent `CaptureStd` class:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureStd
with CaptureStd() as cs:
function_that_writes_to_stdout_and_stderr()
print(cs.err, cs.out)
```
Also, to aid debugging test issues, by default these context managers automatically replay the captured streams on exit
from the context.
### Capturing logger stream
If you need to validate the output of a logger, you can use `CaptureLogger`:
```python
from transformers import logging
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureLogger
msg = "Testing 1, 2, 3"
logging.set_verbosity_info()
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers.models.bart.tokenization_bart")
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cl:
logger.info(msg)
assert cl.out, msg + "\n"
```
### Testing with environment variables
If you want to test the impact of environment variables for a specific test you can use a helper decorator
`transformers.testing_utils.mockenv`
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import mockenv
class HfArgumentParserTest(unittest.TestCase):
@mockenv(TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY="error")
def test_env_override(self):
env_level_str = os.getenv("TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY", None)
```
At times an external program needs to be called, which requires setting `PYTHONPATH` in `os.environ` to include
multiple local paths. A helper class `transformers.test_utils.TestCasePlus` comes to help:
```python
from transformers.testing_utils import TestCasePlus
class EnvExampleTest(TestCasePlus):
def test_external_prog(self):
env = self.get_env()
# now call the external program, passing `env` to it
```
Depending on whether the test file was under the `tests` test suite or `examples` it'll correctly set up
`env[PYTHONPATH]` to include one of these two directories, and also the `src` directory to ensure the testing is
done against the current repo, and finally with whatever `env[PYTHONPATH]` was already set to before the test was
called if anything.
This helper method creates a copy of the `os.environ` object, so the original remains intact.
### Getting reproducible results
In some situations you may want to remove randomness for your tests. To get identical reproducible results set, you
will need to fix the seed:
```python
seed = 42
# python RNG
import random
random.seed(seed)
# pytorch RNGs
import torch
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
# numpy RNG
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(seed)
# tf RNG
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(seed)
```
### Debugging tests
To start a debugger at the point of the warning, do this:
```bash
pytest tests/utils/test_logging.py -W error::UserWarning --pdb
```
## Working with github actions workflows
To trigger a self-push workflow CI job, you must:
1. Create a new branch on `transformers` origin (not a fork!).
2. The branch name has to start with either `ci_` or `ci-` (`main` triggers it too, but we can't do PRs on
`main`). It also gets triggered only for specific paths - you can find the up-to-date definition in case it
changed since this document has been written [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/.github/workflows/self-push.yml) under *push:*
3. Create a PR from this branch.
4. Then you can see the job appear [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/actions/workflows/self-push.yml). It may not run right away if there
is a backlog.
## Testing Experimental CI Features
Testing CI features can be potentially problematic as it can interfere with the normal CI functioning. Therefore if a
new CI feature is to be added, it should be done as following.
1. Create a new dedicated job that tests what needs to be tested
2. The new job must always succeed so that it gives us a green ✓ (details below).
3. Let it run for some days to see that a variety of different PR types get to run on it (user fork branches,
non-forked branches, branches originating from github.com UI direct file edit, various forced pushes, etc. - there
are so many) while monitoring the experimental job's logs (not the overall job green as it's purposefully always
green)
4. When it's clear that everything is solid, then merge the new changes into existing jobs.
That way experiments on CI functionality itself won't interfere with the normal workflow.
Now how can we make the job always succeed while the new CI feature is being developed?
Some CIs, like TravisCI support ignore-step-failure and will report the overall job as successful, but CircleCI and
Github Actions as of this writing don't support that.
So the following workaround can be used:
1. `set +euo pipefail` at the beginning of the run command to suppress most potential failures in the bash script.
2. the last command must be a success: `echo "done"` or just `true` will do
Here is an example:
```yaml
- run:
name: run CI experiment
command: |
set +euo pipefail
echo "setting run-all-despite-any-errors-mode"
this_command_will_fail
echo "but bash continues to run"
# emulate another failure
false
# but the last command must be a success
echo "during experiment do not remove: reporting success to CI, even if there were failures"
```
For simple commands you could also do:
```bash
cmd_that_may_fail || true
```
Of course, once satisfied with the results, integrate the experimental step or job with the rest of the normal jobs,
while removing `set +euo pipefail` or any other things you may have added to ensure that the experimental job doesn't
interfere with the normal CI functioning.
This whole process would have been much easier if we only could set something like `allow-failure` for the
experimental step, and let it fail without impacting the overall status of PRs. But as mentioned earlier CircleCI and
Github Actions don't support it at the moment.
You can vote for this feature and see where it is at these CI-specific threads:
- [Github Actions:](https://github.com/actions/toolkit/issues/399)
- [CircleCI:](https://ideas.circleci.com/ideas/CCI-I-344)
## DeepSpeed integration
For a PR that involves the DeepSpeed integration, keep in mind our CircleCI PR CI setup doesn't have GPUs. Tests requiring GPUs are run on a different CI nightly. This means if you get a passing CI report in your PR, it doesn’t mean the DeepSpeed tests pass.
To run DeepSpeed tests:
```bash
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest tests/deepspeed/test_deepspeed.py
```
Any changes to the modeling or PyTorch examples code requires running the model zoo tests as well.
```bash
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest tests/deepspeed
```
|
transformers/docs/source/en/testing.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/en/testing.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 13559
}
| 32 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Plantillas para Modelos de Chat
## Introducción
Un caso de uso cada vez más común para LLMs es **el chat**. En un contexto de chat, en lugar de continuar una única cadena de texto (como es el caso con un modelo de lenguaje estándar), el modelo continúa una conversación que consta de uno o más **mensajes**, cada uno de los cuales incluye un **rol**, como "usuario" o "asistente", así como el texto del mensaje.
Al igual que con la tokenización, diferentes modelos esperan formatos de entrada muy diferentes para el chat. Esta es la razón por la que agregamos las plantillas de chat como una característica. Las plantillas de chat son parte del tokenizador. Especifican cómo convertir conversaciones, representadas como listas de mensajes, en una única cadena tokenizable en el formato que el modelo espera.
Vamos a hacer esto con un ejemplo concreto utilizando el modelo `BlenderBot`. BlenderBot tiene una plantilla predeterminada extremadamente simple, que principalmente solo agrega espacios en blanco entre rondas de diálogo:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/blenderbot-400M-distill")
>>> chat = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to show off how chat templating works!"},
... ]
>>> tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False)
" Hello, how are you? I'm doing great. How can I help you today? I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>"
```
Observa cómo todo el chat se condensa en una sola cadena. Si usamos `tokenize=True`, que es la configuración predeterminada, esa cadena también será tokenizada para nosotros. Sin embargo, para ver una plantilla más compleja en acción, usemos el modelo `mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1`
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1")
>>> chat = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to show off how chat templating works!"},
... ]
>>> tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False)
"<s>[INST] Hello, how are you? [/INST]I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s> [INST] I'd like to show off how chat templating works! [/INST]"
```
Ten en cuenta que esta vez, el tokenizador ha añadido los tokens de control [INST] y [/INST] para indicar el inicio y el final de los mensajes de usuario (¡pero no de los mensajes del asistente!). Mistral-instruct fue entrenado con estos tokens, pero BlenderBot no lo fue.
## ¿Cómo uso las plantillas de chat?
Como puedes ver en el ejemplo anterior, las plantillas de chat son fáciles de usar. Simplemente construye una lista de mensajes, con claves de `rol` y `contenido`, y luego pásala al método [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`]. Una vez que hagas eso, ¡obtendrás una salida lista para usar! Al utilizar plantillas de chat como entrada para la generación de modelos, también es una buena idea usar `add_generation_prompt=True` para agregar una [indicación de generación](#¿Qué-son-los-"generation-prompts"?).
Aquí tienes un ejemplo de cómo preparar la entrada para `model.generate()` utilizando el modelo de asistente `Zephyr`:
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
checkpoint = "HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint) # You may want to use bfloat16 and/or move to GPU here
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate",
},
{"role": "user", "content": "How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?"},
]
tokenized_chat = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt")
print(tokenizer.decode(tokenized_chat[0]))
```
Esto generará una cadena en el formato de entrada que Zephyr espera.
```text
<|system|>
You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate</s>
<|user|>
How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?</s>
<|assistant|>
```
Ahora que nuestra entrada está formateada correctamente para Zephyr, podemos usar el modelo para generar una respuesta a la pregunta del usuario:
```python
outputs = model.generate(tokenized_chat, max_new_tokens=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
Esto producirá:
```text
<|system|>
You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate</s>
<|user|>
How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?</s>
<|assistant|>
Matey, I'm afraid I must inform ye that humans cannot eat helicopters. Helicopters are not food, they are flying machines. Food is meant to be eaten, like a hearty plate o' grog, a savory bowl o' stew, or a delicious loaf o' bread. But helicopters, they be for transportin' and movin' around, not for eatin'. So, I'd say none, me hearties. None at all.
```
¡Arr, al final resultó ser fácil!
## ¿Existe un pipeline automatizado para chats?
Sí, lo hay! Nuestros canales de generación de texto admiten entradas de chat, cual facilita más facíl utilizar los modelos de chat. En el pasado, solíamos utilizar una clase dedicada "ConversationalPipeline", pero ahora ha quedado obsoleta y su funcionalidad se ha fusionado en [`TextGenerationPipeline`]. Este pipeline está diseñado para facilitar el uso de modelos de chat. Intentemos el ejemplo de `Zephyr` de nuevo, pero esta vez utilizando el pipeline:
```python
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline("conversational", "HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta")
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate",
},
{"role": "user", "content": "How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?"},
]
print(pipe(messages, max_new_tokens=128)[0]['generated_text'][-1]) # Print the assistant's response
```
```text
{'role': 'assistant', 'content': "Matey, I'm afraid I must inform ye that humans cannot eat helicopters. Helicopters are not food, they are flying machines. Food is meant to be eaten, like a hearty plate o' grog, a savory bowl o' stew, or a delicious loaf o' bread. But helicopters, they be for transportin' and movin' around, not for eatin'. So, I'd say none, me hearties. None at all."}
```
La canalización se encargará de todos los detalles de la tokenización y de llamar a `apply_chat_template` por ti. Una vez que el modelo tenga una plantilla de chat, ¡todo lo que necesitas hacer es inicializar el pipeline y pasarle la lista de mensajes!
# ¿Qué son los "generation prompts"?
Puede que hayas notado que el método `apply_chat_template` tiene un argumento `add_generation_prompt`. Este argumento indica a la plantilla que agregue tokens que indiquen el inicio de una respuesta del bot. Por ejemplo, considera el siguiente chat:
```python
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Hi there!"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Nice to meet you!"},
{"role": "user", "content": "Can I ask a question?"}
]
```
Así es cómo se verá esto sin un "generation prompt", usando la plantilla ChatML que vimos en el ejemplo de Zephyr:
```python
tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=False)
"""<|im_start|>user
Hi there!<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
Nice to meet you!<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
Can I ask a question?<|im_end|>
"""
```
Y así es como se ve **con** un "generation prompt":
```python
tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
"""<|im_start|>user
Hi there!<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
Nice to meet you!<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
Can I ask a question?<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
"""
```
Ten en cuenta que esta vez, hemos agregado los tokens que indican el inicio de una respuesta del bot. Esto asegura que cuando el modelo genere texto, escribirá una respuesta del bot en lugar de hacer algo inesperado, como continuar el mensaje del usuario. Recuerda, los modelos de chat siguen siendo solo modelos de lenguaje: están entrenados para continuar texto, ¡y el chat es solo un tipo especial de texto para ellos! Necesitas guiarlos con los tokens de control apropiados para que sepan lo que se supone que deben estar haciendo.
No todos los modelos requieren "generation prompts". Algunos modelos, como BlenderBot y LLaMA, no tienen ningún token especial antes de las respuestas del bot. En estos casos, el argumento `add_generation_prompt` no tendrá ningún efecto. El efecto exacto que tiene `add_generation_prompt` dependerá de la plantilla que se esté utilizando.
## ¿Puedo usar plantillas de chat en el entrenamiento?
¡Sí! Recomendamos que apliques la plantilla de chat como un paso de preprocesamiento para tu conjunto de datos. Después de esto, simplemente puedes continuar como cualquier otra tarea de entrenamiento de modelos de lenguaje. Durante el entrenamiento, generalmente deberías establecer `add_generation_prompt=False`, porque los tokens añadidos para solicitar una respuesta del asistente no serán útiles durante el entrenamiento. Veamos un ejemplo:
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from datasets import Dataset
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta")
chat1 = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Which is bigger, the moon or the sun?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "The sun."}
]
chat2 = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Which is bigger, a virus or a bacterium?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "A bacterium."}
]
dataset = Dataset.from_dict({"chat": [chat1, chat2]})
dataset = dataset.map(lambda x: {"formatted_chat": tokenizer.apply_chat_template(x["chat"], tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=False)})
print(dataset['formatted_chat'][0])
```
Y obtenemos:
```text
<|user|>
Which is bigger, the moon or the sun?</s>
<|assistant|>
The sun.</s>
```
Desde aquí, simplemente continúa el entrenamiento como lo harías con una tarea estándar de modelado de lenguaje, utilizando la columna `formatted_chat`.
## Avanzado: ¿Cómo funcionan las plantillas de chat?
La plantilla de chat para un modelo se almacena en el atributo `tokenizer.chat_template`. Si no se establece ninguna plantilla de chat, se utiliza en su lugar la plantilla predeterminada para esa clase de modelo. Echemos un vistazo a la plantilla para `BlenderBot`:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/blenderbot-400M-distill")
>>> tokenizer.chat_template
"{% for message in messages %}{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}{{ ' ' }}{% endif %}{{ message['content'] }}{% if not loop.last %}{{ ' ' }}{% endif %}{% endfor %}{{ eos_token }}"
```
¡Es un poco intimidante! Vamos a agregar algunas líneas nuevas y sangria para que sea más legible. Ten en cuenta que la primera línea nueva después de cada bloque, así como cualquier espacio en blanco anterior a un bloque, se ignoran de forma predeterminada, utilizando las banderas `trim_blocks` y `lstrip_blocks` de Jinja. Sin embargo, ¡ten cuidado! Aunque el espacio en blanco inicial en cada línea se elimina, los espacios entre bloques en la misma línea no. ¡Te recomendamos encarecidamente que verifiques que tu plantilla no esté imprimiendo espacios adicionales donde no debería estarlo!
```
{% for message in messages %}
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
{{ ' ' }}
{% endif %}
{{ message['content'] }}
{% if not loop.last %}
{{ ' ' }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{{ eos_token }}
```
Si nunca has visto uno de estos antes, esto es una [plantilla de Jinja](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/). Jinja es un lenguaje de plantillas que te permite escribir código simple que genera texto. En muchos aspectos, el código y la sintaxis se asemejan a Python. En Python puro, esta plantilla se vería algo así:
```python
for idx, message in enumerate(messages):
if message['role'] == 'user':
print(' ')
print(message['content'])
if not idx == len(messages) - 1: # Check for the last message in the conversation
print(' ')
print(eos_token)
```
Efectivamente, la plantilla hace tres cosas:
1. Para cada mensaje, si el mensaje es un mensaje de usuario, añade un espacio en blanco antes de él, de lo contrario no imprime nada.
2. Añade el contenido del mensaje.
3. Si el mensaje no es el último mensaje, añade dos espacios después de él. Después del último mensaje, imprime el token EOS.
Esta es una plantilla bastante simple: no añade ningún token de control y no admite mensajes "del sistema", que son una forma común de dar al modelo directivas sobre cómo debe comportarse en la conversación posterior. ¡Pero Jinja te brinda mucha flexibilidad para hacer esas cosas! Veamos una plantilla de Jinja que pueda formatear las entradas de manera similar a la forma en que LLaMA las formatea (nota que la plantilla real de LLaMA incluye el manejo de mensajes del sistema predeterminados y el manejo de mensajes del sistema ligeramente diferentes en general; ¡no uses esta en tu código real!)
```
{% for message in messages %}
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
{{ bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/INST]' }}
{% elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
{{ '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'] + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
{% elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
{{ ' ' + message['content'] + ' ' + eos_token }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
```
Si observas esto por un momento, puedas ver lo que esta plantilla está haciendo: añade tokens específicos basados en el "rol" de cada mensaje, que representa quién lo envió. Los mensajes de usuario, asistente y sistema son claramente distinguibles para el modelo debido a los tokens en los que están envueltos.
## Avanzado: Añadiendo y editando plantillas de chat
### ¿Cómo creo una plantilla de chat?
Simple, solo escribe una plantilla de Jinja y establece `tokenizer.chat_template`. ¡Puede resultarte más fácil comenzar con una plantilla existente de otro modelo y simplemente editarla según tus necesidades! Por ejemplo, podríamos tomar la plantilla de LLaMA de arriba y añadir "[ASST]" y "[/ASST]" a los mensajes del asistente:
```
{% for message in messages %}
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
{{ bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'].strip() + ' [/INST]' }}
{% elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
{{ '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'].strip() + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
{% elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
{{ '[ASST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/ASST]' + eos_token }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
```
Ahora, simplemente establece el atributo `tokenizer.chat_template`. ¡La próxima vez que uses [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`], se utilizará tu nueva plantilla! Este atributo se guardará en el archivo tokenizer_config.json, por lo que puedes usar [`~utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] para cargar tu nueva plantilla en el Hub y asegurarte de que todos estén utilizando la plantilla correcta para tu modelo.
```python
template = tokenizer.chat_template
template = template.replace("SYS", "SYSTEM") # Change the system token
tokenizer.chat_template = template # Set the new template
tokenizer.push_to_hub("model_name") # Upload your new template to the Hub!
```
El método [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`], que utiliza tu plantilla de chat, es llamado por la clase [`TextGenerationPipeline`], así que una vez que configures la plantilla de chat correcta, tu modelo se volverá automáticamente compatible con [`TextGenerationPipeline`].
<Tip>
Si estás ajustando finamente un modelo para chat, además de establecer una plantilla de chat, probablemente deberías agregar cualquier nuevo token de control de chat como los tokens especiales en el tokenizador. Los tokens especiales nunca se dividen, asegurando que tus tokens de control siempre se manejen como tokens únicos en lugar de ser tokenizados en piezas. También deberías establecer el atributo `eos_token` del tokenizador con el token que marca el final de las generaciones del asistente en tu plantilla. Esto asegurará que las herramientas de generación de texto puedan determinar correctamente cuándo detener la generación de texto.
</Tip>
### ¿Qué plantilla debería usar?
Cuando establezcas la plantilla para un modelo que ya ha sido entrenado para chat, debes asegurarte de que la plantilla coincida exactamente con el formato de mensajes que el modelo vio durante el entrenamiento, o de lo contrario es probable que experimentes degradación del rendimiento. Esto es cierto incluso si estás entrenando aún más el modelo; probablemente obtendrás el mejor rendimiento si mantienes constantes los tokens de chat. Esto es muy análogo a la tokenización: generalmente obtienes el mejor rendimiento para la inferencia o el ajuste fino cuando coincides precisamente con la tokenización utilizada durante el entrenamiento.
Si estás entrenando un modelo desde cero o ajustando finamente un modelo de lenguaje base para chat, por otro lado, ¡tienes mucha libertad para elegir una plantilla apropiada! Los LLM son lo suficientemente inteligentes como para aprender a manejar muchos formatos de entrada diferentes. Nuestra plantilla predeterminada para modelos que no tienen una plantilla específica de clase sigue el formato ChatML, y esta es una buena elección flexible para muchos casos de uso. Se ve así:
```
{% for message in messages %}
{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n'}}
{% endfor %}
```
Si te gusta esta plantilla, aquí está en forma de una sola línea, lista para copiar en tu código. La versión de una sola línea también incluye un práctico soporte para [prompts de generación](#¿Qué-son-los-"generation-prompts"?), ¡pero ten en cuenta que no añade tokens de BOS o EOS! Si tu modelo espera esos tokens, no se agregarán automáticamente por `apply_chat_template`, en otras palabras, el texto será tokenizado con `add_special_tokens=False`. Esto es para evitar posibles conflictos entre la plantilla y la lógica de `add_special_tokens`. ¡Si tu modelo espera tokens especiales, asegúrate de añadirlos a la plantilla!
```python
tokenizer.chat_template = "{% if not add_generation_prompt is defined %}{% set add_generation_prompt = false %}{% endif %}{% for message in messages %}{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n'}}{% endfor %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}{{ '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }}{% endif %}"
```
Esta plantilla envuelve cada mensaje en tokens `<|im_start|>` y `<|im_end|>`, y simplemente escribe el rol como una cadena, lo que permite flexibilidad en los roles con los que entrenas. La salida se ve así:
```text
<|im_start|>system
You are a helpful chatbot that will do its best not to say anything so stupid that people tweet about it.<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
How are you?<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
I'm doing great!<|im_end|>
```
Los roles "usuario", "sistema" y "asistente" son los estándar para chat, y recomendamos usarlos cuando tenga sentido, particularmente si deseas que tu modelo funcione bien con [`TextGenerationPipeline`]. Sin embargo, no estás limitado a estos roles: la plantilla es extremadamente flexible y cualquier cadena puede ser un rol.
### ¡Quiero añadir algunas plantillas de chat! ¿Cómo debo empezar?
Si tienes algún modelo de chat, debes establecer su atributo `tokenizer.chat_template` y probarlo usando [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`], luego subir el tokenizador actualizado al Hub. Esto se aplica incluso si no eres el propietario del modelo: si estás usando un modelo con una plantilla de chat vacía o que todavía está utilizando la plantilla predeterminada de clase, por favor abre una solicitud de extracción [pull request](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-pull-requests-discussions) al repositorio del modelo para que este atributo se pueda establecer correctamente.
Una vez que se establece el atributo, ¡eso es todo, has terminado! `tokenizer.apply_chat_template` ahora funcionará correctamente para ese modelo, ¡lo que significa que también es compatible automáticamente en lugares como `TextGenerationPipeline`!
Al asegurarnos de que los modelos tengan este atributo, podemos garantizar que toda la comunidad pueda utilizar todo el poder de los modelos de código abierto. Los desajustes de formato han estado acechando el campo y dañando silenciosamente el rendimiento durante demasiado tiempo: ¡es hora de ponerles fin!
## Avanzado: Consejos para escribir plantillas
Si no estás familiarizado con Jinja, generalmente encontramos que la forma más fácil de escribir una plantilla de chat es primero escribir un script de Python corto que formatee los mensajes como desees, y luego convertir ese script en una plantilla.
Recuerda que el manejador de plantillas recibirá el historial de conversación como una variable llamada mensajes. Cada mensaje es un diccionario con dos claves, `role` y `content`. Podrás acceder a los `mensajes` en tu plantilla tal como lo harías en Python, lo que significa que puedes recorrerlo con `{% for message in messages %}` o acceder a mensajes individuales con, por ejemplo, `{{ messages[0] }}`.
También puedes usar los siguientes consejos para convertir tu código a Jinja:
### Bucles For
Los bucles For en Jinja se ven así:
```
{% for message in messages %}
{{ message['content'] }}
{% endfor %}
```
Ten en cuenta que todo lo que esté dentro del {{bloque de expresión}} se imprimirá en la salida. Puedes usar operadores como `+` para combinar cadenas dentro de bloques de expresión.
### Declaraciones if
Las declaraciones if en Jinja se ven así:
```
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
{{ message['content'] }}
{% endif %}
```
Observa cómo donde Python utiliza espacios en blanco para marcar el inicio y el final de los bloques `for` e `if`, Jinja requiere que los termines explícitamente con `{% endfor %}` y `{% endif %}`.
### Variables especiales
Dentro de tu plantilla, tendrás acceso a la lista de `mensajes`, pero también puedes acceder a varias otras variables especiales. Estas incluyen tokens especiales como `bos_token` y `eos_token`, así como la variable `add_generation_prompt` que discutimos anteriormente. También puedes usar la variable `loop` para acceder a información sobre la iteración actual del bucle, por ejemplo, usando `{% if loop.last %}` para verificar si el mensaje actual es el último mensaje en la conversación. Aquí tienes un ejemplo que combina estas ideas para agregar un prompt de generación al final de la conversación si add_generation_prompt es `True`:
```
{% if loop.last and add_generation_prompt %}
{{ bos_token + 'Assistant:\n' }}
{% endif %}
```
### Notas sobre los espacios en blanco
Hemos intentado que Jinja ignore los espacios en blanco fuera de las {{expresiones}} tanto como sea posible. Sin embargo, ten en cuenta que Jinja es un motor de plantillas de propósito general y puede tratar el espacio en blanco entre bloques en la misma línea como significativo e imprimirlo en la salida. ¡Te recomendamos **encarecidamente** que verifiques que tu plantilla no esté imprimiendo espacios adicionales donde no debería antes de subirla!
|
transformers/docs/source/es/chat_templating.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/es/chat_templating.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 8513
}
| 33 |
<!--Copyright 2020 de The HuggingFace Team. Todos los derechos reservados
Con licencia bajo la Licencia Apache, Versión 2.0 (la "Licencia"); No puedes usar este archivo excepto de conformidad con la Licencia.
Puedes obtener una copia de la Licencia en
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Al menos que sea requrido por la ley aplicable o acordado por escrito, el software distribuido bajo la Licencia es distribuido sobre una BASE "AS IS", SIN GARANTIAS O CONDICIONES DE
NINGÚN TIPO. Ver la Licencia para el idioma específico que rige los permisos y limitaciones bajo la Licencia.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Filosofía
🤗 Transformers es una biblioteca construida para:
- Los investigadores y educadores de NLP que busquen usar/estudiar/extender modelos transformers a gran escala
- Profesionales que quieren optimizar esos modelos y/o ponerlos en producción
- Ingenieros que solo quieren descargar un modelo preentrenado y usarlo para resolver una tarea NLP dada.
La biblioteca fue diseñada con dos fuertes objetivos en mente:
- Que sea tan fácil y rápida de utilizar como sea posible:
- Hemos limitado enormemente el número de abstracciones que el usuario tiene que aprender. De hecho, no hay casi abstracciones,
solo tres clases estándar necesarias para usar cada modelo: [configuration](main_classes/configuration),
[models](main_classes/model) y [tokenizer](main_classes/tokenizer).
- Todas estas clases pueden ser inicializadas de forma simple y unificada a partir de ejemplos pre-entrenados mediante el uso de un método
`from_pretrained()` común de solicitud que se encargará de descargar (si es necesario), almacenar y cargar la solicitud de clase relacionada y datos asociados
(configurations' hyper-parameters, tokenizers' vocabulary, and models' weights) a partir de un control pre-entrenado proporcionado en
[Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) o de tu propio control guardado.
- Por encima de esas tres clases estándar, la biblioteca proporciona dos APIs: [`pipeline`] para usar rápidamente un modelo (junto a su configuracion y tokenizer asociados)
sobre una tarea dada, y [`Trainer`]/`Keras.fit` para entrenar u optimizar de forma rápida un modelo dado.
- Como consecuencia, esta biblioteca NO es una caja de herramientas modular de bloques individuales para redes neuronales. Si quieres extender/construir sobre la biblioteca,
usa simplemente los módulos regulares de Python/PyTorch/TensorFlow/Keras y emplea las clases estándar de la biblioteca como punto de partida para reutilizar funcionalidades
tales como abrir/guardar modelo.
- Proporciona modelos modernos con rendimientos lo más parecido posible a los modelos originales:
- Proporcionamos al menos un ejemplo para cada arquitectura que reproduce un resultado proporcionado por los autores de dicha arquitectura.
- El código normalmente es parecido al código base original, lo cual significa que algún código Pytorch puede no ser tan
*pytorchic* como podría ser por haber sido convertido a código TensorFlow, y viceversa.
Unos cuantos objetivos adicionales:
- Exponer las características internas de los modelos de la forma más coherente posible:
- Damos acceso, mediante una sola API, a todos los estados ocultos y pesos de atención.
- Tokenizer y el modelo de API base están estandarizados para cambiar fácilmente entre modelos.
- Incorporar una selección subjetiva de herramientas de gran potencial para la optimización/investigación de estos modelos:
- Una forma sencilla/coherente de añadir nuevos tokens al vocabulario e incrustraciones (embeddings, en inglés) para optimización.
- Formas sencillas de camuflar y reducir "transformer heads".
- Cambiar fácilmente entre PyTorch y TensorFlow 2.0, permitiendo el entrenamiento usando un marco y la inferencia usando otro.
## Conceptos principales
La biblioteca está construida alrededor de tres tipos de clases para cada modelo:
- **Model classes** como [`BertModel`], que consisten en más de 30 modelos PyTorch ([torch.nn.Module](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module)) o modelos Keras ([tf.keras.Model](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model)) que funcionan con pesos pre-entrenados proporcionados en la
biblioteca.
- **Configuration classes** como [`BertConfig`], que almacena todos los parámetros necesarios para construir un modelo.
No siempre tienes que generarla tu. En particular, si estas usando un modelo pre-entrenado sin ninguna modificación,
la creación del modelo se encargará automáticamente de generar la configuración (que es parte del modelo).
- **Tokenizer classes** como [`BertTokenizer`], que almacena el vocabulario para cada modelo y proporciona métodos para
codificar/decodificar strings en una lista de índices de "token embeddings" para ser empleados en un modelo.
Todas estas clases pueden ser generadas a partir de ejemplos pre-entrenados, y guardados localmente usando dos métodos:
- `from_pretrained()` permite generar un modelo/configuración/tokenizer a partir de una versión pre-entrenada proporcionada ya sea por
la propia biblioteca (los modelos compatibles se pueden encontrar en [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models)) o
guardados localmente (o en un servidor) por el usuario.
- `save_pretrained()` permite guardar un modelo/configuración/tokenizer localmente, de forma que puede ser empleado de nuevo usando
`from_pretrained()`.
|
transformers/docs/source/es/philosophy.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/es/philosophy.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1964
}
| 34 |
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Pipelines pour l'inférence
L'objet [`pipeline`] rend simple l'utilisation de n'importe quel modèle du [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) pour l'inférence sur n'importe quelle langue, tâches de vision par ordinateur, d'audio et multimodales. Même si vous n'avez pas d'expérience avec une modalité spécifique ou si vous n'êtes pas familier avec le code ci-dessous des modèles, vous pouvez toujours les utiliser pour l'inférence avec la [`pipeline`] ! Ce tutoriel vous apprendra à :
* Utiliser un [`pipeline`] pour l'inférence.
* Utiliser un tokenizer ou modèle spécifique.
* Utiliser un [`pipeline`] pour des tâches audio, de vision et multimodales.
<Tip>
Consultez la documentation du [`pipeline`] pour une liste complète des tâches prises en charge et des paramètres disponibles.
</Tip>
## Utilisation du pipeline
Bien que chaque tâche ait son propre [`pipeline`], il est plus simple d'utiliser le [`pipeline`] générale qui inclut tous les pipelines spécifiques aux différentes tâches. Cette approche charge automatiquement un modèle par défaut et une classe de prétraitement adaptée à votre tâche, simplifiant ainsi votre utilisation. Prenons l'exemple de l'utilisation du [`pipeline`] pour la reconnaissance automatique de la parole (ASR) ou de la transcription de la parole en texte.
1. Commencez par créer un [`pipeline`] et spécifiez la tâche d'inférence :
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> transcriber = pipeline(task="automatic-speech-recognition")
```
2. Passez votre entrée au [`pipeline`]. Dans le cas de la reconnaissance vocale, il s'agit d'un fichier audio :
```py
>>> transcriber("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
{'text': 'I HAVE A DREAM BUT ONE DAY THIS NATION WILL RISE UP LIVE UP THE TRUE MEANING OF ITS TREES'}
```
Pas le résultat que vous aviez en tête ? Consultez certains des [modèles de reconnaissance vocale automatique les plus téléchargés](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=automatic-speech-recognition&sort=trending)
sur le Hub pour voir si vous pouvez obtenir une meilleure transcription.
Essayons le modèle [Whisper large-v2](https://huggingface.co/openai/whisper-large) de OpenAI. Whisper a été publié 2 ans après Wav2Vec2 et a été entraîné sur près de 10 fois plus de données. En tant que tel, il surpasse Wav2Vec2 sur la plupart des benchmarks en aval. Il a également l'avantage supplémentaire de prédire la ponctuation et la casse, ce qui n'est pas possible avec Wav2Vec2.
Essayons-le ici pour voir comment il fonctionne :
```py
>>> transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2")
>>> transcriber("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
{'text': ' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.'}
```
Maintenant, ce résultat semble plus précis ! Pour une comparaison approfondie entre Wav2Vec2 et Whisper, consultez le [cours Audio Transformers](https://huggingface.co/learn/audio-course/chapter5/asr_models).
Nous vous encourageons vraiment à consulter le Hub pour des modèles dans différentes langues, des modèles spécialisés dans votre domaine, et plus encore.
Vous pouvez consulter et comparer les résultats des modèles directement depuis votre navigateur sur le Hub pour voir s'ils conviennent ou gèrent mieux les cas particuliers que d'autres.
Et si vous ne trouvez pas de modèle pour votre cas d'utilisation, vous pouvez toujours commencer à [entraîner](training) le vôtre !
Si vous avez plusieurs entrées, vous pouvez passer votre entrée sous forme de liste :
```py
transcriber(
[
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac",
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/1.flac",
]
)
```
Les pipelines sont excellents pour l'expérimentation car passer d'un modèle à un autre est trivial ; cependant, il existe des moyens de les optimiser pour des charges de travail plus importantes que l'expérimentation. Consultez les guides suivants qui expliquent comment itérer sur des ensembles de données complets ou utiliser des pipelines dans un serveur web :
de la documentation :
* [Utilisation des pipelines sur un ensemble de données](#using-pipelines-on-a-dataset)
* [Utilisation des pipelines pour un serveur web](./pipeline_webserver)
## Paramètres
[`pipeline`] prend en charge de nombreux paramètres ; certains sont spécifiques à la tâche et d'autres sont généraux pour tous les pipelines.
En général, vous pouvez spécifier les paramètres où vous le souhaitez :
```py
transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", my_parameter=1)
out = transcriber(...) # This will use `my_parameter=1`.
out = transcriber(..., my_parameter=2) # This will override and use `my_parameter=2`.
out = transcriber(...) # This will go back to using `my_parameter=1`.
```
Voyons 3 paramètres importants :
### Device
Si vous utilisez `device=n`, le pipeline met automatiquement le modèle sur l'appareil spécifié.
Cela fonctionnera que vous utilisiez PyTorch ou Tensorflow.
```py
transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", device=0)
```
Si le modèle est trop grand pour un seul GPU et que vous utilisez PyTorch, vous pouvez définir `device_map="auto"` pour déterminer automatiquement comment charger et stocker les poids du modèle. L'utilisation de l'argument `device_map` nécessite le package 🤗 [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) :
```bash
pip install --upgrade accelerate
```
Le code suivant charge et stocke automatiquement les poids du modèle sur plusieurs appareils :
```py
transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", device_map="auto")
```
Notez que si `device_map="auto"` est passé, il n'est pas nécessaire d'ajouter l'argument `device=device` lors de l'instanciation de votre `pipeline` car vous pourriez rencontrer des comportements inattendus !
### Batch size
Par défaut, les pipelines ne feront pas d'inférence en batch pour des raisons expliquées en détail [ici](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/pipelines#pipeline-batching). La raison est que le batching n'est pas nécessairement plus rapide, et peut en fait être beaucoup plus lent dans certains cas.
Mais si cela fonctionne dans votre cas d'utilisation, vous pouvez utiliser :
```py
transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", device=0, batch_size=2)
audio_filenames = [f"https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/{i}.flac" for i in range(1, 5)]
texts = transcriber(audio_filenames)
```
Cela exécute le pipeline sur les 4 fichiers audio fournis, mais les passera par batch de 2 au modèle (qui est sur un GPU, où le batching est plus susceptible d'aider) sans nécessiter de code supplémentaire de votre part.
La sortie doit toujours correspondre à ce que vous auriez reçu sans batching. Il s'agit uniquement d'un moyen de vous aider à obtenir plus de vitesse avec un pipeline.
Les pipelines peuvent également atténuer certaines des complexités du batching car, pour certains pipelines, un seul élément (comme un long fichier audio) doit être divisé en plusieurs parties pour être traité par un modèle. Le pipeline effectue ce [*batching par morceaux*](./main_classes/pipelines#pipeline-chunk-batching) pour vous.
### Paramètres spécifiques à la tâche
Toutes les tâches fournissent des paramètres spécifiques à la tâche qui permettent une flexibilité et des options supplémentaires pour vous aider à accomplir votre travail.
Par exemple, la méthode [`transformers.AutomaticSpeechRecognitionPipeline.__call__`] dispose d'un paramètre `return_timestamps` qui semble prometteur pour le sous-titrage des vidéos :
```py
>>> transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", return_timestamps=True)
>>> transcriber("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
{'text': ' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.', 'chunks': [{'timestamp': (0.0, 11.88), 'text': ' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its'}, {'timestamp': (11.88, 12.38), 'text': ' creed.'}]}
```
Comme vous pouvez le voir, le modèle a inféré le texte et a également indiqué **quand** les différentes phrases ont été prononcées.
Il existe de nombreux paramètres disponibles pour chaque tâche, alors consultez la référence API de chaque tâche pour voir ce que vous pouvez ajuster !
Par exemple, le [`~transformers.AutomaticSpeechRecognitionPipeline`] dispose d'un paramètre `chunk_length_s` qui est utile pour travailler sur des fichiers audio très longs (par exemple, le sous-titrage de films entiers ou de vidéos d'une heure) qu'un modèle ne peut généralement pas gérer seul :
```python
>>> transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", chunk_length_s=30)
>>> transcriber("https://huggingface.co/datasets/reach-vb/random-audios/resolve/main/ted_60.wav")
{'text': " So in college, I was a government major, which means I had to write a lot of papers. Now, when a normal student writes a paper, they might spread the work out a little like this. So, you know. You get started maybe a little slowly, but you get enough done in the first week that with some heavier days later on, everything gets done and things stay civil. And I would want to do that like that. That would be the plan. I would have it all ready to go, but then actually the paper would come along, and then I would kind of do this. And that would happen every single paper. But then came my 90-page senior thesis, a paper you're supposed to spend a year on. I knew for a paper like that, my normal workflow was not an option, it was way too big a project. So I planned things out and I decided I kind of had to go something like this. This is how the year would go. So I'd start off light and I'd bump it up"}
```
Si vous ne trouvez pas un paramètre qui vous aiderait vraiment, n'hésitez pas à [le demander](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=feature&template=feature-request.yml) !
## Utilisation des pipelines sur un ensemble de données
Le pipeline peut également exécuter des inférences sur un grand ensemble de données. Le moyen le plus simple que nous recommandons pour cela est d'utiliser un itérateur :
```py
def data():
for i in range(1000):
yield f"My example {i}"
pipe = pipeline(model="openai-community/gpt2", device=0)
generated_characters = 0
for out in pipe(data()):
generated_characters += len(out[0]["generated_text"])
```
L'itérateur `data()` génère chaque résultat, et le pipeline reconnaît automatiquement que l'entrée est itérable et commencera à récupérer les données tout en continuant à les traiter sur le GPU (cela utilise [DataLoader](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#torch.utils.data.DataLoader) sous le capot).
C'est important car vous n'avez pas besoin d'allouer de mémoire pour l'ensemble de données complet et vous pouvez alimenter le GPU aussi rapidement que possible.
Étant donné que le lotissement pourrait accélérer les choses, il peut être utile d'essayer de régler le paramètre `batch_size` ici.
La façon la plus simple d'itérer sur un ensemble de données est d'en charger un depuis 🤗 [Datasets](https://github.com/huggingface/datasets) :
```py
# KeyDataset is a util that will just output the item we're interested in.
from transformers.pipelines.pt_utils import KeyDataset
from datasets import load_dataset
pipe = pipeline(model="hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-wav2vec2", device=0)
dataset = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_dummy", "clean", split="validation[:10]")
for out in pipe(KeyDataset(dataset, "audio")):
print(out)
```
## Utilisation des pipelines pour un serveur web
<Tip>
Créer un moteur d'inférence est un sujet complexe qui mérite sa propre page.
</Tip>
[Lien](./pipeline_webserver)
## Pipeline de vision
Utiliser un [`pipeline`] pour les tâches de vision est pratiquement identique.
Spécifiez votre tâche et passez votre image au classificateur. L'image peut être un lien, un chemin local ou une image encodée en base64. Par exemple, quelle espèce de chat est montrée ci-dessous ?

```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> vision_classifier = pipeline(model="google/vit-base-patch16-224")
>>> preds = vision_classifier(
... images="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
... )
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
>>> preds
[{'score': 0.4335, 'label': 'lynx, catamount'}, {'score': 0.0348, 'label': 'cougar, puma, catamount, mountain lion, painter, panther, Felis concolor'}, {'score': 0.0324, 'label': 'snow leopard, ounce, Panthera uncia'}, {'score': 0.0239, 'label': 'Egyptian cat'}, {'score': 0.0229, 'label': 'tiger cat'}]
```
## Pipeline de texte
Utiliser un [`pipeline`] pour les tâches de NLP est pratiquement identique.
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> # This model is a `zero-shot-classification` model.
>>> # It will classify text, except you are free to choose any label you might imagine
>>> classifier = pipeline(model="facebook/bart-large-mnli")
>>> classifier(
... "I have a problem with my iphone that needs to be resolved asap!!",
... candidate_labels=["urgent", "not urgent", "phone", "tablet", "computer"],
... )
{'sequence': 'I have a problem with my iphone that needs to be resolved asap!!', 'labels': ['urgent', 'phone', 'computer', 'not urgent', 'tablet'], 'scores': [0.504, 0.479, 0.013, 0.003, 0.002]}
```
## Pipeline multimodal
Le [`pipeline`] prend en charge plus d'une modalité. Par exemple, une tâche de réponse à des questions visuelles (VQA) combine texte et image. N'hésitez pas à utiliser n'importe quel lien d'image que vous aimez et une question que vous souhaitez poser à propos de l'image. L'image peut être une URL ou un chemin local vers l'image.
Par exemple, si vous utilisez cette [image de facture](https://huggingface.co/spaces/impira/docquery/resolve/2359223c1837a7587402bda0f2643382a6eefeab/invoice.png) :
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> vqa = pipeline(model="impira/layoutlm-document-qa")
>>> output = vqa(
... image="https://huggingface.co/spaces/impira/docquery/resolve/2359223c1837a7587402bda0f2643382a6eefeab/invoice.png",
... question="What is the invoice number?",
... )
>>> output[0]["score"] = round(output[0]["score"], 3)
>>> output
[{'score': 0.425, 'answer': 'us-001', 'start': 16, 'end': 16}]
```
<Tip>
Pour exécuter l'exemple ci-dessus, vous devez avoir [`pytesseract`](https://pypi.org/project/pytesseract/) installé en plus de 🤗 Transformers :
```bash
sudo apt install -y tesseract-ocr
pip install pytesseract
```
</Tip>
## Utilisation de `pipeline` sur de grands modèles avec 🤗 `accelerate` :
Vous pouvez facilement exécuter `pipeline` sur de grands modèles en utilisant 🤗 `accelerate` ! Assurez-vous d'abord d'avoir installé `accelerate` avec `pip install accelerate`.
Chargez d'abord votre modèle en utilisant `device_map="auto"` ! Nous utiliserons `facebook/opt-1.3b` pour notre exemple.
```py
# pip install accelerate
import torch
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline(model="facebook/opt-1.3b", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
output = pipe("This is a cool example!", do_sample=True, top_p=0.95)
```
Vous pouvez également passer des modèles chargés en 8 bits si vous installez `bitsandbytes` et ajoutez l'argument `load_in_8bit=True`
Notez que vous pouvez remplacer le point de contrôle par n'importe quel modèle.
```py
# pip install accelerate bitsandbytes
import torch
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline(model="facebook/opt-1.3b", device_map="auto", model_kwargs={"load_in_8bit": True})
output = pipe("This is a cool example!", do_sample=True, top_p=0.95)
```
## Création de démonstrations web à partir de pipelines avec `gradio`
Hugging Face prenant en charge le chargement de grands modèles, comme BLOOM.
Les pipelines sont automatiquement pris en charge dans [Gradio](https://github.com/gradio-app/gradio/), une bibliothèque qui facilite la création d'applications d'apprentissage automatique belles et conviviales sur le web. Tout d'abord, assurez-vous que Gradio est installé :
```
pip install gradio
```
Ensuite, vous pouvez créer une démonstration web autour d'un pipeline de classification d'images (ou tout autre pipeline) en une seule ligne de code en appelant la fonction [`Interface.from_pipeline`](https://www.gradio.app/docs/interface#interface-from-pipeline) de Gradio pour lancer le pipeline. Cela crée une interface intuitive de glisser-déposer dans votre navigateur :
```py
from transformers import pipeline
import gradio as gr
pipe = pipeline("image-classification", model="google/vit-base-patch16-224")
gr.Interface.from_pipeline(pipe).launch()
```
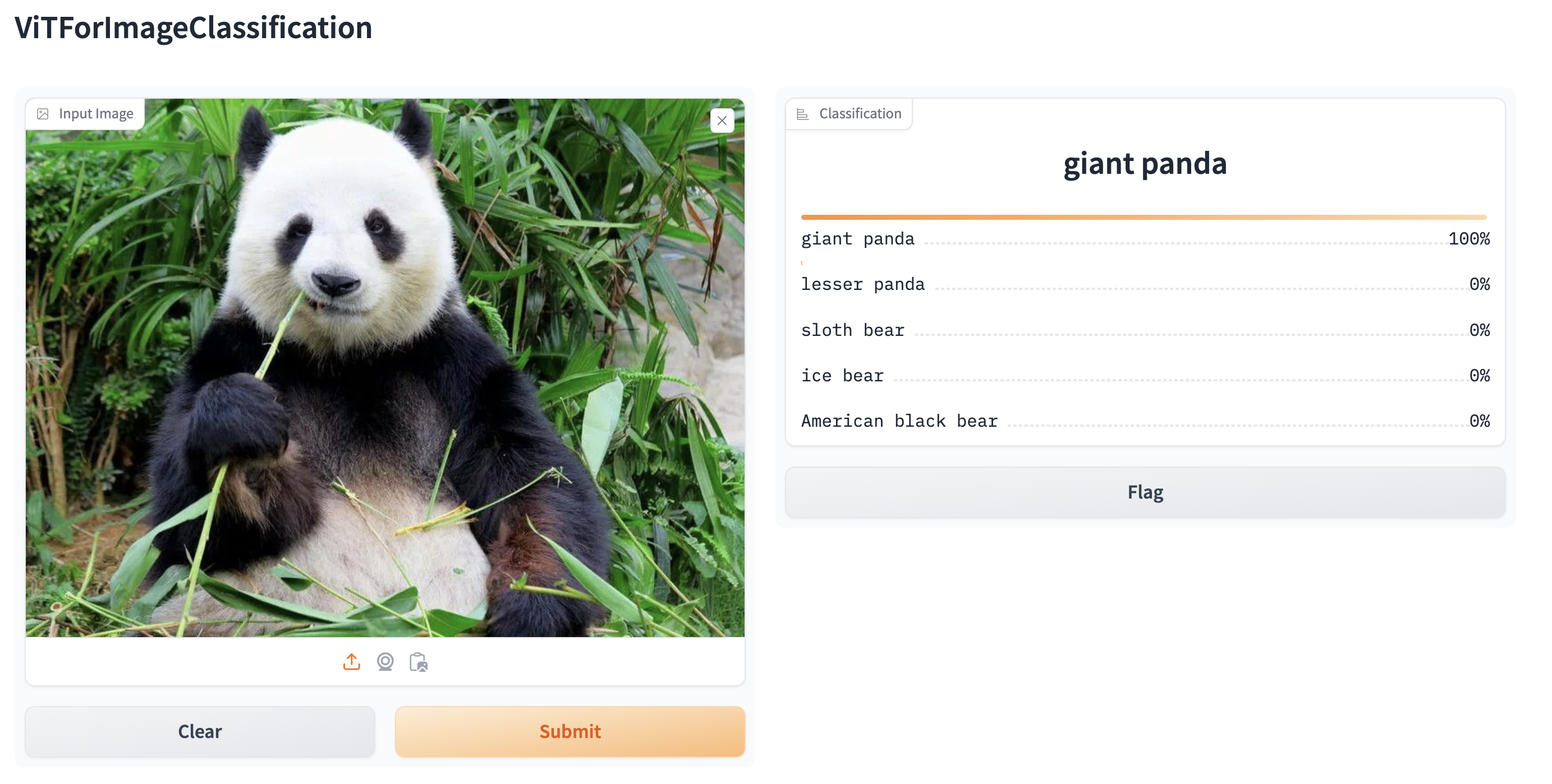
Par défaut, la démonstration web s'exécute sur un serveur local. Si vous souhaitez la partager avec d'autres, vous pouvez générer un lien public temporaire en définissant `share=True` dans `launch()`. Vous pouvez également héberger votre démonstration sur [Hugging Face Spaces](https://huggingface.co/spaces) pour obtenir un lien permanent.
|
transformers/docs/source/fr/tutoriel_pipeline.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/fr/tutoriel_pipeline.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 6226
}
| 35 |
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Debugging
## Debug dei problemi di rete multi-GPU
Quando addestri o fai inferenza con `DistributedDataParallel` e GPU multiple, se si verificano problemi di intercomunicazione tra processi e/o nodi, puoi utilizzare il seguente script per diagnosticare i problemi della rete.
```bash
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/transformers/main/scripts/distributed/torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
```
Per esempio per testare come 2 GPU interagiscono fai:
```bash
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 --nnodes 1 torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
```
Se entrambi i processi sono in grado di comunicare tra loro e di allocare la memoria della GPU, ciascuno di essi stamperà lo stato OK.
Per più GPU o nodi adatta gli argumenti nello script.
All'interno dello script di diagnostica troverai molti altri dettagli e anche una guida per eseguirlo in ambiente SLURM.
Un livello di debug superiore è aggiungere la variabile d'ambiente `NCCL_DEBUG=INFO` come di seguito:
```bash
NCCL_DEBUG=INFO python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 --nnodes 1 torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
```
In questo modo si scaricano molte informazioni di debug relative a NCCL, che puoi cercare online in caso di problemi. Oppure, se non hai la sicurezza di come interpretare l'output, puoi condividere il file di log in una Issue.
## Rilevamento di Underflow e Overflow
<Tip>
Questa funzionalità al momento è disponibile solo per PyTorch.
</Tip>
<Tip>
Per addestramento multi-GPU richiede DDP (`torch.distributed.launch`).
</Tip>
<Tip>
Questa funzionalità può essere usata con modelli basati su `nn.Module`.
</Tip>
Se inizi a ottenere `loss=NaN` o il modello presenta qualche altro comportamento anomalo a causa di valori `inf` o `nan` in
attivazioni o nei pesi, è necessario scoprire dove si verifica il primo underflow o overflow e cosa lo ha determinato. Fortunatamente
è possibile farlo facilmente attivando un modulo speciale che effettuerà il rilevamento automaticamente.
Se stai usando [`Trainer`], hai bisogno di aggiungere solo:
```bash
--debug underflow_overflow
```
ai normali argomenti della riga di comando, o passa `debug="underflow_overflow"` quando viene creato l'oggetto
[`TrainingArguments`].
Se stai usando il tuo ciclo di allenamento o un altro trainer, puoi ottenere lo stesso risultato con:
```python
from .debug_utils import DebugUnderflowOverflow
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model)
```
[`~debug_utils.DebugUnderflowOverflow`] inserisce dei ganci nel modello che dopo ogni chiamata
testeranno le variabili di ingresso e di uscita e anche i pesi del modulo corrispondente. Non appena viene rilevato `inf` o
o `nan` in almeno un elemento delle attivazioni o dei pesi, il programma lo notifica e stampa un rapporto come il seguente (questo è stato rilevato con `google/mt5-small` sotto fp16 mixed precision):
```
Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0
Last 21 forward frames:
abs min abs max metadata
encoder.block.1.layer.1.DenseReluDense.dropout Dropout
0.00e+00 2.57e+02 input[0]
0.00e+00 2.85e+02 output
[...]
encoder.block.2.layer.0 T5LayerSelfAttention
6.78e-04 3.15e+03 input[0]
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 output[0]
None output[1]
2.25e-01 1.00e+04 output[2]
encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm T5LayerNorm
8.69e-02 4.18e-01 weight
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 input[0]
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_0 Linear
2.17e-07 4.50e+00 weight
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
2.68e-06 3.70e+01 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_1 Linear
8.08e-07 2.66e+01 weight
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
1.27e-04 2.37e+02 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.dropout Dropout
0.00e+00 8.76e+03 input[0]
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo Linear
1.01e-06 6.44e+00 weight
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 input[0]
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense T5DenseGatedGeluDense
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.dropout Dropout
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 input[0]
0.00e+00 inf output
```
L'output di esempio è stato tagliato al centro per brevità.
La seconda colonna mostra il valore dell'elemento più grande in assoluto,così se osserviamo da vicino gli ultimi istanti,
input e output sono nel range di `1e4`. Questo addestramento è stato eseguito con una mixed precision fp16 e l'ultimo passo usciva fuori (sotto `fp16` il valore più grande prima di `inf` è `64e3`). Per evitare overflows sotto `fp16` le attivazionioni devono rimanere molto al di sotto di `1e4`, perché `1e4 * 1e4 = 1e8` quindi qualsiasi moltiplicazione di matrice con grandi attivazioni porterà a una condizione di overflow numerico.
All'inizio della traccia è possibile scoprire a quale lotto si è verificato il problema (questo `Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0` significa che il problema si è verificato nel primo lotto).
Ogni frame segnalato inizia dichiarando la voce completamente qualificata per il modulo corrispondente per il quale il frame è stato segnalato.
Se osserviamo il seguente frame:
```
encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm T5LayerNorm
8.69e-02 4.18e-01 weight
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 input[0]
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 output
```
Questo, `encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm` indica che si tratta di un layer norm nel primo layer, del secondo blocco dell'encoder. E le chiamata specifica di `forward` è `T5LayerNorm`.
Osserviamo gli ultimi frame del report:
```
Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0
Last 21 forward frames:
abs min abs max metadata
[...]
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_0 Linear
2.17e-07 4.50e+00 weight
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
2.68e-06 3.70e+01 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_1 Linear
8.08e-07 2.66e+01 weight
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
1.27e-04 2.37e+02 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo Linear
1.01e-06 6.44e+00 weight
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 input[0]
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense T5DenseGatedGeluDense
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
encoder.block.2.layer.1.dropout Dropout
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 input[0]
0.00e+00 inf output
```
L'ultimo frame report per la funzione `Dropout.forward` con la prima voce per l'unico input e la seconda per l'unico output. Si può notare che è stato richiamato da un attibuto `dropout` dentro la classe `DenseReluDense`. Si può notare che ciò è avvenuto durante il primo strato, del 2° blocco, durante il primissimo lotto. Infine, gli elementi di input più grandi in assoluto sono stati `6.27e+04` e l'equivalente per l'output era `inf`.
Puoi vedere qui, che `T5DenseGatedGeluDense.forward` risulta in output activations, il cui valore massimo assoluto era circa 62,7K, che è molto vicino al limite massimo di 64K di fp16. Nel prossimo frame abbiamo `Dropout` che rinormalizza i pesi, dopo aver azzerato alcuni elementi, il che spinge il valore massimo assoluto a più di 64K e si verifica un overflow.(`inf`).
Come puoi notare, è nei frames precedenti che occorre esaminare quando i numeri iniziano a diventare molto grandi per i valori fp16.
Confrontiamo il report al codice `models/t5/modeling_t5.py`:
```python
class T5DenseGatedGeluDense(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.wi_0 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_ff, bias=False)
self.wi_1 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_ff, bias=False)
self.wo = nn.Linear(config.d_ff, config.d_model, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout_rate)
self.gelu_act = ACT2FN["gelu_new"]
def forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_gelu = self.gelu_act(self.wi_0(hidden_states))
hidden_linear = self.wi_1(hidden_states)
hidden_states = hidden_gelu * hidden_linear
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.wo(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
```
Ora è facile vedere la chiamata `dropout`, e tutte le chiamate precedenti.
Poiché il rilevamento avviene in un avanzamento (forward hook in eng.), i rapporti vengono creati immeditamente dopo ogni rientro da `forward` (forward returns in eng.).
Tornando al rapporto completo, per agire e risolvere il problema, dobbiamo andare qualche frame più in alto, dove i numeri hanno iniziato a salire, e probabilmente passare alla modalità `fp32`, in modo che i numeri non trabocchino quando vengono moltiplicati o sommati. Naturalmente, potrebbero esserci altre soluzioni. Per esempio, potremmo spegnere temporanemante `amp` se è abilitato, successivamente spostare `forward` in un helper wrapper, come:
```python
def _forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_gelu = self.gelu_act(self.wi_0(hidden_states))
hidden_linear = self.wi_1(hidden_states)
hidden_states = hidden_gelu * hidden_linear
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.wo(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
import torch
def forward(self, hidden_states):
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=False):
return self._forward(hidden_states)
else:
return self._forward(hidden_states)
```
Poiché il rilevatore automatico riporta solo gli ingressi e le uscite di fotogrammi completi, una volta che si sa dove cercare, si può
analizzare anche le fasi intermedie di una specifica funzione `forward`. In alcuni casi puoi usare la funzione di supporto `detect_overflow` per indirizzare il rilevatore dove preferisci, ad esempio:
```python
from debug_utils import detect_overflow
class T5LayerFF(nn.Module):
[...]
def forward(self, hidden_states):
forwarded_states = self.layer_norm(hidden_states)
detect_overflow(forwarded_states, "after layer_norm")
forwarded_states = self.DenseReluDense(forwarded_states)
detect_overflow(forwarded_states, "after DenseReluDense")
return hidden_states + self.dropout(forwarded_states)
```
Si può vedere che abbiamo aggiunto 2 di questi e ora teniamo traccia se `inf` o `nan` per `forwarded_states` è stato rilevato
da qualche parte.
In realtà, il rilevatore li riporta già, perché ciascuna delle chiamate nell'esempio precedente è un `nn.Module`, ma
diciamo che se avessimo dei calcoli diretti locali, questo è il modo in cui lo faremmo.
Inoltre, se si istanzia il debugger nel proprio codice, è possibile modificare il numero di fotogrammi stampati rispetto a
predefinito, ad esempio.:
```python
from .debug_utils import DebugUnderflowOverflow
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, max_frames_to_save=100)
```
### Tracciamento della mistura assoluta del lotto specifico e del valore massimo
La stessa classe di debug può essere utilizzata per il tracciamento per-batch con la funzione di rilevamento di underflow/overflow disattivata.
Supponiamo di voler osservare i valori minimi e massimi assoluti per tutti gli ingredienti di ogni chiamata `forward` di un dato lotto.
lotto, e che lo si voglia fare solo per i lotti 1 e 3. Si istanzia questa classe come:
```python
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, trace_batch_nums=[1, 3])
```
Ora i batch completi 1 e 3 saranno tracciati utilizzando lo stesso formato del rilevatore di underflow/overflow.
I batches sono 0-indexed.
Questo è utile se si sa che il programma inizia a comportarsi male dopo un certo numero di batch, in modo da poter avanzare velocemente fino a quell'area.
direttamente a quell'area. Ecco un esempio di output troncato per questa configurazione:
```
*** Starting batch number=1 ***
abs min abs max metadata
shared Embedding
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
0.00e+00 2.47e+04 input[0]
5.36e-05 7.92e+02 output
[...]
decoder.dropout Dropout
1.60e-07 2.27e+01 input[0]
0.00e+00 2.52e+01 output
decoder T5Stack
not a tensor output
lm_head Linear
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
0.00e+00 1.11e+00 input[0]
6.06e-02 8.39e+01 output
T5ForConditionalGeneration
not a tensor output
*** Starting batch number=3 ***
abs min abs max metadata
shared Embedding
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
0.00e+00 2.78e+04 input[0]
5.36e-05 7.92e+02 output
[...]
```
Qui verrà scaricato un numero enorme di fotogrammi, tanti quanti sono le chiamate in avanti nel modello, quindi può essere o non essere quello che volete, ma a volte può essere più utile usarlo di un classico debugger. Per esempio, se il problema inizia a verificarsi a partire dal lotto numero 150. Quindi è possibile scaricare le tracce dei lotti 149 e 150 e confrontare i punti in cui i numeri hanno iniziato a divergere.
È inoltre possibile specificare il numero di batch dopo il quale interrompere l'addestramento, con:
```python
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, trace_batch_nums=[1, 3], abort_after_batch_num=3)
```
|
transformers/docs/source/it/debugging.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/it/debugging.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 5635
}
| 36 |
<!---
Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Controlli su una Pull Request
Quando apri una pull request sui 🤗 Transformers, vengono eseguiti un discreto numero di controlli per assicurarsi che la patch che stai aggiungendo non stia rompendo qualcosa di esistente. Questi controlli sono di quattro tipi:
- test regolari
- costruzione della documentazione
- stile del codice e della documentazione
- coerenza generale del repository
In questo documento, cercheremo di spiegare quali sono i vari controlli e le loro ragioni, oltre a spiegare come eseguire il debug locale se uno di essi fallisce sulla tua PR.
Nota che tutti richiedono un'installazione dev:
```bash
pip install transformers[dev]
```
o un'installazione modificabile:
```bash
pip install -e .[dev]
```
all'interno del repo Transformers.
## Tests
Tutti i job che iniziano con `ci/circleci: run_tests_` eseguono parti della suite di test dei Transformers. Ognuno di questi job si concentra su una parte della libreria in un determinato ambiente: per esempio `ci/circleci: run_tests_pipelines_tf` esegue il test delle pipeline in un ambiente in cui è installato solo TensorFlow.
Nota che per evitare di eseguire i test quando non ci sono cambiamenti reali nei moduli che si stanno testando, ogni volta viene eseguita solo una parte della suite di test: viene eseguita una utility per determinare le differenze nella libreria tra prima e dopo la PR (ciò che GitHub mostra nella scheda "Files changes") e sceglie i test che sono stati impattati dalla diff. Questa utility può essere eseguita localmente con:
```bash
python utils/tests_fetcher.py
```
dalla root del repo Transformers. Di seguito ciò che farà:
1. Controlla per ogni file nel diff se le modifiche sono nel codice o solo nei commenti o nelle docstrings. Vengono mantenuti solo i file con modifiche reali al codice.
2. Costruisce una mappa interna che fornisce per ogni file del codice sorgente della libreria tutti i file su cui ha un impatto ricorsivo. Si dice che il modulo A ha un impatto sul modulo B se il modulo B importa il modulo A. Per l'impatto ricorsivo, abbiamo bisogno di una catena di moduli che va dal modulo A al modulo B in cui ogni modulo importa il precedente.
3. Applica questa mappa ai file raccolti nel passaggio 1, si ottiene l'elenco dei file del modello interessati dalla PR.
4. Mappa ciascuno di questi file con i corrispondenti file di test e ottiene l'elenco dei test da eseguire.
Quando esegui lo script in locale, dovresti ottenere la stampa dei risultati dei passi 1, 3 e 4 e quindi sapere quali test sono stati eseguiti. Lo script creerà anche un file chiamato `test_list.txt` che contiene l'elenco dei test da eseguire e che puoi eseguire localmente con il seguente comando:
```bash
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s $(cat test_list.txt)
```
Nel caso in cui qualcosa sia sfuggito, l'intera suite di test viene eseguita quotidianamente.
## Build della documentazione
Il job `ci/circleci: build_doc` esegue una build della documentazione per assicurarsi che tutto sia a posto una volta che la PR è stata unita. Se questo passaggio fallisce, puoi controllare localmente entrando nella cartella `docs` del repo Transformers e digitare
```bash
make html
```
Sphinx non è noto per i suoi messaggi di errore chiari, quindi potrebbe essere necessario che provi alcune cose per trovare davvero la fonte dell'errore.
## Stile del codice e della documentazione
La formattazione del codice viene applicata a tutti i file sorgenti, agli esempi e ai test usando `black` e `isort`. Abbiamo anche uno strumento personalizzato che si occupa della formattazione delle docstring e dei file `rst` (`utils/style_doc.py`), così come dell'ordine dei lazy imports eseguiti nei file `__init__.py` dei Transformers (`utils/custom_init_isort.py`). Tutto questo può essere lanciato eseguendo
```bash
make style
```
I controlli della CI sono applicati all'interno del controllo `ci/circleci: check_code_quality`. Esegue anche `flake8`, che dà un'occhiata di base al codice e si lamenta se trova una variabile non definita o non utilizzata. Per eseguire questo controllo localmente, usare
```bash
make quality
```
Questa operazione può richiedere molto tempo, quindi per eseguire la stessa operazione solo sui file modificati nel branch corrente, eseguire
```bash
make fixup
```
Quest'ultimo comando eseguirà anche tutti i controlli aggiuntivi per la consistenza del repository. Diamogli un'occhiata.
## Coerenza del repository
All'interno sono raggruppati tutti i test per assicurarsi che la tua PR lasci il repository in un buono stato ed è eseguito dal controllo `ci/circleci: check_repository_consistency`. Puoi eseguire localmente questo controllo eseguendo quanto segue:
```bash
make repo-consistency
```
Questo verifica che:
- Tutti gli oggetti aggiunti all'init sono documentati (eseguito da `utils/check_repo.py`)
- Tutti i file `__init__.py` hanno lo stesso contenuto nelle loro due sezioni (eseguito da `utils/check_inits.py`)
- Tutto il codice identificato come copia da un altro modulo è coerente con l'originale (eseguito da `utils/check_copies.py`)
- Le traduzioni dei README e l'indice della documentazione hanno lo stesso elenco di modelli del README principale (eseguito da `utils/check_copies.py`)
- Le tabelle autogenerate nella documentazione sono aggiornate (eseguito da `utils/check_table.py`)
- La libreria ha tutti gli oggetti disponibili anche se non tutte le dipendenze opzionali sono installate (eseguito da `utils/check_dummies.py`)
Se questo controllo fallisce, le prime due voci richiedono una correzione manuale, mentre le ultime quattro possono essere corrette automaticamente per te eseguendo il comando
```bash
make fix-copies
```
Ulteriori controlli riguardano le PR che aggiungono nuovi modelli, principalmente che:
- Tutti i modelli aggiunti sono in un Auto-mapping (eseguita da `utils/check_repo.py`)
<!-- TODO Sylvain, add a check that makes sure the common tests are implemented.-->
- Tutti i modelli sono testati correttamente (eseguito da `utils/check_repo.py`)
<!-- TODO Sylvain, add the following
- All models are added to the main README, inside the main doc
- All checkpoints used actually exist on the Hub
-->
|
transformers/docs/source/it/pr_checks.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/it/pr_checks.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2370
}
| 37 |
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Sharing custom models
🤗 Transformersライブラリは、簡単に拡張できるように設計されています。すべてのモデルはリポジトリの特定のサブフォルダに完全にコード化されており、抽象化はありません。したがって、モデリングファイルをコピーして調整することが簡単です。
新しいモデルを書いている場合、ゼロから始める方が簡単かもしれません。このチュートリアルでは、カスタムモデルとその設定をどのように書き、Transformers内で使用できるようにし、コードに依存する共同体と共有する方法を説明します。ライブラリに存在しない場合でも、誰でも使用できるようにします。
これを実証するために、[timmライブラリ](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models)のResNetクラスを[`PreTrainedModel`]にラップすることによって、ResNetモデルを使用します。
## Writing a custom configuration
モデルに取り組む前に、まずその設定を書きましょう。モデルの設定は、モデルを構築するために必要なすべての情報を含むオブジェクトです。次のセクションで見るように、モデルは初期化するために`config`しか受け取ることができないため、そのオブジェクトができるだけ完全である必要があります。
この例では、ResNetクラスのいくつかの引数を取得し、調整したいかもしれないとします。異なる設定は、異なるタイプのResNetを提供します。その後、これらの引数を確認した後、それらの引数を単に格納します。
```python
from transformers import PretrainedConfig
from typing import List
class ResnetConfig(PretrainedConfig):
model_type = "resnet"
def __init__(
self,
block_type="bottleneck",
layers: List[int] = [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes: int = 1000,
input_channels: int = 3,
cardinality: int = 1,
base_width: int = 64,
stem_width: int = 64,
stem_type: str = "",
avg_down: bool = False,
**kwargs,
):
if block_type not in ["basic", "bottleneck"]:
raise ValueError(f"`block_type` must be 'basic' or bottleneck', got {block_type}.")
if stem_type not in ["", "deep", "deep-tiered"]:
raise ValueError(f"`stem_type` must be '', 'deep' or 'deep-tiered', got {stem_type}.")
self.block_type = block_type
self.layers = layers
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.cardinality = cardinality
self.base_width = base_width
self.stem_width = stem_width
self.stem_type = stem_type
self.avg_down = avg_down
super().__init__(**kwargs)
```
重要なことを3つ覚えておくべきポイントは次のとおりです:
- `PretrainedConfig` を継承する必要があります。
- あなたの `PretrainedConfig` の `__init__` は任意の kwargs を受け入れる必要があります。
- これらの `kwargs` は親クラスの `__init__` に渡す必要があります。
継承は、🤗 Transformers ライブラリのすべての機能を取得できるようにするためです。他の2つの制約は、
`PretrainedConfig` が設定しているフィールド以外にも多くのフィールドを持っていることから来ています。
`from_pretrained` メソッドで設定を再ロードする場合、これらのフィールドはあなたの設定に受け入れられ、
その後、親クラスに送信される必要があります。
設定の `model_type` を定義すること(ここでは `model_type="resnet"`)は、
自動クラスにモデルを登録したい場合を除いては必須ではありません(最後のセクションを参照)。
これで、ライブラリの他のモデル設定と同様に、設定を簡単に作成して保存できます。
以下は、resnet50d 設定を作成して保存する方法の例です:
```py
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
resnet50d_config.save_pretrained("custom-resnet")
```
これにより、`custom-resnet` フォルダ内に `config.json` という名前のファイルが保存されます。その後、`from_pretrained` メソッドを使用して構成を再ロードできます。
```py
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig.from_pretrained("custom-resnet")
```
また、[`PretrainedConfig`] クラスの他のメソッドを使用することもできます。たとえば、[`~PretrainedConfig.push_to_hub`] を使用して、設定を直接 Hub にアップロードできます。
## Writing a custom model
ResNet の設定ができたので、モデルを書き始めることができます。実際には2つのモデルを書きます。1つはバッチの画像から隠れた特徴を抽出するモデル([`BertModel`] のようなもの)で、もう1つは画像分類に適したモデル([`BertForSequenceClassification`] のようなもの)です。
前述したように、この例をシンプルに保つために、モデルの緩いラッパーのみを書きます。このクラスを書く前に行う必要がある唯一のことは、ブロックタイプと実際のブロッククラスの間のマップです。その後、すべてを `ResNet` クラスに渡して設定からモデルを定義します:
```py
from transformers import PreTrainedModel
from timm.models.resnet import BasicBlock, Bottleneck, ResNet
from .configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
BLOCK_MAPPING = {"basic": BasicBlock, "bottleneck": Bottleneck}
class ResnetModel(PreTrainedModel):
config_class = ResnetConfig
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
self.model = ResNet(
block_layer,
config.layers,
num_classes=config.num_classes,
in_chans=config.input_channels,
cardinality=config.cardinality,
base_width=config.base_width,
stem_width=config.stem_width,
stem_type=config.stem_type,
avg_down=config.avg_down,
)
def forward(self, tensor):
return self.model.forward_features(tensor)
```
画像を分類するモデルの場合、forwardメソッドを変更するだけです:
```py
import torch
class ResnetModelForImageClassification(PreTrainedModel):
config_class = ResnetConfig
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
self.model = ResNet(
block_layer,
config.layers,
num_classes=config.num_classes,
in_chans=config.input_channels,
cardinality=config.cardinality,
base_width=config.base_width,
stem_width=config.stem_width,
stem_type=config.stem_type,
avg_down=config.avg_down,
)
def forward(self, tensor, labels=None):
logits = self.model(tensor)
if labels is not None:
loss = torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(logits, labels)
return {"loss": loss, "logits": logits}
return {"logits": logits}
```
両方の場合、`PreTrainedModel`から継承し、`config`を使用してスーパークラスの初期化を呼び出します(通常の`torch.nn.Module`を書くときのような感じです)。
`config_class`を設定する行は必須ではありませんが、(最後のセクションを参照)、モデルを自動クラスに登録したい場合に使用できます。
<Tip>
モデルがライブラリ内のモデルと非常に似ている場合、このモデルと同じ構成を再利用できます。
</Tip>
モデルが返す内容は何でも構いませんが、ラベルが渡されるときに損失を含む辞書を返す(`ResnetModelForImageClassification`のように行ったもの)と、
モデルを[`Trainer`]クラス内で直接使用できるようになります。独自のトレーニングループまたは他のライブラリを使用する予定である限り、
別の出力形式を使用することも問題ありません。
さて、モデルクラスができたので、1つ作成しましょう:
```py
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
```
再度、[`PreTrainedModel`]のいずれかのメソッド、例えば[`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]や
[`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]などを使用できます。次のセクションでは、モデルの重みをコードと一緒に
Hugging Face Hub にプッシュする方法を見てみます。
しかし、まずはモデル内に事前学習済みの重みをロードしましょう。
独自のユースケースでは、おそらく独自のデータでカスタムモデルをトレーニングすることになるでしょう。
このチュートリアルではスピードアップのために、resnet50dの事前学習済みバージョンを使用します。
私たちのモデルはそれをラップするだけなので、これらの重みを転送するのは簡単です:
```py
import timm
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
```
さて、[`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]または[`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]を実行したときに、
モデルのコードが保存されるようにする方法を見てみましょう。
## Sending the code to the Hub
<Tip warning={true}>
このAPIは実験的であり、次のリリースでわずかな変更があるかもしれません。
</Tip>
まず、モデルが`.py`ファイルに完全に定義されていることを確認してください。
ファイルは相対インポートを他のファイルに依存できますが、すべてのファイルが同じディレクトリにある限り(まだこの機能ではサブモジュールはサポートしていません)、問題ありません。
この例では、現在の作業ディレクトリ内に名前が「resnet_model」のフォルダを作成し、その中に`modeling_resnet.py`ファイルと`configuration_resnet.py`ファイルを定義します。
構成ファイルには`ResnetConfig`のコードが含まれ、モデリングファイルには`ResnetModel`と`ResnetModelForImageClassification`のコードが含まれています。
```
.
└── resnet_model
├── __init__.py
├── configuration_resnet.py
└── modeling_resnet.py
```
`__init__.py`は空であっても問題ありません。Pythonが`resnet_model`をモジュールとして検出できるようにするために存在します。
<Tip warning={true}>
ライブラリからモデリングファイルをコピーする場合、ファイルの先頭にあるすべての相対インポートを`transformers`パッケージからインポートに置き換える必要があります。
</Tip>
既存の設定やモデルを再利用(またはサブクラス化)できることに注意してください。
コミュニティとモデルを共有するために、次の手順に従ってください:まず、新しく作成したファイルからResNetモデルと設定をインポートします:
```py
from resnet_model.configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
from resnet_model.modeling_resnet import ResnetModel, ResnetModelForImageClassification
```
次に、`save_pretrained`メソッドを使用してこれらのオブジェクトのコードファイルをコピーし、特定のAutoクラス(特にモデルの場合)に正しく登録するようライブラリに指示する必要があります。次のように実行します:
```py
ResnetConfig.register_for_auto_class()
ResnetModel.register_for_auto_class("AutoModel")
ResnetModelForImageClassification.register_for_auto_class("AutoModelForImageClassification")
```
注意: 設定については自動クラスを指定する必要はありません(設定用の自動クラスは1つしかなく、[`AutoConfig`]です)が、
モデルについては異なります。カスタムモデルは多くの異なるタスクに適している可能性があるため、
モデルが正確な自動クラスのうちどれに適しているかを指定する必要があります。
次に、前述のように設定とモデルを作成しましょう:
```py
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
```
モデルをHubに送信するには、ログインしていることを確認してください。ターミナルで次のコマンドを実行します:
```bash
huggingface-cli login
```
またはノートブックから:
```py
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()
```
次に、次のようにして、独自の名前空間にプッシュできます(または、メンバーである組織にプッシュできます):
```py
resnet50d.push_to_hub("custom-resnet50d")
```
モデリングの重みとJSON形式の構成に加えて、このフォルダー「custom-resnet50d」内のモデリングおよび構成「.py」ファイルもコピーされ、結果はHubにアップロードされました。結果はこの[model repo](https://huggingface.co/sgugger/custom-resnet50d)で確認できます。
詳細については、[Hubへのプッシュ方法](model_sharing)を参照してください。
## Using a model with custom code
自動クラスと `from_pretrained` メソッドを使用して、リポジトリ内のカスタムコードファイルと共に任意の構成、モデル、またはトークナイザを使用できます。 Hubにアップロードされるすべてのファイルとコードはマルウェアのスキャンが実施されます(詳細は[Hubセキュリティ](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security#malware-scanning)ドキュメンテーションを参照してください)、しかし、依然として悪意のあるコードを実行しないために、モデルコードと作者を確認する必要があります。
`trust_remote_code=True` を設定してカスタムコードを持つモデルを使用できます:
```py
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True)
```
コミットハッシュを「revision」として渡すことも強く推奨されています。これにより、モデルの作者がコードを悪意のある新しい行で更新しなかったことを確認できます(モデルの作者を完全に信頼している場合を除きます)。
```py
commit_hash = "ed94a7c6247d8aedce4647f00f20de6875b5b292"
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
"sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True, revision=commit_hash
)
```
モデルリポジトリのコミット履歴をブラウジングする際には、任意のコミットのコミットハッシュを簡単にコピーできるボタンがあります。
## Registering a model with custom code to the auto classes
🤗 Transformersを拡張するライブラリを作成している場合、独自のモデルを含めるために自動クラスを拡張したい場合があります。
これはコードをHubにプッシュすることとは異なり、ユーザーはカスタムモデルを取得するためにあなたのライブラリをインポートする必要があります
(Hubからモデルコードを自動的にダウンロードするのとは対照的です)。
構成に既存のモデルタイプと異なる `model_type` 属性がある限り、またあなたのモデルクラスが適切な `config_class` 属性を持っている限り、
次のようにそれらを自動クラスに追加できます:
```py
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoModelForImageClassification
AutoConfig.register("resnet", ResnetConfig)
AutoModel.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModel)
AutoModelForImageClassification.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModelForImageClassification)
```
注意: `AutoConfig` にカスタム設定を登録する際の最初の引数は、カスタム設定の `model_type` と一致する必要があります。
また、任意の自動モデルクラスにカスタムモデルを登録する際の最初の引数は、それらのモデルの `config_class` と一致する必要があります。
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/custom_models.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/custom_models.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 7503
}
| 38 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Processors
Transformers ライブラリでは、プロセッサは 2 つの異なる意味を持ちます。
- [Wav2Vec2](../model_doc/wav2vec2) などのマルチモーダル モデルの入力を前処理するオブジェクト (音声とテキスト)
または [CLIP](../model_doc/clip) (テキストとビジョン)
- 古いバージョンのライブラリで GLUE または SQUAD のデータを前処理するために使用されていたオブジェクトは非推奨になりました。
## Multi-modal processors
マルチモーダル モデルでは、オブジェクトが複数のモダリティ (テキスト、
視覚と音声)。これは、2 つ以上の処理オブジェクトをグループ化するプロセッサーと呼ばれるオブジェクトによって処理されます。
トークナイザー (テキスト モダリティ用)、画像プロセッサー (視覚用)、特徴抽出器 (オーディオ用) など。
これらのプロセッサは、保存およびロード機能を実装する次の基本クラスを継承します。
[[autodoc]] ProcessorMixin
## Deprecated processors
すべてのプロセッサは、同じアーキテクチャに従っています。
[`~data.processors.utils.DataProcessor`]。プロセッサは次のリストを返します。
[`~data.processors.utils.InputExample`]。これら
[`~data.processors.utils.InputExample`] は次のように変換できます。
[`~data.processors.utils.Input features`] をモデルにフィードします。
[[autodoc]] data.processors.utils.DataProcessor
[[autodoc]] data.processors.utils.InputExample
[[autodoc]] data.processors.utils.InputFeatures
## GLUE
[一般言語理解評価 (GLUE)](https://gluebenchmark.com/) は、
既存の NLU タスクの多様なセットにわたるモデルのパフォーマンス。紙と同時発売された [GLUE: A
自然言語理解のためのマルチタスクベンチマークおよび分析プラットフォーム](https://openreview.net/pdf?id=rJ4km2R5t7)
このライブラリは、MRPC、MNLI、MNLI (不一致)、CoLA、SST2、STSB、
QQP、QNLI、RTE、WNLI。
それらのプロセッサは次のとおりです。
- [`~data.processors.utils.MrpcProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.MnliProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.MnliMismatchedProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.Sst2Processor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.StsbProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.QqpProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.QnliProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.RteProcessor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.WnliProcessor`]
さらに、次のメソッドを使用して、データ ファイルから値をロードし、それらをリストに変換することができます。
[`~data.processors.utils.InputExample`]。
[[autodoc]] data.processors.glue.glue_convert_examples_to_features
## XNLI
[クロスリンガル NLI コーパス (XNLI)](https://www.nyu.edu/projects/bowman/xnli/) は、
言語を超えたテキスト表現の品質。 XNLI は、[*MultiNLI*](http://www.nyu.edu/projects/bowman/multinli/) に基づくクラウドソースのデータセットです。テキストのペアには、15 個のテキスト含意アノテーションがラベル付けされています。
さまざまな言語 (英語などの高リソース言語とスワヒリ語などの低リソース言語の両方を含む)。
論文 [XNLI: Evaluating Cross-lingual Sentence Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.05053) と同時にリリースされました。
このライブラリは、XNLI データをロードするプロセッサをホストします。
- [`~data.processors.utils.XnliProcessor`]
テストセットにはゴールドラベルが付いているため、評価はテストセットで行われますのでご了承ください。
これらのプロセッサを使用する例は、[run_xnli.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/text-classification/run_xnli.py) スクリプトに示されています。
## SQuAD
[The Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD)](https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer//) は、次のベンチマークです。
質問応答に関するモデルのパフォーマンスを評価します。 v1.1 と v2.0 の 2 つのバージョンが利用可能です。最初のバージョン
(v1.1) は、論文 [SQuAD: 100,000+ question for Machine Comprehension of Text](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05250) とともにリリースされました。 2 番目のバージョン (v2.0) は、論文 [Know What You Don't と同時にリリースされました。
知っておくべき: SQuAD の答えられない質問](https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.03822)。
このライブラリは、次の 2 つのバージョンのそれぞれのプロセッサをホストします。
### Processors
それらのプロセッサは次のとおりです。
- [`~data.processors.utils.SquadV1Processor`]
- [`~data.processors.utils.SquadV2Processor`]
どちらも抽象クラス [`~data.processors.utils.SquadProcessor`] を継承しています。
[[autodoc]] data.processors.squad.SquadProcessor
- all
さらに、次のメソッドを使用して、SQuAD の例を次の形式に変換できます。
モデルの入力として使用できる [`~data.processors.utils.SquadFeatures`]。
[[autodoc]] data.processors.squad.squad_convert_examples_to_features
これらのプロセッサと前述の方法は、データを含むファイルだけでなく、
*tensorflow_datasets* パッケージ。以下に例を示します。
### Example usage
以下にプロセッサを使用した例と、データ ファイルを使用した変換方法を示します。
```python
# Loading a V2 processor
processor = SquadV2Processor()
examples = processor.get_dev_examples(squad_v2_data_dir)
# Loading a V1 processor
processor = SquadV1Processor()
examples = processor.get_dev_examples(squad_v1_data_dir)
features = squad_convert_examples_to_features(
examples=examples,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
doc_stride=args.doc_stride,
max_query_length=max_query_length,
is_training=not evaluate,
)
```
*tensorflow_datasets* の使用は、データ ファイルを使用するのと同じくらい簡単です。
```python
# tensorflow_datasets only handle Squad V1.
tfds_examples = tfds.load("squad")
examples = SquadV1Processor().get_examples_from_dataset(tfds_examples, evaluate=evaluate)
features = squad_convert_examples_to_features(
examples=examples,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
doc_stride=args.doc_stride,
max_query_length=max_query_length,
is_training=not evaluate,
)
```
これらのプロセッサを使用する別の例は、[run_squad.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/legacy/question-answering/run_squad.py) スクリプトに示されています。
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/main_classes/processors.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/main_classes/processors.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3103
}
| 39 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# BertGeneration
## Overview
BertGeneration モデルは、次を使用してシーケンス間のタスクに利用できる BERT モデルです。
[Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) で提案されている [`EncoderDecoderModel`]
タスク、Sascha Rothe、Sishi Nagayan、Aliaksei Severyn 著。
論文の要約は次のとおりです。
*大規模なニューラル モデルの教師なし事前トレーニングは、最近、自然言語処理に革命をもたらしました。による
NLP 実践者は、公開されたチェックポイントからウォームスタートして、複数の項目で最先端の技術を推進してきました。
コンピューティング時間を大幅に節約しながらベンチマークを実行します。これまでのところ、主に自然言語に焦点を当ててきました。
タスクを理解する。この論文では、シーケンス生成のための事前トレーニングされたチェックポイントの有効性を実証します。私たちは
公開されている事前トレーニング済み BERT と互換性のある Transformer ベースのシーケンス間モデルを開発しました。
GPT-2 および RoBERTa チェックポイントを使用し、モデルの初期化の有用性について広範な実証研究を実施しました。
エンコーダとデコーダ、これらのチェックポイント。私たちのモデルは、機械翻訳に関する新しい最先端の結果をもたらします。
テキストの要約、文の分割、および文の融合。*
## Usage examples and tips
- モデルを [`EncoderDecoderModel`] と組み合わせて使用して、2 つの事前トレーニングされたモデルを活用できます。
後続の微調整のための BERT チェックポイント。
```python
>>> # leverage checkpoints for Bert2Bert model...
>>> # use BERT's cls token as BOS token and sep token as EOS token
>>> encoder = BertGenerationEncoder.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-large-uncased", bos_token_id=101, eos_token_id=102)
>>> # add cross attention layers and use BERT's cls token as BOS token and sep token as EOS token
>>> decoder = BertGenerationDecoder.from_pretrained(
... "google-bert/bert-large-uncased", add_cross_attention=True, is_decoder=True, bos_token_id=101, eos_token_id=102
... )
>>> bert2bert = EncoderDecoderModel(encoder=encoder, decoder=decoder)
>>> # create tokenizer...
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-large-uncased")
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(
... "This is a long article to summarize", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt"
... ).input_ids
>>> labels = tokenizer("This is a short summary", return_tensors="pt").input_ids
>>> # train...
>>> loss = bert2bert(input_ids=input_ids, decoder_input_ids=labels, labels=labels).loss
>>> loss.backward()
```
- 事前トレーニングされた [`EncoderDecoderModel`] もモデル ハブで直接利用できます。
```python
>>> # instantiate sentence fusion model
>>> sentence_fuser = EncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("google/roberta2roberta_L-24_discofuse")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/roberta2roberta_L-24_discofuse")
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(
... "This is the first sentence. This is the second sentence.", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt"
... ).input_ids
>>> outputs = sentence_fuser.generate(input_ids)
>>> print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
チップ:
- [`BertGenerationEncoder`] と [`BertGenerationDecoder`] は、
[`EncoderDecoder`] と組み合わせます。
- 要約、文の分割、文の融合、および翻訳の場合、入力に特別なトークンは必要ありません。
したがって、入力の末尾に EOS トークンを追加しないでください。
このモデルは、[patrickvonplaten](https://huggingface.co/patrickvonplaten) によって提供されました。元のコードは次のとおりです
[ここ](https://tfhub.dev/s?module-type=text-generation&subtype=module,placeholder) があります。
## BertGenerationConfig
[[autodoc]] BertGenerationConfig
## BertGenerationTokenizer
[[autodoc]] BertGenerationTokenizer
- save_vocabulary
## BertGenerationEncoder
[[autodoc]] BertGenerationEncoder
- forward
## BertGenerationDecoder
[[autodoc]] BertGenerationDecoder
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/model_doc/bert-generation.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/model_doc/bert-generation.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 1974
}
| 40 |
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# ByT5
## Overview
ByT5 モデルは、[ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir
Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
論文の要約は次のとおりです。
*最も広く使用されている事前トレーニング済み言語モデルは、単語またはサブワード単位に対応するトークンのシーケンスで動作します。
テキストをトークンのシーケンスとしてエンコードするには、トークナイザーが必要です。トークナイザーは通常、
モデル。代わりに生のテキスト (バイトまたは文字) を直接操作するトークンフリー モデルには多くの利点があります。
すぐに使用できるあらゆる言語のテキストを処理でき、ノイズに対してより堅牢であり、技術的負債を最小限に抑えます。
複雑でエラーが発生しやすいテキスト前処理パイプラインを削除します。バイトまたは文字列がトークンより長いため
トークンフリー モデルに関する過去の研究では、シーケンスのコストを償却するように設計された新しいモデル アーキテクチャが導入されることがよくありました。
生のテキストを直接操作します。この論文では、標準的な Transformer アーキテクチャが次のようなもので使用できることを示します。
バイトシーケンスを処理するための最小限の変更。パラメータ数の観点からトレードオフを注意深く特徴付けます。
FLOP のトレーニングと推論速度を調べ、バイトレベルのモデルがトークンレベルと競合できることを示します。
対応者。また、バイトレベルのモデルはノイズに対して大幅に堅牢であり、より優れたパフォーマンスを発揮することも示しています。
スペルと発音に敏感なタスク。私たちの貢献の一環として、新しいセットをリリースします。
T5 アーキテクチャに基づいた事前トレーニング済みのバイトレベルの Transformer モデルと、そこで使用されるすべてのコードとデータ
実験。*
このモデルは、[patrickvonplaten](https://huggingface.co/patrickvonplaten) によって提供されました。元のコードは次のとおりです
[ここ](https://github.com/google-research/byt5) にあります。
<Tip>
ByT5 のアーキテクチャは T5v1.1 モデルに基づいています。API リファレンスについては、[T5v1.1 のドキュメント ページ](t5v1.1) を参照してください。彼らは
モデルの入力を準備する方法が異なるだけです。以下のコード例を参照してください。
</Tip>
ByT5 は教師なしで事前トレーニングされているため、単一タスク中にタスク プレフィックスを使用する利点はありません。
微調整。マルチタスクの微調整を行う場合は、プレフィックスを使用する必要があります。
## Usage Examples
ByT5 は生の UTF-8 バイトで動作するため、トークナイザーなしで使用できます。
```python
>>> from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration
>>> import torch
>>> model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("google/byt5-small")
>>> num_special_tokens = 3
>>> # Model has 3 special tokens which take up the input ids 0,1,2 of ByT5.
>>> # => Need to shift utf-8 character encodings by 3 before passing ids to model.
>>> input_ids = torch.tensor([list("Life is like a box of chocolates.".encode("utf-8"))]) + num_special_tokens
>>> labels = torch.tensor([list("La vie est comme une boîte de chocolat.".encode("utf-8"))]) + num_special_tokens
>>> loss = model(input_ids, labels=labels).loss
>>> loss.item()
2.66
```
ただし、バッチ推論とトレーニングの場合は、トークナイザーを使用することをお勧めします。
```python
>>> from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("google/byt5-small")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/byt5-small")
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer(
... ["Life is like a box of chocolates.", "Today is Monday."], padding="longest", return_tensors="pt"
... )
>>> labels_dict = tokenizer(
... ["La vie est comme une boîte de chocolat.", "Aujourd'hui c'est lundi."], padding="longest", return_tensors="pt"
... )
>>> labels = labels_dict.input_ids
>>> loss = model(**model_inputs, labels=labels).loss
>>> loss.item()
17.9
```
[T5](t5) と同様に、ByT5 はスパンマスクノイズ除去タスクでトレーニングされました。しかし、
モデルはキャラクターに直接作用するため、事前トレーニングタスクは少し複雑です
違う。のいくつかの文字を破損してみましょう
`"The dog chases a ball in the park."`という文を入力し、ByT5 に予測してもらいます。
わたしたちのため。
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/byt5-base")
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google/byt5-base")
>>> input_ids_prompt = "The dog chases a ball in the park."
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(input_ids_prompt).input_ids
>>> # Note that we cannot add "{extra_id_...}" to the string directly
>>> # as the Byte tokenizer would incorrectly merge the tokens
>>> # For ByT5, we need to work directly on the character level
>>> # Contrary to T5, ByT5 does not use sentinel tokens for masking, but instead
>>> # uses final utf character ids.
>>> # UTF-8 is represented by 8 bits and ByT5 has 3 special tokens.
>>> # => There are 2**8+2 = 259 input ids and mask tokens count down from index 258.
>>> # => mask to "The dog [258]a ball [257]park."
>>> input_ids = torch.tensor([input_ids[:8] + [258] + input_ids[14:21] + [257] + input_ids[28:]])
>>> input_ids
tensor([[ 87, 107, 104, 35, 103, 114, 106, 35, 258, 35, 100, 35, 101, 100, 111, 111, 257, 35, 115, 100, 117, 110, 49, 1]])
>>> # ByT5 produces only one char at a time so we need to produce many more output characters here -> set `max_length=100`.
>>> output_ids = model.generate(input_ids, max_length=100)[0].tolist()
>>> output_ids
[0, 258, 108, 118, 35, 119, 107, 104, 35, 114, 113, 104, 35, 122, 107, 114, 35, 103, 114, 104, 118, 257, 35, 108, 113, 35, 119, 107, 104, 35, 103, 108, 118, 102, 114, 256, 108, 113, 35, 119, 107, 104, 35, 115, 100, 117, 110, 49, 35, 87, 107, 104, 35, 103, 114, 106, 35, 108, 118, 35, 119, 107, 104, 35, 114, 113, 104, 35, 122, 107, 114, 35, 103, 114, 104, 118, 35, 100, 35, 101, 100, 111, 111, 35, 108, 113, 255, 35, 108, 113, 35, 119, 107, 104, 35, 115, 100, 117, 110, 49]
>>> # ^- Note how 258 descends to 257, 256, 255
>>> # Now we need to split on the sentinel tokens, let's write a short loop for this
>>> output_ids_list = []
>>> start_token = 0
>>> sentinel_token = 258
>>> while sentinel_token in output_ids:
... split_idx = output_ids.index(sentinel_token)
... output_ids_list.append(output_ids[start_token:split_idx])
... start_token = split_idx
... sentinel_token -= 1
>>> output_ids_list.append(output_ids[start_token:])
>>> output_string = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_ids_list)
>>> output_string
['<pad>', 'is the one who does', ' in the disco', 'in the park. The dog is the one who does a ball in', ' in the park.']
```
## ByT5Tokenizer
[[autodoc]] ByT5Tokenizer
詳細については、[`ByT5Tokenizer`] を参照してください。
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/model_doc/byt5.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/model_doc/byt5.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3268
}
| 41 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# CTRL
<div class="flex flex-wrap space-x-1">
<a href="https://huggingface.co/models?filter=Salesforce/ctrl">
<img alt="Models" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/All_model_pages-ctrl-blueviolet">
</a>
<a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/docs-demos/tiny-ctrl">
<img alt="Spaces" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue">
</a>
</div>
## Overview
CTRL モデルは、Nitish Shirish Keskar*、Bryan McCann*、Lav R. Varshney、Caiming Xiong, Richard Socher によって [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) で提案されました。
リチャード・ソーチャー。これは、非常に大規模なコーパスの言語モデリングを使用して事前トレーニングされた因果的 (一方向) トランスフォーマーです
最初のトークンが制御コード (リンク、書籍、Wikipedia など) として予約されている、約 140 GB のテキスト データ。
論文の要約は次のとおりです。
*大規模な言語モデルは有望なテキスト生成機能を示していますが、ユーザーは特定の言語モデルを簡単に制御できません
生成されたテキストの側面。 16 億 3,000 万パラメータの条件付きトランスフォーマー言語モデルである CTRL をリリースします。
スタイル、コンテンツ、タスク固有の動作を制御する制御コードを条件付けるように訓練されています。制御コードは
生のテキストと自然に共生する構造から派生し、教師なし学習の利点を維持しながら、
テキスト生成をより明示的に制御できるようになります。これらのコードを使用すると、CTRL でどの部分が予測されるのかを予測することもできます。
トレーニング データにはシーケンスが与えられる可能性が最も高くなります。これにより、大量のデータを分析するための潜在的な方法が提供されます。
モデルベースのソース帰属を介して。*
このモデルは、[keskarnitishr](https://huggingface.co/keskarnitishr) によって提供されました。元のコードが見つかる
[こちら](https://github.com/salesforce/Salesforce/ctrl)。
## Usage tips
- CTRL は制御コードを利用してテキストを生成します。生成を特定の単語や文で開始する必要があります。
またはリンクして一貫したテキストを生成します。 [元の実装](https://github.com/salesforce/Salesforce/ctrl) を参照してください。
詳しくは。
- CTRL は絶対位置埋め込みを備えたモデルであるため、通常は入力を右側にパディングすることをお勧めします。
左。
- CTRL は因果言語モデリング (CLM) の目的でトレーニングされているため、次の予測に強力です。
シーケンス内のトークン。この機能を利用すると、CTRL は構文的に一貫したテキストを生成できるようになります。
*run_generation.py* サンプル スクリプトで確認できます。
- PyTorch モデルは、以前に計算されたキーと値のアテンション ペアである`past_key_values`を入力として受け取ることができます。
TensorFlow モデルは`past`を入力として受け入れます。 `past_key_values`値を使用すると、モデルが再計算されなくなります。
テキスト生成のコンテキストで事前に計算された値。 [`forward`](model_doc/ctrl#transformers.CTRLModel.forward) を参照してください。
この引数の使用法の詳細については、メソッドを参照してください。
## Resources
- [テキスト分類タスクガイド](../tasks/sequence_classification)
- [因果言語モデリング タスク ガイド](../tasks/language_modeling)
## CTRLConfig
[[autodoc]] CTRLConfig
## CTRLTokenizer
[[autodoc]] CTRLTokenizer
- save_vocabulary
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
## CTRLModel
[[autodoc]] CTRLModel
- forward
## CTRLLMHeadModel
[[autodoc]] CTRLLMHeadModel
- forward
## CTRLForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] CTRLForSequenceClassification
- forward
</pt>
<tf>
## TFCTRLModel
[[autodoc]] TFCTRLModel
- call
## TFCTRLLMHeadModel
[[autodoc]] TFCTRLLMHeadModel
- call
## TFCTRLForSequenceClassification
[[autodoc]] TFCTRLForSequenceClassification
- call
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/model_doc/ctrl.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/model_doc/ctrl.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 2127
}
| 42 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# 推論のための多言語モデル
[[open-in-colab]]
🤗 Transformers にはいくつかの多言語モデルがあり、それらの推論の使用方法は単一言語モデルとは異なります。ただし、多言語モデルの使用方法がすべて異なるわけではありません。 [google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-uncased](https://huggingface.co/google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-uncased) などの一部のモデルは、単一言語モデルと同様に使用できます。 このガイドでは、推論のために使用方法が異なる多言語モデルをどのように使うかを示します。
## XLM
XLM には10の異なるチェックポイントがあり、そのうちの1つだけが単一言語です。 残りの9つのモデルチェックポイントは、言語埋め込みを使用するチェックポイントと使用しないチェックポイントの2つのカテゴリに分けることができます。
### 言語の埋め込みがある XLM
次の XLM モデルは、言語の埋め込みを使用して、推論で使用される言語を指定します。
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-ende-1024` (マスク化された言語モデリング、英語-ドイツ語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-enfr-1024` (マスク化された言語モデリング、英語-フランス語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-enro-1024` (マスク化された言語モデリング、英語-ルーマニア語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-xnli15-1024` (マスク化された言語モデリング、XNLI 言語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-tlm-xnli15-1024` (マスク化された言語モデリング + 翻訳 + XNLI 言語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-clm-enfr-1024` (因果言語モデリング、英語-フランス語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-clm-ende-1024` (因果言語モデリング、英語-ドイツ語)
言語の埋め込みは、モデルに渡される `input_ids` と同じ形状のテンソルとして表されます。 これらのテンソルの値は、使用される言語に依存し、トークナイザーの `lang2id` および `id2lang` 属性によって識別されます。
この例では、`FacebookAI/xlm-clm-enfr-1024` チェックポイントをロードします (因果言語モデリング、英語-フランス語)。
```py
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import XLMTokenizer, XLMWithLMHeadModel
>>> tokenizer = XLMTokenizer.from_pretrained("FacebookAI/xlm-clm-enfr-1024")
>>> model = XLMWithLMHeadModel.from_pretrained("FacebookAI/xlm-clm-enfr-1024")
```
トークナイザーの `lang2id` 属性は、このモデルの言語とその ID を表示します。
```py
>>> print(tokenizer.lang2id)
{'en': 0, 'fr': 1}
```
次に、入力例を作成します。
```py
>>> input_ids = torch.tensor([tokenizer.encode("Wikipedia was used to")]) # batch size of 1
```
言語 ID を `en` に設定し、それを使用して言語の埋め込みを定義します。 言語の埋め込みは、英語の言語 ID であるため、`0` で埋められたテンソルです。 このテンソルは `input_ids` と同じサイズにする必要があります。
```py
>>> language_id = tokenizer.lang2id["en"] # 0
>>> langs = torch.tensor([language_id] * input_ids.shape[1]) # torch.tensor([0, 0, 0, ..., 0])
>>> # We reshape it to be of size (batch_size, sequence_length)
>>> langs = langs.view(1, -1) # is now of shape [1, sequence_length] (we have a batch size of 1)
```
これで、`input_ids` と言語の埋め込みをモデルに渡すことができます。
```py
>>> outputs = model(input_ids, langs=langs)
```
[run_generation.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/text-generation/run_generation.py) スクリプトは、`xlm-clm` チェックポイントを使用して、言語が埋め込まれたテキストを生成できます。
### 言語の埋め込みがないXLM
次の XLM モデルは、推論中に言語の埋め込みを必要としません。
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-17-1280` (マスク化された言語モデリング、17の言語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-100-1280` (マスク化された言語モデリング、100の言語)
これらのモデルは、以前の XLM チェックポイントとは異なり、一般的な文の表現に使用されます。
## BERT
以下の BERT モデルは、多言語タスクに使用できます。
- `google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-uncased` (マスク化された言語モデリング + 次の文の予測、102の言語)
- `google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-cased` (マスク化された言語モデリング + 次の文の予測、104の言語)
これらのモデルは、推論中に言語の埋め込みを必要としません。 文脈から言語を識別し、それに応じて推測する必要があります。
## XLM-RoBERTa
次の XLM-RoBERTa モデルは、多言語タスクに使用できます。
- `FacebookAI/xlm-roberta-base` (マスク化された言語モデリング、100の言語)
- `FacebookAI/xlm-roberta-large` (マスク化された言語モデリング、100の言語)
XLM-RoBERTa は、100の言語で新しく作成およびクリーニングされた2.5 TB の CommonCrawl データでトレーニングされました。 これは、分類、シーケンスのラベル付け、質問応答などのダウンストリームタスクで、mBERT や XLM などの以前にリリースされた多言語モデルを大幅に改善します。
## M2M100
次の M2M100 モデルは、多言語翻訳に使用できます。
- `facebook/m2m100_418M` (翻訳)
- `facebook/m2m100_1.2B` (翻訳)
この例では、`facebook/m2m100_418M` チェックポイントをロードして、中国語から英語に翻訳します。 トークナイザーでソース言語を設定できます。
```py
>>> from transformers import M2M100ForConditionalGeneration, M2M100Tokenizer
>>> en_text = "Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards, for they are subtle and quick to anger."
>>> chinese_text = "不要插手巫師的事務, 因為他們是微妙的, 很快就會發怒."
>>> tokenizer = M2M100Tokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/m2m100_418M", src_lang="zh")
>>> model = M2M100ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("facebook/m2m100_418M")
```
テキストをトークン化します。
```py
>>> encoded_zh = tokenizer(chinese_text, return_tensors="pt")
```
M2M100 は、最初に生成されたトークンとしてターゲット言語 ID を強制的にターゲット言語に翻訳します。 英語に翻訳するには、`generate` メソッドで `forced_bos_token_id` を `en` に設定します。
```py
>>> generated_tokens = model.generate(**encoded_zh, forced_bos_token_id=tokenizer.get_lang_id("en"))
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
'Do not interfere with the matters of the witches, because they are delicate and will soon be angry.'
```
## MBart
多言語翻訳には、次の MBart モデルを使用できます。
- `facebook/mbart-large-50-one-to-many-mmt` (One-to-many multilingual machine translation, 50 languages)
- `facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt` (Many-to-many multilingual machine translation, 50 languages)
- `facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt` (Many-to-one multilingual machine translation, 50 languages)
- `facebook/mbart-large-50` (Multilingual translation, 50 languages)
- `facebook/mbart-large-cc25`
この例では、`facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt` チェックポイントをロードして、フィンランド語を英語に翻訳します。トークナイザーでソース言語を設定できます。
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> en_text = "Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards, for they are subtle and quick to anger."
>>> fi_text = "Älä sekaannu velhojen asioihin, sillä ne ovat hienovaraisia ja nopeasti vihaisia."
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt", src_lang="fi_FI")
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt")
```
テキストをトークン化します。
```py
>>> encoded_en = tokenizer(en_text, return_tensors="pt")
```
MBart は、最初に生成されたトークンとしてターゲット言語 ID を強制的にターゲット言語に翻訳します。 英語に翻訳するには、`generate` メソッドで `forced_bos_token_id` を `en` に設定します。
```py
>>> generated_tokens = model.generate(**encoded_en, forced_bos_token_id=tokenizer.lang_code_to_id("en_XX"))
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
"Don't interfere with the wizard's affairs, because they are subtle, will soon get angry."
```
`facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt` チェックポイントを使用している場合、最初に生成されたトークンとしてターゲット言語 ID を強制する必要はありません。それ以外の場合、使用方法は同じです。
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/multilingual.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/multilingual.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 4144
}
| 43 |
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Image classification
[[open-in-colab]]
<Youtube id="tjAIM7BOYhw"/>
画像分類では、画像にラベルまたはクラスを割り当てます。テキストや音声の分類とは異なり、入力は
画像を構成するピクセル値。損傷の検出など、画像分類には多くの用途があります
自然災害の後、作物の健康状態を監視したり、病気の兆候がないか医療画像をスクリーニングしたりするのに役立ちます。
このガイドでは、次の方法を説明します。
1. [Food-101](https://huggingface.co/datasets/food101) データセットの [ViT](model_doc/vit) を微調整して、画像内の食品を分類します。
2. 微調整したモデルを推論に使用します。
<Tip>
このタスクと互換性のあるすべてのアーキテクチャとチェックポイントを確認するには、[タスクページ](https://huggingface.co/tasks/image-classification) を確認することをお勧めします。
</Tip>
始める前に、必要なライブラリがすべてインストールされていることを確認してください。
```bash
pip install transformers datasets evaluate
```
Hugging Face アカウントにログインして、モデルをアップロードしてコミュニティと共有することをお勧めします。プロンプトが表示されたら、トークンを入力してログインします。
```py
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
>>> notebook_login()
```
## Load Food-101 dataset
Datasets、🤗 データセット ライブラリから Food-101 データセットの小さいサブセットを読み込みます。これにより、次の機会が得られます
完全なデータセットのトレーニングにさらに時間を費やす前に、実験してすべてが機能することを確認してください。
```py
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> food = load_dataset("food101", split="train[:5000]")
```
[`~datasets.Dataset.train_test_split`] メソッドを使用して、データセットの `train` 分割をトレイン セットとテスト セットに分割します。
```py
>>> food = food.train_test_split(test_size=0.2)
```
次に、例を見てみましょう。
```py
>>> food["train"][0]
{'image': <PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile image mode=RGB size=512x512 at 0x7F52AFC8AC50>,
'label': 79}
```
データセット内の各例には 2 つのフィールドがあります。
- `image`: 食品の PIL 画像
- `label`: 食品のラベルクラス
モデルがラベル ID からラベル名を取得しやすくするために、ラベル名をマップする辞書を作成します。
整数への変換、またはその逆:
```py
>>> labels = food["train"].features["label"].names
>>> label2id, id2label = dict(), dict()
>>> for i, label in enumerate(labels):
... label2id[label] = str(i)
... id2label[str(i)] = label
```
これで、ラベル ID をラベル名に変換できるようになりました。
```py
>>> id2label[str(79)]
'prime_rib'
```
## Preprocess
次のステップでは、ViT 画像プロセッサをロードして画像をテンソルに処理します。
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
>>> checkpoint = "google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k"
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
```
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
いくつかの画像変換を画像に適用して、モデルの過学習に対する堅牢性を高めます。ここでは torchvision の [`transforms`](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html) モジュールを使用しますが、任意の画像ライブラリを使用することもできます。
画像のランダムな部分をトリミングし、サイズを変更し、画像の平均と標準偏差で正規化します。
```py
>>> from torchvision.transforms import RandomResizedCrop, Compose, Normalize, ToTensor
>>> normalize = Normalize(mean=image_processor.image_mean, std=image_processor.image_std)
>>> size = (
... image_processor.size["shortest_edge"]
... if "shortest_edge" in image_processor.size
... else (image_processor.size["height"], image_processor.size["width"])
... )
>>> _transforms = Compose([RandomResizedCrop(size), ToTensor(), normalize])
```
次に、変換を適用し、画像の `pixel_values` (モデルへの入力) を返す前処理関数を作成します。
```py
>>> def transforms(examples):
... examples["pixel_values"] = [_transforms(img.convert("RGB")) for img in examples["image"]]
... del examples["image"]
... return examples
```
データセット全体に前処理関数を適用するには、🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.with_transform`] メソッドを使用します。変換は、データセットの要素を読み込むときにオンザフライで適用されます。
```py
>>> food = food.with_transform(transforms)
```
次に、[`DefaultDataCollator`] を使用してサンプルのバッチを作成します。 🤗 Transformers の他のデータ照合器とは異なり、`DefaultDataCollator` はパディングなどの追加の前処理を適用しません。
```py
>>> from transformers import DefaultDataCollator
>>> data_collator = DefaultDataCollator()
```
</pt>
</frameworkcontent>
<frameworkcontent>
<tf>
過剰適合を回避し、モデルをより堅牢にするために、データセットのトレーニング部分にデータ拡張を追加します。
ここでは、Keras 前処理レイヤーを使用してトレーニング データの変換 (データ拡張を含む) を定義します。
検証データの変換 (中央のトリミング、サイズ変更、正規化のみ)。 `tf.image` または
他のライブラリでも構いません。
```py
>>> from tensorflow import keras
>>> from tensorflow.keras import layers
>>> size = (image_processor.size["height"], image_processor.size["width"])
>>> train_data_augmentation = keras.Sequential(
... [
... layers.RandomCrop(size[0], size[1]),
... layers.Rescaling(scale=1.0 / 127.5, offset=-1),
... layers.RandomFlip("horizontal"),
... layers.RandomRotation(factor=0.02),
... layers.RandomZoom(height_factor=0.2, width_factor=0.2),
... ],
... name="train_data_augmentation",
... )
>>> val_data_augmentation = keras.Sequential(
... [
... layers.CenterCrop(size[0], size[1]),
... layers.Rescaling(scale=1.0 / 127.5, offset=-1),
... ],
... name="val_data_augmentation",
... )
```
次に、一度に 1 つの画像ではなく、画像のバッチに適切な変換を適用する関数を作成します。
```py
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> def convert_to_tf_tensor(image: Image):
... np_image = np.array(image)
... tf_image = tf.convert_to_tensor(np_image)
... # `expand_dims()` is used to add a batch dimension since
... # the TF augmentation layers operates on batched inputs.
... return tf.expand_dims(tf_image, 0)
>>> def preprocess_train(example_batch):
... """Apply train_transforms across a batch."""
... images = [
... train_data_augmentation(convert_to_tf_tensor(image.convert("RGB"))) for image in example_batch["image"]
... ]
... example_batch["pixel_values"] = [tf.transpose(tf.squeeze(image)) for image in images]
... return example_batch
... def preprocess_val(example_batch):
... """Apply val_transforms across a batch."""
... images = [
... val_data_augmentation(convert_to_tf_tensor(image.convert("RGB"))) for image in example_batch["image"]
... ]
... example_batch["pixel_values"] = [tf.transpose(tf.squeeze(image)) for image in images]
... return example_batch
```
🤗 データセット [`~datasets.Dataset.set_transform`] を使用して、その場で変換を適用します。
```py
food["train"].set_transform(preprocess_train)
food["test"].set_transform(preprocess_val)
```
最後の前処理ステップとして、`DefaultDataCollator`を使用してサンプルのバッチを作成します。 🤗 Transformers の他のデータ照合機能とは異なり、
`DefaultDataCollator` は、パディングなどの追加の前処理を適用しません。
```py
>>> from transformers import DefaultDataCollator
>>> data_collator = DefaultDataCollator(return_tensors="tf")
```
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
## Evaluate
トレーニング中にメトリクスを含めると、多くの場合、モデルのパフォーマンスを評価するのに役立ちます。すぐにロードできます
🤗 [Evaluate](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/index) ライブラリを使用した評価方法。このタスクでは、ロードします
[accuracy](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/accuracy) 指標 (詳細については、🤗 評価 [クイック ツアー](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/a_quick_tour) を参照してくださいメトリクスをロードして計算する方法):
```py
>>> import evaluate
>>> accuracy = evaluate.load("accuracy")
```
次に、予測とラベルを [`~evaluate.EvaluationModule.compute`] に渡して精度を計算する関数を作成します。
```py
>>> import numpy as np
>>> def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
... predictions, labels = eval_pred
... predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
... return accuracy.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
```
これで `compute_metrics`関数の準備が整いました。トレーニングを設定するときにこの関数に戻ります。
## Train
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
<Tip>
[`Trainer`] を使用したモデルの微調整に慣れていない場合は、[こちら](../training#train-with-pytorch-trainer) の基本的なチュートリアルをご覧ください。
</Tip>
これでモデルのトレーニングを開始する準備が整いました。 [`AutoModelForImageClassification`] を使用して ViT をロードします。ラベルの数と予想されるラベルの数、およびラベル マッピングを指定します。
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification, TrainingArguments, Trainer
>>> model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
... checkpoint,
... num_labels=len(labels),
... id2label=id2label,
... label2id=label2id,
... )
```
この時点で残っているステップは 3 つだけです。
1. [`TrainingArguments`] でトレーニング ハイパーパラメータを定義します。 `image` 列が削除されるため、未使用の列を削除しないことが重要です。 `image` 列がないと、`pixel_values` を作成できません。この動作を防ぐには、`remove_unused_columns=False`を設定してください。他に必要なパラメータは、モデルの保存場所を指定する `output_dir` だけです。 `push_to_hub=True`を設定して、このモデルをハブにプッシュします (モデルをアップロードするには、Hugging Face にサインインする必要があります)。各エポックの終了時に、[`Trainer`] は精度を評価し、トレーニング チェックポイントを保存します。
2. トレーニング引数を、モデル、データセット、トークナイザー、データ照合器、および `compute_metrics` 関数とともに [`Trainer`] に渡します。
3. [`~Trainer.train`] を呼び出してモデルを微調整します。
```py
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(
... output_dir="my_awesome_food_model",
... remove_unused_columns=False,
... eval_strategy="epoch",
... save_strategy="epoch",
... learning_rate=5e-5,
... per_device_train_batch_size=16,
... gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
... per_device_eval_batch_size=16,
... num_train_epochs=3,
... warmup_ratio=0.1,
... logging_steps=10,
... load_best_model_at_end=True,
... metric_for_best_model="accuracy",
... push_to_hub=True,
... )
>>> trainer = Trainer(
... model=model,
... args=training_args,
... data_collator=data_collator,
... train_dataset=food["train"],
... eval_dataset=food["test"],
... processing_class=image_processor,
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
... )
>>> trainer.train()
```
トレーニングが完了したら、 [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] メソッドを使用してモデルをハブに共有し、誰もがモデルを使用できるようにします。
```py
>>> trainer.push_to_hub()
```
</pt>
</frameworkcontent>
<frameworkcontent>
<tf>
<Tip>
Keras を使用したモデルの微調整に慣れていない場合は、まず [基本チュートリアル](./training#train-a-tensorflow-model-with-keras) を確認してください。
</Tip>
TensorFlow でモデルを微調整するには、次の手順に従います。
1. トレーニングのハイパーパラメータを定義し、オプティマイザーと学習率スケジュールを設定します。
2. 事前トレーニングされたモデルをインスタンス化します。
3. 🤗 データセットを `tf.data.Dataset` に変換します。
4. モデルをコンパイルします。
5. コールバックを追加し、`fit()` メソッドを使用してトレーニングを実行します。
6. モデルを 🤗 Hub にアップロードしてコミュニティと共有します。
まず、ハイパーパラメーター、オプティマイザー、学習率スケジュールを定義します。
```py
>>> from transformers import create_optimizer
>>> batch_size = 16
>>> num_epochs = 5
>>> num_train_steps = len(food["train"]) * num_epochs
>>> learning_rate = 3e-5
>>> weight_decay_rate = 0.01
>>> optimizer, lr_schedule = create_optimizer(
... init_lr=learning_rate,
... num_train_steps=num_train_steps,
... weight_decay_rate=weight_decay_rate,
... num_warmup_steps=0,
... )
```
次に、ラベル マッピングとともに [`TFAutoModelForImageClassification`] を使用して ViT を読み込みます。
```py
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForImageClassification
>>> model = TFAutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
... checkpoint,
... id2label=id2label,
... label2id=label2id,
... )
```
Convert your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format using the [`~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`] and your `data_collator`:
```py
>>> # converting our train dataset to tf.data.Dataset
>>> tf_train_dataset = food["train"].to_tf_dataset(
... columns="pixel_values", label_cols="label", shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, collate_fn=data_collator
... )
>>> # converting our test dataset to tf.data.Dataset
>>> tf_eval_dataset = food["test"].to_tf_dataset(
... columns="pixel_values", label_cols="label", shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, collate_fn=data_collator
... )
```
`compile()` を使用してトレーニング用にモデルを設定します。
```py
>>> from tensorflow.keras.losses import SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
>>> loss = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
>>> model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss)
```
予測から精度を計算し、モデルを 🤗 ハブにプッシュするには、[Keras callbacks](../main_classes/keras_callbacks) を使用します。
`compute_metrics` 関数を [KerasMetricCallback](../main_classes/keras_callbacks#transformers.KerasMetricCallback) に渡します。
[PushToHubCallback](../main_classes/keras_callbacks#transformers.PushToHubCallback) を使用してモデルをアップロードします。
```py
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import KerasMetricCallback, PushToHubCallback
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_eval_dataset)
>>> push_to_hub_callback = PushToHubCallback(
... output_dir="food_classifier",
... tokenizer=image_processor,
... save_strategy="no",
... )
>>> callbacks = [metric_callback, push_to_hub_callback]
```
ついに、モデルをトレーニングする準備が整いました。トレーニングおよび検証データセット、エポック数、
モデルを微調整するためのコールバック:
```py
>>> model.fit(tf_train_dataset, validation_data=tf_eval_dataset, epochs=num_epochs, callbacks=callbacks)
Epoch 1/5
250/250 [==============================] - 313s 1s/step - loss: 2.5623 - val_loss: 1.4161 - accuracy: 0.9290
Epoch 2/5
250/250 [==============================] - 265s 1s/step - loss: 0.9181 - val_loss: 0.6808 - accuracy: 0.9690
Epoch 3/5
250/250 [==============================] - 252s 1s/step - loss: 0.3910 - val_loss: 0.4303 - accuracy: 0.9820
Epoch 4/5
250/250 [==============================] - 251s 1s/step - loss: 0.2028 - val_loss: 0.3191 - accuracy: 0.9900
Epoch 5/5
250/250 [==============================] - 238s 949ms/step - loss: 0.1232 - val_loss: 0.3259 - accuracy: 0.9890
```
おめでとう!モデルを微調整し、🤗 Hub で共有しました。これで推論に使用できるようになりました。
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
<Tip>
画像分類用のモデルを微調整する方法の詳細な例については、対応する [PyTorch ノートブック](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb)
</Tip>
## Inference
モデルを微調整したので、それを推論に使用できるようになりました。
推論を実行したい画像を読み込みます。
```py
>>> ds = load_dataset("food101", split="validation[:10]")
>>> image = ds["image"][0]
```
<div class="flex justify-center">
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/beignets-task-guide.png" alt="image of beignets"/>
</div>
推論用に微調整されたモデルを試す最も簡単な方法は、それを [`pipeline`] で使用することです。モデルを使用して画像分類用の`pipeline`をインスタンス化し、それに画像を渡します。
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> classifier = pipeline("image-classification", model="my_awesome_food_model")
>>> classifier(image)
[{'score': 0.31856709718704224, 'label': 'beignets'},
{'score': 0.015232225880026817, 'label': 'bruschetta'},
{'score': 0.01519392803311348, 'label': 'chicken_wings'},
{'score': 0.013022331520915031, 'label': 'pork_chop'},
{'score': 0.012728818692266941, 'label': 'prime_rib'}]
```
必要に応じて、`pipeline`の結果を手動で複製することもできます。
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
画像プロセッサをロードして画像を前処理し、`input`を PyTorch テンソルとして返します。
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
>>> import torch
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("my_awesome_food_model")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
```
入力をモデルに渡し、ロジットを返します。
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
>>> model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("my_awesome_food_model")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
```
最も高い確率で予測されたラベルを取得し、モデルの `id2label` マッピングを使用してラベルに変換します。
```py
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> model.config.id2label[predicted_label]
'beignets'
```
</pt>
</frameworkcontent>
<frameworkcontent>
<tf>
画像プロセッサをロードして画像を前処理し、`input`を TensorFlow テンソルとして返します。
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("MariaK/food_classifier")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="tf")
```
入力をモデルに渡し、ロジットを返します。
```py
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForImageClassification
>>> model = TFAutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("MariaK/food_classifier")
>>> logits = model(**inputs).logits
```
最も高い確率で予測されたラベルを取得し、モデルの `id2label` マッピングを使用してラベルに変換します。
```py
>>> predicted_class_id = int(tf.math.argmax(logits, axis=-1)[0])
>>> model.config.id2label[predicted_class_id]
'beignets'
```
</tf>
</frameworkcontent>
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/tasks/image_classification.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/tasks/image_classification.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 8613
}
| 44 |
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Video classification
[[open-in-colab]]
ビデオ分類は、ビデオ全体にラベルまたはクラスを割り当てるタスクです。ビデオには、各ビデオに 1 つのクラスのみが含まれることが期待されます。ビデオ分類モデルはビデオを入力として受け取り、ビデオがどのクラスに属するかについての予測を返します。これらのモデルを使用して、ビデオの内容を分類できます。ビデオ分類の実際のアプリケーションはアクション/アクティビティ認識であり、フィットネス アプリケーションに役立ちます。また、視覚障害のある人にとって、特に通勤時に役立ちます。
このガイドでは、次の方法を説明します。
1. [UCF101](https://www.crcv.ucf.edu/) のサブセットで [VideoMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/videomae) を微調整します。 data/UCF101.php) データセット。
2. 微調整したモデルを推論に使用します。
<Tip>
このタスクと互換性のあるすべてのアーキテクチャとチェックポイントを確認するには、[タスクページ](https://huggingface.co/tasks/video-classification) を確認することをお勧めします。
</Tip>
始める前に、必要なライブラリがすべてインストールされていることを確認してください。
```bash
pip install -q pytorchvideo transformers evaluate
```
[PyTorchVideo](https://pytorchvideo.org/) (`pytorchvideo` と呼ばれます) を使用してビデオを処理し、準備します。
モデルをアップロードしてコミュニティと共有できるように、Hugging Face アカウントにログインすることをお勧めします。プロンプトが表示されたら、トークンを入力してログインします。
```py
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
>>> notebook_login()
```
## Load UCF101 dataset
まず、[UCF-101 データセット](https://www.crcv.ucf.edu/data/UCF101.php) のサブセットをロードします。これにより、完全なデータセットのトレーニングにさらに時間を費やす前に、実験してすべてが機能することを確認する機会が得られます。
```py
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
>>> hf_dataset_identifier = "sayakpaul/ucf101-subset"
>>> filename = "UCF101_subset.tar.gz"
>>> file_path = hf_hub_download(repo_id=hf_dataset_identifier, filename=filename, repo_type="dataset")
```
サブセットをダウンロードした後、圧縮アーカイブを抽出する必要があります。
```py
>>> import tarfile
>>> with tarfile.open(file_path) as t:
... t.extractall(".")
```
大まかに言うと、データセットは次のように構成されています。
```bash
UCF101_subset/
train/
BandMarching/
video_1.mp4
video_2.mp4
...
Archery
video_1.mp4
video_2.mp4
...
...
val/
BandMarching/
video_1.mp4
video_2.mp4
...
Archery
video_1.mp4
video_2.mp4
...
...
test/
BandMarching/
video_1.mp4
video_2.mp4
...
Archery
video_1.mp4
video_2.mp4
...
...
```
(`sorted`)された ビデオ パスは次のように表示されます。
```bash
...
'UCF101_subset/train/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g07_c04.avi',
'UCF101_subset/train/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g07_c06.avi',
'UCF101_subset/train/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g08_c01.avi',
'UCF101_subset/train/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g09_c02.avi',
'UCF101_subset/train/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g09_c06.avi'
...
```
同じグループ/シーンに属するビデオ クリップがあり、ビデオ ファイル パスではグループが`g`で示されていることがわかります。たとえば、`v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g07_c04.avi`や`v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g07_c06.avi`などです。
検証と評価の分割では、[データ漏洩](https://www.kaggle.com/code/alexisbcook/data-leakage) を防ぐために、同じグループ/シーンからのビデオ クリップを使用しないでください。このチュートリアルで使用しているサブセットでは、この情報が考慮されています。
次に、データセット内に存在するラベルのセットを取得します。また、モデルを初期化するときに役立つ 2 つの辞書を作成します。
* `label2id`: クラス名を整数にマップします。
* `id2label`: 整数をクラス名にマッピングします。
```py
>>> class_labels = sorted({str(path).split("/")[2] for path in all_video_file_paths})
>>> label2id = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(class_labels)}
>>> id2label = {i: label for label, i in label2id.items()}
>>> print(f"Unique classes: {list(label2id.keys())}.")
# Unique classes: ['ApplyEyeMakeup', 'ApplyLipstick', 'Archery', 'BabyCrawling', 'BalanceBeam', 'BandMarching', 'BaseballPitch', 'Basketball', 'BasketballDunk', 'BenchPress'].
```
個性的なクラスが10種類あります。トレーニング セットには、クラスごとに 30 個のビデオがあります。
## Load a model to fine-tune
事前トレーニングされたチェックポイントとそれに関連する画像プロセッサからビデオ分類モデルをインスタンス化します。モデルのエンコーダーには事前トレーニングされたパラメーターが付属しており、分類ヘッドはランダムに初期化されます。画像プロセッサは、データセットの前処理パイプラインを作成するときに役立ちます。
```py
>>> from transformers import VideoMAEImageProcessor, VideoMAEForVideoClassification
>>> model_ckpt = "MCG-NJU/videomae-base"
>>> image_processor = VideoMAEImageProcessor.from_pretrained(model_ckpt)
>>> model = VideoMAEForVideoClassification.from_pretrained(
... model_ckpt,
... label2id=label2id,
... id2label=id2label,
... ignore_mismatched_sizes=True, # provide this in case you're planning to fine-tune an already fine-tuned checkpoint
... )
```
モデルのロード中に、次の警告が表示される場合があります。
```bash
Some weights of the model checkpoint at MCG-NJU/videomae-base were not used when initializing VideoMAEForVideoClassification: [..., 'decoder.decoder_layers.1.attention.output.dense.bias', 'decoder.decoder_layers.2.attention.attention.key.weight']
- This IS expected if you are initializing VideoMAEForVideoClassification from the checkpoint of a model trained on another task or with another architecture (e.g. initializing a BertForSequenceClassification model from a BertForPreTraining model).
- This IS NOT expected if you are initializing VideoMAEForVideoClassification from the checkpoint of a model that you expect to be exactly identical (initializing a BertForSequenceClassification model from a BertForSequenceClassification model).
Some weights of VideoMAEForVideoClassification were not initialized from the model checkpoint at MCG-NJU/videomae-base and are newly initialized: ['classifier.bias', 'classifier.weight']
You should probably TRAIN this model on a down-stream task to be able to use it for predictions and inference.
```
この警告は、一部の重み (たとえば、`classifier`層の重みとバイアス) を破棄し、他のいくつかの重み (新しい`classifier`層の重みとバイアス) をランダムに初期化していることを示しています。この場合、これは予想されることです。事前にトレーニングされた重みを持たない新しい頭部を追加しているため、推論に使用する前にこのモデルを微調整する必要があるとライブラリが警告します。これはまさに私たちが行おうとしているものです。する。
**注意** [このチェックポイント](https://huggingface.co/MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics) は、同様のダウンストリームで微調整されてチェックポイントが取得されたため、このタスクのパフォーマンスが向上することに注意してください。かなりのドメインの重複があるタスク。 `MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics` を微調整して取得した [このチェックポイント](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics-finetuned-ucf101-subset) を確認できます。 -キネティクス`。
## Prepare the datasets for training
ビデオの前処理には、[PyTorchVideo ライブラリ](https://pytorchvideo.org/) を利用します。まず、必要な依存関係をインポートします。
```py
>>> import pytorchvideo.data
>>> from pytorchvideo.transforms import (
... ApplyTransformToKey,
... Normalize,
... RandomShortSideScale,
... RemoveKey,
... ShortSideScale,
... UniformTemporalSubsample,
... )
>>> from torchvision.transforms import (
... Compose,
... Lambda,
... RandomCrop,
... RandomHorizontalFlip,
... Resize,
... )
```
トレーニング データセットの変換には、均一な時間サブサンプリング、ピクセル正規化、ランダム クロッピング、およびランダムな水平反転を組み合わせて使用します。検証および評価のデータセット変換では、ランダムなトリミングと水平反転を除き、同じ変換チェーンを維持します。これらの変換の詳細については、[PyTorchVideo の公式ドキュメント](https://pytorchvideo.org) を参照してください。
事前トレーニングされたモデルに関連付けられた`image_processor`を使用して、次の情報を取得します。
* ビデオ フレームのピクセルが正規化される画像の平均値と標準偏差。
* ビデオ フレームのサイズが変更される空間解像度。
まず、いくつかの定数を定義します。
```py
>>> mean = image_processor.image_mean
>>> std = image_processor.image_std
>>> if "shortest_edge" in image_processor.size:
... height = width = image_processor.size["shortest_edge"]
>>> else:
... height = image_processor.size["height"]
... width = image_processor.size["width"]
>>> resize_to = (height, width)
>>> num_frames_to_sample = model.config.num_frames
>>> sample_rate = 4
>>> fps = 30
>>> clip_duration = num_frames_to_sample * sample_rate / fps
```
次に、データセット固有の変換とデータセットをそれぞれ定義します。トレーニングセットから始めます:
```py
>>> train_transform = Compose(
... [
... ApplyTransformToKey(
... key="video",
... transform=Compose(
... [
... UniformTemporalSubsample(num_frames_to_sample),
... Lambda(lambda x: x / 255.0),
... Normalize(mean, std),
... RandomShortSideScale(min_size=256, max_size=320),
... RandomCrop(resize_to),
... RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
... ]
... ),
... ),
... ]
... )
>>> train_dataset = pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101(
... data_path=os.path.join(dataset_root_path, "train"),
... clip_sampler=pytorchvideo.data.make_clip_sampler("random", clip_duration),
... decode_audio=False,
... transform=train_transform,
... )
```
同じ一連のワークフローを検証セットと評価セットに適用できます。
```py
>>> val_transform = Compose(
... [
... ApplyTransformToKey(
... key="video",
... transform=Compose(
... [
... UniformTemporalSubsample(num_frames_to_sample),
... Lambda(lambda x: x / 255.0),
... Normalize(mean, std),
... Resize(resize_to),
... ]
... ),
... ),
... ]
... )
>>> val_dataset = pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101(
... data_path=os.path.join(dataset_root_path, "val"),
... clip_sampler=pytorchvideo.data.make_clip_sampler("uniform", clip_duration),
... decode_audio=False,
... transform=val_transform,
... )
>>> test_dataset = pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101(
... data_path=os.path.join(dataset_root_path, "test"),
... clip_sampler=pytorchvideo.data.make_clip_sampler("uniform", clip_duration),
... decode_audio=False,
... transform=val_transform,
... )
```
**注意**: 上記のデータセット パイプラインは、[公式 PyTorchVideo サンプル](https://pytorchvideo.org/docs/tutorial_classification#dataset) から取得したものです。 [`pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101()`](https://pytorchvideo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/data/data.html#pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101) 関数を使用しています。 UCF-101 データセット。内部では、[`pytorchvideo.data.labeled_video_dataset.LabeledVideoDataset`](https://pytorchvideo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/data/data.html#pytorchvideo.data.LabeledVideoDataset) オブジェクトを返します。 `LabeledVideoDataset` クラスは、PyTorchVideo データセット内のすべてのビデオの基本クラスです。したがって、PyTorchVideo で既製でサポートされていないカスタム データセットを使用したい場合は、それに応じて `LabeledVideoDataset` クラスを拡張できます。詳細については、`data`API [ドキュメント](https://pytorchvideo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/data/data.html)を参照してください。また、データセットが同様の構造 (上に示したもの) に従っている場合は、`pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101()` を使用すると問題なく動作するはずです。
`num_videos` 引数にアクセスすると、データセット内のビデオの数を知ることができます。
```py
>>> print(train_dataset.num_videos, val_dataset.num_videos, test_dataset.num_videos)
# (300, 30, 75)
```
## Visualize the preprocessed video for better debugging
```py
>>> import imageio
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from IPython.display import Image
>>> def unnormalize_img(img):
... """Un-normalizes the image pixels."""
... img = (img * std) + mean
... img = (img * 255).astype("uint8")
... return img.clip(0, 255)
>>> def create_gif(video_tensor, filename="sample.gif"):
... """Prepares a GIF from a video tensor.
...
... The video tensor is expected to have the following shape:
... (num_frames, num_channels, height, width).
... """
... frames = []
... for video_frame in video_tensor:
... frame_unnormalized = unnormalize_img(video_frame.permute(1, 2, 0).numpy())
... frames.append(frame_unnormalized)
... kargs = {"duration": 0.25}
... imageio.mimsave(filename, frames, "GIF", **kargs)
... return filename
>>> def display_gif(video_tensor, gif_name="sample.gif"):
... """Prepares and displays a GIF from a video tensor."""
... video_tensor = video_tensor.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)
... gif_filename = create_gif(video_tensor, gif_name)
... return Image(filename=gif_filename)
>>> sample_video = next(iter(train_dataset))
>>> video_tensor = sample_video["video"]
>>> display_gif(video_tensor)
```
<div class="flex justify-center">
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tasks/sample_gif.gif" alt="Person playing basketball"/>
</div>
## Train the model
🤗 Transformers の [`Trainer`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/trainer) をモデルのトレーニングに利用します。 `Trainer`をインスタンス化するには、トレーニング構成と評価メトリクスを定義する必要があります。最も重要なのは [`TrainingArguments`](https://huggingface.co/transformers/main_classes/trainer.html#transformers.TrainingArguments) で、これはトレーニングを構成するためのすべての属性を含むクラスです。モデルのチェックポイントを保存するために使用される出力フォルダー名が必要です。また、🤗 Hub 上のモデル リポジトリ内のすべての情報を同期するのにも役立ちます。
トレーニング引数のほとんどは一目瞭然ですが、ここで非常に重要なのは`remove_unused_columns=False`です。これにより、モデルの呼び出し関数で使用されない機能が削除されます。デフォルトでは`True`です。これは、通常、未使用の特徴列を削除し、モデルの呼び出し関数への入力を解凍しやすくすることが理想的であるためです。ただし、この場合、`pixel_values` (モデルが入力で期待する必須キーです) を作成するには、未使用の機能 (特に`video`) が必要です。
```py
>>> from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
>>> model_name = model_ckpt.split("/")[-1]
>>> new_model_name = f"{model_name}-finetuned-ucf101-subset"
>>> num_epochs = 4
>>> args = TrainingArguments(
... new_model_name,
... remove_unused_columns=False,
... eval_strategy="epoch",
... save_strategy="epoch",
... learning_rate=5e-5,
... per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
... per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
... warmup_ratio=0.1,
... logging_steps=10,
... load_best_model_at_end=True,
... metric_for_best_model="accuracy",
... push_to_hub=True,
... max_steps=(train_dataset.num_videos // batch_size) * num_epochs,
... )
```
`pytorchvideo.data.Ucf101()` によって返されるデータセットは `__len__` メソッドを実装していません。そのため、`TrainingArguments`をインスタンス化するときに`max_steps`を定義する必要があります。
次に、予測からメトリクスを計算する関数を定義する必要があります。これは、これからロードする`metric`を使用します。必要な前処理は、予測されたロジットの argmax を取得することだけです。
```py
import evaluate
metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
predictions = np.argmax(eval_pred.predictions, axis=1)
return metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=eval_pred.label_ids)
```
**評価に関する注意事項**:
[VideoMAE 論文](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12602) では、著者は次の評価戦略を使用しています。彼らはテスト ビデオからのいくつかのクリップでモデルを評価し、それらのクリップにさまざまなクロップを適用して、合計スコアを報告します。ただし、単純さと簡潔さを保つために、このチュートリアルではそれを考慮しません。
また、サンプルをまとめてバッチ処理するために使用される `collate_fn` を定義します。各バッチは、`pixel_values` と `labels` という 2 つのキーで構成されます。
```py
>>> def collate_fn(examples):
... # permute to (num_frames, num_channels, height, width)
... pixel_values = torch.stack(
... [example["video"].permute(1, 0, 2, 3) for example in examples]
... )
... labels = torch.tensor([example["label"] for example in examples])
... return {"pixel_values": pixel_values, "labels": labels}
```
次に、これらすべてをデータセットとともに`Trainer`に渡すだけです。
```py
>>> trainer = Trainer(
... model,
... args,
... train_dataset=train_dataset,
... eval_dataset=val_dataset,
... processing_class=image_processor,
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
... data_collator=collate_fn,
... )
```
すでにデータを前処理しているのに、なぜトークナイザーとして`image_processor`を渡したのか不思議に思うかもしれません。これは、イメージ プロセッサ構成ファイル (JSON として保存) もハブ上のリポジトリにアップロードされるようにするためだけです。
次に、`train` メソッドを呼び出してモデルを微調整します。
```py
>>> train_results = trainer.train()
```
トレーニングが完了したら、 [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] メソッドを使用してモデルをハブに共有し、誰もがモデルを使用できるようにします。
```py
>>> trainer.push_to_hub()
```
## Inference
モデルを微調整したので、それを推論に使用できるようになりました。
推論のためにビデオをロードします。
```py
>>> sample_test_video = next(iter(test_dataset))
```
<div class="flex justify-center">
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tasks/sample_gif_two.gif" alt="Teams playing basketball"/>
</div>
推論用に微調整されたモデルを試す最も簡単な方法は、それを [`pipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/pipelines#transformers.VideoClassificationPipeline). で使用することです。モデルを使用してビデオ分類用の` pipeline`をインスタンス化し、それにビデオを渡します。
```py
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> video_cls = pipeline(model="my_awesome_video_cls_model")
>>> video_cls("https://huggingface.co/datasets/sayakpaul/ucf101-subset/resolve/main/v_BasketballDunk_g14_c06.avi")
[{'score': 0.9272987842559814, 'label': 'BasketballDunk'},
{'score': 0.017777055501937866, 'label': 'BabyCrawling'},
{'score': 0.01663011871278286, 'label': 'BalanceBeam'},
{'score': 0.009560945443809032, 'label': 'BandMarching'},
{'score': 0.0068979403004050255, 'label': 'BaseballPitch'}]
```
必要に応じて、`pipeline`の結果を手動で複製することもできます。
```py
>>> def run_inference(model, video):
... # (num_frames, num_channels, height, width)
... perumuted_sample_test_video = video.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)
... inputs = {
... "pixel_values": perumuted_sample_test_video.unsqueeze(0),
... "labels": torch.tensor(
... [sample_test_video["label"]]
... ), # this can be skipped if you don't have labels available.
... }
... device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
... inputs = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
... model = model.to(device)
... # forward pass
... with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
... logits = outputs.logits
... return logits
```
次に、入力をモデルに渡し、`logits `を返します。
```py
>>> logits = run_inference(trained_model, sample_test_video["video"])
```
`logits` をデコードすると、次のようになります。
```py
>>> predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
# Predicted class: BasketballDunk
```
|
transformers/docs/source/ja/tasks/video_classification.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ja/tasks/video_classification.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 10027
}
| 45 |
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Hugging Face Transformers를 추가하는 방법은 무엇인가요? [[how-to-add-a-model-to-transformers]]
Hugging Face Transformers 라이브러리는 커뮤니티 기여자들 덕분에 새로운 모델을 제공할 수 있는 경우가 많습니다. 하지만 이는 도전적인 프로젝트이며 Hugging Face Transformers 라이브러리와 구현할 모델에 대한 깊은 이해가 필요합니다. Hugging Face에서는 더 많은 커뮤니티 멤버가 모델을 적극적으로 추가할 수 있도록 지원하고자 하며, 이 가이드를 통해 PyTorch 모델을 추가하는 과정을 안내하고 있습니다 (PyTorch가 설치되어 있는지 확인해주세요).
이 과정을 진행하면 다음과 같은 내용을 이해하게 됩니다:
- 오픈 소스의 모범 사례에 대한 통찰력을 얻습니다.
- 가장 인기 있는 딥러닝 라이브러리의 설계 원칙을 이해합니다.
- 대규모 모델을 효율적으로 테스트하는 방법을 배웁니다.
- `black`, `ruff`, `make fix-copies`와 같은 Python 유틸리티를 통합하여 깔끔하고 가독성 있는 코드를 작성하는 방법을 배웁니다.
Hugging Face 팀은 항상 도움을 줄 준비가 되어 있으므로 혼자가 아니라는 점을 기억하세요. 🤗 ❤️
시작에 앞서 🤗 Transformers에 원하는 모델을 추가하기 위해 [New model addition](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model&template=new-model-addition.yml) 이슈를 열어야 합니다. 특정 모델을 기여하는 데 특별히 까다로운 기준을 가지지 않는 경우 [New model label](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/labels/New%20model)을 필터링하여 요청되지 않은 모델이 있는지 확인하고 작업할 수 있습니다.
새로운 모델 요청을 열었다면 첫 번째 단계는 🤗 Transformers에 익숙해지는 것입니다!
## 🤗 Transformers의 전반적인 개요 [[general-overview-of-transformers]]
먼저 🤗 Transformers에 대한 전반적인 개요를 파악해야 합니다. 🤗 Transformers는 매우 주관적인 라이브러리이기 때문에 해당 라이브러리의 철학이나 설계 선택 사항에 동의하지 않을 수도 있습니다. 그러나 우리의 경험상 라이브러리의 기본적인 설계 선택과 철학은 🤗 Transformers의 규모를 효율적으로 확장하면서 유지 보수 비용을 합리적인 수준으로 유지하는 것입니다.
[라이브러리의 철학에 대한 문서](philosophy)를 읽는 것이 라이브러리를 더 잘 이해하는 좋은 시작점입니다. 모든 모델에 적용하려는 몇 가지 작업 방식에 대한 선택 사항이 있습니다:
- 일반적으로 추상화보다는 구성을 선호합니다.
- 코드를 복제하는 것이 항상 나쁜 것은 아닙니다. 코드의 가독성이나 접근성을 크게 향상시킨다면 복제하는 것은 좋습니다.
- 모델 파일은 가능한 한 독립적으로 유지되어야 합니다. 따라서 특정 모델의 코드를 읽을 때 해당 `modeling_....py` 파일만 확인하면 됩니다.
우리는 라이브러리의 코드가 제품을 제공하는 수단뿐만 아니라 개선하고자 하는 제품이라고도 생각합니다. 따라서 모델을 추가할 때, 사용자는 모델을 사용할 사람뿐만 아니라 코드를 읽고 이해하고 필요한 경우 조정할 수 있는 모든 사람까지도 포함한다는 점을 기억해야 합니다.
이를 염두에 두고 일반적인 라이브러리 설계에 대해 조금 더 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
### 모델 개요 [[overview-of-models]]
모델을 성공적으로 추가하려면 모델과 해당 구성인 [`PreTrainedModel`] 및 [`PretrainedConfig`] 간의 상호작용을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다. 예를 들어, 🤗 Transformers에 추가하려는 모델을 `BrandNewBert`라고 부르겠습니다.
다음을 살펴보겠습니다:
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers_overview.png"/>
보다시피, 🤗 Transformers에서는 상속을 사용하지만 추상화 수준을 최소한으로 유지합니다. 라이브러리의 어떤 모델에서도 두 수준 이상의 추상화가 존재하지 않습니다. `BrandNewBertModel`은 `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`에서 상속받고, 이 클래스는 [`PreTrainedModel`]에서 상속받습니다. 이로써 새로운 모델은 [`PreTrainedModel`]에만 의존하도록 하려고 합니다. 모든 새로운 모델에 자동으로 제공되는 중요한 기능은 [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] 및 [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]입니다. 이러한 기능 외에도 `BrandNewBertModel.forward`와 같은 다른 중요한 기능은 새로운 `modeling_brand_new_bert.py` 스크립트에서 완전히 정의되어야 합니다. 또한 `BrandNewBertForMaskedLM`과 같은 특정 헤드 레이어를 가진 모델은 `BrandNewBertModel`을 상속받지 않고 forward pass에서 호출할 수 있는 `BrandNewBertModel`을 사용하여 추상화 수준을 낮게 유지합니다. 모든 새로운 모델은 `BrandNewBertConfig`라는 구성 클래스를 필요로 합니다. 이 구성은 항상 [`PreTrainedModel`]의 속성으로 저장되며, 따라서 `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`을 상속받는 모든 클래스에서 `config` 속성을 통해 액세스할 수 있습니다:
```python
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("brandy/brand_new_bert")
model.config # model has access to its config
```
모델과 마찬가지로 구성은 [`PretrainedConfig`]에서 기본 직렬화 및 역직렬화 기능을 상속받습니다. 구성과 모델은 항상 *pytorch_model.bin* 파일과 *config.json* 파일로 각각 별도로 직렬화됩니다. [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]를 호출하면 자동으로 [`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`]도 호출되므로 모델과 구성이 모두 저장됩니다.
### 코드 스타일 [[code-style]]
새로운 모델을 작성할 때, Transformers는 주관적인 라이브러리이며 몇 가지 독특한 코딩 스타일이 있습니다:
1. 모델의 forward pass는 모델 파일에 완전히 작성되어야 합니다. 라이브러리의 다른 모델에서 블록을 재사용하려면 코드를 복사하여 위에 `# Copied from` 주석과 함께 붙여넣으면 됩니다 (예: [여기](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/v4.17.0/src/transformers/models/roberta/modeling_roberta.py#L160)를 참조하세요).
2. 코드는 완전히 이해하기 쉬워야 합니다. 변수 이름을 명확하게 지정하고 약어를 사용하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. 예를 들어, `act`보다는 `activation`을 선호합니다. 한 글자 변수 이름은 루프의 인덱스인 경우를 제외하고 권장되지 않습니다.
3. 더 일반적으로, 짧은 마법 같은 코드보다는 길고 명시적인 코드를 선호합니다.
4. PyTorch에서 `nn.Sequential`을 하위 클래스로 만들지 말고 `nn.Module`을 하위 클래스로 만들고 forward pass를 작성하여 다른 사람이 코드를 빠르게 디버그할 수 있도록 합니다. print 문이나 중단점을 추가할 수 있습니다.
5. 함수 시그니처에는 타입 주석을 사용해야 합니다. 그 외에는 타입 주석보다 변수 이름이 훨씬 읽기 쉽고 이해하기 쉽습니다.
### 토크나이저 개요 [[overview-of-tokenizers]]
아직 준비되지 않았습니다 :-( 이 섹션은 곧 추가될 예정입니다!
## 🤗 Transformers에 모델 추가하는 단계별 방법 [[stepbystep-recipe-to-add-a-model-to-transformers]]
각자 모델을 이식하는 방법에 대한 선호가 다르기 때문에 다른 기여자들이 Hugging Face에 모델을 이식하는 방법에 대한 요약을 살펴보는 것이 매우 유용할 수 있습니다. 다음은 모델을 이식하는 방법에 대한 커뮤니티 블로그 게시물 목록입니다:
1. [GPT2 모델 이식하기](https://medium.com/huggingface/from-tensorflow-to-pytorch-265f40ef2a28) - [Thomas](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf)
2. [WMT19 MT 모델 이식하기](https://huggingface.co/blog/porting-fsmt) - [Stas](https://huggingface.co/stas)
경험상 모델을 추가할 때 주의해야 할 가장 중요한 사항은 다음과 같습니다:
- 같은 일을 반복하지 마세요! 새로운 🤗 Transformers 모델을 위해 추가할 코드의 대부분은 이미 🤗 Transformers 어딘가에 존재합니다. 이미 존재하는 복사할 수 있는 유사한 모델과 토크나이저를 찾는데 시간을 투자하세요. [grep](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/)와 [rg](https://github.com/BurntSushi/ripgrep)를 참고하세요. 모델의 토크나이저가 한 모델을 기반으로 하고 모델링 코드가 다른 모델을 기반으로 하는 경우가 존재할 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어 FSMT의 모델링 코드는 BART를 기반으로 하고 FSMT의 토크나이저 코드는 XLM을 기반으로 합니다.
- 이것은 과학적인 도전보다는 공학적인 도전입니다. 논문의 모델의 모든 이론적 측면을 이해하려는 것보다 효율적인 디버깅 환경을 만드는 데 더 많은 시간을 소비해야 합니다.
- 막힐 때 도움을 요청하세요! 모델은 🤗 Transformers의 핵심 구성 요소이므로 Hugging Face의 우리는 당신이 모델을 추가하는 각 단계에서 기꺼이 도움을 줄 준비가 되어 있습니다. 진전이 없다고 느끼면 주저하지 말고 도움을 요청하세요.
다음에서는 모델을 🤗 Transformers로 이식하는 데 가장 유용한 일반적인 절차를 제공하려고 노력합니다.
다음 목록은 모델을 추가하는 데 수행해야 할 모든 작업의 요약이며 To-Do 목록으로 사용할 수 있습니다:
☐ (선택 사항) BrandNewBert의 이론적 측면 이해<br>
☐ Hugging Face 개발 환경 준비<br>
☐ 원본 리포지토리의 디버깅 환경 설정<br>
☐ 원본 리포지토리와 체크포인트를 사용하여 `forward()` pass가 성공적으로 실행되는 스크립트 작성<br>
☐ 🤗 Transformers에 모델 스켈레톤 성공적으로 추가<br>
☐ 원본 체크포인트를 🤗 Transformers 체크포인트로 성공적으로 변환<br>
☐ 🤗 Transformers에서 원본 체크포인트와 동일한 출력을 내주는 `forward()` pass 성공적으로 실행<br>
☐ 🤗 Transformers에서 모델 테스트 완료<br>
☐ 🤗 Transformers에 토크나이저 성공적으로 추가<br>
☐ 종단 간 통합 테스트 실행<br>
☐ 문서 작성 완료<br>
☐ 모델 가중치를 허브에 업로드<br>
☐ Pull request 제출<br>
☐ (선택 사항) 데모 노트북 추가
우선, 일반적으로는 `BrandNewBert`의 이론적인 이해로 시작하는 것을 권장합니다. 그러나 이론적 측면을 직접 이해하는 대신 *직접 해보면서* 모델의 이론적 측면을 이해하는 것을 선호하는 경우 바로 `BrandNewBert` 코드 베이스로 빠져드는 것도 괜찮습니다. 이 옵션은 엔지니어링 기술이 이론적 기술보다 더 뛰어난 경우, `BrandNewBert`의 논문을 이해하는 데 어려움이 있는 경우, 또는 과학적인 논문을 읽는 것보다 프로그래밍에 훨씬 더 흥미 있는 경우에 더 적합할 수 있습니다.
### 1. (선택 사항) BrandNewBert의 이론적 측면 [[1-optional-theoretical-aspects-of-brandnewbert]]
만약 그런 서술적인 작업이 존재한다면, *BrandNewBert*의 논문을 읽어보는 시간을 가져야 합니다. 이해하기 어려운 섹션이 많을 수 있습니다. 그렇더라도 걱정하지 마세요! 목표는 논문의 깊은 이론적 이해가 아니라 *BrandNewBert*를 🤗 Transformers에서 효과적으로 재구현하기 위해 필요한 정보를 추출하는 것입니다. 이를 위해 이론적 측면에 너무 많은 시간을 투자할 필요는 없지만 다음과 같은 실제적인 측면에 집중해야 합니다:
- *BrandNewBert*는 어떤 유형의 모델인가요? BERT와 유사한 인코더 모델인가요? GPT2와 유사한 디코더 모델인가요? BART와 유사한 인코더-디코더 모델인가요? 이들 간의 차이점에 익숙하지 않은 경우[model_summary](model_summary)를 참조하세요.
- *BrandNewBert*의 응용 분야는 무엇인가요? 텍스트 분류인가요? 텍스트 생성인가요? 요약과 같은 Seq2Seq 작업인가요?
- *brand_new_bert*와 BERT/GPT-2/BART의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
- *brand_new_bert*와 가장 유사한 [🤗 Transformers 모델](https://huggingface.co/transformers/#contents)은 무엇인가요?
- 어떤 종류의 토크나이저가 사용되나요? Sentencepiece 토크나이저인가요? Word piece 토크나이저인가요? BERT 또는 BART에 사용되는 동일한 토크나이저인가요?
모델의 아키텍처에 대해 충분히 이해했다는 생각이 든 후, 궁금한 사항이 있으면 Hugging Face 팀에 문의하십시오. 이는 모델의 아키텍처, 어텐션 레이어 등에 관한 질문을 포함할 수 있습니다. Hugging Face의 유지 관리자들은 보통 코드를 검토하는 것에 대해 매우 기뻐하므로 당신을 돕는 일을 매우 환영할 것입니다!
### 2. 개발 환경 설정 [[2-next-prepare-your-environment]]
1. 저장소 페이지에서 "Fork" 버튼을 클릭하여 저장소의 사본을 GitHub 사용자 계정으로 만듭니다.
2. `transformers` fork를 로컬 디스크에 클론하고 베이스 저장소를 원격 저장소로 추가합니다:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/[your Github handle]/transformers.git
cd transformers
git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
```
3. 개발 환경을 설정합니다. 다음 명령을 실행하여 개발 환경을 설정할 수 있습니다:
```bash
python -m venv .env
source .env/bin/activate
pip install -e ".[dev]"
```
각 운영 체제에 따라 Transformers의 선택적 의존성이 개수가 증가하면 이 명령이 실패할 수 있습니다. 그런 경우에는 작업 중인 딥 러닝 프레임워크 (PyTorch, TensorFlow 및/또는 Flax)을 설치한 후, 다음 명령을 수행하면 됩니다:
```bash
pip install -e ".[quality]"
```
대부분의 경우에는 이것으로 충분합니다. 그런 다음 상위 디렉토리로 돌아갑니다.
```bash
cd ..
```
4. Transformers에 *brand_new_bert*의 PyTorch 버전을 추가하는 것을 권장합니다. PyTorch를 설치하려면 다음 링크의 지침을 따르십시오: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
**참고:** CUDA를 설치할 필요는 없습니다. 새로운 모델이 CPU에서 작동하도록 만드는 것으로 충분합니다.
5. *brand_new_bert*를 이식하기 위해서는 해당 원본 저장소에 접근할 수 있어야 합니다:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/org_that_created_brand_new_bert_org/brand_new_bert.git
cd brand_new_bert
pip install -e .
```
이제 *brand_new_bert*를 🤗 Transformers로 이식하기 위한 개발 환경을 설정하였습니다.
### 3.-4. 원본 저장소에서 사전 훈련된 체크포인트 실행하기 [[3.-4.-run-a-pretrained-checkpoint-using-the-original-repository]]
먼저, 원본 *brand_new_bert* 저장소에서 작업을 시작합니다. 원본 구현은 보통 "연구용"으로 많이 사용됩니다. 즉, 문서화가 부족하고 코드가 이해하기 어려울 수 있습니다. 그러나 이것이 바로 *brand_new_bert*를 다시 구현하려는 동기가 되어야 합니다. Hugging Face에서의 주요 목표 중 하나는 **거인의 어깨 위에 서는 것**이며, 이는 여기에서 쉽게 해석되어 동작하는 모델을 가져와서 가능한 한 **접근 가능하고 사용자 친화적이며 아름답게** 만드는 것입니다. 이것은 🤗 Transformers에서 모델을 다시 구현하는 가장 중요한 동기입니다 - 새로운 복잡한 NLP 기술을 **모두에게** 접근 가능하게 만드는 것을 목표로 합니다.
따라서 원본 저장소에 대해 자세히 살펴보는 것으로 시작해야 합니다.
원본 저장소에서 공식 사전 훈련된 모델을 성공적으로 실행하는 것은 종종 **가장 어려운** 단계입니다. 우리의 경험에 따르면, 원본 코드 베이스에 익숙해지는 데 시간을 투자하는 것이 매우 중요합니다. 다음을 파악해야 합니다:
- 사전 훈련된 가중치를 어디서 찾을 수 있는지?
- 사전 훈련된 가중치를 해당 모델에로드하는 방법은?
- 모델과 독립적으로 토크나이저를 실행하는 방법은?
- 간단한 forward pass에 필요한 클래스와 함수를 파악하기 위해 forward pass를 한 번 추적해 보세요. 일반적으로 해당 함수들만 다시 구현하면 됩니다.
- 모델의 중요한 구성 요소를 찾을 수 있어야 합니다. 모델 클래스는 어디에 있나요? 모델 하위 클래스(*EncoderModel*, *DecoderModel* 등)가 있나요? self-attention 레이어는 어디에 있나요? self-attention, cross-attention 등 여러 가지 다른 어텐션 레이어가 있나요?
- 원본 환경에서 모델을 디버그할 수 있는 방법은 무엇인가요? *print* 문을 추가해야 하나요? *ipdb*와 같은 대화식 디버거를 사용할 수 있나요? PyCharm과 같은 효율적인 IDE를 사용해 모델을 디버그할 수 있나요?
원본 저장소에서 코드를 이식하는 작업을 시작하기 전에 원본 저장소에서 코드를 **효율적으로** 디버그할 수 있어야 합니다! 또한, 오픈 소스 라이브러리로 작업하고 있다는 것을 기억해야 합니다. 따라서 원본 저장소에서 issue를 열거나 pull request를 열기를 주저하지 마십시오. 이 저장소의 유지 관리자들은 누군가가 자신들의 코드를 살펴본다는 것에 대해 매우 기뻐할 것입니다!
현재 시점에서, 원래 모델을 디버깅하기 위해 어떤 디버깅 환경과 전략을 선호하는지는 당신에게 달렸습니다. 우리는 고가의 GPU 환경을 구축하는 것은 비추천합니다. 대신, 원래 저장소로 들어가서 작업을 시작할 때와 🤗 Transformers 모델의 구현을 시작할 때에도 CPU에서 작업하는 것이 좋습니다. 모델이 이미 🤗 Transformers로 성공적으로 이식되었을 때에만 모델이 GPU에서도 예상대로 작동하는지 확인해야합니다.
일반적으로, 원래 모델을 실행하기 위한 두 가지 가능한 디버깅 환경이 있습니다.
- [Jupyter 노트북](https://jupyter.org/) / [Google Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/intro.ipynb)
- 로컬 Python 스크립트
Jupyter 노트북의 장점은 셀 단위로 실행할 수 있다는 것입니다. 이는 논리적인 구성 요소를 더 잘 분리하고 중간 결과를 저장할 수 있으므로 디버깅 사이클이 더 빨라질 수 있습니다. 또한, 노트북은 다른 기여자와 쉽게 공유할 수 있으므로 Hugging Face 팀의 도움을 요청하려는 경우 매우 유용할 수 있습니다. Jupyter 노트북에 익숙하다면 이를 사용하는 것을 강력히 추천합니다.
Jupyter 노트북의 단점은 사용에 익숙하지 않은 경우 새로운 프로그래밍 환경에 적응하는 데 시간을 할애해야 하며, `ipdb`와 같은 알려진 디버깅 도구를 더 이상 사용할 수 없을 수도 있다는 것입니다.
각 코드 베이스에 대해 좋은 첫 번째 단계는 항상 **작은** 사전 훈련된 체크포인트를 로드하고 더미 정수 벡터 입력을 사용하여 단일 forward pass를 재현하는 것입니다. 이와 같은 스크립트는 다음과 같을 수 있습니다(의사 코드로 작성):
```python
model = BrandNewBertModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
input_ids = [0, 4, 5, 2, 3, 7, 9] # vector of input ids
original_output = model.predict(input_ids)
```
다음으로, 디버깅 전략에 대해 일반적으로 다음과 같은 몇 가지 선택지가 있습니다:
- 원본 모델을 많은 작은 테스트 가능한 구성 요소로 분해하고 각각에 대해 forward pass를 실행하여 검증합니다.
- 원본 모델을 원본 *tokenizer*과 원본 *model*로만 분해하고 해당 부분에 대해 forward pass를 실행한 후 검증을 위해 중간 출력(print 문 또는 중단점)을 사용합니다.
다시 말하지만, 어떤 전략을 선택할지는 당신에게 달려 있습니다. 원본 코드 베이스에 따라 하나 또는 다른 전략이 유리할 수 있습니다.
원본 코드 베이스를 모델의 작은 하위 구성 요소로 분해할 수 있는지 여부, 예를 들어 원본 코드 베이스가 즉시 실행 모드에서 간단히 실행될 수 있는 경우, 그런 경우에는 그 노력이 가치가 있다는 것이 일반적입니다. 초기에 더 어려운 방법을 선택하는 것에는 몇 가지 중요한 장점이 있습니다.
- 원본 모델을 🤗 Transformers 구현과 비교할 때 각 구성 요소가 일치하는지 자동으로 확인할 수 있습니다. 즉, 시각적인 비교(print 문을 통한 비교가 아닌) 대신 🤗 Transformers 구현과 그에 대응하는 원본 구성 요소가 일치하는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 전체 모델을 모듈별로, 즉 작은 구성 요소로 분해함으로써 모델을 이식하는 큰 문제를 단순히 개별 구성 요소를 이식하는 작은 문제로 분해할 수 있으므로 작업을 더 잘 구조화할 수 있습니다.
- 모델을 논리적으로 의미 있는 구성 요소로 분리하는 것은 모델의 설계에 대한 더 나은 개요를 얻고 모델을 더 잘 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 이러한 구성 요소별 테스트를 통해 코드를 변경하면서 회귀가 발생하지 않도록 보장할 수 있습니다.
[Lysandre의 ELECTRA 통합 검사](https://gist.github.com/LysandreJik/db4c948f6b4483960de5cbac598ad4ed)는 이를 수행하는 좋은 예제입니다.
그러나 원본 코드 베이스가 매우 복잡하거나 중간 구성 요소를 컴파일된 모드에서 실행하는 것만 허용하는 경우, 모델을 테스트 가능한 작은 하위 구성 요소로 분해하는 것이 시간이 많이 소요되거나 불가능할 수도 있습니다. [T5의 MeshTensorFlow](https://github.com/tensorflow/mesh/tree/master/mesh_tensorflow) 라이브러리는 매우 복잡하며 모델을 하위 구성 요소로 분해하는 간단한 방법을 제공하지 않습니다. 이러한 라이브러리의 경우, 보통 print 문을 통해 확인합니다.
어떤 전략을 선택하더라도 권장되는 절차는 동일합니다. 먼저 시작 레이어를 디버그하고 마지막 레이어를 마지막에 디버그하는 것이 좋습니다.
다음 순서로 각 레이어의 출력을 검색하는 것이 좋습니다:
1. 모델에 전달된 입력 ID 가져오기
2. 워드 임베딩 가져오기
3. 첫 번째 Transformer 레이어의 입력 가져오기
4. 첫 번째 Transformer 레이어의 출력 가져오기
5. 다음 n-1개의 Transformer 레이어의 출력 가져오기
6. BrandNewBert 모델의 출력 가져오기
입력 ID는 정수 배열로 구성되며, 예를 들어 `input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]`와 같을 수 있습니다.
다음 레이어의 출력은 종종 다차원 실수 배열로 구성되며, 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있습니다:
```
[[
[-0.1465, -0.6501, 0.1993, ..., 0.1451, 0.3430, 0.6024],
[-0.4417, -0.5920, 0.3450, ..., -0.3062, 0.6182, 0.7132],
[-0.5009, -0.7122, 0.4548, ..., -0.3662, 0.6091, 0.7648],
...,
[-0.5613, -0.6332, 0.4324, ..., -0.3792, 0.7372, 0.9288],
[-0.5416, -0.6345, 0.4180, ..., -0.3564, 0.6992, 0.9191],
[-0.5334, -0.6403, 0.4271, ..., -0.3339, 0.6533, 0.8694]]],
```
🤗 Transformers에 추가되는 모든 모델은 통합 테스트를 통과해야 합니다. 즉, 원본 모델과 🤗 Transformers의 재구현 버전이 0.001의 정밀도로 정확히 동일한 출력을 내야 합니다! 동일한 모델이 다른 라이브러리에서 작성되었을 때 라이브러리 프레임워크에 따라 약간 다른 출력을 얻는 것은 정상이므로 1e-3(0.001)의 오차는 허용합니다. 거의 동일한 출력을 내는 것만으로는 충분하지 않으며, 완벽히 일치하는 수준이어야 합니다. 따라서 🤗 Transformers 버전의 중간 출력을 *brand_new_bert*의 원래 구현의 중간 출력과 여러 번 비교해야 합니다. 이 경우 원본 저장소의 **효율적인** 디버깅 환경이 절대적으로 중요합니다. 디버깅 환경을 가능한 한 효율적으로 만드는 몇 가지 조언을 제시합니다.
- 중간 결과를 디버그하는 가장 좋은 방법을 찾으세요. 원본 저장소가 PyTorch로 작성되었다면 원본 모델을 더 작은 하위 구성 요소로 분해하여 중간 값을 검색하는 긴 스크립트를 작성하는 것에 시간을 투자할 가치가 있습니다. 원본 저장소가 Tensorflow 1로 작성되었다면 [tf.print](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/print)와 같은 Tensorflow 출력 작업을 사용하여 중간 값을 출력해야 할 수도 있습니다. 원본 저장소가 Jax로 작성되었다면 forward pass를 실행할 때 모델이 **jit 되지 않도록** 해야 합니다. 예를 들어 [이 링크](https://github.com/google/jax/issues/196)를 확인해 보세요.
- 사용 가능한 가장 작은 사전 훈련된 체크포인트를 사용하세요. 체크포인트가 작을수록 디버그 사이클이 더 빨라집니다. 전반적으로 forward pass에 10초 이상이 걸리는 경우 효율적이지 않습니다. 매우 큰 체크포인트만 사용할 수 있는 경우, 새 환경에서 임의로 초기화된 가중치로 더미 모델을 만들고 해당 가중치를 🤗 Transformers 버전과 비교하기 위해 저장하는 것이 더 의미가 있을 수 있습니다.
- 디버깅 설정에서 가장 쉽게 forward pass를 호출하는 방법을 사용하세요. 원본 저장소에서 **단일** forward pass만 호출하는 함수를 찾는 것이 이상적입니다. 이 함수는 일반적으로 `predict`, `evaluate`, `forward`, `__call__`과 같이 호출됩니다. `autoregressive_sample`과 같은 텍스트 생성에서 `forward`를 여러 번 호출하여 텍스트를 생성하는 등의 작업을 수행하는 함수를 디버그하고 싶지 않을 것입니다.
- 토큰화 과정을 모델의 *forward* pass와 분리하려고 노력하세요. 원본 저장소에서 입력 문자열을 입력해야 하는 예제가 있는 경우, 입력 문자열이 입력 ID로 변경되는 순간을 찾아서 시작하세요. 이 경우 직접 ID를 입력할 수 있도록 작은 스크립트를 작성하거나 원본 코드를 수정해야 할 수도 있습니다.
- 디버깅 설정에서 모델이 훈련 모드가 아니라는 것을 확인하세요. 훈련 모드에서는 모델의 여러 드롭아웃 레이어 때문에 무작위 출력이 생성될 수 있습니다. 디버깅 환경에서 forward pass가 **결정론적**이도록 해야 합니다. 또는 동일한 프레임워크에 있는 경우 *transformers.utils.set_seed*를 사용하세요.
다음 섹션에서는 *brand_new_bert*에 대해 이 작업을 수행하는 데 더 구체적인 세부 사항/팁을 제공합니다.
### 5.-14. 🤗 Transformers에 BrandNewBert를 이식하기 [[5.-14.-port-brandnewbert-to-transformers]]
이제, 마침내 🤗 Transformers에 새로운 코드를 추가할 수 있습니다. 🤗 Transformers 포크의 클론으로 이동하세요:
```bash
cd transformers
```
다음과 같이 이미 존재하는 모델의 모델 아키텍처와 정확히 일치하는 모델을 추가하는 특별한 경우에는 [이 섹션](#write-a-conversion-script)에 설명된대로 변환 스크립트만 추가하면 됩니다. 이 경우에는 이미 존재하는 모델의 전체 모델 아키텍처를 그대로 재사용할 수 있습니다.
그렇지 않으면 새 모델 생성을 시작하겠습니다. 다음 스크립트를 사용하여 다음에서 시작하는 모델을 추가하는 것이 좋습니다.
기존 모델:
```bash
transformers-cli add-new-model-like
```
모델의 기본 정보를 입력하는 설문지가 표시됩니다.
**huggingface/transformers 메인 저장소에 Pull Request 열기**
자동으로 생성된 코드를 수정하기 전에, 지금은 "작업 진행 중 (WIP)" 풀 리퀘스트를 열기 위한 시기입니다. 예를 들어, 🤗 Transformers에 "*brand_new_bert* 추가"라는 제목의 "[WIP] Add *brand_new_bert*" 풀 리퀘스트를 엽니다. 이렇게 하면 당신과 Hugging Face 팀이 🤗 Transformers에 모델을 통합하는 작업을 함께할 수 있습니다.
다음을 수행해야 합니다:
1. 메인 브랜치에서 작업을 잘 설명하는 이름으로 브랜치 생성
```bash
git checkout -b add_brand_new_bert
```
2. 자동으로 생성된 코드 커밋
```bash
git add .
git commit
```
3. 현재 메인을 가져오고 리베이스
```bash
git fetch upstream
git rebase upstream/main
```
4. 변경 사항을 계정에 푸시
```bash
git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
```
5. 만족스럽다면, GitHub에서 자신의 포크한 웹 페이지로 이동합니다. "Pull request"를 클릭합니다. Hugging Face 팀의 일부 멤버의 GitHub 핸들을 리뷰어로 추가하여 Hugging Face 팀이 앞으로의 변경 사항에 대해 알림을 받을 수 있도록 합니다.
6. GitHub 풀 리퀘스트 웹 페이지 오른쪽에 있는 "Convert to draft"를 클릭하여 PR을 초안으로 변경합니다.
다음으로, 어떤 진전을 이루었다면 작업을 커밋하고 계정에 푸시하여 풀 리퀘스트에 표시되도록 해야 합니다. 또한, 다음과 같이 현재 메인과 작업을 업데이트해야 합니다:
```bash
git fetch upstream
git merge upstream/main
```
일반적으로, 모델 또는 구현에 관한 모든 질문은 자신의 PR에서 해야 하며, PR에서 토론되고 해결되어야 합니다. 이렇게 하면 Hugging Face 팀이 새로운 코드를 커밋하거나 질문을 할 때 항상 알림을 받을 수 있습니다. Hugging Face 팀에게 문제 또는 질문을 효율적으로 이해할 수 있도록 추가한 코드를 명시하는 것이 도움이 될 때가 많습니다.
이를 위해, 변경 사항을 모두 볼 수 있는 "Files changed" 탭으로 이동하여 질문하고자 하는 줄로 이동한 다음 "+" 기호를 클릭하여 코멘트를 추가할 수 있습니다. 질문이나 문제가 해결되면, 생성된 코멘트의 "Resolve" 버튼을 클릭할 수 있습니다.
마찬가지로, Hugging Face 팀은 코드를 리뷰할 때 코멘트를 남길 것입니다. 우리는 PR에서 대부분의 질문을 GitHub에서 묻는 것을 권장합니다. 공개에 크게 도움이 되지 않는 매우 일반적인 질문의 경우, Slack이나 이메일을 통해 Hugging Face 팀에게 문의할 수 있습니다.
**5. brand_new_bert에 대해 생성된 모델 코드를 적용하기**
먼저, 우리는 모델 자체에만 초점을 맞추고 토크나이저에 대해서는 신경 쓰지 않을 것입니다. 모든 관련 코드는 다음의 생성된 파일에서 찾을 수 있습니다: `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` 및 `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/configuration_brand_new_bert.py`.
이제 마침내 코딩을 시작할 수 있습니다 :). `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py`의 생성된 코드는 인코더 전용 모델인 경우 BERT와 동일한 아키텍처를 가지거나, 인코더-디코더 모델인 경우 BART와 동일한 아키텍처를 가질 것입니다. 이 시점에서, 모델의 이론적 측면에 대해 배운 내용을 다시 상기해야 합니다: *모델이 BERT 또는 BART와 어떻게 다른가요?*. 자주 변경해야 하는 것은 *self-attention* 레이어, 정규화 레이어의 순서 등을 변경하는 것입니다. 다시 말하지만, 자신의 모델을 구현하는 데 도움이 되도록 Transformers에서 이미 존재하는 모델의 유사한 아키텍처를 살펴보는 것이 유용할 수 있습니다.
**참고로** 이 시점에서, 코드가 완전히 정확하거나 깨끗하다고 확신할 필요는 없습니다. 오히려 처음에는 원본 코드의 첫 번째 *불완전하고* 복사된 버전을 `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py`에 추가하는 것이 좋습니다. 필요한 모든 코드가 추가될 때까지 이러한 작업을 진행한 후, 다음 섹션에서 설명한 변환 스크립트를 사용하여 코드를 점진적으로 개선하고 수정하는 것이 훨씬 효율적입니다. 이 시점에서 작동해야 하는 유일한 것은 다음 명령이 작동하는 것입니다:
```python
from transformers import BrandNewBertModel, BrandNewBertConfig
model = BrandNewBertModel(BrandNewBertConfig())
```
위의 명령은 `BrandNewBertConfig()`에 정의된 기본 매개변수에 따라 무작위 가중치로 모델을 생성하며, 이로써 모든 구성 요소의 `init()` 메서드가 작동함을 보장합니다.
모든 무작위 초기화는 `BrandnewBertPreTrainedModel` 클래스의 `_init_weights` 메서드에서 수행되어야 합니다. 이 메서드는 구성 설정 변수에 따라 모든 리프 모듈을 초기화해야 합니다. BERT의 `_init_weights` 메서드 예제는 다음과 같습니다:
```py
def _init_weights(self, module):
"""Initialize the weights"""
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.padding_idx is not None:
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
module.bias.data.zero_()
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
```
몇 가지 모듈에 대해 특별한 초기화가 필요한 경우 사용자 정의 방식을 사용할 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어, `Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining`에서 마지막 두 개의 선형 레이어는 일반적인 PyTorch `nn.Linear`의 초기화를 가져야 하지만, 다른 모든 레이어는 위와 같은 초기화를 사용해야 합니다. 이는 다음과 같이 코드화됩니다:
```py
def _init_weights(self, module):
"""Initialize the weights"""
if isinstance(module, Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining):
module.project_hid.reset_parameters()
module.project_q.reset_parameters()
module.project_hid._is_hf_initialized = True
module.project_q._is_hf_initialized = True
elif isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
```
`_is_hf_initialized` 플래그는 서브모듈을 한 번만 초기화하도록 내부적으로 사용됩니다. `module.project_q` 및 `module.project_hid`에 대해 `True`로 설정함으로써, 우리가 수행한 사용자 정의 초기화가 이후에 덮어쓰이지 않도록 합니다. 즉, `_init_weights` 함수가 이들에게 적용되지 않습니다.
**6. 변환 스크립트 작성하기**
다음으로, 디버그에 사용한 체크포인트를 기존 저장소에서 만든 🤗 Transformers 구현과 호환되는 체크포인트로 변환할 수 있는 변환 스크립트를 작성해야 합니다. 변환 스크립트를 처음부터 작성하는 것보다는 *brand_new_bert*와 동일한 프레임워크로 작성된 유사한 모델을 변환한 기존 변환 스크립트를 찾아보는 것이 좋습니다. 일반적으로 기존 변환 스크립트를 복사하여 사용 사례에 맞게 약간 수정하는 것으로 충분합니다. 모델에 대해 유사한 기존 변환 스크립트를 어디에서 찾을 수 있는지 Hugging Face 팀에게 문의하는 것을 망설이지 마세요.
- TensorFlow에서 PyTorch로 모델을 이전하는 경우, 좋은 참고 자료로 BERT의 변환 스크립트 [여기](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/7acfa95afb8194f8f9c1f4d2c6028224dbed35a2/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_bert.py#L91)를 참조할 수 있습니다.
- PyTorch에서 PyTorch로 모델을 이전하는 경우, 좋은 참고 자료로 BART의 변환 스크립트 [여기](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/bart/convert_bart_original_pytorch_checkpoint_to_pytorch.py)를 참조할 수 있습니다.
다음에서는 PyTorch 모델이 레이어 가중치를 저장하고 레이어 이름을 정의하는 방법에 대해 간단히 설명하겠습니다. PyTorch에서 레이어의 이름은 레이어에 지정한 클래스 속성의 이름으로 정의됩니다. 다음과 같이 PyTorch에서 `SimpleModel`이라는 더미 모델을 정의해 봅시다:
```python
from torch import nn
class SimpleModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.intermediate = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(10)
```
이제 이 모델 정의의 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있으며 `dense`, `intermediate`, `layer_norm` 등의 가중치가 랜덤하게 할당됩니다. 모델을 출력하여 아키텍처를 확인할 수 있습니다.
```python
model = SimpleModel()
print(model)
```
이는 다음과 같이 출력됩니다:
```
SimpleModel(
(dense): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
(intermediate): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
(layer_norm): LayerNorm((10,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
```
우리는 레이어의 이름이 PyTorch에서 클래스 속성의 이름으로 정의되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 특정 레이어의 가중치 값을 출력하여 확인할 수 있습니다:
```python
print(model.dense.weight.data)
```
가중치가 무작위로 초기화되었음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
```
tensor([[-0.0818, 0.2207, -0.0749, -0.0030, 0.0045, -0.1569, -0.1598, 0.0212,
-0.2077, 0.2157],
[ 0.1044, 0.0201, 0.0990, 0.2482, 0.3116, 0.2509, 0.2866, -0.2190,
0.2166, -0.0212],
[-0.2000, 0.1107, -0.1999, -0.3119, 0.1559, 0.0993, 0.1776, -0.1950,
-0.1023, -0.0447],
[-0.0888, -0.1092, 0.2281, 0.0336, 0.1817, -0.0115, 0.2096, 0.1415,
-0.1876, -0.2467],
[ 0.2208, -0.2352, -0.1426, -0.2636, -0.2889, -0.2061, -0.2849, -0.0465,
0.2577, 0.0402],
[ 0.1502, 0.2465, 0.2566, 0.0693, 0.2352, -0.0530, 0.1859, -0.0604,
0.2132, 0.1680],
[ 0.1733, -0.2407, -0.1721, 0.1484, 0.0358, -0.0633, -0.0721, -0.0090,
0.2707, -0.2509],
[-0.1173, 0.1561, 0.2945, 0.0595, -0.1996, 0.2988, -0.0802, 0.0407,
0.1829, -0.1568],
[-0.1164, -0.2228, -0.0403, 0.0428, 0.1339, 0.0047, 0.1967, 0.2923,
0.0333, -0.0536],
[-0.1492, -0.1616, 0.1057, 0.1950, -0.2807, -0.2710, -0.1586, 0.0739,
0.2220, 0.2358]]).
```
변환 스크립트에서는 이러한 무작위로 초기화된 가중치를 체크포인트의 해당 레이어의 정확한 가중치로 채워야 합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다:
```python
# retrieve matching layer weights, e.g. by
# recursive algorithm
layer_name = "dense"
pretrained_weight = array_of_dense_layer
model_pointer = getattr(model, "dense")
model_pointer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(pretrained_weight)
```
이렇게 하면 PyTorch 모델의 무작위로 초기화된 각 가중치와 해당 체크포인트 가중치가 **모양과 이름** 모두에서 정확히 일치하는지 확인해야 합니다. 이를 위해 모양에 대한 assert 문을 추가하고 체크포인트 가중치의 이름을 출력해야 합니다. 예를 들어 다음과 같은 문장을 추가해야 합니다:
```python
assert (
model_pointer.weight.shape == pretrained_weight.shape
), f"Pointer shape of random weight {model_pointer.shape} and array shape of checkpoint weight {pretrained_weight.shape} mismatched"
```
또한 두 가중치의 이름을 출력하여 일치하는지 확인해야 합니다. *예시*:
```python
logger.info(f"Initialize PyTorch weight {layer_name} from {pretrained_weight.name}")
```
모양 또는 이름이 일치하지 않는 경우, 랜덤으로 초기화된 레이어에 잘못된 체크포인트 가중치를 할당한 것으로 추측됩니다.
잘못된 모양은 `BrandNewBertConfig()`의 구성 매개변수 설정이 변환하려는 체크포인트에 사용된 설정과 정확히 일치하지 않기 때문일 가능성이 가장 큽니다. 그러나 PyTorch의 레이어 구현 자체에서 가중치를 전치해야 할 수도 있습니다.
마지막으로, **모든** 필요한 가중치가 초기화되었는지 확인하고 초기화에 사용되지 않은 모든 체크포인트 가중치를 출력하여 모델이 올바르게 변환되었는지 확인해야 합니다. 잘못된 모양 문장이나 잘못된 이름 할당으로 인해 변환 시도가 실패하는 것은 완전히 정상입니다. 이는 `BrandNewBertConfig()`에서 잘못된 매개변수를 사용하거나 🤗 Transformers 구현에서 잘못된 아키텍처, 🤗 Transformers 구현의 구성 요소 중 하나의 `init()` 함수에 버그가 있는 경우이거나 체크포인트 가중치 중 하나를 전치해야 하는 경우일 가능성이 가장 높습니다.
이 단계는 이전 단계와 함께 반복되어야 하며 모든 체크포인트의 가중치가 Transformers 모델에 올바르게 로드되었을 때까지 계속되어야 합니다. 🤗 Transformers 구현에 체크포인트를 올바르게 로드한 후에는 `/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder`와 같은 원하는 폴더에 모델을 저장할 수 있어야 합니다. 해당 폴더에는 `pytorch_model.bin` 파일과 `config.json` 파일이 모두 포함되어야 합니다.
```python
model.save_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
```
**7. 순방향 패스 구현하기**
🤗 Transformers 구현에 사전 훈련된 가중치를 정확하게 로드한 후에는 순방향 패스가 올바르게 구현되었는지 확인해야 합니다. [원본 저장소에 익숙해지기](#3-4-run-a-pretrained-checkpoint-using-the-original-repository)에서 이미 원본 저장소를 사용하여 모델의 순방향 패스를 실행하는 스크립트를 만들었습니다. 이제 원본 대신 🤗 Transformers 구현을 사용하는 유사한 스크립트를 작성해야 합니다. 다음과 같이 작성되어야 합니다:
```python
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]
output = model(input_ids).last_hidden_states
```
🤗 Transformers 구현과 원본 모델 구현이 처음부터 정확히 동일한 출력을 제공하지 않거나 순방향 패스에서 오류가 발생할 가능성이 매우 높습니다. 실망하지 마세요. 예상된 일입니다! 먼저, 순방향 패스에서 오류가 발생하지 않도록 해야 합니다. 종종 잘못된 차원이 사용되어 *차원 불일치* 오류가 발생하거나 잘못된 데이터 유형 개체가 사용되는 경우가 있습니다. 예를 들면 `torch.long` 대신에 `torch.float32`가 사용된 경우입니다. 해결할 수 없는 오류가 발생하면 Hugging Face 팀에 도움을 요청하는 것이 좋습니다.
🤗 Transformers 구현이 올바르게 작동하는지 확인하는 마지막 단계는 출력이 `1e-3`의 정밀도로 동일한지 확인하는 것입니다. 먼저, 출력 모양이 동일하도록 보장해야 합니다. 즉, 🤗 Transformers 구현 스크립트와 원본 구현 사이에서 `outputs.shape`는 동일한 값을 반환해야 합니다. 그 다음으로, 출력 값이 동일하도록 해야 합니다. 이는 새로운 모델을 추가할 때 가장 어려운 부분 중 하나입니다. 출력이 동일하지 않은 일반적인 실수 사례는 다음과 같습니다:
- 일부 레이어가 추가되지 않았습니다. 즉, *활성화* 레이어가 추가되지 않았거나 잔차 연결이 빠졌습니다.
- 단어 임베딩 행렬이 연결되지 않았습니다.
- 잘못된 위치 임베딩이 사용되었습니다. 원본 구현에서는 오프셋을 사용합니다.
- 순방향 패스 중에 Dropout이 적용되었습니다. 이를 수정하려면 *model.training이 False*인지 확인하고 순방향 패스 중에 Dropout 레이어가 잘못 활성화되지 않도록 하세요. 즉, [PyTorch의 기능적 Dropout](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.functional.html?highlight=dropout#torch.nn.functional.dropout)에 *self.training*을 전달하세요.
문제를 해결하는 가장 좋은 방법은 일반적으로 원본 구현과 🤗 Transformers 구현의 순방향 패스를 나란히 놓고 차이점이 있는지 확인하는 것입니다. 이상적으로는 순방향 패스의 중간 출력을 디버그/출력하여 원본 구현과 🤗 Transformers 구현의 정확한 위치를 찾을 수 있어야 합니다. 먼저, 두 스크립트의 하드코딩된 `input_ids`가 동일한지 확인하세요. 다음으로, `input_ids`의 첫 번째 변환의 출력(일반적으로 단어 임베딩)이 동일한지 확인하세요. 그런 다음 네트워크의 가장 마지막 레이어까지 진행해보세요. 어느 시점에서 두 구현 사이에 차이가 있는 것을 알게 되는데, 이는 🤗 Transformers 구현의 버그 위치를 가리킬 것입니다. 저희 경험상으로는 원본 구현과 🤗 Transformers 구현 모두에서 동일한 위치에 많은 출력 문을 추가하고 이들의 중간 표현에 대해 동일한 값을 보이는 출력 문을 연속적으로 제거하는 것이 간단하고 효과적인 방법입니다.
`torch.allclose(original_output, output, atol=1e-3)`로 출력을 확인하여 두 구현이 동일한 출력을 하는 것을 확신한다면, 가장 어려운 부분은 끝났습니다! 축하드립니다. 남은 작업은 쉬운 일이 될 것입니다 😊.
**8. 필요한 모든 모델 테스트 추가하기**
이 시점에서 새로운 모델을 성공적으로 추가했습니다. 그러나 해당 모델이 요구되는 디자인에 완전히 부합하지 않을 수도 있습니다. 🤗 Transformers와 완벽하게 호환되는 구현인지 확인하기 위해 모든 일반 테스트를 통과해야 합니다. Cookiecutter는 아마도 모델을 위한 테스트 파일을 자동으로 추가했을 것입니다. 아마도 `tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py`와 같은 경로에 위치할 것입니다. 이 테스트 파일을 실행하여 일반 테스트가 모두 통과하는지 확인하세요.
```bash
pytest tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py
```
모든 일반 테스트를 수정한 후, 이제 수행한 작업을 충분히 테스트하여 다음 사항을 보장해야 합니다.
- a) 커뮤니티가 *brand_new_bert*의 특정 테스트를 살펴봄으로써 작업을 쉽게 이해할 수 있도록 함
- b) 모델에 대한 향후 변경 사항이 모델의 중요한 기능을 손상시키지 않도록 함
먼저 통합 테스트를 추가해야 합니다. 이러한 통합 테스트는 이전에 모델을 🤗 Transformers로 구현하기 위해 사용한 디버깅 스크립트와 동일한 작업을 수행합니다. Cookiecutter에 이미 이러한 모델 테스트의 템플릿인 `BrandNewBertModelIntegrationTests`가 추가되어 있으며, 여러분이 작성해야 할 내용으로만 채워 넣으면 됩니다. 이러한 테스트가 통과하는지 확인하려면 다음을 실행하세요.
```bash
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -sv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py::BrandNewBertModelIntegrationTests
```
<Tip>
Windows를 사용하는 경우 `RUN_SLOW=1`을 `SET RUN_SLOW=1`로 바꿔야 합니다.
</Tip>
둘째로, *brand_new_bert*에 특화된 모든 기능도 별도의 테스트에서 추가로 테스트해야 합니다. 이 부분은 종종 잊히는데, 두 가지 측면에서 굉장히 유용합니다.
- *brand_new_bert*의 특수 기능이 어떻게 작동해야 하는지 보여줌으로써 커뮤니티에게 모델 추가 과정에서 습득한 지식을 전달하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 향후 기여자는 이러한 특수 테스트를 실행하여 모델에 대한 변경 사항을 빠르게 테스트할 수 있습니다.
**9. 토크나이저 구현하기**
다음으로, *brand_new_bert*의 토크나이저를 추가해야 합니다. 보통 토크나이저는 🤗 Transformers의 기존 토크나이저와 동일하거나 매우 유사합니다.
토크나이저가 올바르게 작동하는지 확인하기 위해 먼저 원본 리포지토리에서 문자열을 입력하고 `input_ids`를 반환하는 스크립트를 생성하는 것이 좋습니다. 다음과 같은 유사한 스크립트일 수 있습니다 (의사 코드로 작성):
```python
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
model = BrandNewBertModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
input_ids = model.tokenize(input_str)
```
원본 리포지토리를 자세히 살펴보고 올바른 토크나이저 함수를 찾거나, 복제본에서 변경 사항을 적용하여 `input_ids`만 출력하도록 해야 합니다. 원본 리포지토리를 사용하는 기능적인 토큰화 스크립트를 작성한 후, 🤗 Transformers의 유사한 스크립트를 생성해야 합니다. 다음과 같이 작성되어야 합니다:
```python
from transformers import BrandNewBertTokenizer
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
tokenizer = BrandNewBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("/path/to/tokenizer/folder/")
input_ids = tokenizer(input_str).input_ids
```
두 개의 `input_ids`가 동일한 값을 반환할 때, 마지막 단계로 토크나이저 테스트 파일도 추가해야 합니다.
*brand_new_bert*의 모델링 테스트 파일과 유사하게, *brand_new_bert*의 토크나이제이션 테스트 파일에는 몇 가지 하드코딩된 통합 테스트가 포함되어야 합니다.
**10. 종단 간 통합 테스트 실행**
토크나이저를 추가한 후에는 모델과 토크나이저를 사용하여 몇 가지 종단 간 통합 테스트를 추가해야 합니다. `tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py`에 추가해주세요. 이러한 테스트는 🤗 Transformers 구현이 예상대로 작동하는지를 의미 있는 text-to-text 예시로 보여줘야 합니다. 그 예시로는 *예를 들어* source-to-target 번역 쌍, article-to-summary 쌍, question-to-answer 쌍 등이 포함될 수 있습니다. 불러온 체크포인트 중 어느 것도 다운스트림 작업에서 미세 조정되지 않았다면, 모델 테스트만으로 충분합니다. 모델이 완전히 기능을 갖추었는지 확인하기 위해 마지막 단계로 GPU에서 모든 테스트를 실행하는 것이 좋습니다. 모델의 내부 텐서의 일부에 `.to(self.device)` 문을 추가하는 것을 잊었을 수 있으며, 이 경우 테스트에서 오류로 표시됩니다. GPU에 액세스할 수 없는 경우, Hugging Face 팀이 테스트를 대신 실행할 수 있습니다.
**11. 기술문서 추가**
이제 *brand_new_bert*에 필요한 모든 기능이 추가되었습니다. 거의 끝났습니다! 추가해야 할 것은 멋진 기술문서과 기술문서 페이지입니다. Cookiecutter가 `docs/source/model_doc/brand_new_bert.md`라는 템플릿 파일을 추가해줬을 것입니다. 이 페이지를 사용하기 전에 모델을 사용하는 사용자들은 일반적으로 이 페이지를 먼저 확인합니다. 따라서 문서는 이해하기 쉽고 간결해야 합니다. 모델을 사용하는 방법을 보여주기 위해 *팁*을 추가하는 것이 커뮤니티에 매우 유용합니다. 독스트링에 관련하여 Hugging Face 팀에 문의하는 것을 주저하지 마세요.
다음으로, `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py`에 추가된 독스트링이 올바르며 필요한 모든 입력 및 출력을 포함하도록 확인하세요. [여기](writing-documentation)에서 우리의 문서 작성 가이드와 독스트링 형식에 대한 상세 가이드가 있습니다. 문서는 일반적으로 커뮤니티와 모델의 첫 번째 접점이기 때문에, 문서는 적어도 코드만큼의 주의를 기울여야 합니다.
**코드 리팩토링**
좋아요, 이제 *brand_new_bert*를 위한 모든 필요한 코드를 추가했습니다. 이 시점에서 다음을 실행하여 잠재적으로 잘못된 코드 스타일을 수정해야 합니다:
그리고 코딩 스타일이 품질 점검을 통과하는지 확인하기 위해 다음을 실행하고 확인해야 합니다:
```bash
make style
```
🤗 Transformers에는 여전히 실패할 수 있는 몇 가지 매우 엄격한 디자인 테스트가 있습니다. 이는 독스트링에 누락된 정보나 잘못된 명명 때문에 종종 발생합니다. 여기서 막히면 Hugging Face 팀이 도움을 줄 것입니다.
```bash
make quality
```
마지막으로, 코드가 정확히 작동하는 것을 확인한 후에는 항상 코드를 리팩토링하는 것이 좋은 생각입니다. 모든 테스트가 통과된 지금은 추가한 코드를 다시 검토하고 리팩토링하는 좋은 시기입니다.
이제 코딩 부분을 완료했습니다. 축하합니다! 🎉 멋져요! 😎
**12. 모델을 모델 허브에 업로드하세요**
이 마지막 파트에서는 모든 체크포인트를 변환하여 모델 허브에 업로드하고 각 업로드된 모델 체크포인트에 대한 모델 카드를 추가해야 합니다. [Model sharing and uploading Page](model_sharing)를 읽고 허브 기능에 익숙해지세요. *brand_new_bert*의 저자 조직 아래에 모델을 업로드할 수 있는 필요한 액세스 권한을 얻기 위해 Hugging Face 팀과 협업해야 합니다. `transformers`의 모든 모델에 있는 `push_to_hub` 메서드는 체크포인트를 허브에 빠르고 효율적으로 업로드하는 방법입니다. 아래에 작은 코드 조각이 붙여져 있습니다:
각 체크포인트에 적합한 모델 카드를 만드는 데 시간을 할애하는 것은 가치가 있습니다. 모델 카드는 체크포인트의 특성을 강조해야 합니다. *예를 들어* 이 체크포인트는 어떤 데이터셋에서 사전 훈련/세부 훈련되었는지? 이 모델은 어떤 하위 작업에서 사용해야 하는지? 그리고 모델을 올바르게 사용하는 방법에 대한 몇 가지 코드도 포함해야 합니다.
```python
brand_new_bert.push_to_hub("brand_new_bert")
# Uncomment the following line to push to an organization.
# brand_new_bert.push_to_hub("<organization>/brand_new_bert")
```
**13. (선택 사항) 노트북 추가**
*brand_new_bert*를 다운스트림 작업에서 추론 또는 미세 조정에 사용하는 방법을 자세히 보여주는 노트북을 추가하는 것이 매우 유용합니다. 이것은 PR을 병합하는 데 필수적이지는 않지만 커뮤니티에 매우 유용합니다.
**14. 완료된 PR 제출**
이제 프로그래밍을 마쳤으며, 마지막 단계로 PR을 메인 브랜치에 병합해야 합니다. 보통 Hugging Face 팀은 이미 여기까지 도움을 주었을 것입니다. 그러나 PR에 멋진 설명을 추가하고 리뷰어에게 특정 디자인 선택 사항을 강조하려면 완료된 PR에 약간의 설명을 추가하는 시간을 할애하는 것이 가치가 있습니다.
### 작업물을 공유하세요!! [[share-your-work]]
이제 커뮤니티에서 작업물을 인정받을 시간입니다! 모델 추가 작업을 완료하는 것은 Transformers와 전체 NLP 커뮤니티에 큰 기여입니다. 당신의 코드와 이식된 사전 훈련된 모델은 수백, 심지어 수천 명의 개발자와 연구원에 의해 확실히 사용될 것입니다. 당신의 작업에 자랑스러워해야 하며 이를 커뮤니티와 공유해야 합니다.
**당신은 커뮤니티 내 모든 사람들에게 매우 쉽게 접근 가능한 또 다른 모델을 만들었습니다! 🤯**
|
transformers/docs/source/ko/add_new_model.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ko/add_new_model.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 43040
}
| 46 |
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Text generation strategies[[text-generation-strategies]]
텍스트 생성은 개방형 텍스트 작성, 요약, 번역 등 다양한 자연어 처리(NLP) 작업에 필수적입니다. 이는 또한 음성-텍스트 변환, 시각-텍스트 변환과 같이 텍스트를 출력으로 하는 여러 혼합 모달리티 응용 프로그램에서도 중요한 역할을 합니다. 텍스트 생성을 가능하게 하는 몇몇 모델로는 GPT2, XLNet, OpenAI GPT, CTRL, TransformerXL, XLM, Bart, T5, GIT, Whisper 등이 있습니다.
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] 메서드를 활용하여 다음과 같은 다양한 작업들에 대해 텍스트 결과물을 생성하는 몇 가지 예시를 살펴보세요:
* [텍스트 요약](./tasks/summarization#inference)
* [이미지 캡셔닝](./model_doc/git#transformers.GitForCausalLM.forward.example)
* [오디오 전사](./model_doc/whisper#transformers.WhisperForConditionalGeneration.forward.example)
generate 메소드에 입력되는 값들은 모델의 데이터 형태에 따라 달라집니다. 이 값들은 AutoTokenizer나 AutoProcessor와 같은 모델의 전처리 클래스에 의해 반환됩니다. 모델의 전처리 장치가 하나 이상의 입력 유형을 생성하는 경우, 모든 입력을 generate()에 전달해야 합니다. 각 모델의 전처리 장치에 대해서는 해당 모델의 문서에서 자세히 알아볼 수 있습니다.
텍스트를 생성하기 위해 출력 토큰을 선택하는 과정을 디코딩이라고 하며, `generate()` 메소드가 사용할 디코딩 전략을 사용자가 커스터마이징할 수 있습니다. 디코딩 전략을 수정하는 것은 훈련 가능한 매개변수의 값들을 변경하지 않지만, 생성된 출력의 품질에 눈에 띄는 영향을 줄 수 있습니다. 이는 텍스트에서 반복을 줄이고, 더 일관성 있게 만드는 데 도움을 줄 수 있습니다.
이 가이드에서는 다음과 같은 내용을 다룹니다:
* 기본 생성 설정
* 일반적인 디코딩 전략과 주요 파라미터
* 🤗 Hub에서 미세 조정된 모델과 함께 사용자 정의 생성 설정을 저장하고 공유하는 방법
## 기본 텍스트 생성 설정[[default-text-generation-configuration]]
모델의 디코딩 전략은 생성 설정에서 정의됩니다. 사전 훈련된 모델을 [`pipeline`] 내에서 추론에 사용할 때, 모델은 내부적으로 기본 생성 설정을 적용하는 `PreTrainedModel.generate()` 메소드를 호출합니다. 사용자가 모델과 함께 사용자 정의 설정을 저장하지 않았을 경우에도 기본 설정이 사용됩니다.
모델을 명시적으로 로드할 때, `model.generation_config`을 통해 제공되는 생성 설정을 검사할 수 있습니다.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilgpt2")
>>> model.generation_config
GenerationConfig {
"bos_token_id": 50256,
"eos_token_id": 50256,
}
```
`model.generation_config`를 출력하면 기본 설정과 다른 값들만 표시되고, 기본값들은 나열되지 않습니다.
기본 생성 설정은 입력 프롬프트와 출력을 합친 최대 크기를 20 토큰으로 제한하여 리소스 부족을 방지합니다. 기본 디코딩 전략은 탐욕 탐색(greedy search)으로, 다음 토큰으로 가장 높은 확률을 가진 토큰을 선택하는 가장 단순한 디코딩 전략입니다. 많은 작업과 작은 출력 크기에 대해서는 이 방법이 잘 작동하지만, 더 긴 출력을 생성할 때 사용하면 매우 반복적인 결과를 생성하게 될 수 있습니다.
## 텍스트 생성 사용자 정의[[customize-text-generation]]
파라미터와 해당 값을 [`generate`] 메소드에 직접 전달하여 `generation_config`을 재정의할 수 있습니다:
```python
>>> my_model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=4, do_sample=True) # doctest: +SKIP
```
기본 디코딩 전략이 대부분의 작업에 잘 작동한다 하더라도, 조정할 수 있는 몇 가지 파라미터가 있습니다. 일반적으로 조정되는 파라미터에는 다음과 같은 것들이 포함됩니다:
- `max_new_tokens`: 생성할 최대 토큰 수입니다. 즉, 프롬프트에 있는 토큰을 제외한 출력 시퀀스의 크기입니다. 출력의 길이를 중단 기준으로 사용하는 대신, 전체 생성물이 일정 시간을 초과할 때 생성을 중단하기로 선택할 수도 있습니다. 더 알아보려면 [`StoppingCriteria`]를 확인하세요.
- `num_beams`: 1보다 큰 수의 빔을 지정함으로써, 탐욕 탐색(greedy search)에서 빔 탐색(beam search)으로 전환하게 됩니다. 이 전략은 각 시간 단계에서 여러 가설을 평가하고 결국 전체 시퀀스에 대해 가장 높은 확률을 가진 가설을 선택합니다. 이는 초기 토큰의 확률이 낮아 탐욕 탐색에 의해 무시되었을 높은 확률의 시퀀스를 식별할 수 있는 장점을 가집니다.
- `do_sample`: 이 매개변수를 `True`로 설정하면, 다항 샘플링, 빔 탐색 다항 샘플링, Top-K 샘플링 및 Top-p 샘플링과 같은 디코딩 전략을 활성화합니다. 이러한 전략들은 전체 어휘에 대한 확률 분포에서 다음 토큰을 선택하며, 전략별로 특정 조정이 적용됩니다.
- `num_return_sequences`: 각 입력에 대해 반환할 시퀀스 후보의 수입니다. 이 옵션은 빔 탐색(beam search)의 변형과 샘플링과 같이 여러 시퀀스 후보를 지원하는 디코딩 전략에만 사용할 수 있습니다. 탐욕 탐색(greedy search)과 대조 탐색(contrastive search) 같은 디코딩 전략은 단일 출력 시퀀스를 반환합니다.
## 모델에 사용자 정의 디코딩 전략 저장[[save-a-custom-decoding-strategy-with-your-model]]
특정 생성 설정을 가진 미세 조정된 모델을 공유하고자 할 때, 다음 단계를 따를 수 있습니다:
* [`GenerationConfig`] 클래스 인스턴스를 생성합니다.
* 디코딩 전략 파라미터를 설정합니다.
* 생성 설정을 [`GenerationConfig.save_pretrained`]를 사용하여 저장하며, `config_file_name` 인자는 비워둡니다.
* 모델의 저장소에 설정을 업로드하기 위해 `push_to_hub`를 `True`로 설정합니다.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, GenerationConfig
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("my_account/my_model") # doctest: +SKIP
>>> generation_config = GenerationConfig(
... max_new_tokens=50, do_sample=True, top_k=50, eos_token_id=model.config.eos_token_id
... )
>>> generation_config.save_pretrained("my_account/my_model", push_to_hub=True) # doctest: +SKIP
```
단일 디렉토리에 여러 생성 설정을 저장할 수 있으며, 이때 [`GenerationConfig.save_pretrained`]의 `config_file_name` 인자를 사용합니다. 나중에 [`GenerationConfig.from_pretrained`]로 이들을 인스턴스화할 수 있습니다. 이는 단일 모델에 대해 여러 생성 설정을 저장하고 싶을 때 유용합니다(예: 샘플링을 이용한 창의적 텍스트 생성을 위한 하나, 빔 탐색을 이용한 요약을 위한 다른 하나 등). 모델에 설정 파일을 추가하기 위해 적절한 Hub 권한을 가지고 있어야 합니다.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, GenerationConfig
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-t5/t5-small")
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google-t5/t5-small")
>>> translation_generation_config = GenerationConfig(
... num_beams=4,
... early_stopping=True,
... decoder_start_token_id=0,
... eos_token_id=model.config.eos_token_id,
... pad_token=model.config.pad_token_id,
... )
>>> # 팁: Hub에 push하려면 `push_to_hub=True`를 추가
>>> translation_generation_config.save_pretrained("/tmp", "translation_generation_config.json")
>>> # 명명된 생성 설정 파일을 사용하여 생성을 매개변수화할 수 있습니다.
>>> generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained("/tmp", "translation_generation_config.json")
>>> inputs = tokenizer("translate English to French: Configuration files are easy to use!", return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, generation_config=generation_config)
>>> print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
['Les fichiers de configuration sont faciles à utiliser!']
```
## 스트리밍[[streaming]]
`generate()` 메소드는 `streamer` 입력을 통해 스트리밍을 지원합니다. `streamer` 입력은 `put()`과 `end()` 메소드를 가진 클래스의 인스턴스와 호환됩니다. 내부적으로, `put()`은 새 토큰을 추가하는 데 사용되며, `end()`는 텍스트 생성의 끝을 표시하는 데 사용됩니다.
<Tip warning={true}>
스트리머 클래스의 API는 아직 개발 중이며, 향후 변경될 수 있습니다.
</Tip>
실제로 다양한 목적을 위해 자체 스트리밍 클래스를 만들 수 있습니다! 또한, 기본적인 스트리밍 클래스들도 준비되어 있어 바로 사용할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, [`TextStreamer`] 클래스를 사용하여 `generate()`의 출력을 화면에 한 단어씩 스트리밍할 수 있습니다:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, TextStreamer
>>> tok = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
>>> inputs = tok(["An increasing sequence: one,"], return_tensors="pt")
>>> streamer = TextStreamer(tok)
>>> # 스트리머는 평소와 같은 출력값을 반환할 뿐만 아니라 생성된 텍스트도 표준 출력(stdout)으로 출력합니다.
>>> _ = model.generate(**inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=20)
An increasing sequence: one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten, eleven,
```
## 디코딩 전략[[decoding-strategies]]
`generate()` 매개변수와 궁극적으로 `generation_config`의 특정 조합을 사용하여 특정 디코딩 전략을 활성화할 수 있습니다. 이 개념이 처음이라면, 흔히 사용되는 디코딩 전략이 어떻게 작동하는지 설명하는 [이 블로그 포스트](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-generate)를 읽어보는 것을 추천합니다.
여기서는 디코딩 전략을 제어하는 몇 가지 매개변수를 보여주고, 이를 어떻게 사용할 수 있는지 설명하겠습니다.
### 탐욕 탐색(Greedy Search)[[greedy-search]]
[`generate`]는 기본적으로 탐욕 탐색 디코딩을 사용하므로 이를 활성화하기 위해 별도의 매개변수를 지정할 필요가 없습니다. 이는 `num_beams`가 1로 설정되고 `do_sample=False`로 되어 있다는 의미입니다."
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> prompt = "I look forward to"
>>> checkpoint = "distilbert/distilgpt2"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
['I look forward to seeing you all again!\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n']
```
### 대조 탐색(Contrastive search)[[contrastive-search]]
2022년 논문 [A Contrastive Framework for Neural Text Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.06417)에서 제안된 대조 탐색 디코딩 전략은 반복되지 않으면서도 일관된 긴 출력을 생성하는 데 있어 우수한 결과를 보였습니다. 대조 탐색이 작동하는 방식을 알아보려면 [이 블로그 포스트](https://huggingface.co/blog/introducing-csearch)를 확인하세요. 대조 탐색의 동작을 가능하게 하고 제어하는 두 가지 주요 매개변수는 `penalty_alpha`와 `top_k`입니다:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> checkpoint = "openai-community/gpt2-large"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> prompt = "Hugging Face Company is"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, penalty_alpha=0.6, top_k=4, max_new_tokens=100)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
['Hugging Face Company is a family owned and operated business. We pride ourselves on being the best
in the business and our customer service is second to none.\n\nIf you have any questions about our
products or services, feel free to contact us at any time. We look forward to hearing from you!']
```
### 다항 샘플링(Multinomial sampling)[[multinomial-sampling]]
탐욕 탐색(greedy search)이 항상 가장 높은 확률을 가진 토큰을 다음 토큰으로 선택하는 것과 달리, 다항 샘플링(multinomial sampling, 조상 샘플링(ancestral sampling)이라고도 함)은 모델이 제공하는 전체 어휘에 대한 확률 분포를 기반으로 다음 토큰을 무작위로 선택합니다. 0이 아닌 확률을 가진 모든 토큰은 선택될 기회가 있으므로, 반복의 위험을 줄일 수 있습니다.
다항 샘플링을 활성화하려면 `do_sample=True` 및 `num_beams=1`을 설정하세요.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, set_seed
>>> set_seed(0) # 재현성을 위해
>>> checkpoint = "openai-community/gpt2-large"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> prompt = "Today was an amazing day because"
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=True, num_beams=1, max_new_tokens=100)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
['Today was an amazing day because when you go to the World Cup and you don\'t, or when you don\'t get invited,
that\'s a terrible feeling."']
```
### 빔 탐색(Beam-search) 디코딩[[beam-search-decoding]]
탐욕 검색(greedy search)과 달리, 빔 탐색(beam search) 디코딩은 각 시간 단계에서 여러 가설을 유지하고 결국 전체 시퀀스에 대해 가장 높은 확률을 가진 가설을 선택합니다. 이는 낮은 확률의 초기 토큰으로 시작하고 그리디 검색에서 무시되었을 가능성이 높은 시퀀스를 식별하는 이점이 있습니다.
이 디코딩 전략을 활성화하려면 `num_beams` (추적할 가설 수라고도 함)를 1보다 크게 지정하세요.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> prompt = "It is astonishing how one can"
>>> checkpoint = "openai-community/gpt2-medium"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, max_new_tokens=50)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
['It is astonishing how one can have such a profound impact on the lives of so many people in such a short period of
time."\n\nHe added: "I am very proud of the work I have been able to do in the last few years.\n\n"I have']
```
### 빔 탐색 다항 샘플링(Beam-search multinomial sampling)[[beam-search-multinomial-sampling]]
이 디코딩 전략은 이름에서 알 수 있듯이 빔 탐색과 다항 샘플링을 결합한 것입니다. 이 디코딩 전략을 사용하기 위해서는 `num_beams`를 1보다 큰 값으로 설정하고, `do_sample=True`로 설정해야 합니다.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, set_seed
>>> set_seed(0) # 재현성을 위해
>>> prompt = "translate English to German: The house is wonderful."
>>> checkpoint = "google-t5/t5-small"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
'Das Haus ist wunderbar.'
```
### 다양한 빔 탐색 디코딩(Diverse beam search decoding)[[diverse-beam-search-decoding]]
다양한 빔 탐색(Decoding) 전략은 선택할 수 있는 더 다양한 빔 시퀀스 집합을 생성할 수 있게 해주는 빔 탐색 전략의 확장입니다. 이 방법은 어떻게 작동하는지 알아보려면, [다양한 빔 탐색: 신경 시퀀스 모델에서 다양한 솔루션 디코딩하기](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02424.pdf)를 참조하세요. 이 접근 방식은 세 가지 주요 매개변수를 가지고 있습니다: `num_beams`, `num_beam_groups`, 그리고 `diversity_penalty`. 다양성 패널티는 그룹 간에 출력이 서로 다르게 하기 위한 것이며, 각 그룹 내에서 빔 탐색이 사용됩니다.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> checkpoint = "google/pegasus-xsum"
>>> prompt = (
... "The Permaculture Design Principles are a set of universal design principles "
... "that can be applied to any location, climate and culture, and they allow us to design "
... "the most efficient and sustainable human habitation and food production systems. "
... "Permaculture is a design system that encompasses a wide variety of disciplines, such "
... "as ecology, landscape design, environmental science and energy conservation, and the "
... "Permaculture design principles are drawn from these various disciplines. Each individual "
... "design principle itself embodies a complete conceptual framework based on sound "
... "scientific principles. When we bring all these separate principles together, we can "
... "create a design system that both looks at whole systems, the parts that these systems "
... "consist of, and how those parts interact with each other to create a complex, dynamic, "
... "living system. Each design principle serves as a tool that allows us to integrate all "
... "the separate parts of a design, referred to as elements, into a functional, synergistic, "
... "whole system, where the elements harmoniously interact and work together in the most "
... "efficient way possible."
... )
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, num_beam_groups=5, max_new_tokens=30, diversity_penalty=1.0)
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
'The Design Principles are a set of universal design principles that can be applied to any location, climate and
culture, and they allow us to design the'
```
이 가이드에서는 다양한 디코딩 전략을 가능하게 하는 주요 매개변수를 보여줍니다. [`generate`] 메서드에 대한 고급 매개변수가 존재하므로 [`generate`] 메서드의 동작을 더욱 세부적으로 제어할 수 있습니다. 사용 가능한 매개변수의 전체 목록은 [API 문서](./main_classes/text_generation.md)를 참조하세요.
### 추론 디코딩(Speculative Decoding)[[speculative-decoding]]
추론 디코딩(보조 디코딩(assisted decoding)으로도 알려짐)은 동일한 토크나이저를 사용하는 훨씬 작은 보조 모델을 활용하여 몇 가지 후보 토큰을 생성하는 상위 모델의 디코딩 전략을 수정한 것입니다. 주 모델은 단일 전방 통과로 후보 토큰을 검증함으로써 디코딩 과정을 가속화합니다. `do_sample=True`일 경우, [추론 디코딩 논문](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.17192.pdf)에 소개된 토큰 검증과 재샘플링 방식이 사용됩니다.
현재, 탐욕 검색(greedy search)과 샘플링만이 지원되는 보조 디코딩(assisted decoding) 기능을 통해, 보조 디코딩은 배치 입력을 지원하지 않습니다. 보조 디코딩에 대해 더 알고 싶다면, [이 블로그 포스트](https://huggingface.co/blog/assisted-generation)를 확인해 주세요.
보조 디코딩을 활성화하려면 모델과 함께 `assistant_model` 인수를 설정하세요.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> prompt = "Alice and Bob"
>>> checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-1.4b-deduped"
>>> assistant_checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-160m-deduped"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(assistant_checkpoint)
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
['Alice and Bob are sitting in a bar. Alice is drinking a beer and Bob is drinking a']
```
샘플링 방법과 함께 보조 디코딩을 사용하는 경우 다항 샘플링과 마찬가지로 `temperature` 인수를 사용하여 무작위성을 제어할 수 있습니다. 그러나 보조 디코딩에서는 `temperature`를 낮추면 대기 시간을 개선하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, set_seed
>>> set_seed(42) # 재현성을 위해
>>> prompt = "Alice and Bob"
>>> checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-1.4b-deduped"
>>> assistant_checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-160m-deduped"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
>>> assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(assistant_checkpoint)
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model, do_sample=True, temperature=0.5)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
['Alice and Bob, who were both in their early twenties, were both in the process of']
```
|
transformers/docs/source/ko/generation_strategies.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ko/generation_strategies.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 13395
}
| 47 |
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# 대규모 언어 모델로 생성하기 [[generation-with-llms]]
[[open-in-colab]]
LLM 또는 대규모 언어 모델은 텍스트 생성의 핵심 구성 요소입니다. 간단히 말하면, 주어진 입력 텍스트에 대한 다음 단어(정확하게는 토큰)를 예측하기 위해 훈련된 대규모 사전 훈련 변환기 모델로 구성됩니다. 토큰을 한 번에 하나씩 예측하기 때문에 새로운 문장을 생성하려면 모델을 호출하는 것 외에 더 복잡한 작업을 수행해야 합니다. 즉, 자기회귀 생성을 수행해야 합니다.
자기회귀 생성은 몇 개의 초기 입력값을 제공한 후, 그 출력을 다시 모델에 입력으로 사용하여 반복적으로 호출하는 추론 과정입니다. 🤗 Transformers에서는 [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] 메소드가 이 역할을 하며, 이는 생성 기능을 가진 모든 모델에서 사용 가능합니다.
이 튜토리얼에서는 다음 내용을 다루게 됩니다:
* LLM으로 텍스트 생성
* 일반적으로 발생하는 문제 해결
* LLM을 최대한 활용하기 위한 다음 단계
시작하기 전에 필요한 모든 라이브러리가 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요:
```bash
pip install transformers bitsandbytes>=0.39.0 -q
```
## 텍스트 생성 [[generate-text]]
[인과적 언어 모델링(causal language modeling)](tasks/language_modeling)을 목적으로 학습된 언어 모델은 일련의 텍스트 토큰을 입력으로 사용하고, 그 결과로 다음 토큰이 나올 확률 분포를 제공합니다.
<!-- [GIF 1 -- FWD PASS] -->
<figure class="image table text-center m-0 w-full">
<video
style="max-width: 90%; margin: auto;"
autoplay loop muted playsinline
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/blog/assisted-generation/gif_1_1080p.mov"
></video>
<figcaption>"LLM의 전방 패스"</figcaption>
</figure>
LLM과 자기회귀 생성을 함께 사용할 때 핵심적인 부분은 이 확률 분포로부터 다음 토큰을 어떻게 고를 것인지입니다. 다음 반복 과정에 사용될 토큰을 결정하는 한, 어떠한 방법도 가능합니다. 확률 분포에서 가장 가능성이 높은 토큰을 선택하는 것처럼 간단할 수도 있고, 결과 분포에서 샘플링하기 전에 수십 가지 변환을 적용하는 것처럼 복잡할 수도 있습니다.
<!-- [GIF 2 -- TEXT GENERATION] -->
<figure class="image table text-center m-0 w-full">
<video
style="max-width: 90%; margin: auto;"
autoplay loop muted playsinline
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/blog/assisted-generation/gif_2_1080p.mov"
></video>
<figcaption>"자기회귀 생성은 확률 분포에서 다음 토큰을 반복적으로 선택하여 텍스트를 생성합니다."</figcaption>
</figure>
위에서 설명한 과정은 어떤 종료 조건이 충족될 때까지 반복적으로 수행됩니다. 모델이 시퀀스의 끝(EOS 토큰)을 출력할 때까지를 종료 조건으로 하는 것이 이상적입니다. 그렇지 않은 경우에는 미리 정의된 최대 길이에 도달했을 때 생성이 중단됩니다.
모델이 예상대로 동작하기 위해선 토큰 선택 단계와 정지 조건을 올바르게 설정하는 것이 중요합니다. 이러한 이유로, 각 모델에는 기본 생성 설정이 잘 정의된 [`~generation.GenerationConfig`] 파일이 함께 제공됩니다.
코드를 확인해봅시다!
<Tip>
기본 LLM 사용에 관심이 있다면, 우리의 [`Pipeline`](pipeline_tutorial) 인터페이스로 시작하는 것을 추천합니다. 그러나 LLM은 양자화나 토큰 선택 단계에서의 미세한 제어와 같은 고급 기능들을 종종 필요로 합니다. 이러한 작업은 [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`]를 통해 가장 잘 수행될 수 있습니다. LLM을 이용한 자기회귀 생성은 자원을 많이 소모하므로, 적절한 처리량을 위해 GPU에서 실행되어야 합니다.
</Tip>
먼저, 모델을 불러오세요.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
... "mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", device_map="auto", load_in_4bit=True
... )
```
`from_pretrained` 함수를 호출할 때 2개의 플래그를 주목하세요:
- `device_map`은 모델이 GPU로 이동되도록 합니다.
- `load_in_4bit`는 리소스 요구 사항을 크게 줄이기 위해 [4비트 동적 양자화](main_classes/quantization)를 적용합니다.
이 외에도 모델을 초기화하는 다양한 방법이 있지만, LLM을 처음 시작할 때 이 설정을 추천합니다.
이어서 텍스트 입력을 [토크나이저](tokenizer_summary)으로 전처리하세요.
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
>>> import torch
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer(["A list of colors: red, blue"], return_tensors="pt").to(device)
```
`model_inputs` 변수에는 토큰화된 텍스트 입력과 함께 어텐션 마스크가 들어 있습니다. [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`]는 어텐션 마스크가 제공되지 않았을 경우에도 이를 추론하려고 노력하지만, 최상의 성능을 위해서는 가능하면 어텐션 마스크를 전달하는 것을 권장합니다.
마지막으로 [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] 메소드를 호출해 생성된 토큰을 얻은 후, 이를 출력하기 전에 텍스트 형태로 변환하세요.
```python
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
'A list of colors: red, blue, green, yellow, black, white, and brown'
```
이게 전부입니다! 몇 줄의 코드만으로 LLM의 능력을 활용할 수 있게 되었습니다.
## 일반적으로 발생하는 문제 [[common-pitfalls]]
[생성 전략](generation_strategies)이 많고, 기본값이 항상 사용 사례에 적합하지 않을 수 있습니다. 출력이 예상과 다를 때 흔히 발생하는 문제와 이를 해결하는 방법에 대한 목록을 만들었습니다.
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token # Mistral has no pad token by default
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
... "mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", device_map="auto", load_in_4bit=True
... )
```
### 생성된 출력이 너무 짧거나 길다 [[generated-output-is-too-shortlong]]
[`~generation.GenerationConfig`] 파일에서 별도로 지정하지 않으면, `generate`는 기본적으로 최대 20개의 토큰을 반환합니다. `generate` 호출에서 `max_new_tokens`을 수동으로 설정하여 반환할 수 있는 새 토큰의 최대 수를 설정하는 것이 좋습니다. LLM(정확하게는 [디코더 전용 모델](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/chapter1/6?fw=pt))은 입력 프롬프트도 출력의 일부로 반환합니다.
```py
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer(["A sequence of numbers: 1, 2"], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> # By default, the output will contain up to 20 tokens
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
'A sequence of numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5'
>>> # Setting `max_new_tokens` allows you to control the maximum length
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id, max_new_tokens=50)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
'A sequence of numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,'
```
### 잘못된 생성 모드 [[incorrect-generation-mode]]
기본적으로 [`~generation.GenerationConfig`] 파일에서 별도로 지정하지 않으면, `generate`는 각 반복에서 가장 확률이 높은 토큰을 선택합니다(그리디 디코딩). 하려는 작업에 따라 이 방법은 바람직하지 않을 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 챗봇이나 에세이 작성과 같은 창의적인 작업은 샘플링이 적합할 수 있습니다. 반면, 오디오를 텍스트로 변환하거나 번역과 같은 입력 기반 작업은 그리디 디코딩이 더 적합할 수 있습니다. `do_sample=True`로 샘플링을 활성화할 수 있으며, 이 주제에 대한 자세한 내용은 이 [블로그 포스트](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-generate)에서 볼 수 있습니다.
```python
>>> # Set seed or reproducibility -- you don't need this unless you want full reproducibility
>>> from transformers import set_seed
>>> set_seed(0)
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer(["I am a cat."], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> # LLM + greedy decoding = repetitive, boring output
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
'I am a cat. I am a cat. I am a cat. I am a cat'
>>> # With sampling, the output becomes more creative!
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
'I am a cat.\nI just need to be. I am always.\nEvery time'
```
### 잘못된 패딩 [[wrong-padding-side]]
LLM은 [디코더 전용](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/chapter1/6?fw=pt) 구조를 가지고 있어, 입력 프롬프트에 대해 지속적으로 반복 처리를 합니다. 입력 데이터의 길이가 다르면 패딩 작업이 필요합니다. LLM은 패딩 토큰에서 작동을 이어가도록 설계되지 않았기 때문에, 입력 왼쪽에 패딩이 추가 되어야 합니다. 그리고 어텐션 마스크도 꼭 `generate` 함수에 전달되어야 합니다!
```python
>>> # The tokenizer initialized above has right-padding active by default: the 1st sequence,
>>> # which is shorter, has padding on the right side. Generation fails.
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer(
... ["1, 2, 3", "A, B, C, D, E"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt"
... ).to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids[0], skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
''
>>> # With left-padding, it works as expected!
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openlm-research/open_llama_7b", padding_side="left")
>>> tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token # Llama has no pad token by default
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer(
... ["1, 2, 3", "A, B, C, D, E"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt"
... ).to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
'1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,'
```
<!-- TODO: when the prompting guide is ready, mention the importance of setting the right prompt in this section -->
## 추가 자료 [[further-resources]]
자기회귀 생성 프로세스는 상대적으로 단순한 편이지만, LLM을 최대한 활용하려면 여러 가지 요소를 고려해야 하므로 쉽지 않을 수 있습니다. LLM에 대한 더 깊은 이해와 활용을 위한 다음 단계는 아래와 같습니다:
<!-- TODO: complete with new guides -->
### 고급 생성 사용 [[advanced-generate-usage]]
1. [가이드](generation_strategies)는 다양한 생성 방법을 제어하는 방법, 생성 설정 파일을 설정하는 방법, 출력을 스트리밍하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다.
2. [`~generation.GenerationConfig`]와 [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`], [generate-related classes](internal/generation_utils)를 참조해보세요.
### LLM 리더보드 [[llm-leaderboards]]
1. [Open LLM Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/HuggingFaceH4/open_llm_leaderboard)는 오픈 소스 모델의 품질에 중점을 둡니다.
2. [Open LLM-Perf Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/optimum/llm-perf-leaderboard)는 LLM 처리량에 중점을 둡니다.
### 지연 시간 및 처리량 [[latency-and-throughput]]
1. 메모리 요구 사항을 줄이려면, 동적 양자화에 대한 [가이드](main_classes/quantization)를 참조하세요.
### 관련 라이브러리 [[related-libraries]]
1. [`text-generation-inference`](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference)는 LLM을 위한 실제 운영 환경에 적합한 서버입니다.
2. [`optimum`](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum)은 특정 하드웨어 장치에서 LLM을 최적화하기 위해 🤗 Transformers를 확장한 것입니다.
|
transformers/docs/source/ko/llm_tutorial.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ko/llm_tutorial.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 8185
}
| 48 |
# AltCLIP
## 개요[[overview]]
AltCLIP 모델은 Zhongzhi Chen, Guang Liu, Bo-Wen Zhang, Fulong Ye, Qinghong Yang, Ledell Wu의 [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679v2) 논문에서 제안되었습니다. AltCLIP(CLIP의 언어 인코더를 변경하여 언어 기능 확장)은 다양한 이미지-텍스트 및 텍스트-텍스트 쌍으로 훈련된 신경망입니다. CLIP의 텍스트 인코더를 사전 훈련된 다국어 텍스트 인코더 XLM-R로 교체하여, 거의 모든 작업에서 CLIP과 유사한 성능을 얻을 수 있었으며, 원래 CLIP의 다국어 이해와 같은 기능도 확장되었습니다.
논문의 초록은 다음과 같습니다:
*본 연구에서는 강력한 이중 언어 멀티모달 표현 모델을 훈련하는 개념적으로 간단하고 효과적인 방법을 제시합니다. OpenAI에서 출시한 사전 훈련된 멀티모달 표현 모델 CLIP에서 시작하여, 그 텍스트 인코더를 사전 훈련된 다국어 텍스트 인코더 XLM-R로 교체하고, 교사 학습과 대조 학습으로 구성된 2단계 훈련 스키마를 통해 언어와 이미지 표현을 정렬했습니다. 우리는 광범위한 작업 평가를 통해 우리의 방법을 검증했습니다. ImageNet-CN, Flicker30k-CN, COCO-CN을 포함한 여러 작업에서 새로운 최고 성능을 달성했으며, 거의 모든 작업에서 CLIP과 유사한 성능을 얻었습니다. 이는 CLIP의 텍스트 인코더를 단순히 변경하여 다국어 이해와 같은 확장 기능을 얻을 수 있음을 시사합니다.*
이 모델은 [jongjyh](https://huggingface.co/jongjyh)에 의해 기여되었습니다.
## 사용 팁과 예제[[usage-tips-and-example]]
AltCLIP의 사용법은 CLIP과 매우 유사하며, 차이점은 텍스트 인코더에 있습니다. 일반적인 어텐션 대신 양방향 어텐션을 사용하며, XLM-R의 [CLS] 토큰을 사용하여 텍스트 임베딩을 나타냅니다.
AltCLIP은 멀티모달 비전 및 언어 모델입니다. 이미지와 텍스트 간의 유사성 계산 및 제로샷 이미지 분류에 사용할 수 있습니다. AltCLIP은 ViT와 같은 트랜스포머를 사용하여 시각적 특징을 얻고, 양방향 언어 모델을 사용하여 텍스트 특징을 얻습니다. 이후 텍스트와 시각적 특징 모두 동일한 차원의 잠재 공간으로 투사됩니다. 투사된 이미지와 텍스트 특징 간의 내적을 유사도 점수로 사용합니다.
이미지를 트랜스포머 인코더에 입력하기 위해, 각 이미지를 일정한 크기의 겹치지 않는 패치 시퀀스로 분할한 뒤, 이를 선형 임베딩합니다. 전체 이미지를 나타내기 위해 [CLS] 토큰이 추가됩니다. 저자들은 절대 위치 임베딩도 추가하여 결과 벡터 시퀀스를 표준 트랜스포머 인코더에 입력합니다. [`CLIPImageProcessor`]는 모델을 위해 이미지를 크기 조정하고 정규화하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
[`AltCLIPProcessor`]는 [`CLIPImageProcessor`]와 [`XLMRobertaTokenizer`]를 하나의 인스턴스로 묶어 텍스트를 인코딩하고 이미지를 준비합니다. 다음 예제는 [`AltCLIPProcessor`]와 [`AltCLIPModel`]을 사용하여 이미지와 텍스트 간의 유사성 점수를 얻는 방법을 보여줍니다.
```python
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AltCLIPModel, AltCLIPProcessor
>>> model = AltCLIPModel.from_pretrained("BAAI/AltCLIP")
>>> processor = AltCLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("BAAI/AltCLIP")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(text=["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits_per_image = outputs.logits_per_image # 이미지-텍스트 유사도 점수
>>> probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1) # 라벨 마다 확률을 얻기 위해 softmax 적용
```
<Tip>
이 모델은 `CLIPModel`을 기반으로 하므로, 원래 CLIP처럼 사용할 수 있습니다.
</Tip>
## AltCLIPConfig
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPConfig
- from_text_vision_configs
## AltCLIPTextConfig
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPTextConfig
## AltCLIPVisionConfig
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPVisionConfig
## AltCLIPProcessor
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPProcessor
## AltCLIPModel
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPModel
- forward
- get_text_features
- get_image_features
## AltCLIPTextModel
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPTextModel
- forward
## AltCLIPVisionModel
[[autodoc]] AltCLIPVisionModel
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/ko/model_doc/altclip.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ko/model_doc/altclip.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3274
}
| 49 |
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
-->
# DBRX[[dbrx]]
## 개요[[overview]]
DBRX는 [트랜스포머 기반의](https://www.isattentionallyouneed.com/) 다음 토큰을 예측하는 디코더 전용 LLM 모델입니다.
총 132B 매개변수를 가진 *세밀한* 전문가 혼합(MoE) 아키텍처를 사용하며, 이 중 36B 매개변수가 입력마다 활성화됩니다.
12T 토큰의 텍스트와 코드 데이터로 사전 학습되었습니다.
Mixtral-8x7B와 Grok-1과 같은 다른 공개 MoE 모델들과 비교했을 때, DBRX는 더 많은 수의 작은 전문가들을 사용하는 세밀한 구조를 가지고 있습니다. DBRX는 16개의 전문가 중 4개를 선택하는 반면, Mixtral-8x7B와 Grok-1은 8개의 전문가 중 2개를 선택합니다.
이는 65배 더 많은 전문가 조합을 가능하게 하며, 이를 통해 모델의 품질이 향상되는 것을 발견했습니다.
DBRX는 회전 위치 인코딩(RoPE), 게이트 선형 유닛(GLU), 그룹 쿼리 어텐션(GQA)을 사용합니다.
BPE 기반 모델이며 [tiktoken](https://github.com/openai/tiktoken) 저장소에 설명된 GPT-4 토크나이저를 사용합니다.
이러한 선택들은 철저한 평가와 스케일링 실험을 기반으로 이루어졌습니다.
DBRX는 신중하게 선별된 12T 토큰의 데이터로 사전 학습되었으며, 최대 문맥 길이는 32K 토큰입니다.
이 데이터는 토큰 대비 MPT 계열 모델 학습에 사용된 데이터보다 최소 2배 이상 더 좋은 것으로 추정됩니다.
이 새로운 데이터셋은 데이터 처리를 위한 Apache Spark™와 Databricks 노트북, 그리고 데이터 관리와 거버넌스를 위한 Unity Catalog를 포함한 Databricks 도구 전체를 활용하여 개발되었습니다.
우리는 사전 학습을 위해 커리큘럼 학습을 사용했으며, 학습 중 데이터 믹스를 변경하는 방식이 모델 품질을 상당히 개선한다는 것을 발견했습니다.
DBRX Instruct와 DBRX Base에 대한 더 자세한 정보는 이 [기술 블로그 포스트](https://www.databricks.com/blog/introducing-dbrx-new-state-art-open-llm)에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
이 모델은 [eitan-turok](https://huggingface.co/eitanturok)와 [abhi-db](https://huggingface.co/abhi-db)가 기여했습니다. 원본 코드는 [이곳](https://github.com/databricks/dbrx-instruct)에서 찾을 수 있지만, 최신 버전이 아닐 수 있습니다.
## 사용 예[[usage-examples]]
`generate()` 메소드는 DBRX를 사용하여 텍스트를 생성하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다. 표준 어텐션 구현, 플래시 어텐션, PyTorch의 스케일된 내적 어텐션(Scaled Dot-Product Attention)을 사용하여 생성할 수 있습니다. 후자의 두 어텐션 구현 방식은 처리 속도를 크게 높여줍니다.
```python
from transformers import DbrxForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("databricks/dbrx-instruct", token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN")
model = DbrxForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"databricks/dbrx-instruct",
device_map="auto",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN",
)
input_text = "What does it take to build a great LLM?"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": input_text}]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_dict=True, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=200)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
`pip install flash-attn`를 통해 플래시 어텐션을 설치하면, 더 빠른 생성이 가능합니다. (플래시 어텐션에 대한 HuggingFace 문서는 [이곳](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_infer_gpu_one#flashattention-2)에서 확인할 수 있습니다.)
```python
from transformers import DbrxForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("databricks/dbrx-instruct", token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN")
model = DbrxForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"databricks/dbrx-instruct",
device_map="auto",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN",
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
input_text = "What does it take to build a great LLM?"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": input_text}]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_dict=True, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=200)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
PyTorch의 스케일된 내적 어텐션을 사용하여도 더 빠른 생성이 가능합니다. (스케일된 내적 어텐션에 대한 HuggingFace 문서는 [이곳](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)에서 확인할 수 있습니다.)
```python
from transformers import DbrxForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("databricks/dbrx-instruct", token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN")
model = DbrxForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"databricks/dbrx-instruct",
device_map="auto",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
token="YOUR_HF_TOKEN",
attn_implementation="sdpa",
)
input_text = "What does it take to build a great LLM?"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": input_text}]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_dict=True, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=200)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
## DbrxConfig[[transformers.DbrxConfig]]
[[autodoc]] DbrxConfig
## DbrxModel[[transformers.DbrxModel]]
[[autodoc]] DbrxModel
- forward
## DbrxForCausalLM[[transformers.DbrxForCausalLM]]
[[autodoc]] DbrxForCausalLM
- forward
|
transformers/docs/source/ko/model_doc/dbrx.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ko/model_doc/dbrx.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 3617
}
| 50 |
<!--Copyright 2023 Mistral AI and The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See thze License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# Mistral[[mistral]]
## 개요[[overview]]
미스트랄은 Albert Jiang, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Arthur Mensch, Chris Bamford, Devendra Singh Chaplot, Diego de las Casas, Florian Bressand, Gianna Lengyel, Guillaume Lample, Lélio Renard Lavaud, Lucile Saulnier, Marie-Anne Lachaux, Pierre Stock, Teven Le Scao, Thibaut Lavril, Thomas Wang, Timothée Lacroix, William El Sayed가 작성한 [이 블로그 포스트](https://mistral.ai/news/announcing-mistral-7b/)에서 소개되었습니다.
블로그 포스트의 서두는 다음과 같습니다:
*미스트랄 AI팀은 현존하는 언어 모델 중 크기 대비 가장 강력한 미스트랄7B를 출시하게 되어 자랑스럽습니다.*
미스트랄-7B는 [mistral.ai](https://mistral.ai/)에서 출시한 첫 번째 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)입니다.
### 아키텍처 세부사항[[architectural-details]]
미스트랄-7B는 다음과 같은 구조적 특징을 가진 디코더 전용 트랜스포머입니다:
- 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션: 8k 컨텍스트 길이와 고정 캐시 크기로 훈련되었으며, 이론상 128K 토큰의 어텐션 범위를 가집니다.
- GQA(Grouped Query Attention): 더 빠른 추론이 가능하고 더 작은 크기의 캐시를 사용합니다.
- 바이트 폴백(Byte-fallback) BPE 토크나이저: 문자들이 절대 어휘 목록 외의 토큰으로 매핑되지 않도록 보장합니다.
더 자세한 내용은 [출시 블로그 포스트](https://mistral.ai/news/announcing-mistral-7b/)를 참조하세요.
### 라이선스[[license]]
`미스트랄-7B`는 아파치 2.0 라이선스로 출시되었습니다.
## 사용 팁[[usage-tips]]
미스트랄 AI팀은 다음 3가지 체크포인트를 공개했습니다:
- 기본 모델인 [미스트랄-7B-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1)은 인터넷 규모의 데이터에서 다음 토큰을 예측하도록 사전 훈련되었습니다.
- 지시 조정 모델인 [미스트랄-7B-Instruct-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1)은 지도 미세 조정(SFT)과 직접 선호도 최적화(DPO)를 사용한 채팅에 최적화된 기본 모델입니다.
- 개선된 지시 조정 모델인 [미스트랄-7B-Instruct-v0.2](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2)는 v1을 개선한 버전입니다.
기본 모델은 다음과 같이 사용할 수 있습니다:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"My favourite condiment is to ..."
```
지시 조정 모델은 다음과 같이 사용할 수 있습니다:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2")
>>> messages = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "What is your favourite condiment?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "Well, I'm quite partial to a good squeeze of fresh lemon juice. It adds just the right amount of zesty flavour to whatever I'm cooking up in the kitchen!"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "Do you have mayonnaise recipes?"}
... ]
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"Mayonnaise can be made as follows: (...)"
```
지시 조정 모델은 입력이 올바른 형식으로 준비되도록 [채팅 템플릿](../chat_templating)을 적용해야 합니다.
## 플래시 어텐션을 이용한 미스트랄 속도향상[[speeding-up-mistral-by-using-flash-attention]]
위의 코드 스니펫들은 어떤 최적화 기법도 사용하지 않은 추론 과정을 보여줍니다. 하지만 모델 내부에서 사용되는 어텐션 메커니즘의 더 빠른 구현인 [플래시 어텐션2](../perf_train_gpu_one.md#flash-attention-2)을 활용하면 모델의 속도를 크게 높일 수 있습니다.
먼저, 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션 기능을 포함하는 플래시 어텐션2의 최신 버전을 설치해야 합니다.
```bash
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
```
하드웨어와 플래시 어텐션2의 호환여부를 확인하세요. 이에 대한 자세한 내용은 [플래시 어텐션 저장소](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention)의 공식 문서에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한 모델을 반정밀도(예: `torch.float16`)로 불러와야합니다.
플래시 어텐션2를 사용하여 모델을 불러오고 실행하려면 아래 코드 스니펫을 참조하세요:
```python
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"My favourite condiment is to (...)"
```
### 기대하는 속도 향상[[expected-speedups]]
다음은 `mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1` 체크포인트를 사용한 트랜스포머의 기본 구현과 플래시 어텐션2 버전 모델 사이의 순수 추론 시간을 비교한 예상 속도 향상 다이어그램입니다.
<div style="text-align: center">
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/ybelkada/documentation-images/resolve/main/mistral-7b-inference-large-seqlen.png">
</div>
### 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션[[sliding-window-attention]]
현재 구현은 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션 메커니즘과 메모리 효율적인 캐시 관리 기능을 지원합니다. 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션을 활성화하려면, 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션과 호환되는`flash-attn`(`>=2.3.0`)버전을 사용하면 됩니다.
또한 플래시 어텐션2 모델은 더 메모리 효율적인 캐시 슬라이싱 메커니즘을 사용합니다. 미스트랄 모델의 공식 구현에서 권장하는 롤링 캐시 메커니즘을 따라, 캐시 크기를 고정(`self.config.sliding_window`)으로 유지하고, `padding_side="left"`인 경우에만 배치 생성(batch generation)을 지원하며, 현재 토큰의 절대 위치를 사용해 위치 임베딩을 계산합니다.
## 양자화로 미스트랄 크기 줄이기[[shrinking-down-mistral-using-quantization]]
미스트랄 모델은 70억 개의 파라미터를 가지고 있어, 절반의 정밀도(float16)로 약 14GB의 GPU RAM이 필요합니다. 각 파라미터가 2바이트로 저장되기 때문입니다. 하지만 [양자화](../quantization.md)를 사용하면 모델 크기를 줄일 수 있습니다. 모델을 4비트(즉, 파라미터당 반 바이트)로 양자화하면 약 3.5GB의 RAM만 필요합니다.
모델을 양자화하는 것은 `quantization_config`를 모델에 전달하는 것만큼 간단합니다. 아래에서는 BitsAndBytes 양자화를 사용하지만, 다른 양자화 방법은 [이 페이지](../quantization.md)를 참고하세요:
```python
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
>>> # specify how to quantize the model
>>> quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
... load_in_4bit=True,
... bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
... bnb_4bit_compute_dtype="torch.float16",
... )
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", quantization_config=True, device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> messages = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "What is your favourite condiment?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "Well, I'm quite partial to a good squeeze of fresh lemon juice. It adds just the right amount of zesty flavour to whatever I'm cooking up in the kitchen!"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "Do you have mayonnaise recipes?"}
... ]
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"The expected output"
```
이 모델은 [Younes Belkada](https://huggingface.co/ybelkada)와 [Arthur Zucker](https://huggingface.co/ArthurZ)가 기여했습니다.
원본 코드는 [이곳](https://github.com/mistralai/mistral-src)에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
## 리소스[[resources]]
미스트랄을 시작하는 데 도움이 되는 Hugging Face와 community 자료 목록(🌎로 표시됨) 입니다. 여기에 포함될 자료를 제출하고 싶으시다면 PR(Pull Request)를 열어주세요. 리뷰해 드리겠습니다! 자료는 기존 자료를 복제하는 대신 새로운 내용을 담고 있어야 합니다.
<PipelineTag pipeline="text-generation"/>
- 미스트랄-7B의 지도형 미세조정(SFT)을 수행하는 데모 노트북은 [이곳](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/Mistral/Supervised_fine_tuning_(SFT)_of_an_LLM_using_Hugging_Face_tooling.ipynb)에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 🌎
- 2024년에 Hugging Face 도구를 사용해 LLM을 미세 조정하는 방법에 대한 [블로그 포스트](https://www.philschmid.de/fine-tune-llms-in-2024-with-trl). 🌎
- Hugging Face의 [정렬(Alignment) 핸드북](https://github.com/huggingface/alignment-handbook)에는 미스트랄-7B를 사용한 지도형 미세 조정(SFT) 및 직접 선호 최적화(DPO)를 수행하기 위한 스크립트와 레시피가 포함되어 있습니다. 여기에는 단일 GPU에서 QLoRa 및 다중 GPU를 사용한 전체 미세 조정을 위한 스크립트가 포함되어 있습니다.
- [인과적 언어 모델링 작업 가이드](../tasks/language_modeling)
## MistralConfig[[transformers.MistralConfig]]
[[autodoc]] MistralConfig
## MistralModel[[transformers.MistralModel]]
[[autodoc]] MistralModel
- forward
## MistralForCausalLM[[transformers.MistralForCausalLM]]
[[autodoc]] MistralForCausalLM
- forward
## MistralForSequenceClassification[[transformers.MistralForSequenceClassification]]
[[autodoc]] MistralForSequenceClassification
- forward
## MistralForTokenClassification[[transformers.MistralForTokenClassification]]
[[autodoc]] MistralForTokenClassification
- forward
## FlaxMistralModel[[transformers.FlaxMistralModel]]
[[autodoc]] FlaxMistralModel
- __call__
## FlaxMistralForCausalLM[[transformers.FlaxMistralForCausalLM]]
[[autodoc]] FlaxMistralForCausalLM
- __call__
## TFMistralModel[[transformers.TFMistralModel]]
[[autodoc]] TFMistralModel
- call
## TFMistralForCausalLM[[transformers.TFMistralForCausalLM]]
[[autodoc]] TFMistralForCausalLM
- call
## TFMistralForSequenceClassification[[transformers.TFMistralForSequenceClassification]]
[[autodoc]] TFMistralForSequenceClassification
- call
|
transformers/docs/source/ko/model_doc/mistral.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "transformers/docs/source/ko/model_doc/mistral.md",
"repo_id": "transformers",
"token_count": 7040
}
| 51 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.