Datasets:
license: mit
dataset_info:
features:
- name: id
dtype: string
- name: t
dtype: string
- name: t_tc
dtype: string
- name: fm
dtype: string
- name: fm_fc
dtype: string
- name: fm_fc_c
dtype: string
- name: fm_fc_c_m
dtype: string
- name: fm_fc_c_m_f
dtype: string
splits:
- name: train
num_bytes: 5271949886
num_examples: 624022
- name: test
num_bytes: 709543564
num_examples: 78388
- name: validation
num_bytes: 702878290
num_examples: 78534
download_size: 836317231
dataset_size: 6684371740
configs:
- config_name: default
data_files:
- split: train
path: data/train-*
- split: test
path: data/test-*
- split: validation
path: data/validation-*
task_categories:
- text-generation
language:
- en
tags:
- unit test
- java
- code
Dataset Description
Microsoft created the methods2test dataset, consisting of Java Junit test cases with its corresponding focal methods. It contains 780k pairs of JUnit test cases and focal methods which were extracted from a total of 91K Java open source project hosted on GitHub.
This is an alternative version of the methods2test dataset. It provides convenient access to the different context levels based on the raw source code (e.g. newlines are preserved). The test cases and associated classes are also made available.
The mapping between test case and focal methods are based heuristics rules and Java developer's best practice.
More information could be found here:
Dataset Schema
t: <TEST_CASE>
t_tc: <TEST_CASE> <TEST_CLASS_NAME>
fm: <FOCAL_METHOD>
fm_fc: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD>
fm_fc_c: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD> <CONTRSUCTORS>
fm_fc_c_m: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD> <CONTRSUCTORS> <METHOD_SIGNATURES>
fm_fc_c_m_f: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD> <CONTRSUCTORS> <METHOD_SIGNATURES> <FIELDS>
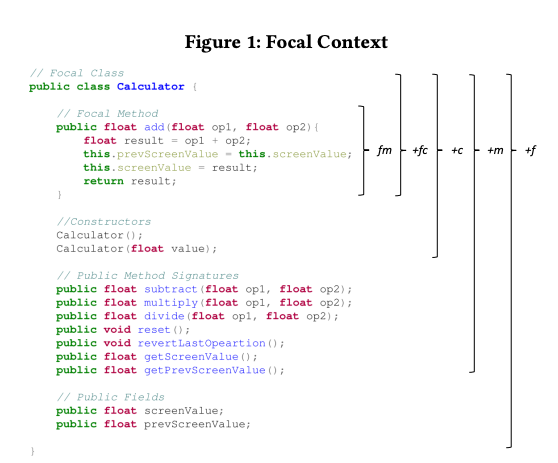
Focal Context
- fm: this representation incorporates exclusively the source code of the focal method. Intuitively, this contains the most important information for generating accurate test cases for the given method.
- fm+fc: this representations adds the focal class name, which can provide meaningful semantic information to the model.
- fm+fc+c: this representation adds the signatures of the constructor methods of the focal class. The idea behind this augmentation is that the test case may require instantiating an object of the focal class in order to properly test the focal method.
- fm+fc+c+m: this representation adds the signatures of the other public methods in the focal class. The rationale which motivated this inclusion is that the test case may need to invoke other auxiliary methods within the class (e.g., getters, setters) to set up or tear down the testing environment.
- fm+fc+c+m+f : this representation adds the public fields of the focal class. The motivation is that test cases may need to inspect the status of the public fields to properly test a focal method.
The different levels of focal contexts are the following:
T: test case
T_TC: test case + test class name
FM: focal method
FM_FC: focal method + focal class name
FM_FC_C: focal method + focal class name + constructor signatures
FM_FC_C_M: focal method + focal class name + constructor signatures + public method signatures
FM_FC_C_M_F: focal method + focal class name + constructor signatures + public method signatures + public fields
Limitations
The original authors validate the heuristics by inspecting a statistically significant sample (confidence level of 95% within 10% margin of error) of 97 samples from the training set. Two authors independently evaluated the sample, then met to discuss the disagreements. We found that 90.72% of the samples have a correct link between the test case and the corresponding focal method
Contribution
All thanks to the original authors.