Faster Stable Diffusion with Core ML on iPhone, iPad, and Mac
WWDC’23 (Apple Worldwide Developers Conference) was held last week. A lot of the news focused on the Vision Pro announcement during the keynote, but there’s much more to it. Like every year, WWDC week is packed with more than 200 technical sessions that dive deep inside the upcoming features across Apple operating systems and frameworks. This year we are particularly excited about changes in Core ML devoted to compression and optimization techniques. These changes make running models such as Stable Diffusion faster and with less memory use! As a taste, consider the following test I ran on my iPhone 13 back in December, compared with the current speed using 6-bit palettization:
 Stable Diffusion on iPhone, back in December and now with 6-bit palettization
Stable Diffusion on iPhone, back in December and now with 6-bit palettization
Contents
- New Core ML Optimizations
- Using Quantized and Optimized Stable Diffusion Models
- Converting and Optimizing Custom Models
- Using Less than 6 bits
- Conclusion
New Core ML Optimizations
Core ML is a mature framework that allows machine learning models to run efficiently on-device, taking advantage of all the compute hardware in Apple devices: the CPU, the GPU, and the Neural Engine specialized in ML tasks. On-device execution is going through a period of extraordinary interest triggered by the popularity of models such as Stable Diffusion and Large Language Models with chat interfaces. Many people want to run these models on their hardware for a variety of reasons, including convenience, privacy, and API cost savings. Naturally, many developers are exploring ways to run these models efficiently on-device and creating new apps and use cases. Core ML improvements that contribute to achieving that goal are big news for the community!
The Core ML optimization changes encompass two different (but complementary) software packages:
- The Core ML framework itself. This is the engine that runs ML models on Apple hardware and is part of the operating system. Models have to be exported in a special format supported by the framework, and this format is also referred to as “Core ML”.
- The
coremltoolsconversion package. This is an open-source Python module whose mission is to convert PyTorch or Tensorflow models to the Core ML format.
coremltools now includes a new submodule called coremltools.optimize with all the compression and optimization tools. For full details on this package, please take a look at this WWDC session. In the case of Stable Diffusion, we’ll be using 6-bit palettization, a type of quantization that compresses model weights from a 16-bit floating-point representation to just 6 bits per parameter. The name “palettization” refers to a technique similar to the one used in computer graphics to work with a limited set of colors: the color table (or “palette”) contains a fixed number of colors, and the colors in the image are replaced with the indexes of the closest colors available in the palette. This immediately provides the benefit of drastically reducing storage size, and thus reducing download time and on-device disk use.
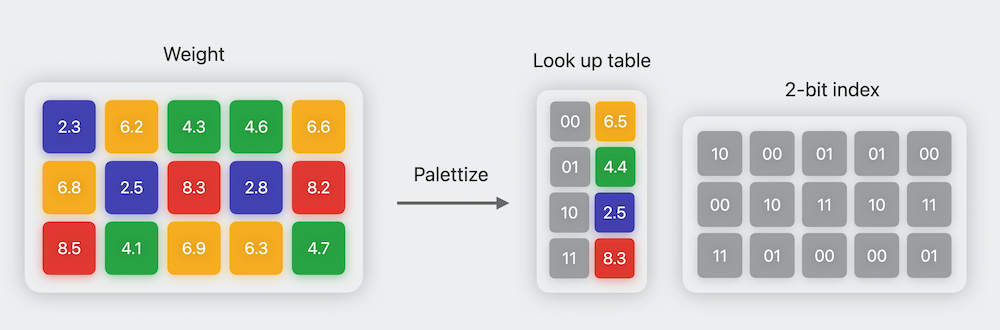 Illustration of 2-bit palettization. Image credit: Apple WWDC’23 Session Use Core ML Tools for machine learning model compression.
Illustration of 2-bit palettization. Image credit: Apple WWDC’23 Session Use Core ML Tools for machine learning model compression.
The compressed 6-bit weights cannot be used for computation, because they are just indices into a table and no longer represent the magnitude of the original weights. Therefore, Core ML needs to uncompress the palletized weights before use. In previous versions of Core ML, uncompression took place when the model was first loaded from disk, so the amount of memory used was equal to the uncompressed model size. With the new improvements, weights are kept as 6-bit numbers and converted on the fly as inference progresses from layer to layer. This might seem slow – an inference run requires a lot of uncompressing operations –, but it’s typically more efficient than preparing all the weights in 16-bit mode! The reason is that memory transfers are in the critical path of execution, and transferring less memory is faster than transferring uncompressed data.
Using Quantized and Optimized Stable Diffusion Models
Last December, Apple introduced ml-stable-diffusion, an open-source repo based on diffusers to easily convert Stable Diffusion models to Core ML. It also applies optimizations to the transformers attention layers that make inference faster on the Neural Engine (on devices where it’s available). ml-stable-diffusion has just been updated after WWDC with the following:
- Quantization is supported using
--quantize-nbitsduring conversion. You can quantize to 8, 6, 4, or even 2 bits! For best results, we recommend using 6-bit quantization, as the precision loss is small while achieving fast inference and significant memory savings. If you want to go lower than that, please check this section for advanced techniques. - Additional optimizations of the attention layers that achieve even better performance on the Neural Engine! The trick is to split the query sequences into chunks of 512 to avoid the creation of large intermediate tensors. This method is called
SPLIT_EINSUM_V2in the code and can improve performance between 10% to 30%.
In order to make it easy for everyone to take advantage of these improvements, we have converted the four official Stable Diffusion models and pushed them to the Hub. These are all the variants:
| Model | Uncompressed | Palettized |
|---|---|---|
| Stable Diffusion 1.4 | Core ML, float16 |
Core ML, 6-bit palettized |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 | Core ML, float16 |
Core ML, 6-bit palettized |
| Stable Diffusion 2 base | Core ML, float16 |
Core ML, 6-bit palettized |
| Stable Diffusion 2.1 base | Core ML, float16 |
Core ML, 6-bit palettized |
In order to use 6-bit models, you need the development versions of iOS/iPadOS 17 or macOS 14 (Sonoma) because those are the ones that contain the latest Core ML framework. You can download them from the Apple developer site if you are a registered developer, or you can sign up for the public beta that will be released in a few weeks.
Note that each variant is available in Core ML format and also as a zip archive. Zip files are ideal for native apps, such as our open-source demo app and other third party tools. If you just want to run the models on your own hardware, the easiest way is to use our demo app and select the quantized model you want to test. You need to compile the app using Xcode, but an update will be available for download in the App Store soon. For more details, check our previous post.
 Running 6-bit stable-diffusion-2-1-base model in demo app
Running 6-bit stable-diffusion-2-1-base model in demo app
If you want to download a particular Core ML package to integrate it in your own Xcode project, you can clone the repos or just download the version of interest using code like the following.
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
from pathlib import Path
repo_id = "apple/coreml-stable-diffusion-2-1-base-palettized"
variant = "original/packages"
model_path = Path("./models") / (repo_id.split("/")[-1] + "_" + variant.replace("/", "_"))
snapshot_download(repo_id, allow_patterns=f"{variant}/*", local_dir=model_path, local_dir_use_symlinks=False)
print(f"Model downloaded at {model_path}")
Converting and Optimizing Custom Models
If you want to use a personalized Stable Diffusion model (for example, if you have fine-tuned or dreamboothed your own models), you can use Apple’s ml-stable-diffusion repo to do the conversion yourself. This is a brief summary of how you’d go about it, but we recommend you read the documentation details.
If you want to apply quantization, you need the latest versions of coremltools, apple/ml-stable-diffusion and Xcode in order to do the conversion.
- Download
coremltools7.0 beta from the releases page in GitHub. - Download Xcode 15.0 beta from Apple developer site.
- Download
apple/ml-stable-diffusionfrom the repo and follow the installation instructions.
- Select the model you want to convert. You can train your own or choose one from the Hugging Face Diffusers Models Gallery. For example, let’s convert
prompthero/openjourney-v4. - Install
apple/ml-stable-diffusionand run a first conversion using theORIGINALattention implementation like this:
python -m python_coreml_stable_diffusion.torch2coreml \
--model-version prompthero/openjourney-v4 \
--convert-unet \
--convert-text-encoder \
--convert-vae-decoder \
--convert-vae-encoder \
--convert-safety-checker \
--quantize-nbits 6 \
--attention-implementation ORIGINAL \
--compute-unit CPU_AND_GPU \
--bundle-resources-for-swift-cli \
--check-output-correctness \
-o models/original/openjourney-6-bit
- Use
--convert-vae-encoderif you want to use image-to-image tasks. - Do not use
--chunk-unetwith--quantized-nbits 6(or less), as the quantized model is small enough to work fine on both iOS and macOS.
- Repeat the conversion for the
SPLIT_EINSUM_V2attention implementation:
python -m python_coreml_stable_diffusion.torch2coreml \
--model-version prompthero/openjourney-v4 \
--convert-unet \
--convert-text-encoder \
--convert-vae-decoder \
--convert-safety-checker \
--quantize-nbits 6 \
--attention-implementation SPLIT_EINSUM_V2 \
--compute-unit ALL \
--bundle-resources-for-swift-cli \
--check-output-correctness \
-o models/split_einsum_v2/openjourney-6-bit
Test the converted models on the desired hardware. As a rule of thumb, the
ORIGINALversion usually works better on macOS, whereasSPLIT_EINSUM_V2is usually faster on iOS. For more details and additional data points, see these tests contributed by the community on the previous version of Stable Diffusion for Core ML.To integrate the desired model in your own app:
- If you are going to distribute the model inside the app, use the
.mlpackagefiles. Note that this will increase the size of your app binary. - Otherwise, you can use the compiled
Resourcesto download them dynamically when your app starts.
- If you are going to distribute the model inside the app, use the
If you don’t use the --quantize-nbits option, weights will be represented as 16-bit floats. This is compatible with the current version of Core ML so you won’t need to install the betas of iOS, macOS or Xcode.
Using Less than 6 bits
6-bit quantization is a sweet spot between model quality, model size and convenience – you just need to provide a conversion option in order to be able to quantize any pre-trained model. This is an example of post-training compression.
The beta version of coremltools released last week also includes training-time compression methods. The idea here is that you can fine-tune a pre-trained Stable Diffusion model and perform the weights compression while fine-tuning is taking place. This allows you to use 4- or even 2-bit compression while minimizing the loss in quality. The reason this works is because weight clustering is performed using a differentiable algorithm, and therefore we can apply the usual training optimizers to find the quantization table while minimizing model loss.
We have plans to evaluate this method soon, and can’t wait to see how 4-bit optimized models work and how fast they run. If you beat us to it, please drop us a note and we’ll be happy to check 🙂
Conclusion
Quantization methods can be used to reduce the size of Stable Diffusion models, make them run faster on-device and consume less resources. The latest versions of Core ML and coremltools support techniques like 6-bit palettization that are easy to apply and that have a minimal impact on quality. We have added 6-bit palettized models to the Hub, which are small enough to run on both iOS and macOS. We've also shown how you can convert fine-tuned models yourself, and can't wait to see what you do with these tools and techniques!

