Spaces:
Sleeping
title: Sentiment Analysis App
emoji: 🚀
colorFrom: green
colorTo: purple
sdk: streamlit
sdk_version: 1.17.0
app_file: app.py
pinned: false
AI Project: Finetuning Language Models - Toxic Tweets
Hello! This is a project for CS-UY 4613: Artificial Intelligence. I'm providing a step-by-step instruction on finetuning language models for detecting toxic tweets.
Milestone 3
This milestone includes finetuning a language model in HuggingFace for sentiment analysis.
Link to app: https://huggingface.co/spaces/andyqin18/sentiment-analysis-app
Here's the setup block that includes all modules:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import torch
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, TrainingArguments, Trainer
device = torch.device('cuda') if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device('cpu')
1. Prepare Data
First we extract comment strings and labels from train.csv and split them into training data and validation data with a percentage of 80% vs 20%. We also create 2 dictionaries that map labels to integers and back.
df = pd.read_csv("milestone3/comp/train.csv")
train_texts = df["comment_text"].values
labels = df.columns[2:]
id2label = {idx:label for idx, label in enumerate(labels)}
label2id = {label:idx for idx, label in enumerate(labels)}
train_labels = df[labels].values
# Randomly select 20000 samples within the data
np.random.seed(18)
small_train_texts = np.random.choice(train_texts, size=20000, replace=False)
np.random.seed(18)
small_train_labels_idx = np.random.choice(train_labels.shape[0], size=20000, replace=False)
small_train_labels = train_labels[small_train_labels_idx, :]
# Separate training data and validation data
train_texts, val_texts, train_labels, val_labels = train_test_split(small_train_texts, small_train_labels, test_size=.2)
2. Data Preprocessing
As models like BERT don't expect text as direct input, but rather input_ids, etc., we tokenize the text using the tokenizer. The AutoTokenizer will automatically load the appropriate tokenizer based on the checkpoint on the hub. We can now merge the labels and texts to datasets as a class we defined.
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
class TextDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,texts,labels):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
def __getitem__(self,idx):
encodings = tokenizer(self.texts[idx], truncation=True, padding="max_length")
item = {key: torch.tensor(val) for key, val in encodings.items()}
item['labels'] = torch.tensor(self.labels[idx],dtype=torch.float32)
del encodings
return item
def __len__(self):
return len(self.labels)
train_dataset = TextDataset(train_texts, train_labels)
val_dataset = TextDataset(val_texts, val_labels)
3. Train the model using Trainer
We define a model that includes a pre-trained base and also set the problem to multi_label_classification. Then we train the model using Trainer, which requires TrainingArguments beforehand that specify training hyperparameters, where we can set learning rate, batch sizes and push_to_hub=True.
After verifying Token with HuggingFace, the model is now pushed to the hub.
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased",
problem_type="multi_label_classification",
num_labels=len(labels),
id2label=id2label,
label2id=label2id)
model.to(device)
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="finetuned-bert-uncased",
evaluation_strategy = "epoch",
save_strategy = "epoch",
learning_rate=2e-5,
per_device_train_batch_size=16,
per_device_eval_batch_size=16,
num_train_epochs=5,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
push_to_hub=True
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=val_dataset,
tokenizer=tokenizer
)
trainer.train()
trainer.push_to_hub()
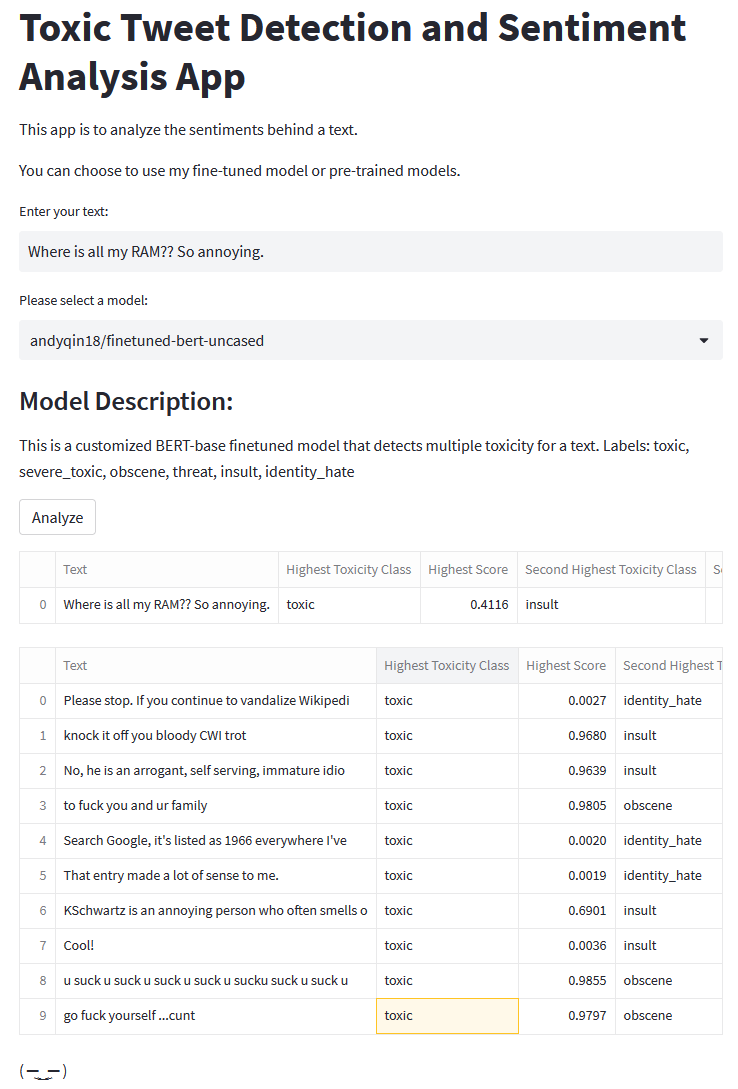
4. Update the app
Modify app.py so that it takes in one text and generate an analysis using one of the provided models. Details are explained in comment lines. The app should look like this: