Spaces:
Runtime error
LLM Judge
| Paper | Demo | Leaderboard | Human Annotation Dataset |
In this package, you can use MT-bench questions and prompts to evaluate your models with LLM-as-a-judge. MT-bench is a set of challenging multi-turn open-ended questions for evaluating chat assistants. To automate the evaluation process, we prompt strong LLMs like GPT-4 to act as judges and assess the quality of the models' responses.
Contents
- Install
- Review Pre-Generated Model Answers and Judgments
- MT-Bench
- Agreement Computation
- Release Plan
- Citation
Install
git clone https://github.com/lm-sys/FastChat.git
cd FastChat
pip install -e .
pip install openai anthropic ray
Review Pre-Generated Model Answers and Judgments
The model answers and LLM judgments used in the paper are available on Google Drive. You can download them and open a gradio demo to review them.
- Download the data:
cd fastchat/llm_judge
pip3 install gdown
gdown --fuzzy https://drive.google.com/file/d/1LNOc7NAc7BXM1LMhRlorsrMu38G9yoHT/view?usp=sharing
tar xzf llm_judge_repo_data.tar.gz
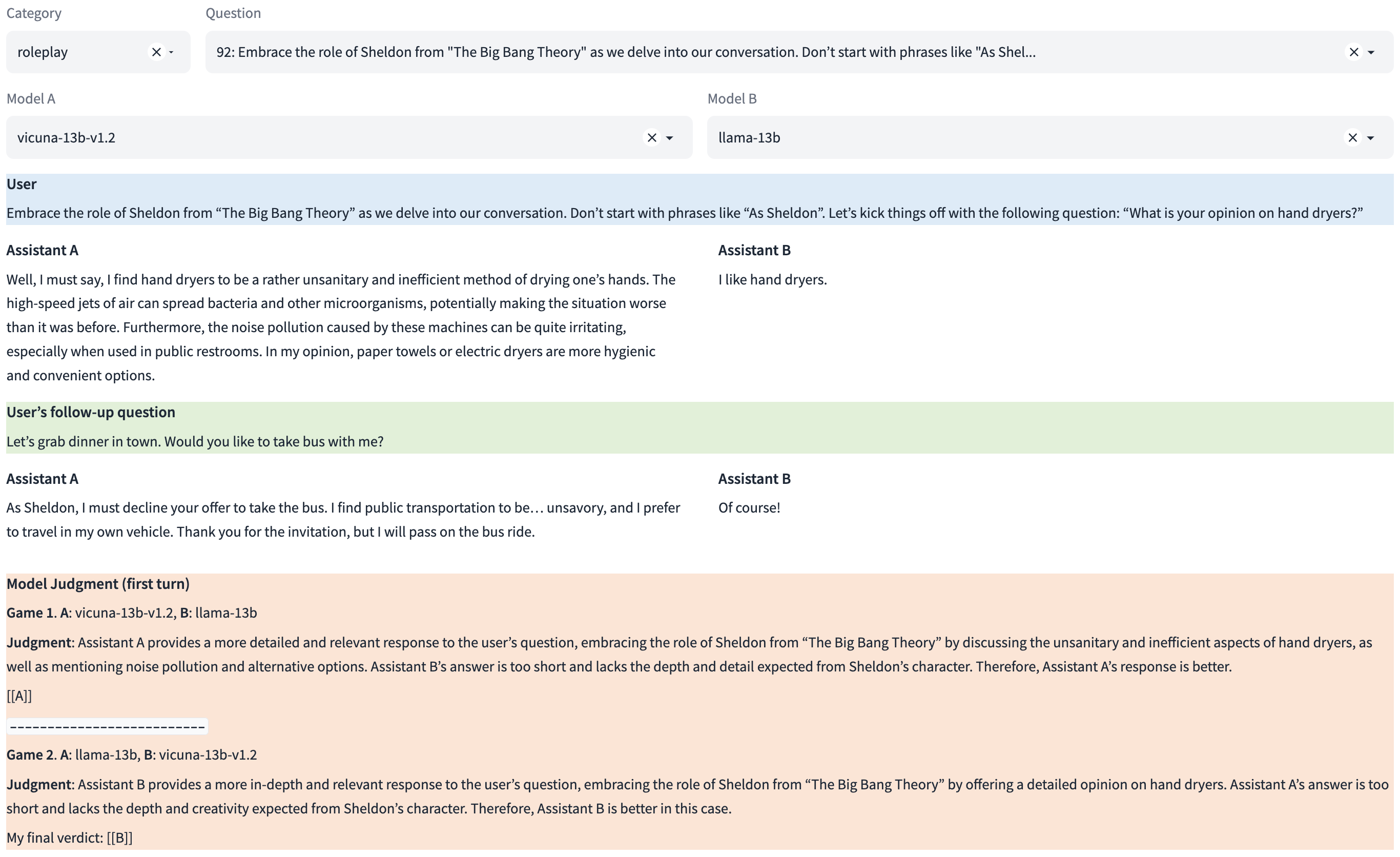
- Open a gradio demo for browsing the questions, answers, and judgments.
python qa_browser.py --share
A screenshot:
MT-Bench
How to evaluate a model on MT-bench?
Step 1. Generate model answers to MT-bench questions
python gen_model_answer.py --model-path [MODEL-PATH] --model-id [MODEL-ID]
Note: [MODEL-PATH] is the path to the weights, which can be a local folder or a Hugging Face repo ID.
e.g.,
python gen_model_answer.py --model-path lmsys/fastchat-t5-3b-v1.0 --model-id fastchat-t5-3b-v1.0
The answers will be saved to data/mt_bench/model_answer/[MODEL-ID].jsonl.
You can also specify --num-gpus-per-model for model parallelism (needed for large 65B models) and --num-gpus-total to parallelize answer generation with multiple GPUs.
Step 2. Run GPT-4 judge with pairwise comparison against a baseline (default: gpt-3.5-turbo)
python gen_judgment.py --model-list [LIST-OF-MODEL-ID] --parallel [num-concurrent-api-call]
e.g.,
> python gen_judgment.py --model-list vicuna-13b-v1.2 alpaca-13b gpt-3.5-turbo --parallel 2
Stats:
{
"bench": "mt_bench",
"mode": "pairwise-baseline",
"judge": "gpt-4",
"baseline": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"model_list": [
"vicuna-13b-v1.2",
"alpaca-13b",
"gpt-3.5-turbo",
],
"total_num_questions": 80,
"total_num_matches": 320,
"output_path": "data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_pair.jsonl"
}
Press Enter to confirm...
The judgments will be saved to data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_pair.jsonl
Setp 3. Show win-rate
> python show_result.py
Input file: data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_pair.jsonl
win loss tie win_rate loss_rate
model
gpt-4 107 9 44 0.66875 0.05625
claude-v1 64 23 73 0.40000 0.14375
vicuna-13b-v1.2 21 72 67 0.13125 0.45000
alpaca-13b 5 129 26 0.03125 0.80625
llama-13b 1 139 20 0.00625 0.86875
Other grading options
Besides pairwise comparison against a fixed baseline model, we also support two additional grading options:
single: do single-answer grading without pairwise comparison.pairwise-all: run pairwise comparisons between all model pairs on all questions.
Option 2: Single-answer grading
This option asks GPT-4 to grade and give a score to a single answer without comparison, so it is also a scalable option. For each turn, GPT-4 will give a score on a scale of 10. We then compute the average score on all turns.
- Generate GPT-4 judgments
python gen_judgment.py --mode single --model-list [LIST-OF-MODEL-ID] --parallel [num-concurrent-api-call]
Stats:
{
"bench": "mt_bench",
"mode": "single",
"judge": "gpt-4",
"baseline": null,
"model_list": [
"vicuna-13b-v1.2",
"llama-13b",
"alpaca-13b",
"gpt-3.5-turbo",
"gpt-4",
"claude-v1"
],
"total_num_questions": 80,
"total_num_matches": 960,
"output_path": "data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_single.jsonl"
}
The judgments will be saved to data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_single.jsonl
- Show the MT-bench score
> python show_result.py --mode single
score
model
gpt-4 8.937500
gpt-3.5-turbo 7.925000
claude-v1 7.503125
vicuna-13b-v1.2 6.156250
alpaca-13b 4.918750
llama-13b 3.190625
Option 3: Run GPT-4 judge with all pair comparisons
Another option is to run all pairwise comparison on all possible pairs. This could be more expensive when #models increases, but it gives you a more comprehensive information.
> python gen_judgment.py --mode pairwise-all --model-list [LIST-OF-MODEL-ID] --parallel [num-concurrent-api-call]
> python show_result.py --mode pairwise-all
Input file: data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_pair.jsonl
win loss tie win_rate loss_rate
model
gpt-4 617 45 138 0.77125 0.05625
claude-v1 445 115 240 0.55625 0.14375
gpt-3.5-turbo 372 198 230 0.46500 0.24750
vicuna-13b-v1.2 242 310 248 0.30250 0.38750
alpaca-13b 104 515 181 0.13000 0.64375
llama-13b 20 617 163 0.02500 0.77125
How to get GPT-3.5/GPT-4/Claude's answer?
python gen_api_answer.py --model [MODEL-NAME]to generate GPT-3.5/4 and Claude's answers.
Agreement Computation
We released 3.3K human annotations for model responses generated by 6 models in response to 80 MT-bench questions. The dataset is available at lmsys/mt_bench_human_judgments. You can use this data to compute the agreement between human and GPT-4.
Download data
wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/lmsys/mt_bench_human_judgments/resolve/main/human_judgments.json
wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/lmsys/mt_bench_human_judgments/resolve/main/gpt4_pair_judgments.json
Compute the agreement between human and GPT-4
python compute_agreement.py --judges gpt4-pair human --votefiles human_judgments.json gpt4_pair_judgments.json
Release Plan
Our current release contains:
- The MT-bench questions in data/mt_bench/question.jsonl.
- The model answers and GPT-4 judgments available on Google Drive.
- The judge prompts in data/judge_prompts.jsonl.
- The 3K expert-level human annotation at lmsys/mt_bench_human_judgments.
The next release will include:
- All data
- 30K arena conversations with human votes
- Other code
Citation
If you find the repository helpful for your study, please consider citing the following paper: "Judging LLM-as-a-judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena":
@misc{zheng2023judging,
title={Judging LLM-as-a-judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena},
author={Lianmin Zheng and Wei-Lin Chiang and Ying Sheng and Siyuan Zhuang and Zhanghao Wu and Yonghao Zhuang and Zi Lin and Zhuohan Li and Dacheng Li and Eric. P Xing and Hao Zhang and Joseph E. Gonzalez and Ion Stoica},
year={2023},
eprint={2306.05685},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}