tags:
- monai
- medical
library_name: monai
license: apache-2.0
Model Overview
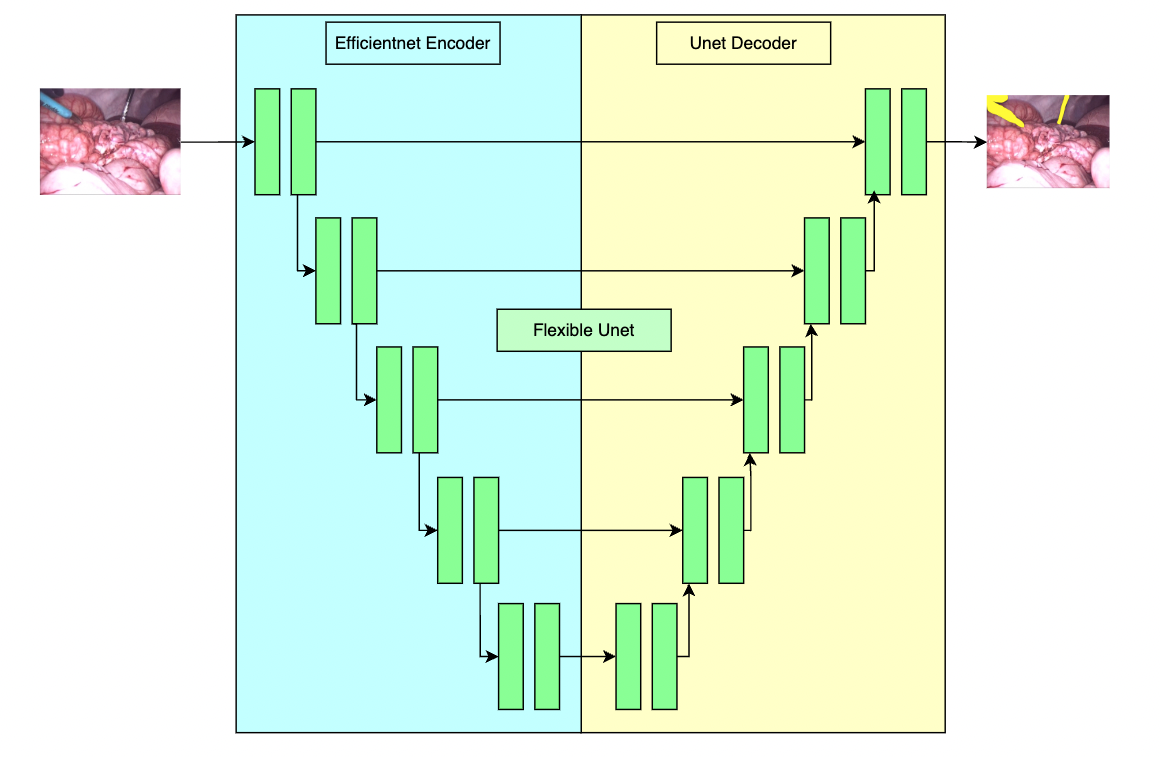
A pre-trained model for the endoscopic tool segmentation task and is trained using a flexible unet structure with an efficient-b2 [1] as the backbone and a UNet architecture [2] as the decoder. Datasets use private samples from Activ Surgical.
The PyTorch model and torchscript model are shared in google drive. Details can be found in large_files.yml file. Modify the "bundle_root" parameter specified in configs/train.json and configs/inference.json to reflect where models are downloaded. Expected directory path to place downloaded models is "models/" under "bundle_root".
Data
Datasets used in this work were provided by Activ Surgical.
Since datasets are private, existing public datasets like EndoVis 2017 can be used to train a similar model.
Preprocessing
When using EndoVis or any other dataset, it should be divided into "train", "valid" and "test" folders. Samples in each folder would better be images and converted to jpg format. Otherwise, "images", "labels", "val_images" and "val_labels" parameters in "configs/train.json" and "datalist" in "configs/inference.json" should be modified to fit given dataset. After that, "dataset_dir" parameter in "configs/train.json" and "configs/inference.json" should be changed to root folder which contains previous "train", "valid" and "test" folders.
Please notice that loading data operation in this bundle is adaptive. If images and labels are not in the same format, it may lead to a mismatching problem. For example, if images are in jpg format and labels are in npy format, PIL and Numpy readers will be used separately to load images and labels. Since these two readers have their own way to parse file's shape, loaded labels will be transpose of the correct ones and incur a missmatching problem.
Training configuration
The training as performed with the following:
- GPU: At least 12GB of GPU memory
- Actual Model Input: 736 x 480 x 3
- Optimizer: Adam
- Learning Rate: 1e-4
Input
A three channel video frame
Output
Two channels:
- Label 1: tools
- Label 0: everything else
Performance
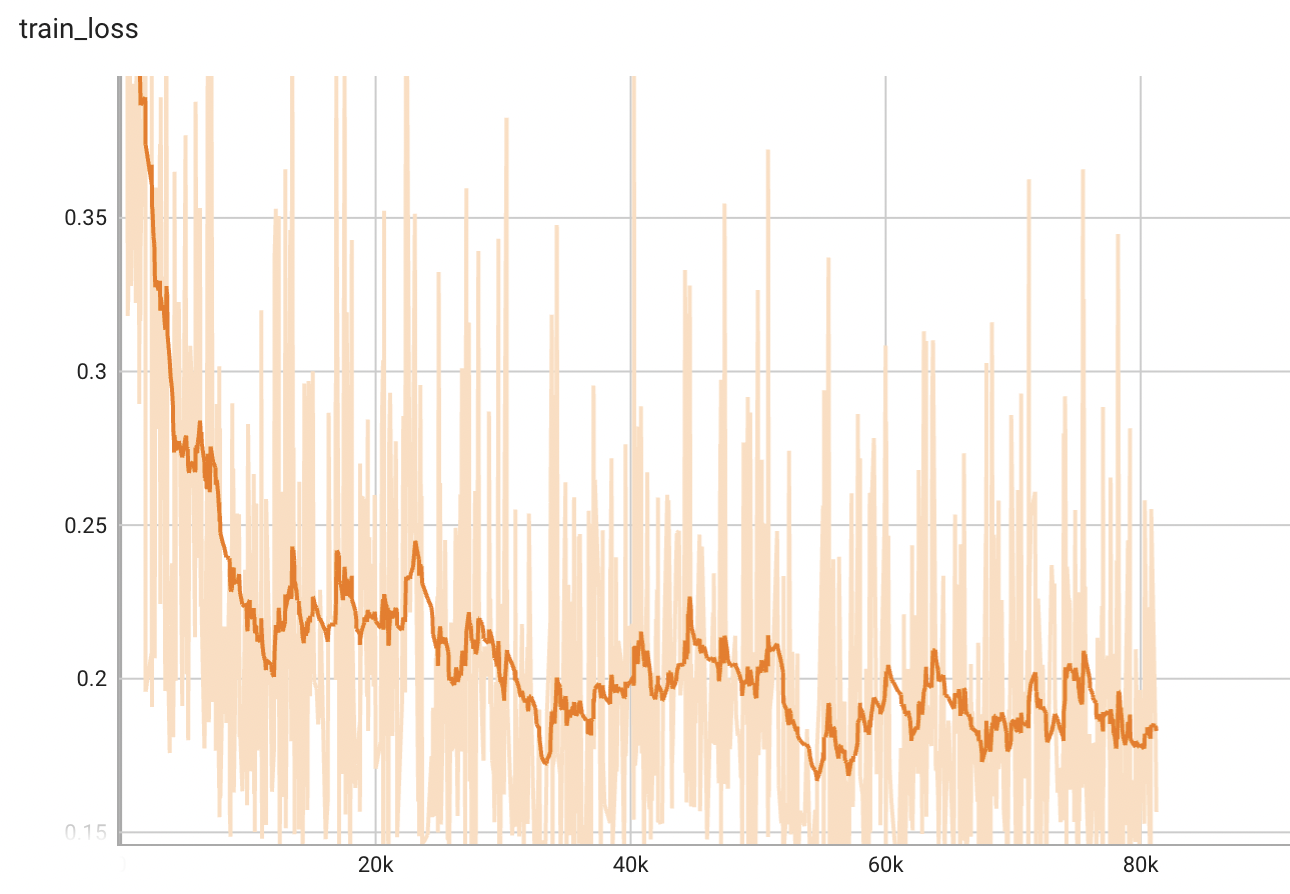
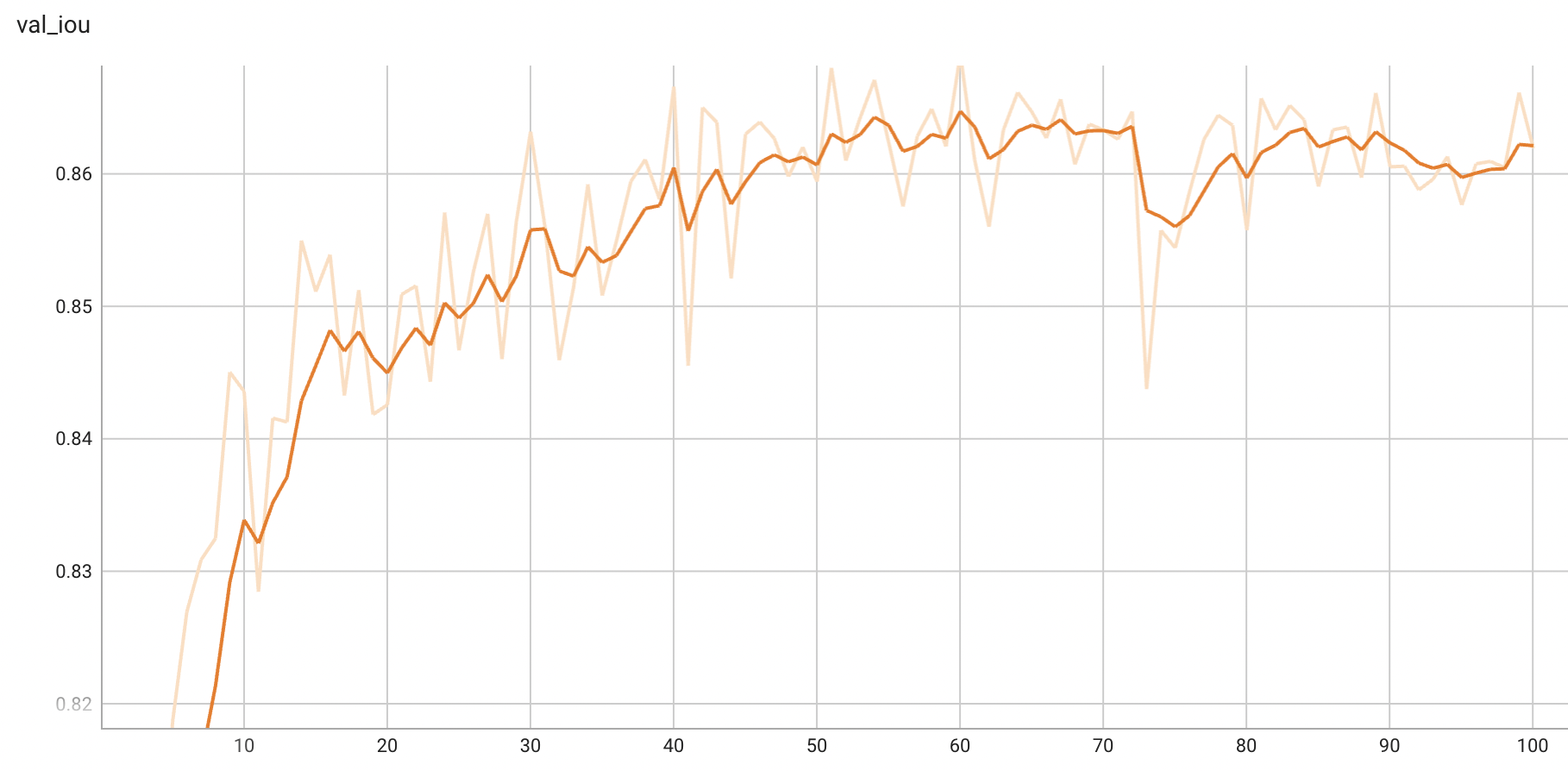
IoU was used for evaluating the performance of the model. This model achieves a mean IoU score of 0.87.
Training Loss
Validation IoU
TensorRT speedup
The endoscopic_tool_segmentation bundle supports the TensorRT acceleration. The table below shows the speedup ratios benchmarked on an A100 80G GPU, in which the model computation means the speedup ratio of model's inference with a random input without preprocessing and postprocessing and the end2end means run the bundle end to end with the TensorRT based model. The torch_fp32 and torch_amp is for the pytorch model with or without amp mode. The trt_fp32 and trt_fp16 is for the TensorRT based model converted in corresponding precision. The speedup amp, speedup fp32 and speedup fp16 is the speedup ratio of corresponding models versus the pytorch float32 model, while the amp vs fp16 is between the pytorch amp model and the TensorRT float16 based model.
| method | torch_fp32(ms) | torch_amp(ms) | trt_fp32(ms) | trt_fp16(ms) | speedup amp | speedup fp32 | speedup fp16 | amp vs fp16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model computation | 12.00 | 14.06 | 6.59 | 5.20 | 0.85 | 1.82 | 2.31 | 2.70 |
| end2end | 170.04 | 172.20 | 155.26 | 155.57 | 0.99 | 1.10 | 1.09 | 1.11 |
This result is benchmarked under:
- TensorRT: 8.5.3+cuda11.8
- Torch-TensorRT Version: 1.4.0
- CPU Architecture: x86-64
- OS: ubuntu 20.04
- Python version:3.8.10
- CUDA version: 11.8
- GPU models and configuration: A100 80G
MONAI Bundle Commands
In addition to the Pythonic APIs, a few command line interfaces (CLI) are provided to interact with the bundle. The CLI supports flexible use cases, such as overriding configs at runtime and predefining arguments in a file.
For more details usage instructions, visit the MONAI Bundle Configuration Page.
Execute training:
python -m monai.bundle run training --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file configs/train.json --logging_file configs/logging.conf
Override the train config to execute multi-GPU training:
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=2 -m monai.bundle run training --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/multi_gpu_train.json']" --logging_file configs/logging.conf
Please note that the distributed training-related options depend on the actual running environment; thus, users may need to remove --standalone, modify --nnodes, or do some other necessary changes according to the machine used. For more details, please refer to pytorch's official tutorial.
Override the train config to execute evaluation with the trained model:
python -m monai.bundle run evaluating --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/evaluate.json']" --logging_file configs/logging.conf
Override the train config and evaluate config to execute multi-GPU evaluation:
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=2 -m monai.bundle run evaluating --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/evaluate.json','configs/multi_gpu_evaluate.json']" --logging_file configs/logging.conf
Execute inference:
python -m monai.bundle run evaluating --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file configs/inference.json --logging_file configs/logging.conf
Export checkpoint to TorchScript file:
python -m monai.bundle ckpt_export network_def --filepath models/model.ts --ckpt_file models/model.pt --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file configs/inference.json
Export checkpoint to TensorRT based models with fp32 or fp16 precision:
python -m monai.bundle trt_export --net_id network_def --filepath models/model_trt.ts --ckpt_file models/model.pt --meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file configs/inference.json --precision <fp32/fp16>
References
[1] Tan, M. and Le, Q. V. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. ICML, 2019a. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.11946.pdf
[2] O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, and T. Brox. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pages 234–241. Springer, 2015. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.04597.pdf
License
Copyright (c) MONAI Consortium
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.