創建自己的數據集
有時,不存在合適的數據集適用於您構建 NLP 應用,因此您需要自己創建。在本節中,我們將向您展示如何創建一個GitHub issues的語料庫,GitHub issues通常用於跟蹤 GitHub 存儲庫中的錯誤或功能。該語料庫可用於各種目的,包括:
- 探索關閉未解決的issue或拉取請求需要多長時間
- 訓練一個多標籤分類器可以根據issue的描述(例如,“錯誤”、“增強”或“issue”)用元數據標記issue
- 創建語義搜索引擎以查找與用戶查詢匹配的issue
在這裡,我們將專注於創建語料庫,在下一節中,我們將探索語義搜索。我們將使用與流行的開源項目相關的 GitHub issue:🤗 Datasets!接下來讓我們看看如何獲取數據並探索這些issue中包含的信息。
獲取數據
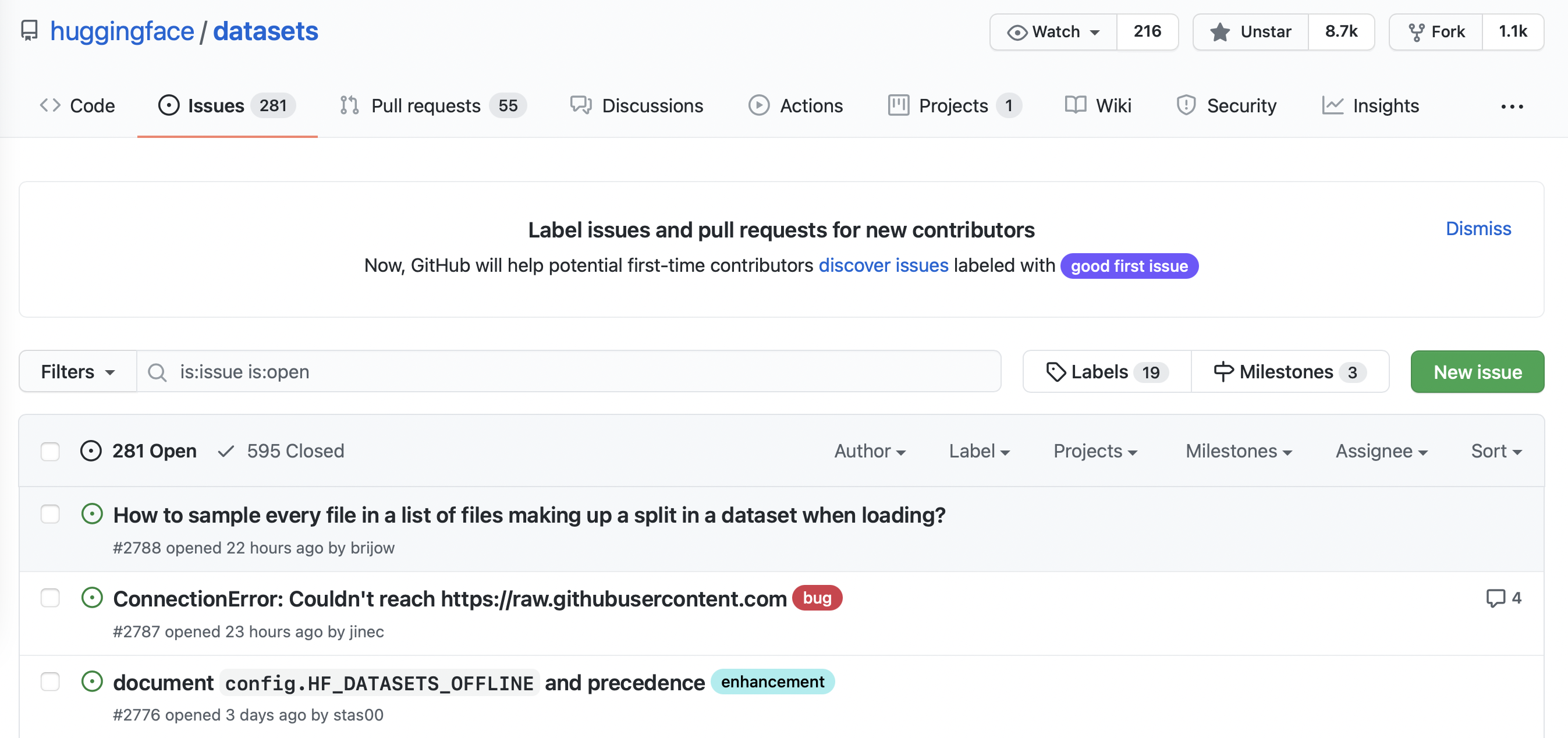
您可以瀏覽 🤗 Datasets 中的所有issueIssues tab.如以下屏幕截圖所示,在撰寫本文時,有 331 個未解決的issue和 668 個已關閉的issue。
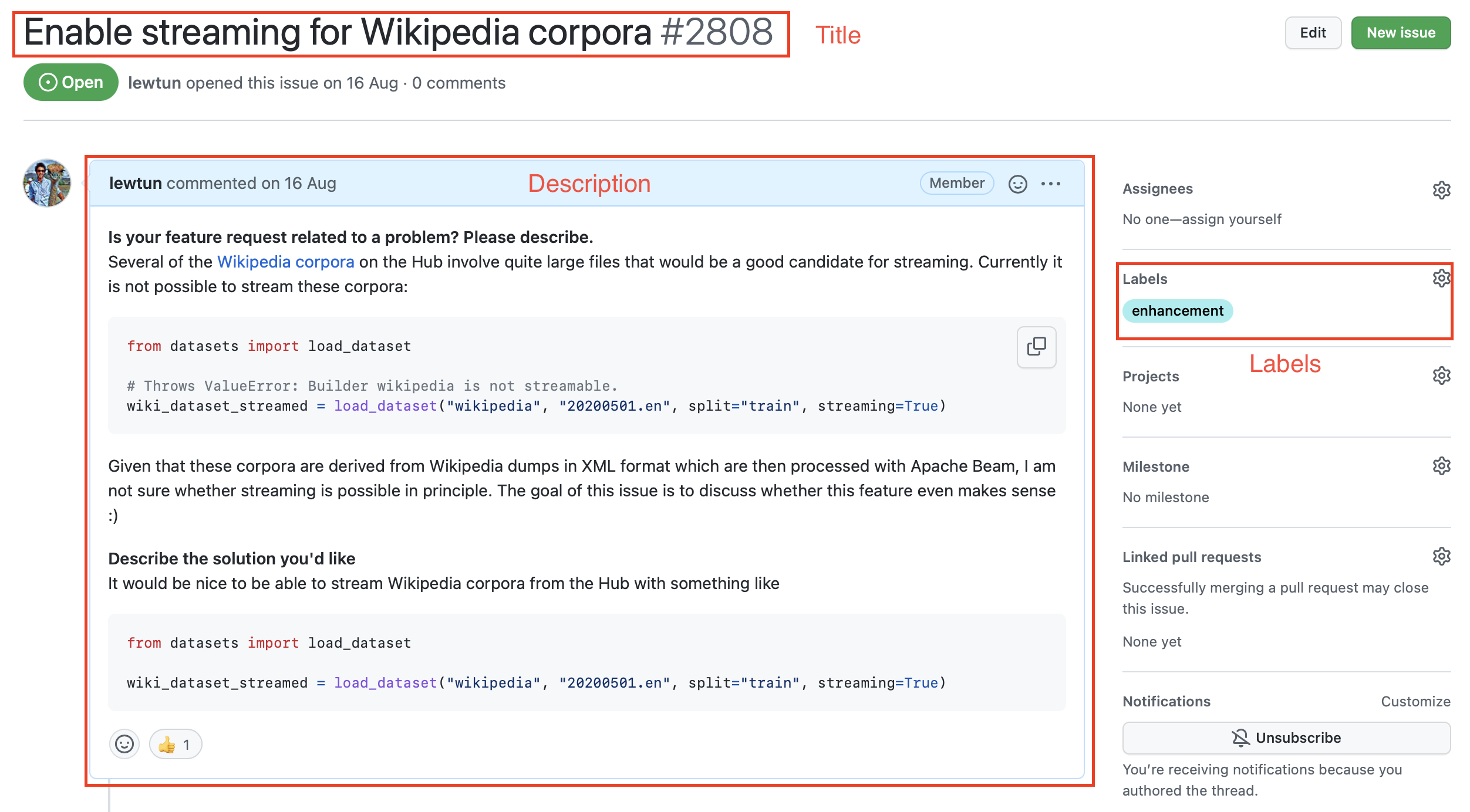
如果您單擊其中一個issue,您會發現它包含一個標題、一個描述和一組表徵該issue的標籤。下面的屏幕截圖顯示了一個示例.
要下載所有存儲庫的issue,我們將使用GitHub REST API投票Issues endpoint.此節點返回一個 JSON 對象列表,每個對象包含大量字段,其中包括標題和描述以及有關issue狀態的元數據等。
下載issue的一種便捷方式是通過 requests 庫,這是用 Python 中發出 HTTP 請求的標準方式。您可以通過運行以下的代碼來安裝庫:
!pip install requests
安裝庫後,您通過調用 requests.get() 功能來獲取Issues節點。例如,您可以運行以下命令來獲取第一頁上的第一個Issues:
import requests
url = "https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues?page=1&per_page=1"
response = requests.get(url)這 response 對象包含很多關於請求的有用信息,包括 HTTP 狀態碼:
response.status_code
200其中一個狀態碼 200 表示請求成功(您可以在這裡找到可能的 HTTP 狀態代碼列表)。然而,我們真正感興趣的是有效的信息,由於我們知道我們的issues是 JSON 格式,讓我們按如下方式查看所有的信息:
response.json()
[{'url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/2792',
'repository_url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets',
'labels_url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/2792/labels{/name}',
'comments_url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/2792/comments',
'events_url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/2792/events',
'html_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/2792',
'id': 968650274,
'node_id': 'MDExOlB1bGxSZXF1ZXN0NzEwNzUyMjc0',
'number': 2792,
'title': 'Update GooAQ',
'user': {'login': 'bhavitvyamalik',
'id': 19718818,
'node_id': 'MDQ6VXNlcjE5NzE4ODE4',
'avatar_url': 'https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/19718818?v=4',
'gravatar_id': '',
'url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik',
'html_url': 'https://github.com/bhavitvyamalik',
'followers_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/followers',
'following_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/following{/other_user}',
'gists_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/gists{/gist_id}',
'starred_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/starred{/owner}{/repo}',
'subscriptions_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/subscriptions',
'organizations_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/orgs',
'repos_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/repos',
'events_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/events{/privacy}',
'received_events_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/received_events',
'type': 'User',
'site_admin': False},
'labels': [],
'state': 'open',
'locked': False,
'assignee': None,
'assignees': [],
'milestone': None,
'comments': 1,
'created_at': '2021-08-12T11:40:18Z',
'updated_at': '2021-08-12T12:31:17Z',
'closed_at': None,
'author_association': 'CONTRIBUTOR',
'active_lock_reason': None,
'pull_request': {'url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/pulls/2792',
'html_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/2792',
'diff_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/2792.diff',
'patch_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/2792.patch'},
'body': '[GooAQ](https://github.com/allenai/gooaq) dataset was recently updated after splits were added for the same. This PR contains new updated GooAQ with train/val/test splits and updated README as well.',
'performed_via_github_app': None}]哇,這是很多信息!我們可以看到有用的字段,例如 標題 , 內容 , 參與的成員, issue的描述信息,以及打開issue的GitHub 用戶的信息。
✏️ 試試看!單擊上面 JSON 中的幾個 URL,以瞭解每個 GitHub issue中我url鏈接到的實際的地址。
如 GitHub文檔 中所述,未經身份驗證的請求限制為每小時 60 個請求。雖然你可以增加 per_page 查詢參數以減少您發出的請求數量,您仍然會遭到任何超過幾千個issue的存儲庫的速率限制。因此,您應該關注 GitHub 的創建個人身份令牌,創建一個個人訪問令牌這樣您就可以將速率限制提高到每小時 5,000 個請求。獲得令牌後,您可以將其包含在請求標頭中:
GITHUB_TOKEN = xxx # Copy your GitHub token here
headers = {"Authorization": f"token {GITHUB_TOKEN}"}⚠️ 不要與陌生人共享存在GITHUB令牌的筆記本。我們建議您在使用完後將GITHUB令牌刪除,以避免意外洩漏此信息。一個更好的做法是,將令牌存儲在.env文件中,並使用 python-dotenv library 為您自動將其作為環境變量加載。
現在我們有了訪問令牌,讓我們創建一個可以從 GitHub 存儲庫下載所有issue的函數:
import time
import math
from pathlib import Path
import pandas as pd
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
def fetch_issues(
owner="huggingface",
repo="datasets",
num_issues=10_000,
rate_limit=5_000,
issues_path=Path("."),
):
if not issues_path.is_dir():
issues_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
batch = []
all_issues = []
per_page = 100 # Number of issues to return per page
num_pages = math.ceil(num_issues / per_page)
base_url = "https://api.github.com/repos"
for page in tqdm(range(num_pages)):
# Query with state=all to get both open and closed issues
query = f"issues?page={page}&per_page={per_page}&state=all"
issues = requests.get(f"{base_url}/{owner}/{repo}/{query}", headers=headers)
batch.extend(issues.json())
if len(batch) > rate_limit and len(all_issues) < num_issues:
all_issues.extend(batch)
batch = [] # Flush batch for next time period
print(f"Reached GitHub rate limit. Sleeping for one hour ...")
time.sleep(60 * 60 + 1)
all_issues.extend(batch)
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(all_issues)
df.to_json(f"{issues_path}/{repo}-issues.jsonl", orient="records", lines=True)
print(
f"Downloaded all the issues for {repo}! Dataset stored at {issues_path}/{repo}-issues.jsonl"
)現在我們可以調用 fetch_issues() 批量下載所有issue,避免超過GitHub每小時的請求數限制;結果將存儲在repository_name-issues.jsonl文件,其中每一行都是一個 JSON 對象,代表一個issue。讓我們使用這個函數從 🤗 Datasets中抓取所有issue:
# Depending on your internet connection, this can take several minutes to run...
fetch_issues()下載issue後,我們可以使用我們 section 2新學會的方法在本地加載它們:
issues_dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files="datasets-issues.jsonl", split="train")
issues_datasetDataset({
features: ['url', 'repository_url', 'labels_url', 'comments_url', 'events_url', 'html_url', 'id', 'node_id', 'number', 'title', 'user', 'labels', 'state', 'locked', 'assignee', 'assignees', 'milestone', 'comments', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'closed_at', 'author_association', 'active_lock_reason', 'pull_request', 'body', 'timeline_url', 'performed_via_github_app'],
num_rows: 3019
})太好了,我們已經從頭開始創建了我們的第一個數據集!但是為什麼會有幾千個issue,而🤗 Datasets存儲庫中的Issues 選項卡總共卻只顯示了大約 1,000 個issue🤔?如 GitHub 文檔中所述,那是因為我們也下載了所有的拉取請求:
Git Hub的REST API v3認為每個pull請求都是一個issue,但並不是每個issue都是一個pull請求。因此,“Issues”節點可能在響應中同時返回issue和拉取請求。你可以通過pull_request 的 key來辨別pull請求。請注意,從“Issues”節點返回的pull請求的id將是一個issue id。
由於issue和pull request的內容有很大的不同,我們先做一些小的預處理,讓我們能夠區分它們。
清理數據
上面來自 GitHub 文檔的片段告訴我們, pull_request 列可用於區分issue和拉取請求。讓我們隨機挑選一些樣本,看看有什麼不同。我們將使用在第三節, 學習的方法,使用 Dataset.shuffle() 和 Dataset.select() 抽取一個隨機樣本,然後將 html_url 和 pull_request 列使用zip函數打包,以便我們可以比較各種 URL:
sample = issues_dataset.shuffle(seed=666).select(range(3))
# Print out the URL and pull request entries
for url, pr in zip(sample["html_url"], sample["pull_request"]):
print(f">> URL: {url}")
print(f">> Pull request: {pr}\n")>> URL: https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/850
>> Pull request: {'url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/pulls/850', 'html_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/850', 'diff_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/850.diff', 'patch_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/850.patch'}
>> URL: https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/issues/2773
>> Pull request: None
>> URL: https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/783
>> Pull request: {'url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/pulls/783', 'html_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/783', 'diff_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/783.diff', 'patch_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/783.patch'}這裡我們可以看到,每個pull請求都與各種url相關聯,而普通issue只有一個None條目。我們可以使用這一點不同來創建一個新的is_pull_request列通過檢查pull_request字段是否為None來區分它們:
issues_dataset = issues_dataset.map(
lambda x: {"is_pull_request": False if x["pull_request"] is None else True}
)✏️ 試試看!計算在 🤗 Datasets中解決issue所需的平均時間。您可能會發現 Dataset.filter()函數對於過濾拉取請求和未解決的issue很有用,並且您可以使用Dataset.set_format()函數將數據集轉換為DataFrame,以便您可以輕鬆地按照需求修改創建和關閉的時間的格式(以時間戳格式)。
儘管我們可以通過刪除或重命名某些列來進一步清理數據集,但在此階段儘可能保持數據集“原始”狀態通常是一個很好的做法,以便它可以在多個應用程序中輕鬆使用。在我們將數據集推送到 Hugging Face Hub 之前,讓我們再添加一些缺少的數據:與每個issue和拉取請求相關的評論。我們接下來將添加它們——你猜對了——我們將依然使用GitHub REST API!
擴充數據集
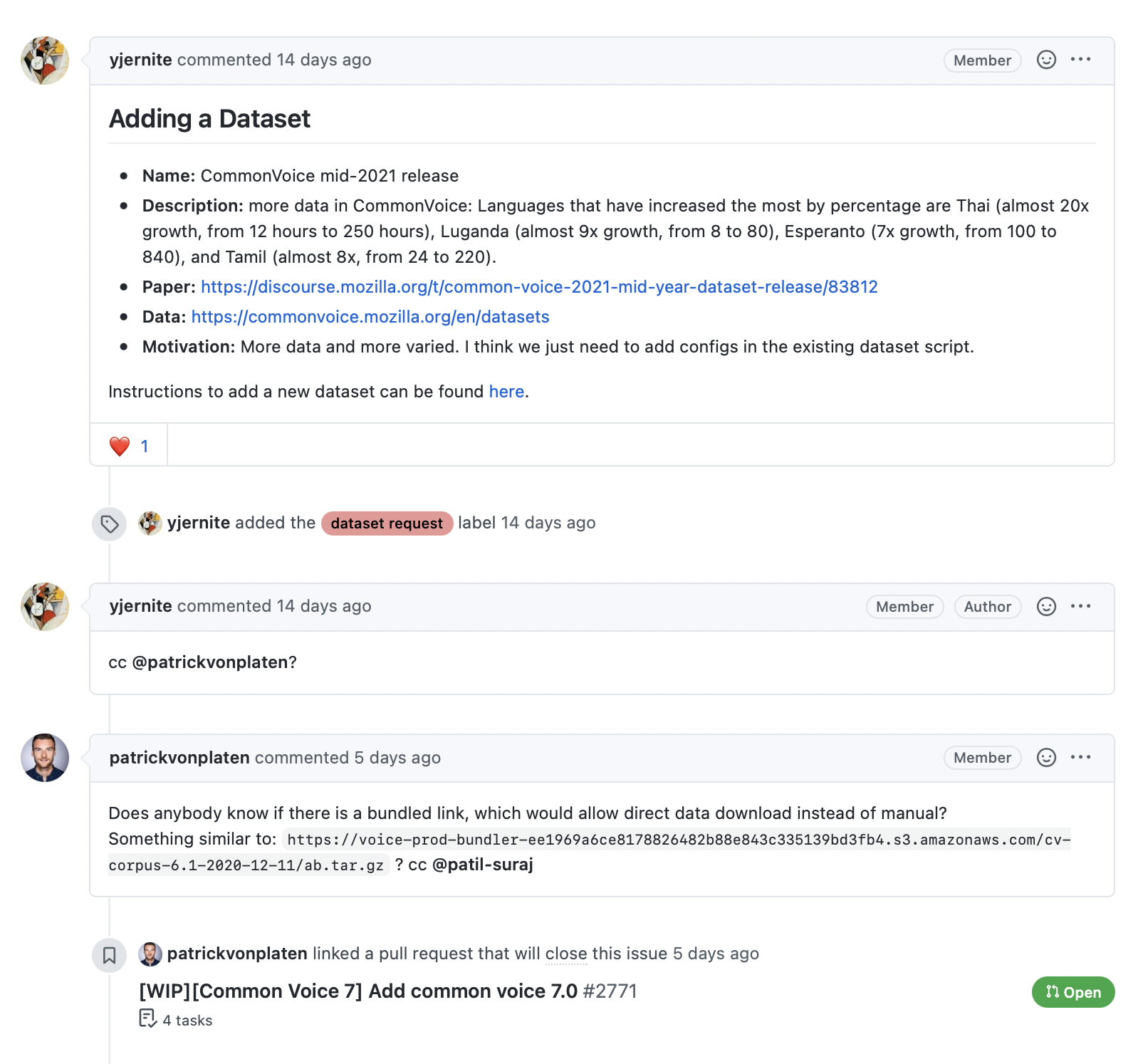
如以下屏幕截圖所示,與issue或拉取請求相關的評論提供了豐富的信息,特別是如果我們有興趣構建搜索引擎來回答用戶對這個項目的疑問。
GitHub REST API 提供了一個 評論節點 返回與issue編號相關的所有評論。讓我們測試節點以查看它返回的內容:
issue_number = 2792
url = f"https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/{issue_number}/comments"
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.json()[{'url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/comments/897594128',
'html_url': 'https://github.com/huggingface/datasets/pull/2792#issuecomment-897594128',
'issue_url': 'https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/2792',
'id': 897594128,
'node_id': 'IC_kwDODunzps41gDMQ',
'user': {'login': 'bhavitvyamalik',
'id': 19718818,
'node_id': 'MDQ6VXNlcjE5NzE4ODE4',
'avatar_url': 'https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/19718818?v=4',
'gravatar_id': '',
'url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik',
'html_url': 'https://github.com/bhavitvyamalik',
'followers_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/followers',
'following_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/following{/other_user}',
'gists_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/gists{/gist_id}',
'starred_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/starred{/owner}{/repo}',
'subscriptions_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/subscriptions',
'organizations_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/orgs',
'repos_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/repos',
'events_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/events{/privacy}',
'received_events_url': 'https://api.github.com/users/bhavitvyamalik/received_events',
'type': 'User',
'site_admin': False},
'created_at': '2021-08-12T12:21:52Z',
'updated_at': '2021-08-12T12:31:17Z',
'author_association': 'CONTRIBUTOR',
'body': "@albertvillanova my tests are failing here:\r\n```\r\ndataset_name = 'gooaq'\r\n\r\n def test_load_dataset(self, dataset_name):\r\n configs = self.dataset_tester.load_all_configs(dataset_name, is_local=True)[:1]\r\n> self.dataset_tester.check_load_dataset(dataset_name, configs, is_local=True, use_local_dummy_data=True)\r\n\r\ntests/test_dataset_common.py:234: \r\n_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ \r\ntests/test_dataset_common.py:187: in check_load_dataset\r\n self.parent.assertTrue(len(dataset[split]) > 0)\r\nE AssertionError: False is not true\r\n```\r\nWhen I try loading dataset on local machine it works fine. Any suggestions on how can I avoid this error?",
'performed_via_github_app': None}]我們可以看到註釋存儲在body字段中,所以讓我們編寫一個簡單的函數,通過在response.json()中為每個元素挑選body內容來返回與某個issue相關的所有評論:
def get_comments(issue_number):
url = f"https://api.github.com/repos/huggingface/datasets/issues/{issue_number}/comments"
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
return [r["body"] for r in response.json()]
# Test our function works as expected
get_comments(2792)["@albertvillanova my tests are failing here:\r\n```\r\ndataset_name = 'gooaq'\r\n\r\n def test_load_dataset(self, dataset_name):\r\n configs = self.dataset_tester.load_all_configs(dataset_name, is_local=True)[:1]\r\n> self.dataset_tester.check_load_dataset(dataset_name, configs, is_local=True, use_local_dummy_data=True)\r\n\r\ntests/test_dataset_common.py:234: \r\n_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ \r\ntests/test_dataset_common.py:187: in check_load_dataset\r\n self.parent.assertTrue(len(dataset[split]) > 0)\r\nE AssertionError: False is not true\r\n```\r\nWhen I try loading dataset on local machine it works fine. Any suggestions on how can I avoid this error?"]這看起來不錯,所以讓我們使用 Dataset.map() 方法在我們數據集中每個issue的添加一個comments列:
# Depending on your internet connection, this can take a few minutes...
issues_with_comments_dataset = issues_dataset.map(
lambda x: {"comments": get_comments(x["number"])}
)最後一步是將增強數據集與原始數據保存在一起,以便我們可以將它們都推送到 Hub:
issues_with_comments_dataset.to_json("issues-datasets-with-comments.jsonl")將數據集上傳到 Hugging Face Hub
現在我們有了我們的增強數據集,是時候將它推送到 Hub 並且與社區共享它!要上傳數據集,我們將使用🤗 Hub 庫,它允許我們通過 Python API 與 Hugging Face Hub 進行交互。 🤗 Hub 預裝了🤗 Transformers,所以我們可以直接使用它。例如,我們可以使用 list_datasets() 獲取有關當前託管在 Hub 上的所有公共數據集的信息的函數:
from huggingface_hub import list_datasets
all_datasets = list_datasets()
print(f"Number of datasets on Hub: {len(all_datasets)}")
print(all_datasets[0])Number of datasets on Hub: 1487
Dataset Name: acronym_identification, Tags: ['annotations_creators:expert-generated', 'language_creators:found', 'languages:en', 'licenses:mit', 'multilinguality:monolingual', 'size_categories:10K<n<100K', 'source_datasets:original', 'task_categories:structure-prediction', 'task_ids:structure-prediction-other-acronym-identification']我們可以看到 Hub 上目前有近 1,500 個數據集, list_datasets() 函數還提供了有關每個數據集存儲庫的一些基本元數據。
為了上傳我們的數據集,我們需要做的第一件事是在 Hub 上創建一個新的數據集存儲庫。為此,我們需要一個身份驗證令牌,可以通過首先使用notebook_login() 函數登錄 Hugging Face Hub 獲得:
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()這將創建一個小部件,您可以在其中輸入您的用戶名和密碼, API 令牌將保存在~/.huggingface/令牌.如果您在終端中運行代碼,則可以改為通過 CLI 登錄:
huggingface-cli login
完成此操作後,我們可以創建一個新的數據集存儲庫 create_repo() 功能:
from huggingface_hub import create_repo
repo_url = create_repo(name="github-issues", repo_type="dataset")
repo_url'https://huggingface.co/datasets/lewtun/github-issues'在此示例中,我們創建了一個名為的空數據集存儲庫 github-issues 在下面 lewtun 用戶名(當您運行此代碼時,用戶名應該是您的 Hub 用戶名!)。
✏️ 試試看!使用您的 Hugging Face Hub 用戶名和密碼獲取令牌並創建一個名為 github-issues.請記住永遠不要將您的憑據保存在 Colab 或任何其他存儲庫中,因為這些信息可能會被不法分子利用。
接下來,讓我們將存儲庫從 Hub 克隆到我們的本地機器,並將我們的數據集文件複製到其中。 🤗 Hub 提供了一個方便的 Repository 類,它包含許多常見 Git 命令的類,因此要克隆遠程存儲庫,我們只需要提供我們要克隆的 URL 和本地路徑:
from huggingface_hub import Repository
repo = Repository(local_dir="github-issues", clone_from=repo_url)
!cp datasets-issues-with-comments.jsonl github-issues/默認情況下,使用Git LFS跟蹤各種文件擴展名(如.bin、.gz和.zip),以便在同一Git工作流中對大型文件進行版本控制。您可以在存儲庫的.gitattributes文件找到跟蹤文件擴展名的列表。要在列表中包含JSON行格式,我們可以運行以下命令:
repo.lfs_track("*.jsonl")然後我們可以使用 Repository.push_to_hub() 將數據集推送到 Hub:
repo.push_to_hub()
如果我們導航到包含在 repo_url ,我們現在應該看到我們的數據集文件已經上傳。
從這裡,任何人都可以通過簡單地提供來下載數據集 load_dataset() 以存儲庫 ID 作為 path 爭論:
remote_dataset = load_dataset("lewtun/github-issues", split="train")
remote_datasetDataset({
features: ['url', 'repository_url', 'labels_url', 'comments_url', 'events_url', 'html_url', 'id', 'node_id', 'number', 'title', 'user', 'labels', 'state', 'locked', 'assignee', 'assignees', 'milestone', 'comments', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'closed_at', 'author_association', 'active_lock_reason', 'pull_request', 'body', 'performed_via_github_app', 'is_pull_request'],
num_rows: 2855
})很酷,我們已經將我們的數據集推送到 Hub,其他人可以使用它!只剩下一件重要的事情要做:添加一個數據卡這解釋了語料庫是如何創建的,併為使用數據集的其他提供一些其他有用的信息。
💡 您還可以使用一些 Git 魔法直接從終端將數據集上傳到 Hugging Face Hub。有關如何執行此操作的詳細信息,請參閱 🤗 Datasets guide 指南。
創建數據集卡片
有據可查的數據集更有可能對其他人(包括你未來的自己!)有用,因為它們提供了上下文,使用戶能夠決定數據集是否與他們的任務相關,並評估任何潛在的偏見或與使用相關的風險。在 Hugging Face Hub 上,此信息存儲在每個數據集存儲庫的自述文件文件。在創建此文件之前,您應該執行兩個主要步驟:
- 使用數據集標籤應用程序 創建YAML格式的元數據標籤。這些標籤用於各種各樣的搜索功能,並確保您的數據集可以很容易地被社區成員找到。因為我們已經在這裡創建了一個自定義數據集,所以您需要克隆數據集標籤存儲庫並在本地運行應用程序。它的界面是這樣的:

2.閱讀🤗 Datasets guide 關於創建信息性數據集卡片的指南,並將其作為模板使用。
您可以創建自述文件文件直接在Hub上,你可以在裡面找到模板數據集卡片 lewtun/github-issues 數據集存儲庫。填寫好的數據集卡片的屏幕截圖如下所示。!
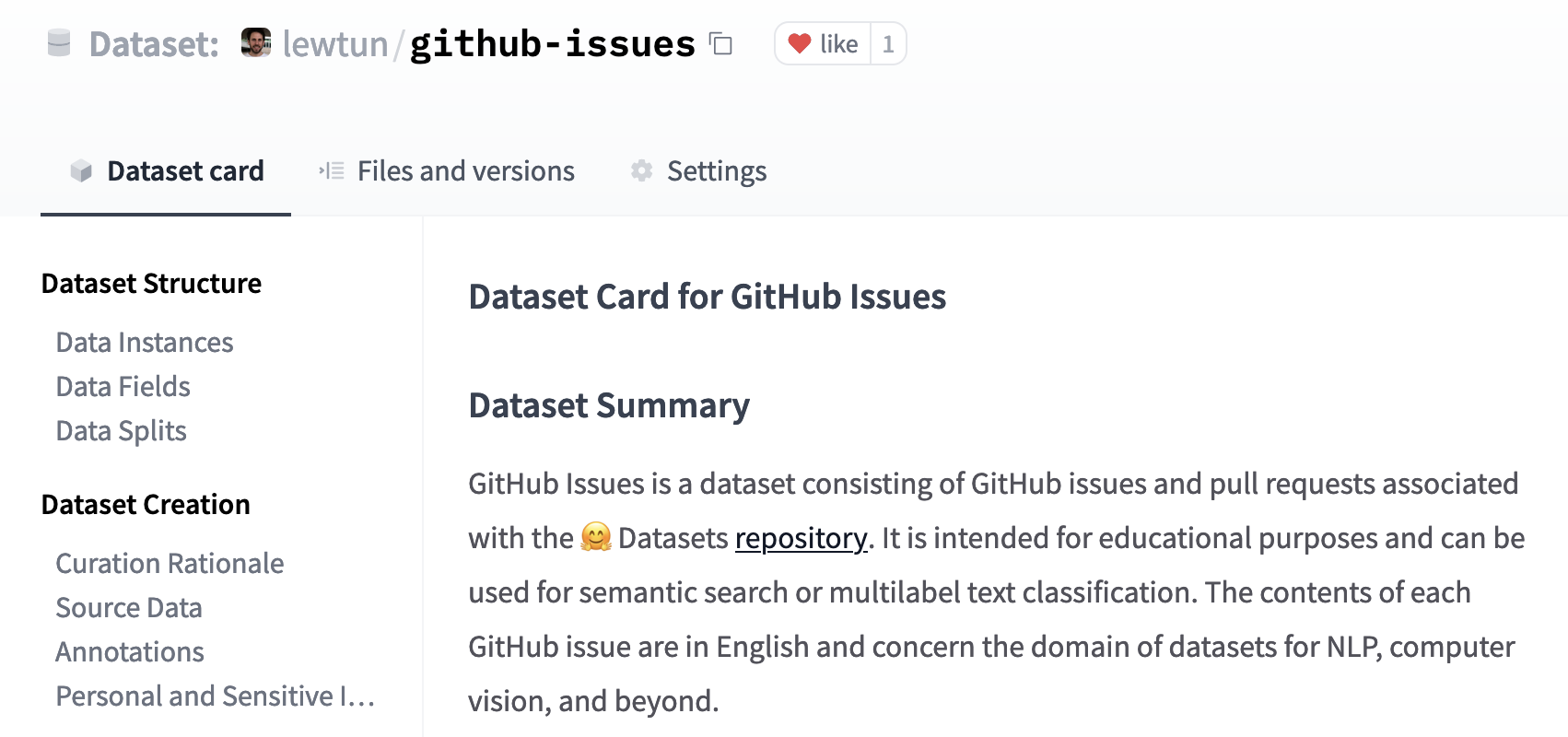
✏️試試看!使用應用程序和 🤗 Datasets guide 指南來完成 GitHub issue數據集的 README.md 文件。
很好! 我們在本節中看到,創建一個好的數據集可能非常複雜,但幸運的是,將其上傳並與社區共享會很容易實現。在下一節中,我們將使用我們的新數據集創建一個帶有 🤗 Datasets的語義搜索引擎,該數據集可以將issue與最相關的issue和評論進行匹配。
✏️ 試試看!按照我們在本節中採取的步驟為您最喜歡的開源庫創建一個 GitHub issue數據集(當然,選擇 🤗 Datasets以外的其他東西!)。對於獎勵積分,微調多標籤分類器以預測該領域中存在的標籤。
