TRL documentation
Examples of using peft with trl to finetune 8-bit models with Low Rank Adaption (LoRA)
Examples of using peft with trl to finetune 8-bit models with Low Rank Adaption (LoRA)
The notebooks and scripts in this examples show how to use Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to fine-tune models in a memory efficient manner. Most of PEFT methods supported in peft library but note that some PEFT methods such as Prompt tuning are not supported. For more information on LoRA, see the original paper.
Here’s an overview of the peft-enabled notebooks and scripts in the trl repository:
| File | Task | Description |
|---|---|---|
gpt2-sentiment_peft.py |
Sentiment | Same as the sentiment analysis example, but learning a low rank adapter on a 8-bit base model |
cm_finetune_peft_imdb.py |
Sentiment | Fine tuning a low rank adapter on a frozen 8-bit model for text generation on the imdb dataset. |
merge_peft_adapter.py |
🤗 Hub | Merging of the adapter layers into the base model’s weights and storing these on the hub. |
gpt-neo-20b_sentiment_peft.py |
Sentiment | Sentiment fine-tuning of a low rank adapter to create positive reviews. |
gpt-neo-1b_peft.py |
Sentiment | Sentiment fine-tuning of a low rank adapter to create positive reviews using 2 GPUs. |
stack_llama/rl_training.py |
RLHF | Distributed fine-tuning of the 7b parameter LLaMA models with a learned reward model and peft. |
stack_llama/reward_modeling.py |
Reward Modeling | Distributed training of the 7b parameter LLaMA reward model with peft. |
stack_llama/supervised_finetuning.py |
SFT | Distributed instruction/supervised fine-tuning of the 7b parameter LLaMA model with peft. |
Installation
Note: peft is in active development, so we install directly from their Github page. Peft also relies on the latest version of transformers.pip install trl[peft]
pip install bitsandbytes loralib
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@main
#optional: wandb
pip install wandbNote: if you don’t want to log with wandb remove log_with="wandb" in the scripts/notebooks. You can also replace it with your favourite experiment tracker that’s supported by accelerate.
How to use it?
Simply declare a PeftConfig object in your script and pass it through .from_pretrained to load the TRL+PEFT model.
from peft import LoraConfig
from trl import AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead
model_id = "edbeeching/gpt-neo-125M-imdb"
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=16,
lora_alpha=32,
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
model_id,
peft_config=lora_config,
)And if you want to load your model in 8bit precision:
pretrained_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
config.model_name,
load_in_8bit=True,
peft_config=lora_config,
)… or in 4bit precision:
pretrained_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
config.model_name,
peft_config=lora_config,
load_in_4bit=True,
)Launch scripts
The trl library is powered by accelerate. As such it is best to configure and launch trainings with the following commands:
accelerate config # will prompt you to define the training configuration
accelerate launch scripts/gpt2-sentiment_peft.py # launches training
Using trl + peft and Data Parallelism
You can scale up to as many GPUs as you want, as long as you are able to fit the training process in a single device. The only tweak you need to apply is to load the model as follows:
from peft import LoraConfig
...
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=16,
lora_alpha=32,
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
)
pretrained_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
config.model_name,
peft_config=lora_config,
)And if you want to load your model in 8bit precision:
pretrained_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
config.model_name,
peft_config=lora_config,
load_in_8bit=True,
)… or in 4bit precision:
pretrained_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
config.model_name,
peft_config=lora_config,
load_in_4bit=True,
)Finally, make sure that the rewards are computed on correct device as well, for that you can use ppo_trainer.model.current_device.
Naive pipeline parallelism (NPP) for large models (>60B models)
The trl library also supports naive pipeline parallelism (NPP) for large models (>60B models). This is a simple way to parallelize the model across multiple GPUs.
This paradigm, termed as “Naive Pipeline Parallelism” (NPP) is a simple way to parallelize the model across multiple GPUs. We load the model and the adapters across multiple GPUs and the activations and gradients will be naively communicated across the GPUs. This supports int8 models as well as other dtype models.
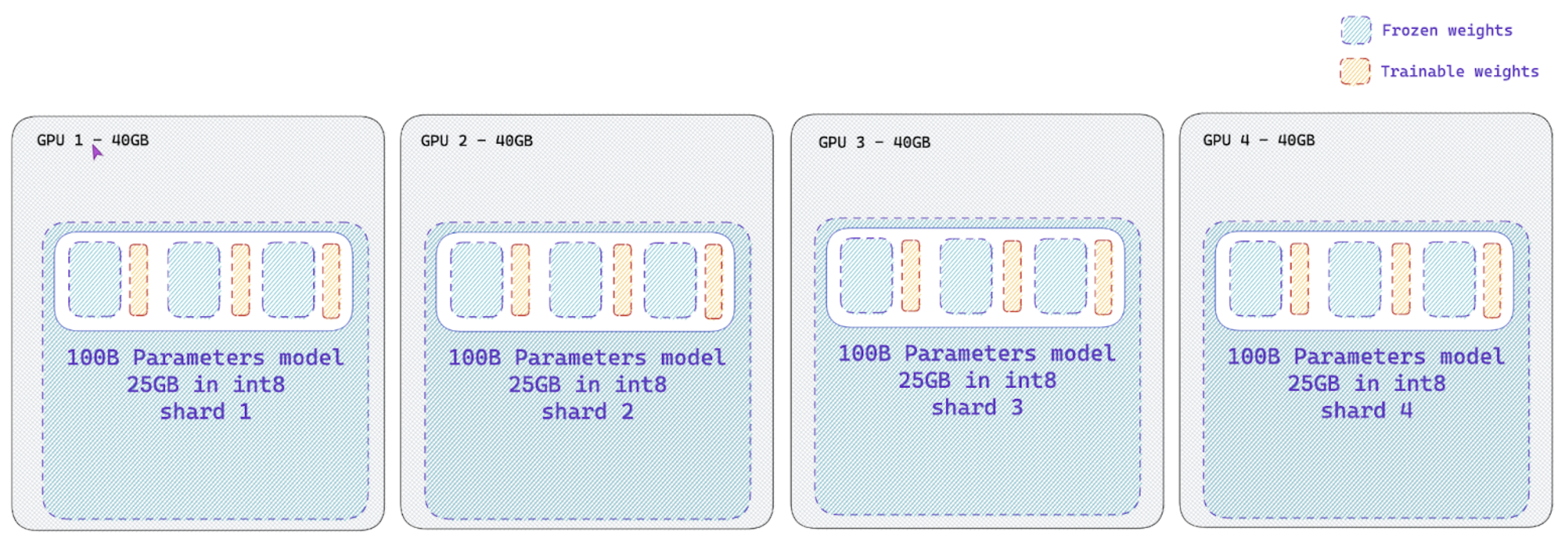
How to use NPP?
Simply load your model with a custom device_map argument on the from_pretrained to split your model across multiple devices. Check out this nice tutorial on how to properly create a device_map for your model.
Also make sure to have the lm_head module on the first GPU device as it may throw an error if it is not on the first device. As this time of writing, you need to install the main branch of accelerate: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git@main and peft: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git@main.
That all you need to do to use NPP. Check out the gpt-neo-1b_peft.py example for a more details usage of NPP.
Launch scripts
Although trl library is powered by accelerate, you should run your training script in a single process. Note that we do not support Data Parallelism together with NPP yet.
python PATH_TO_SCRIPT