Transformers documentation
LLaVA-NeXT
LLaVA-NeXT



Overview
The LLaVA-NeXT model was proposed in LLaVA-NeXT: Improved reasoning, OCR, and world knowledge by Haotian Liu, Chunyuan Li, Yuheng Li, Bo Li, Yuanhan Zhang, Sheng Shen, Yong Jae Lee. LLaVa-NeXT (also called LLaVa-1.6) improves upon LLaVa by increasing the input image resolution and training on an improved visual instruction tuning dataset to improve OCR and common sense reasoning.
The introduction from the blog is the following:
*In October 2023, we released LLaVA-1.5 with a simple and efficient design along with great performance on a benchmark suite of 12 datasets. It has since served as the foundation of many comprehensive studies of data, model, and capabilities of large multimodal models (LMM), and has enabled various new applications.
Today, we are thrilled to present LLaVA-NeXT, with improved reasoning, OCR, and world knowledge. LLaVA-NeXT even exceeds Gemini Pro on several benchmarks.
Compared with LLaVA-1.5, LLaVA-NeXT has several improvements:
Increasing the input image resolution to 4x more pixels. This allows it to grasp more visual details. It supports three aspect ratios, up to 672x672, 336x1344, 1344x336 resolution. Better visual reasoning and OCR capability with an improved visual instruction tuning data mixture. Better visual conversation for more scenarios, covering different applications. Better world knowledge and logical reasoning. Efficient deployment and inference with SGLang. Along with performance improvements, LLaVA-NeXT maintains the minimalist design and data efficiency of LLaVA-1.5. It re-uses the pretrained connector of LLaVA-1.5, and still uses less than 1M visual instruction tuning samples. The largest 34B variant finishes training in ~1 day with 32 A100s.*
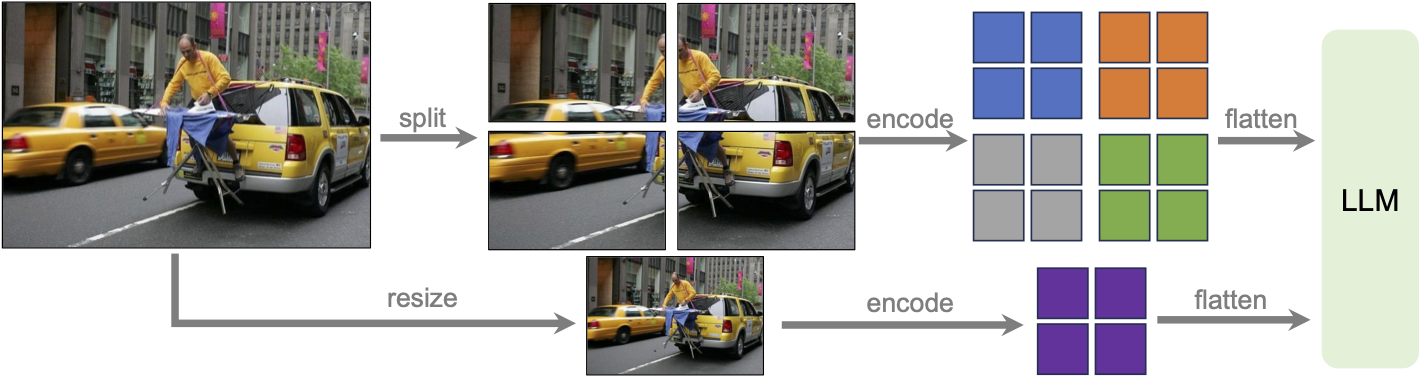 LLaVa-NeXT incorporates a higher input resolution by encoding various patches of the input image. Taken from the original paper.
LLaVa-NeXT incorporates a higher input resolution by encoding various patches of the input image. Taken from the original paper. This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Usage tips
- We advise users to use
padding_side="left"when computing batched generation as it leads to more accurate results. Simply make sure to callprocessor.tokenizer.padding_side = "left"before generating.
- Llava-Next uses different number of patches for images and thus has to pad the inputs inside modeling code, aside from the padding done when processing the inputs. The default setting is “left-padding” if model is in
eval()mode, otherwise “right-padding”.
[!NOTE] LLaVA models after release v4.46 will raise warnings about adding
processor.patch_size = {{patch_size}},processor.num_additional_image_tokens = {{num_additional_image_tokens}}and processor.vision_feature_select_strategy = {{vision_feature_select_strategy}}. It is strongly recommended to add the attributes to the processor if you own the model checkpoint, or open a PR if it is not owned by you. Adding these attributes means that LLaVA will try to infer the number of image tokens required per image and expand the text with as many<image>placeholders as there will be tokens. Usually it is around 500 tokens per image, so make sure that the text is not truncated as otherwise there will be failure when merging the embeddings. The attributes can be obtained from model config, asmodel.config.vision_config.patch_sizeormodel.config.vision_feature_select_strategy. Thenum_additional_image_tokensshould be1if the vision backbone adds a CLS token or0` if nothing extra is added to the vision patches.
Formatting Prompts with Chat Templates
Each checkpoint is trained with a specific prompt format, depending on the underlying large language model backbone. To ensure correct formatting, use the processor’s apply_chat_template method.
Important:
- You must construct a conversation history — passing a plain string won’t work.
- Each message should be a dictionary with
"role"and"content"keys. - The
"content"should be a list of dictionaries for different modalities like"text"and"image".
Here’s an example of how to structure your input. We will use llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf and a conversation history of text and image.
from transformers import LlavaNextProcessor
processor = LlavaNextProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf")
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What’s shown in this image?"},
],
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": [{"type": "text", "text": "This image shows a red stop sign."},]
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe the image in more details."},
],
},
]
text_prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
# Note that the template simply formats your prompt, you still have to tokenize it and obtain pixel values for your images
print(text_prompt)
>>> "[INST] <image>\nWhat's shown in this image? [/INST] This image shows a red stop sign. [INST] Describe the image in more details. [/INST]"- If you want to construct a chat prompt yourself, below is a list of possible formats . llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf requires the following format:
"[INST] <image>\nWhat is shown in this image? [/INST]"llava-v1.6-vicuna-7b-hf and llava-v1.6-vicuna-13b-hf require the following format:
"A chat between a curious human and an artificial intelligence assistant. The assistant gives helpful, detailed, and polite answers to the human's questions. USER: <image>\nWhat is shown in this image? ASSISTANT:"llava-v1.6-34b-hf requires the following format:
"<|im_start|>system\nAnswer the questions.<|im_end|><|im_start|>user\n<image>\nWhat is shown in this image?<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistant\n"llama3-llava-next-8b-hf requires the following format:
"<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>\n\nYou are a helpful language and vision assistant. You are able to understand the visual content that the user provides, and assist the user with a variety of tasks using natural language.<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>\n\n<image>\nWhat is shown in this image?<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>\n\n"llava-next-72b-hf and llava-next-110b-hf require the following format:
"<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n<image>\nWhat is shown in this image?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n"🚀 Bonus: If you’re using transformers>=4.49.0, you can also get a vectorized output from apply_chat_template. See the Usage Examples below for more details on how to use it.
Usage example
Single image inference
Here’s how to load the model and perform inference in half-precision (torch.float16):
from transformers import LlavaNextProcessor, LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration
import torch
from PIL import Image
import requests
processor = LlavaNextProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf")
model = LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
model.to("cuda:0")
# prepare image and text prompt, using the appropriate prompt template
url = "https://github.com/haotian-liu/LLaVA/blob/1a91fc274d7c35a9b50b3cb29c4247ae5837ce39/images/llava_v1_5_radar.jpg?raw=true"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"},
],
},
]
prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
inputs = processor(image, prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda:0")
# autoregressively complete prompt
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100)
print(processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))Multi image inference
LLaVa-Next can perform inference with multiple images as input, where images either belong to the same prompt or different prompts (in batched inference). Here is how you can do it:
import requests
from PIL import Image
import torch
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForImageTextToText
# Load the model in half-precision
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf")
# Get three different images
url = "https://www.ilankelman.org/stopsigns/australia.jpg"
image_stop = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
image_cats = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
url = "https://huggingface.co/microsoft/kosmos-2-patch14-224/resolve/main/snowman.jpg"
image_snowman = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
# Prepare a batch of two prompts, where the first one is a multi-turn conversation and the second is not
conversation_1 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"},
],
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "There is a red stop sign in the image."},
],
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What about this image? How many cats do you see?"},
],
},
]
conversation_2 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"},
],
},
]
prompt_1 = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation_1, add_generation_prompt=True)
prompt_2 = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation_2, add_generation_prompt=True)
prompts = [prompt_1, prompt_2]
# We can simply feed images in the order they have to be used in the text prompt
# Each "<image>" token uses one image leaving the next for the subsequent "<image>" tokens
inputs = processor(images=[image_stop, image_cats, image_snowman], text=prompts, padding=True, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# Generate
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=30)
processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)Model optimization
Quantization using Bitsandbytes
The model can be loaded in 8 or 4 bits, greatly reducing the memory requirements while maintaining the performance of the original model. First make sure to install bitsandbytes, pip install bitsandbytes, and to have access to a GPU/accelerator that is supported by the library.
bitsandbytes is being refactored to support multiple backends beyond CUDA. Currently, ROCm (AMD GPU) and Intel CPU implementations are mature, with Intel XPU in progress and Apple Silicon support expected by Q4/Q1. For installation instructions and the latest backend updates, visit this link.
We value your feedback to help identify bugs before the full release! Check out these docs for more details and feedback links.
Simply change the snippet above with:
from transformers import AutoModelForImageTextToText, BitsAndBytesConfig
# specify how to quantize the model
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,
)
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf", quantization_config=quantization_config, device_map="auto")Use Flash-Attention 2 to further speed-up generation
First make sure to install flash-attn. Refer to the original repository of Flash Attention regarding that package installation. Simply change the snippet above with:
from transformers import AutoModelForImageTextToText
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
model_id,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
use_flash_attention_2=True
).to(0)LlavaNextConfig
class transformers.LlavaNextConfig
< source >( vision_config = None text_config = None image_token_index = 32000 projector_hidden_act = 'gelu' vision_feature_select_strategy = 'default' vision_feature_layer = -2 image_grid_pinpoints = None tie_word_embeddings = False image_seq_length = 576 multimodal_projector_bias = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- vision_config (
Union[AutoConfig, dict], optional, defaults toCLIPVisionConfig) — The config object or dictionary of the vision backbone. - text_config (
Union[AutoConfig, dict], optional, defaults toLlamaConfig) — The config object or dictionary of the text backbone. - image_token_index (
int, optional, defaults to 32000) — The image token index to encode the image prompt. - projector_hidden_act (
str, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The activation function used by the multimodal projector. - vision_feature_select_strategy (
str, optional, defaults to"default") — The feature selection strategy used to select the vision feature from the vision backbone. Can be one of"default"or"full". If"default", the CLS token is removed from the vision features. If"full", the full vision features are used. - vision_feature_layer (
Union[int, list[int]], optional, defaults to -2) — The index of the layer to select the vision feature. If multiple indices are provided, the vision feature of the corresponding indices will be concatenated to form the vision features. - image_grid_pinpoints (
List, optional, defaults to[[336, 672], [672, 336], [672, 672], [1008, 336], [336, 1008]]) — A list of possible resolutions to use for processing high resolution images. Each item in the list should be a tuple or list of the form(height, width). - tie_word_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether the model’s input and output word embeddings should be tied. - image_seq_length (
int, optional, defaults to 576) — Sequence length of one image embedding. - multimodal_projector_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to use bias in the multimodal projector.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration. It is used to instantiate an Llava-NeXT model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf model.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration, LlavaNextConfig, CLIPVisionConfig, LlamaConfig
>>> # Initializing a CLIP-vision config
>>> vision_config = CLIPVisionConfig()
>>> # Initializing a Llama config
>>> text_config = LlamaConfig()
>>> # Initializing a Llava-Next llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf style configuration
>>> configuration = LlavaNextConfig(vision_config, text_config)
>>> # Initializing a model from the llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf style configuration
>>> model = LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configLlavaNextImageProcessor
class transformers.LlavaNextImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None image_grid_pinpoints: typing.Optional[list] = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BICUBIC: 3> do_center_crop: bool = True crop_size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None do_pad: typing.Optional[bool] = True do_convert_rgb: bool = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden bydo_resizein thepreprocessmethod. - size (
dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"shortest_edge" -- 224}): Size of the image after resizing. The shortest edge of the image is resized to size[“shortest_edge”], with the longest edge resized to keep the input aspect ratio. Can be overridden bysizein thepreprocessmethod. - image_grid_pinpoints (
Listoptional, defaults to[[672, 336], [336, 672], [672, 672], [336, 1008], [1008, 336]]) — A list of possible resolutions to use for processing high resolution images. The best resolution is selected based on the original size of the image. Can be overridden byimage_grid_pinpointsin thepreprocessmethod. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toResampling.BICUBIC) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden byresamplein thepreprocessmethod. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to center crop the image to the specifiedcrop_size. Can be overridden bydo_center_cropin thepreprocessmethod. - crop_size (
dict[str, int]optional, defaults to 224) — Size of the output image after applyingcenter_crop. Can be overridden bycrop_sizein thepreprocessmethod. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden bydo_rescalein thepreprocessmethod. - rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden byrescale_factorin thepreprocessmethod. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden bydo_normalizein thepreprocessmethod. - image_mean (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults to[0.48145466, 0.4578275, 0.40821073]) — Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_std (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults to[0.26862954, 0.26130258, 0.27577711]) — Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to pad the image. IfTrue, will pad the patch dimension of the images in the batch to the largest number of patches in the batch. Padding will be applied to the bottom and right with zeros. - do_convert_rgb (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to convert the image to RGB.
Constructs a LLaVa-NeXT image processor. Based on CLIPImageProcessor with incorporation of additional techniques for processing high resolution images as explained in the LLaVa paper.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None image_grid_pinpoints: typing.Optional[list] = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: typing.Optional[bool] = None crop_size: typing.Optional[int] = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None do_pad: typing.Optional[bool] = None do_convert_rgb: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Optional[transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None )
Parameters
- images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the image after resizing. Shortest edge of the image is resized to size[“shortest_edge”], with the longest edge resized to keep the input aspect ratio. - image_grid_pinpoints (
Listoptional, defaults toself.image_grid_pinpoints) — A list of possible resolutions to use for processing high resolution images. The best resolution is selected based on the original size of the image. - resample (
int, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_center_crop) — Whether to center crop the image. - crop_size (
dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — Size of the center crop. Only has an effect ifdo_center_cropis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - image_std (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_pad) — Whether to pad the image. IfTrue, will pad the patch dimension of the images in the batch to the largest number of patches in the batch. Padding will be applied to the bottom and right with zeros. - do_convert_rgb (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_convert_rgb) — Whether to convert the image to RGB. - return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:- Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray. TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
- Unset: Return a list of
- data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.- Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
LlavaNextImageProcessorFast
class transformers.LlavaNextImageProcessorFast
< source >( **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.llava_next.image_processing_llava_next_fast.LlavaNextFastImageProcessorKwargs] )
Constructs a fast Llava Next image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.llava_next.image_processing_llava_next_fast.LlavaNextFastImageProcessorKwargs] ) → <class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
Parameters
- images (
Union[PIL.Image.Image, numpy.ndarray, torch.Tensor, list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']]) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
dict[str, int], optional) — Describes the maximum input dimensions to the model. - default_to_square (
bool, optional) — Whether to default to a square image when resizing, if size is an int. - resample (
Union[PILImageResampling, F.InterpolationMode, NoneType]) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional) — Whether to center crop the image. - crop_size (
dict[str, int], optional) — Size of the output image after applyingcenter_crop. - do_rescale (
bool, optional) — Whether to rescale the image. - rescale_factor (
Union[int, float, NoneType]) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
Union[float, list[float], NoneType]) — Image mean to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - image_std (
Union[float, list[float], NoneType]) — Image standard deviation to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - do_convert_rgb (
bool, optional) — Whether to convert the image to RGB. - return_tensors (
Union[str, ~utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType]) — Returns stacked tensors if set to `pt, otherwise returns a list of tensors. - data_format (
~image_utils.ChannelDimension, optional) — OnlyChannelDimension.FIRSTis supported. Added for compatibility with slow processors. - input_data_format (
Union[str, ~image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType]) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
- device (
torch.device, optional) — The device to process the images on. If unset, the device is inferred from the input images. - disable_grouping (
bool, optional) — Whether to disable grouping of images by size to process them individually and not in batches. If None, will be set to True if the images are on CPU, and False otherwise. This choice is based on empirical observations, as detailed here: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/38157 - image_grid_pinpoints (
list[list[int]], optional) — A list of possible resolutions to use for processing high resolution images. The best resolution is selected based on the original size of the image. Can be overridden byimage_grid_pinpointsin thepreprocessmethod. - do_pad (
bool, optional) — Whether to pad the image. IfTrue, will pad the patch dimension of the images in the batch to the largest number of patches in the batch. Padding will be applied to the bottom and right with zeros.
Returns
<class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
- data (
dict) — Dictionary of lists/arrays/tensors returned by the call method (‘pixel_values’, etc.). - tensor_type (
Union[None, str, TensorType], optional) — You can give a tensor_type here to convert the lists of integers in PyTorch/TensorFlow/Numpy Tensors at initialization.
LlavaNextProcessor
class transformers.LlavaNextProcessor
< source >( image_processor = None tokenizer = None patch_size = None vision_feature_select_strategy = None chat_template = None image_token = '<image>' num_additional_image_tokens = 0 **kwargs )
Parameters
- image_processor (LlavaNextImageProcessor, optional) — The image processor is a required input.
- tokenizer (LlamaTokenizerFast, optional) — The tokenizer is a required input.
- patch_size (
int, optional) — Patch size from the vision tower. - vision_feature_select_strategy (
str, optional) — The feature selection strategy used to select the vision feature from the vision backbone. Should be same as in model’s config - chat_template (
str, optional) — A Jinja template which will be used to convert lists of messages in a chat into a tokenizable string. - image_token (
str, optional, defaults to"<image>") — Special token used to denote image location. - num_additional_image_tokens (
int, optional, defaults to 0) — Number of additional tokens added to the image embeddings, such as CLS (+1). If the backbone has no CLS or other extra tokens appended, no need to set this arg.
Constructs a LLaVa-NeXT processor which wraps a LLaVa-NeXT image processor and a LLaMa tokenizer into a single processor.
LlavaNextProcessor offers all the functionalities of LlavaNextImageProcessor and LlamaTokenizerFast. See the
__call__() and decode() for more information.
This method forwards all its arguments to LlamaTokenizerFast’s batch_decode(). Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
This method forwards all its arguments to LlamaTokenizerFast’s decode(). Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
LlavaNextModel
class transformers.LlavaNextModel
< source >( config: LlavaNextConfig )
Parameters
- config (LlavaNextConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The Llava-Next model which consists of a vision backbone and a language model without language modeling head.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( input_ids: LongTensor = None pixel_values: FloatTensor = None image_sizes: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[list[torch.FloatTensor]] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None vision_feature_layer: typing.Union[int, list[int], NoneType] = None vision_feature_select_strategy: typing.Optional[str] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None cache_position: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.modeling_flash_attention_utils.FlashAttentionKwargs] ) → transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.LlavaNextModelOutputWithPast or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using{image_processor_class}. See{image_processor_class}.__call__for details ({processor_class}uses{image_processor_class}for processing images). - image_sizes (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, 2), optional) — The sizes of the images in the batch, being (height, width) for each image. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
list[torch.FloatTensor], optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.Two formats are allowed:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
The model will output the same cache format that is fed as input. If no
past_key_valuesare passed, the legacy cache format will be returned.If
past_key_valuesare used, the user can optionally input only the lastinput_ids(those that don’t have their past key value states given to this model) of shape(batch_size, 1)instead of allinput_idsof shape(batch_size, sequence_length). - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix. - vision_feature_layer (
Union[int, list[int], NoneType]) — The index of the layer to select the vision feature. If multiple indices are provided, the vision feature of the corresponding indices will be concatenated to form the vision features. - vision_feature_select_strategy (
str, optional, defaults to"default") — The feature selection strategy used to select the vision feature from the vision backbone. Can be one of"default"or"full". If"default", the CLS token is removed from the vision features. If"full", the full vision features are used. - use_cache (
bool, optional) — If set toTrue,past_key_valueskey value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (seepast_key_values). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — Indices depicting the position of the input sequence tokens in the sequence. Contrarily toposition_ids, this tensor is not affected by padding. It is used to update the cache in the correct position and to infer the complete sequence length.
Returns
transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.LlavaNextModelOutputWithPast or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.LlavaNextModelOutputWithPast or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (LlavaNextConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenuse_cache=Trueis passed or whenconfig.use_cache=True) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head))Contains pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks) that can be used (see
past_key_valuesinput) to speed up sequential decoding. -
hidden_states (
tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...], optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...], optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
image_hidden_states (
torch.FloatTensor, optional) — Atorch.FloatTensorof size(batch_size, num_images, sequence_length, hidden_size). image_hidden_states of the model produced by the vision encoder and after projecting the last hidden state.
The LlavaNextModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
get_image_features
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor image_sizes: Tensor vision_feature_layer: typing.Union[int, list[int], NoneType] = None vision_feature_select_strategy: typing.Optional[str] = None ) → image_features (listtorch.Tensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensor]of shape(batch_size, num_patches, channels, height, width)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. - image_sizes (
torch.Tensorof shape(num_images, 2)) — Actual image size of each images (H, W). - vision_feature_layer (
Union[int, list[int]], optional) — The index of the layer to select the vision feature. If multiple indices are provided, the vision feature of the corresponding indices will be concatenated to form the vision features. - vision_feature_select_strategy (
str, optional) — The feature selection strategy used to select the vision feature from the vision backbone. Can be one of"default"or"full"
Returns
image_features (listtorch.Tensor)
List of image feature tensor, each contains all the visual feature of all patches
and are of shape (num_patches, image_length, embed_dim)).
Obtains image last hidden states from the vision tower and apply multimodal projection.
pack_image_features
< source >( image_features image_sizes vision_feature_select_strategy image_newline = None )
Parameters
- image_features (
list[torch.Tensor]of length num_images, each of shape(num_patches, image_length, embed_dim)) — List of image feature tensor, each contains all the visual feature of all patches. - image_sizes (
torch.Tensorof shape(num_images, 2)) — Actual image size of each images (H, W). - vision_feature_select_strategy (
str) — The feature selection strategy used to select the vision feature from the vision backbone. - image_newline (
torch.Tensorof shape(embed_dim)) — New line embedding vector.
Reshape, unpad and then pack each image_feature into a single image_features tensor containing all visual vectors.
LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration
class transformers.LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration
< source >( config: LlavaNextConfig )
Parameters
- config (LlavaNextConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The LLAVA-NeXT model which consists of a vision backbone and a language model.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( input_ids: LongTensor = None pixel_values: FloatTensor = None image_sizes: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[list[torch.FloatTensor]] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None vision_feature_layer: typing.Union[int, list[int], NoneType] = None vision_feature_select_strategy: typing.Optional[str] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None cache_position: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None logits_to_keep: typing.Union[int, torch.Tensor] = 0 **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.KwargsForCausalLM] ) → transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.LlavaNextCausalLMOutputWithPast or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using{image_processor_class}. See{image_processor_class}.__call__for details ({processor_class}uses{image_processor_class}for processing images). - image_sizes (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, 2), optional) — The sizes of the images in the batch, being (height, width) for each image. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - past_key_values (
list[torch.FloatTensor], optional) — Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in thepast_key_valuesreturned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, whenuse_cache=Trueorconfig.use_cache=True.Two formats are allowed:
- a Cache instance, see our kv cache guide;
- Tuple of
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)). This is also known as the legacy cache format.
The model will output the same cache format that is fed as input. If no
past_key_valuesare passed, the legacy cache format will be returned.If
past_key_valuesare used, the user can optionally input only the lastinput_ids(those that don’t have their past key value states given to this model) of shape(batch_size, 1)instead of allinput_idsof shape(batch_size, sequence_length). - inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix. - vision_feature_layer (
Union[int, list[int], NoneType]) — The index of the layer to select the vision feature. If multiple indices are provided, the vision feature of the corresponding indices will be concatenated to form the vision features. - vision_feature_select_strategy (
str, optional, defaults to"default") — The feature selection strategy used to select the vision feature from the vision backbone. Can be one of"default"or"full". If"default", the CLS token is removed from the vision features. If"full", the full vision features are used. - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Labels for computing the masked language modeling loss. Indices should either be in[0, ..., config.vocab_size]or -100 (seeinput_idsdocstring). Tokens with indices set to-100are ignored (masked), the loss is only computed for the tokens with labels in[0, ..., config.vocab_size]. - use_cache (
bool, optional) — If set toTrue,past_key_valueskey value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (seepast_key_values). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - cache_position (
torch.LongTensorof shape(sequence_length), optional) — Indices depicting the position of the input sequence tokens in the sequence. Contrarily toposition_ids, this tensor is not affected by padding. It is used to update the cache in the correct position and to infer the complete sequence length. - logits_to_keep (
Union[int, torch.Tensor], defaults to0) — If anint, compute logits for the lastlogits_to_keeptokens. If0, calculate logits for allinput_ids(special case). Only last token logits are needed for generation, and calculating them only for that token can save memory, which becomes pretty significant for long sequences or large vocabulary size. If atorch.Tensor, must be 1D corresponding to the indices to keep in the sequence length dimension. This is useful when using packed tensor format (single dimension for batch and sequence length).
Returns
transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.LlavaNextCausalLMOutputWithPast or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.llava_next.modeling_llava_next.LlavaNextCausalLMOutputWithPast or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (LlavaNextConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Language modeling loss (for next-token prediction). -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax). -
past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenuse_cache=Trueis passed or whenconfig.use_cache=True) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head))Contains pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks) that can be used (see
past_key_valuesinput) to speed up sequential decoding. -
hidden_states (
tuple[torch.FloatTensor], optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple[torch.FloatTensor], optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
-
image_hidden_states (
torch.FloatTensor, optional) — Atorch.FloatTensorof size (batch_size * num_patches, num_images, sequence_length, hidden_size)`. image_hidden_states of the model produced by the vision encoder and after projecting the last hidden state.
The LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration
>>> model = LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-v1.6-mistral-7b-hf")
>>> prompt = "[INST] <image>\nWhat is shown in this image? [/INST]"
>>> url = "https://www.ilankelman.org/stopsigns/australia.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, text=prompt, return_tensors="pt")
>>> # Generate
>>> generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=30)
>>> processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
"[INST] \nWhat is shown in this image? [/INST] The image appears to be a radar chart, which is a type of multi-dimensional plot (...)"