Transformers documentation
AWQ
AWQ
Try AWQ quantization with this notebook!
Activation-aware Weight Quantization (AWQ) doesn’t quantize all the weights in a model, and instead, it preserves a small percentage of weights that are important for LLM performance. This significantly reduces quantization loss such that you can run models in 4-bit precision without experiencing any performance degradation.
There are several libraries for quantizing models with the AWQ algorithm, such as llm-awq, autoawq or optimum-intel. Transformers supports loading models quantized with the llm-awq and autoawq libraries. This guide will show you how to load models quantized with autoawq, but the process is similar for llm-awq quantized models.
Make sure you have autoawq installed:
pip install autoawq
AWQ-quantized models can be identified by checking the quantization_config attribute in the model’s config.json file:
{
"_name_or_path": "/workspace/process/huggingfaceh4_zephyr-7b-alpha/source",
"architectures": [
"MistralForCausalLM"
],
...
...
...
"quantization_config": {
"quant_method": "awq",
"zero_point": true,
"group_size": 128,
"bits": 4,
"version": "gemm"
}
}A quantized model is loaded with the from_pretrained() method. If you loaded your model on the CPU, make sure to move it to a GPU device first. Use the device_map parameter to specify where to place the model:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_id = "TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map="cuda:0")Loading an AWQ-quantized model automatically sets other weights to fp16 by default for performance reasons. If you want to load these other weights in a different format, use the torch_dtype parameter:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_id = "TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float32)AWQ quantization can also be combined with FlashAttention-2 to further accelerate inference:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ", attn_implementation="flash_attention_2", device_map="cuda:0")Fused modules
Fused modules offers improved accuracy and performance and it is supported out-of-the-box for AWQ modules for Llama and Mistral architectures, but you can also fuse AWQ modules for unsupported architectures.
Fused modules cannot be combined with other optimization techniques such as FlashAttention-2.
To enable fused modules for supported architectures, create an AwqConfig and set the parameters fuse_max_seq_len and do_fuse=True. The fuse_max_seq_len parameter is the total sequence length and it should include the context length and the expected generation length. You can set it to a larger value to be safe.
For example, to fuse the AWQ modules of the TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ model.
import torch
from transformers import AwqConfig, AutoModelForCausalLM
model_id = "TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ"
quantization_config = AwqConfig(
bits=4,
fuse_max_seq_len=512,
do_fuse=True,
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=quantization_config).to(0)The TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ model was benchmarked with batch_size=1 with and without fused modules.
| Batch Size | Prefill Length | Decode Length | Prefill tokens/s | Decode tokens/s | Memory (VRAM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 32 | 60.0984 | 38.4537 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 64 | 64 | 1333.67 | 31.6604 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 128 | 128 | 2434.06 | 31.6272 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 256 | 256 | 3072.26 | 38.1731 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 512 | 512 | 3184.74 | 31.6819 | 4.59 GB (5.80%) |
| 1 | 1024 | 1024 | 3148.18 | 36.8031 | 4.81 GB (6.07%) |
| 1 | 2048 | 2048 | 2927.33 | 35.2676 | 5.73 GB (7.23%) |
| Batch Size | Prefill Length | Decode Length | Prefill tokens/s | Decode tokens/s | Memory (VRAM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 32 | 81.4899 | 80.2569 | 4.00 GB (5.05%) |
| 1 | 64 | 64 | 1756.1 | 106.26 | 4.00 GB (5.05%) |
| 1 | 128 | 128 | 2479.32 | 105.631 | 4.00 GB (5.06%) |
| 1 | 256 | 256 | 1813.6 | 85.7485 | 4.01 GB (5.06%) |
| 1 | 512 | 512 | 2848.9 | 97.701 | 4.11 GB (5.19%) |
| 1 | 1024 | 1024 | 3044.35 | 87.7323 | 4.41 GB (5.57%) |
| 1 | 2048 | 2048 | 2715.11 | 89.4709 | 5.57 GB (7.04%) |
The speed and throughput of fused and unfused modules were also tested with the optimum-benchmark library.
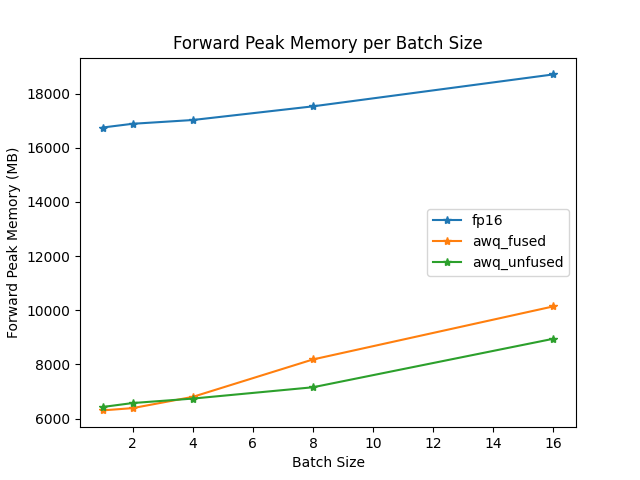
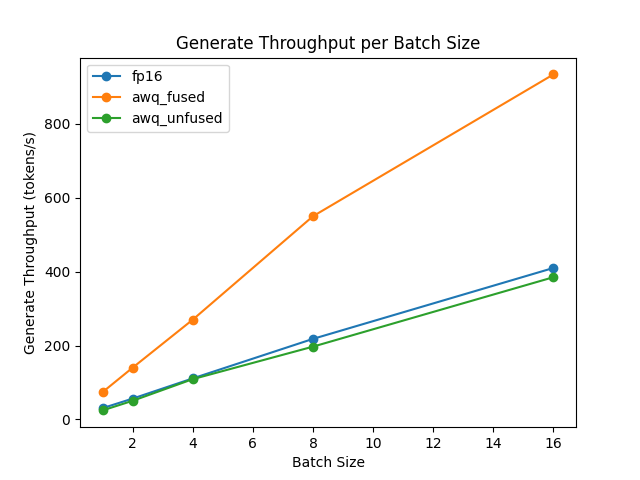
ExLlama-v2 support
Recent versions of autoawq supports ExLlama-v2 kernels for faster prefill and decoding. To get started, first install the latest version of autoawq by running:
pip install git+https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ.git
Get started by passing an AwqConfig() with version="exllama".
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, AwqConfig
quantization_config = AwqConfig(version="exllama")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1-AWQ",
quantization_config=quantization_config,
device_map="auto",
)
input_ids = torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 128), dtype=torch.long, device="cuda")
output = model(input_ids)
print(output.logits)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1-AWQ")
input_ids = tokenizer.encode("How to make a cake", return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
output = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True, max_length=50, pad_token_id=50256)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))Note this feature is supported on AMD GPUs.