Transformers documentation
CLIPSeg
CLIPSeg

개요
CLIPSeg 모델은 Timo Lüddecke와 Alexander Ecker가 Image Segmentation Using Text and Image Prompts 논문에서 제안했습니다. CLIPSeg는 가중치가 고정된 CLIP 모델에 최소한의 디코더를 결합하여 제로샷 및 원샷 이미지 분할을 수행합니다.
논문 초록은 다음과 같습니다.
이미지 분할은 일반적으로 사전에 정의된 객체 클래스 집합에 대해 모델을 훈련시키는 방식으로 접근합니다. 하지만 새로운 클래스를 추가하거나 보다 복잡한 질의를 처리하려면, 해당 내용을 포함한 데이터 세트로 모델을 다시 훈련해야 하므로 비용이 많이 듭니다. 이에 본 논문에서는 테스트 시점에 텍스트나 이미지로 구성된 임의의 프롬프트만으로 이미지 분할을 수행할 수 있는 시스템을 제안합니다. 이 접근 방식을 통해 서로 다른 과제를 갖는 세 가지 주요 이미지 분할 태스크—지시 표현 분할(referring expression segmentation), 제로샷 분할(zero-shot segmentation), 원샷 분할(one-shot segmentation)—을 단일 통합 모델로 처리할 수 있습니다. 이를 위해 우리는 CLIP 모델을 백본으로 삼고, 고해상도 예측을 가능하게 하는 트랜스포머 기반 디코더를 추가해 이를 확장했습니다. 확장된 PhraseCut 데이터 세트를 활용해 훈련한 본 시스템은 자유 형식의 텍스트 프롬프트나 특정 목적을 표현하는 이미지를 입력으로 받아, 입력 이미지에 대한 이진 분할 맵을 생성합니다. 특히 이미지 기반 프롬프트의 다양한 구성 방식과 그 효과를 자세히 분석하였습니다. 이 새로운 하이브리드 입력 방식은 앞서 언급한 세 가지 태스크뿐만 아니라, 텍스트 또는 이미지로 질의할 수 있는 모든 이진 분할 문제에 유연하게 대응할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, 본 시스템이 어포던스(affordance)나 객체 속성과 같은 일반화된 질의에도 높은 적응력을 보임을 확인하였습니다.
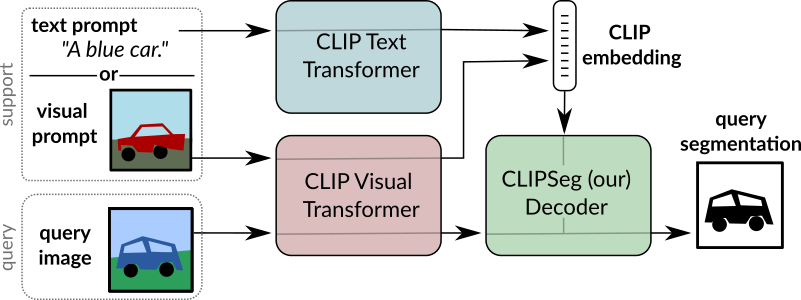 CLIPSeg 개요. 원본 논문에서 발췌.
CLIPSeg 개요. 원본 논문에서 발췌. 이 모델은 nielsr님이 기여했습니다. 원본 코드는 여기에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
사용 팁
- CLIPSegForImageSegmentation은 CLIPSegModel과 동일한, CLIPSegModel 위에 디코더를 추가한 모델입니다.
- CLIPSegForImageSegmentation은 테스트 시점에 임의의 프롬프트를 기반으로 이미지 분할을 생성합니다. 이때 프롬프트는 텍스트(
input_ids), 이미지(conditional_pixel_values), 사용자 정의 조건부 임베딩(conditional_embeddings)을 사용할 수 있습니다.
리소스
CLIPSeg를 시작하는 데 도움이 될 Hugging Face 공식 자료와 커뮤니티(🌎 아이콘으로 표시)의 유용한 리소스 목록을 아래에 정리했습니다. 혹시 목록에 없는 새로운 자료나 튜토리얼을 공유하고 싶으시다면, 언제든지 Pull Request를 통해 제안해 주세요. 저희가 검토 후 소중히 반영하겠습니다! 기존 자료와 중복되지 않는 새로운 내용이라면 더욱 좋습니다.
- zero-shot image segmentation with CLIPSeg을 시연하는 노트북.
CLIPSegConfig
class transformers.CLIPSegConfig
< source >( text_config = None vision_config = None projection_dim = 512 logit_scale_init_value = 2.6592 extract_layers = [3, 6, 9] reduce_dim = 64 decoder_num_attention_heads = 4 decoder_attention_dropout = 0.0 decoder_hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' decoder_intermediate_size = 2048 conditional_layer = 0 use_complex_transposed_convolution = False **kwargs )
Parameters
- text_config (
dict, optional) — Dictionary of configuration options used to initialize CLIPSegTextConfig. - vision_config (
dict, optional) — Dictionary of configuration options used to initialize CLIPSegVisionConfig. - projection_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — Dimensionality of text and vision projection layers. - logit_scale_init_value (
float, optional, defaults to 2.6592) — The initial value of the logit_scale parameter. Default is used as per the original CLIPSeg implementation. - extract_layers (
list[int], optional, defaults to[3, 6, 9]) — Layers to extract when forwarding the query image through the frozen visual backbone of CLIP. - reduce_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 64) — Dimensionality to reduce the CLIP vision embedding. - decoder_num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — Number of attention heads in the decoder of CLIPSeg. - decoder_attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - decoder_hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new""quick_gelu"are supported. - decoder_intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layers in the Transformer decoder. - conditional_layer (
int, optional, defaults to 0) — The layer to use of the Transformer encoder whose activations will be combined with the condition embeddings using FiLM (Feature-wise Linear Modulation). If 0, the last layer is used. - use_complex_transposed_convolution (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use a more complex transposed convolution in the decoder, enabling more fine-grained segmentation. - kwargs (optional) — Dictionary of keyword arguments.
CLIPSegConfig is the configuration class to store the configuration of a CLIPSegModel. It is used to instantiate a CLIPSeg model according to the specified arguments, defining the text model and vision model configs. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the CLIPSeg CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import CLIPSegConfig, CLIPSegModel
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegConfig with CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 style configuration
>>> configuration = CLIPSegConfig()
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegModel (with random weights) from the CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 style configuration
>>> model = CLIPSegModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.config
>>> # We can also initialize a CLIPSegConfig from a CLIPSegTextConfig and a CLIPSegVisionConfig
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegText and CLIPSegVision configuration
>>> config_text = CLIPSegTextConfig()
>>> config_vision = CLIPSegVisionConfig()
>>> config = CLIPSegConfig.from_text_vision_configs(config_text, config_vision)from_text_vision_configs
< source >( text_config vision_config **kwargs ) → PreTrainedConfig
Returns
PreTrainedConfig
An instance of a configuration object
Instantiate a model config (or a derived class) from text model configuration and vision model configuration.
CLIPSegTextConfig
class transformers.CLIPSegTextConfig
< source >( vocab_size = 49408 hidden_size = 512 intermediate_size = 2048 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 8 max_position_embeddings = 77 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 pad_token_id = 1 bos_token_id = 49406 eos_token_id = 49407 **kwargs )
Parameters
- vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 49408) — Vocabulary size of the CLIPSeg text model. Defines the number of different tokens that can be represented by theinputs_idspassed when calling CLIPSegModel. - hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. - intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, defaults to 77) — The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048). - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new""quick_gelu"are supported. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - initializer_factor (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — A factor for initializing all weight matrices (should be kept to 1, used internally for initialization testing). - pad_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — Padding token id. - bos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 49406) — Beginning of stream token id. - eos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 49407) — End of stream token id.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a CLIPSegModel. It is used to instantiate an CLIPSeg model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the CLIPSeg CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import CLIPSegTextConfig, CLIPSegTextModel
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegTextConfig with CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 style configuration
>>> configuration = CLIPSegTextConfig()
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegTextModel (with random weights) from the CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 style configuration
>>> model = CLIPSegTextModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configCLIPSegVisionConfig
class transformers.CLIPSegVisionConfig
< source >( hidden_size = 768 intermediate_size = 3072 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 num_channels = 3 image_size = 224 patch_size = 32 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 **kwargs )
Parameters
- hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. - intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels. - image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — The size (resolution) of each image. - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — The size (resolution) of each patch. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new""quick_gelu"are supported. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - initializer_factor (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — A factor for initializing all weight matrices (should be kept to 1, used internally for initialization testing).
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a CLIPSegModel. It is used to instantiate an CLIPSeg model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the CLIPSeg CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import CLIPSegVisionConfig, CLIPSegVisionModel
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegVisionConfig with CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 style configuration
>>> configuration = CLIPSegVisionConfig()
>>> # Initializing a CLIPSegVisionModel (with random weights) from the CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 style configuration
>>> model = CLIPSegVisionModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configCLIPSegProcessor
class transformers.CLIPSegProcessor
< source >( image_processor = None tokenizer = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- image_processor (ViTImageProcessor, optional) — The image processor is a required input.
- tokenizer (CLIPTokenizerFast, optional) — The tokenizer is a required input.
Constructs a CLIPSeg processor which wraps a CLIPSeg image processor and a CLIP tokenizer into a single processor.
CLIPSegProcessor offers all the functionalities of ViTImageProcessor and CLIPTokenizerFast. See the
__call__() and decode() for more information.
CLIPSegModel
class transformers.CLIPSegModel
< source >( config: CLIPSegConfig )
Parameters
- config (CLIPSegConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Clipseg Model outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None return_loss: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = True return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size), optional) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using ViTImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details (CLIPSegProcessor uses ViTImageProcessor for processing images). - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - return_loss (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the contrastive loss. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, defaults toTrue) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (CLIPSegConfig) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenreturn_lossisTrue) — Contrastive loss for image-text similarity. - logits_per_image (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(image_batch_size, text_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweenimage_embedsandtext_embeds. This represents the image-text similarity scores. - logits_per_text (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(text_batch_size, image_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweentext_embedsandimage_embeds. This represents the text-image similarity scores. - text_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegTextModel. - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegVisionModel. - text_model_output (
<class '~modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling'>.text_model_output, defaults toNone) — The output of the CLIPSegTextModel. - vision_model_output (
<class '~modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling'>.vision_model_output, defaults toNone) — The output of the CLIPSegVisionModel.
The CLIPSegModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPSegModel
>>> from transformers.image_utils import load_image
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> model = CLIPSegModel.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = load_image(url)
>>> inputs = processor(
... text=["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True
... )
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits_per_image = outputs.logits_per_image # this is the image-text similarity score
>>> probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1) # we can take the softmax to get the label probabilitiesget_text_features
< source >( input_ids: Tensor attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None ) → text_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1].
Returns
text_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegTextModel.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, CLIPSegModel
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> model = CLIPSegModel.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... text_features = model.get_text_features(**inputs)get_image_features
< source >( pixel_values: FloatTensor interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = True ) → image_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using ViTImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details (CLIPSegProcessor uses ViTImageProcessor for processing images). - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, defaults toTrue) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings.
Returns
image_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegVisionModel.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPSegModel
>>> from transformers.image_utils import load_image
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> model = CLIPSegModel.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = load_image(url)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... image_features = model.get_image_features(**inputs)CLIPSegTextModel
forward
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
- attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (CLIPSegConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The CLIPSegTextModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, CLIPSegTextModel
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> model = CLIPSegTextModel.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled (EOS token) statesCLIPSegVisionModel
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: typing.Optional[bool] = True return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size), optional) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using ViTImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details (CLIPSegProcessor uses ViTImageProcessor for processing images). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (CLIPSegConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The CLIPSegVisionModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPSegVisionModel
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> model = CLIPSegVisionModel.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled CLS statesCLIPSegForImageSegmentation
class transformers.CLIPSegForImageSegmentation
< source >( config: CLIPSegConfig )
Parameters
- config (CLIPSegConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
CLIPSeg model with a Transformer-based decoder on top for zero-shot and one-shot image segmentation.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None conditional_pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None conditional_embeddings: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = True return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size), optional) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using ViTImageProcessor. See ViTImageProcessor.call() for details (CLIPSegProcessor uses ViTImageProcessor for processing images). - conditional_pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensor, optional) — The pixel values of the conditional images. - conditional_embeddings (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.projection_dim), optional) — The conditional embeddings for the query images. If provided, the model will use this instead of computing the embeddings from the conditional_pixel_values. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
- position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.n_positions - 1]. - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the sequence classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, defaults toTrue) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (CLIPSegConfig) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenreturn_lossisTrue) — Contrastive loss for image-text similarity. - logits_per_image (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(image_batch_size, text_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweenimage_embedsandtext_embeds. This represents the image-text similarity scores. - logits_per_text (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(text_batch_size, image_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweentext_embedsandimage_embeds. This represents the text-image similarity scores. - text_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegTextModel. - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegVisionModel. - text_model_output (
<class '~modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling'>.text_model_output, defaults toNone) — The output of the CLIPSegTextModel. - vision_model_output (
<class '~modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling'>.vision_model_output, defaults toNone) — The output of the CLIPSegVisionModel.
The CLIPSegForImageSegmentation forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPSegForImageSegmentation
>>> from transformers.image_utils import load_image
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> model = CLIPSegForImageSegmentation.from_pretrained("CIDAS/clipseg-rd64-refined")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = load_image(url)
>>> texts = ["a cat", "a remote", "a blanket"]
>>> inputs = processor(text=texts, images=[image] * len(texts), padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> print(logits.shape)
torch.Size([3, 352, 352])