Accelerate documentation
DeepSpeed
DeepSpeed
DeepSpeed implements everything described in the ZeRO paper. Some of the salient optimizations are:
- Optimizer state partitioning (ZeRO stage 1)
- Gradient partitioning (ZeRO stage 2)
- Parameter partitioning (ZeRO stage 3)
- Custom mixed precision training handling
- A range of fast CUDA-extension-based optimizers
- ZeRO-Offload to CPU and Disk/NVMe
- Hierarchical partitioning of model parameters (ZeRO++)
ZeRO-Offload has its own dedicated paper: ZeRO-Offload: Democratizing Billion-Scale Model Training. And NVMe-support is described in the paper ZeRO-Infinity: Breaking the GPU Memory Wall for Extreme Scale Deep Learning.
DeepSpeed ZeRO-2 is primarily used only for training, as its features are of no use to inference.
DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 can be used for inference as well since it allows huge models to be loaded on multiple GPUs, which won’t be possible on a single GPU.
Accelerate integrates DeepSpeed via 2 options:
- Integration of the DeepSpeed features via
deepspeed config filespecification inaccelerate config. You just supply your custom config file or use our template. Most of this document is focused on this feature. This supports all the core features of DeepSpeed and gives user a lot of flexibility. User may have to change a few lines of code depending on the config. - Integration via
deepspeed_plugin.This supports subset of the DeepSpeed features and uses default options for the rest of the configurations. User need not change any code and is good for those who are fine with most of the default settings of DeepSpeed.
What is integrated?
Training:
- Accelerate integrates all features of DeepSpeed ZeRO. This includes all the ZeRO stages 1, 2 and 3 as well as ZeRO-Offload, ZeRO-Infinity (which can offload to disk/NVMe) and ZeRO++.
Below is a short description of Data Parallelism using ZeRO - Zero Redundancy Optimizer along with diagram from this blog post
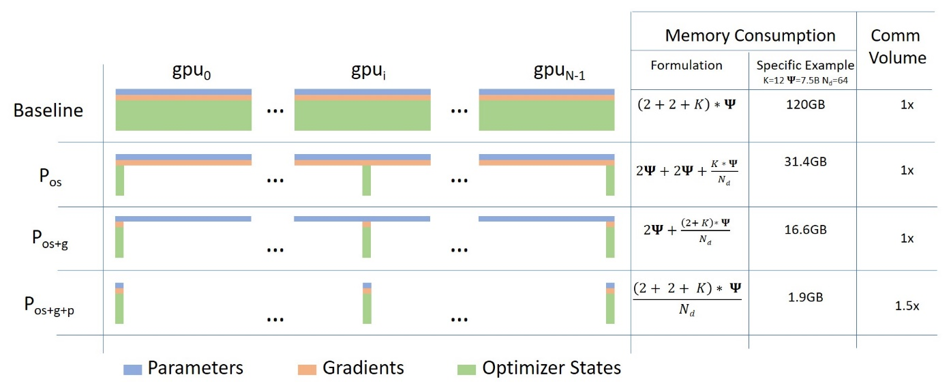
(Source: link)
a. Stage 1 : Shards optimizer states across data parallel workers/GPUs
b. Stage 2 : Shards optimizer states + gradients across data parallel workers/GPUs
c. Stage 3: Shards optimizer states + gradients + model parameters across data parallel workers/GPUs
d. Optimizer Offload: Offloads the gradients + optimizer states to CPU/Disk building on top of ZERO Stage 2
e. Param Offload: Offloads the model parameters to CPU/Disk building on top of ZERO Stage 3
f. Hierarchical Partitioning: Enables efficient multi-node training with data-parallel training across nodes and ZeRO-3 sharding within a node, built on top of ZeRO Stage 3.
Note: With respect to Disk Offload, the disk should be an NVME for decent speed but it technically works on any DiskInference:
- DeepSpeed ZeRO Inference supports ZeRO stage 3 with ZeRO-Infinity. It uses the same ZeRO protocol as training, but it doesn’t use an optimizer and a lr scheduler and only stage 3 is relevant. For more details see: deepspeed-zero-inference.
How it works?
Pre-Requisites: Install DeepSpeed version >=0.6.5. Please refer to the DeepSpeed Installation details for more information.
We will first look at easy to use integration via accelerate config.
Followed by more flexible and feature rich deepspeed config file integration.
Accelerate DeepSpeed Plugin
On your machine(s) just run:
accelerate config
and answer the questions asked. It will ask whether you want to use a config file for DeepSpeed to which you should answer no. Then answer the following questions to generate a basic DeepSpeed config. This will generate a config file that will be used automatically to properly set the default options when doing
accelerate launch my_script.py --args_to_my_script
For instance, here is how you would run the NLP example examples/nlp_example.py (from the root of the repo) with DeepSpeed Plugin:
ZeRO Stage-2 DeepSpeed Plugin Example
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
gradient_clipping: 1.0
offload_optimizer_device: none
offload_param_device: none
zero3_init_flag: true
zero_stage: 2
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
fsdp_config: {}
machine_rank: 0
main_process_ip: null
main_process_port: null
main_training_function: main
mixed_precision: fp16
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 2
use_cpu: falseaccelerate launch examples/nlp_example.py --mixed_precision fp16
ZeRO Stage-3 with CPU Offload DeepSpeed Plugin Example
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
gradient_clipping: 1.0
offload_optimizer_device: cpu
offload_param_device: cpu
zero3_init_flag: true
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
zero_stage: 3
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
fsdp_config: {}
machine_rank: 0
main_process_ip: null
main_process_port: null
main_training_function: main
mixed_precision: fp16
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 2
use_cpu: falseaccelerate launch examples/nlp_example.py --mixed_precision fp16
Currently, Accelerate supports following config through the CLI:
`zero_stage`: [0] Disabled, [1] optimizer state partitioning, [2] optimizer+gradient state partitioning and [3] optimizer+gradient+parameter partitioning
`gradient_accumulation_steps`: Number of training steps to accumulate gradients before averaging and applying them.
`gradient_clipping`: Enable gradient clipping with value.
`offload_optimizer_device`: [none] Disable optimizer offloading, [cpu] offload optimizer to CPU, [nvme] offload optimizer to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO >= Stage-2.
`offload_optimizer_nvme_path`: Decides Nvme Path to offload optimizer states. If unspecified, will default to 'none'.
`offload_param_device`: [none] Disable parameter offloading, [cpu] offload parameters to CPU, [nvme] offload parameters to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3.
`offload_param_nvme_path`: Decides Nvme Path to offload parameters. If unspecified, will default to 'none'.
`zero3_init_flag`: Decides whether to enable `deepspeed.zero.Init` for constructing massive models. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3.
`zero3_save_16bit_model`: Decides whether to save 16-bit model weights when using ZeRO Stage-3.
`mixed_precision`: `no` for FP32 training, `fp16` for FP16 mixed-precision training and `bf16` for BF16 mixed-precision training.
`deepspeed_moe_layer_cls_names`: Comma-separated list of transformer Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layer class names (case-sensitive) to wrap ,e.g, `MixtralSparseMoeBlock`, `Qwen2MoeSparseMoeBlock`, `JetMoEAttention,JetMoEBlock` ...
`deepspeed_hostfile`: DeepSpeed hostfile for configuring multi-node compute resources.
`deepspeed_exclusion_filter`: DeepSpeed exclusion filter string when using mutli-node setup.
`deepspeed_inclusion_filter`: DeepSpeed inclusion filter string when using mutli-node setup.
`deepspeed_multinode_launcher`: DeepSpeed multi-node launcher to use. If unspecified, will default to `pdsh`.
`deepspeed_config_file`: path to the DeepSpeed config file in `json` format. See the next section for more details on this.To be able to tweak more options, you will need to use a DeepSpeed config file.
DeepSpeed Config File
On your machine(s) just run:
accelerate config
and answer the questions asked. It will ask whether you want to use a config file for deepspeed to which you answer yes and provide the path to the deepspeed config file. This will generate a config file that will be used automatically to properly set the default options when doing
accelerate launch my_script.py --args_to_my_script
For instance, here is how you would run the NLP example examples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.py (from the root of the repo) with DeepSpeed Config File:
ZeRO Stage-2 DeepSpeed Config File Example
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
deepspeed_config_file: /home/ubuntu/accelerate/examples/configs/deepspeed_config_templates/zero_stage2_config.json
zero3_init_flag: true
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
fsdp_config: {}
machine_rank: 0
main_process_ip: null
main_process_port: null
main_training_function: main
mixed_precision: fp16
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 2
use_cpu: falsewith the contents of zero_stage2_config.json being:
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": true,
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto",
"torch_adam": true,
"adam_w_mode": true
}
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupDecayLR",
"params": {
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto",
"total_num_steps": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 2,
"allgather_partitions": true,
"allgather_bucket_size": 2e8,
"overlap_comm": true,
"reduce_scatter": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"contiguous_gradients": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": 1,
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false
}accelerate launch examples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.py \
--config_name "gpt2-large" \
--tokenizer_name "gpt2-large" \
--dataset_name "wikitext" \
--dataset_config_name "wikitext-2-raw-v1" \
--block_size 128 \
--output_dir "./clm/clm_deepspeed_stage2_accelerate" \
--learning_rate 5e-4 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 24 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 24 \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--with_tracking \
--report_to "wandb"\ZeRO Stage-3 with CPU offload DeepSpeed Config File Example
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
deepspeed_config_file: /home/ubuntu/accelerate/examples/configs/deepspeed_config_templates/zero_stage3_offload_config.json
zero3_init_flag: true
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
fsdp_config: {}
machine_rank: 0
main_process_ip: null
main_process_port: null
main_training_function: main
mixed_precision: fp16
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 2
use_cpu: falsewith the contents of zero_stage3_offload_config.json being:
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": true,
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupDecayLR",
"params": {
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto",
"total_num_steps": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"overlap_comm": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": "auto",
"sub_group_size": 1e9,
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 1e9,
"stage3_max_reuse_distance": 1e9,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": "auto"
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": 1,
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false
}accelerate launch examples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.py \
--config_name "gpt2-large" \
--tokenizer_name "gpt2-large" \
--dataset_name "wikitext" \
--dataset_config_name "wikitext-2-raw-v1" \
--block_size 128 \
--output_dir "./clm/clm_deepspeed_stage3_offload_accelerate" \
--learning_rate 5e-4 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 32 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 32 \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--with_tracking \
--report_to "wandb"\ZeRO++ Config Example You can use the features of ZeRO++ by using the appropriate config parameters. Note that ZeRO++ is an extension for ZeRO Stage 3. Here is how the config file can be modified, from DeepSpeed’s ZeRO++ tutorial:
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"zero_quantized_weights": true,
"zero_hpz_partition_size": 8,
"zero_quantized_gradients": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"overlap_comm": true
}
}For hierarchical partitioning, the partition size zero_hpz_partition_size should ideally be set to the number of GPUs per node. (For example, the above config file assumes 8 GPUs per node)
Important code changes when using DeepSpeed Config File
DeepSpeed Optimizers and Schedulers. For more information on these, see the DeepSpeed Optimizers and DeepSpeed Schedulers documentation. We will look at the changes needed in the code when using these.
a. DS Optim + DS Scheduler: The case when both
optimizerandschedulerkeys are present in the DeepSpeed config file. In this situation, those will be used and the user has to useaccelerate.utils.DummyOptimandaccelerate.utils.DummySchedulerto replace the PyTorch/Custom optimizers and schedulers in their code. Below is the snippet fromexamples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.pyshowing this:# Creates Dummy Optimizer if `optimizer` was specified in the config file else creates Adam Optimizer optimizer_cls = ( torch.optim.AdamW if accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin is None or "optimizer" not in accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config else DummyOptim ) optimizer = optimizer_cls(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=args.learning_rate) # Creates Dummy Scheduler if `scheduler` was specified in the config file else creates `args.lr_scheduler_type` Scheduler if ( accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin is None or "scheduler" not in accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config ): lr_scheduler = get_scheduler( name=args.lr_scheduler_type, optimizer=optimizer, num_warmup_steps=args.num_warmup_steps, num_training_steps=args.max_train_steps, ) else: lr_scheduler = DummyScheduler( optimizer, total_num_steps=args.max_train_steps, warmup_num_steps=args.num_warmup_steps )b. Custom Optim + Custom Scheduler: The case when both
optimizerandschedulerkeys are absent in the DeepSpeed config file. In this situation, no code changes are needed from the user and this is the case when using integration via DeepSpeed Plugin. In the above example we can see that the code remains unchanged if theoptimizerandschedulerkeys are absent in the DeepSpeed config file.c. Custom Optim + DS Scheduler: The case when only
schedulerkey is present in the DeepSpeed config file. In this situation, the user has to useaccelerate.utils.DummySchedulerto replace the PyTorch/Custom scheduler in their code.d. DS Optim + Custom Scheduler: The case when only
optimizerkey is present in the DeepSpeed config file. This will result in an error because you can only use DS Scheduler when using DS Optim.Notice the
autovalues in the above example DeepSpeed config files. These are automatically handled bypreparemethod based on model, dataloaders, dummy optimizer and dummy schedulers provided topreparemethod. Only theautofields specified in above examples are handled bypreparemethod and the rest have to be explicitly specified by the user.
The auto values are calculated as:
reduce_bucket_size:hidden_size * hidden_sizestage3_prefetch_bucket_size:int(0.9 * hidden_size * hidden_size)stage3_param_persistence_threshold:10 * hidden_size
For the auto feature to work for these 3 config entries - Accelerate will use model.config.hidden_size or max(model.config.hidden_sizes) as hidden_size. If neither of these is available, the launching will fail and you will have to set these 3 config entries manually. Remember the first 2 config entries are the communication buffers - the larger they are the more efficient the comms will be, and the larger they are the more GPU memory they will consume, so it’s a tunable performance trade-off.
Things to note when using DeepSpeed Config File
Below is a sample script using deepspeed_config_file in different scenarios.
Code test.py:
from accelerate import Accelerator
from accelerate.state import AcceleratorState
def main():
accelerator = Accelerator()
accelerator.print(f"{AcceleratorState()}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Scenario 1: Manually tampered accelerate config file having deepspeed_config_file along with other entries.
- Content of the
accelerateconfig:
command_file: null
commands: null
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
gradient_clipping: 1.0
offload_optimizer_device: 'cpu'
offload_param_device: 'cpu'
zero3_init_flag: true
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
zero_stage: 3
deepspeed_config_file: 'ds_config.json'
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
downcast_bf16: 'no'
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
fsdp_config: {}
gpu_ids: null
machine_rank: 0
main_process_ip: null
main_process_port: null
main_training_function: main
megatron_lm_config: {}
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 2
rdzv_backend: static
same_network: true
tpu_name: null
tpu_zone: null
use_cpu: falseds_config.json:
{
"bf16": {
"enabled": true
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": false,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "none"
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "none"
}
},
"gradient_clipping": 1.0,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"gradient_accumulation_steps": 10,
"steps_per_print": 2000000
}- Output of
accelerate launch test.py:
ValueError: When using `deepspeed_config_file`, the following accelerate config variables will be ignored:
['gradient_accumulation_steps', 'gradient_clipping', 'zero_stage', 'offload_optimizer_device', 'offload_param_device',
'zero3_save_16bit_model', 'mixed_precision'].
Please specify them appropriately in the DeepSpeed config file.
If you are using an accelerate config file, remove other config variables mentioned in the above specified list.
The easiest method is to create a new config following the questionnaire via `accelerate config`.
It will only ask for the necessary config variables when using `deepspeed_config_file`.Scenario 2: Use the solution of the error to create new accelerate config and check that no ambiguity error is now thrown.
- Run
accelerate config:
$ accelerate config
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In which compute environment are you running?
This machine
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Which type of machine are you using?
multi-GPU
How many different machines will you use (use more than 1 for multi-node training)? [1]:
Do you wish to optimize your script with torch dynamo?[yes/NO]:
Do you want to use DeepSpeed? [yes/NO]: yes
Do you want to specify a json file to a DeepSpeed config? [yes/NO]: yes
Please enter the path to the json DeepSpeed config file: ds_config.json
Do you want to enable `deepspeed.zero.Init` when using ZeRO Stage-3 for constructing massive models? [yes/NO]: yes
How many GPU(s) should be used for distributed training? [1]:4
accelerate configuration saved at ds_config_sample.yaml- Content of the
accelerateconfig:
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
deepspeed_config_file: ds_config.json
zero3_init_flag: true
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
downcast_bf16: 'no'
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
fsdp_config: {}
machine_rank: 0
main_training_function: main
megatron_lm_config: {}
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 4
rdzv_backend: static
same_network: true
use_cpu: false- Output of
accelerate launch test.py:
Distributed environment: DEEPSPEED Backend: nccl
Num processes: 4
Process index: 0
Local process index: 0
Device: cuda:0
Mixed precision type: bf16
ds_config: {'bf16': {'enabled': True}, 'zero_optimization': {'stage': 3, 'stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save': False, 'offload_optimizer': {'device': 'none'}, 'offload_param': {'device': 'none'}}, 'gradient_clipping': 1.0, 'train_batch_size': 'auto', 'train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu': 'auto', 'gradient_accumulation_steps': 10, 'steps_per_print': inf, 'fp16': {'enabled': False}}Scenario 3: Setting the accelerate launch command arguments related to DeepSpeed as "auto" in the DeepSpeed` configuration file and check that things work as expected.
- New
ds_config.jsonwith"auto"for theaccelerate launchDeepSpeed command arguments:
{
"bf16": {
"enabled": "auto"
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": "auto",
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": "auto",
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "auto"
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "auto"
}
},
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000000
}- Output of
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" --zero_stage=3 --gradient_accumulation_steps=5 --gradient_clipping=1.0 --offload_param_device="cpu" --offload_optimizer_device="nvme" --zero3_save_16bit_model="true" test.py:
Distributed environment: DEEPSPEED Backend: nccl
Num processes: 4
Process index: 0
Local process index: 0
Device: cuda:0
Mixed precision type: fp16
ds_config: {'bf16': {'enabled': False}, 'zero_optimization': {'stage': 3, 'stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save': True, 'offload_optimizer': {'device': 'nvme'}, 'offload_param': {'device': 'cpu'}}, 'gradient_clipping': 1.0, 'train_batch_size': 'auto', 'train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu': 'auto', 'gradient_accumulation_steps': 5, 'steps_per_print': inf, 'fp16': {'enabled': True, 'auto_cast': True}}Note:
- Remaining
"auto"values are handled inaccelerator.prepare()call as explained in point 2 ofImportant code changes when using DeepSpeed Config File. - Only when
gradient_accumulation_stepsisauto, the value passed while creatingAcceleratorobject viaAccelerator(gradient_accumulation_steps=k)will be used. When using DeepSpeed Plugin, the value from it will be used and it will overwrite the value passed while creating Accelerator object.
Saving and loading
Saving and loading of models is unchanged for ZeRO Stage-1 and Stage-2.
under ZeRO Stage-3,
state_dictcontains just the placeholders since the model weights are partitioned across multiple GPUs. ZeRO Stage-3 has 2 options:a. Saving the entire 16bit model weights to directly load later on using
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pytorch_model.bin)). For this, either setzero_optimization.stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_saveto True in DeepSpeed Config file or setzero3_save_16bit_modelto True in DeepSpeed Plugin. Note that this option requires consolidation of the weights on one GPU it can be slow and memory demanding, so only use this feature when needed. Below is the snippet fromexamples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.pyshowing this:unwrapped_model = accelerator.unwrap_model(model) # New Code # # Saves the whole/unpartitioned fp16 model when in ZeRO Stage-3 to the output directory if # `stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save` is True in DeepSpeed Config file or # `zero3_save_16bit_model` is True in DeepSpeed Plugin. # For Zero Stages 1 and 2, models are saved as usual in the output directory. # The model name saved is `pytorch_model.bin` unwrapped_model.save_pretrained( args.output_dir, is_main_process=accelerator.is_main_process, save_function=accelerator.save, state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(model), )b. To get 32bit weights, first save the model using
model.save_checkpoint(). Below is the snippet fromexamples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.pyshowing this:success = model.save_checkpoint(PATH, ckpt_id, checkpoint_state_dict) status_msg = f"checkpointing: PATH={PATH}, ckpt_id={ckpt_id}" if success: logging.info(f"Success {status_msg}") else: logging.warning(f"Failure {status_msg}")This will create ZeRO model and optimizer partitions along with
zero_to_fp32.pyscript in checkpoint directory. You can use this script to do offline consolidation. It requires no configuration files or GPUs. Here is an example of its usage:$ cd /path/to/checkpoint_dir $ ./zero_to_fp32.py . pytorch_model.bin Processing zero checkpoint at global_step1 Detected checkpoint of type zero stage 3, world_size: 2 Saving fp32 state dict to pytorch_model.bin (total_numel=60506624)To get 32bit model for saving/inference, you can perform:
from deepspeed.utils.zero_to_fp32 import load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint unwrapped_model = accelerator.unwrap_model(model) fp32_model = load_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint(unwrapped_model, checkpoint_dir)If you are only interested in the
state_dict, you can do the following:from deepspeed.utils.zero_to_fp32 import get_fp32_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint state_dict = get_fp32_state_dict_from_zero_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir)Note that all these functions require ~2x memory (general RAM) of the size of the final checkpoint.
ZeRO Inference
DeepSpeed ZeRO Inference supports ZeRO stage 3 with ZeRO-Infinity. It uses the same ZeRO protocol as training, but it doesn’t use an optimizer and a lr scheduler and only stage 3 is relevant. With accelerate integration, you just need to prepare the model and dataloader as shown below:
model, eval_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(model, eval_dataloader)
Few caveats to be aware of
- Current integration doesn’t support Pipeline Parallelism of DeepSpeed.
- Current integration doesn’t support
mpu, limiting the tensor parallelism which is supported in Megatron-LM. - Current integration doesn’t support multiple models.
DeepSpeed Resources
The documentation for the internals related to deepspeed can be found here.
Papers:
- ZeRO: Memory Optimizations Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models
- ZeRO-Offload: Democratizing Billion-Scale Model Training
- ZeRO-Infinity: Breaking the GPU Memory Wall for Extreme Scale Deep Learning
- ZeRO++: Extremely Efficient Collective Communication for Giant Model Training
Finally, please, remember that Accelerate only integrates DeepSpeed, therefore if you
have any problems or questions with regards to DeepSpeed usage, please, file an issue with DeepSpeed GitHub.
For those interested in the similarities and differences between FSDP and DeepSpeed, please check out the concept guide here!