Datasets:
annotations_creators:
- expert-generated
language_creators:
- found
languages:
- en
licenses:
- unknown
multilinguality:
- monolingual
size_categories:
- 1K<n<10K
source_datasets:
- original
- extended|yelp_review_full
- extended|other-amazon_reviews_ucsd
- extended|other-tripadvisor_reviews
task_categories:
- question-answering
task_ids:
- extractive-qa
paperswithcode_id: subjqa
pretty_name: subjqa
Dataset Card for subjqa
Table of Contents
- Dataset Description
- Dataset Structure
- Dataset Creation
- Considerations for Using the Data
- Additional Information
Dataset Description
- Repository: https://github.com/lewtun/SubjQA
- Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.14283
- Point of Contact: Lewis Tunstall
Dataset Summary
SubjQA is a question answering dataset that focuses on subjective (as opposed to factual) questions and answers. The dataset consists of roughly 10,000 questions over reviews from 6 different domains: books, movies, grocery, electronics, TripAdvisor (i.e. hotels), and restaurants. Each question is paired with a review and a span is highlighted as the answer to the question (with some questions having no answer). Moreover, both questions and answer spans are assigned a subjectivity label by annotators. Questions such as "How much does this product weigh?" is a factual question (i.e., low subjectivity), while "Is this easy to use?" is a subjective question (i.e., high subjectivity).
In short, SubjQA provides a setting to study how well extractive QA systems perform on finding answer that are less factual and to what extent modeling subjectivity can improve the performance of QA systems.
Note: Much of the information provided on this dataset card is taken from the README provided by the authors in their GitHub repository (link).
To load a domain with datasets you can run the following:
from datasets import load_dataset
# other options include: electronics, grocery, movies, restaurants, tripadvisor
dataset = load_dataset("subjqa", "books")
Supported Tasks and Leaderboards
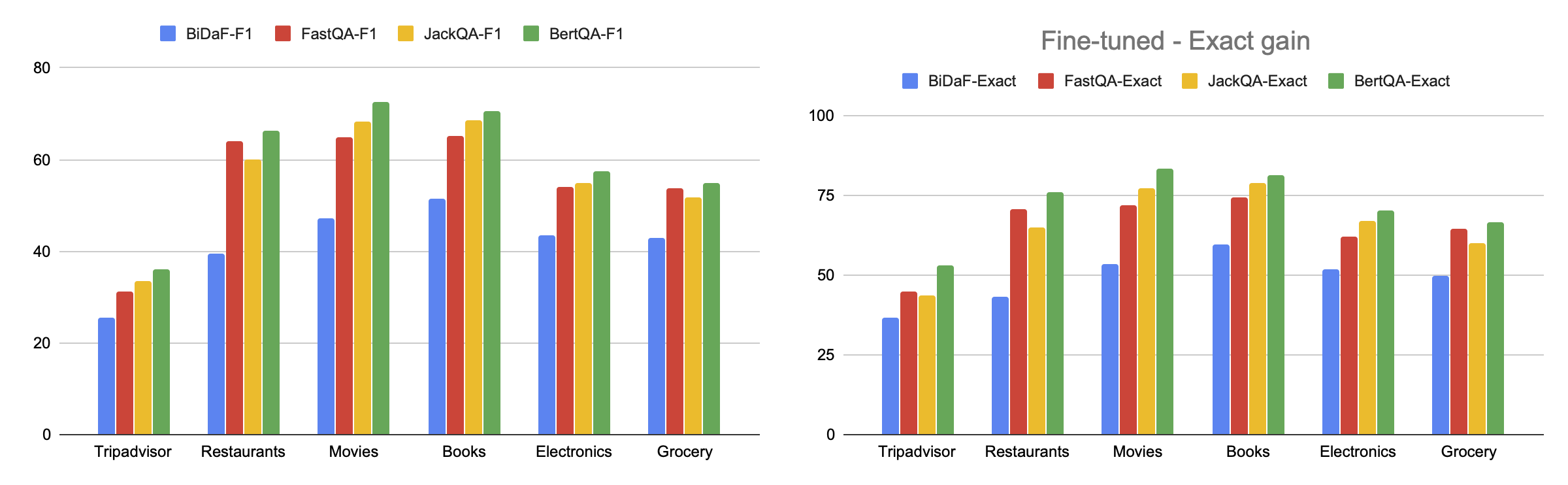
question-answering: The dataset can be used to train a model for extractive question answering, which involves questions whose answer can be identified as a span of text in a review. Success on this task is typically measured by achieving a high Exact Match or F1 score. The BERT model that is first fine-tuned on SQuAD 2.0 and then further fine-tuned on SubjQA achieves the scores shown in the figure below.
Languages
The text in the dataset is in English and the associated BCP-47 code is en.
Dataset Structure
Data Instances
An example from books domain is shown below:
{
"answers": {
"ans_subj_score": [1.0],
"answer_start": [324],
"answer_subj_level": [2],
"is_ans_subjective": [true],
"text": ["This is a wonderfully written book"],
},
"context": "While I would not recommend this book to a young reader due to a couple pretty explicate scenes I would recommend it to any adult who just loves a good book. Once I started reading it I could not put it down. I hesitated reading it because I didn't think that the subject matter would be interesting, but I was so wrong. This is a wonderfully written book.",
"domain": "books",
"id": "0255768496a256c5ed7caed9d4e47e4c",
"is_ques_subjective": false,
"nn_asp": "matter",
"nn_mod": "interesting",
"q_reviews_id": "a907837bafe847039c8da374a144bff9",
"query_asp": "part",
"query_mod": "fascinating",
"ques_subj_score": 0.0,
"question": "What are the parts like?",
"question_subj_level": 2,
"review_id": "a7f1a2503eac2580a0ebbc1d24fffca1",
"title": "0002007770",
}
Data Fields
Each domain and split consists of the following columns:
title: The id of the item/business discussed in the review.question: The question (written based on a query opinion).id: A unique id assigned to the question-review pair.q_reviews_id: A unique id assigned to all question-review pairs with a shared question.question_subj_level: The subjectiviy level of the question (on a 1 to 5 scale with 1 being the most subjective).ques_subj_score: The subjectivity score of the question computed using the TextBlob package.context: The review (that mentions the neighboring opinion).review_id: A unique id associated with the review.answers.text: The span labeled by annotators as the answer.answers.answer_start: The (character-level) start index of the answer span highlighted by annotators.is_ques_subjective: A boolean subjectivity label derived fromquestion_subj_level(i.e., scores below 4 are considered as subjective)answers.answer_subj_level: The subjectiviy level of the answer span (on a 1 to 5 scale with 5 being the most subjective).answers.ans_subj_score: The subjectivity score of the answer span computed usign the TextBlob package.answers.is_ans_subjective: A boolean subjectivity label derived fromanswer_subj_level(i.e., scores below 4 are considered as subjective)domain: The category/domain of the review (e.g., hotels, books, ...).nn_mod: The modifier of the neighboring opinion (which appears in the review).nn_asp: The aspect of the neighboring opinion (which appears in the review).query_mod: The modifier of the query opinion (around which a question is manually written).query_asp: The aspect of the query opinion (around which a question is manually written).
Data Splits
The question-review pairs from each domain are split into training, development, and test sets. The table below shows the size of the dataset per each domain and split.
| Domain | Train | Dev | Test | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TripAdvisor | 1165 | 230 | 512 | 1686 |
| Restaurants | 1400 | 267 | 266 | 1683 |
| Movies | 1369 | 261 | 291 | 1677 |
| Books | 1314 | 256 | 345 | 1668 |
| Electronics | 1295 | 255 | 358 | 1659 |
| Grocery | 1124 | 218 | 591 | 1725 |
Based on the subjectivity labels provided by annotators, one observes that 73% of the questions and 74% of the answers in the dataset are subjective. This provides a substantial number of subjective QA pairs as well as a reasonable number of factual questions to compare and constrast the performance of QA systems on each type of QA pairs.
Finally, the next table summarizes the average length of the question, the review, and the highlighted answer span for each category.
| Domain | Review Len | Question Len | Answer Len | % answerable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TripAdvisor | 187.25 | 5.66 | 6.71 | 78.17 |
| Restaurants | 185.40 | 5.44 | 6.67 | 60.72 |
| Movies | 331.56 | 5.59 | 7.32 | 55.69 |
| Books | 285.47 | 5.78 | 7.78 | 52.99 |
| Electronics | 249.44 | 5.56 | 6.98 | 58.89 |
| Grocery | 164.75 | 5.44 | 7.25 | 64.69 |
Dataset Creation
Curation Rationale
Most question-answering datasets like SQuAD and Natural Questions focus on answering questions over factual data such as Wikipedia and news articles. However, in domains like e-commerce the questions and answers are often subjective, that is, they depend on the personal experience of the users. For example, a customer on Amazon may ask "Is the sound quality any good?", which is more difficult to answer than a factoid question like "What is the capital of Australia?" These considerations motivate the creation of SubjQA as a tool to investigate the relationship between subjectivity and question-answering.
Source Data
Initial Data Collection and Normalization
The SubjQA dataset is constructed based on publicly available review datasets. Specifically, the movies, books, electronics, and grocery categories are constructed using reviews from the Amazon Review dataset. The TripAdvisor category, as the name suggests, is constructed using reviews from TripAdvisor which can be found here. Finally, the restaurants category is constructed using the Yelp Dataset which is also publicly available.
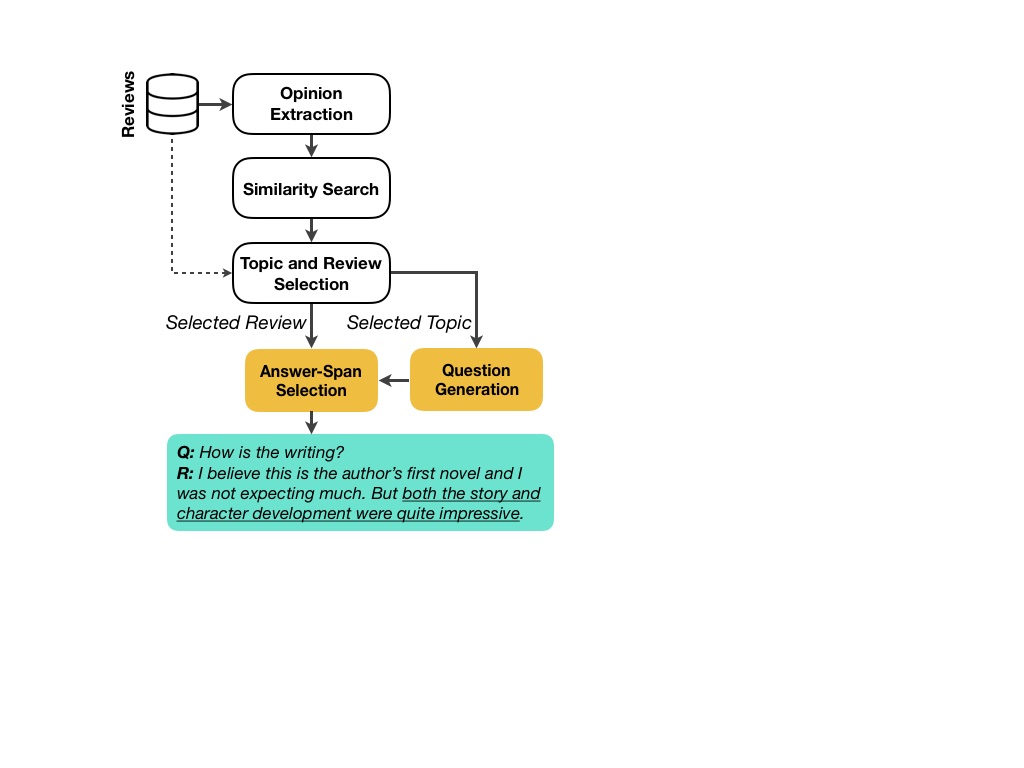
The process of constructing SubjQA is discussed in detail in the paper. In a nutshell, the dataset construction consists of the following steps:
- First, all opinions expressed in reviews are extracted. In the pipeline, each opinion is modeled as a (modifier, aspect) pair which is a pair of spans where the former describes the latter. (good, hotel), and (terrible, acting) are a few examples of extracted opinions.
- Using Matrix Factorization techniques, implication relationships between different expressed opinions are mined. For instance, the system mines that "responsive keys" implies "good keyboard". In our pipeline, we refer to the conclusion of an implication (i.e., "good keyboard" in this examples) as the query opinion, and we refer to the premise (i.e., "responsive keys") as its neighboring opinion.
- Annotators are then asked to write a question based on query opinions. For instance given "good keyboard" as the query opinion, they might write "Is this keyboard any good?"
- Each question written based on a query opinion is then paired with a review that mentions its neighboring opinion. In our example, that would be a review that mentions "responsive keys".
- The question and review pairs are presented to annotators to select the correct answer span, and rate the subjectivity level of the question as well as the subjectivity level of the highlighted answer span.
A visualisation of the data collection pipeline is shown in the image below.
Who are the source language producers?
As described above, the source data for SubjQA is customer reviews of products and services on e-commerce websites like Amazon and TripAdvisor.
Annotations
Annotation process
The generation of questions and answer span labels were obtained through the Appen platform. From the SubjQA paper:
The platform provides quality control by showing the workers 5 questions at a time, out of which one is labeled by the experts. A worker who fails to maintain 70% accuracy is kicked out by the platform and his judgements are ignored ... To ensure good quality labels, we paid each worker 5 cents per annotation.
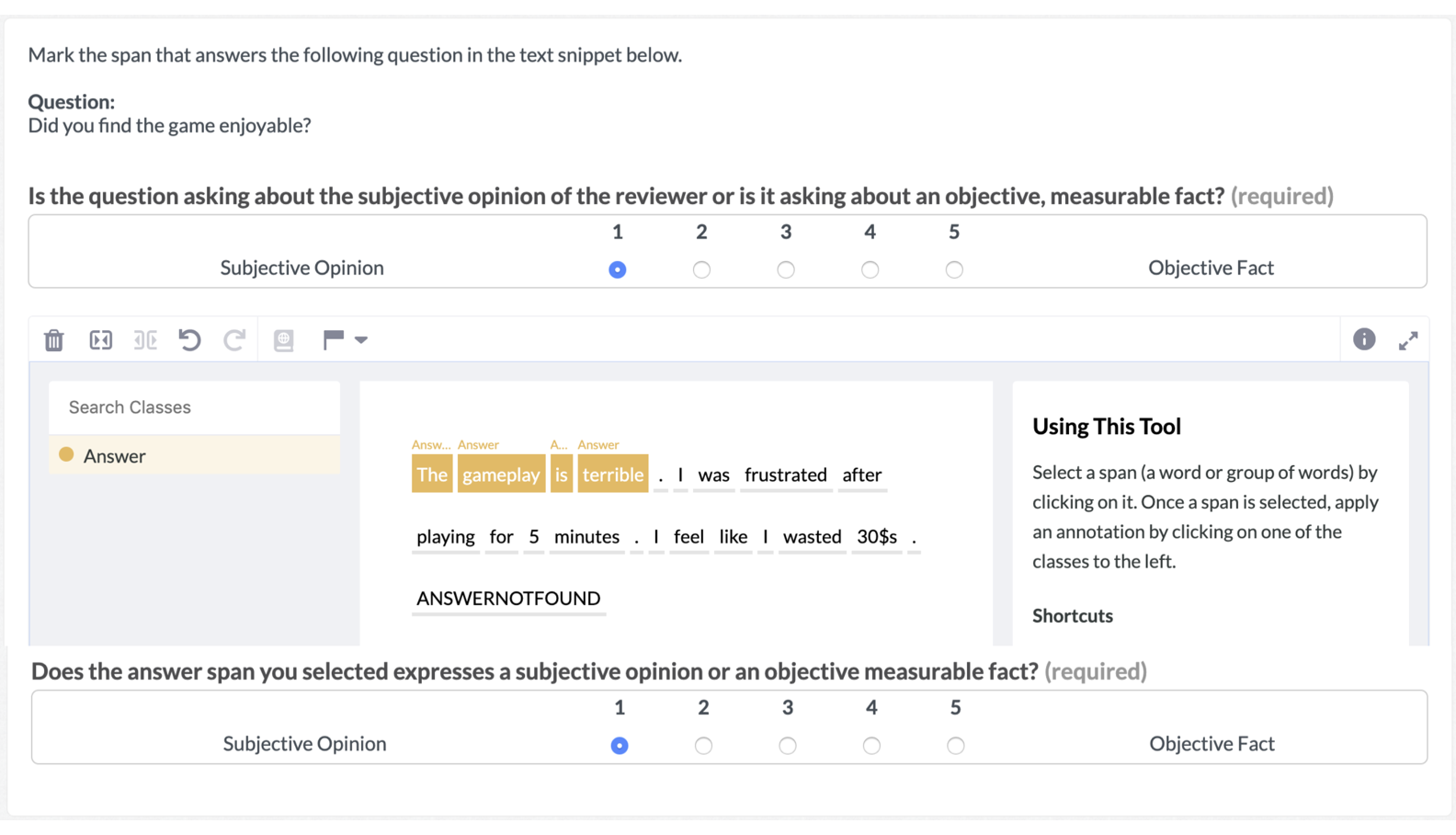
The instructions for generating a question are shown in the following figure:

Similarly, the interface for the answer span and subjectivity labelling tasks is shown below:
As described in the SubjQA paper, the workers assign subjectivity scores (1-5) to each question and the selected answer span. They can also indicate if a question cannot be answered from the given review.
Who are the annotators?
Workers on the Appen platform.
Personal and Sensitive Information
[Needs More Information]
Considerations for Using the Data
Social Impact of Dataset
The SubjQA dataset can be used to develop question-answering systems that can provide better on-demand answers to e-commerce customers who are interested in subjective questions about products and services.
Discussion of Biases
[Needs More Information]
Other Known Limitations
[Needs More Information]
Additional Information
Dataset Curators
The people involved in creating the SubjQA dataset are the authors of the accompanying paper:
- Johannes Bjerva1, Department of Computer Science, University of Copenhagen, Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University
- Nikita Bhutani, Megagon Labs, Mountain View
- Behzad Golshan, Megagon Labs, Mountain View
- Wang-Chiew Tan, Megagon Labs, Mountain View
- Isabelle Augenstein, Department of Computer Science, University of Copenhagen
Licensing Information
The SubjQA dataset is provided "as-is", and its creators make no representation as to its accuracy.
The SubjQA dataset is constructed based on the following datasets and thus contains subsets of their data:
- Amazon Review Dataset from UCSD
- Used for books, movies, grocery, and electronics domains
- The TripAdvisor Dataset from UIUC's Database and Information Systems Laboratory
- Used for the TripAdvisor domain
- The Yelp Dataset
- Used for the restaurants domain
Consequently, the data within each domain of the SubjQA dataset should be considered under the same license as the dataset it was built upon.
Citation Information
If you are using the dataset, please cite the following in your work:
@inproceedings{bjerva20subjqa,
title = "SubjQA: A Dataset for Subjectivity and Review Comprehension",
author = "Bjerva, Johannes and
Bhutani, Nikita and
Golahn, Behzad and
Tan, Wang-Chiew and
Augenstein, Isabelle",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing",
month = November,
year = "2020",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
}
Contributions
Thanks to @lewtun for adding this dataset.