GLM-4-9B-Chat
Model Introduction
GLM-4-9B is the open-source version of the latest generation of pre-trained models in the GLM-4 series launched by Zhipu AI. In the evaluation of data sets in semantics, mathematics, reasoning, code, and knowledge, GLM-4-9B and its human preference-aligned version GLM-4-9B-Chat have shown superior performance beyond Llama-3-8B. In addition to multi-round conversations, GLM-4-9B-Chat also has advanced features such as web browsing, code execution, custom tool calls (Function Call), and long text reasoning (supporting up to 128K context). This generation of models has added multi-language support, supporting 26 languages including Japanese, Korean, and German. We have also launched the GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M model that supports 1M context length (about 2 million Chinese characters) and the multimodal model GLM-4V-9B based on GLM-4-9B. GLM-4V-9B possesses dialogue capabilities in both Chinese and English at a high resolution of 1120*1120. In various multimodal evaluations, including comprehensive abilities in Chinese and English, perception & reasoning, text recognition, and chart understanding, GLM-4V-9B demonstrates superior performance compared to GPT-4-turbo-2024-04-09, Gemini 1.0 Pro, Qwen-VL-Max, and Claude 3 Opus.
Benchmark
We evaluated the GLM-4-9B-Chat model on some classic tasks and obtained the following results:
| Model | AlignBench-v2 | MT-Bench | IFEval | MMLU | C-Eval | GSM8K | MATH | HumanEval | NCB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 5.12 | 8.00 | 68.58 | 68.4 | 51.3 | 79.6 | 30.0 | 62.2 | 24.7 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 3.97 | 5.50 | 28.1 | 66.4 | 69.0 | 72.3 | 25.7 | 58.5 | 11.3 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 6.61 | 8.35 | 69.0 | 72.4 | 75.6 | 79.6 | 50.6 | 71.8 | 32.2 |
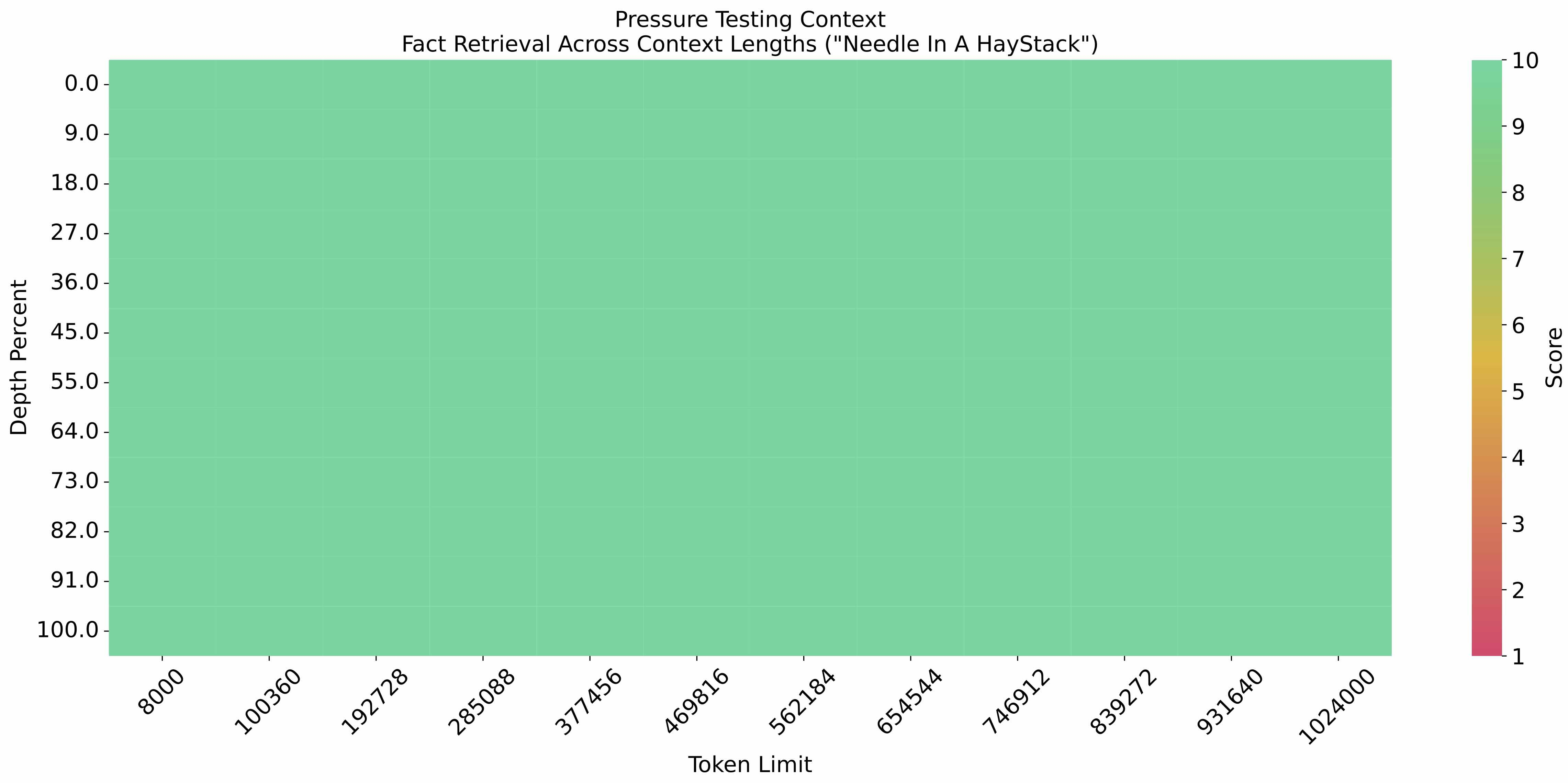
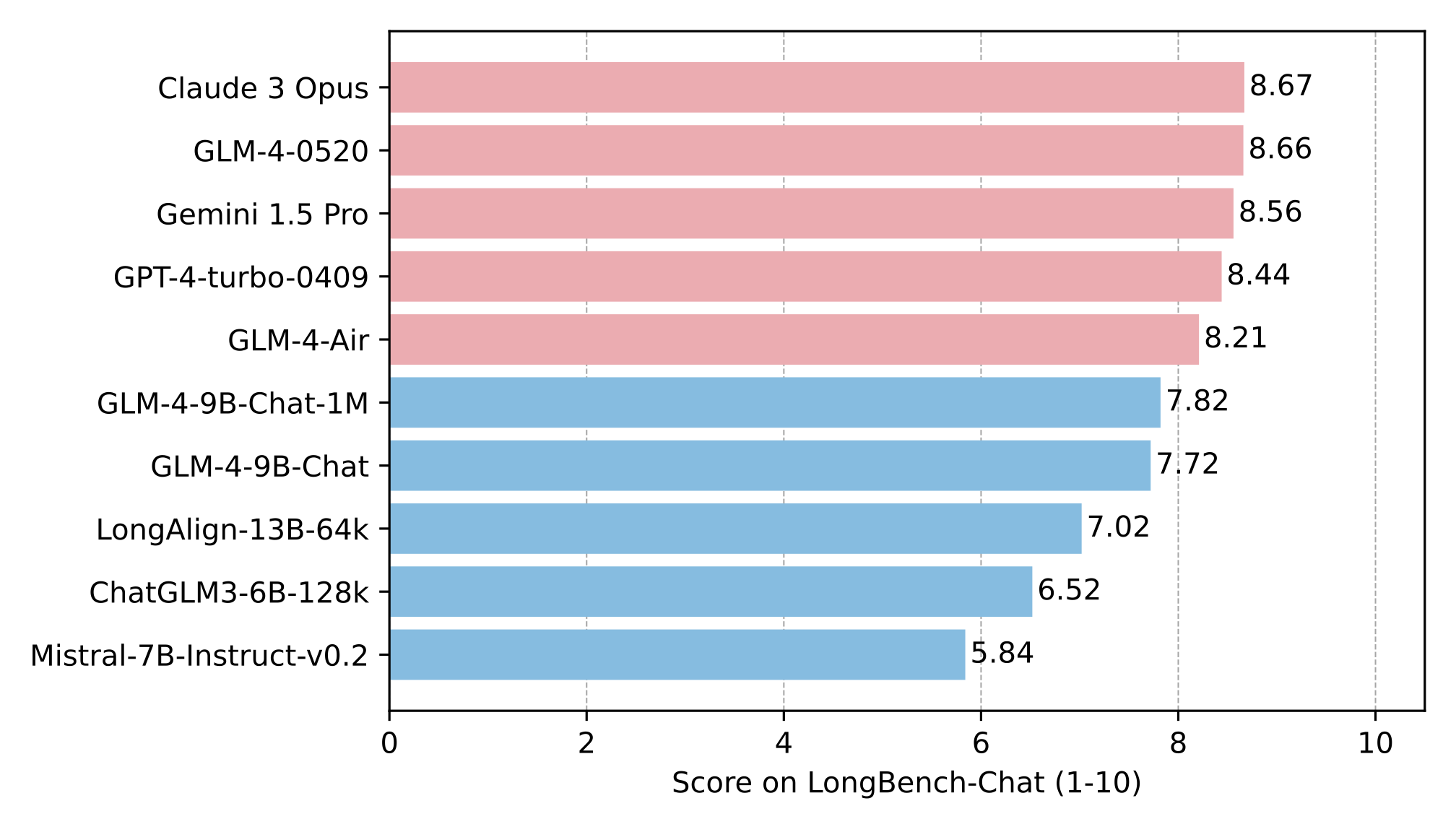
Long Context
The eval_needle experiment was conducted with a context length of 1M, and the results are as follows:
The long text capability was further evaluated on LongBench, and the results are as follows:
Multi Language
The tests for GLM-4-9B-Chat and Llama-3-8B-Instruct are conducted on six multilingual datasets. The test results and the corresponding languages selected for each dataset are shown in the table below:
| Dataset | Llama-3-8B-Instruct | GLM-4-9B-Chat | Languages |
|---|---|---|---|
| M-MMLU | 49.6 | 56.6 | all |
| FLORES | 25.0 | 28.8 | ru, es, de, fr, it, pt, pl, ja, nl, ar, tr, cs, vi, fa, hu, el, ro, sv, uk, fi, ko, da, bg, no |
| MGSM | 54.0 | 65.3 | zh, en, bn, de, es, fr, ja, ru, sw, te, th |
| XWinograd | 61.7 | 73.1 | zh, en, fr, jp, ru, pt |
| XStoryCloze | 84.7 | 90.7 | zh, en, ar, es, eu, hi, id, my, ru, sw, te |
| XCOPA | 73.3 | 80.1 | zh, et, ht, id, it, qu, sw, ta, th, tr, vi |
Function Call
Tested on Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard.
| Model | Overall Acc. | AST Summary | Exec Summary | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 58.88 | 59.25 | 70.01 | 45.83 |
| gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 81.24 | 82.14 | 78.61 | 88.75 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 57.88 | 62.18 | 69.78 | 5.42 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 81.00 | 80.26 | 84.40 | 87.92 |
This repository is the model repository of GLM-4-9B-Chat, supporting 128K context length.
Quick call
For hardware configuration and system requirements, please check here.
Use the following method to quickly call the GLM-4-9B-Chat language model
Use the transformers backend for inference:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat", trust_remote_code=True)
query = "Hello"
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([{"role": "user", "content": query}],
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True
)
inputs = inputs.to(device)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
trust_remote_code=True
).to(device).eval()
gen_kwargs = {"max_length": 2500, "do_sample": True, "top_k": 1}
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, **gen_kwargs)
outputs = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
Use the vLLM backend for inference:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M
# max_model_len, tp_size = 1048576, 4
# GLM-4-9B-Chat
# If you encounter OOM, it is recommended to reduce max_model_len or increase tp_size
max_model_len, tp_size = 131072, 1
model_name = "THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat"
prompt = [{"role": "user", "content": "hello"}]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
tensor_parallel_size=tp_size,
max_model_len=max_model_len,
trust_remote_code=True,
enforce_eager=True,
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M If you encounter OOM phenomenon, it is recommended to enable the following parameters
# enable_chunked_prefill=True,
# max_num_batched_tokens=8192
)
stop_token_ids = [151329, 151336, 151338]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.95, max_tokens=1024, stop_token_ids=stop_token_ids)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(prompt, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
outputs = llm.generate(prompts=inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
print(outputs[0].outputs[0].text)
LICENSE
The weights of the GLM-4 model are available under the terms of LICENSE.
Citations
If you find our work useful, please consider citing the following paper.
@article{zeng2022glm,
title={Glm-130b: An open bilingual pre-trained model},
author={Zeng, Aohan and Liu, Xiao and Du, Zhengxiao and Wang, Zihan and Lai, Hanyu and Ding, Ming and Yang, Zhuoyi and Xu, Yifan and Zheng, Wendi and Xia, Xiao and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.02414},
year={2022}
}
@inproceedings{du2022glm,
title={GLM: General Language Model Pretraining with Autoregressive Blank Infilling},
author={Du, Zhengxiao and Qian, Yujie and Liu, Xiao and Ding, Ming and Qiu, Jiezhong and Yang, Zhilin and Tang, Jie},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)},
pages={320--335},
year={2022}
}