license: other
license_name: glm-4
license_link: https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m/blob/main/LICENSE
language:
- zh
- en
tags:
- glm
- chatglm
- thudm
inference: false
glm-4-9b-chat
GLM-4-9B 是智谱 AI 推出的最新一代预训练模型 GLM-4 系列中的开源版本。 在语义、数学、推理、代码和知识等多方面的数据集测评中,GLM-4-9B 及其人类偏好对齐的版本 GLM-4-9B-Chat 均表现出较高的性能。 除了能进行多轮对话,GLM-4-9B-Chat 还具备网页浏览、代码执行、自定义工具调用(Function Call)和长文本推理(支持最大 128K 上下文)等高级功能。 本代模型增加了多语言支持,支持包括日语,韩语,德语在内的 26 种语言。我们还推出了支持 1M 上下文长度(约 200 万中文字符)的模型。
评测结果
我们在一些经典任务上对 GLM-4-9B 模型进行了评测,并得到了如下的结果
典型任务
| Model | AlignBench-v2 | MT-Bench | IFEval | MMLU | C-Eval | GSM8K | MATH | HumanEval | NCB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 5.12 | 8.00 | 68.58 | 68.4 | 51.3 | 79.6 | 30.0 | 62.2 | 24.7 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 3.97 | 5.50 | 28.1 | 66.4 | 69.0 | 72.3 | 25.7 | 58.5 | 11.3 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 6.61 | 8.35 | 69.0 | 72.4 | 75.6 | 79.6 | 50.6 | 71.8 | 32.2 |
长文本
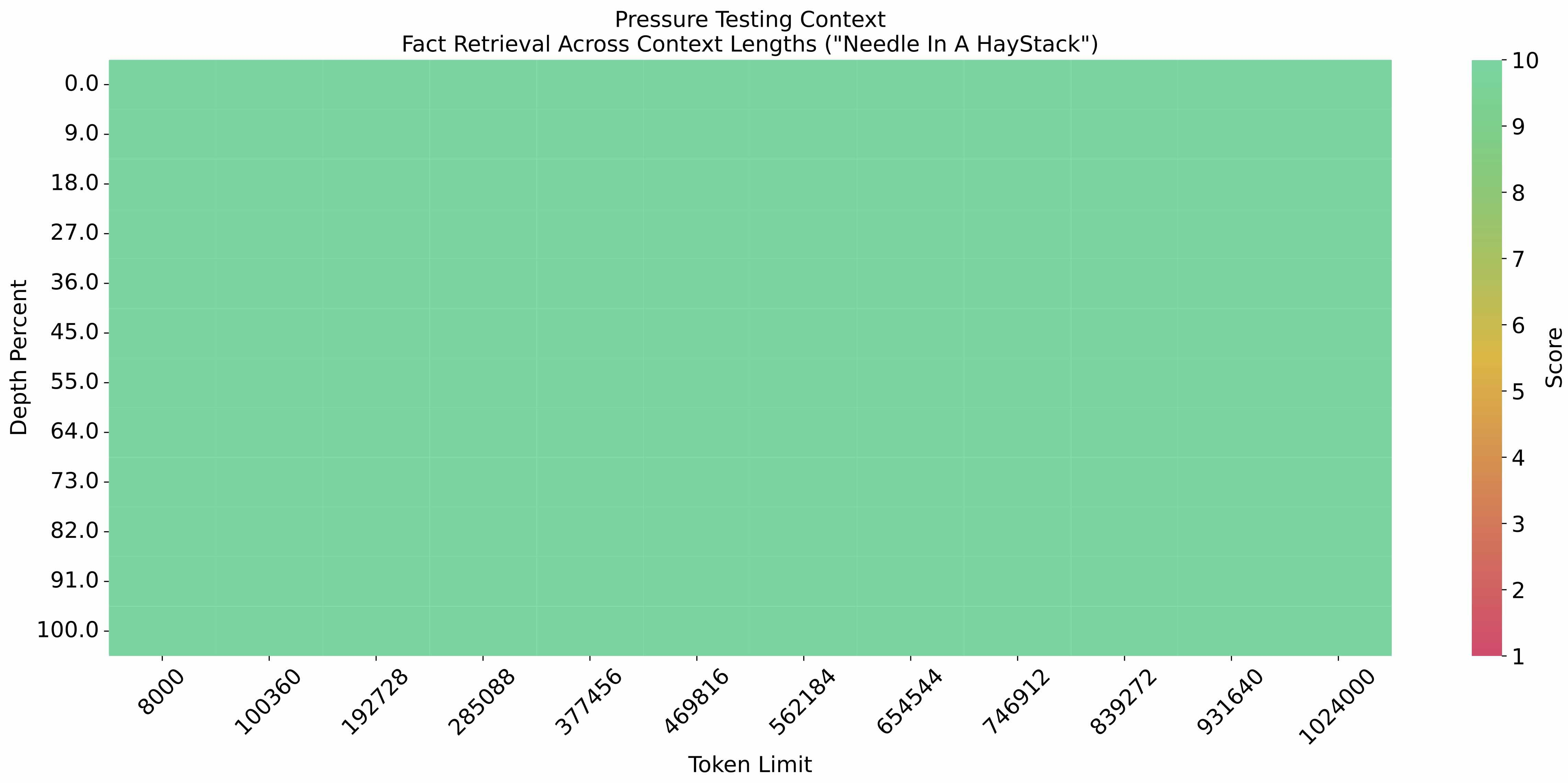
在 1M 的上下文长度下进行大海捞针实验,结果如下:
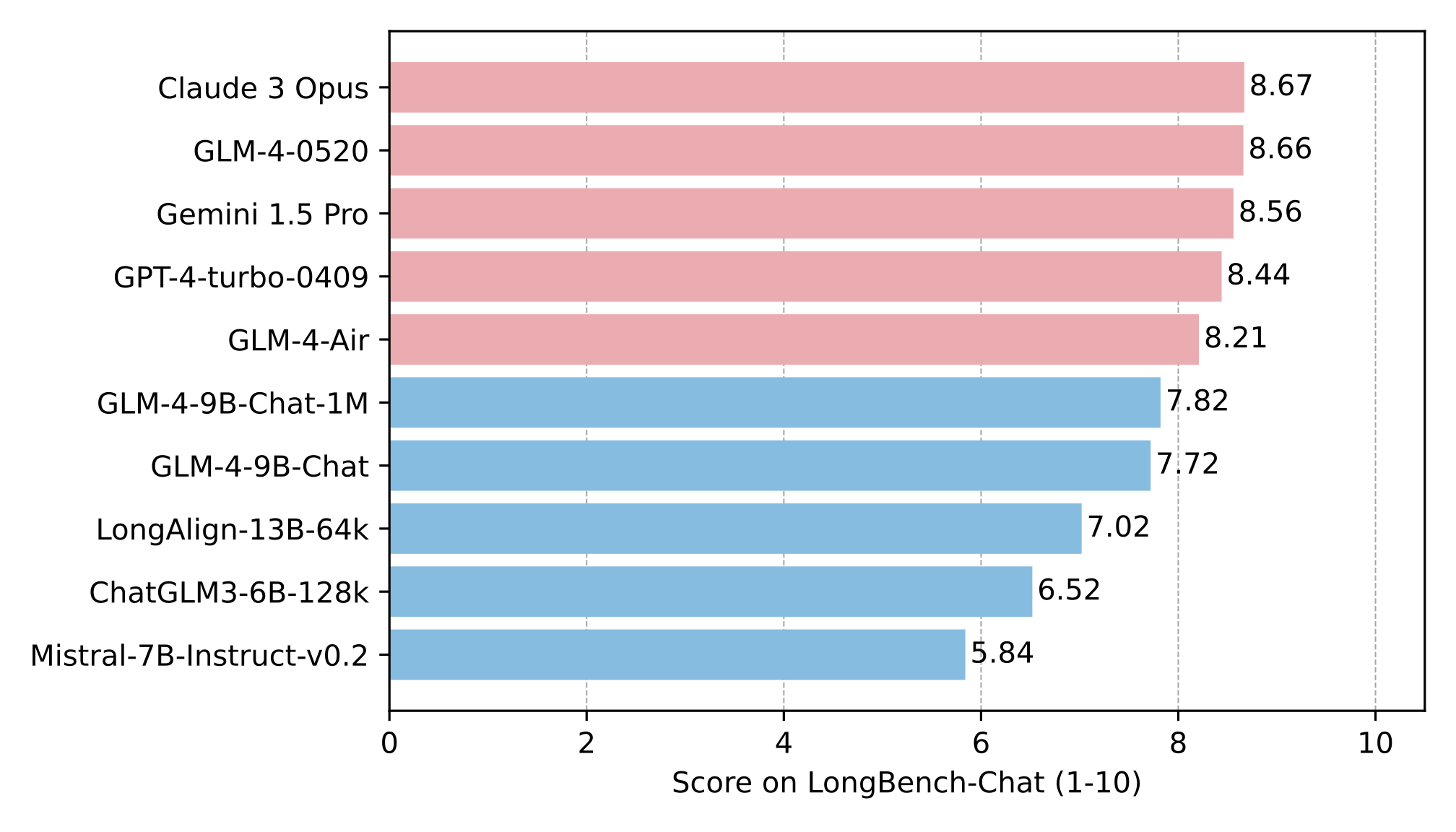
在 LongBench-Chat 上对长文本能力进行了进一步评测,结果如下:
多语言能力
在六个多语言数据集上对 GLM-4-9B-Chat 和 Llama-3-8B-Instruct 进行了 0-shot 测试。具体来说,M-MMLU测试了数据集提供的全部 34 种语言;FLORES测试了中英与另外 24 种语言(包括 ru, es, de, fr, it, pt, pl, ja, nl, ar, tr, cs, vi, fa, hu, el, ro, sv, uk, fi, ko, da, bg, no)之间的互译能力(中/英↔其他语言、中↔英);MGSM测试了 11 种语言的数学能力(包括 zh, en, bn, de, es, fr, ja, ru, sw, te, th);XWinograd测试了 6 种语言的指代消解能力(包括 zh, en, fr, jp, ru, pt);XStoryCloze测试了 11 种语言的故事结局预测能力(包括 zh, en, ar, es, eu, hi, id, my, ru, sw, te);XCOPA测试了 11 种语言的因果推理能力(包括 zh, et, ht, id, it, qu, sw, ta, th, tr, vi)。
| Model | M-MMLU | FLORES | MGSM | XWinograd | XStoryCloze | XCOPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 学科知识 | 翻译 | 数学 | 指代消解 | 故事结局预测 | 因果推理 | |
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 49.6 | 25.0 | 54.0 | 61.7 | 84.7 | 73.3 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 56.6 | 28.8 | 65.3 | 73.1 | 90.7 | 80.1 |
工具调用能力
| Model | Overall Acc. | AST Summary | Exec Summary | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 58.88 | 59.25 | 70.01 | 45.83 |
| GPT-4-turbo-0409 | 81.24 | 82.14 | 78.61 | 88.75 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 57.88 | 62.18 | 69.78 | 5.42 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 81.00 | 80.26 | 84.40 | 87.92 |
本仓库是 GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M 的模型仓库,支持1M上下文长度。
运行模型
使用 transformers 后端进行推理:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m",trust_remote_code=True)
query = "你好"
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([{"role": "user", "content": query}],
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True
)
inputs = inputs.to(device)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
trust_remote_code=True
).to(device).eval()
gen_kwargs = {"max_length": 2500, "do_sample": True, "top_k": 1}
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, **gen_kwargs)
outputs = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
使用 VLLM后端进行推理:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
max_model_len, tp_size = 1048576, 4
model_name = "THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m"
prompt = '你好'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
tensor_parallel_size=tp_size,
max_model_len=max_model_len,
trust_remote_code=True,
enforce_eager=True,
enable_chunked_prefill=True,
max_num_batched_tokens=8192
)
stop_token_ids = [151329, 151336, 151338]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.95, max_tokens=1024, stop_token_ids=stop_token_ids)
inputs = tokenizer.build_chat_input(prompt, history=None, role='user')['input_ids'].tolist()
outputs = llm.generate(prompt_token_ids=inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
generated_text = [output.outputs[0].text for output in outputs]
print(generated_text)
协议
GLM-4 模型的权重的使用则需要遵循 LICENSE。
Rhe use of the GLM-4 model weights needs to comply with the LICENSE.
引用
如果你觉得我们的工作有帮助的话,请考虑引用下列论文。
@article{zeng2022glm,
title={Glm-130b: An open bilingual pre-trained model},
author={Zeng, Aohan and Liu, Xiao and Du, Zhengxiao and Wang, Zihan and Lai, Hanyu and Ding, Ming and Yang, Zhuoyi and Xu, Yifan and Zheng, Wendi and Xia, Xiao and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.02414},
year={2022}
}
@inproceedings{du2022glm,
title={GLM: General Language Model Pretraining with Autoregressive Blank Infilling},
author={Du, Zhengxiao and Qian, Yujie and Liu, Xiao and Ding, Ming and Qiu, Jiezhong and Yang, Zhilin and Tang, Jie},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)},
pages={320--335},
year={2022}
}