Spaces:
Running
Running
Update Space (evaluate main: 7e21410f)
Browse files
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,12 +1,112 @@
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
| 2 |
-
title:
|
| 3 |
-
emoji:
|
| 4 |
-
colorFrom:
|
| 5 |
-
colorTo:
|
| 6 |
sdk: gradio
|
| 7 |
-
sdk_version: 3.
|
| 8 |
app_file: app.py
|
| 9 |
pinned: false
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
---
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
| 2 |
+
title: sMAPE
|
| 3 |
+
emoji: 🤗
|
| 4 |
+
colorFrom: blue
|
| 5 |
+
colorTo: red
|
| 6 |
sdk: gradio
|
| 7 |
+
sdk_version: 3.0.2
|
| 8 |
app_file: app.py
|
| 9 |
pinned: false
|
| 10 |
+
tags:
|
| 11 |
+
- evaluate
|
| 12 |
+
- metric
|
| 13 |
+
description: >-
|
| 14 |
+
Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error (sMAPE) is the symmetric mean percentage error difference between the predicted and actual values defined by Chen and Yang (2004).
|
| 15 |
---
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
+
# Metric Card for sMAPE
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
## Metric Description
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
Symmetric Mean Absolute Error (sMAPE) is the symmetric mean of the percentage error of difference between the predicted $x_i$ and actual $y_i$ numeric values:
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
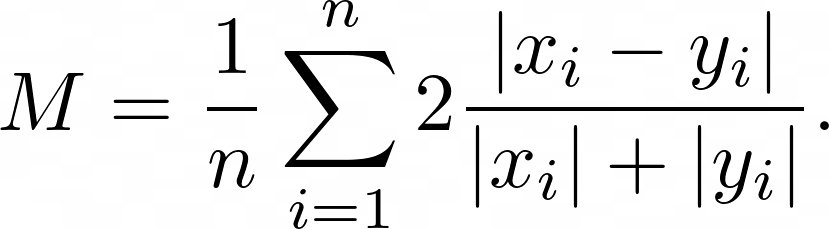
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
## How to Use
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
At minimum, this metric requires predictions and references as inputs.
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
```python
|
| 32 |
+
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape")
|
| 33 |
+
>>> predictions = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
|
| 34 |
+
>>> references = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
|
| 35 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
|
| 36 |
+
```
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
### Inputs
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
Mandatory inputs:
|
| 41 |
+
- `predictions`: numeric array-like of shape (`n_samples,`) or (`n_samples`, `n_outputs`), representing the estimated target values.
|
| 42 |
+
- `references`: numeric array-like of shape (`n_samples,`) or (`n_samples`, `n_outputs`), representing the ground truth (correct) target values.
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
Optional arguments:
|
| 45 |
+
- `sample_weight`: numeric array-like of shape (`n_samples,`) representing sample weights. The default is `None`.
|
| 46 |
+
- `multioutput`: `raw_values`, `uniform_average` or numeric array-like of shape (`n_outputs,`), which defines the aggregation of multiple output values. The default value is `uniform_average`.
|
| 47 |
+
- `raw_values` returns a full set of errors in case of multioutput input.
|
| 48 |
+
- `uniform_average` means that the errors of all outputs are averaged with uniform weight.
|
| 49 |
+
- the array-like value defines weights used to average errors.
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
### Output Values
|
| 52 |
+
This metric outputs a dictionary, containing the mean absolute error score, which is of type:
|
| 53 |
+
- `float`: if multioutput is `uniform_average` or an ndarray of weights, then the weighted average of all output errors is returned.
|
| 54 |
+
- numeric array-like of shape (`n_outputs,`): if multioutput is `raw_values`, then the score is returned for each output separately.
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
Each sMAPE `float` value ranges from `0.0` to `2.0`, with the best value being 0.0.
|
| 57 |
+
|
| 58 |
+
Output Example(s):
|
| 59 |
+
```python
|
| 60 |
+
{'smape': 0.5}
|
| 61 |
+
```
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
If `multioutput="raw_values"`:
|
| 64 |
+
```python
|
| 65 |
+
{'smape': array([0.5, 1.5 ])}
|
| 66 |
+
```
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
#### Values from Popular Papers
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
### Examples
|
| 72 |
+
|
| 73 |
+
Example with the `uniform_average` config:
|
| 74 |
+
```python
|
| 75 |
+
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape")
|
| 76 |
+
>>> predictions = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
|
| 77 |
+
>>> references = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
|
| 78 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
|
| 79 |
+
>>> print(results)
|
| 80 |
+
{'smape': 0.5787...}
|
| 81 |
+
```
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
Example with multi-dimensional lists, and the `raw_values` config:
|
| 84 |
+
```python
|
| 85 |
+
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape", "multilist")
|
| 86 |
+
>>> predictions = [[0.5, 1], [-1, 1], [7, -6]]
|
| 87 |
+
>>> references = [[0.1, 2], [-1, 2], [8, -5]]
|
| 88 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
|
| 89 |
+
>>> print(results)
|
| 90 |
+
{'smape': 0.8874...}
|
| 91 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references, multioutput='raw_values')
|
| 92 |
+
>>> print(results)
|
| 93 |
+
{'smape': array([1.3749..., 0.4])}
|
| 94 |
+
```
|
| 95 |
+
|
| 96 |
+
## Limitations and Bias
|
| 97 |
+
This metric is called a measure of "percentage error" even though there is no multiplier of 100. The range is between (0, 2) with it being two when the target and prediction are both zero.
|
| 98 |
+
|
| 99 |
+
## Citation(s)
|
| 100 |
+
|
| 101 |
+
```bibtex
|
| 102 |
+
@article{article,
|
| 103 |
+
author = {Chen, Zhuo and Yang, Yuhong},
|
| 104 |
+
year = {2004},
|
| 105 |
+
month = {04},
|
| 106 |
+
pages = {},
|
| 107 |
+
title = {Assessing forecast accuracy measures}
|
| 108 |
+
}
|
| 109 |
+
```
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
## Further References
|
| 112 |
+
- [Symmetric Mean absolute percentage error - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symmetric_mean_absolute_percentage_error)
|
app.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import evaluate
|
| 2 |
+
from evaluate.utils import launch_gradio_widget
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
|
| 5 |
+
module = evaluate.load("smape")
|
| 6 |
+
launch_gradio_widget(module)
|
requirements.txt
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
git+https://github.com/huggingface/evaluate@7e21410f9bcff651452f188b702cc80ecd3530e6
|
| 2 |
+
sklearn
|
smape.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Datasets Authors and the current dataset script contributor.
|
| 2 |
+
#
|
| 3 |
+
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
| 4 |
+
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
| 5 |
+
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
| 6 |
+
#
|
| 7 |
+
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
| 8 |
+
#
|
| 9 |
+
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
| 10 |
+
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
| 11 |
+
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
| 12 |
+
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
| 13 |
+
# limitations under the License.
|
| 14 |
+
"""sMAPE - Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error Metric"""
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
import datasets
|
| 17 |
+
import numpy as np
|
| 18 |
+
from sklearn.metrics._regression import _check_reg_targets
|
| 19 |
+
from sklearn.utils.validation import check_consistent_length
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
import evaluate
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
_CITATION = """\
|
| 25 |
+
@article{article,
|
| 26 |
+
author = {Chen, Zhuo and Yang, Yuhong},
|
| 27 |
+
year = {2004},
|
| 28 |
+
month = {04},
|
| 29 |
+
pages = {},
|
| 30 |
+
title = {Assessing forecast accuracy measures}
|
| 31 |
+
}
|
| 32 |
+
"""
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
_DESCRIPTION = """\
|
| 35 |
+
Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error (sMAPE) is the symmetric mean percentage error
|
| 36 |
+
difference between the predicted and actual values as defined by Chen and Yang (2004),
|
| 37 |
+
based on the metric by Armstrong (1985) and Makridakis (1993).
|
| 38 |
+
"""
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
_KWARGS_DESCRIPTION = """
|
| 42 |
+
Args:
|
| 43 |
+
predictions: array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
|
| 44 |
+
Estimated target values.
|
| 45 |
+
references: array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
|
| 46 |
+
Ground truth (correct) target values.
|
| 47 |
+
sample_weight: array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
|
| 48 |
+
Sample weights.
|
| 49 |
+
multioutput: {"raw_values", "uniform_average"} or array-like of shape (n_outputs,), default="uniform_average"
|
| 50 |
+
Defines aggregating of multiple output values. Array-like value defines weights used to average errors.
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
"raw_values" : Returns a full set of errors in case of multioutput input.
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
"uniform_average" : Errors of all outputs are averaged with uniform weight.
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
Returns:
|
| 57 |
+
smape : symmetric mean absolute percentage error.
|
| 58 |
+
If multioutput is "raw_values", then symmetric mean absolute percentage error is returned for each output separately. If multioutput is "uniform_average" or an ndarray of weights, then the weighted average of all output errors is returned.
|
| 59 |
+
sMAPE output is non-negative floating point in the range (0, 2). The best value is 0.0.
|
| 60 |
+
Examples:
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape")
|
| 63 |
+
>>> predictions = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
|
| 64 |
+
>>> references = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
|
| 65 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
|
| 66 |
+
>>> print(results)
|
| 67 |
+
{'smape': 0.5787878787878785}
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
If you're using multi-dimensional lists, then set the config as follows :
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape", "multilist")
|
| 72 |
+
>>> predictions = [[0.5, 1], [-1, 1], [7, -6]]
|
| 73 |
+
>>> references = [[0.1, 2], [-1, 2], [8, -5]]
|
| 74 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
|
| 75 |
+
>>> print(results)
|
| 76 |
+
{'smape': 0.49696969558995985}
|
| 77 |
+
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references, multioutput='raw_values')
|
| 78 |
+
>>> print(results)
|
| 79 |
+
{'smape': array([0.48888889, 0.50505051])}
|
| 80 |
+
"""
|
| 81 |
+
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
def symmetric_mean_absolute_percentage_error(y_true, y_pred, *, sample_weight=None, multioutput="uniform_average"):
|
| 84 |
+
"""Symmetric Mean absolute percentage error (sMAPE) metric using sklearn's api and helpers.
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
Parameters
|
| 87 |
+
----------
|
| 88 |
+
y_true : array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
|
| 89 |
+
Ground truth (correct) target values.
|
| 90 |
+
y_pred : array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
|
| 91 |
+
Estimated target values.
|
| 92 |
+
sample_weight : array-like of shape (n_samples,), default=None
|
| 93 |
+
Sample weights.
|
| 94 |
+
multioutput : {'raw_values', 'uniform_average'} or array-like
|
| 95 |
+
Defines aggregating of multiple output values.
|
| 96 |
+
Array-like value defines weights used to average errors.
|
| 97 |
+
If input is list then the shape must be (n_outputs,).
|
| 98 |
+
'raw_values' :
|
| 99 |
+
Returns a full set of errors in case of multioutput input.
|
| 100 |
+
'uniform_average' :
|
| 101 |
+
Errors of all outputs are averaged with uniform weight.
|
| 102 |
+
Returns
|
| 103 |
+
-------
|
| 104 |
+
loss : float or ndarray of floats
|
| 105 |
+
If multioutput is 'raw_values', then mean absolute percentage error
|
| 106 |
+
is returned for each output separately.
|
| 107 |
+
If multioutput is 'uniform_average' or an ndarray of weights, then the
|
| 108 |
+
weighted average of all output errors is returned.
|
| 109 |
+
sMAPE output is non-negative floating point. The best value is 0.0.
|
| 110 |
+
"""
|
| 111 |
+
y_type, y_true, y_pred, multioutput = _check_reg_targets(y_true, y_pred, multioutput)
|
| 112 |
+
check_consistent_length(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight)
|
| 113 |
+
epsilon = np.finfo(np.float64).eps
|
| 114 |
+
smape = 2 * np.abs(y_pred - y_true) / (np.maximum(np.abs(y_true), epsilon) + np.maximum(np.abs(y_pred), epsilon))
|
| 115 |
+
output_errors = np.average(smape, weights=sample_weight, axis=0)
|
| 116 |
+
if isinstance(multioutput, str):
|
| 117 |
+
if multioutput == "raw_values":
|
| 118 |
+
return output_errors
|
| 119 |
+
elif multioutput == "uniform_average":
|
| 120 |
+
# pass None as weights to np.average: uniform mean
|
| 121 |
+
multioutput = None
|
| 122 |
+
|
| 123 |
+
return np.average(output_errors, weights=multioutput)
|
| 124 |
+
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
@evaluate.utils.file_utils.add_start_docstrings(_DESCRIPTION, _KWARGS_DESCRIPTION)
|
| 127 |
+
class Smape(evaluate.Metric):
|
| 128 |
+
def _info(self):
|
| 129 |
+
return evaluate.MetricInfo(
|
| 130 |
+
description=_DESCRIPTION,
|
| 131 |
+
citation=_CITATION,
|
| 132 |
+
inputs_description=_KWARGS_DESCRIPTION,
|
| 133 |
+
features=datasets.Features(self._get_feature_types()),
|
| 134 |
+
reference_urls=["https://robjhyndman.com/hyndsight/smape/"],
|
| 135 |
+
)
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
def _get_feature_types(self):
|
| 138 |
+
if self.config_name == "multilist":
|
| 139 |
+
return {
|
| 140 |
+
"predictions": datasets.Sequence(datasets.Value("float")),
|
| 141 |
+
"references": datasets.Sequence(datasets.Value("float")),
|
| 142 |
+
}
|
| 143 |
+
else:
|
| 144 |
+
return {
|
| 145 |
+
"predictions": datasets.Value("float"),
|
| 146 |
+
"references": datasets.Value("float"),
|
| 147 |
+
}
|
| 148 |
+
|
| 149 |
+
def _compute(self, predictions, references, sample_weight=None, multioutput="uniform_average"):
|
| 150 |
+
|
| 151 |
+
smape_score = symmetric_mean_absolute_percentage_error(
|
| 152 |
+
references,
|
| 153 |
+
predictions,
|
| 154 |
+
sample_weight=sample_weight,
|
| 155 |
+
multioutput=multioutput,
|
| 156 |
+
)
|
| 157 |
+
|
| 158 |
+
return {"smape": smape_score}
|