에러가 발생했을 때 대응 방법
이번 장에서는 Transformer 모델을 새롭게 튜닝 후 예측을 하려고 할 때 발생할 수 있는 몇가지 일반적인 에러를 살펴보겠습니다.
이번 장에서 모델의 저장소 템플릿이 준비되어 있습니다. 만약 이번 단원에서 코드를 실행하려면 모델을 Huggingface Hub의 개인 계정에 모델을 복사해야 합니다. 모델을 계정의 저장소에 복제하기 위해 주피터 노트북에서 아래의 코드를 실행하거나:
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()또는 아래의 스크립트를 원하는 터미널에서 실행합니다:
huggingface-cli login
터미널에서 아이디와 비밀번호를 입력하는 프롬프트가 나타나며, 식별 토큰은 ~/.cache/huggingface/에 저장됩니다. 한번 로그인 하고 나면 모델의 저장소 템플릿을 아래의 함수를 사용해 복사할 수 있습니다:
from distutils.dir_util import copy_tree
from huggingface_hub import Repository, snapshot_download, create_repo, get_full_repo_name
def copy_repository_template():
# Clone the repo and extract the local path
template_repo_id = "lewtun/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28"
commit_hash = "be3eaffc28669d7932492681cd5f3e8905e358b4"
template_repo_dir = snapshot_download(template_repo_id, revision=commit_hash)
# Create an empty repo on the Hub
model_name = template_repo_id.split("/")[1]
create_repo(model_name, exist_ok=True)
# Clone the empty repo
new_repo_id = get_full_repo_name(model_name)
new_repo_dir = model_name
repo = Repository(local_dir=new_repo_dir, clone_from=new_repo_id)
# Copy files
copy_tree(template_repo_dir, new_repo_dir)
# Push to Hub
repo.push_to_hub()이제 copy_repository_template()를 호출하면 모델 저장소의 템플릿이 계정에 복사 됩니다.
🤗 Transformers의 파이프라인 디버깅
Transformer 모델들의 멋진 디버깅 세계로 여정을 떠나기 위해, 다음의 시나리오를 생각해보세요: 여러분은 E-commerce 사이트의 고객이 소비자 상품에 대한 답변을 찾기 위한 질문 및 답변 프로젝트에서 동료와 함께 일하고 있으며, 동료가 당신에게 다음과 같은 메세지를 보냈습니다:
안녕하세요! Hugging Face 코스에 있는 7 단원의 기술을 활용해서 실험을 해봤는데, SQuAD에서 좋은 결과를 얻었습니다. 저희 프로젝트를 이 모델로 시작할 수 있다고 생각이 됩니다. 허브에 있는 모델 아이디는 “lewtun/distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28” 입니다. 마음 껏 테스트 해보세요. :)
🤗 Transformers의 pipeline을 사용는 모델을 불러오기 위해 우선 고려해야 할 것이 있습니다:
from transformers import pipeline
model_checkpoint = get_full_repo_name("distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28")
reader = pipeline("question-answering", model=model_checkpoint)"""
OSError: Can't load config for 'lewtun/distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28'. make sure that:
- 'lewtun/distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28'이라는 모델명이 'https://huggingface.co/models'에 존재하는지 확인하거나
'lewtun/distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28'이라는 경로 또는 폴더가 config.json 파일 포함하고 있는지 확인하세요.
"""아 이런, 뭔가 잘못된 것 같네요! 만약 프로그래밍이 처음이라면, 이런 종류의 에러가 처음에는 다소 신비하게(OSError란 도대체..) 보일 수도 있습니다. 여기에서 보이는 에러는 파이썬의 traceback(stack trace로 알려져있음)으로 불리는 좀 더 큰 에러 리포트의 마지막 부분 입니다. 예를 들어 이 코드를 Google의 Colab에서 실행한다면 아래와 같은 스크린샷을 보게 될겁니다:
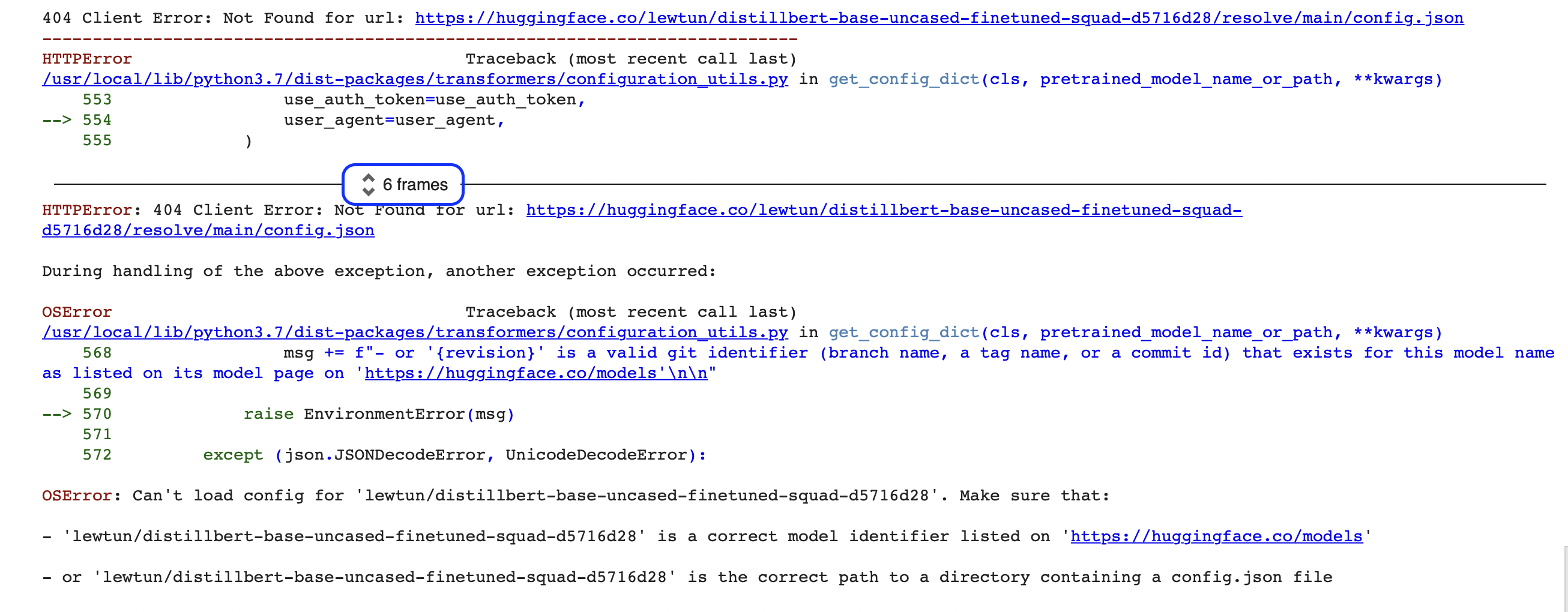
이 리포트에는 많은 정보를 담고 있으니, 같이 핵심 부분을 살펴보겠습니다. 우선 명심해야할 것은 tracebacks은 아래부터 위로 읽어야 합니다. 이러한 말은 영어 텍스트를 위에서 아래로 읽어오곤 했다면 이상하게 들릴 수 있겠지만 모델과 토크나이저를 다운로드 할 때 pipeline이 만드는 함수 호출 순서를 보여주는 traceback을 반영했기 때문입니다. 내부에서 pipeline이 작동하는 방식에 대한 자세한 내용은 단원 2를 참고하세요.
Google Colab의 traceback에서 “6 frames” 주변의 파란 상자를 보셨나요? traceback을 “frames”로 압축하는 Colab의 특별한 기능입니다. 만약 오류의 원인을 찾을 수 없다면, 두개의 작은 화살표를 클릭해서 전체 traceback을 확장되어 있는지 여부를 확인하세요.
즉 마지막 에러 메시지와 발생한 예외의 이름을 가리키는 traceback의 마지막 줄을 뜻합니다. 이 경우의 예외 유형은 시스템 관련 오류를 나타내는 OS Error 입니다. 첨부된 오류 메시지를 읽으면 모델의 config.json 파일에 문제가 있는 것으로 보이며 이를 수정하기 위해 두 가지 선택지가 있습니다:
"""
make sure that:
- 'lewtun/distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28' is a correct model identifier listed on 'https://huggingface.co/models'
- or 'lewtun/distillbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28' is the correct path to a directory containing a config.json file
"""💡 이해하기 어려운 에러 메시지를 접하게 된다면, 메세지를 복사해서 Google 또는 스택오버플로우 검색창에 붙여 넣기만 하세요(네 진짭니다!). 이는 오류가 발생한 첫 사람이 아닐 가능성이 높을뿐더러, 커뮤니티의 다른 사람들이 게시한 솔루션을 찾는 좋은 방법입니다. 예를 들어, 스택오버플로우에서 ‘OSError: Can’t load config for’를 검색하면 여러 해답을 제공하며 문제 해결을 위한 출발점으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
첫 번째 제안은 모델 ID가 실제로 정확한지 확인하도록 요청하는 것으로 비즈니스의 첫 순서는 식별자(모델 이름)를 복사하여 Hub의 검색 창에 붙여넣는 것입니다:
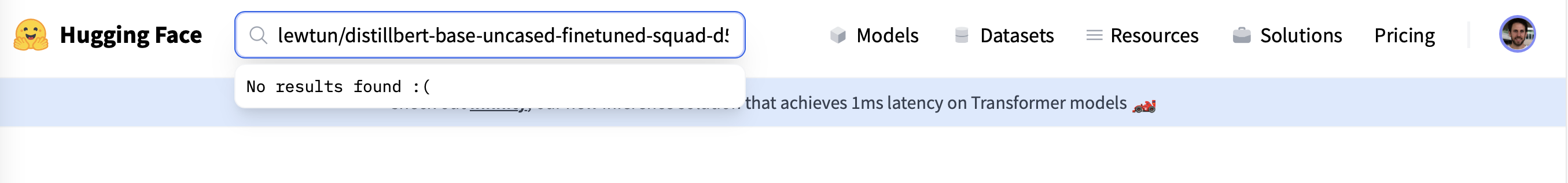
음, 동료의 모델이 허브에 없는 것 같습니다… 아하, 모델의 이름에 오타가 있었습니다! DistilBERT는 이름에 “l”이 하나만 있으므로 이를 수정하고 대신 “lewtun/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28”을 찾아보겠습니다:
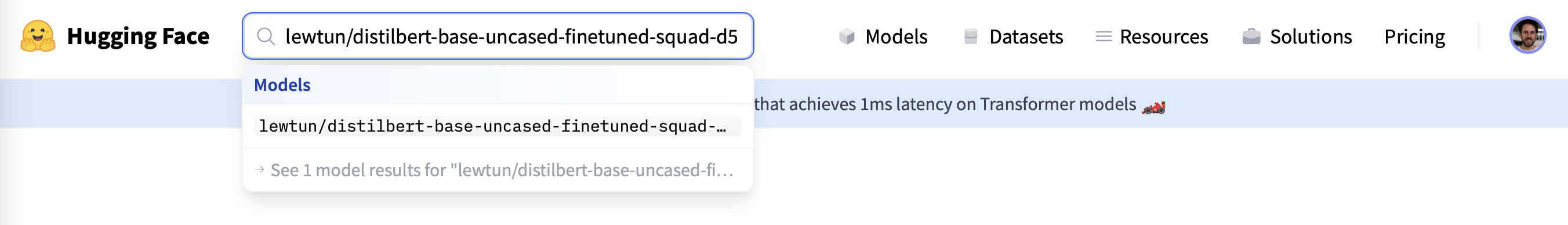
좋습니다, 성공했군요. 이제 올바른 모델 ID로 모델을 다시 다운로드 해봅시다:
model_checkpoint = get_full_repo_name("distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28")
reader = pipeline("question-answering", model=model_checkpoint)"""
OSError: Can't load config for 'lewtun/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28'. Make sure that:
- 'lewtun/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28' is a correct model identifier listed on 'https://huggingface.co/models'
- or 'lewtun/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-squad-d5716d28' is the correct path to a directory containing a config.json file
"""아오 또 실패입니다. 머신러닝 엔지니어의 일상에 오신 것을 환영합니다! 모델 ID를 수정했으므로 문제는 저장소 자체에 있어야 합니다. 🤗 Hub의 저장소 컨텐츠에 빠르게 액세스하는 방법은 huggingface_hub 라이브러리의 list_repo_files() 함수를 사용하는 것입니다:
from huggingface_hub import list_repo_files
list_repo_files(repo_id=model_checkpoint)['.gitattributes', 'README.md', 'pytorch_model.bin', 'special_tokens_map.json', 'tokenizer_config.json', 'training_args.bin', 'vocab.txt']흥미롭네요 — 이 저장소에는 config.json가 보이지 않습니다! 우리의 pipeline이 모델을 불러올 수 없는 것이 당연했군요; 동료가 파인튜닝 후에 허브에 푸시하는 것을 잊어버린 모양입니다. 이 경우, 문제는 매우 간단하게 해결할 수 있습니다: 동료에게 파일을 추가하도록 요청하거나, 사전 훈련(pretrained)된 모델이 distilbert-base-uncased인 것을 확인 할 수 있으므로, 이 모델에 대한 config를 다운로드하고 저장소에 푸시하여 문제가 해결되는지 확인할 수 있습니다. 시도 해봅시다. 단원 2에서 배운 기술을 사용해 AutoConfig 클래스로 모델의 config 파일을 다운로드할 수 있습니다.
from transformers import AutoConfig
pretrained_checkpoint = "distilbert-base-uncased"
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(pretrained_checkpoint)🚨 여기에서 하는 접근 방식은 동료가 ‘distilbert-base-uncased’의 config를 수정했을 수 있으므로 이 접근 방식은 완전하지 않습니다. 우리는 동료에게 먼저 확인하고 싶겠지만, 이번 장에서의 목적상, 동료가 디폴트 config를 사용했다고 가정하겠습니다.
그런 다음 config 클래스의 push_to_hub() 기능을 사용해서 config 파일을 모델 저장소로 푸시할 수 있습니다:
We can then push this to our model repository with the configuration’s push_to_hub() function:
config.push_to_hub(model_checkpoint, commit_message="Add config.json")이제 main 브랜치의 최신 커밋에서 모델을 로드해서 작동 여부를 테스트할 수 있습니다:
reader = pipeline("question-answering", model=model_checkpoint, revision="main")
context = r"""
Extractive Question Answering is the task of extracting an answer from a text
given a question. An example of a question answering dataset is the SQuAD
dataset, which is entirely based on that task. If you would like to fine-tune a
model on a SQuAD task, you may leverage the
examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_squad.py script.
🤗 Transformers is interoperable with the PyTorch, TensorFlow, and JAX
frameworks, so you can use your favourite tools for a wide variety of tasks!
"""
question = "What is extractive question answering?"
reader(question=question, context=context){'score': 0.38669535517692566,
'start': 34,
'end': 95,
'answer': 'the task of extracting an answer from a text given a question'}유후, 동작하네요! 방금 배운 내용을 요약 해보겠습니다:
- Python의 오류 메시지는 tracebacks로 알려져 있으며 아래에서 위로 읽습니다. 오류 메시지의 마지막 줄에는 일반적으로 문제의 원인을 찾는 데 필요한 정보가 포함되어 있습니다.
- 마지막 줄에 충분한 정보가 포함되어 있지 않으면 traceback을 위로 훑어보고 소스 코드에서 오류가 발생한 위치를 식별할 수 있는지 확인합니다.
- 오류 메시지가 문제를 디버그하는 데 도움이 되지 않으면 온라인에서 유사한 문제에 대한 해결책을 검색해 보세요.
huggingface_hub// 🤗 Hub? 이 라이브러리는 허브의 저장소와 상호 작용하고 디버그하는 데 사용할 수 있는 툴들을 제공합니다.
이제 파이프라인을 디버깅하는 방법을 알았으니 모델 자체의 forward pass에서 더 까다로운 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
모델의 foward pass 디버깅
‘pipeline’은 빠르게 예측을 생성해야 하는 대부분의 애플리케이션에 적합하지만 때로는 모델의 logits값에 접근해야 할 수도 있습니다(예: 적용하려는 커스텀 후처리 과정이 있는 경우). 이 경우 무엇이 잘못될 수 있는지 알아보기 위해 먼저 pipeline에서 모델과 토크나이저를 가져와 보겠습니다:
tokenizer = reader.tokenizer model = reader.model
다음으로 질문이 필요합니다. 선호하는 프레임워크가 지원되는지 살펴보겠습니다:
question = "Which frameworks can I use?"단원 7에서 보았듯이 일반적인 단계는 입력을 토큰화하고 시작과 마지막 토큰의 logits를 추출한 다음 응답 부분을 디코딩하는 것입니다:
import torch
inputs = tokenizer(question, context, add_special_tokens=True)
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"][0]
outputs = model(**inputs)
answer_start_scores = outputs.start_logits
answer_end_scores = outputs.end_logits
# Get the most likely beginning of answer with the argmax of the score
answer_start = torch.argmax(answer_start_scores)
# Get the most likely end of answer with the argmax of the score
answer_end = torch.argmax(answer_end_scores) + 1
answer = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_string(
tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids[answer_start:answer_end])
)
print(f"Question: {question}")
print(f"Answer: {answer}")"""
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
/var/folders/28/k4cy5q7s2hs92xq7_h89_vgm0000gn/T/ipykernel_75743/2725838073.py in <module>
1 inputs = tokenizer(question, text, add_special_tokens=True)
2 input_ids = inputs["input_ids"]
----> 3 outputs = model(**inputs)
4 answer_start_scores = outputs.start_logits
5 answer_end_scores = outputs.end_logits
~/miniconda3/envs/huggingface/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py in _call_impl(self, *input, **kwargs)
1049 if not (self._backward_hooks or self._forward_hooks or self._forward_pre_hooks or _global_backward_hooks
1050 or _global_forward_hooks or _global_forward_pre_hooks):
-> 1051 return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
1052 # Do not call functions when jit is used
1053 full_backward_hooks, non_full_backward_hooks = [], []
~/miniconda3/envs/huggingface/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/distilbert/modeling_distilbert.py in forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, head_mask, inputs_embeds, start_positions, end_positions, output_attentions, output_hidden_states, return_dict)
723 return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
724
--> 725 distilbert_output = self.distilbert(
726 input_ids=input_ids,
727 attention_mask=attention_mask,
~/miniconda3/envs/huggingface/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py in _call_impl(self, *input, **kwargs)
1049 if not (self._backward_hooks or self._forward_hooks or self._forward_pre_hooks or _global_backward_hooks
1050 or _global_forward_hooks or _global_forward_pre_hooks):
-> 1051 return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
1052 # Do not call functions when jit is used
1053 full_backward_hooks, non_full_backward_hooks = [], []
~/miniconda3/envs/huggingface/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/distilbert/modeling_distilbert.py in forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, head_mask, inputs_embeds, output_attentions, output_hidden_states, return_dict)
471 raise ValueError("You cannot specify both input_ids and inputs_embeds at the same time")
472 elif input_ids is not None:
--> 473 input_shape = input_ids.size()
474 elif inputs_embeds is not None:
475 input_shape = inputs_embeds.size()[:-1]
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'size'
"""이런, 코드에 버그가 있는 것 같네요! 하지만 약간의 디버깅은 두렵지 않습니다. 노트북에서 파이썬 디버거를 사용 할 수 있습니다:
또는 터미널에서:
여기에서 오류 메시지를 읽으면 'list' 객체에는 'size' 속성이 없으며 model(**inputs)‘에서 문제가 발생한 라인을 가리키는 --> 화살표를 볼 수 있습니다. .Python 디버거를 사용하여 대화식으로 디버그할 수 있지만 지금은 단순히 inputs` 부분을 슬라이스하여 어떤 값이 있는지 볼 것입니다:
inputs["input_ids"][:5][101, 2029, 7705, 2015, 2064]확실히 일반적인 Python list처럼 보이지만 타입을 다시 확인합시다:
type(inputs["input_ids"])list네, 확실히 파이썬의 list입니다. 무엇이 잘못되었을까요? 단원 2에서 🤗 Transformers의 AutoModelForXxx 클래스는 tensors(PyTorch 또는 TensorFlow 포함)에서 작동하며 tensor의 dimensions를 추출하기 위해 일반적인 방법으로 PyTorch의 Tensor.size()를 활용합니다. 어떤 라인이 예외를 발생시켰는지 알아보기 위해 traceback을 다시 살펴보겠습니다:
~/miniconda3/envs/huggingface/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/distilbert/modeling_distilbert.py in forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, head_mask, inputs_embeds, output_attentions, output_hidden_states, return_dict)
471 raise ValueError("You cannot specify both input_ids and inputs_embeds at the same time")
472 elif input_ids is not None:
--> 473 input_shape = input_ids.size()
474 elif inputs_embeds is not None:
475 input_shape = inputs_embeds.size()[:-1]
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'size'코드가 input_ids.size()를 호출하려고 하지만, Python list에서는 절대 동작하지 않습니다. 이 문제를 어떻게 해결할 수 있을까요? 스택오버플로우에서 오류 메시지를 검색하면 꽤 많은 관련 해결책을 제공합니다. 첫 번째 질문을 클릭하면 아래 스크린샷에 표시된 답변과 함께 우리와 유사한 질문이 표시됩니다:
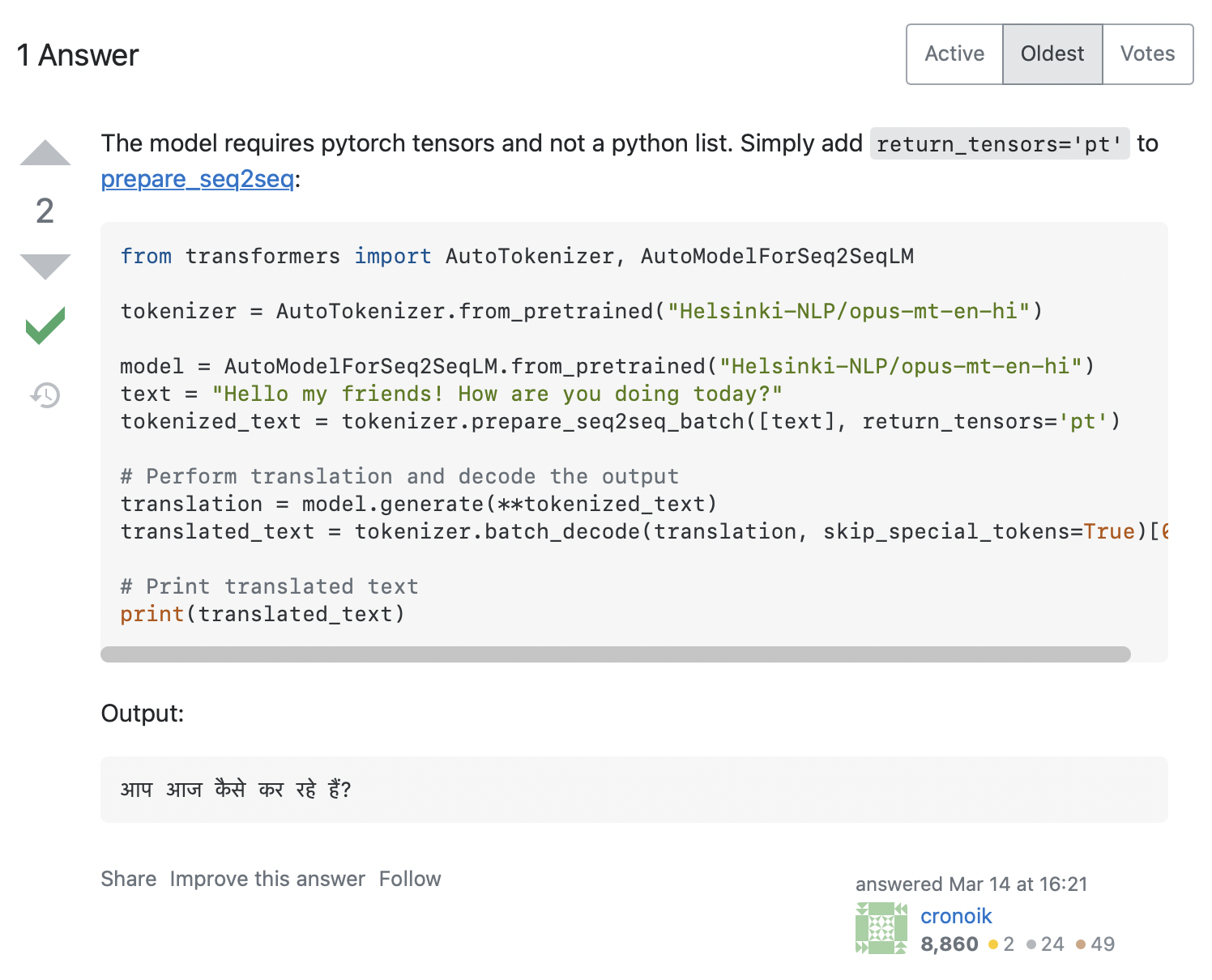
대답은 토크나이저에 return_tensors='pt'를 추가할 것을 권장하는데, 이게 작동하는지 확인해 보겠습니다:
inputs = tokenizer(question, context, add_special_tokens=True, return_tensors="pt")
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"][0]
outputs = model(**inputs)
answer_start_scores = outputs.start_logits
answer_end_scores = outputs.end_logits
# Get the most likely beginning of answer with the argmax of the score
answer_start = torch.argmax(answer_start_scores)
# Get the most likely end of answer with the argmax of the score
answer_end = torch.argmax(answer_end_scores) + 1
answer = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_string(
tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids[answer_start:answer_end])
)
print(f"Question: {question}")
print(f"Answer: {answer}")"""
Question: Which frameworks can I use?
Answer: pytorch, tensorflow, and jax
"""잘 동작하네요! 이게 바로 스택오버플로우가 얼마나 유용한지 보여주는 좋은 예입니다. 유사한 문제를 식별하여 커뮤니티의 다른 사람들의 경험을 활용할 수 있었습니다. 그러나 이와 같은 검색이 항상 적절한 답변을 제공하는 것은 아닙니다. 이러한 경우에 무엇을 할 수 있을까요? 다행히도 Hugging Face forums에 여러분을 반기고 도와줄 수 있는 개발자 커뮤니티가 있습니다! 다음 장에서는 답변을 얻을 수 있는 좋은 포럼 질문을 만드는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
