text
stringlengths 5
631k
| id
stringlengths 14
178
| metadata
dict | __index_level_0__
int64 0
647
|
|---|---|---|---|
import gc
import inspect
import random
import unittest
import numpy as np
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, CLIPTextConfig, CLIPTextModelWithProjection, CLIPTokenizer, T5EncoderModel
from diffusers import (
AutoencoderKL,
AutoPipelineForImage2Image,
FlowMatchEulerDiscreteScheduler,
SD3Transformer2DModel,
StableDiffusion3Img2ImgPipeline,
StableDiffusion3PAGImg2ImgPipeline,
)
from diffusers.utils.testing_utils import (
backend_empty_cache,
enable_full_determinism,
floats_tensor,
load_image,
require_torch_accelerator,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ..pipeline_params import (
IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_IMAGE_PARAMS,
TEXT_GUIDED_IMAGE_VARIATION_BATCH_PARAMS,
TEXT_GUIDED_IMAGE_VARIATION_PARAMS,
TEXT_TO_IMAGE_CALLBACK_CFG_PARAMS,
)
from ..test_pipelines_common import (
PipelineTesterMixin,
)
enable_full_determinism()
class StableDiffusion3PAGImg2ImgPipelineFastTests(unittest.TestCase, PipelineTesterMixin):
pipeline_class = StableDiffusion3PAGImg2ImgPipeline
params = TEXT_GUIDED_IMAGE_VARIATION_PARAMS.union({"pag_scale", "pag_adaptive_scale"}) - {"height", "width"}
required_optional_params = PipelineTesterMixin.required_optional_params - {"latents"}
batch_params = TEXT_GUIDED_IMAGE_VARIATION_BATCH_PARAMS
image_params = IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_IMAGE_PARAMS
image_latens_params = IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_IMAGE_PARAMS
callback_cfg_params = TEXT_TO_IMAGE_CALLBACK_CFG_PARAMS
test_xformers_attention = False
def get_dummy_components(self):
torch.manual_seed(0)
transformer = SD3Transformer2DModel(
sample_size=32,
patch_size=1,
in_channels=4,
num_layers=2,
attention_head_dim=8,
num_attention_heads=4,
caption_projection_dim=32,
joint_attention_dim=32,
pooled_projection_dim=64,
out_channels=4,
)
clip_text_encoder_config = CLIPTextConfig(
bos_token_id=0,
eos_token_id=2,
hidden_size=32,
intermediate_size=37,
layer_norm_eps=1e-05,
num_attention_heads=4,
num_hidden_layers=5,
pad_token_id=1,
vocab_size=1000,
hidden_act="gelu",
projection_dim=32,
)
torch.manual_seed(0)
text_encoder = CLIPTextModelWithProjection(clip_text_encoder_config)
torch.manual_seed(0)
text_encoder_2 = CLIPTextModelWithProjection(clip_text_encoder_config)
text_encoder_3 = T5EncoderModel.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-t5")
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-clip")
tokenizer_2 = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-clip")
tokenizer_3 = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-t5")
torch.manual_seed(0)
vae = AutoencoderKL(
sample_size=32,
in_channels=3,
out_channels=3,
block_out_channels=(4,),
layers_per_block=1,
latent_channels=4,
norm_num_groups=1,
use_quant_conv=False,
use_post_quant_conv=False,
shift_factor=0.0609,
scaling_factor=1.5035,
)
scheduler = FlowMatchEulerDiscreteScheduler()
return {
"scheduler": scheduler,
"text_encoder": text_encoder,
"text_encoder_2": text_encoder_2,
"text_encoder_3": text_encoder_3,
"tokenizer": tokenizer,
"tokenizer_2": tokenizer_2,
"tokenizer_3": tokenizer_3,
"transformer": transformer,
"vae": vae,
}
def get_dummy_inputs(self, device, seed=0):
image = floats_tensor((1, 3, 32, 32), rng=random.Random(seed)).to(device)
image = image / 2 + 0.5
if str(device).startswith("mps"):
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
else:
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(seed)
inputs = {
"prompt": "A painting of a squirrel eating a burger",
"image": image,
"generator": generator,
"num_inference_steps": 2,
"guidance_scale": 5.0,
"output_type": "np",
"pag_scale": 0.7,
}
return inputs
def test_pag_disable_enable(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
# base pipeline (expect same output when pag is disabled)
pipe_sd = StableDiffusion3Img2ImgPipeline(**components)
pipe_sd = pipe_sd.to(device)
pipe_sd.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
del inputs["pag_scale"]
assert "pag_scale" not in inspect.signature(pipe_sd.__call__).parameters, (
f"`pag_scale` should not be a call parameter of the base pipeline {pipe_sd.__class__.__name__}."
)
out = pipe_sd(**inputs).images[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
components = self.get_dummy_components()
# pag disabled with pag_scale=0.0
pipe_pag = self.pipeline_class(**components)
pipe_pag = pipe_pag.to(device)
pipe_pag.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
inputs["pag_scale"] = 0.0
out_pag_disabled = pipe_pag(**inputs).images[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert np.abs(out.flatten() - out_pag_disabled.flatten()).max() < 1e-3
def test_pag_inference(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
pipe_pag = self.pipeline_class(**components, pag_applied_layers=["blocks.0"])
pipe_pag = pipe_pag.to(device)
pipe_pag.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
image = pipe_pag(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (
1,
32,
32,
3,
), f"the shape of the output image should be (1, 32, 32, 3) but got {image.shape}"
expected_slice = np.array(
[0.66063476, 0.44838923, 0.5484299, 0.7242875, 0.5970012, 0.6015729, 0.53080845, 0.52220416, 0.56397927]
)
max_diff = np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max()
self.assertLessEqual(max_diff, 1e-3)
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
class StableDiffusion3PAGImg2ImgPipelineIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
pipeline_class = StableDiffusion3PAGImg2ImgPipeline
repo_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-3-medium-diffusers"
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def tearDown(self):
super().tearDown()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def get_inputs(
self, device, generator_device="cpu", dtype=torch.float32, seed=0, guidance_scale=7.0, pag_scale=0.7
):
img_url = (
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdxl-text2img.png"
)
init_image = load_image(img_url)
generator = torch.Generator(device=generator_device).manual_seed(seed)
inputs = {
"prompt": "an astronaut in a space suit walking through a jungle",
"generator": generator,
"image": init_image,
"num_inference_steps": 12,
"strength": 0.6,
"guidance_scale": guidance_scale,
"pag_scale": pag_scale,
"output_type": "np",
}
return inputs
def test_pag_cfg(self):
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id, enable_pag=True, torch_dtype=torch.float16, pag_applied_layers=["blocks.17"]
)
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload(device=torch_device)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_inputs(torch_device)
image = pipeline(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1].flatten()
assert image.shape == (1, 1024, 1024, 3)
expected_slice = np.array(
[
0.16772461,
0.17626953,
0.18432617,
0.17822266,
0.18359375,
0.17626953,
0.17407227,
0.17700195,
0.17822266,
]
)
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-3, (
f"output is different from expected, {image_slice.flatten()}"
)
def test_pag_uncond(self):
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id, enable_pag=True, torch_dtype=torch.float16, pag_applied_layers=["blocks.(4|17)"]
)
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload(device=torch_device)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_inputs(torch_device, guidance_scale=0.0, pag_scale=1.8)
image = pipeline(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1].flatten()
assert image.shape == (1, 1024, 1024, 3)
expected_slice = np.array(
[0.1508789, 0.16210938, 0.17138672, 0.16210938, 0.17089844, 0.16137695, 0.16235352, 0.16430664, 0.16455078]
)
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-3, (
f"output is different from expected, {image_slice.flatten()}"
)
|
diffusers/tests/pipelines/pag/test_pag_sd3_img2img.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/pipelines/pag/test_pag_sd3_img2img.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 4767
}
| 200
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import gc
import unittest
import numpy as np
import torch
from transformers import CLIPTextConfig, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
from diffusers import (
AutoencoderKL,
DDIMScheduler,
EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
EulerDiscreteScheduler,
LMSDiscreteScheduler,
PNDMScheduler,
StableDiffusionPipeline,
UNet2DConditionModel,
logging,
)
from diffusers.utils.testing_utils import (
CaptureLogger,
backend_empty_cache,
backend_max_memory_allocated,
backend_reset_peak_memory_stats,
enable_full_determinism,
load_numpy,
nightly,
numpy_cosine_similarity_distance,
require_torch_accelerator,
skip_mps,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from ..pipeline_params import (
TEXT_TO_IMAGE_BATCH_PARAMS,
TEXT_TO_IMAGE_CALLBACK_CFG_PARAMS,
TEXT_TO_IMAGE_IMAGE_PARAMS,
TEXT_TO_IMAGE_PARAMS,
)
from ..test_pipelines_common import (
PipelineKarrasSchedulerTesterMixin,
PipelineLatentTesterMixin,
PipelineTesterMixin,
SDFunctionTesterMixin,
)
enable_full_determinism()
class StableDiffusion2PipelineFastTests(
SDFunctionTesterMixin,
PipelineLatentTesterMixin,
PipelineKarrasSchedulerTesterMixin,
PipelineTesterMixin,
unittest.TestCase,
):
pipeline_class = StableDiffusionPipeline
params = TEXT_TO_IMAGE_PARAMS
batch_params = TEXT_TO_IMAGE_BATCH_PARAMS
image_params = TEXT_TO_IMAGE_IMAGE_PARAMS
image_latents_params = TEXT_TO_IMAGE_IMAGE_PARAMS
callback_cfg_params = TEXT_TO_IMAGE_CALLBACK_CFG_PARAMS
test_layerwise_casting = True
test_group_offloading = True
def get_dummy_components(self):
torch.manual_seed(0)
unet = UNet2DConditionModel(
block_out_channels=(32, 64),
layers_per_block=2,
sample_size=32,
in_channels=4,
out_channels=4,
down_block_types=("DownBlock2D", "CrossAttnDownBlock2D"),
up_block_types=("CrossAttnUpBlock2D", "UpBlock2D"),
cross_attention_dim=32,
# SD2-specific config below
attention_head_dim=(2, 4),
use_linear_projection=True,
)
scheduler = DDIMScheduler(
beta_start=0.00085,
beta_end=0.012,
beta_schedule="scaled_linear",
clip_sample=False,
set_alpha_to_one=False,
)
torch.manual_seed(0)
vae = AutoencoderKL(
block_out_channels=[32, 64],
in_channels=3,
out_channels=3,
down_block_types=["DownEncoderBlock2D", "DownEncoderBlock2D"],
up_block_types=["UpDecoderBlock2D", "UpDecoderBlock2D"],
latent_channels=4,
sample_size=128,
)
torch.manual_seed(0)
text_encoder_config = CLIPTextConfig(
bos_token_id=0,
eos_token_id=2,
hidden_size=32,
intermediate_size=37,
layer_norm_eps=1e-05,
num_attention_heads=4,
num_hidden_layers=5,
pad_token_id=1,
vocab_size=1000,
# SD2-specific config below
hidden_act="gelu",
projection_dim=512,
)
text_encoder = CLIPTextModel(text_encoder_config)
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-clip")
components = {
"unet": unet,
"scheduler": scheduler,
"vae": vae,
"text_encoder": text_encoder,
"tokenizer": tokenizer,
"safety_checker": None,
"feature_extractor": None,
"image_encoder": None,
}
return components
def get_dummy_inputs(self, device, seed=0):
generator_device = "cpu" if not device.startswith("cuda") else "cuda"
if not str(device).startswith("mps"):
generator = torch.Generator(device=generator_device).manual_seed(seed)
else:
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
inputs = {
"prompt": "A painting of a squirrel eating a burger",
"generator": generator,
"num_inference_steps": 2,
"guidance_scale": 6.0,
"output_type": "np",
}
return inputs
def test_stable_diffusion_ddim(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (1, 64, 64, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.5753, 0.6113, 0.5005, 0.5036, 0.5464, 0.4725, 0.4982, 0.4865, 0.4861])
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-2
def test_stable_diffusion_pndm(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
components["scheduler"] = PNDMScheduler(skip_prk_steps=True)
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (1, 64, 64, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.5121, 0.5714, 0.4827, 0.5057, 0.5646, 0.4766, 0.5189, 0.4895, 0.4990])
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-2
def test_stable_diffusion_k_lms(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
components["scheduler"] = LMSDiscreteScheduler.from_config(components["scheduler"].config)
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (1, 64, 64, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.4865, 0.5439, 0.4840, 0.4995, 0.5543, 0.4846, 0.5199, 0.4942, 0.5061])
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-2
def test_stable_diffusion_k_euler_ancestral(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
components["scheduler"] = EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler.from_config(components["scheduler"].config)
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (1, 64, 64, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.4864, 0.5440, 0.4842, 0.4994, 0.5543, 0.4846, 0.5196, 0.4942, 0.5063])
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-2
def test_stable_diffusion_k_euler(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
components["scheduler"] = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_config(components["scheduler"].config)
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (1, 64, 64, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.4865, 0.5439, 0.4840, 0.4995, 0.5543, 0.4846, 0.5199, 0.4942, 0.5061])
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-2
def test_stable_diffusion_unflawed(self):
device = "cpu" # ensure determinism for the device-dependent torch.Generator
components = self.get_dummy_components()
components["scheduler"] = DDIMScheduler.from_config(
components["scheduler"].config, timestep_spacing="trailing"
)
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_dummy_inputs(device)
inputs["guidance_rescale"] = 0.7
inputs["num_inference_steps"] = 10
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1]
assert image.shape == (1, 64, 64, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.4736, 0.5405, 0.4705, 0.4955, 0.5675, 0.4812, 0.5310, 0.4967, 0.5064])
assert np.abs(image_slice.flatten() - expected_slice).max() < 1e-2
def test_stable_diffusion_long_prompt(self):
components = self.get_dummy_components()
components["scheduler"] = LMSDiscreteScheduler.from_config(components["scheduler"].config)
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline(**components)
sd_pipe = sd_pipe.to(torch_device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
do_classifier_free_guidance = True
negative_prompt = None
num_images_per_prompt = 1
logger = logging.get_logger("diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion")
logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
prompt = 25 * "@"
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cap_logger_3:
text_embeddings_3, negeative_text_embeddings_3 = sd_pipe.encode_prompt(
prompt, torch_device, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance, negative_prompt
)
if negeative_text_embeddings_3 is not None:
text_embeddings_3 = torch.cat([negeative_text_embeddings_3, text_embeddings_3])
prompt = 100 * "@"
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cap_logger:
text_embeddings, negative_embeddings = sd_pipe.encode_prompt(
prompt, torch_device, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance, negative_prompt
)
if negative_embeddings is not None:
text_embeddings = torch.cat([negative_embeddings, text_embeddings])
negative_prompt = "Hello"
with CaptureLogger(logger) as cap_logger_2:
text_embeddings_2, negative_text_embeddings_2 = sd_pipe.encode_prompt(
prompt, torch_device, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance, negative_prompt
)
if negative_text_embeddings_2 is not None:
text_embeddings_2 = torch.cat([negative_text_embeddings_2, text_embeddings_2])
assert text_embeddings_3.shape == text_embeddings_2.shape == text_embeddings.shape
assert text_embeddings.shape[1] == 77
assert cap_logger.out == cap_logger_2.out
# 100 - 77 + 1 (BOS token) + 1 (EOS token) = 25
assert cap_logger.out.count("@") == 25
assert cap_logger_3.out == ""
def test_attention_slicing_forward_pass(self):
super().test_attention_slicing_forward_pass(expected_max_diff=3e-3)
def test_inference_batch_single_identical(self):
super().test_inference_batch_single_identical(expected_max_diff=3e-3)
def test_encode_prompt_works_in_isolation(self):
extra_required_param_value_dict = {
"device": torch.device(torch_device).type,
"do_classifier_free_guidance": self.get_dummy_inputs(device=torch_device).get("guidance_scale", 1.0) > 1.0,
}
return super().test_encode_prompt_works_in_isolation(extra_required_param_value_dict)
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
@skip_mps
class StableDiffusion2PipelineSlowTests(unittest.TestCase):
def tearDown(self):
super().tearDown()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def get_inputs(self, device, generator_device="cpu", dtype=torch.float32, seed=0):
if not str(device).startswith("mps"):
generator = torch.Generator(device=generator_device).manual_seed(seed)
else:
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
latents = np.random.RandomState(seed).standard_normal((1, 4, 64, 64))
latents = torch.from_numpy(latents).to(device=device, dtype=dtype)
inputs = {
"prompt": "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse",
"latents": latents,
"generator": generator,
"num_inference_steps": 3,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"output_type": "np",
}
return inputs
def test_stable_diffusion_default_ddim(self):
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-base")
pipe.to(torch_device)
pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_inputs(torch_device)
image = pipe(**inputs).images
image_slice = image[0, -3:, -3:, -1].flatten()
assert image.shape == (1, 512, 512, 3)
expected_slice = np.array([0.49493, 0.47896, 0.40798, 0.54214, 0.53212, 0.48202, 0.47656, 0.46329, 0.48506])
assert np.abs(image_slice - expected_slice).max() < 7e-3
@require_torch_accelerator
def test_stable_diffusion_attention_slicing(self):
backend_reset_peak_memory_stats(torch_device)
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-base", torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
pipe.unet.set_default_attn_processor()
pipe = pipe.to(torch_device)
pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
# enable attention slicing
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
inputs = self.get_inputs(torch_device, dtype=torch.float16)
image_sliced = pipe(**inputs).images
mem_bytes = backend_max_memory_allocated(torch_device)
backend_reset_peak_memory_stats(torch_device)
# make sure that less than 3.3 GB is allocated
assert mem_bytes < 3.3 * 10**9
# disable slicing
pipe.disable_attention_slicing()
pipe.unet.set_default_attn_processor()
inputs = self.get_inputs(torch_device, dtype=torch.float16)
image = pipe(**inputs).images
# make sure that more than 3.3 GB is allocated
mem_bytes = backend_max_memory_allocated(torch_device)
assert mem_bytes > 3.3 * 10**9
max_diff = numpy_cosine_similarity_distance(image.flatten(), image_sliced.flatten())
assert max_diff < 5e-3
@nightly
@require_torch_accelerator
@skip_mps
class StableDiffusion2PipelineNightlyTests(unittest.TestCase):
def tearDown(self):
super().tearDown()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def get_inputs(self, device, generator_device="cpu", dtype=torch.float32, seed=0):
_generator_device = "cpu" if not generator_device.startswith("cuda") else "cuda"
if not str(device).startswith("mps"):
generator = torch.Generator(device=_generator_device).manual_seed(seed)
else:
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
latents = np.random.RandomState(seed).standard_normal((1, 4, 64, 64))
latents = torch.from_numpy(latents).to(device=device, dtype=dtype)
inputs = {
"prompt": "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse",
"latents": latents,
"generator": generator,
"num_inference_steps": 2,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"output_type": "np",
}
return inputs
def test_stable_diffusion_2_1_default(self):
sd_pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-base").to(torch_device)
sd_pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_inputs(torch_device)
image = sd_pipe(**inputs).images[0]
expected_image = load_numpy(
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/test-arrays/resolve/main"
"/stable_diffusion_2_text2img/stable_diffusion_2_0_pndm.npy"
)
max_diff = np.abs(expected_image - image).max()
assert max_diff < 1e-3
|
diffusers/tests/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2/test_stable_diffusion.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2/test_stable_diffusion.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 7767
}
| 201
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
import numpy as np
from diffusers.utils import is_flax_available
from diffusers.utils.testing_utils import require_flax, slow
if is_flax_available():
import jax
import jax.numpy as jnp
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
from diffusers import FlaxDDIMScheduler, FlaxDiffusionPipeline, FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
@require_flax
class DownloadTests(unittest.TestCase):
def test_download_only_pytorch(self):
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
# pipeline has Flax weights
_ = FlaxDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-stable-diffusion-pipe", safety_checker=None, cache_dir=tmpdirname
)
all_root_files = [t[-1] for t in os.walk(os.path.join(tmpdirname, os.listdir(tmpdirname)[0], "snapshots"))]
files = [item for sublist in all_root_files for item in sublist]
# None of the downloaded files should be a PyTorch file even if we have some here:
# https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing/tiny-stable-diffusion-pipe/blob/main/unet/diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
assert not any(f.endswith(".bin") for f in files)
@slow
@require_flax
class FlaxPipelineTests(unittest.TestCase):
def test_dummy_all_tpus(self):
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"hf-internal-testing/tiny-stable-diffusion-pipe", safety_checker=None
)
prompt = (
"A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of"
" field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
)
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
num_inference_steps = 4
num_samples = jax.device_count()
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
# shard inputs and rng
params = replicate(params)
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, num_samples)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
assert images.shape == (num_samples, 1, 64, 64, 3)
if jax.device_count() == 8:
assert np.abs(np.abs(images[0, 0, :2, :2, -2:], dtype=np.float32).sum() - 4.1514745) < 1e-3
assert np.abs(np.abs(images, dtype=np.float32).sum() - 49947.875) < 5e-1
images_pil = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
assert len(images_pil) == num_samples
def test_stable_diffusion_v1_4(self):
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", revision="flax", safety_checker=None
)
prompt = (
"A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of"
" field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
)
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
num_inference_steps = 50
num_samples = jax.device_count()
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
# shard inputs and rng
params = replicate(params)
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, num_samples)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
assert images.shape == (num_samples, 1, 512, 512, 3)
if jax.device_count() == 8:
assert np.abs((np.abs(images[0, 0, :2, :2, -2:], dtype=np.float32).sum() - 0.05652401)) < 1e-2
assert np.abs((np.abs(images, dtype=np.float32).sum() - 2383808.2)) < 5e-1
def test_stable_diffusion_v1_4_bfloat_16(self):
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", variant="bf16", dtype=jnp.bfloat16, safety_checker=None
)
prompt = (
"A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of"
" field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
)
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
num_inference_steps = 50
num_samples = jax.device_count()
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
# shard inputs and rng
params = replicate(params)
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, num_samples)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
assert images.shape == (num_samples, 1, 512, 512, 3)
if jax.device_count() == 8:
assert np.abs((np.abs(images[0, 0, :2, :2, -2:], dtype=np.float32).sum() - 0.04003906)) < 5e-2
assert np.abs((np.abs(images, dtype=np.float32).sum() - 2373516.75)) < 5e-1
def test_stable_diffusion_v1_4_bfloat_16_with_safety(self):
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", variant="bf16", dtype=jnp.bfloat16
)
prompt = (
"A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of"
" field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
)
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
num_inference_steps = 50
num_samples = jax.device_count()
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
# shard inputs and rng
params = replicate(params)
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, num_samples)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
assert images.shape == (num_samples, 1, 512, 512, 3)
if jax.device_count() == 8:
assert np.abs((np.abs(images[0, 0, :2, :2, -2:], dtype=np.float32).sum() - 0.04003906)) < 5e-2
assert np.abs((np.abs(images, dtype=np.float32).sum() - 2373516.75)) < 5e-1
def test_stable_diffusion_v1_4_bfloat_16_ddim(self):
scheduler = FlaxDDIMScheduler(
beta_start=0.00085,
beta_end=0.012,
beta_schedule="scaled_linear",
set_alpha_to_one=False,
steps_offset=1,
)
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
variant="bf16",
dtype=jnp.bfloat16,
scheduler=scheduler,
safety_checker=None,
)
scheduler_state = scheduler.create_state()
params["scheduler"] = scheduler_state
prompt = (
"A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of"
" field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
)
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
num_inference_steps = 50
num_samples = jax.device_count()
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
# shard inputs and rng
params = replicate(params)
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, num_samples)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
assert images.shape == (num_samples, 1, 512, 512, 3)
if jax.device_count() == 8:
assert np.abs((np.abs(images[0, 0, :2, :2, -2:], dtype=np.float32).sum() - 0.045043945)) < 5e-2
assert np.abs((np.abs(images, dtype=np.float32).sum() - 2347693.5)) < 5e-1
def test_jax_memory_efficient_attention(self):
prompt = (
"A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of"
" field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
)
num_samples = jax.device_count()
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
prng_seed = jax.random.split(jax.random.PRNGKey(0), num_samples)
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
variant="bf16",
dtype=jnp.bfloat16,
safety_checker=None,
)
params = replicate(params)
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, jit=True).images
assert images.shape == (num_samples, 1, 512, 512, 3)
slice = images[2, 0, 256, 10:17, 1]
# With memory efficient attention
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
variant="bf16",
dtype=jnp.bfloat16,
safety_checker=None,
use_memory_efficient_attention=True,
)
params = replicate(params)
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
images_eff = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, jit=True).images
assert images_eff.shape == (num_samples, 1, 512, 512, 3)
slice_eff = images[2, 0, 256, 10:17, 1]
# I checked the results visually and they are very similar. However, I saw that the max diff is `1` and the `sum`
# over the 8 images is exactly `256`, which is very suspicious. Testing a random slice for now.
assert abs(slice_eff - slice).max() < 1e-2
|
diffusers/tests/pipelines/test_pipelines_flax.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/pipelines/test_pipelines_flax.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 4559
}
| 202
|
import torch
from diffusers import DDIMScheduler
from .test_schedulers import SchedulerCommonTest
class DDIMSchedulerTest(SchedulerCommonTest):
scheduler_classes = (DDIMScheduler,)
forward_default_kwargs = (("eta", 0.0), ("num_inference_steps", 50))
def get_scheduler_config(self, **kwargs):
config = {
"num_train_timesteps": 1000,
"beta_start": 0.0001,
"beta_end": 0.02,
"beta_schedule": "linear",
"clip_sample": True,
}
config.update(**kwargs)
return config
def full_loop(self, **config):
scheduler_class = self.scheduler_classes[0]
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config(**config)
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
num_inference_steps, eta = 10, 0.0
model = self.dummy_model()
sample = self.dummy_sample_deter
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
for t in scheduler.timesteps:
residual = model(sample, t)
sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample, eta).prev_sample
return sample
def test_timesteps(self):
for timesteps in [100, 500, 1000]:
self.check_over_configs(num_train_timesteps=timesteps)
def test_steps_offset(self):
for steps_offset in [0, 1]:
self.check_over_configs(steps_offset=steps_offset)
scheduler_class = self.scheduler_classes[0]
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config(steps_offset=1)
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
scheduler.set_timesteps(5)
assert torch.equal(scheduler.timesteps, torch.LongTensor([801, 601, 401, 201, 1]))
def test_betas(self):
for beta_start, beta_end in zip([0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1], [0.002, 0.02, 0.2, 2]):
self.check_over_configs(beta_start=beta_start, beta_end=beta_end)
def test_schedules(self):
for schedule in ["linear", "squaredcos_cap_v2"]:
self.check_over_configs(beta_schedule=schedule)
def test_prediction_type(self):
for prediction_type in ["epsilon", "v_prediction"]:
self.check_over_configs(prediction_type=prediction_type)
def test_clip_sample(self):
for clip_sample in [True, False]:
self.check_over_configs(clip_sample=clip_sample)
def test_timestep_spacing(self):
for timestep_spacing in ["trailing", "leading"]:
self.check_over_configs(timestep_spacing=timestep_spacing)
def test_rescale_betas_zero_snr(self):
for rescale_betas_zero_snr in [True, False]:
self.check_over_configs(rescale_betas_zero_snr=rescale_betas_zero_snr)
def test_thresholding(self):
self.check_over_configs(thresholding=False)
for threshold in [0.5, 1.0, 2.0]:
for prediction_type in ["epsilon", "v_prediction"]:
self.check_over_configs(
thresholding=True,
prediction_type=prediction_type,
sample_max_value=threshold,
)
def test_time_indices(self):
for t in [1, 10, 49]:
self.check_over_forward(time_step=t)
def test_inference_steps(self):
for t, num_inference_steps in zip([1, 10, 50], [10, 50, 500]):
self.check_over_forward(time_step=t, num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps)
def test_eta(self):
for t, eta in zip([1, 10, 49], [0.0, 0.5, 1.0]):
self.check_over_forward(time_step=t, eta=eta)
def test_variance(self):
scheduler_class = self.scheduler_classes[0]
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config()
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(scheduler._get_variance(0, 0) - 0.0)) < 1e-5
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(scheduler._get_variance(420, 400) - 0.14771)) < 1e-5
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(scheduler._get_variance(980, 960) - 0.32460)) < 1e-5
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(scheduler._get_variance(0, 0) - 0.0)) < 1e-5
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(scheduler._get_variance(487, 486) - 0.00979)) < 1e-5
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(scheduler._get_variance(999, 998) - 0.02)) < 1e-5
def test_full_loop_no_noise(self):
sample = self.full_loop()
result_sum = torch.sum(torch.abs(sample))
result_mean = torch.mean(torch.abs(sample))
assert abs(result_sum.item() - 172.0067) < 1e-2
assert abs(result_mean.item() - 0.223967) < 1e-3
def test_full_loop_with_v_prediction(self):
sample = self.full_loop(prediction_type="v_prediction")
result_sum = torch.sum(torch.abs(sample))
result_mean = torch.mean(torch.abs(sample))
assert abs(result_sum.item() - 52.5302) < 1e-2
assert abs(result_mean.item() - 0.0684) < 1e-3
def test_full_loop_with_set_alpha_to_one(self):
# We specify different beta, so that the first alpha is 0.99
sample = self.full_loop(set_alpha_to_one=True, beta_start=0.01)
result_sum = torch.sum(torch.abs(sample))
result_mean = torch.mean(torch.abs(sample))
assert abs(result_sum.item() - 149.8295) < 1e-2
assert abs(result_mean.item() - 0.1951) < 1e-3
def test_full_loop_with_no_set_alpha_to_one(self):
# We specify different beta, so that the first alpha is 0.99
sample = self.full_loop(set_alpha_to_one=False, beta_start=0.01)
result_sum = torch.sum(torch.abs(sample))
result_mean = torch.mean(torch.abs(sample))
assert abs(result_sum.item() - 149.0784) < 1e-2
assert abs(result_mean.item() - 0.1941) < 1e-3
def test_full_loop_with_noise(self):
scheduler_class = self.scheduler_classes[0]
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config()
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
num_inference_steps, eta = 10, 0.0
t_start = 8
model = self.dummy_model()
sample = self.dummy_sample_deter
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
# add noise
noise = self.dummy_noise_deter
timesteps = scheduler.timesteps[t_start * scheduler.order :]
sample = scheduler.add_noise(sample, noise, timesteps[:1])
for t in timesteps:
residual = model(sample, t)
sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample, eta).prev_sample
result_sum = torch.sum(torch.abs(sample))
result_mean = torch.mean(torch.abs(sample))
assert abs(result_sum.item() - 354.5418) < 1e-2, f" expected result sum 218.4379, but get {result_sum}"
assert abs(result_mean.item() - 0.4616) < 1e-3, f" expected result mean 0.2844, but get {result_mean}"
|
diffusers/tests/schedulers/test_scheduler_ddim.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/schedulers/test_scheduler_ddim.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 3127
}
| 203
|
import tempfile
import unittest
import torch
from diffusers import IPNDMScheduler
from .test_schedulers import SchedulerCommonTest
class IPNDMSchedulerTest(SchedulerCommonTest):
scheduler_classes = (IPNDMScheduler,)
forward_default_kwargs = (("num_inference_steps", 50),)
def get_scheduler_config(self, **kwargs):
config = {"num_train_timesteps": 1000}
config.update(**kwargs)
return config
def check_over_configs(self, time_step=0, **config):
kwargs = dict(self.forward_default_kwargs)
num_inference_steps = kwargs.pop("num_inference_steps", None)
sample = self.dummy_sample
residual = 0.1 * sample
dummy_past_residuals = [residual + 0.2, residual + 0.15, residual + 0.1, residual + 0.05]
for scheduler_class in self.scheduler_classes:
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config(**config)
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
# copy over dummy past residuals
scheduler.ets = dummy_past_residuals[:]
if time_step is None:
time_step = scheduler.timesteps[len(scheduler.timesteps) // 2]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
scheduler.save_config(tmpdirname)
new_scheduler = scheduler_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
new_scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
# copy over dummy past residuals
new_scheduler.ets = dummy_past_residuals[:]
output = scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
new_output = new_scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(output - new_output)) < 1e-5, "Scheduler outputs are not identical"
output = scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
new_output = new_scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(output - new_output)) < 1e-5, "Scheduler outputs are not identical"
@unittest.skip("Test not supported.")
def test_from_save_pretrained(self):
pass
def check_over_forward(self, time_step=0, **forward_kwargs):
kwargs = dict(self.forward_default_kwargs)
num_inference_steps = kwargs.pop("num_inference_steps", None)
sample = self.dummy_sample
residual = 0.1 * sample
dummy_past_residuals = [residual + 0.2, residual + 0.15, residual + 0.1, residual + 0.05]
for scheduler_class in self.scheduler_classes:
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config()
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
# copy over dummy past residuals (must be after setting timesteps)
scheduler.ets = dummy_past_residuals[:]
if time_step is None:
time_step = scheduler.timesteps[len(scheduler.timesteps) // 2]
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
scheduler.save_config(tmpdirname)
new_scheduler = scheduler_class.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
# copy over dummy past residuals
new_scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
# copy over dummy past residual (must be after setting timesteps)
new_scheduler.ets = dummy_past_residuals[:]
output = scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
new_output = new_scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(output - new_output)) < 1e-5, "Scheduler outputs are not identical"
output = scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
new_output = new_scheduler.step(residual, time_step, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
assert torch.sum(torch.abs(output - new_output)) < 1e-5, "Scheduler outputs are not identical"
def full_loop(self, **config):
scheduler_class = self.scheduler_classes[0]
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config(**config)
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
num_inference_steps = 10
model = self.dummy_model()
sample = self.dummy_sample_deter
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
for i, t in enumerate(scheduler.timesteps):
residual = model(sample, t)
sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample).prev_sample
scheduler._step_index = None
for i, t in enumerate(scheduler.timesteps):
residual = model(sample, t)
sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample).prev_sample
return sample
def test_step_shape(self):
kwargs = dict(self.forward_default_kwargs)
num_inference_steps = kwargs.pop("num_inference_steps", None)
for scheduler_class in self.scheduler_classes:
scheduler_config = self.get_scheduler_config()
scheduler = scheduler_class(**scheduler_config)
sample = self.dummy_sample
residual = 0.1 * sample
if num_inference_steps is not None and hasattr(scheduler, "set_timesteps"):
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
elif num_inference_steps is not None and not hasattr(scheduler, "set_timesteps"):
kwargs["num_inference_steps"] = num_inference_steps
# copy over dummy past residuals (must be done after set_timesteps)
dummy_past_residuals = [residual + 0.2, residual + 0.15, residual + 0.1, residual + 0.05]
scheduler.ets = dummy_past_residuals[:]
time_step_0 = scheduler.timesteps[5]
time_step_1 = scheduler.timesteps[6]
output_0 = scheduler.step(residual, time_step_0, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
output_1 = scheduler.step(residual, time_step_1, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
self.assertEqual(output_0.shape, sample.shape)
self.assertEqual(output_0.shape, output_1.shape)
output_0 = scheduler.step(residual, time_step_0, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
output_1 = scheduler.step(residual, time_step_1, sample, **kwargs).prev_sample
self.assertEqual(output_0.shape, sample.shape)
self.assertEqual(output_0.shape, output_1.shape)
def test_timesteps(self):
for timesteps in [100, 1000]:
self.check_over_configs(num_train_timesteps=timesteps, time_step=None)
def test_inference_steps(self):
for t, num_inference_steps in zip([1, 5, 10], [10, 50, 100]):
self.check_over_forward(num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps, time_step=None)
def test_full_loop_no_noise(self):
sample = self.full_loop()
result_mean = torch.mean(torch.abs(sample))
assert abs(result_mean.item() - 2540529) < 10
|
diffusers/tests/schedulers/test_scheduler_ipndm.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/schedulers/test_scheduler_ipndm.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 3140
}
| 204
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import gc
import unittest
import torch
from diffusers import (
AutoencoderDC,
)
from diffusers.utils.testing_utils import (
backend_empty_cache,
enable_full_determinism,
load_hf_numpy,
numpy_cosine_similarity_distance,
require_torch_accelerator,
slow,
torch_device,
)
enable_full_determinism()
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
class AutoencoderDCSingleFileTests(unittest.TestCase):
model_class = AutoencoderDC
ckpt_path = "https://huggingface.co/mit-han-lab/dc-ae-f32c32-sana-1.0/blob/main/model.safetensors"
repo_id = "mit-han-lab/dc-ae-f32c32-sana-1.0-diffusers"
main_input_name = "sample"
base_precision = 1e-2
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def tearDown(self):
super().tearDown()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def get_file_format(self, seed, shape):
return f"gaussian_noise_s={seed}_shape={'_'.join([str(s) for s in shape])}.npy"
def get_sd_image(self, seed=0, shape=(4, 3, 512, 512), fp16=False):
dtype = torch.float16 if fp16 else torch.float32
image = torch.from_numpy(load_hf_numpy(self.get_file_format(seed, shape))).to(torch_device).to(dtype)
return image
def test_single_file_inference_same_as_pretrained(self):
model_1 = self.model_class.from_pretrained(self.repo_id).to(torch_device)
model_2 = self.model_class.from_single_file(self.ckpt_path, config=self.repo_id).to(torch_device)
image = self.get_sd_image(33)
with torch.no_grad():
sample_1 = model_1(image).sample
sample_2 = model_2(image).sample
assert sample_1.shape == sample_2.shape
output_slice_1 = sample_1.flatten().float().cpu()
output_slice_2 = sample_2.flatten().float().cpu()
assert numpy_cosine_similarity_distance(output_slice_1, output_slice_2) < 1e-4
def test_single_file_components(self):
model = self.model_class.from_pretrained(self.repo_id)
model_single_file = self.model_class.from_single_file(self.ckpt_path)
PARAMS_TO_IGNORE = ["torch_dtype", "_name_or_path", "_use_default_values", "_diffusers_version"]
for param_name, param_value in model_single_file.config.items():
if param_name in PARAMS_TO_IGNORE:
continue
assert model.config[param_name] == param_value, (
f"{param_name} differs between pretrained loading and single file loading"
)
def test_single_file_in_type_variant_components(self):
# `in` variant checkpoints require passing in a `config` parameter
# in order to set the scaling factor correctly.
# `in` and `mix` variants have the same keys and we cannot automatically infer a scaling factor.
# We default to using the `mix` config
repo_id = "mit-han-lab/dc-ae-f128c512-in-1.0-diffusers"
ckpt_path = "https://huggingface.co/mit-han-lab/dc-ae-f128c512-in-1.0/blob/main/model.safetensors"
model = self.model_class.from_pretrained(repo_id)
model_single_file = self.model_class.from_single_file(ckpt_path, config=repo_id)
PARAMS_TO_IGNORE = ["torch_dtype", "_name_or_path", "_use_default_values", "_diffusers_version"]
for param_name, param_value in model_single_file.config.items():
if param_name in PARAMS_TO_IGNORE:
continue
assert model.config[param_name] == param_value, (
f"{param_name} differs between pretrained loading and single file loading"
)
def test_single_file_mix_type_variant_components(self):
repo_id = "mit-han-lab/dc-ae-f128c512-mix-1.0-diffusers"
ckpt_path = "https://huggingface.co/mit-han-lab/dc-ae-f128c512-mix-1.0/blob/main/model.safetensors"
model = self.model_class.from_pretrained(repo_id)
model_single_file = self.model_class.from_single_file(ckpt_path, config=repo_id)
PARAMS_TO_IGNORE = ["torch_dtype", "_name_or_path", "_use_default_values", "_diffusers_version"]
for param_name, param_value in model_single_file.config.items():
if param_name in PARAMS_TO_IGNORE:
continue
assert model.config[param_name] == param_value, (
f"{param_name} differs between pretrained loading and single file loading"
)
|
diffusers/tests/single_file/test_model_autoencoder_dc_single_file.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/single_file/test_model_autoencoder_dc_single_file.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 2115
}
| 205
|
import gc
import tempfile
import unittest
import torch
from diffusers import (
StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline,
T2IAdapter,
)
from diffusers.loaders.single_file_utils import _extract_repo_id_and_weights_name
from diffusers.utils import load_image
from diffusers.utils.testing_utils import (
backend_empty_cache,
enable_full_determinism,
numpy_cosine_similarity_distance,
require_torch_accelerator,
slow,
torch_device,
)
from .single_file_testing_utils import (
SDXLSingleFileTesterMixin,
download_diffusers_config,
download_original_config,
download_single_file_checkpoint,
)
enable_full_determinism()
@slow
@require_torch_accelerator
class StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipelineSingleFileSlowTests(unittest.TestCase, SDXLSingleFileTesterMixin):
pipeline_class = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline
ckpt_path = "https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0/blob/main/sd_xl_base_1.0.safetensors"
repo_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
original_config = (
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Stability-AI/generative-models/main/configs/inference/sd_xl_base.yaml"
)
def setUp(self):
super().setUp()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def tearDown(self):
super().tearDown()
gc.collect()
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
def get_inputs(self):
prompt = "toy"
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(0)
image = load_image(
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/t2i_adapter/toy_canny.png"
)
inputs = {
"prompt": prompt,
"image": image,
"generator": generator,
"num_inference_steps": 2,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"output_type": "np",
}
return inputs
def test_single_file_format_inference_is_same_as_pretrained(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe_single_file = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline.from_single_file(
self.ckpt_path,
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None,
)
pipe_single_file.enable_model_cpu_offload(device=torch_device)
pipe_single_file.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
inputs = self.get_inputs()
images_single_file = pipe_single_file(**inputs).images[0]
pipe = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None,
)
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload(device=torch_device)
inputs = self.get_inputs()
images = pipe(**inputs).images[0]
assert images_single_file.shape == (768, 512, 3)
assert images.shape == (768, 512, 3)
max_diff = numpy_cosine_similarity_distance(images.flatten(), images_single_file.flatten())
assert max_diff < 5e-3
def test_single_file_components(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
variant="fp16",
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
pipe_single_file = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(self.ckpt_path, safety_checker=None, adapter=adapter)
super().test_single_file_components(pipe, pipe_single_file)
def test_single_file_components_local_files_only(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
variant="fp16",
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
repo_id, weight_name = _extract_repo_id_and_weights_name(self.ckpt_path)
local_ckpt_path = download_single_file_checkpoint(repo_id, weight_name, tmpdir)
single_file_pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(
local_ckpt_path, adapter=adapter, safety_checker=None, local_files_only=True
)
self._compare_component_configs(pipe, single_file_pipe)
def test_single_file_components_with_diffusers_config(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
variant="fp16",
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None,
)
pipe_single_file = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(self.ckpt_path, config=self.repo_id, adapter=adapter)
self._compare_component_configs(pipe, pipe_single_file)
def test_single_file_components_with_diffusers_config_local_files_only(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
variant="fp16",
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
repo_id, weight_name = _extract_repo_id_and_weights_name(self.ckpt_path)
local_ckpt_path = download_single_file_checkpoint(repo_id, weight_name, tmpdir)
local_diffusers_config = download_diffusers_config(self.repo_id, tmpdir)
pipe_single_file = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(
local_ckpt_path,
config=local_diffusers_config,
adapter=adapter,
safety_checker=None,
local_files_only=True,
)
self._compare_component_configs(pipe, pipe_single_file)
def test_single_file_components_with_original_config(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
variant="fp16",
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None,
)
pipe_single_file = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(
self.ckpt_path, original_config=self.original_config, adapter=adapter
)
self._compare_component_configs(pipe, pipe_single_file)
def test_single_file_components_with_original_config_local_files_only(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_pretrained(
self.repo_id,
variant="fp16",
adapter=adapter,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
repo_id, weight_name = _extract_repo_id_and_weights_name(self.ckpt_path)
local_ckpt_path = download_single_file_checkpoint(repo_id, weight_name, tmpdir)
local_original_config = download_original_config(self.original_config, tmpdir)
pipe_single_file = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(
local_ckpt_path,
original_config=local_original_config,
adapter=adapter,
safety_checker=None,
local_files_only=True,
)
self._compare_component_configs(pipe, pipe_single_file)
def test_single_file_setting_pipeline_dtype_to_fp16(self):
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-lineart-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
single_file_pipe = self.pipeline_class.from_single_file(
self.ckpt_path, adapter=adapter, torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
super().test_single_file_setting_pipeline_dtype_to_fp16(single_file_pipe)
|
diffusers/tests/single_file/test_stable_diffusion_xl_adapter_single_file.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/tests/single_file/test_stable_diffusion_xl_adapter_single_file.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 3851
}
| 206
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import requests
from packaging.version import parse
# GitHub repository details
USER = "huggingface"
REPO = "diffusers"
def fetch_all_branches(user, repo):
branches = [] # List to store all branches
page = 1 # Start from first page
while True:
# Make a request to the GitHub API for the branches
response = requests.get(
f"https://api.github.com/repos/{user}/{repo}/branches",
params={"page": page},
timeout=60,
)
# Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 200:
# Add the branches from the current page to the list
branches.extend([branch["name"] for branch in response.json()])
# Check if there is a 'next' link for pagination
if "next" in response.links:
page += 1 # Move to the next page
else:
break # Exit loop if there is no next page
else:
print("Failed to retrieve branches:", response.status_code)
break
return branches
def main():
# Fetch all branches
branches = fetch_all_branches(USER, REPO)
# Filter branches.
# print(f"Total branches: {len(branches)}")
filtered_branches = []
for branch in branches:
if branch.startswith("v") and ("-release" in branch or "-patch" in branch):
filtered_branches.append(branch)
# print(f"Filtered: {branch}")
sorted_branches = sorted(filtered_branches, key=lambda x: parse(x.split("-")[0][1:]), reverse=True)
latest_branch = sorted_branches[0]
# print(f"Latest branch: {latest_branch}")
return latest_branch
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(main())
|
diffusers/utils/fetch_latest_release_branch.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "diffusers/utils/fetch_latest_release_branch.py",
"repo_id": "diffusers",
"token_count": 873
}
| 207
|
from lerobot.datasets.lerobot_dataset import LeRobotDataset
from lerobot.datasets.utils import hw_to_dataset_features
from lerobot.record import record_loop
from lerobot.robots.lekiwi.config_lekiwi import LeKiwiClientConfig
from lerobot.robots.lekiwi.lekiwi_client import LeKiwiClient
from lerobot.teleoperators.keyboard import KeyboardTeleop, KeyboardTeleopConfig
from lerobot.teleoperators.so100_leader import SO100Leader, SO100LeaderConfig
from lerobot.utils.control_utils import init_keyboard_listener
from lerobot.utils.utils import log_say
from lerobot.utils.visualization_utils import _init_rerun
NUM_EPISODES = 3
FPS = 30
EPISODE_TIME_SEC = 30
RESET_TIME_SEC = 10
TASK_DESCRIPTION = "My task description"
# Create the robot and teleoperator configurations
robot_config = LeKiwiClientConfig(remote_ip="172.18.134.136", id="lekiwi")
leader_arm_config = SO100LeaderConfig(port="/dev/tty.usbmodem585A0077581", id="my_awesome_leader_arm")
keyboard_config = KeyboardTeleopConfig()
robot = LeKiwiClient(robot_config)
leader_arm = SO100Leader(leader_arm_config)
keyboard = KeyboardTeleop(keyboard_config)
# Configure the dataset features
action_features = hw_to_dataset_features(robot.action_features, "action")
obs_features = hw_to_dataset_features(robot.observation_features, "observation")
dataset_features = {**action_features, **obs_features}
# Create the dataset
dataset = LeRobotDataset.create(
repo_id="<hf_username>/<dataset_repo_id>",
fps=FPS,
features=dataset_features,
robot_type=robot.name,
use_videos=True,
image_writer_threads=4,
)
# To connect you already should have this script running on LeKiwi: `python -m lerobot.robots.lekiwi.lekiwi_host --robot.id=my_awesome_kiwi`
robot.connect()
leader_arm.connect()
keyboard.connect()
_init_rerun(session_name="lekiwi_record")
listener, events = init_keyboard_listener()
if not robot.is_connected or not leader_arm.is_connected or not keyboard.is_connected:
raise ValueError("Robot, leader arm of keyboard is not connected!")
recorded_episodes = 0
while recorded_episodes < NUM_EPISODES and not events["stop_recording"]:
log_say(f"Recording episode {recorded_episodes}")
# Run the record loop
record_loop(
robot=robot,
events=events,
fps=FPS,
dataset=dataset,
teleop=[leader_arm, keyboard],
control_time_s=EPISODE_TIME_SEC,
single_task=TASK_DESCRIPTION,
display_data=True,
)
# Logic for reset env
if not events["stop_recording"] and (
(recorded_episodes < NUM_EPISODES - 1) or events["rerecord_episode"]
):
log_say("Reset the environment")
record_loop(
robot=robot,
events=events,
fps=FPS,
teleop=[leader_arm, keyboard],
control_time_s=RESET_TIME_SEC,
single_task=TASK_DESCRIPTION,
display_data=True,
)
if events["rerecord_episode"]:
log_say("Re-record episode")
events["rerecord_episode"] = False
events["exit_early"] = False
dataset.clear_episode_buffer()
continue
dataset.save_episode()
recorded_episodes += 1
# Upload to hub and clean up
dataset.push_to_hub()
robot.disconnect()
leader_arm.disconnect()
keyboard.disconnect()
listener.stop()
|
lerobot/examples/lekiwi/record.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/examples/lekiwi/record.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 1318
}
| 208
|
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import datetime as dt
import logging
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from pathlib import Path
from lerobot import envs, policies # noqa: F401
from lerobot.configs import parser
from lerobot.configs.default import EvalConfig
from lerobot.configs.policies import PreTrainedConfig
@dataclass
class EvalPipelineConfig:
# Either the repo ID of a model hosted on the Hub or a path to a directory containing weights
# saved using `Policy.save_pretrained`. If not provided, the policy is initialized from scratch
# (useful for debugging). This argument is mutually exclusive with `--config`.
env: envs.EnvConfig
eval: EvalConfig = field(default_factory=EvalConfig)
policy: PreTrainedConfig | None = None
output_dir: Path | None = None
job_name: str | None = None
seed: int | None = 1000
def __post_init__(self):
# HACK: We parse again the cli args here to get the pretrained path if there was one.
policy_path = parser.get_path_arg("policy")
if policy_path:
cli_overrides = parser.get_cli_overrides("policy")
self.policy = PreTrainedConfig.from_pretrained(policy_path, cli_overrides=cli_overrides)
self.policy.pretrained_path = policy_path
else:
logging.warning(
"No pretrained path was provided, evaluated policy will be built from scratch (random weights)."
)
if not self.job_name:
if self.env is None:
self.job_name = f"{self.policy.type}"
else:
self.job_name = f"{self.env.type}_{self.policy.type}"
if not self.output_dir:
now = dt.datetime.now()
eval_dir = f"{now:%Y-%m-%d}/{now:%H-%M-%S}_{self.job_name}"
self.output_dir = Path("outputs/eval") / eval_dir
@classmethod
def __get_path_fields__(cls) -> list[str]:
"""This enables the parser to load config from the policy using `--policy.path=local/dir`"""
return ["policy"]
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/configs/eval.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/configs/eval.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 972
}
| 209
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import contextlib
import importlib.resources
import json
import logging
from collections.abc import Iterator
from itertools import accumulate
from pathlib import Path
from pprint import pformat
from types import SimpleNamespace
from typing import Any
import datasets
import jsonlines
import numpy as np
import packaging.version
import torch
from datasets.table import embed_table_storage
from huggingface_hub import DatasetCard, DatasetCardData, HfApi
from huggingface_hub.errors import RevisionNotFoundError
from PIL import Image as PILImage
from torchvision import transforms
from lerobot.configs.types import DictLike, FeatureType, PolicyFeature
from lerobot.datasets.backward_compatibility import (
V21_MESSAGE,
BackwardCompatibilityError,
ForwardCompatibilityError,
)
from lerobot.utils.utils import is_valid_numpy_dtype_string
DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE = 1000 # Max number of episodes per chunk
INFO_PATH = "meta/info.json"
EPISODES_PATH = "meta/episodes.jsonl"
STATS_PATH = "meta/stats.json"
EPISODES_STATS_PATH = "meta/episodes_stats.jsonl"
TASKS_PATH = "meta/tasks.jsonl"
DEFAULT_VIDEO_PATH = "videos/chunk-{episode_chunk:03d}/{video_key}/episode_{episode_index:06d}.mp4"
DEFAULT_PARQUET_PATH = "data/chunk-{episode_chunk:03d}/episode_{episode_index:06d}.parquet"
DEFAULT_IMAGE_PATH = "images/{image_key}/episode_{episode_index:06d}/frame_{frame_index:06d}.png"
DATASET_CARD_TEMPLATE = """
---
# Metadata will go there
---
This dataset was created using [LeRobot](https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot).
## {}
"""
DEFAULT_FEATURES = {
"timestamp": {"dtype": "float32", "shape": (1,), "names": None},
"frame_index": {"dtype": "int64", "shape": (1,), "names": None},
"episode_index": {"dtype": "int64", "shape": (1,), "names": None},
"index": {"dtype": "int64", "shape": (1,), "names": None},
"task_index": {"dtype": "int64", "shape": (1,), "names": None},
}
def flatten_dict(d: dict, parent_key: str = "", sep: str = "/") -> dict:
"""Flatten a nested dictionary structure by collapsing nested keys into one key with a separator.
For example:
```
>>> dct = {"a": {"b": 1, "c": {"d": 2}}, "e": 3}`
>>> print(flatten_dict(dct))
{"a/b": 1, "a/c/d": 2, "e": 3}
"""
items = []
for k, v in d.items():
new_key = f"{parent_key}{sep}{k}" if parent_key else k
if isinstance(v, dict):
items.extend(flatten_dict(v, new_key, sep=sep).items())
else:
items.append((new_key, v))
return dict(items)
def unflatten_dict(d: dict, sep: str = "/") -> dict:
outdict = {}
for key, value in d.items():
parts = key.split(sep)
d = outdict
for part in parts[:-1]:
if part not in d:
d[part] = {}
d = d[part]
d[parts[-1]] = value
return outdict
def get_nested_item(obj: DictLike, flattened_key: str, sep: str = "/") -> Any:
split_keys = flattened_key.split(sep)
getter = obj[split_keys[0]]
if len(split_keys) == 1:
return getter
for key in split_keys[1:]:
getter = getter[key]
return getter
def serialize_dict(stats: dict[str, torch.Tensor | np.ndarray | dict]) -> dict:
serialized_dict = {}
for key, value in flatten_dict(stats).items():
if isinstance(value, (torch.Tensor, np.ndarray)):
serialized_dict[key] = value.tolist()
elif isinstance(value, np.generic):
serialized_dict[key] = value.item()
elif isinstance(value, (int, float)):
serialized_dict[key] = value
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"The value '{value}' of type '{type(value)}' is not supported.")
return unflatten_dict(serialized_dict)
def embed_images(dataset: datasets.Dataset) -> datasets.Dataset:
# Embed image bytes into the table before saving to parquet
format = dataset.format
dataset = dataset.with_format("arrow")
dataset = dataset.map(embed_table_storage, batched=False)
dataset = dataset.with_format(**format)
return dataset
def load_json(fpath: Path) -> Any:
with open(fpath) as f:
return json.load(f)
def write_json(data: dict, fpath: Path) -> None:
fpath.parent.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
with open(fpath, "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
def load_jsonlines(fpath: Path) -> list[Any]:
with jsonlines.open(fpath, "r") as reader:
return list(reader)
def write_jsonlines(data: dict, fpath: Path) -> None:
fpath.parent.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
with jsonlines.open(fpath, "w") as writer:
writer.write_all(data)
def append_jsonlines(data: dict, fpath: Path) -> None:
fpath.parent.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
with jsonlines.open(fpath, "a") as writer:
writer.write(data)
def write_info(info: dict, local_dir: Path):
write_json(info, local_dir / INFO_PATH)
def load_info(local_dir: Path) -> dict:
info = load_json(local_dir / INFO_PATH)
for ft in info["features"].values():
ft["shape"] = tuple(ft["shape"])
return info
def write_stats(stats: dict, local_dir: Path):
serialized_stats = serialize_dict(stats)
write_json(serialized_stats, local_dir / STATS_PATH)
def cast_stats_to_numpy(stats) -> dict[str, dict[str, np.ndarray]]:
stats = {key: np.array(value) for key, value in flatten_dict(stats).items()}
return unflatten_dict(stats)
def load_stats(local_dir: Path) -> dict[str, dict[str, np.ndarray]]:
if not (local_dir / STATS_PATH).exists():
return None
stats = load_json(local_dir / STATS_PATH)
return cast_stats_to_numpy(stats)
def write_task(task_index: int, task: dict, local_dir: Path):
task_dict = {
"task_index": task_index,
"task": task,
}
append_jsonlines(task_dict, local_dir / TASKS_PATH)
def load_tasks(local_dir: Path) -> tuple[dict, dict]:
tasks = load_jsonlines(local_dir / TASKS_PATH)
tasks = {item["task_index"]: item["task"] for item in sorted(tasks, key=lambda x: x["task_index"])}
task_to_task_index = {task: task_index for task_index, task in tasks.items()}
return tasks, task_to_task_index
def write_episode(episode: dict, local_dir: Path):
append_jsonlines(episode, local_dir / EPISODES_PATH)
def load_episodes(local_dir: Path) -> dict:
episodes = load_jsonlines(local_dir / EPISODES_PATH)
return {item["episode_index"]: item for item in sorted(episodes, key=lambda x: x["episode_index"])}
def write_episode_stats(episode_index: int, episode_stats: dict, local_dir: Path):
# We wrap episode_stats in a dictionary since `episode_stats["episode_index"]`
# is a dictionary of stats and not an integer.
episode_stats = {"episode_index": episode_index, "stats": serialize_dict(episode_stats)}
append_jsonlines(episode_stats, local_dir / EPISODES_STATS_PATH)
def load_episodes_stats(local_dir: Path) -> dict:
episodes_stats = load_jsonlines(local_dir / EPISODES_STATS_PATH)
return {
item["episode_index"]: cast_stats_to_numpy(item["stats"])
for item in sorted(episodes_stats, key=lambda x: x["episode_index"])
}
def backward_compatible_episodes_stats(
stats: dict[str, dict[str, np.ndarray]], episodes: list[int]
) -> dict[str, dict[str, np.ndarray]]:
return dict.fromkeys(episodes, stats)
def load_image_as_numpy(
fpath: str | Path, dtype: np.dtype = np.float32, channel_first: bool = True
) -> np.ndarray:
img = PILImage.open(fpath).convert("RGB")
img_array = np.array(img, dtype=dtype)
if channel_first: # (H, W, C) -> (C, H, W)
img_array = np.transpose(img_array, (2, 0, 1))
if np.issubdtype(dtype, np.floating):
img_array /= 255.0
return img_array
def hf_transform_to_torch(items_dict: dict[torch.Tensor | None]):
"""Get a transform function that convert items from Hugging Face dataset (pyarrow)
to torch tensors. Importantly, images are converted from PIL, which corresponds to
a channel last representation (h w c) of uint8 type, to a torch image representation
with channel first (c h w) of float32 type in range [0,1].
"""
for key in items_dict:
first_item = items_dict[key][0]
if isinstance(first_item, PILImage.Image):
to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
items_dict[key] = [to_tensor(img) for img in items_dict[key]]
elif first_item is None:
pass
else:
items_dict[key] = [x if isinstance(x, str) else torch.tensor(x) for x in items_dict[key]]
return items_dict
def is_valid_version(version: str) -> bool:
try:
packaging.version.parse(version)
return True
except packaging.version.InvalidVersion:
return False
def check_version_compatibility(
repo_id: str,
version_to_check: str | packaging.version.Version,
current_version: str | packaging.version.Version,
enforce_breaking_major: bool = True,
) -> None:
v_check = (
packaging.version.parse(version_to_check)
if not isinstance(version_to_check, packaging.version.Version)
else version_to_check
)
v_current = (
packaging.version.parse(current_version)
if not isinstance(current_version, packaging.version.Version)
else current_version
)
if v_check.major < v_current.major and enforce_breaking_major:
raise BackwardCompatibilityError(repo_id, v_check)
elif v_check.minor < v_current.minor:
logging.warning(V21_MESSAGE.format(repo_id=repo_id, version=v_check))
def get_repo_versions(repo_id: str) -> list[packaging.version.Version]:
"""Returns available valid versions (branches and tags) on given repo."""
api = HfApi()
repo_refs = api.list_repo_refs(repo_id, repo_type="dataset")
repo_refs = [b.name for b in repo_refs.branches + repo_refs.tags]
repo_versions = []
for ref in repo_refs:
with contextlib.suppress(packaging.version.InvalidVersion):
repo_versions.append(packaging.version.parse(ref))
return repo_versions
def get_safe_version(repo_id: str, version: str | packaging.version.Version) -> str:
"""
Returns the version if available on repo or the latest compatible one.
Otherwise, will throw a `CompatibilityError`.
"""
target_version = (
packaging.version.parse(version) if not isinstance(version, packaging.version.Version) else version
)
hub_versions = get_repo_versions(repo_id)
if not hub_versions:
raise RevisionNotFoundError(
f"""Your dataset must be tagged with a codebase version.
Assuming _version_ is the codebase_version value in the info.json, you can run this:
```python
from huggingface_hub import HfApi
hub_api = HfApi()
hub_api.create_tag("{repo_id}", tag="_version_", repo_type="dataset")
```
"""
)
if target_version in hub_versions:
return f"v{target_version}"
compatibles = [
v for v in hub_versions if v.major == target_version.major and v.minor <= target_version.minor
]
if compatibles:
return_version = max(compatibles)
if return_version < target_version:
logging.warning(f"Revision {version} for {repo_id} not found, using version v{return_version}")
return f"v{return_version}"
lower_major = [v for v in hub_versions if v.major < target_version.major]
if lower_major:
raise BackwardCompatibilityError(repo_id, max(lower_major))
upper_versions = [v for v in hub_versions if v > target_version]
assert len(upper_versions) > 0
raise ForwardCompatibilityError(repo_id, min(upper_versions))
def get_hf_features_from_features(features: dict) -> datasets.Features:
hf_features = {}
for key, ft in features.items():
if ft["dtype"] == "video":
continue
elif ft["dtype"] == "image":
hf_features[key] = datasets.Image()
elif ft["shape"] == (1,):
hf_features[key] = datasets.Value(dtype=ft["dtype"])
elif len(ft["shape"]) == 1:
hf_features[key] = datasets.Sequence(
length=ft["shape"][0], feature=datasets.Value(dtype=ft["dtype"])
)
elif len(ft["shape"]) == 2:
hf_features[key] = datasets.Array2D(shape=ft["shape"], dtype=ft["dtype"])
elif len(ft["shape"]) == 3:
hf_features[key] = datasets.Array3D(shape=ft["shape"], dtype=ft["dtype"])
elif len(ft["shape"]) == 4:
hf_features[key] = datasets.Array4D(shape=ft["shape"], dtype=ft["dtype"])
elif len(ft["shape"]) == 5:
hf_features[key] = datasets.Array5D(shape=ft["shape"], dtype=ft["dtype"])
else:
raise ValueError(f"Corresponding feature is not valid: {ft}")
return datasets.Features(hf_features)
def _validate_feature_names(features: dict[str, dict]) -> None:
invalid_features = {name: ft for name, ft in features.items() if "/" in name}
if invalid_features:
raise ValueError(f"Feature names should not contain '/'. Found '/' in '{invalid_features}'.")
def hw_to_dataset_features(
hw_features: dict[str, type | tuple], prefix: str, use_video: bool = True
) -> dict[str, dict]:
features = {}
joint_fts = {key: ftype for key, ftype in hw_features.items() if ftype is float}
cam_fts = {key: shape for key, shape in hw_features.items() if isinstance(shape, tuple)}
if joint_fts and prefix == "action":
features[prefix] = {
"dtype": "float32",
"shape": (len(joint_fts),),
"names": list(joint_fts),
}
if joint_fts and prefix == "observation":
features[f"{prefix}.state"] = {
"dtype": "float32",
"shape": (len(joint_fts),),
"names": list(joint_fts),
}
for key, shape in cam_fts.items():
features[f"{prefix}.images.{key}"] = {
"dtype": "video" if use_video else "image",
"shape": shape,
"names": ["height", "width", "channels"],
}
_validate_feature_names(features)
return features
def build_dataset_frame(
ds_features: dict[str, dict], values: dict[str, Any], prefix: str
) -> dict[str, np.ndarray]:
frame = {}
for key, ft in ds_features.items():
if key in DEFAULT_FEATURES or not key.startswith(prefix):
continue
elif ft["dtype"] == "float32" and len(ft["shape"]) == 1:
frame[key] = np.array([values[name] for name in ft["names"]], dtype=np.float32)
elif ft["dtype"] in ["image", "video"]:
frame[key] = values[key.removeprefix(f"{prefix}.images.")]
return frame
def dataset_to_policy_features(features: dict[str, dict]) -> dict[str, PolicyFeature]:
# TODO(aliberts): Implement "type" in dataset features and simplify this
policy_features = {}
for key, ft in features.items():
shape = ft["shape"]
if ft["dtype"] in ["image", "video"]:
type = FeatureType.VISUAL
if len(shape) != 3:
raise ValueError(f"Number of dimensions of {key} != 3 (shape={shape})")
names = ft["names"]
# Backward compatibility for "channel" which is an error introduced in LeRobotDataset v2.0 for ported datasets.
if names[2] in ["channel", "channels"]: # (h, w, c) -> (c, h, w)
shape = (shape[2], shape[0], shape[1])
elif key == "observation.environment_state":
type = FeatureType.ENV
elif key.startswith("observation"):
type = FeatureType.STATE
elif key.startswith("action"):
type = FeatureType.ACTION
else:
continue
policy_features[key] = PolicyFeature(
type=type,
shape=shape,
)
return policy_features
def create_empty_dataset_info(
codebase_version: str,
fps: int,
features: dict,
use_videos: bool,
robot_type: str | None = None,
) -> dict:
return {
"codebase_version": codebase_version,
"robot_type": robot_type,
"total_episodes": 0,
"total_frames": 0,
"total_tasks": 0,
"total_videos": 0,
"total_chunks": 0,
"chunks_size": DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE,
"fps": fps,
"splits": {},
"data_path": DEFAULT_PARQUET_PATH,
"video_path": DEFAULT_VIDEO_PATH if use_videos else None,
"features": features,
}
def get_episode_data_index(
episode_dicts: dict[dict], episodes: list[int] | None = None
) -> dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
episode_lengths = {ep_idx: ep_dict["length"] for ep_idx, ep_dict in episode_dicts.items()}
if episodes is not None:
episode_lengths = {ep_idx: episode_lengths[ep_idx] for ep_idx in episodes}
cumulative_lengths = list(accumulate(episode_lengths.values()))
return {
"from": torch.LongTensor([0] + cumulative_lengths[:-1]),
"to": torch.LongTensor(cumulative_lengths),
}
def check_timestamps_sync(
timestamps: np.ndarray,
episode_indices: np.ndarray,
episode_data_index: dict[str, np.ndarray],
fps: int,
tolerance_s: float,
raise_value_error: bool = True,
) -> bool:
"""
This check is to make sure that each timestamp is separated from the next by (1/fps) +/- tolerance
to account for possible numerical error.
Args:
timestamps (np.ndarray): Array of timestamps in seconds.
episode_indices (np.ndarray): Array indicating the episode index for each timestamp.
episode_data_index (dict[str, np.ndarray]): A dictionary that includes 'to',
which identifies indices for the end of each episode.
fps (int): Frames per second. Used to check the expected difference between consecutive timestamps.
tolerance_s (float): Allowed deviation from the expected (1/fps) difference.
raise_value_error (bool): Whether to raise a ValueError if the check fails.
Returns:
bool: True if all checked timestamp differences lie within tolerance, False otherwise.
Raises:
ValueError: If the check fails and `raise_value_error` is True.
"""
if timestamps.shape != episode_indices.shape:
raise ValueError(
"timestamps and episode_indices should have the same shape. "
f"Found {timestamps.shape=} and {episode_indices.shape=}."
)
# Consecutive differences
diffs = np.diff(timestamps)
within_tolerance = np.abs(diffs - (1.0 / fps)) <= tolerance_s
# Mask to ignore differences at the boundaries between episodes
mask = np.ones(len(diffs), dtype=bool)
ignored_diffs = episode_data_index["to"][:-1] - 1 # indices at the end of each episode
mask[ignored_diffs] = False
filtered_within_tolerance = within_tolerance[mask]
# Check if all remaining diffs are within tolerance
if not np.all(filtered_within_tolerance):
# Track original indices before masking
original_indices = np.arange(len(diffs))
filtered_indices = original_indices[mask]
outside_tolerance_filtered_indices = np.nonzero(~filtered_within_tolerance)[0]
outside_tolerance_indices = filtered_indices[outside_tolerance_filtered_indices]
outside_tolerances = []
for idx in outside_tolerance_indices:
entry = {
"timestamps": [timestamps[idx], timestamps[idx + 1]],
"diff": diffs[idx],
"episode_index": episode_indices[idx].item()
if hasattr(episode_indices[idx], "item")
else episode_indices[idx],
}
outside_tolerances.append(entry)
if raise_value_error:
raise ValueError(
f"""One or several timestamps unexpectedly violate the tolerance inside episode range.
This might be due to synchronization issues during data collection.
\n{pformat(outside_tolerances)}"""
)
return False
return True
def check_delta_timestamps(
delta_timestamps: dict[str, list[float]], fps: int, tolerance_s: float, raise_value_error: bool = True
) -> bool:
"""This will check if all the values in delta_timestamps are multiples of 1/fps +/- tolerance.
This is to ensure that these delta_timestamps added to any timestamp from a dataset will themselves be
actual timestamps from the dataset.
"""
outside_tolerance = {}
for key, delta_ts in delta_timestamps.items():
within_tolerance = [abs(ts * fps - round(ts * fps)) / fps <= tolerance_s for ts in delta_ts]
if not all(within_tolerance):
outside_tolerance[key] = [
ts for ts, is_within in zip(delta_ts, within_tolerance, strict=True) if not is_within
]
if len(outside_tolerance) > 0:
if raise_value_error:
raise ValueError(
f"""
The following delta_timestamps are found outside of tolerance range.
Please make sure they are multiples of 1/{fps} +/- tolerance and adjust
their values accordingly.
\n{pformat(outside_tolerance)}
"""
)
return False
return True
def get_delta_indices(delta_timestamps: dict[str, list[float]], fps: int) -> dict[str, list[int]]:
delta_indices = {}
for key, delta_ts in delta_timestamps.items():
delta_indices[key] = [round(d * fps) for d in delta_ts]
return delta_indices
def cycle(iterable):
"""The equivalent of itertools.cycle, but safe for Pytorch dataloaders.
See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/23900 for information on why itertools.cycle is not safe.
"""
iterator = iter(iterable)
while True:
try:
yield next(iterator)
except StopIteration:
iterator = iter(iterable)
def create_branch(repo_id, *, branch: str, repo_type: str | None = None) -> None:
"""Create a branch on a existing Hugging Face repo. Delete the branch if it already
exists before creating it.
"""
api = HfApi()
branches = api.list_repo_refs(repo_id, repo_type=repo_type).branches
refs = [branch.ref for branch in branches]
ref = f"refs/heads/{branch}"
if ref in refs:
api.delete_branch(repo_id, repo_type=repo_type, branch=branch)
api.create_branch(repo_id, repo_type=repo_type, branch=branch)
def create_lerobot_dataset_card(
tags: list | None = None,
dataset_info: dict | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> DatasetCard:
"""
Keyword arguments will be used to replace values in src/lerobot/datasets/card_template.md.
Note: If specified, license must be one of https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-licenses.
"""
card_tags = ["LeRobot"]
if tags:
card_tags += tags
if dataset_info:
dataset_structure = "[meta/info.json](meta/info.json):\n"
dataset_structure += f"```json\n{json.dumps(dataset_info, indent=4)}\n```\n"
kwargs = {**kwargs, "dataset_structure": dataset_structure}
card_data = DatasetCardData(
license=kwargs.get("license"),
tags=card_tags,
task_categories=["robotics"],
configs=[
{
"config_name": "default",
"data_files": "data/*/*.parquet",
}
],
)
card_template = (importlib.resources.files("lerobot.datasets") / "card_template.md").read_text()
return DatasetCard.from_template(
card_data=card_data,
template_str=card_template,
**kwargs,
)
class IterableNamespace(SimpleNamespace):
"""
A namespace object that supports both dictionary-like iteration and dot notation access.
Automatically converts nested dictionaries into IterableNamespaces.
This class extends SimpleNamespace to provide:
- Dictionary-style iteration over keys
- Access to items via both dot notation (obj.key) and brackets (obj["key"])
- Dictionary-like methods: items(), keys(), values()
- Recursive conversion of nested dictionaries
Args:
dictionary: Optional dictionary to initialize the namespace
**kwargs: Additional keyword arguments passed to SimpleNamespace
Examples:
>>> data = {"name": "Alice", "details": {"age": 25}}
>>> ns = IterableNamespace(data)
>>> ns.name
'Alice'
>>> ns.details.age
25
>>> list(ns.keys())
['name', 'details']
>>> for key, value in ns.items():
... print(f"{key}: {value}")
name: Alice
details: IterableNamespace(age=25)
"""
def __init__(self, dictionary: dict[str, Any] = None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
if dictionary is not None:
for key, value in dictionary.items():
if isinstance(value, dict):
setattr(self, key, IterableNamespace(value))
else:
setattr(self, key, value)
def __iter__(self) -> Iterator[str]:
return iter(vars(self))
def __getitem__(self, key: str) -> Any:
return vars(self)[key]
def items(self):
return vars(self).items()
def values(self):
return vars(self).values()
def keys(self):
return vars(self).keys()
def validate_frame(frame: dict, features: dict):
expected_features = set(features) - set(DEFAULT_FEATURES)
actual_features = set(frame)
error_message = validate_features_presence(actual_features, expected_features)
common_features = actual_features & expected_features
for name in common_features - {"task"}:
error_message += validate_feature_dtype_and_shape(name, features[name], frame[name])
if error_message:
raise ValueError(error_message)
def validate_features_presence(actual_features: set[str], expected_features: set[str]):
error_message = ""
missing_features = expected_features - actual_features
extra_features = actual_features - expected_features
if missing_features or extra_features:
error_message += "Feature mismatch in `frame` dictionary:\n"
if missing_features:
error_message += f"Missing features: {missing_features}\n"
if extra_features:
error_message += f"Extra features: {extra_features}\n"
return error_message
def validate_feature_dtype_and_shape(name: str, feature: dict, value: np.ndarray | PILImage.Image | str):
expected_dtype = feature["dtype"]
expected_shape = feature["shape"]
if is_valid_numpy_dtype_string(expected_dtype):
return validate_feature_numpy_array(name, expected_dtype, expected_shape, value)
elif expected_dtype in ["image", "video"]:
return validate_feature_image_or_video(name, expected_shape, value)
elif expected_dtype == "string":
return validate_feature_string(name, value)
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"The feature dtype '{expected_dtype}' is not implemented yet.")
def validate_feature_numpy_array(
name: str, expected_dtype: str, expected_shape: list[int], value: np.ndarray
):
error_message = ""
if isinstance(value, np.ndarray):
actual_dtype = value.dtype
actual_shape = value.shape
if actual_dtype != np.dtype(expected_dtype):
error_message += f"The feature '{name}' of dtype '{actual_dtype}' is not of the expected dtype '{expected_dtype}'.\n"
if actual_shape != expected_shape:
error_message += f"The feature '{name}' of shape '{actual_shape}' does not have the expected shape '{expected_shape}'.\n"
else:
error_message += f"The feature '{name}' is not a 'np.ndarray'. Expected type is '{expected_dtype}', but type '{type(value)}' provided instead.\n"
return error_message
def validate_feature_image_or_video(name: str, expected_shape: list[str], value: np.ndarray | PILImage.Image):
# Note: The check of pixels range ([0,1] for float and [0,255] for uint8) is done by the image writer threads.
error_message = ""
if isinstance(value, np.ndarray):
actual_shape = value.shape
c, h, w = expected_shape
if len(actual_shape) != 3 or (actual_shape != (c, h, w) and actual_shape != (h, w, c)):
error_message += f"The feature '{name}' of shape '{actual_shape}' does not have the expected shape '{(c, h, w)}' or '{(h, w, c)}'.\n"
elif isinstance(value, PILImage.Image):
pass
else:
error_message += f"The feature '{name}' is expected to be of type 'PIL.Image' or 'np.ndarray' channel first or channel last, but type '{type(value)}' provided instead.\n"
return error_message
def validate_feature_string(name: str, value: str):
if not isinstance(value, str):
return f"The feature '{name}' is expected to be of type 'str', but type '{type(value)}' provided instead.\n"
return ""
def validate_episode_buffer(episode_buffer: dict, total_episodes: int, features: dict):
if "size" not in episode_buffer:
raise ValueError("size key not found in episode_buffer")
if "task" not in episode_buffer:
raise ValueError("task key not found in episode_buffer")
if episode_buffer["episode_index"] != total_episodes:
# TODO(aliberts): Add option to use existing episode_index
raise NotImplementedError(
"You might have manually provided the episode_buffer with an episode_index that doesn't "
"match the total number of episodes already in the dataset. This is not supported for now."
)
if episode_buffer["size"] == 0:
raise ValueError("You must add one or several frames with `add_frame` before calling `add_episode`.")
buffer_keys = set(episode_buffer.keys()) - {"task", "size"}
if not buffer_keys == set(features):
raise ValueError(
f"Features from `episode_buffer` don't match the ones in `features`."
f"In episode_buffer not in features: {buffer_keys - set(features)}"
f"In features not in episode_buffer: {set(features) - buffer_keys}"
)
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/datasets/utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/datasets/utils.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 12408
}
| 210
|
from .motors_bus import Motor, MotorCalibration, MotorNormMode, MotorsBus
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/motors/__init__.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/motors/__init__.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 21
}
| 211
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 Tony Z. Zhao and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Action Chunking Transformer Policy
As per Learning Fine-Grained Bimanual Manipulation with Low-Cost Hardware (https://huggingface.co/papers/2304.13705).
The majority of changes here involve removing unused code, unifying naming, and adding helpful comments.
"""
import math
from collections import deque
from collections.abc import Callable
from itertools import chain
import einops
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F # noqa: N812
import torchvision
from torch import Tensor, nn
from torchvision.models._utils import IntermediateLayerGetter
from torchvision.ops.misc import FrozenBatchNorm2d
from lerobot.constants import ACTION, OBS_IMAGES
from lerobot.policies.act.configuration_act import ACTConfig
from lerobot.policies.normalize import Normalize, Unnormalize
from lerobot.policies.pretrained import PreTrainedPolicy
class ACTPolicy(PreTrainedPolicy):
"""
Action Chunking Transformer Policy as per Learning Fine-Grained Bimanual Manipulation with Low-Cost
Hardware (paper: https://huggingface.co/papers/2304.13705, code: https://github.com/tonyzhaozh/act)
"""
config_class = ACTConfig
name = "act"
def __init__(
self,
config: ACTConfig,
dataset_stats: dict[str, dict[str, Tensor]] | None = None,
):
"""
Args:
config: Policy configuration class instance or None, in which case the default instantiation of
the configuration class is used.
dataset_stats: Dataset statistics to be used for normalization. If not passed here, it is expected
that they will be passed with a call to `load_state_dict` before the policy is used.
"""
super().__init__(config)
config.validate_features()
self.config = config
self.normalize_inputs = Normalize(config.input_features, config.normalization_mapping, dataset_stats)
self.normalize_targets = Normalize(
config.output_features, config.normalization_mapping, dataset_stats
)
self.unnormalize_outputs = Unnormalize(
config.output_features, config.normalization_mapping, dataset_stats
)
self.model = ACT(config)
if config.temporal_ensemble_coeff is not None:
self.temporal_ensembler = ACTTemporalEnsembler(config.temporal_ensemble_coeff, config.chunk_size)
self.reset()
def get_optim_params(self) -> dict:
# TODO(aliberts, rcadene): As of now, lr_backbone == lr
# Should we remove this and just `return self.parameters()`?
return [
{
"params": [
p
for n, p in self.named_parameters()
if not n.startswith("model.backbone") and p.requires_grad
]
},
{
"params": [
p
for n, p in self.named_parameters()
if n.startswith("model.backbone") and p.requires_grad
],
"lr": self.config.optimizer_lr_backbone,
},
]
def reset(self):
"""This should be called whenever the environment is reset."""
if self.config.temporal_ensemble_coeff is not None:
self.temporal_ensembler.reset()
else:
self._action_queue = deque([], maxlen=self.config.n_action_steps)
@torch.no_grad()
def select_action(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> Tensor:
"""Select a single action given environment observations.
This method wraps `select_actions` in order to return one action at a time for execution in the
environment. It works by managing the actions in a queue and only calling `select_actions` when the
queue is empty.
"""
self.eval() # keeping the policy in eval mode as it could be set to train mode while queue is consumed
if self.config.temporal_ensemble_coeff is not None:
actions = self.predict_action_chunk(batch)
action = self.temporal_ensembler.update(actions)
return action
# Action queue logic for n_action_steps > 1. When the action_queue is depleted, populate it by
# querying the policy.
if len(self._action_queue) == 0:
actions = self.predict_action_chunk(batch)[:, : self.config.n_action_steps]
# `self.model.forward` returns a (batch_size, n_action_steps, action_dim) tensor, but the queue
# effectively has shape (n_action_steps, batch_size, *), hence the transpose.
self._action_queue.extend(actions.transpose(0, 1))
return self._action_queue.popleft()
@torch.no_grad()
def predict_action_chunk(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> Tensor:
"""Predict a chunk of actions given environment observations."""
self.eval()
batch = self.normalize_inputs(batch)
if self.config.image_features:
batch = dict(batch) # shallow copy so that adding a key doesn't modify the original
batch[OBS_IMAGES] = [batch[key] for key in self.config.image_features]
actions = self.model(batch)[0]
actions = self.unnormalize_outputs({ACTION: actions})[ACTION]
return actions
def forward(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> tuple[Tensor, dict]:
"""Run the batch through the model and compute the loss for training or validation."""
batch = self.normalize_inputs(batch)
if self.config.image_features:
batch = dict(batch) # shallow copy so that adding a key doesn't modify the original
batch[OBS_IMAGES] = [batch[key] for key in self.config.image_features]
batch = self.normalize_targets(batch)
actions_hat, (mu_hat, log_sigma_x2_hat) = self.model(batch)
l1_loss = (
F.l1_loss(batch[ACTION], actions_hat, reduction="none") * ~batch["action_is_pad"].unsqueeze(-1)
).mean()
loss_dict = {"l1_loss": l1_loss.item()}
if self.config.use_vae:
# Calculate Dₖₗ(latent_pdf || standard_normal). Note: After computing the KL-divergence for
# each dimension independently, we sum over the latent dimension to get the total
# KL-divergence per batch element, then take the mean over the batch.
# (See App. B of https://huggingface.co/papers/1312.6114 for more details).
mean_kld = (
(-0.5 * (1 + log_sigma_x2_hat - mu_hat.pow(2) - (log_sigma_x2_hat).exp())).sum(-1).mean()
)
loss_dict["kld_loss"] = mean_kld.item()
loss = l1_loss + mean_kld * self.config.kl_weight
else:
loss = l1_loss
return loss, loss_dict
class ACTTemporalEnsembler:
def __init__(self, temporal_ensemble_coeff: float, chunk_size: int) -> None:
"""Temporal ensembling as described in Algorithm 2 of https://huggingface.co/papers/2304.13705.
The weights are calculated as wᵢ = exp(-temporal_ensemble_coeff * i) where w₀ is the oldest action.
They are then normalized to sum to 1 by dividing by Σwᵢ. Here's some intuition around how the
coefficient works:
- Setting it to 0 uniformly weighs all actions.
- Setting it positive gives more weight to older actions.
- Setting it negative gives more weight to newer actions.
NOTE: The default value for `temporal_ensemble_coeff` used by the original ACT work is 0.01. This
results in older actions being weighed more highly than newer actions (the experiments documented in
https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot/pull/319 hint at why highly weighing new actions might be
detrimental: doing so aggressively may diminish the benefits of action chunking).
Here we use an online method for computing the average rather than caching a history of actions in
order to compute the average offline. For a simple 1D sequence it looks something like:
```
import torch
seq = torch.linspace(8, 8.5, 100)
print(seq)
m = 0.01
exp_weights = torch.exp(-m * torch.arange(len(seq)))
print(exp_weights)
# Calculate offline
avg = (exp_weights * seq).sum() / exp_weights.sum()
print("offline", avg)
# Calculate online
for i, item in enumerate(seq):
if i == 0:
avg = item
continue
avg *= exp_weights[:i].sum()
avg += item * exp_weights[i]
avg /= exp_weights[: i + 1].sum()
print("online", avg)
```
"""
self.chunk_size = chunk_size
self.ensemble_weights = torch.exp(-temporal_ensemble_coeff * torch.arange(chunk_size))
self.ensemble_weights_cumsum = torch.cumsum(self.ensemble_weights, dim=0)
self.reset()
def reset(self):
"""Resets the online computation variables."""
self.ensembled_actions = None
# (chunk_size,) count of how many actions are in the ensemble for each time step in the sequence.
self.ensembled_actions_count = None
def update(self, actions: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Takes a (batch, chunk_size, action_dim) sequence of actions, update the temporal ensemble for all
time steps, and pop/return the next batch of actions in the sequence.
"""
self.ensemble_weights = self.ensemble_weights.to(device=actions.device)
self.ensemble_weights_cumsum = self.ensemble_weights_cumsum.to(device=actions.device)
if self.ensembled_actions is None:
# Initializes `self._ensembled_action` to the sequence of actions predicted during the first
# time step of the episode.
self.ensembled_actions = actions.clone()
# Note: The last dimension is unsqueeze to make sure we can broadcast properly for tensor
# operations later.
self.ensembled_actions_count = torch.ones(
(self.chunk_size, 1), dtype=torch.long, device=self.ensembled_actions.device
)
else:
# self.ensembled_actions will have shape (batch_size, chunk_size - 1, action_dim). Compute
# the online update for those entries.
self.ensembled_actions *= self.ensemble_weights_cumsum[self.ensembled_actions_count - 1]
self.ensembled_actions += actions[:, :-1] * self.ensemble_weights[self.ensembled_actions_count]
self.ensembled_actions /= self.ensemble_weights_cumsum[self.ensembled_actions_count]
self.ensembled_actions_count = torch.clamp(self.ensembled_actions_count + 1, max=self.chunk_size)
# The last action, which has no prior online average, needs to get concatenated onto the end.
self.ensembled_actions = torch.cat([self.ensembled_actions, actions[:, -1:]], dim=1)
self.ensembled_actions_count = torch.cat(
[self.ensembled_actions_count, torch.ones_like(self.ensembled_actions_count[-1:])]
)
# "Consume" the first action.
action, self.ensembled_actions, self.ensembled_actions_count = (
self.ensembled_actions[:, 0],
self.ensembled_actions[:, 1:],
self.ensembled_actions_count[1:],
)
return action
class ACT(nn.Module):
"""Action Chunking Transformer: The underlying neural network for ACTPolicy.
Note: In this code we use the terms `vae_encoder`, 'encoder', `decoder`. The meanings are as follows.
- The `vae_encoder` is, as per the literature around variational auto-encoders (VAE), the part of the
model that encodes the target data (a sequence of actions), and the condition (the robot
joint-space).
- A transformer with an `encoder` (not the VAE encoder) and `decoder` (not the VAE decoder) with
cross-attention is used as the VAE decoder. For these terms, we drop the `vae_` prefix because we
have an option to train this model without the variational objective (in which case we drop the
`vae_encoder` altogether, and nothing about this model has anything to do with a VAE).
Transformer
Used alone for inference
(acts as VAE decoder
during training)
┌───────────────────────┐
│ Outputs │
│ ▲ │
│ ┌─────►┌───────┐ │
┌──────┐ │ │ │Transf.│ │
│ │ │ ├─────►│decoder│ │
┌────┴────┐ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ ┌───┴───┬─►│ │ │
│ VAE │ │ │ │ │ └───────┘ │
│ encoder │ │ │ │Transf.│ │
│ │ │ │ │encoder│ │
└───▲─────┘ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ └▲──▲─▲─┘ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │
inputs └─────┼──┘ │ image emb. │
│ state emb. │
└───────────────────────┘
"""
def __init__(self, config: ACTConfig):
# BERT style VAE encoder with input tokens [cls, robot_state, *action_sequence].
# The cls token forms parameters of the latent's distribution (like this [*means, *log_variances]).
super().__init__()
self.config = config
if self.config.use_vae:
self.vae_encoder = ACTEncoder(config, is_vae_encoder=True)
self.vae_encoder_cls_embed = nn.Embedding(1, config.dim_model)
# Projection layer for joint-space configuration to hidden dimension.
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
self.vae_encoder_robot_state_input_proj = nn.Linear(
self.config.robot_state_feature.shape[0], config.dim_model
)
# Projection layer for action (joint-space target) to hidden dimension.
self.vae_encoder_action_input_proj = nn.Linear(
self.config.action_feature.shape[0],
config.dim_model,
)
# Projection layer from the VAE encoder's output to the latent distribution's parameter space.
self.vae_encoder_latent_output_proj = nn.Linear(config.dim_model, config.latent_dim * 2)
# Fixed sinusoidal positional embedding for the input to the VAE encoder. Unsqueeze for batch
# dimension.
num_input_token_encoder = 1 + config.chunk_size
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
num_input_token_encoder += 1
self.register_buffer(
"vae_encoder_pos_enc",
create_sinusoidal_pos_embedding(num_input_token_encoder, config.dim_model).unsqueeze(0),
)
# Backbone for image feature extraction.
if self.config.image_features:
backbone_model = getattr(torchvision.models, config.vision_backbone)(
replace_stride_with_dilation=[False, False, config.replace_final_stride_with_dilation],
weights=config.pretrained_backbone_weights,
norm_layer=FrozenBatchNorm2d,
)
# Note: The assumption here is that we are using a ResNet model (and hence layer4 is the final
# feature map).
# Note: The forward method of this returns a dict: {"feature_map": output}.
self.backbone = IntermediateLayerGetter(backbone_model, return_layers={"layer4": "feature_map"})
# Transformer (acts as VAE decoder when training with the variational objective).
self.encoder = ACTEncoder(config)
self.decoder = ACTDecoder(config)
# Transformer encoder input projections. The tokens will be structured like
# [latent, (robot_state), (env_state), (image_feature_map_pixels)].
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
self.encoder_robot_state_input_proj = nn.Linear(
self.config.robot_state_feature.shape[0], config.dim_model
)
if self.config.env_state_feature:
self.encoder_env_state_input_proj = nn.Linear(
self.config.env_state_feature.shape[0], config.dim_model
)
self.encoder_latent_input_proj = nn.Linear(config.latent_dim, config.dim_model)
if self.config.image_features:
self.encoder_img_feat_input_proj = nn.Conv2d(
backbone_model.fc.in_features, config.dim_model, kernel_size=1
)
# Transformer encoder positional embeddings.
n_1d_tokens = 1 # for the latent
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
n_1d_tokens += 1
if self.config.env_state_feature:
n_1d_tokens += 1
self.encoder_1d_feature_pos_embed = nn.Embedding(n_1d_tokens, config.dim_model)
if self.config.image_features:
self.encoder_cam_feat_pos_embed = ACTSinusoidalPositionEmbedding2d(config.dim_model // 2)
# Transformer decoder.
# Learnable positional embedding for the transformer's decoder (in the style of DETR object queries).
self.decoder_pos_embed = nn.Embedding(config.chunk_size, config.dim_model)
# Final action regression head on the output of the transformer's decoder.
self.action_head = nn.Linear(config.dim_model, self.config.action_feature.shape[0])
self._reset_parameters()
def _reset_parameters(self):
"""Xavier-uniform initialization of the transformer parameters as in the original code."""
for p in chain(self.encoder.parameters(), self.decoder.parameters()):
if p.dim() > 1:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(p)
def forward(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> tuple[Tensor, tuple[Tensor, Tensor] | tuple[None, None]]:
"""A forward pass through the Action Chunking Transformer (with optional VAE encoder).
`batch` should have the following structure:
{
[robot_state_feature] (optional): (B, state_dim) batch of robot states.
[image_features]: (B, n_cameras, C, H, W) batch of images.
AND/OR
[env_state_feature]: (B, env_dim) batch of environment states.
[action_feature] (optional, only if training with VAE): (B, chunk_size, action dim) batch of actions.
}
Returns:
(B, chunk_size, action_dim) batch of action sequences
Tuple containing the latent PDF's parameters (mean, log(σ²)) both as (B, L) tensors where L is the
latent dimension.
"""
if self.config.use_vae and self.training:
assert "action" in batch, (
"actions must be provided when using the variational objective in training mode."
)
if "observation.images" in batch:
batch_size = batch["observation.images"][0].shape[0]
else:
batch_size = batch["observation.environment_state"].shape[0]
# Prepare the latent for input to the transformer encoder.
if self.config.use_vae and "action" in batch and self.training:
# Prepare the input to the VAE encoder: [cls, *joint_space_configuration, *action_sequence].
cls_embed = einops.repeat(
self.vae_encoder_cls_embed.weight, "1 d -> b 1 d", b=batch_size
) # (B, 1, D)
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
robot_state_embed = self.vae_encoder_robot_state_input_proj(batch["observation.state"])
robot_state_embed = robot_state_embed.unsqueeze(1) # (B, 1, D)
action_embed = self.vae_encoder_action_input_proj(batch["action"]) # (B, S, D)
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
vae_encoder_input = [cls_embed, robot_state_embed, action_embed] # (B, S+2, D)
else:
vae_encoder_input = [cls_embed, action_embed]
vae_encoder_input = torch.cat(vae_encoder_input, axis=1)
# Prepare fixed positional embedding.
# Note: detach() shouldn't be necessary but leaving it the same as the original code just in case.
pos_embed = self.vae_encoder_pos_enc.clone().detach() # (1, S+2, D)
# Prepare key padding mask for the transformer encoder. We have 1 or 2 extra tokens at the start of the
# sequence depending whether we use the input states or not (cls and robot state)
# False means not a padding token.
cls_joint_is_pad = torch.full(
(batch_size, 2 if self.config.robot_state_feature else 1),
False,
device=batch["observation.state"].device,
)
key_padding_mask = torch.cat(
[cls_joint_is_pad, batch["action_is_pad"]], axis=1
) # (bs, seq+1 or 2)
# Forward pass through VAE encoder to get the latent PDF parameters.
cls_token_out = self.vae_encoder(
vae_encoder_input.permute(1, 0, 2),
pos_embed=pos_embed.permute(1, 0, 2),
key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask,
)[0] # select the class token, with shape (B, D)
latent_pdf_params = self.vae_encoder_latent_output_proj(cls_token_out)
mu = latent_pdf_params[:, : self.config.latent_dim]
# This is 2log(sigma). Done this way to match the original implementation.
log_sigma_x2 = latent_pdf_params[:, self.config.latent_dim :]
# Sample the latent with the reparameterization trick.
latent_sample = mu + log_sigma_x2.div(2).exp() * torch.randn_like(mu)
else:
# When not using the VAE encoder, we set the latent to be all zeros.
mu = log_sigma_x2 = None
# TODO(rcadene, alexander-soare): remove call to `.to` to speedup forward ; precompute and use buffer
latent_sample = torch.zeros([batch_size, self.config.latent_dim], dtype=torch.float32).to(
batch["observation.state"].device
)
# Prepare transformer encoder inputs.
encoder_in_tokens = [self.encoder_latent_input_proj(latent_sample)]
encoder_in_pos_embed = list(self.encoder_1d_feature_pos_embed.weight.unsqueeze(1))
# Robot state token.
if self.config.robot_state_feature:
encoder_in_tokens.append(self.encoder_robot_state_input_proj(batch["observation.state"]))
# Environment state token.
if self.config.env_state_feature:
encoder_in_tokens.append(
self.encoder_env_state_input_proj(batch["observation.environment_state"])
)
if self.config.image_features:
# For a list of images, the H and W may vary but H*W is constant.
# NOTE: If modifying this section, verify on MPS devices that
# gradients remain stable (no explosions or NaNs).
for img in batch["observation.images"]:
cam_features = self.backbone(img)["feature_map"]
cam_pos_embed = self.encoder_cam_feat_pos_embed(cam_features).to(dtype=cam_features.dtype)
cam_features = self.encoder_img_feat_input_proj(cam_features)
# Rearrange features to (sequence, batch, dim).
cam_features = einops.rearrange(cam_features, "b c h w -> (h w) b c")
cam_pos_embed = einops.rearrange(cam_pos_embed, "b c h w -> (h w) b c")
# Extend immediately instead of accumulating and concatenating
# Convert to list to extend properly
encoder_in_tokens.extend(list(cam_features))
encoder_in_pos_embed.extend(list(cam_pos_embed))
# Stack all tokens along the sequence dimension.
encoder_in_tokens = torch.stack(encoder_in_tokens, axis=0)
encoder_in_pos_embed = torch.stack(encoder_in_pos_embed, axis=0)
# Forward pass through the transformer modules.
encoder_out = self.encoder(encoder_in_tokens, pos_embed=encoder_in_pos_embed)
# TODO(rcadene, alexander-soare): remove call to `device` ; precompute and use buffer
decoder_in = torch.zeros(
(self.config.chunk_size, batch_size, self.config.dim_model),
dtype=encoder_in_pos_embed.dtype,
device=encoder_in_pos_embed.device,
)
decoder_out = self.decoder(
decoder_in,
encoder_out,
encoder_pos_embed=encoder_in_pos_embed,
decoder_pos_embed=self.decoder_pos_embed.weight.unsqueeze(1),
)
# Move back to (B, S, C).
decoder_out = decoder_out.transpose(0, 1)
actions = self.action_head(decoder_out)
return actions, (mu, log_sigma_x2)
class ACTEncoder(nn.Module):
"""Convenience module for running multiple encoder layers, maybe followed by normalization."""
def __init__(self, config: ACTConfig, is_vae_encoder: bool = False):
super().__init__()
self.is_vae_encoder = is_vae_encoder
num_layers = config.n_vae_encoder_layers if self.is_vae_encoder else config.n_encoder_layers
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([ACTEncoderLayer(config) for _ in range(num_layers)])
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model) if config.pre_norm else nn.Identity()
def forward(
self, x: Tensor, pos_embed: Tensor | None = None, key_padding_mask: Tensor | None = None
) -> Tensor:
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, pos_embed=pos_embed, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
class ACTEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: ACTConfig):
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(config.dim_model, config.n_heads, dropout=config.dropout)
# Feed forward layers.
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(config.dim_model, config.dim_feedforward)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(config.dim_feedforward, config.dim_model)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.activation = get_activation_fn(config.feedforward_activation)
self.pre_norm = config.pre_norm
def forward(self, x, pos_embed: Tensor | None = None, key_padding_mask: Tensor | None = None) -> Tensor:
skip = x
if self.pre_norm:
x = self.norm1(x)
q = k = x if pos_embed is None else x + pos_embed
x = self.self_attn(q, k, value=x, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask)
x = x[0] # note: [0] to select just the output, not the attention weights
x = skip + self.dropout1(x)
if self.pre_norm:
skip = x
x = self.norm2(x)
else:
x = self.norm1(x)
skip = x
x = self.linear2(self.dropout(self.activation(self.linear1(x))))
x = skip + self.dropout2(x)
if not self.pre_norm:
x = self.norm2(x)
return x
class ACTDecoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: ACTConfig):
"""Convenience module for running multiple decoder layers followed by normalization."""
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([ACTDecoderLayer(config) for _ in range(config.n_decoder_layers)])
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model)
def forward(
self,
x: Tensor,
encoder_out: Tensor,
decoder_pos_embed: Tensor | None = None,
encoder_pos_embed: Tensor | None = None,
) -> Tensor:
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(
x, encoder_out, decoder_pos_embed=decoder_pos_embed, encoder_pos_embed=encoder_pos_embed
)
if self.norm is not None:
x = self.norm(x)
return x
class ACTDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: ACTConfig):
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(config.dim_model, config.n_heads, dropout=config.dropout)
self.multihead_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(config.dim_model, config.n_heads, dropout=config.dropout)
# Feed forward layers.
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(config.dim_model, config.dim_feedforward)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(config.dim_feedforward, config.dim_model)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model)
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(config.dim_model)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.activation = get_activation_fn(config.feedforward_activation)
self.pre_norm = config.pre_norm
def maybe_add_pos_embed(self, tensor: Tensor, pos_embed: Tensor | None) -> Tensor:
return tensor if pos_embed is None else tensor + pos_embed
def forward(
self,
x: Tensor,
encoder_out: Tensor,
decoder_pos_embed: Tensor | None = None,
encoder_pos_embed: Tensor | None = None,
) -> Tensor:
"""
Args:
x: (Decoder Sequence, Batch, Channel) tensor of input tokens.
encoder_out: (Encoder Sequence, B, C) output features from the last layer of the encoder we are
cross-attending with.
decoder_pos_embed: (ES, 1, C) positional embedding for keys (from the encoder).
encoder_pos_embed: (DS, 1, C) Positional_embedding for the queries (from the decoder).
Returns:
(DS, B, C) tensor of decoder output features.
"""
skip = x
if self.pre_norm:
x = self.norm1(x)
q = k = self.maybe_add_pos_embed(x, decoder_pos_embed)
x = self.self_attn(q, k, value=x)[0] # select just the output, not the attention weights
x = skip + self.dropout1(x)
if self.pre_norm:
skip = x
x = self.norm2(x)
else:
x = self.norm1(x)
skip = x
x = self.multihead_attn(
query=self.maybe_add_pos_embed(x, decoder_pos_embed),
key=self.maybe_add_pos_embed(encoder_out, encoder_pos_embed),
value=encoder_out,
)[0] # select just the output, not the attention weights
x = skip + self.dropout2(x)
if self.pre_norm:
skip = x
x = self.norm3(x)
else:
x = self.norm2(x)
skip = x
x = self.linear2(self.dropout(self.activation(self.linear1(x))))
x = skip + self.dropout3(x)
if not self.pre_norm:
x = self.norm3(x)
return x
def create_sinusoidal_pos_embedding(num_positions: int, dimension: int) -> Tensor:
"""1D sinusoidal positional embeddings as in Attention is All You Need.
Args:
num_positions: Number of token positions required.
Returns: (num_positions, dimension) position embeddings (the first dimension is the batch dimension).
"""
def get_position_angle_vec(position):
return [position / np.power(10000, 2 * (hid_j // 2) / dimension) for hid_j in range(dimension)]
sinusoid_table = np.array([get_position_angle_vec(pos_i) for pos_i in range(num_positions)])
sinusoid_table[:, 0::2] = np.sin(sinusoid_table[:, 0::2]) # dim 2i
sinusoid_table[:, 1::2] = np.cos(sinusoid_table[:, 1::2]) # dim 2i+1
return torch.from_numpy(sinusoid_table).float()
class ACTSinusoidalPositionEmbedding2d(nn.Module):
"""2D sinusoidal positional embeddings similar to what's presented in Attention Is All You Need.
The variation is that the position indices are normalized in [0, 2π] (not quite: the lower bound is 1/H
for the vertical direction, and 1/W for the horizontal direction.
"""
def __init__(self, dimension: int):
"""
Args:
dimension: The desired dimension of the embeddings.
"""
super().__init__()
self.dimension = dimension
self._two_pi = 2 * math.pi
self._eps = 1e-6
# Inverse "common ratio" for the geometric progression in sinusoid frequencies.
self._temperature = 10000
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Args:
x: A (B, C, H, W) batch of 2D feature map to generate the embeddings for.
Returns:
A (1, C, H, W) batch of corresponding sinusoidal positional embeddings.
"""
not_mask = torch.ones_like(x[0, :1]) # (1, H, W)
# Note: These are like range(1, H+1) and range(1, W+1) respectively, but in most implementations
# they would be range(0, H) and range(0, W). Keeping it at as is to match the original code.
y_range = not_mask.cumsum(1, dtype=torch.float32)
x_range = not_mask.cumsum(2, dtype=torch.float32)
# "Normalize" the position index such that it ranges in [0, 2π].
# Note: Adding epsilon on the denominator should not be needed as all values of y_embed and x_range
# are non-zero by construction. This is an artifact of the original code.
y_range = y_range / (y_range[:, -1:, :] + self._eps) * self._two_pi
x_range = x_range / (x_range[:, :, -1:] + self._eps) * self._two_pi
inverse_frequency = self._temperature ** (
2 * (torch.arange(self.dimension, dtype=torch.float32, device=x.device) // 2) / self.dimension
)
x_range = x_range.unsqueeze(-1) / inverse_frequency # (1, H, W, 1)
y_range = y_range.unsqueeze(-1) / inverse_frequency # (1, H, W, 1)
# Note: this stack then flatten operation results in interleaved sine and cosine terms.
# pos_embed_x and pos_embed_y are (1, H, W, C // 2).
pos_embed_x = torch.stack((x_range[..., 0::2].sin(), x_range[..., 1::2].cos()), dim=-1).flatten(3)
pos_embed_y = torch.stack((y_range[..., 0::2].sin(), y_range[..., 1::2].cos()), dim=-1).flatten(3)
pos_embed = torch.cat((pos_embed_y, pos_embed_x), dim=3).permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # (1, C, H, W)
return pos_embed
def get_activation_fn(activation: str) -> Callable:
"""Return an activation function given a string."""
if activation == "relu":
return F.relu
if activation == "gelu":
return F.gelu
if activation == "glu":
return F.glu
raise RuntimeError(f"activation should be relu/gelu/glu, not {activation}.")
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/policies/act/modeling_act.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/policies/act/modeling_act.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 15801
}
| 212
|
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import abc
import builtins
import logging
import os
from importlib.resources import files
from pathlib import Path
from tempfile import TemporaryDirectory
from typing import TypeVar
import packaging
import safetensors
from huggingface_hub import HfApi, ModelCard, ModelCardData, hf_hub_download
from huggingface_hub.constants import SAFETENSORS_SINGLE_FILE
from huggingface_hub.errors import HfHubHTTPError
from safetensors.torch import load_model as load_model_as_safetensor, save_model as save_model_as_safetensor
from torch import Tensor, nn
from lerobot.configs.policies import PreTrainedConfig
from lerobot.configs.train import TrainPipelineConfig
from lerobot.policies.utils import log_model_loading_keys
from lerobot.utils.hub import HubMixin
T = TypeVar("T", bound="PreTrainedPolicy")
class PreTrainedPolicy(nn.Module, HubMixin, abc.ABC):
"""
Base class for policy models.
"""
config_class: None
name: None
def __init__(self, config: PreTrainedConfig, *inputs, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
if not isinstance(config, PreTrainedConfig):
raise ValueError(
f"Parameter config in `{self.__class__.__name__}(config)` should be an instance of class "
"`PreTrainedConfig`. To create a model from a pretrained model use "
f"`model = {self.__class__.__name__}.from_pretrained(PRETRAINED_MODEL_NAME)`"
)
self.config = config
def __init_subclass__(cls, **kwargs):
super().__init_subclass__(**kwargs)
if not getattr(cls, "config_class", None):
raise TypeError(f"Class {cls.__name__} must define 'config_class'")
if not getattr(cls, "name", None):
raise TypeError(f"Class {cls.__name__} must define 'name'")
def _save_pretrained(self, save_directory: Path) -> None:
self.config._save_pretrained(save_directory)
model_to_save = self.module if hasattr(self, "module") else self
save_model_as_safetensor(model_to_save, str(save_directory / SAFETENSORS_SINGLE_FILE))
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(
cls: builtins.type[T],
pretrained_name_or_path: str | Path,
*,
config: PreTrainedConfig | None = None,
force_download: bool = False,
resume_download: bool | None = None,
proxies: dict | None = None,
token: str | bool | None = None,
cache_dir: str | Path | None = None,
local_files_only: bool = False,
revision: str | None = None,
strict: bool = False,
**kwargs,
) -> T:
"""
The policy is set in evaluation mode by default using `policy.eval()` (dropout modules are
deactivated). To train it, you should first set it back in training mode with `policy.train()`.
"""
if config is None:
config = PreTrainedConfig.from_pretrained(
pretrained_name_or_path=pretrained_name_or_path,
force_download=force_download,
resume_download=resume_download,
proxies=proxies,
token=token,
cache_dir=cache_dir,
local_files_only=local_files_only,
revision=revision,
**kwargs,
)
model_id = str(pretrained_name_or_path)
instance = cls(config, **kwargs)
if os.path.isdir(model_id):
print("Loading weights from local directory")
model_file = os.path.join(model_id, SAFETENSORS_SINGLE_FILE)
policy = cls._load_as_safetensor(instance, model_file, config.device, strict)
else:
try:
model_file = hf_hub_download(
repo_id=model_id,
filename=SAFETENSORS_SINGLE_FILE,
revision=revision,
cache_dir=cache_dir,
force_download=force_download,
proxies=proxies,
resume_download=resume_download,
token=token,
local_files_only=local_files_only,
)
policy = cls._load_as_safetensor(instance, model_file, config.device, strict)
except HfHubHTTPError as e:
raise FileNotFoundError(
f"{SAFETENSORS_SINGLE_FILE} not found on the HuggingFace Hub in {model_id}"
) from e
policy.to(config.device)
policy.eval()
return policy
@classmethod
def _load_as_safetensor(cls, model: T, model_file: str, map_location: str, strict: bool) -> T:
# Create base kwargs
kwargs = {"strict": strict}
# Add device parameter for newer versions that support it
if packaging.version.parse(safetensors.__version__) >= packaging.version.parse("0.4.3"):
kwargs["device"] = map_location
# Load the model with appropriate kwargs
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = load_model_as_safetensor(model, model_file, **kwargs)
log_model_loading_keys(missing_keys, unexpected_keys)
# For older versions, manually move to device if needed
if "device" not in kwargs and map_location != "cpu":
logging.warning(
"Loading model weights on other devices than 'cpu' is not supported natively in your version of safetensors."
" This means that the model is loaded on 'cpu' first and then copied to the device."
" This leads to a slower loading time."
" Please update safetensors to version 0.4.3 or above for improved performance."
)
model.to(map_location)
return model
@abc.abstractmethod
def get_optim_params(self) -> dict:
"""
Returns the policy-specific parameters dict to be passed on to the optimizer.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abc.abstractmethod
def reset(self):
"""To be called whenever the environment is reset.
Does things like clearing caches.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
# TODO(aliberts, rcadene): split into 'forward' and 'compute_loss'?
@abc.abstractmethod
def forward(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> tuple[Tensor, dict | None]:
"""_summary_
Args:
batch (dict[str, Tensor]): _description_
Returns:
tuple[Tensor, dict | None]: The loss and potentially other information. Apart from the loss which
is a Tensor, all other items should be logging-friendly, native Python types.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abc.abstractmethod
def predict_action_chunk(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> Tensor:
"""Returns the action chunk (for action chunking policies) for a given observation, potentially in batch mode.
Child classes using action chunking should use this method within `select_action` to form the action chunk
cached for selection.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abc.abstractmethod
def select_action(self, batch: dict[str, Tensor]) -> Tensor:
"""Return one action to run in the environment (potentially in batch mode).
When the model uses a history of observations, or outputs a sequence of actions, this method deals
with caching.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def push_model_to_hub(
self,
cfg: TrainPipelineConfig,
):
api = HfApi()
repo_id = api.create_repo(
repo_id=self.config.repo_id, private=self.config.private, exist_ok=True
).repo_id
# Push the files to the repo in a single commit
with TemporaryDirectory(ignore_cleanup_errors=True) as tmp:
saved_path = Path(tmp) / repo_id
self.save_pretrained(saved_path) # Calls _save_pretrained and stores model tensors
card = self.generate_model_card(
cfg.dataset.repo_id, self.config.type, self.config.license, self.config.tags
)
card.save(str(saved_path / "README.md"))
cfg.save_pretrained(saved_path) # Calls _save_pretrained and stores train config
commit_info = api.upload_folder(
repo_id=repo_id,
repo_type="model",
folder_path=saved_path,
commit_message="Upload policy weights, train config and readme",
allow_patterns=["*.safetensors", "*.json", "*.yaml", "*.md"],
ignore_patterns=["*.tmp", "*.log"],
)
logging.info(f"Model pushed to {commit_info.repo_url.url}")
def generate_model_card(
self, dataset_repo_id: str, model_type: str, license: str | None, tags: list[str] | None
) -> ModelCard:
base_model = "lerobot/smolvla_base" if model_type == "smolvla" else None # Set a base model
card_data = ModelCardData(
license=license or "apache-2.0",
library_name="lerobot",
pipeline_tag="robotics",
tags=list(set(tags or []).union({"robotics", "lerobot", model_type})),
model_name=model_type,
datasets=dataset_repo_id,
base_model=base_model,
)
template_card = files("lerobot.templates").joinpath("lerobot_modelcard_template.md").read_text()
card = ModelCard.from_template(card_data, template_str=template_card)
card.validate()
return card
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/policies/pretrained.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/policies/pretrained.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 4306
}
| 213
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 Seungjae Lee and Yibin Wang and Haritheja Etukuru
# and H. Jin Kim and Nur Muhammad Mahi Shafiullah and Lerrel Pinto
# and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import math
from collections.abc import Callable
from functools import partial
from math import ceil
from random import randrange
import torch
import torch.distributed as distributed
import torch.nn.functional as F # noqa: N812
from einops import pack, rearrange, reduce, repeat, unpack
from torch import einsum, nn
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast
from torch.optim import Optimizer
from lerobot.policies.vqbet.configuration_vqbet import VQBeTConfig
# ruff: noqa: N806
"""
This file is part of a VQ-BeT that utilizes code from the following repositories:
- Vector Quantize PyTorch code is licensed under the MIT License:
Original source: https://github.com/lucidrains/vector-quantize-pytorch
- nanoGPT part is an adaptation of Andrej Karpathy's nanoGPT implementation in PyTorch.
Original source: https://github.com/karpathy/nanoGPT
We also made some changes to the original code to adapt it to our needs. The changes are described in the code below.
"""
"""
This is a part for nanoGPT that utilizes code from the following repository:
- Andrej Karpathy's nanoGPT implementation in PyTorch.
Original source: https://github.com/karpathy/nanoGPT
- The nanoGPT code is licensed under the MIT License:
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2022 Andrej Karpathy
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
- We've made some changes to the original code to adapt it to our needs.
Changed variable names:
- n_head -> gpt_n_head
- n_embd -> gpt_hidden_dim
- block_size -> gpt_block_size
- n_layer -> gpt_n_layer
class GPT(nn.Module):
- removed unused functions `def generate`, `def estimate_mfu`, and `def from_pretrained`
- changed the `configure_optimizers` to `def configure_parameters` and made it to return only the parameters of the model: we use an external optimizer in our training loop.
- in the function `forward`, we removed target loss calculation parts, since it will be calculated in the training loop (after passing through bin prediction and offset prediction heads).
"""
class CausalSelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
assert config.gpt_hidden_dim % config.gpt_n_head == 0
# key, query, value projections for all heads, but in a batch
self.c_attn = nn.Linear(config.gpt_hidden_dim, 3 * config.gpt_hidden_dim)
# output projection
self.c_proj = nn.Linear(config.gpt_hidden_dim, config.gpt_hidden_dim)
# regularization
self.attn_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.resid_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
# causal mask to ensure that attention is only applied to the left in the input sequence
self.register_buffer(
"bias",
torch.tril(torch.ones(config.gpt_block_size, config.gpt_block_size)).view(
1, 1, config.gpt_block_size, config.gpt_block_size
),
)
self.gpt_n_head = config.gpt_n_head
self.gpt_hidden_dim = config.gpt_hidden_dim
def forward(self, x):
(
B,
T,
C,
) = x.size() # batch size, sequence length, embedding dimensionality (gpt_hidden_dim)
# calculate query, key, values for all heads in batch and move head forward to be the batch dim
q, k, v = self.c_attn(x).split(self.gpt_hidden_dim, dim=2)
k = k.view(B, T, self.gpt_n_head, C // self.gpt_n_head).transpose(1, 2) # (B, nh, T, hs)
q = q.view(B, T, self.gpt_n_head, C // self.gpt_n_head).transpose(1, 2) # (B, nh, T, hs)
v = v.view(B, T, self.gpt_n_head, C // self.gpt_n_head).transpose(1, 2) # (B, nh, T, hs)
# causal self-attention; Self-attend: (B, nh, T, hs) x (B, nh, hs, T) -> (B, nh, T, T)
att = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * (1.0 / math.sqrt(k.size(-1)))
att = att.masked_fill(self.bias[:, :, :T, :T] == 0, float("-inf"))
att = F.softmax(att, dim=-1)
att = self.attn_dropout(att)
y = att @ v # (B, nh, T, T) x (B, nh, T, hs) -> (B, nh, T, hs)
y = y.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(B, T, C) # re-assemble all head outputs side by side
# output projection
y = self.resid_dropout(self.c_proj(y))
return y
class Block(nn.Module):
# causual self-attention block for GPT
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.ln_1 = nn.LayerNorm(config.gpt_hidden_dim)
self.attn = CausalSelfAttention(config)
self.ln_2 = nn.LayerNorm(config.gpt_hidden_dim)
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(config.gpt_hidden_dim, 4 * config.gpt_hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(4 * config.gpt_hidden_dim, config.gpt_hidden_dim),
nn.Dropout(config.dropout),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.attn(self.ln_1(x))
x = x + self.mlp(self.ln_2(x))
return x
class GPT(nn.Module):
"""
Original comments:
Full definition of a GPT Language Model, all of it in this single file.
References:
1) the official GPT-2 TensorFlow implementation released by OpenAI:
https://github.com/openai/gpt-2/blob/master/src/model.py
2) huggingface/transformers PyTorch implementation:
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/gpt2/modeling_gpt2.py
"""
def __init__(self, config: VQBeTConfig):
"""
GPT model gets hyperparameters from a config object. Please refer configuration_vqbet.py for more details.
"""
super().__init__()
assert config.gpt_output_dim is not None
assert config.gpt_block_size is not None
self.config = config
self.transformer = nn.ModuleDict(
{
"wte": nn.Linear(config.gpt_input_dim, config.gpt_hidden_dim),
"wpe": nn.Embedding(config.gpt_block_size, config.gpt_hidden_dim),
"drop": nn.Dropout(config.dropout),
"h": nn.ModuleList([Block(config) for _ in range(config.gpt_n_layer)]),
"ln_f": nn.LayerNorm(config.gpt_hidden_dim),
}
)
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.gpt_hidden_dim, config.gpt_output_dim, bias=False)
# init all weights, and apply a special scaled init to the residual projections, per GPT-2 paper
self.apply(self._init_weights)
for pn, p in self.named_parameters():
if pn.endswith("c_proj.weight"):
torch.nn.init.normal_(p, mean=0.0, std=0.02 / math.sqrt(2 * config.gpt_n_layer))
# report number of parameters
n_params = sum(p.numel() for p in self.parameters())
print(f"number of parameters: {n_params / 1e6:.2f}M")
def forward(self, input, targets=None):
device = input.device
b, t, d = input.size()
assert t <= self.config.gpt_block_size, (
f"Cannot forward sequence of length {t}, block size is only {self.config.gpt_block_size}"
)
# positional encodings that are added to the input embeddings
pos = torch.arange(0, t, dtype=torch.long, device=device).unsqueeze(0) # shape (1, t)
# forward the GPT model itself
tok_emb = self.transformer.wte(input) # token embeddings of shape (b, t, gpt_hidden_dim)
pos_emb = self.transformer.wpe(pos) # position embeddings of shape (1, t, gpt_hidden_dim)
x = self.transformer.drop(tok_emb + pos_emb)
for block in self.transformer.h:
x = block(x)
x = self.transformer.ln_f(x)
logits = self.lm_head(x)
return logits
def _init_weights(self, module):
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
torch.nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.02)
if module.bias is not None:
torch.nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
torch.nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.02)
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
torch.nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
torch.nn.init.ones_(module.weight)
def crop_block_size(self, gpt_block_size):
# model surgery to decrease the block size if necessary
# e.g. we may load the GPT2 pretrained model checkpoint (block size 1024)
# but want to use a smaller block size for some smaller, simpler model
assert gpt_block_size <= self.config.gpt_block_size
self.config.gpt_block_size = gpt_block_size
self.transformer.wpe.weight = nn.Parameter(self.transformer.wpe.weight[:gpt_block_size])
for block in self.transformer.h:
block.attn.bias = block.attn.bias[:, :, :gpt_block_size, :gpt_block_size]
def configure_parameters(self):
"""
This long function is unfortunately doing something very simple and is being very defensive:
We are separating out all parameters of the model into two buckets: those that will experience
weight decay for regularization and those that won't (biases, and layernorm/embedding weights).
"""
# separate out all parameters to those that will and won't experience regularizing weight decay
decay = set()
no_decay = set()
whitelist_weight_modules = (torch.nn.Linear,)
blacklist_weight_modules = (torch.nn.LayerNorm, torch.nn.Embedding)
for mn, m in self.named_modules():
for pn, _p in m.named_parameters():
fpn = f"{mn}.{pn}" if mn else pn # full param name
if pn.endswith("bias"):
# all biases will not be decayed
no_decay.add(fpn)
elif pn.endswith("weight") and isinstance(m, whitelist_weight_modules):
# weights of whitelist modules will be weight decayed
decay.add(fpn)
elif pn.endswith("weight") and isinstance(m, blacklist_weight_modules):
# weights of blacklist modules will NOT be weight decayed
no_decay.add(fpn)
# validate that we considered every parameter
param_dict = dict(self.named_parameters())
inter_params = decay & no_decay
union_params = decay | no_decay
assert len(inter_params) == 0, "parameters {} made it into both decay/no_decay sets!".format(
str(inter_params)
)
assert len(param_dict.keys() - union_params) == 0, (
"parameters {} were not separated into either decay/no_decay set!".format(
str(param_dict.keys() - union_params),
)
)
decay = [param_dict[pn] for pn in sorted(decay)]
no_decay = [param_dict[pn] for pn in sorted(no_decay)]
# return the parameters that require weight decay, and the parameters that don't separately.
return decay, no_decay
"""
This file is a part for Residual Vector Quantization that utilizes code from the following repository:
- Phil Wang's vector-quantize-pytorch implementation in PyTorch.
Original source: https://github.com/lucidrains/vector-quantize-pytorch
- The vector-quantize-pytorch code is licensed under the MIT License:
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2020 Phil Wang
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
- We've made some changes to the original code to adapt it to our needs.
class ResidualVQ(nn.Module):
- added `self.register_buffer('freeze_codebook', torch.tensor(False))` to the __init__ method:
This enables the user to save an indicator whether the codebook is frozen or not.
- changed the name of function `get_codes_from_indices` → `get_codebook_vector_from_indices`:
This is to make the function name more descriptive.
class VectorQuantize(nn.Module):
- removed the `use_cosine_sim` and `layernorm_after_project_in` parameters from the __init__ method:
These parameters are not used in the code.
- changed the name of function `get_codes_from_indices` → `get_codebook_vector_from_indices`:
This is to make the function name more descriptive.
"""
class ResidualVQ(nn.Module):
"""
Residual VQ is composed of multiple VectorQuantize layers.
Follows Algorithm 1. in https://huggingface.co/papers/2107.03312
"Residual Vector Quantizer (a.k.a. multi-stage vector quantizer [36]) cascades Nq layers of VQ as follows. The unquantized input vector is
passed through a first VQ and quantization residuals are computed. The residuals are then iteratively quantized by a sequence of additional
Nq -1 vector quantizers, as described in Algorithm 1."
self.project_in: function for projecting input to codebook dimension
self.project_out: function for projecting codebook dimension to output dimension
self.layers: nn.ModuleList of VectorQuantize layers that contains Nq layers of VQ as described in the paper.
self.freeze_codebook: buffer to save an indicator whether the codebook is frozen or not. VQ-BeT will check this to determine whether to update the codebook or not.
"""
def __init__(
self,
*,
dim,
num_quantizers,
codebook_dim=None,
shared_codebook=False,
heads=1,
quantize_dropout=False,
quantize_dropout_cutoff_index=0,
quantize_dropout_multiple_of=1,
accept_image_fmap=False,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__()
assert heads == 1, "residual vq is not compatible with multi-headed codes"
codebook_dim = codebook_dim if (codebook_dim is not None) else dim
codebook_input_dim = codebook_dim * heads
requires_projection = codebook_input_dim != dim
self.project_in = nn.Linear(dim, codebook_input_dim) if requires_projection else nn.Identity()
self.project_out = nn.Linear(codebook_input_dim, dim) if requires_projection else nn.Identity()
self.num_quantizers = num_quantizers
self.accept_image_fmap = accept_image_fmap
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[
VectorQuantize(
dim=codebook_dim, codebook_dim=codebook_dim, accept_image_fmap=accept_image_fmap, **kwargs
)
for _ in range(num_quantizers)
]
)
self.quantize_dropout = quantize_dropout and num_quantizers > 1
assert quantize_dropout_cutoff_index >= 0
self.register_buffer("freeze_codebook", torch.tensor(False))
self.quantize_dropout_cutoff_index = quantize_dropout_cutoff_index
self.quantize_dropout_multiple_of = quantize_dropout_multiple_of # encodec paper proposes structured dropout, believe this was set to 4
if not shared_codebook:
return
first_vq, *rest_vq = self.layers
codebook = first_vq._codebook
for vq in rest_vq:
vq._codebook = codebook
@property
def codebooks(self):
codebooks = [layer._codebook.embed for layer in self.layers]
codebooks = torch.stack(codebooks, dim=0)
codebooks = rearrange(codebooks, "q 1 c d -> q c d")
return codebooks
def get_codebook_vector_from_indices(self, indices):
# this function will return the codes from all codebooks across layers corresponding to the indices
batch, quantize_dim = indices.shape[0], indices.shape[-1]
# may also receive indices in the shape of 'b h w q' (accept_image_fmap)
indices, ps = pack([indices], "b * q")
# because of quantize dropout, one can pass in indices that are coarse
# and the network should be able to reconstruct
if quantize_dim < self.num_quantizers:
assert self.quantize_dropout > 0.0, (
"quantize dropout must be greater than 0 if you wish to reconstruct from a signal with less fine quantizations"
)
indices = F.pad(indices, (0, self.num_quantizers - quantize_dim), value=-1)
# get ready for gathering
codebooks = repeat(self.codebooks, "q c d -> q b c d", b=batch)
gather_indices = repeat(indices, "b n q -> q b n d", d=codebooks.shape[-1])
# take care of quantizer dropout
mask = gather_indices == -1.0
gather_indices = gather_indices.masked_fill(
mask, 0
) # have it fetch a dummy code to be masked out later
all_codes = codebooks.gather(2, gather_indices) # gather all codes
# mask out any codes that were dropout-ed
all_codes = all_codes.masked_fill(mask, 0.0)
# if (accept_image_fmap = True) then return shape (quantize, batch, height, width, dimension)
(all_codes,) = unpack(all_codes, ps, "q b * d")
return all_codes
def forward(self, x, indices=None, return_all_codes=False, sample_codebook_temp=None):
"""
For given input tensor x, this function will return the quantized output, the indices of the quantized output, and the loss.
First, the input tensor x is projected to the codebook dimension. Then, the input tensor x is passed through Nq layers of VectorQuantize.
The residual value of each layer is fed to the next layer.
"""
num_quant, quant_dropout_multiple_of, return_loss, device = (
self.num_quantizers,
self.quantize_dropout_multiple_of,
(indices is not None),
x.device,
)
x = self.project_in(x)
assert not (self.accept_image_fmap and (indices is not None))
quantized_out = 0.0
residual = x
all_losses = []
all_indices = []
if return_loss:
assert not torch.any(indices == -1), (
"some of the residual vq indices were dropped out. please use indices derived when the module is in eval mode to derive cross entropy loss"
)
ce_losses = []
should_quantize_dropout = self.training and self.quantize_dropout and not return_loss
# sample a layer index at which to dropout further residual quantization
# also prepare null indices and loss
if should_quantize_dropout:
rand_quantize_dropout_index = randrange(self.quantize_dropout_cutoff_index, num_quant)
if quant_dropout_multiple_of != 1:
rand_quantize_dropout_index = (
ceil((rand_quantize_dropout_index + 1) / quant_dropout_multiple_of)
* quant_dropout_multiple_of
- 1
)
null_indices_shape = (x.shape[0], *x.shape[-2:]) if self.accept_image_fmap else tuple(x.shape[:2])
null_indices = torch.full(null_indices_shape, -1.0, device=device, dtype=torch.long)
null_loss = torch.full((1,), 0.0, device=device, dtype=x.dtype)
# go through the layers
for quantizer_index, layer in enumerate(self.layers):
if should_quantize_dropout and quantizer_index > rand_quantize_dropout_index:
all_indices.append(null_indices)
all_losses.append(null_loss)
continue
layer_indices = None
if return_loss:
layer_indices = indices[..., quantizer_index]
quantized, *rest = layer(
residual,
indices=layer_indices,
sample_codebook_temp=sample_codebook_temp,
freeze_codebook=self.freeze_codebook,
)
residual = residual - quantized.detach()
quantized_out = quantized_out + quantized
if return_loss:
ce_loss = rest[0]
ce_losses.append(ce_loss)
continue
embed_indices, loss = rest
all_indices.append(embed_indices)
all_losses.append(loss)
# project out, if needed
quantized_out = self.project_out(quantized_out)
# whether to early return the cross entropy loss
if return_loss:
return quantized_out, sum(ce_losses)
# stack all losses and indices
all_losses, all_indices = map(partial(torch.stack, dim=-1), (all_losses, all_indices))
ret = (quantized_out, all_indices, all_losses)
if return_all_codes:
# whether to return all codes from all codebooks across layers
all_codes = self.get_codebook_vector_from_indices(all_indices)
# will return all codes in shape (quantizer, batch, sequence length, codebook dimension)
ret = (*ret, all_codes)
return ret
class VectorQuantize(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
dim,
codebook_size,
codebook_dim=None,
heads=1,
separate_codebook_per_head=False,
decay=0.8,
eps=1e-5,
kmeans_init=False,
kmeans_iters=10,
sync_kmeans=True,
threshold_ema_dead_code=0,
channel_last=True,
accept_image_fmap=False,
commitment_weight=1.0,
commitment_use_cross_entropy_loss=False,
orthogonal_reg_weight=0.0,
orthogonal_reg_active_codes_only=False,
orthogonal_reg_max_codes=None,
stochastic_sample_codes=False,
sample_codebook_temp=1.0,
straight_through=False,
reinmax=False, # using reinmax for improved straight-through, assuming straight through helps at all
sync_codebook=None,
sync_affine_param=False,
ema_update=True,
learnable_codebook=False,
in_place_codebook_optimizer: Callable[
..., Optimizer
] = None, # Optimizer used to update the codebook embedding if using learnable_codebook
affine_param=False,
affine_param_batch_decay=0.99,
affine_param_codebook_decay=0.9,
sync_update_v=0.0, # the v that controls optimistic vs pessimistic update for synchronous update rule (21) https://minyoungg.github.io/vqtorch/assets/draft_050523.pdf
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.heads = heads
self.separate_codebook_per_head = separate_codebook_per_head
codebook_dim = codebook_dim if (codebook_dim is not None) else dim
codebook_input_dim = codebook_dim * heads
requires_projection = codebook_input_dim != dim
self.project_in = nn.Linear(dim, codebook_input_dim) if requires_projection else nn.Identity()
self.project_out = nn.Linear(codebook_input_dim, dim) if requires_projection else nn.Identity()
self.eps = eps
self.commitment_weight = commitment_weight
self.commitment_use_cross_entropy_loss = commitment_use_cross_entropy_loss # whether to use cross entropy loss to codebook as commitment loss
self.learnable_codebook = learnable_codebook
has_codebook_orthogonal_loss = orthogonal_reg_weight > 0
self.has_codebook_orthogonal_loss = has_codebook_orthogonal_loss
self.orthogonal_reg_weight = orthogonal_reg_weight
self.orthogonal_reg_active_codes_only = orthogonal_reg_active_codes_only
self.orthogonal_reg_max_codes = orthogonal_reg_max_codes
assert not (ema_update and learnable_codebook), "learnable codebook not compatible with EMA update"
assert 0 <= sync_update_v <= 1.0
assert not (sync_update_v > 0.0 and not learnable_codebook), "learnable codebook must be turned on"
self.sync_update_v = sync_update_v
gumbel_sample_fn = partial(
gumbel_sample,
stochastic=stochastic_sample_codes,
reinmax=reinmax,
straight_through=straight_through,
)
if sync_codebook is None:
sync_codebook = distributed.is_initialized() and distributed.get_world_size() > 1
codebook_kwargs = {
"dim": codebook_dim,
"num_codebooks": heads if separate_codebook_per_head else 1,
"codebook_size": codebook_size,
"kmeans_init": kmeans_init,
"kmeans_iters": kmeans_iters,
"sync_kmeans": sync_kmeans,
"decay": decay,
"eps": eps,
"threshold_ema_dead_code": threshold_ema_dead_code,
"use_ddp": sync_codebook,
"learnable_codebook": has_codebook_orthogonal_loss or learnable_codebook,
"sample_codebook_temp": sample_codebook_temp,
"gumbel_sample": gumbel_sample_fn,
"ema_update": ema_update,
}
if affine_param:
codebook_kwargs = dict(
**codebook_kwargs,
affine_param=True,
sync_affine_param=sync_affine_param,
affine_param_batch_decay=affine_param_batch_decay,
affine_param_codebook_decay=affine_param_codebook_decay,
)
self._codebook = EuclideanCodebook(**codebook_kwargs)
self.in_place_codebook_optimizer = (
in_place_codebook_optimizer(self._codebook.parameters())
if (in_place_codebook_optimizer is not None)
else None
)
self.codebook_size = codebook_size
self.accept_image_fmap = accept_image_fmap
self.channel_last = channel_last
@property
def codebook(self):
codebook = self._codebook.embed
if self.separate_codebook_per_head:
return codebook
return rearrange(codebook, "1 ... -> ...")
@codebook.setter
def codebook(self, codes):
if not self.separate_codebook_per_head:
codes = rearrange(codes, "... -> 1 ...")
self._codebook.embed.copy_(codes)
def get_codebook_vector_from_indices(self, indices):
codebook = self.codebook
is_multiheaded = codebook.ndim > 2
if not is_multiheaded:
codes = codebook[indices]
return rearrange(codes, "... h d -> ... (h d)")
indices, ps = pack_one(indices, "b * h")
indices = rearrange(indices, "b n h -> b h n")
indices = repeat(indices, "b h n -> b h n d", d=codebook.shape[-1])
codebook = repeat(codebook, "h n d -> b h n d", b=indices.shape[0])
codes = codebook.gather(2, indices)
codes = rearrange(codes, "b h n d -> b n (h d)")
codes = unpack_one(codes, ps, "b * d")
return codes
def forward(
self,
x,
indices=None,
mask=None,
sample_codebook_temp=None,
freeze_codebook=False,
):
orig_input = x
only_one = x.ndim == 2
if only_one:
assert mask is None
x = rearrange(x, "b d -> b 1 d")
shape, device, heads, is_multiheaded, _codebook_size, return_loss = (
x.shape,
x.device,
self.heads,
self.heads > 1,
self.codebook_size,
(indices is not None),
)
need_transpose = not self.channel_last and not self.accept_image_fmap
should_inplace_optimize = self.in_place_codebook_optimizer is not None
# rearrange inputs
if self.accept_image_fmap:
height, width = x.shape[-2:]
x = rearrange(x, "b c h w -> b (h w) c")
if need_transpose:
x = rearrange(x, "b d n -> b n d")
# project input
x = self.project_in(x)
# handle multi-headed separate codebooks
if is_multiheaded:
ein_rhs_eq = "h b n d" if self.separate_codebook_per_head else "1 (b h) n d"
x = rearrange(x, f"b n (h d) -> {ein_rhs_eq}", h=heads)
# l2norm for cosine sim, otherwise identity
x = self._codebook.transform_input(x)
# codebook forward kwargs
codebook_forward_kwargs = {
"sample_codebook_temp": sample_codebook_temp,
"mask": mask,
"freeze_codebook": freeze_codebook,
}
# quantize
quantize, embed_ind, distances = self._codebook(x, **codebook_forward_kwargs)
# one step in-place update
if should_inplace_optimize and self.training and not freeze_codebook:
if mask is not None:
loss = F.mse_loss(quantize, x.detach(), reduction="none")
loss_mask = mask
if is_multiheaded:
loss_mask = repeat(
mask,
"b n -> c (b h) n",
c=loss.shape[0],
h=loss.shape[1] // mask.shape[0],
)
loss = loss[loss_mask].mean()
else:
loss = F.mse_loss(quantize, x.detach())
loss.backward()
self.in_place_codebook_optimizer.step()
self.in_place_codebook_optimizer.zero_grad()
# quantize again
quantize, embed_ind, distances = self._codebook(x, **codebook_forward_kwargs)
if self.training:
# determine code to use for commitment loss
maybe_detach = torch.detach if not self.learnable_codebook or freeze_codebook else identity
commit_quantize = maybe_detach(quantize)
# straight through
quantize = x + (quantize - x).detach()
if self.sync_update_v > 0.0:
# (21) in https://minyoungg.github.io/vqtorch/assets/draft_050523.pdf
quantize = quantize + self.sync_update_v * (quantize - quantize.detach())
# function for calculating cross entropy loss to distance matrix
# used for (1) naturalspeech2 training residual vq latents to be close to the correct codes and (2) cross-entropy based commitment loss
def calculate_ce_loss(codes):
if not is_multiheaded:
dist_einops_eq = "1 b n l -> b l n"
elif self.separate_codebook_per_head:
dist_einops_eq = "c b n l -> b l n c"
else:
dist_einops_eq = "1 (b h) n l -> b l n h"
ce_loss = F.cross_entropy(
rearrange(distances, dist_einops_eq, b=shape[0]), codes, ignore_index=-1
)
return ce_loss
# if returning cross entropy loss on codes that were passed in
if return_loss:
return quantize, calculate_ce_loss(indices)
# transform embedding indices
if is_multiheaded:
if self.separate_codebook_per_head:
embed_ind = rearrange(embed_ind, "h b n -> b n h", h=heads)
else:
embed_ind = rearrange(embed_ind, "1 (b h) n -> b n h", h=heads)
if self.accept_image_fmap:
embed_ind = rearrange(embed_ind, "b (h w) ... -> b h w ...", h=height, w=width)
if only_one:
embed_ind = rearrange(embed_ind, "b 1 -> b")
# aggregate loss
loss = torch.tensor([0.0], device=device, requires_grad=self.training)
if self.training:
if self.commitment_weight > 0:
if self.commitment_use_cross_entropy_loss:
if mask is not None:
ce_loss_mask = mask
if is_multiheaded:
ce_loss_mask = repeat(ce_loss_mask, "b n -> b n h", h=heads)
embed_ind.masked_fill_(~ce_loss_mask, -1)
commit_loss = calculate_ce_loss(embed_ind)
else:
if mask is not None:
# with variable lengthed sequences
commit_loss = F.mse_loss(commit_quantize, x, reduction="none")
loss_mask = mask
if is_multiheaded:
loss_mask = repeat(
loss_mask,
"b n -> c (b h) n",
c=commit_loss.shape[0],
h=commit_loss.shape[1] // mask.shape[0],
)
commit_loss = commit_loss[loss_mask].mean()
else:
commit_loss = F.mse_loss(commit_quantize, x)
loss = loss + commit_loss * self.commitment_weight
if self.has_codebook_orthogonal_loss:
codebook = self._codebook.embed
# only calculate orthogonal loss for the activated codes for this batch
if self.orthogonal_reg_active_codes_only:
assert not (is_multiheaded and self.separate_codebook_per_head), (
"orthogonal regularization for only active codes not compatible with multi-headed with separate codebooks yet"
)
unique_code_ids = torch.unique(embed_ind)
codebook = codebook[:, unique_code_ids]
num_codes = codebook.shape[-2]
if (self.orthogonal_reg_max_codes is not None) and num_codes > self.orthogonal_reg_max_codes:
rand_ids = torch.randperm(num_codes, device=device)[: self.orthogonal_reg_max_codes]
codebook = codebook[:, rand_ids]
orthogonal_reg_loss = orthogonal_loss_fn(codebook)
loss = loss + orthogonal_reg_loss * self.orthogonal_reg_weight
# handle multi-headed quantized embeddings
if is_multiheaded:
if self.separate_codebook_per_head:
quantize = rearrange(quantize, "h b n d -> b n (h d)", h=heads)
else:
quantize = rearrange(quantize, "1 (b h) n d -> b n (h d)", h=heads)
# project out
quantize = self.project_out(quantize)
# rearrange quantized embeddings
if need_transpose:
quantize = rearrange(quantize, "b n d -> b d n")
if self.accept_image_fmap:
quantize = rearrange(quantize, "b (h w) c -> b c h w", h=height, w=width)
if only_one:
quantize = rearrange(quantize, "b 1 d -> b d")
# if masking, only return quantized for where mask has True
if mask is not None:
quantize = torch.where(rearrange(mask, "... -> ... 1"), quantize, orig_input)
return quantize, embed_ind, loss
def noop(*args, **kwargs):
pass
def identity(t):
return t
def cdist(x, y):
x2 = reduce(x**2, "b n d -> b n", "sum")
y2 = reduce(y**2, "b n d -> b n", "sum")
xy = einsum("b i d, b j d -> b i j", x, y) * -2
return (rearrange(x2, "b i -> b i 1") + rearrange(y2, "b j -> b 1 j") + xy).sqrt()
def log(t, eps=1e-20):
return torch.log(t.clamp(min=eps))
def ema_inplace(old, new, decay):
is_mps = str(old.device).startswith("mps:")
if not is_mps:
old.lerp_(new, 1 - decay)
else:
old.mul_(decay).add_(new * (1 - decay))
def pack_one(t, pattern):
return pack([t], pattern)
def unpack_one(t, ps, pattern):
return unpack(t, ps, pattern)[0]
def uniform_init(*shape):
t = torch.empty(shape)
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(t)
return t
def gumbel_noise(t):
noise = torch.zeros_like(t).uniform_(0, 1)
return -log(-log(noise))
def gumbel_sample(
logits,
temperature=1.0,
stochastic=False,
straight_through=False,
reinmax=False,
dim=-1,
training=True,
):
dtype, size = logits.dtype, logits.shape[dim]
if training and stochastic and temperature > 0:
sampling_logits = (logits / temperature) + gumbel_noise(logits)
else:
sampling_logits = logits
ind = sampling_logits.argmax(dim=dim)
one_hot = F.one_hot(ind, size).type(dtype)
assert not (reinmax and not straight_through), (
"reinmax can only be turned on if using straight through gumbel softmax"
)
if not straight_through or temperature <= 0.0 or not training:
return ind, one_hot
# use reinmax for better second-order accuracy - https://huggingface.co/papers/2304.08612
# algorithm 2
if reinmax:
π0 = logits.softmax(dim=dim)
π1 = (one_hot + (logits / temperature).softmax(dim=dim)) / 2
π1 = ((log(π1) - logits).detach() + logits).softmax(dim=1)
π2 = 2 * π1 - 0.5 * π0
one_hot = π2 - π2.detach() + one_hot
else:
π1 = (logits / temperature).softmax(dim=dim)
one_hot = one_hot + π1 - π1.detach()
return ind, one_hot
def laplace_smoothing(x, n_categories, eps=1e-5, dim=-1):
denom = x.sum(dim=dim, keepdim=True)
return (x + eps) / (denom + n_categories * eps)
def sample_vectors(samples, num):
num_samples, device = samples.shape[0], samples.device
if num_samples >= num:
indices = torch.randperm(num_samples, device=device)[:num]
else:
indices = torch.randint(0, num_samples, (num,), device=device)
return samples[indices]
def batched_sample_vectors(samples, num):
return torch.stack([sample_vectors(sample, num) for sample in samples.unbind(dim=0)], dim=0)
def pad_shape(shape, size, dim=0):
return [size if i == dim else s for i, s in enumerate(shape)]
def sample_multinomial(total_count, probs):
device = probs.device
probs = probs.cpu()
total_count = probs.new_full((), total_count)
remainder = probs.new_ones(())
sample = torch.empty_like(probs, dtype=torch.long)
for i, p in enumerate(probs):
s = torch.binomial(total_count, p / remainder)
sample[i] = s
total_count -= s
remainder -= p
return sample.to(device)
def all_gather_sizes(x, dim):
size = torch.tensor(x.shape[dim], dtype=torch.long, device=x.device)
all_sizes = [torch.empty_like(size) for _ in range(distributed.get_world_size())]
distributed.all_gather(all_sizes, size)
return torch.stack(all_sizes)
def all_gather_variably_sized(x, sizes, dim=0):
rank = distributed.get_rank()
all_x = []
for i, size in enumerate(sizes):
t = x if i == rank else x.new_empty(pad_shape(x.shape, size, dim))
distributed.broadcast(t, src=i, async_op=True)
all_x.append(t)
distributed.barrier()
return all_x
def sample_vectors_distributed(local_samples, num):
local_samples = rearrange(local_samples, "1 ... -> ...")
rank = distributed.get_rank()
all_num_samples = all_gather_sizes(local_samples, dim=0)
if rank == 0:
samples_per_rank = sample_multinomial(num, all_num_samples / all_num_samples.sum())
else:
samples_per_rank = torch.empty_like(all_num_samples)
distributed.broadcast(samples_per_rank, src=0)
samples_per_rank = samples_per_rank.tolist()
local_samples = sample_vectors(local_samples, samples_per_rank[rank])
all_samples = all_gather_variably_sized(local_samples, samples_per_rank, dim=0)
out = torch.cat(all_samples, dim=0)
return rearrange(out, "... -> 1 ...")
def batched_bincount(x, *, minlength):
batch, dtype, device = x.shape[0], x.dtype, x.device
target = torch.zeros(batch, minlength, dtype=dtype, device=device)
values = torch.ones_like(x)
target.scatter_add_(-1, x, values)
return target
def kmeans(
samples,
num_clusters,
num_iters=10,
sample_fn=batched_sample_vectors,
all_reduce_fn=noop,
):
num_codebooks, dim, dtype, _device = (
samples.shape[0],
samples.shape[-1],
samples.dtype,
samples.device,
)
means = sample_fn(samples, num_clusters)
for _ in range(num_iters):
dists = -torch.cdist(samples, means, p=2)
buckets = torch.argmax(dists, dim=-1)
bins = batched_bincount(buckets, minlength=num_clusters)
all_reduce_fn(bins)
zero_mask = bins == 0
bins_min_clamped = bins.masked_fill(zero_mask, 1)
new_means = buckets.new_zeros(num_codebooks, num_clusters, dim, dtype=dtype)
new_means.scatter_add_(1, repeat(buckets, "h n -> h n d", d=dim), samples)
new_means = new_means / rearrange(bins_min_clamped, "... -> ... 1")
all_reduce_fn(new_means)
means = torch.where(rearrange(zero_mask, "... -> ... 1"), means, new_means)
return means, bins
def batched_embedding(indices, embeds):
batch, dim = indices.shape[1], embeds.shape[-1]
indices = repeat(indices, "h b n -> h b n d", d=dim)
embeds = repeat(embeds, "h c d -> h b c d", b=batch)
return embeds.gather(2, indices)
def orthogonal_loss_fn(t):
# eq (2) from https://huggingface.co/papers/2112.00384
h, n = t.shape[:2]
normed_codes = F.normalize(t, p=2, dim=-1)
cosine_sim = einsum("h i d, h j d -> h i j", normed_codes, normed_codes)
return (cosine_sim**2).sum() / (h * n**2) - (1 / n)
class EuclideanCodebook(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
dim,
codebook_size,
num_codebooks=1,
kmeans_init=False,
kmeans_iters=10,
sync_kmeans=True,
decay=0.8,
eps=1e-5,
threshold_ema_dead_code=2,
reset_cluster_size=None,
use_ddp=False,
learnable_codebook=False,
gumbel_sample=gumbel_sample,
sample_codebook_temp=1.0,
ema_update=True,
affine_param=False,
sync_affine_param=False,
affine_param_batch_decay=0.99,
affine_param_codebook_decay=0.9,
):
super().__init__()
self.transform_input = identity
self.decay = decay
self.ema_update = ema_update
init_fn = uniform_init if not kmeans_init else torch.zeros
embed = init_fn(num_codebooks, codebook_size, dim)
self.codebook_size = codebook_size
self.num_codebooks = num_codebooks
self.kmeans_iters = kmeans_iters
self.eps = eps
self.threshold_ema_dead_code = threshold_ema_dead_code
self.reset_cluster_size = (
reset_cluster_size if (reset_cluster_size is not None) else threshold_ema_dead_code
)
assert callable(gumbel_sample)
self.gumbel_sample = gumbel_sample
self.sample_codebook_temp = sample_codebook_temp
assert not (use_ddp and num_codebooks > 1 and kmeans_init), (
"kmeans init is not compatible with multiple codebooks in distributed environment for now"
)
self.sample_fn = sample_vectors_distributed if use_ddp and sync_kmeans else batched_sample_vectors
self.kmeans_all_reduce_fn = distributed.all_reduce if use_ddp and sync_kmeans else noop
self.all_reduce_fn = distributed.all_reduce if use_ddp else noop
self.register_buffer("initted", torch.Tensor([not kmeans_init]))
self.register_buffer("cluster_size", torch.zeros(num_codebooks, codebook_size))
self.register_buffer("embed_avg", embed.clone())
self.learnable_codebook = learnable_codebook
if learnable_codebook:
self.embed = nn.Parameter(embed)
else:
self.register_buffer("embed", embed)
# affine related params
self.affine_param = affine_param
self.sync_affine_param = sync_affine_param
if not affine_param:
return
self.affine_param_batch_decay = affine_param_batch_decay
self.affine_param_codebook_decay = affine_param_codebook_decay
self.register_buffer("batch_mean", None)
self.register_buffer("batch_variance", None)
self.register_buffer("codebook_mean_needs_init", torch.Tensor([True]))
self.register_buffer("codebook_mean", torch.empty(num_codebooks, 1, dim))
self.register_buffer("codebook_variance_needs_init", torch.Tensor([True]))
self.register_buffer("codebook_variance", torch.empty(num_codebooks, 1, dim))
@torch.jit.ignore
def init_embed_(self, data, mask=None):
if self.initted:
return
if mask is not None:
c = data.shape[0]
data = rearrange(data[mask], "(c n) d -> c n d", c=c)
embed, cluster_size = kmeans(
data,
self.codebook_size,
self.kmeans_iters,
sample_fn=self.sample_fn,
all_reduce_fn=self.kmeans_all_reduce_fn,
)
embed_sum = embed * rearrange(cluster_size, "... -> ... 1")
self.embed.data.copy_(embed)
self.embed_avg.data.copy_(embed_sum)
self.cluster_size.data.copy_(cluster_size)
self.initted.data.copy_(torch.Tensor([True]))
@torch.jit.ignore
def update_with_decay(self, buffer_name, new_value, decay):
old_value = getattr(self, buffer_name)
needs_init = getattr(self, buffer_name + "_needs_init", False)
if needs_init:
self.register_buffer(buffer_name + "_needs_init", torch.Tensor([False]))
if not (old_value is not None) or needs_init:
self.register_buffer(buffer_name, new_value.detach())
return
value = old_value * decay + new_value.detach() * (1 - decay)
self.register_buffer(buffer_name, value)
@torch.jit.ignore
def update_affine(self, data, embed, mask=None):
assert self.affine_param
var_fn = partial(torch.var, unbiased=False)
# calculate codebook mean and variance
embed = rearrange(embed, "h ... d -> h (...) d")
if self.training:
self.update_with_decay(
"codebook_mean",
reduce(embed, "h n d -> h 1 d", "mean"),
self.affine_param_codebook_decay,
)
self.update_with_decay(
"codebook_variance",
reduce(embed, "h n d -> h 1 d", var_fn),
self.affine_param_codebook_decay,
)
# prepare batch data, which depends on whether it has masking
data = rearrange(data, "h ... d -> h (...) d")
if mask is not None:
c = data.shape[0]
data = rearrange(data[mask], "(c n) d -> c n d", c=c)
# calculate batch mean and variance
if not self.sync_affine_param:
self.update_with_decay(
"batch_mean",
reduce(data, "h n d -> h 1 d", "mean"),
self.affine_param_batch_decay,
)
self.update_with_decay(
"batch_variance",
reduce(data, "h n d -> h 1 d", var_fn),
self.affine_param_batch_decay,
)
return
num_vectors, device, dtype = data.shape[-2], data.device, data.dtype
# number of vectors, for denominator
num_vectors = torch.tensor([num_vectors], device=device, dtype=dtype)
distributed.all_reduce(num_vectors)
# calculate distributed mean
batch_sum = reduce(data, "h n d -> h 1 d", "sum")
distributed.all_reduce(batch_sum)
batch_mean = batch_sum / num_vectors
self.update_with_decay("batch_mean", batch_mean, self.affine_param_batch_decay)
# calculate distributed variance
variance_number = reduce((data - batch_mean) ** 2, "h n d -> h 1 d", "sum")
distributed.all_reduce(variance_number)
batch_variance = variance_number / num_vectors
self.update_with_decay("batch_variance", batch_variance, self.affine_param_batch_decay)
def replace(self, batch_samples, batch_mask):
for ind, (samples, mask) in enumerate(
zip(batch_samples.unbind(dim=0), batch_mask.unbind(dim=0), strict=False)
):
if not torch.any(mask):
continue
sampled = self.sample_fn(rearrange(samples, "... -> 1 ..."), mask.sum().item())
sampled = rearrange(sampled, "1 ... -> ...")
self.embed.data[ind][mask] = sampled
self.cluster_size.data[ind][mask] = self.reset_cluster_size
self.embed_avg.data[ind][mask] = sampled * self.reset_cluster_size
def expire_codes_(self, batch_samples):
if self.threshold_ema_dead_code == 0:
return
expired_codes = self.cluster_size < self.threshold_ema_dead_code
if not torch.any(expired_codes):
return
batch_samples = rearrange(batch_samples, "h ... d -> h (...) d")
self.replace(batch_samples, batch_mask=expired_codes)
@autocast(enabled=False)
def forward(self, x, sample_codebook_temp=None, mask=None, freeze_codebook=False):
needs_codebook_dim = x.ndim < 4
sample_codebook_temp = (
sample_codebook_temp if (sample_codebook_temp is not None) else self.sample_codebook_temp
)
x = x.float()
if needs_codebook_dim:
x = rearrange(x, "... -> 1 ...")
flatten, ps = pack_one(x, "h * d")
if mask is not None:
mask = repeat(
mask,
"b n -> c (b h n)",
c=flatten.shape[0],
h=flatten.shape[-2] // (mask.shape[0] * mask.shape[1]),
)
self.init_embed_(flatten, mask=mask)
if self.affine_param:
self.update_affine(flatten, self.embed, mask=mask)
embed = self.embed if self.learnable_codebook else self.embed.detach()
if self.affine_param:
codebook_std = self.codebook_variance.clamp(min=1e-5).sqrt()
batch_std = self.batch_variance.clamp(min=1e-5).sqrt()
embed = (embed - self.codebook_mean) * (batch_std / codebook_std) + self.batch_mean
dist = -cdist(flatten, embed)
embed_ind, embed_onehot = self.gumbel_sample(
dist, dim=-1, temperature=sample_codebook_temp, training=self.training
)
embed_ind = unpack_one(embed_ind, ps, "h *")
if self.training:
unpacked_onehot = unpack_one(embed_onehot, ps, "h * c")
quantize = einsum("h b n c, h c d -> h b n d", unpacked_onehot, embed)
else:
quantize = batched_embedding(embed_ind, embed)
if self.training and self.ema_update and not freeze_codebook:
if self.affine_param:
flatten = (flatten - self.batch_mean) * (codebook_std / batch_std) + self.codebook_mean
if mask is not None:
embed_onehot[~mask] = 0.0
cluster_size = embed_onehot.sum(dim=1)
self.all_reduce_fn(cluster_size)
ema_inplace(self.cluster_size.data, cluster_size, self.decay)
embed_sum = einsum("h n d, h n c -> h c d", flatten, embed_onehot)
self.all_reduce_fn(embed_sum.contiguous())
ema_inplace(self.embed_avg.data, embed_sum, self.decay)
cluster_size = laplace_smoothing(
self.cluster_size, self.codebook_size, self.eps
) * self.cluster_size.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
embed_normalized = self.embed_avg / rearrange(cluster_size, "... -> ... 1")
self.embed.data.copy_(embed_normalized)
self.expire_codes_(x)
if needs_codebook_dim:
quantize, embed_ind = tuple(rearrange(t, "1 ... -> ...") for t in (quantize, embed_ind))
dist = unpack_one(dist, ps, "h * d")
return quantize, embed_ind, dist
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/policies/vqbet/vqbet_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/policies/vqbet/vqbet_utils.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 24273
}
| 214
|
# SO-100
In the steps below, we explain how to assemble the SO-100 robot.
## Source the parts
Follow this [README](https://github.com/TheRobotStudio/SO-ARM100/blob/main/SO100.md). It contains the bill of materials, with a link to source the parts, as well as the instructions to 3D print the parts. And advise if it's your first time printing or if you don't own a 3D printer.
## Install LeRobot 🤗
To install LeRobot, follow our [Installation Guide](./installation)
In addition to these instructions, you need to install the Feetech SDK:
```bash
pip install -e ".[feetech]"
```
## Configure the motors
**Note:**
Unlike the SO-101, the motor connectors are not easily accessible once the arm is assembled, so the configuration step must be done beforehand.
### 1. Find the USB ports associated with each arm
To find the port for each bus servo adapter, run this script:
```bash
lerobot-find-port
```
<hfoptions id="example">
<hfoption id="Mac">
Example output:
```
Finding all available ports for the MotorBus.
['/dev/tty.usbmodem575E0032081', '/dev/tty.usbmodem575E0031751']
Remove the USB cable from your MotorsBus and press Enter when done.
[...Disconnect corresponding leader or follower arm and press Enter...]
The port of this MotorsBus is /dev/tty.usbmodem575E0032081
Reconnect the USB cable.
```
Where the found port is: `/dev/tty.usbmodem575E0032081` corresponding to your leader or follower arm.
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Linux">
On Linux, you might need to give access to the USB ports by running:
```bash
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyACM0
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyACM1
```
Example output:
```
Finding all available ports for the MotorBus.
['/dev/ttyACM0', '/dev/ttyACM1']
Remove the usb cable from your MotorsBus and press Enter when done.
[...Disconnect corresponding leader or follower arm and press Enter...]
The port of this MotorsBus is /dev/ttyACM1
Reconnect the USB cable.
```
Where the found port is: `/dev/ttyACM1` corresponding to your leader or follower arm.
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
### 2. Set the motors ids and baudrates
Each motor is identified by a unique id on the bus. When brand new, motors usually come with a default id of `1`. For the communication to work properly between the motors and the controller, we first need to set a unique, different id to each motor. Additionally, the speed at which data is transmitted on the bus is determined by the baudrate. In order to talk to each other, the controller and all the motors need to be configured with the same baudrate.
To that end, we first need to connect to each motor individually with the controller in order to set these. Since we will write these parameters in the non-volatile section of the motors' internal memory (EEPROM), we'll only need to do this once.
If you are repurposing motors from another robot, you will probably also need to perform this step as the ids and baudrate likely won't match.
#### Follower
Connect the usb cable from your computer and the power supply to the follower arm's controller board. Then, run the following command or run the API example with the port you got from the previous step. You'll also need to give your leader arm a name with the `id` parameter.
For a visual reference on how to set the motor ids please refer to [this video](https://huggingface.co/docs/lerobot/en/so101#setup-motors-video) where we follow the process for the SO101 arm.
<hfoptions id="setup_motors">
<hfoption id="Command">
```bash
lerobot-setup-motors \
--robot.type=so100_follower \
--robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem585A0076841 # <- paste here the port found at previous step
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="API example">
<!-- prettier-ignore-start -->
```python
from lerobot.robots.so100_follower import SO100Follower, SO100FollowerConfig
config = SO100FollowerConfig(
port="/dev/tty.usbmodem585A0076841",
id="my_awesome_follower_arm",
)
follower = SO100Follower(config)
follower.setup_motors()
```
<!-- prettier-ignore-end -->
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
You should see the following instruction
```
Connect the controller board to the 'gripper' motor only and press enter.
```
As instructed, plug the gripper's motor. Make sure it's the only motor connected to the board, and that the motor itself is not yet daisy-chained to any other motor. As you press `[Enter]`, the script will automatically set the id and baudrate for that motor.
<details>
<summary>Troubleshooting</summary>
If you get an error at that point, check your cables and make sure they are plugged in properly:
<ul>
<li>Power supply</li>
<li>USB cable between your computer and the controller board</li>
<li>The 3-pin cable from the controller board to the motor</li>
</ul>
If you are using a Waveshare controller board, make sure that the two jumpers are set on the `B` channel (USB).
</details>
You should then see the following message:
```
'gripper' motor id set to 6
```
Followed by the next instruction:
```
Connect the controller board to the 'wrist_roll' motor only and press enter.
```
You can disconnect the 3-pin cable from the controller board, but you can leave it connected to the gripper motor on the other end, as it will already be in the right place. Now, plug in another 3-pin cable to the wrist roll motor and connect it to the controller board. As with the previous motor, make sure it is the only motor connected to the board and that the motor itself isn't connected to any other one.
Repeat the operation for each motor as instructed.
> [!TIP]
> Check your cabling at each step before pressing Enter. For instance, the power supply cable might disconnect as you manipulate the board.
When you are done, the script will simply finish, at which point the motors are ready to be used. You can now plug the 3-pin cable from each motor to the next one, and the cable from the first motor (the 'shoulder pan' with id=1) to the controller board, which can now be attached to the base of the arm.
#### Leader
Do the same steps for the leader arm.
<hfoptions id="setup_motors">
<hfoption id="Command">
```bash
lerobot-setup-motors \
--teleop.type=so100_leader \
--teleop.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem575E0031751 # <- paste here the port found at previous step
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="API example">
<!-- prettier-ignore-start -->
```python
from lerobot.teleoperators.so100_leader import SO100Leader, SO100LeaderConfig
config = SO100LeaderConfig(
port="/dev/tty.usbmodem585A0076841",
id="my_awesome_leader_arm",
)
leader = SO100Leader(config)
leader.setup_motors()
```
<!-- prettier-ignore-end -->
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
## Step-by-Step Assembly Instructions
## Remove the gears of the 6 leader motors
<details>
<summary><strong>Video removing gears</strong></summary>
<div class="video-container">
<video controls width="600">
<source
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0c95b88c-5b85-413d-ba19-aee2f864f2a7"
type="video/mp4"
/>
</video>
</div>
</details>
Follow the video for removing gears. You need to remove the gear for the motors of the leader arm. As a result, you will only use the position encoding of the motor and reduce friction to more easily operate the leader arm.
### Clean Parts
Remove all support material from the 3D-printed parts. The easiest way to do this is using a small screwdriver to get underneath the support material.
### Additional Guidance
<details>
<summary><strong>Video assembling arms</strong></summary>
<div class="video-container">
<video controls width="600">
<source
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/488a39de-0189-4461-9de3-05b015f90cca"
type="video/mp4"
/>
</video>
</div>
</details>
**Note:**
This video provides visual guidance for assembling the arms, but it doesn't specify when or how to do the wiring. Inserting the cables beforehand is much easier than doing it afterward. The first arm may take a bit more than 1 hour to assemble, but once you get used to it, you can assemble the second arm in under 1 hour.
---
### First Motor
**Step 2: Insert Wires**
- Insert two wires into the first motor.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_1.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 3: Install in Base**
- Place the first motor into the base.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_2.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 4: Secure Motor**
- Fasten the motor with 4 screws. Two from the bottom and two from top.
**Step 5: Attach Motor Holder**
- Slide over the first motor holder and fasten it using two screws (one on each side).
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_4.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 6: Attach Motor Horns**
- Install both motor horns, securing the top horn with a screw. Try not to move the motor position when attaching the motor horn, especially for the leader arms, where we removed the gears.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_5.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
<details>
<summary>
<strong>Video adding motor horn</strong>
</summary>
<video src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/ef3391a4-ad05-4100-b2bd-1699bf86c969"></video>
</details>
**Step 7: Attach Shoulder Part**
- Route one wire to the back of the robot and the other to the left or towards you (see photo).
- Attach the shoulder part.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_6.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 8: Secure Shoulder**
- Tighten the shoulder part with 4 screws on top and 4 on the bottom
_(access bottom holes by turning the shoulder)._
---
### Second Motor Assembly
**Step 9: Install Motor 2**
- Slide the second motor in from the top and link the wire from motor 1 to motor 2.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_8.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 10: Attach Shoulder Holder**
- Add the shoulder motor holder.
- Ensure the wire from motor 1 to motor 2 goes behind the holder while the other wire is routed upward (see photo).
- This part can be tight to assemble, you can use a workbench like the image or a similar setup to push the part around the motor.
<div style="display: flex;">
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_9.webp"
style="height:250px;"
/>
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_10.webp"
style="height:250px;"
/>
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_12.webp"
style="height:250px;"
/>
</div>
**Step 11: Secure Motor 2**
- Fasten the second motor with 4 screws.
**Step 12: Attach Motor Horn**
- Attach both motor horns to motor 2, again use the horn screw.
**Step 13: Attach Base**
- Install the base attachment using 2 screws.
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_11.webp" style="height:300px;">
**Step 14: Attach Upper Arm**
- Attach the upper arm with 4 screws on each side.
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_13.webp" style="height:300px;">
---
### Third Motor Assembly
**Step 15: Install Motor 3**
- Route the motor cable from motor 2 through the cable holder to motor 3, then secure motor 3 with 4 screws.
**Step 16: Attach Motor Horn**
- Attach both motor horns to motor 3 and secure one again with a horn screw.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_14.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 17: Attach Forearm**
- Connect the forearm to motor 3 using 4 screws on each side.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_15.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
---
### Fourth Motor Assembly
**Step 18: Install Motor 4**
- Slide in motor 4, attach the cable from motor 3, and secure the cable in its holder with a screw.
<div style="display: flex;">
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_16.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_19.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
</div>
**Step 19: Attach Motor Holder 4**
- Install the fourth motor holder (a tight fit). Ensure one wire is routed upward and the wire from motor 3 is routed downward (see photo).
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_17.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 20: Secure Motor 4 & Attach Horn**
- Fasten motor 4 with 4 screws and attach its motor horns, use for one a horn screw.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_18.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
---
### Wrist Assembly
**Step 21: Install Motor 5**
- Insert motor 5 into the wrist holder and secure it with 2 front screws.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_20.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 22: Attach Wrist**
- Connect the wire from motor 4 to motor 5. And already insert the other wire for the gripper.
- Secure the wrist to motor 4 using 4 screws on both sides.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_22.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 23: Attach Wrist Horn**
- Install only one motor horn on the wrist motor and secure it with a horn screw.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_23.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
---
### Follower Configuration
**Step 24: Attach Gripper**
- Attach the gripper to motor 5.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_24.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 25: Install Gripper Motor**
- Insert the gripper motor, connect the motor wire from motor 5 to motor 6, and secure it with 3 screws on each side.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_25.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 26: Attach Gripper Horn & Claw**
- Attach the motor horns and again use a horn screw.
- Install the gripper claw and secure it with 4 screws on both sides.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_26.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 27: Mount Controller**
- Attach the motor controller to the back of the robot.
<div style="display: flex;">
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_27.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_28.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
</div>
_Assembly complete – proceed to Leader arm assembly._
---
### Leader Configuration
For the leader configuration, perform **Steps 1–23**. Make sure that you removed the motor gears from the motors.
**Step 24: Attach Leader Holder**
- Mount the leader holder onto the wrist and secure it with a screw.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_29.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 25: Attach Handle**
- Attach the handle to motor 5 using 4 screws.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_30.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 26: Install Gripper Motor**
- Insert the gripper motor, secure it with 3 screws on each side, attach a motor horn using a horn screw, and connect the motor wire.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_31.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 27: Attach Trigger**
- Attach the follower trigger with 4 screws.
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_32.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
**Step 28: Mount Controller**
- Attach the motor controller to the back of the robot.
<div style="display: flex;">
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_27.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
<img
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/lerobot/so100_assembly_28.webp"
style="height:300px;"
/>
</div>
## Calibrate
Next, you'll need to calibrate your robot to ensure that the leader and follower arms have the same position values when they are in the same physical position.
The calibration process is very important because it allows a neural network trained on one robot to work on another.
#### Follower
Run the following command or API example to calibrate the follower arm:
<hfoptions id="calibrate_follower">
<hfoption id="Command">
```bash
lerobot-calibrate \
--robot.type=so100_follower \
--robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem58760431551 \ # <- The port of your robot
--robot.id=my_awesome_follower_arm # <- Give the robot a unique name
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="API example">
<!-- prettier-ignore-start -->
```python
from lerobot.robots.so100_follower import SO100FollowerConfig, SO100Follower
config = SO100FollowerConfig(
port="/dev/tty.usbmodem585A0076891",
id="my_awesome_follower_arm",
)
follower = SO100Follower(config)
follower.connect(calibrate=False)
follower.calibrate()
follower.disconnect()
```
<!-- prettier-ignore-end -->
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
We unified the calibration method for most robots. Thus, the calibration steps for this SO100 arm are the same as the steps for the Koch and SO101. First, we have to move the robot to the position where each joint is in the middle of its range, then we press `Enter`. Secondly, we move all joints through their full range of motion. A video of this same process for the SO101 as reference can be found [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/lerobot/en/so101#calibration-video)
#### Leader
Do the same steps to calibrate the leader arm, run the following command or API example:
<hfoptions id="calibrate_leader">
<hfoption id="Command">
```bash
lerobot-calibrate \
--teleop.type=so100_leader \
--teleop.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem58760431551 \ # <- The port of your robot
--teleop.id=my_awesome_leader_arm # <- Give the robot a unique name
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="API example">
<!-- prettier-ignore-start -->
```python
from lerobot.teleoperators.so100_leader import SO100LeaderConfig, SO100Leader
config = SO100LeaderConfig(
port="/dev/tty.usbmodem58760431551",
id="my_awesome_leader_arm",
)
leader = SO100Leader(config)
leader.connect(calibrate=False)
leader.calibrate()
leader.disconnect()
```
<!-- prettier-ignore-end -->
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
Congrats 🎉, your robot is all set to learn a task on its own. Start training it by following this tutorial: [Getting started with real-world robots](./getting_started_real_world_robot)
> [!TIP]
> If you have any questions or need help, please reach out on [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/s3KuuzsPFb).
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/robots/so100_follower/so100.mdx/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/robots/so100_follower/so100.mdx",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 6468
}
| 215
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Use this script to get a quick summary of your system config.
It should be able to run without any of LeRobot's dependencies or LeRobot itself installed.
"""
import platform
HAS_HF_HUB = True
HAS_HF_DATASETS = True
HAS_NP = True
HAS_TORCH = True
HAS_LEROBOT = True
try:
import huggingface_hub
except ImportError:
HAS_HF_HUB = False
try:
import datasets
except ImportError:
HAS_HF_DATASETS = False
try:
import numpy as np
except ImportError:
HAS_NP = False
try:
import torch
except ImportError:
HAS_TORCH = False
try:
import lerobot
except ImportError:
HAS_LEROBOT = False
lerobot_version = lerobot.__version__ if HAS_LEROBOT else "N/A"
hf_hub_version = huggingface_hub.__version__ if HAS_HF_HUB else "N/A"
hf_datasets_version = datasets.__version__ if HAS_HF_DATASETS else "N/A"
np_version = np.__version__ if HAS_NP else "N/A"
torch_version = torch.__version__ if HAS_TORCH else "N/A"
torch_cuda_available = torch.cuda.is_available() if HAS_TORCH else "N/A"
cuda_version = torch._C._cuda_getCompiledVersion() if HAS_TORCH and torch.version.cuda is not None else "N/A"
# TODO(aliberts): refactor into an actual command `lerobot env`
def display_sys_info() -> dict:
"""Run this to get basic system info to help for tracking issues & bugs."""
info = {
"`lerobot` version": lerobot_version,
"Platform": platform.platform(),
"Python version": platform.python_version(),
"Huggingface_hub version": hf_hub_version,
"Dataset version": hf_datasets_version,
"Numpy version": np_version,
"PyTorch version (GPU?)": f"{torch_version} ({torch_cuda_available})",
"Cuda version": cuda_version,
"Using GPU in script?": "<fill in>",
# "Using distributed or parallel set-up in script?": "<fill in>",
}
print("\nCopy-and-paste the text below in your GitHub issue and FILL OUT the last point.\n")
print(format_dict(info))
return info
def format_dict(d: dict) -> str:
return "\n".join([f"- {prop}: {val}" for prop, val in d.items()]) + "\n"
if __name__ == "__main__":
display_sys_info()
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/scripts/display_sys_info.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/scripts/display_sys_info.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 998
}
| 216
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
""" Visualize data of **all** frames of any episode of a dataset of type LeRobotDataset.
Note: The last frame of the episode doesnt always correspond to a final state.
That's because our datasets are composed of transition from state to state up to
the antepenultimate state associated to the ultimate action to arrive in the final state.
However, there might not be a transition from a final state to another state.
Note: This script aims to visualize the data used to train the neural networks.
~What you see is what you get~. When visualizing image modality, it is often expected to observe
lossly compression artifacts since these images have been decoded from compressed mp4 videos to
save disk space. The compression factor applied has been tuned to not affect success rate.
Example of usage:
- Visualize data stored on a local machine:
```bash
local$ python -m lerobot.scripts.visualize_dataset_html \
--repo-id lerobot/pusht
local$ open http://localhost:9090
```
- Visualize data stored on a distant machine with a local viewer:
```bash
distant$ python -m lerobot.scripts.visualize_dataset_html \
--repo-id lerobot/pusht
local$ ssh -L 9090:localhost:9090 distant # create a ssh tunnel
local$ open http://localhost:9090
```
- Select episodes to visualize:
```bash
python -m lerobot.scripts.visualize_dataset_html \
--repo-id lerobot/pusht \
--episodes 7 3 5 1 4
```
"""
import argparse
import csv
import json
import logging
import re
import shutil
import tempfile
from io import StringIO
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import requests
from flask import Flask, redirect, render_template, request, url_for
from lerobot import available_datasets
from lerobot.datasets.lerobot_dataset import LeRobotDataset
from lerobot.datasets.utils import IterableNamespace
from lerobot.utils.utils import init_logging
def run_server(
dataset: LeRobotDataset | IterableNamespace | None,
episodes: list[int] | None,
host: str,
port: str,
static_folder: Path,
template_folder: Path,
):
app = Flask(__name__, static_folder=static_folder.resolve(), template_folder=template_folder.resolve())
app.config["SEND_FILE_MAX_AGE_DEFAULT"] = 0 # specifying not to cache
@app.route("/")
def hommepage(dataset=dataset):
if dataset:
dataset_namespace, dataset_name = dataset.repo_id.split("/")
return redirect(
url_for(
"show_episode",
dataset_namespace=dataset_namespace,
dataset_name=dataset_name,
episode_id=0,
)
)
dataset_param, episode_param = None, None
all_params = request.args
if "dataset" in all_params:
dataset_param = all_params["dataset"]
if "episode" in all_params:
episode_param = int(all_params["episode"])
if dataset_param:
dataset_namespace, dataset_name = dataset_param.split("/")
return redirect(
url_for(
"show_episode",
dataset_namespace=dataset_namespace,
dataset_name=dataset_name,
episode_id=episode_param if episode_param is not None else 0,
)
)
featured_datasets = [
"lerobot/aloha_static_cups_open",
"lerobot/columbia_cairlab_pusht_real",
"lerobot/taco_play",
]
return render_template(
"visualize_dataset_homepage.html",
featured_datasets=featured_datasets,
lerobot_datasets=available_datasets,
)
@app.route("/<string:dataset_namespace>/<string:dataset_name>")
def show_first_episode(dataset_namespace, dataset_name):
first_episode_id = 0
return redirect(
url_for(
"show_episode",
dataset_namespace=dataset_namespace,
dataset_name=dataset_name,
episode_id=first_episode_id,
)
)
@app.route("/<string:dataset_namespace>/<string:dataset_name>/episode_<int:episode_id>")
def show_episode(dataset_namespace, dataset_name, episode_id, dataset=dataset, episodes=episodes):
repo_id = f"{dataset_namespace}/{dataset_name}"
try:
if dataset is None:
dataset = get_dataset_info(repo_id)
except FileNotFoundError:
return (
"Make sure to convert your LeRobotDataset to v2 & above. See how to convert your dataset at https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot/pull/461",
400,
)
dataset_version = (
str(dataset.meta._version) if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset) else dataset.codebase_version
)
match = re.search(r"v(\d+)\.", dataset_version)
if match:
major_version = int(match.group(1))
if major_version < 2:
return "Make sure to convert your LeRobotDataset to v2 & above."
episode_data_csv_str, columns, ignored_columns = get_episode_data(dataset, episode_id)
dataset_info = {
"repo_id": f"{dataset_namespace}/{dataset_name}",
"num_samples": dataset.num_frames
if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset)
else dataset.total_frames,
"num_episodes": dataset.num_episodes
if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset)
else dataset.total_episodes,
"fps": dataset.fps,
}
if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset):
video_paths = [
dataset.meta.get_video_file_path(episode_id, key) for key in dataset.meta.video_keys
]
videos_info = [
{
"url": url_for("static", filename=str(video_path).replace("\\", "/")),
"filename": video_path.parent.name,
}
for video_path in video_paths
]
tasks = dataset.meta.episodes[episode_id]["tasks"]
else:
video_keys = [key for key, ft in dataset.features.items() if ft["dtype"] == "video"]
videos_info = [
{
"url": f"https://huggingface.co/datasets/{repo_id}/resolve/main/"
+ dataset.video_path.format(
episode_chunk=int(episode_id) // dataset.chunks_size,
video_key=video_key,
episode_index=episode_id,
),
"filename": video_key,
}
for video_key in video_keys
]
response = requests.get(
f"https://huggingface.co/datasets/{repo_id}/resolve/main/meta/episodes.jsonl", timeout=5
)
response.raise_for_status()
# Split into lines and parse each line as JSON
tasks_jsonl = [json.loads(line) for line in response.text.splitlines() if line.strip()]
filtered_tasks_jsonl = [row for row in tasks_jsonl if row["episode_index"] == episode_id]
tasks = filtered_tasks_jsonl[0]["tasks"]
videos_info[0]["language_instruction"] = tasks
if episodes is None:
episodes = list(
range(dataset.num_episodes if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset) else dataset.total_episodes)
)
return render_template(
"visualize_dataset_template.html",
episode_id=episode_id,
episodes=episodes,
dataset_info=dataset_info,
videos_info=videos_info,
episode_data_csv_str=episode_data_csv_str,
columns=columns,
ignored_columns=ignored_columns,
)
app.run(host=host, port=port)
def get_ep_csv_fname(episode_id: int):
ep_csv_fname = f"episode_{episode_id}.csv"
return ep_csv_fname
def get_episode_data(dataset: LeRobotDataset | IterableNamespace, episode_index):
"""Get a csv str containing timeseries data of an episode (e.g. state and action).
This file will be loaded by Dygraph javascript to plot data in real time."""
columns = []
selected_columns = [col for col, ft in dataset.features.items() if ft["dtype"] in ["float32", "int32"]]
selected_columns.remove("timestamp")
ignored_columns = []
for column_name in selected_columns:
shape = dataset.features[column_name]["shape"]
shape_dim = len(shape)
if shape_dim > 1:
selected_columns.remove(column_name)
ignored_columns.append(column_name)
# init header of csv with state and action names
header = ["timestamp"]
for column_name in selected_columns:
dim_state = (
dataset.meta.shapes[column_name][0]
if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset)
else dataset.features[column_name].shape[0]
)
if "names" in dataset.features[column_name] and dataset.features[column_name]["names"]:
column_names = dataset.features[column_name]["names"]
while not isinstance(column_names, list):
column_names = list(column_names.values())[0]
else:
column_names = [f"{column_name}_{i}" for i in range(dim_state)]
columns.append({"key": column_name, "value": column_names})
header += column_names
selected_columns.insert(0, "timestamp")
if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset):
from_idx = dataset.episode_data_index["from"][episode_index]
to_idx = dataset.episode_data_index["to"][episode_index]
data = (
dataset.hf_dataset.select(range(from_idx, to_idx))
.select_columns(selected_columns)
.with_format("pandas")
)
else:
repo_id = dataset.repo_id
url = f"https://huggingface.co/datasets/{repo_id}/resolve/main/" + dataset.data_path.format(
episode_chunk=int(episode_index) // dataset.chunks_size, episode_index=episode_index
)
df = pd.read_parquet(url)
data = df[selected_columns] # Select specific columns
rows = np.hstack(
(
np.expand_dims(data["timestamp"], axis=1),
*[np.vstack(data[col]) for col in selected_columns[1:]],
)
).tolist()
# Convert data to CSV string
csv_buffer = StringIO()
csv_writer = csv.writer(csv_buffer)
# Write header
csv_writer.writerow(header)
# Write data rows
csv_writer.writerows(rows)
csv_string = csv_buffer.getvalue()
return csv_string, columns, ignored_columns
def get_episode_video_paths(dataset: LeRobotDataset, ep_index: int) -> list[str]:
# get first frame of episode (hack to get video_path of the episode)
first_frame_idx = dataset.episode_data_index["from"][ep_index].item()
return [
dataset.hf_dataset.select_columns(key)[first_frame_idx][key]["path"]
for key in dataset.meta.video_keys
]
def get_episode_language_instruction(dataset: LeRobotDataset, ep_index: int) -> list[str]:
# check if the dataset has language instructions
if "language_instruction" not in dataset.features:
return None
# get first frame index
first_frame_idx = dataset.episode_data_index["from"][ep_index].item()
language_instruction = dataset.hf_dataset[first_frame_idx]["language_instruction"]
# TODO (michel-aractingi) hack to get the sentence, some strings in openx are badly stored
# with the tf.tensor appearing in the string
return language_instruction.removeprefix("tf.Tensor(b'").removesuffix("', shape=(), dtype=string)")
def get_dataset_info(repo_id: str) -> IterableNamespace:
response = requests.get(
f"https://huggingface.co/datasets/{repo_id}/resolve/main/meta/info.json", timeout=5
)
response.raise_for_status() # Raises an HTTPError for bad responses
dataset_info = response.json()
dataset_info["repo_id"] = repo_id
return IterableNamespace(dataset_info)
def visualize_dataset_html(
dataset: LeRobotDataset | None,
episodes: list[int] | None = None,
output_dir: Path | None = None,
serve: bool = True,
host: str = "127.0.0.1",
port: int = 9090,
force_override: bool = False,
) -> Path | None:
init_logging()
template_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent / "templates"
if output_dir is None:
# Create a temporary directory that will be automatically cleaned up
output_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp(prefix="lerobot_visualize_dataset_")
output_dir = Path(output_dir)
if output_dir.exists():
if force_override:
shutil.rmtree(output_dir)
else:
logging.info(f"Output directory already exists. Loading from it: '{output_dir}'")
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
static_dir = output_dir / "static"
static_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
if dataset is None:
if serve:
run_server(
dataset=None,
episodes=None,
host=host,
port=port,
static_folder=static_dir,
template_folder=template_dir,
)
else:
# Create a simlink from the dataset video folder containing mp4 files to the output directory
# so that the http server can get access to the mp4 files.
if isinstance(dataset, LeRobotDataset):
ln_videos_dir = static_dir / "videos"
if not ln_videos_dir.exists():
ln_videos_dir.symlink_to((dataset.root / "videos").resolve().as_posix())
if serve:
run_server(dataset, episodes, host, port, static_dir, template_dir)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--repo-id",
type=str,
default=None,
help="Name of hugging face repositery containing a LeRobotDataset dataset (e.g. `lerobot/pusht` for https://huggingface.co/datasets/lerobot/pusht).",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--root",
type=Path,
default=None,
help="Root directory for a dataset stored locally (e.g. `--root data`). By default, the dataset will be loaded from hugging face cache folder, or downloaded from the hub if available.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--load-from-hf-hub",
type=int,
default=0,
help="Load videos and parquet files from HF Hub rather than local system.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--episodes",
type=int,
nargs="*",
default=None,
help="Episode indices to visualize (e.g. `0 1 5 6` to load episodes of index 0, 1, 5 and 6). By default loads all episodes.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--output-dir",
type=Path,
default=None,
help="Directory path to write html files and kickoff a web server. By default write them to 'outputs/visualize_dataset/REPO_ID'.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--serve",
type=int,
default=1,
help="Launch web server.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--host",
type=str,
default="127.0.0.1",
help="Web host used by the http server.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--port",
type=int,
default=9090,
help="Web port used by the http server.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--force-override",
type=int,
default=0,
help="Delete the output directory if it exists already.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--tolerance-s",
type=float,
default=1e-4,
help=(
"Tolerance in seconds used to ensure data timestamps respect the dataset fps value"
"This is argument passed to the constructor of LeRobotDataset and maps to its tolerance_s constructor argument"
"If not given, defaults to 1e-4."
),
)
args = parser.parse_args()
kwargs = vars(args)
repo_id = kwargs.pop("repo_id")
load_from_hf_hub = kwargs.pop("load_from_hf_hub")
root = kwargs.pop("root")
tolerance_s = kwargs.pop("tolerance_s")
dataset = None
if repo_id:
dataset = (
LeRobotDataset(repo_id, root=root, tolerance_s=tolerance_s)
if not load_from_hf_hub
else get_dataset_info(repo_id)
)
visualize_dataset_html(dataset, **vars(args))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/scripts/visualize_dataset_html.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/scripts/visualize_dataset_html.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 7555
}
| 217
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import logging
import threading
from collections import deque
from pprint import pformat
from typing import Deque
import serial
from lerobot.errors import DeviceAlreadyConnectedError, DeviceNotConnectedError
from lerobot.motors import MotorCalibration
from lerobot.motors.motors_bus import MotorNormMode
from lerobot.teleoperators.homunculus.joints_translation import homunculus_glove_to_hope_jr_hand
from lerobot.utils.utils import enter_pressed, move_cursor_up
from ..teleoperator import Teleoperator
from .config_homunculus import HomunculusGloveConfig
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
LEFT_HAND_INVERSIONS = [
"thumb_cmc",
"index_dip",
"middle_mcp_abduction",
"middle_dip",
"pinky_mcp_abduction",
"pinky_dip",
]
RIGHT_HAND_INVERSIONS = [
"thumb_mcp",
"thumb_cmc",
"thumb_pip",
"thumb_dip",
"index_mcp_abduction",
# "index_dip",
"middle_mcp_abduction",
# "middle_dip",
"ring_mcp_abduction",
"ring_mcp_flexion",
# "ring_dip",
"pinky_mcp_abduction",
]
class HomunculusGlove(Teleoperator):
"""
Homunculus Glove designed by NepYope & Hugging Face.
"""
config_class = HomunculusGloveConfig
name = "homunculus_glove"
def __init__(self, config: HomunculusGloveConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.config = config
self.serial = serial.Serial(config.port, config.baud_rate, timeout=1)
self.serial_lock = threading.Lock()
self.joints = {
"thumb_cmc": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"thumb_mcp": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"thumb_pip": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"thumb_dip": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"index_mcp_abduction": MotorNormMode.RANGE_M100_100,
"index_mcp_flexion": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"index_dip": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"middle_mcp_abduction": MotorNormMode.RANGE_M100_100,
"middle_mcp_flexion": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"middle_dip": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"ring_mcp_abduction": MotorNormMode.RANGE_M100_100,
"ring_mcp_flexion": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"ring_dip": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"pinky_mcp_abduction": MotorNormMode.RANGE_M100_100,
"pinky_mcp_flexion": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
"pinky_dip": MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100,
}
self.inverted_joints = RIGHT_HAND_INVERSIONS if config.side == "right" else LEFT_HAND_INVERSIONS
n = 10
# EMA parameters ---------------------------------------------------
self.n: int = n
self.alpha: float = 2 / (n + 1)
# one deque *per joint* so we can inspect raw history if needed
self._buffers: dict[str, Deque[int]] = {joint: deque(maxlen=n) for joint in self.joints}
# running EMA value per joint – lazily initialised on first read
self._ema: dict[str, float | None] = dict.fromkeys(self._buffers)
self._state: dict[str, float] | None = None
self.new_state_event = threading.Event()
self.stop_event = threading.Event()
self.thread = threading.Thread(target=self._read_loop, daemon=True, name=f"{self} _read_loop")
self.state_lock = threading.Lock()
@property
def action_features(self) -> dict:
return {f"{joint}.pos": float for joint in self.joints}
@property
def feedback_features(self) -> dict:
return {}
@property
def is_connected(self) -> bool:
with self.serial_lock:
return self.serial.is_open and self.thread.is_alive()
def connect(self, calibrate: bool = True) -> None:
if self.is_connected:
raise DeviceAlreadyConnectedError(f"{self} already connected")
if not self.serial.is_open:
self.serial.open()
self.thread.start()
# wait for the thread to ramp up & 1st state to be ready
if not self.new_state_event.wait(timeout=2):
raise TimeoutError(f"{self}: Timed out waiting for state after 2s.")
if not self.is_calibrated and calibrate:
self.calibrate()
logger.info(f"{self} connected.")
@property
def is_calibrated(self) -> bool:
return self.calibration_fpath.is_file()
def calibrate(self) -> None:
range_mins, range_maxes = {}, {}
for finger in ["thumb", "index", "middle", "ring", "pinky"]:
print(
f"\nMove {finger} through its entire range of motion."
"\nRecording positions. Press ENTER to stop..."
)
finger_joints = [joint for joint in self.joints if joint.startswith(finger)]
finger_mins, finger_maxes = self._record_ranges_of_motion(finger_joints)
range_mins.update(finger_mins)
range_maxes.update(finger_maxes)
self.calibration = {}
for id_, joint in enumerate(self.joints):
self.calibration[joint] = MotorCalibration(
id=id_,
drive_mode=1 if joint in self.inverted_joints else 0,
homing_offset=0,
range_min=range_mins[joint],
range_max=range_maxes[joint],
)
self._save_calibration()
print("Calibration saved to", self.calibration_fpath)
# TODO(Steven): This function is copy/paste from the `HomunculusArm` class. Consider moving it to an utility to reduce duplicated code.
def _record_ranges_of_motion(
self, joints: list[str] | None = None, display_values: bool = True
) -> tuple[dict[str, int], dict[str, int]]:
"""Interactively record the min/max encoder values of each joint.
Move the joints while the method streams live positions. Press :kbd:`Enter` to finish.
Args:
joints (list[str] | None, optional): Joints to record. Defaults to every joint (`None`).
display_values (bool, optional): When `True` (default) a live table is printed to the console.
Raises:
TypeError: `joints` is not `None` or a list.
ValueError: any joint's recorded min and max are the same.
Returns:
tuple[dict[str, int], dict[str, int]]: Two dictionaries *mins* and *maxes* with the extreme values
observed for each joint.
"""
if joints is None:
joints = list(self.joints)
elif not isinstance(joints, list):
raise TypeError(joints)
display_len = max(len(key) for key in joints)
start_positions = self._read(joints, normalize=False)
mins = start_positions.copy()
maxes = start_positions.copy()
user_pressed_enter = False
while not user_pressed_enter:
positions = self._read(joints, normalize=False)
mins = {joint: int(min(positions[joint], min_)) for joint, min_ in mins.items()}
maxes = {joint: int(max(positions[joint], max_)) for joint, max_ in maxes.items()}
if display_values:
print("\n-------------------------------------------")
print(f"{'NAME':<{display_len}} | {'MIN':>6} | {'POS':>6} | {'MAX':>6}")
for joint in joints:
print(
f"{joint:<{display_len}} | {mins[joint]:>6} | {positions[joint]:>6} | {maxes[joint]:>6}"
)
if enter_pressed():
user_pressed_enter = True
if display_values and not user_pressed_enter:
# Move cursor up to overwrite the previous output
move_cursor_up(len(joints) + 3)
same_min_max = [joint for joint in joints if mins[joint] == maxes[joint]]
if same_min_max:
raise ValueError(f"Some joints have the same min and max values:\n{pformat(same_min_max)}")
return mins, maxes
def configure(self) -> None:
pass
# TODO(Steven): This function is copy/paste from the `HomunculusArm` class. Consider moving it to an utility to reduce duplicated code.
def _normalize(self, values: dict[str, int]) -> dict[str, float]:
if not self.calibration:
raise RuntimeError(f"{self} has no calibration registered.")
normalized_values = {}
for joint, val in values.items():
min_ = self.calibration[joint].range_min
max_ = self.calibration[joint].range_max
drive_mode = self.calibration[joint].drive_mode
bounded_val = min(max_, max(min_, val))
if self.joints[joint] is MotorNormMode.RANGE_M100_100:
norm = (((bounded_val - min_) / (max_ - min_)) * 200) - 100
normalized_values[joint] = -norm if drive_mode else norm
elif self.joints[joint] is MotorNormMode.RANGE_0_100:
norm = ((bounded_val - min_) / (max_ - min_)) * 100
normalized_values[joint] = 100 - norm if drive_mode else norm
return normalized_values
def _apply_ema(self, raw: dict[str, int]) -> dict[str, int]:
"""Update buffers & running EMA values; return smoothed dict as integers."""
smoothed: dict[str, int] = {}
for joint, value in raw.items():
# maintain raw history
self._buffers[joint].append(value)
# initialise on first run
if self._ema[joint] is None:
self._ema[joint] = float(value)
else:
self._ema[joint] = self.alpha * value + (1 - self.alpha) * self._ema[joint]
# Convert back to int for compatibility with normalization
smoothed[joint] = int(round(self._ema[joint]))
return smoothed
def _read(
self, joints: list[str] | None = None, normalize: bool = True, timeout: float = 1
) -> dict[str, int | float]:
"""
Return the most recent (single) values from self.last_d,
optionally applying calibration.
"""
if not self.new_state_event.wait(timeout=timeout):
raise TimeoutError(f"{self}: Timed out waiting for state after {timeout}s.")
with self.state_lock:
state = self._state
self.new_state_event.clear()
if state is None:
raise RuntimeError(f"{self} Internal error: Event set but no state available.")
if joints is not None:
state = {k: v for k, v in state.items() if k in joints}
# Apply EMA smoothing to raw values first
state = self._apply_ema(state)
# Then normalize if requested
if normalize:
state = self._normalize(state)
return state
def _read_loop(self):
"""
Continuously read from the serial buffer in its own thread and sends values to the main thread through
a queue.
"""
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
try:
positions = None
with self.serial_lock:
if self.serial.in_waiting > 0:
self.serial.flush()
positions = self.serial.readline().decode("utf-8").strip().split(" ")
if positions is None or len(positions) != len(self.joints):
continue
joint_positions = {joint: int(pos) for joint, pos in zip(self.joints, positions, strict=True)}
with self.state_lock:
self._state = joint_positions
self.new_state_event.set()
except Exception as e:
logger.debug(f"Error reading frame in background thread for {self}: {e}")
def get_action(self) -> dict[str, float]:
joint_positions = self._read()
return homunculus_glove_to_hope_jr_hand(
{f"{joint}.pos": pos for joint, pos in joint_positions.items()}
)
def send_feedback(self, feedback: dict[str, float]) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError
def disconnect(self) -> None:
if not self.is_connected:
DeviceNotConnectedError(f"{self} is not connected.")
self.stop_event.set()
self.thread.join(timeout=1)
self.serial.close()
logger.info(f"{self} disconnected.")
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/teleoperators/homunculus/homunculus_glove.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/teleoperators/homunculus/homunculus_glove.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 5686
}
| 218
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import time
import numpy as np
from stretch_body.gamepad_teleop import GamePadTeleop
from stretch_body.robot_params import RobotParams
from lerobot.errors import DeviceAlreadyConnectedError
from ..teleoperator import Teleoperator
from .configuration_stretch3 import Stretch3GamePadConfig
# from stretch_body.gamepad_controller.GamePadController
GAMEPAD_BUTTONS = [
"middle_led_ring_button_pressed",
"left_stick_x",
"left_stick_y",
"right_stick_x",
"right_stick_y",
"left_stick_button_pressed",
"right_stick_button_pressed",
"bottom_button_pressed",
"top_button_pressed",
"left_button_pressed",
"right_button_pressed",
"left_shoulder_button_pressed",
"right_shoulder_button_pressed",
"select_button_pressed",
"start_button_pressed",
"left_trigger_pulled",
"right_trigger_pulled",
"bottom_pad_pressed",
"top_pad_pressed",
"left_pad_pressed",
"right_pad_pressed",
]
class Stretch3GamePad(Teleoperator):
"""[Stretch 3](https://hello-robot.com/stretch-3-product), by Hello Robot."""
config_class = Stretch3GamePadConfig
name = "stretch3"
def __init__(self, config: Stretch3GamePadConfig):
raise NotImplementedError
super().__init__(config)
self.config = config
self.robot_type = self.config.type
self.api = GamePadTeleop(robot_instance=False)
self.is_connected = False
self.logs = {}
# TODO(aliberts): test this
RobotParams.set_logging_level("WARNING")
RobotParams.set_logging_formatter("brief_console_formatter")
@property
def action_features(self) -> dict:
return {
"dtype": "float32",
"shape": (len(GAMEPAD_BUTTONS),),
"names": {"buttons": GAMEPAD_BUTTONS},
}
@property
def feedback_features(self) -> dict:
return {}
def connect(self) -> None:
if self.is_connected:
raise DeviceAlreadyConnectedError(
"ManipulatorRobot is already connected. Do not run `robot.connect()` twice."
)
self.api.startup()
self.api._update_state() # Check controller can be read & written
self.api._update_modes()
self.is_connected = True
def calibrate(self) -> None:
pass
def get_action(self) -> np.ndarray:
# Read Stretch state
before_read_t = time.perf_counter()
action = self.api.gamepad_controller.get_state()
self.logs["read_pos_dt_s"] = time.perf_counter() - before_read_t
action = np.asarray(list(action.values()))
return action
def send_feedback(self, feedback: np.ndarray) -> None:
pass
def print_logs(self) -> None:
pass
# TODO(aliberts): move robot-specific logs logic here
def disconnect(self) -> None:
self.api.stop()
self.is_connected = False
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/teleoperators/stretch3_gamepad/stretch3_gamepad.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/teleoperators/stretch3_gamepad/stretch3_gamepad.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 1385
}
| 219
|
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
def encode_sign_magnitude(value: int, sign_bit_index: int):
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signed_number_representations#Sign%E2%80%93magnitude
"""
max_magnitude = (1 << sign_bit_index) - 1
magnitude = abs(value)
if magnitude > max_magnitude:
raise ValueError(f"Magnitude {magnitude} exceeds {max_magnitude} (max for {sign_bit_index=})")
direction_bit = 1 if value < 0 else 0
return (direction_bit << sign_bit_index) | magnitude
def decode_sign_magnitude(encoded_value: int, sign_bit_index: int):
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signed_number_representations#Sign%E2%80%93magnitude
"""
direction_bit = (encoded_value >> sign_bit_index) & 1
magnitude_mask = (1 << sign_bit_index) - 1
magnitude = encoded_value & magnitude_mask
return -magnitude if direction_bit else magnitude
def encode_twos_complement(value: int, n_bytes: int):
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signed_number_representations#Two%27s_complement
"""
bit_width = n_bytes * 8
min_val = -(1 << (bit_width - 1))
max_val = (1 << (bit_width - 1)) - 1
if not (min_val <= value <= max_val):
raise ValueError(
f"Value {value} out of range for {n_bytes}-byte two's complement: [{min_val}, {max_val}]"
)
if value >= 0:
return value
return (1 << bit_width) + value
def decode_twos_complement(value: int, n_bytes: int) -> int:
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signed_number_representations#Two%27s_complement
"""
bits = n_bytes * 8
sign_bit = 1 << (bits - 1)
if value & sign_bit:
value -= 1 << bits
return value
|
lerobot/src/lerobot/utils/encoding_utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/src/lerobot/utils/encoding_utils.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 827
}
| 220
|
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import math
import pickle
import time
import numpy as np
import torch
from lerobot.configs.types import FeatureType, PolicyFeature
from lerobot.scripts.server.helpers import (
FPSTracker,
TimedAction,
TimedObservation,
observations_similar,
prepare_image,
prepare_raw_observation,
raw_observation_to_observation,
resize_robot_observation_image,
)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# FPSTracker
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
def test_fps_tracker_first_observation():
"""First observation should initialize timestamp and return 0 FPS."""
tracker = FPSTracker(target_fps=30.0)
timestamp = 1000.0
metrics = tracker.calculate_fps_metrics(timestamp)
assert tracker.first_timestamp == timestamp
assert tracker.total_obs_count == 1
assert metrics["avg_fps"] == 0.0
assert metrics["target_fps"] == 30.0
def test_fps_tracker_single_interval():
"""Two observations 1 second apart should give 1 FPS."""
tracker = FPSTracker(target_fps=30.0)
# First observation at t=0
metrics1 = tracker.calculate_fps_metrics(0.0)
assert metrics1["avg_fps"] == 0.0
# Second observation at t=1 (1 second later)
metrics2 = tracker.calculate_fps_metrics(1.0)
expected_fps = 1.0 # (2-1) observations / 1.0 seconds = 1 FPS
assert math.isclose(metrics2["avg_fps"], expected_fps, rel_tol=1e-6)
def test_fps_tracker_multiple_intervals():
"""Multiple observations should calculate correct average FPS."""
tracker = FPSTracker(target_fps=30.0)
# Simulate 5 observations over 2 seconds (should be 2 FPS average)
timestamps = [0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
for i, ts in enumerate(timestamps):
metrics = tracker.calculate_fps_metrics(ts)
if i == 0:
assert metrics["avg_fps"] == 0.0
elif i == len(timestamps) - 1:
# After 5 observations over 2 seconds: (5-1)/2 = 2 FPS
expected_fps = 2.0
assert math.isclose(metrics["avg_fps"], expected_fps, rel_tol=1e-6)
def test_fps_tracker_irregular_intervals():
"""FPS calculation should work with irregular time intervals."""
tracker = FPSTracker(target_fps=30.0)
# Irregular timestamps: 0, 0.1, 0.5, 2.0, 3.0 seconds
timestamps = [0.0, 0.1, 0.5, 2.0, 3.0]
for ts in timestamps:
metrics = tracker.calculate_fps_metrics(ts)
# 5 observations over 3 seconds: (5-1)/3 = 1.333... FPS
expected_fps = 4.0 / 3.0
assert math.isclose(metrics["avg_fps"], expected_fps, rel_tol=1e-6)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# TimedData helpers
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
def test_timed_action_getters():
"""TimedAction stores & returns timestamp, action tensor and timestep."""
ts = time.time()
action = torch.arange(10)
ta = TimedAction(timestamp=ts, action=action, timestep=0)
assert math.isclose(ta.get_timestamp(), ts, rel_tol=0, abs_tol=1e-6)
torch.testing.assert_close(ta.get_action(), action)
assert ta.get_timestep() == 0
def test_timed_observation_getters():
"""TimedObservation stores & returns timestamp, dict and timestep."""
ts = time.time()
obs_dict = {"observation.state": torch.ones(6)}
to = TimedObservation(timestamp=ts, observation=obs_dict, timestep=0)
assert math.isclose(to.get_timestamp(), ts, rel_tol=0, abs_tol=1e-6)
assert to.get_observation() is obs_dict
assert to.get_timestep() == 0
def test_timed_data_deserialization_data_getters():
"""TimedAction / TimedObservation survive a round-trip through ``pickle``.
The async-inference stack uses ``pickle.dumps`` to move these objects across
the gRPC boundary (see RobotClient.send_observation and PolicyServer.StreamActions).
This test ensures that the payload keeps its content intact after
the (de)serialization round-trip.
"""
ts = time.time()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# TimedAction
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
original_action = torch.randn(6)
ta_in = TimedAction(timestamp=ts, action=original_action, timestep=13)
# Serialize → bytes → deserialize
ta_bytes = pickle.dumps(ta_in) # nosec
ta_out: TimedAction = pickle.loads(ta_bytes) # nosec B301
# Identity & content checks
assert math.isclose(ta_out.get_timestamp(), ts, rel_tol=0, abs_tol=1e-6)
assert ta_out.get_timestep() == 13
torch.testing.assert_close(ta_out.get_action(), original_action)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# TimedObservation
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
obs_dict = {"observation.state": torch.arange(4).float()}
to_in = TimedObservation(timestamp=ts, observation=obs_dict, timestep=7, must_go=True)
to_bytes = pickle.dumps(to_in) # nosec
to_out: TimedObservation = pickle.loads(to_bytes) # nosec B301
assert math.isclose(to_out.get_timestamp(), ts, rel_tol=0, abs_tol=1e-6)
assert to_out.get_timestep() == 7
assert to_out.must_go is True
assert to_out.get_observation().keys() == obs_dict.keys()
torch.testing.assert_close(to_out.get_observation()["observation.state"], obs_dict["observation.state"])
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# observations_similar()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
def _make_obs(state: torch.Tensor) -> TimedObservation:
"""Create a TimedObservation with raw robot observation format."""
return TimedObservation(
timestamp=time.time(),
observation={
"shoulder": state[0].item() if len(state) > 0 else 0.0,
"elbow": state[1].item() if len(state) > 1 else 0.0,
"wrist": state[2].item() if len(state) > 2 else 0.0,
"gripper": state[3].item() if len(state) > 3 else 0.0,
},
timestep=0,
)
def test_observations_similar_true():
"""Distance below atol → observations considered similar."""
# Create mock lerobot features for the similarity check
lerobot_features = {
"observation.state": {
"dtype": "float32",
"shape": [4],
"names": ["shoulder", "elbow", "wrist", "gripper"],
}
}
obs1 = _make_obs(torch.zeros(4))
obs2 = _make_obs(0.5 * torch.ones(4))
assert observations_similar(obs1, obs2, lerobot_features, atol=2.0)
obs3 = _make_obs(2.0 * torch.ones(4))
assert not observations_similar(obs1, obs3, lerobot_features, atol=2.0)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# raw_observation_to_observation and helpers
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
def _create_mock_robot_observation():
"""Create a mock robot observation with motor positions and camera images."""
return {
"shoulder": 1.0,
"elbow": 2.0,
"wrist": 3.0,
"gripper": 0.5,
"laptop": np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8),
"phone": np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8),
}
def _create_mock_lerobot_features():
"""Create mock lerobot features mapping similar to what hw_to_dataset_features returns."""
return {
"observation.state": {
"dtype": "float32",
"shape": [4],
"names": ["shoulder", "elbow", "wrist", "gripper"],
},
"observation.images.laptop": {
"dtype": "image",
"shape": [480, 640, 3],
"names": ["height", "width", "channels"],
},
"observation.images.phone": {
"dtype": "image",
"shape": [480, 640, 3],
"names": ["height", "width", "channels"],
},
}
def _create_mock_policy_image_features():
"""Create mock policy image features with different resolutions."""
return {
"observation.images.laptop": PolicyFeature(
type=FeatureType.VISUAL,
shape=(3, 224, 224), # Policy expects smaller resolution
),
"observation.images.phone": PolicyFeature(
type=FeatureType.VISUAL,
shape=(3, 160, 160), # Different resolution for second camera
),
}
def test_prepare_image():
"""Test image preprocessing: int8 → float32, normalization to [0,1]."""
# Create mock int8 image data
image_int8 = torch.randint(0, 256, size=(3, 224, 224), dtype=torch.uint8)
processed = prepare_image(image_int8)
# Check dtype conversion
assert processed.dtype == torch.float32
# Check normalization range
assert processed.min() >= 0.0
assert processed.max() <= 1.0
# Check that values are scaled correctly (255 → 1.0, 0 → 0.0)
if image_int8.max() == 255:
assert torch.isclose(processed.max(), torch.tensor(1.0), atol=1e-6)
if image_int8.min() == 0:
assert torch.isclose(processed.min(), torch.tensor(0.0), atol=1e-6)
# Check memory contiguity
assert processed.is_contiguous()
def test_resize_robot_observation_image():
"""Test image resizing from robot resolution to policy resolution."""
# Create mock image: (H=480, W=640, C=3)
original_image = torch.randint(0, 256, size=(480, 640, 3), dtype=torch.uint8)
target_shape = (3, 224, 224) # (C, H, W)
resized = resize_robot_observation_image(original_image, target_shape)
# Check output shape matches target
assert resized.shape == target_shape
# Check that original image had different dimensions
assert original_image.shape != resized.shape
# Check that resizing preserves value range
assert resized.min() >= 0
assert resized.max() <= 255
def test_prepare_raw_observation():
"""Test the preparation of raw robot observation to lerobot format."""
robot_obs = _create_mock_robot_observation()
lerobot_features = _create_mock_lerobot_features()
policy_image_features = _create_mock_policy_image_features()
prepared = prepare_raw_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features)
# Check that state is properly extracted and batched
assert "observation.state" in prepared
state = prepared["observation.state"]
assert isinstance(state, torch.Tensor)
assert state.shape == (1, 4) # Batched state
# Check that images are processed and resized
assert "observation.images.laptop" in prepared
assert "observation.images.phone" in prepared
laptop_img = prepared["observation.images.laptop"]
phone_img = prepared["observation.images.phone"]
# Check image shapes match policy requirements
assert laptop_img.shape == policy_image_features["observation.images.laptop"].shape
assert phone_img.shape == policy_image_features["observation.images.phone"].shape
# Check that images are tensors
assert isinstance(laptop_img, torch.Tensor)
assert isinstance(phone_img, torch.Tensor)
def test_raw_observation_to_observation_basic():
"""Test the main raw_observation_to_observation function."""
robot_obs = _create_mock_robot_observation()
lerobot_features = _create_mock_lerobot_features()
policy_image_features = _create_mock_policy_image_features()
device = "cpu"
observation = raw_observation_to_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features, device)
# Check that all expected keys are present
assert "observation.state" in observation
assert "observation.images.laptop" in observation
assert "observation.images.phone" in observation
# Check state processing
state = observation["observation.state"]
assert isinstance(state, torch.Tensor)
assert state.device.type == device
assert state.shape == (1, 4) # Batched
# Check image processing
laptop_img = observation["observation.images.laptop"]
phone_img = observation["observation.images.phone"]
# Images should have batch dimension: (B, C, H, W)
assert laptop_img.shape == (1, 3, 224, 224)
assert phone_img.shape == (1, 3, 160, 160)
# Check device placement
assert laptop_img.device.type == device
assert phone_img.device.type == device
# Check image dtype and range (should be float32 in [0, 1])
assert laptop_img.dtype == torch.float32
assert phone_img.dtype == torch.float32
assert laptop_img.min() >= 0.0 and laptop_img.max() <= 1.0
assert phone_img.min() >= 0.0 and phone_img.max() <= 1.0
def test_raw_observation_to_observation_with_non_tensor_data():
"""Test that non-tensor data (like task strings) is preserved."""
robot_obs = _create_mock_robot_observation()
robot_obs["task"] = "pick up the red cube" # Add string instruction
lerobot_features = _create_mock_lerobot_features()
policy_image_features = _create_mock_policy_image_features()
device = "cpu"
observation = raw_observation_to_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features, device)
# Check that task string is preserved
assert "task" in observation
assert observation["task"] == "pick up the red cube"
assert isinstance(observation["task"], str)
@torch.no_grad()
def test_raw_observation_to_observation_device_handling():
"""Test that tensors are properly moved to the specified device."""
device = "mps" if torch.backends.mps.is_available() else "cpu"
robot_obs = _create_mock_robot_observation()
lerobot_features = _create_mock_lerobot_features()
policy_image_features = _create_mock_policy_image_features()
observation = raw_observation_to_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features, device)
# Check that all tensors are on the correct device
for key, value in observation.items():
if isinstance(value, torch.Tensor):
assert value.device.type == device, f"Tensor {key} not on {device}"
def test_raw_observation_to_observation_deterministic():
"""Test that the function produces consistent results for the same input."""
robot_obs = _create_mock_robot_observation()
lerobot_features = _create_mock_lerobot_features()
policy_image_features = _create_mock_policy_image_features()
device = "cpu"
# Run twice with same input
obs1 = raw_observation_to_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features, device)
obs2 = raw_observation_to_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features, device)
# Results should be identical
assert set(obs1.keys()) == set(obs2.keys())
for key in obs1:
if isinstance(obs1[key], torch.Tensor):
torch.testing.assert_close(obs1[key], obs2[key])
else:
assert obs1[key] == obs2[key]
def test_image_processing_pipeline_preserves_content():
"""Test that the image processing pipeline preserves recognizable patterns."""
# Create an image with a specific pattern
original_img = np.zeros((100, 100, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
original_img[25:75, 25:75, :] = 255 # White square in center
robot_obs = {"shoulder": 1.0, "elbow": 1.0, "wrist": 1.0, "gripper": 1.0, "laptop": original_img}
lerobot_features = {
"observation.state": {
"dtype": "float32",
"shape": [4],
"names": ["shoulder", "elbow", "wrist", "gripper"],
},
"observation.images.laptop": {
"dtype": "image",
"shape": [100, 100, 3],
"names": ["height", "width", "channels"],
},
}
policy_image_features = {
"observation.images.laptop": PolicyFeature(
type=FeatureType.VISUAL,
shape=(3, 50, 50), # Downsamples from 100x100
)
}
observation = raw_observation_to_observation(robot_obs, lerobot_features, policy_image_features, "cpu")
processed_img = observation["observation.images.laptop"].squeeze(0) # Remove batch dim
# Check that the center region has higher values than corners
# Due to bilinear interpolation, exact values will change but pattern should remain
center_val = processed_img[:, 25, 25].mean() # Center of 50x50 image
corner_val = processed_img[:, 5, 5].mean() # Corner
assert center_val > corner_val, "Image processing should preserve recognizable patterns"
|
lerobot/tests/async_inference/test_helpers.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/tests/async_inference/test_helpers.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 6275
}
| 221
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import importlib
import gymnasium as gym
import pytest
import torch
from gymnasium.utils.env_checker import check_env
import lerobot
from lerobot.envs.factory import make_env, make_env_config
from lerobot.envs.utils import preprocess_observation
from tests.utils import require_env
OBS_TYPES = ["state", "pixels", "pixels_agent_pos"]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("obs_type", OBS_TYPES)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("env_name, env_task", lerobot.env_task_pairs)
@require_env
def test_env(env_name, env_task, obs_type):
if env_name == "aloha" and obs_type == "state":
pytest.skip("`state` observations not available for aloha")
package_name = f"gym_{env_name}"
importlib.import_module(package_name)
env = gym.make(f"{package_name}/{env_task}", obs_type=obs_type)
check_env(env.unwrapped, skip_render_check=True)
env.close()
@pytest.mark.parametrize("env_name", lerobot.available_envs)
@require_env
def test_factory(env_name):
cfg = make_env_config(env_name)
env = make_env(cfg, n_envs=1)
obs, _ = env.reset()
obs = preprocess_observation(obs)
# test image keys are float32 in range [0,1]
for key in obs:
if "image" not in key:
continue
img = obs[key]
assert img.dtype == torch.float32
# TODO(rcadene): we assume for now that image normalization takes place in the model
assert img.max() <= 1.0
assert img.min() >= 0.0
env.close()
|
lerobot/tests/envs/test_envs.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/tests/envs/test_envs.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 765
}
| 222
|
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import pytest
import torch
from lerobot.constants import (
OPTIMIZER_PARAM_GROUPS,
OPTIMIZER_STATE,
)
from lerobot.optim.optimizers import (
AdamConfig,
AdamWConfig,
MultiAdamConfig,
SGDConfig,
load_optimizer_state,
save_optimizer_state,
)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"config_cls, expected_class",
[
(AdamConfig, torch.optim.Adam),
(AdamWConfig, torch.optim.AdamW),
(SGDConfig, torch.optim.SGD),
(MultiAdamConfig, dict),
],
)
def test_optimizer_build(config_cls, expected_class, model_params):
config = config_cls()
if config_cls == MultiAdamConfig:
params_dict = {"default": model_params}
optimizer = config.build(params_dict)
assert isinstance(optimizer, expected_class)
assert isinstance(optimizer["default"], torch.optim.Adam)
assert optimizer["default"].defaults["lr"] == config.lr
else:
optimizer = config.build(model_params)
assert isinstance(optimizer, expected_class)
assert optimizer.defaults["lr"] == config.lr
def test_save_optimizer_state(optimizer, tmp_path):
save_optimizer_state(optimizer, tmp_path)
assert (tmp_path / OPTIMIZER_STATE).is_file()
assert (tmp_path / OPTIMIZER_PARAM_GROUPS).is_file()
def test_save_and_load_optimizer_state(model_params, optimizer, tmp_path):
save_optimizer_state(optimizer, tmp_path)
loaded_optimizer = AdamConfig().build(model_params)
loaded_optimizer = load_optimizer_state(loaded_optimizer, tmp_path)
torch.testing.assert_close(optimizer.state_dict(), loaded_optimizer.state_dict())
@pytest.fixture
def base_params_dict():
return {
"actor": [torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(10, 10))],
"critic": [torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(5, 5))],
"temperature": [torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3, 3))],
}
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"config_params, expected_values",
[
# Test 1: Basic configuration with different learning rates
(
{
"lr": 1e-3,
"weight_decay": 1e-4,
"optimizer_groups": {
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3},
},
},
{
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.9, 0.999)},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.9, 0.999)},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.9, 0.999)},
},
),
# Test 2: Different weight decays and beta values
(
{
"lr": 1e-3,
"weight_decay": 1e-4,
"optimizer_groups": {
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-5},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-6},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3, "betas": (0.95, 0.999)},
},
},
{
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-5, "betas": (0.9, 0.999)},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-6, "betas": (0.9, 0.999)},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.95, 0.999)},
},
),
# Test 3: Epsilon parameter customization
(
{
"lr": 1e-3,
"weight_decay": 1e-4,
"optimizer_groups": {
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4, "eps": 1e-6},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4, "eps": 1e-7},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3, "eps": 1e-8},
},
},
{
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.9, 0.999), "eps": 1e-6},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.9, 0.999), "eps": 1e-7},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "betas": (0.9, 0.999), "eps": 1e-8},
},
),
],
)
def test_multi_adam_configuration(base_params_dict, config_params, expected_values):
# Create config with the given parameters
config = MultiAdamConfig(**config_params)
optimizers = config.build(base_params_dict)
# Verify optimizer count and keys
assert len(optimizers) == len(expected_values)
assert set(optimizers.keys()) == set(expected_values.keys())
# Check that all optimizers are Adam instances
for opt in optimizers.values():
assert isinstance(opt, torch.optim.Adam)
# Verify hyperparameters for each optimizer
for name, expected in expected_values.items():
optimizer = optimizers[name]
for param, value in expected.items():
assert optimizer.defaults[param] == value
@pytest.fixture
def multi_optimizers(base_params_dict):
config = MultiAdamConfig(
lr=1e-3,
optimizer_groups={
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3},
},
)
return config.build(base_params_dict)
def test_save_multi_optimizer_state(multi_optimizers, tmp_path):
# Save optimizer states
save_optimizer_state(multi_optimizers, tmp_path)
# Verify that directories were created for each optimizer
for name in multi_optimizers:
assert (tmp_path / name).is_dir()
assert (tmp_path / name / OPTIMIZER_STATE).is_file()
assert (tmp_path / name / OPTIMIZER_PARAM_GROUPS).is_file()
def test_save_and_load_multi_optimizer_state(base_params_dict, multi_optimizers, tmp_path):
# Option 1: Add a minimal backward pass to populate optimizer states
for name, params in base_params_dict.items():
if name in multi_optimizers:
# Create a dummy loss and do backward
dummy_loss = params[0].sum()
dummy_loss.backward()
# Perform an optimization step
multi_optimizers[name].step()
# Zero gradients for next steps
multi_optimizers[name].zero_grad()
# Save optimizer states
save_optimizer_state(multi_optimizers, tmp_path)
# Create new optimizers with the same config
config = MultiAdamConfig(
lr=1e-3,
optimizer_groups={
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3},
},
)
new_optimizers = config.build(base_params_dict)
# Load optimizer states
loaded_optimizers = load_optimizer_state(new_optimizers, tmp_path)
# Verify state dictionaries match
for name in multi_optimizers:
torch.testing.assert_close(multi_optimizers[name].state_dict(), loaded_optimizers[name].state_dict())
def test_save_and_load_empty_multi_optimizer_state(base_params_dict, tmp_path):
"""Test saving and loading optimizer states even when the state is empty (no backward pass)."""
# Create config and build optimizers
config = MultiAdamConfig(
lr=1e-3,
optimizer_groups={
"actor": {"lr": 1e-4},
"critic": {"lr": 5e-4},
"temperature": {"lr": 2e-3},
},
)
optimizers = config.build(base_params_dict)
# Save optimizer states without any backward pass (empty state)
save_optimizer_state(optimizers, tmp_path)
# Create new optimizers with the same config
new_optimizers = config.build(base_params_dict)
# Load optimizer states
loaded_optimizers = load_optimizer_state(new_optimizers, tmp_path)
# Verify hyperparameters match even with empty state
for name, optimizer in optimizers.items():
assert optimizer.defaults["lr"] == loaded_optimizers[name].defaults["lr"]
assert optimizer.defaults["weight_decay"] == loaded_optimizers[name].defaults["weight_decay"]
assert optimizer.defaults["betas"] == loaded_optimizers[name].defaults["betas"]
# Verify state dictionaries match (they will be empty)
torch.testing.assert_close(
optimizer.state_dict()["param_groups"], loaded_optimizers[name].state_dict()["param_groups"]
)
|
lerobot/tests/optim/test_optimizers.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/tests/optim/test_optimizers.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 3922
}
| 223
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from lerobot.calibrate import CalibrateConfig, calibrate
from lerobot.record import DatasetRecordConfig, RecordConfig, record
from lerobot.replay import DatasetReplayConfig, ReplayConfig, replay
from lerobot.teleoperate import TeleoperateConfig, teleoperate
from tests.fixtures.constants import DUMMY_REPO_ID
from tests.mocks.mock_robot import MockRobotConfig
from tests.mocks.mock_teleop import MockTeleopConfig
def test_calibrate():
robot_cfg = MockRobotConfig()
cfg = CalibrateConfig(robot=robot_cfg)
calibrate(cfg)
def test_teleoperate():
robot_cfg = MockRobotConfig()
teleop_cfg = MockTeleopConfig()
cfg = TeleoperateConfig(
robot=robot_cfg,
teleop=teleop_cfg,
teleop_time_s=0.1,
)
teleoperate(cfg)
def test_record_and_resume(tmp_path):
robot_cfg = MockRobotConfig()
teleop_cfg = MockTeleopConfig()
dataset_cfg = DatasetRecordConfig(
repo_id=DUMMY_REPO_ID,
single_task="Dummy task",
root=tmp_path / "record",
num_episodes=1,
episode_time_s=0.1,
reset_time_s=0,
push_to_hub=False,
)
cfg = RecordConfig(
robot=robot_cfg,
dataset=dataset_cfg,
teleop=teleop_cfg,
play_sounds=False,
)
dataset = record(cfg)
assert dataset.fps == 30
assert dataset.meta.total_episodes == dataset.num_episodes == 1
assert dataset.meta.total_frames == dataset.num_frames == 3
assert dataset.meta.total_tasks == 1
cfg.resume = True
dataset = record(cfg)
assert dataset.meta.total_episodes == dataset.num_episodes == 2
assert dataset.meta.total_frames == dataset.num_frames == 6
assert dataset.meta.total_tasks == 1
def test_record_and_replay(tmp_path):
robot_cfg = MockRobotConfig()
teleop_cfg = MockTeleopConfig()
record_dataset_cfg = DatasetRecordConfig(
repo_id=DUMMY_REPO_ID,
single_task="Dummy task",
root=tmp_path / "record_and_replay",
num_episodes=1,
episode_time_s=0.1,
push_to_hub=False,
)
record_cfg = RecordConfig(
robot=robot_cfg,
dataset=record_dataset_cfg,
teleop=teleop_cfg,
play_sounds=False,
)
replay_dataset_cfg = DatasetReplayConfig(
repo_id=DUMMY_REPO_ID,
episode=0,
root=tmp_path / "record_and_replay",
)
replay_cfg = ReplayConfig(
robot=robot_cfg,
dataset=replay_dataset_cfg,
play_sounds=False,
)
record(record_cfg)
replay(replay_cfg)
|
lerobot/tests/test_control_robot.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "lerobot/tests/test_control_robot.py",
"repo_id": "lerobot",
"token_count": 1294
}
| 224
|
# Config for 16 nodes of 8 H100s with FSDP1
# Model arguments
model_name_or_path: Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct
model_revision: main
torch_dtype: bfloat16
attn_implementation: flash_attention_2
# Data training arguments
dataset_name: open-r1/codeforces-cots
dataset_config: solutions_decontaminated
dataset_num_proc: 12
# SFT trainer config
bf16: true
do_eval: false
eval_strategy: 'no'
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
gradient_checkpointing: true
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs:
use_reentrant: false
hub_always_push: true
hub_model_id: OlympicCoder-32B
hub_strategy: every_save
learning_rate: 4.0e-05
log_level: info
logging_steps: 1
logging_strategy: steps
lr_scheduler_type: cosine_with_min_lr
lr_scheduler_kwargs:
min_lr_rate: 0.1
packing: false
max_grad_norm: 0.2
max_length: 22528 # we were unable to train at 32k due to OOM. See https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/35983 for context parallelism support.
max_steps: -1
num_train_epochs: 10
optim: paged_adamw_8bit
output_dir: data/OlympicCoder-32B
overwrite_output_dir: true
per_device_eval_batch_size: 1
per_device_train_batch_size: 1
push_to_hub: true
report_to:
- wandb
save_only_model: true # needed to bypass FSDP errors with saving paged optimizers
save_strategy: epoch
save_total_limit: 1
seed: 42
use_liger_kernel: false # fails on multi-node
warmup_ratio: 0.03
|
open-r1/recipes/OlympicCoder-32B/sft/config_v00.00.yaml/0
|
{
"file_path": "open-r1/recipes/OlympicCoder-32B/sft/config_v00.00.yaml",
"repo_id": "open-r1",
"token_count": 505
}
| 225
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""
This script is used to decontaminate a dataset by checking for n-gram overlap with other datasets.
It uses the same approach presented in https://huggingface.co/papers/2501.19393,
as found in: https://github.com/simplescaling/s1/blob/main/data/decontaminate_util.py
Usage:
python scripts/decontaminate.py \
--dataset open-r1/verifiable-coding-problems-python \
--split train \
--ngram_size 8 \
--problem_column problem \
--cleanup
"""
import collections
from tqdm import tqdm
def normalize_string(text: str) -> str:
"""Basic string normalization."""
# Convert to lowercase and normalize whitespace
text = text.lower().strip()
# Replace multiple spaces with single space
text = " ".join(text.split())
return text
def word_ngrams(text: str, n: int) -> list:
"""Generate word-level n-grams from text."""
words = text.split()
return [" ".join(words[i : i + n]) for i in range(len(words) - n + 1)]
def build_ngram_lookup(documents: list[str], ngram_size: int = 8) -> dict[str, set[int]]:
"""Build ngram lookup for documents."""
lookup = collections.defaultdict(set)
for doc_id, document in enumerate(tqdm(documents)):
normalized_text = normalize_string(document)
ngrams = word_ngrams(normalized_text, ngram_size)
for ngram in ngrams:
lookup[ngram].add(doc_id)
return lookup
def build_ngram_single(document: str, ngram_size: int = 8) -> set[str]:
normalized_text = normalize_string(document)
ngrams = word_ngrams(normalized_text, ngram_size)
return set(ngrams)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--dataset", type=str, required=True, help="Name of the dataset to check for contamination.")
parser.add_argument("--config", type=str, default=None, help="Name of the dataset config to load.")
parser.add_argument("--split", type=str, default="train", help="Split to check for contamination, defaults to `train`.")
parser.add_argument("--ngram_size", type=int, default=8, help="Size of n-grams to build, defaults to 8.")
parser.add_argument(
"--problem_column", type=str, default="problem", help="Name of the column containing the problem (prompt)."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--cleanup",
action="store_true",
help="Whether to remove the contaminated rows before pushing the dataset.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--new_dataset_name",
type=str,
default=None,
help="New name for the dataset. If not provided, will reuse the name and add a `_decontaminated` to the name."
)
args = parser.parse_args()
from datasets import load_dataset, Dataset
# Load the dataset to check for contamination
ds = load_dataset(args.dataset, name=args.config, split=args.split)
eval_datasets = {
"aime_2024": (load_dataset("HuggingFaceH4/aime_2024", split="train"), "problem"),
"aime_2025": (load_dataset("yentinglin/aime_2025", split="train"), "problem"),
"math_500": (load_dataset("HuggingFaceH4/MATH-500", split="test"), "problem"),
"gpqa": (load_dataset("Idavidrein/gpqa", "gpqa_diamond", split="train", trust_remote_code=True), "Question"),
"lcb": (
load_dataset(
"livecodebench/code_generation_lite", split="test", version_tag="v4_v5", trust_remote_code=True
),
"question_content",
),
}
ngram_lookups = {}
for ds_name, (eval_dataset, problem_col) in eval_datasets.items():
ngram_lookups[ds_name] = build_ngram_lookup(eval_dataset[problem_col], ngram_size=args.ngram_size)
for eval_name, ngram_lookup in ngram_lookups.items():
# Update the ngram_lookup variable for each dataset
def find_contaminated(row):
# For each example we have to build the ngrams and check for all of them on each row
ngrams = build_ngram_single(row[args.problem_column], ngram_size=args.ngram_size)
row[f"contaminated_{eval_name}"] = any(set(ngram in ngram_lookup for ngram in ngrams))
return row
ds = ds.map(find_contaminated, num_proc=8)
# Allow cleaning up via CLI args (removing the contaminated examples and dropping the columns)
def cleanup(dataset: Dataset) -> Dataset:
initial_size = len(dataset)
contamination_cols = [col for col in dataset.column_names if col.startswith("contaminated_")]
for col in contamination_cols:
if col.startswith("contaminated_"):
size_prior = len(dataset)
dataset = dataset.filter(lambda x: not x[col], num_proc=8)
if len(dataset) < size_prior:
print(f"Removed {size_prior - len(dataset)} samples from '{col.replace('contaminated_', '')}'")
dataset = dataset.remove_columns(contamination_cols)
print(f"Initial size: {initial_size}, Final size: {len(dataset)}")
return dataset
if args.cleanup:
ds = cleanup(ds)
new_ds_name = args.new_dataset_name or f"{args.dataset}_decontaminated"
config_name = args.config if args.config is not None else "default"
url = ds.push_to_hub(new_ds_name, config_name=config_name, split="train")
print(f"Decontaminated dataset: {url}")
|
open-r1/scripts/decontaminate.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "open-r1/scripts/decontaminate.py",
"repo_id": "open-r1",
"token_count": 2308
}
| 226
|
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=r1-vllm
#SBATCH --partition=hopper-prod
#SBATCH --qos=normal
#SBATCH --nodes=4
#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=8
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --output=./logs/%x_%j_%n.out
#SBATCH --error=./logs/%x_%j_%n.err
#SBATCH --time=7-00:00:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1
set -exuo pipefail
MODEL_PATH="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1"
CONDA_ENV="vllm7"
SERVER_PORT=8000
RAY_PORT=6379
RAY_DASHBOARD_PORT=8265
while getopts "m:e:h" opt; do
case $opt in
m) MODEL_PATH="$OPTARG" ;;
e) CONDA_ENV="$OPTARG" ;;
h|?) echo "Usage: sbatch $0 [-m MODEL_PATH] [-e CONDA_ENV]"; exit 1 ;;
esac
done
# Environment setup
module load cuda/12.1
source ~/.bashrc
source "$CONDA_PREFIX/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "$CONDA_ENV" || { echo "Failed to activate conda env $CONDA_ENV"; exit 1; }
# Get nodes information
NODES=($(scontrol show hostnames "$SLURM_JOB_NODELIST"))
HEAD_NODE="${NODES[0]}"
HEAD_NODE_IP=$(srun --nodes=1 --ntasks=1 -w "$HEAD_NODE" hostname --ip-address)
echo "SLURM_JOB_ID: $SLURM_JOB_ID"
echo "SLURM_JOB_NODELIST: $SLURM_JOB_NODELIST"
echo "Head node: $HEAD_NODE ($HEAD_NODE_IP)"
# Start Ray head node
echo "Starting Ray head node at $HEAD_NODE"
srun --nodes=1 --ntasks=1 -w "$HEAD_NODE" \
ray start --head \
--node-ip-address="$HEAD_NODE_IP" \
--port=$RAY_PORT \
--dashboard-host=0.0.0.0 \
--dashboard-port=$RAY_DASHBOARD_PORT \
--block &
sleep 10
# Start Ray worker nodes
WORKER_COUNT=$((SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES - 1))
for ((i = 1; i <= WORKER_COUNT; i++)); do
WORKER_NODE="${NODES[$i]}"
echo "Starting Ray worker $i at $WORKER_NODE"
srun --nodes=1 --ntasks=1 -w "$WORKER_NODE" \
ray start --address "$HEAD_NODE_IP:$RAY_PORT" \
--block &
sleep 5
done
echo "Waiting for Ray cluster to initialize..."
sleep 60
# Start vLLM server
echo "Starting vLLM server..."
RAY_ADDRESS="http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$RAY_DASHBOARD_PORT" ray job submit \
--working-dir src/open_r1 \
--no-wait \
--job-id vllm-server \
-- vllm serve "$MODEL_PATH" \
--tensor-parallel-size 8 \
--pipeline-parallel-size 4 \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.90 \
--max-model-len 32768 \
--max-num-batched-tokens 262144 \
--max-num-seqs 128 \
--max-seq-len-to-capture 32768 \
--enable-chunked-prefill true \
--preemption-mode recompute \
--swap-space 128 \
--trust-remote-code \
--distributed-executor-backend ray
# Wait for server with timeout
TIMEOUT=3600 # 1h
START_TIME=$(date +%s)
echo "Waiting for vLLM server (http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$SERVER_PORT)..."
while true; do
if curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" "http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$SERVER_PORT/health" >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "Server is ready at http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$SERVER_PORT"
break
fi
CURRENT_TIME=$(date +%s)
if [ $((CURRENT_TIME - START_TIME)) -gt $TIMEOUT ]; then
echo "Error: Server failed to start within $TIMEOUT seconds"
exit 1
fi
echo "Still waiting... ($(($CURRENT_TIME - $START_TIME)) seconds elapsed)"
sleep 60
done
echo "Checking available models..."
curl "http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$SERVER_PORT/v1/models"
sleep 10
echo "Executing sanity check..."
curl "http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$SERVER_PORT/v1/completions" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"model\": \"default\",
\"prompt\": \"<|begin▁of▁sentence|><|User|>hi, how are you?<|Assistant|>\",
\"max_tokens\": 2048,
\"temperature\": 0.6
}"
# Keep the job running with health checks
while true; do
if ! curl -s -o /dev/null "http://$HEAD_NODE_IP:$SERVER_PORT/health"; then
echo "Error: Server health check failed"
exit 1
fi
sleep 300
done
|
open-r1/slurm/experimental/serve_r1_vllm.slurm/0
|
{
"file_path": "open-r1/slurm/experimental/serve_r1_vllm.slurm",
"repo_id": "open-r1",
"token_count": 1729
}
| 227
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import subprocess
from typing import List
from transformers import TrainerCallback
from transformers.trainer_callback import TrainerControl, TrainerState
from transformers.training_args import TrainingArguments
from .evaluation import run_benchmark_jobs
from .hub import push_to_hub_revision
def is_slurm_available() -> bool:
# returns true if a slurm queueing system is available
try:
subprocess.run(["sinfo"], check=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
return True
except FileNotFoundError:
return False
class DummyConfig:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
for k, v in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, k, v)
class PushToHubRevisionCallback(TrainerCallback):
def __init__(self, model_config) -> None:
self.model_config = model_config
def on_save(
self,
args: TrainingArguments,
state: TrainerState,
control: TrainerControl,
**kwargs,
):
if state.is_world_process_zero:
global_step = state.global_step
# WARNING: if you use dataclasses.replace(args, ...) the accelerator dist state will be broken, so I do this workaround
# Also if you instantiate a new SFTConfig, the accelerator dist state will be broken
dummy_config = DummyConfig(
hub_model_id=args.hub_model_id,
hub_model_revision=f"{args.hub_model_revision}-step-{global_step:09d}",
output_dir=f"{args.output_dir}/checkpoint-{global_step}",
system_prompt=args.system_prompt,
)
future = push_to_hub_revision(
dummy_config, extra_ignore_patterns=["*.pt"]
) # don't push the optimizer states
if is_slurm_available():
dummy_config.benchmarks = args.benchmarks
def run_benchmark_callback(_):
print(f"Checkpoint {global_step} pushed to hub.")
run_benchmark_jobs(dummy_config, self.model_config)
future.add_done_callback(run_benchmark_callback)
CALLBACKS = {
"push_to_hub_revision": PushToHubRevisionCallback,
}
def get_callbacks(train_config, model_config) -> List[TrainerCallback]:
callbacks = []
for callback_name in train_config.callbacks:
if callback_name not in CALLBACKS:
raise ValueError(f"Callback {callback_name} not found in CALLBACKS.")
callbacks.append(CALLBACKS[callback_name](model_config))
return callbacks
|
open-r1/src/open_r1/utils/callbacks.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "open-r1/src/open_r1/utils/callbacks.py",
"repo_id": "open-r1",
"token_count": 1242
}
| 228
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from typing import List, Optional
import requests
from e2b_code_interpreter.models import Execution, ExecutionError, Result
class RoutedSandbox:
"""
A sandbox environment that routes code execution requests to the E2B Router.
This class is designed for batched execution of scripts, primarily for Python code.
It mimics the usage of 'Sandbox' from 'e2b_code_interpreter', but adds support for batch processing.
Attributes:
router_url (str): The URL of the E2B Router to which code execution requests are sent.
"""
def __init__(self, router_url: str):
"""
Initializes the RoutedSandbox with the specified router URL.
Args:
router_url (str): The URL of the E2B Router.
"""
self.router_url = router_url
def run_code(
self,
scripts: list[str],
languages: Optional[List[str]] = None,
timeout: Optional[int] = None,
request_timeout: Optional[int] = None,
) -> list[Execution]:
"""
Executes a batch of scripts in the sandbox environment.
Args:
scripts (list[str]): A list of code scripts to execute.
languages (list[str], optional): List of programming languages for each script. If None, defaults to Python for all scripts.
timeout (Optional[int], optional): The maximum execution time for each script in seconds. Defaults to 300 seconds.
request_timeout (Optional[int], optional): The timeout for the HTTP request in seconds. Defaults to 30 seconds.
Returns:
list[Execution]: A list of Execution objects containing the results, logs, and errors (if any) for each script.
"""
# Set default values for timeouts if not provided
if timeout is None:
timeout = 300 # Default to 5 minutes
if request_timeout is None:
request_timeout = 30 # Default to 30 seconds
# Default to Python for all scripts if languages is not provided
if languages is None:
languages = ["python"] * len(scripts)
# Prepare the payload for the HTTP POST request
payload = {
"scripts": scripts,
"languages": languages,
"timeout": timeout,
"request_timeout": request_timeout,
}
# Send the request to the E2B Router
response = requests.post(f"http://{self.router_url}/execute_batch", json=payload)
if not response.ok:
print(f"Request failed with status code: {response.status_code}")
# Parse the response and construct Execution objects
results = response.json()
output = []
for result in results:
if result["execution"] is None:
# If execution is None, create an empty Execution object
# This can happen when a script times out or fails to execute
execution = Execution()
else:
execution = Execution(
results=[Result(**r) for r in result["execution"]["results"]],
logs=result["execution"]["logs"],
error=(ExecutionError(**result["execution"]["error"]) if result["execution"]["error"] else None),
execution_count=result["execution"]["execution_count"],
)
output.append(execution)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
# for local testing launch an E2B router with: python scripts/e2b_router.py
sbx = RoutedSandbox(router_url="0.0.0.0:8000")
codes = ["print('hello world')", "print('hello world)"]
executions = sbx.run_code(codes) # Execute Python inside the sandbox
print(executions)
|
open-r1/src/open_r1/utils/routed_sandbox.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "open-r1/src/open_r1/utils/routed_sandbox.py",
"repo_id": "open-r1",
"token_count": 1629
}
| 229
|
# docstyle-ignore
INSTALL_CONTENT = """
# PEFT installation
! pip install peft accelerate transformers
# To install from source instead of the last release, comment the command above and uncomment the following one.
# ! pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
"""
|
peft/docs/source/_config.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/docs/source/_config.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 75
}
| 230
|
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# torch.compile
In PEFT, [torch.compile](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) works for some but not all features. The reason why it won't always work is because PEFT is highly dynamic in certain places (loading and switching between multiple adapters, for instance), which can cause trouble for `torch.compile`. In other places, `torch.compile` may work, but won't be as fast as expected because of graph breaks.
If you don't see an error, it doesn't necessarily mean that `torch.compile` worked correctly. It might give you an output, but the output is incorrect. This guide describes what works with `torch.compile` and what doesn't. For your own testing, we recommend using the latest PyTorch version, as `torch.compile` is constantly being improved.
> [!TIP]
> Unless indicated otherwise, the default `torch.compile` settings were used.
## Training and inference with `torch.compile`
These features **work** with `torch.compile`. Everything listed below was tested with a causal LM:
- Training with `Trainer` from 🤗 transformers
- Training with a custom PyTorch loop
- Inference
- Generation
The following adapters were tested successfully:
- AdaLoRA
- BOFT
- Bone
- IA³
- Layer Norm Tuning
- LoHa
- LoKr
- LoRA
- LoRA + DoRA
- LoRA applied to embedding layers
- OFT
- VeRA
- HRA
## Advanced PEFT features with `torch.compile`
Below are some of the more advanced PEFT features that **work**. They were all tested with LoRA.
- `modules_to_save` (i.e. `config = LoraConfig(..., modules_to_save=...)`)
- Merging adapters (one or multiple)
- Merging multiple adapters into one adapter (i.e. calling `model.add_weighted_adapter(...)`)
- Using PEFT adapters with quantization (bitsandbytes)
- Disabling adapters (i.e. using `with model.disable_adapter()`)
- Unloading (i.e. calling `model.merge_and_unload()`)
- Mixed adapter batches (i.e. calling `model(batch, adapter_names=["__base__", "default", "other", ...])`)
- Inference with multiple adapters (i.e. using `model.add_adapter` or `model.load_adapter` to load more than 1 adapter); for this, only call `torch.compile` _after_ loading all adapters
Generally, we can expect that if a feature works correctly with LoRA and is also supported by other adapter types, it should also work for that adapter type.
## Test cases
All the use cases listed above are tested inside of [`peft/tests/test_torch_compile.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/tests/test_torch_compile.py). If you want to check in more detail how we tested a certain feature, please go to that file and check the test that corresponds to your use case.
> [!TIP]
> If you have another use case where you know that `torch.compile` does or does not work with PEFT, please contribute by letting us know or by opening a PR to add this use case to the covered test cases.
|
peft/docs/source/developer_guides/torch_compile.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/docs/source/developer_guides/torch_compile.md",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 1014
}
| 231
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# The implementation is based on "Parameter-Efficient Orthogonal Finetuning
# via Butterfly Factorization" (https://huggingface.co/papers/2311.06243) in ICLR 2024.
import glob
import os
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import face_alignment
import numpy as np
import torch
from accelerate import Accelerator
from skimage.io import imread
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from tqdm import tqdm
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from utils.args_loader import parse_args
from utils.dataset import make_dataset
# Determine the best available device
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda:0"
else:
# TODO: xpu support in facealignment will be ready after this PR is merged:https://github.com/1adrianb/face-alignment/pull/371
device = "cpu"
detect_model = face_alignment.FaceAlignment(face_alignment.LandmarksType.TWO_D, device=device, flip_input=False)
# with open('./data/celebhq-text/prompt_val_blip_full.json', 'rt') as f: # fill50k, COCO
# for line in f:
# val_data = json.loads(line)
end_list = np.array([17, 22, 27, 42, 48, 31, 36, 68], dtype=np.int32) - 1
def count_txt_files(directory):
pattern = os.path.join(directory, "*.txt")
txt_files = glob.glob(pattern)
return len(txt_files)
def plot_kpts(image, kpts, color="g"):
"""Draw 68 key points
Args:
image: the input image
kpt: (68, 3).
"""
if color == "r":
c = (255, 0, 0)
elif color == "g":
c = (0, 255, 0)
elif color == "b":
c = (255, 0, 0)
image = image.copy()
kpts = kpts.copy()
radius = max(int(min(image.shape[0], image.shape[1]) / 200), 1)
for i in range(kpts.shape[0]):
st = kpts[i, :2]
if kpts.shape[1] == 4:
if kpts[i, 3] > 0.5:
c = (0, 255, 0)
else:
c = (0, 0, 255)
image = cv2.circle(image, (int(st[0]), int(st[1])), radius, c, radius * 2)
if i in end_list:
continue
ed = kpts[i + 1, :2]
image = cv2.line(image, (int(st[0]), int(st[1])), (int(ed[0]), int(ed[1])), (255, 255, 255), radius)
return image
def generate_landmark2d(dataset, input_dir, pred_lmk_dir, gt_lmk_dir, vis=False):
print("Generate 2d landmarks ...")
os.makedirs(pred_lmk_dir, exist_ok=True)
imagepath_list = sorted(glob.glob(f"{input_dir}/pred*.png"))
for imagepath in tqdm(imagepath_list):
name = Path(imagepath).stem
idx = int(name.split("_")[-1])
pred_txt_path = os.path.join(pred_lmk_dir, f"{idx}.txt")
gt_lmk_path = os.path.join(gt_lmk_dir, f"{idx}_gt_lmk.jpg")
gt_txt_path = os.path.join(gt_lmk_dir, f"{idx}.txt")
gt_img_path = os.path.join(gt_lmk_dir, f"{idx}_gt_img.jpg")
if (not os.path.exists(pred_txt_path)) or (not os.path.exists(gt_txt_path)):
image = imread(imagepath) # [:, :, :3]
out = detect_model.get_landmarks(image)
if out is None:
continue
pred_kpt = out[0].squeeze()
np.savetxt(pred_txt_path, pred_kpt)
# Your existing code for obtaining the image tensor
gt_lmk_img = dataset[idx]["conditioning_pixel_values"]
save_image(gt_lmk_img, gt_lmk_path)
gt_img = (dataset[idx]["pixel_values"]) * 0.5 + 0.5
save_image(gt_img, gt_img_path)
gt_img = (gt_img.permute(1, 2, 0) * 255).type(torch.uint8).cpu().numpy()
out = detect_model.get_landmarks(gt_img)
if out is None:
continue
gt_kpt = out[0].squeeze()
np.savetxt(gt_txt_path, gt_kpt)
# gt_image = cv2.resize(cv2.imread(gt_lmk_path), (512, 512))
if vis:
gt_lmk_image = cv2.imread(gt_lmk_path)
# visualize predicted landmarks
vis_path = os.path.join(pred_lmk_dir, f"{idx}_overlay.jpg")
image = cv2.imread(imagepath)
image_point = plot_kpts(image, pred_kpt)
cv2.imwrite(vis_path, np.concatenate([image_point, gt_lmk_image], axis=1))
# visualize gt landmarks
vis_path = os.path.join(gt_lmk_dir, f"{idx}_overlay.jpg")
image = cv2.imread(gt_img_path)
image_point = plot_kpts(image, gt_kpt)
cv2.imwrite(vis_path, np.concatenate([image_point, gt_lmk_image], axis=1))
def landmark_comparison(val_dataset, lmk_dir, gt_lmk_dir):
print("Calculating reprojection error")
lmk_err = []
pbar = tqdm(range(len(val_dataset)))
for i in pbar:
# line = val_dataset[i]
# img_name = line["image"].split(".")[0]
lmk1_path = os.path.join(gt_lmk_dir, f"{i}.txt")
lmk1 = np.loadtxt(lmk1_path)
lmk2_path = os.path.join(lmk_dir, f"{i}.txt")
if not os.path.exists(lmk2_path):
print(f"{lmk2_path} not exist")
continue
lmk2 = np.loadtxt(lmk2_path)
lmk_err.append(np.mean(np.linalg.norm(lmk1 - lmk2, axis=1)))
pbar.set_description(f"lmk_err: {np.mean(lmk_err):.5f}")
print("Reprojection error:", np.mean(lmk_err))
np.save(os.path.join(lmk_dir, "lmk_err.npy"), lmk_err)
def main(args):
logging_dir = Path(args.output_dir, args.logging_dir)
accelerator = Accelerator(
gradient_accumulation_steps=args.gradient_accumulation_steps,
mixed_precision=args.mixed_precision,
log_with=args.report_to,
project_dir=logging_dir,
)
# Load the tokenizer
if args.tokenizer_name:
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.tokenizer_name, revision=args.revision, use_fast=False)
elif args.pretrained_model_name_or_path:
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path,
subfolder="tokenizer",
revision=args.revision,
use_fast=False,
)
val_dataset = make_dataset(args, tokenizer, accelerator, "test")
gt_lmk_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, "gt_lmk")
if not os.path.exists(gt_lmk_dir):
os.makedirs(gt_lmk_dir, exist_ok=True)
pred_lmk_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, "pred_lmk")
if not os.path.exists(pred_lmk_dir):
os.makedirs(pred_lmk_dir, exist_ok=True)
input_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, "results")
generate_landmark2d(val_dataset, input_dir, pred_lmk_dir, gt_lmk_dir, args.vis_overlays)
if count_txt_files(pred_lmk_dir) == len(val_dataset) and count_txt_files(gt_lmk_dir) == len(val_dataset):
landmark_comparison(val_dataset, pred_lmk_dir, gt_lmk_dir)
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parse_args()
main(args)
|
peft/examples/boft_controlnet/eval.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/boft_controlnet/eval.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 3474
}
| 232
|
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
-->
# DreamBooth fine-tuning with BOFT
This guide demonstrates how to use BOFT, an orthogonal fine-tuning method, to fine-tune Dreambooth with either `stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1` or `runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5` model.
By using BOFT from 🤗 PEFT, we can significantly reduce the number of trainable parameters while still achieving impressive results in various fine-tuning tasks across different foundation models. BOFT enhances model efficiency by integrating full-rank orthogonal matrices with a butterfly structure into specific model blocks, such as attention blocks, mirroring the approach used in LoRA. During fine-tuning, only these inserted matrices are trained, leaving the original model parameters untouched. During inference, the trainable BOFT parameters can be merged into the original model, eliminating any additional computational costs.
As a member of the **orthogonal finetuning** class, BOFT presents a systematic and principled method for fine-tuning. It possesses several unique properties and has demonstrated superior performance compared to LoRA in a variety of scenarios. For further details on BOFT, please consult the [PEFT's GitHub repo's concept guide OFT](https://https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/index), the [original BOFT paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2311.06243) and the [original OFT paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2306.07280).
In this guide we provide a Dreambooth fine-tuning script that is available in [PEFT's GitHub repo examples](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/tree/main/examples/boft_dreambooth). This implementation is adapted from [peft's lora_dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/tree/main/examples/lora_dreambooth). You can try it out and finetune on your custom images.
## Set up your environment
Start by cloning the PEFT repository:
```bash
git clone --recursive https://github.com/huggingface/peft
```
Navigate to the directory containing the training scripts for fine-tuning Dreambooth with BOFT:
```bash
cd peft/examples/boft_dreambooth
```
Set up your environment: install PEFT, and all the required libraries. At the time of writing this guide we recommend installing PEFT from source. The following environment setup should work on A100 and H100:
### CUDA
```bash
conda create --name peft python=3.10
conda activate peft
conda install pytorch==2.1.2 torchvision==0.16.2 torchaudio==2.1.2 pytorch-cuda=11.8 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install xformers -c xformers
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
```
The follwing environment setuo is validated work on Intel XPU:
### Intel XPU
```bash
conda create --name peft python=3.10
conda activate peft
pip install pip install torch==2.8.0.dev20250615+xpu torchvision==0.23.0.dev20250615+xpu torchaudio==2.8.0.dev20250615+xpu --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/xpu --no-cache-dir
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
```
## Download the data
[dreambooth](https://github.com/google/dreambooth) dataset should have been automatically cloned in the following structure when running the training script.
```
boft_dreambooth
├── data
│ ├── data_dir
│ └── dreambooth
│ └── data
│ ├── backpack
│ └── backpack_dog
│ ...
```
You can also put your custom images into `boft_dreambooth/data/dreambooth`.
## Finetune Dreambooth with BOFT
```bash
./train_dreambooth.sh
```
or using the following script arguments:
```bash
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
export CLASS_DIR="path-to-class-images"
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
```
Here:
- `INSTANCE_DIR`: The directory containing the images that you intend to use for training your model.
- `CLASS_DIR`: The directory containing class-specific images. In this example, we use prior preservation to avoid overfitting and language-drift. For prior preservation, you need other images of the same class as part of the training process. However, these images can be generated and the training script will save them to a local path you specify here.
- `OUTPUT_DIR`: The destination folder for storing the trained model's weights.
To learn more about DreamBooth fine-tuning with prior-preserving loss, check out the [Diffusers documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/training/dreambooth#finetuning-with-priorpreserving-loss).
Launch the training script with `accelerate` and pass hyperparameters, as well as LoRa-specific arguments to it such as:
- `use_boft`: Enables BOFT in the training script.
- `boft_block_size`: the BOFT matrix block size across different layers, expressed in `int`. Smaller block size results in sparser update matrices with fewer trainable parameters. **Note**, please choose it to be dividable to most layer `in_features` dimension, e.g., 4, 8, 16. Also, you can only specify either `boft_block_size` or `boft_block_num`, but not both simultaneously, because `boft_block_size` x `boft_block_num` = layer dimension.
- `boft_block_num`: the number of BOFT matrix blocks across different layers, expressed in `int`. Fewer blocks result in sparser update matrices with fewer trainable parameters. **Note**, please choose it to be dividable to most layer `in_features` dimension, e.g., 4, 8, 16. Also, you can only specify either `boft_block_size` or `boft_block_num`, but not both simultaneously, because `boft_block_size` x `boft_block_num` = layer dimension.
- `boft_n_butterfly_factor`: the number of butterfly factors. **Note**, for `boft_n_butterfly_factor=1`, BOFT is the same as vanilla OFT, for `boft_n_butterfly_factor=2`, the effective block size of OFT becomes twice as big and the number of blocks becomes half.
- `bias`: specify if the `bias` parameters should be trained. Can be `none`, `all` or `boft_only`.
- `boft_dropout`: specify the probability of multiplicative dropout.
Here's what the full set of script arguments may look like:
```bash
PEFT_TYPE="boft"
BLOCK_NUM=8
BLOCK_SIZE=0
N_BUTTERFLY_FACTOR=1
VALIDATION_PROMPT=${PROMPT_LIST[@]}
INSTANCE_PROMPT="a photo of ${UNIQUE_TOKEN} ${CLASS_TOKEN}"
CLASS_PROMPT="a photo of ${CLASS_TOKEN}"
export MODEL_NAME="stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1"
# export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
export PROJECT_NAME="dreambooth_${PEFT_TYPE}"
export RUN_NAME="${SELECTED_SUBJECT}_${PEFT_TYPE}_${BLOCK_NUM}${BLOCK_SIZE}${N_BUTTERFLY_FACTOR}"
export INSTANCE_DIR="./data/dreambooth/dataset/${SELECTED_SUBJECT}"
export CLASS_DIR="./data/class_data/${CLASS_TOKEN}"
export OUTPUT_DIR="./data/output/${PEFT_TYPE}"
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
--class_data_dir="$CLASS_DIR" \
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
--wandb_project_name=$PROJECT_NAME \
--wandb_run_name=$RUN_NAME \
--with_prior_preservation --prior_loss_weight=1.0 \
--instance_prompt="$INSTANCE_PROMPT" \
--validation_prompt="$VALIDATION_PROMPT" \
--class_prompt="$CLASS_PROMPT" \
--resolution=512 \
--train_batch_size=1 \
--num_dataloader_workers=2 \
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
--num_class_images=200 \
--use_boft \
--boft_block_num=$BLOCK_NUM \
--boft_block_size=$BLOCK_SIZE \
--boft_n_butterfly_factor=$N_BUTTERFLY_FACTOR \
--boft_dropout=0.1 \
--boft_bias="boft_only" \
--learning_rate=3e-5 \
--max_train_steps=1010 \
--checkpointing_steps=200 \
--validation_steps=200 \
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention \
--report_to="wandb" \
```
or use this training script:
```bash
./train_dreambooth.sh $idx
```
with the `$idx` corresponds to different subjects.
If you are running this script on Windows, you may need to set the `--num_dataloader_workers` to 0.
## Inference with a single adapter
To run inference with the fine-tuned model, simply run the jupyter notebook `dreambooth_inference.ipynb` for visualization with `jupyter notebook` under `./examples/boft_dreambooth`.
|
peft/examples/boft_dreambooth/boft_dreambooth.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/boft_dreambooth/boft_dreambooth.md",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 2789
}
| 233
|
# Copyright 2024-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import torch
from datautils import get_calib_data
from tqdm import tqdm
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from peft import get_peft_model
from peft.tuners.lora.config import CordaConfig, LoraConfig
from peft.tuners.lora.corda import preprocess_corda
@torch.no_grad()
def run_model(model, calib_loader):
model.eval()
for batch in tqdm(calib_loader):
batch = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in batch.items()}
model(**batch)
def main(args):
# Setting random seed of numpy and torch
np.random.seed(args.seed)
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(args.seed)
elif torch.xpu.is_available():
torch.xpu.manual_seed_all(args.seed)
torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
# Load model
model_id = args.model_id
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_id, device_map="auto", torch_dtype=torch.float16, trust_remote_code=True
)
# Collect data
calib_loader = get_calib_data(args.calib_dataset, tokenizer, model_id, args.calib_loader_size, seed=args.seed)
# Evaluate the original model
print("\n---- model before svd ---\n")
print(model)
# Perform decomposition
corda_config = CordaConfig(
corda_method="ipm" if args.first_eigen else "kpm",
)
lora_config = LoraConfig(
init_lora_weights="corda",
target_modules=["q_proj", "o_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"],
r=args.r,
lora_alpha=args.r,
corda_config=corda_config,
)
preprocess_corda(
model,
lora_config,
run_model=lambda: run_model(model, calib_loader),
)
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
# Evaluate again to check if the model is consistent
# Using `model.model` here because `get_peft_model` wraps a layer to the model
print("\n---- model after svd ---\n")
print(model)
# Save as hugging face model
if args.save_model:
assert args.save_path is not None
save_path = args.save_path
# Save CorDA modules
model.peft_config["default"].init_lora_weights = True
model.save_pretrained(os.path.join(save_path, "corda_init"))
# Save residual model
model = model.unload()
model.save_pretrained(save_path)
# Save tokenizer
tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_path)
print(f"Done building CorDA huggingface model in {save_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--model_id",
type=str,
default="meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf",
help="Pretrained model ID",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--calib_loader_size",
type=int,
default=256,
help="number of samples used for covariance matrices",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--calib_dataset",
type=str,
default="wikitext2",
choices=[
"wikitext2",
"c4",
"ptb",
"traivia_qa",
"nqopen",
"MetaMATH",
"codefeedback",
"WizLMinstruct",
"alpaca",
],
help="calibration dataset",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--eval_mmlu",
action="store_true",
help="evaluate mmlu",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--seed",
type=int,
default=233,
help="random seed",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--r",
type=int,
default=None,
)
parser.add_argument(
"--first_eigen",
action="store_true",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--save_model",
action="store_true",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--save_path",
type=str,
default=None,
)
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)
|
peft/examples/corda_finetuning/preprocess.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/corda_finetuning/preprocess.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 2033
}
| 234
|
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import transformers
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0" # force to use CUDA GPU device 0
os.environ["ZE_AFFINITY_MASK"] = "0" # force to use Intel XPU device 0
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""Finetune-opt-bnb-peft.ipynb
Automatically generated by Colaboratory.
Original file is located at
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1jCkpikz0J2o20FBQmYmAGdiKmJGOMo-o
## Fine-tune large models using 🤗 `peft` adapters, `transformers` & `bitsandbytes`
In this tutorial we will cover how we can fine-tune large language models using the very recent `peft` library and `bitsandbytes` for loading large models in 8-bit.
The fine-tuning method will rely on a recent method called "Low Rank Adapters" (LoRA), instead of fine-tuning the entire model you just have to fine-tune these adapters and load them properly inside the model.
After fine-tuning the model you can also share your adapters on the 🤗 Hub and load them very easily. Let's get started!
### Install requirements
First, run the cells below to install the requirements:
"""
"""### Model loading
Here let's load the `opt-6.7b` model, its weights in half-precision (float16) are about 13GB on the Hub! If we load them in 8-bit we would require around 7GB of memory instead.
"""
device_type = torch.accelerator.current_accelerator().type if hasattr(torch, "accelerator") else "cuda"
device_module = getattr(torch, device_type, torch.cuda)
free_in_GB = int(device_module.mem_get_info()[0] / 1024**3)
max_memory = f"{free_in_GB - 2}GB"
n_gpus = device_module.device_count()
max_memory = {i: max_memory for i in range(n_gpus)}
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"facebook/opt-350m",
max_memory=max_memory,
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
llm_int8_threshold=6.0,
llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
),
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
"""### Post-processing on the model
Finally, we need to apply some post-processing on the 8-bit model to enable training, let's freeze all our layers, and cast the layer-norm in `float32` for stability. We also cast the output of the last layer in `float32` for the same reasons.
"""
print(model)
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False # freeze the model - train adapters later
if param.ndim == 1:
# cast the small parameters (e.g. layernorm) to fp32 for stability
param.data = param.data.to(torch.float32)
# model.gradient_checkpointing_enable() # reduce number of stored activations
# model.model.decoder.project_in = lambda x: x.requires_grad_(True)
class CastOutputToFloat(nn.Sequential):
def forward(self, x):
return super().forward(x).to(torch.float32)
model.lm_head = CastOutputToFloat(model.lm_head)
"""### Apply LoRA
Here comes the magic with `peft`! Let's load a `PeftModel` and specify that we are going to use low-rank adapters (LoRA) using `get_peft_model` utility function from `peft`.
"""
def print_trainable_parameters(model):
"""
Prints the number of trainable parameters in the model.
"""
trainable_params = 0
all_param = 0
for _, param in model.named_parameters():
all_param += param.numel()
if param.requires_grad:
trainable_params += param.numel()
print(
f"trainable params: {trainable_params} || all params: {all_param} || trainable%: {100 * trainable_params / all_param}"
)
config = LoraConfig(
r=64,
lora_alpha=32,
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj", "out_proj", "fc1", "fc2"],
lora_dropout=0.01,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
print_trainable_parameters(model)
# Verifying the datatypes.
dtypes = {}
for _, p in model.named_parameters():
dtype = p.dtype
if dtype not in dtypes:
dtypes[dtype] = 0
dtypes[dtype] += p.numel()
total = 0
for k, v in dtypes.items():
total += v
for k, v in dtypes.items():
print(k, v, v / total)
"""### Training"""
data = load_dataset("Abirate/english_quotes")
data = data.map(lambda samples: tokenizer(samples["quote"]), batched=True)
trainer = transformers.Trainer(
model=model,
train_dataset=data["train"],
args=transformers.TrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
warmup_steps=10,
max_steps=20,
learning_rate=3e-4,
fp16=True,
logging_steps=1,
output_dir="outputs",
),
data_collator=transformers.DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(tokenizer, mlm=False),
)
model.config.use_cache = False # silence the warnings. Please re-enable for inference!
trainer.train()
# from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
# notebook_login()
# model.push_to_hub("ybelkada/opt-6.7b-lora", use_auth_token=True)
"""## Load adapters from the Hub
You can also directly load adapters from the Hub using the commands below:
"""
# import torch
# from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig
# from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
#
# peft_model_id = "ybelkada/opt-6.7b-lora"
# config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)
# model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path, return_dict=True, quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True), device_map='auto')
# tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)
#
## Load the Lora model
# model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)
#
# """## Inference
#
# You can then directly use the trained model or the model that you have loaded from the 🤗 Hub for inference as you would do it usually in `transformers`.
# """
#
batch = tokenizer("Two things are infinite: ", return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
model.config.use_cache = False # silence the warnings. Please re-enable for inference!
model.eval()
with torch.amp.autocast(device_type=device_type):
output_tokens = model.generate(**batch, max_new_tokens=50)
print("\n\n", tokenizer.decode(output_tokens[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
# model.save('./test.pt')
# """As you can see by fine-tuning for few steps we have almost recovered the quote from Albert Einstein that is present in the [training data](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Abirate/english_quotes)."""
|
peft/examples/fp4_finetuning/finetune_fp4_opt_bnb_peft.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/fp4_finetuning/finetune_fp4_opt_bnb_peft.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 2428
}
| 235
|
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
debug: false
distributed_type: MULTI_XPU
downcast_bf16: 'no'
enable_cpu_affinity: false
gpu_ids: all
ipex_config:
ipex: false
machine_rank: 0
main_training_function: main
mixed_precision: 'no'
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 4
rdzv_backend: static
same_network: true
tpu_env: []
tpu_use_cluster: false
tpu_use_sudo: false
use_cpu: false
|
peft/examples/int8_training/config.yaml/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/int8_training/config.yaml",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 151
}
| 236
|
# LoRA-FA: Memory-efficient Low-rank Adaptation for Large Language Models Fine-tuning
## Introduction
[LoRA-FA](https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.03303) is a noval Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning method, which freezes the projection down layer (matrix A) during LoRA training process and thus lead to less accelerator memory consumption by eliminating the need for storing the activations of input tensors (X). Furthermore, LoRA-FA narrows the gap between the update amount of pre-trained weights when using the low-rank fine-tuning method and the full fine-tuning method. In conclusion, LoRA-FA reduces the memory consumption and leads to superior performance compared to vanilla LoRA.
## Quick start
```python
import torch
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
from peft.optimizers import create_lorafa_optimizer
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, Trainer
from datasets import load_dataset
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct")
dataset = load_dataset("timdettmers/openassistant-guanaco", split="train")
lora_rank = 16
lora_alpha = 32
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=lora_rank,
lora_alpha=lora_alpha,
bias="none",
)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
optimizer = create_lorafa_optimizer(
model=peft_model,
r=lora_rank,
lora_alpha=lora_alpha,
lr=7e-5,
)
# you can also use scheduler, we recommend get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup from transformers
# for better model performance
scheduler = None
trainer = transformers.Trainer(
model=peft_model,
train_dataset=dataset,
dataset_text_field="text",
max_seq_length=2048,
processing_class=tokenizer,
optimizers=(optimizer, None),
)
trainer.train()
peft_model.save_pretrained("lorafa-llama-3-8b-inst")
```
The only change in your code is to pass the LoRA-FA optimizer to the trainer (if training with trainer). Do not forget `from peft.optimizers import create_lorafa_optimizer`!
## Example
In this dir, we also provide you a simple example for fine-tuning with LoRA-FA optimizer.
### Run on CPU, single-accelerator or multi-accelerator
This 👇 by default will load the model in peft set up with LoRA config, and train the model with LoRA-FA optimizer.
0. CPU
You can simply run LoRA-FA as below:
```bash
python lorafa_finetuning.py --base_model_name_or_path meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B --dataset_name_or_path meta-math/MetaMathQA-40K --output_dir path/to/output --lorafa
```
1. Single-accelerator
Run the finetuning script on 1 accelerator:
```bash
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 # force to use CUDA GPU 0
export ZE_AFFINITY_MASK=0 # force to use Intel XPU 0
python lorafa_finetuning.py --base_model_name_or_path meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B --dataset_name_or_path meta-math/MetaMathQA-40K --output_dir path/to/output --lorafa
```
2. Multi-accelerator
LoRA-FA can also be run on multi-accelerator, with 🤗 Accelerate:
```bash
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 # force to use CUDA GPU 0,1,2,3
export ZE_AFFINITY_MASK=0,1,2,3 # force to use Intel XPU 0,1,2,3
accelerate launch lorafa_finetuning.py --base_model_name_or_path meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B --dataset_name_or_path meta-math/MetaMathQA-40K --output_dir path/to/output --lorafa
```
The `accelerate launch` will automatically configure multi-accelerator for you. You can also utilize `accelerate launch` in single-accelerator scenario.
### Use the model from 🤗
You can load and use the model as any other 🤗 models.
```python
from transformers import AutoModel
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf")
```
## Best practice in fine-tuning Llama using LoRA-FA: the hyper-params
Sometimes, achieving optimal LoRA fine-tuning can be challenging due to the larger number of hyperparameters to consider compared to full fine-tuning. For instance, not only do we need to adjust the commonly used learning rate, but the ideal LoRA rank may also vary depending on the specific model and task. Additionally, there are other factors to consider, such as LoRA alpha and sequence length. To assist with this, we have created a repository of reproducible best practices in the [LoRA-FA examples](https://github.com/AaronZLT/lorafa) for reference. This resource showcases the optimal LoRA-FA fine-tuning hyperparameters for different models across various datasets. By doing so, we significantly reduce the time and effort spent on hyperparameter tuning, and it may also provide insights for tuning other training hyperparameters. We encourage you to experiment and fine-tune on your own downstream tasks as well.
## LoRA-FA's advantages and limitations
By eliminating the activation of adapter A, LoRA-FA uses less memory for fine-tuning compared to LoRA. For instance, when fine-tuning Llama-2-7b-chat-hf with a batch size of 8 and a sequence length of 1024, LoRA-FA requires 36GB of memory to store activations. This allows it to run successfully on an 80GB accelerator. In contrast, LoRA requires at least 60GB of memory for activations, leading to an Out of Memory (OOM) error. Additionally, the memory consumption of LoRA-FA is not sensitive to the rank, allowing for performance improvements by increasing the LoRA rank without additional memory usage. LoRA-FA further narrows the performance gap with Full-FT by minimizing the discrepancy between the low-rank gradient and the full gradient, enabling it to achieve performance that is on par with or even superior to vanilla LoRA.
Despite its advantages, LoRA-FA is inherently limited by its low-rank approximation nature and potential issues with catastrophic forgetting. The gradient approximation can impact training throughput. Addressing these limitations, especially in terms of approximation accuracy and forgetting phenomena, presents a promising direction for future research.
## Citation
```
@misc{zhang2023lorafamemoryefficientlowrankadaptation,
title={LoRA-FA: Memory-efficient Low-rank Adaptation for Large Language Models Fine-tuning},
author={Longteng Zhang and Lin Zhang and Shaohuai Shi and Xiaowen Chu and Bo Li},
year={2023},
eprint={2308.03303},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.03303},
}
```
|
peft/examples/lorafa_finetune/README.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/lorafa_finetune/README.md",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 1944
}
| 237
|
<jupyter_start><jupyter_code>%env CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 # force using CUDA GPU device 0
%env ZE_AFFINITY_MASK=0 # force using Intel XPU device 0
%env TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM=false<jupyter_output>env: CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 # force using CUDA GPU device 0
env: ZE_AFFINITY_MASK=0 # force using Intel XPU device 0
env: TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM=false<jupyter_text>Initialize PolyModel<jupyter_code>import torch
from transformers import (
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
AutoTokenizer,
default_data_collator,
Seq2SeqTrainingArguments,
Seq2SeqTrainer,
)
from datasets import load_dataset, concatenate_datasets
from peft import PolyConfig, get_peft_model, TaskType, PeftModel, PeftConfig
model_name_or_path = "google/flan-t5-xl"
r = 8 # rank of lora in poly
n_tasks = 4 # number of tasks
n_skills = 2 # number of skills (loras)
n_splits = 4 # number of heads
batch_size = 8
lr = 5e-5
num_epochs = 8
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=True)
base_model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=True)
peft_config = PolyConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM,
poly_type="poly",
r=r,
n_tasks=n_tasks,
n_skills=n_skills,
n_splits=n_splits,
)
model = get_peft_model(base_model, peft_config)
model.print_trainable_parameters()<jupyter_output>trainable params: 9,441,792 || all params: 2,859,198,976 || trainable%: 0.3302<jupyter_text>Prepare datasetsFor this example, we selected four `SuperGLUE` benchmark datasets: `boolq`, `multirc`, `rte`, and `wic`, each with a training set of 1,000 examples and an evaluation set of 100 examples.<jupyter_code># boolq
boolq_dataset = (
load_dataset("super_glue", "boolq")
.map(
lambda x: {
"input": f"{x['passage']}\nQuestion: {x['question']}\nA. Yes\nB. No\nAnswer:",
# 0 - False
# 1 - True
"output": ["B", "A"][int(x["label"])],
"task_name": "boolq",
}
)
.select_columns(["input", "output", "task_name"])
)
print("boolq example: ")
print(boolq_dataset["train"][0])
# multirc
multirc_dataset = (
load_dataset("super_glue", "multirc")
.map(
lambda x: {
"input": (
f"{x['paragraph']}\nQuestion: {x['question']}\nAnswer: {x['answer']}\nIs it"
" true?\nA. Yes\nB. No\nAnswer:"
),
# 0 - False
# 1 - True
"output": ["B", "A"][int(x["label"])],
"task_name": "multirc",
}
)
.select_columns(["input", "output", "task_name"])
)
print("multirc example: ")
print(multirc_dataset["train"][0])
# rte
rte_dataset = (
load_dataset("super_glue", "rte")
.map(
lambda x: {
"input": (
f"{x['premise']}\n{x['hypothesis']}\nIs the sentence below entailed by the"
" sentence above?\nA. Yes\nB. No\nAnswer:"
),
# 0 - entailment
# 1 - not_entailment
"output": ["A", "B"][int(x["label"])],
"task_name": "rte",
}
)
.select_columns(["input", "output", "task_name"])
)
print("rte example: ")
print(rte_dataset["train"][0])
# wic
wic_dataset = (
load_dataset("super_glue", "wic")
.map(
lambda x: {
"input": (
f"Sentence 1: {x['sentence1']}\nSentence 2: {x['sentence2']}\nAre '{x['word']}'"
" in the above two sentences the same?\nA. Yes\nB. No\nAnswer:"
),
# 0 - False
# 1 - True
"output": ["B", "A"][int(x["label"])],
"task_name": "wic",
}
)
.select_columns(["input", "output", "task_name"])
)
print("wic example: ")
print(wic_dataset["train"][0])
# define a task2id map
TASK2ID = {
"boolq": 0,
"multirc": 1,
"rte": 2,
"wic": 3,
}
def tokenize(examples):
inputs, targets = examples["input"], examples["output"]
features = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=512, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
labels = tokenizer(targets, max_length=2, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
labels = labels["input_ids"]
labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100
features["labels"] = labels
features["task_ids"] = torch.tensor([[TASK2ID[t]] for t in examples["task_name"]]).long()
return features
def get_superglue_dataset(
split="train",
n_samples=500,
):
ds = concatenate_datasets(
[
boolq_dataset[split].shuffle().select(range(n_samples)),
multirc_dataset[split].shuffle().select(range(n_samples)),
rte_dataset[split].shuffle().select(range(n_samples)),
wic_dataset[split].shuffle().select(range(n_samples)),
]
)
ds = ds.map(
tokenize,
batched=True,
remove_columns=["input", "output", "task_name"],
load_from_cache_file=False,
)
return ds<jupyter_output><empty_output><jupyter_text>As a toy example, we only select 1,000 from each subdataset for training and 100 each for eval.<jupyter_code>superglue_train_dataset = get_superglue_dataset(split="train", n_samples=1000)
superglue_eval_dataset = get_superglue_dataset(split="test", n_samples=100)<jupyter_output>Map: 0%| | 0/4000 [00:00<?, ? examples/s]<jupyter_text>Train and evaluate<jupyter_code># training and evaluation
def compute_metrics(eval_preds):
preds, labels = eval_preds
preds = [[i for i in seq if i != -100] for seq in preds]
labels = [[i for i in seq if i != -100] for seq in labels]
preds = tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True)
labels = tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
correct = 0
total = 0
for pred, true in zip(preds, labels):
if pred.strip() == true.strip():
correct += 1
total += 1
accuracy = correct / total
return {"accuracy": accuracy}
training_args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments(
"output",
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
learning_rate=lr,
num_train_epochs=num_epochs,
eval_strategy="epoch",
logging_strategy="epoch",
save_strategy="no",
report_to=[],
predict_with_generate=True,
generation_max_length=2,
remove_unused_columns=False,
)
trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
model=model,
processing_class=tokenizer,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=superglue_train_dataset,
eval_dataset=superglue_eval_dataset,
data_collator=default_data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
trainer.train()
# saving model
model_name_or_path = "google/flan-t5-xl"
peft_model_id = f"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}"
model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)
!ls -lh $peft_model_id<jupyter_output>total 37M
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5.1K Aug 4 20:25 README.md
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 381 Aug 4 20:25 adapter_config.json
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 37M Aug 4 20:25 adapter_model.safetensors<jupyter_text>Load and infer<jupyter_code>device_type = torch.accelerator.current_accelerator().type if hasattr(torch, "accelerator") else "cuda"
device = f"{device_type}:0" if device_type != "cpu" else "cpu"
peft_model_id = f"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}"
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)
model = model.to(device)
model = model.eval()
i = 5
inputs = tokenizer(rte_dataset["validation"]["input"][i], return_tensors="pt")
inputs["task_ids"] = torch.LongTensor([TASK2ID["rte"]])
inputs = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
print(rte_dataset["validation"]["input"][i])
print(rte_dataset["validation"]["output"][i])
print(inputs)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=2)
print(outputs[0])
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)[0])<jupyter_output>In 1979, the leaders signed the Egypt-Israel peace treaty on the White House lawn. Both President Begin and Sadat received the Nobel Peace Prize for their work. The two nations have enjoyed peaceful relations to this day.
The Israel-Egypt Peace Agreement was signed in 1979.
Is the sentence below entailed by the sentence above?
A. Yes
B. No
Answer:
A
{'input_ids': tensor([[ 86, 15393, 6, 8, 2440, 3814, 8, 10438, 18, 30387,
3065, 2665, 63, 30, 8, 1945, 1384, 8652, 5, 2867,
1661, 10129, 77, 11, 18875, 144, 1204, 8, 22232, 11128,
11329, 21, 70, 161, 5, 37, 192, 9352, 43, 2994,
9257, 5836, 12, 48, 239, 5, 37, 3352, 18, 427,
122, 63, 102, 17, 11128, 7139, 47, 3814, 16, 15393,
5, 27, 7, 8, 7142, 666, 3, 295, 10990, 57,
8, 7142, 756, 58, 71, 5, 2163, 272, 5, 465,
[...]
|
peft/examples/poly/peft_poly_seq2seq_with_generate.ipynb/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/examples/poly/peft_poly_seq2seq_with_generate.ipynb",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 4174
}
| 238
|
{
"auto_mapping": null,
"base_model_name_or_path": null,
"bias": "none",
"exclude_modules": null,
"fan_in_fan_out": false,
"inference_mode": false,
"init_weights": false,
"layers_pattern": null,
"layers_to_transform": null,
"modules_to_save": null,
"n_frequency": 1000,
"n_frequency_pattern": {},
"peft_type": "FOURIERFT",
"random_loc_seed": 777,
"revision": null,
"scaling": 300,
"target_modules": [
"v_proj",
"q_proj"
],
"task_type": null
}
|
peft/method_comparison/MetaMathQA/experiments/fourierft/llama-3.2-3B-default/adapter_config.json/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/method_comparison/MetaMathQA/experiments/fourierft/llama-3.2-3B-default/adapter_config.json",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 213
}
| 239
|
{
"auto_mapping": null,
"base_model_name_or_path": null,
"encoder_hidden_size": 3072,
"inference_mode": false,
"num_attention_heads": 24,
"num_layers": 28,
"num_transformer_submodules": 1,
"num_virtual_tokens": 200,
"peft_type": "PREFIX_TUNING",
"prefix_projection": false,
"revision": null,
"task_type": "CAUSAL_LM",
"token_dim": 3072
}
|
peft/method_comparison/MetaMathQA/experiments/prefixtuning/llama-3.2-3B-lr_0.001/adapter_config.json/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/method_comparison/MetaMathQA/experiments/prefixtuning/llama-3.2-3B-lr_0.001/adapter_config.json",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 157
}
| 240
|
# Copyright 2025-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""
Main entry point to run the experiments. Contains general setup and the proper inference code.
"""
import argparse
import gc
import json
import os
import sys
import time
from typing import Optional
import bitsandbytes
import torch
import transformers
from data import prepare_benchmark_prompts
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig, set_seed
from utils import (
BenchmarkConfig,
BenchmarkResult,
BenchmarkStatus,
get_memory_usage,
init_accelerator,
log_results,
validate_experiment_path,
)
import peft
from peft import PeftConfig, get_peft_model
def load_base_results(model_id: str) -> Optional[dict]:
"""Load base model results if they exist."""
base_results_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "base_results")
model_name = model_id.replace("/", "_").replace("-", "_")
filename = f"base_{model_name}.json"
filepath = os.path.join(base_results_dir, filename)
if os.path.exists(filepath):
with open(filepath) as f:
return json.load(f)
return None
def measure_inference_time(model, tokenizer, prompts, max_new_tokens, num_runs, print_fn, category_generation_params):
"""Measure inference time for each prompt category."""
inference_times = {}
time_per_token = {}
generated_tokens = {}
individual_samples = {}
for category, category_prompts in prompts.items():
print_fn(f"\nMeasuring inference time for {category} prompts...")
category_times = []
category_tokens = []
category_time_per_token = []
category_samples = []
for prompt in category_prompts:
prompt_times = []
prompt_tokens = []
prompt_time_per_token = []
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
cat_max_new_tokens = category_generation_params.get(category, {}).get("max_new_tokens", max_new_tokens)
for _ in range(num_runs):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
outputs = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=cat_max_new_tokens,
min_new_tokens=cat_max_new_tokens,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.pad_token_id,
)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
# Calculate metrics
inference_time = end_time - start_time
num_tokens = len(outputs[0]) - len(inputs["input_ids"][0])
time_per_token_val = inference_time / num_tokens if num_tokens > 0 else 0
prompt_times.append(inference_time)
prompt_tokens.append(num_tokens)
prompt_time_per_token.append(time_per_token_val)
# Calculate averages for this prompt
avg_time = sum(prompt_times) / len(prompt_times)
avg_tokens = sum(prompt_tokens) / len(prompt_tokens)
avg_time_per_token = sum(prompt_time_per_token) / len(prompt_time_per_token)
sample_result = {
"inference_time": avg_time,
"generated_tokens": avg_tokens,
"time_per_token": avg_time_per_token,
"individual_runs": [
{"inference_time": t, "generated_tokens": tok, "time_per_token": tpt}
for t, tok, tpt in zip(prompt_times, prompt_tokens, prompt_time_per_token)
],
}
category_samples.append(sample_result)
category_times.append(avg_time)
category_tokens.append(avg_tokens)
category_time_per_token.append(avg_time_per_token)
if category_times:
avg_category_time = sum(category_times) / len(category_times)
avg_category_tokens = sum(category_tokens) / len(category_tokens)
avg_category_time_per_token = sum(category_time_per_token) / len(category_time_per_token)
inference_times[category] = avg_category_time
generated_tokens[category] = avg_category_tokens
time_per_token[category] = avg_category_time_per_token
individual_samples[category] = category_samples
return {
"inference_times": inference_times,
"time_per_token": time_per_token,
"generated_tokens": generated_tokens,
"individual_samples": individual_samples,
}
def run_benchmark(
benchmark_config: BenchmarkConfig, experiment_name: str, experiment_path: str, print_fn=print
) -> BenchmarkResult:
"""Run benchmarks for the specified PEFT method configuration."""
result = BenchmarkResult(
experiment_name=experiment_name,
status=BenchmarkStatus.RUNNING,
model_id=benchmark_config.model_id,
)
result.save()
start_time = time.perf_counter()
e_main_benchmark: Optional[Exception] = None
try:
print_fn("Initializing accelerator...")
accelerator_allocated_init, accelerator_reserved_init = init_accelerator()
set_seed(benchmark_config.seed)
print_fn(f"Loading base model: {benchmark_config.model_id}")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(benchmark_config.model_id)
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
model_kwargs = {
"device_map": "auto" if (torch.cuda.is_available() or torch.xpu.is_available()) else None,
}
if benchmark_config.dtype == "float32":
model_kwargs["torch_dtype"] = torch.float32
elif benchmark_config.dtype == "float16":
model_kwargs["torch_dtype"] = torch.float16
elif benchmark_config.dtype == "bfloat16":
model_kwargs["torch_dtype"] = torch.bfloat16
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported dtype: {benchmark_config.dtype}")
if benchmark_config.use_8bit:
model_kwargs["quantization_config"] = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_8bit=True, llm_int8_enable_fp32_cpu_offload=True
)
elif benchmark_config.use_4bit:
model_kwargs["quantization_config"] = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=model_kwargs.get("torch_dtype", torch.float16),
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
)
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(benchmark_config.model_id, **model_kwargs)
base_results = load_base_results(benchmark_config.model_id)
print_fn("Preparing benchmark prompts...")
prompts = prepare_benchmark_prompts(
config=benchmark_config,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_input_length=None,
seed=benchmark_config.seed,
)
if base_results:
print_fn("Using cached base model results...")
base_inference_times = base_results["inference_results"]
else:
raise FileNotFoundError(
"No cached base results found. Please run `python run_base.py` first to generate base model results."
)
try:
print_fn(f"Loading PEFT config from {experiment_path}")
peft_config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(experiment_path)
print_fn(f"Loaded PEFT config: {peft_config.peft_type}, with parameters: {vars(peft_config)}")
model = get_peft_model(base_model, peft_config)
except Exception as exc:
error_msg = f"Error loading PEFT config: {str(exc)}"
print_fn(error_msg)
del base_model
gc.collect()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
elif torch.xpu.is_available():
torch.xpu.empty_cache()
ram, accelerator_allocated, accelerator_reserved = get_memory_usage()
result.add_memory_log("peft_model_loaded", ram, accelerator_allocated, accelerator_reserved)
# Calculate PEFT model metrics
trainable_params = model.get_nb_trainable_parameters()[0]
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
base_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.base_model.parameters())
dtype_bytes = 2 if benchmark_config.dtype in ["float16", "bfloat16"] else 4
adapter_size_mb = trainable_params * dtype_bytes / (1024 * 1024)
base_model_size_mb = base_params * dtype_bytes / (1024 * 1024)
param_ratio = trainable_params / total_params if total_params > 0 else 0
result.update_meta_info(
param_counts={
"base_params": base_params,
"trainable_params": trainable_params,
"total_params": total_params,
"param_ratio": param_ratio,
},
size_info={"base_model_size_mb": base_model_size_mb, "adapter_size_mb": adapter_size_mb},
package_info={
"transformers-version": transformers.__version__,
"peft-version": peft.__version__,
"bitsandbytes-version": bitsandbytes.__version__ if hasattr(bitsandbytes, "__version__") else None,
},
)
print_fn("Measuring PEFT model inference times...")
peft_inference_times = measure_inference_time(
model,
tokenizer,
prompts,
max_new_tokens=benchmark_config.max_new_tokens,
num_runs=benchmark_config.num_inference_runs,
print_fn=print_fn,
category_generation_params=benchmark_config.category_generation_params,
)
# Calculate inference overhead for each category
inference_overhead = {
k: (peft_inference_times["inference_times"][k] - base_inference_times["inference_times"][k])
/ base_inference_times["inference_times"][k]
* 100
for k in base_inference_times["inference_times"]
}
for category in prompts:
category_metrics = {
"inference_time": peft_inference_times["inference_times"][category],
"base_inference_time": base_inference_times["inference_times"][category],
"inference_overhead_pct": inference_overhead[category],
"time_per_token": peft_inference_times["time_per_token"][category],
"generated_tokens": peft_inference_times["generated_tokens"][category],
}
result.add_metrics_for_category(
category, category_metrics, individual_samples=peft_inference_times["individual_samples"][category]
)
result.update_generation_info(
memory_data={
"peak_accelerator_memory_mb": max(
(log["accelerator_allocated_mb"] for log in result.generation_info["memory"]["memory_logs"]), default=0
),
"peak_ram_memory_mb": max(
(log["ram_mb"] for log in result.generation_info["memory"]["memory_logs"]), default=0
),
}
)
ram, accelerator_allocated, accelerator_reserved = get_memory_usage()
result.add_memory_log("benchmark_complete", ram, accelerator_allocated, accelerator_reserved)
result.status = BenchmarkStatus.SUCCESS
except Exception as exc:
print_fn(f"Benchmark failed with error: {exc}")
result.status = BenchmarkStatus.FAILED
e_main_benchmark = exc
end_time = time.perf_counter()
error_message = str(e_main_benchmark) if e_main_benchmark is not None else None
peft_config_dict = peft_config.to_dict() if "peft_config" in locals() else None
if peft_config_dict:
for key, value in peft_config_dict.items():
if isinstance(value, set):
peft_config_dict[key] = list(value)
result.update_run_info(
duration=end_time - start_time,
status=result.status,
error=error_message,
peft_config=peft_config_dict,
benchmark_config=benchmark_config.to_dict(),
)
return result
def main() -> None:
"""Main entry point for the benchmark runner."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run PEFT method benchmarks")
parser.add_argument("experiment_path", help="Path to experiment directory")
parser.add_argument("--verbose", "-v", action="store_true", help="Enable verbose output")
args = parser.parse_args()
print_fn = print if args.verbose else lambda *args, **kwargs: None
experiment_path = args.experiment_path
allowed_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__)))
abs_experiment_path = os.path.abspath(experiment_path)
if not abs_experiment_path.startswith(allowed_root):
print(f"Experiment path must be inside {allowed_root}, got: {abs_experiment_path}. Skipping execution.")
return 0
if not os.path.exists(abs_experiment_path):
print(f"Experiment path not found: {abs_experiment_path}. Skipping execution.")
return 0
experiment_path = abs_experiment_path
experiment_name, benchmark_config = validate_experiment_path(experiment_path)
print_fn(f"Running benchmark for experiment: {experiment_name}")
result = run_benchmark(
benchmark_config=benchmark_config,
experiment_name=experiment_name,
experiment_path=experiment_path,
print_fn=print_fn,
)
log_results(experiment_name, result, print_fn=print)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.exit(main())
|
peft/method_comparison/text_generation_benchmark/run.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/method_comparison/text_generation_benchmark/run.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 6187
}
| 241
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import inspect
from contextlib import contextmanager
from copy import deepcopy
from functools import update_wrapper
from types import MethodType
from torch import nn
from .peft_model import PeftConfig, PeftModel
from .tuners.lora import LoraLayer
from .tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer
def update_forward_signature(model: PeftModel) -> None:
"""
Updates the forward signature of the PeftModel to include parents class signature
model (`PeftModel`): Peft model to update the forward signature
Example:
```python
>>> from transformers import WhisperForConditionalGeneration
>>> from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, update_forward_signature
>>> model = WhisperForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-tiny.en")
>>> peft_config = LoraConfig(r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1, target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"])
>>> peft_model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
>>> update_forward_signature(peft_model)
```
"""
# Only update signature when the current forward signature only has *args and **kwargs
current_signature = inspect.signature(model.forward)
if (
len(current_signature.parameters) == 2
and "args" in current_signature.parameters
and "kwargs" in current_signature.parameters
):
forward = deepcopy(model.forward.__func__)
update_wrapper(
forward, type(model.get_base_model()).forward, assigned=("__doc__", "__name__", "__annotations__")
)
model.forward = MethodType(forward, model)
def update_generate_signature(model: PeftModel) -> None:
"""
Updates the generate signature of a PeftModel with overriding generate to include parents class signature
model (`PeftModel`): Peft model to update the generate signature
Example:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType, update_generate_signature
>>> model_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
>>> peft_config = LoraConfig(
... task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
... )
>>> peft_model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
>>> update_generate_signature(peft_model)
>>> help(peft_model.generate)
```
"""
if not hasattr(model, "generate"):
return
current_signature = inspect.signature(model.generate)
if (
len(current_signature.parameters) == 2
and "args" in current_signature.parameters
and "kwargs" in current_signature.parameters
) or (len(current_signature.parameters) == 1 and "kwargs" in current_signature.parameters):
generate = deepcopy(model.generate.__func__)
update_wrapper(
generate,
type(model.get_base_model()).generate,
assigned=("__doc__", "__name__", "__annotations__"),
)
model.generate = MethodType(generate, model)
def update_signature(model: PeftModel, method: str = "all") -> None:
"""
Updates the signature of a PeftModel include parents class signature for forward or generate method
model (`PeftModel`): Peft model to update generate or forward signature method (`str`): method to update
signature choose one of "forward", "generate", "all"
Example:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType, update_signature
>>> model_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
>>> peft_config = LoraConfig(
... task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
... )
>>> peft_model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
>>> update_signature(peft_model)
>>> help(peft_model.generate)
```
"""
if method == "forward":
update_forward_signature(model)
elif method == "generate":
update_generate_signature(model)
elif method == "all":
update_forward_signature(model)
update_generate_signature(model)
else:
raise ValueError(f"method {method} is not supported please choose one of ['forward', 'generate', 'all']")
def check_if_peft_model(model_name_or_path: str) -> bool:
"""
Check if the model is a PEFT model.
Args:
model_name_or_path (`str`):
Model id to check, can be local or on the Hugging Face Hub.
Returns:
`bool`: True if the model is a PEFT model, False otherwise.
"""
is_peft_model = True
try:
PeftConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
except Exception:
# allow broad exceptions so that this works even if new exceptions are added on HF Hub side
is_peft_model = False
return is_peft_model
@contextmanager
def rescale_adapter_scale(model, multiplier):
"""
Context manager to temporarily rescale the scaling of the LoRA adapter in a model.
The original scaling values are restored when the context manager exits. This context manager works with the
transformers and diffusers models that have directly loaded LoRA adapters.
For LoRA, applying this context manager with multiplier in [0, 1] is strictly equivalent to applying
[wise-ft](https://huggingface.co/papers/2109.01903) (see [#1940](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/issues/1940)
for details). It can improve the performances of the model if there is a distribution shiftbetween the training
data used for fine-tuning, and the test data used during inference.
Warning: It has been reported that when using Apple's MPS backend for PyTorch, it is necessary to add a short sleep
time after exiting the context before the scales are fully restored.
Args:
model: The model containing `LoraLayer` modules whose scaling is to be adjusted.
multiplier (float or int):
The multiplier that rescales the `scaling` attribute. Must be of type float or int.
Raises:
ValueError: If the model does not contain any `LoraLayer`
instances, indicating that the model does not support scaling.
Example:
```python
>>> model = ModelWithLoraLayer()
>>> multiplier = 0.5
>>> with rescale_adapter_scale(model, multiplier):
... outputs = model(**inputs) # Perform operations with the scaled model
>>> outputs = model(**inputs) # The original scaling values are restored here
```
"""
# check if multiplier has a valid data type
if not isinstance(multiplier, (float, int)):
raise TypeError(f"Argument multiplier should be of type float, got {type(multiplier)}")
# iterate on the model's modules and grab the original scaling attribute
# from the lora layers if present
original_scaling = {}
for module in model.modules():
if isinstance(module, LoraLayer):
original_scaling[module] = module.scaling.copy()
module.scaling = {k: v * multiplier for k, v in module.scaling.items()}
# check whether scaling is prohibited on model
# the original scaling dictionary should be empty
# if there were no lora layers
if not original_scaling:
raise ValueError("scaling is only supported for models with `LoraLayer`s")
try:
yield
finally:
# restore original scaling values after exiting the context
for module, scaling in original_scaling.items():
module.scaling = scaling
@contextmanager
def disable_input_dtype_casting(model: nn.Module, active: bool = True):
"""
Context manager disables input dtype casting to the dtype of the weight.
Parameters:
model (nn.Module):
The model containing PEFT modules whose input dtype casting is to be adjusted.
active (bool):
Whether the context manager is active (default) or inactive.
"""
# Additional info: Normally, the dtype of the weight and input need to match, which is why the dtype is cast.
# However, in certain circumustances, this is handled by forward hooks, e.g. when using layerwise casting in
# diffusers. In that case, PEFT casting the dtype interferes with the layerwise casting, which is why the option to
# disable it is given.
if not active:
yield
return
original_values = {}
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if not isinstance(module, BaseTunerLayer):
continue
original_values[name] = module.cast_input_dtype_enabled
module.cast_input_dtype_enabled = False
try:
yield
finally:
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if not isinstance(module, BaseTunerLayer):
continue
if name in original_values:
module.cast_input_dtype_enabled = original_values[name]
|
peft/src/peft/helpers.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/helpers.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 3462
}
| 242
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import warnings
from typing import Any, Optional
import packaging
import torch
import transformers
from torch import nn
from peft.tuners.lora import LoraLayer
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import check_adapters_to_merge
from peft.utils import transpose
if packaging.version.parse(transformers.__version__) >= packaging.version.parse("4.33.0"):
from transformers.integrations import deepspeed_config
else:
from transformers.deepspeed import deepspeed_config
class AdaLoraLayer(LoraLayer):
# List all names of layers that may contain adapter weights
# Note: ranknum doesn't need to be included as it is not an nn.Module
adapter_layer_names = ("lora_A", "lora_B", "lora_E", "lora_embedding_A", "lora_embedding_B")
# All names of other parameters that may contain adapter-related parameters
other_param_names = ("r", "lora_alpha", "scaling", "lora_dropout", "ranknum")
def __init__(self, base_layer: nn.Module) -> None:
super().__init__(base_layer)
self.lora_E = nn.ParameterDict({})
self.lora_A = nn.ParameterDict({})
self.lora_B = nn.ParameterDict({})
self.ranknum = nn.ParameterDict({})
def update_layer(self, adapter_name, r, lora_alpha, lora_dropout, init_lora_weights):
if r < 0:
# note: r == 0 is allowed for AdaLora, see #1539
raise ValueError(f"`r` should be a positive integer or 0, but the value passed is {r}")
self.r[adapter_name] = r
self.lora_alpha[adapter_name] = lora_alpha
if lora_dropout > 0.0:
lora_dropout_layer = nn.Dropout(p=lora_dropout)
else:
lora_dropout_layer = nn.Identity()
self.lora_dropout[adapter_name] = lora_dropout_layer
# Actual trainable parameters
# Right singular vectors
self.lora_A[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(r, self.in_features))
# Singular values
self.lora_E[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(r, 1))
# Left singular vectors
self.lora_B[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.out_features, r))
# The current rank
self.ranknum[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1), requires_grad=False)
self.ranknum[adapter_name].data.fill_(float(r))
self.ranknum[adapter_name].requires_grad = False
self.scaling[adapter_name] = lora_alpha if lora_alpha > 0 else float(r)
if init_lora_weights:
self.reset_lora_parameters(adapter_name)
self._move_adapter_to_device_of_base_layer(adapter_name)
self.set_adapter(self.active_adapters)
def reset_lora_parameters(self, adapter_name):
if adapter_name in self.lora_A.keys():
nn.init.zeros_(self.lora_E[adapter_name])
nn.init.normal_(self.lora_A[adapter_name], mean=0.0, std=0.02)
nn.init.normal_(self.lora_B[adapter_name], mean=0.0, std=0.02)
class SVDLinear(nn.Module, AdaLoraLayer):
# SVD-based adaptation by a dense layer
def __init__(
self,
base_layer: nn.Module,
adapter_name: str,
r: int = 0,
lora_alpha: int = 1,
lora_dropout: float = 0.0,
fan_in_fan_out: bool = False,
init_lora_weights: bool = True,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
AdaLoraLayer.__init__(self, base_layer)
# Freezing the pre-trained weight matrix
self.get_base_layer().weight.requires_grad = False
self.fan_in_fan_out = fan_in_fan_out
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(adapter_name, r, lora_alpha, lora_dropout, init_lora_weights)
def merge(self, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> None:
"""
Merge the active adapter weights into the base weights
Args:
safe_merge (`bool`, *optional*):
If True, the merge operation will be performed in a copy of the original weights and check for NaNs
before merging the weights. This is useful if you want to check if the merge operation will produce
NaNs. Defaults to `False`.
adapter_names (`List[str]`, *optional*):
The list of adapter names that should be merged. If None, all active adapters will be merged. Defaults
to `None`.
"""
adapter_names = check_adapters_to_merge(self, adapter_names)
if not adapter_names:
# no adapter to merge
return
for active_adapter in adapter_names:
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
if active_adapter in self.lora_A.keys():
if safe_merge:
# Note that safe_merge will be slower than the normal merge
# because of the copy operation.
orig_weights = base_layer.weight.data.clone()
orig_weights += self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
if not torch.isfinite(orig_weights).all():
raise ValueError(
f"NaNs detected in the merged weights. The adapter {active_adapter} seems to be broken"
)
base_layer.weight.data = orig_weights
else:
base_layer.weight.data += self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
self.merged_adapters.append(active_adapter)
def unmerge(self) -> None:
"""
This method unmerges all merged adapter layers from the base weights.
"""
if not self.merged:
warnings.warn("Already unmerged. Nothing to do.")
return
while len(self.merged_adapters) > 0:
active_adapter = self.merged_adapters.pop()
if active_adapter in self.lora_A.keys():
self.get_base_layer().weight.data -= self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
def get_delta_weight(self, adapter) -> torch.Tensor:
return (
transpose(self.lora_B[adapter] @ (self.lora_A[adapter] * self.lora_E[adapter]), self.fan_in_fan_out)
* self.scaling[adapter]
/ (self.ranknum[adapter] + 1e-5)
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.disable_adapters:
if self.merged:
self.unmerge()
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
elif self.merged:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
else:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.lora_A.keys():
continue
lora_A = self.lora_A[active_adapter]
lora_B = self.lora_B[active_adapter]
lora_E = self.lora_E[active_adapter]
dropout = self.lora_dropout[active_adapter]
scaling = self.scaling[active_adapter]
ranknum = self.ranknum[active_adapter] + 1e-5
x = self._cast_input_dtype(x, lora_A.dtype)
result += (dropout(x) @ (lora_A * lora_E).T @ lora_B.T) * scaling / ranknum
return result
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "adalora." + rep
class RankAllocator:
"""
The RankAllocator for AdaLoraModel. Paper: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=lq62uWRJjiY
Args:
config ([`AdaLoraConfig`]): The configuration of the AdaLora model.
model: the model that we apply AdaLoRA to.
"""
def __init__(self, model, peft_config, adapter_name):
self.peft_config = peft_config
self.adapter_name = adapter_name
self.beta1 = peft_config.beta1
self.beta2 = peft_config.beta2
assert self.beta1 > 0 and self.beta1 < 1
assert self.beta2 > 0 and self.beta2 < 1
self.reset_ipt()
self._set_budget_scheduler(model)
def set_total_step(self, total_step):
self.peft_config.total_step = total_step
def reset_ipt(self):
self.ipt = {}
self.exp_avg_ipt = {}
self.exp_avg_unc = {}
def _set_budget_scheduler(self, model):
self.init_bgt = 0
self.name_set = set()
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if f"lora_A.{self.adapter_name}" in n:
self.init_bgt += p.size(0)
self.name_set.add(n.replace("lora_A", "%s"))
self.name_set = sorted(self.name_set)
# The total final rank budget
self.target_bgt = self.peft_config.target_r * len(self.name_set)
def budget_schedule(self, step: int):
tinit = self.peft_config.tinit
tfinal = self.peft_config.tfinal
total_step = self.peft_config.total_step
# Initial warmup
if step <= tinit:
budget = self.init_bgt
mask_ind = False
# Final fine-tuning
elif step > total_step - tfinal:
budget = self.target_bgt
mask_ind = True
else:
# Budget decreasing with a cubic scheduler
mul_coeff = 1 - (step - tinit) / (total_step - tfinal - tinit)
budget = int((self.init_bgt - self.target_bgt) * (mul_coeff**3) + self.target_bgt)
mask_ind = True if step % self.peft_config.deltaT == 0 else False
return budget, mask_ind
def update_ipt(self, model):
# Update the sensitivity and uncertainty for every weight
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if "lora_" in n and self.adapter_name in n:
if n not in self.ipt:
self.ipt[n] = torch.zeros_like(p)
self.exp_avg_ipt[n] = torch.zeros_like(p)
self.exp_avg_unc[n] = torch.zeros_like(p)
with torch.no_grad():
if deepspeed_config() is not None:
import deepspeed
grad = deepspeed.utils.safe_get_full_grad(p)
self.ipt[n] = (p * grad).abs().detach()
else:
self.ipt[n] = (p * p.grad).abs().detach()
# Sensitivity smoothing
self.exp_avg_ipt[n] = self.beta1 * self.exp_avg_ipt[n] + (1 - self.beta1) * self.ipt[n]
# Uncertainty quantification
self.exp_avg_unc[n] = (
self.beta2 * self.exp_avg_unc[n] + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.ipt[n] - self.exp_avg_ipt[n]).abs()
)
def _element_score(self, n):
return self.exp_avg_ipt[n] * self.exp_avg_unc[n]
def _combine_ipt(self, ipt_E, ipt_AB):
ipt_AB = ipt_AB.sum(dim=1, keepdim=False)
sum_ipt = ipt_E.view(-1) + ipt_AB.view(-1)
return sum_ipt
def mask_to_budget(self, model, budget):
value_ipt = {}
vector_ipt = {}
triplet_ipt = {}
# Get the importance score for A, E, B
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if f"lora_A.{self.adapter_name}" in n:
entry_ipt = self._element_score(n)
comb_ipt = torch.mean(entry_ipt, dim=1, keepdim=True)
name_m = n.replace("lora_A", "%s")
if name_m not in vector_ipt:
vector_ipt[name_m] = [comb_ipt]
else:
vector_ipt[name_m].append(comb_ipt)
if f"lora_B.{self.adapter_name}" in n:
entry_ipt = self._element_score(n)
comb_ipt = torch.mean(entry_ipt, dim=0, keepdim=False).view(-1, 1)
name_m = n.replace("lora_B", "%s")
if name_m not in vector_ipt:
vector_ipt[name_m] = [comb_ipt]
else:
vector_ipt[name_m].append(comb_ipt)
if f"lora_E.{self.adapter_name}" in n:
entry_ipt = self._element_score(n)
name_m = n.replace("lora_E", "%s")
value_ipt[name_m] = entry_ipt
all_score = []
# Calculate the score for each triplet
for name_m in vector_ipt:
ipt_E = value_ipt[name_m]
ipt_AB = torch.cat(vector_ipt[name_m], dim=1)
sum_ipt = self._combine_ipt(ipt_E, ipt_AB)
name_E = name_m % "lora_E"
triplet_ipt[name_E] = sum_ipt.view(-1, 1)
all_score.append(sum_ipt.view(-1))
# Get the threshold by ranking ipt
mask_threshold = torch.kthvalue(
torch.cat(all_score),
k=self.init_bgt - budget,
)[0].item()
rank_pattern = {}
# Mask the unimportant triplets
with torch.no_grad():
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if f"lora_E.{self.adapter_name}" in n:
p.masked_fill_(triplet_ipt[n] <= mask_threshold, 0.0)
rank_pattern[n] = (~(triplet_ipt[n] <= mask_threshold)).view(-1).tolist()
return rank_pattern
def update_and_allocate(self, model, global_step, force_mask=False):
# # Update the importance score and allocate the budget
if global_step < self.peft_config.total_step - self.peft_config.tfinal:
self.update_ipt(model)
budget, mask_ind = self.budget_schedule(global_step)
# Allocate the budget according to importance scores
if mask_ind or force_mask:
rank_pattern = self.mask_to_budget(model, budget)
else:
rank_pattern = None
return budget, rank_pattern
def mask_using_rank_pattern(self, model, rank_pattern):
# Mask the unimportant triplets
is_adapter_name_truncated = False
if self.adapter_name not in next(iter(rank_pattern.keys())):
is_adapter_name_truncated = True
with torch.no_grad():
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if f"lora_E.{self.adapter_name}" in n:
key = n if not is_adapter_name_truncated else n.replace(f".{self.adapter_name}", "")
mask = torch.Tensor(rank_pattern[key]).unsqueeze(-1).to(p.device)
p.masked_fill_(~mask.bool(), 0.0)
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/adalora/layer.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/adalora/layer.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 7172
}
| 243
|
# Copyright 2024-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import math
import warnings
from typing import Any, Optional, Union
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer, check_adapters_to_merge
class BoneLayer(BaseTunerLayer):
# All names of layers that may contain (trainable) adapter weights
adapter_layer_names = ("bone_block",)
# All names of other parameters that may contain adapter-related parameters
other_param_names = ("bone_r",)
def __init__(self, base_layer: nn.Module, **kwargs) -> None:
self.base_layer = base_layer
self.bone_r = {}
self.bone_block = nn.ParameterDict({})
# Mark the weight as unmerged
self._disable_adapters = False
self.merged_adapters = []
# flag to enable/disable casting of input to weight dtype during forward call
self.cast_input_dtype_enabled = True
self.kwargs = kwargs
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
if isinstance(base_layer, nn.Linear):
self.in_features, self.out_features = base_layer.in_features, base_layer.out_features
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported layer type {type(base_layer)}")
def update_layer(
self,
adapter_name: str,
r: int,
init_weights: bool,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
"""Internal function to create bone adapter
Args:
adapter_name (`str`): Name for the adapter to add.
r (`int`): Rank for the added adapter.
init_weights (`bool`): Whether to initialize weights.
"""
if r <= 0:
raise ValueError(f"`r` should be a positive integer value but the value passed is {r}")
self.bone_r[adapter_name] = r
# Determine shape of Bone weights
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
if isinstance(base_layer, nn.Linear):
self.bone_block[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(r, self.out_features), requires_grad=True)
else:
raise TypeError(f"Bone is not implemented for base layers of type {type(base_layer).__name__}")
# Initialize weights
if init_weights == "bat":
if self.in_features % r != 0 or self.out_features % r != 0:
raise ValueError("The weight matrix must be fully divisible into [r, r] blocks.")
self.reset_bat_parameters(adapter_name, r)
elif init_weights:
self.reset_bone_parameters(adapter_name, r)
else:
self.reset_bone_parameters_random(adapter_name)
# Move new weights to device
self._move_adapter_to_device_of_base_layer(adapter_name)
self.set_adapter(self.active_adapters)
def reset_bone_parameters(self, adapter_name: str, r):
self.bone_block[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(r, self.out_features), requires_grad=True)
def reset_bat_parameters(self, adapter_name: str, r):
self.bone_block[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(self.out_features // r, r, r), requires_grad=True)
def reset_bone_parameters_random(self, adapter_name: str):
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.bone_block[adapter_name], a=math.sqrt(5))
def scale_layer(self, scale: float) -> None:
if scale == 1:
return
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.bone_block.keys():
continue
warnings.warn("Scaling operation for Bone not supported! Automatically set scale to 1.")
def unscale_layer(self, scale=None) -> None:
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.bone_block.keys():
continue
warnings.warn("Unscaling operation for Bone not supported! Keeping scale at 1.")
class BoneLinear(nn.Module, BoneLayer):
"""
Bone implemented in a dense layer.
"""
def __init__(
self,
base_layer,
adapter_name: str,
r: int = 0,
init_weights: Union[bool, str] = True,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
BoneLayer.__init__(self, base_layer, **kwargs)
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(adapter_name, r, init_weights, **kwargs)
self.bone_fn = init_weights
def merge(self, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> None:
"""
Merge the active adapter weights into the base weights
Args:
safe_merge (`bool`, *optional*):
If `True`, the merge operation will be performed in a copy of the original weights and check for NaNs
before merging the weights. This is useful if you want to check if the merge operation will produce
NaNs. Defaults to `False`.
adapter_names (`List[str]`, *optional*):
The list of adapter names that should be merged. If `None`, all active adapters will be merged.
Defaults to `None`.
"""
adapter_names = check_adapters_to_merge(self, adapter_names)
if not adapter_names:
# no adapter to merge
return
for active_adapter in adapter_names:
if active_adapter in self.bone_block.keys():
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
orig_dtype = base_layer.weight.dtype
if safe_merge:
# Note that safe_merge will be slower than the normal merge
# because of the copy operation.
orig_weight = base_layer.weight.data.clone()
if self.bone_fn == "bat":
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter, orig_weight)
orig_weight += delta_weight
else:
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight_bone(active_adapter, self.base_layer.weight.data)
orig_weight = delta_weight
if not torch.isfinite(orig_weight).all():
raise ValueError(
f"NaNs detected in the merged weights. The adapter {active_adapter} seems to be broken"
)
base_layer.weight.data = orig_weight.to(orig_dtype)
else:
if self.bone_fn == "bat":
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter, self.base_layer.weight.data)
base_layer.weight.data += delta_weight.to(orig_dtype)
else:
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight_bone(active_adapter, self.base_layer.weight.data)
base_layer.weight.data = delta_weight.to(orig_dtype)
self.merged_adapters.append(active_adapter)
def unmerge(self) -> None:
"""
This method unmerges all merged adapter layers from the base weights.
"""
if not self.merged:
warnings.warn("Already unmerged. Nothing to do.")
return
while len(self.merged_adapters) > 0:
active_adapter = self.merged_adapters.pop()
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
orig_dtype = base_layer.weight.dtype
if active_adapter in self.bone_block.keys():
orig_weight = self.get_base_layer().weight.data.clone()
if self.bone_fn == "bat":
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter, orig_weight, re=True)
else:
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight_bone(active_adapter, orig_weight, re=True)
base_layer.weight.data = delta_weight.to(orig_dtype)
def get_delta_weight(self, adapter, orig_weight, re: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Compute the delta weight for the given adapter.
Args:
adapter (str):
The name of the adapter for which the delta weight should be computed.
"""
device = self.bone_block[adapter].device
dtype = self.bone_block[adapter].dtype
# In case users wants to merge the adapter weights that are in
# (b)float16 while being on CPU, we need to cast the weights to float32, perform the merge and then cast back to
# (b)float16 because some CPUs have slow bf16/fp16 matmuls.
cast_to_fp32 = device.type == "cpu" and (dtype == torch.float16 or dtype == torch.bfloat16)
weight_bone = self.bone_block[adapter]
if cast_to_fp32:
weight_bone = weight_bone.float()
orig_weight = orig_weight.to(weight_bone.dtype)
r = weight_bone.size(-1)
if re:
o = orig_weight.reshape(orig_weight.size(0) // r, r, orig_weight.size(1) // r, r).permute(2, 0, 1, 3)
one = torch.eye(weight_bone.size(-1)).to(weight_bone.device)
# inverse must be in float32, after that the dtype can be adjusted if needed
inv_I_plus_b = torch.inverse(one + weight_bone)
inv_I_plus_b = inv_I_plus_b.to(weight_bone.dtype)
w = (o - weight_bone) @ inv_I_plus_b
output_tensor = w.permute(1, 2, 0, 3).reshape(*orig_weight.shape)
else:
w = (
orig_weight.reshape(orig_weight.size(0) // r, r, orig_weight.size(1) // r, r).permute(2, 0, 1, 3)
@ weight_bone
+ weight_bone
)
output_tensor = w.permute(1, 2, 0, 3).reshape(*orig_weight.shape)
if cast_to_fp32:
output_tensor = output_tensor.to(dtype=dtype)
# cast back the weights
self.bone_block[adapter].data = weight_bone.to(dtype)
return output_tensor
def get_delta_weight_bone(self, adapter, orig_weight, re: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Compute the delta weight for the given adapter.
Args:
adapter (str):
The name of the adapter for which the delta weight should be computed.
"""
device = self.bone_block[adapter].device
dtype = self.bone_block[adapter].dtype
# In case users wants to merge the adapter weights that are in
# (b)float16 while being on CPU, we need to cast the weights to float32, perform the merge and then cast back to
# (b)float16 because some CPUs have slow bf16/fp16 matmuls.
cast_to_fp32 = device.type == "cpu" and (dtype == torch.float16 or dtype == torch.bfloat16)
weight_bone = self.bone_block[adapter]
if cast_to_fp32:
weight_bone = weight_bone.float()
in_features = orig_weight.size(-1)
r = weight_bone.size(0)
if in_features % r != 0:
last_size = in_features % r
n_block = in_features // r
n_block_size = n_block * r
if re:
orig_weight[:, :n_block_size] = (
(orig_weight[:, :n_block_size].reshape(-1, n_block, r).permute(1, 2, 0) - weight_bone)
.permute(2, 0, 1)
.reshape(*orig_weight[:, :n_block_size].shape)
)
orig_weight[:, n_block_size:] = (
orig_weight[:, n_block_size:] - (weight_bone.transpose(0, 1))[:, :last_size]
)
else:
orig_weight[:, :n_block_size] = (
(orig_weight[:, :n_block_size].reshape(-1, n_block, r).permute(1, 2, 0) + weight_bone)
.permute(2, 0, 1)
.reshape(*orig_weight[:, :n_block_size].shape)
)
orig_weight[:, n_block_size:] = (
orig_weight[:, n_block_size:] + (weight_bone.transpose(0, 1))[:, :last_size]
)
output_tensor = orig_weight
else:
if re:
w = orig_weight.reshape(-1, orig_weight.size(1) // r, r).permute(1, 2, 0) - weight_bone
output_tensor = w.permute(2, 0, 1).reshape(*orig_weight.shape)
else:
w = orig_weight.reshape(-1, orig_weight.size(1) // r, r).permute(1, 2, 0) + weight_bone
output_tensor = w.permute(2, 0, 1).reshape(*orig_weight.shape)
if cast_to_fp32:
output_tensor = output_tensor.to(dtype=dtype)
# cast back the weights
self.bone_block[adapter].data = weight_bone.to(dtype)
return output_tensor
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> torch.Tensor:
previous_dtype = x.dtype
if self.disable_adapters:
if self.merged:
self.unmerge()
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
elif self.merged:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
else:
if self.bone_fn == "bat":
orig_weight = self.base_layer.weight.data.clone()
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.bone_block.keys():
continue
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter, orig_weight)
orig_weight = orig_weight + delta_weight
x = self._cast_input_dtype(x, orig_weight.dtype)
bias = self._cast_input_dtype(self.base_layer.bias, orig_weight.dtype)
result = F.linear(input=x, weight=orig_weight, bias=bias)
else:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.bone_block.keys():
continue
bone = self.bone_block[active_adapter]
r = bone.size(0)
if x.size(-1) % r != 0:
padding_size = (r - x.size(-1) % r) % r
x = F.pad(x, (0, padding_size))
x = self._cast_input_dtype(x, bone.dtype)
result = result + torch.sum(x.reshape(*x.shape[:-1], x.size(-1) // r, r), dim=-2) @ bone
result = result.to(previous_dtype)
return result
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "bone." + rep
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/bone/layer.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/bone/layer.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 7038
}
| 244
|
# Copyright 2024-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import math
import warnings
from typing import Any, Optional, Union
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer, check_adapters_to_merge
class HRALayer(BaseTunerLayer):
# All names of layers that may contain (trainable) adapter weights
adapter_layer_names = ("hra_u",)
# All names of other parameters that may contain adapter-related parameters
other_param_names = ("hra_r", "hra_apply_GS")
def __init__(self, base_layer: nn.Module, **kwargs) -> None:
self.base_layer = base_layer
self.hra_r = {}
self.hra_apply_GS = {}
self.hra_u = nn.ParameterDict({})
# Mark the weight as unmerged
self._disable_adapters = False
self.merged_adapters = []
# flag to enable/disable casting of input to weight dtype during forward call
self.cast_input_dtype_enabled = True
self.kwargs = kwargs
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
if isinstance(base_layer, nn.Linear):
self.in_features, self.out_features = base_layer.in_features, base_layer.out_features
elif isinstance(base_layer, nn.Conv2d):
self.in_features, self.out_features = base_layer.in_channels, base_layer.out_channels
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported layer type {type(base_layer)}")
def update_layer(
self,
adapter_name: str,
r: int,
apply_GS: bool,
init_weights: bool,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
"""Internal function to create hra adapter
Args:
adapter_name (`str`): Name for the adapter to add.
r (`int`): Rank for the added adapter.
init_weights (`bool`): Whether to initialize weights.
apply_GS (`bool`): Whether to apply Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization or not.
"""
if r <= 0:
raise ValueError(f"`r` should be a positive integer value but the value passed is {r}")
self.hra_r[adapter_name] = r
self.hra_apply_GS[adapter_name] = apply_GS
# Determine shape of HRA weights
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
if isinstance(base_layer, nn.Linear):
self.hra_u[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.in_features, r), requires_grad=True)
elif isinstance(base_layer, nn.Conv2d):
self.hra_u[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(
torch.empty(self.in_features * base_layer.kernel_size[0] * base_layer.kernel_size[0], r),
requires_grad=True,
)
else:
raise TypeError(f"HRA is not implemented for base layers of type {type(base_layer).__name__}")
# Initialize weights
if init_weights:
self.reset_hra_parameters(adapter_name)
else:
self.reset_hra_parameters_random(adapter_name)
# Move new weights to device
self._move_adapter_to_device_of_base_layer(adapter_name)
self.set_adapter(self.active_adapters)
def reset_hra_parameters(self, adapter_name: str):
if self.hra_r[adapter_name] % 2 != 0:
warnings.warn("The symmetric initialization can NOT be performed when r is odd!")
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.hra_u[adapter_name], a=math.sqrt(5))
else:
shape = self.hra_u[adapter_name].shape
half_u = torch.zeros(shape[0], shape[1] // 2)
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(half_u, a=math.sqrt(5))
self.hra_u[adapter_name] = nn.Parameter(torch.repeat_interleave(half_u, 2, dim=1))
def reset_hra_parameters_random(self, adapter_name: str):
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.hra_u[adapter_name], a=math.sqrt(5))
def scale_layer(self, scale: float) -> None:
if scale == 1:
return
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.hra_u.keys():
continue
warnings.warn("Scaling operation for HRA not supported! Automatically set scale to 1.")
def unscale_layer(self, scale=None) -> None:
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.hra_u.keys():
continue
warnings.warn("Unscaling operation for HRA not supported! Keeping scale at 1.")
class HRALinear(nn.Module, HRALayer):
"""
HRA implemented in a dense layer.
"""
def __init__(
self,
base_layer,
adapter_name: str,
r: int = 0,
apply_GS: bool = False,
init_weights: Union[bool, str] = True,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
HRALayer.__init__(self, base_layer, **kwargs)
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(adapter_name, r, apply_GS, init_weights, **kwargs)
def merge(self, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> None:
"""
Merge the active adapter weights into the base weights
Args:
safe_merge (`bool`, *optional*):
If `True`, the merge operation will be performed in a copy of the original weights and check for NaNs
before merging the weights. This is useful if you want to check if the merge operation will produce
NaNs. Defaults to `False`.
adapter_names (`List[str]`, *optional*):
The list of adapter names that should be merged. If `None`, all active adapters will be merged.
Defaults to `None`.
"""
adapter_names = check_adapters_to_merge(self, adapter_names)
if not adapter_names:
# no adapter to merge
return
for active_adapter in adapter_names:
if active_adapter in self.hra_u.keys():
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
orig_dtype = base_layer.weight.dtype
if safe_merge:
# Note that safe_merge will be slower than the normal merge
# because of the copy operation.
orig_weight = base_layer.weight.data.clone()
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
orig_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
if not torch.isfinite(orig_weight).all():
raise ValueError(
f"NaNs detected in the merged weights. The adapter {active_adapter} seems to be broken"
)
base_layer.weight.data = orig_weight.to(orig_dtype)
else:
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
new_weight = torch.mm(base_layer.weight.data.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
base_layer.weight.data = new_weight.to(orig_dtype)
self.merged_adapters.append(active_adapter)
def unmerge(self) -> None:
"""
This method unmerges all merged adapter layers from the base weights.
"""
if not self.merged:
warnings.warn("Already unmerged. Nothing to do.")
return
while len(self.merged_adapters) > 0:
active_adapter = self.merged_adapters.pop()
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
orig_dtype = base_layer.weight.dtype
if active_adapter in self.hra_u.keys():
orig_weight = base_layer.weight.data.clone()
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter, reverse=True)
new_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
base_layer.weight.data = new_weight.to(orig_dtype)
def get_delta_weight(self, adapter_name: str, reverse: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
rank = self.hra_r[adapter_name]
apply_GS = self.hra_apply_GS[adapter_name]
opt_u = self.hra_u[adapter_name]
shape = opt_u.shape
if apply_GS:
weight = [(opt_u[:, 0] / opt_u[:, 0].norm()).view(-1, 1)]
for i in range(1, rank):
ui = opt_u[:, i].view(-1, 1)
for j in range(i):
ui = ui - (weight[j].t() @ ui) * weight[j]
weight.append((ui / ui.norm()).view(-1, 1))
weight = torch.cat(weight, dim=1)
weight = torch.eye(shape[0], device=opt_u.device, dtype=opt_u.dtype) - 2 * weight @ weight.t()
else:
opt_u = opt_u / opt_u.norm(dim=0)
weight = torch.eye(shape[0], device=opt_u.device, dtype=opt_u.dtype)
if reverse:
indices = range(rank - 1, -1, -1)
else:
indices = range(rank)
for i in indices:
ui = opt_u[:, i].view(-1, 1)
weight = weight - 2 * weight @ ui @ ui.t()
return weight
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> torch.Tensor:
previous_dtype = x.dtype
if self.disable_adapters:
if self.merged:
self.unmerge()
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
elif self.merged:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
else:
new_weight = torch.eye(self.in_features, device=x.device)
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.hra_u.keys():
continue
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
new_weight = torch.mm(new_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
orig_weight = self.get_base_layer().weight.data
orig_weight = self._cast_input_dtype(orig_weight, new_weight.dtype)
new_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight, new_weight)
bias = self._cast_input_dtype(self.base_layer.bias, new_weight.dtype)
if self.cast_input_dtype_enabled:
x = self._cast_input_dtype(x, new_weight.dtype)
else:
x = x.to(self.get_base_layer().weight.data.dtype)
result = F.linear(input=x, weight=new_weight, bias=bias)
result = result.to(previous_dtype)
return result
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "hra." + rep
class HRAConv2d(nn.Module, HRALayer):
"""HRA implemented in Conv2d layer"""
def __init__(
self,
base_layer,
adapter_name: str,
r: int = 0,
apply_GS: bool = False,
init_weights: Union[bool, str] = True,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__()
HRALayer.__init__(self, base_layer)
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(adapter_name, r, apply_GS, init_weights, **kwargs)
def merge(self, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> None:
"""
Merge the active adapter weights into the base weights
Args:
safe_merge (`bool`, *optional*):
If `True`, the merge operation will be performed in a copy of the original weights and check for NaNs
before merging the weights. This is useful if you want to check if the merge operation will produce
NaNs. Defaults to `False`.
adapter_names (`List[str]`, *optional*):
The list of adapter names that should be merged. If `None`, all active adapters will be merged.
Defaults to `None`.
"""
adapter_names = check_adapters_to_merge(self, adapter_names)
if not adapter_names:
# no adapter to merge
return
for active_adapter in adapter_names:
if active_adapter in self.hra_u.keys():
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
orig_dtype = base_layer.weight.dtype
if safe_merge:
# Note that safe_merge will be slower than the normal merge
# because of the copy operation.
orig_weight = base_layer.weight.data.clone()
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features * base_layer.kernel_size[0] * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
orig_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features,
base_layer.kernel_size[0],
base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
if not torch.isfinite(orig_weight).all():
raise ValueError(
f"NaNs detected in the merged weights. The adapter {active_adapter} seems to be broken"
)
base_layer.weight.data = orig_weight.to(orig_dtype)
else:
orig_weight = base_layer.weight.data
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0] * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
orig_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features,
base_layer.kernel_size[0],
base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
base_layer.weight.data = orig_weight.to(orig_dtype)
self.merged_adapters.append(active_adapter)
def unmerge(self) -> None:
"""
This method unmerges all merged adapter layers from the base weights.
"""
if not self.merged:
warnings.warn("Already unmerged. Nothing to do.")
return
while len(self.merged_adapters) > 0:
active_adapter = self.merged_adapters.pop()
base_layer = self.get_base_layer()
orig_dtype = base_layer.weight.dtype
if active_adapter in self.hra_u.keys():
orig_weight = base_layer.weight.data.clone()
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features * base_layer.kernel_size[0] * base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter, reverse=True)
orig_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features, self.in_features, base_layer.kernel_size[0], base_layer.kernel_size[0]
)
base_layer.weight.data = orig_weight.to(orig_dtype)
def get_delta_weight(self, adapter_name: str, reverse: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
rank = self.hra_r[adapter_name]
apply_GS = self.hra_apply_GS[adapter_name]
opt_u = self.hra_u[adapter_name]
shape = opt_u.shape
if apply_GS:
weight = [(opt_u[:, 0] / opt_u[:, 0].norm()).view(-1, 1)]
for i in range(1, rank):
ui = opt_u[:, i].view(-1, 1)
for j in range(i):
ui = ui - (weight[j].t() @ ui) * weight[j]
weight.append((ui / ui.norm()).view(-1, 1))
weight = torch.cat(weight, dim=1)
weight = torch.eye(shape[0], device=opt_u.device, dtype=opt_u.dtype) - 2 * weight @ weight.t()
else:
opt_u = opt_u / opt_u.norm(dim=0)
weight = torch.eye(shape[0], device=opt_u.device, dtype=opt_u.dtype)
if reverse:
indices = range(rank - 1, -1, -1)
else:
indices = range(rank)
for i in indices:
ui = opt_u[:, i].view(-1, 1)
weight = weight - 2 * weight @ ui @ ui.t()
return weight
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> torch.Tensor:
previous_dtype = x.dtype
if self.disable_adapters:
if self.merged:
self.unmerge()
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
elif self.merged:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
else:
new_weight = torch.eye(
self.in_features * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0] * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0],
device=x.device,
)
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.hra_u.keys():
continue
delta_weight = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
new_weight = torch.mm(new_weight.to(delta_weight.dtype), delta_weight)
orig_weight = self.base_layer.weight.data
orig_weight = orig_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0] * self.base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
orig_weight = self._cast_input_dtype(orig_weight, new_weight.dtype)
bias = self._cast_input_dtype(self.base_layer.bias, new_weight.dtype)
new_weight = torch.mm(orig_weight, new_weight)
new_weight = new_weight.view(
self.out_features,
self.in_features,
self.base_layer.kernel_size[0],
self.base_layer.kernel_size[0],
)
if self.cast_input_dtype_enabled:
x = self._cast_input_dtype(x, new_weight.dtype)
else:
x = x.to(self.get_base_layer().weight.data.dtype)
result = F.conv2d(
input=x,
weight=new_weight,
bias=bias,
padding=self.base_layer.padding[0],
stride=self.base_layer.stride[0],
)
result = result.to(previous_dtype)
return result
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "hra." + rep
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/hra/layer.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/hra/layer.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 9358
}
| 245
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import annotations
import math
import operator
import warnings
from contextlib import contextmanager
from dataclasses import asdict, replace
from enum import Enum
from functools import partial, reduce
from typing import Literal, Optional
import torch
from torch import nn
from tqdm import tqdm
from peft.import_utils import is_bnb_4bit_available, is_bnb_available
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import (
BaseTuner,
BaseTunerLayer,
check_target_module_exists,
onload_layer,
replicate_layers,
)
from peft.utils import (
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper,
ModulesToSaveWrapper,
_freeze_adapter,
_get_submodules,
get_peft_model_state_dict,
get_quantization_config,
)
from peft.utils.merge_utils import dare_linear, dare_ties, magnitude_prune, task_arithmetic, ties
from peft.utils.other import get_pattern_key
from .aqlm import dispatch_aqlm
from .awq import dispatch_awq
from .config import LoraConfig
from .eetq import dispatch_eetq
from .gptq import dispatch_gptq
from .hqq import dispatch_hqq
from .inc import dispatch_inc
from .layer import Conv2d, LoraLayer, ParamWrapper, dispatch_default
from .torchao import dispatch_torchao
from .tp_layer import dispatch_megatron
def _adapter_names_pre_forward_hook(target, args, kwargs, adapter_names):
# pre-forward hook to inject the adapter_names argument when using mixed adapter batches inference
kwargs["adapter_names"] = adapter_names
return args, kwargs
class LoraModel(BaseTuner):
"""
Creates Low Rank Adapter (LoRA) model from a pretrained transformers model.
The method is described in detail in https://huggingface.co/papers/2106.09685.
Args:
model ([`torch.nn.Module`]): The model to be adapted.
config ([`LoraConfig`]): The configuration of the Lora model.
adapter_name (`str`): The name of the adapter, defaults to `"default"`.
low_cpu_mem_usage (`bool`, `optional`, defaults to `False`):
Create empty adapter weights on meta device. Useful to speed up the loading process.
Returns:
`torch.nn.Module`: The Lora model.
Example:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
>>> from peft import LoraModel, LoraConfig
>>> config = LoraConfig(
... task_type="SEQ_2_SEQ_LM",
... r=8,
... lora_alpha=32,
... target_modules=["q", "v"],
... lora_dropout=0.01,
... )
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-base")
>>> lora_model = LoraModel(model, config, "default")
```
```py
>>> import torch
>>> import transformers
>>> from peft import LoraConfig, PeftModel, get_peft_model, prepare_model_for_kbit_training
>>> rank = ...
>>> target_modules = ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "out_proj", "fc_in", "fc_out", "wte"]
>>> config = LoraConfig(
... r=4, lora_alpha=16, target_modules=target_modules, lora_dropout=0.1, bias="none", task_type="CAUSAL_LM"
... )
>>> quantization_config = transformers.BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True)
>>> tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
... "kakaobrain/kogpt",
... revision="KoGPT6B-ryan1.5b-float16", # or float32 version: revision=KoGPT6B-ryan1.5b
... bos_token="[BOS]",
... eos_token="[EOS]",
... unk_token="[UNK]",
... pad_token="[PAD]",
... mask_token="[MASK]",
... )
>>> model = transformers.GPTJForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
... "kakaobrain/kogpt",
... revision="KoGPT6B-ryan1.5b-float16", # or float32 version: revision=KoGPT6B-ryan1.5b
... pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
... use_cache=False,
... device_map={"": rank},
... torch_dtype=torch.float16,
... quantization_config=quantization_config,
... )
>>> model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model)
>>> lora_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
```
**Attributes**:
- **model** ([`~transformers.PreTrainedModel`]) -- The model to be adapted.
- **peft_config** ([`LoraConfig`]): The configuration of the Lora model.
"""
prefix: str = "lora_"
def _check_new_adapter_config(self, config: LoraConfig) -> None:
"""
A helper method to check the config when a new adapter is being added.
Raise a ValueError if there is something wrong with the config or if it conflicts with existing adapters.
"""
# TODO: there should be a check if any of the existing adapters actually has bias != "none", or else the check
# does not fully correspond to the error message.
if (len(self.peft_config) > 1) and (config.bias != "none"):
raise ValueError(
f"{self.__class__.__name__} supports only 1 adapter with bias. When using multiple adapters, "
"set bias to 'none' for all adapters."
)
@staticmethod
def _check_target_module_exists(lora_config, key):
return check_target_module_exists(lora_config, key)
def _prepare_model(self, peft_config: LoraConfig, model: nn.Module):
r"""
A private method to modify the model structure before adapter is applied.
Args:
peft_config (`PeftConfig`):
The prepared adapter config.
model (`nn.Module`):
The model that is going to be adapted.
"""
if peft_config.layer_replication:
replicate_layers(model, peft_config.layer_replication)
def _create_and_replace(
self,
lora_config,
adapter_name,
target,
target_name,
parent,
current_key,
*,
parameter_name: Optional[str] = None,
) -> None:
if current_key is None:
raise ValueError("Current Key shouldn't be `None`")
if lora_config.target_parameters:
# Right now, unfortunately, we don't support multiple adapters with target_parameters on the same model.
other_configs_use_target_params = any(
conf.target_parameters for key, conf in self.peft_config.items() if key != adapter_name
)
if other_configs_use_target_params:
raise ValueError(
f"Adding a LoRA config with `target_parameters={lora_config.target_parameters}` but there are "
"already other LoRA adapters on this model that use `target_parameters`. At the moment, only "
"one LoRA adapter per model with `target_parameters` is allowed."
)
# Regexp matching - Find key which matches current target_name in patterns provided
r_key = get_pattern_key(lora_config.rank_pattern.keys(), current_key)
alpha_key = get_pattern_key(lora_config.alpha_pattern.keys(), current_key)
r = lora_config.rank_pattern.get(r_key, lora_config.r)
alpha = lora_config.alpha_pattern.get(alpha_key, lora_config.lora_alpha)
kwargs = {
"r": r,
"lora_alpha": alpha,
"lora_dropout": lora_config.lora_dropout,
"fan_in_fan_out": lora_config.fan_in_fan_out,
"init_lora_weights": lora_config.init_lora_weights,
"use_rslora": lora_config.use_rslora,
"use_dora": lora_config.use_dora,
"use_qalora": lora_config.use_qalora,
"qalora_group_size": lora_config.qalora_group_size,
"ephemeral_gpu_offload": lora_config.runtime_config.ephemeral_gpu_offload,
"lora_bias": lora_config.lora_bias,
"loaded_in_8bit": getattr(self.model, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False),
"loaded_in_4bit": getattr(self.model, "is_loaded_in_4bit", False),
"parameter_name": parameter_name,
}
# for torchao merging, we need the get_apply_tensor_subclass from the quantization config
try:
kwargs["get_apply_tensor_subclass"] = operator.attrgetter(
"hf_quantizer.quantization_config.get_apply_tensor_subclass"
)(self.model)
except AttributeError:
pass
quant_methods = ["gptq", "aqlm", "awq"]
for quant_method in quant_methods:
quantization_config = get_quantization_config(self.model, method=quant_method)
if quantization_config is not None:
kwargs[f"{quant_method}_quantization_config"] = quantization_config
# note: AdaLoraLayer is a subclass of LoraLayer, we need to exclude it
from peft.tuners.adalora import AdaLoraLayer
# if the target is a ParamWrapper, we nest it to allow targeting multiple nn.Parameter on the same module
wrap_target_param = isinstance(target, ParamWrapper) and (adapter_name in target.lora_A)
if isinstance(target, LoraLayer) and not isinstance(target, AdaLoraLayer) and not wrap_target_param:
target.update_layer(
adapter_name,
r,
lora_alpha=alpha,
lora_dropout=lora_config.lora_dropout,
init_lora_weights=lora_config.init_lora_weights,
use_rslora=lora_config.use_rslora,
use_dora=lora_config.use_dora,
lora_bias=lora_config.lora_bias,
)
else:
if isinstance(target, ParamWrapper) and (parameter_name == target.parameter_name):
raise ValueError(
"Trying to target the same nn.Parameter twice, this should not happen. Please open an issue on the "
"PEFT repo: https://github.com/huggingface/peft/issues"
)
device_map = self.model.hf_device_map if hasattr(self.model, "hf_device_map") else None
new_module = self._create_new_module(lora_config, adapter_name, target, device_map=device_map, **kwargs)
if adapter_name not in self.active_adapters:
# adding an additional adapter: it is not automatically trainable
new_module.requires_grad_(False)
self._replace_module(parent, target_name, new_module, target)
def _replace_module(self, parent, child_name, new_module, child):
setattr(parent, child_name, new_module)
# It's not necessary to set requires_grad here, as that is handled by
# _mark_only_adapters_as_trainable
# child layer wraps the original module, unpack it
if hasattr(child, "base_layer"):
child = child.base_layer
meta = torch.device("meta")
# dispatch to correct device
for name, module in new_module.named_modules():
if (self.prefix in name) or ("ranknum" in name):
if hasattr(child, "qweight"):
weight = child.qweight
elif hasattr(child, "W_q"):
weight = child.W_q
elif hasattr(child, "weight"):
weight = child.weight
elif getattr(child, "in_proj_weight", None) is not None: # MHA
weight = child.in_proj_weight
else:
weight = next(child.parameters())
if not any(p.device == meta for p in module.parameters()):
module.to(weight.device)
def _mark_only_adapters_as_trainable(self, model: nn.Module) -> None:
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if self.prefix not in n:
p.requires_grad = False
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
bias = self.peft_config[active_adapter].bias
if bias == "none":
continue
if bias == "all":
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if "bias" in n:
p.requires_grad = True
elif bias == "lora_only":
for m in model.modules():
if isinstance(m, LoraLayer) and hasattr(m, "bias") and m.bias is not None:
m.bias.requires_grad = True
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Requested bias: {bias}, is not implemented.")
@staticmethod
def _create_new_module(lora_config, adapter_name, target, **kwargs):
# Collect dispatcher functions to decide what backend to use for the replaced LoRA layer. The order matters,
# because the first match is always used. Therefore, the default layers should be checked last.
dispatchers = []
if lora_config._custom_modules:
# Experimental custom LoRA module support. Allows users to pass a custom mapping for unsupported layer
# types by impelementing their own LoRA layers.
def dynamic_dispatch_func(target, adapter_name, lora_config, **kwargs):
new_module = None
if isinstance(target, BaseTunerLayer):
target_base_layer = target.get_base_layer()
else:
target_base_layer = target
for key, custom_cls in lora_config._custom_modules.items():
if isinstance(target_base_layer, key):
new_module = custom_cls(target, adapter_name, **kwargs)
break
return new_module
dispatchers.append(dynamic_dispatch_func)
# avoid eager bnb import
if is_bnb_available():
from .bnb import dispatch_bnb_8bit
dispatchers.append(dispatch_bnb_8bit)
if is_bnb_4bit_available():
from .bnb import dispatch_bnb_4bit
dispatchers.append(dispatch_bnb_4bit)
dispatchers.extend(
[
dispatch_eetq,
dispatch_aqlm,
dispatch_awq,
dispatch_gptq,
dispatch_hqq,
dispatch_inc,
dispatch_torchao,
dispatch_megatron,
dispatch_default,
]
)
new_module = None
for dispatcher in dispatchers:
new_module = dispatcher(target, adapter_name, lora_config=lora_config, **kwargs)
if new_module is not None: # first match wins
break
if new_module is None:
# no module could be matched
raise ValueError(
f"Target module {target} is not supported. Currently, only the following modules are supported: "
"`torch.nn.Linear`, `torch.nn.Embedding`, `torch.nn.Conv1d`, `torch.nn.Conv2d`, `torch.nn.Conv3d`, "
"`transformers.pytorch_utils.Conv1D`, `torch.nn.MultiheadAttention.`."
)
return new_module
def __getattr__(self, name: str):
"""Forward missing attributes to the wrapped module."""
try:
return super().__getattr__(name) # defer to nn.Module's logic
except AttributeError:
if name == "model": # see #1892: prevent infinite recursion if class is not initialized
raise
return getattr(self.model, name)
def get_peft_config_as_dict(self, inference: bool = False):
config_dict = {}
for key, value in self.peft_config.items():
config = {k: v.value if isinstance(v, Enum) else v for k, v in asdict(value).items()}
if inference:
config["inference_mode"] = True
config_dict[key] = config
return config
def _set_adapter_layers(self, enabled: bool = True) -> None:
for module in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(module, (BaseTunerLayer, AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper)):
module.enable_adapters(enabled)
def enable_adapter_layers(self) -> None:
"""Enable all adapters.
Call this if you have previously disabled all adapters and want to re-enable them.
"""
self._set_adapter_layers(enabled=True)
def disable_adapter_layers(self) -> None:
"""Disable all adapters.
When disabling all adapters, the model output corresponds to the output of the base model.
"""
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
val = self.peft_config[active_adapter].bias
if val != "none":
msg = (
f"Careful, disabling adapter layers with bias configured to be '{val}' does not produce the same "
"output as the base model would without adaption."
)
warnings.warn(msg)
self._set_adapter_layers(enabled=False)
def set_adapter(self, adapter_name: str | list[str]) -> None:
"""Set the active adapter(s).
Additionally, this function will set the specified adapters to trainable (i.e., requires_grad=True). If this is
not desired, use the following code.
```py
>>> for name, param in model_peft.named_parameters():
... if ...: # some check on name (ex. if 'lora' in name)
... param.requires_grad = False
```
Args:
adapter_name (`str` or `list[str]`): Name of the adapter(s) to be activated.
"""
for module in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(module, LoraLayer):
if module.merged:
warnings.warn("Adapter cannot be set when the model is merged. Unmerging the model first.")
module.unmerge()
module.set_adapter(adapter_name)
self.active_adapter = adapter_name
@contextmanager
def _enable_peft_forward_hooks(self, *args, **kwargs):
# If adapter_names is passed as an argument, we inject it into the forward arguments.
adapter_names = kwargs.pop("adapter_names", None)
if adapter_names is None:
# nothing to do
yield
return
if self.training:
raise ValueError("Cannot pass `adapter_names` when the model is in training mode.")
# Check that users only passed actually existing adapters.
# Note: We cannot do this on the layer level, as each individual layer may not have each adapter. Still, we want
# to check that there is at least one layer with the given name, or else something like typos can easily slip.
expected_adapters = set()
for layer in self.modules():
if isinstance(layer, LoraLayer):
expected_adapters |= layer.lora_A.keys()
expected_adapters |= layer.lora_embedding_A.keys()
unique_adapters = {name for name in adapter_names if name != "__base__"}
unexpected_adapters = unique_adapters - expected_adapters
if unexpected_adapters:
raise ValueError(f"Trying to infer with non-existing adapter(s): {', '.join(sorted(unexpected_adapters))}")
# deal with beam search
num_beams = kwargs.get("num_beams", None)
uses_beam_search = isinstance(num_beams, int) and (num_beams > 1)
original_adapter_names = adapter_names[:]
if uses_beam_search:
if not isinstance(adapter_names, (list, tuple)):
raise TypeError(f"Got adapter names of type {type(adapter_names)}, expected a list of str.")
# When there is beam search, the inputs are repeated n times, thus we repeat each adapter name n times and
# then flatten the nested list. For encoder-decoder models, this extended list should not be applied to the
# encoder part. Further below, the original argument is thus restored for the encoder.
adapter_names = sum(([n] * kwargs["num_beams"] for n in adapter_names), [])
hook_handles = []
for module in self.modules():
if isinstance(module, LoraLayer) or isinstance(module, AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper):
pre_forward = partial(_adapter_names_pre_forward_hook, adapter_names=adapter_names)
handle = module.register_forward_pre_hook(pre_forward, with_kwargs=True)
hook_handles.append(handle)
if uses_beam_search and hasattr(self.model, "get_encoder"):
# For encoder-decoder models, even when applying beam search, the encoder part of the model should not use
# the extended adapter_names. This is because the encoder still uses the original, non-extended samples.
for module in self.model.get_encoder().modules():
if isinstance(module, LoraLayer) or isinstance(module, AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper):
# Add another hook to overwrite the kwargs with the original adapter names -- this is easier than
# trying to exclude the encoder.
pre_forward = partial(_adapter_names_pre_forward_hook, adapter_names=original_adapter_names)
handle = module.register_forward_pre_hook(pre_forward, with_kwargs=True)
hook_handles.append(handle)
yield
for handle in hook_handles:
handle.remove()
def _check_merge_allowed(self):
"""Verify that the configuration supports merging.
Currently gptq quantization and replicated layers do not support merging.
"""
super()._check_merge_allowed()
if getattr(self.model, "quantization_method", None) == "gptq":
raise ValueError("Cannot merge LORA layers when the model is gptq quantized")
if self.peft_config.get("layer_replication"):
raise ValueError("Cannot merge LORA layers when base model layers are replicated")
@staticmethod
def _prepare_adapter_config(peft_config, model_config):
if peft_config.target_modules is None:
if model_config["model_type"] in TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING:
peft_config.target_modules = set(
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING[model_config["model_type"]]
)
elif not peft_config.target_parameters:
raise ValueError("Please specify `target_modules` or `target_parameters`in `peft_config`")
return peft_config
def _unload_and_optionally_merge(
self,
merge=True,
progressbar: bool = False,
safe_merge: bool = False,
adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None,
):
if merge:
self._check_merge_allowed()
key_list = [key for key, _ in self.model.named_modules() if self.prefix not in key]
desc = "Unloading " + ("and merging " if merge else "") + "model"
for key in tqdm(key_list, disable=not progressbar, desc=desc):
try:
parent, target, target_name = _get_submodules(self.model, key)
except AttributeError:
continue
with onload_layer(target):
if hasattr(target, "unload_and_optionally_merge_module"):
# if layers have special unloading method, like MultiheadAttention, use that
unloaded_module = target.unload_and_optionally_merge_module(
merge=merge, safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names
)
self._replace_module(parent, target_name, unloaded_module, target)
elif hasattr(target, "base_layer"):
if merge:
target.merge(safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names)
self._replace_module(parent, target_name, target.get_base_layer(), target)
return self.model
def _check_add_weighted_adapter(
self, adapters: list[str], combination_type: str, svd_rank: int | None
) -> tuple[str, int, str]:
"""
Helper function to check if the arguments to add_weighted_adapter are valid and compatible with the underlying
model.
"""
for adapter in adapters:
if adapter not in list(self.peft_config.keys()):
raise ValueError(f"Adapter {adapter} does not exist")
for adapter in adapters:
if self.peft_config[adapter].target_parameters:
raise ValueError(
f"add_weighted_adapter does not support targeting nn.Parameter (problematic adapter '{adapter}')"
)
# If more than one of the adapters targets the same module with modules_to_save, raise an error, as these
# modules cannot be merged. First, find the ModulesToSaveWrapper instances in the model, then check if they
# have modules for the adapters to be merged.
modules_to_save_wrappers = [module for module in self.modules() if isinstance(module, ModulesToSaveWrapper)]
problematic_wrappers = [
wrapper
for wrapper in modules_to_save_wrappers
if sum(adapter in wrapper.modules_to_save for adapter in adapters) > 1
]
if problematic_wrappers:
raise ValueError(
"Cannot add weighted adapters if they target the same module with modules_to_save, but found "
f"{len(problematic_wrappers)} such instance(s)."
)
# if there is only one adapter, we can only use linear merging
combination_type = "linear" if len(adapters) == 1 else combination_type
adapters_ranks: list[int] = [
# When allocating tensors for the new adapter, we need the maximum possible rank to not overflow
config.r if not config.rank_pattern else max(config.r, *config.rank_pattern.values())
for config in (self.peft_config[adapter] for adapter in adapters)
]
if combination_type in ("linear", "ties", "dare_ties", "dare_linear", "magnitude_prune"):
# all adapters ranks should be same, new rank is just this value
if len(set(adapters_ranks)) != 1:
raise ValueError(
"All adapters must have the same r value when using combination_type linear, ties, dare_ties or "
"dare_linear."
)
new_rank = adapters_ranks[0]
elif combination_type == "cat":
# adapters ranks may be different, new rank is sum of all ranks
# be careful, because output adapter rank may be really big if mixing a lot of adapters
new_rank = sum(adapters_ranks)
elif combination_type.endswith("svd"):
# new rank is the max of all ranks of the adapters if not provided
new_rank = svd_rank or max(adapters_ranks)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid combination_type: {combination_type}")
target_module_types = [type(self.peft_config[adapter].target_modules) for adapter in adapters]
if not target_module_types:
raise ValueError(f"Found no adapter matching the names in {adapters}")
if len(set(target_module_types)) > 1:
raise ValueError(
"all adapter configs should follow the same target modules type. "
"Combining adapters with `target_modules` type being a mix of list/set and string is not supported."
)
if target_module_types[0] is str:
new_target_modules = "|".join(f"({self.peft_config[adapter].target_modules})" for adapter in adapters)
elif target_module_types[0] is set:
new_target_modules = reduce(
operator.or_, (self.peft_config[adapter].target_modules for adapter in adapters)
)
else:
raise TypeError(f"Invalid type {target_module_types[0]} found in target_modules")
return combination_type, new_rank, new_target_modules
def add_weighted_adapter(
self,
adapters: list[str],
weights: list[float],
adapter_name: str,
combination_type: str = "svd",
svd_rank: int | None = None,
svd_clamp: int | None = None,
svd_full_matrices: bool = True,
svd_driver: str | None = None,
density: float | None = None,
majority_sign_method: Literal["total", "frequency"] = "total",
) -> None:
"""
This method adds a new adapter by merging the given adapters with the given weights.
When using the `cat` combination_type you should be aware that rank of the resulting adapter will be equal to
the sum of all adapters ranks. So it's possible that the mixed adapter may become too big and result in OOM
errors.
Args:
adapters (`list`):
List of adapter names to be merged.
weights (`list`):
List of weights for each adapter.
adapter_name (`str`):
Name of the new adapter.
combination_type (`str`):
The merging type can be one of [`svd`, `linear`, `cat`, `ties`, `ties_svd`, `dare_ties`, `dare_linear`,
`dare_ties_svd`, `dare_linear_svd`, `magnitude_prune`, `magnitude_prune_svd`]. When using the `cat`
combination_type, the rank of the resulting adapter is equal to the sum of all adapters ranks (the
mixed adapter may be too big and result in OOM errors).
svd_rank (`int`, *optional*):
Rank of output adapter for svd. If None provided, will use max rank of merging adapters.
svd_clamp (`float`, *optional*):
A quantile threshold for clamping SVD decomposition output. If None is provided, do not perform
clamping. Defaults to None.
svd_full_matrices (`bool`, *optional*):
Controls whether to compute the full or reduced SVD, and consequently, the shape of the returned
tensors U and Vh. Defaults to True.
svd_driver (`str`, *optional*):
Name of the cuSOLVER method to be used. This keyword argument only works when merging on CUDA. Can be
one of [None, `gesvd`, `gesvdj`, `gesvda`]. For more info please refer to `torch.linalg.svd`
documentation. Defaults to None.
density (`float`, *optional*):
Value between 0 and 1. 0 means all values are pruned and 1 means no values are pruned. Should be used
with [`ties`, `ties_svd`, `dare_ties`, `dare_linear`, `dare_ties_svd`, `dare_linear_svd`,
`magnintude_prune`, `magnitude_prune_svd`]
majority_sign_method (`str`):
The method, should be one of ["total", "frequency"], to use to get the magnitude of the sign values.
Should be used with [`ties`, `ties_svd`, `dare_ties`, `dare_ties_svd`]
"""
if adapter_name in list(self.peft_config.keys()):
return
combination_type, new_rank, new_target_modules = self._check_add_weighted_adapter(
adapters=adapters,
combination_type=combination_type,
svd_rank=svd_rank,
)
self.peft_config[adapter_name] = replace(
self.peft_config[adapters[0]],
r=new_rank,
lora_alpha=new_rank,
target_modules=new_target_modules,
alpha_pattern={},
rank_pattern={},
)
self.inject_adapter(self.model, adapter_name)
# Do we really need that?
_freeze_adapter(self.model, adapter_name)
key_list = [key for key, _ in self.model.named_modules() if self.prefix not in key]
for key in key_list:
_, target, _ = _get_submodules(self.model, key)
if isinstance(target, LoraLayer):
if adapter_name in target.lora_A:
target_lora_A = target.lora_A[adapter_name].weight
target_lora_B = target.lora_B[adapter_name].weight
elif adapter_name in target.lora_embedding_A:
target_lora_A = target.lora_embedding_A[adapter_name]
target_lora_B = target.lora_embedding_B[adapter_name]
else:
continue
target_lora_A.data = target_lora_A.data * 0.0
target_lora_B.data = target_lora_B.data * 0.0
if combination_type == "cat":
loras_A, loras_B = [], []
for adapter, weight in zip(adapters, weights):
if adapter in target.lora_A:
current_adapter_lora_A = target.lora_A[adapter].weight
current_adapter_lora_B = target.lora_B[adapter].weight
elif adapter in target.lora_embedding_A:
current_adapter_lora_A = target.lora_embedding_A[adapter]
current_adapter_lora_B = target.lora_embedding_B[adapter]
else:
continue
loras_A.append(current_adapter_lora_A.data * weight * target.scaling[adapter])
loras_B.append(current_adapter_lora_B.data)
if len(loras_A) == 0:
raise ValueError("No matching LoRAs found. Please raise an issue on GitHub.")
loras_A = torch.cat(loras_A, dim=0)
loras_B = torch.cat(loras_B, dim=1)
target_lora_A.data[: loras_A.shape[0], :] = loras_A
target_lora_B.data[:, : loras_B.shape[1]] = loras_B
elif combination_type in [
"svd",
"ties_svd",
"dare_linear_svd",
"dare_ties_svd",
"magnitude_prune_svd",
]:
target_lora_A.data, target_lora_B.data = self._svd_generalized_task_arithmetic_weighted_adapter(
combination_type,
adapters,
weights,
new_rank,
target,
target_lora_A,
target_lora_B,
density,
majority_sign_method,
svd_clamp,
full_matrices=svd_full_matrices,
driver=svd_driver,
)
elif combination_type in ["linear", "ties", "dare_linear", "dare_ties", "magnitude_prune"]:
target_lora_A.data, target_lora_B.data = self._generalized_task_arithmetic_weighted_adapter(
combination_type, adapters, weights, target, density, majority_sign_method
)
def _svd_generalized_task_arithmetic_weighted_adapter(
self,
combination_type,
adapters,
weights,
new_rank,
target,
target_lora_A,
target_lora_B,
density,
majority_sign_method,
clamp=None,
full_matrices=True,
driver=None,
):
valid_adapters = []
valid_weights = []
is_embedding = any(adapter in target.lora_embedding_A for adapter in adapters)
for adapter, weight in zip(adapters, weights):
if adapter in target.lora_A or adapter in target.lora_embedding_A:
valid_adapters.append(adapter)
valid_weights.append(weight * target.scaling[adapter])
# if no valid adapter, nothing to do
if len(valid_adapters) == 0:
raise ValueError("No matching LoRAs found. Please raise an issue on Github.")
delta_weight = [target.get_delta_weight(adapter) for adapter in valid_adapters]
valid_weights = torch.tensor(valid_weights).to(delta_weight[0].device)
if combination_type == "svd":
delta_weight = task_arithmetic(delta_weight, valid_weights)
elif combination_type == "ties_svd":
delta_weight = ties(delta_weight, valid_weights, density, majority_sign_method)
elif combination_type == "dare_linear_svd":
delta_weight = dare_linear(delta_weight, valid_weights, density)
elif combination_type == "dare_ties_svd":
delta_weight = dare_ties(delta_weight, valid_weights, density, majority_sign_method)
elif combination_type == "magnitude_prune_svd":
delta_weight = magnitude_prune(delta_weight, valid_weights, density)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid value passed to combination type: {combination_type}")
conv2d = isinstance(target, Conv2d)
if conv2d:
conv2d_1x1 = target.weight.size()[2:4] == (1, 1)
if not conv2d_1x1:
delta_weight = delta_weight.flatten(start_dim=1)
else:
delta_weight = delta_weight.squeeze()
if (hasattr(target, "fan_in_fan_out") and target.fan_in_fan_out) or is_embedding:
delta_weight = delta_weight.T
# based on https://github.com/kohya-ss/sd-scripts/blob/main/networks/svd_merge_lora.py#L114-L131
U, S, Vh = torch.linalg.svd(delta_weight, full_matrices=full_matrices, driver=driver)
U = U[:, :new_rank]
S = S[:new_rank]
U = U @ torch.diag(S)
Vh = Vh[:new_rank, :]
if clamp is not None:
dist = torch.cat([U.flatten(), Vh.flatten()])
hi_val = torch.quantile(dist, clamp)
low_val = -hi_val
U = U.clamp(low_val, hi_val)
Vh = Vh.clamp(low_val, hi_val)
if conv2d:
U = U.reshape(target_lora_B.data.shape)
Vh = Vh.reshape(target_lora_A.data.shape)
return Vh, U
def _generalized_task_arithmetic_weighted_adapter(
self,
combination_type,
adapters,
weights,
target,
density,
majority_sign_method,
):
# account weights for LoRA A and B layers.
valid_weights = []
lora_A_deltas = []
lora_B_deltas = []
for adapter, weight in zip(adapters, weights):
if adapter in target.lora_A:
current_adapter_lora_A = target.lora_A[adapter].weight
current_adapter_lora_B = target.lora_B[adapter].weight
elif adapter in target.lora_embedding_A:
current_adapter_lora_A = target.lora_embedding_A[adapter]
current_adapter_lora_B = target.lora_embedding_B[adapter]
else:
continue
valid_weights.append(math.sqrt(weight * target.scaling[adapter]))
lora_A_deltas.append(current_adapter_lora_A.data)
lora_B_deltas.append(current_adapter_lora_B.data)
valid_weights = torch.tensor(valid_weights).to(lora_A_deltas[0].device)
lora_deltas = [lora_A_deltas, lora_B_deltas]
dtype = lora_A_deltas[0].dtype
for i, task_tensors in enumerate(lora_deltas):
if combination_type == "linear":
lora_deltas[i] = task_arithmetic(task_tensors, valid_weights)
elif combination_type == "ties":
lora_deltas[i] = ties(task_tensors, valid_weights, density, majority_sign_method)
elif combination_type == "dare_linear":
lora_deltas[i] = dare_linear(task_tensors, valid_weights, density)
elif combination_type == "dare_ties":
lora_deltas[i] = dare_ties(task_tensors, valid_weights, density, majority_sign_method)
elif combination_type == "magnitude_prune":
lora_deltas[i] = magnitude_prune(task_tensors, valid_weights, density)
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid combination type")
lora_deltas = [delta.to(dtype) for delta in lora_deltas]
return lora_deltas
def delete_adapter(self, adapter_name: str) -> None:
"""
Deletes an existing adapter.
Args:
adapter_name (str): Name of the adapter to be deleted.
"""
if adapter_name not in list(self.peft_config.keys()):
raise ValueError(f"Adapter {adapter_name} does not exist")
del self.peft_config[adapter_name]
key_list = [key for key, _ in self.model.named_modules() if self.prefix not in key]
new_adapter = None
for key in key_list:
_, target, _ = _get_submodules(self.model, key)
if isinstance(target, LoraLayer):
target.delete_adapter(adapter_name)
if new_adapter is None:
new_adapter = target.active_adapters[:]
self.active_adapter = new_adapter or []
self._delete_auxiliary_adapter(adapter_name, new_active_adapters=new_adapter)
def merge_and_unload(
self, progressbar: bool = False, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None
) -> torch.nn.Module:
r"""
This method merges the LoRa layers into the base model. This is needed if someone wants to use the base model
as a standalone model.
Args:
progressbar (`bool`):
whether to show a progressbar indicating the unload and merge process
safe_merge (`bool`):
whether to activate the safe merging check to check if there is any potential Nan in the adapter
weights
adapter_names (`List[str]`, *optional*):
The list of adapter names that should be merged. If None, all active adapters will be merged. Defaults
to `None`.
Example:
```py
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> from peft import PeftModel
>>> base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("tiiuae/falcon-40b")
>>> peft_model_id = "smangrul/falcon-40B-int4-peft-lora-sfttrainer-sample"
>>> model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_model_id)
>>> merged_model = model.merge_and_unload()
```
"""
return self._unload_and_optionally_merge(
progressbar=progressbar, safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names
)
def unload(self) -> torch.nn.Module:
"""
Gets back the base model by removing all the lora modules without merging. This gives back the original base
model.
"""
return self._unload_and_optionally_merge(merge=False)
def subtract_mutated_init(self, output_state_dict: dict[str, torch.Tensor], adapter_name: str, kwargs=None):
"""
This function can calculate the updates of the PiSSA/CorDA/OLoRA by comparing the parameters of the
PiSSA/CorDA/OLoRA adapter in `output_state_dict` with the initial values of PiSSA/CorDA/OLoRA in
`adapter_name`, thus converting PiSSA/CorDA/OLoRA to LoRA.
"""
for name, param in self.model.named_parameters():
if (
param.data.dtype != torch.float32
and param.data.dtype != torch.float16
and param.data.dtype != torch.bfloat16
) and adapter_name.startswith("pissa"):
warnings.warn(
r"Note that Quant(W_res) + AB != Quant(W) + \Delta(AB); "
"the converted LoRA, when combined with W or Quant(W), may introduce a certain gap in the fine-tuned model. "
"Therefore, we recommend directly using the Quant(W_res) in conjunction with the PiSSA adapter. "
)
mutated_init_state_dict = get_peft_model_state_dict(
self,
state_dict=kwargs.get("state_dict", None),
adapter_name=adapter_name,
)
tensors_lora = {}
for name in output_state_dict.keys():
## W = W^{res} + A_0 \times B_0,
## W + \Delta W = W^{res} + A \times B,
## \Delta W = A \times B - A_0 \times B_0 = [A | A_0] \times [B | -B_0]^T = A'B'.
if "lora_A" in name:
tensors_lora[name] = torch.cat(
[output_state_dict[name], mutated_init_state_dict[".".join(name.split(".")[1:])]], dim=0
)
elif "lora_B" in name:
tensors_lora[name] = torch.cat(
[output_state_dict[name], -mutated_init_state_dict[".".join(name.split(".")[1:])]], dim=1
)
return tensors_lora
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/lora/model.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/lora/model.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 20708
}
| 246
|
# Copyright 2025-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import importlib.metadata as importlib_metadata
from typing import Any, Optional
import packaging.version
import torch
from peft.import_utils import is_auto_awq_available
from peft.tuners.oft.layer import OFTLayer
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer
class AwqOFTLinear(torch.nn.Module, OFTLayer):
def __init__(
self,
base_layer,
adapter_name,
r: int = 0,
oft_block_size: int = 32,
module_dropout: float = 0.0,
coft: bool = False,
eps: float = 6e-5,
block_share: bool = False,
fan_in_fan_out: bool = False, # Set this to True if the layer to replace stores weight like (fan_in, fan_out)
init_weights: bool = True,
use_cayley_neumann: bool = False,
num_cayley_neumann_terms: int = 5,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__()
OFTLayer.__init__(self, base_layer)
# self.base_layer and self.quant_linear_module are the same; we need the former for consistency and the latter
# for backwards compatibility
self.quant_linear_module = base_layer
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(
adapter_name,
r,
oft_block_size=oft_block_size,
module_dropout=module_dropout,
coft=coft,
eps=eps,
block_share=block_share,
init_weights=init_weights,
use_cayley_neumann=use_cayley_neumann,
num_cayley_neumann_terms=num_cayley_neumann_terms,
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
if self.disable_adapters:
result = self.quant_linear_module(x)
return result
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.oft_R.keys():
continue
oft_R = self.oft_R[active_adapter]
requires_conversion = not torch.is_autocast_enabled()
if requires_conversion:
expected_dtype = x.dtype
x = self._cast_input_dtype(x, oft_R.weight.dtype)
x = oft_R(x)
if requires_conversion:
x = x.to(expected_dtype)
result = self.quant_linear_module(x)
return result
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "oft." + rep
def dispatch_awq(
target: torch.nn.Module,
adapter_name: str,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> Optional[torch.nn.Module]:
new_module = None
if isinstance(target, BaseTunerLayer):
target_base_layer = target.get_base_layer()
else:
target_base_layer = target
if is_auto_awq_available():
from awq.modules.linear import WQLinear_GEMM
if isinstance(target_base_layer, WQLinear_GEMM):
# Raise the error only at the dispatch level
AUTOAWQ_MINIMUM_VERSION = packaging.version.parse("0.2.0")
version_autoawq = packaging.version.parse(importlib_metadata.version("autoawq"))
if AUTOAWQ_MINIMUM_VERSION > version_autoawq:
raise ImportError(
f"Found an incompatible version of auto-awq. Found version {version_autoawq}, "
f"but only versions above {AUTOAWQ_MINIMUM_VERSION} are supported for PEFT."
)
new_module = AwqOFTLinear(target, adapter_name, **kwargs)
target.qweight = target_base_layer.qweight
return new_module
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/oft/awq.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/oft/awq.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 1781
}
| 247
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.distributions.relaxed_bernoulli import RelaxedBernoulli
from .config import PolyConfig
EPS = 1e-12
def get_router(poly_config: PolyConfig) -> nn.Module:
if poly_config.poly_type == "poly":
return PolyRouter(poly_config)
else:
raise ValueError(
f"Unsupported poly_type: {poly_config.poly_type}. "
"Currently, only the following types are supported: "
"`poly`."
)
class Router(nn.Module, ABC):
@abstractmethod
def reset(self): ...
@abstractmethod
def forward(self, task_ids: torch.Tensor, input_ids: torch.Tensor): ...
class PolyRouter(Router):
# It's a simplified implementation of
# https://github.com/microsoft/mttl/blob/ce4ca51dbca73be656feb9b3e5233633e3c5dec7/mttl/models/poly.py#L138
def __init__(self, poly_config: PolyConfig):
super().__init__()
self.poly_type = poly_config.poly_type
self.n_tasks = poly_config.n_tasks
self.n_skills = poly_config.n_skills
self.n_splits = poly_config.n_splits
self.module_logits = nn.Parameter(torch.empty((self.n_tasks, self.n_splits * self.n_skills)))
def reset(self):
torch.nn.init.uniform_(self.module_logits, -1e-3, 1e-3)
def forward(self, task_ids: torch.Tensor, input_ids: torch.Tensor):
if task_ids is None:
raise ValueError("task_ids should not be None.")
if task_ids.max().item() >= self.n_tasks:
raise ValueError(f"Only {self.n_tasks} tasks available. Found task id = {task_ids.max().item()}")
# move task id to input's device
task_ids = task_ids.to(self.module_logits.device)
module_logits = self.module_logits[task_ids]
module_logits = module_logits.view(-1, self.n_splits, self.n_skills)
if self.training:
module_logits = RelaxedBernoulli(temperature=1.0, logits=module_logits).rsample()
else:
module_logits = torch.sigmoid(module_logits)
module_weights = module_logits / (module_logits.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True) + EPS)
return module_weights
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/poly/router.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/poly/router.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 1101
}
| 248
|
# Copyright 2025-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import annotations
import operator
from contextlib import contextmanager
from functools import partial
from typing import Optional
import torch
from torch import nn
from tqdm import tqdm
from peft.import_utils import is_bnb_4bit_available, is_bnb_available
from peft.tuners.road.config import RoadConfig
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import (
BaseTuner,
BaseTunerLayer,
check_target_module_exists,
onload_layer,
)
from peft.utils import (
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
ModulesToSaveWrapper,
_get_submodules,
)
from .layer import RoadLayer, dispatch_default
def _adapter_names_pre_forward_hook(target, args, kwargs, adapter_names):
# pre-forward hook to inject the adapter_names argument when using mixed adapter batches inference
kwargs["adapter_names"] = adapter_names
return args, kwargs
class RoadModel(BaseTuner):
""" """
prefix: str = "road_"
@staticmethod
def _prepare_adapter_config(road_config: RoadConfig, model_config: dict) -> RoadConfig:
if road_config.target_modules is None:
if model_config["model_type"] not in TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING:
raise ValueError("Please specify `target_modules` in `peft_config`")
road_config.target_modules = set(
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING[model_config["model_type"]]
)
return road_config
@staticmethod
def _check_target_module_exists(road_config, key):
return check_target_module_exists(road_config, key)
def _create_and_replace(
self,
road_config: RoadConfig,
adapter_name: str,
target: nn.Module,
target_name: str,
parent: nn.Module,
current_key,
) -> None:
if current_key is None:
raise ValueError("Current Key shouldn't be `None`")
# Regexp matching - Find key which matches current target_name in patterns provided
variant = road_config.variant
group_size = road_config.group_size
kwargs = {
"variant": variant,
"group_size": group_size,
"init_weights": road_config.init_weights,
"loaded_in_8bit": getattr(self.model, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False),
"loaded_in_4bit": getattr(self.model, "is_loaded_in_4bit", False),
}
# for torchao merging, we need the get_apply_tensor_subclass from the quantization config
try:
kwargs["get_apply_tensor_subclass"] = operator.attrgetter(
"hf_quantizer.quantization_config.get_apply_tensor_subclass"
)(self.model)
except AttributeError:
pass
if isinstance(target, RoadLayer):
target.update_layer(
adapter_name,
variant,
group_size,
init_weights=road_config.init_weights,
)
else:
device_map = self.model.hf_device_map if hasattr(self.model, "hf_device_map") else None
new_module = self._create_new_module(road_config, adapter_name, target, device_map=device_map, **kwargs)
if adapter_name not in self.active_adapters:
# adding an additional adapter: it is not automatically trainable
new_module.requires_grad_(False)
self._replace_module(parent, target_name, new_module, target)
def _replace_module(self, parent, child_name, new_module, child):
setattr(parent, child_name, new_module)
# It's not necessary to set requires_grad here, as that is handled by
# _mark_only_adapters_as_trainable
# child layer wraps the original module, unpack it
if hasattr(child, "base_layer"):
child = child.base_layer
meta = torch.device("meta")
# dispatch to correct device
for name, module in new_module.named_modules():
if (self.prefix in name) or ("ranknum" in name):
if hasattr(child, "qweight"):
weight = child.qweight
elif hasattr(child, "W_q"):
weight = child.W_q
elif hasattr(child, "weight"):
weight = child.weight
elif getattr(child, "in_proj_weight", None) is not None: # MHA
weight = child.in_proj_weight
else:
weight = next(child.parameters())
if not any(p.device == meta for p in module.parameters()):
module.to(weight.device)
@staticmethod
def _create_new_module(road_config: RoadConfig, adapter_name, target, **kwargs):
dispatchers = []
# avoid eager bnb import
if is_bnb_available():
from .bnb import dispatch_bnb_8bit
dispatchers.append(dispatch_bnb_8bit)
if is_bnb_4bit_available():
from .bnb import dispatch_bnb_4bit
dispatchers.append(dispatch_bnb_4bit)
dispatchers.extend(
[
dispatch_default,
]
)
new_module = None
for dispatcher in dispatchers:
new_module = dispatcher(target, adapter_name, road_config=road_config, **kwargs)
if new_module is not None: # first match wins
break
if new_module is None:
# no module could be matched
raise ValueError(
f"Target module {target} is not supported. Currently, only the following modules are supported: "
"`torch.nn.Linear`."
)
return new_module
def _mark_only_adapters_as_trainable(self, model: nn.Module):
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if self.prefix not in n:
p.requires_grad = False
def _set_adapter_layers(self, enabled: bool = True) -> None:
for module in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(module, (BaseTunerLayer, ModulesToSaveWrapper)):
module.enable_adapters(enabled)
def disable_adapter_layers(self) -> None:
self._set_adapter_layers(enabled=False)
def enable_adapter_layers(self) -> None:
self._set_adapter_layers(enabled=True)
def set_adapter(self, adapter_name: str | list[str]) -> None:
"""Set the active adapter(s).
Additionally, this function will set the specified adapters to trainable (i.e., requires_grad=True). If this is
not desired, use the following code.
```py
>>> for name, param in model_peft.named_parameters():
... if ...: # some check on name (ex. if 'lora' in name)
... param.requires_grad = False
```
Args:
adapter_name (`str` or `list[str]`): Name of the adapter(s) to be activated.
"""
for module in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(module, RoadLayer):
module.set_adapter(adapter_name)
self.active_adapter = adapter_name
def __getattr__(self, name: str):
"""Forward missing attributes to the wrapped module."""
try:
return super().__getattr__(name) # defer to nn.Module's logic
except AttributeError:
if name == "model": # see #1892: prevent infinite recursion if class is not initialized
raise
return getattr(self.model, name)
@contextmanager
def _enable_peft_forward_hooks(self, *args, **kwargs):
# If adapter_names is passed as an argument, we inject it into the forward arguments.
adapter_names = kwargs.pop("adapter_names", None)
if adapter_names is None:
# nothing to do
yield
return
if self.training:
raise ValueError("Cannot pass `adapter_names` when the model is in training mode.")
# Check that users only passed actually existing adapters.
# Note: We cannot do this on the layer level, as each individual layer may not have each adapter. Still, we want
# to check that there is at least one layer with the given name, or else something like typos can easily slip.
expected_adapters = set()
for layer in self.modules():
if isinstance(layer, RoadLayer):
expected_adapters |= layer.road_theta.keys()
unique_adapters = {name for name in adapter_names if name != "__base__"}
unexpected_adapters = unique_adapters - expected_adapters
if unexpected_adapters:
raise ValueError(f"Trying to infer with non-existing adapter(s): {', '.join(sorted(unexpected_adapters))}")
hook_handles = []
for module in self.modules():
if isinstance(module, RoadLayer):
pre_forward = partial(_adapter_names_pre_forward_hook, adapter_names=adapter_names)
handle = module.register_forward_pre_hook(pre_forward, with_kwargs=True)
hook_handles.append(handle)
# TODO LoRA also has hooks for beam search, ignore this for now
yield
for handle in hook_handles:
handle.remove()
def _unload_and_optionally_merge(
self,
merge=True,
progressbar: bool = False,
safe_merge: bool = False,
adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None,
):
if merge:
self._check_merge_allowed()
key_list = [key for key, _ in self.model.named_modules() if self.prefix not in key]
desc = "Unloading " + ("and merging " if merge else "") + "model"
for key in tqdm(key_list, disable=not progressbar, desc=desc):
try:
parent, target, target_name = _get_submodules(self.model, key)
except AttributeError:
continue
with onload_layer(target):
if hasattr(target, "base_layer"):
if merge:
target.merge(safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names)
self._replace_module(parent, target_name, target.get_base_layer(), target)
elif isinstance(target, ModulesToSaveWrapper):
# save any additional trainable modules part of `modules_to_save`
new_module = target.modules_to_save[target.active_adapter]
if hasattr(new_module, "base_layer"):
# check if the module is itself a tuner layer
if merge:
new_module.merge(safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names)
new_module = new_module.get_base_layer()
setattr(parent, target_name, new_module)
return self.model
def delete_adapter(self, adapter_name: str) -> None:
"""
Deletes an existing adapter.
Args:
adapter_name (str): Name of the adapter to be deleted.
"""
if adapter_name not in list(self.peft_config.keys()):
raise ValueError(f"Adapter {adapter_name} does not exist")
del self.peft_config[adapter_name]
key_list = [key for key, _ in self.model.named_modules() if self.prefix not in key]
new_adapter = None
for key in key_list:
_, target, _ = _get_submodules(self.model, key)
if isinstance(target, RoadLayer):
target.delete_adapter(adapter_name)
if new_adapter is None:
new_adapter = target.active_adapters[:]
self.active_adapter = new_adapter or []
self._delete_auxiliary_adapter(adapter_name, new_active_adapters=new_adapter)
def merge_and_unload(
self, progressbar: bool = False, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None
) -> torch.nn.Module:
r"""
This method merges the RoAd layers into the base model. This is needed if someone wants to use the base model
as a standalone model.
Args:
progressbar (`bool`):
whether to show a progressbar indicating the unload and merge process
safe_merge (`bool`):
whether to activate the safe merging check to check if there is any potential Nan in the adapter
weights
adapter_names (`List[str]`, *optional*):
The list of adapter names that should be merged. If None, all active adapters will be merged. Defaults
to `None`.
"""
return self._unload_and_optionally_merge(
progressbar=progressbar, safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names
)
def unload(self) -> torch.nn.Module:
"""
Gets back the base model by removing all the road modules without merging. This gives back the original base
model.
"""
return self._unload_and_optionally_merge(merge=False)
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/road/model.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/road/model.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 5898
}
| 249
|
# Copyright 2024-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import annotations
import warnings
from typing import Optional
import bitsandbytes as bnb
import torch
from peft.import_utils import is_bnb_4bit_available, is_bnb_available
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import check_adapters_to_merge
from peft.utils.integrations import dequantize_bnb_weight
from peft.utils.other import transpose
from .layer import VeraLayer
if is_bnb_available():
class Linear8bitLt(torch.nn.Module, VeraLayer):
def __init__(
self,
base_layer: torch.nn.Module,
adapter_name: str,
vera_A,
vera_B,
r: int = 0,
vera_dropout: float = 0.0,
fan_in_fan_out: bool = False,
init_weights: bool = True,
d_initial: float = 0.1,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
VeraLayer.__init__(self, base_layer)
self.fan_in_fan_out = fan_in_fan_out
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(
adapter_name,
vera_A,
vera_B,
r,
vera_dropout=vera_dropout,
init_weights=init_weights,
d_initial=d_initial,
)
def merge(self, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> None:
if self.merged:
warnings.warn(
f"Already following adapters were merged {','.join(self.merged_adapters)}. "
f"You are now additionally merging {','.join(self.active_adapters)}."
)
adapter_names = check_adapters_to_merge(self, adapter_names)
if not adapter_names:
return
for active_adapter in adapter_names:
if active_adapter not in self.vera_lambda_d.keys():
continue
warnings.warn(
"Merge vera module to 8-bit linear may get different generations due to rounding errors."
)
vera_data = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
weight = self.get_base_layer().weight
state = self.get_base_layer().state
if state.SCB is None:
state.SCB = weight.SCB
output = dequantize_bnb_weight(weight, state)
w_data = output.to(vera_data.dtype).to(vera_data.device) + vera_data
if safe_merge and not torch.isfinite(w_data).all():
raise ValueError(
f"NaNs detected in the merged weights. The adapter {active_adapter} seems to be broken"
)
self.get_base_layer().weight = bnb.nn.Int8Params(
w_data.to("cpu"), requires_grad=False, has_fp16_weights=weight.has_fp16_weights
).to(weight.device)
state.reset_grads()
self.merged_adapters.append(active_adapter)
def unmerge(self) -> None:
if not self.merged:
warnings.warn("Already unmerged. Nothing to do")
return
while len(self.merged_adapters) > 0:
active_adapter = self.merged_adapters.pop()
if active_adapter not in self.vera_lambda_d.keys():
continue
warnings.warn(
"Unmerge vera module to 8-bit linear may get different generations due to rounding errors."
)
vera_data = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
weight = self.get_base_layer().weight
state = self.get_base_layer().state
if state.SCB is None:
state.SCB = weight.SCB
output = dequantize_bnb_weight(weight, state=state)
w_data = output.to(vera_data.dtype).to(vera_data.device) - vera_data
self.get_base_layer().weight = bnb.nn.Int8Params(
w_data.to("cpu"), requires_grad=False, has_fp16_weights=weight.has_fp16_weights
).to(weight.device)
state.reset_grads()
def get_delta_weight(self, adapter) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Compute the delta weight for the given adapter.
Args:
adapter (str): The name of the adapter for which the delta weight should be computed.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: The computed delta weight for the VeRA adapter.
Note:
This method implements the VeRA-specific weight update. Unlike LoRA, VeRA uses shared projection
matrices (vera_A and vera_B) across all layers, along with per-layer trainable parameters (lambda_d and
lambda_b).
"""
# Retrieve shared projection matrices
vera_A = self.vera_A[adapter]
vera_B = self.vera_B[adapter]
# Retrieve per-layer trainable parameters
device = vera_B.device
dtype = vera_B.dtype
# In case users wants to merge the adapter weights that are in
# (b)float16 while being on CPU, we need to cast the weights to float32, perform the merge and then cast back to
# (b)float16 because some CPUs have slow bf16/fp16 matmuls.
cast_to_fp32 = device.type == "cpu" and (dtype == torch.float16 or dtype == torch.bfloat16)
lambda_d = self.vera_lambda_d[adapter]
lambda_b = self.vera_lambda_b[adapter]
if cast_to_fp32:
vera_A = vera_A.float()
vera_B = vera_B.float()
lambda_d = lambda_d.float()
lambda_b = lambda_b.float()
sliced_A = vera_A[:, : self.in_features].to(lambda_d.device)
sliced_B = vera_B[: self.out_features, :].to(lambda_d.device)
lambda_b = lambda_b.unsqueeze(-1)
lambda_d = lambda_d.unsqueeze(-1)
# VeRA-specific computation:
# 1. Apply lambda_d to the input projection (vera_A)
# 2. Apply lambda_b to the output projection (vera_B)
# 3. Compute the outer product of the scaled projections
output_tensor = transpose((lambda_b * sliced_B) @ (lambda_d * sliced_A), self.fan_in_fan_out)
if cast_to_fp32:
output_tensor = output_tensor.to(dtype=dtype)
return output_tensor
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args, **kwargs) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Perform the forward pass using the VeRA adapter.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Input tensor.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Output tensor after applying the VeRA adaptation.
Note:
This method implements the VeRA-specific forward pass. It applies the shared projections (vera_A and
vera_B) along with the per-layer trainable parameters (lambda_d and lambda_b) to compute the adapter
output.
"""
if self.disable_adapters:
if self.merged:
self.unmerge()
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
elif self.merged:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
else:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.vera_lambda_d.keys():
continue
lambda_d = self.vera_lambda_d[active_adapter]
lambda_b = self.vera_lambda_b[active_adapter]
vera_A = self.vera_A[active_adapter]
vera_B = self.vera_B[active_adapter]
dropout = self.vera_dropout[active_adapter]
requires_conversion = not torch.is_autocast_enabled()
if requires_conversion:
expected_dtype = result.dtype
compute_dtype = lambda_d.dtype
if x.dtype != compute_dtype:
x = x.to(compute_dtype)
sliced_A = vera_A[:, : self.in_features].to(x.device)
sliced_B = vera_B[: self.out_features, :].to(x.device)
x_temp = dropout(x.to(lambda_d.dtype))
adapter_output = lambda_b * torch.nn.functional.linear(
lambda_d * torch.nn.functional.linear(x_temp, sliced_A), sliced_B
)
if requires_conversion:
adapter_output = adapter_output.to(expected_dtype)
result = result + adapter_output
# Ensure the output tensor has the same dtype as the input tensor
return result.to(x.dtype)
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "vera." + rep
if is_bnb_4bit_available():
class Linear4bit(torch.nn.Module, VeraLayer):
def __init__(
self,
base_layer: torch.nn.Module,
adapter_name: str,
vera_A,
vera_B,
r: int = 0,
vera_dropout: float = 0.0,
fan_in_fan_out: bool = False,
init_weights: bool = True,
d_initial: float = 0.1,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
VeraLayer.__init__(self, base_layer)
self.fan_in_fan_out = fan_in_fan_out
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
self.update_layer(
adapter_name,
vera_A,
vera_B,
r,
vera_dropout=vera_dropout,
init_weights=init_weights,
d_initial=d_initial,
)
def merge(self, safe_merge: bool = False, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> None:
if self.merged:
warnings.warn(
f"Already following adapters were merged {','.join(self.merged_adapters)}. "
f"You are now additionally merging {','.join(self.active_adapters)}."
)
adapter_names = check_adapters_to_merge(self, adapter_names)
if not adapter_names:
return
for active_adapter in adapter_names:
if active_adapter not in self.vera_lambda_d.keys():
continue
warnings.warn(
"Merge vera module to 4-bit linear may get different generations due to rounding errors."
)
vera_data = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
weight = self.get_base_layer().weight
kwargs = weight.__dict__
# torch.compile can introduce attributes preceded by '_', remove them
kwargs = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if not k.startswith("_")}
w_data = bnb.functional.dequantize_4bit(weight.data, weight.quant_state) + vera_data
if safe_merge and not torch.isfinite(w_data).all():
raise ValueError(
f"NaNs detected in the merged weights. The adapter {active_adapter} seems to be broken"
)
self.get_base_layer().weight = bnb.nn.Params4bit(w_data.to("cpu"), requires_grad=False, **kwargs).to(
weight.device
)
self.merged_adapters.append(active_adapter)
def unmerge(self) -> None:
if not self.merged:
warnings.warn("Already unmerged. Nothing to do")
return
while len(self.merged_adapters) > 0:
active_adapter = self.merged_adapters.pop()
if active_adapter not in self.vera_lambda_d.keys():
continue
warnings.warn(
"Unmerge vera module to 4-bit linear may get different generations due to rounding errors."
)
vera_data = self.get_delta_weight(active_adapter)
weight = self.get_base_layer().weight
kwargs = weight.__dict__
w_data = bnb.functional.dequantize_4bit(weight.data, weight.quant_state) - vera_data
self.get_base_layer().weight = bnb.nn.Params4bit(w_data.to("cpu"), requires_grad=False, **kwargs).to(
weight.device
)
def get_delta_weight(self, adapter) -> torch.Tensor:
vera_A = self.vera_A[adapter]
vera_B = self.vera_B[adapter]
device = vera_B.device
dtype = vera_B.dtype
cast_to_fp32 = device.type == "cpu" and (dtype == torch.float16 or dtype == torch.bfloat16)
lambda_d = self.vera_lambda_d[adapter]
lambda_b = self.vera_lambda_b[adapter]
if cast_to_fp32:
vera_A = vera_A.float()
vera_B = vera_B.float()
lambda_d = lambda_d.float()
lambda_b = lambda_b.float()
sliced_A = vera_A[:, : self.in_features].to(lambda_d.device)
sliced_B = vera_B[: self.out_features, :].to(lambda_d.device)
lambda_b = lambda_b.unsqueeze(-1)
lambda_d = lambda_d.unsqueeze(-1)
output_tensor = transpose((lambda_b * sliced_B) @ (lambda_d * sliced_A), self.fan_in_fan_out)
if cast_to_fp32:
output_tensor = output_tensor.to(dtype=dtype)
return output_tensor
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args, **kwargs) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.disable_adapters:
if self.merged:
self.unmerge()
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
elif self.merged:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
else:
result = self.base_layer(x, *args, **kwargs)
result = result.clone()
for active_adapter in self.active_adapters:
if active_adapter not in self.vera_lambda_d.keys():
continue
lambda_d = self.vera_lambda_d[active_adapter]
lambda_b = self.vera_lambda_b[active_adapter]
vera_A = self.vera_A[active_adapter]
vera_B = self.vera_B[active_adapter]
dropout = self.vera_dropout[active_adapter]
requires_conversion = not torch.is_autocast_enabled()
if requires_conversion:
expected_dtype = result.dtype
compute_dtype = lambda_d.dtype
if x.dtype != compute_dtype:
x = x.to(compute_dtype)
sliced_A = vera_A[:, : self.in_features].to(x.device)
sliced_B = vera_B[: self.out_features, :].to(x.device)
x_temp = dropout(x.to(lambda_d.dtype))
adapter_output = lambda_b * torch.nn.functional.linear(
lambda_d * torch.nn.functional.linear(x_temp, sliced_A), sliced_B
)
if requires_conversion:
adapter_output = adapter_output.to(expected_dtype)
result = result + adapter_output
# Ensure the output tensor has the same dtype as the input tensor
return result.to(x.dtype)
def __repr__(self) -> str:
rep = super().__repr__()
return "vera." + rep
|
peft/src/peft/tuners/vera/bnb.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/tuners/vera/bnb.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 8510
}
| 250
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import annotations
import copy
import functools
import inspect
import os
import re
import warnings
from collections.abc import Sequence
from contextlib import nullcontext
from typing import Any, Optional, Union
import accelerate
import torch
import transformers
from accelerate import FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin
from accelerate.hooks import add_hook_to_module, remove_hook_from_module
from accelerate.utils import is_npu_available, is_xpu_available
from huggingface_hub import file_exists
from huggingface_hub.errors import EntryNotFoundError, HFValidationError
from packaging import version
from safetensors.torch import storage_ptr, storage_size
from transformers import PreTrainedModel
from ..import_utils import is_auto_gptq_available, is_gptqmodel_available, is_torch_tpu_available
from .constants import (
CONFIG_NAME,
EMBEDDING_LAYER_NAMES,
INCLUDE_LINEAR_LAYERS_SHORTHAND,
SAFETENSORS_WEIGHTS_NAME,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_ADALORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_C3A_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_FOURIERFT_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_IA3_FEEDFORWARD_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_IA3_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LNTUNING_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LOHA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LOKR_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_PREFIX_TUNING_POSTPROCESS_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_RANDLORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_SHIRA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_VBLORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_VERA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING,
WEIGHTS_NAME,
bloom_model_postprocess_past_key_value,
starcoder_model_postprocess_past_key_value,
)
mlu_available = False
if version.parse(accelerate.__version__) >= version.parse("0.29.0"):
from accelerate.utils import is_mlu_available
mlu_available = is_mlu_available()
__all__ = [
"CONFIG_NAME",
"EMBEDDING_LAYER_NAMES",
"INCLUDE_LINEAR_LAYERS_SHORTHAND",
"SAFETENSORS_WEIGHTS_NAME",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_ADALORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_C3A_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_FOURIERFT_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_IA3_FEEDFORWARD_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_IA3_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LNTUNING_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LOHA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LOKR_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_PREFIX_TUNING_POSTPROCESS_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_RANDLORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_SHIRA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_VBLORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_VERA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING",
"WEIGHTS_NAME",
"bloom_model_postprocess_past_key_value",
"starcoder_model_postprocess_past_key_value",
]
# Get current device name based on available devices
def infer_device() -> str:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
return "cuda"
elif hasattr(torch.backends, "mps") and torch.backends.mps.is_available():
return "mps"
elif mlu_available:
return "mlu"
elif is_xpu_available():
return "xpu"
elif is_npu_available():
return "npu"
return "cpu"
def prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model, use_gradient_checkpointing=True, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=None):
r"""
Note this method only works for `transformers` models.
This method wraps the entire protocol for preparing a model before running a training. This includes:
1- Cast the layernorm in fp32 2- making output embedding layer require grads 3- Add the upcasting of the lm
head to fp32 4- Freezing the base model layers to ensure they are not updated during training
Args:
model (`transformers.PreTrainedModel`):
The loaded model from `transformers`
use_gradient_checkpointing (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
If True, use gradient checkpointing to save memory at the expense of slower backward pass.
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs (`dict`, *optional*, defaults to `None`):
Keyword arguments to pass to the gradient checkpointing function, please refer to the documentation of
`torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint` for more details about the arguments that you can pass to that method.
Note this is only available in the latest transformers versions (> 4.34.1).
"""
loaded_in_kbit = getattr(model, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False) or getattr(model, "is_loaded_in_4bit", False)
is_gptq_quantized = getattr(model, "quantization_method", None) == "gptq"
is_aqlm_quantized = getattr(model, "quantization_method", None) == "aqlm"
is_eetq_quantized = getattr(model, "quantization_method", None) == "eetq"
is_torchao_quantized = getattr(model, "quantization_method", None) == "torchao"
is_hqq_quantized = getattr(model, "quantization_method", None) == "hqq" or getattr(model, "hqq_quantized", False)
if gradient_checkpointing_kwargs is None:
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs = {}
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
# freeze base model's layers
param.requires_grad = False
if (
not is_gptq_quantized
and not is_aqlm_quantized
and not is_eetq_quantized
and not is_hqq_quantized
and not is_torchao_quantized
):
# cast all non INT8 parameters to fp32
for param in model.parameters():
if (
(param.dtype == torch.float16) or (param.dtype == torch.bfloat16)
) and param.__class__.__name__ != "Params4bit":
param.data = param.data.to(torch.float32)
if (
loaded_in_kbit
or is_gptq_quantized
or is_aqlm_quantized
or is_eetq_quantized
or is_hqq_quantized
or is_torchao_quantized
) and use_gradient_checkpointing:
# When having `use_reentrant=False` + gradient_checkpointing, there is no need for this hack
if "use_reentrant" not in gradient_checkpointing_kwargs or gradient_checkpointing_kwargs["use_reentrant"]:
# For backward compatibility
if hasattr(model, "enable_input_require_grads"):
model.enable_input_require_grads()
else:
def make_inputs_require_grad(module, input, output):
output.requires_grad_(True)
model.get_input_embeddings().register_forward_hook(make_inputs_require_grad)
# To support older transformers versions, check if the model supports gradient_checkpointing_kwargs
_supports_gc_kwargs = "gradient_checkpointing_kwargs" in list(
inspect.signature(model.gradient_checkpointing_enable).parameters
)
if not _supports_gc_kwargs and len(gradient_checkpointing_kwargs) > 0:
warnings.warn(
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs is not supported in this version of transformers. The passed kwargs will be ignored."
" if you want to use that feature, please upgrade to the latest version of transformers.",
FutureWarning,
)
gc_enable_kwargs = (
{} if not _supports_gc_kwargs else {"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs": gradient_checkpointing_kwargs}
)
# enable gradient checkpointing for memory efficiency
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable(**gc_enable_kwargs)
return model
# copied from transformers.models.bart.modeling_bart
def shift_tokens_right(input_ids: torch.Tensor, pad_token_id: int, decoder_start_token_id: int):
"""
Shift input ids one token to the right.
Args:
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`): input ids
pad_token_id (`int`): The id of the `padding` token.
decoder_start_token_id (`int`): The id of the `start` token.
"""
shifted_input_ids = input_ids.new_zeros(input_ids.shape)
shifted_input_ids[:, 1:] = input_ids[:, :-1].clone()
shifted_input_ids[:, 0] = decoder_start_token_id
if pad_token_id is None:
raise ValueError("self.model.config.pad_token_id has to be defined.")
# replace possible -100 values in labels by `pad_token_id`
shifted_input_ids.masked_fill_(shifted_input_ids == -100, pad_token_id)
return shifted_input_ids
class AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
"""Wrap a specific module so that it can be trained and saved in a way that is tangential to how
PEFT normally works, e.g. fully training a classification layer instead of using an adapter.
"""
def __init__(self, module_to_save, adapter_name, **kwargs):
"""Extra kwargs will be passed to `self.init_modules` and `self.update`."""
super().__init__()
self.original_module = module_to_save
self._active_adapter = [adapter_name]
self._disable_adapters = False
self._adapters = set()
self.init_modules(adapter_name, **kwargs)
self.update(adapter_name, **kwargs)
self.check_module()
def init_modules(self, adapter_name, **kwargs):
"""A place to initialize PyTorch modules in `__init__` before the call to `self.update()`."""
raise NotImplementedError
def _error_message_name(self):
"""Returns a user friendly identifier for error messages, e.g. for type compatibility error messages from
`check_module()` so that the user can backtrack where the error comes from. A generic "training wrapper" is
less helpful than "modules_to_save", for example.
"""
return "training wrapper"
def check_module(self):
"""Perform some sanity checks on the module to ensure that it works"""
# Try to anticipate some modules that users could try to target that would not work.
# Note: It's not possible to check hasattr(module, "forward"), since that returns True for ModuleDict and
# ModuleList, even though their forward methods cannot be called
forbidden_classes = (torch.nn.ModuleDict, torch.nn.ModuleList, torch.nn.ParameterDict, torch.nn.ParameterList)
if isinstance(self.original_module, forbidden_classes):
cls_name = self.original_module.__class__
raise TypeError(f"{self._error_message_name()} cannot be applied to modules of type {cls_name}")
# local import to avoid circular import
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer
if isinstance(self.original_module, BaseTunerLayer):
# e.g. applying a training wrapper to a lora layer makes no sense
cls_name = self.original_module.__class__
raise TypeError(f"{self._error_message_name()} cannot be applied to modules of type {cls_name}")
@property
def disable_adapters(self) -> bool:
# use a property to ensure that disable_adapters is not set directly, instead use the enable_adapters method
return self._disable_adapters
@property
def active_adapter(self) -> Union[list[str], str]:
# use a property to ensure that active_adapter is not set directly, instead use the set_adapter method
return self._active_adapter
@property
def active_adapters(self) -> list[str]:
if isinstance(self._active_adapter, str):
return [self._active_adapter]
return self._active_adapter
def _hasattr_wrapped(self, name, modules):
"""Infrastructure to enable the implementing class to delegate attributes to other modules.
Returns True if the implementing class knows how to handle attribute `name`.
Gets passed `modules` which is PyTorch's internal list of assigned modules from `nn.Module`.
"""
return False
def _getattr_wrapped(self, name, modules):
"""If `_hasattr_wrapped` returns True for `name`, then this function should return the corresponding
value associated with `name`.
"""
return None
def __getattr__(self, name: str):
# Note: This whole method may seem overly complex at first but PyTorch messes with __getattr__ in a way that
# requires very careful handling to avoid infinite recursion.
try:
return super().__getattr__(name)
except AttributeError:
pass
if "_modules" not in self.__dict__:
raise AttributeError(f"'{type(self).__name__}' object has no attribute '{name}'")
# Could not find the attribute the PyTorch way. So let's check if it's an attribute on the
# original_module or the module further down (e.g., `modules_to_save[active_adapter]`).
modules = self.__dict__["_modules"]
if self.disable_adapters:
return getattr(self.original_module, name)
elif self._hasattr_wrapped(name, modules):
return self._getattr_wrapped(name, modules)
# For some reason, there is no module corresponding to the active adapter; this should normally not be
# reached and exists as a failsafe (otherwise, a KeyError would be raised)
raise AttributeError(f"'{type(self).__name__}' object has no attribute '{name}'")
def update(self, adapter_name, **kwargs):
"""Called when this instance should be part of an adapter's training.
Adds the given adapter to the list of adapters that this instance is training along with.
Additional kwargs are expected to be the same kwargs that are also passed for initializing this class.
"""
if adapter_name not in self._adapters:
self._adapters.add(adapter_name)
def _create_new_hook(self, old_hook):
r"""
Creates a new hook based on the old hook. Use it only if you know what you are doing !
"""
old_hook_cls = getattr(accelerate.hooks, old_hook.__class__.__name__)
old_hook_attr = old_hook.__dict__
filtered_old_hook_attr = {}
old_hook_init_signature = inspect.signature(old_hook_cls.__init__)
for k in old_hook_attr.keys():
if k in old_hook_init_signature.parameters:
filtered_old_hook_attr[k] = old_hook_attr[k]
new_hook = old_hook_cls(**filtered_old_hook_attr)
return new_hook
def _check_forward_args(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
"""Check if the arguments are compatible with the configs and state of the model"""
adapter_names = kwargs.get("adapter_names", None)
if adapter_names is None:
return
if len(x) != len(adapter_names):
msg = (
"Length of `adapter_names` should be the same as the number of inputs, but got "
f"{len(adapter_names)} and {len(x)} respectively."
)
raise ValueError(msg)
def _forward_wrapped(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> torch.Tensor:
raise NotImplementedError
def _forward_wrapped_mixed_batch(
self, x: torch.Tensor, active_adapter: str, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> torch.Tensor:
raise NotImplementedError
def _forward_wrapped_passthrough(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> torch.Tensor:
"""The forward call when no adapter is involved in the forward computation, only the base model"""
raise NotImplementedError
def _mixed_batch_forward(
self, input: torch.Tensor, *args: Any, adapter_names: list[str], **kwargs: Any
) -> torch.Tensor:
# This is a special method that handles the case when users pass the argument `adapter_names`. This is an
# extra argument that allows mixing different adapters in the same batch at inference time.
SUPPORTED_MODULES = (torch.nn.Linear, torch.nn.Embedding, torch.nn.Conv1d, torch.nn.Conv2d, torch.nn.Conv3d)
module_names = ", ".join([module.__name__ for module in SUPPORTED_MODULES])
if not isinstance(self.original_module, SUPPORTED_MODULES):
raise TypeError(f"Mixed batching is only supported for the following modules: {module_names}.")
unique_adapters = set(adapter_names)
sub_batch_indices_list = []
for adapter in unique_adapters:
sub_batch_indices_list.append([index for index, item in enumerate(adapter_names) if item == adapter])
results = [0 for _ in range(len(input))]
for i, active_adapter in enumerate(unique_adapters):
sub_batch = input[sub_batch_indices_list[i]]
if active_adapter == "__base__":
output = self.original_module(sub_batch, *args, **kwargs)
else:
output = self._forward_wrapped_mixed_batch(sub_batch, active_adapter, *args, **kwargs)
for index, j in enumerate(sub_batch_indices_list[i]):
results[j] = output[index]
return torch.stack(results)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, *args, **kwargs):
self._check_forward_args(x, *args, **kwargs)
adapter_names = kwargs.pop("adapter_names", None)
if self.disable_adapters or any(adapter not in self._adapters for adapter in self.active_adapters):
return self._forward_wrapped_passthrough(x, *args, **kwargs)
if adapter_names is None:
return self._forward_wrapped(x, *args, **kwargs)
return self._mixed_batch_forward(x, *args, adapter_names=adapter_names, **kwargs)
def enable_adapters(self, enabled: bool):
"""Toggle the enabling and disabling of adapters
Args:
enabled (bool): True to enable adapters, False to disable adapters
"""
if enabled:
self._disable_adapters = False
else:
self._disable_adapters = True
def set_adapter(self, adapter_names: Union[str, list[str]]):
"""Set the active adapter
Args:
adapter_name (str): The name of the adapter to set as active
"""
if isinstance(adapter_names, str):
self._active_adapter = adapter_names
else:
self._active_adapter = []
for adapter_name in adapter_names:
if adapter_name not in self._adapters:
raise ValueError(f"Adapter {adapter_name} not found in {self._adapters}")
self._active_adapter.append(adapter_name)
def delete_adapter(self, adapter_name: str, new_active_adapters: Optional[list[str]]) -> None:
"""Delete an adapter from the layer, set a new active adapter if necessary"""
raise NotImplementedError
def adapter_state_dict(self, adapter_name):
"""Return the state dict of this module for a given adapter."""
raise NotImplementedError
def adapter_state_dict_load_map(self, adapter_name):
"""Return a mapping from the key present in disk-loaded state dict
and how it should be represented in the loaded model's state dict.
The default should be a 1:1 mapping but it is important to define a mapping as it also serves as the
ground-truth for which keys are supposed to be loaded from a saved state dict.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def unload_and_optionally_merge_module(
self, merge: bool, safe_merge: bool, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]]
) -> torch.nn.Module:
"""Handles unloading when called from PEFT models. Returns the wrapped module
and handles merging onto the wrapped module if requested.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
class ModulesToSaveWrapper(AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper):
"""Wraps a module that is supposed to be trained (i.e. `requires_grad_(True)`) and saved after training."""
def __init__(self, module_to_save, adapter_name):
super().__init__(module_to_save, adapter_name)
def init_modules(self, adapter_name):
# we treat each adapter separately, so we have multiple adapters, same (copied) module for each
self.modules_to_save = torch.nn.ModuleDict({})
def _error_message_name(self):
return "modules_to_save"
def _forward_wrapped(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
if not self.active_adapters:
return self._forward_wrapped_passthrough(x, *args, **kwargs)
return self.modules_to_save[self.active_adapters[0]](x, *args, **kwargs)
def _forward_wrapped_mixed_batch(self, x, active_adapter, *args, **kwargs):
return self.modules_to_save[active_adapter](x, *args, **kwargs)
def _forward_wrapped_passthrough(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
return self.original_module(x, *args, **kwargs)
def _hasattr_wrapped(self, name, modules):
return self.active_adapters[0] in modules["modules_to_save"]
def _getattr_wrapped(self, name, modules):
return getattr(modules["modules_to_save"][self.active_adapters[0]], name)
def update(self, adapter_name, **kwargs):
super().update(adapter_name)
context_manager = nullcontext()
for _, param in self.original_module.named_parameters():
num_params = param.numel()
# if using DS Zero 3 and the weights are initialized empty
if num_params == 0 and hasattr(param, "ds_numel"):
import deepspeed
context_manager = deepspeed.zero.GatheredParameters(self.original_module.parameters(), modifier_rank=0)
break
if adapter_name not in self.modules_to_save:
with context_manager:
self.modules_to_save[adapter_name] = copy.deepcopy(self.original_module)
if hasattr(self.modules_to_save[adapter_name], "_hf_hook"):
old_hook = self.modules_to_save[adapter_name]._hf_hook
new_hook = self._create_new_hook(old_hook)
remove_hook_from_module(self.modules_to_save[adapter_name])
add_hook_to_module(self.modules_to_save[adapter_name], new_hook)
self.original_module.requires_grad_(False)
# note that there currently cannot be more than one active adapter for the same layer with modules to save
# since there would be no clear way to decide which adapter's weights are the correct ones. therefore we
# assume that there is only one active adapter. this precondition is enforced by _set_adapter.
if adapter_name == self.active_adapter:
self.modules_to_save[adapter_name].requires_grad_(True)
def enable_adapters(self, enabled: bool):
"""Takes care of setting the required_grad flag on the wrapped module.
If adapters are enabled, gradients for the module are required as well.
"""
super().enable_adapters(enabled)
if enabled:
self.original_module.requires_grad_(False)
self.modules_to_save[self.active_adapter].requires_grad_(True)
else:
self.original_module.requires_grad_(True)
self.modules_to_save.requires_grad_(False)
def set_adapter(self, adapter_names: Union[str, list[str]]):
"""Set the active adapter
Additionally, this function will set the specified adapter to trainable (i.e., requires_grad=True). If this is
not desired, use the following code.
```py
>>> for name, param in model_peft.named_parameters():
... if ...: # some check on name (ex. if 'lora' in name)
... param.requires_grad = False
```
Args:
adapter_names (list[str], str): The name of the adapter to set as active
"""
if isinstance(adapter_names, str):
adapter_names = [adapter_names]
if len(adapter_names) > 1:
raise ValueError(f"Attempted to set multiple ({adapter_names}) adapters at once for modules_to_save.")
adapter_name = adapter_names[0]
if adapter_name not in self._adapters:
raise ValueError(f"Adapter {adapter_name} not found in {self._adapters}")
self.modules_to_save[self.active_adapters[0]].requires_grad_(False)
self.modules_to_save[adapter_name].requires_grad_(True)
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
def delete_adapter(self, adapter_name: str, new_active_adapters: Optional[list[str]]) -> None:
"""
Delete the adapter if present.
This method will also set a new active adapter if the deleted adapter was the active adapter. It is important
that the new adapter is chosen by the caller in a deterministic way, so that the same adapter is chosen on all
layers.
"""
if adapter_name not in self.modules_to_save:
return
# set new active adapter, if necessary
# note: there can only ever be one active adapter, unlike for LoRA etc.
if isinstance(new_active_adapters, (list, tuple)) and len(new_active_adapters) > 1:
name = self.__class__.__name__
raise ValueError(
f"Attempted to set multiple ({new_active_adapters}) adapters at once for {name}, which is not allowed."
)
if adapter_name in self._adapters:
self._adapters.remove(adapter_name)
if not new_active_adapters:
# no active adapter now
del self.modules_to_save[adapter_name]
self._active_adapter = []
return
new_active_adapter = new_active_adapters[0]
if new_active_adapter not in self.modules_to_save:
# a new active adapter was chosen but it seems like it has no modules_to_save
del self.modules_to_save[adapter_name]
self._active_adapter = []
return
if new_active_adapter != self.active_adapters[0]:
self.set_adapter(new_active_adapter)
del self.modules_to_save[adapter_name]
def adapter_state_dict_load_map(self, adapter_name):
# Maps the module keys as they are in the saved state dict to the in-memory state dict.
# Must contain all keys that are supposed to be loaded.
if adapter_name not in self._adapters:
# In caes of multiple adapters, each bringing their own modules to save, each
# ModulesToSaveWrapper will be queried but not every wrapper is obliged to serve the same adapters.
return {}
return {k: f"modules_to_save.{adapter_name}.{k}" for k in self.modules_to_save[adapter_name].state_dict()}
def adapter_state_dict(self, adapter_name, state_dict):
if adapter_name not in self._adapters:
# In caes of multiple adapters, each bringing their own modules to save, each
# ModulesToSaveWrapper will be queried but not every wrapper is obliged to serve the same adapters.
return {}
return {
k: state_dict[f"modules_to_save.{adapter_name}.{k}"]
for k in self.modules_to_save[adapter_name].state_dict()
}
def unload_and_optionally_merge_module(
self, merge: bool, safe_merge: bool, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]]
) -> torch.nn.Module:
"""Unloading in case of `ModulesToSave` means to simply return the wrapped module.
However, if the wrapped module is itself a tuner, we'll call merge on it before.
"""
new_module = self.modules_to_save[self.active_adapter]
# TODO: not sure if this is still a sensible thing to do. We would basically have to
# do the same checks as `_unload_and_optionally_merge` to support MHA, for example.
if hasattr(new_module, "base_layer"):
# check if the module is itself a tuner layer
if merge:
new_module.merge(safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names)
new_module = new_module.get_base_layer()
return new_module
class TrainableTokensWrapper(AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper):
"""Wraps a module (typically an embedding layer) that is supposed to be re-trained selectively (i.e.
solely updating a few columns) using the `TrainableTokensLayer` PEFT method.
Supports weight-tying to another adapter when passed a `tied_adapter` which is expected to be a
`TrainableTokensLayer`.
"""
def __init__(
self,
module_to_save: torch.nn.Module,
adapter_name: str,
token_indices: list[int],
tied_adapter=None,
) -> None:
super().__init__(module_to_save, adapter_name, token_indices=token_indices, tied_adapter=tied_adapter)
# unset the original_module attribute since we're using a property to remove this from the state dict.
self.original_module = None
@property
def original_module(self):
# use a property instead of an attribute to exclude this pointer from the state dict
# to make sure that it will not be saved.
return self.token_adapter.base_layer
def init_modules(self, adapter_name, token_indices, tied_adapter):
# use a local import to avoid potential circular imports
from peft.tuners.trainable_tokens import TrainableTokensLayer
# since super().__init__() calls update before we have a chance to initialise the adapter we would
# need here, we do the initialization here.
self.token_adapter = TrainableTokensLayer(self.original_module, adapter_name, token_indices, tied_adapter)
def _error_message_name(self):
return "trainable_token_indices"
def _hasattr_wrapped(self, name, modules):
return name == "weight"
def _getattr_wrapped(self, name, modules):
# some models query self.wte.weight.dtype, some may query the weights directly. for the first case it is not
# necessary to do anything special but we don't know if is going to be `.dtype`. so we need to get the merged
# weights from the adapter.
if name == "weight":
return modules["token_adapter"].get_merged_weights(self.token_adapter.active_adapters)
raise RuntimeError(
f"This code should've never been reached, probably a bad check in `_hasattr_wrapped` for {name}. "
"Please file an issue under https://github.com/huggingface/peft/issues."
)
def _forward_wrapped(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
if not self.active_adapters:
return self._forward_wrapped_passthrough(x, *args, **kwargs)
return self.token_adapter(x)
def _forward_wrapped_mixed_batch(self, x, active_adapter, *args, **kwargs):
return self.token_adapter.forward_adapters(x, [active_adapter])
def _forward_wrapped_passthrough(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
# the token adapter knows how to deal with disabled adapter / no active adapter, don't call original_module
# directly
return self.token_adapter(x, *args, **kwargs)
def update(self, active_adapter, **kwargs):
# TODO this does not support deepspeed/fsdp since it is missing a context manager
# see ModulesToSaveWrapper implementation
if active_adapter not in self._adapters:
self.token_adapter.update_layer(active_adapter, **kwargs)
super().update(active_adapter)
def adapter_state_dict_load_map(self, adapter_name):
if self.token_adapter.tied_adapter:
return {}
return {"token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta": f"token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta.{adapter_name}"}
def adapter_state_dict(self, adapter_name, state_dict):
if self.token_adapter.tied_adapter:
# storing of weight-tied layers is not up to us and will be handled by
# transformers. we're just here to keep those layers in sync during training.
# therefore we return an empty state dict.
return {}
return {
f"token_adapter.{k}": state_dict[f"token_adapter.{k}.{adapter_name}"] for k in ["trainable_tokens_delta"]
}
def enable_adapters(self, enabled: bool):
"""Enables/disables the underlying `TrainableTokens` adapter.
Also handles the internal adapter disable flag.
"""
super().enable_adapters(enabled)
self.token_adapter.enable_adapters(enabled)
def set_adapter(self, adapter_names: Union[str, list[str]]):
super().set_adapter(adapter_names)
self.token_adapter.set_adapter(adapter_names)
def delete_adapter(self, adapter_name: str, new_active_adapters: Optional[list[str]]) -> None:
"""
Delete the adapter if present.
This method will also set a new active adapter if the deleted adapter was the active adapter. It is important
that the new adapter is chosen by the caller in a deterministic way, so that the same adapter is chosen on all
layers.
"""
self.token_adapter.delete_adapter(adapter_name)
# set new active adapter, if necessary
# note: there can only ever be one active adapter, unlike for LoRA etc.
if isinstance(new_active_adapters, (list, tuple)) and len(new_active_adapters) > 1:
name = self.__class__.__name__
raise ValueError(
f"Attempted to set multiple ({new_active_adapters}) adapters at once for {name}, which is not allowed."
)
if adapter_name in self._adapters:
self._adapters.remove(adapter_name)
if not new_active_adapters:
self._active_adapter = []
return
if new_active_adapters[0] not in self.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta:
# a new active adapter was chosen but it seems like it has no trainable_tokens
self._active_adapter = []
return
new_active_adapter = new_active_adapters[0]
self.set_adapter(new_active_adapter)
def unload_and_optionally_merge_module(
self, merge: bool, safe_merge: bool, adapter_names: Optional[list[str]]
) -> torch.nn.Module:
"""Unloading for `TrainableTokensWrapper` means to return the wrapped module, e.g. the embedding layer and,
if requested, merging the `TrainableTokens` adapter onto the wrapped module.
"""
if merge:
self.token_adapter.merge(safe_merge=safe_merge, adapter_names=adapter_names)
return self.token_adapter.get_base_layer()
def _get_input_embeddings_name(model, default=None):
if not hasattr(model, "get_input_embeddings"):
return default
input_embeddings = model.get_input_embeddings()
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if module is input_embeddings:
return name
return default
def _get_submodules(model, key):
parent = model.get_submodule(".".join(key.split(".")[:-1]))
target_name = key.split(".")[-1]
target = model.get_submodule(key)
return parent, target, target_name
def _freeze_adapter(model, adapter_name):
for n, p in model.named_parameters():
if adapter_name in n:
p.requires_grad = False
def _set_trainable(
model,
adapter_name,
module_names,
strict_module_check=False,
wrapper_cls: Optional[AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper] = None,
**wrapper_kwargs,
):
"""Wraps modules that are supposed to be re-trained either normally, i.e. marking them to require gradients and
saving them alongside other modules, or with certain methods that go alongside PEFT methods, such as retraining
specific token indices using selective read/write.
Note that you need to validate beforehand if there are layers targeted by multiple wrappers, e.g. if the
'embedding' layer is configured for both `ModulesToSaveWrapper` and `TrainableTokensWrapper` there would be
conflicts down the line.
The default is to wrap the module in a `ModulesToSaveWrapper` wrapper.
If `strict_module_check` is set, this method raises an ValueError, similar to BaseTuner.inject_adapter when none of
the requested modules in `module_names` is not found in the model.
"""
if wrapper_cls is None:
wrapper_cls = ModulesToSaveWrapper
if not module_names:
# This is useful for the case that the PEFT config does not have `modules_to_save`, e.g.
# in the case of prompt tuning and friends.
return
trainable_modules = []
found_modules = set()
# disable removal of duplicates to support targeting tied weights
key_list = [key for key, _ in model.named_modules(remove_duplicate=False)]
for key in key_list:
target_module_found = any(key.endswith(target_key) for target_key in module_names)
if target_module_found:
parent, target, target_name = _get_submodules(model, key)
if isinstance(target, wrapper_cls):
target.update(adapter_name, **wrapper_kwargs)
target.set_adapter(target.active_adapter)
else:
new_module = wrapper_cls(target, adapter_name, **wrapper_kwargs)
new_module.set_adapter(adapter_name)
setattr(parent, target_name, new_module)
trainable_modules.append(new_module)
found_modules.add(target_name)
not_found = set(module_names).difference(found_modules)
if strict_module_check and not found_modules:
raise ValueError(
f"Target modules {not_found} not found in the base model. Please check the target modules and try again."
)
return trainable_modules
def _set_adapter(model, adapter_name):
def check_adapter_name(adapter_name):
if isinstance(adapter_name, str):
return adapter_name
# adapter_name is a list of str
if len(adapter_name) > 1:
raise ValueError("Only one adapter can be set at a time for modules_to_save")
elif len(adapter_name) == 0:
raise ValueError("Please specify at least one adapter to set")
adapter_name = adapter_name[0]
return adapter_name
for module in model.modules():
if isinstance(module, AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper):
# only check the adapter_name if we actually encounter a AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper, otherwise we don't care
adapter_name = check_adapter_name(adapter_name)
# if the adapter is found in this module, set it as the active adapter, else disable the adapters of this
# module
if adapter_name in module._adapters:
module.enable_adapters(True)
module.set_adapter(adapter_name)
else:
module.enable_adapters(False)
def _prepare_prompt_learning_config(peft_config, model_config):
# In case of VLM we focus on the language model portion of the model.
if "text_config" in model_config:
model_config = model_config["text_config"]
if peft_config.num_layers is None:
if "num_hidden_layers" in model_config:
num_layers = model_config["num_hidden_layers"]
elif "num_layers" in model_config:
num_layers = model_config["num_layers"]
elif "n_layer" in model_config:
num_layers = model_config["n_layer"]
else:
raise ValueError("Please specify `num_layers` in `peft_config`")
peft_config.num_layers = num_layers
if peft_config.token_dim is None:
if "hidden_size" in model_config:
token_dim = model_config["hidden_size"]
elif "n_embd" in model_config:
token_dim = model_config["n_embd"]
elif "d_model" in model_config:
token_dim = model_config["d_model"]
else:
raise ValueError("Please specify `token_dim` in `peft_config`")
peft_config.token_dim = token_dim
if peft_config.num_attention_heads is None:
if "num_attention_heads" in model_config:
num_attention_heads = model_config["num_attention_heads"]
elif "n_head" in model_config:
num_attention_heads = model_config["n_head"]
elif "num_heads" in model_config:
num_attention_heads = model_config["num_heads"]
elif "encoder_attention_heads" in model_config:
num_attention_heads = model_config["encoder_attention_heads"]
else:
raise ValueError("Please specify `num_attention_heads` in `peft_config`")
peft_config.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
# For grouped-query attention, see #1901.
if peft_config.peft_type == "PREFIX_TUNING" and "num_key_value_heads" in model_config:
num_key_value_heads = model_config["num_key_value_heads"]
peft_config.token_dim = peft_config.token_dim // peft_config.num_attention_heads * num_key_value_heads
peft_config.num_attention_heads = num_key_value_heads
if getattr(peft_config, "encoder_hidden_size", None) is None:
setattr(peft_config, "encoder_hidden_size", peft_config.token_dim)
return peft_config
def _get_no_split_modules(model) -> set[str]:
"""
Get the modules of the model that should not be split when using device_map. We iterate through the modules to get
the underlying `_no_split_modules`.
Returns:
`List[str]`: List of modules that should not be split
"""
# After discussion in https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/38141, based on:
# https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/1e921a3a9cea92b383ca4b0484ee45596bbdadc3/src/transformers/modeling_utils.py#L2677-L2704
_no_split_modules: set[str] = set()
if not hasattr(model, "_no_split_modules"):
return _no_split_modules
modules_to_check = [model]
while len(modules_to_check) > 0:
module = modules_to_check.pop(-1)
# if the module does not appear in _no_split_modules, we also check the children
if module.__class__.__name__ not in _no_split_modules:
if isinstance(module, PreTrainedModel):
if module._no_split_modules is not None:
_no_split_modules = _no_split_modules | set(module._no_split_modules)
modules_to_check += list(module.children())
return _no_split_modules
def fsdp_auto_wrap_policy(model):
if hasattr(FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin, "get_module_class_from_name"):
get_module_class_from_name = FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin.get_module_class_from_name
else:
from accelerate.utils.dataclasses import get_module_class_from_name
from torch.distributed.fsdp.wrap import _or_policy, lambda_auto_wrap_policy, transformer_auto_wrap_policy
from ..tuners import PrefixEncoder, PromptEmbedding, PromptEncoder
default_transformer_cls_names_to_wrap = ",".join(_get_no_split_modules(model))
transformer_cls_names_to_wrap = os.environ.get(
"FSDP_TRANSFORMER_CLS_TO_WRAP", default_transformer_cls_names_to_wrap
).split(",")
transformer_cls_to_wrap = {PrefixEncoder, PromptEncoder, PromptEmbedding}
for layer_class in transformer_cls_names_to_wrap:
if len(layer_class) == 0:
continue
transformer_cls = get_module_class_from_name(model, layer_class)
if transformer_cls is None:
raise Exception("Could not find the transformer layer class to wrap in the model.")
else:
transformer_cls_to_wrap.add(transformer_cls)
def lambda_policy_fn(module):
if (
len(list(module.named_children())) == 0
and getattr(module, "weight", None) is not None
and module.weight.requires_grad
):
return True
return False
lambda_policy = functools.partial(lambda_auto_wrap_policy, lambda_fn=lambda_policy_fn)
transformer_wrap_policy = functools.partial(
transformer_auto_wrap_policy,
transformer_layer_cls=transformer_cls_to_wrap,
)
auto_wrap_policy = functools.partial(_or_policy, policies=[lambda_policy, transformer_wrap_policy])
return auto_wrap_policy
def transpose(weight, fan_in_fan_out):
if not fan_in_fan_out:
return weight
if isinstance(weight, torch.nn.Parameter):
return torch.nn.Parameter(weight.T)
return weight.T
def _is_valid_match(key: str, target_key: str):
"""
Helper function to match module names target_key and key. Makes sure that either the key is exactly the target_key
or the target_key is a submodule of key
"""
if key.endswith(target_key):
if len(key) > len(target_key):
return key.endswith("." + target_key) # must be a sub module
return True
return False
def _get_batch_size(input_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor], inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor]) -> int:
"""Get the batch size based on either input_ids or input_embeds
Raises an ValueError if both are None.
"""
if (input_ids is None) and (inputs_embeds is None):
raise ValueError("You have to provide either input_ids or inputs_embeds")
if input_ids is not None:
batch_size = input_ids.shape[0]
else:
batch_size = inputs_embeds.shape[0]
return batch_size
def get_quantization_config(model: torch.nn.Module, method: str):
"""
Get the quantization config of the related quantization method
"""
if (
hasattr(model, "config")
and hasattr(model.config, "quantization_config")
and (getattr(model, "quantization_method", None) == method)
):
return model.config.quantization_config
return None
def get_auto_gptq_quant_linear(gptq_quantization_config):
"""
Get the right AutoGPTQQuantLinear class based on the quantization config file
"""
if gptq_quantization_config is None:
return None
if is_auto_gptq_available():
from auto_gptq.utils.import_utils import dynamically_import_QuantLinear
else:
return None
desc_act = gptq_quantization_config.desc_act
group_size = gptq_quantization_config.group_size
bits = gptq_quantization_config.bits
if hasattr(gptq_quantization_config, "use_exllama"):
use_exllama = gptq_quantization_config.use_exllama
else:
use_exllama = not gptq_quantization_config.disable_exllama
if hasattr(gptq_quantization_config, "exllama_config"):
exllama_version = gptq_quantization_config.exllama_config["version"]
else:
exllama_version = 1
QuantLinear = dynamically_import_QuantLinear(
use_triton=False,
desc_act=desc_act,
group_size=group_size,
bits=bits,
disable_exllama=not (use_exllama and exllama_version == 1),
disable_exllamav2=not (use_exllama and exllama_version == 2),
)
return QuantLinear
def get_gptqmodel_quant_linear(gptq_quantization_config, device_map=None):
"""
Get the right GPTQQuantLinear class based on the quantization config file
"""
if gptq_quantization_config is None:
return None
if not is_gptqmodel_available():
return None
from gptqmodel.utils.importer import hf_select_quant_linear
desc_act = gptq_quantization_config.desc_act
group_size = gptq_quantization_config.group_size
bits = gptq_quantization_config.bits
checkpoint_format = (
gptq_quantization_config.checkpoint_format
if hasattr(gptq_quantization_config, "checkpoint_format")
else "gptq"
)
sym = gptq_quantization_config.sym
meta = gptq_quantization_config.meta if hasattr(gptq_quantization_config, "meta") else None
QuantLinear = hf_select_quant_linear(
bits=bits,
group_size=group_size,
desc_act=desc_act,
sym=sym,
device_map=device_map,
checkpoint_format=checkpoint_format,
meta=meta,
backend="auto_trainable",
)
return QuantLinear
def id_tensor_storage(tensor: torch.Tensor) -> tuple[torch.device, int, int]:
"""
Unique identifier to a tensor storage. Multiple different tensors can share the same underlying storage. For
example, "meta" tensors all share the same storage, and thus their identifier will all be equal. This identifier is
guaranteed to be unique and constant for this tensor's storage during its lifetime. Two tensor storages with
non-overlapping lifetimes may have the same id.
This method is the exact same copy of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/pytorch_utils.py#L282C1-L300C58 but we added
it here manually to avoid import issue with old versions of transformers.
"""
if tensor.device.type == "xla" and is_torch_tpu_available():
# NOTE: xla tensors dont have storage
# use some other unique id to distinguish.
# this is a XLA tensor, it must be created using torch_xla's
# device. So the following import is safe:
import torch_xla
unique_id = torch_xla._XLAC._xla_get_tensor_id(tensor)
else:
unique_id = storage_ptr(tensor)
return tensor.device, unique_id, storage_size(tensor)
def cast_mixed_precision_params(model, dtype):
"""
Cast all non-trainable parameters of the model to the given `dtype`. The `dtype` can be `torch.float16` or
`torch.bfloat16` as per the mixed-precision training you are performing. The trainable parameters are cast to full
precision. This is meant to reduce the GPU memory usage when using PEFT methods by using half-precision dtype for
non-trainable parameters. Having the trainable parameters in full-precision preserves training stability when using
automatic mixed-precision training.
Args:
model (`torch.nn.Module`):
The model to cast the non-trainable parameters of.
dtype (`torch.dtype`):
The dtype to cast the non-trainable parameters to. The `dtype` can be `torch.float16` or
`torch.bfloat16` as per the mixed-precision training you are performing.
"""
for p in model.parameters():
if not p.requires_grad:
p.data = p.to(dtype)
else:
p.data = p.to(torch.float32)
def str_to_bool(value: str) -> int:
"""
Converts a string representation of truth to `True` (1) or `False` (0).
True values are `y`, `yes`, `t`, `true`, `on`, and `1`; False value are `n`, `no`, `f`, `false`, `off`, and `0`;
"""
# same as function as in accelerate.utils, which replaces the deprecated distutils.util.strtobool
value = value.lower()
if value in ("y", "yes", "t", "true", "on", "1"):
return 1
elif value in ("n", "no", "f", "false", "off", "0"):
return 0
else:
raise ValueError(f"invalid truth value {value}")
def check_file_exists_on_hf_hub(repo_id: str, filename: str, **kwargs) -> Optional[bool]:
"""Check if a file exists on HF Hub, if check was not successful returns None instead of erroring.
Respect offline mode if set.
"""
exists: Optional[bool] = None
if str_to_bool(os.environ.get("HF_HUB_OFFLINE", "0")):
# user set offline mode, cannot check
return exists
try:
exists = file_exists(repo_id, filename, **kwargs)
except (HFValidationError, EntryNotFoundError):
# error, exists stays None
pass
except Exception as e:
warnings.warn(
f"Unable to fetch remote file due to the following error {e} - silently ignoring the lookup"
f" for the file {filename} in {repo_id}."
)
return exists
def match_target_against_key(target_pattern: str, key: str):
"""Backing function for `target_modules` config parameter.
Having this as its own function ensures that target key matching can be implemented in the same way everywhere.
"""
return re.fullmatch(target_pattern, key)
def get_pattern_key(pattern_keys: Sequence[str], key_to_match: str) -> str:
"""Match a substring of key_to_match in pattern keys"""
for key in pattern_keys:
match = re.match(rf"(.*\.)?({key})$", key_to_match)
if not match:
continue
return key
return key_to_match
def set_additional_trainable_modules(model, peft_config, model_config, adapter_name):
"""Handle the resolution of additional trainable modules (also called AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper)
by checking the config if such modules are requested and adding them to the model.
Currently trainable tokens and modules to save are considered additional trainable modules.
"""
if getattr(peft_config, "modules_to_save", None) is not None:
# this may add a new ModulesToSaveWrapper
_set_trainable(model, adapter_name, module_names=getattr(peft_config, "modules_to_save", None))
if getattr(peft_config, "trainable_token_indices", None) is not None:
if isinstance(peft_config.trainable_token_indices, dict):
target_layers = peft_config.trainable_token_indices
else:
layer_name = _get_input_embeddings_name(model, "embed_tokens")
target_layers = {layer_name: peft_config.trainable_token_indices}
modules_to_save = getattr(peft_config, "modules_to_save", None)
if modules_to_save is not None:
for target_layer in target_layers:
if target_layer in modules_to_save:
raise ValueError(
"The embedding layer is already marked to be trained fully, either specify "
f'`modules_to_save=[..., "{target_layer}", ...]` or '
f"`trainable_tokens={{'{target_layer}': x}}` but not both."
)
for target_layer, token_indices in target_layers.items():
_set_trainable(
model,
adapter_name,
module_names=[target_layer],
strict_module_check=True,
wrapper_cls=TrainableTokensWrapper,
token_indices=token_indices,
)
# There might be the possibility that we have output weights that are tied to the input weights.
# In that case we will tie any module that wants tied weights to the token adapter to make sure that
# any modification is reflected in the tied layers as well.
if (
model_config.get("tie_word_embeddings", False)
# some models may be misconfigured to have weight tying enabled but don't define tied weights keys
and model._tied_weights_keys is not None
and isinstance(model.get_input_embeddings(), TrainableTokensWrapper)
):
# the embedding layer is modified and we want weight tying.
module_keys = [".".join(n.split(".")[:-1]) for n in model._tied_weights_keys]
token_adapter = model.get_input_embeddings().token_adapter
_set_trainable(
model,
adapter_name,
module_names=module_keys,
strict_module_check=True,
wrapper_cls=TrainableTokensWrapper,
token_indices=token_adapter.token_indices[adapter_name],
tied_adapter=model.get_input_embeddings().token_adapter,
)
def create_attention_mask(
model, *, model_input, attention_mask, past_key_values, cache_position, batch_size, sequence_length, position_ids
):
# adapted from:
# https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/cb4c56ce0dfa1350267ed28e57760986a58a9ba4/src/transformers/generation/utils.py#L644-L680
# In PEFT, we sometimes need to re-create the attention mask. This is because some prompt learning methods insert
# new items into the sequence, which results in the attention mask needing an update. We re-use transformers code
# for this as much as possible.
transformers_ge_4_53_1 = version.parse(transformers.__version__) >= version.parse("4.53.1")
if transformers_ge_4_53_1:
# the function already exists in v4.53.0 but has a different signature, so we check for 4.53.1
from transformers.masking_utils import create_masks_for_generate
else:
raise ImportError("Your transformers version is too old, please upgrade it to >= 4.53.1")
# Create the causal mask with fixed shape in advance, to reduce recompilations. If the function to create
# the 4D causal mask exists, it should be present in the base model (XXXModel class) or in its decoder.
base_model = getattr(model, model.base_model_prefix, model)
decoder = base_model.get_decoder() if hasattr(base_model, "get_decoder") else None
causal_mask_creation_function = getattr(base_model, "_prepare_4d_causal_attention_mask_with_cache_position", None)
if causal_mask_creation_function is None and decoder is not None: # it may be in the decoder
causal_mask_creation_function = getattr(decoder, "_prepare_4d_causal_attention_mask_with_cache_position", None)
# If it's not defined, it means the model uses the new general mask API
if causal_mask_creation_function is None: # can't be found
token_type_ids = getattr(model_input, "token_type_ids", None)
# Some models may overwrite the general one
causal_mask_creation_function = getattr(model, "create_masks_for_generate", create_masks_for_generate)
attention_mask = causal_mask_creation_function(
config=model.config,
# we only need batch size, seq_length and dtype here - we don't care about the values of the embeddings
input_embeds=torch.empty((batch_size, sequence_length), dtype=model.dtype),
attention_mask=attention_mask,
cache_position=cache_position,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
else:
attention_mask = causal_mask_creation_function(
attention_mask,
sequence_length=sequence_length,
target_length=past_key_values.get_max_cache_shape(),
dtype=model.dtype,
cache_position=cache_position,
batch_size=batch_size,
config=model.config,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
return attention_mask
|
peft/src/peft/utils/other.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/src/peft/utils/other.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 23318
}
| 251
|
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import copy
import os
import platform
import re
import shutil
import tempfile
import time
from contextlib import contextmanager
from functools import partial
import pytest
import torch
from safetensors.torch import load_file as safe_load_file
from torch import nn
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
from transformers.pytorch_utils import Conv1D
from peft import (
AdaLoraConfig,
BOFTConfig,
BoneConfig,
C3AConfig,
FourierFTConfig,
HRAConfig,
IA3Config,
LNTuningConfig,
LoHaConfig,
LoKrConfig,
LoraConfig,
MissConfig,
OFTConfig,
PeftModel,
PeftWarning,
RandLoraConfig,
RoadConfig,
ShiraConfig,
TaskType,
TrainableTokensConfig,
VBLoRAConfig,
VeraConfig,
get_peft_model,
)
from peft.tuners.tuners_utils import BaseTunerLayer
from peft.utils import AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper, infer_device
from .testing_common import PeftCommonTester
from .testing_utils import get_state_dict, require_non_cpu, set_init_weights_false
# MLP is a vanilla FF network with only linear layers
# EmbConv1D has an embedding and a Conv1D layer
# Conv2D has a Conv2D layer
TEST_CASES = [
########
# LoRA #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 LoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 LoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 LoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 LoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 LoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"]}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 LoRA",
"MLP",
LoraConfig,
{
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"lora_alpha": 4,
"lora_dropout": 0.1,
},
),
("Vanilla MLP 7 LoRA with DoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "use_dora": True}),
("Vanilla MLP 8 LoRA with DoRA", "MLP", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "use_dora": True}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 9 LoRA with DoRA",
"MLP",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": "lin1", "use_dora": True, "lora_alpha": 32},
),
("Embedding + transformers Conv1D 1 LoRA", "EmbConv1D", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv1d"]}),
("Embedding + transformers Conv1D 2 LoRA", "EmbConv1D", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["emb"]}),
("Embedding + transformers Conv1D 3 LoRA", "EmbConv1D", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["emb", "conv1d"]}),
(
"Embedding + transformers Conv1D 1 DoRA",
"EmbConv1D",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d"], "use_dora": True},
),
("Embedding + transformers Conv1D 2 DoRA", "EmbConv1D", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["emb"], "use_dora": True}),
(
"Embedding + transformers Conv1D 3 DoRA",
"EmbConv1D",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["emb", "conv1d"], "use_dora": True},
),
(
"Embedding + transformers Conv1D 1 LoRA trainable_tokens",
"EmbConv1D",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d"], "trainable_token_indices": {"emb": [0, 10]}},
),
("Conv1d LoRA", "Conv1d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv1d"]}),
("Conv1d LoRA with DoRA", "Conv1d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv1d"], "use_dora": True}),
("Conv2d 1 LoRA", "Conv2d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
("Conv2d 2 LoRA", "Conv2d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"]}),
("Conv2d 1 LoRA with DoRA", "Conv2d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "use_dora": True}),
("Conv2d 2 LoRA with DoRA", "Conv2d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "use_dora": True}),
("Conv2d Groups LoRA", "Conv2dGroups", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
("Conv2d Groups2 LoRA", "Conv2dGroups2", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
("Conv2d Groups LoRA with DoRA", "Conv2dGroups", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "use_dora": True}),
("Conv2d Groups2 LoRA with DoRA", "Conv2dGroups2", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "use_dora": True}),
("Conv3d 1 LoRA", "Conv3d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv3d"]}),
("Conv3d 2 LoRA", "Conv3d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv3d", "lin0"]}),
("Conv3d 1 LoRA with DoRA", "Conv3d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv3d"], "use_dora": True}),
("Conv3d 2 LoRA with DoRA", "Conv3d", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv3d", "lin0"], "use_dora": True}),
# LoRA with lora_B bias enabled (note: embedding is not supported)
# It's important to set lora_alpha != r to ensure that scaling is taken into account correctly
(
"Vanilla MLP 1 LoRA with lora_b bias",
"MLP",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "lora_bias": True, "lora_alpha": 32},
),
(
"Conv2d 1 LoRA with lora_b bias",
"Conv2d",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "lora_bias": True, "lora_alpha": 32},
),
(
"Conv3d 1 LoRA with lora_b bias",
"Conv3d",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv3d"], "lora_bias": True, "lora_alpha": 32},
),
("MHA 1 LoRA", "MHA", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["mha"]}),
("MHA 2 LoRA", "MHA", LoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["mha", "lin0"]}),
# targeting parameters directly
("MLP 1 using nn.Parameter LoRA", "MlpUsingParameters", LoraConfig, {"target_parameters": ["lin0.weight"]}),
(
"MLP 2 using nn.Parameter LoRA",
"MLP",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "target_parameters": ["lin1.weight"]},
),
#######
# IA³ #
#######
("Vanilla MLP 1 IA3", "MLP", IA3Config, {"target_modules": "lin0", "feedforward_modules": []}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 IA3", "MLP", IA3Config, {"target_modules": "lin0", "feedforward_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 IA3", "MLP", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "feedforward_modules": []}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 IA3", "MLP", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "feedforward_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 IA3", "MLP", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["lin1"], "feedforward_modules": []}),
("Vanilla MLP 6 IA3", "MLP", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["lin1"], "feedforward_modules": ["lin1"]}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 7 IA3",
"MLP",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "feedforward_modules": []},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 8 IA3",
"MLP",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "feedforward_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"]},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 9 IA3",
"MLP",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "feedforward_modules": ["lin0"]},
),
(
"transformers Conv1D 1 IA3",
"EmbConv1D",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv1d"]},
),
(
"transformers Conv1D 2 IA3",
"EmbConv1D",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv1d", "lin0"]},
),
(
"transformers Conv1D 1 IA3",
"EmbConv1D",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv1d"], "modules_to_save": ["lin0"]},
),
("Conv2d 1 IA3", "Conv2d", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "feedforward_modules": []}),
("Conv2d 2 IA3", "Conv2d", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
(
"Conv2d 3 IA3",
"Conv2d",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": []},
),
(
"Conv2d 4 IA3",
"Conv2d",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv2d"]},
),
(
"Conv2d 5 IA3",
"Conv2d",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"]},
),
("Conv3d 1 IA3", "Conv3d", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["conv3d"], "feedforward_modules": []}),
("Conv3d 2 IA3", "Conv3d", IA3Config, {"target_modules": ["conv3d"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv3d"]}),
(
"Conv3d 3 IA3",
"Conv3d",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv3d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": []},
),
(
"Conv3d 4 IA3",
"Conv3d",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv3d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv3d"]},
),
(
"Conv3d 5 IA3",
"Conv3d",
IA3Config,
{"target_modules": ["conv3d", "lin0"], "feedforward_modules": ["conv3d", "lin0"]},
),
########
# LoHa #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 LOHA", "MLP", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 LOHA", "MLP", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 LOHA", "MLP", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 LOHA", "MLP", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 LOHA", "MLP", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"]}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 LOHA",
"MLP",
LoHaConfig,
{
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"alpha": 4,
"module_dropout": 0.1,
},
),
("Vanilla MLP 7 LOHA", "MLP", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "rank_dropout": 0.5}),
("Conv2d 1 LOHA", "Conv2d", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
("Conv2d 2 LOHA", "Conv2d", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"]}),
("Conv2d 3 LOHA", "Conv2d", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "use_effective_conv2d": True}),
("Conv2d 4 LOHA", "Conv2d", LoHaConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "use_effective_conv2d": True}),
# LoKr
("Vanilla MLP 1 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"]}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 LOKR",
"MLP",
LoKrConfig,
{
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"alpha": 4,
"module_dropout": 0.1,
},
),
("Vanilla MLP 7 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "rank_dropout": 0.5}),
("Vanilla MLP 8 LOKR", "MLP", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "decompose_both": True, "r": 1, "alpha": 1}),
("Conv2d 1 LOKR", "Conv2d", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
("Conv2d 2 LOKR", "Conv2d", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"]}),
("Conv2d 3 LOKR", "Conv2d", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "use_effective_conv2d": True}),
("Conv2d 4 LOKR", "Conv2d", LoKrConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "use_effective_conv2d": True}),
(
"Conv2d 5 LOKR",
"Conv2d",
LoKrConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "use_effective_conv2d": True, "decompose_both": True},
),
(
"Conv2d 6 LOKR",
"Conv2d",
LoKrConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"], "use_effective_conv2d": True, "decompose_factor": 4},
),
(
"Conv2d 7 LOKR",
"Conv2d",
LoKrConfig,
{
"target_modules": ["conv2d", "lin0"],
"use_effective_conv2d": True,
"decompose_both": True,
"decompose_factor": 4,
},
),
########
# OFT #
########
(
"Vanilla MLP 1 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 2, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": "lin0", "use_cayley_neumann": False},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 2 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 2, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "use_cayley_neumann": False},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{
"r": 2,
"oft_block_size": 0,
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"modules_to_save": ["lin1"],
"use_cayley_neumann": False,
},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{
"r": 2,
"oft_block_size": 0,
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"module_dropout": 0.1,
"use_cayley_neumann": False,
},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 7 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 2, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "coft": True, "eps": 1e-2},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 8 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 2, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "block_share": True, "use_cayley_neumann": False},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 9 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 2, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "coft": True, "eps": 1e-2, "block_share": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 10 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 0, "oft_block_size": 2, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "use_cayley_neumann": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 11 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 0, "oft_block_size": 2, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "use_cayley_neumann": False},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 12 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{
"r": 0,
"oft_block_size": 2,
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"coft": True,
"eps": 1e-2,
"block_share": True,
"use_cayley_neumann": True,
},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 13 OFT",
"MLP",
OFTConfig,
{
"r": 0,
"oft_block_size": 2,
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"coft": True,
"eps": 1e-2,
"block_share": True,
"use_cayley_neumann": False,
},
),
("Conv2d 1 OFT", "Conv2d", OFTConfig, {"r": 5, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
("Conv2d 3 OFT", "Conv2d", OFTConfig, {"r": 5, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["conv2d"], "coft": True}),
(
"Conv2d 4 OFT",
"Conv2d",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 5, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["conv2d"], "block_share": True},
),
(
"Conv2d 5 OFT",
"Conv2d",
OFTConfig,
{"r": 5, "oft_block_size": 0, "target_modules": ["conv2d"], "coft": True, "block_share": True},
),
########
# HRA #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 HRA", "MLP", HRAConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 HRA", "MLP", HRAConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 HRA", "MLP", HRAConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 HRA", "MLP", HRAConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"]}),
("Conv2d 1 HRA", "Conv2d", HRAConfig, {"target_modules": ["conv2d"]}),
########
# Bone #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 1 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 Bone", "MLP", BoneConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 Bone",
"MLP",
BoneConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"},
),
########
# MiSS #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "r": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 1 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 MiSS", "MLP", MissConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 MiSS",
"MLP",
MissConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "r": 2, "init_weights": "bat"},
),
#############
# LN Tuning #
#############
("LayerNorm 1 LNTuning", "MLP_LayerNorm", LNTuningConfig, {"target_modules": "layernorm0"}),
("LayerNorm 2 LNTuning", "MLP_LayerNorm", LNTuningConfig, {"target_modules": ["layernorm0"]}),
(
"LayerNorm 3 LNTuning",
"MLP_LayerNorm",
LNTuningConfig,
{"target_modules": ["layernorm0"], "modules_to_save": ["layernorm1"]},
),
("Linear 4 LNTuning", "MLP_LayerNorm", LNTuningConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Linear 5 LNTuning", "MLP_LayerNorm", LNTuningConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
########
# BOFT #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 BOFT", "MLP", BOFTConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"], "boft_block_size": 2}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 2 BOFT",
"MLP",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "modules_to_save": ["lin0"], "boft_block_size": 2},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 3 BOFT",
"MLP",
BOFTConfig,
{
"target_modules": ["lin1"],
"boft_block_size": 2,
"boft_dropout": 0.1,
},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 4 BOFT",
"MLP",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "boft_block_size": 2, "boft_block_num": 0, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 1},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 BOFT",
"MLP",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "boft_block_size": 0, "boft_block_num": 2, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 1},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 BOFT",
"MLP",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "boft_block_size": 10, "boft_block_num": 0, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 2},
),
(
"Conv2d 1 BOFT",
"Conv2d",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "boft_block_size": 45, "boft_block_num": 0, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 1},
),
(
"Conv2d 2 BOFT",
"Conv2d",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "boft_block_size": 0, "boft_block_num": 1, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 1},
),
(
"MLP2 1 BOFT",
"MLP2",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "boft_block_size": 2, "boft_block_num": 0, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 3},
),
(
"MLP2 2 BOFT",
"MLP2",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "boft_block_size": 0, "boft_block_num": 8, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 3},
),
(
"Conv2d2 1 BOFT",
"Conv2d2",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "boft_block_size": 2, "boft_block_num": 0, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 2},
),
(
"Conv2d2 1 BOFT",
"Conv2d2",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv2d"], "boft_block_size": 2, "boft_block_num": 0, "boft_n_butterfly_factor": 3},
),
#########
# SHiRA #
#########
("Vanilla MLP 1 SHiRA", "MLP", ShiraConfig, {"r": 1, "target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 SHiRA", "MLP", ShiraConfig, {"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 SHiRA", "MLP", ShiraConfig, {"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin1"]}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 4 SHiRA",
"MLP",
ShiraConfig,
{"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "random_seed": 56},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 SHiRA",
"MLP",
ShiraConfig,
{"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin0"]},
),
########
# VeRA #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 VeRA", "MLP", VeraConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0"}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 VeRA", "MLP", VeraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 VeRA", "MLP", VeraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"]}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 VeRA", "MLP", VeraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"]}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 VeRA",
"MLP",
VeraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"]},
),
(
"Embedding + transformers Conv1D 1 VeRA",
"EmbConv1D",
VeraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d"]},
),
#############
# FourierFT #
#############
# FourierFT is not initialized as an identity transform by default, hence set init_weights=True
(
"Vanilla MLP 1 FourierFT",
"MLP",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": "lin0", "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 2 FourierFT",
"MLP",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 3 FourierFT",
"MLP",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 FourierFT",
"MLP",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 FourierFT",
"MLP",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 7 FourierFT",
"MLP",
FourierFTConfig,
{
"n_frequency_pattern": {"lin0": 5, "lin1": 10},
"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"],
"modules_to_save": ["lin1"],
"init_weights": True,
},
),
##########
# VBLoRA #
##########
("Vanilla MLP 1 VBLoRA", "MLP", VBLoRAConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "vector_length": 1, "num_vectors": 5}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 VBLoRA", "MLP", VBLoRAConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "vector_length": 1, "num_vectors": 5}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 VBLoRA", "MLP", VBLoRAConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"], "vector_length": 2, "num_vectors": 5}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 4 VBLoRA",
"MLP",
VBLoRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "vector_length": 1, "num_vectors": 5},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 VBLoRA",
"MLP",
VBLoRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "vector_length": 1, "num_vectors": 5},
),
(
"Embedding + transformers Conv1D 1 VBLoRA",
"EmbConv1D",
VBLoRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["conv1d"], "vector_length": 1, "num_vectors": 2},
),
###################
# TrainableTokens #
###################
(
"Embedding + transformers Conv1D 1 trainable_tokens",
"EmbConv1D",
TrainableTokensConfig,
{"target_modules": ["emb"], "token_indices": [0, 1, 3], "init_weights": False},
),
############
# RandLora #
############
# We have to reduce the default scaling parameter to avoid nans when using large learning rates
("Vanilla MLP 1 RandLora", "MLP", RandLoraConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "randlora_alpha": 1}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 RandLora", "MLP", RandLoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "randlora_alpha": 1}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 RandLora", "MLP", RandLoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"], "randlora_alpha": 1}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 RandLora", "MLP", RandLoraConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "randlora_alpha": 1}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 RandLora",
"MLP",
RandLoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "sparse": True, "randlora_alpha": 1},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 RandLora",
"MLP",
RandLoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "very_sparse": True, "randlora_alpha": 1},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 7 RandLora",
"MLP",
RandLoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "randlora_alpha": 1},
),
#######
# C3A #
#######
# note: C3A is not initialized as an identity transform by default, hence set init_weights=True
("Vanilla MLP 1 C3A", "MLP", C3AConfig, {"block_size": 2, "target_modules": "lin0", "init_weights": True}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 C3A", "MLP", C3AConfig, {"block_size": 2, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": True}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 C3A", "MLP", C3AConfig, {"block_size": 2, "target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": True}),
(
"Vanilla MLP 5 C3A",
"MLP",
C3AConfig,
{"block_size": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 6 C3A",
"MLP",
C3AConfig,
{"block_size": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "modules_to_save": ["lin1"], "init_weights": True},
),
(
"Vanilla MLP 7 C3A",
"MLP",
C3AConfig,
{
"block_size_pattern": {"lin0": 5, "lin1": 10},
"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"],
"modules_to_save": ["lin1"],
"init_weights": True,
},
),
########
# RoAd #
########
("Vanilla MLP 1 RoAd", "MLP", RoadConfig, {"target_modules": "lin0", "group_size": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 2 RoAd", "MLP", RoadConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "group_size": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 3 RoAd", "MLP", RoadConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin1"], "group_size": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 4 RoAd", "MLP", RoadConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0", "lin1"], "group_size": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 5 RoAd", "MLP", RoadConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "variant": "road_2", "group_size": 2}),
("Vanilla MLP 6 RoAd", "MLP", RoadConfig, {"target_modules": ["lin0"], "variant": "road_4", "group_size": 2}),
]
# For this test matrix, each tuple consists of:
# - test name
# - tuner method
# - config_cls
# - 1st config kwargs
# - 2nd config kwargs
# The model used for this test is `MLP`, which uses linear layers `lin0` and `lin1`
MULTIPLE_ACTIVE_ADAPTERS_TEST_CASES = [
(
"LoRA Same",
"lora",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False},
),
(
"LoRA Different",
"lora",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_lora_weights": False},
),
(
"LoRA + trainable tokens Same",
"lora+trainable_tokens",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False, "trainable_token_indices": {"emb": [0, 1, 2]}},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False, "trainable_token_indices": {"emb": [3, 4, 5, 6]}},
),
(
"LoRA + trainable tokens Different",
"lora+trainable_tokens",
LoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False, "trainable_token_indices": {"emb": [0, 1, 2]}},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_lora_weights": False, "trainable_token_indices": {"emb": [3, 4, 5, 6]}},
),
(
"LoRA targeting nn.Parameter Same",
"lora",
LoraConfig,
{"target_parameters": ["lin0.weight"], "init_lora_weights": False},
{"target_parameters": ["lin0.weight"], "init_lora_weights": False},
),
(
"LoRA targeting nn.Parameter Different",
"lora",
LoraConfig,
{"target_parameters": ["lin0.weight"], "init_lora_weights": False},
{"target_parameters": ["lin1.weight"], "init_lora_weights": False},
),
(
"IA3 Same",
"ia3",
IA3Config,
{
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"feedforward_modules": ["lin0"],
"init_ia3_weights": False,
},
{
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"feedforward_modules": ["lin0"],
"init_ia3_weights": False,
},
),
(
"IA3 Different",
"ia3",
IA3Config,
{
"target_modules": ["lin0"],
"feedforward_modules": ["lin0"],
"init_ia3_weights": False,
},
{
"target_modules": ["lin1"],
"feedforward_modules": ["lin1"],
"init_ia3_weights": False,
},
),
(
"AdaLora Same",
"adalora",
AdaLoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False, "inference_mode": True, "total_step": 1},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False, "inference_mode": True, "total_step": 1},
),
(
"AdaLora Different",
"adalora",
AdaLoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_lora_weights": False, "inference_mode": True, "total_step": 1},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_lora_weights": False, "inference_mode": True, "total_step": 1},
),
(
"FourierFT Same",
"fourierft",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0"]},
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0"]},
),
(
"FourierFT Different",
"fourierft",
FourierFTConfig,
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin0"]},
{"n_frequency": 10, "target_modules": ["lin1"]},
),
(
"SHiRA Same",
"shira",
ShiraConfig,
{"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
{"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
),
(
"SHiRA Different",
"shira",
ShiraConfig,
{"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
{"r": 1, "target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False},
),
# Note: Currently, we cannot target lin0 and lin1 with different adapters when using VeRA. The reason is that the
# first adapter being created will result in a vera_A or vera_B shape that is too small for the next adapter
# (remember that VeRA shares these parameters across all layers), which results in an error.
(
"VeRA Same",
"vera",
VeraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
),
# Note: RandLora may present the same problem mentioned above for Vera.
(
"RandLora Same",
"randlora",
RandLoraConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
),
(
"HRA Same",
"hra",
HRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
),
(
"HRA Different",
"hra",
HRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False},
),
(
"Bone Same",
"bone",
BoneConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
),
(
"Bone Different",
"bone",
BoneConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
),
(
"MiSS Same",
"miss",
MissConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
),
(
"MiSS Different",
"miss",
MissConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False, "r": 2},
),
# Not testing "mini" initialization targeting the same layer, because The matrix is initialized to all zeros in MiSS-mini mode.
(
"VBLoRA Same",
"vblora",
VBLoRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "vector_length": 2, "init_vector_bank_bound": 0.1},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "vector_length": 2, "init_vector_bank_bound": 0.1},
),
(
"VBLoRA Different",
"vblora",
VBLoRAConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "vector_length": 2, "init_vector_bank_bound": 0.1},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "vector_length": 2, "init_vector_bank_bound": 0.1},
),
(
"BOFT Same",
"boft",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "boft_block_size": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "boft_block_size": 2},
),
(
"BOFT Different",
"boft",
BOFTConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "boft_block_size": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False, "boft_block_size": 2},
),
(
"RoAd Same",
"road",
RoadConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "group_size": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "group_size": 2},
),
(
"RoAd Different",
"road",
RoadConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "group_size": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False, "group_size": 2},
),
(
"RoAd 2 Different",
"road",
RoadConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "variant": "road_1", "group_size": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False, "variant": "road_2", "group_size": 2},
),
(
"RoAd 4 Different",
"road",
RoadConfig,
{"target_modules": ["lin0"], "init_weights": False, "variant": "road_1", "group_size": 2},
{"target_modules": ["lin1"], "init_weights": False, "variant": "road_4", "group_size": 2},
),
]
PREFIXES = {
IA3Config: "ia3_",
LoraConfig: "lora_",
LoHaConfig: "hada_",
LoKrConfig: "lokr_",
OFTConfig: "oft_",
BOFTConfig: "boft_",
LNTuningConfig: "ln_tuning_",
VeraConfig: "vera_lambda_",
RandLoraConfig: "randlora_",
FourierFTConfig: "fourierft_",
C3AConfig: "c3a_",
HRAConfig: "hra_",
ShiraConfig: "shira_",
VBLoRAConfig: "vblora_",
BoneConfig: "bone_",
RoadConfig: "road_",
MissConfig: "miss_",
TrainableTokensConfig: "trainable_tokens_",
}
def _skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs):
if (config_cls == LoraConfig) and config_kwargs.get("target_parameters"):
pytest.skip("LoRA with multiple adapters with target_parameters is not supported")
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.drop(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class MLPWithGRU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size=20, hidden_size=20, num_layers=1, batch_first=True, bias=bias)
self.fc = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.drop(X)
X = X.unsqueeze(1)
X, _ = self.gru(X)
X = X.squeeze(1)
X = self.fc(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class MLP_LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.layernorm0 = nn.LayerNorm(10, 10)
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.layernorm1 = nn.LayerNorm(20, 20)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.layernorm0(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.drop(X)
X = self.layernorm1(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class MLP2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 32, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(32, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.drop(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 10, bias=bias)
def forward(self, X):
X = X.float()
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.drop(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
return X
class DeepMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True, num_hidden_layers=12):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([Block(bias=bias) for _ in range(num_hidden_layers)])
self.out = nn.Linear(10, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = X.float(X)
for layer in self.layers:
X = layer(X)
X = self.out(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelEmbConv1D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, emb_size=100):
super().__init__()
self.emb = nn.Embedding(emb_size, 5)
self.conv1d = Conv1D(1, 5)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = self.emb(X)
X = self.conv1d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelEmbWithEmbeddingUtils(nn.Module):
# Adds `get_input_embeddings` and `get_output_embeddings` methods to mimic 🤗 transformers models
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(100, 5)
self.conv1d = Conv1D(1, 5)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = self.embed_tokens(X)
X = self.conv1d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
def get_input_embeddings(self):
return self.embed_tokens
def get_output_embeddings(self):
return None
class ModelConv1D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1d = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, 2)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(9, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = X.reshape(-1, 1, 10)
X = self.conv1d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelConv2D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(5, 10, 3, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = X.reshape(-1, 5, 3, 3)
X = self.conv2d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelConv2D2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 40)
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(8, 32, 3)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(32, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = X.reshape(-1, 8, 3, 3)
X = self.conv2d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelConv2DGroups(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(90, 288)
# groups is set as 8 since default r=8
# hence to make r divisible by groups
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(16, 16, 3, groups=8)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(16, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = X.flatten()
X = self.lin0(X)
X = X.reshape(2, 16, 3, 3)
X = self.conv2d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelConv2DGroups2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, padding=1, groups=2)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(12800, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
# Note: needs a different input shape, thus ignore original input
X = torch.arange(9 * 16 * 20 * 20).view([9, 16, 20, 20]).to(self.conv2d.weight.device)
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.conv2d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelConv3D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv3d = nn.Conv3d(5, 10, 3)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
# If necessary, convert from 2D image to 3D volume
if X.dim() == 2:
X = torch.stack([X] * 3, dim=-1)
X = X.reshape(-1, 5, 3, 3, 3)
X = self.conv3d(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.flat(X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class ModelMha(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.mha = nn.MultiheadAttention(10, 2)
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 2)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X, _ = self.mha(X, X, X)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class _LinearUsingParameter(nn.Module):
# Linear layer equivalent
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, bias=None):
super().__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(in_features, out_features))
if bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(out_features))
def forward(self, x):
return x @ self.weight + self.bias
class MlpUsingParameters(nn.Module):
# MLP that uses layers whose parameters need to be targeted with target_parameters
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = _LinearUsingParameter(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.lin1 = _LinearUsingParameter(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
self.dtype = torch.float
def forward(self, X):
X = X.to(self.dtype)
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.drop(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
class MockTransformerWrapper:
"""Mock class to behave like a transformers model.
This is needed because the tests initialize the model by calling transformers_class.from_pretrained.
"""
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(cls, model_id, torch_dtype=None):
# set the seed so that from_pretrained always returns the same model
torch.manual_seed(0)
if torch_dtype is None:
torch_dtype = torch.float32
if model_id == "MLP":
return MLP().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "EmbConv1D":
return ModelEmbConv1D().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "Conv1d":
return ModelConv1D().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "Conv2d":
return ModelConv2D().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "Conv2dGroups":
return ModelConv2DGroups().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "Conv2dGroups2":
return ModelConv2DGroups2().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "Conv3d":
return ModelConv3D().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "MLP_LayerNorm":
return MLP_LayerNorm().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "MLP2":
return MLP2().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "Conv2d2":
return ModelConv2D2().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "MHA":
return ModelMha().to(torch_dtype)
if model_id == "MlpUsingParameters":
return MlpUsingParameters().to(torch_dtype)
raise ValueError(f"model_id {model_id} not implemented")
class TestPeftCustomModel(PeftCommonTester):
"""
Implements the tests for custom models.
Most tests should just call the parent class, e.g. test_save_pretrained calls self._test_save_pretrained. Override
this if custom models don't work with the parent test method.
"""
transformers_class = MockTransformerWrapper
def prepare_inputs_for_testing(self):
X = torch.arange(90).view(9, 10).to(self.torch_device)
return {"X": X}
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_attributes_parametrized(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_model_attr(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_adapter_name(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_adapter_name(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_prepare_for_training_parametrized(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# This test does not work with custom models because it assumes that
# there is always a method get_input_embeddings that returns a layer
# which does not need updates. Instead, a new test is added below that
# checks that LoRA works as expected.
pass
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_save_pretrained(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_save_pretrained(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_save_pretrained_pickle(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_save_pretrained(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs, safe_serialization=False)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_load_model_low_cpu_mem_usage(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_load_model_low_cpu_mem_usage(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_from_pretrained_config_construction(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_from_pretrained_config_construction(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_load_multiple_adapters(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_load_multiple_adapters(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_merge_layers(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
pytest.skip(
f"Skipping test for {model_id} as merging is not supported. (See https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403 for details)"
)
config_kwargs = set_init_weights_false(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_merge_layers(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_merge_layers_fp16(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
pytest.skip(
f"Skipping test for {model_id} as merging is not supported. (See https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403 for details)"
)
config_kwargs = set_init_weights_false(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_merge_layers_fp16(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_merge_layers_is_idempotent(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# calling merge twice with the same arguments should not change the output
# https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
pytest.skip(
f"Skipping test for {model_id} as merging is not supported. (See https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403 for details)"
)
config_kwargs = set_init_weights_false(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_merge_layers_is_idempotent(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_safe_merge(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
pytest.skip(
f"Skipping test for {model_id} as merging is not supported. (See https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403 for details)"
)
config_kwargs = set_init_weights_false(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_safe_merge(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("safe_merge", [False, True])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("module_type", ["linear", "conv2d"])
def test_merge_with_lora_bias_when_base_layer_has_no_bias_warns_and_raises(self, safe_merge, module_type):
# It is not possible to merge the lora_B bias if the base layer doesn't have a bias itself.
if module_type == "linear":
model = MLP(bias=False)
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"], lora_bias=True)
warn_msg = re.escape("`lora_bias=True` was passed but the targeted layer of type Linear has no bias")
elif module_type == "conv2d":
model = ModelConv2D(bias=False)
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv2d"], lora_bias=True)
warn_msg = re.escape("`lora_bias=True` was passed but the targeted layer of type Conv2d has no bias")
else:
raise ValueError(f"Wrong module_type passed, expected 'linear' or 'conv2d', got {module_type}")
with pytest.warns(PeftWarning, match=warn_msg):
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
err_msg = "Impossible to merge LoRA with `lora_bias=True` because the base layer has no bias"
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError, match=err_msg):
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=safe_merge)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_generate(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# Custom models do not (necessarily) have a generate method, so this test is not performed
pass
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_generate_half_prec(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# Custom models do not (necessarily) have a generate method, so this test is not performed
pass
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_training_custom_models(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_training(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_training_custom_models_layer_indexing(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# At the moment, layer indexing only works when layer names conform to a specific pattern, which is not
# guaranteed here. Therefore, this test is not performed.
pass
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_training_custom_models_gradient_checkpointing(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_training_gradient_checkpointing(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_inference_safetensors(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_inference_safetensors(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_peft_model_device_map(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_peft_model_device_map(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_forward_output_finite(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(**X)
assert torch.isfinite(output).all()
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_forward_float16(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# The user manually sets the dtype of the base model to fp16 precision. This should not cause an error for the
# different PEFT methods.
try:
torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.float16)
except Exception:
# skip this test if float16 is not supported on this machine
pytest.skip(reason="Test requires float16 support")
# skip on MacOS
if platform.system() == "Darwin":
pytest.skip(reason="MacOS does not support multiple ops in float16")
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to(self.torch_device)
model.dtype = torch.float16
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model.eval()
# check that none of this raises an error
model(**X)
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
# this model does not support merging
return
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=False)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=True)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model = model.merge_and_unload()
model(**X)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_forward_bfloat16(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# The user manually sets the dtype of the base model to bf16 precision. This should not cause an error for the
# different PEFT methods.
try:
torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.bfloat16)
except Exception:
# skip this test if float16 is not supported on this machine
pytest.skip(reason="Test requires bfloat16 support")
# skip on MacOS
if platform.system() == "Darwin":
pytest.skip(reason="MacOS does not support multiple ops in bfloat16")
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).to(self.torch_device)
model.dtype = torch.bfloat16
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model.eval()
# check that none of this raises an error
model(**X)
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
# this model does not support merging
return
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=False)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=True)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model = model.merge_and_unload()
model(**X)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_forward_float16_no_autocast(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# Same as above but don't autocast adapter weights to float32 automatically
try:
torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.float16)
except Exception:
# skip this test if float16 is not supported on this machine
pytest.skip(reason="Test requires float16 support")
# skip on MacOS
if platform.system() == "Darwin":
pytest.skip(reason="MacOS does not support multiple ops in float16")
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to(self.torch_device)
model.dtype = torch.float16
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config, autocast_adapter_dtype=False)
model.eval()
# check that none of this raises an error
model(**X)
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
# this model does not support merging
return
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=False)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=True)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model = model.merge_and_unload()
model(**X)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_forward_bfloat16_no_autocast(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# Same as above but don't autocast adapter weights to float32 automatically
try:
torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.bfloat16)
except Exception:
# skip this test if float16 is not supported on this machine
pytest.skip(reason="Test requires bfloat16 support")
# skip on MacOS
if platform.system() == "Darwin":
pytest.skip(reason="MacOS does not support multiple ops in bfloat16")
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).to(self.torch_device)
model.dtype = torch.bfloat16
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config, autocast_adapter_dtype=False)
model.eval()
# check that none of this raises an error
model(**X)
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
# this model does not support merging
return
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=False)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model.merge_adapter(safe_merge=True)
model(**X)
model.unmerge_adapter()
model(**X)
model = model.merge_and_unload()
model(**X)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_only_params_are_updated(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# An explicit test that when using an adapter on a custom model, only the adapter parameters are updated during
# training
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model_before = copy.deepcopy(model)
model.train()
lr = 0.5
if (config_kwargs.get("use_dora") and model_id == "EmbConv1D") or issubclass(config_cls, VBLoRAConfig):
# this high learning rate was found through testing to be necessary to avoid flakiness
lr = 100
elif "mha" in model_id.lower():
# we get exploding gradients with MHA when learning rate is too high
lr = 1e-3
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
# train at least 3 steps for all parameters to be updated (probably this is required because of symmetry
# breaking of some LoRA layers that are initialized with constants)
for _ in range(3):
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(**X)
loss = y_pred.sum()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
tol = 1e-4
params_before = dict(model_before.named_parameters())
params_after = dict(model.named_parameters())
assert params_before.keys() == params_after.keys()
prefix = PREFIXES[config_cls]
for name, param_before in params_before.items():
param_after = params_after[name]
if (prefix in name) or ("modules_to_save" in name) or ("token_adapter.trainable_tokens" in name):
# target_modules, modules_to_save and modules of `NewTokensWrapper` _are_ updated
assert not torch.allclose(param_before, param_after, atol=tol, rtol=tol)
else:
assert torch.allclose(param_before, param_after, atol=tol, rtol=tol)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_parameters_after_loading_model(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# An explicit test that when loading a trained model, the parameters are loaded correctly
# see issue #808
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model.train()
lr = 0.5
if config_kwargs.get("use_dora"):
lr = 0.1 # otherwise we get nan
elif "mha" in model_id.lower():
lr = 1e-3 # we get exploding gradients with MHA when learning rate is too high
elif issubclass(config_cls, VBLoRAConfig) or issubclass(config_cls, RandLoraConfig):
lr = 0.01 # otherwise we get nan
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
# train at least 3 steps for all parameters to be updated (probably this is required because of symmetry
# breaking of some LoRA layers that are initialized with constants)
for _ in range(3):
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(**X)
loss = y_pred.sum()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
tol = 1e-4
params_before = get_state_dict(model)
# note: no need to sanity check if parameters were updated at all, this
# is already covered in the previous test
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
model_from_pretrained = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
model_from_pretrained = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model_from_pretrained, tmp_dirname)
params_after = get_state_dict(model_from_pretrained)
assert params_before.keys() == params_after.keys()
for name, param_before in params_before.items():
param_after = params_after[name]
assert torch.allclose(param_before, param_after, atol=tol, rtol=tol)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_disable_adapters(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# Test that it's possible to disable the adapter, in which case the model output should be identical to that of
# the base model.
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device).eval()
outputs_base = model(**X)
if issubclass(config_cls, (TrainableTokensConfig,)):
config_kwargs = config_kwargs.copy()
# override the default value and make PEFT operation a no-op
config_kwargs["init_weights"] = True
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
if issubclass(config_cls, VBLoRAConfig):
# Manually set the `vblora_vector_bank` to zero so that VB-LoRA functions as an identity operation.
torch.nn.init.zeros_(model.vblora_vector_bank["default"])
model.eval()
outputs_before = model(**X)
assert torch.allclose(outputs_base, outputs_before)
if issubclass(config_cls, VBLoRAConfig):
# initialize `vblora_vector_bank` so it can be trained
model._init_vblora_vector_bank(config, "default")
model.train()
# EmbConv1D is slow to learn for some reason
lr = 0.01 if model_id != "EmbConv1D" else 1.0
if isinstance(config, TrainableTokensConfig):
# TrainableTokens is only changing a small subset, so we need a higher lr to see the difference
lr = 2.0
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
# train at least 3 steps for all parameters to be updated (probably this is required because of symmetry
# breaking of some LoRA layers that are initialized with constants)
for _ in range(3):
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(**X)
y = torch.arange(len(y_pred)).to(self.torch_device) % 2
loss = nn.functional.nll_loss(y_pred, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.eval()
outputs_after = model(**X)
with model.disable_adapter():
outputs_disabled = model(**X)
# check that after leaving the disable_adapter context, everything is enabled again
outputs_enabled_after_disable = model(**X)
if self.torch_device == "cpu":
# LayerNorm is running float32 on cpu, so difference in outputs are smaller
rtol, atol = 1e-8, 1e-8
else:
rtol, atol = 1e-5, 1e-8
assert not torch.allclose(outputs_before, outputs_after, rtol=rtol, atol=atol)
assert torch.allclose(outputs_before, outputs_disabled)
assert torch.allclose(outputs_after, outputs_enabled_after_disable)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_disable_adapters_with_merging(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# Same test as test_disable_adapters, but additionally merge the trained adapter.
# https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403
if model_id in ["Conv2dGroups", "Conv2dGroups2"]:
pytest.skip(
f"Skipping test for {model_id} as merging is not supported. (See https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2403 for details)"
)
# same as test_disable_adapters, but with merging
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
if issubclass(config_cls, VBLoRAConfig):
# Manually set the `vblora_vector_bank` to zero so that VB-LoRA functions as an identity operation.
torch.nn.init.zeros_(model.vblora_vector_bank["default"])
model.eval()
outputs_before = model(**X)
if issubclass(config_cls, VBLoRAConfig):
# initialize `vblora_vector_bank` so it can be trained
model._init_vblora_vector_bank(config, "default")
model.train()
if isinstance(config_cls, LNTuningConfig):
# LayerNorm tuning is slow to learn
lr = 1.0
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
else:
# Adam optimizer since SGD isn't great for small models with IA3 + Conv1D
lr = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
# train at least 3 steps for all parameters to be updated (probably this is required because of symmetry
# breaking of some LoRA layers that are initialized with constants)
for _ in range(3):
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(**X)
y = torch.arange(len(y_pred)).to(self.torch_device) % 2
loss = nn.functional.nll_loss(y_pred, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.eval()
outputs_unmerged = model(**X)
model.merge_adapter()
outputs_after = model(**X)
with model.disable_adapter():
outputs_disabled = model(**X)
# check that after leaving the disable_adapter context, everything is enabled again
outputs_enabled_after_disable = model(**X)
atol, rtol = 1e-5, 1e-5 # tolerances higher than defaults since merging introduces some numerical instability
conv_ids = ["Conv2d", "Conv3d", "Conv2d2"]
if issubclass(config_cls, (IA3Config, LoraConfig)) and model_id in conv_ids: # more instability with Conv
atol, rtol = 1e-3, 1e-3
if issubclass(config_cls, OFTConfig):
atol, rtol = 1e-4, 1e-4
if config_kwargs.get("use_dora") and model_id == "EmbConv1D":
atol, rtol = 1e-4, 1e-4
# check that there is a difference in results after training
assert not torch.allclose(outputs_before, outputs_after, atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
if self.torch_device in ["mlu"] and model_id in conv_ids:
atol, rtol = 1e-3, 1e-2 # MLU
# unmerged or merged should make no difference
assert torch.allclose(outputs_after, outputs_unmerged, atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
# check that disabling adapters gives the same results as before training
assert torch.allclose(outputs_before, outputs_disabled, atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
# check that enabling + disabling adapters does not change the results
assert torch.allclose(outputs_after, outputs_enabled_after_disable, atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_disable_adapter_with_bias_warns(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# When training biases in lora, disabling adapters does not reset the biases, so the output is not what users
# might expect. Therefore, a warning should be given.
# Note: We test only with custom models since they run really fast. There is really no point in testing the same
# thing with decoder, encoder_decoder, etc.
if config_cls != LoraConfig or config_cls != BOFTConfig:
# skip this test for other configs as bias is specific to Lora
pytest.skip("Testing bias warnings only for LoraConfig or BOFTConfig")
if not issubclass(config_cls, (LoraConfig, BOFTConfig)):
pytest.skip("Bias argument is only supported for LoRA or BOFT models")
def run_with_disable(config_kwargs, bias):
config_kwargs = config_kwargs.copy()
config_kwargs["bias"] = bias
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
pass # there is nothing to be done
if config_cls == LoraConfig:
# check that bias=all and bias=lora_only give a warning with the correct message
msg_start = "Careful, disabling adapter layers with bias configured to be"
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=msg_start):
run_with_disable(config_kwargs, bias="lora_only")
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=msg_start):
run_with_disable(config_kwargs, bias="all")
if config_cls == BOFTConfig:
# check that bias=all and bias=boft_only give a warning with the correct message
msg_start = "Careful, disabling adapter layers with bias configured to be"
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=msg_start):
run_with_disable(config_kwargs, bias="boft_only")
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=msg_start):
run_with_disable(config_kwargs, bias="all")
# For bias=none, there is no warning. Unfortunately, AFAIK unittest has no option to assert that no warning is
# given, therefore, we check that the unittest gives us an AssertionError if we check for a warning
bias_warning_was_given = False
try:
with pytest.warns(UserWarning) as cm:
run_with_disable(config_kwargs, bias="none")
# if we get here, it means there was no AssertionError, i.e. there are warnings -- let's check that they
# are not related to the bias setting
if any(warning.message.args[0].startswith(msg_start) for warning in cm.warnings):
bias_warning_was_given = True
except AssertionError:
# This is good, there was an AssertionError, i.e. there was no warning
pass
if bias_warning_was_given:
# This is bad, there was a warning about the bias when there should not have been any.
self.fail("There should be no warning when bias is set to 'none'")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_active_adapter(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs)
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
assert model.active_adapters == ["default"]
assert model.active_adapter == "default"
# at this stage, "default" is still the activate adapter, "other" is disabled
model.add_adapter("other", config)
assert model.active_adapters == ["default"]
assert model.active_adapter == "default"
# set "other" as the active adapter
model.set_adapter("other")
assert model.active_adapters == ["other"]
assert model.active_adapter == "other"
# set both adapters as active
# Note: On the PeftModel, there cannot be multiple active adapters, so we have to go through model.base_model
# instead.
model.base_model.set_adapter(["default", "other"])
# model.active_adapters works, as it delegates to the base_model
assert model.active_adapters == ["default", "other"]
# model.active_adapter would not work, thus we have to check the base_model directly
assert model.base_model.active_adapter == ["default", "other"]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_disable_adapters_exiting_context_restores_previous_state(
self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs
):
# Test that when we exit the disable_adapter context, we correctly restore the enabled state of the modules as
# they were before the context.
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
tuner_modules = [module for module in model.modules() if isinstance(module, BaseTunerLayer)]
# all layers should be enabled
assert all(not module.disable_adapters for module in tuner_modules)
with model.disable_adapter():
pass
# this should not change after exiting the context
assert all(not module.disable_adapters for module in tuner_modules)
# now disable all layers
model.disable_adapter_layers()
assert all(module.disable_adapters for module in tuner_modules)
with model.disable_adapter():
pass
assert all(module.disable_adapters for module in tuner_modules)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_disable_adapters_exiting_context_irregular_state(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
# When we have a model where some adapters are enabled and others are disabled, we should get a warning when
# entering the disable_adapter context because we cannot correctly restore the state of the adapters from
# before the context. After exiting the context, all adapters will be enabled, which is the status quo of how
# we deal with this.
model = self.transformers_class.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config = config_cls(
base_model_name_or_path=model_id,
**config_kwargs,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
tuner_modules = [module for module in model.modules() if isinstance(module, BaseTunerLayer)]
# now we mix the states, some enabled some not
if len(tuner_modules) < 2:
# next check only works with more than 1 tuner module
return
# disable a single layer
tuner_modules[0].enable_adapters(False)
# sanity check that we have both enabled and disabled layers
assert {module.disable_adapters for module in tuner_modules} == {True, False}
# check that we get a warning with irregular states
msg = "The model contains some adapter layers that are enabled and others that are disabled"
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=msg):
with model.disable_adapter():
pass
# when encountering irregular adapters, we enable all adapters at the end of the context
assert all(not module.disable_adapters for module in tuner_modules)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_delete_adapter(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_delete_adapter(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_delete_inactive_adapter(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs)
self._test_delete_inactive_adapter(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_delete_unknown_adapter_raises(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_delete_unknown_adapter_raises(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
def test_delete_adapter_with_multiple_adapters_works(self):
# Add 3 adapters, delete the active one, the next one should be active, delete the inactive one, the active one
# should stay the same.
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
config2 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0, adapter_name="adapter0").to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
model.add_adapter("adapter2", config2)
inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter0"]
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete the active adapter, next one should become active
model.delete_adapter("adapter0")
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter1"]
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete an inactive adapter, should not affect the active adapter
model.delete_adapter("adapter2")
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter1"]
model(**inputs) # does not raise
def test_delete_adapter_multiple_adapters_with_modules_to_save(self):
# There are 3 adapters. Adapter 0 has modules_to_save. Delete it, we should switch to adapter 1, which does not
# have modules_to_save. Then, we delete it too, switching to adapter 2, which has modules_to_save. Finally, we
# delete the last adapter (state is updated but forward is no longer possible).
model = MLP()
inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
config2 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
model = get_peft_model(model, config0, adapter_name="adapter0").to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
model.add_adapter("adapter2", config2)
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter0"]
assert model.modules_to_save == {"lin1"}
assert set(model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save) == {"adapter0", "adapter2"}
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete active adapter, should switch to the next adapter (which does not have modules_to_save)
model.delete_adapter("adapter0")
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter1"]
assert model.modules_to_save == {"lin1"}
assert set(model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save) == {"adapter2"}
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete active adapter, should switch to the next adapter (which *does* have modules_to_save)
model.delete_adapter("adapter1")
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter2"]
assert model.modules_to_save == {"lin1"}
assert set(model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save) == {"adapter2"}
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete last adapter
model.delete_adapter("adapter2")
assert model.active_adapters == []
assert model.modules_to_save is None
assert set(model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save) == set()
def test_delete_adapter_multiple_adapters_with_trainable_token_indices(self):
# Same as the previous test, just using trainable_token_indices instead of modules_to_save
# Note that we need to use a transformers model for trainable_token_indices
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-OPTForCausalLM")
inputs = {"input_ids": torch.arange(10).view(-1, 1).to(self.torch_device)}
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["q_proj"], trainable_token_indices=[0, 1])
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["q_proj"])
config2 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["q_proj"], trainable_token_indices=[1, 3])
model = get_peft_model(model, config0, adapter_name="adapter0").to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
model.add_adapter("adapter2", config2)
embed_tokens = model.base_model.model.model.decoder.embed_tokens
lm_head = model.base_model.model.lm_head
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter0"]
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == {"adapter0", "adapter2"}
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == {"adapter0", "adapter2"}
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == {"adapter0", "adapter2"}
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == {"adapter0", "adapter2"}
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete active adapter, should switch to the next adapter (which does not have modules_to_save)
model.delete_adapter("adapter0")
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter1"]
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == {"adapter2"}
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == {"adapter2"}
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == {"adapter2"}
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == {"adapter2"}
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete active adapter, should switch to the next adapter (which *does* have modules_to_save)
model.delete_adapter("adapter1")
assert model.active_adapters == ["adapter2"]
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == {"adapter2"}
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == {"adapter2"}
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == {"adapter2"}
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == {"adapter2"}
model(**inputs) # does not raise
# delete last adapter
model.delete_adapter("adapter2")
assert model.active_adapters == []
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == set()
assert set(embed_tokens.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == set()
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta) == set()
assert set(lm_head.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_original) == set()
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs", TEST_CASES)
def test_adding_multiple_adapters_with_bias_raises(self, test_name, model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs):
self._test_adding_multiple_adapters_with_bias_raises(model_id, config_cls, config_kwargs)
def test_weight_bias_attributes(self):
model = MLP()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
assert hasattr(model.base_model.model.lin0, "weight")
assert hasattr(model.base_model.model.lin0, "bias")
def test_multiple_adapters_automatic_modules_to_save(self):
# See issue 1574
# When we use certain task types, PeftModel.modules_to_save is automatically updated to include some extra
# layers not specified in the PeftConfig. This attribute should be honored for all adapters, not just for
# the default adapter.
config0 = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS)
config1 = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS)
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
model = get_peft_model(model, config0)
# sanity check
assert model.modules_to_save
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
assert "default" in model.base_model.classifier.modules_to_save
assert "other" in model.base_model.classifier.modules_to_save
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"config_cls", [IA3Config, LoHaConfig, LoKrConfig, LoraConfig, HRAConfig, BoneConfig, ShiraConfig, MissConfig]
)
def test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save(self, config_cls):
# See issue 1574
# Check that we can have a model where one adapter has modules_to_save and the other doesn't. It should be
# possible to switch between those adapters and to use them.
if hasattr(config_cls, "feedforward_modules"): # IA³
config_cls = partial(config_cls, feedforward_modules=["lin0"])
if config_cls == BoneConfig or config_cls == MissConfig:
config_cls = partial(config_cls, r=2)
if config_cls == ShiraConfig:
config_cls = partial(config_cls, r=1)
config0 = config_cls(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
config1 = config_cls(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = MLP()
model = get_peft_model(model, config0).to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
assert "default" in model.base_model.lin1.modules_to_save
assert "other" not in model.base_model.lin1.modules_to_save
# check that switching adapters and predicting does not raise
inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
# "default" adapter is active
model(**inputs)
# switch to "other" adapter
model.set_adapter("other")
model(**inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"config_cls", [IA3Config, LoHaConfig, LoKrConfig, LoraConfig, HRAConfig, BoneConfig, ShiraConfig]
)
def test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save_order_switched(self, config_cls):
# See issue 1574
# Same test as test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save, but this time the 2nd adapter has modules_to_save.
if hasattr(config_cls, "feedforward_modules"): # IA³
config_cls = partial(config_cls, feedforward_modules=["lin0"])
if config_cls == BoneConfig or config_cls == MissConfig:
config_cls = partial(config_cls, r=2)
if config_cls == ShiraConfig:
config_cls = partial(config_cls, r=1)
config0 = config_cls(target_modules=["lin0"])
config1 = config_cls(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
model = MLP()
model = get_peft_model(model, config0).to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
assert "default" not in model.base_model.lin1.modules_to_save
assert "other" in model.base_model.lin1.modules_to_save
# check that switching adapters and predicting does not raise
inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
# "default" adapter is active
model(**inputs)
# switch to "other" adapter
model.set_adapter("other")
model(**inputs)
def test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save_merging_adapters(self):
# See issue 1574
# This test is similar to test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save, but it also checks that merging adapter
# weights works when one adapter has a modules_to_save and the other hasn't
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = MLP()
model = get_peft_model(model, config0).to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
# check that this does not raise
model.add_weighted_adapter(["default", "other"], weights=[1.0, 1.0], adapter_name="merged")
# since one of the adapters that was merged has a modules_to_save, that one should be used for the merged
# adapter
assert "default" in model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save
assert "other" not in model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save
assert "merged" in model.base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save
# check that using the merged adapter does not raise
model.set_adapter("merged")
inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model(**inputs)
def test_multiple_adapters_same_modules_to_save_merging_adapters_raises(self):
# See issue 1574
# This test is similar to test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save_merging_adapters but here the two
# adapters target the same module with modules_to_save. In this case, trying to merge the adapter weights
# should raise an error.
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
model = MLP()
model = get_peft_model(model, config0).to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
msg = re.escape(
"Cannot add weighted adapters if they target the same module with modules_to_save, but found 1 such "
"instance(s)."
)
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
model.add_weighted_adapter(["default", "other"], weights=[1.0, 1.0], adapter_name="merged")
def test_multiple_adapters_seq_cls_mixed_modules_to_save_merging_adapters(self):
# See issue 1574
# This test is similar to test_multiple_adapters_mixed_modules_to_save_merging_adapters but uses a SEQ_CLS
# model like in test_multiple_adapters_automatic_modules_to_save. This should raise an error because the same
# module is implicitly targeted by modules_to_save twice.
config0 = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS)
config1 = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS)
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
model = get_peft_model(model, config0)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
msg = re.escape(
"Cannot add weighted adapters if they target the same module with modules_to_save, but found 1 such "
"instance(s)."
)
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
model.add_weighted_adapter(["default", "other"], weights=[1.0, 1.0], adapter_name="merged")
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"config_cls", [IA3Config, LoHaConfig, LoKrConfig, LoraConfig, HRAConfig, BoneConfig, MissConfig]
)
def test_add_weighted_adapter_cat_with_rank_pattern(self, config_cls):
# Fixes a bug described in #2512, which resulted from the rank_pattern not being taken into account
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"], r=8, rank_pattern={"lin0": 2})
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"], r=8, rank_pattern={"lin0": 16})
model = MLP()
model = get_peft_model(model, config0).to(self.torch_device)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
model.add_weighted_adapter(
["default", "other"], weights=[1.0, 1.0], adapter_name="merged", combination_type="cat"
)
def test_multiple_adapters_no_needless_copy_modules_to_save(self):
# See 2206
# The problem was that we keep a "global" modules_to_save on the model which contains all possible
# modules_to_save for each adapter. When the first adapter targets embed_tokens with modules_to_save and the
# second adapter targets lm_head, then embed_tokens will create a copy of the original module for the second
# adapter, even though it's not needed. The copy still acts as expected but uses unnecessary memory.
model_id = "hf-internal-testing/tiny-random-OPTForCausalLM"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id).to(self.torch_device)
config0 = LoraConfig(modules_to_save=["embed_tokens"])
config1 = LoraConfig(modules_to_save=["lm_head"])
model = get_peft_model(model, config0)
model.add_adapter("other", config1)
lm_head_keys = list(model.base_model.model.lm_head.modules_to_save.keys())
assert lm_head_keys == ["other"]
embed_token_keys = list(model.base_model.model.model.decoder.embed_tokens.modules_to_save.keys())
# before the fix, this would be: ['default', 'other']
assert embed_token_keys == ["default"]
def test_existing_model_card(self):
# ensure that if there is already a model card, it is not overwritten
model = MLP()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dirname:
# create a model card
text = "---\nmeta: hello\n---\nThis is a model card\n"
with open(os.path.join(tmp_dirname, "README.md"), "w") as f:
f.write(text)
model.save_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
with open(os.path.join(tmp_dirname, "README.md")) as f:
model_card = f.read()
assert "library_name: peft" in model_card
assert "meta: hello" in model_card
assert "This is a model card" in model_card
def test_non_existing_model_card(self):
# ensure that if there is already a model card, it is not overwritten
model = MLP()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dirname:
model.save_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
with open(os.path.join(tmp_dirname, "README.md")) as f:
model_card = f.read()
assert "library_name: peft" in model_card
# rough check that the model card is pre-filled
assert len(model_card) > 1000
@pytest.mark.parametrize("save_embedding_layers", ["auto", True, False])
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"peft_config",
[
(LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "embed_tokens"], init_lora_weights=False)),
(LoraConfig(target_modules=r"^embed_tokens", init_lora_weights=False)),
],
)
def test_save_pretrained_targeting_lora_to_embedding_layer(self, save_embedding_layers, tmp_path, peft_config):
model = ModelEmbWithEmbeddingUtils()
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
if save_embedding_layers == "auto":
# assert warning
msg_start = "Setting `save_embedding_layers` to `True` as embedding layers found in `target_modules`."
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=msg_start):
model.save_pretrained(tmp_path, save_embedding_layers=save_embedding_layers)
else:
model.save_pretrained(tmp_path, save_embedding_layers=save_embedding_layers)
state_dict = safe_load_file(tmp_path / "adapter_model.safetensors")
contains_embedding = "base_model.model.embed_tokens.base_layer.weight" in state_dict
if save_embedding_layers in ["auto", True]:
assert contains_embedding
assert torch.allclose(
model.base_model.model.embed_tokens.base_layer.weight,
state_dict["base_model.model.embed_tokens.base_layer.weight"],
)
else:
assert not contains_embedding
@pytest.mark.parametrize("save_embedding_layers", ["auto", True, False])
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"peft_config",
[
(LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "emb"], init_lora_weights=False)),
(LoraConfig(target_modules=r"^emb", init_lora_weights=False)),
],
)
def test_save_pretrained_targeting_lora_to_embedding_layer_non_transformers(
self, save_embedding_layers, tmp_path, peft_config
):
model = ModelEmbConv1D()
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
if save_embedding_layers is True:
with pytest.warns(
UserWarning,
match=r"Could not identify embedding layer\(s\) because the model is not a 🤗 transformers model\.",
):
model.save_pretrained(tmp_path, save_embedding_layers=save_embedding_layers)
else:
model.save_pretrained(tmp_path, save_embedding_layers=save_embedding_layers)
state_dict = safe_load_file(tmp_path / "adapter_model.safetensors")
assert "base_model.model.emb.base_layer.weight" not in state_dict
def test_load_resized_embedding_ignore_mismatched_sizes(self):
# issue #1605
# Make it possible to load a LoRA layer that targets an embedding layer even if the sizes mismatch by passing
# ignore_mismatched_sizes=True
model = ModelEmbConv1D(emb_size=100)
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb", "lin0"], init_lora_weights=False)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
# note: not using the context manager here because it fails on Windows CI for some reason
tmp_dirname = tempfile.mkdtemp()
try:
model.save_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
model = ModelEmbConv1D(emb_size=105)
# first check that this raises
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as exc:
PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, tmp_dirname)
msg = exc.value.args[0]
assert "size mismatch" in msg and "100" in msg and "105" in msg
# does not raise
PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, tmp_dirname, ignore_mismatched_sizes=True)
finally:
try:
shutil.rmtree(tmp_dirname)
except PermissionError:
# windows error
pass
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"config0",
[
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoKrConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False),
LoHaConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False),
AdaLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False, total_step=1),
IA3Config(target_modules=["lin0"], feedforward_modules=["lin0"], init_ia3_weights=False),
OFTConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False, r=2, oft_block_size=0),
BOFTConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False, boft_block_size=2),
HRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False),
BoneConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False, r=2),
MissConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_weights=False, r=2),
],
)
def test_adapter_name_makes_no_difference(self, config0):
# It should not matter whether we use the default adapter name or a custom one
model_cls = MLP
input = torch.arange(90).reshape(9, 10).to(self.torch_device)
# base model
torch.manual_seed(0)
base_model = model_cls().eval().to(self.torch_device)
output_base = base_model(input)
# default name
torch.manual_seed(0)
base_model = model_cls().eval().to(self.torch_device)
torch.manual_seed(0)
peft_model_default = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, adapter_name="default").eval().to(self.torch_device)
output_default = peft_model_default(input)
sd_default = peft_model_default.state_dict()
# custom name 1
torch.manual_seed(0)
base_model = model_cls().eval().to(self.torch_device)
torch.manual_seed(0)
peft_model_custom1 = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, adapter_name="adapter").eval().to(self.torch_device)
output_custom1 = peft_model_custom1(input)
sd_custom1 = peft_model_custom1.state_dict()
# custom name 2
torch.manual_seed(0)
base_model = model_cls().eval().to(self.torch_device)
torch.manual_seed(0)
peft_model_custom2 = (
get_peft_model(base_model, config0, adapter_name="other-name").eval().to(self.torch_device)
)
output_custom2 = peft_model_custom2(input)
sd_custom2 = peft_model_custom2.state_dict()
assert len(sd_default) == len(sd_custom1) == len(sd_custom2)
for key in sd_default:
key1 = key.replace("default", "adapter")
key2 = key.replace("default", "other-name")
assert key1 in sd_custom1
assert key2 in sd_custom2
for k0, k1, k2 in zip(sd_default, sd_custom1, sd_custom2):
assert torch.allclose(sd_default[k0], sd_custom1[k1])
assert torch.allclose(sd_default[k0], sd_custom2[k2])
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output_default)
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output_custom1)
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output_custom2)
assert torch.allclose(output_custom1, output_custom2)
assert torch.allclose(output_default, output_custom1)
def test_gpt2_dora_merge_and_unload(self):
# see https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/1588#discussion_r1537914207
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2")
config = LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", use_dora=True)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
# should not raise an error
model.merge_and_unload()
def test_gpt2_dora_merge_and_unload_safe_merge(self):
# see https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/1588#discussion_r1537914207
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2")
config = LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", use_dora=True)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
# should not raise an error
model.merge_and_unload(safe_merge=True)
def test_unload_adapter_multihead_attention(self):
# MultiheadAttention has special logic for unloading, that logic is covered by this test
self._test_unload_adapter(
model_id="MHA",
config_cls=LoraConfig,
config_kwargs={"target_modules": ["mha"], "init_lora_weights": False},
)
def test_dora_save_and_load_remapping(self):
# Here we test the refactor of DoRA which changed lora_magnitude_vector from a ParameterDict to a ModuleDict
# with a DoraLayer instance. The old parameter is now the "weight" attribute of that layer. Since we want the
# state_dict format not to change, we ensure that the ".weight" part of the key is removed.
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m")
config = LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", use_dora=True)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
state_dict = model.state_dict()
# sanity check: state dict contains "lora_magnitude_vector.default.weight" keys
assert any("lora_magnitude_vector.default.weight" in k for k in state_dict)
# save the model, check the state dict
# note: not using the context manager here because it fails on Windows CI for some reason
tmp_dirname = tempfile.mkdtemp()
try:
model.save_pretrained(tmp_dirname)
state_dict_adapter = safe_load_file(os.path.join(tmp_dirname, "adapter_model.safetensors"))
# note that in the state dict, the "default" part of the key is removed
assert not any("lora_magnitude_vector.weight" in k for k in state_dict_adapter)
del model
loaded = PeftModel.from_pretrained(AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m"), tmp_dirname)
finally:
try:
shutil.rmtree(tmp_dirname)
except PermissionError:
# windows error
pass
state_dict_loaded = loaded.state_dict()
assert state_dict.keys() == state_dict_loaded.keys()
for k in state_dict:
assert torch.allclose(state_dict[k], state_dict_loaded[k])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("with_forward_call", [False, True])
def test_mha_gradients_set_correctly(self, with_forward_call):
# check for this bug: https://github.com/huggingface/peft/issues/761#issuecomment-1893804738
base_model = ModelMha()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["mha"])
model = get_peft_model(base_model, config)
model = model.to(self.torch_device)
if with_forward_call:
# after the merge-unmerge roundtrip happening in forward of lora MHA, the base weights should be set to
# requires_grad=False
inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model(**inputs)
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.out_proj.base_layer.weight.requires_grad is False
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.in_proj_weight.requires_grad is False
# _restore_weights used to ignore the gradient, this checks that it is indeed considered
model.base_model.model.mha._restore_weights()
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.out_proj.base_layer.weight.requires_grad is False
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.in_proj_weight.requires_grad is False
model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.out_proj.base_layer.weight.requires_grad = True
model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.in_proj_weight.requires_grad = True
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.out_proj.base_layer.weight.requires_grad is True
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.in_proj_weight.requires_grad is True
model.base_model.model.mha._restore_weights()
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.out_proj.base_layer.weight.requires_grad is True
assert model.base_model.model.mha.base_layer.in_proj_weight.requires_grad is True
class TestMultiRankAdapter:
"""Tests related to multirank LoRA adapters"""
def test_multirank(self):
config_1 = LoraConfig(
r=8,
lora_alpha=8,
init_lora_weights=False,
target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"],
)
config_2 = LoraConfig(
r=8,
lora_alpha=8,
init_lora_weights=False,
target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"],
rank_pattern={"lin0": 4},
alpha_pattern={"lin0": 4},
)
# Add first adapter
model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config_1, adapter_name="first")
# Add second adapter
model.add_adapter("second", config_2)
# Extract current and expected ranks
rank_current = model.lin0.lora_A["second"].weight.shape[0]
rank_expected = config_2.rank_pattern["lin0"]
assert rank_current == rank_expected, f"Rank {rank_current} is not equal to expected {rank_expected}"
def test_multirank_2(self):
rank_pattern = {}
alpha_pattern = {}
r = 4
lora_alpha = 8
for i in range(10):
rank = 64 // (i + 1)
for j in range(2):
rank_pattern[f"layers.{i}.lin{j}"] = rank
alpha_pattern[f"layers.{i}.lin{j}"] = 2 * rank
config = LoraConfig(
r=r,
lora_alpha=lora_alpha,
init_lora_weights=False,
target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"],
rank_pattern=rank_pattern,
alpha_pattern=alpha_pattern,
)
# Add first adapter
model = get_peft_model(DeepMLP(), config, adapter_name="first")
# Add second adapter
model.add_adapter("second", config)
for adapter in ["first", "second"]:
for key, module in model.base_model.model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, BaseTunerLayer):
rank_expected = rank_pattern.get(key, r)
rank_current = module.lora_A[adapter].weight.shape[0]
assert rank_current == rank_expected, (
f"Rank {rank_current} is not equal to expected {rank_expected}"
)
class TestLayerRepr:
"""Tests related to the repr of adapted models"""
def test_repr_lora_linear(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config)
print_output = repr(model.model.lin0)
assert print_output.startswith("lora.Linear")
assert "in_features=10" in print_output
assert "out_features=20" in print_output
assert "lora_A" in print_output
assert "lora_B" in print_output
assert "default" in print_output
def test_repr_lora_embedding(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb"])
model = get_peft_model(ModelEmbConv1D(), config)
print_output = repr(model.model.emb)
assert print_output.startswith("lora.Embedding")
assert "100, 5" in print_output
assert "lora_embedding_A" in print_output
assert "lora_embedding_B" in print_output
assert "default" in print_output
def test_repr_lora_conv1d(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv1d"])
model = get_peft_model(ModelEmbConv1D(), config)
print_output = repr(model.model.conv1d)
assert print_output.startswith("lora.Linear")
assert "in_features=5" in print_output
assert "out_features=1" in print_output
assert "lora_A" in print_output
assert "lora_B" in print_output
assert "default" in print_output
def test_repr_lora_conv2d(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv2d"])
model = get_peft_model(ModelConv2D(), config)
print_output = repr(model.model.conv2d)
assert print_output.startswith("lora.Conv2d")
assert "5, 10" in print_output
assert "kernel_size=(3, 3)" in print_output
assert "stride=(1, 1)" in print_output
assert "lora_A" in print_output
assert "lora_B" in print_output
assert "default" in print_output
def test_repr_lora_paramwrapper(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_parameters=["lin0.weight"])
model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config)
print_output = repr(model.model.lin0)
assert print_output.startswith("lora.ParamWrapper")
# important: targeted parameter should be contained:
assert "parameter_name='weight'" in print_output
assert "in_features=10" in print_output
assert "out_features=20" in print_output
assert "lora_A" in print_output
assert "lora_B" in print_output
assert "default" in print_output
class TestMultipleActiveAdapters:
"""
A test class to test the functionality of multiple active adapters.
This is not specifically tied to custom models, it's just easy to test here and testing it on all types of models
would be overkill.
"""
torch_device = infer_device()
def prepare_inputs_for_testing(self):
X = torch.arange(90).view(9, 10).to(self.torch_device)
return {"X": X}
def set_multiple_active_adapters(self, model, adapter_names):
for module in model.modules():
if isinstance(module, (BaseTunerLayer, AuxiliaryTrainingWrapper)):
module.set_adapter(adapter_names)
def resolve_model_cls(self, tuner_method):
if tuner_method == "lora+trainable_tokens":
# for this method we need an Embedding layer to target
return ModelEmbConv1D()
if tuner_method == "ia3":
return MLP(bias=False)
return MLP(bias=True)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, tuner_method, config_cls, config_kwargs_1, config_kwargs_2", MULTIPLE_ACTIVE_ADAPTERS_TEST_CASES
)
def test_multiple_active_adapters_forward(
self, test_name, tuner_method, config_cls, config_kwargs_1, config_kwargs_2
):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs_2)
torch.manual_seed(0)
model = self.resolve_model_cls(tuner_method)
model = model.to(self.torch_device).eval()
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
config_1 = config_cls(**config_kwargs_1)
config_2 = config_cls(**config_kwargs_2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config_1, adapter_name="adapter_1")
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter_2", config_2)
# the assumption that the output of the combined output of two adapters is != to the output of one
# adapter is not true for unmodified trainable tokens as they just mimic the existing embedding matrix.
# therefore, we modify the weights so that the adapter weights differs from the embedding weights.
#
# We do it this way because we have no way to pass something like `init_weights=False` to the token adapter.
if "trainable_tokens" in tuner_method:
peft_model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["adapter_1"].data = torch.rand_like(
peft_model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["adapter_1"].data
)
peft_model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["adapter_2"].data = torch.rand_like(
peft_model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["adapter_2"].data
)
# set adapter_1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter_1")
adapter_1_output = peft_model(**X)
# set adapter_2
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter_2")
adapter_2_output = peft_model(**X)
# set ["adapter_1", "adapter_2"]
self.set_multiple_active_adapters(peft_model, ["adapter_1", "adapter_2"])
combined_output = peft_model(**X)
assert not torch.allclose(adapter_1_output, adapter_2_output, atol=1e-5)
assert not torch.allclose(adapter_1_output, combined_output, atol=1e-5)
assert not torch.allclose(adapter_2_output, combined_output, atol=1e-5)
if (tuner_method == "lora") and not (config_1.target_parameters or config_2.target_parameters):
# Create a weighted adapter combining both adapters and check that its output is same as setting multiple
# active adapters. `target_parameters` is not supported.
peft_model.add_weighted_adapter(
["adapter_1", "adapter_2"], [1.0, 1.0], "new_combined_adapter", combination_type="cat"
)
peft_model.set_adapter("new_combined_adapter")
new_combined_output = peft_model(**X)
assert torch.allclose(new_combined_output, combined_output, atol=1e-5)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, tuner_method, config_cls, config_kwargs_1, config_kwargs_2", MULTIPLE_ACTIVE_ADAPTERS_TEST_CASES
)
def test_multiple_active_adapters_merge_and_unmerge(
self, test_name, tuner_method, config_cls, config_kwargs_1, config_kwargs_2
):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs_2)
torch.manual_seed(0)
model = self.resolve_model_cls(tuner_method)
model = model.to(self.torch_device).eval()
X = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
base_output = model(**X)
config_1 = config_cls(**config_kwargs_1)
config_2 = config_cls(**config_kwargs_2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config_1, adapter_name="adapter_1")
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter_2", config_2)
# set ["adapter_1", "adapter_2"]
self.set_multiple_active_adapters(peft_model, ["adapter_1", "adapter_2"])
combined_output = peft_model(**X)
peft_model.merge_adapter()
merged_combined_output = peft_model(**X)
assert torch.allclose(merged_combined_output, combined_output, atol=1e-4)
peft_model.unmerge_adapter()
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
disabled_adapter_output = peft_model(**X)
assert torch.allclose(disabled_adapter_output, base_output, atol=1e-4)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, tuner_method, config_cls, config_kwargs_1, config_kwargs_2", MULTIPLE_ACTIVE_ADAPTERS_TEST_CASES
)
def test_merge_layers_multi(self, test_name, tuner_method, config_cls, config_kwargs_1, config_kwargs_2):
_skip_tests_with_multiple_adapters_with_target_parameters(config_cls, config_kwargs_2)
torch.manual_seed(0)
model = self.resolve_model_cls(tuner_method)
model = model.to(self.torch_device).eval()
config_1 = config_cls(**config_kwargs_1)
config_2 = config_cls(**config_kwargs_2)
model = get_peft_model(model, config_1)
# the assumption that the output of the combined output of two adapters is != to the output of one
# adapter is not true for unmodified trainable tokens as they just mimic the existing embedding matrix.
# therefore, we modify the weights so that the adapter weights differs from the embedding weights. in this
# case we even use 20*rand to be very distinct to adapter 2 since we're comparing outputs and not embeddings
# with rather high tolerance values. this is also the reason why `init_weights` is not sufficient here and
# when using `<peft method>.trainable_token_indices` we do not have the utility of `init_weights` anyway.
if "trainable_tokens" in tuner_method:
model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["default"].data = 20 * torch.rand_like(
model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["default"].data
)
dummy_input = self.prepare_inputs_for_testing()
model.eval()
with torch.inference_mode():
logits_adapter_1 = model(**dummy_input)[0]
model.add_adapter("adapter-2", config_2)
model.set_adapter("adapter-2")
# same as above but for adapter 2
if "trainable_tokens" in tuner_method:
model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["adapter-2"].data = 2 * torch.rand_like(
model.emb.token_adapter.trainable_tokens_delta["adapter-2"].data
)
model.eval()
with torch.inference_mode():
logits_adapter_2 = model(**dummy_input)[0]
assert not torch.allclose(logits_adapter_1, logits_adapter_2, atol=1e-3, rtol=1e-3)
model.set_adapter("default")
with torch.inference_mode():
logits_adapter_1_after_set = model(**dummy_input)[0]
assert torch.allclose(logits_adapter_1_after_set, logits_adapter_1, atol=1e-3, rtol=1e-3)
model_copy = copy.deepcopy(model)
model_copy_2 = copy.deepcopy(model)
model_merged_all = model.merge_and_unload(adapter_names=["adapter-2", "default"])
with torch.inference_mode():
logits_merged_all = model_merged_all(**dummy_input)[0]
assert not torch.allclose(logits_merged_all, logits_adapter_2, atol=1e-3, rtol=1e-3)
assert not torch.allclose(logits_merged_all, logits_adapter_1, atol=1e-3, rtol=1e-3)
model_merged_adapter_2 = model_copy.merge_and_unload(adapter_names=["adapter-2"])
with torch.inference_mode():
logits_merged_adapter_2 = model_merged_adapter_2(**dummy_input)[0]
assert torch.allclose(logits_merged_adapter_2, logits_adapter_2, atol=1e-3, rtol=1e-3)
model_merged_adapter_default = model_copy_2.merge_and_unload(adapter_names=["default"])
with torch.inference_mode():
logits_merged_adapter_default = model_merged_adapter_default(**dummy_input)[0]
assert torch.allclose(logits_merged_adapter_default, logits_adapter_1, atol=1e-3, rtol=1e-3)
class TestRequiresGrad:
"""Test that requires_grad is set correctly in specific circumstances
# See issue #899.
This is not specifically tied to custom models, it's just easy to test here and testing it on all types of models
would be overkill.
"""
def check_requires_grad(self, model, *params_expected: str):
# Check that only the given parameters have requires_grad=True, and all others have requires_grad=False.
# Calling without arguments besides the model means that all parameters should have requires_grad=False.
params_with_requires_grad = [name for name, param in model.named_parameters() if param.requires_grad]
diff = set(params_expected).symmetric_difference(set(params_with_requires_grad))
msg = f"Expected {params_expected} to require gradients, got {params_with_requires_grad}"
assert len(diff) == 0, msg
def test_requires_grad_modules_to_save_default(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config)
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.bias",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_modules_to_save_disabling(self):
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config)
# when disabling the adapter, the original module's grad should be enabled and vice versa
peft_model.disable_adapter_layers()
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.original_module.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.original_module.bias",
)
# when re-enabling the adapter, the original module's grad should be disabled and vice versa
peft_model.enable_adapter_layers()
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.bias",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# when using the disable_adapter context, the original module's grad should be enabled and vice versa
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.original_module.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.original_module.bias",
)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.bias",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_modules_to_save_multiple_adapters(self):
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.bias",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.default.bias",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# set config1 as active, should lead to adapter1 requiring grad
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.modules_to_save.adapter1.bias",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_lora_different_targets(self):
# test two different LoRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin1"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_lora_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that LoRA adapters target the same layer
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_ia3_different_targets(self):
# test two different IA3 adapters that target different modules
config0 = IA3Config(target_modules=["lin0"], feedforward_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = IA3Config(target_modules=["lin1"], feedforward_modules=["lin1"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_ia3_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that IA3 adapters target the same layer
config0 = IA3Config(target_modules=["lin0"], feedforward_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = IA3Config(target_modules=["lin0"], feedforward_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_adalora_different_targets(self):
# test two different AdaLora adapters that target different modules
config0 = AdaLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], total_step=1)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = AdaLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], total_step=1, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_E.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_E.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_E.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.lora_E.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_adalora_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that AdaLora adapters target the same layer
config0 = AdaLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], total_step=1)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = AdaLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], total_step=1, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_E.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_E.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_E.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_E.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_lora_conv2d(self):
# test two different LoRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv2d"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(ModelConv2D(), config0)
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv2d.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.conv2d.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv2d.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.conv2d.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_A.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.lin0.lora_B.adapter1.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_lora_emb_conv1d(self):
# test two different LoRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv1d"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(ModelEmbConv1D(), config0)
config1 = LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv1d.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.conv1d.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv1d.lora_A.default.weight",
"base_model.model.conv1d.lora_B.default.weight",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.emb.lora_embedding_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.emb.lora_embedding_B.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.emb.lora_embedding_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.emb.lora_embedding_B.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_ia3_conv1d(self):
# test two different LoRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = IA3Config(target_modules=["conv1d"], feedforward_modules=[])
peft_model = get_peft_model(ModelEmbConv1D(), config0)
config1 = IA3Config(target_modules=["lin0"], feedforward_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv1d.ia3_l.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv1d.ia3_l.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_ia3_conv2d(self):
# test two different LoRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = IA3Config(target_modules=["conv2d"], feedforward_modules=["conv2d"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(ModelConv2D(), config0)
config1 = IA3Config(target_modules=["lin0"], feedforward_modules=[])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv2d.ia3_l.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.conv2d.ia3_l.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.ia3_l.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_loha_different_targets(self):
# test two different LoHa adapters that target different modules
config0 = LoHaConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoHaConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_b.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_b.default",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w1_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w1_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w2_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w2_b.adapter1",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w1_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w1_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w2_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.hada_w2_b.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_loha_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that LoHa adapters target the same layer
config0 = LoHaConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoHaConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_b.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_a.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_b.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_b.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w1_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_a.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.hada_w2_b.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_lokr_different_targets(self):
# test two different LoKr adapters that target different modules
config0 = LoKrConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoKrConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w1.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w2.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w1.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w2.default",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.lokr_w1.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.lokr_w2.adapter1",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.lokr_w1.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.lokr_w2.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_lokr_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that LoKr adapters target the same layer
config0 = LoKrConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = LoKrConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w1.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w2.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w1.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w2.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w1.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w2.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w1.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.lokr_w2.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_oft_different_targets(self):
# test two different OFT adapters that target different modules
config0 = OFTConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2, oft_block_size=0)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = OFTConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], r=2, oft_block_size=0, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.oft_R.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.oft_R.default.weight",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.oft_R.adapter1.weight",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.oft_R.adapter1.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_oft_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that OFT adapters target the same layer
config0 = OFTConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2, oft_block_size=0)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = OFTConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2, oft_block_size=0, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.oft_R.default.weight",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.oft_R.default.weight",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.oft_R.adapter1.weight",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.oft_R.adapter1.weight",
)
def test_requires_grad_hra_different_targets(self):
# test two different HRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = HRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = HRAConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hra_u.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hra_u.default",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.hra_u.adapter1",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.hra_u.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_hra_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that HRA adapters target the same layer
config0 = HRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = HRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hra_u.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hra_u.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hra_u.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.hra_u.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_bone_different_targets(self):
# test two different HRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = BoneConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = BoneConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], r=2, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.bone_block.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.bone_block.default",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.bone_block.adapter1",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.bone_block.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_bone_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that HRA adapters target the same layer
config0 = BoneConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = BoneConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.bone_block.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.bone_block.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.bone_block.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.bone_block.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_miss_different_targets(self):
# test two different HRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = MissConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = MissConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], r=2, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.miss_block.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.miss_block.default",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.miss_block.adapter1",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.miss_block.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_miss_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that HRA adapters target the same layer
config0 = MissConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = MissConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=2, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.miss_block.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.miss_block.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.miss_block.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.miss_block.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_boft_different_targets(self):
# test two different OFT adapters that target different modules
config0 = BOFTConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], boft_block_size=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP2(), config0)
config1 = BOFTConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], boft_block_size=2, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active pter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.boft_R.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.boft_s.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.boft_R.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.boft_s.default",
)
# change activate pter to pter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_R.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_s.adapter1",
)
# disable all pters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_R.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_s.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_boft_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that BOFT adapters target the same layer
config0 = BOFTConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], boft_block_size=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = BOFTConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], boft_block_size=2, inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_R.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_s.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_R.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_s.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_R.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_s.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_R.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.boft_s.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_lntuning_different_targets(self):
config0 = LNTuningConfig(
target_modules=["layernorm0"],
)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP_LayerNorm(), config0)
config1 = LNTuningConfig(
target_modules=["layernorm1"],
inference_mode=True,
)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.bias",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.bias",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm1.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm1.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.bias",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm1.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm1.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.bias",
)
def test_requires_grad_lntuning_same_targets(self):
config0 = LNTuningConfig(
target_modules=["layernorm0"],
)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP_LayerNorm(), config0)
config1 = LNTuningConfig(target_modules=["layernorm0"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.bias",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.default.bias",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.bias",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.weight",
"base_model.model.layernorm0.ln_tuning_layers.adapter1.bias",
)
def test_requires_grad_vera_different_targets(self):
# Test two different VeRA adapters that target different modules. Most notably, ensure that vera_A and vera_B
# don't require grads.
# requires a model with at least 2 layers with the same shapes
class MLP2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias) # lin1 and lin2 have same shape
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = X.float()
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin2(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin3(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
config0 = VeraConfig(target_modules=["lin1"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP2(), config0)
config1 = VeraConfig(target_modules=["lin2"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_d.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_d.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_d.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_d.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_vera_same_targets(self):
# Test two different VeRA adapters that target the same module. Most notably, ensure that vera_A and vera_B
# don't require grads.
# requires a model with at least 2 layers with the same shapes
class MLP2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias) # lin1 and lin2 have same shape
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = X.float()
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin2(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin3(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
config0 = VeraConfig(target_modules=["lin1", "lin2"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP2(), config0)
config1 = VeraConfig(target_modules=["lin1", "lin2"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_d.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_d.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_d.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_b.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_d.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_d.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_d.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.vera_lambda_d.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_b.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.vera_lambda_d.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_randlora_different_targets(self):
# Test two different RandLora adapters that target different modules. Most notably, ensure that randbasis_A and randbasis_B
# don't require grads.
# requires a model with at least 2 layers with the same shapes
class MLP2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias) # lin1 and lin2 have same shape
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = X.float()
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin2(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin3(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
config0 = RandLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin1"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP2(), config0)
config1 = RandLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin2"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_lambda.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_gamma.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_lambda.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_gamma.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_lambda.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_gamma.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_lambda.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_gamma.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_randlora_same_targets(self):
# Test two different RandLora adapters that target the same module. Most notably, ensure that randbasis_A and randbasis_B
# don't require grads.
# requires a model with at least 2 layers with the same shapes
class MLP2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias) # lin1 and lin2 have same shape
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(20, 20, bias=bias)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(20, 2, bias=bias)
self.sm = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, X):
X = X.float()
X = self.lin0(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin1(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin2(X)
X = self.relu(X)
X = self.lin3(X)
X = self.sm(X)
return X
config0 = RandLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin1", "lin2"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP2(), config0)
config1 = RandLoraConfig(target_modules=["lin1", "lin2"])
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_lambda.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_gamma.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_lambda.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_gamma.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_lambda.default",
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_gamma.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_lambda.default",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_gamma.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_lambda.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_gamma.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_lambda.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_gamma.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_lambda.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.randlora_gamma.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_lambda.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin2.randlora_gamma.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_vblora_different_targets(self):
# test two different VBLoRA adapters that target different modules
config0 = VBLoRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], vector_length=1, num_vectors=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = VBLoRAConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], vector_length=1, num_vectors=2)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vblora_logits_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.vblora_logits_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.adapter1", # vblora_vector_bank is shared
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.vblora_logits_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin1.vblora_logits_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.adapter1", # vblora_vector_bank is shared
)
def test_requires_grad_vblora_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that VBLoRA adapters target the same layer
config0 = VBLoRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], vector_length=1, num_vectors=2)
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = VBLoRAConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], vector_length=1, num_vectors=2)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_A.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_B.default",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_A.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_logits_B.adapter1",
"base_model.model.lin0.vblora_vector_bank.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_fourierft_different_targets(self):
# test two different fourierft adapters that target different modules
config0 = FourierFTConfig(n_frequency=10, target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = FourierFTConfig(n_frequency=10, target_modules=["lin1"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.fourierft_spectrum.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.fourierft_spectrum.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.fourierft_spectrum.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin1.fourierft_spectrum.adapter1",
)
def test_requires_grad_fourierft_same_targets(self):
# same as previous test, except that AdaLora adapters target the same layer
config0 = FourierFTConfig(n_frequency=10, target_modules=["lin0"])
peft_model = get_peft_model(MLP(), config0)
config1 = FourierFTConfig(n_frequency=10, target_modules=["lin0"], inference_mode=True)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
# active adapter is still "default"
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.fourierft_spectrum.default",
)
# set config0 as active, should not change anything
peft_model.set_adapter("default")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.fourierft_spectrum.default",
)
# change activate adapter to adapter1
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.fourierft_spectrum.adapter1",
)
# disable all adapters
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
self.check_requires_grad(peft_model)
# after context is exited, return to the previous state
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
self.check_requires_grad(
peft_model,
"base_model.model.lin0.fourierft_spectrum.adapter1",
)
# this is for PEFT methods that support mixed adapter batches.
MIXED_ADAPTER_TEST_CASES = [
(
"LoRA mixed adapter",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], r=16, init_lora_weights=False),
),
(
"RoAd mixed adapter",
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], group_size=2, variant="road_2", init_weights=False),
),
]
class TestMixedAdapterBatches:
torch_device = infer_device()
def get_mlp_peft(self, config0, config1):
"""A simple MLP with 2 LoRA adapters"""
torch.manual_seed(0)
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
return peft_model
def run_checks(self, model, inputs):
# This checks that we can have mixed adapters in a single batch. The test works by creating the outputs for the
# base model, adapter 0, and adapter 1 separately. Then, we create an output with mixed adapters, where the
# sample [0, 3, 6] are for the base model, [1, 4, 7] for adapter 0, and [2, 5, 8] for adapter 1. Finally, we
# check that the outputs of the mixed batch are correct for the corresponding indices.
adapter_name0, adapter_name1 = model.peft_config.keys()
with model.disable_adapter():
output_base = model(**inputs)
model.set_adapter(adapter_name0)
output0 = model(**inputs)
# sanity check, outputs are not the same
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output0)
model.set_adapter(adapter_name1)
output1 = model(**inputs)
# sanity check, outputs have the right shape and are not the same
assert len(output_base) >= 3
assert len(output_base) == len(output0) == len(output1)
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output0)
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output1)
# set adapter_indices so that it alternates between base, adapter 0, and adapter 1
adapters = ["__base__", adapter_name0, adapter_name1]
inputs["adapter_names"] = [adapters[i % 3] for i in (range(len(inputs["X"])))]
output_mixed = model.forward(**inputs)
assert torch.allclose(output_base[::3], output_mixed[::3])
assert torch.allclose(output0[1::3], output_mixed[1::3])
assert torch.allclose(output1[2::3], output_mixed[2::3])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, config0, config1", MIXED_ADAPTER_TEST_CASES)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_mlp(self, test_name, config0, config1):
mlp_peft = self.get_mlp_peft(config0, config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(mlp_peft, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with different target layers",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], init_lora_weights=False),
),
(
"RoAd mixed adapter with different target layers",
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin1"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_different_target_layers(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with modules to save",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"], init_lora_weights=False),
),
(
"RoAd mixed adapter with modules to save",
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["lin1"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_multiple_modules_to_save(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with unsupported layer",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["gru"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], modules_to_save=["gru"], init_lora_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_unsupported_layer_raises(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = MLPWithGRU().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
SUPPORTED_MODULES = (torch.nn.Linear, torch.nn.Embedding, torch.nn.Conv1d, torch.nn.Conv2d, torch.nn.Conv3d)
module_names = ", ".join([module.__name__ for module in SUPPORTED_MODULES])
with pytest.raises(
TypeError, match=f"Mixed batching is only supported for the following modules: {module_names}."
):
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with overlapping layers",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"], init_lora_weights=False),
),
(
"RoAd mixed adapter with overlapping layers",
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "lin1"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_partly_overlapping_target_layers(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
# target different lora layers
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with conv1d",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb", "conv1d"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb", "conv1d"], r=16, init_lora_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_conv1d_emb(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = ModelEmbConv1D().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with conv1d and emb and modules to save",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb", "conv1d"], modules_to_save=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["emb", "conv1d"], modules_to_save=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_conv1d_emb_multiple_modules_to_save(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = ModelEmbConv1D().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with conv2d",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv2d"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["conv2d"], r=16, init_lora_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_conv2d(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = ModelConv2D().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(270).view(6, 5, 3, 3).to(self.torch_device)}
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter with mha",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["mha"], init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(target_modules=["mha"], r=16, init_lora_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_mha_raises(self, test_name, config0, config1):
base_model = ModelMha().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter0").eval()
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter1", config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
msg = "lora.MultiheadAttention does not support mixed adapter batches"
with pytest.raises(TypeError, match=msg):
self.run_checks(peft_model, inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, config0, config1", MIXED_ADAPTER_TEST_CASES)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_length_mismatch_raises(self, test_name, config0, config1):
mlp_peft = self.get_mlp_peft(config0, config1)
inputs = {
"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device),
"adapter_names": ["__base__"] * 5, # wrong length!
}
msg = r"Length of `adapter_names` should be the same as the number of inputs, but got "
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
mlp_peft.forward(**inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, config0, config1", MIXED_ADAPTER_TEST_CASES)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_training_mode_raises(self, test_name, config0, config1):
mlp_peft = self.get_mlp_peft(config0, config1)
inputs = {
"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device),
"adapter_names": ["__base__"] * 9,
}
mlp_peft = mlp_peft.train()
msg = r"Cannot pass `adapter_names` when the model is in training mode."
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
mlp_peft.forward(**inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, config0, config1", MIXED_ADAPTER_TEST_CASES)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_disabled(self, test_name, config0, config1):
# Disabling adapters should have precedence over passing adapter names
mlp_peft = self.get_mlp_peft(config0, config1)
inputs = {"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)}
with mlp_peft.disable_adapter():
output_disabled = mlp_peft(**inputs)
adapters = ["__base__", "adapter0", "adapter1"]
inputs["adapter_names"] = [adapters[i % 3] for i in (range(len(inputs["X"])))]
with mlp_peft.disable_adapter():
output_mixed = mlp_peft.forward(**inputs)
assert torch.allclose(output_disabled, output_mixed)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_name, config0, config1", MIXED_ADAPTER_TEST_CASES)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_merged_raises(self, test_name, config0, config1):
# When there are merged adapters, passing adapter names should raise an error
mlp_peft = self.get_mlp_peft(config0, config1)
inputs = {
"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device),
"adapter_names": ["adapter0"] * 9,
}
mlp_peft.merge_adapter(["adapter0"])
msg = r"Cannot pass `adapter_names` when there are merged adapters, please call `unmerge_adapter` first."
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
mlp_peft.forward(**inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config",
[
(
"LoRA mixed batch wrong adapter name",
LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False),
),
(
"RoAD mixed batch wrong adapter name",
RoadConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], group_size=2, init_weights=False),
),
],
)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_wrong_adapter_name_raises(self, test_name, config):
# Ensure that all of the adapter names that are being passed actually exist
torch.manual_seed(0)
x = torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device)
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config).eval()
peft_model.add_adapter(adapter_name="other", peft_config=config)
# sanity check: this works
peft_model.forward(x, adapter_names=["default"] * 5 + ["other"] * 4)
# check one correct and one incorrect adapter
msg = re.escape("Trying to infer with non-existing adapter(s): does-not-exist")
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
peft_model.forward(x, adapter_names=["default"] * 5 + ["does-not-exist"] * 4)
# check two correct adapters and one incorrect adapter
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
peft_model.forward(x, adapter_names=["default"] * 3 + ["does-not-exist"] * 4 + ["other"] * 2)
# check only incorrect adapters
msg = re.escape("Trying to infer with non-existing adapter(s): does-not-exist, other-does-not-exist")
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
peft_model.forward(x, adapter_names=["does-not-exist"] * 5 + ["other-does-not-exist"] * 4)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_with_dora_raises(self):
# When there are DoRA adapters, passing adapter names should raise an error
torch.manual_seed(0)
inputs = {
"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device),
"adapter_names": ["default"] * 9,
}
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False, use_dora=True)
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config).eval()
msg = r"Cannot pass `adapter_names` when DoRA is enabled."
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=msg):
peft_model.forward(**inputs)
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_with_dora_but_dora_not_included_works(self):
# When there are DoRA adapters, passing adapter names should raise an error, see previous test. However, when
# the adapter that uses DoRA is not included in adapter_names, it's actually fine.
torch.manual_seed(0)
base_model = MLP().to(self.torch_device).eval()
config_dora = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False, use_dora=True)
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config_dora)
config_no_dora = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0"], init_lora_weights=False, use_dora=False)
peft_model.add_adapter(adapter_name="other", peft_config=config_no_dora)
peft_model.eval()
# The "default" adapter uses DoRA but "other" is not using it, so using "other" is fine. Also, "__base__" is
# fine since it uses the base model and thus DoRA is not involved either.
inputs = {
"X": torch.arange(90).view(-1, 10).to(self.torch_device),
"adapter_names": ["other"] * 4 + ["__base__"] * 5,
}
peft_model.forward(**inputs)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_name, config0, config1, factor",
[
(
"LoRA mixed adapter timing",
LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", init_lora_weights=False),
LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", r=16, init_lora_weights=False),
2.0,
),
(
"RoAd mixed adapter timing",
RoadConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", init_weights=False),
RoadConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", variant="road_2", init_weights=False),
3.0,
),
],
)
@require_non_cpu
def test_mixed_adapter_batches_lora_opt_timing(self, test_name, config0, config1, factor):
# Use a more realistic model (opt-125m) and do a simple runtime check to ensure that mixed adapter batches
# don't add too much overhead. These types of tests are inherently flaky, so we try to add in some robustness.
logs = [] # store the time it takes to run each forward pass here
@contextmanager
def timed():
tic = time.perf_counter()
yield
toc = time.perf_counter()
logs.append(toc - tic)
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(self.torch_device).eval()
inputs = {"input_ids": torch.randint(0, 1000, (16, 64)).to(self.torch_device)}
with timed():
output_base = base_model(**inputs).logits
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, config0, "adapter1").eval()
with timed():
output0 = peft_model(**inputs).logits
# sanity check, outputs are not the same
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output0)
peft_model.add_adapter("adapter2", config1)
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter2")
with timed():
output1 = peft_model(**inputs).logits
# sanity check, outputs are not the same
assert not torch.allclose(output_base, output1)
# set adapter_indices so that it alternates between 0 (base), lora 1, and lora 2
adapters = ["__base__", "adapter1", "adapter2"]
inputs["adapter_names"] = [adapters[i % 3] for i in (range(len(inputs["input_ids"])))]
with timed():
output_mixed = peft_model.forward(**inputs).logits
atol, rtol = 1e-4, 1e-4
assert torch.allclose(output_base[::3], output_mixed[::3], atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
assert torch.allclose(output0[1::3], output_mixed[1::3], atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
assert torch.allclose(output1[2::3], output_mixed[2::3], atol=atol, rtol=rtol)
# Check that the overhead in time added by mixed batches is not too high.
# To prevent flakiness, we measure mixed inference 3 times and take the lowest value, then compare it to the mean
# of the non-mixed inference times. We also grant a generous margin of 2x the mean time.
with timed():
output_mixed = peft_model.forward(**inputs).logits
with timed():
output_mixed = peft_model.forward(**inputs).logits
time_base, time0, time1, *time_mixed = logs
time_non_mixed = (time_base + time0 + time1) / 3
time_mixed = min(time_mixed)
assert time_mixed < factor * time_non_mixed
# Measure timing of running base and adapter separately vs using a mixed batch. Note that on CPU, the
# differences are quite small, so this test requires GPU to avoid flakiness.
for _ in range(3):
with timed():
with peft_model.disable_adapter():
peft_model(**{k: v[::3] for k, v in inputs.items()})
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter1")
peft_model(**{k: v[1::3] for k, v in inputs.items()})
peft_model.set_adapter("adapter2")
peft_model(**{k: v[2::3] for k, v in inputs.items()})
times_separate = logs[-3:]
time_separate = sum(times_separate) / 3
assert time_separate > time_mixed
class TestDynamicDispatch:
# These are tests for the dynamic dispatch feature for LoRA. We create a custom module and a custom LoRA layer
# that targets it.
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def custom_module_cls(self):
class MyModule(nn.Module):
# A custom layer that just behaves like an nn.Linear layer but is not an instance of nn.Linear. Therefore,
# it would normally fail to be targeted.
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.in_features = 10
self.out_features = 20
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(20, 10))
def forward(self, x):
return nn.functional.linear(x, self.weight)
return MyModule
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def custom_lora_cls(self):
from peft.tuners import lora
class MyLora(lora.Linear):
# just re-use the lora.Linear code here
pass
return MyLora
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def model_cls(self, custom_module_cls):
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.lin0 = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.my_module = custom_module_cls()
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(20, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.lin0(x))
x = self.relu(self.my_module(x))
x = self.lin1(x)
return x
return MyModel
def test_custom_lora_layer_used(self, custom_module_cls, custom_lora_cls, model_cls):
# check that when we register custom lora layers, they are indeed being used for the intended module
model = model_cls()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "my_module", "lin1"])
config._register_custom_module({custom_module_cls: custom_lora_cls})
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
assert isinstance(peft_model.base_model.model.my_module, custom_lora_cls)
assert isinstance(peft_model.base_model.model.my_module.base_layer, custom_module_cls)
# sanity check that the other lora layer types are still the default ones
assert not isinstance(peft_model.base_model.model.lin0.base_layer, custom_module_cls)
assert not isinstance(peft_model.base_model.model.lin1.base_layer, custom_module_cls)
def test_training_works(self, model_cls, custom_module_cls, custom_lora_cls):
# check that when we train with custom lora layers, they are indeed updated
model = model_cls()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "my_module", "lin1"])
config._register_custom_module({custom_module_cls: custom_lora_cls})
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
sd_before = copy.deepcopy(peft_model.state_dict())
inputs = torch.randn(16, 10)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(peft_model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
for _ in range(5):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = peft_model(inputs)
loss = output.sum() ** 2
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
sd_after = peft_model.state_dict()
# sanity check that for finite results, since nan != nan, which would make the test pass trivially
for val in sd_before.values():
assert torch.isfinite(val).all()
for val in sd_after.values():
assert torch.isfinite(val).all()
assert not torch.allclose(
sd_before["base_model.model.my_module.lora_A.default.weight"],
sd_after["base_model.model.my_module.lora_A.default.weight"],
)
assert not torch.allclose(
sd_before["base_model.model.my_module.lora_B.default.weight"],
sd_after["base_model.model.my_module.lora_B.default.weight"],
)
def test_saving_and_loading(self, custom_module_cls, custom_lora_cls, model_cls, tmp_path):
# check that we can successfully save and load the custom lora cls
torch.manual_seed(0)
model = model_cls()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "my_module", "lin1"])
config._register_custom_module({custom_module_cls: custom_lora_cls})
torch.manual_seed(1)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
inputs = torch.randn(5, 10)
outputs_before = peft_model(inputs) # does not raise
sd_before = peft_model.state_dict()
peft_model.save_pretrained(tmp_path / "lora-custom-module")
del model, peft_model
torch.manual_seed(0) # same seed for base model
model = model_cls()
# custom lora mapping is not persisted at the moment, so as a workaround this is needed
config = LoraConfig.from_pretrained(tmp_path / "lora-custom-module")
config._register_custom_module({custom_module_cls: custom_lora_cls})
# different seed for adapter to ensure it is not identical just because of seed
torch.manual_seed(123)
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, tmp_path / "lora-custom-module", config=config)
assert isinstance(peft_model.base_model.model.my_module, custom_lora_cls)
assert isinstance(peft_model.base_model.model.my_module.base_layer, custom_module_cls)
outputs_after = peft_model(inputs) # does not raise
assert torch.allclose(outputs_before, outputs_after)
sd_after = peft_model.state_dict()
assert sd_before.keys() == sd_after.keys()
for key in sd_before.keys():
assert torch.allclose(sd_before[key], sd_after[key])
def test_override_lora_linear(self, custom_lora_cls):
# in this test, we check if users can override default PEFT behavior by supplying a custom lora class that is
# being used instead of lora.Linear
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m")
config = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM)
config._register_custom_module({nn.Linear: custom_lora_cls})
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
layers = peft_model.base_model.model.model.decoder.layers
for layer in layers:
assert isinstance(layer.self_attn.v_proj, custom_lora_cls)
assert isinstance(layer.self_attn.q_proj, custom_lora_cls)
def test_custom_lora_layer_issues_warning(self, custom_module_cls, custom_lora_cls, model_cls, recwarn):
# users will get a warning if they target a layer type that is not officially supported
model = model_cls()
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lin0", "my_module", "lin1"])
config._register_custom_module({custom_module_cls: custom_lora_cls})
get_peft_model(model, config)
# check warning message
msg = (
"Unsupported layer type '<class 'tests.test_custom_models.TestDynamicDispatch.custom_module_cls."
"<locals>.MyModule'>' encountered, proceed at your own risk."
)
assert str(recwarn.list[-1].message) == msg
def test_target_layer_without_in_features_out_features(self, recwarn):
# It should be possible for users to target layers even if we cannot determine in_features and out_features.
# Those are only needed to initialize the LoRA layer via update_layer, so as long as users take care of that,
# they should be good and not require those attributes to exist
from peft.tuners import lora
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(10, 20)
class MyLora(nn.Module, lora.LoraLayer):
def __init__(self, base_layer, adapter_name, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
lora.LoraLayer.__init__(self, base_layer, **kwargs)
self._active_adapter = adapter_name
model = MyModel()
# check that in_features and out_features attributes don't exist on LSTM
assert not hasattr(model.lstm, "in_features")
assert not hasattr(model.lstm, "out_features")
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=["lstm"])
config._register_custom_module({nn.LSTM: MyLora})
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
# check that custom LoRA layer is correctly applied
assert isinstance(peft_model.base_model.lstm, MyLora)
assert isinstance(peft_model.base_model.lstm.base_layer, nn.LSTM)
# we should still get a warning message
msg = "Unsupported layer type '<class 'torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM'>' encountered, proceed at your own risk."
assert str(recwarn.list[-1].message) == msg
|
peft/tests/test_custom_models.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/tests/test_custom_models.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 100426
}
| 252
|
# Copyright 2025-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import pytest
import torch
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
class TestGetPeftModel:
RELOAD_WARNING_EXPECTED_MATCH = r"You are trying to modify a model .*"
@pytest.fixture
def lora_config_0(self):
return LoraConfig(target_modules="0")
@pytest.fixture
def base_model(self):
return torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(10, 2), torch.nn.Linear(2, 10))
def test_get_peft_model_warns_when_reloading_model(self, lora_config_0, base_model):
get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config_0)
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=self.RELOAD_WARNING_EXPECTED_MATCH):
get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config_0)
def test_get_peft_model_proposed_fix_in_warning_helps(self, lora_config_0, base_model, recwarn):
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config_0)
peft_model.unload()
get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config_0)
warning_checker = pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=self.RELOAD_WARNING_EXPECTED_MATCH)
for warning in recwarn:
if warning_checker.matches(warning):
pytest.fail("Warning raised even though model was unloaded.")
def test_get_peft_model_repeated_invocation(self, lora_config_0, base_model):
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config_0)
# use direct-addressing of the other layer to accomodate for the nested model
lora_config_1 = LoraConfig(target_modules="base_model.model.1")
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match=self.RELOAD_WARNING_EXPECTED_MATCH):
get_peft_model(peft_model, lora_config_1)
|
peft/tests/test_mapping.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/tests/test_mapping.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 851
}
| 253
|
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os
from functools import wraps
import huggingface_hub
import pytest
import torch
from safetensors.torch import load_file
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from peft import LoraConfig, PeftType, TaskType, XLoraConfig, get_peft_model
from peft.peft_model import PeftModel
from peft.utils import infer_device
def flaky(num_tries: int):
"""Decorator for test functions that are flaky"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
for _ in range(num_tries):
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except AssertionError as e:
print(f"Failed test {func.__name__} with error: {e}")
continue
raise AssertionError(f"Failed test {func.__name__} after {num_tries} tries")
return wrapper
return decorator
class TestXlora:
torch_device = infer_device()
model_id = "facebook/opt-125m"
num_loras = 4
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def lora_dir(self, tmp_path_factory):
return tmp_path_factory.mktemp("lora")
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def lora_embedding_dir(self, tmp_path_factory):
return tmp_path_factory.mktemp("lora_embedding")
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def saved_lora_adapters(self, lora_dir):
file_names = []
lora_configs = [
LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"], init_lora_weights=False)
for _ in range(self.num_loras)
]
# have 1 LoRA with different target modules
lora_configs[-1] = LoraConfig(
task_type="CAUSAL_LM", target_modules=["k_proj", "q_proj", "v_proj"], init_lora_weights=False
)
for i, lora_config in enumerate(lora_configs, start=1):
torch.manual_seed(i)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
file_name = os.path.join(lora_dir, f"checkpoint-{i}")
peft_model.save_pretrained(file_name)
file_names.append(file_name)
return file_names
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def saved_lora_embedding_adapters(self, lora_embedding_dir):
file_names = []
for i in range(1, self.num_loras + 1):
torch.manual_seed(i)
lora_config = LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", init_lora_weights=False, target_modules=["embed_tokens"])
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
file_name = os.path.join(lora_embedding_dir, f"checkpoint-{i}")
peft_model.save_pretrained(file_name)
file_names.append(file_name)
return file_names
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def tokenizer(self):
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(self.model_id, trust_remote_code=True, device_map=self.torch_device)
return tokenizer
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def embedding_model(self, saved_lora_embedding_adapters):
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
model.config.use_cache = False
adapters = {str(i): file_name for i, file_name in enumerate(saved_lora_embedding_adapters)}
peft_config = XLoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
peft_type=PeftType.XLORA,
hidden_size=model.config.hidden_size,
xlora_depth=8,
adapters=adapters,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config).to(self.torch_device)
return model
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def model(self, saved_lora_adapters):
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
model.config.use_cache = False
adapters = {str(i): file_name for i, file_name in enumerate(saved_lora_adapters)}
peft_config = XLoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
peft_type=PeftType.XLORA,
hidden_size=model.config.hidden_size,
xlora_depth=8,
adapters=adapters,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config).to(self.torch_device)
return model
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def model_layerwise(self, saved_lora_adapters):
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
model.config.use_cache = False
adapters = {str(i): file_name for i, file_name in enumerate(saved_lora_adapters)}
peft_config = XLoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
peft_type=PeftType.XLORA,
hidden_size=model.config.hidden_size,
xlora_depth=8,
adapters=adapters,
layerwise_scalings=True,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config).to(self.torch_device)
return model
def test_functional(self, tokenizer, model):
model.enable_scalings_logging()
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
def test_scalings_logging_methods(self, tokenizer, model):
model.enable_scalings_logging()
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
_ = model.get_latest_scalings()
# 32 is the numeber of max scalings. 3 is the number of prompt tokens.
assert 32 + 3 >= len(model.get_scalings_log()) > 0
model.disable_scalings_logging()
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
assert 32 >= len(model.get_scalings_log()) > 0
bucketed = model.get_bucketed_scalings_log()
keys = bucketed.keys()
# Once bucket for each token as we aren't using cache
assert len(bucketed) == 32 == len(keys)
seq_len = inputs.shape[1]
for key in keys:
assert len(bucketed[key][0]) == 1
assert len(bucketed[key][1]) == 1
assert bucketed[key][0][0] == key - seq_len
model.clear_scalings_log()
assert len(model.get_scalings_log()) == 0
def test_misc_methods(self, tokenizer, model):
model.set_global_scaling_weight(1.5)
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.global_scaling_weight == 1.5
assert model.get_global_scaling_weight() == 1.5
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
assert str(model) is not None
# On CI (but not locally), this test is flaky since transformers v4.45.0.
@flaky(num_tries=5)
def test_save_load_functional(self, tokenizer, model, tmp_path):
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
before_logits = outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]
assert torch.isfinite(before_logits).all()
model.save_pretrained(save_directory=tmp_path)
del model
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
model.config.use_cache = False
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model=model, model_id=tmp_path).to(self.torch_device)
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
after_logits = outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]
assert torch.isfinite(after_logits).all()
assert torch.equal(after_logits, before_logits)
def test_save_load_functional_pt(self, tokenizer, model, tmp_path):
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
before_logits = outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]
assert torch.isfinite(before_logits).all()
model.save_pretrained(save_directory=tmp_path, safe_serialization=False)
del model
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
model.config.use_cache = False
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model=model, model_id=tmp_path, safe_serialization=False).to(
self.torch_device
)
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
after_logits = outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]
assert torch.isfinite(after_logits).all()
assert torch.equal(after_logits, before_logits), (after_logits, before_logits)
def test_topk_lora(self, tokenizer, model):
model.set_topk_lora(2)
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.top_k_lora == 2
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
def test_softmax_topk(self, tokenizer, model):
# Just reach in to set the config
model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.top_k_lora = 2
model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.enable_softmax = False
model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.enable_softmax_topk = True
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
def test_set_override_scaling_pass_value(self, model):
# Defaults to 0
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.override_scaling_pass_value == 0.0
# Set it to 2 and make sure it actually is
model.set_scaling_pass_value(2)
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.override_scaling_pass_value == 2
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.scaling_pass_value == 2
# Set it to None and make sure it is 1/n
model.set_scaling_pass_value(None)
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.override_scaling_pass_value == 1 / self.num_loras
assert model.internal_xlora_classifier.config.scaling_pass_value == 1 / self.num_loras
def test_functional_layerwise(self, tokenizer, model_layerwise):
model_layerwise.enable_scalings_logging()
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model_layerwise.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
def test_disable_adapter(self, tokenizer, model):
model.enable_scalings_logging()
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
with model.disable_adapter():
outputs_disabled = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs_disabled[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
assert not torch.equal(outputs, outputs_disabled)
def test_functional_embedding(self, tokenizer, embedding_model):
inputs = tokenizer.encode("Python is a", add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = embedding_model.generate(
input_ids=inputs.to(self.torch_device),
max_new_tokens=32,
)
assert torch.isfinite(outputs[: inputs.shape[1] :]).all()
def test_xlora_loading_valid(self):
# This test also simulatenously tests the loading-from-hub functionality!
torch.manual_seed(123)
model_id = "facebook/opt-125m"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
model.config.use_cache = False
adapters = [
"peft-internal-testing/opt-125m-dummy-lora",
"peft-internal-testing/opt-125m-dummy-lora",
]
adapters = {str(i): file_name for i, file_name in enumerate(adapters)}
peft_config = XLoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
peft_type=PeftType.XLORA,
hidden_size=model.config.hidden_size,
adapters=adapters,
xlora_depth=8,
xlora_size=2048,
layerwise_scalings=True,
xlora_dropout_p=0.2,
)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
downloaded = huggingface_hub.hf_hub_download(repo_id=adapters["0"], filename="adapter_model.safetensors")
sd = load_file(downloaded)
w0 = model.base_model.model.model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn.q_proj.lora_A["0"].weight
w1 = sd["base_model.model.model.decoder.layers.0.self_attn.q_proj.lora_A.weight"]
assert torch.allclose(w0, w1)
|
peft/tests/test_xlora.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "peft/tests/test_xlora.py",
"repo_id": "peft",
"token_count": 6705
}
| 254
|
# Upgrading from previous versions
I generally try to maintain code interface and especially model weight compatibility across many `timm` versions. Sometimes there are exceptions.
## Checkpoint remapping
Pretrained weight remapping is handled by `checkpoint_filter_fn` in a model implementation module. This remaps old pretrained checkpoints to new, and also 3rd party (original) checkpoints to `timm` format if the model was modified when brought into `timm`.
The `checkpoint_filter_fn` is automatically called when loading pretrained weights via `pretrained=True`, but they can be called manually if you call the fn directly with the current model instance and old state dict.
## Upgrading from 0.6 and earlier
Many changes were made since the 0.6.x stable releases. They were previewed in 0.8.x dev releases but not everyone transitioned.
* `timm.models.layers` moved to `timm.layers`:
* `from timm.models.layers import name` will still work via deprecation mapping (but please transition to `timm.layers`).
* `import timm.models.layers.module` or `from timm.models.layers.module import name` needs to be changed now.
* Builder, helper, non-model modules in `timm.models` have a `_` prefix added, ie `timm.models.helpers` -> `timm.models._helpers`, there are temporary deprecation mapping files but those will be removed.
* All models now support `architecture.pretrained_tag` naming (ex `resnet50.rsb_a1`).
* The pretrained_tag is the specific weight variant (different head) for the architecture.
* Using only `architecture` defaults to the first weights in the default_cfgs for that model architecture.
* In adding pretrained tags, many model names that existed to differentiate were renamed to use the tag (ex: `vit_base_patch16_224_in21k` -> `vit_base_patch16_224.augreg_in21k`). There are deprecation mappings for these.
* A number of models had their checkpoints remapped to match architecture changes needed to better support `features_only=True`, there are `checkpoint_filter_fn` methods in any model module that was remapped. These can be passed to `timm.models.load_checkpoint(..., filter_fn=timm.models.swin_transformer_v2.checkpoint_filter_fn)` to remap your existing checkpoint.
* The Hugging Face Hub (https://huggingface.co/timm) is now the primary source for `timm` weights. Model cards include link to papers, original source, license.
* Previous 0.6.x can be cloned from [0.6.x](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/tree/0.6.x) branch or installed via pip with version.
|
pytorch-image-models/UPGRADING.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/UPGRADING.md",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 692
}
| 255
|
# Adversarial Inception v3
**Inception v3** is a convolutional neural network architecture from the Inception family that makes several improvements including using [Label Smoothing](https://paperswithcode.com/method/label-smoothing), Factorized 7 x 7 convolutions, and the use of an [auxiliary classifier](https://paperswithcode.com/method/auxiliary-classifier) to propagate label information lower down the network (along with the use of batch normalization for layers in the sidehead). The key building block is an [Inception Module](https://paperswithcode.com/method/inception-v3-module).
This particular model was trained for study of adversarial examples (adversarial training).
The weights from this model were ported from [Tensorflow/Models](https://github.com/tensorflow/models).
## How do I use this model on an image?
To load a pretrained model:
```py
>>> import timm
>>> model = timm.create_model('adv_inception_v3', pretrained=True)
>>> model.eval()
```
To load and preprocess the image:
```py
>>> import urllib
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> from timm.data import resolve_data_config
>>> from timm.data.transforms_factory import create_transform
>>> config = resolve_data_config({}, model=model)
>>> transform = create_transform(**config)
>>> url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> img = Image.open(filename).convert('RGB')
>>> tensor = transform(img).unsqueeze(0) # transform and add batch dimension
```
To get the model predictions:
```py
>>> import torch
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... out = model(tensor)
>>> probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(out[0], dim=0)
>>> print(probabilities.shape)
>>> # prints: torch.Size([1000])
```
To get the top-5 predictions class names:
```py
>>> # Get imagenet class mappings
>>> url, filename = ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/hub/master/imagenet_classes.txt", "imagenet_classes.txt")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> with open("imagenet_classes.txt", "r") as f:
... categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()]
>>> # Print top categories per image
>>> top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5)
>>> for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)):
... print(categories[top5_catid[i]], top5_prob[i].item())
>>> # prints class names and probabilities like:
>>> # [('Samoyed', 0.6425196528434753), ('Pomeranian', 0.04062102362513542), ('keeshond', 0.03186424449086189), ('white wolf', 0.01739676296710968), ('Eskimo dog', 0.011717947199940681)]
```
Replace the model name with the variant you want to use, e.g. `adv_inception_v3`. You can find the IDs in the model summaries at the top of this page.
To extract image features with this model, follow the [timm feature extraction examples](../feature_extraction), just change the name of the model you want to use.
## How do I finetune this model?
You can finetune any of the pre-trained models just by changing the classifier (the last layer).
```py
>>> model = timm.create_model('adv_inception_v3', pretrained=True, num_classes=NUM_FINETUNE_CLASSES)
```
To finetune on your own dataset, you have to write a training loop or adapt [timm's training
script](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/train.py) to use your dataset.
## How do I train this model?
You can follow the [timm recipe scripts](../training_script) for training a new model afresh.
## Citation
```BibTeX
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-1804-00097,
author = {Alexey Kurakin and
Ian J. Goodfellow and
Samy Bengio and
Yinpeng Dong and
Fangzhou Liao and
Ming Liang and
Tianyu Pang and
Jun Zhu and
Xiaolin Hu and
Cihang Xie and
Jianyu Wang and
Zhishuai Zhang and
Zhou Ren and
Alan L. Yuille and
Sangxia Huang and
Yao Zhao and
Yuzhe Zhao and
Zhonglin Han and
Junjiajia Long and
Yerkebulan Berdibekov and
Takuya Akiba and
Seiya Tokui and
Motoki Abe},
title = {Adversarial Attacks and Defences Competition},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1804.00097},
year = {2018},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.00097},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {1804.00097},
timestamp = {Thu, 31 Oct 2019 16:31:22 +0100},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-1804-00097.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}
```
<!--
Type: model-index
Collections:
- Name: Adversarial Inception v3
Paper:
Title: Adversarial Attacks and Defences Competition
URL: https://paperswithcode.com/paper/adversarial-attacks-and-defences-competition
Models:
- Name: adv_inception_v3
In Collection: Adversarial Inception v3
Metadata:
FLOPs: 7352418880
Parameters: 23830000
File Size: 95549439
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Auxiliary Classifier
- Average Pooling
- Average Pooling
- Batch Normalization
- Convolution
- Dense Connections
- Dropout
- Inception-v3 Module
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: adv_inception_v3
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '299'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/inception_v3.py#L456
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-weights/adv_inception_v3-9e27bd63.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 77.58%
Top 5 Accuracy: 93.74%
-->
|
pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/adversarial-inception-v3.mdx/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/adversarial-inception-v3.mdx",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 2250
}
| 256
|
# (Gluon) ResNet
**Residual Networks**, or **ResNets**, learn residual functions with reference to the layer inputs, instead of learning unreferenced functions. Instead of hoping each few stacked layers directly fit a desired underlying mapping, residual nets let these layers fit a residual mapping. They stack [residual blocks](https://paperswithcode.com/method/residual-block) ontop of each other to form network: e.g. a ResNet-50 has fifty layers using these blocks.
The weights from this model were ported from [Gluon](https://cv.gluon.ai/model_zoo/classification.html).
## How do I use this model on an image?
To load a pretrained model:
```py
>>> import timm
>>> model = timm.create_model('gluon_resnet101_v1b', pretrained=True)
>>> model.eval()
```
To load and preprocess the image:
```py
>>> import urllib
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> from timm.data import resolve_data_config
>>> from timm.data.transforms_factory import create_transform
>>> config = resolve_data_config({}, model=model)
>>> transform = create_transform(**config)
>>> url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> img = Image.open(filename).convert('RGB')
>>> tensor = transform(img).unsqueeze(0) # transform and add batch dimension
```
To get the model predictions:
```py
>>> import torch
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... out = model(tensor)
>>> probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(out[0], dim=0)
>>> print(probabilities.shape)
>>> # prints: torch.Size([1000])
```
To get the top-5 predictions class names:
```py
>>> # Get imagenet class mappings
>>> url, filename = ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/hub/master/imagenet_classes.txt", "imagenet_classes.txt")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> with open("imagenet_classes.txt", "r") as f:
... categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()]
>>> # Print top categories per image
>>> top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5)
>>> for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)):
... print(categories[top5_catid[i]], top5_prob[i].item())
>>> # prints class names and probabilities like:
>>> # [('Samoyed', 0.6425196528434753), ('Pomeranian', 0.04062102362513542), ('keeshond', 0.03186424449086189), ('white wolf', 0.01739676296710968), ('Eskimo dog', 0.011717947199940681)]
```
Replace the model name with the variant you want to use, e.g. `gluon_resnet101_v1b`. You can find the IDs in the model summaries at the top of this page.
To extract image features with this model, follow the [timm feature extraction examples](../feature_extraction), just change the name of the model you want to use.
## How do I finetune this model?
You can finetune any of the pre-trained models just by changing the classifier (the last layer).
```py
>>> model = timm.create_model('gluon_resnet101_v1b', pretrained=True, num_classes=NUM_FINETUNE_CLASSES)
```
To finetune on your own dataset, you have to write a training loop or adapt [timm's training
script](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/train.py) to use your dataset.
## How do I train this model?
You can follow the [timm recipe scripts](../training_script) for training a new model afresh.
## Citation
```BibTeX
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/HeZRS15,
author = {Kaiming He and
Xiangyu Zhang and
Shaoqing Ren and
Jian Sun},
title = {Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1512.03385},
year = {2015},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {1512.03385},
timestamp = {Wed, 17 Apr 2019 17:23:45 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/HeZRS15.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}
```
<!--
Type: model-index
Collections:
- Name: Gloun ResNet
Paper:
Title: Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
URL: https://paperswithcode.com/paper/deep-residual-learning-for-image-recognition
Models:
- Name: gluon_resnet101_v1b
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 10068547584
Parameters: 44550000
File Size: 178723172
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet101_v1b
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L89
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet101_v1b-3b017079.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 79.3%
Top 5 Accuracy: 94.53%
- Name: gluon_resnet101_v1c
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 10376567296
Parameters: 44570000
File Size: 178802575
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet101_v1c
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L113
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet101_v1c-1f26822a.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 79.53%
Top 5 Accuracy: 94.59%
- Name: gluon_resnet101_v1d
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 10377018880
Parameters: 44570000
File Size: 178802755
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet101_v1d
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L138
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet101_v1d-0f9c8644.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 80.4%
Top 5 Accuracy: 95.02%
- Name: gluon_resnet101_v1s
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 11805511680
Parameters: 44670000
File Size: 179221777
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet101_v1s
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L166
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet101_v1s-60fe0cc1.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 80.29%
Top 5 Accuracy: 95.16%
- Name: gluon_resnet152_v1b
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 14857660416
Parameters: 60190000
File Size: 241534001
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet152_v1b
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L97
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet152_v1b-c1edb0dd.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 79.69%
Top 5 Accuracy: 94.73%
- Name: gluon_resnet152_v1c
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 15165680128
Parameters: 60210000
File Size: 241613404
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet152_v1c
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L121
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet152_v1c-a3bb0b98.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 79.91%
Top 5 Accuracy: 94.85%
- Name: gluon_resnet152_v1d
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 15166131712
Parameters: 60210000
File Size: 241613584
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet152_v1d
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L147
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet152_v1d-bd354e12.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 80.48%
Top 5 Accuracy: 95.2%
- Name: gluon_resnet152_v1s
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 16594624512
Parameters: 60320000
File Size: 242032606
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet152_v1s
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L175
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet152_v1s-dcc41b81.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 81.02%
Top 5 Accuracy: 95.42%
- Name: gluon_resnet18_v1b
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 2337073152
Parameters: 11690000
File Size: 46816736
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet18_v1b
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L65
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet18_v1b-0757602b.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 70.84%
Top 5 Accuracy: 89.76%
- Name: gluon_resnet34_v1b
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 4718469120
Parameters: 21800000
File Size: 87295112
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet34_v1b
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L73
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet34_v1b-c6d82d59.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 74.59%
Top 5 Accuracy: 92.0%
- Name: gluon_resnet50_v1b
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 5282531328
Parameters: 25560000
File Size: 102493763
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet50_v1b
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L81
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet50_v1b-0ebe02e2.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 77.58%
Top 5 Accuracy: 93.72%
- Name: gluon_resnet50_v1c
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 5590551040
Parameters: 25580000
File Size: 102573166
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet50_v1c
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L105
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet50_v1c-48092f55.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 78.01%
Top 5 Accuracy: 93.99%
- Name: gluon_resnet50_v1d
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 5591002624
Parameters: 25580000
File Size: 102573346
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet50_v1d
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L129
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet50_v1d-818a1b1b.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 79.06%
Top 5 Accuracy: 94.46%
- Name: gluon_resnet50_v1s
In Collection: Gloun ResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 7019495424
Parameters: 25680000
File Size: 102992368
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Bottleneck Residual Block
- Convolution
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- ReLU
- Residual Block
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Data:
- ImageNet
ID: gluon_resnet50_v1s
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Image Size: '224'
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/d8e69206be253892b2956341fea09fdebfaae4e3/timm/models/gluon_resnet.py#L156
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-pretrained-gluonresnet/releases/download/v0.1/gluon_resnet50_v1s-1762acc0.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 78.7%
Top 5 Accuracy: 94.25%
-->
|
pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/gloun-resnet.mdx/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/gloun-resnet.mdx",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 7213
}
| 257
|
# MobileNet v3
**MobileNetV3** is a convolutional neural network that is designed for mobile phone CPUs. The network design includes the use of a [hard swish activation](https://paperswithcode.com/method/hard-swish) and [squeeze-and-excitation](https://paperswithcode.com/method/squeeze-and-excitation-block) modules in the [MBConv blocks](https://paperswithcode.com/method/inverted-residual-block).
## How do I use this model on an image?
To load a pretrained model:
```py
>>> import timm
>>> model = timm.create_model('mobilenetv3_large_100', pretrained=True)
>>> model.eval()
```
To load and preprocess the image:
```py
>>> import urllib
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> from timm.data import resolve_data_config
>>> from timm.data.transforms_factory import create_transform
>>> config = resolve_data_config({}, model=model)
>>> transform = create_transform(**config)
>>> url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> img = Image.open(filename).convert('RGB')
>>> tensor = transform(img).unsqueeze(0) # transform and add batch dimension
```
To get the model predictions:
```py
>>> import torch
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... out = model(tensor)
>>> probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(out[0], dim=0)
>>> print(probabilities.shape)
>>> # prints: torch.Size([1000])
```
To get the top-5 predictions class names:
```py
>>> # Get imagenet class mappings
>>> url, filename = ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/hub/master/imagenet_classes.txt", "imagenet_classes.txt")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> with open("imagenet_classes.txt", "r") as f:
... categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()]
>>> # Print top categories per image
>>> top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5)
>>> for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)):
... print(categories[top5_catid[i]], top5_prob[i].item())
>>> # prints class names and probabilities like:
>>> # [('Samoyed', 0.6425196528434753), ('Pomeranian', 0.04062102362513542), ('keeshond', 0.03186424449086189), ('white wolf', 0.01739676296710968), ('Eskimo dog', 0.011717947199940681)]
```
Replace the model name with the variant you want to use, e.g. `mobilenetv3_large_100`. You can find the IDs in the model summaries at the top of this page.
To extract image features with this model, follow the [timm feature extraction examples](../feature_extraction), just change the name of the model you want to use.
## How do I finetune this model?
You can finetune any of the pre-trained models just by changing the classifier (the last layer).
```py
>>> model = timm.create_model('mobilenetv3_large_100', pretrained=True, num_classes=NUM_FINETUNE_CLASSES)
```
To finetune on your own dataset, you have to write a training loop or adapt [timm's training
script](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/train.py) to use your dataset.
## How do I train this model?
You can follow the [timm recipe scripts](../training_script) for training a new model afresh.
## Citation
```BibTeX
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-1905-02244,
author = {Andrew Howard and
Mark Sandler and
Grace Chu and
Liang{-}Chieh Chen and
Bo Chen and
Mingxing Tan and
Weijun Wang and
Yukun Zhu and
Ruoming Pang and
Vijay Vasudevan and
Quoc V. Le and
Hartwig Adam},
title = {Searching for MobileNetV3},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1905.02244},
year = {2019},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {1905.02244},
timestamp = {Tue, 12 Jan 2021 15:30:06 +0100},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-1905-02244.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}
```
<!--
Type: model-index
Collections:
- Name: MobileNet V3
Paper:
Title: Searching for MobileNetV3
URL: https://paperswithcode.com/paper/searching-for-mobilenetv3
Models:
- Name: mobilenetv3_large_100
In Collection: MobileNet V3
Metadata:
FLOPs: 287193752
Parameters: 5480000
File Size: 22076443
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Convolution
- Dense Connections
- Depthwise Separable Convolution
- Dropout
- Global Average Pooling
- Hard Swish
- Inverted Residual Block
- ReLU
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
- Squeeze-and-Excitation Block
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Techniques:
- RMSProp
- Weight Decay
Training Data:
- ImageNet
Training Resources: 4x4 TPU Pod
ID: mobilenetv3_large_100
LR: 0.1
Dropout: 0.8
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Momentum: 0.9
Batch Size: 4096
Image Size: '224'
Weight Decay: 1.0e-05
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/9a25fdf3ad0414b4d66da443fe60ae0aa14edc84/timm/models/mobilenetv3.py#L363
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-weights/mobilenetv3_large_100_ra-f55367f5.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 75.77%
Top 5 Accuracy: 92.54%
- Name: mobilenetv3_rw
In Collection: MobileNet V3
Metadata:
FLOPs: 287190638
Parameters: 5480000
File Size: 22064048
Architecture:
- 1x1 Convolution
- Batch Normalization
- Convolution
- Dense Connections
- Depthwise Separable Convolution
- Dropout
- Global Average Pooling
- Hard Swish
- Inverted Residual Block
- ReLU
- Residual Connection
- Softmax
- Squeeze-and-Excitation Block
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Techniques:
- RMSProp
- Weight Decay
Training Data:
- ImageNet
Training Resources: 4x4 TPU Pod
ID: mobilenetv3_rw
LR: 0.1
Dropout: 0.8
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Momentum: 0.9
Batch Size: 4096
Image Size: '224'
Weight Decay: 1.0e-05
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/9a25fdf3ad0414b4d66da443fe60ae0aa14edc84/timm/models/mobilenetv3.py#L384
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-weights/mobilenetv3_100-35495452.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 75.62%
Top 5 Accuracy: 92.71%
-->
|
pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/mobilenet-v3.mdx/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/mobilenet-v3.mdx",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 2582
}
| 258
|
# SK-ResNet
**SK ResNet** is a variant of a [ResNet](https://www.paperswithcode.com/method/resnet) that employs a [Selective Kernel](https://paperswithcode.com/method/selective-kernel) unit. In general, all the large kernel convolutions in the original bottleneck blocks in ResNet are replaced by the proposed [SK convolutions](https://paperswithcode.com/method/selective-kernel-convolution), enabling the network to choose appropriate receptive field sizes in an adaptive manner.
## How do I use this model on an image?
To load a pretrained model:
```py
>>> import timm
>>> model = timm.create_model('skresnet18', pretrained=True)
>>> model.eval()
```
To load and preprocess the image:
```py
>>> import urllib
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> from timm.data import resolve_data_config
>>> from timm.data.transforms_factory import create_transform
>>> config = resolve_data_config({}, model=model)
>>> transform = create_transform(**config)
>>> url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> img = Image.open(filename).convert('RGB')
>>> tensor = transform(img).unsqueeze(0) # transform and add batch dimension
```
To get the model predictions:
```py
>>> import torch
>>> with torch.inference_mode():
... out = model(tensor)
>>> probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(out[0], dim=0)
>>> print(probabilities.shape)
>>> # prints: torch.Size([1000])
```
To get the top-5 predictions class names:
```py
>>> # Get imagenet class mappings
>>> url, filename = ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/hub/master/imagenet_classes.txt", "imagenet_classes.txt")
>>> urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
>>> with open("imagenet_classes.txt", "r") as f:
... categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()]
>>> # Print top categories per image
>>> top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5)
>>> for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)):
... print(categories[top5_catid[i]], top5_prob[i].item())
>>> # prints class names and probabilities like:
>>> # [('Samoyed', 0.6425196528434753), ('Pomeranian', 0.04062102362513542), ('keeshond', 0.03186424449086189), ('white wolf', 0.01739676296710968), ('Eskimo dog', 0.011717947199940681)]
```
Replace the model name with the variant you want to use, e.g. `skresnet18`. You can find the IDs in the model summaries at the top of this page.
To extract image features with this model, follow the [timm feature extraction examples](../feature_extraction), just change the name of the model you want to use.
## How do I finetune this model?
You can finetune any of the pre-trained models just by changing the classifier (the last layer).
```py
>>> model = timm.create_model('skresnet18', pretrained=True, num_classes=NUM_FINETUNE_CLASSES)
```
To finetune on your own dataset, you have to write a training loop or adapt [timm's training
script](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/train.py) to use your dataset.
## How do I train this model?
You can follow the [timm recipe scripts](../training_script) for training a new model afresh.
## Citation
```BibTeX
@misc{li2019selective,
title={Selective Kernel Networks},
author={Xiang Li and Wenhai Wang and Xiaolin Hu and Jian Yang},
year={2019},
eprint={1903.06586},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
```
<!--
Type: model-index
Collections:
- Name: SKResNet
Paper:
Title: Selective Kernel Networks
URL: https://paperswithcode.com/paper/selective-kernel-networks
Models:
- Name: skresnet18
In Collection: SKResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 2333467136
Parameters: 11960000
File Size: 47923238
Architecture:
- Convolution
- Dense Connections
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- Residual Connection
- Selective Kernel
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Techniques:
- SGD with Momentum
- Weight Decay
Training Data:
- ImageNet
Training Resources: 8x GPUs
ID: skresnet18
LR: 0.1
Epochs: 100
Layers: 18
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Momentum: 0.9
Batch Size: 256
Image Size: '224'
Weight Decay: 4.0e-05
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/a7f95818e44b281137503bcf4b3e3e94d8ffa52f/timm/models/sknet.py#L148
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-weights/skresnet18_ra-4eec2804.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 73.03%
Top 5 Accuracy: 91.17%
- Name: skresnet34
In Collection: SKResNet
Metadata:
FLOPs: 4711849952
Parameters: 22280000
File Size: 89299314
Architecture:
- Convolution
- Dense Connections
- Global Average Pooling
- Max Pooling
- Residual Connection
- Selective Kernel
- Softmax
Tasks:
- Image Classification
Training Techniques:
- SGD with Momentum
- Weight Decay
Training Data:
- ImageNet
Training Resources: 8x GPUs
ID: skresnet34
LR: 0.1
Epochs: 100
Layers: 34
Crop Pct: '0.875'
Momentum: 0.9
Batch Size: 256
Image Size: '224'
Weight Decay: 4.0e-05
Interpolation: bicubic
Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/a7f95818e44b281137503bcf4b3e3e94d8ffa52f/timm/models/sknet.py#L165
Weights: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-weights/skresnet34_ra-bdc0ccde.pth
Results:
- Task: Image Classification
Dataset: ImageNet
Metrics:
Top 1 Accuracy: 76.93%
Top 5 Accuracy: 93.32%
-->
|
pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/skresnet.mdx/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/models/skresnet.mdx",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 2085
}
| 259
|
# Data
[[autodoc]] timm.data.create_dataset
[[autodoc]] timm.data.create_loader
[[autodoc]] timm.data.create_transform
[[autodoc]] timm.data.resolve_data_config
|
pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/reference/data.mdx/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/hfdocs/source/reference/data.mdx",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 67
}
| 260
|
"""Patch-level random erasing augmentation for NaFlex Vision Transformers.
This module implements random erasing specifically designed for patchified images,
operating at the patch granularity rather than pixel level. It supports two modes:
- 'patch': Randomly erases individual patches (speckle-like noise)
- 'region': Erases contiguous rectangular regions of patches (similar to original RandomErasing)
The implementation is coordinate-aware, respecting valid patch boundaries and supporting
variable patch sizes in NaFlex training.
Hacked together by / Copyright 2025, Ross Wightman, Hugging Face
"""
import random
import math
from typing import Optional, Union, Tuple
import torch
class PatchRandomErasing:
"""Random erasing for patchified images in NaFlex format.
Supports two modes:
1. 'patch': Simple mode that erases randomly selected valid patches
2. 'region': Erases rectangular regions at patch granularity
"""
def __init__(
self,
erase_prob: float = 0.5,
patch_drop_prob: float = 0.0,
min_count: int = 1,
max_count: Optional[int] = None,
min_area: float = 0.02,
max_area: float = 1 / 3,
min_aspect: float = 0.3,
max_aspect: Optional[float] = None,
mode: str = 'const',
value: float = 0.,
spatial_mode: str = 'region',
num_splits: int = 0,
device: Union[str, torch.device] = 'cuda',
) -> None:
"""Initialize PatchRandomErasing.
Args:
erase_prob: Probability that the Random Erasing operation will be performed.
patch_drop_prob: Patch dropout probability. Remove random patches instead of erasing.
min_count: Minimum number of erasing operations.
max_count: Maximum number of erasing operations.
min_area: Minimum percentage of valid patches/area to erase.
max_area: Maximum percentage of valid patches/area to erase.
min_aspect: Minimum aspect ratio of erased area (only used in 'region' mode).
max_aspect: Maximum aspect ratio of erased area (only used in 'region' mode).
mode: Patch content mode, one of 'const', 'rand', or 'pixel'.
value: Constant value for 'const' mode.
spatial_mode: Erasing strategy, one of 'patch' or 'region'.
num_splits: Number of splits to apply erasing to (0 for all).
device: Computation device.
"""
self.erase_prob = erase_prob
self.patch_drop_prob = patch_drop_prob
self.min_count = min_count
self.max_count = max_count or min_count
self.min_area = min_area
self.max_area = max_area
# Aspect ratio params (for region mode)
max_aspect = max_aspect or 1 / min_aspect
self.log_aspect_ratio = (math.log(min_aspect), math.log(max_aspect))
# Number of splits
self.num_splits = num_splits
self.device = device
# Strategy mode
self.spatial_mode = spatial_mode
assert self.spatial_mode in ('patch', 'region')
# Value generation mode flags
self.erase_mode = mode.lower()
assert self.erase_mode in ('rand', 'pixel', 'const')
self.const_value = value
self.unique_noise_per_patch = True
def _get_values(
self,
shape: Union[Tuple[int, ...], torch.Size],
value: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
dtype: torch.dtype = torch.float32,
device: Optional[Union[str, torch.device]] = None
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Generate values for erased patches based on the specified mode.
Args:
shape: Shape of patches to erase.
value: Value to use in const (or rand) mode.
dtype: Data type to use.
device: Device to use.
Returns:
Tensor with values for erasing patches.
"""
device = device or self.device
if self.erase_mode == 'pixel':
# only mode with erase shape that includes pixels
return torch.empty(shape, dtype=dtype, device=device).normal_()
else:
shape = (1, 1, shape[-1]) if len(shape) == 3 else (1, shape[-1])
if self.erase_mode == 'const' or value is not None:
erase_value = value or self.const_value
if isinstance(erase_value, (int, float)):
values = torch.full(shape, erase_value, dtype=dtype, device=device)
else:
erase_value = torch.tensor(erase_value, dtype=dtype, device=device)
values = torch.expand_copy(erase_value, shape)
else:
values = torch.empty(shape, dtype=dtype, device=device).normal_()
return values
def _drop_patches(
self,
patches: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
patch_valid: torch.Tensor,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""Patch Dropout.
Fully drops patches from datastream. Only mode that saves compute BUT requires support
for non-contiguous patches and associated patch coordinate and valid handling.
Args:
patches: Tensor of patches.
patch_coord: Tensor of patch coordinates.
patch_valid: Tensor indicating which patches are valid.
Returns:
Tuple of (patches, patch_coord, patch_valid) with some patches dropped.
"""
# FIXME WIP, not completed. Downstream support in model needed for non-contiguous valid patches
if random.random() > self.erase_prob:
return
# Get indices of valid patches
valid_indices = torch.nonzero(patch_valid, as_tuple=True)[0].tolist()
# Skip if no valid patches
if not valid_indices:
return patches, patch_coord, patch_valid
num_valid = len(valid_indices)
if self.patch_drop_prob:
# patch dropout mode, completely remove dropped patches (FIXME needs downstream support in model)
num_keep = max(1, int(num_valid * (1. - self.patch_drop_prob)))
keep_indices = torch.argsort(torch.randn(1, num_valid, device=self.device), dim=-1)[:, :num_keep]
# maintain patch order, possibly useful for debug / visualization
keep_indices = keep_indices.sort(dim=-1)[0]
patches = patches.gather(1, keep_indices.unsqueeze(-1).expand((-1, -1) + patches.shape[2:]))
return patches, patch_coord, patch_valid
def _erase_patches(
self,
patches: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
patch_valid: torch.Tensor,
patch_shape: torch.Size,
dtype: torch.dtype = torch.float32,
) -> None:
"""Apply erasing by selecting individual patches randomly.
The simplest mode, aligned on patch boundaries. Behaves similarly to speckle or 'sprinkles'
noise augmentation at patch size.
Args:
patches: Tensor of patches to modify in-place.
patch_coord: Tensor of patch coordinates.
patch_valid: Tensor indicating which patches are valid.
patch_shape: Shape of individual patches.
dtype: Data type for generated values.
"""
if random.random() > self.erase_prob:
return
# Get indices of valid patches
valid_indices = torch.nonzero(patch_valid, as_tuple=True)[0]
num_valid = len(valid_indices)
if num_valid == 0:
return
count = random.randint(self.min_count, self.max_count)
# Determine how many valid patches to erase from RE min/max count and area args
max_erase = min(num_valid, max(1, int(num_valid * count * self.max_area)))
min_erase = max(1, int(num_valid * count * self.min_area))
num_erase = random.randint(min_erase, max_erase)
# Randomly select valid patches to erase
erase_idx = valid_indices[torch.randperm(num_valid, device=patches.device)[:num_erase]]
if self.unique_noise_per_patch and self.erase_mode == 'pixel':
# generate unique noise for the whole selection of patches
fill_shape = (num_erase,) + patch_shape
else:
fill_shape = patch_shape
patches[erase_idx] = self._get_values(fill_shape, dtype=dtype)
def _erase_region(
self,
patches: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
patch_valid: torch.Tensor,
patch_shape: torch.Size,
dtype: torch.dtype = torch.float32,
) -> None:
"""Apply erasing by selecting rectangular regions of patches randomly.
Closer to the original RandomErasing implementation. Erases
spatially contiguous rectangular regions of patches (aligned with patches).
Args:
patches: Tensor of patches to modify in-place.
patch_coord: Tensor of patch coordinates.
patch_valid: Tensor indicating which patches are valid.
patch_shape: Shape of individual patches.
dtype: Data type for generated values.
"""
if random.random() > self.erase_prob:
return
# Determine grid dimensions from coordinates
valid_coord = patch_coord[patch_valid]
if len(valid_coord) == 0:
return # No valid patches
max_y = valid_coord[:, 0].max().item() + 1
max_x = valid_coord[:, 1].max().item() + 1
grid_h, grid_w = max_y, max_x
total_area = grid_h * grid_w
ys, xs = patch_coord[:, 0], patch_coord[:, 1]
count = random.randint(self.min_count, self.max_count)
for _ in range(count):
# Try to select a valid region to erase (multiple attempts)
for attempt in range(10):
# Sample random area and aspect ratio
target_area = random.uniform(self.min_area, self.max_area) * total_area
aspect_ratio = math.exp(random.uniform(*self.log_aspect_ratio))
# Calculate region height and width
h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
if h > grid_h or w > grid_w:
continue # try again
# Calculate region patch bounds
top = random.randint(0, grid_h - h)
left = random.randint(0, grid_w - w)
bottom, right = top + h, left + w
# Region test
region_mask = (
(ys >= top) & (ys < bottom) &
(xs >= left) & (xs < right) &
patch_valid
)
num_selected = int(region_mask.sum().item())
if not num_selected:
continue # no patch actually falls inside – try again
if self.unique_noise_per_patch and self.erase_mode == 'pixel':
# generate unique noise for the whole region
fill_shape = (num_selected,) + patch_shape
else:
fill_shape = patch_shape
patches[region_mask] = self._get_values(fill_shape, dtype=dtype)
# Successfully applied erasing, exit the loop
break
def __call__(
self,
patches: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Apply random patch erasing.
Args:
patches: Tensor of shape [B, N, P*P, C] or [B, N, Ph, Pw, C].
patch_coord: Tensor of shape [B, N, 2] with (y, x) coordinates.
patch_valid: Boolean tensor of shape [B, N] indicating which patches are valid.
Returns:
Erased patches tensor of same shape as input.
"""
if patches.ndim == 4:
batch_size, num_patches, patch_dim, channels = patches.shape
elif patches.ndim == 5:
batch_size, num_patches, patch_h, patch_w, channels = patches.shape
else:
assert False
patch_shape = patches.shape[2:]
# patch_shape ==> shape of patches to fill (h, w, c) or (h * w, c)
# Create default valid mask if not provided
if patch_valid is None:
patch_valid = torch.ones((batch_size, num_patches), dtype=torch.bool, device=patches.device)
# Skip the first part of the batch if num_splits is set
batch_start = batch_size // self.num_splits if self.num_splits > 1 else 0
# Apply erasing to each batch element
for i in range(batch_start, batch_size):
if self.patch_drop_prob:
assert False, "WIP, not completed"
self._drop_patches(
patches[i],
patch_coord[i],
patch_valid[i],
)
elif self.spatial_mode == 'patch':
# FIXME we could vectorize patch mode across batch, worth the effort?
self._erase_patches(
patches[i],
patch_coord[i],
patch_valid[i],
patch_shape,
patches.dtype
)
elif self.spatial_mode == 'region':
self._erase_region(
patches[i],
patch_coord[i],
patch_valid[i],
patch_shape,
patches.dtype
)
else:
assert False
return patches
def __repr__(self) -> str:
"""Return string representation of PatchRandomErasing.
Returns:
String representation of the object.
"""
fs = self.__class__.__name__ + f'(p={self.erase_prob}, mode={self.erase_mode}'
fs += f', spatial={self.spatial_mode}, area=({self.min_area}, {self.max_area}))'
fs += f', count=({self.min_count}, {self.max_count}))'
return fs
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/data/naflex_random_erasing.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/data/naflex_random_erasing.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 6484
}
| 261
|
""" Real labels evaluator for ImageNet
Paper: `Are we done with ImageNet?` - https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.07159
Based on Numpy example at https://github.com/google-research/reassessed-imagenet
Hacked together by / Copyright 2020 Ross Wightman
"""
import os
import json
import numpy as np
import pkgutil
class RealLabelsImagenet:
def __init__(self, filenames, real_json=None, topk=(1, 5)):
if real_json is not None:
with open(real_json) as real_labels:
real_labels = json.load(real_labels)
else:
real_labels = json.loads(
pkgutil.get_data(__name__, os.path.join('_info', 'imagenet_real_labels.json')).decode('utf-8'))
real_labels = {f'ILSVRC2012_val_{i + 1:08d}.JPEG': labels for i, labels in enumerate(real_labels)}
self.real_labels = real_labels
self.filenames = filenames
assert len(self.filenames) == len(self.real_labels)
self.topk = topk
self.is_correct = {k: [] for k in topk}
self.sample_idx = 0
def add_result(self, output):
maxk = max(self.topk)
_, pred_batch = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
pred_batch = pred_batch.cpu().numpy()
for pred in pred_batch:
filename = self.filenames[self.sample_idx]
filename = os.path.basename(filename)
if self.real_labels[filename]:
for k in self.topk:
self.is_correct[k].append(
any([p in self.real_labels[filename] for p in pred[:k]]))
self.sample_idx += 1
def get_accuracy(self, k=None):
if k is None:
return {k: float(np.mean(self.is_correct[k])) * 100 for k in self.topk}
else:
return float(np.mean(self.is_correct[k])) * 100
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/data/real_labels.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/data/real_labels.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 854
}
| 262
|
""" Classifier head and layer factory
Hacked together by / Copyright 2020 Ross Wightman
"""
from collections import OrderedDict
from functools import partial
from typing import Optional, Union, Callable
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from .adaptive_avgmax_pool import SelectAdaptivePool2d
from .create_act import get_act_layer
from .create_norm import get_norm_layer
def _create_pool(
num_features: int,
num_classes: int,
pool_type: str = 'avg',
use_conv: bool = False,
input_fmt: Optional[str] = None,
):
flatten_in_pool = not use_conv # flatten when we use a Linear layer after pooling
if not pool_type:
flatten_in_pool = False # disable flattening if pooling is pass-through (no pooling)
global_pool = SelectAdaptivePool2d(
pool_type=pool_type,
flatten=flatten_in_pool,
input_fmt=input_fmt,
)
num_pooled_features = num_features * global_pool.feat_mult()
return global_pool, num_pooled_features
def _create_fc(num_features, num_classes, use_conv=False):
if num_classes <= 0:
fc = nn.Identity() # pass-through (no classifier)
elif use_conv:
fc = nn.Conv2d(num_features, num_classes, 1, bias=True)
else:
fc = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes, bias=True)
return fc
def create_classifier(
num_features: int,
num_classes: int,
pool_type: str = 'avg',
use_conv: bool = False,
input_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
drop_rate: Optional[float] = None,
):
global_pool, num_pooled_features = _create_pool(
num_features,
num_classes,
pool_type,
use_conv=use_conv,
input_fmt=input_fmt,
)
fc = _create_fc(
num_pooled_features,
num_classes,
use_conv=use_conv,
)
if drop_rate is not None:
dropout = nn.Dropout(drop_rate)
return global_pool, dropout, fc
return global_pool, fc
class ClassifierHead(nn.Module):
"""Classifier head w/ configurable global pooling and dropout."""
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int,
num_classes: int,
pool_type: str = 'avg',
drop_rate: float = 0.,
use_conv: bool = False,
input_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
):
"""
Args:
in_features: The number of input features.
num_classes: The number of classes for the final classifier layer (output).
pool_type: Global pooling type, pooling disabled if empty string ('').
drop_rate: Pre-classifier dropout rate.
"""
super(ClassifierHead, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.use_conv = use_conv
self.input_fmt = input_fmt
global_pool, fc = create_classifier(
in_features,
num_classes,
pool_type,
use_conv=use_conv,
input_fmt=input_fmt,
)
self.global_pool = global_pool
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop_rate)
self.fc = fc
self.flatten = nn.Flatten(1) if use_conv and pool_type else nn.Identity()
def reset(self, num_classes: int, pool_type: Optional[str] = None):
if pool_type is not None and pool_type != self.global_pool.pool_type:
self.global_pool, self.fc = create_classifier(
self.in_features,
num_classes,
pool_type=pool_type,
use_conv=self.use_conv,
input_fmt=self.input_fmt,
)
self.flatten = nn.Flatten(1) if self.use_conv and pool_type else nn.Identity()
else:
num_pooled_features = self.in_features * self.global_pool.feat_mult()
self.fc = _create_fc(
num_pooled_features,
num_classes,
use_conv=self.use_conv,
)
def forward(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
x = self.global_pool(x)
x = self.drop(x)
if pre_logits:
return self.flatten(x)
x = self.fc(x)
return self.flatten(x)
class NormMlpClassifierHead(nn.Module):
""" A Pool -> Norm -> Mlp Classifier Head for '2D' NCHW tensors
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int,
num_classes: int,
hidden_size: Optional[int] = None,
pool_type: str = 'avg',
drop_rate: float = 0.,
norm_layer: Union[str, Callable] = 'layernorm2d',
act_layer: Union[str, Callable] = 'tanh',
):
"""
Args:
in_features: The number of input features.
num_classes: The number of classes for the final classifier layer (output).
hidden_size: The hidden size of the MLP (pre-logits FC layer) if not None.
pool_type: Global pooling type, pooling disabled if empty string ('').
drop_rate: Pre-classifier dropout rate.
norm_layer: Normalization layer type.
act_layer: MLP activation layer type (only used if hidden_size is not None).
"""
super().__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_features = in_features
self.use_conv = not pool_type
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_layer)
act_layer = get_act_layer(act_layer)
linear_layer = partial(nn.Conv2d, kernel_size=1) if self.use_conv else nn.Linear
self.global_pool = SelectAdaptivePool2d(pool_type=pool_type)
self.norm = norm_layer(in_features)
self.flatten = nn.Flatten(1) if pool_type else nn.Identity()
if hidden_size:
self.pre_logits = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('fc', linear_layer(in_features, hidden_size)),
('act', act_layer()),
]))
self.num_features = hidden_size
else:
self.pre_logits = nn.Identity()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop_rate)
self.fc = linear_layer(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def reset(self, num_classes: int, pool_type: Optional[str] = None):
if pool_type is not None:
self.global_pool = SelectAdaptivePool2d(pool_type=pool_type)
self.flatten = nn.Flatten(1) if pool_type else nn.Identity()
self.use_conv = self.global_pool.is_identity()
linear_layer = partial(nn.Conv2d, kernel_size=1) if self.use_conv else nn.Linear
if self.hidden_size:
if ((isinstance(self.pre_logits.fc, nn.Conv2d) and not self.use_conv) or
(isinstance(self.pre_logits.fc, nn.Linear) and self.use_conv)):
with torch.no_grad():
new_fc = linear_layer(self.in_features, self.hidden_size)
new_fc.weight.copy_(self.pre_logits.fc.weight.reshape(new_fc.weight.shape))
new_fc.bias.copy_(self.pre_logits.fc.bias)
self.pre_logits.fc = new_fc
self.fc = linear_layer(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
x = self.global_pool(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.pre_logits(x)
x = self.drop(x)
if pre_logits:
return x
x = self.fc(x)
return x
class ClNormMlpClassifierHead(nn.Module):
""" A Pool -> Norm -> Mlp Classifier Head for n-D NxxC tensors
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int,
num_classes: int,
hidden_size: Optional[int] = None,
pool_type: str = 'avg',
drop_rate: float = 0.,
norm_layer: Union[str, Callable] = 'layernorm',
act_layer: Union[str, Callable] = 'gelu',
input_fmt: str = 'NHWC',
):
"""
Args:
in_features: The number of input features.
num_classes: The number of classes for the final classifier layer (output).
hidden_size: The hidden size of the MLP (pre-logits FC layer) if not None.
pool_type: Global pooling type, pooling disabled if empty string ('').
drop_rate: Pre-classifier dropout rate.
norm_layer: Normalization layer type.
act_layer: MLP activation layer type (only used if hidden_size is not None).
"""
super().__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_features = in_features
assert pool_type in ('', 'avg', 'max', 'avgmax')
self.pool_type = pool_type
assert input_fmt in ('NHWC', 'NLC')
self.pool_dim = 1 if input_fmt == 'NLC' else (1, 2)
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_layer)
act_layer = get_act_layer(act_layer)
self.norm = norm_layer(in_features)
if hidden_size:
self.pre_logits = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('fc', nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_size)),
('act', act_layer()),
]))
self.num_features = hidden_size
else:
self.pre_logits = nn.Identity()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop_rate)
self.fc = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def reset(self, num_classes: int, pool_type: Optional[str] = None, reset_other: bool = False):
if pool_type is not None:
self.pool_type = pool_type
if reset_other:
self.pre_logits = nn.Identity()
self.norm = nn.Identity()
self.fc = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def _global_pool(self, x):
if self.pool_type:
if self.pool_type == 'avg':
x = x.mean(dim=self.pool_dim)
elif self.pool_type == 'max':
x = x.amax(dim=self.pool_dim)
elif self.pool_type == 'avgmax':
x = 0.5 * (x.amax(dim=self.pool_dim) + x.mean(dim=self.pool_dim))
return x
def forward(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
x = self._global_pool(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.pre_logits(x)
x = self.drop(x)
if pre_logits:
return x
x = self.fc(x)
return x
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/classifier.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/classifier.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 5047
}
| 263
|
""" Gather-Excite Attention Block
Paper: `Gather-Excite: Exploiting Feature Context in CNNs` - https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.12348
Official code here, but it's only partial impl in Caffe: https://github.com/hujie-frank/GENet
I've tried to support all of the extent both w/ and w/o params. I don't believe I've seen another
impl that covers all of the cases.
NOTE: extent=0 + extra_params=False is equivalent to Squeeze-and-Excitation
Hacked together by / Copyright 2021 Ross Wightman
"""
import math
from torch import nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from .create_act import create_act_layer, get_act_layer
from .create_conv2d import create_conv2d
from .helpers import make_divisible
from .mlp import ConvMlp
class GatherExcite(nn.Module):
""" Gather-Excite Attention Module
"""
def __init__(
self, channels, feat_size=None, extra_params=False, extent=0, use_mlp=True,
rd_ratio=1./16, rd_channels=None, rd_divisor=1, add_maxpool=False,
act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, gate_layer='sigmoid'):
super(GatherExcite, self).__init__()
self.add_maxpool = add_maxpool
act_layer = get_act_layer(act_layer)
self.extent = extent
if extra_params:
self.gather = nn.Sequential()
if extent == 0:
assert feat_size is not None, 'spatial feature size must be specified for global extent w/ params'
self.gather.add_module(
'conv1', create_conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=feat_size, stride=1, depthwise=True))
if norm_layer:
self.gather.add_module(f'norm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(channels))
else:
assert extent % 2 == 0
num_conv = int(math.log2(extent))
for i in range(num_conv):
self.gather.add_module(
f'conv{i + 1}',
create_conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, depthwise=True))
if norm_layer:
self.gather.add_module(f'norm{i + 1}', nn.BatchNorm2d(channels))
if i != num_conv - 1:
self.gather.add_module(f'act{i + 1}', act_layer(inplace=True))
else:
self.gather = None
if self.extent == 0:
self.gk = 0
self.gs = 0
else:
assert extent % 2 == 0
self.gk = self.extent * 2 - 1
self.gs = self.extent
if not rd_channels:
rd_channels = make_divisible(channels * rd_ratio, rd_divisor, round_limit=0.)
self.mlp = ConvMlp(channels, rd_channels, act_layer=act_layer) if use_mlp else nn.Identity()
self.gate = create_act_layer(gate_layer)
def forward(self, x):
size = x.shape[-2:]
if self.gather is not None:
x_ge = self.gather(x)
else:
if self.extent == 0:
# global extent
x_ge = x.mean(dim=(2, 3), keepdims=True)
if self.add_maxpool:
# experimental codepath, may remove or change
x_ge = 0.5 * x_ge + 0.5 * x.amax((2, 3), keepdim=True)
else:
x_ge = F.avg_pool2d(
x, kernel_size=self.gk, stride=self.gs, padding=self.gk // 2, count_include_pad=False)
if self.add_maxpool:
# experimental codepath, may remove or change
x_ge = 0.5 * x_ge + 0.5 * F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=self.gk, stride=self.gs, padding=self.gk // 2)
x_ge = self.mlp(x_ge)
if x_ge.shape[-1] != 1 or x_ge.shape[-2] != 1:
x_ge = F.interpolate(x_ge, size=size)
return x * self.gate(x_ge)
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/gather_excite.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/gather_excite.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 1956
}
| 264
|
""" Bilinear-Attention-Transform and Non-Local Attention
Paper: `Non-Local Neural Networks With Grouped Bilinear Attentional Transforms`
- https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/html/Chi_Non-Local_Neural_Networks_With_Grouped_Bilinear_Attentional_Transforms_CVPR_2020_paper.html
Adapted from original code: https://github.com/BA-Transform/BAT-Image-Classification
"""
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from ._fx import register_notrace_module
from .conv_bn_act import ConvNormAct
from .helpers import make_divisible
from .trace_utils import _assert
class NonLocalAttn(nn.Module):
"""Spatial NL block for image classification.
This was adapted from https://github.com/BA-Transform/BAT-Image-Classification
Their NonLocal impl inspired by https://github.com/facebookresearch/video-nonlocal-net.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, use_scale=True, rd_ratio=1/8, rd_channels=None, rd_divisor=8, **kwargs):
super(NonLocalAttn, self).__init__()
if rd_channels is None:
rd_channels = make_divisible(in_channels * rd_ratio, divisor=rd_divisor)
self.scale = in_channels ** -0.5 if use_scale else 1.0
self.t = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, rd_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True)
self.p = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, rd_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True)
self.g = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, rd_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True)
self.z = nn.Conv2d(rd_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True)
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels)
self.reset_parameters()
def forward(self, x):
shortcut = x
t = self.t(x)
p = self.p(x)
g = self.g(x)
B, C, H, W = t.size()
t = t.view(B, C, -1).permute(0, 2, 1)
p = p.view(B, C, -1)
g = g.view(B, C, -1).permute(0, 2, 1)
att = torch.bmm(t, p) * self.scale
att = F.softmax(att, dim=2)
x = torch.bmm(att, g)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1).reshape(B, C, H, W)
x = self.z(x)
x = self.norm(x) + shortcut
return x
def reset_parameters(self):
for name, m in self.named_modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(
m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if len(list(m.parameters())) > 1:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.GroupNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
@register_notrace_module
class BilinearAttnTransform(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, block_size, groups, act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
super(BilinearAttnTransform, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = ConvNormAct(in_channels, groups, 1, act_layer=act_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer)
self.conv_p = nn.Conv2d(groups, block_size * block_size * groups, kernel_size=(block_size, 1))
self.conv_q = nn.Conv2d(groups, block_size * block_size * groups, kernel_size=(1, block_size))
self.conv2 = ConvNormAct(in_channels, in_channels, 1, act_layer=act_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer)
self.block_size = block_size
self.groups = groups
self.in_channels = in_channels
def resize_mat(self, x, t: int):
B, C, block_size, block_size1 = x.shape
_assert(block_size == block_size1, '')
if t <= 1:
return x
x = x.view(B * C, -1, 1, 1)
x = x * torch.eye(t, t, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
x = x.view(B * C, block_size, block_size, t, t)
x = torch.cat(torch.split(x, 1, dim=1), dim=3)
x = torch.cat(torch.split(x, 1, dim=2), dim=4)
x = x.view(B, C, block_size * t, block_size * t)
return x
def forward(self, x):
_assert(x.shape[-1] % self.block_size == 0, '')
_assert(x.shape[-2] % self.block_size == 0, '')
B, C, H, W = x.shape
out = self.conv1(x)
rp = F.adaptive_max_pool2d(out, (self.block_size, 1))
cp = F.adaptive_max_pool2d(out, (1, self.block_size))
p = self.conv_p(rp).view(B, self.groups, self.block_size, self.block_size).sigmoid()
q = self.conv_q(cp).view(B, self.groups, self.block_size, self.block_size).sigmoid()
p = p / p.sum(dim=3, keepdim=True)
q = q / q.sum(dim=2, keepdim=True)
p = p.view(B, self.groups, 1, self.block_size, self.block_size).expand(x.size(
0), self.groups, C // self.groups, self.block_size, self.block_size).contiguous()
p = p.view(B, C, self.block_size, self.block_size)
q = q.view(B, self.groups, 1, self.block_size, self.block_size).expand(x.size(
0), self.groups, C // self.groups, self.block_size, self.block_size).contiguous()
q = q.view(B, C, self.block_size, self.block_size)
p = self.resize_mat(p, H // self.block_size)
q = self.resize_mat(q, W // self.block_size)
y = p.matmul(x)
y = y.matmul(q)
y = self.conv2(y)
return y
class BatNonLocalAttn(nn.Module):
""" BAT
Adapted from: https://github.com/BA-Transform/BAT-Image-Classification
"""
def __init__(
self, in_channels, block_size=7, groups=2, rd_ratio=0.25, rd_channels=None, rd_divisor=8,
drop_rate=0.2, act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, **_):
super().__init__()
if rd_channels is None:
rd_channels = make_divisible(in_channels * rd_ratio, divisor=rd_divisor)
self.conv1 = ConvNormAct(in_channels, rd_channels, 1, act_layer=act_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer)
self.ba = BilinearAttnTransform(rd_channels, block_size, groups, act_layer=act_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer)
self.conv2 = ConvNormAct(rd_channels, in_channels, 1, act_layer=act_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p=drop_rate)
def forward(self, x):
xl = self.conv1(x)
y = self.ba(xl)
y = self.conv2(y)
y = self.dropout(y)
return y + x
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/non_local_attn.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/non_local_attn.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 3047
}
| 265
|
""" Squeeze-and-Excitation Channel Attention
An SE implementation originally based on PyTorch SE-Net impl.
Has since evolved with additional functionality / configuration.
Paper: `Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks` - https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01507
Also included is Effective Squeeze-Excitation (ESE).
Paper: `CenterMask : Real-Time Anchor-Free Instance Segmentation` - https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.06667
Hacked together by / Copyright 2021 Ross Wightman
"""
from torch import nn as nn
from .create_act import create_act_layer
from .helpers import make_divisible
class SEModule(nn.Module):
""" SE Module as defined in original SE-Nets with a few additions
Additions include:
* divisor can be specified to keep channels % div == 0 (default: 8)
* reduction channels can be specified directly by arg (if rd_channels is set)
* reduction channels can be specified by float rd_ratio (default: 1/16)
* global max pooling can be added to the squeeze aggregation
* customizable activation, normalization, and gate layer
"""
def __init__(
self, channels, rd_ratio=1. / 16, rd_channels=None, rd_divisor=8, add_maxpool=False,
bias=True, act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=None, gate_layer='sigmoid'):
super(SEModule, self).__init__()
self.add_maxpool = add_maxpool
if not rd_channels:
rd_channels = make_divisible(channels * rd_ratio, rd_divisor, round_limit=0.)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(channels, rd_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=bias)
self.bn = norm_layer(rd_channels) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
self.act = create_act_layer(act_layer, inplace=True)
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(rd_channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=bias)
self.gate = create_act_layer(gate_layer)
def forward(self, x):
x_se = x.mean((2, 3), keepdim=True)
if self.add_maxpool:
# experimental codepath, may remove or change
x_se = 0.5 * x_se + 0.5 * x.amax((2, 3), keepdim=True)
x_se = self.fc1(x_se)
x_se = self.act(self.bn(x_se))
x_se = self.fc2(x_se)
return x * self.gate(x_se)
SqueezeExcite = SEModule # alias
class EffectiveSEModule(nn.Module):
""" 'Effective Squeeze-Excitation
From `CenterMask : Real-Time Anchor-Free Instance Segmentation` - https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.06667
"""
def __init__(self, channels, add_maxpool=False, gate_layer='hard_sigmoid', **_):
super(EffectiveSEModule, self).__init__()
self.add_maxpool = add_maxpool
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
self.gate = create_act_layer(gate_layer)
def forward(self, x):
x_se = x.mean((2, 3), keepdim=True)
if self.add_maxpool:
# experimental codepath, may remove or change
x_se = 0.5 * x_se + 0.5 * x.amax((2, 3), keepdim=True)
x_se = self.fc(x_se)
return x * self.gate(x_se)
EffectiveSqueezeExcite = EffectiveSEModule # alias
class SqueezeExciteCl(nn.Module):
""" SE Module as defined in original SE-Nets with a few additions
Additions include:
* divisor can be specified to keep channels % div == 0 (default: 8)
* reduction channels can be specified directly by arg (if rd_channels is set)
* reduction channels can be specified by float rd_ratio (default: 1/16)
* global max pooling can be added to the squeeze aggregation
* customizable activation, normalization, and gate layer
"""
def __init__(
self, channels, rd_ratio=1. / 16, rd_channels=None, rd_divisor=8,
bias=True, act_layer=nn.ReLU, gate_layer='sigmoid'):
super().__init__()
if not rd_channels:
rd_channels = make_divisible(channels * rd_ratio, rd_divisor, round_limit=0.)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(channels, rd_channels, bias=bias)
self.act = create_act_layer(act_layer, inplace=True)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(rd_channels, channels, bias=bias)
self.gate = create_act_layer(gate_layer)
def forward(self, x):
x_se = x.mean((1, 2), keepdims=True) # FIXME avg dim [1:n-1], don't assume 2D NHWC
x_se = self.fc1(x_se)
x_se = self.act(x_se)
x_se = self.fc2(x_se)
return x * self.gate(x_se)
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/squeeze_excite.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/layers/squeeze_excite.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 1859
}
| 266
|
""" PyTorch Feature Extraction Helpers
A collection of classes, functions, modules to help extract features from models
and provide a common interface for describing them.
The return_layers, module re-writing idea inspired by torchvision IntermediateLayerGetter
https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/d88d8961ae51507d0cb680329d985b1488b1b76b/torchvision/models/_utils.py
Hacked together by / Copyright 2020 Ross Wightman
"""
from collections import OrderedDict, defaultdict
from copy import deepcopy
from functools import partial
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Sequence, Tuple, Union
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.layers import Format, _assert
from ._manipulate import checkpoint
__all__ = [
'FeatureInfo', 'FeatureHooks', 'FeatureDictNet', 'FeatureListNet', 'FeatureHookNet', 'FeatureGetterNet',
'feature_take_indices'
]
def feature_take_indices(
num_features: int,
indices: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,
as_set: bool = False,
) -> Tuple[List[int], int]:
""" Determine the absolute feature indices to 'take' from.
Note: This function can be called in forward() so must be torchscript compatible,
which requires some incomplete typing and workaround hacks.
Args:
num_features: total number of features to select from
indices: indices to select,
None -> select all
int -> select last n
list/tuple of int -> return specified (-ve indices specify from end)
as_set: return as a set
Returns:
List (or set) of absolute (from beginning) indices, Maximum index
"""
if indices is None:
indices = num_features # all features if None
if isinstance(indices, int):
# convert int -> last n indices
_assert(0 < indices <= num_features, f'last-n ({indices}) is out of range (1 to {num_features})')
take_indices = [num_features - indices + i for i in range(indices)]
else:
take_indices: List[int] = []
for i in indices:
idx = num_features + i if i < 0 else i
_assert(0 <= idx < num_features, f'feature index {idx} is out of range (0 to {num_features - 1})')
take_indices.append(idx)
if not torch.jit.is_scripting() and as_set:
return set(take_indices), max(take_indices)
return take_indices, max(take_indices)
def _out_indices_as_tuple(x: Union[int, Tuple[int, ...]]) -> Tuple[int, ...]:
if isinstance(x, int):
# if indices is an int, take last N features
return tuple(range(-x, 0))
return tuple(x)
OutIndicesT = Union[int, Tuple[int, ...]]
class FeatureInfo:
def __init__(
self,
feature_info: List[Dict],
out_indices: OutIndicesT,
):
out_indices = _out_indices_as_tuple(out_indices)
prev_reduction = 1
for i, fi in enumerate(feature_info):
# sanity check the mandatory fields, there may be additional fields depending on the model
assert 'num_chs' in fi and fi['num_chs'] > 0
assert 'reduction' in fi and fi['reduction'] >= prev_reduction
prev_reduction = fi['reduction']
assert 'module' in fi
fi.setdefault('index', i)
self.out_indices = out_indices
self.info = feature_info
def from_other(self, out_indices: OutIndicesT):
out_indices = _out_indices_as_tuple(out_indices)
return FeatureInfo(deepcopy(self.info), out_indices)
def get(self, key: str, idx: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None):
""" Get value by key at specified index (indices)
if idx == None, returns value for key at each output index
if idx is an integer, return value for that feature module index (ignoring output indices)
if idx is a list/tuple, return value for each module index (ignoring output indices)
"""
if idx is None:
return [self.info[i][key] for i in self.out_indices]
if isinstance(idx, (tuple, list)):
return [self.info[i][key] for i in idx]
else:
return self.info[idx][key]
def get_dicts(self, keys: Optional[List[str]] = None, idx: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None):
""" return info dicts for specified keys (or all if None) at specified indices (or out_indices if None)
"""
if idx is None:
if keys is None:
return [self.info[i] for i in self.out_indices]
else:
return [{k: self.info[i][k] for k in keys} for i in self.out_indices]
if isinstance(idx, (tuple, list)):
return [self.info[i] if keys is None else {k: self.info[i][k] for k in keys} for i in idx]
else:
return self.info[idx] if keys is None else {k: self.info[idx][k] for k in keys}
def channels(self, idx: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None):
""" feature channels accessor
"""
return self.get('num_chs', idx)
def reduction(self, idx: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None):
""" feature reduction (output stride) accessor
"""
return self.get('reduction', idx)
def module_name(self, idx: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None):
""" feature module name accessor
"""
return self.get('module', idx)
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.info[item]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.info)
class FeatureHooks:
""" Feature Hook Helper
This module helps with the setup and extraction of hooks for extracting features from
internal nodes in a model by node name.
FIXME This works well in eager Python but needs redesign for torchscript.
"""
def __init__(
self,
hooks: Sequence[Union[str, Dict]],
named_modules: dict,
out_map: Sequence[Union[int, str]] = None,
default_hook_type: str = 'forward',
):
# setup feature hooks
self._feature_outputs = defaultdict(OrderedDict)
self._handles = []
modules = {k: v for k, v in named_modules}
for i, h in enumerate(hooks):
hook_name = h if isinstance(h, str) else h['module']
m = modules[hook_name]
hook_id = out_map[i] if out_map else hook_name
hook_fn = partial(self._collect_output_hook, hook_id)
hook_type = default_hook_type
if isinstance(h, dict):
hook_type = h.get('hook_type', default_hook_type)
if hook_type == 'forward_pre':
handle = m.register_forward_pre_hook(hook_fn)
elif hook_type == 'forward':
handle = m.register_forward_hook(hook_fn)
else:
assert False, "Unsupported hook type"
self._handles.append(handle)
def _collect_output_hook(self, hook_id, *args):
x = args[-1] # tensor we want is last argument, output for fwd, input for fwd_pre
if isinstance(x, tuple):
x = x[0] # unwrap input tuple
self._feature_outputs[x.device][hook_id] = x
def get_output(self, device) -> Dict[str, torch.tensor]:
output = self._feature_outputs[device]
self._feature_outputs[device] = OrderedDict() # clear after reading
return output
def _module_list(module, flatten_sequential=False):
# a yield/iter would be better for this but wouldn't be compatible with torchscript
ml = []
for name, module in module.named_children():
if flatten_sequential and isinstance(module, nn.Sequential):
# first level of Sequential containers is flattened into containing model
for child_name, child_module in module.named_children():
combined = [name, child_name]
ml.append(('_'.join(combined), '.'.join(combined), child_module))
else:
ml.append((name, name, module))
return ml
def _get_feature_info(net, out_indices: OutIndicesT):
feature_info = getattr(net, 'feature_info')
if isinstance(feature_info, FeatureInfo):
return feature_info.from_other(out_indices)
elif isinstance(feature_info, (list, tuple)):
return FeatureInfo(net.feature_info, out_indices)
else:
assert False, "Provided feature_info is not valid"
def _get_return_layers(feature_info, out_map):
module_names = feature_info.module_name()
return_layers = {}
for i, name in enumerate(module_names):
return_layers[name] = out_map[i] if out_map is not None else feature_info.out_indices[i]
return return_layers
class FeatureDictNet(nn.ModuleDict):
""" Feature extractor with OrderedDict return
Wrap a model and extract features as specified by the out indices, the network is
partially re-built from contained modules.
There is a strong assumption that the modules have been registered into the model in the same
order as they are used. There should be no reuse of the same nn.Module more than once, including
trivial modules like `self.relu = nn.ReLU`.
Only submodules that are directly assigned to the model class (`model.feature1`) or at most
one Sequential container deep (`model.features.1`, with flatten_sequent=True) can be captured.
All Sequential containers that are directly assigned to the original model will have their
modules assigned to this module with the name `model.features.1` being changed to `model.features_1`
"""
def __init__(
self,
model: nn.Module,
out_indices: OutIndicesT = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4),
out_map: Sequence[Union[int, str]] = None,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
feature_concat: bool = False,
flatten_sequential: bool = False,
):
"""
Args:
model: Model from which to extract features.
out_indices: Output indices of the model features to extract.
out_map: Return id mapping for each output index, otherwise str(index) is used.
feature_concat: Concatenate intermediate features that are lists or tuples instead of selecting
first element e.g. `x[0]`
flatten_sequential: Flatten first two-levels of sequential modules in model (re-writes model modules)
"""
super(FeatureDictNet, self).__init__()
self.feature_info = _get_feature_info(model, out_indices)
self.output_fmt = Format(output_fmt)
self.concat = feature_concat
self.grad_checkpointing = False
self.return_layers = {}
return_layers = _get_return_layers(self.feature_info, out_map)
modules = _module_list(model, flatten_sequential=flatten_sequential)
remaining = set(return_layers.keys())
layers = OrderedDict()
for new_name, old_name, module in modules:
layers[new_name] = module
if old_name in remaining:
# return id has to be consistently str type for torchscript
self.return_layers[new_name] = str(return_layers[old_name])
remaining.remove(old_name)
if not remaining:
break
assert not remaining and len(self.return_layers) == len(return_layers), \
f'Return layers ({remaining}) are not present in model'
self.update(layers)
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable: bool = True):
self.grad_checkpointing = enable
def _collect(self, x) -> (Dict[str, torch.Tensor]):
out = OrderedDict()
for i, (name, module) in enumerate(self.items()):
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
# Skipping checkpoint of first module because need a gradient at input
# Skipping last because networks with in-place ops might fail w/ checkpointing enabled
# NOTE: first_or_last module could be static, but recalc in is_scripting guard to avoid jit issues
first_or_last_module = i == 0 or i == max(len(self) - 1, 0)
x = module(x) if first_or_last_module else checkpoint(module, x)
else:
x = module(x)
if name in self.return_layers:
out_id = self.return_layers[name]
if isinstance(x, (tuple, list)):
# If model tap is a tuple or list, concat or select first element
# FIXME this may need to be more generic / flexible for some nets
out[out_id] = torch.cat(x, 1) if self.concat else x[0]
else:
out[out_id] = x
return out
def forward(self, x) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
return self._collect(x)
class FeatureListNet(FeatureDictNet):
""" Feature extractor with list return
A specialization of FeatureDictNet that always returns features as a list (values() of dict).
"""
def __init__(
self,
model: nn.Module,
out_indices: OutIndicesT = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4),
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
feature_concat: bool = False,
flatten_sequential: bool = False,
):
"""
Args:
model: Model from which to extract features.
out_indices: Output indices of the model features to extract.
feature_concat: Concatenate intermediate features that are lists or tuples instead of selecting
first element e.g. `x[0]`
flatten_sequential: Flatten first two-levels of sequential modules in model (re-writes model modules)
"""
super().__init__(
model,
out_indices=out_indices,
output_fmt=output_fmt,
feature_concat=feature_concat,
flatten_sequential=flatten_sequential,
)
def forward(self, x) -> (List[torch.Tensor]):
return list(self._collect(x).values())
class FeatureHookNet(nn.ModuleDict):
""" FeatureHookNet
Wrap a model and extract features specified by the out indices using forward/forward-pre hooks.
If `no_rewrite` is True, features are extracted via hooks without modifying the underlying
network in any way.
If `no_rewrite` is False, the model will be re-written as in the
FeatureList/FeatureDict case by folding first to second (Sequential only) level modules into this one.
FIXME this does not currently work with Torchscript, see FeatureHooks class
"""
def __init__(
self,
model: nn.Module,
out_indices: OutIndicesT = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4),
out_map: Optional[Sequence[Union[int, str]]] = None,
return_dict: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
no_rewrite: Optional[bool] = None,
flatten_sequential: bool = False,
default_hook_type: str = 'forward',
):
"""
Args:
model: Model from which to extract features.
out_indices: Output indices of the model features to extract.
out_map: Return id mapping for each output index, otherwise str(index) is used.
return_dict: Output features as a dict.
no_rewrite: Enforce that model is not re-written if True, ie no modules are removed / changed.
flatten_sequential arg must also be False if this is set True.
flatten_sequential: Re-write modules by flattening first two levels of nn.Sequential containers.
default_hook_type: The default hook type to use if not specified in model.feature_info.
"""
super().__init__()
assert not torch.jit.is_scripting()
self.feature_info = _get_feature_info(model, out_indices)
self.return_dict = return_dict
self.output_fmt = Format(output_fmt)
self.grad_checkpointing = False
if no_rewrite is None:
no_rewrite = not flatten_sequential
layers = OrderedDict()
hooks = []
if no_rewrite:
assert not flatten_sequential
if hasattr(model, 'reset_classifier'): # make sure classifier is removed?
model.reset_classifier(0)
layers['body'] = model
hooks.extend(self.feature_info.get_dicts())
else:
modules = _module_list(model, flatten_sequential=flatten_sequential)
remaining = {
f['module']: f['hook_type'] if 'hook_type' in f else default_hook_type
for f in self.feature_info.get_dicts()
}
for new_name, old_name, module in modules:
layers[new_name] = module
for fn, fm in module.named_modules(prefix=old_name):
if fn in remaining:
hooks.append(dict(module=fn, hook_type=remaining[fn]))
del remaining[fn]
if not remaining:
break
assert not remaining, f'Return layers ({remaining}) are not present in model'
self.update(layers)
self.hooks = FeatureHooks(hooks, model.named_modules(), out_map=out_map)
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable: bool = True):
self.grad_checkpointing = enable
def forward(self, x):
for i, (name, module) in enumerate(self.items()):
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
# Skipping checkpoint of first module because need a gradient at input
# Skipping last because networks with in-place ops might fail w/ checkpointing enabled
# NOTE: first_or_last module could be static, but recalc in is_scripting guard to avoid jit issues
first_or_last_module = i == 0 or i == max(len(self) - 1, 0)
x = module(x) if first_or_last_module else checkpoint(module, x)
else:
x = module(x)
out = self.hooks.get_output(x.device)
return out if self.return_dict else list(out.values())
class FeatureGetterNet(nn.ModuleDict):
""" FeatureGetterNet
Wrap models with a feature getter method, like 'get_intermediate_layers'
"""
def __init__(
self,
model: nn.Module,
out_indices: OutIndicesT = 4,
out_map: Optional[Sequence[Union[int, str]]] = None,
return_dict: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
norm: bool = False,
prune: bool = True,
):
"""
Args:
model: Model to wrap.
out_indices: Indices of features to extract.
out_map: Remap feature names for dict output (WIP, not supported).
return_dict: Return features as dictionary instead of list (WIP, not supported).
norm: Apply final model norm to all output features (if possible).
"""
super().__init__()
if prune and hasattr(model, 'prune_intermediate_layers'):
# replace out_indices after they've been normalized, -ve indices will be invalid after prune
out_indices = model.prune_intermediate_layers(
out_indices,
prune_norm=not norm,
)
self.feature_info = _get_feature_info(model, out_indices)
self.model = model
self.out_indices = out_indices
self.out_map = out_map
self.return_dict = return_dict
self.output_fmt = Format(output_fmt)
self.norm = norm
def forward(self, x):
features = self.model.forward_intermediates(
x,
indices=self.out_indices,
norm=self.norm,
output_fmt=self.output_fmt,
intermediates_only=True,
)
return features
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/_features.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/_features.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 8419
}
| 267
|
""" Class-Attention in Image Transformers (CaiT)
Paper: 'Going deeper with Image Transformers' - https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.17239
Original code and weights from https://github.com/facebookresearch/deit, copyright below
Modifications and additions for timm hacked together by / Copyright 2021, Ross Wightman
"""
# Copyright (c) 2015-present, Facebook, Inc.
# All rights reserved.
from functools import partial
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple, Union
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.data import IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD
from timm.layers import PatchEmbed, Mlp, DropPath, trunc_normal_, use_fused_attn
from ._builder import build_model_with_cfg
from ._features import feature_take_indices
from ._manipulate import checkpoint, checkpoint_seq
from ._registry import register_model, generate_default_cfgs
__all__ = ['Cait', 'ClassAttn', 'LayerScaleBlockClassAttn', 'LayerScaleBlock', 'TalkingHeadAttn']
class ClassAttn(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
# with slight modifications to do CA
fused_attn: torch.jit.Final[bool]
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
self.fused_attn = use_fused_attn()
self.q = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.k = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.v = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
q = self.q(x[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).reshape(B, 1, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
k = self.k(x).reshape(B, N, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
v = self.v(x).reshape(B, N, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
if self.fused_attn:
x_cls = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(
q, k, v,
dropout_p=self.attn_drop.p if self.training else 0.,
)
else:
q = q * self.scale
attn = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x_cls = attn @ v
x_cls = x_cls.transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, 1, C)
x_cls = self.proj(x_cls)
x_cls = self.proj_drop(x_cls)
return x_cls
class LayerScaleBlockClassAttn(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
# with slight modifications to add CA and LayerScale
def __init__(
self,
dim,
num_heads,
mlp_ratio=4.,
qkv_bias=False,
proj_drop=0.,
attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
attn_block=ClassAttn,
mlp_block=Mlp,
init_values=1e-4,
):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = attn_block(
dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
proj_drop=proj_drop,
)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = mlp_block(
in_features=dim,
hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer,
drop=proj_drop,
)
self.gamma_1 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones(dim))
self.gamma_2 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones(dim))
def forward(self, x, x_cls):
u = torch.cat((x_cls, x), dim=1)
x_cls = x_cls + self.drop_path(self.gamma_1 * self.attn(self.norm1(u)))
x_cls = x_cls + self.drop_path(self.gamma_2 * self.mlp(self.norm2(x_cls)))
return x_cls
class TalkingHeadAttn(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
# with slight modifications to add Talking Heads Attention (https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.02436v1.pdf)
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_l = nn.Linear(num_heads, num_heads)
self.proj_w = nn.Linear(num_heads, num_heads)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0] * self.scale, qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)
attn = self.proj_l(attn.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.proj_w(attn.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class LayerScaleBlock(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
# with slight modifications to add layerScale
def __init__(
self,
dim,
num_heads,
mlp_ratio=4.,
qkv_bias=False,
proj_drop=0.,
attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
attn_block=TalkingHeadAttn,
mlp_block=Mlp,
init_values=1e-4,
):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = attn_block(
dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
proj_drop=proj_drop,
)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = mlp_block(
in_features=dim,
hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer,
drop=proj_drop,
)
self.gamma_1 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones(dim))
self.gamma_2 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones(dim))
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.gamma_1 * self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.gamma_2 * self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
class Cait(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
# with slight modifications to adapt to our cait models
def __init__(
self,
img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
in_chans=3,
num_classes=1000,
global_pool='token',
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
mlp_ratio=4.,
qkv_bias=True,
drop_rate=0.,
pos_drop_rate=0.,
proj_drop_rate=0.,
attn_drop_rate=0.,
drop_path_rate=0.,
block_layers=LayerScaleBlock,
block_layers_token=LayerScaleBlockClassAttn,
patch_layer=PatchEmbed,
norm_layer=partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6),
act_layer=nn.GELU,
attn_block=TalkingHeadAttn,
mlp_block=Mlp,
init_values=1e-4,
attn_block_token_only=ClassAttn,
mlp_block_token_only=Mlp,
depth_token_only=2,
mlp_ratio_token_only=4.0
):
super().__init__()
assert global_pool in ('', 'token', 'avg')
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.global_pool = global_pool
self.num_features = self.head_hidden_size = self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.grad_checkpointing = False
self.patch_embed = patch_layer(
img_size=img_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
r = self.patch_embed.feat_ratio() if hasattr(self.patch_embed, 'feat_ratio') else patch_size
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim))
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=pos_drop_rate)
dpr = [drop_path_rate for i in range(depth)]
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[block_layers(
dim=embed_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
proj_drop=proj_drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[i],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
attn_block=attn_block,
mlp_block=mlp_block,
init_values=init_values,
) for i in range(depth)])
self.feature_info = [dict(num_chs=embed_dim, reduction=r, module=f'blocks.{i}') for i in range(depth)]
self.blocks_token_only = nn.ModuleList([block_layers_token(
dim=embed_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio_token_only,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
attn_block=attn_block_token_only,
mlp_block=mlp_block_token_only,
init_values=init_values,
) for _ in range(depth_token_only)])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
self.head_drop = nn.Dropout(drop_rate)
self.head = nn.Linear(embed_dim, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=.02)
trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=.02)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
@torch.jit.ignore
def no_weight_decay(self):
return {'pos_embed', 'cls_token'}
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable=True):
self.grad_checkpointing = enable
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse=False):
def _matcher(name):
if any([name.startswith(n) for n in ('cls_token', 'pos_embed', 'patch_embed')]):
return 0
elif name.startswith('blocks.'):
return int(name.split('.')[1]) + 1
elif name.startswith('blocks_token_only.'):
# overlap token only blocks with last blocks
to_offset = len(self.blocks) - len(self.blocks_token_only) + 1
return int(name.split('.')[1]) + to_offset
elif name.startswith('norm.'):
return len(self.blocks)
else:
return float('inf')
return _matcher
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.head
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: Optional[str] = None):
self.num_classes = num_classes
if global_pool is not None:
assert global_pool in ('', 'token', 'avg')
self.global_pool = global_pool
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def forward_intermediates(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
indices: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,
norm: bool = False,
stop_early: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
intermediates_only: bool = False,
) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]]]:
""" Forward features that returns intermediates.
Args:
x: Input image tensor
indices: Take last n blocks if int, all if None, select matching indices if sequence
norm: Apply norm layer to all intermediates
stop_early: Stop iterating over blocks when last desired intermediate hit
output_fmt: Shape of intermediate feature outputs
intermediates_only: Only return intermediate features
"""
assert output_fmt in ('NCHW', 'NLC'), 'Output format must be one of NCHW or NLC.'
reshape = output_fmt == 'NCHW'
intermediates = []
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.blocks), indices)
# forward pass
B, _, height, width = x.shape
x = self.patch_embed(x)
x = x + self.pos_embed
x = self.pos_drop(x)
if torch.jit.is_scripting() or not stop_early: # can't slice blocks in torchscript
blocks = self.blocks
else:
blocks = self.blocks[:max_index + 1]
for i, blk in enumerate(blocks):
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint(blk, x)
else:
x = blk(x)
if i in take_indices:
# normalize intermediates with final norm layer if enabled
intermediates.append(self.norm(x) if norm else x)
# process intermediates
if reshape:
# reshape to BCHW output format
H, W = self.patch_embed.dynamic_feat_size((height, width))
intermediates = [y.reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous() for y in intermediates]
if intermediates_only:
return intermediates
# NOTE not supporting return of class tokens
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
for i, blk in enumerate(self.blocks_token_only):
cls_tokens = blk(x, cls_tokens)
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, intermediates
def prune_intermediate_layers(
self,
indices: Union[int, List[int]] = 1,
prune_norm: bool = False,
prune_head: bool = True,
):
""" Prune layers not required for specified intermediates.
"""
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.blocks), indices)
self.blocks = self.blocks[:max_index + 1] # truncate blocks
if prune_norm:
self.norm = nn.Identity()
if prune_head:
self.blocks_token_only = nn.ModuleList() # prune token blocks with head
self.reset_classifier(0, '')
return take_indices
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.patch_embed(x)
x = x + self.pos_embed
x = self.pos_drop(x)
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint_seq(self.blocks, x)
else:
x = self.blocks(x)
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
for i, blk in enumerate(self.blocks_token_only):
cls_tokens = blk(x, cls_tokens)
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
if self.global_pool:
x = x[:, 1:].mean(dim=1) if self.global_pool == 'avg' else x[:, 0]
x = self.head_drop(x)
return x if pre_logits else self.head(x)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
def checkpoint_filter_fn(state_dict, model=None):
if 'model' in state_dict:
state_dict = state_dict['model']
checkpoint_no_module = {}
for k, v in state_dict.items():
checkpoint_no_module[k.replace('module.', '')] = v
return checkpoint_no_module
def _create_cait(variant, pretrained=False, **kwargs):
out_indices = kwargs.pop('out_indices', 3)
model = build_model_with_cfg(
Cait,
variant,
pretrained,
pretrained_filter_fn=checkpoint_filter_fn,
feature_cfg=dict(out_indices=out_indices, feature_cls='getter'),
**kwargs,
)
return model
def _cfg(url='', **kwargs):
return {
'url': url,
'num_classes': 1000, 'input_size': (3, 384, 384), 'pool_size': None,
'crop_pct': 1.0, 'interpolation': 'bicubic', 'fixed_input_size': True,
'mean': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, 'std': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD,
'first_conv': 'patch_embed.proj', 'classifier': 'head',
**kwargs
}
default_cfgs = generate_default_cfgs({
'cait_xxs24_224.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/XXS24_224.pth',
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
),
'cait_xxs24_384.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/XXS24_384.pth',
),
'cait_xxs36_224.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/XXS36_224.pth',
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
),
'cait_xxs36_384.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/XXS36_384.pth',
),
'cait_xs24_384.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/XS24_384.pth',
),
'cait_s24_224.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/S24_224.pth',
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
),
'cait_s24_384.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/S24_384.pth',
),
'cait_s36_384.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/S36_384.pth',
),
'cait_m36_384.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/M36_384.pth',
),
'cait_m48_448.fb_dist_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
url='https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/deit/M48_448.pth',
input_size=(3, 448, 448),
),
})
@register_model
def cait_xxs24_224(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=192, depth=24, num_heads=4, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_xxs24_224', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_xxs24_384(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=192, depth=24, num_heads=4, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_xxs24_384', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_xxs36_224(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=192, depth=36, num_heads=4, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_xxs36_224', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_xxs36_384(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=192, depth=36, num_heads=4, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_xxs36_384', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_xs24_384(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=288, depth=24, num_heads=6, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_xs24_384', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_s24_224(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=384, depth=24, num_heads=8, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_s24_224', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_s24_384(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=384, depth=24, num_heads=8, init_values=1e-5)
model = _create_cait('cait_s24_384', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_s36_384(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=384, depth=36, num_heads=8, init_values=1e-6)
model = _create_cait('cait_s36_384', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_m36_384(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=768, depth=36, num_heads=16, init_values=1e-6)
model = _create_cait('cait_m36_384', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
@register_model
def cait_m48_448(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> Cait:
model_args = dict(patch_size=16, embed_dim=768, depth=48, num_heads=16, init_values=1e-6)
model = _create_cait('cait_m48_448', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
return model
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/cait.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/cait.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 10699
}
| 268
|
""" EfficientViT (by MIT Song Han's Lab)
Paper: `Efficientvit: Enhanced linear attention for high-resolution low-computation visual recognition`
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14756
Adapted from official impl at https://github.com/mit-han-lab/efficientvit
"""
__all__ = ['EfficientVit', 'EfficientVitLarge']
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple, Union
from functools import partial
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from timm.data import IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD
from timm.layers import SelectAdaptivePool2d, create_conv2d, GELUTanh
from ._builder import build_model_with_cfg
from ._features import feature_take_indices
from ._features_fx import register_notrace_module
from ._manipulate import checkpoint_seq
from ._registry import register_model, generate_default_cfgs
def val2list(x: list or tuple or any, repeat_time=1):
if isinstance(x, (list, tuple)):
return list(x)
return [x for _ in range(repeat_time)]
def val2tuple(x: list or tuple or any, min_len: int = 1, idx_repeat: int = -1):
# repeat elements if necessary
x = val2list(x)
if len(x) > 0:
x[idx_repeat:idx_repeat] = [x[idx_repeat] for _ in range(min_len - len(x))]
return tuple(x)
def get_same_padding(kernel_size: int or tuple[int, ...]) -> int or tuple[int, ...]:
if isinstance(kernel_size, tuple):
return tuple([get_same_padding(ks) for ks in kernel_size])
else:
assert kernel_size % 2 > 0, "kernel size should be odd number"
return kernel_size // 2
class ConvNormAct(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
dilation=1,
groups=1,
bias=False,
dropout=0.,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
act_layer=nn.ReLU,
):
super(ConvNormAct, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout, inplace=False)
self.conv = create_conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
dilation=dilation,
groups=groups,
bias=bias,
)
self.norm = norm_layer(num_features=out_channels) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
self.act = act_layer(inplace=True) if act_layer is not None else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.act(x)
return x
class DSConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
use_bias=False,
norm_layer=(nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.BatchNorm2d),
act_layer=(nn.ReLU6, None),
):
super(DSConv, self).__init__()
use_bias = val2tuple(use_bias, 2)
norm_layer = val2tuple(norm_layer, 2)
act_layer = val2tuple(act_layer, 2)
self.depth_conv = ConvNormAct(
in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
groups=in_channels,
norm_layer=norm_layer[0],
act_layer=act_layer[0],
bias=use_bias[0],
)
self.point_conv = ConvNormAct(
in_channels,
out_channels,
1,
norm_layer=norm_layer[1],
act_layer=act_layer[1],
bias=use_bias[1],
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.depth_conv(x)
x = self.point_conv(x)
return x
class ConvBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
mid_channels=None,
expand_ratio=1,
use_bias=False,
norm_layer=(nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.BatchNorm2d),
act_layer=(nn.ReLU6, None),
):
super(ConvBlock, self).__init__()
use_bias = val2tuple(use_bias, 2)
norm_layer = val2tuple(norm_layer, 2)
act_layer = val2tuple(act_layer, 2)
mid_channels = mid_channels or round(in_channels * expand_ratio)
self.conv1 = ConvNormAct(
in_channels,
mid_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
norm_layer=norm_layer[0],
act_layer=act_layer[0],
bias=use_bias[0],
)
self.conv2 = ConvNormAct(
mid_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
1,
norm_layer=norm_layer[1],
act_layer=act_layer[1],
bias=use_bias[1],
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
return x
class MBConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
mid_channels=None,
expand_ratio=6,
use_bias=False,
norm_layer=(nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.BatchNorm2d),
act_layer=(nn.ReLU6, nn.ReLU6, None),
):
super(MBConv, self).__init__()
use_bias = val2tuple(use_bias, 3)
norm_layer = val2tuple(norm_layer, 3)
act_layer = val2tuple(act_layer, 3)
mid_channels = mid_channels or round(in_channels * expand_ratio)
self.inverted_conv = ConvNormAct(
in_channels,
mid_channels,
1,
stride=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer[0],
act_layer=act_layer[0],
bias=use_bias[0],
)
self.depth_conv = ConvNormAct(
mid_channels,
mid_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=stride,
groups=mid_channels,
norm_layer=norm_layer[1],
act_layer=act_layer[1],
bias=use_bias[1],
)
self.point_conv = ConvNormAct(
mid_channels,
out_channels,
1,
norm_layer=norm_layer[2],
act_layer=act_layer[2],
bias=use_bias[2],
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.inverted_conv(x)
x = self.depth_conv(x)
x = self.point_conv(x)
return x
class FusedMBConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
mid_channels=None,
expand_ratio=6,
groups=1,
use_bias=False,
norm_layer=(nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.BatchNorm2d),
act_layer=(nn.ReLU6, None),
):
super(FusedMBConv, self).__init__()
use_bias = val2tuple(use_bias, 2)
norm_layer = val2tuple(norm_layer, 2)
act_layer = val2tuple(act_layer, 2)
mid_channels = mid_channels or round(in_channels * expand_ratio)
self.spatial_conv = ConvNormAct(
in_channels,
mid_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=stride,
groups=groups,
norm_layer=norm_layer[0],
act_layer=act_layer[0],
bias=use_bias[0],
)
self.point_conv = ConvNormAct(
mid_channels,
out_channels,
1,
norm_layer=norm_layer[1],
act_layer=act_layer[1],
bias=use_bias[1],
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.spatial_conv(x)
x = self.point_conv(x)
return x
class LiteMLA(nn.Module):
"""Lightweight multi-scale linear attention"""
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
heads: int or None = None,
heads_ratio: float = 1.0,
dim=8,
use_bias=False,
norm_layer=(None, nn.BatchNorm2d),
act_layer=(None, None),
kernel_func=nn.ReLU,
scales=(5,),
eps=1e-5,
):
super(LiteMLA, self).__init__()
self.eps = eps
heads = heads or int(in_channels // dim * heads_ratio)
total_dim = heads * dim
use_bias = val2tuple(use_bias, 2)
norm_layer = val2tuple(norm_layer, 2)
act_layer = val2tuple(act_layer, 2)
self.dim = dim
self.qkv = ConvNormAct(
in_channels,
3 * total_dim,
1,
bias=use_bias[0],
norm_layer=norm_layer[0],
act_layer=act_layer[0],
)
self.aggreg = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
3 * total_dim,
3 * total_dim,
scale,
padding=get_same_padding(scale),
groups=3 * total_dim,
bias=use_bias[0],
),
nn.Conv2d(3 * total_dim, 3 * total_dim, 1, groups=3 * heads, bias=use_bias[0]),
)
for scale in scales
])
self.kernel_func = kernel_func(inplace=False)
self.proj = ConvNormAct(
total_dim * (1 + len(scales)),
out_channels,
1,
bias=use_bias[1],
norm_layer=norm_layer[1],
act_layer=act_layer[1],
)
def _attn(self, q, k, v):
dtype = v.dtype
q, k, v = q.float(), k.float(), v.float()
kv = k.transpose(-1, -2) @ v
out = q @ kv
out = out[..., :-1] / (out[..., -1:] + self.eps)
return out.to(dtype)
def forward(self, x):
B, _, H, W = x.shape
# generate multi-scale q, k, v
qkv = self.qkv(x)
multi_scale_qkv = [qkv]
for op in self.aggreg:
multi_scale_qkv.append(op(qkv))
multi_scale_qkv = torch.cat(multi_scale_qkv, dim=1)
multi_scale_qkv = multi_scale_qkv.reshape(B, -1, 3 * self.dim, H * W).transpose(-1, -2)
q, k, v = multi_scale_qkv.chunk(3, dim=-1)
# lightweight global attention
q = self.kernel_func(q)
k = self.kernel_func(k)
v = F.pad(v, (0, 1), mode="constant", value=1.)
if not torch.jit.is_scripting():
with torch.autocast(device_type=v.device.type, enabled=False):
out = self._attn(q, k, v)
else:
out = self._attn(q, k, v)
# final projection
out = out.transpose(-1, -2).reshape(B, -1, H, W)
out = self.proj(out)
return out
register_notrace_module(LiteMLA)
class EfficientVitBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels,
heads_ratio=1.0,
head_dim=32,
expand_ratio=4,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
act_layer=nn.Hardswish,
):
super(EfficientVitBlock, self).__init__()
self.context_module = ResidualBlock(
LiteMLA(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=in_channels,
heads_ratio=heads_ratio,
dim=head_dim,
norm_layer=(None, norm_layer),
),
nn.Identity(),
)
self.local_module = ResidualBlock(
MBConv(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=in_channels,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
use_bias=(True, True, False),
norm_layer=(None, None, norm_layer),
act_layer=(act_layer, act_layer, None),
),
nn.Identity(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.context_module(x)
x = self.local_module(x)
return x
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
main: Optional[nn.Module],
shortcut: Optional[nn.Module] = None,
pre_norm: Optional[nn.Module] = None,
):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.pre_norm = pre_norm if pre_norm is not None else nn.Identity()
self.main = main
self.shortcut = shortcut
def forward(self, x):
res = self.main(self.pre_norm(x))
if self.shortcut is not None:
res = res + self.shortcut(x)
return res
def build_local_block(
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
stride: int,
expand_ratio: float,
norm_layer: str,
act_layer: str,
fewer_norm: bool = False,
block_type: str = "default",
):
assert block_type in ["default", "large", "fused"]
if expand_ratio == 1:
if block_type == "default":
block = DSConv(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=stride,
use_bias=(True, False) if fewer_norm else False,
norm_layer=(None, norm_layer) if fewer_norm else norm_layer,
act_layer=(act_layer, None),
)
else:
block = ConvBlock(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=stride,
use_bias=(True, False) if fewer_norm else False,
norm_layer=(None, norm_layer) if fewer_norm else norm_layer,
act_layer=(act_layer, None),
)
else:
if block_type == "default":
block = MBConv(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=stride,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
use_bias=(True, True, False) if fewer_norm else False,
norm_layer=(None, None, norm_layer) if fewer_norm else norm_layer,
act_layer=(act_layer, act_layer, None),
)
else:
block = FusedMBConv(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=stride,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
use_bias=(True, False) if fewer_norm else False,
norm_layer=(None, norm_layer) if fewer_norm else norm_layer,
act_layer=(act_layer, None),
)
return block
class Stem(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_chs, out_chs, depth, norm_layer, act_layer, block_type='default'):
super().__init__()
self.stride = 2
self.add_module(
'in_conv',
ConvNormAct(
in_chs, out_chs,
kernel_size=3, stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer,
)
)
stem_block = 0
for _ in range(depth):
self.add_module(f'res{stem_block}', ResidualBlock(
build_local_block(
in_channels=out_chs,
out_channels=out_chs,
stride=1,
expand_ratio=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
block_type=block_type,
),
nn.Identity(),
))
stem_block += 1
class EfficientVitStage(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_chs,
out_chs,
depth,
norm_layer,
act_layer,
expand_ratio,
head_dim,
vit_stage=False,
):
super(EfficientVitStage, self).__init__()
blocks = [ResidualBlock(
build_local_block(
in_channels=in_chs,
out_channels=out_chs,
stride=2,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
fewer_norm=vit_stage,
),
None,
)]
in_chs = out_chs
if vit_stage:
# for stage 3, 4
for _ in range(depth):
blocks.append(
EfficientVitBlock(
in_channels=in_chs,
head_dim=head_dim,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
)
)
else:
# for stage 1, 2
for i in range(1, depth):
blocks.append(ResidualBlock(
build_local_block(
in_channels=in_chs,
out_channels=out_chs,
stride=1,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer
),
nn.Identity(),
))
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks)
def forward(self, x):
return self.blocks(x)
class EfficientVitLargeStage(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_chs,
out_chs,
depth,
norm_layer,
act_layer,
head_dim,
vit_stage=False,
fewer_norm=False,
):
super(EfficientVitLargeStage, self).__init__()
blocks = [ResidualBlock(
build_local_block(
in_channels=in_chs,
out_channels=out_chs,
stride=2,
expand_ratio=24 if vit_stage else 16,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
fewer_norm=vit_stage or fewer_norm,
block_type='default' if fewer_norm else 'fused',
),
None,
)]
in_chs = out_chs
if vit_stage:
# for stage 4
for _ in range(depth):
blocks.append(
EfficientVitBlock(
in_channels=in_chs,
head_dim=head_dim,
expand_ratio=6,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
)
)
else:
# for stage 1, 2, 3
for i in range(depth):
blocks.append(ResidualBlock(
build_local_block(
in_channels=in_chs,
out_channels=out_chs,
stride=1,
expand_ratio=4,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
fewer_norm=fewer_norm,
block_type='default' if fewer_norm else 'fused',
),
nn.Identity(),
))
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks)
def forward(self, x):
return self.blocks(x)
class ClassifierHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
widths: List[int],
num_classes: int = 1000,
dropout: float = 0.,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
act_layer=nn.Hardswish,
pool_type: str = 'avg',
norm_eps: float = 1e-5,
):
super(ClassifierHead, self).__init__()
self.widths = widths
self.num_features = widths[-1]
assert pool_type, 'Cannot disable pooling'
self.in_conv = ConvNormAct(in_channels, widths[0], 1, norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer)
self.global_pool = SelectAdaptivePool2d(pool_type=pool_type, flatten=True)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(widths[0], widths[1], bias=False),
nn.LayerNorm(widths[1], eps=norm_eps),
act_layer(inplace=True) if act_layer is not None else nn.Identity(),
nn.Dropout(dropout, inplace=False),
nn.Linear(widths[1], num_classes, bias=True) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity(),
)
def reset(self, num_classes: int, pool_type: Optional[str] = None):
if pool_type is not None:
assert pool_type, 'Cannot disable pooling'
self.global_pool = SelectAdaptivePool2d(pool_type=pool_type, flatten=True,)
if num_classes > 0:
self.classifier[-1] = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes, bias=True)
else:
self.classifier[-1] = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
x = self.in_conv(x)
x = self.global_pool(x)
if pre_logits:
# cannot slice or iterate with torchscript so, this
x = self.classifier[0](x)
x = self.classifier[1](x)
x = self.classifier[2](x)
x = self.classifier[3](x)
else:
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
class EfficientVit(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_chans=3,
widths=(),
depths=(),
head_dim=32,
expand_ratio=4,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
act_layer=nn.Hardswish,
global_pool='avg',
head_widths=(),
drop_rate=0.0,
num_classes=1000,
):
super(EfficientVit, self).__init__()
self.grad_checkpointing = False
self.global_pool = global_pool
self.num_classes = num_classes
# input stem
self.stem = Stem(in_chans, widths[0], depths[0], norm_layer, act_layer)
stride = self.stem.stride
# stages
self.feature_info = []
self.stages = nn.Sequential()
in_channels = widths[0]
for i, (w, d) in enumerate(zip(widths[1:], depths[1:])):
self.stages.append(EfficientVitStage(
in_channels,
w,
depth=d,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
head_dim=head_dim,
vit_stage=i >= 2,
))
stride *= 2
in_channels = w
self.feature_info += [dict(num_chs=in_channels, reduction=stride, module=f'stages.{i}')]
self.num_features = in_channels
self.head = ClassifierHead(
self.num_features,
widths=head_widths,
num_classes=num_classes,
dropout=drop_rate,
pool_type=self.global_pool,
)
self.head_hidden_size = self.head.num_features
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse=False):
matcher = dict(
stem=r'^stem',
blocks=r'^stages\.(\d+)' if coarse else [
(r'^stages\.(\d+).downsample', (0,)),
(r'^stages\.(\d+)\.\w+\.(\d+)', None),
]
)
return matcher
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable=True):
self.grad_checkpointing = enable
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.head.classifier[-1]
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: Optional[str] = None):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.head.reset(num_classes, global_pool)
def forward_intermediates(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
indices: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,
norm: bool = False,
stop_early: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
intermediates_only: bool = False,
) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]]]:
""" Forward features that returns intermediates.
Args:
x: Input image tensor
indices: Take last n blocks if int, all if None, select matching indices if sequence
norm: Apply norm layer to compatible intermediates
stop_early: Stop iterating over blocks when last desired intermediate hit
output_fmt: Shape of intermediate feature outputs
intermediates_only: Only return intermediate features
Returns:
"""
assert output_fmt in ('NCHW',), 'Output shape must be NCHW.'
intermediates = []
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.stages), indices)
# forward pass
x = self.stem(x)
if torch.jit.is_scripting() or not stop_early: # can't slice blocks in torchscript
stages = self.stages
else:
stages = self.stages[:max_index + 1]
for feat_idx, stage in enumerate(stages):
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint_seq(stages, x)
else:
x = stage(x)
if feat_idx in take_indices:
intermediates.append(x)
if intermediates_only:
return intermediates
return x, intermediates
def prune_intermediate_layers(
self,
indices: Union[int, List[int]] = 1,
prune_norm: bool = False,
prune_head: bool = True,
):
""" Prune layers not required for specified intermediates.
"""
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.stages), indices)
self.stages = self.stages[:max_index + 1] # truncate blocks w/ stem as idx 0
if prune_head:
self.reset_classifier(0, '')
return take_indices
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.stem(x)
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint_seq(self.stages, x)
else:
x = self.stages(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
return self.head(x, pre_logits=pre_logits) if pre_logits else self.head(x)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
class EfficientVitLarge(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_chans=3,
widths=(),
depths=(),
head_dim=32,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d,
act_layer=GELUTanh,
global_pool='avg',
head_widths=(),
drop_rate=0.0,
num_classes=1000,
norm_eps=1e-7,
):
super(EfficientVitLarge, self).__init__()
self.grad_checkpointing = False
self.global_pool = global_pool
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.norm_eps = norm_eps
norm_layer = partial(norm_layer, eps=self.norm_eps)
# input stem
self.stem = Stem(in_chans, widths[0], depths[0], norm_layer, act_layer, block_type='large')
stride = self.stem.stride
# stages
self.feature_info = []
self.stages = nn.Sequential()
in_channels = widths[0]
for i, (w, d) in enumerate(zip(widths[1:], depths[1:])):
self.stages.append(EfficientVitLargeStage(
in_channels,
w,
depth=d,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
head_dim=head_dim,
vit_stage=i >= 3,
fewer_norm=i >= 2,
))
stride *= 2
in_channels = w
self.feature_info += [dict(num_chs=in_channels, reduction=stride, module=f'stages.{i}')]
self.num_features = in_channels
self.head = ClassifierHead(
self.num_features,
widths=head_widths,
num_classes=num_classes,
dropout=drop_rate,
pool_type=self.global_pool,
act_layer=act_layer,
norm_eps=self.norm_eps,
)
self.head_hidden_size = self.head.num_features
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse=False):
matcher = dict(
stem=r'^stem',
blocks=r'^stages\.(\d+)' if coarse else [
(r'^stages\.(\d+).downsample', (0,)),
(r'^stages\.(\d+)\.\w+\.(\d+)', None),
]
)
return matcher
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable=True):
self.grad_checkpointing = enable
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.head.classifier[-1]
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: Optional[str] = None):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.head.reset(num_classes, global_pool)
def forward_intermediates(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
indices: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,
norm: bool = False,
stop_early: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
intermediates_only: bool = False,
) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]]]:
""" Forward features that returns intermediates.
Args:
x: Input image tensor
indices: Take last n blocks if int, all if None, select matching indices if sequence
norm: Apply norm layer to compatible intermediates
stop_early: Stop iterating over blocks when last desired intermediate hit
output_fmt: Shape of intermediate feature outputs
intermediates_only: Only return intermediate features
Returns:
"""
assert output_fmt in ('NCHW',), 'Output shape must be NCHW.'
intermediates = []
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.stages), indices)
# forward pass
x = self.stem(x)
if torch.jit.is_scripting() or not stop_early: # can't slice blocks in torchscript
stages = self.stages
else:
stages = self.stages[:max_index + 1]
for feat_idx, stage in enumerate(stages):
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint_seq(stages, x)
else:
x = stage(x)
if feat_idx in take_indices:
intermediates.append(x)
if intermediates_only:
return intermediates
return x, intermediates
def prune_intermediate_layers(
self,
indices: Union[int, List[int]] = 1,
prune_norm: bool = False,
prune_head: bool = True,
):
""" Prune layers not required for specified intermediates.
"""
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.stages), indices)
self.stages = self.stages[:max_index + 1] # truncate blocks w/ stem as idx 0
if prune_head:
self.reset_classifier(0, '')
return take_indices
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.stem(x)
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint_seq(self.stages, x)
else:
x = self.stages(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
return self.head(x, pre_logits=pre_logits) if pre_logits else self.head(x)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
def _cfg(url='', **kwargs):
return {
'url': url,
'num_classes': 1000,
'mean': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN,
'std': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD,
'first_conv': 'stem.in_conv.conv',
'classifier': 'head.classifier.4',
'crop_pct': 0.95,
'input_size': (3, 224, 224),
'pool_size': (7, 7),
**kwargs,
}
default_cfgs = generate_default_cfgs({
'efficientvit_b0.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'efficientvit_b1.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'efficientvit_b1.r256_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 256, 256), pool_size=(8, 8), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_b1.r288_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 288, 288), pool_size=(9, 9), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_b2.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'efficientvit_b2.r256_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 256, 256), pool_size=(8, 8), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_b2.r288_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 288, 288), pool_size=(9, 9), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_b3.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'efficientvit_b3.r256_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 256, 256), pool_size=(8, 8), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_b3.r288_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 288, 288), pool_size=(9, 9), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l1.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l2.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l2.r256_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 256, 256), pool_size=(8, 8), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l2.r288_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 288, 288), pool_size=(9, 9), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l2.r384_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 384, 384), pool_size=(12, 12), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l3.r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l3.r256_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 256, 256), pool_size=(8, 8), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l3.r320_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 320, 320), pool_size=(10, 10), crop_pct=1.0,
),
'efficientvit_l3.r384_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 384, 384), pool_size=(12, 12), crop_pct=1.0,
),
# 'efficientvit_l0_sam.sam': _cfg(
# # hf_hub_id='timm/',
# input_size=(3, 512, 512), crop_pct=1.0,
# num_classes=0,
# ),
# 'efficientvit_l1_sam.sam': _cfg(
# # hf_hub_id='timm/',
# input_size=(3, 512, 512), crop_pct=1.0,
# num_classes=0,
# ),
# 'efficientvit_l2_sam.sam': _cfg(
# # hf_hub_id='timm/',f
# input_size=(3, 512, 512), crop_pct=1.0,
# num_classes=0,
# ),
})
def _create_efficientvit(variant, pretrained=False, **kwargs):
out_indices = kwargs.pop('out_indices', (0, 1, 2, 3))
model = build_model_with_cfg(
EfficientVit,
variant,
pretrained,
feature_cfg=dict(flatten_sequential=True, out_indices=out_indices),
**kwargs
)
return model
def _create_efficientvit_large(variant, pretrained=False, **kwargs):
out_indices = kwargs.pop('out_indices', (0, 1, 2, 3))
model = build_model_with_cfg(
EfficientVitLarge,
variant,
pretrained,
feature_cfg=dict(flatten_sequential=True, out_indices=out_indices),
**kwargs
)
return model
@register_model
def efficientvit_b0(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(8, 16, 32, 64, 128), depths=(1, 2, 2, 2, 2), head_dim=16, head_widths=(1024, 1280))
return _create_efficientvit('efficientvit_b0', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def efficientvit_b1(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(16, 32, 64, 128, 256), depths=(1, 2, 3, 3, 4), head_dim=16, head_widths=(1536, 1600))
return _create_efficientvit('efficientvit_b1', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def efficientvit_b2(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(24, 48, 96, 192, 384), depths=(1, 3, 4, 4, 6), head_dim=32, head_widths=(2304, 2560))
return _create_efficientvit('efficientvit_b2', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def efficientvit_b3(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), depths=(1, 4, 6, 6, 9), head_dim=32, head_widths=(2304, 2560))
return _create_efficientvit('efficientvit_b3', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def efficientvit_l1(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), depths=(1, 1, 1, 6, 6), head_dim=32, head_widths=(3072, 3200))
return _create_efficientvit_large('efficientvit_l1', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def efficientvit_l2(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), depths=(1, 2, 2, 8, 8), head_dim=32, head_widths=(3072, 3200))
return _create_efficientvit_large('efficientvit_l2', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def efficientvit_l3(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model_args = dict(
widths=(64, 128, 256, 512, 1024), depths=(1, 2, 2, 8, 8), head_dim=32, head_widths=(6144, 6400))
return _create_efficientvit_large('efficientvit_l3', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
# FIXME will wait for v2 SAM models which are pending
# @register_model
# def efficientvit_l0_sam(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
# # only backbone for segment-anything-model weights
# model_args = dict(
# widths=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), depths=(1, 1, 1, 4, 4), head_dim=32, num_classes=0, norm_eps=1e-6)
# return _create_efficientvit_large('efficientvit_l0_sam', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
#
#
# @register_model
# def efficientvit_l1_sam(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
# # only backbone for segment-anything-model weights
# model_args = dict(
# widths=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), depths=(1, 1, 1, 6, 6), head_dim=32, num_classes=0, norm_eps=1e-6)
# return _create_efficientvit_large('efficientvit_l1_sam', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
#
#
# @register_model
# def efficientvit_l2_sam(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
# # only backbone for segment-anything-model weights
# model_args = dict(
# widths=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), depths=(1, 2, 2, 8, 8), head_dim=32, num_classes=0, norm_eps=1e-6)
# return _create_efficientvit_large('efficientvit_l2_sam', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/efficientvit_mit.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/efficientvit_mit.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 20134
}
| 269
|
""" HRNet
Copied from https://github.com/HRNet/HRNet-Image-Classification
Original header:
Copyright (c) Microsoft
Licensed under the MIT License.
Written by Bin Xiao (Bin.Xiao@microsoft.com)
Modified by Ke Sun (sunk@mail.ustc.edu.cn)
"""
import logging
from typing import List
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.data import IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD
from timm.layers import create_classifier
from ._builder import build_model_with_cfg, pretrained_cfg_for_features
from ._features import FeatureInfo
from ._registry import register_model, generate_default_cfgs
from .resnet import BasicBlock, Bottleneck # leveraging ResNet block_types w/ additional features like SE
__all__ = ['HighResolutionNet', 'HighResolutionNetFeatures'] # model_registry will add each entrypoint fn to this
_BN_MOMENTUM = 0.1
_logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
cfg_cls = dict(
hrnet_w18_small=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(1,),
num_channels=(32,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(2, 2),
num_channels=(16, 32),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(2, 2, 2),
num_channels=(16, 32, 64),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(2, 2, 2, 2),
num_channels=(16, 32, 64, 128),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w18_small_v2=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(2,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(2, 2),
num_channels=(18, 36),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(2, 2, 2),
num_channels=(18, 36, 72),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=2,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(2, 2, 2, 2),
num_channels=(18, 36, 72, 144),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w18=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(18, 36),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(18, 36, 72),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(18, 36, 72, 144),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w30=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(30, 60),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(30, 60, 120),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(30, 60, 120, 240),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w32=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(32, 64),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(32, 64, 128),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(32, 64, 128, 256),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w40=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(40, 80),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(40, 80, 160),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(40, 80, 160, 320),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w44=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(44, 88),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(44, 88, 176),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(44, 88, 176, 352),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w48=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(48, 96),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(48, 96, 192),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(48, 96, 192, 384),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
),
hrnet_w64=dict(
stem_width=64,
stage1=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=1,
block_type='BOTTLENECK',
num_blocks=(4,),
num_channels=(64,),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
stage2=dict(
num_modules=1,
num_branches=2,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4),
num_channels=(64, 128),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage3=dict(
num_modules=4,
num_branches=3,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(64, 128, 256),
fuse_method='SUM'
),
stage4=dict(
num_modules=3,
num_branches=4,
block_type='BASIC',
num_blocks=(4, 4, 4, 4),
num_channels=(64, 128, 256, 512),
fuse_method='SUM',
),
)
)
class HighResolutionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
num_branches,
block_types,
num_blocks,
num_in_chs,
num_channels,
fuse_method,
multi_scale_output=True,
):
super(HighResolutionModule, self).__init__()
self._check_branches(
num_branches,
block_types,
num_blocks,
num_in_chs,
num_channels,
)
self.num_in_chs = num_in_chs
self.fuse_method = fuse_method
self.num_branches = num_branches
self.multi_scale_output = multi_scale_output
self.branches = self._make_branches(
num_branches,
block_types,
num_blocks,
num_channels,
)
self.fuse_layers = self._make_fuse_layers()
self.fuse_act = nn.ReLU(False)
def _check_branches(self, num_branches, block_types, num_blocks, num_in_chs, num_channels):
error_msg = ''
if num_branches != len(num_blocks):
error_msg = 'num_branches({}) <> num_blocks({})'.format(num_branches, len(num_blocks))
elif num_branches != len(num_channels):
error_msg = 'num_branches({}) <> num_channels({})'.format(num_branches, len(num_channels))
elif num_branches != len(num_in_chs):
error_msg = 'num_branches({}) <> num_in_chs({})'.format(num_branches, len(num_in_chs))
if error_msg:
_logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
def _make_one_branch(self, branch_index, block_type, num_blocks, num_channels, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.num_in_chs[branch_index] != num_channels[branch_index] * block_type.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
self.num_in_chs[branch_index], num_channels[branch_index] * block_type.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels[branch_index] * block_type.expansion, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
)
layers = [block_type(self.num_in_chs[branch_index], num_channels[branch_index], stride, downsample)]
self.num_in_chs[branch_index] = num_channels[branch_index] * block_type.expansion
for i in range(1, num_blocks[branch_index]):
layers.append(block_type(self.num_in_chs[branch_index], num_channels[branch_index]))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_branches(self, num_branches, block_type, num_blocks, num_channels):
branches = []
for i in range(num_branches):
branches.append(self._make_one_branch(i, block_type, num_blocks, num_channels))
return nn.ModuleList(branches)
def _make_fuse_layers(self):
if self.num_branches == 1:
return nn.Identity()
num_branches = self.num_branches
num_in_chs = self.num_in_chs
fuse_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches if self.multi_scale_output else 1):
fuse_layer = []
for j in range(num_branches):
if j > i:
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_in_chs[j], num_in_chs[i], 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_in_chs[i], momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2 ** (j - i), mode='nearest')))
elif j == i:
fuse_layer.append(nn.Identity())
else:
conv3x3s = []
for k in range(i - j):
if k == i - j - 1:
num_out_chs_conv3x3 = num_in_chs[i]
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_in_chs[j], num_out_chs_conv3x3, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_out_chs_conv3x3, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM)
))
else:
num_out_chs_conv3x3 = num_in_chs[j]
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_in_chs[j], num_out_chs_conv3x3, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_out_chs_conv3x3, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(False)
))
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
fuse_layers.append(nn.ModuleList(fuse_layer))
return nn.ModuleList(fuse_layers)
def get_num_in_chs(self):
return self.num_in_chs
def forward(self, x: List[torch.Tensor]) -> List[torch.Tensor]:
if self.num_branches == 1:
return [self.branches[0](x[0])]
for i, branch in enumerate(self.branches):
x[i] = branch(x[i])
x_fuse = []
for i, fuse_outer in enumerate(self.fuse_layers):
y = None
for j, f in enumerate(fuse_outer):
if y is None:
y = f(x[j])
else:
y = y + f(x[j])
x_fuse.append(self.fuse_act(y))
return x_fuse
class SequentialList(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, *args):
super(SequentialList, self).__init__(*args)
@torch.jit._overload_method # noqa: F811
def forward(self, x):
# type: (List[torch.Tensor]) -> (List[torch.Tensor])
pass
@torch.jit._overload_method # noqa: F811
def forward(self, x):
# type: (torch.Tensor) -> (List[torch.Tensor])
pass
def forward(self, x) -> List[torch.Tensor]:
for module in self:
x = module(x)
return x
@torch.jit.interface
class ModuleInterface(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor: # `input` has a same name in Sequential forward
pass
block_types_dict = {
'BASIC': BasicBlock,
'BOTTLENECK': Bottleneck
}
class HighResolutionNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
cfg,
in_chans=3,
num_classes=1000,
output_stride=32,
global_pool='avg',
drop_rate=0.0,
head='classification',
**kwargs,
):
super(HighResolutionNet, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
assert output_stride == 32 # FIXME support dilation
cfg.update(**kwargs)
stem_width = cfg['stem_width']
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, stem_width, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(stem_width, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM)
self.act1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(stem_width, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM)
self.act2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.stage1_cfg = cfg['stage1']
num_channels = self.stage1_cfg['num_channels'][0]
block_type = block_types_dict[self.stage1_cfg['block_type']]
num_blocks = self.stage1_cfg['num_blocks'][0]
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block_type, 64, num_channels, num_blocks)
stage1_out_channel = block_type.expansion * num_channels
self.stage2_cfg = cfg['stage2']
num_channels = self.stage2_cfg['num_channels']
block_type = block_types_dict[self.stage2_cfg['block_type']]
num_channels = [num_channels[i] * block_type.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels))]
self.transition1 = self._make_transition_layer([stage1_out_channel], num_channels)
self.stage2, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(self.stage2_cfg, num_channels)
self.stage3_cfg = cfg['stage3']
num_channels = self.stage3_cfg['num_channels']
block_type = block_types_dict[self.stage3_cfg['block_type']]
num_channels = [num_channels[i] * block_type.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels))]
self.transition2 = self._make_transition_layer(pre_stage_channels, num_channels)
self.stage3, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(self.stage3_cfg, num_channels)
self.stage4_cfg = cfg['stage4']
num_channels = self.stage4_cfg['num_channels']
block_type = block_types_dict[self.stage4_cfg['block_type']]
num_channels = [num_channels[i] * block_type.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels))]
self.transition3 = self._make_transition_layer(pre_stage_channels, num_channels)
self.stage4, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(self.stage4_cfg, num_channels, multi_scale_output=True)
self.head = head
self.head_channels = None # set if _make_head called
head_conv_bias = cfg.pop('head_conv_bias', True)
if head == 'classification':
# Classification Head
self.num_features = self.head_hidden_size = 2048
self.incre_modules, self.downsamp_modules, self.final_layer = self._make_head(
pre_stage_channels,
conv_bias=head_conv_bias,
)
self.global_pool, self.head_drop, self.classifier = create_classifier(
self.num_features,
self.num_classes,
pool_type=global_pool,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
)
else:
if head == 'incre':
self.num_features = self.head_hidden_size = 2048
self.incre_modules, _, _ = self._make_head(pre_stage_channels, incre_only=True)
else:
self.num_features = self.head_hidden_size = 256
self.incre_modules = None
self.global_pool = nn.Identity()
self.head_drop = nn.Identity()
self.classifier = nn.Identity()
curr_stride = 2
# module names aren't actually valid here, hook or FeatureNet based extraction would not work
self.feature_info = [dict(num_chs=64, reduction=curr_stride, module='stem')]
for i, c in enumerate(self.head_channels if self.head_channels else num_channels):
curr_stride *= 2
c = c * 4 if self.head_channels else c # head block_type expansion factor of 4
self.feature_info += [dict(num_chs=c, reduction=curr_stride, module=f'stage{i + 1}')]
self.init_weights()
def _make_head(self, pre_stage_channels, incre_only=False, conv_bias=True):
head_block_type = Bottleneck
self.head_channels = [32, 64, 128, 256]
# Increasing the #channels on each resolution
# from C, 2C, 4C, 8C to 128, 256, 512, 1024
incre_modules = []
for i, channels in enumerate(pre_stage_channels):
incre_modules.append(self._make_layer(head_block_type, channels, self.head_channels[i], 1, stride=1))
incre_modules = nn.ModuleList(incre_modules)
if incre_only:
return incre_modules, None, None
# downsampling modules
downsamp_modules = []
for i in range(len(pre_stage_channels) - 1):
in_channels = self.head_channels[i] * head_block_type.expansion
out_channels = self.head_channels[i + 1] * head_block_type.expansion
downsamp_module = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=conv_bias),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
downsamp_modules.append(downsamp_module)
downsamp_modules = nn.ModuleList(downsamp_modules)
final_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=self.head_channels[3] * head_block_type.expansion, out_channels=self.num_features,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=conv_bias),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.num_features, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
return incre_modules, downsamp_modules, final_layer
def _make_transition_layer(self, num_channels_pre_layer, num_channels_cur_layer):
num_branches_cur = len(num_channels_cur_layer)
num_branches_pre = len(num_channels_pre_layer)
transition_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches_cur):
if i < num_branches_pre:
if num_channels_cur_layer[i] != num_channels_pre_layer[i]:
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_channels_pre_layer[i], num_channels_cur_layer[i], 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels_cur_layer[i], momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
else:
transition_layers.append(nn.Identity())
else:
conv3x3s = []
for j in range(i + 1 - num_branches_pre):
_in_chs = num_channels_pre_layer[-1]
_out_chs = num_channels_cur_layer[i] if j == i - num_branches_pre else _in_chs
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(_in_chs, _out_chs, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(_out_chs, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
return nn.ModuleList(transition_layers)
def _make_layer(self, block_type, inplanes, planes, block_types, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or inplanes != planes * block_type.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes * block_type.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block_type.expansion, momentum=_BN_MOMENTUM),
)
layers = [block_type(inplanes, planes, stride, downsample)]
inplanes = planes * block_type.expansion
for i in range(1, block_types):
layers.append(block_type(inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_stage(self, layer_config, num_in_chs, multi_scale_output=True):
num_modules = layer_config['num_modules']
num_branches = layer_config['num_branches']
num_blocks = layer_config['num_blocks']
num_channels = layer_config['num_channels']
block_type = block_types_dict[layer_config['block_type']]
fuse_method = layer_config['fuse_method']
modules = []
for i in range(num_modules):
# multi_scale_output is only used last module
reset_multi_scale_output = multi_scale_output or i < num_modules - 1
modules.append(HighResolutionModule(
num_branches, block_type, num_blocks, num_in_chs, num_channels, fuse_method, reset_multi_scale_output)
)
num_in_chs = modules[-1].get_num_in_chs()
return SequentialList(*modules), num_in_chs
@torch.jit.ignore
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(
m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse=False):
matcher = dict(
stem=r'^conv[12]|bn[12]',
block_types=r'^(?:layer|stage|transition)(\d+)' if coarse else [
(r'^layer(\d+)\.(\d+)', None),
(r'^stage(\d+)\.(\d+)', None),
(r'^transition(\d+)', (99999,)),
],
)
return matcher
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable=True):
assert not enable, "gradient checkpointing not supported"
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.classifier
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: str = 'avg'):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.global_pool, self.classifier = create_classifier(
self.num_features, self.num_classes, pool_type=global_pool)
def stages(self, x) -> List[torch.Tensor]:
x = self.layer1(x)
xl = [t(x) for i, t in enumerate(self.transition1)]
yl = self.stage2(xl)
xl = [t(yl[-1]) if not isinstance(t, nn.Identity) else yl[i] for i, t in enumerate(self.transition2)]
yl = self.stage3(xl)
xl = [t(yl[-1]) if not isinstance(t, nn.Identity) else yl[i] for i, t in enumerate(self.transition3)]
yl = self.stage4(xl)
return yl
def forward_features(self, x):
# Stem
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.act2(x)
# Stages
yl = self.stages(x)
if self.incre_modules is None or self.downsamp_modules is None:
return yl
y = None
for i, incre in enumerate(self.incre_modules):
if y is None:
y = incre(yl[i])
else:
down: ModuleInterface = self.downsamp_modules[i - 1] # needed for torchscript module indexing
y = incre(yl[i]) + down.forward(y)
y = self.final_layer(y)
return y
def forward_head(self, x, pre_logits: bool = False):
# Classification Head
x = self.global_pool(x)
x = self.head_drop(x)
return x if pre_logits else self.classifier(x)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(y)
return x
class HighResolutionNetFeatures(HighResolutionNet):
"""HighResolutionNet feature extraction
The design of HRNet makes it easy to grab feature maps, this class provides a simple wrapper to do so.
It would be more complicated to use the FeatureNet helpers.
The `feature_location=incre` allows grabbing increased channel count features using part of the
classification head. If `feature_location=''` the default HRNet features are returned. First stem
conv is used for stride 2 features.
"""
def __init__(
self,
cfg,
in_chans=3,
num_classes=1000,
output_stride=32,
global_pool='avg',
drop_rate=0.0,
feature_location='incre',
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3, 4),
**kwargs,
):
assert feature_location in ('incre', '')
super(HighResolutionNetFeatures, self).__init__(
cfg,
in_chans=in_chans,
num_classes=num_classes,
output_stride=output_stride,
global_pool=global_pool,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
head=feature_location,
**kwargs,
)
self.feature_info = FeatureInfo(self.feature_info, out_indices)
self._out_idx = {f['index'] for f in self.feature_info.get_dicts()}
def forward_features(self, x):
assert False, 'Not supported'
def forward(self, x) -> List[torch.Tensor]:
out = []
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
if 0 in self._out_idx:
out.append(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.act2(x)
x = self.stages(x)
if self.incre_modules is not None:
x = [incre(f) for f, incre in zip(x, self.incre_modules)]
for i, f in enumerate(x):
if i + 1 in self._out_idx:
out.append(f)
return out
def _create_hrnet(variant, pretrained=False, cfg_variant=None, **model_kwargs):
model_cls = HighResolutionNet
features_only = False
kwargs_filter = None
if model_kwargs.pop('features_only', False):
model_cls = HighResolutionNetFeatures
kwargs_filter = ('num_classes', 'global_pool')
features_only = True
cfg_variant = cfg_variant or variant
pretrained_strict = model_kwargs.pop(
'pretrained_strict',
not features_only and model_kwargs.get('head', 'classification') == 'classification'
)
model = build_model_with_cfg(
model_cls,
variant,
pretrained,
model_cfg=cfg_cls[cfg_variant],
pretrained_strict=pretrained_strict,
kwargs_filter=kwargs_filter,
**model_kwargs,
)
if features_only:
model.pretrained_cfg = pretrained_cfg_for_features(model.default_cfg)
model.default_cfg = model.pretrained_cfg # backwards compat
return model
def _cfg(url='', **kwargs):
return {
'url': url,
'num_classes': 1000, 'input_size': (3, 224, 224), 'pool_size': (7, 7),
'crop_pct': 0.875, 'interpolation': 'bilinear',
'mean': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, 'std': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD,
'first_conv': 'conv1', 'classifier': 'classifier',
**kwargs
}
default_cfgs = generate_default_cfgs({
'hrnet_w18_small.gluon_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/', interpolation='bicubic'),
'hrnet_w18_small.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w18_small_v2.gluon_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/', interpolation='bicubic'),
'hrnet_w18_small_v2.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w18.ms_aug_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=0.95,
),
'hrnet_w18.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w30.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w32.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w40.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w44.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w48.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w64.ms_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'hrnet_w18_ssld.paddle_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=0.95, test_crop_pct=1.0, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288)
),
'hrnet_w48_ssld.paddle_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=0.95, test_crop_pct=1.0, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288)
),
})
@register_model
def hrnet_w18_small(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w18_small', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w18_small_v2(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w18_small_v2', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w18(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w18', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w30(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w30', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w32(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w32', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w40(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w40', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w44(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w44', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w48(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w48', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w64(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w64', pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w18_ssld(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
kwargs.setdefault('head_conv_bias', False)
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w18_ssld', cfg_variant='hrnet_w18', pretrained=pretrained, **kwargs)
@register_model
def hrnet_w48_ssld(pretrained=False, **kwargs) -> HighResolutionNet:
kwargs.setdefault('head_conv_bias', False)
return _create_hrnet('hrnet_w48_ssld', cfg_variant='hrnet_w48', pretrained=pretrained, **kwargs)
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/hrnet.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/hrnet.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 17679
}
| 270
|
""" NaFlex Vision Transformer
An improved version of the Vision Transformer with:
1. Encapsulated embedding and position encoding in a single module
2. Support for linear patch embedding on pre-patchified inputs
3. Support for NaFlex variable aspect, variable resolution
4. Support for FlexiViT variable patch size
5. Support for NaViT fractional/factorized position embedding
Based on ideas from:
- Original Vision Transformer: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
- FlexiViT: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.08013
- NaViT: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.06304
- NaFlex (SigLip-2): https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14786
Hacked together by / Copyright 2025, Ross Wightman, Hugging Face
"""
import logging
import math
from dataclasses import dataclass, fields, replace
from functools import partial
from typing import Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Set, Tuple, Type, Union, Any
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from timm.data import IMAGENET_INCEPTION_MEAN, IMAGENET_INCEPTION_STD
from timm.layers import (
AttentionPoolLatent,
Mlp,
LayerNorm,
PatchDropoutWithIndices,
PatchEmbedInterpolator,
_assert,
to_2tuple,
get_act_layer,
get_norm_layer,
apply_keep_indices_nlc,
disable_compiler,
)
from ._builder import build_model_with_cfg
from ._features import feature_take_indices
from ._features_fx import register_notrace_function, register_notrace_module
from ._manipulate import checkpoint, named_apply
from ._registry import register_model, generate_default_cfgs
from .eva import EvaBlock
from .vision_transformer import Block, global_pool_nlc
__all__ = ['NaFlexVitCfg', 'NaFlexVit']
_logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@dataclass
class NaFlexVitCfg:
"""Configuration for FlexVit model.
This dataclass contains the bulk of model configuration parameters,
with core parameters (img_size, in_chans, num_classes, etc.) remaining
as direct constructor arguments for API compatibility.
"""
# Architecture parameters
patch_size: Union[int, Tuple[int, int]] = 16
embed_dim: int = 768
depth: int = 12
num_heads: int = 12
mlp_ratio: float = 4.0
scale_mlp_norm: bool = False # Apply scaling norm to MLP
# Attention parameters
qkv_bias: bool = True
qk_norm: bool = False
proj_bias: bool = True
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.0
scale_attn_inner_norm: bool = False # Apply scaling norm to attn context
# Regularization
init_values: Optional[float] = None # Layer-scale init values (layer-scale enabled if not None)
drop_rate: float = 0.0 # Dropout rate for classifier
pos_drop_rate: float = 0.0 # Dropout rate for position embeddings
patch_drop_rate: float = 0.0 # Dropout rate for patch tokens
proj_drop_rate: float = 0.0 # Dropout rate for linear projections
drop_path_rate: float = 0.0 # Stochastic depth drop rate
# Prefix token configuration
class_token: bool = False # Use class token
reg_tokens: int = 0 # Number of register tokens
# Position embedding configuration
pos_embed: str = 'learned' # Type of position embedding ('learned', 'factorized', 'rope', 'none')
pos_embed_grid_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = (16, 16) # Grid size for position embedding initialization
pos_embed_interp_mode: str = 'bicubic' # Interpolation mode for position embedding resizing
pos_embed_ar_preserving: bool = False # Whether to preserve aspect ratio during position embedding interpolation
pos_embed_use_grid_sample: bool = False # Whether to use grid_sample for naflex position embedding interpolation
# ROPE specific configuration
rope_type: str = '' # ROPE type: '' or 'none' for no ROPE, 'axial' for standard, 'mixed' for learnable frequencies
rope_temperature: float = 10000.0 # Temperature for ROPE frequency computation
rope_ref_feat_shape: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None
rope_grid_offset: float = 0. # Grid offset for non-pixel ROPE mode
rope_grid_indexing: str = 'ij' # Grid indexing mode for ROPE ('ij' or 'xy')
# Image processing
dynamic_img_pad: bool = False # Whether to enable dynamic padding for variable resolution
# Other architecture choices
pre_norm: bool = False # Whether to apply normalization before attention/MLP layers (start of blocks)
final_norm: bool = True # Whether to apply final normalization before pooling and classifier (end of blocks)
fc_norm: Optional[bool] = None # Whether to normalize features before final classifier (after pooling)
# Global pooling setup
global_pool: str = 'map' # Type of global pooling for final sequence
pool_include_prefix: bool = False # Whether to include class/register prefix tokens in global pooling
attn_pool_num_heads: Optional[int] = None # Override num_heads for attention pool
attn_pool_mlp_ratio: Optional[float] = None # Override mlp_ratio for attention pool
# Weight initialization
weight_init: str = '' # Weight initialization scheme
fix_init: bool = True # Apply weight initialization fix (scaling w/ layer index)
# Embedding configuration
embed_proj_type: str = 'linear' # Type of embedding layer ('conv' or 'linear')
input_norm_layer: Optional[str] = None # Normalization layer for embeddings input (before input projection)
embed_norm_layer: Optional[str] = None # Normalization layer for embeddings (after input projection)
# Layer implementations
norm_layer: Optional[str] = None # Normalization layer for transformer blocks
act_layer: Optional[str] = None # Activation layer for MLP blocks
block_fn: Optional[str] = None # Transformer block implementation class name
mlp_layer: Optional[str] = None # MLP implementation class name
# EVA-specific parameters
attn_type: str = 'standard' # Attention type: 'standard', 'eva', 'rope'
swiglu_mlp: bool = False # Use SwiGLU MLP variant
qkv_fused: bool = True # Whether to use fused QKV projections
# Variable patch size support
enable_patch_interpolator: bool = False # Enable dynamic patch size support
def _overlay_kwargs(cfg: NaFlexVitCfg, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVitCfg:
"""Overlay kwargs onto config, replacing config values with provided kwargs."""
# Only update fields that exist in the config
config_fields = set(cfg.__dataclass_fields__.keys())
config_kwargs = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if k in config_fields}
if config_kwargs:
cfg = replace(cfg, **config_kwargs)
return cfg
def batch_patchify(
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_size: Tuple[int, int],
pad: bool = True,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Tuple[int, int]]:
"""Patchify a batch of images.
Args:
x: Input tensor of shape [B, C, H, W].
patch_size: Patch dimensions (patch_h, patch_w).
pad: Whether to pad images to be divisible by patch size.
Returns:
Tuple of (patches, grid_size) where patches has shape [B, N, P*P*C]
and grid_size is (num_patches_h, num_patches_w).
"""
B, C, H, W = x.shape
ph, pw = patch_size
# Ensure the image is divisible by patch size
if pad and (H % ph != 0 or W % pw != 0):
pad_h = (ph - H % ph) % ph
pad_w = (pw - W % pw) % pw
x = F.pad(x, (0, pad_w, 0, pad_h))
nh, nw = H // ph, W // pw
patches = x.view(B, C, nh, ph, nw, pw).permute(0, 2, 4, 3, 5, 1).reshape(B, nh * nw, ph * pw * C)
# FIXME confirm we want 'channels last' in the patch channel layout, egg ph, ph, C instead of C, ph, hw
return patches, (nh, nw)
def calculate_naflex_grid_sizes(_coord: torch.Tensor):
# Calculate the appropriate grid size from coords
max_y = _coord[:, :, 0].amax(dim=1) + 1
max_x = _coord[:, :, 1].amax(dim=1) + 1
return [(int(h.item()), int(w.item())) for h, w in zip(max_y, max_x)]
class NaFlexRopeIterator:
"""Iterator for generating batched ROPE embeddings for mixed mode with multiple grid sizes."""
def __init__(
self,
rope_module,
size_to_indices: Dict[Tuple[int, int], List[int]],
unique_sizes: List[Tuple[int, int]],
batch_size: int,
seq_len: int,
dtype: torch.dtype,
device: torch.device,
):
self.rope = rope_module
self.size_to_indices = size_to_indices
self.unique_sizes = unique_sizes
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.seq_len = seq_len
self.dtype = dtype
self.device = device
self.depth = rope_module.depth
self.num_heads = rope_module.num_heads
self.head_dim = 2 * rope_module.dim // rope_module.num_heads
self._depth_idx = 0
# Pre-compute embeddings for each unique size
self._embeddings_per_size = {}
for grid_size in unique_sizes:
# get_embed returns all depths at once for mixed mode
rope_embed = rope_module.get_embed(shape=grid_size)
self._embeddings_per_size[grid_size] = rope_embed
def __iter__(self):
self._depth_idx = 0
return self
@disable_compiler
def __next__(self):
if self._depth_idx >= self.depth:
raise StopIteration
# Create batch tensor for current depth
batch_embed = torch.zeros(
self.batch_size, self.num_heads, self.seq_len, self.head_dim,
dtype=self.dtype, device=self.device
)
# Fill in embeddings for each unique grid size
for grid_size in self.unique_sizes:
h, w = grid_size
actual_len = h * w
batch_indices = self.size_to_indices[grid_size]
# Get pre-computed embeddings for this size at current depth
embed = self._embeddings_per_size[grid_size][self._depth_idx] # [num_heads, H*W, dim]
# Assign to batch indices
for bi in batch_indices:
batch_embed[bi, :, :actual_len, :] = embed[:, :actual_len, :]
self._depth_idx += 1
return batch_embed
def get_block_fn(cfg: NaFlexVitCfg) -> Callable:
"""Get appropriate block function based on configuration.
Returns a partially applied block constructor with EVA-specific
or conflicting parameters pre-configured if needed.
"""
# Check if we need EVA block features
use_eva_features = (
cfg.attn_type in ('eva', 'rope') or
cfg.rope_type not in ('', 'none') or # Any ROPE type requires EVA blocks
cfg.swiglu_mlp
)
if use_eva_features:
# Determine attention type based on rope_type if not explicitly set
attn_type = cfg.attn_type
if attn_type == 'standard' and cfg.rope_type not in ('', 'none'):
attn_type = 'rope'
num_prefix_tokens = (1 if cfg.class_token else 0) + cfg.reg_tokens
return partial(
EvaBlock,
attn_type=attn_type,
swiglu_mlp=cfg.swiglu_mlp,
scale_mlp=cfg.scale_mlp_norm,
scale_attn_inner=cfg.scale_attn_inner_norm,
qkv_fused=cfg.qkv_fused,
num_prefix_tokens=num_prefix_tokens,
)
else:
# Standard ViT block
block_fn = cfg.block_fn or Block
if cfg.scale_mlp_norm or cfg.scale_attn_inner_norm:
# param names differ between EVA vs non-EVA block types
block_fn = partial(
block_fn,
scale_mlp_norm=cfg.scale_mlp_norm,
scale_attn_norm=cfg.scale_attn_inner_norm
)
return block_fn
@register_notrace_module
class NaFlexEmbeds(nn.Module):
"""NaFlex Embedding module for Vision Transformers.
This module encapsulates the complete embedding process for Vision Transformers,
supporting both standard and NaFlex (NaViT + FlexiViT) functionality:
1. Patch embedding (via Conv2d or Linear)
2. Class and register token preparation
3. Position embedding addition with interpolation support
4. Pre-normalization (if requested)
5. Dropout application
NaFlex capabilities include:
- Variable aspect ratio and resolution via patch coordinates
- Patch type indicators for handling padding tokens in attention
- Flexible position embedding interpolation for arbitrary grid sizes
- Support for factorized position embeddings
The patch embedding can be one of two types:
- Conv2d-based (default): For standard image inputs [B, C, H, W]
- Linear-based: For pre-patchified inputs [B, N, P*P*C]
Args:
patch_size: Size of patches for patch embedding
in_chans: Number of input image channels
embed_dim: Dimensionality of patch embedding
proj_type: Type of embedding projection layer ('conv' or 'linear')
input_norm_layer: Normalization layer applied to input (linear mode only)
proj_norm_layer: Normalization layer applied after projection
pos_embed: Type of position embedding ('learned', 'factorized', 'none')
pos_drop_rate: Dropout rate for position embeddings
class_token: Whether to include a class token
reg_tokens: Number of register tokens to include
bias: Whether to use bias in projection layers
dynamic_img_pad: Whether to enable dynamic padding for variable resolution
pos_embed_grid_size: Grid size for position embedding initialization
pos_embed_interp_mode: Interpolation mode for position embedding resizing
pos_embed_ar_preserving: Whether to preserve aspect ratio during position embedding interpolation
default_img_size: Default image size for position embedding grid calculation
"""
def __init__(
self,
patch_size: Union[int, Tuple[int, int]] = 16,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 768,
proj_type: Optional[str] = None,
proj_bias: bool = True,
class_token: bool = True,
reg_tokens: int = 0,
dynamic_img_pad: bool = False,
default_img_size: Optional[Union[int, Tuple[int, int]]] = None,
pos_embed: str = 'learned',
pos_embed_grid_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = (14, 14),
pos_embed_interp_mode: str = 'bicubic',
pos_embed_ar_preserving: bool = False,
pos_embed_use_grid_sample: bool = False,
input_norm_layer: Optional[Type[nn.Module]] = None,
proj_norm_layer: Union[bool, Optional[Type[nn.Module]]] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Type[nn.Module]] = None,
pos_drop_rate: float = 0.,
enable_patch_interpolator: bool = False,
) -> None:
"""Initialize NaFlexEmbeds module.
Args:
patch_size: Size of patches for patch embedding.
in_chans: Number of input image channels.
embed_dim: Dimensionality of patch embedding.
proj_type: Type of embedding projection layer ('conv' or 'linear').
proj_bias: Whether to use bias in projection layers.
class_token: Whether to include a class token.
reg_tokens: Number of register tokens to include.
dynamic_img_pad: Whether to enable dynamic padding for variable resolution.
default_img_size: Default image size for position embedding grid calculation.
pos_embed: Type of position embedding ('learned', 'factorized', 'none').
pos_embed_grid_size: Grid size for position embedding initialization.
pos_embed_interp_mode: Interpolation mode for position embedding resizing.
pos_embed_ar_preserving: Whether to preserve aspect ratio during interpolation.
input_norm_layer: Normalization layer applied to input (linear mode only).
proj_norm_layer: Normalization layer applied after projection.
norm_layer: Default normalization layer.
pos_drop_rate: Dropout rate for position embeddings.
enable_patch_interpolator: Enable dynamic patch size support.
"""
super().__init__()
self.has_class_token = class_token
self.num_reg_tokens = reg_tokens
self.pos_embed_interp_mode = pos_embed_interp_mode
self.pos_embed_ar_preserving = pos_embed_ar_preserving
self.pos_embed_use_grid_sample = pos_embed_use_grid_sample
self.patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
self.in_chans = in_chans
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.dynamic_img_pad = dynamic_img_pad
self.enable_patch_interpolator = enable_patch_interpolator
# Calculate number of prefix tokens
self.num_prefix_tokens = 1 if class_token else 0
self.num_prefix_tokens += reg_tokens
# Create class and register tokens
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim)) if class_token else None
self.reg_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, reg_tokens, embed_dim)) if reg_tokens else None
# Calculate grid size and number of patches
self.default_img_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None
self.pos_embed_grid_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None # Grid size used for learned pos embed init
if pos_embed_grid_size is not None:
# Highest priority, use provided pos_embed_grid_size
self.pos_embed_grid_size = pos_embed_grid_size
elif default_img_size is not None:
# Fallback to calculating grid size from img_size + patch_size if img size provided.
self.default_img_size = to_2tuple(default_img_size)
self.pos_embed_grid_size = tuple([s // p for s, p in zip(self.default_img_size, self.patch_size)])
# Determine patch embedding type (linear or conv2d)
if proj_type == 'linear':
# Create linear projection for pre-patchified inputs
# Input dimension is patch_size^2 * in_chans
patch_dim = self.patch_size[0] * self.patch_size[1] * in_chans
assert not (input_norm_layer is True and norm_layer is None), \
"`norm_layer` must be given when input_norm_layer=True"
input_norm_layer = norm_layer if input_norm_layer is True else (input_norm_layer or None)
self.norm_input = input_norm_layer(patch_dim) if input_norm_layer else None
self.proj = nn.Linear(patch_dim, embed_dim, bias=proj_bias)
self.flatten = False
self.is_linear = True
else:
# Default to convolutional patch embedding for image inputs
assert not input_norm_layer
self.norm_input = None
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(
in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size, bias=proj_bias
)
self.flatten = True
self.is_linear = False
# Create patch embedding interpolator if enabled
if self.enable_patch_interpolator:
self.patch_interpolator = PatchEmbedInterpolator(
base_patch_size=self.patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
interpolation=pos_embed_interp_mode,
antialias=True,
)
else:
self.patch_interpolator = None
# Create normalization layer after the projection
assert not (proj_norm_layer is True and norm_layer is None), \
"`norm_layer` must be given when proj_norm_layer=True"
proj_norm_layer = norm_layer if proj_norm_layer is True else (proj_norm_layer or None)
self.norm = proj_norm_layer(embed_dim) if proj_norm_layer else nn.Identity()
# Create position embedding if needed - only for patches, never for prefix tokens
if pos_embed in ('factorized', 'learned') and self.pos_embed_grid_size is None:
raise ValueError(
"Cannot initialize position embeddings without grid_size."
"Please provide img_size or pos_embed_grid_size.")
self.pos_embed: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
self.pos_embed_y: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
self.pos_embed_x: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
if not pos_embed or pos_embed == 'none':
self.pos_embed_type = 'none'
elif pos_embed == 'factorized':
assert self.pos_embed_grid_size is not None
h, w = self.pos_embed_grid_size
self.pos_embed_type = 'factorized'
self.pos_embed_y = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, h, embed_dim) * .02)
self.pos_embed_x = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, w, embed_dim) * .02)
else:
assert self.pos_embed_grid_size is not None
h, w = self.pos_embed_grid_size
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, h, w, embed_dim) * .02)
self.pos_embed_type = 'learned'
# Dropout layer
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=pos_drop_rate)
def feature_info(self, location) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get feature information for feature extraction.
Args:
location: Feature extraction location identifier
Returns:
Dictionary containing feature channel count and reduction factor
"""
return dict(num_chs=self.embed_dim, reduction=self.patch_size)
def feat_ratio(self, as_scalar: bool = True) -> Union[int, Tuple[int, int]]:
"""Get the feature reduction ratio (stride) of the patch embedding.
Args:
as_scalar: Whether to return the maximum dimension as a scalar
Returns:
Feature reduction ratio as scalar or tuple
"""
if as_scalar:
return max(self.patch_size)
else:
return self.patch_size
def dynamic_feat_size(self, img_size: Tuple[int, int]) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""Calculate grid (feature) size for given image size.
Takes into account dynamic padding when enabled.
Args:
img_size: Input image size as (height, width)
Returns:
Grid size as (grid_height, grid_width)
"""
if self.dynamic_img_pad:
return math.ceil(img_size[0] / self.patch_size[0]), math.ceil(img_size[1] / self.patch_size[1])
else:
return img_size[0] // self.patch_size[0], img_size[1] // self.patch_size[1]
@disable_compiler
def _apply_learned_naflex_pos_embed(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
) -> None:
"""Apply learned position embeddings to NaFlex batch in-place.
Interpolates learned 2D position embeddings for each sample in the batch
based on their individual grid sizes.
Args:
x: Input tensor to add position embeddings to [B, N, C]
patch_coord: Patch coordinates [B, N, 2] with (y, x) values
"""
# Calculate grid sizes from patch coordinates
naflex_grid_sizes = calculate_naflex_grid_sizes(patch_coord)
orig_h, orig_w = self.pos_embed.shape[1:3]
pos_embed_nchw = self.pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float() # B,C,H,W
def _interp2d(size):
"""
Return a flattened positional-embedding grid at an arbitrary spatial resolution.
Converts the learned 2-D table stored in NCHW format (pos_embed_nchw) into
a (1, H*W, C) sequence that matches the requested size.
"""
if (size[0] == orig_h) and (size[1] == orig_w):
pos_embed_flat = self.pos_embed.reshape(1, orig_h * orig_w, -1)
else:
_interp_size = to_2tuple(max(size)) if self.pos_embed_ar_preserving else size
pos_embed_flat = F.interpolate(
pos_embed_nchw,
size=_interp_size,
mode=self.pos_embed_interp_mode,
align_corners=False,
antialias=True,
)[:, :, :size[0], :size[1]].flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
return pos_embed_flat.to(dtype=x.dtype)
# Determine unique grid sizes to avoid duplicate interpolation
size_to_indices: Dict[Tuple[int, int], List[int]] = {}
for bi, k in enumerate(naflex_grid_sizes):
# k = h << 16 | w # FIXME can get jit compat with this
size_to_indices.setdefault(k, []).append(bi)
for k, batch_indices in size_to_indices.items():
# h, w = k >> 16, k & 0xFFFF # FIXME can get jit compat with this
# Interpolate only once for this (h, w)
pos_embed_flat = _interp2d(k)
seq_len = min(x.shape[1], pos_embed_flat.shape[1])
x[:, :seq_len].index_add_(
0,
torch.as_tensor(batch_indices, device=x.device),
pos_embed_flat[:, :seq_len].expand(len(batch_indices), -1, -1)
)
@disable_compiler
def _apply_learned_naflex_pos_embed_grid_sample(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
) -> None:
"""Apply learned position embeddings to NaFlex batch using grid_sample.
Uses F.grid_sample for efficient interpolation of learned 2D position embeddings
based on patch coordinates. Based on proposal by https://github.com/stas-sl
Args:
x: Input tensor to add position embeddings to [B, N, C]
patch_coord: Patch coordinates [B, N, 2] with (y, x) values
"""
device = x.device
B, N, C = x.shape
shapes = patch_coord.max(dim=1).values + 1 # (B, 2) containing [h_i, w_i]
if self.pos_embed_ar_preserving:
L_i = shapes.amax(dim=1) # (B,) max(h_i, w_i)
L_global = L_i.amax()
grid_size_y = grid_size_x = L_global
scale_x = scale_y = L_global / L_i # uniform zoom (B,)
else:
grid_size_y, grid_size_x = shapes.amax(dim=0) # (2,)
scale_y = grid_size_y / shapes[:, 0] # vertical zoom (B,)
scale_x = grid_size_x / shapes[:, 1] # horizontal zoom (B,)
theta = torch.zeros(B, 2, 3, device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
theta[:, 0, 0] = scale_x
theta[:, 1, 1] = scale_y
theta[:, 0, 2] = scale_x - 1 # translate x
theta[:, 1, 2] = scale_y - 1 # translate y
grid = F.affine_grid(theta, (B, C, grid_size_y, grid_size_x), align_corners=False)
pos_embed = F.grid_sample(
self.pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).expand(B, -1, -1, -1).float(),
grid,
mode=self.pos_embed_interp_mode,
align_corners=False,
padding_mode='border',
).to(dtype=x.dtype) # (B, C, H_out, W_out)
bi = torch.arange(B, device=device).unsqueeze(1)
x += pos_embed[bi, :, patch_coord[..., 0], patch_coord[..., 1]] # NOTE leave as '+='
def _apply_learned_pos_embed(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
grid_size: List[int],
) -> None:
"""Apply learned position embeddings to standard 2D batch in-place.
Interpolates learned 2D position embeddings to match the specified grid size.
Args:
x: Input tensor to add position embeddings to [B, H*W, C]
grid_size: Target grid size as [height, width]
"""
orig_h, orig_w = self.pos_embed.shape[1:3]
if grid_size[0] == orig_h and grid_size[1] == orig_w:
# No resize needed, just flatten
pos_embed_flat = self.pos_embed.reshape(1, orig_h * orig_w, -1)
else:
# Resize if needed - directly using F.interpolate
if self.pos_embed_ar_preserving:
L = max(grid_size)
_interp_size = L, L
else:
_interp_size = grid_size
pos_embed_flat = F.interpolate(
self.pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float(), # B,C,H,W
size=_interp_size,
mode=self.pos_embed_interp_mode,
align_corners=False,
antialias=True,
)[:, :, :grid_size[0], :grid_size[1]].flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
pos_embed_flat = pos_embed_flat.to(dtype=x.dtype)
x.add_(pos_embed_flat)
@disable_compiler
def _apply_factorized_naflex_pos_embed(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
) -> None:
"""Apply factorized position embeddings to NaFlex batch in-place.
Uses separate Y and X position embedding tables that are interpolated
and combined for each sample's grid size.
Args:
x: Input tensor to add position embeddings to [B, N, C]
patch_coord: Patch coordinates [B, N, 2] with (y, x) values
"""
# Calculate grid sizes from patch coordinates
naflex_grid_sizes = calculate_naflex_grid_sizes(patch_coord)
assert len(naflex_grid_sizes) == x.size(0) # one (H,W) per sample
# Handle each batch element separately with its own grid size
orig_h, orig_w = self.pos_embed_y.shape[1], self.pos_embed_x.shape[1]
# bucket samples that share the same (H, W) so we build each grid once
size_to_indices: Dict[Tuple[int, int], List[int]] = {}
for bi, k in enumerate(naflex_grid_sizes):
size_to_indices.setdefault(k, []).append(bi)
def _interp1d(table: torch.Tensor, new_length: int, orig_length: int) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Resample a 1-D positional-embedding table to specified length
and return it in (1, L, C) layout, dtype matching x.
"""
if new_length == orig_length:
return table.to(dtype=x.dtype)
return F.interpolate(
table.permute(0, 2, 1).float(), # (1,C,L) → (1,C,L_out)
size=new_length,
mode='linear',
align_corners=False,
).permute(0, 2, 1).to(dtype=x.dtype) # → (1,L_out,C)
for k, batch_indices in size_to_indices.items():
target_h, target_w = k
if self.pos_embed_ar_preserving:
len_y = len_x = max(target_h, target_w)
else:
len_y, len_x = target_h, target_w
pe_y = _interp1d(self.pos_embed_y, len_y, orig_h)[:, :target_h] # (1,H,C)
pe_x = _interp1d(self.pos_embed_x, len_x, orig_w)[:, :target_w] # (1,W,C)
# Broadcast, add and flatten to sequence layout (row major)
pos = pe_y.unsqueeze(2) + pe_x.unsqueeze(1) # (1,H,W,C)
pos = pos.flatten(1, 2)
seq_len = min(x.shape[1], pos.shape[1])
x[:, :seq_len].index_add_(
0,
torch.as_tensor(batch_indices, device=x.device),
pos[:, :seq_len].expand(len(batch_indices), -1, -1)
)
@disable_compiler
def _apply_factorized_naflex_pos_embed_grid_sample(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
) -> None:
"""Apply factorized position embeddings to NaFlex batch using grid_sample.
Uses F.grid_sample for efficient interpolation of separate Y and X position
embedding tables based on patch coordinates. Based on proposal by https://github.com/stas-sl
Args:
x: Input tensor to add position embeddings to [B, N, C]
patch_coord: Patch coordinates [B, N, 2] with (y, x) values
"""
device = x.device
B, _, C = x.shape
shapes = patch_coord.amax(dim=1) + 1
if self.pos_embed_ar_preserving:
# Aspect ratio preserving mode: use square grid with uniform scaling
L_i = shapes.amax(dim=1) # (B,) max(h_i, w_i)
L_global = L_i.amax()
grid_size_y = grid_size_x = L_global
scale_x = scale_y = L_global / L_i # uniform zoom (B,)
else:
# Standard mode: different scaling for x and y
grid_size_y, grid_size_x = shapes.amax(0)
scale_x = grid_size_x / shapes[:, 1] # horizontal zoom (B,)
scale_y = grid_size_y / shapes[:, 0] # vertical zoom (B,)
def _interp1d(table: torch.Tensor, scale: torch.Tensor, out_length: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
pe = table.permute(0, 2, 1).unsqueeze(2).expand(B, -1, -1, -1).float() # (1, L, C) -> (B, C, 1, L)
theta = torch.zeros(B, 2, 3, device=x.device)
theta[:, 0, 0] = scale
theta[:, 0, 2] = scale - 1
theta[:, 1, 1] = 1
grid = F.affine_grid(theta, (B, C, 1, out_length), align_corners=False)
pe = F.grid_sample(pe, grid, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False, padding_mode='border')
return pe.to(x.dtype)
# Interpolate along each axis
pe_x = _interp1d(self.pos_embed_x, scale=scale_x, out_length=grid_size_x)
pe_y = _interp1d(self.pos_embed_y, scale=scale_y, out_length=grid_size_y)
bi = torch.arange(B, device=device).unsqueeze(1)
x += pe_x[bi, :, 0, patch_coord[..., 1]] + pe_y[bi, :, 0, patch_coord[..., 0]]
def _apply_factorized_pos_embed(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
grid_size: List[int],
) -> None:
"""Apply factorized position embeddings to standard 2D batch in-place.
Uses separate Y and X position embedding tables that are interpolated
and combined for the specified grid size.
Args:
x: Input tensor to add position embeddings to [B, H*W, C]
grid_size: Target grid size as [height, width]
"""
orig_h, orig_w = self.pos_embed_y.shape[1], self.pos_embed_x.shape[1]
target_h, target_w = grid_size
if self.pos_embed_ar_preserving:
len_y = len_x = max(target_h, target_w)
else:
len_y, len_x = target_h, target_w
def _interp1d(table: torch.Tensor, new_length: int, orig_length: int) -> torch.Tensor:
if new_length == orig_length:
return table.to(dtype=x.dtype)
return F.interpolate(
table.permute(0, 2, 1).float(), # (1,L,C) -> (1,C,L)
size=new_length,
mode='linear',
align_corners=False,
).permute(0, 2, 1).to(dtype=x.dtype) # (1,L,C)
# Interpolate embeddings
pe_y = _interp1d(self.pos_embed_y, len_y, orig_h)[:, :target_h] # (1,H,C)
pe_x = _interp1d(self.pos_embed_x, len_x, orig_w)[:, :target_w] # (1,W,C)
# Broadcast, add and flatten to sequence layout (row major)
pos_embed = pe_y.unsqueeze(2) + pe_x.unsqueeze(1) # (1, H, W, C)
pos_embed_flat = pos_embed.flatten(1, 2) # (1, H*W, C)
x.add_(pos_embed_flat)
def forward(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[Tuple[int, int]]]:
"""Forward pass for patch embedding with position encoding.
Args:
x: Input tensor. Supported formats:
- [B, C, H, W] for conv mode
- [B, N, P*P*C] for pre-patchified linear mode (normal)
- [B, N, Ph, Pw, C] for pre-patchified linear mode (variable patch size)
patch_coord: Optional patch coordinates [B, N, 2] for NaFlex mode.
patch_valid: Optional validity mask for patches [B, N] for NaFlex mode.
Returns:
Tuple of (embedded_tensor, grid_size) where:
- embedded_tensor: [B, num_prefix_tokens + N, embed_dim]
- grid_size: (H, W) tuple for standard mode, None for NaFlex mode
"""
grid_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None
B = x.shape[0]
if self.is_linear:
# Linear embedding path, works with NaFlex mode or standard 2D mode
if patch_coord is None:
# Standard 2D (B, C, H, W) mode
_assert(x.ndim == 4, 'Expecting 2D image input with input ndim == 4')
x, grid_size = batch_patchify(x, self.patch_size, pad=self.dynamic_img_pad)
else:
# Pre-patchified NaFlex mode
# Variable patch size mode: [B, N, Ph, Pw, C], normal mode: [B, N, P*P*C]
_assert(x.ndim == 5 or x.ndim == 3, 'Expecting patchified input with ndim == 3 or 5.')
# Handle variable patch size projection
if self.enable_patch_interpolator and x.ndim == 5:
_assert(self.norm_input is None, 'input norm not supported with patch resizing')
# Apply projection with interpolation
x = self.patch_interpolator(
x,
self.proj.weight,
self.proj.bias,
patch_size=tuple(x.shape[2:4]), # patch size from [B, N, Ph, Pw, C] shape
is_linear=True,
)
else:
# Standard projection
x = x.flatten(2) # ensure [B, N, P*P*C], flatten Ph*Pw*C if separate
if self.norm_input is not None:
x = self.norm_input(x)
x = self.proj(x)
else:
_assert(x.ndim == 4, 'Convolutional input must be 4D')
if self.dynamic_img_pad:
H, W = x.shape[-2:]
pad_h = (self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0]) % self.patch_size[0]
pad_w = (self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1]) % self.patch_size[1]
x = F.pad(x, (0, pad_w, 0, pad_h))
x = self.proj(x)
grid_size = x.shape[-2:]
if self.flatten:
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # NCHW -> NLC
# Apply normalization after flattening
x = self.norm(x)
if self.pos_embed_type == 'learned':
if grid_size is not None:
# Standard 2D mode
self._apply_learned_pos_embed(x, grid_size=grid_size)
else:
# NaFlex mode
if self.pos_embed_use_grid_sample:
self._apply_learned_naflex_pos_embed_grid_sample(x, patch_coord=patch_coord)
else:
self._apply_learned_naflex_pos_embed(x, patch_coord=patch_coord)
elif self.pos_embed_type == 'factorized':
if grid_size is not None:
# Standard 2D mode
self._apply_factorized_pos_embed(x, grid_size=grid_size)
else:
# NaFlex mode
if self.pos_embed_use_grid_sample:
self._apply_factorized_naflex_pos_embed_grid_sample(x, patch_coord=patch_coord)
else:
self._apply_factorized_naflex_pos_embed(x, patch_coord=patch_coord)
# Prepare and add class and register tokens
to_cat = []
if self.cls_token is not None:
to_cat.append(self.cls_token.expand(B, -1, -1))
if self.reg_token is not None:
to_cat.append(self.reg_token.expand(B, -1, -1))
# Add tokens to the beginning
if to_cat:
x = torch.cat(to_cat + [x], dim=1)
# Apply dropout
x = self.pos_drop(x)
return x, grid_size
@register_notrace_function
def create_attention_mask(
patch_valid: torch.Tensor,
num_prefix_tokens: int = 0,
symmetric: bool = True,
q_len: Optional[int] = None,
dtype: torch.dtype = torch.float32,
) -> Optional[torch.Tensor]:
"""Creates an attention mask from patch validity information.
Supports two modes controlled by `symmetric`:
1. `symmetric=True` (default): Creates a symmetric mask of shape
[B, 1, seq_len, seq_len]. An attention pair (i, j) is allowed only if
both token i and token j are valid. Suitable for standard self-attention.
2. `symmetric=False`: Creates a potentially non-square mask of shape
[B, 1, q_len, kv_len]. An attention pair (q, k) is allowed only if
the key/value token k is valid. Query token validity is not checked
in the mask itself. Useful for cross-attention or specific self-attention
implementations `q_len` can be specified.
Used for NaFlex mode to handle variable token counts and padding tokens.
Args:
patch_valid: Tensor of shape [B, N] with True for valid patches, False for padding.
num_prefix_tokens: Number of prefix tokens (class token, register tokens)
to prepend, which are always considered valid.
symmetric: If True, create a symmetric mask.
If False, create an expanded mask based only on key/value validity.
q_len: Query sequence length override. Only used when `symmetric` is False.
Defaults to the key/value sequence length (`kv_len`) if None.
dtype: Dtype of the output attention mask (e.g., torch.float32).
Returns:
Attention mask tensor. Additive mask (-inf for masked, 0 for unmasked).
Shape is [B, 1, seq_len, seq_len] if symmetric=True,
or [B, 1, q_len, kv_len] if symmetric=False.
"""
if patch_valid is None:
return None
patch_valid = patch_valid.bool() # Ensure boolean type
B, N = patch_valid.shape
kv_len = N # Initial key/value length is the number of patches
# Prepend prefix tokens if any
if num_prefix_tokens > 0:
# Create prefix validity tensor on the same device/dtype base as patch_valid
prefix_valid = patch_valid.new_ones((B, num_prefix_tokens), dtype=torch.bool)
# Concatenate prefix and patch validity. Shape becomes [B, num_prefix_tokens + N]
patch_valid = torch.cat([prefix_valid, patch_valid], dim=1)
kv_len += num_prefix_tokens # Update total key/value sequence length
if symmetric:
# Symmetric mask is True where BOTH query and key are valid
mask_bool = patch_valid.unsqueeze(-1) & patch_valid.unsqueeze(1)
mask_bool = mask_bool.unsqueeze(1) # Add head dimension: [B, 1, seq_len, seq_len]
else:
# Expanded mask
q_len = q_len or kv_len
mask_bool = patch_valid[:, None, None, :].expand(B, 1, q_len, kv_len)
# Create the float mask and apply masking using additive mask convention
mask_float = torch.zeros_like(mask_bool, dtype=dtype)
# Fill with negative infinity where mask_bool is False (masked positions)
mask_float.masked_fill_(~mask_bool, torch.finfo(dtype).min)
return mask_float
@register_notrace_function
def global_pool_naflex(
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
pool_type: str = 'token',
num_prefix_tokens: int = 1,
reduce_include_prefix: bool = False,
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Global pooling with NaFlex support for masked tokens.
Applies global pooling while respecting patch validity masks to exclude
padding tokens from pooling operations.
Args:
x: Input tensor with shape [B, N, C]
patch_valid: Optional validity mask for patches [B, N-num_prefix_tokens]
pool_type: Type of pooling ('token', 'avg', 'avgmax', 'max')
num_prefix_tokens: Number of prefix tokens (class/register)
reduce_include_prefix: Whether to include prefix tokens in pooling reduction
Returns:
Pooled tensor with shape [B, C]
"""
if patch_valid is None or pool_type not in ('avg', 'avgmax', 'max'):
# Fall back to standard pooling
x = global_pool_nlc(
x,
pool_type=pool_type,
num_prefix_tokens=num_prefix_tokens,
reduce_include_prefix=reduce_include_prefix,
)
return x
# For NaFlex mode, we need to apply masked pooling to exclude padding tokens
if num_prefix_tokens > 0:
if reduce_include_prefix:
# Include prefix tokens in pooling - they are always considered valid
# patch_valid only covers patch tokens, so create combined validity mask
prefix_valid = patch_valid.new_ones(x.shape[0], num_prefix_tokens)
patch_valid = torch.cat([prefix_valid, patch_valid], dim=1)
else:
# Exclude prefix tokens from pooling (default behavior)
x = x[:, num_prefix_tokens:]
patch_valid_float = patch_valid.to(x.dtype)
if pool_type == 'avg':
# Compute masked average pooling, sum valid tokens and divide by count of valid tokens
masked_sums = (x * patch_valid_float.unsqueeze(-1)).sum(dim=1)
valid_counts = patch_valid_float.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).clamp(min=1)
pooled = masked_sums / valid_counts
return pooled
elif pool_type == 'avgmax':
# For avgmax, compute masked average and masked max
masked_sums = (x * patch_valid_float.unsqueeze(-1)).sum(dim=1)
valid_counts = patch_valid_float.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).clamp(min=1)
masked_avg = masked_sums / valid_counts
# For max pooling we set masked positions to large negative value
masked_x = x.clone()
masked_x[~patch_valid] = torch.finfo(masked_x.dtype).min
masked_max = masked_x.amax(dim=1)
# Combine average and max
return 0.5 * (masked_avg + masked_max)
elif pool_type == 'max':
# For max pooling we set masked positions to large negative value
masked_x = x.clone()
masked_x[~patch_valid] = torch.finfo(masked_x.dtype).min
return masked_x.amax(dim=1)
else:
assert False
class NaFlexVit(nn.Module):
"""NaFlexVit: Vision Transformer with NaFlex support for flexible input handling.
A flexible implementation of Vision Transformer that supports:
- Standard image classification with various pooling strategies
- NaFlex functionality for variable aspect ratios and resolutions
- Linear patch embedding for pre-patchified inputs
- Multiple position embedding strategies (learned, factorized, rope)
- Comprehensive attention masking for efficient batch processing
- Encapsulated embedding and position encoding in FlexEmbeds module
- Compatible with standard ViT checkpoints through checkpoint filtering
"""
def __init__(
self,
cfg: Optional[NaFlexVitCfg] = None,
in_chans: int = 3,
num_classes: int = 1000,
img_size: Optional[Union[int, Tuple[int, int]]] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
"""Initialize NaFlexVit model.
Args:
cfg: Model configuration. If None, uses default NaFlexVitCfg.
in_chans: Number of input image channels.
num_classes: Number of classification classes.
img_size: Input image size (for backwards compatibility with classic vit).
**kwargs: Additional config parameters to override cfg values.
"""
super().__init__()
# Initialize config
cfg = cfg or NaFlexVitCfg()
if kwargs:
cfg = _overlay_kwargs(cfg, **kwargs)
# Validate configuration
assert cfg.global_pool in ('', 'avg', 'avgmax', 'max', 'token', 'map')
assert cfg.class_token or cfg.global_pool != 'token'
assert cfg.pos_embed in ('', 'none', 'learned', 'factorized')
# Resolve layer implementations
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(cfg.norm_layer) or LayerNorm
embed_norm_layer = get_norm_layer(cfg.embed_norm_layer)
act_layer = get_act_layer(cfg.act_layer) or nn.GELU
block_fn = get_block_fn(cfg)
mlp_layer = cfg.mlp_layer or Mlp # TODO: Support configurable mlp_layer via string lookup
# Store instance variables
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.global_pool = cfg.global_pool
self.num_features = self.head_hidden_size = self.embed_dim = cfg.embed_dim # for consistency with other models
self.num_prefix_tokens = 1 if cfg.class_token else 0
self.num_prefix_tokens += cfg.reg_tokens
self.num_reg_tokens = cfg.reg_tokens
self.has_class_token = cfg.class_token
self.pool_include_prefix = cfg.pool_include_prefix
self.grad_checkpointing = False
# Initialize embedding module (includes patch, position embedding, and class/reg tokens)
# FlexEmbeds is always used - handles both linear and conv embedding
self.embeds = NaFlexEmbeds(
patch_size=cfg.patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=cfg.embed_dim,
proj_type=cfg.embed_proj_type,
proj_bias=not cfg.pre_norm, # disable bias if pre-norm is used (e.g. CLIP)
class_token=cfg.class_token,
reg_tokens=cfg.reg_tokens,
default_img_size=img_size,
dynamic_img_pad=cfg.dynamic_img_pad,
pos_embed=cfg.pos_embed,
pos_embed_grid_size=cfg.pos_embed_grid_size,
pos_embed_interp_mode=cfg.pos_embed_interp_mode,
pos_embed_ar_preserving=cfg.pos_embed_ar_preserving,
pos_embed_use_grid_sample=cfg.pos_embed_use_grid_sample,
proj_norm_layer=embed_norm_layer,
pos_drop_rate=cfg.pos_drop_rate,
enable_patch_interpolator=getattr(cfg, 'enable_patch_interpolator', False),
)
self.norm_pre = norm_layer(cfg.embed_dim) if cfg.pre_norm else nn.Identity()
# ROPE position embeddings at model level
self.rope: Optional[nn.Module] = None
self.rope_is_mixed = False
if cfg.rope_type and cfg.rope_type != 'none':
from timm.layers.pos_embed_sincos import RotaryEmbeddingCat, RotaryEmbeddingMixed
if cfg.rope_type == 'mixed':
self.rope = RotaryEmbeddingMixed(
cfg.embed_dim,
depth=cfg.depth,
num_heads=cfg.num_heads,
temperature=cfg.rope_temperature,
feat_shape=None, # Dynamic shapes for NaFlex
grid_indexing=cfg.rope_grid_indexing,
)
self.rope_is_mixed = True
elif cfg.rope_type == 'axial':
self.rope = RotaryEmbeddingCat(
cfg.embed_dim // cfg.num_heads,
temperature=cfg.rope_temperature,
in_pixels=False,
feat_shape=None, # Dynamic shapes for NaFlex
ref_feat_shape=cfg.rope_ref_feat_shape,
grid_offset=cfg.rope_grid_offset,
grid_indexing=cfg.rope_grid_indexing,
)
self.rope_is_mixed = False
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown rope_type: {cfg.rope_type}")
# Patch dropout
if cfg.patch_drop_rate > 0:
self.patch_drop = PatchDropoutWithIndices(
cfg.patch_drop_rate,
num_prefix_tokens=self.num_prefix_tokens,
)
else:
self.patch_drop = None
# Transformer blocks
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, cfg.drop_path_rate, cfg.depth)] # stochastic depth decay rule
# Create transformer blocks
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[
block_fn(
dim=cfg.embed_dim,
num_heads=cfg.num_heads,
mlp_ratio=cfg.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=cfg.qkv_bias,
qk_norm=cfg.qk_norm,
proj_bias=cfg.proj_bias,
init_values=cfg.init_values,
proj_drop=cfg.proj_drop_rate,
attn_drop=cfg.attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[i],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
mlp_layer=mlp_layer,
)
for i in range(cfg.depth)
])
# Feature info for downstream tasks
patch_reduction = self.embeds.feat_ratio(as_scalar=True)
self.feature_info = [
dict(module=f'blocks.{i}', num_chs=cfg.embed_dim, reduction=patch_reduction)
for i in range(cfg.depth)
]
self.norm = norm_layer(cfg.embed_dim) if cfg.final_norm and not cfg.fc_norm else nn.Identity()
# Classifier Head
if cfg.global_pool == 'map':
self.attn_pool = AttentionPoolLatent(
self.embed_dim,
num_heads=cfg.attn_pool_num_heads or cfg.num_heads,
mlp_ratio=cfg.attn_pool_mlp_ratio or cfg.mlp_ratio,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
)
else:
self.attn_pool = None
# Handle fc_norm default value
fc_norm = cfg.fc_norm
if fc_norm is None:
fc_norm = cfg.global_pool == 'avg'
self.fc_norm = norm_layer(cfg.embed_dim) if cfg.final_norm and fc_norm else nn.Identity()
self.head_drop = nn.Dropout(cfg.drop_rate)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
if cfg.weight_init != 'skip':
self.init_weights(cfg.weight_init)
if cfg.fix_init:
self.fix_init_weight()
def fix_init_weight(self) -> None:
"""Apply initialization weight fix with layer-wise scaling."""
def rescale(param: torch.Tensor, _layer_id: int) -> None:
with torch.no_grad():
param.div_(math.sqrt(2.0 * _layer_id))
for layer_id, layer in enumerate(self.blocks):
if hasattr(layer, 'attn'):
rescale(layer.attn.proj.weight, layer_id + 1)
if hasattr(layer, 'mlp'):
rescale(layer.mlp.fc2.weight, layer_id + 1)
if hasattr(layer, 'attn_out_proj'):
rescale(layer.attn_out_proj.weight, layer_id + 1)
if hasattr(layer, 'mlp_out_proj'):
rescale(layer.mlp_out_proj.weight, layer_id + 1)
def init_weights(self, mode: str = '') -> None:
"""Initialize model weights according to specified scheme.
Args:
mode: Initialization mode ('jax', 'jax_nlhb', 'moco', or '')
"""
assert mode in ('jax', 'jax_nlhb', 'moco', '')
head_bias = -math.log(self.num_classes) if 'nlhb' in mode else 0.
named_apply(get_init_weights_vit(mode, head_bias), self)
@torch.jit.ignore()
def load_pretrained(self, checkpoint_path: str, prefix: str = '') -> None:
# Custom loading for the new model structure
from .vision_transformer import _load_weights as _orig_load_weights
def _load_weights_adapter(model, checkpoint_path, prefix=''):
"""Adapter function to handle the different model structure"""
state_dict = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location='cpu')
if isinstance(state_dict, dict) and 'state_dict' in state_dict:
state_dict = state_dict['state_dict']
# Map original keys to new structure
for k in list(state_dict.keys()):
if k.startswith('cls_token'):
state_dict['embeds.' + k] = state_dict.pop(k)
elif k.startswith('reg_token'):
state_dict['embeds.' + k] = state_dict.pop(k)
elif k.startswith('pos_embed'):
state_dict['embeds.' + k] = state_dict.pop(k)
elif k.startswith('patch_embed'):
state_dict['embeds.' + k[12:]] = state_dict.pop(k)
return _orig_load_weights(model, state_dict, prefix)
_load_weights_adapter(self, checkpoint_path, prefix)
@torch.jit.ignore
def no_weight_decay(self) -> Set:
"""Get set of parameter names that should not have weight decay applied.
Returns:
Set of parameter names to skip during weight decay
"""
skip_list = {'embeds.pos_embed', 'embeds.cls_token', 'embeds.reg_token'}
if self.rope and hasattr(self.rope, 'no_weight_decay'):
skip_list.update(self.rope.no_weight_decay())
return skip_list
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse: bool = False) -> Dict:
"""Get parameter group matcher for optimizer parameter grouping.
Args:
coarse: Whether to use coarse-grained grouping
Returns:
Dictionary mapping group names to regex patterns
"""
return dict(
stem=r'^embeds', # stem and embed
blocks=[(r'^blocks\.(\d+)', None), (r'^norm', (99999,))]
)
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable: bool = True) -> None:
"""Enable or disable gradient checkpointing for memory efficiency.
Args:
enable: Whether to enable gradient checkpointing
"""
self.grad_checkpointing = enable
if hasattr(self.embeds, 'patch_embed') and hasattr(self.embeds.patch_embed, 'set_grad_checkpointing'):
self.embeds.patch_embed.set_grad_checkpointing(enable)
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
"""Get the classification head module.
Returns:
Classification head module
"""
return self.head
@disable_compiler
def _generate_rope_naflex(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: torch.Tensor,
) -> Union[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor], Any]:
"""Generate ROPE position embeddings for NaFlex batch with variable grid sizes.
Args:
x: Input tensor [B, N, C]
patch_coord: Patch coordinates [B, N, 2] with (y, x) values
Returns:
ROPE embeddings:
- Axial mode: Tensor of shape [B, 1, N, dim*2]
- Mixed mode: List of tensors, each of shape [B, num_heads, N, dim], one per depth layer
- Mixed mode with iterator: Iterator yielding tensors per depth
"""
# Calculate grid sizes for each sample
naflex_grid_sizes = calculate_naflex_grid_sizes(patch_coord)
# Build ROPE embeddings for each unique grid size
size_to_indices = {}
unique_sizes = []
for bi, grid_size in enumerate(naflex_grid_sizes):
if grid_size not in size_to_indices:
size_to_indices[grid_size] = []
unique_sizes.append(grid_size)
size_to_indices[grid_size].append(bi)
B, N, C = x.shape
seq_len = N - self.num_prefix_tokens
if self.rope_is_mixed:
# Use an iterator for Mixed mode, returns [batch_size, depth, num_heads, seq_len, dim]
return NaFlexRopeIterator(
self.rope,
size_to_indices,
unique_sizes,
B,
seq_len,
x.dtype,
x.device
)
# Axial mode: [batch_size, seq_len, dim*2]
rope_embeds = torch.zeros(B, seq_len, self.rope.dim * 2, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
if hasattr(self.rope, 'get_batch_embeds'):
# Batch mode - generate unique embeds from one grid and then assign
unique_embeds = self.rope.get_batch_embeds(unique_sizes)
for grid_size, embed, batch_indices in zip(unique_sizes, unique_embeds, size_to_indices.values()):
h, w = grid_size
actual_len = h * w
for bi in batch_indices:
rope_embeds[bi, :actual_len] = embed[:actual_len]
else:
# Generate each unique size separately and assign
for grid_size, bi in size_to_indices.items():
rope_embed = self.rope.get_embed(shape=grid_size)
h, w = grid_size
actual_len = h * w
rope_embeds[bi, :actual_len] = rope_embed[:actual_len]
rope_embeds = rope_embeds.unsqueeze(1)
return rope_embeds
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: Optional[str] = None) -> None:
"""Reset the classification head with new number of classes and pooling.
Args:
num_classes: Number of classes for new classification head
global_pool: Optional new global pooling type
"""
self.num_classes = num_classes
if global_pool is not None:
assert global_pool in ('', 'avg', 'avgmax', 'max', 'token', 'map')
if global_pool == 'map' and self.attn_pool is None:
assert False, "Cannot currently add attention pooling in reset_classifier()."
elif global_pool != 'map' and self.attn_pool is not None:
self.attn_pool = None # remove attention pooling
self.global_pool = global_pool
self.head = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def _forward_embeds(
self,
x,
patch_coord,
patch_valid,
attn_mask,
) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
""" Forward pass through patch / abs pos / rope pos embeds and patch dropout
"""
naflex_mode = patch_coord is not None
# patch embed, abs pos embed, returns global grid size as calculated from 'standard' NCHW batches
x, grid_size = self.embeds(
x,
patch_coord=patch_coord,
patch_valid=patch_valid,
)
# Generate ROPE embeddings at model level
rope_embeds = None
if self.rope is not None:
if patch_coord is not None:
# NaFlex mode - variable grid sizes
rope_embeds = self._generate_rope_naflex(x, patch_coord)
elif grid_size is not None:
# Standard mode - fixed grid size
rope_embeds = self.rope.get_embed(shape=grid_size)
else:
assert False, 'Expected one of patch_coord or grid_size to be valid'
# Apply patch dropout with coordinated updates
keep_indices: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
if self.training and self.patch_drop is not None:
x, keep_indices = self.patch_drop(x)
# keep_indices excludes prefix tokens, can use directly on patch_valid & rope embeds
if patch_valid is not None:
patch_valid = patch_valid.gather(1, keep_indices)
if rope_embeds is not None and not self.rope_is_mixed:
# Update ROPE embeddings to match dropped tokens (only for axial mode)
# Batch dim already present in NaFlex mode, but will be added in standard mode.
rope_embeds = apply_keep_indices_nlc(x, rope_embeds, keep_indices, pos_embed_has_batch=naflex_mode)
if not naflex_mode:
# B, N, dim -> B, 1, N, dim. Need head dim added for standard mode, already added in NaFlex.
rope_embeds = rope_embeds.unsqueeze(1)
# Create attention mask from patch_valid after patch dropout applied
if attn_mask is None:
attn_mask = create_attention_mask(
patch_valid,
num_prefix_tokens=self.num_prefix_tokens,
dtype=x.dtype
)
x = self.norm_pre(x)
return {
'patches': x,
'patch_valid': patch_valid,
'rope_embeds': rope_embeds,
'attn_mask': attn_mask,
'keep_indices': keep_indices,
}
def forward_intermediates(
self,
x: Union[torch.Tensor, Dict[str, torch.Tensor]],
indices: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,
return_prefix_tokens: bool = False,
norm: bool = False,
stop_early: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
intermediates_only: bool = False,
output_dict: bool = False,
patch_coord: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attn_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]], Dict[str, Any]]:
""" Forward features that returns intermediates.
Args:
x: Input image tensor
indices: Take last n blocks if int, all if None, select matching indices if sequence
return_prefix_tokens: Return both prefix and spatial intermediate tokens
norm: Apply norm layer to all intermediates
stop_early: Stop iterating over blocks when last desired intermediate hit
output_fmt: Shape of intermediate feature outputs
intermediates_only: Only return intermediate features
output_dict: Return outputs as a dictionary with 'image_features' and 'image_intermediates' keys
patch_coord: Optional patch coordinates [B, N, 2] for NaFlex mode
patch_valid: Optional patch type indicators (1=patch, 0=padding) for NaFlex
attn_mask: Optional attention mask for masked attention
Returns:
A tuple with (final_features, intermediates), a list of intermediate features, or a dictionary containing
'image_features' and 'image_intermediates' (and optionally 'image_intermediates_prefix')
"""
# FIXME unfinished / untested
assert output_fmt in ('NCHW', 'NLC'), 'Output format must be one of NCHW or NLC.'
reshape = output_fmt == 'NCHW'
intermediates = []
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(len(self.blocks), indices)
if isinstance(x, Dict):
# Handle dictionary input from NaFlex collator
patch_coord = x['patch_coord']
patch_valid = x['patch_valid']
patches = x['patches']
assert False, 'WIP, patch mode needs more work'
else:
patches = x
height, width = x.shape[-2:]
H, W = self.embeds.dynamic_feat_size((height, width))
# Forward pass through patch and abs position embedding
embeds = self._forward_embeds(
patches,
patch_coord=patch_coord,
patch_valid=patch_valid,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
)
x = embeds['patches']
rope_embeds = embeds.get('rope_embeds', None)
keep_indices = embeds.get('keep_indices', None)
attn_mask = embeds.get('attn_mask', None)
# Forward pass through blocks
if torch.jit.is_scripting() or not stop_early: # can't slice blocks in torchscript
blocks = self.blocks
else:
blocks = self.blocks[:max_index + 1]
do_checkpointing = self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting()
if self.rope_is_mixed and rope_embeds is not None:
# Mixed mode with per-layer embeddings (list or iterator)
for i, (blk, rope_embed) in enumerate(zip(self.blocks, rope_embeds)):
# Apply patch dropout to rope_embed if needed
if self.training and self.patch_drop is not None and keep_indices is not None:
# Apply patch dropout to rope_embed if needed (batch dim already present in naflex mode)
rope_embed = apply_keep_indices_nlc(
x,
rope_embed,
keep_indices,
pos_embed_has_batch=embeds.get('naflex_mode', False),
)
if do_checkpointing:
x = checkpoint(blk, x, rope=rope_embed, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, rope=rope_embed, attn_mask=attn_mask)
if i in take_indices:
# normalize intermediates with final norm layer if enabled
intermediates.append(self.norm(x) if norm else x)
else:
for i, blk in enumerate(blocks):
# Axial ROPE mode with shared embeddings
if rope_embeds is not None:
if do_checkpointing:
x = checkpoint(blk, x, rope=rope_embeds, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, rope=rope_embeds, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
if do_checkpointing:
x = checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, attn_mask=attn_mask)
if i in take_indices:
# normalize intermediates with final norm layer if enabled
intermediates.append(self.norm(x) if norm else x)
# Process intermediates
if self.num_prefix_tokens:
# split prefix (e.g. class, distill) and spatial feature tokens
prefix_tokens = [y[:, 0:self.num_prefix_tokens] for y in intermediates]
intermediates = [y[:, self.num_prefix_tokens:] for y in intermediates]
else:
prefix_tokens = None
if reshape:
# reshape to BCHW output format
intermediates = [
y.reshape(y.shape[0], H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
for y in intermediates
]
# FIXME always use dict for NaFlex mode to return masks and more?
# For dictionary output
if output_dict:
result_dict = {}
# Intermediates are always included
result_dict['image_intermediates'] = intermediates
if prefix_tokens is not None and return_prefix_tokens:
result_dict['image_intermediates_prefix'] = prefix_tokens
# Only include features if not intermediates_only
if not intermediates_only:
x_final = self.norm(x)
result_dict['image_features'] = x_final
return result_dict
# For non-dictionary output, maintain the original behavior
if not torch.jit.is_scripting() and return_prefix_tokens and prefix_tokens is not None:
# return_prefix not support in torchscript due to poor type handling
intermediates = list(zip(intermediates, prefix_tokens))
if intermediates_only:
return intermediates
x = self.norm(x)
return x, intermediates
def forward_features(
self,
patches: torch.Tensor,
patch_coord: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attn_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> Union[torch.Tensor, Dict[str, torch.Tensor]]:
"""
"""
naflex_mode = patch_coord is not None
# Pass through patch & abs position embedding module with patch coordinate/type support
embeds = self._forward_embeds(
patches,
patch_coord=patch_coord,
patch_valid=patch_valid,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
)
x = embeds['patches']
rope_embeds = embeds.get('rope_embeds', None)
keep_indices = embeds.get('keep_indices', None)
attn_mask = embeds.get('attn_mask', None)
# Apply transformer blocks with masked attention and/or ROPE if provided
do_checkpointing = self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting()
if self.rope_is_mixed and rope_embeds is not None:
# Mixed mode with per-layer embeddings (list or iterator)
for i, (blk, rope_embed) in enumerate(zip(self.blocks, rope_embeds)):
if self.training and self.patch_drop is not None and keep_indices is not None:
# Apply patch dropout to rope_embed if needed (batch dim already present in naflex mode)
rope_embed = apply_keep_indices_nlc(
x,
rope_embed,
keep_indices,
pos_embed_has_batch=naflex_mode,
)
if do_checkpointing:
x = checkpoint(blk, x, rope=rope_embed, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, rope=rope_embed, attn_mask=attn_mask)
elif rope_embeds is not None:
# Axial ROPE mode with shared embeddings
for blk in self.blocks:
if do_checkpointing:
x = checkpoint(blk, x, rope=rope_embeds, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, rope=rope_embeds, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
for blk in self.blocks:
if do_checkpointing:
x = checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, attn_mask=attn_mask)
x = self.norm(x)
if naflex_mode:
return {
'patches': x,
'patch_valid': embeds.get('patch_valid', None),
}
return x
def _pool(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
pool_type: Optional[str] = None,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.attn_pool is not None:
attn_mask = create_attention_mask(
patch_valid,
num_prefix_tokens=self.num_prefix_tokens if self.pool_include_prefix else 0,
symmetric=False,
q_len=1,
dtype=x.dtype,
)
if not self.pool_include_prefix:
x = x[:, self.num_prefix_tokens:]
x = self.attn_pool(x, attn_mask=attn_mask)
return x
pool_type = self.global_pool if pool_type is None else pool_type
x = global_pool_naflex(
x,
patch_valid,
pool_type=pool_type,
num_prefix_tokens=self.num_prefix_tokens,
reduce_include_prefix=self.pool_include_prefix,
)
return x
def forward_head(
self,
patches: torch.Tensor,
pre_logits: bool = False,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self._pool(patches, patch_valid=patch_valid)
x = self.fc_norm(x)
x = self.head_drop(x)
return x if pre_logits else self.head(x)
def forward(
self,
x: Union[torch.Tensor, Dict[str, torch.Tensor]],
patch_coord: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
patch_valid: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attn_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass with optional NaFlex support.
Args:
x: Input tensor. Supported formats:
- [B, C, H, W] standard image input
- [B, N, P*P*C] pre-patchified tensor (flattened patches)
- [B, N, Ph, Pw, C] pre-patchified tensor (variable patch size)
- Dict from NaFlex collator
patch_coord: Optional patch coordinates [B, N, 2] for NaFlex mode.
patch_valid: Optional patch validity indicators for NaFlex.
attn_mask: Optional attn mask to override defaults generated from patch_valid
Returns:
Model output tensor.
"""
input_is_dict = isinstance(x, Dict)
naflex_mode = input_is_dict or patch_coord is not None
if naflex_mode:
if input_is_dict:
# Handle dictionary input from NaFlex collator, dict inputs take priority over args
patches = x['patches']
patch_valid = x.get('patch_valid', patch_valid)
patch_coord = x.get('patch_coord', patch_coord)
attn_mask = x.get('attn_mask', attn_mask)
else:
patches = x
_assert(patch_coord is not None, "patch_coord is required in naflex mode")
_assert(patch_valid is not None, "patch_valid is required in naflex mode")
features = self.forward_features(
patches=patches,
patch_valid=patch_valid,
patch_coord=patch_coord,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
)
# Pass patches & patch_valid to forward_head for masked pooling
x = self.forward_head(**features)
else:
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
def _debug_dump_patches(x):
# DEBUG, reconstruct patches & save
patch_coord = x['patch_coord']
patch_valid = x['patch_valid']
patches = x['patches']
for i in range(len(patches)):
patch = patches[i][patch_valid[i]]
h = (patch_coord[i, :, 0].max() + 1).item()
w = (patch_coord[i, :, 1].max() + 1).item()
patch = patch.reshape(h, w, 16, 16, 3).permute(4, 0, 2, 1, 3)
patch = patch.reshape(3, h*16, w*16)
from torchvision.utils import save_image
save_image(patch, f'patch_{i}.jpg', normalize=True)
def get_init_weights_vit(mode: str = 'jax', head_bias: float = 0.0) -> Callable:
"""Function imported from vision_transformer.py to maintain compatibility"""
from .vision_transformer import init_weights_vit_jax, init_weights_vit_moco, init_weights_vit_timm
if 'jax' in mode:
return partial(init_weights_vit_jax, head_bias=head_bias)
elif 'moco' in mode:
return init_weights_vit_moco
else:
return init_weights_vit_timm
def checkpoint_filter_fn(state_dict: Dict[str, Any], model: NaFlexVit) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Handle state dict conversion from original ViT to the new version with combined embedding."""
# Handle CombinedEmbed module pattern
out_dict = {}
for k, v in state_dict.items():
# Convert tokens and embeddings to combined_embed structure
if k == 'pos_embed':
# Handle position embedding format conversion - from (1, N, C) to (1, H, W, C)
if hasattr(model.embeds, 'pos_embed') and v.ndim == 3:
num_cls_token = 0
num_reg_token = 0
if 'reg_token' in state_dict:
num_reg_token = state_dict['reg_token'].shape[1]
if 'cls_token' in state_dict:
num_cls_token = state_dict['cls_token'].shape[1]
num_prefix_tokens = num_cls_token + num_reg_token
# Original format is (1, N, C), need to reshape to (1, H, W, C)
num_patches = v.shape[1]
num_patches_no_prefix = num_patches - num_prefix_tokens
grid_size_no_prefix = math.sqrt(num_patches_no_prefix)
grid_size = math.sqrt(num_patches)
if (grid_size_no_prefix != grid_size
and (grid_size_no_prefix.is_integer() and not grid_size.is_integer())
):
# make a decision, did the pos_embed of the original include the prefix tokens?
num_patches = num_patches_no_prefix
cls_token_emb = v[:, 0:num_cls_token]
if cls_token_emb.numel():
state_dict['cls_token'] += cls_token_emb
reg_token_emb = v[:, num_cls_token:num_reg_token]
if reg_token_emb.numel():
state_dict['reg_token'] += reg_token_emb
v = v[:, num_prefix_tokens:]
grid_size = grid_size_no_prefix
grid_size = int(grid_size)
# Check if it's a perfect square for a standard grid
if grid_size * grid_size == num_patches:
# Reshape from (1, N, C) to (1, H, W, C)
v = v.reshape(1, grid_size, grid_size, v.shape[2])
else:
# Not a square grid, we need to get the actual dimensions
if hasattr(model.embeds.patch_embed, 'grid_size'):
h, w = model.embeds.patch_embed.grid_size
if h * w == num_patches:
# We have the right dimensions
v = v.reshape(1, h, w, v.shape[2])
else:
# Dimensions don't match, use interpolation
_logger.warning(
f"Position embedding size mismatch: checkpoint={num_patches}, model={(h * w)}. "
f"Using default initialization and will resize in forward pass."
)
# Keep v as is, the forward pass will handle resizing
out_dict['embeds.pos_embed'] = v
elif k == 'cls_token':
out_dict['embeds.cls_token'] = v
elif k == 'reg_token':
out_dict['embeds.reg_token'] = v
# Convert patch_embed.X to embeds.patch_embed.X
elif k.startswith('patch_embed.'):
suffix = k[12:]
if suffix == 'proj.weight':
v = v.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).flatten(1)
new_key = 'embeds.' + suffix
out_dict[new_key] = v
else:
out_dict[k] = v
return out_dict
def _cfg(url: str = '', **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
'url': url,
'num_classes': 1000,
'input_size': (3, 384, 384),
'pool_size': None,
'crop_pct': 1.0,
'interpolation': 'bicubic',
'mean': IMAGENET_INCEPTION_MEAN,
'std': IMAGENET_INCEPTION_STD,
'first_conv': 'embeds.proj',
'classifier': 'head',
'license': 'apache-2.0',
**kwargs,
}
default_cfgs = generate_default_cfgs({
'naflexvit_base_patch16_gap.e300_s576_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'naflexvit_base_patch16_par_gap.e300_s576_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'naflexvit_base_patch16_parfac_gap.e300_s576_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
),
'naflexvit_base_patch16_map.untrained': _cfg(),
# SigLIP-2 NaFlex vit encoder weights
'naflexvit_base_patch16_siglip.v2_webli': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=0),
'naflexvit_so400m_patch16_siglip.v2_webli': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=0),
})
def _create_naflexvit(variant: str, pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
out_indices = kwargs.pop('out_indices', 3)
cfg = kwargs.pop('cfg', NaFlexVitCfg())
cfg_field_names = {f.name for f in fields(NaFlexVitCfg)}
# pop in-place so the original kwargs is emptied of cfg-specific keys
cfg_updates = {k: kwargs.pop(k) for k in list(kwargs) if k in cfg_field_names}
if cfg_updates:
cfg = _overlay_kwargs(cfg, **cfg_updates)
model = build_model_with_cfg(
NaFlexVit, variant, pretrained,
pretrained_filter_fn=checkpoint_filter_fn,
cfg=cfg,
feature_cfg=dict(out_indices=out_indices, feature_cls='getter'),
**kwargs,
)
return model
def _create_naflexvit_from_classic(
variant: str,
pretrained: bool = False,
**kwargs,
) -> NaFlexVit:
"""Create FlexVit model from classic VisionTransformer configuration.
This function handles the parameter mapping and configuration logic needed
to create FlexVit models that are compatible with classic VisionTransformer
configurations and pretrained weights.
Args:
variant: Model variant name
pretrained: Whether to load pretrained weights
**kwargs: Classic VisionTransformer parameters
Returns:
FlexVit model instance
"""
# Remove VisionTransformer-specific parameters that don't apply to FlexVit
kwargs.pop('no_embed_class', None)
kwargs.pop('dynamic_img_size', None)
# Handle global pooling and fc_norm defaults that differ between ViT and FlexVit
gp = kwargs.pop('global_pool', 'token') # Original ViTs default to cls token pooling
fc_norm = kwargs.pop('fc_norm', None) # Original ViTs used fc_norm when not set and avg pooling used
if fc_norm is None and gp == 'avg':
fc_norm = True
# Set FlexVit-specific defaults that differ from VisionTransformer
flex_kwargs = {
'pos_embed_grid_size': None, # rely on img_size (// patch_size) that will be passed through
'class_token': kwargs.get('class_token', True),
'global_pool': gp,
'fc_norm': fc_norm,
'scale_mlp_norm': kwargs.pop('scale_mlp_norm', False),
'scale_attn_inner_norm': kwargs.pop('scale_attn_norm', False),
**kwargs # User overrides take precedence
}
return _create_naflexvit(variant, pretrained, **flex_kwargs)
def _create_naflexvit_from_eva(
variant: str,
pretrained: bool = False,
**kwargs,
) -> NaFlexVit:
"""Create NaFlexVit model from EVA configuration.
This function handles the parameter mapping and configuration logic needed
to create NaFlexVit models that are compatible with EVA configurations
and pretrained weights.
Args:
variant: Model variant name
pretrained: Whether to load pretrained weights
**kwargs: EVA model parameters
Returns:
NaFlexVit model instance
"""
# Handle EVA's unique parameters & block args
kwargs.pop('no_embed_class', None) # EVA specific, not used in NaFlexVit (always no-embed)
# Map EVA's rope parameters
use_rot_pos_emb = kwargs.pop('use_rot_pos_emb', False)
rope_mixed_mode = kwargs.pop('rope_mixed_mode', False)
rope_temperature = kwargs.pop('rope_temperature', 10000.)
rope_grid_offset = kwargs.pop('rope_grid_offset', 0.)
rope_grid_indexing = kwargs.pop('rope_grid_indexing', 'ij')
if use_rot_pos_emb:
rope_type = 'mixed' if rope_mixed_mode else 'axial'
else:
rope_type = 'none'
# Handle norm/pool resolution logic to mirror EVA
gp = kwargs.pop('global_pool', 'avg')
use_pre_transformer_norm = kwargs.pop('use_pre_transformer_norm', False)
use_post_transformer_norm = kwargs.pop('use_post_transformer_norm', True)
use_fc_norm = kwargs.pop('use_fc_norm', None)
if use_fc_norm is None:
use_fc_norm = gp == 'avg' # default on if avg pool used
# Set NaFlexVit-specific parameters
naflex_kwargs = {
'pos_embed_grid_size': None, # rely on img_size (// patch_size)
'class_token': kwargs.get('class_token', True),
'reg_tokens': kwargs.pop('num_reg_tokens', kwargs.get('reg_tokens', 0)),
'global_pool': gp,
'pre_norm': use_pre_transformer_norm,
'final_norm': use_post_transformer_norm,
'fc_norm': use_fc_norm,
'pos_embed': 'learned' if kwargs.pop('use_abs_pos_emb', True) else 'none',
'rope_type': rope_type,
'rope_temperature': rope_temperature,
'rope_grid_offset': rope_grid_offset,
'rope_grid_indexing': rope_grid_indexing,
'rope_ref_feat_shape': kwargs.get('ref_feat_shape', None),
'attn_type': kwargs.pop('attn_type', 'eva'),
'swiglu_mlp': kwargs.pop('swiglu_mlp', False),
'qkv_fused': kwargs.pop('qkv_fused', True),
'scale_mlp_norm': kwargs.pop('scale_mlp', False),
'scale_attn_inner_norm': kwargs.pop('scale_attn_inner', False),
**kwargs # Pass remaining kwargs through
}
return _create_naflexvit(variant, pretrained, **naflex_kwargs)
@register_model
def naflexvit_base_patch16_gap(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-Base with NaFlex functionality and global average pooling.
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
init_values=1e-5,
global_pool='avg',
reg_tokens=4,
fc_norm=True,
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_base_patch16_gap', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_base_patch16_par_gap(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-Base with NaFlex functionality, aspect preserving pos embed, global average pooling.
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
init_values=1e-5,
pos_embed_ar_preserving=True,
global_pool='avg',
reg_tokens=4,
fc_norm=True,
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_base_patch16_par_gap', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_base_patch16_parfac_gap(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-Base with NaFlex functionality, aspect preserving & factorized pos embed, global average pooling.
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
init_values=1e-5,
pos_embed_ar_preserving=True,
pos_embed='factorized',
global_pool='avg',
reg_tokens=4,
fc_norm=True,
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_base_patch16_parfac_gap', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_base_patch16_map(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-Base with NaFlex functionality and MAP attention pooling.
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
init_values=1e-5,
global_pool='map',
reg_tokens=1,
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_base_patch16_map', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_so150m2_patch16_reg1_gap(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-SO150M2 with NaFlex functionality for variable aspect ratios and resolutions.
This model supports:
1. Variable aspect ratios and resolutions via patch coordinates
2. Position embedding interpolation for arbitrary grid sizes
3. Explicit patch coordinates and valid token masking
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=832,
depth=21,
num_heads=13,
mlp_ratio=34/13,
init_values=1e-5,
qkv_bias=False,
reg_tokens=1,
global_pool='avg',
fc_norm=True,
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_so150m2_patch16_reg1_gap', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_so150m2_patch16_reg1_map(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-SO150M2 with NaFlex functionality for variable aspect ratios and resolutions.
This model supports:
1. Variable aspect ratios and resolutions via patch coordinates
2. Position embedding interpolation for arbitrary grid sizes
3. Explicit patch coordinates and valid token masking
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=832,
depth=21,
num_heads=13,
mlp_ratio=34/13,
init_values=1e-5,
qkv_bias=False,
reg_tokens=1,
global_pool='map',
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_so150m2_patch16_reg1_map', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_base_patch16_siglip(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-Base with NaFlex functionality and SigLIP-style configuration.
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
act_layer='gelu_tanh',
global_pool='map',
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_base_patch16_siglip', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
@register_model
def naflexvit_so400m_patch16_siglip(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs) -> NaFlexVit:
"""ViT-SO400M with NaFlex functionality for variable aspect ratios and resolutions.
"""
cfg = NaFlexVitCfg(
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=1152,
depth=27,
num_heads=16,
mlp_ratio=3.7362,
act_layer='gelu_tanh',
global_pool='map',
)
model = _create_naflexvit('naflexvit_so400m_patch16_siglip', pretrained=pretrained, cfg=cfg, **kwargs)
return model
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/naflexvit.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/naflexvit.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 42781
}
| 271
|
"""Pre-Activation ResNet v2 with GroupNorm and Weight Standardization.
A PyTorch implementation of ResNetV2 adapted from the Google Big-Transfer (BiT) source code
at https://github.com/google-research/big_transfer to match timm interfaces. The BiT weights have
been included here as pretrained models from their original .NPZ checkpoints.
Additionally, supports non pre-activation bottleneck for use as a backbone for Vision Transformers (ViT) and
extra padding support to allow porting of official Hybrid ResNet pretrained weights from
https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer
Thanks to the Google team for the above two repositories and associated papers:
* Big Transfer (BiT): General Visual Representation Learning - https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.11370
* An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale - https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
* Knowledge distillation: A good teacher is patient and consistent - https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05237
Original copyright of Google code below, modifications by Ross Wightman, Copyright 2020.
"""
# Copyright 2020 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from collections import OrderedDict # pylint: disable=g-importing-member
from functools import partial
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.data import IMAGENET_INCEPTION_MEAN, IMAGENET_INCEPTION_STD
from timm.layers import GroupNormAct, BatchNormAct2d, EvoNorm2dS0, FilterResponseNormTlu2d, ClassifierHead, \
DropPath, AvgPool2dSame, create_pool2d, StdConv2d, create_conv2d, get_act_layer, get_norm_act_layer, make_divisible
from ._builder import build_model_with_cfg
from ._features import feature_take_indices
from ._manipulate import checkpoint_seq, named_apply, adapt_input_conv
from ._registry import generate_default_cfgs, register_model, register_model_deprecations
__all__ = ['ResNetV2'] # model_registry will add each entrypoint fn to this
class PreActBasic(nn.Module):
"""Pre-activation basic block (not in typical 'v2' implementations)."""
def __init__(
self,
in_chs: int,
out_chs: Optional[int] = None,
bottle_ratio: float = 1.0,
stride: int = 1,
dilation: int = 1,
first_dilation: Optional[int] = None,
groups: int = 1,
act_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
conv_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
proj_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.,
):
"""Initialize PreActBasic block.
Args:
in_chs: Input channels.
out_chs: Output channels.
bottle_ratio: Bottleneck ratio (not used in basic block).
stride: Stride for convolution.
dilation: Dilation rate.
first_dilation: First dilation rate.
groups: Group convolution size.
act_layer: Activation layer type.
conv_layer: Convolution layer type.
norm_layer: Normalization layer type.
proj_layer: Projection/downsampling layer type.
drop_path_rate: Stochastic depth drop rate.
"""
super().__init__()
first_dilation = first_dilation or dilation
conv_layer = conv_layer or StdConv2d
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(GroupNormAct, num_groups=32)
out_chs = out_chs or in_chs
mid_chs = make_divisible(out_chs * bottle_ratio)
if proj_layer is not None and (stride != 1 or first_dilation != dilation or in_chs != out_chs):
self.downsample = proj_layer(
in_chs,
out_chs,
stride=stride,
dilation=dilation,
first_dilation=first_dilation,
preact=True,
conv_layer=conv_layer,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
else:
self.downsample = None
self.norm1 = norm_layer(in_chs)
self.conv1 = conv_layer(in_chs, mid_chs, 3, stride=stride, dilation=first_dilation, groups=groups)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(mid_chs)
self.conv2 = conv_layer(mid_chs, out_chs, 3, dilation=dilation, groups=groups)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_rate) if drop_path_rate > 0 else nn.Identity()
def zero_init_last(self) -> None:
"""Zero-initialize the last convolution weight (not applicable to basic block)."""
nn.init.zeros_(self.conv2.weight)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output tensor.
"""
x_preact = self.norm1(x)
# shortcut branch
shortcut = x
if self.downsample is not None:
shortcut = self.downsample(x_preact)
# residual branch
x = self.conv1(x_preact)
x = self.conv2(self.norm2(x))
x = self.drop_path(x)
return x + shortcut
class PreActBottleneck(nn.Module):
"""Pre-activation (v2) bottleneck block.
Follows the implementation of "Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks":
https://github.com/KaimingHe/resnet-1k-layers/blob/master/resnet-pre-act.lua
Except it puts the stride on 3x3 conv when available.
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_chs: int,
out_chs: Optional[int] = None,
bottle_ratio: float = 0.25,
stride: int = 1,
dilation: int = 1,
first_dilation: Optional[int] = None,
groups: int = 1,
act_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
conv_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
proj_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.,
):
"""Initialize PreActBottleneck block.
Args:
in_chs: Input channels.
out_chs: Output channels.
bottle_ratio: Bottleneck ratio.
stride: Stride for convolution.
dilation: Dilation rate.
first_dilation: First dilation rate.
groups: Group convolution size.
act_layer: Activation layer type.
conv_layer: Convolution layer type.
norm_layer: Normalization layer type.
proj_layer: Projection/downsampling layer type.
drop_path_rate: Stochastic depth drop rate.
"""
super().__init__()
first_dilation = first_dilation or dilation
conv_layer = conv_layer or StdConv2d
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(GroupNormAct, num_groups=32)
out_chs = out_chs or in_chs
mid_chs = make_divisible(out_chs * bottle_ratio)
if proj_layer is not None:
self.downsample = proj_layer(
in_chs,
out_chs,
stride=stride,
dilation=dilation,
first_dilation=first_dilation,
preact=True,
conv_layer=conv_layer,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
else:
self.downsample = None
self.norm1 = norm_layer(in_chs)
self.conv1 = conv_layer(in_chs, mid_chs, 1)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(mid_chs)
self.conv2 = conv_layer(mid_chs, mid_chs, 3, stride=stride, dilation=first_dilation, groups=groups)
self.norm3 = norm_layer(mid_chs)
self.conv3 = conv_layer(mid_chs, out_chs, 1)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_rate) if drop_path_rate > 0 else nn.Identity()
def zero_init_last(self) -> None:
"""Zero-initialize the last convolution weight."""
nn.init.zeros_(self.conv3.weight)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output tensor.
"""
x_preact = self.norm1(x)
# shortcut branch
shortcut = x
if self.downsample is not None:
shortcut = self.downsample(x_preact)
# residual branch
x = self.conv1(x_preact)
x = self.conv2(self.norm2(x))
x = self.conv3(self.norm3(x))
x = self.drop_path(x)
return x + shortcut
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""Non Pre-activation bottleneck block, equiv to V1.5/V1b Bottleneck. Used for ViT.
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_chs: int,
out_chs: Optional[int] = None,
bottle_ratio: float = 0.25,
stride: int = 1,
dilation: int = 1,
first_dilation: Optional[int] = None,
groups: int = 1,
act_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
conv_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
proj_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.,
):
super().__init__()
first_dilation = first_dilation or dilation
act_layer = act_layer or nn.ReLU
conv_layer = conv_layer or StdConv2d
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(GroupNormAct, num_groups=32)
out_chs = out_chs or in_chs
mid_chs = make_divisible(out_chs * bottle_ratio)
if proj_layer is not None:
self.downsample = proj_layer(
in_chs,
out_chs,
stride=stride,
dilation=dilation,
preact=False,
conv_layer=conv_layer,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
else:
self.downsample = None
self.conv1 = conv_layer(in_chs, mid_chs, 1)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(mid_chs)
self.conv2 = conv_layer(mid_chs, mid_chs, 3, stride=stride, dilation=first_dilation, groups=groups)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(mid_chs)
self.conv3 = conv_layer(mid_chs, out_chs, 1)
self.norm3 = norm_layer(out_chs, apply_act=False)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_rate) if drop_path_rate > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.act3 = act_layer(inplace=True)
def zero_init_last(self) -> None:
"""Zero-initialize the last batch norm weight."""
if getattr(self.norm3, 'weight', None) is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(self.norm3.weight)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output tensor.
"""
# shortcut branch
shortcut = x
if self.downsample is not None:
shortcut = self.downsample(x)
# residual
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.norm1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.norm2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.norm3(x)
x = self.drop_path(x)
x = self.act3(x + shortcut)
return x
class DownsampleConv(nn.Module):
"""1x1 convolution downsampling module."""
def __init__(
self,
in_chs: int,
out_chs: int,
stride: int = 1,
dilation: int = 1,
first_dilation: Optional[int] = None,
preact: bool = True,
conv_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
):
super(DownsampleConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = conv_layer(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=stride)
self.norm = nn.Identity() if preact else norm_layer(out_chs, apply_act=False)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Downsampled tensor.
"""
return self.norm(self.conv(x))
class DownsampleAvg(nn.Module):
"""AvgPool downsampling as in 'D' ResNet variants."""
def __init__(
self,
in_chs: int,
out_chs: int,
stride: int = 1,
dilation: int = 1,
first_dilation: Optional[int] = None,
preact: bool = True,
conv_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
):
super(DownsampleAvg, self).__init__()
avg_stride = stride if dilation == 1 else 1
if stride > 1 or dilation > 1:
avg_pool_fn = AvgPool2dSame if avg_stride == 1 and dilation > 1 else nn.AvgPool2d
self.pool = avg_pool_fn(2, avg_stride, ceil_mode=True, count_include_pad=False)
else:
self.pool = nn.Identity()
self.conv = conv_layer(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=1)
self.norm = nn.Identity() if preact else norm_layer(out_chs, apply_act=False)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Downsampled tensor.
"""
return self.norm(self.conv(self.pool(x)))
class ResNetStage(nn.Module):
"""ResNet Stage."""
def __init__(
self,
in_chs: int,
out_chs: int,
stride: int,
dilation: int,
depth: int,
bottle_ratio: float = 0.25,
groups: int = 1,
avg_down: bool = False,
block_dpr: Optional[List[float]] = None,
block_fn: Callable = PreActBottleneck,
act_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
conv_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable] = None,
**block_kwargs: Any,
):
super(ResNetStage, self).__init__()
self.grad_checkpointing = False
first_dilation = 1 if dilation in (1, 2) else 2
layer_kwargs = dict(act_layer=act_layer, conv_layer=conv_layer, norm_layer=norm_layer)
proj_layer = DownsampleAvg if avg_down else DownsampleConv
prev_chs = in_chs
self.blocks = nn.Sequential()
for block_idx in range(depth):
drop_path_rate = block_dpr[block_idx] if block_dpr else 0.
stride = stride if block_idx == 0 else 1
self.blocks.add_module(str(block_idx), block_fn(
prev_chs,
out_chs,
stride=stride,
dilation=dilation,
bottle_ratio=bottle_ratio,
groups=groups,
first_dilation=first_dilation,
proj_layer=proj_layer,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate,
**layer_kwargs,
**block_kwargs,
))
prev_chs = out_chs
first_dilation = dilation
proj_layer = None
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass through all blocks in the stage.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output tensor.
"""
if self.grad_checkpointing and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
x = checkpoint_seq(self.blocks, x)
else:
x = self.blocks(x)
return x
def is_stem_deep(stem_type: str) -> bool:
"""Check if stem type is deep (has multiple convolutions).
Args:
stem_type: Type of stem to check.
Returns:
True if stem is deep, False otherwise.
"""
return any([s in stem_type for s in ('deep', 'tiered')])
def create_resnetv2_stem(
in_chs: int,
out_chs: int = 64,
stem_type: str = '',
preact: bool = True,
conv_layer: Callable = StdConv2d,
norm_layer: Callable = partial(GroupNormAct, num_groups=32),
) -> nn.Sequential:
stem = OrderedDict()
assert stem_type in ('', 'fixed', 'same', 'deep', 'deep_fixed', 'deep_same', 'tiered')
# NOTE conv padding mode can be changed by overriding the conv_layer def
if is_stem_deep(stem_type):
# A 3 deep 3x3 conv stack as in ResNet V1D models
if 'tiered' in stem_type:
stem_chs = (3 * out_chs // 8, out_chs // 2) # 'T' resnets in resnet.py
else:
stem_chs = (out_chs // 2, out_chs // 2) # 'D' ResNets
stem['conv1'] = conv_layer(in_chs, stem_chs[0], kernel_size=3, stride=2)
stem['norm1'] = norm_layer(stem_chs[0])
stem['conv2'] = conv_layer(stem_chs[0], stem_chs[1], kernel_size=3, stride=1)
stem['norm2'] = norm_layer(stem_chs[1])
stem['conv3'] = conv_layer(stem_chs[1], out_chs, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
if not preact:
stem['norm3'] = norm_layer(out_chs)
else:
# The usual 7x7 stem conv
stem['conv'] = conv_layer(in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size=7, stride=2)
if not preact:
stem['norm'] = norm_layer(out_chs)
if 'fixed' in stem_type:
# 'fixed' SAME padding approximation that is used in BiT models
stem['pad'] = nn.ConstantPad2d(1, 0.)
stem['pool'] = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
elif 'same' in stem_type:
# full, input size based 'SAME' padding, used in ViT Hybrid model
stem['pool'] = create_pool2d('max', kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding='same')
else:
# the usual PyTorch symmetric padding
stem['pool'] = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
return nn.Sequential(stem)
class ResNetV2(nn.Module):
"""Implementation of Pre-activation (v2) ResNet mode.
"""
def __init__(
self,
layers: List[int],
channels: Tuple[int, ...] = (256, 512, 1024, 2048),
num_classes: int = 1000,
in_chans: int = 3,
global_pool: str = 'avg',
output_stride: int = 32,
width_factor: int = 1,
stem_chs: int = 64,
stem_type: str = '',
avg_down: bool = False,
preact: bool = True,
basic: bool = False,
bottle_ratio: float = 0.25,
act_layer: Callable = nn.ReLU,
norm_layer: Callable = partial(GroupNormAct, num_groups=32),
conv_layer: Callable = StdConv2d,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.,
zero_init_last: bool = False,
):
"""
Args:
layers (List[int]) : number of layers in each block
channels (List[int]) : number of channels in each block:
num_classes (int): number of classification classes (default 1000)
in_chans (int): number of input (color) channels. (default 3)
global_pool (str): Global pooling type. One of 'avg', 'max', 'avgmax', 'catavgmax' (default 'avg')
output_stride (int): output stride of the network, 32, 16, or 8. (default 32)
width_factor (int): channel (width) multiplication factor
stem_chs (int): stem width (default: 64)
stem_type (str): stem type (default: '' == 7x7)
avg_down (bool): average pooling in residual downsampling (default: False)
preact (bool): pre-activation (default: True)
act_layer (Union[str, nn.Module]): activation layer
norm_layer (Union[str, nn.Module]): normalization layer
conv_layer (nn.Module): convolution module
drop_rate: classifier dropout rate (default: 0.)
drop_path_rate: stochastic depth rate (default: 0.)
zero_init_last: zero-init last weight in residual path (default: False)
"""
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
wf = width_factor
norm_layer = get_norm_act_layer(norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer)
act_layer = get_act_layer(act_layer)
self.feature_info = []
stem_chs = make_divisible(stem_chs * wf)
self.stem = create_resnetv2_stem(
in_chans,
stem_chs,
stem_type,
preact,
conv_layer=conv_layer,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
stem_feat = ('stem.conv3' if is_stem_deep(stem_type) else 'stem.conv') if preact else 'stem.norm'
self.feature_info.append(dict(num_chs=stem_chs, reduction=2, module=stem_feat))
prev_chs = stem_chs
curr_stride = 4
dilation = 1
block_dprs = [x.tolist() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(layers)).split(layers)]
if preact:
block_fn = PreActBasic if basic else PreActBottleneck
else:
assert not basic
block_fn = Bottleneck
self.stages = nn.Sequential()
for stage_idx, (d, c, bdpr) in enumerate(zip(layers, channels, block_dprs)):
out_chs = make_divisible(c * wf)
stride = 1 if stage_idx == 0 else 2
if curr_stride >= output_stride:
dilation *= stride
stride = 1
stage = ResNetStage(
prev_chs,
out_chs,
stride=stride,
dilation=dilation,
depth=d,
bottle_ratio=bottle_ratio,
avg_down=avg_down,
act_layer=act_layer,
conv_layer=conv_layer,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
block_dpr=bdpr,
block_fn=block_fn,
)
prev_chs = out_chs
curr_stride *= stride
self.feature_info += [dict(num_chs=prev_chs, reduction=curr_stride, module=f'stages.{stage_idx}')]
self.stages.add_module(str(stage_idx), stage)
self.num_features = self.head_hidden_size = prev_chs
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features) if preact else nn.Identity()
self.head = ClassifierHead(
self.num_features,
num_classes,
pool_type=global_pool,
drop_rate=self.drop_rate,
use_conv=True,
)
self.init_weights(zero_init_last=zero_init_last)
@torch.jit.ignore
def init_weights(self, zero_init_last: bool = True) -> None:
"""Initialize model weights."""
named_apply(partial(_init_weights, zero_init_last=zero_init_last), self)
@torch.jit.ignore()
def load_pretrained(self, checkpoint_path: str, prefix: str = 'resnet/') -> None:
"""Load pretrained weights."""
_load_weights(self, checkpoint_path, prefix)
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse: bool = False) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Group parameters for optimization."""
matcher = dict(
stem=r'^stem',
blocks=r'^stages\.(\d+)' if coarse else [
(r'^stages\.(\d+)\.blocks\.(\d+)', None),
(r'^norm', (99999,))
]
)
return matcher
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable: bool = True) -> None:
"""Enable or disable gradient checkpointing."""
for s in self.stages:
s.grad_checkpointing = enable
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
"""Get the classifier head."""
return self.head.fc
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: Optional[str] = None) -> None:
"""Reset the classifier head.
Args:
num_classes: Number of classes for new classifier.
global_pool: Global pooling type.
"""
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.head.reset(num_classes, global_pool)
def forward_intermediates(
self,
x: torch.Tensor,
indices: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,
norm: bool = False,
stop_early: bool = False,
output_fmt: str = 'NCHW',
intermediates_only: bool = False,
) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]]]:
""" Forward features that returns intermediates.
Args:
x: Input image tensor
indices: Take last n blocks if int, all if None, select matching indices if sequence
norm: Apply norm layer to compatible intermediates
stop_early: Stop iterating over blocks when last desired intermediate hit
output_fmt: Shape of intermediate feature outputs
intermediates_only: Only return intermediate features
Returns:
"""
assert output_fmt in ('NCHW',), 'Output shape must be NCHW.'
intermediates = []
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(5, indices)
# forward pass
feat_idx = 0
H, W = x.shape[-2:]
for stem in self.stem:
x = stem(x)
if x.shape[-2:] == (H //2, W //2):
x_down = x
if feat_idx in take_indices:
intermediates.append(x_down)
last_idx = len(self.stages)
if torch.jit.is_scripting() or not stop_early: # can't slice blocks in torchscript
stages = self.stages
else:
stages = self.stages[:max_index]
for feat_idx, stage in enumerate(stages, start=1):
x = stage(x)
if feat_idx in take_indices:
if feat_idx == last_idx:
x_inter = self.norm(x) if norm else x
intermediates.append(x_inter)
else:
intermediates.append(x)
if intermediates_only:
return intermediates
if feat_idx == last_idx:
x = self.norm(x)
return x, intermediates
def prune_intermediate_layers(
self,
indices: Union[int, List[int]] = 1,
prune_norm: bool = False,
prune_head: bool = True,
):
""" Prune layers not required for specified intermediates.
"""
take_indices, max_index = feature_take_indices(5, indices)
self.stages = self.stages[:max_index] # truncate blocks w/ stem as idx 0
if prune_norm:
self.norm = nn.Identity()
if prune_head:
self.reset_classifier(0, '')
return take_indices
def forward_features(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass through feature extraction layers.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Feature tensor.
"""
x = self.stem(x)
x = self.stages(x)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x: torch.Tensor, pre_logits: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass through classifier head.
Args:
x: Input features.
pre_logits: Return features before final linear layer.
Returns:
Classification logits or features.
"""
return self.head(x, pre_logits=pre_logits) if pre_logits else self.head(x)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output logits.
"""
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
def _init_weights(module: nn.Module, name: str = '', zero_init_last: bool = True) -> None:
"""Initialize module weights.
Args:
module: PyTorch module to initialize.
name: Module name.
zero_init_last: Zero-initialize last layer weights.
"""
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear) or ('head.fc' in name and isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d)):
nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
elif isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(module.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if module.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
elif isinstance(module, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.LayerNorm, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.ones_(module.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
elif zero_init_last and hasattr(module, 'zero_init_last'):
module.zero_init_last()
@torch.no_grad()
def _load_weights(model: nn.Module, checkpoint_path: str, prefix: str = 'resnet/'):
import numpy as np
def t2p(conv_weights):
"""Possibly convert HWIO to OIHW."""
if conv_weights.ndim == 4:
conv_weights = conv_weights.transpose([3, 2, 0, 1])
return torch.from_numpy(conv_weights)
weights = np.load(checkpoint_path)
stem_conv_w = adapt_input_conv(
model.stem.conv.weight.shape[1], t2p(weights[f'{prefix}root_block/standardized_conv2d/kernel']))
model.stem.conv.weight.copy_(stem_conv_w)
model.norm.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{prefix}group_norm/gamma']))
model.norm.bias.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{prefix}group_norm/beta']))
if isinstance(getattr(model.head, 'fc', None), nn.Conv2d) and \
model.head.fc.weight.shape[0] == weights[f'{prefix}head/conv2d/kernel'].shape[-1]:
model.head.fc.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{prefix}head/conv2d/kernel']))
model.head.fc.bias.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{prefix}head/conv2d/bias']))
for i, (sname, stage) in enumerate(model.stages.named_children()):
for j, (bname, block) in enumerate(stage.blocks.named_children()):
cname = 'standardized_conv2d'
block_prefix = f'{prefix}block{i + 1}/unit{j + 1:02d}/'
block.conv1.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}a/{cname}/kernel']))
block.conv2.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}b/{cname}/kernel']))
block.conv3.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}c/{cname}/kernel']))
block.norm1.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}a/group_norm/gamma']))
block.norm2.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}b/group_norm/gamma']))
block.norm3.weight.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}c/group_norm/gamma']))
block.norm1.bias.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}a/group_norm/beta']))
block.norm2.bias.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}b/group_norm/beta']))
block.norm3.bias.copy_(t2p(weights[f'{block_prefix}c/group_norm/beta']))
if block.downsample is not None:
w = weights[f'{block_prefix}a/proj/{cname}/kernel']
block.downsample.conv.weight.copy_(t2p(w))
def _create_resnetv2(variant: str, pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""Create a ResNetV2 model.
Args:
variant: Model variant name.
pretrained: Load pretrained weights.
**kwargs: Additional model arguments.
Returns:
ResNetV2 model instance.
"""
feature_cfg = dict(flatten_sequential=True)
return build_model_with_cfg(
ResNetV2, variant, pretrained,
feature_cfg=feature_cfg,
**kwargs,
)
def _create_resnetv2_bit(variant: str, pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""Create a ResNetV2 model with BiT weights.
Args:
variant: Model variant name.
pretrained: Load pretrained weights.
**kwargs: Additional model arguments.
Returns:
ResNetV2 model instance.
"""
return _create_resnetv2(
variant,
pretrained=pretrained,
stem_type='fixed',
conv_layer=partial(StdConv2d, eps=1e-8),
**kwargs,
)
def _cfg(url: str = '', **kwargs: Any) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
'url': url,
'num_classes': 1000, 'input_size': (3, 224, 224), 'pool_size': (7, 7),
'crop_pct': 0.875, 'interpolation': 'bilinear',
'mean': IMAGENET_INCEPTION_MEAN, 'std': IMAGENET_INCEPTION_STD,
'first_conv': 'stem.conv', 'classifier': 'head.fc',
**kwargs
}
default_cfgs = generate_default_cfgs({
# Paper: Knowledge distillation: A good teacher is patient and consistent - https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05237
'resnetv2_50x1_bit.goog_distilled_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_teacher_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_teacher_in21k_ft_in1k_384': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 384, 384), pool_size=(12, 12), crop_pct=1.0, interpolation='bicubic', custom_load=True),
# pretrained on imagenet21k, finetuned on imagenet1k
'resnetv2_50x1_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 448, 448), pool_size=(14, 14), crop_pct=1.0, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_50x3_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 448, 448), pool_size=(14, 14), crop_pct=1.0, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_101x1_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 448, 448), pool_size=(14, 14), crop_pct=1.0, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_101x3_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 448, 448), pool_size=(14, 14), crop_pct=1.0, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 448, 448), pool_size=(14, 14), crop_pct=1.0, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_152x4_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
input_size=(3, 480, 480), pool_size=(15, 15), crop_pct=1.0, custom_load=True), # only one at 480x480?
# trained on imagenet-21k
'resnetv2_50x1_bit.goog_in21k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=21843, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_50x3_bit.goog_in21k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=21843, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_101x1_bit.goog_in21k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=21843, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_101x3_bit.goog_in21k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=21843, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_in21k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=21843, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_152x4_bit.goog_in21k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
num_classes=21843, custom_load=True),
'resnetv2_18.ra4_e3600_r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', crop_pct=0.9, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0),
'resnetv2_18d.ra4_e3600_r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', crop_pct=0.9, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0,
first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_34.ra4_e3600_r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', crop_pct=0.9, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0),
'resnetv2_34d.ra4_e3600_r224_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', crop_pct=0.9, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0,
first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_34d.ra4_e3600_r384_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
crop_pct=1.0, input_size=(3, 384, 384), pool_size=(12, 12), test_input_size=(3, 448, 448),
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_50.a1h_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', crop_pct=0.95, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0),
'resnetv2_50d.untrained': _cfg(
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_50t.untrained': _cfg(
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_101.a1h_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', crop_pct=0.95, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0),
'resnetv2_101d.untrained': _cfg(
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_152.untrained': _cfg(
interpolation='bicubic'),
'resnetv2_152d.untrained': _cfg(
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1'),
'resnetv2_50d_gn.ah_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1',
crop_pct=0.95, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0),
'resnetv2_50d_evos.ah_in1k': _cfg(
hf_hub_id='timm/',
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1',
crop_pct=0.95, test_input_size=(3, 288, 288), test_crop_pct=1.0),
'resnetv2_50d_frn.untrained': _cfg(
interpolation='bicubic', first_conv='stem.conv1'),
})
@register_model
def resnetv2_50x1_bit(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50x1-BiT model."""
return _create_resnetv2_bit(
'resnetv2_50x1_bit', pretrained=pretrained, layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], width_factor=1, **kwargs)
@register_model
def resnetv2_50x3_bit(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50x3-BiT model."""
return _create_resnetv2_bit(
'resnetv2_50x3_bit', pretrained=pretrained, layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], width_factor=3, **kwargs)
@register_model
def resnetv2_101x1_bit(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-101x1-BiT model."""
return _create_resnetv2_bit(
'resnetv2_101x1_bit', pretrained=pretrained, layers=[3, 4, 23, 3], width_factor=1, **kwargs)
@register_model
def resnetv2_101x3_bit(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-101x3-BiT model."""
return _create_resnetv2_bit(
'resnetv2_101x3_bit', pretrained=pretrained, layers=[3, 4, 23, 3], width_factor=3, **kwargs)
@register_model
def resnetv2_152x2_bit(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-152x2-BiT model."""
return _create_resnetv2_bit(
'resnetv2_152x2_bit', pretrained=pretrained, layers=[3, 8, 36, 3], width_factor=2, **kwargs)
@register_model
def resnetv2_152x4_bit(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-152x4-BiT model."""
return _create_resnetv2_bit(
'resnetv2_152x4_bit', pretrained=pretrained, layers=[3, 8, 36, 3], width_factor=4, **kwargs)
@register_model
def resnetv2_18(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-18 model."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[2, 2, 2, 2], channels=(64, 128, 256, 512), basic=True, bottle_ratio=1.0,
conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d
)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_18', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_18d(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-18d model (deep stem variant)."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[2, 2, 2, 2], channels=(64, 128, 256, 512), basic=True, bottle_ratio=1.0,
conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d, stem_type='deep', avg_down=True
)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_18d', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_34(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-34 model."""
model_args = dict(
layers=(3, 4, 6, 3), channels=(64, 128, 256, 512), basic=True, bottle_ratio=1.0,
conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d
)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_34', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_34d(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-34d model (deep stem variant)."""
model_args = dict(
layers=(3, 4, 6, 3), channels=(64, 128, 256, 512), basic=True, bottle_ratio=1.0,
conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d, stem_type='deep', avg_down=True
)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_34d', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_50(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50 model."""
model_args = dict(layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_50', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_50d(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50d model (deep stem variant)."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d,
stem_type='deep', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_50d', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_50t(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50t model (tiered stem variant)."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d,
stem_type='tiered', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_50t', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_101(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-101 model."""
model_args = dict(layers=[3, 4, 23, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_101', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_101d(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-101d model (deep stem variant)."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 4, 23, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d,
stem_type='deep', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_101d', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_152(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-152 model."""
model_args = dict(layers=[3, 8, 36, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_152', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_152d(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-152d model (deep stem variant)."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 8, 36, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=BatchNormAct2d,
stem_type='deep', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_152d', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
# Experimental configs (may change / be removed)
@register_model
def resnetv2_50d_gn(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50d model with Group Normalization."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=GroupNormAct,
stem_type='deep', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_50d_gn', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_50d_evos(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50d model with EvoNorm."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=EvoNorm2dS0,
stem_type='deep', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_50d_evos', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
@register_model
def resnetv2_50d_frn(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> ResNetV2:
"""ResNetV2-50d model with Filter Response Normalization."""
model_args = dict(
layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], conv_layer=create_conv2d, norm_layer=FilterResponseNormTlu2d,
stem_type='deep', avg_down=True)
return _create_resnetv2('resnetv2_50d_frn', pretrained=pretrained, **dict(model_args, **kwargs))
register_model_deprecations(__name__, {
'resnetv2_50x1_bitm': 'resnetv2_50x1_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_50x3_bitm': 'resnetv2_50x3_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_101x1_bitm': 'resnetv2_101x1_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_101x3_bitm': 'resnetv2_101x3_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_152x2_bitm': 'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_152x4_bitm': 'resnetv2_152x4_bit.goog_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_50x1_bitm_in21k': 'resnetv2_50x1_bit.goog_in21k',
'resnetv2_50x3_bitm_in21k': 'resnetv2_50x3_bit.goog_in21k',
'resnetv2_101x1_bitm_in21k': 'resnetv2_101x1_bit.goog_in21k',
'resnetv2_101x3_bitm_in21k': 'resnetv2_101x3_bit.goog_in21k',
'resnetv2_152x2_bitm_in21k': 'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_in21k',
'resnetv2_152x4_bitm_in21k': 'resnetv2_152x4_bit.goog_in21k',
'resnetv2_50x1_bit_distilled': 'resnetv2_50x1_bit.goog_distilled_in1k',
'resnetv2_152x2_bit_teacher': 'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_teacher_in21k_ft_in1k',
'resnetv2_152x2_bit_teacher_384': 'resnetv2_152x2_bit.goog_teacher_in21k_ft_in1k_384',
})
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/resnetv2.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/resnetv2.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 21408
}
| 272
|
"""VGG
Adapted from https://github.com/pytorch/vision 'vgg.py' (BSD-3-Clause) with a few changes for
timm functionality.
Copyright 2021 Ross Wightman
"""
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Type, Union, cast
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from timm.data import IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD
from timm.layers import ClassifierHead
from ._builder import build_model_with_cfg
from ._features_fx import register_notrace_module
from ._registry import register_model, generate_default_cfgs
__all__ = ['VGG']
cfgs: Dict[str, List[Union[str, int]]] = {
'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
}
@register_notrace_module # reason: FX can't symbolically trace control flow in forward method
class ConvMlp(nn.Module):
"""Convolutional MLP block for VGG head.
Replaces traditional Linear layers with Conv2d layers in the classifier.
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int = 512,
out_features: int = 4096,
kernel_size: int = 7,
mlp_ratio: float = 1.0,
drop_rate: float = 0.2,
act_layer: Type[nn.Module] = nn.ReLU,
conv_layer: Type[nn.Module] = nn.Conv2d,
):
"""Initialize ConvMlp.
Args:
in_features: Number of input features.
out_features: Number of output features.
kernel_size: Kernel size for first conv layer.
mlp_ratio: Ratio for hidden layer size.
drop_rate: Dropout rate.
act_layer: Activation layer type.
conv_layer: Convolution layer type.
"""
super(ConvMlp, self).__init__()
self.input_kernel_size = kernel_size
mid_features = int(out_features * mlp_ratio)
self.fc1 = conv_layer(in_features, mid_features, kernel_size, bias=True)
self.act1 = act_layer(True)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop_rate)
self.fc2 = conv_layer(mid_features, out_features, 1, bias=True)
self.act2 = act_layer(True)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output tensor.
"""
if x.shape[-2] < self.input_kernel_size or x.shape[-1] < self.input_kernel_size:
# keep the input size >= 7x7
output_size = (max(self.input_kernel_size, x.shape[-2]), max(self.input_kernel_size, x.shape[-1]))
x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, output_size)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.act2(x)
return x
class VGG(nn.Module):
"""VGG model architecture.
Based on `Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition`
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
"""
def __init__(
self,
cfg: List[Any],
num_classes: int = 1000,
in_chans: int = 3,
output_stride: int = 32,
mlp_ratio: float = 1.0,
act_layer: Type[nn.Module] = nn.ReLU,
conv_layer: Type[nn.Module] = nn.Conv2d,
norm_layer: Optional[Type[nn.Module]] = None,
global_pool: str = 'avg',
drop_rate: float = 0.,
) -> None:
"""Initialize VGG model.
Args:
cfg: Configuration list defining network architecture.
num_classes: Number of classes for classification.
in_chans: Number of input channels.
output_stride: Output stride of network.
mlp_ratio: Ratio for MLP hidden layer size.
act_layer: Activation layer type.
conv_layer: Convolution layer type.
norm_layer: Normalization layer type.
global_pool: Global pooling type.
drop_rate: Dropout rate.
"""
super(VGG, self).__init__()
assert output_stride == 32
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.grad_checkpointing = False
self.use_norm = norm_layer is not None
self.feature_info = []
prev_chs = in_chans
net_stride = 1
pool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d
layers: List[nn.Module] = []
for v in cfg:
last_idx = len(layers) - 1
if v == 'M':
self.feature_info.append(dict(num_chs=prev_chs, reduction=net_stride, module=f'features.{last_idx}'))
layers += [pool_layer(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
net_stride *= 2
else:
v = cast(int, v)
conv2d = conv_layer(prev_chs, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if norm_layer is not None:
layers += [conv2d, norm_layer(v), act_layer(inplace=True)]
else:
layers += [conv2d, act_layer(inplace=True)]
prev_chs = v
self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.feature_info.append(dict(num_chs=prev_chs, reduction=net_stride, module=f'features.{len(layers) - 1}'))
self.num_features = prev_chs
self.head_hidden_size = 4096
self.pre_logits = ConvMlp(
prev_chs,
self.head_hidden_size,
7,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
act_layer=act_layer,
conv_layer=conv_layer,
)
self.head = ClassifierHead(
self.head_hidden_size,
num_classes,
pool_type=global_pool,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
)
self._initialize_weights()
@torch.jit.ignore
def group_matcher(self, coarse: bool = False) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Group matcher for parameter groups.
Args:
coarse: Whether to use coarse grouping.
Returns:
Dictionary of grouped parameters.
"""
# this treats BN layers as separate groups for bn variants, a lot of effort to fix that
return dict(stem=r'^features\.0', blocks=r'^features\.(\d+)')
@torch.jit.ignore
def set_grad_checkpointing(self, enable: bool = True) -> None:
"""Enable or disable gradient checkpointing.
Args:
enable: Whether to enable gradient checkpointing.
"""
assert not enable, 'gradient checkpointing not supported'
@torch.jit.ignore
def get_classifier(self) -> nn.Module:
"""Get the classifier module.
Returns:
Classifier module.
"""
return self.head.fc
def reset_classifier(self, num_classes: int, global_pool: Optional[str] = None) -> None:
"""Reset the classifier.
Args:
num_classes: Number of classes for new classifier.
global_pool: Global pooling type.
"""
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.head.reset(num_classes, global_pool)
def forward_features(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass through feature extraction layers.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Feature tensor.
"""
x = self.features(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x: torch.Tensor, pre_logits: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass through head.
Args:
x: Input features.
pre_logits: Return features before final linear layer.
Returns:
Classification logits or features.
"""
x = self.pre_logits(x)
return self.head(x, pre_logits=pre_logits) if pre_logits else self.head(x)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor.
Returns:
Output logits.
"""
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self) -> None:
"""Initialize model weights."""
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _filter_fn(state_dict: dict) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""Convert patch embedding weight from manual patchify + linear proj to conv.
Args:
state_dict: State dictionary to filter.
Returns:
Filtered state dictionary.
"""
out_dict = {}
for k, v in state_dict.items():
k_r = k
k_r = k_r.replace('classifier.0', 'pre_logits.fc1')
k_r = k_r.replace('classifier.3', 'pre_logits.fc2')
k_r = k_r.replace('classifier.6', 'head.fc')
if 'classifier.0.weight' in k:
v = v.reshape(-1, 512, 7, 7)
if 'classifier.3.weight' in k:
v = v.reshape(-1, 4096, 1, 1)
out_dict[k_r] = v
return out_dict
def _create_vgg(variant: str, pretrained: bool, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
"""Create a VGG model.
Args:
variant: Model variant name.
pretrained: Load pretrained weights.
**kwargs: Additional model arguments.
Returns:
VGG model instance.
"""
cfg = variant.split('_')[0]
# NOTE: VGG is one of few models with stride==1 features w/ 6 out_indices [0..5]
out_indices = kwargs.pop('out_indices', (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5))
model = build_model_with_cfg(
VGG,
variant,
pretrained,
model_cfg=cfgs[cfg],
feature_cfg=dict(flatten_sequential=True, out_indices=out_indices),
pretrained_filter_fn=_filter_fn,
**kwargs,
)
return model
def _cfg(url: str = '', **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Create default configuration dictionary.
Args:
url: Model weight URL.
**kwargs: Additional configuration options.
Returns:
Configuration dictionary.
"""
return {
'url': url,
'num_classes': 1000, 'input_size': (3, 224, 224), 'pool_size': (7, 7),
'crop_pct': 0.875, 'interpolation': 'bilinear',
'mean': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN, 'std': IMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD,
'first_conv': 'features.0', 'classifier': 'head.fc',
**kwargs
}
default_cfgs = generate_default_cfgs({
'vgg11.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg13.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg16.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg19.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg11_bn.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg13_bn.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg16_bn.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
'vgg19_bn.tv_in1k': _cfg(hf_hub_id='timm/'),
})
@register_model
def vgg11(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 11-layer model (configuration "A") from
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(**kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg11', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg11_bn(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 11-layer model (configuration "A") with batch normalization
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, **kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg11_bn', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg13(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 13-layer model (configuration "B")
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(**kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg13', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg13_bn(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 13-layer model (configuration "B") with batch normalization
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, **kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg13_bn', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg16(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 16-layer model (configuration "D")
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(**kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg16', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg16_bn(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 16-layer model (configuration "D") with batch normalization
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, **kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg16_bn', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg19(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 19-layer model (configuration "E")
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(**kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg19', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
@register_model
def vgg19_bn(pretrained: bool = False, **kwargs: Any) -> VGG:
r"""VGG 19-layer model (configuration 'E') with batch normalization
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`._
"""
model_args = dict(norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, **kwargs)
return _create_vgg('vgg19_bn', pretrained=pretrained, **model_args)
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/models/vgg.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/models/vgg.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 6624
}
| 273
|
import math
import torch
from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
class AdaBelief(Optimizer):
r"""Implements AdaBelief algorithm. Modified from Adam in PyTorch
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-3)
betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-16)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
amsgrad (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSGrad variant of this
algorithm from the paper `On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond`_
(default: False)
decoupled_decay (boolean, optional): (default: True) If set as True, then
the optimizer uses decoupled weight decay as in AdamW
fixed_decay (boolean, optional): (default: False) This is used when weight_decouple
is set as True.
When fixed_decay == True, the weight decay is performed as
$W_{new} = W_{old} - W_{old} \times decay$.
When fixed_decay == False, the weight decay is performed as
$W_{new} = W_{old} - W_{old} \times decay \times lr$. Note that in this case, the
weight decay ratio decreases with learning rate (lr).
rectify (boolean, optional): (default: True) If set as True, then perform the rectified
update similar to RAdam
degenerated_to_sgd (boolean, optional) (default:True) If set as True, then perform SGD update
when variance of gradient is high
reference: AdaBelief Optimizer, adapting stepsizes by the belief in observed gradients, NeurIPS 2020
For a complete table of recommended hyperparameters, see https://github.com/juntang-zhuang/Adabelief-Optimizer'
For example train/args for EfficientNet see these gists
- link to train_script: https://gist.github.com/juntang-zhuang/0a501dd51c02278d952cf159bc233037
- link to args.yaml: https://gist.github.com/juntang-zhuang/517ce3c27022b908bb93f78e4f786dc3
"""
def __init__(
self,
params,
lr=1e-3,
betas=(0.9, 0.999),
eps=1e-16,
weight_decay=0,
amsgrad=False,
decoupled_decay=True,
fixed_decay=False,
rectify=True,
degenerated_to_sgd=True,
):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
if not 0.0 <= eps:
raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
if isinstance(params, (list, tuple)) and len(params) > 0 and isinstance(params[0], dict):
for param in params:
if 'betas' in param and (param['betas'][0] != betas[0] or param['betas'][1] != betas[1]):
param['buffer'] = [[None, None, None] for _ in range(10)]
defaults = dict(
lr=lr,
betas=betas,
eps=eps,
weight_decay=weight_decay,
amsgrad=amsgrad,
degenerated_to_sgd=degenerated_to_sgd,
decoupled_decay=decoupled_decay,
rectify=rectify,
fixed_decay=fixed_decay,
buffer=[[None, None, None] for _ in range(10)]
)
super(AdaBelief, self).__init__(params, defaults)
def __setstate__(self, state):
super(AdaBelief, self).__setstate__(state)
for group in self.param_groups:
group.setdefault('amsgrad', False)
@torch.no_grad()
def reset(self):
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
state = self.state[p]
amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
# State initialization
state['step'] = 0
# Exponential moving average of gradient values
state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p)
# Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
state['exp_avg_var'] = torch.zeros_like(p)
if amsgrad:
# Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
state['max_exp_avg_var'] = torch.zeros_like(p)
@torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
grad = p.grad
if grad.dtype in {torch.float16, torch.bfloat16}:
grad = grad.float()
if grad.is_sparse:
raise RuntimeError(
'AdaBelief does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
p_fp32 = p
if p.dtype in {torch.float16, torch.bfloat16}:
p_fp32 = p_fp32.float()
amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
state = self.state[p]
# State initialization
if len(state) == 0:
state['step'] = 0
# Exponential moving average of gradient values
state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p_fp32)
# Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
state['exp_avg_var'] = torch.zeros_like(p_fp32)
if amsgrad:
# Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
state['max_exp_avg_var'] = torch.zeros_like(p_fp32)
# perform weight decay, check if decoupled weight decay
if group['decoupled_decay']:
if not group['fixed_decay']:
p_fp32.mul_(1.0 - group['lr'] * group['weight_decay'])
else:
p_fp32.mul_(1.0 - group['weight_decay'])
else:
if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
grad.add_(p_fp32, alpha=group['weight_decay'])
# get current state variable
exp_avg, exp_avg_var = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_var']
state['step'] += 1
bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
# Update first and second moment running average
exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1)
grad_residual = grad - exp_avg
exp_avg_var.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad_residual, grad_residual, value=1 - beta2)
if amsgrad:
max_exp_avg_var = state['max_exp_avg_var']
# Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
torch.max(max_exp_avg_var, exp_avg_var.add_(group['eps']), out=max_exp_avg_var)
# Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
denom = (max_exp_avg_var.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
else:
denom = (exp_avg_var.add_(group['eps']).sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
# update
if not group['rectify']:
# Default update
step_size = group['lr'] / bias_correction1
p_fp32.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size)
else:
# Rectified update, forked from RAdam
buffered = group['buffer'][int(state['step'] % 10)]
if state['step'] == buffered[0]:
num_sma, step_size = buffered[1], buffered[2]
else:
buffered[0] = state['step']
beta2_t = beta2 ** state['step']
num_sma_max = 2 / (1 - beta2) - 1
num_sma = num_sma_max - 2 * state['step'] * beta2_t / (1 - beta2_t)
buffered[1] = num_sma
# more conservative since it's an approximated value
if num_sma >= 5:
step_size = math.sqrt(
(1 - beta2_t) *
(num_sma - 4) / (num_sma_max - 4) *
(num_sma - 2) / num_sma *
num_sma_max / (num_sma_max - 2)) / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
elif group['degenerated_to_sgd']:
step_size = 1.0 / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
else:
step_size = -1
buffered[2] = step_size
if num_sma >= 5:
denom = exp_avg_var.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
p_fp32.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size * group['lr'])
elif step_size > 0:
p_fp32.add_(exp_avg, alpha=-step_size * group['lr'])
if p.dtype in {torch.float16, torch.bfloat16}:
p.copy_(p_fp32)
return loss
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/optim/adabelief.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/optim/adabelief.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 5278
}
| 274
|
import math
import torch
from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
class NAdamLegacy(Optimizer):
"""Implements Nadam algorithm (a variant of Adam based on Nesterov momentum).
NOTE: This impl has been deprecated in favour of torch.optim.NAdam and remains as a reference
It has been proposed in `Incorporating Nesterov Momentum into Adam`__.
Arguments:
params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
parameter groups
lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 2e-3)
betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
running averages of gradient and its square
eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
schedule_decay (float, optional): momentum schedule decay (default: 4e-3)
__ http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2015/054_report.pdf
__ http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~fritz/absps/momentum.pdf
Originally taken from: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/1408
NOTE: Has potential issues but does work well on some problems.
"""
def __init__(
self,
params,
lr=2e-3,
betas=(0.9, 0.999),
eps=1e-8,
weight_decay=0,
schedule_decay=4e-3,
):
if not 0.0 <= lr:
raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
defaults = dict(
lr=lr,
betas=betas,
eps=eps,
weight_decay=weight_decay,
schedule_decay=schedule_decay,
)
super(NAdamLegacy, self).__init__(params, defaults)
@torch.no_grad()
def step(self, closure=None):
"""Performs a single optimization step.
Arguments:
closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
and returns the loss.
"""
loss = None
if closure is not None:
with torch.enable_grad():
loss = closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is None:
continue
grad = p.grad
state = self.state[p]
# State initialization
if len(state) == 0:
state['step'] = 0
state['m_schedule'] = 1.
state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p)
state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p)
# Warming momentum schedule
m_schedule = state['m_schedule']
schedule_decay = group['schedule_decay']
exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
eps = group['eps']
state['step'] += 1
t = state['step']
bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** t
if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
grad = grad.add(p, alpha=group['weight_decay'])
momentum_cache_t = beta1 * (1. - 0.5 * (0.96 ** (t * schedule_decay)))
momentum_cache_t_1 = beta1 * (1. - 0.5 * (0.96 ** ((t + 1) * schedule_decay)))
m_schedule_new = m_schedule * momentum_cache_t
m_schedule_next = m_schedule * momentum_cache_t * momentum_cache_t_1
state['m_schedule'] = m_schedule_new
# Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1. - beta1)
exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1. - beta2)
denom = (exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(eps)
p.addcdiv_(grad, denom, value=-group['lr'] * (1. - momentum_cache_t) / (1. - m_schedule_new))
p.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-group['lr'] * momentum_cache_t_1 / (1. - m_schedule_next))
return loss
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/optim/nadam.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/optim/nadam.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 2021
}
| 275
|
""" Step Scheduler
Basic step LR schedule with warmup, noise.
Hacked together by / Copyright 2020 Ross Wightman
"""
import math
import torch
from typing import List
from .scheduler import Scheduler
class StepLRScheduler(Scheduler):
"""
"""
def __init__(
self,
optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,
decay_t: float,
decay_rate: float = 1.,
warmup_t=0,
warmup_lr_init=0,
warmup_prefix=True,
t_in_epochs=True,
noise_range_t=None,
noise_pct=0.67,
noise_std=1.0,
noise_seed=42,
initialize=True,
) -> None:
super().__init__(
optimizer,
param_group_field="lr",
t_in_epochs=t_in_epochs,
noise_range_t=noise_range_t,
noise_pct=noise_pct,
noise_std=noise_std,
noise_seed=noise_seed,
initialize=initialize,
)
self.decay_t = decay_t
self.decay_rate = decay_rate
self.warmup_t = warmup_t
self.warmup_lr_init = warmup_lr_init
self.warmup_prefix = warmup_prefix
if self.warmup_t:
self.warmup_steps = [(v - warmup_lr_init) / self.warmup_t for v in self.base_values]
super().update_groups(self.warmup_lr_init)
else:
self.warmup_steps = [1 for _ in self.base_values]
def _get_lr(self, t: int) -> List[float]:
if t < self.warmup_t:
lrs = [self.warmup_lr_init + t * s for s in self.warmup_steps]
else:
if self.warmup_prefix:
t = t - self.warmup_t
lrs = [v * (self.decay_rate ** (t // self.decay_t)) for v in self.base_values]
return lrs
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/scheduler/step_lr.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/scheduler/step_lr.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 951
}
| 276
|
from typing import Optional, Tuple, List
import torch
def onnx_forward(onnx_file, example_input):
import onnxruntime
sess_options = onnxruntime.SessionOptions()
session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnx_file, sess_options)
input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name
output = session.run([], {input_name: example_input.numpy()})
output = output[0]
return output
def onnx_export(
model: torch.nn.Module,
output_file: str,
example_input: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
training: bool = False,
verbose: bool = False,
check: bool = True,
check_forward: bool = False,
batch_size: int = 64,
input_size: Tuple[int, int, int] = None,
opset: Optional[int] = None,
dynamic_size: bool = False,
aten_fallback: bool = False,
keep_initializers: Optional[bool] = None,
use_dynamo: bool = False,
input_names: List[str] = None,
output_names: List[str] = None,
):
import onnx
if training:
training_mode = torch.onnx.TrainingMode.TRAINING
model.train()
else:
training_mode = torch.onnx.TrainingMode.EVAL
model.eval()
if example_input is None:
if not input_size:
assert hasattr(model, 'default_cfg'), 'Cannot file model default config, input size must be provided'
input_size = model.default_cfg.get('input_size')
example_input = torch.randn((batch_size,) + input_size, requires_grad=training)
# Run model once before export trace, sets padding for models with Conv2dSameExport. This means
# that the padding for models with Conv2dSameExport (most models with tf_ prefix) is fixed for
# the input img_size specified in this script.
# Opset >= 11 should allow for dynamic padding, however I cannot get it to work due to
# issues in the tracing of the dynamic padding or errors attempting to export the model after jit
# scripting it (an approach that should work). Perhaps in a future PyTorch or ONNX versions...
with torch.inference_mode():
original_out = model(example_input)
input_names = input_names or ["input0"]
output_names = output_names or ["output0"]
dynamic_axes = {'input0': {0: 'batch'}, 'output0': {0: 'batch'}}
if dynamic_size:
dynamic_axes['input0'][2] = 'height'
dynamic_axes['input0'][3] = 'width'
if aten_fallback:
export_type = torch.onnx.OperatorExportTypes.ONNX_ATEN_FALLBACK
else:
export_type = torch.onnx.OperatorExportTypes.ONNX
if use_dynamo:
export_options = torch.onnx.ExportOptions(dynamic_shapes=dynamic_size)
export_output = torch.onnx.dynamo_export(
model,
example_input,
export_options=export_options,
)
export_output.save(output_file)
else:
torch.onnx.export(
model,
example_input,
output_file,
training=training_mode,
export_params=True,
verbose=verbose,
input_names=input_names,
output_names=output_names,
keep_initializers_as_inputs=keep_initializers,
dynamic_axes=dynamic_axes,
opset_version=opset,
operator_export_type=export_type
)
if check:
onnx_model = onnx.load(output_file)
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model, full_check=True) # assuming throw on error
if check_forward and not training:
import numpy as np
onnx_out = onnx_forward(output_file, example_input)
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(original_out.numpy(), onnx_out, decimal=3)
|
pytorch-image-models/timm/utils/onnx.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "pytorch-image-models/timm/utils/onnx.py",
"repo_id": "pytorch-image-models",
"token_count": 1594
}
| 277
|
# Agents - Guided tour
[[open-in-colab]]
In this guided visit, you will learn how to build an agent, how to run it, and how to customize it to make it work better for your use-case.
## Choosing an agent type: CodeAgent or ToolCallingAgent
`smolagents` comes with two agent classes: [`CodeAgent`] and [`ToolCallingAgent`], which represent two different paradigms for how agents interact with tools.
The key difference lies in how actions are specified and executed: code generation vs structured tool calling.
- [`CodeAgent`] generates tool calls as Python code snippets.
- The code is executed either locally (potentially unsecure) or in a secure sandbox.
- Tools are exposed as Python functions (via bindings).
- Example of tool call:
```py
result = search_docs("What is the capital of France?")
print(result)
```
- Strengths:
- Highly expressive: Allows for complex logic and control flow and can combine tools, loop, transform, reason.
- Flexible: No need to predefine every possible action, can dynamically generate new actions/tools.
- Emergent reasoning: Ideal for multi-step problems or dynamic logic.
- Limitations
- Risk of errors: Must handle syntax errors, exceptions.
- Less predictable: More prone to unexpected or unsafe outputs.
- Requires secure execution environment.
- [`ToolCallingAgent`] writes tool calls as structured JSON.
- This is the common format used in many frameworks (OpenAI API), allowing for structured tool interactions without code execution.
- Tools are defined with a JSON schema: name, description, parameter types, etc.
- Example of tool call:
```json
{
"tool_call": {
"name": "search_docs",
"arguments": {
"query": "What is the capital of France?"
}
}
}
```
- Strengths:
- Reliable: Less prone to hallucination, outputs are structured and validated.
- Safe: Arguments are strictly validated, no risk of arbitrary code running.
- Interoperable: Easy to map to external APIs or services.
- Limitations:
- Low expressivity: Can't easily combine or transform results dynamically, or perform complex logic or control flow.
- Inflexible: Must define all possible actions in advance, limited to predefined tools.
- No code synthesis: Limited to tool capabilities.
When to use which agent type:
- Use [`CodeAgent`] when:
- You need reasoning, chaining, or dynamic composition.
- Tools are functions that can be combined (e.g., parsing + math + querying).
- Your agent is a problem solver or programmer.
- Use [`ToolCallingAgent`] when:
- You have simple, atomic tools (e.g., call an API, fetch a document).
- You want high reliability and clear validation.
- Your agent is like a dispatcher or controller.
## CodeAgent
[`CodeAgent`] generates Python code snippets to perform actions and solve tasks.
By default, the Python code execution is done in your local environment.
This should be safe because the only functions that can be called are the tools you provided (especially if it's only tools by Hugging Face) and a set of predefined safe functions like `print` or functions from the `math` module, so you're already limited in what can be executed.
The Python interpreter also doesn't allow imports by default outside of a safe list, so all the most obvious attacks shouldn't be an issue.
You can authorize additional imports by passing the authorized modules as a list of strings in argument `additional_authorized_imports` upon initialization of your [`CodeAgent`]:
```py
model = InferenceClientModel()
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
```
Additionally, as an extra security layer, access to submodule is forbidden by default, unless explicitly authorized within the import list.
For instance, to access the `numpy.random` submodule, you need to add `'numpy.random'` to the `additional_authorized_imports` list.
This could also be authorized by using `numpy.*`, which will allow `numpy` as well as any subpackage like `numpy.random` and its own subpackages.
> [!WARNING]
> The LLM can generate arbitrary code that will then be executed: do not add any unsafe imports!
The execution will stop at any code trying to perform an illegal operation or if there is a regular Python error with the code generated by the agent.
You can also use [E2B code executor](https://e2b.dev/docs#what-is-e2-b) or Docker instead of a local Python interpreter. For E2B, first [set the `E2B_API_KEY` environment variable](https://e2b.dev/dashboard?tab=keys) and then pass `executor_type="e2b"` upon agent initialization. For Docker, pass `executor_type="docker"` during initialization.
> [!TIP]
> Learn more about code execution [in this tutorial](tutorials/secure_code_execution).
### ToolCallingAgent
[`ToolCallingAgent`] outputs JSON tool calls, which is the common format used in many frameworks (OpenAI API), allowing for structured tool interactions without code execution.
It works much in the same way like [`CodeAgent`], of course without `additional_authorized_imports` since it doesn't execute code:
```py
from smolagents import ToolCallingAgent
agent = ToolCallingAgent(tools=[], model=model)
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
```
## Building your agent
To initialize a minimal agent, you need at least these two arguments:
- `model`, a text-generation model to power your agent - because the agent is different from a simple LLM, it is a system that uses a LLM as its engine. You can use any of these options:
- [`TransformersModel`] takes a pre-initialized `transformers` pipeline to run inference on your local machine using `transformers`.
- [`InferenceClientModel`] leverages a `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` under the hood and supports all Inference Providers on the Hub: Cerebras, Cohere, Fal, Fireworks, HF-Inference, Hyperbolic, Nebius, Novita, Replicate, SambaNova, Together, and more.
- [`LiteLLMModel`] similarly lets you call 100+ different models and providers through [LiteLLM](https://docs.litellm.ai/)!
- [`AzureOpenAIServerModel`] allows you to use OpenAI models deployed in [Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-services/openai-service).
- [`AmazonBedrockServerModel`] allows you to use Amazon Bedrock in [AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/?nc1=h_ls).
- [`MLXModel`] creates a [mlx-lm](https://pypi.org/project/mlx-lm/) pipeline to run inference on your local machine.
- `tools`, a list of `Tools` that the agent can use to solve the task. It can be an empty list. You can also add the default toolbox on top of your `tools` list by defining the optional argument `add_base_tools=True`.
Once you have these two arguments, `tools` and `model`, you can create an agent and run it. You can use any LLM you'd like, either through [Inference Providers](https://huggingface.co/blog/inference-providers), [transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/), [ollama](https://ollama.com/), [LiteLLM](https://www.litellm.ai/), [Azure OpenAI](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-services/openai-service), [Amazon Bedrock](https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/?nc1=h_ls), or [mlx-lm](https://pypi.org/project/mlx-lm/).
All model classes support passing additional keyword arguments (like `temperature`, `max_tokens`, `top_p`, etc.) directly at instantiation time.
These parameters are automatically forwarded to the underlying model's completion calls, allowing you to configure model behavior such as creativity, response length, and sampling strategies.
<hfoptions id="Pick a LLM">
<hfoption id="Inference Providers">
Inference Providers need a `HF_TOKEN` to authenticate, but a free HF account already comes with included credits. Upgrade to PRO to raise your included credits.
To access gated models or rise your rate limits with a PRO account, you need to set the environment variable `HF_TOKEN` or pass `token` variable upon initialization of `InferenceClientModel`. You can get your token from your [settings page](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens)
```python
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id, token="<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>") # You can choose to not pass any model_id to InferenceClientModel to use a default model
# you can also specify a particular provider e.g. provider="together" or provider="sambanova"
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Local Transformers Model">
```python
# !pip install smolagents[transformers]
from smolagents import CodeAgent, TransformersModel
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"
model = TransformersModel(model_id=model_id)
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="OpenAI or Anthropic API">
To use `LiteLLMModel`, you need to set the environment variable `ANTHROPIC_API_KEY` or `OPENAI_API_KEY`, or pass `api_key` variable upon initialization.
```python
# !pip install smolagents[litellm]
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-latest", api_key="YOUR_ANTHROPIC_API_KEY") # Could use 'gpt-4o'
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Ollama">
```python
# !pip install smolagents[litellm]
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
model = LiteLLMModel(
model_id="ollama_chat/llama3.2", # This model is a bit weak for agentic behaviours though
api_base="http://localhost:11434", # replace with 127.0.0.1:11434 or remote open-ai compatible server if necessary
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY", # replace with API key if necessary
num_ctx=8192, # ollama default is 2048 which will fail horribly. 8192 works for easy tasks, more is better. Check https://huggingface.co/spaces/NyxKrage/LLM-Model-VRAM-Calculator to calculate how much VRAM this will need for the selected model.
)
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Azure OpenAI">
To connect to Azure OpenAI, you can either use `AzureOpenAIServerModel` directly, or use `LiteLLMModel` and configure it accordingly.
To initialize an instance of `AzureOpenAIServerModel`, you need to pass your model deployment name and then either pass the `azure_endpoint`, `api_key`, and `api_version` arguments, or set the environment variables `AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT`, `AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY`, and `OPENAI_API_VERSION`.
```python
# !pip install smolagents[openai]
from smolagents import CodeAgent, AzureOpenAIServerModel
model = AzureOpenAIServerModel(model_id="gpt-4o-mini")
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
Similarly, you can configure `LiteLLMModel` to connect to Azure OpenAI as follows:
- pass your model deployment name as `model_id`, and make sure to prefix it with `azure/`
- make sure to set the environment variable `AZURE_API_VERSION`
- either pass the `api_base` and `api_key` arguments, or set the environment variables `AZURE_API_KEY`, and `AZURE_API_BASE`
```python
import os
from smolagents import CodeAgent, LiteLLMModel
AZURE_OPENAI_CHAT_DEPLOYMENT_NAME="gpt-35-turbo-16k-deployment" # example of deployment name
os.environ["AZURE_API_KEY"] = "" # api_key
os.environ["AZURE_API_BASE"] = "" # "https://example-endpoint.openai.azure.com"
os.environ["AZURE_API_VERSION"] = "" # "2024-10-01-preview"
model = LiteLLMModel(model_id="azure/" + AZURE_OPENAI_CHAT_DEPLOYMENT_NAME)
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Amazon Bedrock">
The `AmazonBedrockServerModel` class provides native integration with Amazon Bedrock, allowing for direct API calls and comprehensive configuration.
Basic Usage:
```python
# !pip install smolagents[aws_sdk]
from smolagents import CodeAgent, AmazonBedrockServerModel
model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(model_id="anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0")
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
Advanced Configuration:
```python
import boto3
from smolagents import AmazonBedrockServerModel
# Create a custom Bedrock client
bedrock_client = boto3.client(
'bedrock-runtime',
region_name='us-east-1',
aws_access_key_id='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY',
aws_secret_access_key='YOUR_SECRET_KEY'
)
additional_api_config = {
"inferenceConfig": {
"maxTokens": 3000
},
"guardrailConfig": {
"guardrailIdentifier": "identify1",
"guardrailVersion": 'v1'
},
}
# Initialize with comprehensive configuration
model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
model_id="us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0",
client=bedrock_client, # Use custom client
**additional_api_config
)
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model, add_base_tools=True)
agent.run(
"Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?",
)
```
Using LiteLLMModel:
Alternatively, you can use `LiteLLMModel` with Bedrock models:
```python
from smolagents import LiteLLMModel, CodeAgent
model = LiteLLMModel(model_name="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0")
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], model=model)
agent.run("Explain the concept of quantum computing")
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="mlx-lm">
```python
# !pip install smolagents[mlx-lm]
from smolagents import CodeAgent, MLXModel
mlx_model = MLXModel("mlx-community/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct-4bit")
agent = CodeAgent(model=mlx_model, tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
agent.run("Could you give me the 118th number in the Fibonacci sequence?")
```
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
## Advanced agent configuration
### Customizing agent termination conditions
By default, an agent continues running until it calls the `final_answer` function or reaches the maximum number of steps.
The `final_answer_checks` parameter gives you more control over when and how an agent terminates its execution:
```python
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
# Define a custom final answer check function
def is_integer(final_answer: str, agent_memory=None) -> bool:
"""Return True if final_answer is an integer."""
try:
int(final_answer)
return True
except ValueError:
return False
# Initialize agent with custom final answer check
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[],
model=InferenceClientModel(),
final_answer_checks=[is_integer]
)
agent.run("Calculate the least common multiple of 3 and 7")
```
The `final_answer_checks` parameter accepts a list of functions that each:
- Take the agent's final_answer string the agent's memory as parameters
- Return a boolean indicating whether the final_answer is valid (True) or not (False)
If any function returns `False`, the agent will log the error message and continue the run.
This validation mechanism enables:
- Enforcing output format requirements (e.g., ensuring numeric answers for math problems)
- Implementing domain-specific validation rules
- Creating more robust agents that validate their own outputs
## Inspecting an agent run
Here are a few useful attributes to inspect what happened after a run:
- `agent.logs` stores the fine-grained logs of the agent. At every step of the agent's run, everything gets stored in a dictionary that then is appended to `agent.logs`.
- Running `agent.write_memory_to_messages()` writes the agent's memory as list of chat messages for the Model to view. This method goes over each step of the log and only stores what it's interested in as a message: for instance, it will save the system prompt and task in separate messages, then for each step it will store the LLM output as a message, and the tool call output as another message. Use this if you want a higher-level view of what has happened - but not every log will be transcripted by this method.
## Tools
A tool is an atomic function to be used by an agent. To be used by an LLM, it also needs a few attributes that constitute its API and will be used to describe to the LLM how to call this tool:
- A name
- A description
- Input types and descriptions
- An output type
You can for instance check the [`PythonInterpreterTool`]: it has a name, a description, input descriptions, an output type, and a `forward` method to perform the action.
When the agent is initialized, the tool attributes are used to generate a tool description which is baked into the agent's system prompt. This lets the agent know which tools it can use and why.
**Schema Information**: For tools that have an `output_schema` defined (such as MCP tools with structured output), the `CodeAgent` system prompt automatically includes the JSON schema information. This helps the agent understand the expected structure of tool outputs and access the data appropriately.
### Default toolbox
If you install `smolagents` with the "toolkit" extra, it comes with a default toolbox for empowering agents, that you can add to your agent upon initialization with argument `add_base_tools=True`:
- **DuckDuckGo web search***: performs a web search using DuckDuckGo browser.
- **Python code interpreter**: runs your LLM generated Python code in a secure environment. This tool will only be added to [`ToolCallingAgent`] if you initialize it with `add_base_tools=True`, since code-based agent can already natively execute Python code
- **Transcriber**: a speech-to-text pipeline built on Whisper-Turbo that transcribes an audio to text.
You can manually use a tool by calling it with its arguments.
```python
# !pip install smolagents[toolkit]
from smolagents import WebSearchTool
search_tool = WebSearchTool()
print(search_tool("Who's the current president of Russia?"))
```
### Create a new tool
You can create your own tool for use cases not covered by the default tools from Hugging Face.
For example, let's create a tool that returns the most downloaded model for a given task from the Hub.
You'll start with the code below.
```python
from huggingface_hub import list_models
task = "text-classification"
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
print(most_downloaded_model.id)
```
This code can quickly be converted into a tool, just by wrapping it in a function and adding the `tool` decorator:
This is not the only way to build the tool: you can directly define it as a subclass of [`Tool`], which gives you more flexibility, for instance the possibility to initialize heavy class attributes.
Let's see how it works for both options:
<hfoptions id="build-a-tool">
<hfoption id="Decorate a function with @tool">
```py
from smolagents import tool
@tool
def model_download_tool(task: str) -> str:
"""
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
It returns the name of the checkpoint.
Args:
task: The task for which to get the download count.
"""
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
return most_downloaded_model.id
```
The function needs:
- A clear name. The name should be descriptive enough of what this tool does to help the LLM brain powering the agent. Since this tool returns the model with the most downloads for a task, let's name it `model_download_tool`.
- Type hints on both inputs and output
- A description, that includes an 'Args:' part where each argument is described (without a type indication this time, it will be pulled from the type hint). Same as for the tool name, this description is an instruction manual for the LLM powering your agent, so do not neglect it.
All these elements will be automatically baked into the agent's system prompt upon initialization: so strive to make them as clear as possible!
> [!TIP]
> This definition format is the same as tool schemas used in `apply_chat_template`, the only difference is the added `tool` decorator: read more on our tool use API [here](https://huggingface.co/blog/unified-tool-use#passing-tools-to-a-chat-template).
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="Subclass Tool">
```py
from smolagents import Tool
class ModelDownloadTool(Tool):
name = "model_download_tool"
description = "This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. It returns the name of the checkpoint."
inputs = {"task": {"type": "string", "description": "The task for which to get the download count."}}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, task: str) -> str:
most_downloaded_model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
return most_downloaded_model.id
```
The subclass needs the following attributes:
- A clear `name`. The name should be descriptive enough of what this tool does to help the LLM brain powering the agent. Since this tool returns the model with the most downloads for a task, let's name it `model_download_tool`.
- A `description`. Same as for the `name`, this description is an instruction manual for the LLM powering your agent, so do not neglect it.
- Input types and descriptions
- Output type
All these attributes will be automatically baked into the agent's system prompt upon initialization: so strive to make them as clear as possible!
</hfoption>
</hfoptions>
Then you can directly initialize your agent:
```py
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], model=InferenceClientModel())
agent.run(
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
)
```
You get the following logs:
```text
╭──────────────────────────────────────── New run ─────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ │
│ Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' │
│ task on the Hugging Face Hub? │
│ │
╰─ InferenceClientModel - Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct ───────────────────────────────────────────╯
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Step 0 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
╭─ Executing this code: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ 1 model_name = model_download_tool(task="text-to-video") │
│ 2 print(model_name) │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Execution logs:
ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning
Out: None
[Step 0: Duration 0.27 seconds| Input tokens: 2,069 | Output tokens: 60]
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Step 1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
╭─ Executing this code: ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ 1 final_answer("ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning") │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Out - Final answer: ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning
[Step 1: Duration 0.10 seconds| Input tokens: 4,288 | Output tokens: 148]
Out[20]: 'ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning'
```
> [!TIP]
> Read more on tools in the [dedicated tutorial](./tutorials/tools#what-is-a-tool-and-how-to-build-one).
## Multi-agents
Multi-agent systems have been introduced with Microsoft's framework [Autogen](https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.08155).
In this type of framework, you have several agents working together to solve your task instead of only one.
It empirically yields better performance on most benchmarks. The reason for this better performance is conceptually simple: for many tasks, rather than using a do-it-all system, you would prefer to specialize units on sub-tasks. Here, having agents with separate tool sets and memories allows to achieve efficient specialization. For instance, why fill the memory of the code generating agent with all the content of webpages visited by the web search agent? It's better to keep them separate.
You can easily build hierarchical multi-agent systems with `smolagents`.
To do so, just ensure your agent has `name` and`description` attributes, which will then be embedded in the manager agent's system prompt to let it know how to call this managed agent, as we also do for tools.
Then you can pass this managed agent in the parameter managed_agents upon initialization of the manager agent.
Here's an example of making an agent that managed a specific web search agent using our native [`WebSearchTool`]:
```py
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, WebSearchTool
model = InferenceClientModel()
web_agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[WebSearchTool()],
model=model,
name="web_search_agent",
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument."
)
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[], model=model, managed_agents=[web_agent]
)
manager_agent.run("Who is the CEO of Hugging Face?")
```
> [!TIP]
> For an in-depth example of an efficient multi-agent implementation, see [how we pushed our multi-agent system to the top of the GAIA leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/blog/beating-gaia).
## Talk with your agent and visualize its thoughts in a cool Gradio interface
You can use `GradioUI` to interactively submit tasks to your agent and observe its thought and execution process, here is an example:
```py
from smolagents import (
load_tool,
CodeAgent,
InferenceClientModel,
GradioUI
)
# Import tool from Hub
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image", trust_remote_code=True)
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], model=model)
GradioUI(agent).launch()
```
Under the hood, when the user types a new answer, the agent is launched with `agent.run(user_request, reset=False)`.
The `reset=False` flag means the agent's memory is not flushed before launching this new task, which lets the conversation go on.
You can also use this `reset=False` argument to keep the conversation going in any other agentic application.
In gradio UIs, if you want to allow users to interrupt a running agent, you could do this with a button that triggers method `agent.interrupt()`.
This will stop the agent at the end of its current step, then raise an error.
## Next steps
Finally, when you've configured your agent to your needs, you can share it to the Hub!
```py
agent.push_to_hub("m-ric/my_agent")
```
Similarly, to load an agent that has been pushed to hub, if you trust the code from its tools, use:
```py
agent.from_hub("m-ric/my_agent", trust_remote_code=True)
```
For more in-depth usage, you will then want to check out our tutorials:
- [the explanation of how our code agents work](./tutorials/secure_code_execution)
- [this guide on how to build good agents](./tutorials/building_good_agents).
- [the in-depth guide for tool usage](./tutorials/building_good_agents).
|
smolagents/docs/source/en/guided_tour.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/docs/source/en/guided_tour.md",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 8497
}
| 278
|
# मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम का आयोजन करें 🤖🤝🤖
[[open-in-colab]]
इस नोटबुक में हम एक **मल्टी-एजेंट वेब ब्राउज़र बनाएंगे: एक एजेंटिक सिस्टम जिसमें कई एजेंट वेब का उपयोग करके समस्याओं को हल करने के लिए सहयोग करते हैं!**
यह एक सरल संरचना होगी, जो प्रबंधित वेब खोज एजेंट को रैप करने के लिए `ManagedAgent` ऑब्जेक्ट का उपयोग करता है:
```
+----------------+
| Manager agent |
+----------------+
|
_______________|______________
| |
Code interpreter +--------------------------------+
tool | Managed agent |
| +------------------+ |
| | Web Search agent | |
| +------------------+ |
| | | |
| Web Search tool | |
| Visit webpage tool |
+--------------------------------+
```
आइए इस सिस्टम को सेट करें।
आवश्यक डिपेंडेंसी इंस्टॉल करने के लिए नीचे दी गई लाइन चलाएं:
```
!pip install smolagents[toolkit] --upgrade -q
```
HF Inference API को कॉल करने के लिए लॉगिन करें:
```
from huggingface_hub import login
login()
```
⚡️ हमारा एजेंट [Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct) द्वारा संचालित होगा जो `InferenceClientModel` क्लास का उपयोग करता है जो HF के Inference API का उपयोग करता है: Inference API किसी भी OS मॉडल को जल्दी और आसानी से चलाने की अनुमति देता है।
_नोट:_ The Inference API विभिन्न मानदंडों के आधार पर मॉडल होस्ट करता है, और डिप्लॉय किए गए मॉडल बिना पूर्व सूचना के अपडेट या बदले जा सकते हैं। इसके बारे में अधिक जानें [यहां](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/supported-models)।
```py
model_id = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"
```
## 🔍 एक वेब सर्च टूल बनाएं
वेब ब्राउज़िंग के लिए, हम पहले से मौजूद [`WebSearchTool`] टूल का उपयोग कर सकते हैं जो Google search के समान सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
लेकिन फिर हमें `WebSearchTool` द्वारा खोजे गए पेज को देखने में भी सक्षम होने की आवश्यकता होगी।
ऐसा करने के लिए, हम लाइब्रेरी के बिल्ट-इन `VisitWebpageTool` को इम्पोर्ट कर सकते हैं, लेकिन हम इसे फिर से बनाएंगे यह देखने के लिए कि यह कैसे किया जाता है।
तो आइए `markdownify` का उपयोग करके शुरू से अपना `VisitWebpageTool` टूल बनाएं।
```py
import re
import requests
from markdownify import markdownify
from requests.exceptions import RequestException
from smolagents import tool
@tool
def visit_webpage(url: str) -> str:
"""Visits a webpage at the given URL and returns its content as a markdown string.
Args:
url: The URL of the webpage to visit.
Returns:
The content of the webpage converted to Markdown, or an error message if the request fails.
"""
try:
# Send a GET request to the URL
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an exception for bad status codes
# Convert the HTML content to Markdown
markdown_content = markdownify(response.text).strip()
# Remove multiple line breaks
markdown_content = re.sub(r"\n{3,}", "\n\n", markdown_content)
return markdown_content
except RequestException as e:
return f"Error fetching the webpage: {str(e)}"
except Exception as e:
return f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}"
```
ठीक है, अब चलिए हमारे टूल को टेस्ट करें!
```py
print(visit_webpage("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hugging_Face")[:500])
```
## हमारी मल्टी-एजेंट सिस्टम का निर्माण करें 🤖🤝🤖
अब जब हमारे पास सभी टूल्स `search` और `visit_webpage` हैं, हम उनका उपयोग वेब एजेंट बनाने के लिए कर सकते हैं।
इस एजेंट के लिए कौन सा कॉन्फ़िगरेशन चुनें?
- वेब ब्राउज़िंग एक सिंगल-टाइमलाइन टास्क है जिसे समानांतर टूल कॉल की आवश्यकता नहीं है, इसलिए JSON टूल कॉलिंग इसके लिए अच्छी तरह काम करती है। इसलिए हम `ToolCallingAgent` चुनते हैं।
- साथ ही, चूंकि कभी-कभी वेब सर्च में सही उत्तर खोजने से पहले कई पेजों की सर्च करने की आवश्यकता होती है, हम `max_steps` को बढ़ाकर 10 करना पसंद करते हैं।
```py
from smolagents import (
CodeAgent,
ToolCallingAgent,
InferenceClientModel,
ManagedAgent,
WebSearchTool,
LiteLLMModel,
)
model = InferenceClientModel(model_id=model_id)
web_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
tools=[WebSearchTool(), visit_webpage],
model=model,
max_steps=10,
)
```
फिर हम इस एजेंट को एक `ManagedAgent` में रैप करते हैं जो इसे इसके मैनेजर एजेंट द्वारा कॉल करने योग्य बनाएगा।
```py
managed_web_agent = ManagedAgent(
agent=web_agent,
name="search",
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument.",
)
```
अंत में हम एक मैनेजर एजेंट बनाते हैं, और इनिशियलाइजेशन पर हम अपने मैनेज्ड एजेंट को इसके `managed_agents` आर्गुमेंट में पास करते हैं।
चूंकि यह एजेंट योजना बनाने और सोचने का काम करता है, उन्नत तर्क लाभदायक होगा, इसलिए `CodeAgent` सबसे अच्छा विकल्प होगा।
साथ ही, हम एक ऐसा प्रश्न पूछना चाहते हैं जिसमें वर्तमान वर्ष और अतिरिक्त डेटा गणना शामिल है: इसलिए आइए `additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"]` जोड़ें, यदि एजेंट को इन पैकेजों की आवश्यकता हो।
```py
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[],
model=model,
managed_agents=[managed_web_agent],
additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"],
)
```
बस इतना ही! अब चलिए हमारे सिस्टम को चलाते हैं! हम एक ऐसा प्रश्न चुनते हैं जिसमें गणना और शोध दोनों की आवश्यकता है।
```py
answer = manager_agent.run("If LLM training continues to scale up at the current rhythm until 2030, what would be the electric power in GW required to power the biggest training runs by 2030? What would that correspond to, compared to some countries? Please provide a source for any numbers used.")
```
We get this report as the answer:
```
Based on current growth projections and energy consumption estimates, if LLM trainings continue to scale up at the
current rhythm until 2030:
1. The electric power required to power the biggest training runs by 2030 would be approximately 303.74 GW, which
translates to about 2,660,762 GWh/year.
2. Comparing this to countries' electricity consumption:
- It would be equivalent to about 34% of China's total electricity consumption.
- It would exceed the total electricity consumption of India (184%), Russia (267%), and Japan (291%).
- It would be nearly 9 times the electricity consumption of countries like Italy or Mexico.
3. Source of numbers:
- The initial estimate of 5 GW for future LLM training comes from AWS CEO Matt Garman.
- The growth projection used a CAGR of 79.80% from market research by Springs.
- Country electricity consumption data is from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, primarily for the year
2021.
```
लगता है कि यदि [स्केलिंग हाइपोथिसिस](https://gwern.net/scaling-hypothesis) सत्य बनी रहती है तो हमें कुछ बड़े पावरप्लांट्स की आवश्यकता होगी।
हमारे एजेंट्स ने कार्य को हल करने के लिए कुशलतापूर्वक सहयोग किया! ✅
💡 आप इस ऑर्केस्ट्रेशन को आसानी से अधिक एजेंट्स में विस्तारित कर सकते हैं: एक कोड एक्जीक्यूशन करता है, एक वेब सर्च करता है, एक फाइल लोडिंग को संभालता है।
|
smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/multiagents.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/docs/source/hi/examples/multiagents.md",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 5599
}
| 279
|
# 安全代码执行
[[open-in-colab]]
> [!TIP]
> 如果你是第一次构建 agent,请先阅读 [agent 介绍](../conceptual_guides/intro_agents) 和 [smolagents 导览](../guided_tour)。
### 代码智能体
[多项](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030) [研究](https://huggingface.co/papers/2411.01747) [表明](https://huggingface.co/papers/2401.00812),让大语言模型用代码编写其动作(工具调用)比当前标准的工具调用格式要好得多,目前行业标准是 "将动作写成包含工具名称和参数的 JSON" 的各种变体。
为什么代码更好?因为我们专门为计算机执行的动作而设计编程语言。如果 JSON 片段是更好的方式,那么这个工具包就应该是用 JSON 片段编写的,魔鬼就会嘲笑我们。
代码就是表达计算机动作的更好方式。它具有更好的:
- **组合性**:你能像定义 Python 函数那样,在 JSON 动作中嵌套其他 JSON 动作,或者定义一组 JSON 动作以便以后重用吗?
- **对象管理**:你如何在 JSON 中存储像 `generate_image` 这样的动作的输出?
- **通用性**:代码是为了简单地表达任何可以让计算机做的事情而构建的。
- **在 LLM 训练语料库中的表示**:天赐良机,为什么不利用已经包含在 LLM 训练语料库中的大量高质量动作呢?
下图展示了这一点,取自 [可执行代码动作引出更好的 LLM 智能体](https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.01030)。
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/code_vs_json_actions.png">
这就是为什么我们强调提出代码智能体,在本例中是 Python 智能体,这意味着我们要在构建安全的 Python 解释器上投入更多精力。
### 本地 Python 解释器
默认情况下,`CodeAgent` 会在你的环境中运行 LLM 生成的代码。
这个执行不是由普通的 Python 解释器完成的:我们从零开始重新构建了一个更安全的 `LocalPythonExecutor`。
这个解释器通过以下方式设计以确保安全:
- 将导入限制为用户显式传递的列表
- 限制操作次数以防止无限循环和资源膨胀
- 不会执行任何未预定义的操作
我们已经在许多用例中使用了这个解释器,从未观察到对环境造成任何损害。
然而,这个解决方案并不是万无一失的:可以想象,如果 LLM 被微调用于恶意操作,仍然可能损害你的环境。例如,如果你允许像 `Pillow` 这样无害的包处理图像,LLM 可能会生成数千张图像保存以膨胀你的硬盘。
如果你自己选择了 LLM 引擎,这当然不太可能,但它可能会发生。
所以如果你想格外谨慎,可以使用下面描述的远程代码执行选项。
### E2B 代码执行器
为了最大程度的安全性,你可以使用我们与 E2B 的集成在沙盒环境中运行代码。这是一个远程执行服务,可以在隔离的容器中运行你的代码,使代码无法影响你的本地环境。
为此,你需要设置你的 E2B 账户并在环境变量中设置 `E2B_API_KEY`。请前往 [E2B 快速入门文档](https://e2b.dev/docs/quickstart) 了解更多信息。
然后你可以通过 `pip install e2b-code-interpreter python-dotenv` 安装它。
现在你已经准备好了!
要将代码执行器设置为 E2B,只需在初始化 `CodeAgent` 时传递标志 `executor_type="e2b"`。
请注意,你应该将所有工具的依赖项添加到 `additional_authorized_imports` 中,以便执行器安装它们。
```py
from smolagents import CodeAgent, VisitWebpageTool, InferenceClientModel
agent = CodeAgent(
tools = [VisitWebpageTool()],
model=InferenceClientModel(),
additional_authorized_imports=["requests", "markdownify"],
executor_type="e2b"
)
agent.run("What was Abraham Lincoln's preferred pet?")
```
目前 E2B 代码执行暂不兼容多 agent——因为把 agent 调用放在应该在远程执行的代码块里,是非常混乱的。但我们正在努力做到这件事!
|
smolagents/docs/source/zh/tutorials/secure_code_execution.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/docs/source/zh/tutorials/secure_code_execution.md",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 2540
}
| 280
|
# EXAMPLE COMMAND: from folder examples/open_deep_research, run: python run_gaia.py --concurrency 32 --run-name generate-traces-03-apr-noplanning --model-id gpt-4o
import argparse
import json
import os
import threading
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Any
import datasets
import pandas as pd
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from huggingface_hub import login, snapshot_download
from scripts.reformulator import prepare_response
from scripts.run_agents import (
get_single_file_description,
get_zip_description,
)
from scripts.text_inspector_tool import TextInspectorTool
from scripts.text_web_browser import (
ArchiveSearchTool,
FinderTool,
FindNextTool,
PageDownTool,
PageUpTool,
SimpleTextBrowser,
VisitTool,
)
from scripts.visual_qa import visualizer
from tqdm import tqdm
from smolagents import (
CodeAgent,
GoogleSearchTool,
LiteLLMModel,
Model,
ToolCallingAgent,
)
load_dotenv(override=True)
login(os.getenv("HF_TOKEN"))
append_answer_lock = threading.Lock()
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--concurrency", type=int, default=8)
parser.add_argument("--model-id", type=str, default="o1")
parser.add_argument("--run-name", type=str, required=True)
parser.add_argument("--set-to-run", type=str, default="validation")
parser.add_argument("--use-open-models", type=bool, default=False)
parser.add_argument("--use-raw-dataset", action="store_true")
return parser.parse_args()
### IMPORTANT: EVALUATION SWITCHES
print("Make sure you deactivated any VPN like Tailscale, else some URLs will be blocked!")
custom_role_conversions = {"tool-call": "assistant", "tool-response": "user"}
user_agent = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/119.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/119.0.0.0"
BROWSER_CONFIG = {
"viewport_size": 1024 * 5,
"downloads_folder": "downloads_folder",
"request_kwargs": {
"headers": {"User-Agent": user_agent},
"timeout": 300,
},
"serpapi_key": os.getenv("SERPAPI_API_KEY"),
}
os.makedirs(f"./{BROWSER_CONFIG['downloads_folder']}", exist_ok=True)
def create_agent_team(model: Model):
text_limit = 100000
ti_tool = TextInspectorTool(model, text_limit)
browser = SimpleTextBrowser(**BROWSER_CONFIG)
WEB_TOOLS = [
GoogleSearchTool(provider="serper"),
VisitTool(browser),
PageUpTool(browser),
PageDownTool(browser),
FinderTool(browser),
FindNextTool(browser),
ArchiveSearchTool(browser),
TextInspectorTool(model, text_limit),
]
text_webbrowser_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
model=model,
tools=WEB_TOOLS,
max_steps=20,
verbosity_level=2,
planning_interval=4,
name="search_agent",
description="""A team member that will search the internet to answer your question.
Ask him for all your questions that require browsing the web.
Provide him as much context as possible, in particular if you need to search on a specific timeframe!
And don't hesitate to provide him with a complex search task, like finding a difference between two webpages.
Your request must be a real sentence, not a google search! Like "Find me this information (...)" rather than a few keywords.
""",
provide_run_summary=True,
)
text_webbrowser_agent.prompt_templates["managed_agent"]["task"] += """You can navigate to .txt online files.
If a non-html page is in another format, especially .pdf or a Youtube video, use tool 'inspect_file_as_text' to inspect it.
Additionally, if after some searching you find out that you need more information to answer the question, you can use `final_answer` with your request for clarification as argument to request for more information."""
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
model=model,
tools=[visualizer, ti_tool],
max_steps=12,
verbosity_level=2,
additional_authorized_imports=["*"],
planning_interval=4,
managed_agents=[text_webbrowser_agent],
)
return manager_agent
def load_gaia_dataset(use_raw_dataset: bool, set_to_run: str) -> datasets.Dataset:
if not os.path.exists("data/gaia"):
if use_raw_dataset:
snapshot_download(
repo_id="gaia-benchmark/GAIA",
repo_type="dataset",
local_dir="data/gaia",
ignore_patterns=[".gitattributes", "README.md"],
)
else:
# WARNING: this dataset is gated: make sure you visit the repo to require access.
snapshot_download(
repo_id="smolagents/GAIA-annotated",
repo_type="dataset",
local_dir="data/gaia",
ignore_patterns=[".gitattributes", "README.md"],
)
def preprocess_file_paths(row):
if len(row["file_name"]) > 0:
row["file_name"] = f"data/gaia/{set_to_run}/" + row["file_name"]
return row
eval_ds = datasets.load_dataset(
"data/gaia/GAIA.py",
name="2023_all",
split=set_to_run,
# data_files={"validation": "validation/metadata.jsonl", "test": "test/metadata.jsonl"},
)
eval_ds = eval_ds.rename_columns({"Question": "question", "Final answer": "true_answer", "Level": "task"})
eval_ds = eval_ds.map(preprocess_file_paths)
return eval_ds
def append_answer(entry: dict, jsonl_file: str) -> None:
jsonl_path = Path(jsonl_file)
jsonl_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
with append_answer_lock, open(jsonl_file, "a", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(json.dumps(entry) + "\n")
assert jsonl_path.exists(), "File not found!"
print("Answer exported to file:", jsonl_path.resolve())
def answer_single_question(
example: dict, model_id: str, answers_file: str, visual_inspection_tool: TextInspectorTool
) -> None:
model_params: dict[str, Any] = {
"model_id": model_id,
"custom_role_conversions": custom_role_conversions,
}
if model_id == "o1":
model_params["reasoning_effort"] = "high"
model_params["max_completion_tokens"] = 8192
else:
model_params["max_tokens"] = 4096
model = LiteLLMModel(**model_params)
# model = InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen3-32B", provider="novita", max_tokens=4096)
document_inspection_tool = TextInspectorTool(model, 100000)
agent = create_agent_team(model)
augmented_question = """You have one question to answer. It is paramount that you provide a correct answer.
Give it all you can: I know for a fact that you have access to all the relevant tools to solve it and find the correct answer (the answer does exist).
Failure or 'I cannot answer' or 'None found' will not be tolerated, success will be rewarded.
Run verification steps if that's needed, you must make sure you find the correct answer! Here is the task:
""" + example["question"]
if example["file_name"]:
if ".zip" in example["file_name"]:
prompt_use_files = "\n\nTo solve the task above, you will have to use these attached files:\n"
prompt_use_files += get_zip_description(
example["file_name"], example["question"], visual_inspection_tool, document_inspection_tool
)
else:
prompt_use_files = "\n\nTo solve the task above, you will have to use this attached file:\n"
prompt_use_files += get_single_file_description(
example["file_name"], example["question"], visual_inspection_tool, document_inspection_tool
)
augmented_question += prompt_use_files
start_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
try:
# Run agent 🚀
final_result = agent.run(augmented_question)
agent_memory = agent.write_memory_to_messages()
final_result = prepare_response(augmented_question, agent_memory, reformulation_model=model)
output = str(final_result)
for memory_step in agent.memory.steps:
memory_step.model_input_messages = None
intermediate_steps = agent_memory
# Check for parsing errors which indicate the LLM failed to follow the required format
parsing_error = True if any(["AgentParsingError" in step for step in intermediate_steps]) else False
# check if iteration limit exceeded
iteration_limit_exceeded = True if "Agent stopped due to iteration limit or time limit." in output else False
raised_exception = False
except Exception as e:
print("Error on ", augmented_question, e)
output = None
intermediate_steps = []
parsing_error = False
iteration_limit_exceeded = False
exception = e
raised_exception = True
end_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
token_counts_manager = agent.monitor.get_total_token_counts()
token_counts_web = list(agent.managed_agents.values())[0].monitor.get_total_token_counts()
total_token_counts = {
"input": token_counts_manager["input"] + token_counts_web["input"],
"output": token_counts_manager["output"] + token_counts_web["output"],
}
annotated_example = {
"agent_name": model.model_id,
"question": example["question"],
"augmented_question": augmented_question,
"prediction": output,
"intermediate_steps": intermediate_steps,
"parsing_error": parsing_error,
"iteration_limit_exceeded": iteration_limit_exceeded,
"agent_error": str(exception) if raised_exception else None,
"task": example["task"],
"task_id": example["task_id"],
"true_answer": example["true_answer"],
"start_time": start_time,
"end_time": end_time,
"token_counts": total_token_counts,
}
append_answer(annotated_example, answers_file)
def get_examples_to_answer(answers_file: str, eval_ds: datasets.Dataset) -> list[dict]:
print(f"Loading answers from {answers_file}...")
try:
done_questions = pd.read_json(answers_file, lines=True)["question"].tolist()
print(f"Found {len(done_questions)} previous results!")
except Exception as e:
print("Error when loading records: ", e)
print("No usable records! ▶️ Starting new.")
done_questions = []
return [line for line in eval_ds.to_list() if line["question"] not in done_questions and line["file_name"]]
def main():
args = parse_args()
print(f"Starting run with arguments: {args}")
eval_ds = load_gaia_dataset(args.use_raw_dataset, args.set_to_run)
print("Loaded evaluation dataset:")
print(pd.DataFrame(eval_ds)["task"].value_counts())
answers_file = f"output/{args.set_to_run}/{args.run_name}.jsonl"
tasks_to_run = get_examples_to_answer(answers_file, eval_ds)
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=args.concurrency) as exe:
futures = [
exe.submit(answer_single_question, example, args.model_id, answers_file, visualizer)
for example in tasks_to_run
]
for f in tqdm(as_completed(futures), total=len(tasks_to_run), desc="Processing tasks"):
f.result()
# for example in tasks_to_run:
# answer_single_question(example, args.model_id, answers_file, visualizer)
print("All tasks processed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
smolagents/examples/open_deep_research/run_gaia.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/examples/open_deep_research/run_gaia.py",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 4549
}
| 281
|
from anyio import to_thread
from starlette.applications import Starlette
from starlette.responses import HTMLResponse, JSONResponse
from starlette.routing import Route
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, MCPClient
# Create an MCP client to connect to the MCP server
mcp_server_parameters = {
"url": "https://evalstate-hf-mcp-server.hf.space/mcp",
"transport": "streamable-http",
}
mcp_client = MCPClient(server_parameters=mcp_server_parameters)
# Create a CodeAgent with a specific model and the tools from the MCP client
agent = CodeAgent(
model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"),
tools=mcp_client.get_tools(),
)
# Define the shutdown handler to disconnect the MCP client
async def shutdown():
mcp_client.disconnect()
async def homepage(request):
return HTMLResponse(
r"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Smolagents Demo</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, 'Segoe UI', Roboto, sans-serif;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.container {
background: white;
border-radius: 12px;
padding: 30px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
h1 {
color: #333;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.chat-container {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 8px;
height: 400px;
overflow-y: auto;
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
background-color: #fafafa;
}
.message {
margin-bottom: 15px;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 6px;
}
.user-message {
background-color: #007bff;
color: white;
margin-left: 50px;
}
.agent-message {
background-color: #e9ecef;
color: #333;
margin-right: 50px;
}
.input-container {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
}
input[type="text"] {
flex: 1;
padding: 12px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 6px;
font-size: 16px;
}
button {
padding: 12px 24px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 6px;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
button:disabled {
background-color: #ccc;
cursor: not-allowed;
}
.loading {
color: #666;
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>🤖 Smolagents Demo</h1>
<div class="chat-container" id="chat-container">
<div class="message agent-message">
Hello! I'm a code agent with access to MCP tools. Ask me anything!
</div>
</div>
<div class="input-container">
<input type="text" id="message-input" placeholder="Ask me anything..." autofocus>
<button onclick="sendMessage()" id="send-button">Send</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const chatContainer = document.getElementById('chat-container');
const messageInput = document.getElementById('message-input');
const sendButton = document.getElementById('send-button');
function addMessage(content, isUser = false) {
const messageDiv = document.createElement('div');
messageDiv.className = `message ${isUser ? 'user-message' : 'agent-message'}`;
messageDiv.textContent = content;
chatContainer.appendChild(messageDiv);
chatContainer.scrollTop = chatContainer.scrollHeight;
}
async function sendMessage() {
const message = messageInput.value.trim();
if (!message) return;
// Add user message
addMessage(message, true);
messageInput.value = '';
sendButton.disabled = true;
sendButton.textContent = 'Sending...';
// Add loading indicator
const loadingDiv = document.createElement('div');
loadingDiv.className = 'message agent-message loading';
loadingDiv.textContent = 'Thinking...';
chatContainer.appendChild(loadingDiv);
chatContainer.scrollTop = chatContainer.scrollHeight;
try {
const response = await fetch('/chat', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({ message }),
});
const data = await response.json();
// Remove loading indicator
chatContainer.removeChild(loadingDiv);
// Add agent response
addMessage(data.reply);
} catch (error) {
// Remove loading indicator
chatContainer.removeChild(loadingDiv);
addMessage(`Error: ${error.message}`);
} finally {
sendButton.disabled = false;
sendButton.textContent = 'Send';
messageInput.focus();
}
}
// Send message on Enter key
messageInput.addEventListener('keypress', function(e) {
if (e.key === 'Enter') {
sendMessage();
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
"""
)
async def chat(request):
data = await request.json()
message = data.get("message", "").strip()
# Run in a thread to avoid blocking the event loop
result = await to_thread.run_sync(agent.run, message)
# Format the result if it's a complex data structure
reply = str(result)
return JSONResponse({"reply": reply})
app = Starlette(
debug=True,
routes=[
Route("/", homepage),
Route("/chat", chat, methods=["POST"]),
],
on_shutdown=[shutdown], # Register the shutdown handler: disconnect the MCP client
)
|
smolagents/examples/server/main.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/examples/server/main.py",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 3123
}
| 282
|
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import json
import logging
import os
import re
import uuid
import warnings
from collections.abc import Generator
from copy import deepcopy
from dataclasses import asdict, dataclass
from enum import Enum
from threading import Thread
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any
from .monitoring import TokenUsage
from .tools import Tool
from .utils import RateLimiter, _is_package_available, encode_image_base64, make_image_url, parse_json_blob
if TYPE_CHECKING:
from transformers import StoppingCriteriaList
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
STRUCTURED_GENERATION_PROVIDERS = ["cerebras", "fireworks-ai"]
CODEAGENT_RESPONSE_FORMAT = {
"type": "json_schema",
"json_schema": {
"schema": {
"additionalProperties": False,
"properties": {
"thought": {
"description": "A free form text description of the thought process.",
"title": "Thought",
"type": "string",
},
"code": {
"description": "Valid Python code snippet implementing the thought.",
"title": "Code",
"type": "string",
},
},
"required": ["thought", "code"],
"title": "ThoughtAndCodeAnswer",
"type": "object",
},
"name": "ThoughtAndCodeAnswer",
"strict": True,
},
}
def get_dict_from_nested_dataclasses(obj, ignore_key=None):
def convert(obj):
if hasattr(obj, "__dataclass_fields__"):
return {k: convert(v) for k, v in asdict(obj).items() if k != ignore_key}
return obj
return convert(obj)
@dataclass
class ChatMessageToolCallFunction:
arguments: Any
name: str
description: str | None = None
@dataclass
class ChatMessageToolCall:
function: ChatMessageToolCallFunction
id: str
type: str
def __str__(self) -> str:
return f"Call: {self.id}: Calling {str(self.function.name)} with arguments: {str(self.function.arguments)}"
class MessageRole(str, Enum):
USER = "user"
ASSISTANT = "assistant"
SYSTEM = "system"
TOOL_CALL = "tool-call"
TOOL_RESPONSE = "tool-response"
@classmethod
def roles(cls):
return [r.value for r in cls]
@dataclass
class ChatMessage:
role: MessageRole
content: str | list[dict[str, Any]] | None = None
tool_calls: list[ChatMessageToolCall] | None = None
raw: Any | None = None # Stores the raw output from the API
token_usage: TokenUsage | None = None
def model_dump_json(self):
return json.dumps(get_dict_from_nested_dataclasses(self, ignore_key="raw"))
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, data: dict, raw: Any | None = None, token_usage: TokenUsage | None = None) -> "ChatMessage":
if data.get("tool_calls"):
tool_calls = [
ChatMessageToolCall(
function=ChatMessageToolCallFunction(**tc["function"]), id=tc["id"], type=tc["type"]
)
for tc in data["tool_calls"]
]
data["tool_calls"] = tool_calls
return cls(
role=data["role"],
content=data.get("content"),
tool_calls=data.get("tool_calls"),
raw=raw,
token_usage=token_usage,
)
def dict(self):
return get_dict_from_nested_dataclasses(self)
def render_as_markdown(self) -> str:
rendered = str(self.content) or ""
if self.tool_calls:
rendered += "\n".join(
[
json.dumps({"tool": tool.function.name, "arguments": tool.function.arguments})
for tool in self.tool_calls
]
)
return rendered
def parse_json_if_needed(arguments: str | dict) -> str | dict:
if isinstance(arguments, dict):
return arguments
else:
try:
return json.loads(arguments)
except Exception:
return arguments
@dataclass
class ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta:
"""Represents a streaming delta for tool calls during generation."""
index: int | None = None
id: str | None = None
type: str | None = None
function: ChatMessageToolCallFunction | None = None
@dataclass
class ChatMessageStreamDelta:
content: str | None = None
tool_calls: list[ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta] | None = None
token_usage: TokenUsage | None = None
def agglomerate_stream_deltas(
stream_deltas: list[ChatMessageStreamDelta], role: MessageRole = MessageRole.ASSISTANT
) -> ChatMessage:
"""
Agglomerate a list of stream deltas into a single stream delta.
"""
accumulated_tool_calls: dict[int, ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta] = {}
accumulated_content = ""
total_input_tokens = 0
total_output_tokens = 0
for stream_delta in stream_deltas:
if stream_delta.token_usage:
total_input_tokens += stream_delta.token_usage.input_tokens
total_output_tokens += stream_delta.token_usage.output_tokens
if stream_delta.content:
accumulated_content += stream_delta.content
if stream_delta.tool_calls:
for tool_call_delta in stream_delta.tool_calls: # ?ormally there should be only one call at a time
# Extend accumulated_tool_calls list to accommodate the new tool call if needed
if tool_call_delta.index is not None:
if tool_call_delta.index not in accumulated_tool_calls:
accumulated_tool_calls[tool_call_delta.index] = ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta(
id=tool_call_delta.id,
type=tool_call_delta.type,
function=ChatMessageToolCallFunction(name="", arguments=""),
)
# Update the tool call at the specific index
tool_call = accumulated_tool_calls[tool_call_delta.index]
if tool_call_delta.id:
tool_call.id = tool_call_delta.id
if tool_call_delta.type:
tool_call.type = tool_call_delta.type
if tool_call_delta.function:
if tool_call_delta.function.name and len(tool_call_delta.function.name) > 0:
tool_call.function.name = tool_call_delta.function.name
if tool_call_delta.function.arguments:
tool_call.function.arguments += tool_call_delta.function.arguments
else:
raise ValueError(f"Tool call index is not provided in tool delta: {tool_call_delta}")
return ChatMessage(
role=role,
content=accumulated_content,
tool_calls=[
ChatMessageToolCall(
function=ChatMessageToolCallFunction(
name=tool_call_stream_delta.function.name,
arguments=tool_call_stream_delta.function.arguments,
),
id=tool_call_stream_delta.id or "",
type="function",
)
for tool_call_stream_delta in accumulated_tool_calls.values()
if tool_call_stream_delta.function
],
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=total_input_tokens,
output_tokens=total_output_tokens,
),
)
tool_role_conversions = {
MessageRole.TOOL_CALL: MessageRole.ASSISTANT,
MessageRole.TOOL_RESPONSE: MessageRole.USER,
}
def get_tool_json_schema(tool: Tool) -> dict:
properties = deepcopy(tool.inputs)
required = []
for key, value in properties.items():
if value["type"] == "any":
value["type"] = "string"
if not ("nullable" in value and value["nullable"]):
required.append(key)
return {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.name,
"description": tool.description,
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": properties,
"required": required,
},
},
}
def remove_stop_sequences(content: str, stop_sequences: list[str]) -> str:
for stop_seq in stop_sequences:
if content[-len(stop_seq) :] == stop_seq:
content = content[: -len(stop_seq)]
return content
def get_clean_message_list(
message_list: list[ChatMessage | dict],
role_conversions: dict[MessageRole, MessageRole] | dict[str, str] = {},
convert_images_to_image_urls: bool = False,
flatten_messages_as_text: bool = False,
) -> list[dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Creates a list of messages to give as input to the LLM. These messages are dictionaries and chat template compatible with transformers LLM chat template.
Subsequent messages with the same role will be concatenated to a single message.
Args:
message_list (`list[ChatMessage | dict]`): List of chat messages. Mixed types are allowed.
role_conversions (`dict[MessageRole, MessageRole]`, *optional* ): Mapping to convert roles.
convert_images_to_image_urls (`bool`, default `False`): Whether to convert images to image URLs.
flatten_messages_as_text (`bool`, default `False`): Whether to flatten messages as text.
"""
output_message_list: list[dict[str, Any]] = []
message_list = deepcopy(message_list) # Avoid modifying the original list
for message in message_list:
if isinstance(message, dict):
message = ChatMessage.from_dict(message)
role = message.role
if role not in MessageRole.roles():
raise ValueError(f"Incorrect role {role}, only {MessageRole.roles()} are supported for now.")
if role in role_conversions:
message.role = role_conversions[role] # type: ignore
# encode images if needed
if isinstance(message.content, list):
for element in message.content:
assert isinstance(element, dict), "Error: this element should be a dict:" + str(element)
if element["type"] == "image":
assert not flatten_messages_as_text, f"Cannot use images with {flatten_messages_as_text=}"
if convert_images_to_image_urls:
element.update(
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {"url": make_image_url(encode_image_base64(element.pop("image")))},
}
)
else:
element["image"] = encode_image_base64(element["image"])
if len(output_message_list) > 0 and message.role == output_message_list[-1]["role"]:
assert isinstance(message.content, list), "Error: wrong content:" + str(message.content)
if flatten_messages_as_text:
output_message_list[-1]["content"] += "\n" + message.content[0]["text"]
else:
for el in message.content:
if el["type"] == "text" and output_message_list[-1]["content"][-1]["type"] == "text":
# Merge consecutive text messages rather than creating new ones
output_message_list[-1]["content"][-1]["text"] += "\n" + el["text"]
else:
output_message_list[-1]["content"].append(el)
else:
if flatten_messages_as_text:
content = message.content[0]["text"]
else:
content = message.content
output_message_list.append(
{
"role": message.role,
"content": content,
}
)
return output_message_list
def get_tool_call_from_text(text: str, tool_name_key: str, tool_arguments_key: str) -> ChatMessageToolCall:
tool_call_dictionary, _ = parse_json_blob(text)
try:
tool_name = tool_call_dictionary[tool_name_key]
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(
f"Tool call needs to have a key '{tool_name_key}'. Got keys: {list(tool_call_dictionary.keys())} instead"
) from e
tool_arguments = tool_call_dictionary.get(tool_arguments_key, None)
if isinstance(tool_arguments, str):
tool_arguments = parse_json_if_needed(tool_arguments)
return ChatMessageToolCall(
id=str(uuid.uuid4()),
type="function",
function=ChatMessageToolCallFunction(name=tool_name, arguments=tool_arguments),
)
def supports_stop_parameter(model_id: str) -> bool:
"""
Check if the model supports the `stop` parameter.
Not supported with reasoning models openai/o3, openai/o4-mini, and the openai/gpt-5 series (and their versioned variants).
Args:
model_id (`str`): Model identifier (e.g. "openai/o3", "o4-mini-2025-04-16")
Returns:
bool: True if the model supports the stop parameter, False otherwise
"""
model_name = model_id.split("/")[-1]
# o3, o4-mini, and the gpt-5 series (including versioned variants, o3-2025-04-16) don't support stop parameter
pattern = r"^(o3[-\d]*|o4-mini[-\d]*|gpt-5(-mini|-nano)?[-\d]*)$"
return not re.match(pattern, model_name)
class Model:
"""Base class for all language model implementations.
This abstract class defines the core interface that all model implementations must follow
to work with agents. It provides common functionality for message handling, tool integration,
and model configuration while allowing subclasses to implement their specific generation logic.
Parameters:
flatten_messages_as_text (`bool`, default `False`):
Whether to flatten complex message content into plain text format.
tool_name_key (`str`, default `"name"`):
The key used to extract tool names from model responses.
tool_arguments_key (`str`, default `"arguments"`):
The key used to extract tool arguments from model responses.
model_id (`str`, *optional*):
Identifier for the specific model being used.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying model completion call.
Note:
This is an abstract base class. Subclasses must implement the `generate()` method
to provide actual model inference capabilities.
Example:
```python
class CustomModel(Model):
def generate(self, messages, **kwargs):
# Implementation specific to your model
pass
```
"""
def __init__(
self,
flatten_messages_as_text: bool = False,
tool_name_key: str = "name",
tool_arguments_key: str = "arguments",
model_id: str | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
self.flatten_messages_as_text = flatten_messages_as_text
self.tool_name_key = tool_name_key
self.tool_arguments_key = tool_arguments_key
self.kwargs = kwargs
self.model_id: str | None = model_id
def _prepare_completion_kwargs(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
convert_images_to_image_urls: bool = False,
tool_choice: str | dict | None = "required", # Configurable tool_choice parameter
**kwargs,
) -> dict[str, Any]:
"""
Prepare parameters required for model invocation, handling parameter priorities.
Parameter priority from high to low:
1. Explicitly passed kwargs
2. Specific parameters (stop_sequences, response_format, etc.)
3. Default values in self.kwargs
"""
# Clean and standardize the message list
flatten_messages_as_text = kwargs.pop("flatten_messages_as_text", self.flatten_messages_as_text)
messages_as_dicts = get_clean_message_list(
messages,
role_conversions=custom_role_conversions or tool_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=convert_images_to_image_urls,
flatten_messages_as_text=flatten_messages_as_text,
)
# Use self.kwargs as the base configuration
completion_kwargs = {
**self.kwargs,
"messages": messages_as_dicts,
}
# Handle specific parameters
if stop_sequences is not None:
# Some models do not support stop parameter
if supports_stop_parameter(self.model_id or ""):
completion_kwargs["stop"] = stop_sequences
if response_format is not None:
completion_kwargs["response_format"] = response_format
# Handle tools parameter
if tools_to_call_from:
tools_config = {
"tools": [get_tool_json_schema(tool) for tool in tools_to_call_from],
}
if tool_choice is not None:
tools_config["tool_choice"] = tool_choice
completion_kwargs.update(tools_config)
# Finally, use the passed-in kwargs to override all settings
completion_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return completion_kwargs
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
"""Process the input messages and return the model's response.
Parameters:
messages (`list[dict[str, str | list[dict]]] | list[ChatMessage]`):
A list of message dictionaries to be processed. Each dictionary should have the structure `{"role": "user/system", "content": "message content"}`.
stop_sequences (`List[str]`, *optional*):
A list of strings that will stop the generation if encountered in the model's output.
response_format (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
The response format to use in the model's response.
tools_to_call_from (`List[Tool]`, *optional*):
A list of tools that the model can use to generate responses.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to be passed to the underlying model.
Returns:
`ChatMessage`: A chat message object containing the model's response.
"""
raise NotImplementedError("This method must be implemented in child classes")
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
return self.generate(*args, **kwargs)
def parse_tool_calls(self, message: ChatMessage) -> ChatMessage:
"""Sometimes APIs do not return the tool call as a specific object, so we need to parse it."""
message.role = MessageRole.ASSISTANT # Overwrite role if needed
if not message.tool_calls:
assert message.content is not None, "Message contains no content and no tool calls"
message.tool_calls = [
get_tool_call_from_text(message.content, self.tool_name_key, self.tool_arguments_key)
]
assert len(message.tool_calls) > 0, "No tool call was found in the model output"
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
tool_call.function.arguments = parse_json_if_needed(tool_call.function.arguments)
return message
def to_dict(self) -> dict:
"""
Converts the model into a JSON-compatible dictionary.
"""
model_dictionary = {
**self.kwargs,
"model_id": self.model_id,
}
for attribute in [
"custom_role_conversion",
"temperature",
"max_tokens",
"provider",
"timeout",
"api_base",
"torch_dtype",
"device_map",
"organization",
"project",
"azure_endpoint",
]:
if hasattr(self, attribute):
model_dictionary[attribute] = getattr(self, attribute)
dangerous_attributes = ["token", "api_key"]
for attribute_name in dangerous_attributes:
if hasattr(self, attribute_name):
print(
f"For security reasons, we do not export the `{attribute_name}` attribute of your model. Please export it manually."
)
return model_dictionary
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, model_dictionary: dict[str, Any]) -> "Model":
return cls(**{k: v for k, v in model_dictionary.items()})
class VLLMModel(Model):
"""Model to use [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/) for fast LLM inference and serving.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The Hugging Face model ID to be used for inference.
This can be a path or model identifier from the Hugging Face model hub.
model_kwargs (`dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the vLLM LLM instantiation, such as `revision`, `max_model_len`, etc.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying vLLM model generate call.
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id,
model_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
if not _is_package_available("vllm"):
raise ModuleNotFoundError("Please install 'vllm' extra to use VLLMModel: `pip install 'smolagents[vllm]'`")
from vllm import LLM # type: ignore
from vllm.transformers_utils.tokenizer import get_tokenizer # type: ignore
self.model_kwargs = model_kwargs or {}
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.model_id = model_id
self.model = LLM(model=model_id, **self.model_kwargs)
assert self.model is not None
self.tokenizer = get_tokenizer(model_id)
self._is_vlm = False # VLLMModel does not support vision models yet.
def cleanup(self):
import gc
import torch
from vllm.distributed.parallel_state import ( # type: ignore
destroy_distributed_environment,
destroy_model_parallel,
)
destroy_model_parallel()
if self.model is not None:
# taken from https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/issues/1908#issuecomment-2076870351
del self.model.llm_engine.model_executor.driver_worker
gc.collect()
destroy_distributed_environment()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
from vllm import SamplingParams # type: ignore
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
flatten_messages_as_text=(not self._is_vlm),
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
**kwargs,
)
# Override the OpenAI schema for VLLM compatibility
guided_options_request = {"guided_json": response_format["json_schema"]["schema"]} if response_format else None
messages = completion_kwargs.pop("messages")
prepared_stop_sequences = completion_kwargs.pop("stop", [])
tools = completion_kwargs.pop("tools", None)
completion_kwargs.pop("tool_choice", None)
prompt = self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tools=tools,
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=False,
)
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
n=kwargs.get("n", 1),
temperature=kwargs.get("temperature", 0.0),
max_tokens=kwargs.get("max_tokens", 2048),
stop=prepared_stop_sequences,
)
out = self.model.generate(
prompt,
sampling_params=sampling_params,
guided_options_request=guided_options_request,
**completion_kwargs,
)
output_text = out[0].outputs[0].text
return ChatMessage(
role=MessageRole.ASSISTANT,
content=output_text,
raw={"out": output_text, "completion_kwargs": completion_kwargs},
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=len(out[0].prompt_token_ids),
output_tokens=len(out[0].outputs[0].token_ids),
),
)
class MLXModel(Model):
"""A class to interact with models loaded using MLX on Apple silicon.
> [!TIP]
> You must have `mlx-lm` installed on your machine. Please run `pip install smolagents[mlx-lm]` if it's not the case.
Parameters:
model_id (str):
The Hugging Face model ID to be used for inference. This can be a path or model identifier from the Hugging Face model hub.
tool_name_key (str):
The key, which can usually be found in the model's chat template, for retrieving a tool name.
tool_arguments_key (str):
The key, which can usually be found in the model's chat template, for retrieving tool arguments.
trust_remote_code (bool, default `False`):
Some models on the Hub require running remote code: for this model, you would have to set this flag to True.
load_kwargs (dict[str, Any], *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the `mlx.lm.load` method when loading the model and tokenizer.
apply_chat_template_kwargs (dict, *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the `apply_chat_template` method of the tokenizer.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying MLX model stream_generate call, for instance `max_tokens`.
Example:
```python
>>> engine = MLXModel(
... model_id="mlx-community/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct-4bit",
... max_tokens=10000,
... )
>>> messages = [
... {
... "role": "user",
... "content": "Explain quantum mechanics in simple terms."
... }
... ]
>>> response = engine(messages, stop_sequences=["END"])
>>> print(response)
"Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies..."
```
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str,
trust_remote_code: bool = False,
load_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
apply_chat_template_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
if not _is_package_available("mlx_lm"):
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'mlx-lm' extra to use 'MLXModel': `pip install 'smolagents[mlx-lm]'`"
)
import mlx_lm
self.load_kwargs = load_kwargs or {}
self.load_kwargs.setdefault("tokenizer_config", {}).setdefault("trust_remote_code", trust_remote_code)
self.apply_chat_template_kwargs = apply_chat_template_kwargs or {}
self.apply_chat_template_kwargs.setdefault("add_generation_prompt", True)
# mlx-lm doesn't support vision models: flatten_messages_as_text=True
super().__init__(model_id=model_id, flatten_messages_as_text=True, **kwargs)
self.model, self.tokenizer = mlx_lm.load(self.model_id, **self.load_kwargs)
self.stream_generate = mlx_lm.stream_generate
self.is_vlm = False # mlx-lm doesn't support vision models
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
if response_format is not None:
raise ValueError("MLX does not support structured outputs.")
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
**kwargs,
)
messages = completion_kwargs.pop("messages")
stops = completion_kwargs.pop("stop", [])
tools = completion_kwargs.pop("tools", None)
completion_kwargs.pop("tool_choice", None)
prompt_ids = self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tools=tools, **self.apply_chat_template_kwargs)
output_tokens = 0
text = ""
for response in self.stream_generate(self.model, self.tokenizer, prompt=prompt_ids, **completion_kwargs):
output_tokens += 1
text += response.text
if any((stop_index := text.rfind(stop)) != -1 for stop in stops):
text = text[:stop_index]
break
return ChatMessage(
role=MessageRole.ASSISTANT,
content=text,
raw={"out": text, "completion_kwargs": completion_kwargs},
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=len(prompt_ids),
output_tokens=output_tokens,
),
)
class TransformersModel(Model):
"""A class that uses Hugging Face's Transformers library for language model interaction.
This model allows you to load and use Hugging Face's models locally using the Transformers library. It supports features like stop sequences and grammar customization.
> [!TIP]
> You must have `transformers` and `torch` installed on your machine. Please run `pip install smolagents[transformers]` if it's not the case.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The Hugging Face model ID to be used for inference. This can be a path or model identifier from the Hugging Face model hub.
For example, `"Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"`.
device_map (`str`, *optional*):
The device_map to initialize your model with.
torch_dtype (`str`, *optional*):
The torch_dtype to initialize your model with.
trust_remote_code (bool, default `False`):
Some models on the Hub require running remote code: for this model, you would have to set this flag to True.
model_kwargs (`dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to pass to `AutoModel.from_pretrained` (like revision, model_args, config, etc.).
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying Transformers model generate call, such as `max_new_tokens` or `device`.
Raises:
ValueError:
If the model name is not provided.
Example:
```python
>>> engine = TransformersModel(
... model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct",
... device="cuda",
... max_new_tokens=5000,
... )
>>> messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "Explain quantum mechanics in simple terms."}]
>>> response = engine(messages, stop_sequences=["END"])
>>> print(response)
"Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies..."
```
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str | None = None,
device_map: str | None = None,
torch_dtype: str | None = None,
trust_remote_code: bool = False,
model_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
try:
import torch
from transformers import (
AutoModelForCausalLM,
AutoModelForImageTextToText,
AutoProcessor,
AutoTokenizer,
TextIteratorStreamer,
)
except ModuleNotFoundError:
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'transformers' extra to use 'TransformersModel': `pip install 'smolagents[transformers]'`"
)
if not model_id:
warnings.warn(
"The 'model_id' parameter will be required in version 2.0.0. "
"Please update your code to pass this parameter to avoid future errors. "
"For now, it defaults to 'HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-1.7B-Instruct'.",
FutureWarning,
)
model_id = "HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-1.7B-Instruct"
default_max_tokens = 4096
max_new_tokens = kwargs.get("max_new_tokens") or kwargs.get("max_tokens")
if not max_new_tokens:
kwargs["max_new_tokens"] = default_max_tokens
warnings.warn(
f"`max_new_tokens` not provided, using this default value for `max_new_tokens`: {default_max_tokens}"
)
if device_map is None:
device_map = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
logger.info(f"Using device: {device_map}")
self._is_vlm = False
self.model_kwargs = model_kwargs or {}
try:
self.model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
model_id,
device_map=device_map,
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
trust_remote_code=trust_remote_code,
**self.model_kwargs,
)
self.processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id, trust_remote_code=trust_remote_code)
self._is_vlm = True
self.streamer = TextIteratorStreamer(self.processor.tokenizer, skip_prompt=True, skip_special_tokens=True) # type: ignore
except ValueError as e:
if "Unrecognized configuration class" in str(e):
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_id,
device_map=device_map,
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
trust_remote_code=trust_remote_code,
**self.model_kwargs,
)
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, trust_remote_code=trust_remote_code)
self.streamer = TextIteratorStreamer(self.tokenizer, skip_prompt=True, skip_special_tokens=True) # type: ignore
else:
raise e
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"Failed to load tokenizer and model for {model_id=}: {e}") from e
super().__init__(flatten_messages_as_text=not self._is_vlm, model_id=model_id, **kwargs)
def make_stopping_criteria(self, stop_sequences: list[str], tokenizer) -> "StoppingCriteriaList":
from transformers import StoppingCriteria, StoppingCriteriaList
class StopOnStrings(StoppingCriteria):
def __init__(self, stop_strings: list[str], tokenizer):
self.stop_strings = stop_strings
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.stream = ""
def reset(self):
self.stream = ""
def __call__(self, input_ids, scores, **kwargs):
generated = self.tokenizer.decode(input_ids[0][-1], skip_special_tokens=True)
self.stream += generated
if any([self.stream.endswith(stop_string) for stop_string in self.stop_strings]):
return True
return False
return StoppingCriteriaList([StopOnStrings(stop_sequences, tokenizer)])
def _prepare_completion_args(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> dict[str, Any]:
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
**kwargs,
)
messages = completion_kwargs.pop("messages")
stop_sequences = completion_kwargs.pop("stop", None)
tools = completion_kwargs.pop("tools", None)
max_new_tokens = (
kwargs.get("max_new_tokens")
or kwargs.get("max_tokens")
or self.kwargs.get("max_new_tokens")
or self.kwargs.get("max_tokens")
or 1024
)
prompt_tensor = (self.processor if hasattr(self, "processor") else self.tokenizer).apply_chat_template(
messages,
tools=tools,
return_tensors="pt",
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_dict=True,
)
prompt_tensor = prompt_tensor.to(self.model.device) # type: ignore
if hasattr(prompt_tensor, "input_ids"):
prompt_tensor = prompt_tensor["input_ids"]
model_tokenizer = self.processor.tokenizer if hasattr(self, "processor") else self.tokenizer
stopping_criteria = (
self.make_stopping_criteria(stop_sequences, tokenizer=model_tokenizer) if stop_sequences else None
)
completion_kwargs["max_new_tokens"] = max_new_tokens
return dict(
inputs=prompt_tensor,
use_cache=True,
stopping_criteria=stopping_criteria,
**completion_kwargs,
)
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
if response_format is not None:
raise ValueError("Transformers does not support structured outputs, use VLLMModel for this.")
generation_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_args(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
**kwargs,
)
count_prompt_tokens = generation_kwargs["inputs"].shape[1] # type: ignore
out = self.model.generate(
**generation_kwargs,
)
generated_tokens = out[0, count_prompt_tokens:]
if hasattr(self, "processor"):
output_text = self.processor.decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
else:
output_text = self.tokenizer.decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
if stop_sequences is not None:
output_text = remove_stop_sequences(output_text, stop_sequences)
return ChatMessage(
role=MessageRole.ASSISTANT,
content=output_text,
raw={
"out": output_text,
"completion_kwargs": {key: value for key, value in generation_kwargs.items() if key != "inputs"},
},
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=count_prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=len(generated_tokens),
),
)
def generate_stream(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> Generator[ChatMessageStreamDelta]:
if response_format is not None:
raise ValueError("Transformers does not support structured outputs, use VLLMModel for this.")
generation_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_args(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
response_format=response_format,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
**kwargs,
)
# Get prompt token count once
count_prompt_tokens = generation_kwargs["inputs"].shape[1] # type: ignore
# Start generation in a separate thread
thread = Thread(target=self.model.generate, kwargs={"streamer": self.streamer, **generation_kwargs})
thread.start()
# Process streaming output
is_first_token = True
count_generated_tokens = 0
for new_text in self.streamer:
count_generated_tokens += 1
# Only include input tokens in the first yielded token
input_tokens = count_prompt_tokens if is_first_token else 0
is_first_token = False
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content=new_text,
tool_calls=None,
token_usage=TokenUsage(input_tokens=input_tokens, output_tokens=1),
)
count_prompt_tokens = 0
thread.join()
# Update final output token count
self._last_output_token_count = count_generated_tokens
class ApiModel(Model):
"""
Base class for API-based language models.
This class serves as a foundation for implementing models that interact with
external APIs. It handles the common functionality for managing model IDs,
custom role mappings, and API client connections.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The identifier for the model to be used with the API.
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str`], **optional**):
Mapping to convert between internal role names and API-specific role names. Defaults to None.
client (`Any`, **optional**):
Pre-configured API client instance. If not provided, a default client will be created. Defaults to None.
requests_per_minute (`float`, **optional**):
Rate limit in requests per minute.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying model completion call.
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
client: Any | None = None,
requests_per_minute: float | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(model_id=model_id, **kwargs)
self.custom_role_conversions = custom_role_conversions or {}
self.client = client or self.create_client()
self.rate_limiter = RateLimiter(requests_per_minute)
def create_client(self):
"""Create the API client for the specific service."""
raise NotImplementedError("Subclasses must implement this method to create a client")
def _apply_rate_limit(self):
"""Apply rate limiting before making API calls."""
self.rate_limiter.throttle()
class LiteLLMModel(ApiModel):
"""Model to use [LiteLLM Python SDK](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/#litellm-python-sdk) to access hundreds of LLMs.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The model identifier to use on the server (e.g. "gpt-3.5-turbo").
api_base (`str`, *optional*):
The base URL of the provider API to call the model.
api_key (`str`, *optional*):
The API key to use for authentication.
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
Custom role conversion mapping to convert message roles in others.
Useful for specific models that do not support specific message roles like "system".
flatten_messages_as_text (`bool`, *optional*): Whether to flatten messages as text.
Defaults to `True` for models that start with "ollama", "groq", "cerebras".
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying LiteLLM completion call.
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str | None = None,
api_base: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
flatten_messages_as_text: bool | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
if not model_id:
warnings.warn(
"The 'model_id' parameter will be required in version 2.0.0. "
"Please update your code to pass this parameter to avoid future errors. "
"For now, it defaults to 'anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620'.",
FutureWarning,
)
model_id = "anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620"
self.api_base = api_base
self.api_key = api_key
flatten_messages_as_text = (
flatten_messages_as_text
if flatten_messages_as_text is not None
else model_id.startswith(("ollama", "groq", "cerebras"))
)
super().__init__(
model_id=model_id,
custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions,
flatten_messages_as_text=flatten_messages_as_text,
**kwargs,
)
def create_client(self):
"""Create the LiteLLM client."""
try:
import litellm
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'litellm' extra to use LiteLLMModel: `pip install 'smolagents[litellm]'`"
) from e
return litellm
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
response_format=response_format,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
model=self.model_id,
api_base=self.api_base,
api_key=self.api_key,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
response = self.client.completion(**completion_kwargs)
if not response.choices:
raise RuntimeError(
f"Unexpected API response: model '{self.model_id}' returned no choices. "
" This may indicate a possible API or upstream issue. "
f"Response details: {response.model_dump()}"
)
return ChatMessage.from_dict(
response.choices[0].message.model_dump(include={"role", "content", "tool_calls"}),
raw=response,
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=response.usage.prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=response.usage.completion_tokens,
),
)
def generate_stream(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> Generator[ChatMessageStreamDelta]:
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
response_format=response_format,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
model=self.model_id,
api_base=self.api_base,
api_key=self.api_key,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
for event in self.client.completion(**completion_kwargs, stream=True, stream_options={"include_usage": True}):
if getattr(event, "usage", None):
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content="",
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=event.usage.prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=event.usage.completion_tokens,
),
)
if event.choices:
choice = event.choices[0]
if choice.delta:
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content=choice.delta.content,
tool_calls=[
ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta(
index=delta.index,
id=delta.id,
type=delta.type,
function=delta.function,
)
for delta in choice.delta.tool_calls
]
if choice.delta.tool_calls
else None,
)
else:
if not getattr(choice, "finish_reason", None):
raise ValueError(f"No content or tool calls in event: {event}")
class LiteLLMRouterModel(LiteLLMModel):
"""Router‑based client for interacting with the [LiteLLM Python SDK Router](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/routing).
This class provides a high-level interface for distributing requests among multiple language models using
the LiteLLM SDK's routing capabilities. It is responsible for initializing and configuring the router client,
applying custom role conversions, and managing message formatting to ensure seamless integration with various LLMs.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
Identifier for the model group to use from the model list (e.g., "model-group-1").
model_list (`list[dict[str, Any]]`):
Model configurations to be used for routing.
Each configuration should include the model group name and any necessary parameters.
For more details, refer to the [LiteLLM Routing](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/routing#quick-start) documentation.
client_kwargs (`dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
Additional configuration parameters for the Router client. For more details, see the
[LiteLLM Routing Configurations](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/routing).
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
Custom role conversion mapping to convert message roles in others.
Useful for specific models that do not support specific message roles like "system".
flatten_messages_as_text (`bool`, *optional*): Whether to flatten messages as text.
Defaults to `True` for models that start with "ollama", "groq", "cerebras".
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying LiteLLM Router completion call.
Example:
```python
>>> import os
>>> from smolagents import CodeAgent, WebSearchTool, LiteLLMRouterModel
>>> os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ""
>>> os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = ""
>>> os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = ""
>>> os.environ["AWS_REGION"] = ""
>>> llm_loadbalancer_model_list = [
... {
... "model_name": "model-group-1",
... "litellm_params": {
... "model": "gpt-4o-mini",
... "api_key": os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
... },
... },
... {
... "model_name": "model-group-1",
... "litellm_params": {
... "model": "bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0",
... "aws_access_key_id": os.getenv("AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),
... "aws_secret_access_key": os.getenv("AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"),
... "aws_region_name": os.getenv("AWS_REGION"),
... },
... },
>>> ]
>>> model = LiteLLMRouterModel(
... model_id="model-group-1",
... model_list=llm_loadbalancer_model_list,
... client_kwargs={
... "routing_strategy":"simple-shuffle"
... }
>>> )
>>> agent = CodeAgent(tools=[WebSearchTool()], model=model)
>>> agent.run("How many seconds would it take for a leopard at full speed to run through Pont des Arts?")
```
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str,
model_list: list[dict[str, Any]],
client_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
flatten_messages_as_text: bool | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
self.client_kwargs = {
"model_list": model_list,
**(client_kwargs or {}),
}
super().__init__(
model_id=model_id,
custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions,
flatten_messages_as_text=flatten_messages_as_text,
**kwargs,
)
def create_client(self):
try:
from litellm.router import Router
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'litellm' extra to use LiteLLMRouterModel: `pip install 'smolagents[litellm]'`"
) from e
return Router(**self.client_kwargs)
class InferenceClientModel(ApiModel):
"""A class to interact with Hugging Face's Inference Providers for language model interaction.
This model allows you to communicate with Hugging Face's models using Inference Providers. It can be used in both serverless mode, with a dedicated endpoint, or even with a local URL, supporting features like stop sequences and grammar customization.
Providers include Cerebras, Cohere, Fal, Fireworks, HF-Inference, Hyperbolic, Nebius, Novita, Replicate, SambaNova, Together, and more.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`, *optional*, default `"Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"`):
The Hugging Face model ID to be used for inference.
This can be a model identifier from the Hugging Face model hub or a URL to a deployed Inference Endpoint.
Currently, it defaults to `"Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"`, but this may change in the future.
provider (`str`, *optional*):
Name of the provider to use for inference. A list of supported providers can be found in the [Inference Providers documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/inference-providers/index#partners).
Defaults to "auto" i.e. the first of the providers available for the model, sorted by the user's order [here](https://hf.co/settings/inference-providers).
If `base_url` is passed, then `provider` is not used.
token (`str`, *optional*):
Token used by the Hugging Face API for authentication. This token need to be authorized 'Make calls to the serverless Inference Providers'.
If the model is gated (like Llama-3 models), the token also needs 'Read access to contents of all public gated repos you can access'.
If not provided, the class will try to use environment variable 'HF_TOKEN', else use the token stored in the Hugging Face CLI configuration.
timeout (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 120):
Timeout for the API request, in seconds.
client_kwargs (`dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the Hugging Face InferenceClient.
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
Custom role conversion mapping to convert message roles in others.
Useful for specific models that do not support specific message roles like "system".
api_key (`str`, *optional*):
Token to use for authentication. This is a duplicated argument from `token` to make [`InferenceClientModel`]
follow the same pattern as `openai.OpenAI` client. Cannot be used if `token` is set. Defaults to None.
bill_to (`str`, *optional*):
The billing account to use for the requests. By default the requests are billed on the user's account. Requests can only be billed to
an organization the user is a member of, and which has subscribed to Enterprise Hub.
base_url (`str`, `optional`):
Base URL to run inference. This is a duplicated argument from `model` to make [`InferenceClientModel`]
follow the same pattern as `openai.OpenAI` client. Cannot be used if `model` is set. Defaults to None.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying Hugging Face InferenceClient completion call.
Raises:
ValueError:
If the model name is not provided.
Example:
```python
>>> engine = InferenceClientModel(
... model_id="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct",
... provider="nebius",
... token="your_hf_token_here",
... max_tokens=5000,
... )
>>> messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "Explain quantum mechanics in simple terms."}]
>>> response = engine(messages, stop_sequences=["END"])
>>> print(response)
"Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies..."
```
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct",
provider: str | None = None,
token: str | None = None,
timeout: int = 120,
client_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
bill_to: str | None = None,
base_url: str | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
if token is not None and api_key is not None:
raise ValueError(
"Received both `token` and `api_key` arguments. Please provide only one of them."
" `api_key` is an alias for `token` to make the API compatible with OpenAI's client."
" It has the exact same behavior as `token`."
)
token = token if token is not None else api_key
if token is None:
token = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
self.client_kwargs = {
**(client_kwargs or {}),
"model": model_id,
"provider": provider,
"token": token,
"timeout": timeout,
"bill_to": bill_to,
"base_url": base_url,
}
super().__init__(model_id=model_id, custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions, **kwargs)
def create_client(self):
"""Create the Hugging Face client."""
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
return InferenceClient(**self.client_kwargs)
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
if response_format is not None and self.client_kwargs["provider"] not in STRUCTURED_GENERATION_PROVIDERS:
raise ValueError(
"InferenceClientModel only supports structured outputs with these providers:"
+ ", ".join(STRUCTURED_GENERATION_PROVIDERS)
)
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
# response_format=response_format,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
response = self.client.chat_completion(**completion_kwargs)
return ChatMessage.from_dict(
asdict(response.choices[0].message),
raw=response,
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=response.usage.prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=response.usage.completion_tokens,
),
)
def generate_stream(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> Generator[ChatMessageStreamDelta]:
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
response_format=response_format,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
model=self.model_id,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
for event in self.client.chat.completions.create(
**completion_kwargs, stream=True, stream_options={"include_usage": True}
):
if getattr(event, "usage", None):
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content="",
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=event.usage.prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=event.usage.completion_tokens,
),
)
if event.choices:
choice = event.choices[0]
if choice.delta:
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content=choice.delta.content,
tool_calls=[
ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta(
index=delta.index,
id=delta.id,
type=delta.type,
function=delta.function,
)
for delta in choice.delta.tool_calls
]
if choice.delta.tool_calls
else None,
)
else:
if not getattr(choice, "finish_reason", None):
raise ValueError(f"No content or tool calls in event: {event}")
class OpenAIServerModel(ApiModel):
"""This model connects to an OpenAI-compatible API server.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The model identifier to use on the server (e.g. "gpt-3.5-turbo").
api_base (`str`, *optional*):
The base URL of the OpenAI-compatible API server.
api_key (`str`, *optional*):
The API key to use for authentication.
organization (`str`, *optional*):
The organization to use for the API request.
project (`str`, *optional*):
The project to use for the API request.
client_kwargs (`dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the OpenAI client (like organization, project, max_retries etc.).
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
Custom role conversion mapping to convert message roles in others.
Useful for specific models that do not support specific message roles like "system".
flatten_messages_as_text (`bool`, default `False`):
Whether to flatten messages as text.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying OpenAI API completion call, for instance `temperature`.
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str,
api_base: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
organization: str | None = None,
project: str | None = None,
client_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
flatten_messages_as_text: bool = False,
**kwargs,
):
self.client_kwargs = {
**(client_kwargs or {}),
"api_key": api_key,
"base_url": api_base,
"organization": organization,
"project": project,
}
super().__init__(
model_id=model_id,
custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions,
flatten_messages_as_text=flatten_messages_as_text,
**kwargs,
)
def create_client(self):
try:
import openai
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'openai' extra to use OpenAIServerModel: `pip install 'smolagents[openai]'`"
) from e
return openai.OpenAI(**self.client_kwargs)
def generate_stream(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> Generator[ChatMessageStreamDelta]:
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
response_format=response_format,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
model=self.model_id,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
for event in self.client.chat.completions.create(
**completion_kwargs, stream=True, stream_options={"include_usage": True}
):
if event.usage:
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content="",
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=event.usage.prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=event.usage.completion_tokens,
),
)
if event.choices:
choice = event.choices[0]
if choice.delta:
yield ChatMessageStreamDelta(
content=choice.delta.content,
tool_calls=[
ChatMessageToolCallStreamDelta(
index=delta.index,
id=delta.id,
type=delta.type,
function=delta.function,
)
for delta in choice.delta.tool_calls
]
if choice.delta.tool_calls
else None,
)
else:
if not getattr(choice, "finish_reason", None):
raise ValueError(f"No content or tool calls in event: {event}")
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
completion_kwargs = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=stop_sequences,
response_format=response_format,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
model=self.model_id,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(**completion_kwargs)
return ChatMessage.from_dict(
response.choices[0].message.model_dump(include={"role", "content", "tool_calls"}),
raw=response,
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=response.usage.prompt_tokens,
output_tokens=response.usage.completion_tokens,
),
)
OpenAIModel = OpenAIServerModel
class AzureOpenAIServerModel(OpenAIServerModel):
"""This model connects to an Azure OpenAI deployment.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The model deployment name to use when connecting (e.g. "gpt-4o-mini").
azure_endpoint (`str`, *optional*):
The Azure endpoint, including the resource, e.g. `https://example-resource.azure.openai.com/`. If not provided, it will be inferred from the `AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT` environment variable.
api_key (`str`, *optional*):
The API key to use for authentication. If not provided, it will be inferred from the `AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable.
api_version (`str`, *optional*):
The API version to use. If not provided, it will be inferred from the `OPENAI_API_VERSION` environment variable.
client_kwargs (`dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the AzureOpenAI client (like organization, project, max_retries etc.).
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
Custom role conversion mapping to convert message roles in others.
Useful for specific models that do not support specific message roles like "system".
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying Azure OpenAI API completion call.
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str,
azure_endpoint: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
api_version: str | None = None,
client_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
client_kwargs = client_kwargs or {}
client_kwargs.update(
{
"api_version": api_version,
"azure_endpoint": azure_endpoint,
}
)
super().__init__(
model_id=model_id,
api_key=api_key,
client_kwargs=client_kwargs,
custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions,
**kwargs,
)
def create_client(self):
try:
import openai
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'openai' extra to use AzureOpenAIServerModel: `pip install 'smolagents[openai]'`"
) from e
return openai.AzureOpenAI(**self.client_kwargs)
AzureOpenAIModel = AzureOpenAIServerModel
class AmazonBedrockServerModel(ApiModel):
"""
A model class for interacting with Amazon Bedrock Server models through the Bedrock API.
This class provides an interface to interact with various Bedrock language models,
allowing for customized model inference, guardrail configuration, message handling,
and other parameters allowed by boto3 API.
Authentication:
Amazon Bedrock supports multiple authentication methods:
- Default AWS credentials:
Use the default AWS credential chain (e.g., IAM roles, IAM users).
- API Key Authentication (requires `boto3 >= 1.39.0`):
Set the API key using the `AWS_BEARER_TOKEN_BEDROCK` environment variable.
> [!TIP]
> API key support requires `boto3 >= 1.39.0`.
> For users not relying on API key authentication, the minimum supported version is `boto3 >= 1.36.18`.
Parameters:
model_id (`str`):
The model identifier to use on Bedrock (e.g. "us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0").
client (`boto3.client`, *optional*):
A custom boto3 client for AWS interactions. If not provided, a default client will be created.
client_kwargs (dict[str, Any], *optional*):
Keyword arguments used to configure the boto3 client if it needs to be created internally.
Examples include `region_name`, `config`, or `endpoint_url`.
custom_role_conversions (`dict[str, str]`, *optional*):
Custom role conversion mapping to convert message roles in others.
Useful for specific models that do not support specific message roles like "system".
Defaults to converting all roles to "user" role to enable using all the Bedrock models.
flatten_messages_as_text (`bool`, default `False`):
Whether to flatten messages as text.
**kwargs:
Additional keyword arguments to forward to the underlying Amazon Bedrock model converse call.
Examples:
Creating a model instance with default settings:
```python
>>> bedrock_model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
... model_id='us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0'
... )
```
Creating a model instance with a custom boto3 client:
```python
>>> import boto3
>>> client = boto3.client('bedrock-runtime', region_name='us-west-2')
>>> bedrock_model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
... model_id='us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0',
... client=client
... )
```
Creating a model instance with client_kwargs for internal client creation:
```python
>>> bedrock_model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
... model_id='us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0',
... client_kwargs={'region_name': 'us-west-2', 'endpoint_url': 'https://custom-endpoint.com'}
... )
```
Creating a model instance with inference and guardrail configurations:
```python
>>> additional_api_config = {
... "inferenceConfig": {
... "maxTokens": 3000
... },
... "guardrailConfig": {
... "guardrailIdentifier": "identify1",
... "guardrailVersion": 'v1'
... },
... }
>>> bedrock_model = AmazonBedrockServerModel(
... model_id='anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0',
... **additional_api_config
... )
```
"""
def __init__(
self,
model_id: str,
client=None,
client_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
**kwargs,
):
self.client_kwargs = client_kwargs or {}
# Bedrock only supports `assistant` and `user` roles.
# Many Bedrock models do not allow conversations to start with the `assistant` role, so the default is set to `user/user`.
# This parameter is retained for future model implementations and extended support.
custom_role_conversions = custom_role_conversions or {
MessageRole.SYSTEM: MessageRole.USER,
MessageRole.ASSISTANT: MessageRole.USER,
MessageRole.TOOL_CALL: MessageRole.USER,
MessageRole.TOOL_RESPONSE: MessageRole.USER,
}
super().__init__(
model_id=model_id,
custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions,
flatten_messages_as_text=False, # Bedrock API doesn't support flatten messages, must be a list of messages
client=client,
**kwargs,
)
def _prepare_completion_kwargs(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
custom_role_conversions: dict[str, str] | None = None,
convert_images_to_image_urls: bool = False,
tool_choice: str | dict[Any, Any] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> dict:
"""
Overrides the base method to handle Bedrock-specific configurations.
This implementation adapts the completion keyword arguments to align with
Bedrock's requirements, ensuring compatibility with its unique setup and
constraints.
"""
completion_kwargs = super()._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
stop_sequences=None, # Bedrock support stop_sequence using Inference Config
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
custom_role_conversions=custom_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=convert_images_to_image_urls,
**kwargs,
)
# Not all models in Bedrock support `toolConfig`. Also, smolagents already include the tool call in the prompt,
# so adding `toolConfig` could cause conflicts. We remove it to avoid issues.
completion_kwargs.pop("toolConfig", None)
# The Bedrock API does not support the `type` key in requests.
# This block of code modifies the object to meet Bedrock's requirements.
for message in completion_kwargs.get("messages", []):
for content in message.get("content", []):
if "type" in content:
del content["type"]
return {
"modelId": self.model_id,
**completion_kwargs,
}
def create_client(self):
try:
import boto3 # type: ignore
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
"Please install 'bedrock' extra to use AmazonBedrockServerModel: `pip install 'smolagents[bedrock]'`"
) from e
return boto3.client("bedrock-runtime", **self.client_kwargs)
def generate(
self,
messages: list[ChatMessage | dict],
stop_sequences: list[str] | None = None,
response_format: dict[str, str] | None = None,
tools_to_call_from: list[Tool] | None = None,
**kwargs,
) -> ChatMessage:
if response_format is not None:
raise ValueError("Amazon Bedrock does not support response_format")
completion_kwargs: dict = self._prepare_completion_kwargs(
messages=messages,
tools_to_call_from=tools_to_call_from,
custom_role_conversions=self.custom_role_conversions,
convert_images_to_image_urls=True,
**kwargs,
)
self._apply_rate_limit()
# self.client is created in ApiModel class
response = self.client.converse(**completion_kwargs)
# Get content blocks with "text" key: in case thinking blocks are present, discard them
message_content_blocks_with_text = [
block for block in response["output"]["message"]["content"] if "text" in block
]
if not message_content_blocks_with_text:
raise KeyError("No message content blocks with 'text' key found in response")
# Keep the last one
response["output"]["message"]["content"] = message_content_blocks_with_text[-1]["text"]
return ChatMessage.from_dict(
response["output"]["message"],
raw=response,
token_usage=TokenUsage(
input_tokens=response["usage"]["inputTokens"],
output_tokens=response["usage"]["outputTokens"],
),
)
AmazonBedrockModel = AmazonBedrockServerModel
__all__ = [
"MessageRole",
"tool_role_conversions",
"get_clean_message_list",
"Model",
"MLXModel",
"TransformersModel",
"ApiModel",
"InferenceClientModel",
"LiteLLMModel",
"LiteLLMRouterModel",
"OpenAIServerModel",
"OpenAIModel",
"VLLMModel",
"AzureOpenAIServerModel",
"AzureOpenAIModel",
"AmazonBedrockServerModel",
"AmazonBedrockModel",
"ChatMessage",
]
|
smolagents/src/smolagents/models.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/src/smolagents/models.py",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 35490
}
| 283
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import ast
import os
import re
import shutil
import subprocess
import tempfile
import traceback
from pathlib import Path
import pytest
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from .utils.markers import require_run_all
class SubprocessCallException(Exception):
pass
def run_command(command: list[str], return_stdout=False, env=None):
"""
Runs command with subprocess.check_output and returns stdout if requested.
Properly captures and handles errors during command execution.
"""
for i, c in enumerate(command):
if isinstance(c, Path):
command[i] = str(c)
if env is None:
env = os.environ.copy()
try:
output = subprocess.check_output(command, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, env=env)
if return_stdout:
if hasattr(output, "decode"):
output = output.decode("utf-8")
return output
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
raise SubprocessCallException(
f"Command `{' '.join(command)}` failed with the following error:\n\n{e.output.decode()}"
) from e
class DocCodeExtractor:
"""Handles extraction and validation of Python code from markdown files."""
@staticmethod
def extract_python_code(content: str) -> list[str]:
"""Extract Python code blocks from markdown content."""
pattern = r"```(?:python|py)\n(.*?)\n```"
matches = re.finditer(pattern, content, re.DOTALL)
return [match.group(1).strip() for match in matches]
@staticmethod
def create_test_script(code_blocks: list[str], tmp_dir: str) -> Path:
"""Create a temporary Python script from code blocks."""
combined_code = "\n\n".join(code_blocks)
assert len(combined_code) > 0, "Code is empty!"
tmp_file = Path(tmp_dir) / "test_script.py"
with open(tmp_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(combined_code)
return tmp_file
# Skip: slow tests + require API keys
@require_run_all
class TestDocs:
"""Test case for documentation code testing."""
@classmethod
def setup_class(cls):
cls._tmpdir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
cls.launch_args = ["python3"]
cls.docs_dir = Path(__file__).parent.parent / "docs" / "source" / "en"
cls.extractor = DocCodeExtractor()
if not cls.docs_dir.exists():
raise ValueError(f"Docs directory not found at {cls.docs_dir}")
load_dotenv()
cls.md_files = list(cls.docs_dir.rglob("*.md")) + list(cls.docs_dir.rglob("*.mdx"))
if not cls.md_files:
raise ValueError(f"No markdown files found in {cls.docs_dir}")
@classmethod
def teardown_class(cls):
shutil.rmtree(cls._tmpdir)
@pytest.mark.timeout(100)
def test_single_doc(self, doc_path: Path):
"""Test a single documentation file."""
with open(doc_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
content = f.read()
code_blocks = self.extractor.extract_python_code(content)
excluded_snippets = [
"ToolCollection",
"image_generation_tool", # We don't want to run this expensive operation
"from_langchain", # Langchain is not a dependency
"while llm_should_continue(memory):", # This is pseudo code
"ollama_chat/llama3.2", # Exclude ollama building in guided tour
"model = TransformersModel(model_id=model_id)", # Exclude testing with transformers model
"SmolagentsInstrumentor", # Exclude telemetry since it needs additional installs
]
code_blocks = [
block
for block in code_blocks
if not any(
[snippet in block for snippet in excluded_snippets]
) # Exclude these tools that take longer to run and add dependencies
]
if len(code_blocks) == 0:
pytest.skip(f"No Python code blocks found in {doc_path.name}")
# Validate syntax of each block individually by parsing it
for i, block in enumerate(code_blocks, 1):
ast.parse(block)
# Create and execute test script
print("\n\nCollected code block:==========\n".join(code_blocks))
try:
code_blocks = [
(
block.replace("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>", os.getenv("HF_TOKEN"))
.replace("YOUR_ANTHROPIC_API_KEY", os.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"))
.replace("{your_username}", "m-ric")
)
for block in code_blocks
]
test_script = self.extractor.create_test_script(code_blocks, self._tmpdir)
run_command(self.launch_args + [str(test_script)])
except SubprocessCallException as e:
pytest.fail(f"\nError while testing {doc_path.name}:\n{str(e)}")
except Exception:
pytest.fail(f"\nUnexpected error while testing {doc_path.name}:\n{traceback.format_exc()}")
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
def _setup(self):
"""Fixture to ensure temporary directory exists for each test."""
os.makedirs(self._tmpdir, exist_ok=True)
yield
# Clean up test files after each test
for file in Path(self._tmpdir).glob("*"):
file.unlink()
def pytest_generate_tests(metafunc):
"""Generate test cases for each markdown file."""
if "doc_path" in metafunc.fixturenames:
test_class = metafunc.cls
# Initialize the class if needed
if not hasattr(test_class, "md_files"):
test_class.setup_class()
# Parameterize with the markdown files
metafunc.parametrize("doc_path", test_class.md_files, ids=[f.stem for f in test_class.md_files])
|
smolagents/tests/test_all_docs.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/tests/test_all_docs.py",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 2637
}
| 284
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2024 HuggingFace Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import inspect
import os
import warnings
from textwrap import dedent
from typing import Any, Literal
from unittest.mock import MagicMock, patch
import mcp
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import pytest
from smolagents.agent_types import _AGENT_TYPE_MAPPING
from smolagents.tools import AUTHORIZED_TYPES, Tool, ToolCollection, launch_gradio_demo, tool, validate_tool_arguments
from .utils.markers import require_run_all
class ToolTesterMixin:
def test_inputs_output(self):
assert hasattr(self.tool, "inputs")
assert hasattr(self.tool, "output_type")
inputs = self.tool.inputs
assert isinstance(inputs, dict)
for _, input_spec in inputs.items():
assert "type" in input_spec
assert "description" in input_spec
assert input_spec["type"] in AUTHORIZED_TYPES
assert isinstance(input_spec["description"], str)
output_type = self.tool.output_type
assert output_type in AUTHORIZED_TYPES
def test_common_attributes(self):
assert hasattr(self.tool, "description")
assert hasattr(self.tool, "name")
assert hasattr(self.tool, "inputs")
assert hasattr(self.tool, "output_type")
def test_agent_type_output(self, create_inputs):
inputs = create_inputs(self.tool.inputs)
output = self.tool(**inputs, sanitize_inputs_outputs=True)
if self.tool.output_type != "any":
agent_type = _AGENT_TYPE_MAPPING[self.tool.output_type]
assert isinstance(output, agent_type)
@pytest.fixture
def create_inputs(self, shared_datadir):
def _create_inputs(tool_inputs: dict[str, dict[str | type, str]]) -> dict[str, Any]:
inputs = {}
for input_name, input_desc in tool_inputs.items():
input_type = input_desc["type"]
if input_type == "string":
inputs[input_name] = "Text input"
elif input_type == "image":
inputs[input_name] = PIL.Image.open(shared_datadir / "000000039769.png").resize((512, 512))
elif input_type == "audio":
inputs[input_name] = np.ones(3000)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid type requested: {input_type}")
return inputs
return _create_inputs
class TestTool:
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"type_value, should_raise_error, error_contains",
[
# Valid cases
("string", False, None),
(["string", "number"], False, None),
# Invalid cases
("invalid_type", ValueError, "must be one of"),
(["string", "invalid_type"], ValueError, "must be one of"),
([123, "string"], TypeError, "when type is a list, all elements must be strings"),
(123, TypeError, "must be a string or list of strings"),
],
)
def test_tool_input_type_validation(self, type_value, should_raise_error, error_contains):
"""Test the validation of the type property in tool inputs."""
# Define a tool class with the test type value
def create_tool():
class TestTool(Tool):
name = "test_tool"
description = "A tool for testing type validation"
inputs = {"text": {"type": type_value, "description": "Some input"}}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, text) -> str:
return text
return TestTool()
# Check if we expect this to raise an exception
if should_raise_error:
with pytest.raises(should_raise_error) as exc_info:
create_tool()
# Verify the error message contains expected text
assert error_contains in str(exc_info.value)
else:
# Should not raise an exception
tool = create_tool()
assert isinstance(tool, Tool)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"tool_fixture, expected_output",
[
("no_input_tool", 'def no_input_tool() -> string:\n """Tool with no inputs\n """'),
(
"single_input_tool",
'def single_input_tool(text: string) -> string:\n """Tool with one input\n\n Args:\n text: Input text\n """',
),
(
"multi_input_tool",
'def multi_input_tool(text: string, count: integer) -> object:\n """Tool with multiple inputs\n\n Args:\n text: Text input\n count: Number count\n """',
),
(
"multiline_description_tool",
'def multiline_description_tool(input: string) -> string:\n """This is a tool with\n multiple lines\n in the description\n\n Args:\n input: Some input\n """',
),
],
)
def test_tool_to_code_prompt_output_format(self, tool_fixture, expected_output, request):
"""Test that to_code_prompt generates properly formatted and indented output."""
tool = request.getfixturevalue(tool_fixture)
code_prompt = tool.to_code_prompt()
assert code_prompt == expected_output
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"tool_fixture, expected_output",
[
(
"no_input_tool",
"no_input_tool: Tool with no inputs\n Takes inputs: {}\n Returns an output of type: string",
),
(
"single_input_tool",
"single_input_tool: Tool with one input\n Takes inputs: {'text': {'type': 'string', 'description': 'Input text'}}\n Returns an output of type: string",
),
(
"multi_input_tool",
"multi_input_tool: Tool with multiple inputs\n Takes inputs: {'text': {'type': 'string', 'description': 'Text input'}, 'count': {'type': 'integer', 'description': 'Number count'}}\n Returns an output of type: object",
),
(
"multiline_description_tool",
"multiline_description_tool: This is a tool with\nmultiple lines\nin the description\n Takes inputs: {'input': {'type': 'string', 'description': 'Some input'}}\n Returns an output of type: string",
),
],
)
def test_tool_to_tool_calling_prompt_output_format(self, tool_fixture, expected_output, request):
"""Test that to_tool_calling_prompt generates properly formatted output."""
tool = request.getfixturevalue(tool_fixture)
tool_calling_prompt = tool.to_tool_calling_prompt()
assert tool_calling_prompt == expected_output
def test_tool_init_with_decorator(self):
@tool
def coolfunc(a: str, b: int) -> float:
"""Cool function
Args:
a: The first argument
b: The second one
"""
return b + 2, a
assert coolfunc.output_type == "number"
def test_tool_init_vanilla(self):
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
name = "model_download_counter"
description = """
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
It returns the name of the checkpoint."""
inputs = {
"task": {
"type": "string",
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
}
}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, task: str) -> str:
return "best model"
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
assert list(tool.inputs.keys())[0] == "task"
def test_tool_init_decorator_raises_issues(self):
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
@tool
def coolfunc(a: str, b: int):
"""Cool function
Args:
a: The first argument
b: The second one
"""
return a + b
assert coolfunc.output_type == "number"
assert "Tool return type not found" in str(e)
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
@tool
def coolfunc(a: str, b: int) -> int:
"""Cool function
Args:
a: The first argument
"""
return b + a
assert coolfunc.output_type == "number"
assert "docstring has no description for the argument" in str(e)
def test_saving_tool_raises_error_imports_outside_function(self, tmp_path):
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
import numpy as np
@tool
def get_current_time() -> str:
"""
Gets the current time.
"""
return str(np.random.random())
get_current_time.save(tmp_path)
assert "np" in str(e)
# Also test with classic definition
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
class GetCurrentTimeTool(Tool):
name = "get_current_time_tool"
description = "Gets the current time"
inputs = {}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self):
return str(np.random.random())
get_current_time = GetCurrentTimeTool()
get_current_time.save(tmp_path)
assert "np" in str(e)
def test_tool_definition_raises_no_error_imports_in_function(self):
@tool
def get_current_time() -> str:
"""
Gets the current time.
"""
from datetime import datetime
return str(datetime.now())
class GetCurrentTimeTool(Tool):
name = "get_current_time_tool"
description = "Gets the current time"
inputs = {}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self):
from datetime import datetime
return str(datetime.now())
def test_tool_to_dict_allows_no_arg_in_init(self):
"""Test that a tool cannot be saved with required args in init"""
class FailTool(Tool):
name = "specific"
description = "test description"
inputs = {"string_input": {"type": "string", "description": "input description"}}
output_type = "string"
def __init__(self, url):
super().__init__(self)
self.url = url
def forward(self, string_input: str) -> str:
return self.url + string_input
fail_tool = FailTool("dummy_url")
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
fail_tool.to_dict()
assert "Parameters in __init__ must have default values, found required parameters" in str(e)
class PassTool(Tool):
name = "specific"
description = "test description"
inputs = {"string_input": {"type": "string", "description": "input description"}}
output_type = "string"
def __init__(self, url: str | None = "none"):
super().__init__(self)
self.url = url
def forward(self, string_input: str) -> str:
return self.url + string_input
fail_tool = PassTool()
fail_tool.to_dict()
def test_saving_tool_allows_no_imports_from_outside_methods(self, tmp_path):
# Test that using imports from outside functions fails
import numpy as np
class FailTool(Tool):
name = "specific"
description = "test description"
inputs = {"string_input": {"type": "string", "description": "input description"}}
output_type = "string"
def useless_method(self):
self.client = np.random.random()
return ""
def forward(self, string_input):
return self.useless_method() + string_input
fail_tool = FailTool()
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
fail_tool.save(tmp_path)
assert "'np' is undefined" in str(e)
# Test that putting these imports inside functions works
class SuccessTool(Tool):
name = "specific"
description = "test description"
inputs = {"string_input": {"type": "string", "description": "input description"}}
output_type = "string"
def useless_method(self):
import numpy as np
self.client = np.random.random()
return ""
def forward(self, string_input):
return self.useless_method() + string_input
success_tool = SuccessTool()
success_tool.save(tmp_path)
def test_tool_missing_class_attributes_raises_error(self):
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
class GetWeatherTool(Tool):
name = "get_weather"
description = "Get weather in the next days at given location."
inputs = {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "the location"},
"celsius": {
"type": "string",
"description": "the temperature type",
},
}
def forward(self, location: str, celsius: bool | None = False) -> str:
return "The weather is UNGODLY with torrential rains and temperatures below -10°C"
GetWeatherTool()
assert "You must set an attribute output_type" in str(e)
def test_tool_from_decorator_optional_args(self):
@tool
def get_weather(location: str, celsius: bool | None = False) -> str:
"""
Get weather in the next days at given location.
Secretly this tool does not care about the location, it hates the weather everywhere.
Args:
location: the location
celsius: the temperature type
"""
return "The weather is UNGODLY with torrential rains and temperatures below -10°C"
assert "nullable" in get_weather.inputs["celsius"]
assert get_weather.inputs["celsius"]["nullable"]
assert "nullable" not in get_weather.inputs["location"]
def test_tool_mismatching_nullable_args_raises_error(self):
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
class GetWeatherTool(Tool):
name = "get_weather"
description = "Get weather in the next days at given location."
inputs = {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "the location"},
"celsius": {
"type": "string",
"description": "the temperature type",
},
}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, location: str, celsius: bool | None = False) -> str:
return "The weather is UNGODLY with torrential rains and temperatures below -10°C"
GetWeatherTool()
assert "Nullable" in str(e)
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
class GetWeatherTool2(Tool):
name = "get_weather"
description = "Get weather in the next days at given location."
inputs = {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "the location"},
"celsius": {
"type": "string",
"description": "the temperature type",
},
}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, location: str, celsius: bool = False) -> str:
return "The weather is UNGODLY with torrential rains and temperatures below -10°C"
GetWeatherTool2()
assert "Nullable" in str(e)
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e:
class GetWeatherTool3(Tool):
name = "get_weather"
description = "Get weather in the next days at given location."
inputs = {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "the location"},
"celsius": {
"type": "string",
"description": "the temperature type",
"nullable": True,
},
}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, location, celsius: str) -> str:
return "The weather is UNGODLY with torrential rains and temperatures below -10°C"
GetWeatherTool3()
assert "Nullable" in str(e)
def test_tool_default_parameters_is_nullable(self):
@tool
def get_weather(location: str, celsius: bool = False) -> str:
"""
Get weather in the next days at given location.
Args:
location: The location to get the weather for.
celsius: is the temperature given in celsius?
"""
return "The weather is UNGODLY with torrential rains and temperatures below -10°C"
assert get_weather.inputs["celsius"]["nullable"]
def test_tool_supports_any_none(self, tmp_path):
@tool
def get_weather(location: Any) -> None:
"""
Get weather in the next days at given location.
Args:
location: The location to get the weather for.
"""
return
get_weather.save(tmp_path)
assert get_weather.inputs["location"]["type"] == "any"
assert get_weather.output_type == "null"
def test_tool_supports_array(self):
@tool
def get_weather(locations: list[str], months: tuple[str, str] | None = None) -> dict[str, float]:
"""
Get weather in the next days at given locations.
Args:
locations: The locations to get the weather for.
months: The months to get the weather for
"""
return
assert get_weather.inputs["locations"]["type"] == "array"
assert get_weather.inputs["months"]["type"] == "array"
def test_tool_supports_string_literal(self):
@tool
def get_weather(unit: Literal["celsius", "fahrenheit"] = "celsius") -> None:
"""
Get weather in the next days at given location.
Args:
unit: The unit of temperature
"""
return
assert get_weather.inputs["unit"]["type"] == "string"
assert get_weather.inputs["unit"]["enum"] == ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]
def test_tool_supports_numeric_literal(self):
@tool
def get_choice(choice: Literal[1, 2, 3]) -> None:
"""
Get choice based on the provided numeric literal.
Args:
choice: The numeric choice to be made.
"""
return
assert get_choice.inputs["choice"]["type"] == "integer"
assert get_choice.inputs["choice"]["enum"] == [1, 2, 3]
def test_tool_supports_nullable_literal(self):
@tool
def get_choice(choice: Literal[1, 2, 3, None]) -> None:
"""
Get choice based on the provided value.
Args:
choice: The numeric choice to be made.
"""
return
assert get_choice.inputs["choice"]["type"] == "integer"
assert get_choice.inputs["choice"]["nullable"] is True
assert get_choice.inputs["choice"]["enum"] == [1, 2, 3]
def test_saving_tool_produces_valid_pyhon_code_with_multiline_description(self, tmp_path):
@tool
def get_weather(location: Any) -> None:
"""
Get weather in the next days at given location.
And works pretty well.
Args:
location: The location to get the weather for.
"""
return
get_weather.save(tmp_path)
with open(os.path.join(tmp_path, "tool.py"), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
source_code = f.read()
compile(source_code, f.name, "exec")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("fixture_name", ["boolean_default_tool_class", "boolean_default_tool_function"])
def test_to_dict_boolean_default_input(self, fixture_name, request):
"""Test that boolean input parameter with default value is correctly represented in to_dict output"""
tool = request.getfixturevalue(fixture_name)
result = tool.to_dict()
# Check that the boolean default annotation is preserved
assert "flag: bool = False" in result["code"]
# Check nullable attribute is set for the parameter with default value
assert "'nullable': True" in result["code"]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("fixture_name", ["optional_input_tool_class", "optional_input_tool_function"])
def test_to_dict_optional_input(self, fixture_name, request):
"""Test that Optional/nullable input parameter is correctly represented in to_dict output"""
tool = request.getfixturevalue(fixture_name)
result = tool.to_dict()
# Check the Optional type annotation is preserved
assert "optional_text: str | None = None" in result["code"]
# Check that the input is marked as nullable in the code
assert "'nullable': True" in result["code"]
def test_from_dict_roundtrip(self, example_tool):
# Convert to dict
tool_dict = example_tool.to_dict()
# Create from dict
recreated_tool = Tool.from_dict(tool_dict)
# Verify properties
assert recreated_tool.name == example_tool.name
assert recreated_tool.description == example_tool.description
assert recreated_tool.inputs == example_tool.inputs
assert recreated_tool.output_type == example_tool.output_type
# Verify functionality
test_input = "Hello, world!"
assert recreated_tool(test_input) == test_input.upper()
def test_tool_from_dict_invalid(self):
# Missing code key
with pytest.raises(ValueError) as e:
Tool.from_dict({"name": "invalid_tool"})
assert "must contain 'code' key" in str(e)
def test_tool_decorator_preserves_original_function(self):
# Define a test function with type hints and docstring
def test_function(items: list[str]) -> str:
"""Join a list of strings.
Args:
items: A list of strings to join
Returns:
The joined string
"""
return ", ".join(items)
# Store original function signature, name, and source
original_signature = inspect.signature(test_function)
original_name = test_function.__name__
original_docstring = test_function.__doc__
# Create a tool from the function
test_tool = tool(test_function)
# Check that the original function is unchanged
assert original_signature == inspect.signature(test_function)
assert original_name == test_function.__name__
assert original_docstring == test_function.__doc__
# Verify that the tool's forward method has a different signature (it has 'self')
tool_forward_sig = inspect.signature(test_tool.forward)
assert list(tool_forward_sig.parameters.keys())[0] == "self"
# Original function should not have 'self' parameter
assert "self" not in original_signature.parameters
def test_tool_with_union_type_return(self):
@tool
def union_type_return_tool_function(param: int) -> str | bool:
"""
Tool with output union type.
Args:
param: Input parameter.
"""
return str(param) if param > 0 else False
assert isinstance(union_type_return_tool_function, Tool)
assert union_type_return_tool_function.output_type == "any"
class TestToolDecorator:
def test_tool_decorator_source_extraction_with_multiple_decorators(self):
"""Test that @tool correctly extracts source code with multiple decorators."""
def dummy_decorator(func):
return func
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match="has decorators other than @tool"):
@tool
@dummy_decorator
def multi_decorator_tool(text: str) -> str:
"""Tool with multiple decorators.
Args:
text: Input text
"""
return text.upper()
# Verify the tool works
assert isinstance(multi_decorator_tool, Tool)
assert multi_decorator_tool.name == "multi_decorator_tool"
assert multi_decorator_tool("hello") == "HELLO"
# Verify the source code extraction is correct
forward_source = multi_decorator_tool.forward.__source__
assert "def forward(self, text: str) -> str:" in forward_source
assert "return text.upper()" in forward_source
# Should not contain decorator lines
assert "@tool" not in forward_source
assert "@dummy_decorator" not in forward_source
# Should not contain definition line
assert "def multi_decorator_tool" not in forward_source
def test_tool_decorator_source_extraction_with_multiline_signature(self):
"""Test that @tool correctly extracts source code with multiline function signatures."""
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("error")
@tool
def multiline_signature_tool(
text: str,
count: int = 1,
uppercase: bool = False,
multiline_parameter_1: int = 1_000,
multiline_parameter_2: int = 2_000,
) -> str:
"""Tool with multiline signature.
Args:
text: Input text
count: Number of repetitions
uppercase: Whether to convert to uppercase
multiline_parameter_1: Dummy parameter
multiline_parameter_2: Dummy parameter
"""
result = text * count
return result.upper() if uppercase else result
# Verify the tool works
assert isinstance(multiline_signature_tool, Tool)
assert multiline_signature_tool.name == "multiline_signature_tool"
assert multiline_signature_tool("hello", 2, True) == "HELLOHELLO"
# Verify the source code extraction is correct
forward_source = multiline_signature_tool.forward.__source__
assert (
"def forward(self, text: str, count: int=1, uppercase: bool=False, multiline_parameter_1: int=1000, multiline_parameter_2: int=2000) -> str:"
in forward_source
or "def forward(self, text: str, count: int = 1, uppercase: bool = False, multiline_parameter_1: int = 1000, multiline_parameter_2: int = 2000) -> str:"
in forward_source
)
assert "result = text * count" in forward_source
assert "return result.upper() if uppercase else result" in forward_source
# Should not contain the original multiline function definition
assert "def multiline_signature_tool(" not in forward_source
# Should not contain leftover lines from the original multiline function definition
assert " count: int = 1," not in forward_source
assert " count: int=1," not in forward_source
def test_tool_decorator_source_extraction_with_multiple_decorators_and_multiline(self):
"""Test that @tool works with both multiple decorators and multiline signatures."""
def dummy_decorator_1(func):
return func
def dummy_decorator_2(func):
return func
with pytest.warns(UserWarning, match="has decorators other than @tool"):
@tool
@dummy_decorator_1
@dummy_decorator_2
def complex_tool(
text: str,
multiplier: int = 2,
separator: str = " ",
multiline_parameter_1: int = 1_000,
multiline_parameter_2: int = 2_000,
) -> str:
"""Complex tool with multiple decorators and multiline signature.
Args:
text: Input text
multiplier: How many times to repeat
separator: What to use between repetitions
multiline_parameter_1: Dummy parameter
multiline_parameter_2: Dummy parameter
"""
parts = [text] * multiplier
return separator.join(parts)
# Verify the tool works
assert isinstance(complex_tool, Tool)
assert complex_tool.name == "complex_tool"
assert complex_tool("hello", 3, "-") == "hello-hello-hello"
# Verify the source code extraction is correct
forward_source = complex_tool.forward.__source__
assert (
"def forward(self, text: str, multiplier: int=2, separator: str=' ', multiline_parameter_1: int=1000, multiline_parameter_2: int=2000) -> str:"
in forward_source
or "def forward(self, text: str, multiplier: int = 2, separator: str = ' ', multiline_parameter_1: int = 1000, multiline_parameter_2: int = 2000) -> str:"
in forward_source
)
assert "parts = [text] * multiplier" in forward_source
assert "return separator.join(parts)" in forward_source
# Should not contain any decorator lines
assert "@tool" not in forward_source
assert "@dummy_decorator_1" not in forward_source
assert "@dummy_decorator_2" not in forward_source
# Should not contain leftover lines from the original multiline function definition
assert " multiplier: int = 2," not in forward_source
assert " multiplier: int=2," not in forward_source
@pytest.fixture
def mock_server_parameters():
return MagicMock()
@pytest.fixture
def mock_mcp_adapt():
with patch("mcpadapt.core.MCPAdapt") as mock:
mock.return_value.__enter__.return_value = ["tool1", "tool2"]
mock.return_value.__exit__.return_value = None
yield mock
@pytest.fixture
def mock_smolagents_adapter():
with patch("mcpadapt.smolagents_adapter.SmolAgentsAdapter") as mock:
yield mock
# Ignore FutureWarning about structured_output default value change: this test intentionally uses default behavior
@pytest.mark.filterwarnings("ignore:.*structured_output:FutureWarning")
class TestToolCollection:
def test_from_mcp(self, mock_server_parameters, mock_mcp_adapt, mock_smolagents_adapter):
with ToolCollection.from_mcp(mock_server_parameters, trust_remote_code=True) as tool_collection:
assert isinstance(tool_collection, ToolCollection)
assert len(tool_collection.tools) == 2
assert "tool1" in tool_collection.tools
assert "tool2" in tool_collection.tools
@require_run_all
def test_integration_from_mcp(self):
# define the most simple mcp server with one tool that echoes the input text
mcp_server_script = dedent("""\
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Echo Server")
@mcp.tool()
def echo_tool(text: str) -> str:
return text
mcp.run()
""").strip()
mcp_server_params = mcp.StdioServerParameters(
command="python",
args=["-c", mcp_server_script],
)
with ToolCollection.from_mcp(mcp_server_params, trust_remote_code=True) as tool_collection:
assert len(tool_collection.tools) == 1, "Expected 1 tool"
assert tool_collection.tools[0].name == "echo_tool", "Expected tool name to be 'echo_tool'"
assert tool_collection.tools[0](text="Hello") == "Hello", "Expected tool to echo the input text"
def test_integration_from_mcp_with_streamable_http(self):
import subprocess
import time
# define the most simple mcp server with one tool that echoes the input text
mcp_server_script = dedent("""\
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Echo Server", host="127.0.0.1", port=8000)
@mcp.tool()
def echo_tool(text: str) -> str:
return text
mcp.run(transport="streamable-http")
""").strip()
# start the SSE mcp server in a subprocess
server_process = subprocess.Popen(
["python", "-c", mcp_server_script],
)
# wait for the server to start
time.sleep(1)
try:
with ToolCollection.from_mcp(
{"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp", "transport": "streamable-http"}, trust_remote_code=True
) as tool_collection:
assert len(tool_collection.tools) == 1, "Expected 1 tool"
assert tool_collection.tools[0].name == "echo_tool", "Expected tool name to be 'echo_tool'"
assert tool_collection.tools[0](text="Hello") == "Hello", "Expected tool to echo the input text"
finally:
# clean up the process when test is done
server_process.kill()
server_process.wait()
def test_integration_from_mcp_with_sse(self):
import subprocess
import time
# define the most simple mcp server with one tool that echoes the input text
mcp_server_script = dedent("""\
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Echo Server", host="127.0.0.1", port=8000)
@mcp.tool()
def echo_tool(text: str) -> str:
return text
mcp.run("sse")
""").strip()
# start the SSE mcp server in a subprocess
server_process = subprocess.Popen(
["python", "-c", mcp_server_script],
)
# wait for the server to start
time.sleep(1)
try:
with ToolCollection.from_mcp(
{"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse", "transport": "sse"}, trust_remote_code=True
) as tool_collection:
assert len(tool_collection.tools) == 1, "Expected 1 tool"
assert tool_collection.tools[0].name == "echo_tool", "Expected tool name to be 'echo_tool'"
assert tool_collection.tools[0](text="Hello") == "Hello", "Expected tool to echo the input text"
finally:
# clean up the process when test is done
server_process.kill()
server_process.wait()
@pytest.mark.parametrize("tool_fixture_name", ["boolean_default_tool_class"])
def test_launch_gradio_demo_does_not_raise(tool_fixture_name, request):
tool = request.getfixturevalue(tool_fixture_name)
with patch("gradio.Interface.launch") as mock_launch:
launch_gradio_demo(tool)
assert mock_launch.call_count == 1
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"tool_input_type, expected_input, expects_error",
[
(bool, True, False),
(str, "b", False),
(int, 1, False),
(float, 1, False),
(list, ["a", "b"], False),
(list[str], ["a", "b"], False),
(dict[str, str], {"a": "b"}, False),
(dict[str, str], "b", True),
(bool, "b", True),
(str | int, "a", False),
(str | int, 1, False),
(str | int, None, True),
(str | int, True, True),
],
)
def test_validate_tool_arguments(tool_input_type, expected_input, expects_error):
@tool
def test_tool(argument_a: tool_input_type) -> str:
"""Fake tool
Args:
argument_a: The input
"""
return argument_a
if expects_error:
with pytest.raises((ValueError, TypeError)):
validate_tool_arguments(test_tool, {"argument_a": expected_input})
else:
# Should not raise any exception
validate_tool_arguments(test_tool, {"argument_a": expected_input})
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"scenario, type_hint, default, input_value, expected_error_message",
[
# Required parameters (no default)
# - Valid input
("required_unsupported_none", str, ..., "text", None),
# - None not allowed
("required_unsupported_none", str, ..., None, "Argument param has type 'null' but should be 'string'"),
# - Missing required parameter is not allowed
("required_unsupported_none", str, ..., ..., "Argument param is required"),
#
# Required parameters but supports None
# - Valid input
("required_supported_none", str | None, ..., "text", None),
# - None allowed
("required_supported_none", str | None, ..., None, None),
# - Missing required parameter is not allowed
# TODO: Fix this test case: property is marked as nullable because it can be None, but it can't be missing because it is required
# ("required_supported_none", str | None, ..., ..., "Argument param is required"),
pytest.param(
"required_supported_none",
str | None,
...,
...,
"Argument param is required",
marks=pytest.mark.skip(reason="TODO: Fix this test case"),
),
#
# Optional parameters (has default, doesn't support None)
# - Valid input
("optional_unsupported_none", str, "default", "text", None),
# - None not allowed
# TODO: Fix this test case: property is marked as nullable because it has a default value, but it can't be None
# ("optional_unsupported_none", str, "default", None, "Argument param has type 'null' but should be 'string'"),
pytest.param(
"optional_unsupported_none",
str,
"default",
None,
"Argument param has type 'null' but should be 'string'",
marks=pytest.mark.skip(reason="TODO: Fix this test case"),
),
# - Missing optional parameter is allowed
("optional_unsupported_none", str, "default", ..., None),
#
# Optional and supports None parameters with string default
# - Valid input
("optional_supported_none_str_default", str | None, "default", "text", None),
# - None allowed
("optional_supported_none_str_default", str | None, "default", None, None),
# - Missing optional parameter is allowed
("optional_supported_none_str_default", str | None, "default", ..., None),
#
# Optional and supports None parameters with None default
# - Valid input
("optional_supported_none_none_default", str | None, None, "text", None),
# - None allowed
("optional_supported_none_none_default", str | None, None, None, None),
# - Missing optional parameter is allowed
("optional_supported_none_none_default", str | None, None, ..., None),
],
)
def test_validate_tool_arguments_nullable(scenario, type_hint, default, input_value, expected_error_message):
"""Test validation of tool arguments with focus on nullable properties: optional (with default value) and supporting None value."""
# Create a tool with the appropriate signature
if default is ...: # Using Ellipsis to indicate no default value
@tool
def test_tool(param: type_hint) -> str:
"""Test tool.
Args:
param: Input param
"""
return str(param) if param is not None else "NULL"
else:
@tool
def test_tool(param: type_hint = default) -> str:
"""Test tool.
Args:
param: Input param.
"""
return str(param) if param is not None else "NULL"
# Test with the input dictionary
input_dict = {"param": input_value} if input_value is not ... else {}
if expected_error_message:
with pytest.raises((ValueError, TypeError), match=expected_error_message):
validate_tool_arguments(test_tool, input_dict)
else:
# Should not raise any exception
validate_tool_arguments(test_tool, input_dict)
|
smolagents/tests/test_tools.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "smolagents/tests/test_tools.py",
"repo_id": "smolagents",
"token_count": 18404
}
| 285
|
# Those arguments are required to build the image
ARG HABANA_VERSION=1.21.0
ARG PYTORCH_VERSION=2.6.0
# Rust builder
FROM lukemathwalker/cargo-chef:latest-rust-1.85.1 AS chef
WORKDIR /usr/src
ARG CARGO_REGISTRIES_CRATES_IO_PROTOCOL=sparse
FROM chef AS planner
COPY Cargo.lock Cargo.lock
COPY Cargo.toml Cargo.toml
COPY rust-toolchain.toml rust-toolchain.toml
COPY proto proto
COPY benchmark benchmark
COPY router router
COPY backends backends
COPY launcher launcher
RUN cargo chef prepare --recipe-path recipe.json
FROM chef AS builder
ENV PYO3_PYTHON="/root/.local/bin/python" \
PYTHON_SYS_EXECUTABLE="/root/.local/bin/python" \
PYO3_PYTHON_VERSION="3.10"
RUN curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh \
&& . $HOME/.local/bin/env \
&& uv python install 3.10 --default --preview \
&& test -f /root/.local/bin/python || (echo "Python 3.10 not found at /root/.local/bin/python" && exit 1)
RUN PROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zip && \
curl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIP && \
unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protoc && \
unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*' && \
rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP
COPY --from=planner /usr/src/recipe.json recipe.json
RUN cargo chef cook --profile release-opt --recipe-path recipe.json
ARG GIT_SHA
ARG DOCKER_LABEL
COPY Cargo.toml Cargo.toml
COPY rust-toolchain.toml rust-toolchain.toml
COPY proto proto
COPY benchmark benchmark
COPY router router
COPY backends backends
COPY launcher launcher
RUN cargo build --profile release-opt
# Text Generation Inference base image
ARG HABANA_VERSION
ARG PYTORCH_VERSION
FROM vault.habana.ai/gaudi-docker/${HABANA_VERSION}/ubuntu22.04/habanalabs/pytorch-installer-${PYTORCH_VERSION}:latest AS base
ENV ATTENTION=paged
ENV PREFIX_CACHING=0
ENV PREFILL_CHUNKING=0
ENV PT_HPU_LAZY_MODE=1
ENV PT_HPU_WEIGHT_SHARING=0
ENV VLLM_EXPONENTIAL_BUCKETING=true
# Text Generation Inference base env
ENV HF_HOME=/data \
HF_HUB_ENABLE_HF_TRANSFER=1 \
PORT=80
# Assert that Python 3.10 is installed as the launcher is compiled with Python 3.10
RUN python3.10 --version || (echo "Python 3.10 is not installed" && exit 1)
# libssl.so.1.1 is not installed on Ubuntu 22.04 by default, install it
RUN wget http://nz2.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/o/openssl/libssl1.1_1.1.1f-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb && \
dpkg -i ./libssl1.1_1.1.1f-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
WORKDIR /usr/src
RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
libssl-dev \
ca-certificates \
make \
curl \
git \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Install server
COPY proto proto
COPY backends/gaudi/server server
COPY backends/gaudi/server/Makefile server/Makefile
ARG HABANA_VERSION
RUN cd server && \
make gen-server && \
pip install --no-deps -r requirements.txt && \
bash ./dill-0.3.8-patch.sh && \
pip install . --no-cache-dir
RUN pip install git+https://github.com/sywangyi/vllm-hpu-extension.git@bmax_fix
RUN pip install compressed-tensors==0.9.1
# Install benchmarker
COPY --from=builder /usr/src/target/release-opt/text-generation-benchmark /usr/local/bin/text-generation-benchmark
# Install router
COPY --from=builder /usr/src/target/release-opt/text-generation-router /usr/local/bin/text-generation-router
# Install launcher
COPY --from=builder /usr/src/target/release-opt/text-generation-launcher /usr/local/bin/text-generation-launcher
# AWS Sagemaker compatible image
FROM base AS sagemaker
COPY sagemaker-entrypoint.sh entrypoint.sh
RUN chmod +x entrypoint.sh
ENTRYPOINT ["./entrypoint.sh"]
# Final image
FROM base
ENV HF_HUB_ENABLE_HF_TRANSFER=1
ENV HABANA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all
ENV OMPI_MCA_btl_vader_single_copy_mechanism=NONE
COPY backends/gaudi/tgi-entrypoint.sh /tgi-entrypoint.sh
RUN chmod +x /tgi-entrypoint.sh
ENTRYPOINT ["/tgi-entrypoint.sh"]
CMD ["--json-output"]
|
text-generation-inference/Dockerfile_gaudi/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/Dockerfile_gaudi",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 1593
}
| 286
|
/// Multi shard Client
use crate::{v2, Health, ShardInfo};
use crate::{ClientError, Result};
use crate::v2::InfoResponse;
use async_trait::async_trait;
use futures::future::join_all;
use tonic::transport::Uri;
use tracing::instrument;
use v2::client::{DecodeTimings, PrefillTimings};
use v2::{
Batch, CachedBatch, Client, Generation, GrammarType, HealthResponse,
NextTokenChooserParameters, Request, StoppingCriteriaParameters,
};
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
/// Text Generation Inference gRPC multi client
pub struct ShardedClient {
clients: Vec<Client>,
}
impl ShardedClient {
fn new(clients: Vec<Client>) -> Self {
Self { clients }
}
/// Create a new ShardedClient from a master client. The master client will communicate with
/// the other shards and returns all uris/unix sockets with the `service_discovery` gRPC method.
async fn from_master_client(mut master_client: Client) -> Result<Self> {
// Get all uris/unix sockets from the master client
let uris = master_client.service_discovery().await?;
let futures = uris.into_iter().map(Client::connect_uds);
let clients: Result<Vec<Client>> = join_all(futures).await.into_iter().collect();
Ok(Self::new(clients?))
}
/// Returns a client connected to the given uri
pub async fn connect(uri: Uri) -> Result<Self> {
let master_client = Client::connect(uri).await?;
Self::from_master_client(master_client).await
}
/// Returns a client connected to the given unix socket
pub async fn connect_uds(path: String) -> Result<Self> {
let master_client = Client::connect_uds(path).await?;
Self::from_master_client(master_client).await
}
/// Get the model info
#[instrument(skip(self))]
pub async fn info(&mut self) -> Result<ShardInfo> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| client.info())
.collect();
join_all(futures).await.pop().unwrap().map(ShardInfo::from)
}
/// GRPC health check
#[instrument(skip(self))]
pub async fn health(&mut self) -> Result<HealthResponse> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| client.health())
.collect();
join_all(futures).await.pop().unwrap()
}
/// Clear the past generations cache
#[instrument(skip(self))]
pub async fn clear_cache(&mut self, batch_id: Option<u64>) -> Result<()> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| client.clear_cache(batch_id))
.collect();
join_all(futures).await.into_iter().collect()
}
/// Filter a cached batch
#[instrument(skip(self))]
pub async fn filter_batch(
&mut self,
batch_id: u64,
request_ids: Vec<u64>,
) -> Result<Option<CachedBatch>> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| Box::pin(client.filter_batch(batch_id, request_ids.clone())))
.collect();
// all shards return the same message
join_all(futures).await.pop().unwrap()
}
/// Warmup on a max size batch
///
/// Returns the maximum amount of tokens supported by the hardware
#[instrument(skip(self))]
pub async fn warmup(
&mut self,
max_input_length: u32,
max_prefill_tokens: u32,
max_total_tokens: u32,
max_batch_size: Option<usize>,
) -> Result<Option<u32>> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| {
Box::pin(client.warmup(
max_input_length,
max_prefill_tokens,
max_total_tokens,
max_batch_size,
))
})
.collect();
// Take the minimum value
let results = join_all(futures)
.await
.into_iter()
.collect::<Result<Vec<Option<u32>>>>()?;
Ok(results.into_iter().flatten().min())
}
/// Generate one token for each request in the given batch
///
/// Returns Generation for each request in batch
/// and the next cached batch
#[instrument(skip_all, fields(id = & batch.id, size = & batch.size))]
pub async fn prefill(
&mut self,
batch: Batch,
) -> Result<(Vec<Generation>, Option<CachedBatch>, PrefillTimings)> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| Box::pin(client.prefill(batch.clone())))
.collect();
#[allow(clippy::type_complexity)]
let results: Result<Vec<(Vec<Generation>, Option<CachedBatch>, PrefillTimings)>> =
join_all(futures).await.into_iter().collect();
let mut results = results?;
let (mut generations, next_batch, mut timings) =
results.pop().ok_or(ClientError::EmptyResults)?;
// Merge generations from different model shards
for (mut shard_generations, _, shard_timings) in results.into_iter() {
generations.append(&mut shard_generations);
// Return the timings of the slowest shard
if shard_timings.total > timings.total {
timings = shard_timings;
}
}
Ok((generations, next_batch, timings))
}
/// Generate one token for each request in the given cached batches
///
/// Returns Generation for each request in batches
/// and the next cached batch
#[instrument(skip_all, fields(size = batches.iter().map(| batch | {batch.size}).sum::< u32 > ()))]
pub async fn decode(
&mut self,
batches: Vec<CachedBatch>,
) -> Result<(Vec<Generation>, Option<CachedBatch>, DecodeTimings)> {
let futures: Vec<_> = self
.clients
.iter_mut()
.map(|client| Box::pin(client.decode(batches.clone())))
.collect();
#[allow(clippy::type_complexity)]
let results: Result<Vec<(Vec<Generation>, Option<CachedBatch>, DecodeTimings)>> =
join_all(futures).await.into_iter().collect();
let mut results = results?;
let (mut generations, next_batch, mut timings) =
results.pop().ok_or(ClientError::EmptyResults)?;
// Merge generations from different model shards
for (mut shard_generations, _, shard_timings) in results.into_iter() {
generations.append(&mut shard_generations);
// Return the timings of the slowest shard
if shard_timings.total > timings.total {
timings = shard_timings;
}
}
Ok((generations, next_batch, timings))
}
}
impl From<InfoResponse> for ShardInfo {
fn from(value: InfoResponse) -> Self {
Self {
requires_padding: value.requires_padding,
dtype: value.dtype,
device_type: value.device_type,
window_size: value.window_size,
speculate: value.speculate,
}
}
}
#[async_trait]
impl Health for ShardedClient {
async fn device_health(&self) -> Result<()> {
self.clone().health().await?;
Ok(())
}
async fn model_health(&self) -> Result<()> {
// Dummy batch of 1 token and 1 generated token
let liveness_request = Request {
id: u64::MAX,
inputs: "liveness".to_string(),
truncate: 10,
prefill_logprobs: false,
parameters: Some(NextTokenChooserParameters {
temperature: 1.0,
top_k: 0,
top_p: 1.0,
typical_p: 1.0,
do_sample: false,
seed: 0,
repetition_penalty: 1.0,
frequency_penalty: 0.0,
watermark: false,
grammar: String::new(),
grammar_type: GrammarType::None as i32,
}),
stopping_parameters: Some(StoppingCriteriaParameters {
max_new_tokens: 1,
stop_sequences: vec![],
ignore_eos_token: false,
}),
top_n_tokens: 0,
};
let batch = Batch {
id: u64::MAX,
requests: vec![liveness_request],
size: 1,
max_tokens: 2,
};
self.clone().prefill(batch).await?;
Ok(())
}
}
|
text-generation-inference/backends/client/src/v2/sharded_client.rs/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/client/src/v2/sharded_client.rs",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 3969
}
| 287
|
from dataclasses import dataclass
import torch
from typing import Optional, List, Dict
import collections
import torch.nn.functional as F
_TYPE_CACHE = {}
@dataclass
class HPUPagedAttentionMetadata:
"""Metadata for PagedAttention."""
block_list: Optional[torch.Tensor]
block_mapping: Optional[torch.Tensor]
block_usage: Optional[torch.Tensor]
block_groups: Optional[torch.Tensor]
attn_bias: Optional[torch.Tensor]
slots_in_window_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
block_list_in_window: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
block_mapping_in_window: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
block_usage_in_window: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
block_groups_in_window: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
attn_bias_in_window: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
def subtuple(
obj: object,
typename: str,
to_copy: List[str],
to_override: Optional[Dict[str, object]] = None,
):
if obj is None:
return None
if to_override is None:
to_override = {}
fields = set(to_copy) | set(to_override.keys())
if isinstance(obj, dict):
values = {key: obj[key] for key in fields if key in obj}
else:
values = {f: to_override.get(f, getattr(obj, f)) for f in fields}
if typename not in _TYPE_CACHE:
_TYPE_CACHE[typename] = collections.namedtuple(typename, " ".join(fields))
return _TYPE_CACHE[typename](**values)
def trim_attn_metadata(metadata: HPUPagedAttentionMetadata) -> object:
# NOTE(kzawora): To anyone working on this in the future:
# Trimming metadata is required when using HPUGraphs.
# Attention metadata is going to be hashed by PT bridge, and
# appropriate HPUGraphs will be matched based on all inputs' hash.
# Before you put more keys in here, make sure you know their
# value type and make sure you know how it's going to be hashed.
# You can find that information in input_hash function
# in habana_frameworks/torch/hpu/graphs.py. You can also hash
# it manually with torch.hpu.graphs.input_hash(attention_metadata)
# If you use primitive types here - they will get hashed based
# on their value. You *will* get lots of excessive graph captures
# (and an OOM eventually) if you decide to put something like
# seq_len int here.
# If you absolutely need a scalar, put it in a tensor. Tensors
# get hashed using their metadata, not their values:
# input_hash(torch.tensor(123)) == input_hash(torch.tensor(321))
# input_hash(123) != input_hash(321)
# input_hash("abc") != input_hash("cba")
attention_metadata = subtuple(
metadata,
"TrimmedAttentionMetadata",
[
"block_list",
"block_mapping",
"block_usage",
"block_groups",
"attn_bias",
"slots_in_window_mask",
"block_list_in_window",
"block_mapping_in_window",
"block_usage_in_window",
"block_groups_in_window",
"attn_bias_in_window",
],
)
return attention_metadata
@dataclass
class Seqlen:
input_lengths: torch.Tensor
attn_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None
def __init__(
self,
input_lengths,
):
self.input_lengths = input_lengths
def clamp(self, max):
# Flash decoding doesn't need to clamp
return self
def make_sliding_window_bias(
self,
seq_lens: List[int],
window_size: Optional[int],
dtype: torch.dtype,
padded_input_len: Optional[int],
padded_bs: Optional[int],
) -> List[torch.Tensor]:
attn_biases = []
for seq_len in seq_lens:
if seq_len != 0:
tensor = torch.full(
(1, seq_len, seq_len),
dtype=dtype,
fill_value=1,
)
shift = 0
mask = torch.tril(tensor, diagonal=shift).to(dtype) # type: ignore
if window_size is not None:
mask = torch.triu(mask, diagonal=shift - window_size + 1)
mask = F.pad(
mask,
(
padded_input_len - seq_len,
0,
padded_input_len - seq_len,
0,
0,
0,
),
value=0,
)
else:
mask = torch.full(
(1, padded_input_len, padded_input_len),
dtype=dtype,
fill_value=0,
)
attn_biases.append(mask)
attn_biases = torch.stack(attn_biases, dim=0)
return attn_biases.to(torch.bool)
def _async_h2d_tensor_copy(source, device="hpu"):
if source is None:
return None
if source.device.type == "hpu":
return source
assert source.device.type == "cpu", "Source tensor is not present in host memory!"
target = torch.empty(source.shape, dtype=source.dtype, device=device)
target.copy_(source, non_blocking=True)
return target
def trim_seqlen_metadata(metadata: Seqlen) -> object:
# NOTE(kzawora): To anyone working on this in the future:
# Trimming metadata is required when using HPUGraphs.
# Attention metadata is going to be hashed by PT bridge, and
# appropriate HPUGraphs will be matched based on all inputs' hash.
# Before you put more keys in here, make sure you know their
# value type and make sure you know how it's going to be hashed.
# You can find that information in input_hash function
# in habana_frameworks/torch/hpu/graphs.py. You can also hash
# it manually with torch.hpu.graphs.input_hash(attention_metadata)
# If you use primitive types here - they will get hashed based
# on their value. You *will* get lots of excessive graph captures
# (and an OOM eventually) if you decide to put something like
# seq_len int here.
# If you absolutely need a scalar, put it in a tensor. Tensors
# get hashed using their metadata, not their values:
# input_hash(torch.tensor(123)) == input_hash(torch.tensor(321))
# input_hash(123) != input_hash(321)
# input_hash("abc") != input_hash("cba")
attention_metadata = subtuple(
metadata,
"TrimmedSeqlen",
[
"input_lengths",
"attn_mask",
],
)
return attention_metadata
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/layers/attention/common.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/layers/attention/common.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 2919
}
| 288
|
import torch
# copied from https://github.com/openppl-public/ppq/blob/master/ppq/quantization/measure/norm.py
def torch_snr_error(
y_pred: torch.Tensor, y_real: torch.Tensor, reduction: str = "mean"
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Compute SNR between y_pred(tensor) and y_real(tensor)
SNR can be calcualted as following equation:
SNR(pred, real) = (pred - real) ^ 2 / (real) ^ 2
if x and y are matrixs, SNR error over matrix should be the mean value of SNR error over all elements.
SNR(pred, real) = mean((pred - real) ^ 2 / (real) ^ 2)
Args:
y_pred (torch.Tensor): _description_
y_real (torch.Tensor): _description_
reduction (str, optional): _description_. Defaults to 'mean'.
Raises:
ValueError: _description_
ValueError: _description_
Returns:
torch.Tensor: _description_
"""
if y_pred.shape != y_real.shape:
raise ValueError(
f"Can not compute snr loss for tensors with different shape. "
f"({y_pred.shape} and {y_real.shape})"
)
reduction = str(reduction).lower()
if y_pred.ndim == 1:
y_pred = y_pred.unsqueeze(0)
y_real = y_real.unsqueeze(0)
y_pred = y_pred.flatten(start_dim=1)
y_real = y_real.flatten(start_dim=1)
noise_power = torch.pow(y_pred - y_real, 2).sum(dim=-1)
signal_power = torch.pow(y_real, 2).sum(dim=-1)
snr = (noise_power) / (signal_power + 1e-7)
if reduction == "mean":
return torch.mean(snr)
elif reduction == "sum":
return torch.sum(snr)
elif reduction == "none":
return snr
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported reduction method.")
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/layers/gptq/utils.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/layers/gptq/utils.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 742
}
| 289
|
from typing import Optional, Tuple
import torch
from torch import nn
from transformers.activations import ACT2FN
from transformers.modeling_attn_mask_utils import (
_create_4d_causal_attention_mask,
_prepare_4d_attention_mask,
)
from transformers.modeling_outputs import (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling,
)
from transformers import CLIPConfig, CLIPTextConfig, CLIPVisionConfig
from text_generation_server.layers import (
TensorParallelEmbedding,
TensorParallelColumnLinear,
TensorParallelRowLinear,
)
class CLIPVisionEmbeddings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prefix, config: CLIPVisionConfig, weights):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.image_size = config.image_size
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
# TODO Should we TP this ?
self.class_embedding = weights.get_tensor(f"{prefix}.class_embedding")
self.patch_embedding = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=config.num_channels,
out_channels=self.embed_dim,
kernel_size=self.patch_size,
stride=self.patch_size,
bias=False,
)
self.patch_embedding.weight = nn.Parameter(
weights.get_tensor(f"{prefix}.patch_embedding.weight"), requires_grad=False
)
self.num_patches = (self.image_size // self.patch_size) ** 2
self.num_positions = self.num_patches + 1
self.position_embedding = TensorParallelEmbedding(
prefix=f"{prefix}.position_embedding", weights=weights
)
self.register_buffer(
"position_ids",
torch.arange(self.num_positions, device=weights.device).expand((1, -1)),
persistent=False,
)
def forward(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size = pixel_values.shape[0]
target_dtype = self.patch_embedding.weight.dtype
patch_embeds = self.patch_embedding(
pixel_values.to(dtype=target_dtype)
) # shape = [*, width, grid, grid]
patch_embeds = patch_embeds.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
class_embeds = self.class_embedding.expand(batch_size, 1, -1)
embeddings = torch.cat([class_embeds, patch_embeds], dim=1)
embeddings = embeddings + self.position_embedding(self.position_ids)
return embeddings
class CLIPTextEmbeddings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: CLIPTextConfig):
super().__init__()
embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.token_embedding = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, embed_dim)
self.position_embedding = nn.Embedding(
config.max_position_embeddings, embed_dim
)
# position_ids (1, len position emb) is contiguous in memory and exported when serialized
self.register_buffer(
"position_ids",
torch.arange(config.max_position_embeddings).expand((1, -1)),
persistent=False,
)
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
) -> torch.Tensor:
seq_length = (
input_ids.shape[-1] if input_ids is not None else inputs_embeds.shape[-2]
)
if position_ids is None:
position_ids = self.position_ids[:, :seq_length]
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.token_embedding(input_ids)
position_embeddings = self.position_embedding(position_ids)
embeddings = inputs_embeds + position_embeddings
return embeddings
class CLIPAttention(nn.Module):
"""Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper"""
def __init__(self, prefix, config, weights):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.num_attention_heads
self.head_size = self.embed_dim // self.num_heads
if self.head_size * self.num_heads != self.embed_dim:
raise ValueError(
f"embed_dim must be divisible by num_heads (got `embed_dim`: {self.embed_dim} and `num_heads`:"
f" {self.num_heads})."
)
self.num_heads = self.num_heads // weights.process_group.size()
self.embed_dim = self.embed_dim // weights.process_group.size()
self.scale = self.head_size**-0.5
self.dropout = config.attention_dropout
self.qkv = TensorParallelColumnLinear.load_multi(
config,
prefixes=[f"{prefix}.q_proj", f"{prefix}.k_proj", f"{prefix}.v_proj"],
dim=0,
weights=weights,
bias=True,
)
self.out_proj = TensorParallelRowLinear.load(
config,
prefix=f"{prefix}.out_proj",
weights=weights,
bias=True,
)
def _shape(self, tensor: torch.Tensor, seq_len: int, bsz: int):
return (
tensor.view(bsz, seq_len, self.num_heads, self.head_size)
.transpose(1, 2)
.contiguous()
)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
"""Input shape: Batch x Time x Channel"""
bsz, tgt_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
# get query proj
qkv = self.qkv(hidden_states)
query_states, key_states, value_states = qkv.split(
[
self.head_size * self.num_heads,
]
* 3,
dim=2,
)
query_states = query_states * self.scale
key_states = self._shape(key_states, -1, bsz)
value_states = self._shape(value_states, -1, bsz)
proj_shape = (bsz * self.num_heads, -1, self.head_size)
query_states = self._shape(query_states, tgt_len, bsz).view(*proj_shape)
key_states = key_states.view(*proj_shape)
value_states = value_states.view(*proj_shape)
src_len = key_states.size(1)
attn_weights = torch.bmm(query_states, key_states.transpose(1, 2))
if attn_weights.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len):
raise ValueError(
f"Attention weights should be of size {(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is"
f" {attn_weights.size()}"
)
# apply the causal_attention_mask first
if causal_attention_mask is not None:
if causal_attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len):
raise ValueError(
f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is"
f" {causal_attention_mask.size()}"
)
attn_weights = (
attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
+ causal_attention_mask
)
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
if attention_mask is not None:
if attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len):
raise ValueError(
f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is {attention_mask.size()}"
)
attn_weights = (
attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
+ attention_mask
)
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1)
attn_probs = nn.functional.dropout(
attn_weights, p=self.dropout, training=self.training
)
attn_output = torch.bmm(attn_probs, value_states)
if attn_output.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_size):
raise ValueError(
f"`attn_output` should be of size {(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_size)}, but is"
f" {attn_output.size()}"
)
attn_output = attn_output.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_size)
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2)
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, tgt_len, self.embed_dim)
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, None
class CLIPMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prefix, config, weights):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.activation_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
self.fc1 = TensorParallelColumnLinear.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.fc1", config=config, weights=weights, bias=True
)
self.fc2 = TensorParallelRowLinear.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.fc2", config=config, weights=weights, bias=True
)
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
hidden_states = self.fc1(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.activation_fn(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.fc2(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
class CLIPEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prefix, config: CLIPConfig, weights):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.self_attn = CLIPAttention(
prefix=f"{prefix}.self_attn", config=config, weights=weights
)
self.layer_norm1 = nn.LayerNorm.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.layer_norm1", weights=weights, eps=config.layer_norm_eps
)
self.mlp = CLIPMLP(prefix=f"{prefix}.mlp", config=config, weights=weights)
self.layer_norm2 = nn.LayerNorm.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.layer_norm2", weights=weights, eps=config.layer_norm_eps
)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
causal_attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
):
"""
Args:
hidden_states (`torch.FloatTensor`): input to the layer of shape `(batch, seq_len, embed_dim)`
attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor`): attention mask of size
`(batch, 1, tgt_len, src_len)` where padding elements are indicated by very large negative values.
`(config.encoder_attention_heads,)`.
"""
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.layer_norm1(hidden_states)
hidden_states, attn_weights = self.self_attn(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
causal_attention_mask=causal_attention_mask,
)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.layer_norm2(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
return hidden_states
class CLIPPreTrainedModel(nn.Module):
"""
An abstract class to handle weights initialization and a simple interface for downloading and loading pretrained
models.
"""
config_class = CLIPConfig
base_model_prefix = "clip"
supports_gradient_checkpointing = True
CLIP_START_DOCSTRING = r"""
This model inherits from [`PreTrainedModel`]. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the
library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads
etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch [torch.nn.Module](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module) subclass.
Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage
and behavior.
Parameters:
config ([`CLIPConfig`]): Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model.
Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the
configuration. Check out the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method to load the model weights.
"""
CLIP_TEXT_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
Args:
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide
it.
Indices can be obtained using [`AutoTokenizer`]. See [`PreTrainedTokenizer.encode`] and
[`PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__`] for details.
[What are input IDs?](../glossary#input-ids)
attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
position_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range `[0,
config.max_position_embeddings - 1]`.
[What are position IDs?](../glossary#position-ids)
"""
CLIP_VISION_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
Args:
pixel_values (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)`):
Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using
[`AutoImageProcessor`]. See [`CLIPImageProcessor.__call__`] for details.
"""
CLIP_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
Args:
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide
it.
Indices can be obtained using [`AutoTokenizer`]. See [`PreTrainedTokenizer.encode`] and
[`PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__`] for details.
[What are input IDs?](../glossary#input-ids)
attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
position_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range `[0,
config.max_position_embeddings - 1]`.
[What are position IDs?](../glossary#position-ids)
pixel_values (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)`):
Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using
[`AutoImageProcessor`]. See [`CLIPImageProcessor.__call__`] for details.
return_loss (`bool`, *optional*):
Whether or not to return the contrastive loss.
"""
class CLIPEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
Transformer encoder consisting of `config.num_hidden_layers` self attention layers. Each layer is a
[`CLIPEncoderLayer`].
Args:
config: CLIPConfig
"""
def __init__(self, prefix, config: CLIPConfig, weights):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[
CLIPEncoderLayer(
prefix=f"{prefix}.layers.{i}", config=config, weights=weights
)
for i in range(config.num_hidden_layers)
]
)
def forward(
self,
inputs_embeds,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
):
r"""
Args:
inputs_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)`):
Optionally, instead of passing `input_ids` you can choose to directly pass an embedded representation.
This is useful if you want more control over how to convert `input_ids` indices into associated vectors
than the model's internal embedding lookup matrix.
attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
causal_attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Causal mask for the text model. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
"""
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
for idx, encoder_layer in enumerate(self.layers):
hidden_states = encoder_layer(
hidden_states,
attention_mask,
causal_attention_mask,
)
return hidden_states
class CLIPTextTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prefix: str, config: CLIPTextConfig, weights=None):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.embeddings = CLIPTextEmbeddings(config)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing with `self.post_init()`
self.encoder = CLIPEncoder(
prefix=f"{prefix}.encoder", config=config, weights=weights
)
self.final_layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
# For `pooled_output` computation
self.eos_token_id = config.eos_token_id
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
):
r"""
Returns:
"""
if input_ids is None:
raise ValueError("You have to specify input_ids")
input_shape = input_ids.size()
input_ids = input_ids.view(-1, input_shape[-1])
hidden_states = self.embeddings(input_ids=input_ids, position_ids=position_ids)
# CLIP's text model uses causal mask, prepare it here.
# https://github.com/openai/CLIP/blob/cfcffb90e69f37bf2ff1e988237a0fbe41f33c04/clip/model.py#L324
causal_attention_mask = _create_4d_causal_attention_mask(
input_shape, hidden_states.dtype, device=hidden_states.device
)
# expand attention_mask
if attention_mask is not None:
# [bsz, seq_len] -> [bsz, 1, tgt_seq_len, src_seq_len]
attention_mask = _prepare_4d_attention_mask(
attention_mask, hidden_states.dtype
)
encoder_outputs = self.encoder(
inputs_embeds=hidden_states,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
causal_attention_mask=causal_attention_mask,
)
last_hidden_state = encoder_outputs[0]
last_hidden_state = self.final_layer_norm(last_hidden_state)
if self.eos_token_id == 2:
# The `eos_token_id` was incorrect before PR #24773: Let's keep what have been done here.
# A CLIP model with such `eos_token_id` in the config can't work correctly with extra new tokens added
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# text_embeds.shape = [batch_size, sequence_length, transformer.width]
# take features from the eot embedding (eot_token is the highest number in each sequence)
# casting to torch.int for onnx compatibility: argmax doesn't support int64 inputs with opset 14
last_hidden_state[
torch.arange(
last_hidden_state.shape[0], device=last_hidden_state.device
),
input_ids.to(dtype=torch.int, device=last_hidden_state.device).argmax(
dim=-1
),
]
else:
# The config gets updated `eos_token_id` from PR #24773 (so the use of exta new tokens is possible)
last_hidden_state[
torch.arange(
last_hidden_state.shape[0], device=last_hidden_state.device
),
# We need to get the first position of `eos_token_id` value (`pad_token_ids` might equal to `eos_token_id`)
(
input_ids.to(dtype=torch.int, device=last_hidden_state.device)
== self.eos_token_id
)
.int()
.argmax(dim=-1),
]
return last_hidden_state
class CLIPTextModel(CLIPPreTrainedModel):
config_class = CLIPTextConfig
_no_split_modules = ["CLIPTextEmbeddings", "CLIPEncoderLayer"]
def __init__(self, prefix, config: CLIPTextConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.text_model = CLIPTextTransformer(prefix, config)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
):
r"""
Returns:
Examples:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, CLIPTextModel
>>> model = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled (EOS token) states
```"""
return self.text_model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
class CLIPVisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prefix, config: CLIPVisionConfig, weights):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.embeddings = CLIPVisionEmbeddings(
prefix=f"{prefix}.embeddings", config=config, weights=weights
)
self.pre_layrnorm = nn.LayerNorm.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.pre_layrnorm", weights=weights, eps=config.layer_norm_eps
)
self.encoder = CLIPEncoder(
prefix=f"{prefix}.encoder", config=config, weights=weights
)
# self.post_layernorm = nn.LayerNorm.load(prefix=f"{prefix}.post_layernorm", weights=weights, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
def forward(
self,
pixel_values: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
):
r"""
Returns:
"""
if pixel_values is None:
raise ValueError("You have to specify pixel_values")
hidden_states = self.embeddings(pixel_values)
hidden_states = self.pre_layrnorm(hidden_states)
encoder_outputs = self.encoder(
inputs_embeds=hidden_states,
)
last_hidden_state = encoder_outputs
# pooled_output = last_hidden_state[:, 0, :]
# pooled_output = self.post_layernorm(pooled_output)
return BaseModelOutputWithPooling(
last_hidden_state=last_hidden_state,
# pooler_output=pooled_output,
# hidden_states=encoder_outputs,
)
class CLIPVisionModel(CLIPPreTrainedModel):
config_class = CLIPVisionConfig
main_input_name = "pixel_values"
_no_split_modules = ["CLIPEncoderLayer"]
def __init__(self, config: CLIPVisionConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.vision_model = CLIPVisionTransformer(config)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def get_input_embeddings(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.vision_model.embeddings.patch_embedding
def forward(
self,
pixel_values: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
):
r"""
Returns:
Examples:
```python
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPVisionModel
>>> model = CLIPVisionModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled CLS states
```"""
return self.vision_model(
pixel_values=pixel_values,
)
class CLIPModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prefix, config: CLIPConfig, weights):
super().__init__()
text_config = config.text_config
vision_config = config.vision_config
self.projection_dim = config.projection_dim
self.text_embed_dim = text_config.hidden_size
self.vision_embed_dim = vision_config.hidden_size
self.text_model = CLIPTextTransformer(text_config)
self.vision_model = CLIPVisionTransformer(vision_config)
self.visual_projection = nn.Linear(
self.vision_embed_dim, self.projection_dim, bias=False
)
self.text_projection = nn.Linear(
self.text_embed_dim, self.projection_dim, bias=False
)
self.logit_scale = nn.Parameter(
torch.tensor(self.config.logit_scale_init_value)
)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def get_text_features(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
r"""
Returns:
text_features (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, output_dim`): The text embeddings obtained by
applying the projection layer to the pooled output of [`CLIPTextModel`].
Examples:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, CLIPModel
>>> model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> inputs = tokenizer(["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
>>> text_features = model.get_text_features(**inputs)
```"""
text_outputs = self.text_model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
pooled_output = text_outputs[1]
text_features = self.text_projection(pooled_output)
return text_features
def get_image_features(
self,
pixel_values: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
r"""
Returns:
image_features (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, output_dim`): The image embeddings obtained by
applying the projection layer to the pooled output of [`CLIPVisionModel`].
Examples:
```python
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPModel
>>> model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> image_features = model.get_image_features(**inputs)
```"""
# Use CLIP model's config for some fields (if specified) instead of those of vision & text components.
vision_outputs = self.vision_model(
pixel_values=pixel_values,
)
pooled_output = vision_outputs[1] # pooled_output
image_features = self.visual_projection(pooled_output)
return image_features
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
pixel_values: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
):
r"""
Returns:
Examples:
```python
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, CLIPModel
>>> model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> inputs = processor(
... text=["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True
... )
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits_per_image = outputs.logits_per_image # this is the image-text similarity score
>>> probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1) # we can take the softmax to get the label probabilities
```"""
# Use CLIP model's config for some fields (if specified) instead of those of vision & text components.
vision_outputs = self.vision_model(
pixel_values=pixel_values,
)
text_outputs = self.text_model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
image_embeds = vision_outputs[1]
image_embeds = self.visual_projection(image_embeds)
text_embeds = text_outputs[1]
text_embeds = self.text_projection(text_embeds)
# normalized features
image_embeds = image_embeds / image_embeds.norm(p=2, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
text_embeds = text_embeds / text_embeds.norm(p=2, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
# cosine similarity as logits
logit_scale = self.logit_scale.exp()
logits_per_text = torch.matmul(text_embeds, image_embeds.t()) * logit_scale
logits_per_image = logits_per_text.t()
return logits_per_image, logits_per_text
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling/clip.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling/clip.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 13765
}
| 290
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 EleutherAI and the HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# This code is based on EleutherAI's GPT-NeoX library and the GPT-NeoX
# and OPT implementations in this library. It has been modified from its
# original forms to accommodate minor architectural differences compared
# to GPT-NeoX and OPT used by the Meta AI team that trained the model.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import torch
import torch.distributed
from torch import nn
from transformers.activations import ACT2FN
from transformers.modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
from transformers.models.gpt_neox import GPTNeoXConfig as TransformersGPTNeoXConfig
from typing import Optional, List, Tuple
from text_generation_server.layers.attention import (
paged_attention,
attention,
set_block_mapping,
Seqlen,
HPUPagedAttentionMetadata,
)
from text_generation_server.layers import (
TensorParallelRowLinear,
TensorParallelColumnLinear,
TensorParallelEmbedding,
SpeculativeHead,
get_linear,
)
from text_generation_server.layers.attention.kv_cache import get_kv_scales
from text_generation_server.layers.layernorm import (
FastLayerNorm,
)
from text_generation_server.layers.rotary import (
PositionRotaryEmbedding,
)
from text_generation_server.utils.weights import UnquantizedWeight
import habana_frameworks.torch as htorch
class GPTNeoXConfig(TransformersGPTNeoXConfig):
attribute_map = {
"num_key_value_heads": "num_attention_heads",
}
def load_row(config, prefix: str, weights, bias: bool):
weight = weights.get_weights_row(prefix)
if bias and weights.process_group.rank() == 0:
# Rank is only on the first rank process
bias = weights.get_tensor(f"{prefix}.bias")
else:
bias = None
linear = get_linear(weight, bias)
if config.use_parallel_residual:
return linear
else:
return TensorParallelRowLinear(linear, process_group=weights.process_group)
def load_qkv(config, prefix: str, weights, num_heads, head_size, hidden_size):
weight = weights.get_multi_weights_col([prefix], dim=0)
if isinstance(weight, UnquantizedWeight):
# Only on non quantized versions
weight.weight = (
weight.weight.view(
num_heads,
3,
head_size,
hidden_size,
)
.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)
.reshape(-1, hidden_size)
)
bias = weights.get_sharded(f"{prefix}.bias", dim=0)
bias = bias.view(num_heads, 3, head_size).permute(1, 0, 2).reshape(-1)
linear = get_linear(weight, bias)
if config.use_parallel_residual:
return linear
else:
return TensorParallelColumnLinear(linear)
class FlashNeoxAttention(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, prefix, weights, rotary_emb):
super().__init__()
num_heads = config.num_attention_heads
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.head_size = hidden_size // num_heads
self.rotary_dim = int(config.rotary_pct * self.head_size)
if self.num_heads % weights.process_group.size() != 0:
raise ValueError(
f"`num_heads` must be divisible by `num_shards` (got `num_heads`: {self.num_heads} "
f"and `num_shards`: {weights.process_group.size()}"
)
self.num_heads = self.num_heads // weights.process_group.size()
self.rotary_emb = rotary_emb
self.softmax_scale = self.head_size ** (-0.5)
self.query_key_value = load_qkv(
config,
prefix=f"{prefix}.query_key_value",
weights=weights,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
head_size=self.head_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
)
self.kv_scales = get_kv_scales(weights, f"{prefix}")
self.dense = load_row(
config, prefix=f"{prefix}.dense", weights=weights, bias=True
)
self.kv_head_mapping = torch.arange(
0, self.num_heads, dtype=torch.int32, device=weights.device
)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states,
cos,
sin,
cu_seqlen_prefill,
kv_cache,
slots,
seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta,
):
qkv = self.query_key_value(hidden_states)
qkv = qkv.view(-1, 3, self.num_heads, self.head_size)
# Compute rotary embeddings on rotary_ndims
query_rot = qkv[:, 0][..., : self.rotary_dim]
query_pass = qkv[:, 0][..., self.rotary_dim :]
key_rot = qkv[:, 1][..., : self.rotary_dim]
key_pass = qkv[:, 1][..., self.rotary_dim :]
# Inplace rotary
self.rotary_emb(query_rot, key_rot, cos, sin)
qkv[:, 0] = torch.cat((query_rot, query_pass), dim=-1)
qkv[:, 1] = torch.cat((key_rot, key_pass), dim=-1)
kv_cache.store(
key=qkv[:, 1],
value=qkv[:, 2],
slots=slots,
kv_scales=self.kv_scales,
)
# Prefill
if cu_seqlen_prefill is not None:
# sdpa
attn_output = attention(
query=qkv[:, 0],
key=qkv[:, 1],
value=qkv[:, 2],
kv_cache=kv_cache,
kv_scales=self.kv_scales,
seqlen=seqlen,
softmax_scale=self.softmax_scale,
)
# Decode
else:
attn_output = paged_attention(
qkv[:, 0],
kv_cache,
self.kv_head_mapping,
self.softmax_scale,
seqlen,
kv_scales=self.kv_scales,
hpu_attention_meta=hpu_attention_meta,
)
return self.dense(attn_output.view(-1, self.num_heads * self.head_size))
class FlashMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, prefix, weights):
super().__init__()
act = config.hidden_act
self.act = (
ACT2FN[act]
if "gelu" not in act
else lambda x: torch.nn.functional.gelu(
x,
approximate=(
"tanh" if act in ["gelu_fast", "gelu_pytorch_tanh"] else "none"
),
)
)
self.dense_h_to_4h = TensorParallelColumnLinear.load(
config, prefix=f"{prefix}.dense_h_to_4h", weights=weights, bias=True
)
self.dense_4h_to_h = load_row(
config, prefix=f"{prefix}.dense_4h_to_h", weights=weights, bias=True
)
def forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_states = self.dense_h_to_4h(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.act(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.dense_4h_to_h(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
class FlashNeoXLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer_id, config, weights, rotary_emb):
super().__init__()
layer_norm_eps = config.layer_norm_eps
prefix = f"gpt_neox.layers.{layer_id}"
self.use_parallel_residual = config.use_parallel_residual
self.input_layernorm = FastLayerNorm.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.input_layernorm", weights=weights, eps=layer_norm_eps
)
self.post_attention_layernorm = FastLayerNorm.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.post_attention_layernorm",
weights=weights,
eps=layer_norm_eps,
)
self.attention = FlashNeoxAttention(
config,
prefix=f"{prefix}.attention",
weights=weights,
rotary_emb=rotary_emb,
)
self.mlp = FlashMLP(config, prefix=f"{prefix}.mlp", weights=weights)
self.process_group = weights.process_group
def forward(
self,
hidden_states,
residual,
cos,
sin,
cu_seqlen_prefill,
kv_cache,
slots,
seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta,
):
if self.use_parallel_residual:
ln1_hidden_states, _ = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
attn_output = self.attention(
ln1_hidden_states,
cos,
sin,
cu_seqlen_prefill,
kv_cache,
slots,
seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta,
)
ln2_hidden_states, _ = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states)
mlp_output = self.mlp(ln2_hidden_states)
intermediate = mlp_output + attn_output
if self.process_group.size() > 1:
torch.distributed.all_reduce(intermediate, group=self.process_group)
return intermediate + hidden_states, None
else:
hidden_states, residual = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states, residual)
hidden_states = self.attention(
hidden_states,
cos,
sin,
cu_seqlen_prefill,
kv_cache,
slots,
seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta,
)
hidden_states, residual = self.post_attention_layernorm(
hidden_states, residual
)
mlp_output = self.mlp(hidden_states)
return mlp_output, residual
class FlashGPTNeoXPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
config_class = GPTNeoXConfig
base_model_prefix = "gpt_neox"
supports_gradient_checkpointing = False
_no_split_modules = None
class FlashGPTNeoXModel(FlashGPTNeoXPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, prefix: str, config, weights):
super().__init__(config)
self.config = config
self.embed_in = TensorParallelEmbedding(
prefix=f"{prefix}.embed_in", weights=weights
)
rotary_emb = PositionRotaryEmbedding.static(
config=config,
dim=int(
config.rotary_pct * (config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads)
),
base=config.rotary_emb_base,
device=weights.device,
)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[
FlashNeoXLayer(layer_id, config, weights, rotary_emb)
for layer_id in range(config.num_hidden_layers)
]
)
self.final_layer_norm = FastLayerNorm.load(
prefix=f"{prefix}.final_layer_norm",
weights=weights,
eps=config.layer_norm_eps,
)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
self.head_size = self.layers[0].attention.head_size
self.num_heads = self.layers[0].attention.num_heads
def forward(
self,
input_ids: torch.Tensor,
position_ids: torch.Tensor,
cu_seqlen_prefill: Optional[torch.Tensor],
kv_cache: List[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]],
slots: torch.Tensor,
seqlen: Seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta: Optional[HPUPagedAttentionMetadata],
) -> torch.Tensor:
if hpu_attention_meta is not None:
hpu_attention_meta = set_block_mapping(
hpu_attention_meta, input_ids.shape[0]
)
hidden_states = self.embed_in(input_ids)
# Get rotary cos and sin for this forward
# Avoid to index in each layer
cos, sin = self.layers[0].attention.rotary_emb.get_cos_sin(position_ids)
residual = None
lazy_mode = htorch.utils.internal.is_lazy()
if lazy_mode:
htorch.core.mark_step()
for i, layer in enumerate(self.layers):
hidden_states, residual = layer(
hidden_states,
residual,
cos,
sin,
cu_seqlen_prefill,
kv_cache[i],
slots,
seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta,
)
if lazy_mode:
htorch.core.mark_step()
hidden_states, _ = self.final_layer_norm(hidden_states, residual)
return hidden_states
class FlashGPTNeoXForCausalLM(FlashGPTNeoXPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, prefix, config, weights):
super().__init__(config)
if not prefix:
prefix = "gpt_neox"
else:
prefix = f"{prefix}.gpt_neox"
self.gpt_neox = FlashGPTNeoXModel(prefix, config, weights)
self.embed_out = SpeculativeHead.load(
config, prefix="embed_out", weights=weights
)
def forward(
self,
input_ids: torch.Tensor,
position_ids: torch.Tensor,
cu_seqlen_prefill: Optional[torch.Tensor],
kv_cache: List[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]],
slots: torch.Tensor,
seqlen: Seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta: Optional[HPUPagedAttentionMetadata],
lm_head_indices: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
adapter_data: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> torch.Tensor:
hidden_states = self.gpt_neox(
input_ids,
position_ids,
cu_seqlen_prefill,
kv_cache,
slots,
seqlen,
hpu_attention_meta,
)
if lm_head_indices is not None:
hidden_states = hidden_states[lm_head_indices]
logits = self.embed_out(hidden_states)
return logits
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling/flash_neox_modeling.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling/flash_neox_modeling.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 6849
}
| 291
|
def load_text_model(prefix, config, weights, name=None):
if config.model_type == "llama":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.flash_llama_modeling import (
FlashLlamaForCausalLM,
)
return FlashLlamaForCausalLM(prefix, config, weights, name=name)
elif config.model_type == "mistral":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.flash_mistral_modeling import (
FlashMistralForCausalLM,
)
return FlashMistralForCausalLM(prefix, config, weights, name=name)
elif config.model_type == "gemma":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.flash_gemma_modeling import (
FlashGemmaForCausalLM,
)
return FlashGemmaForCausalLM(prefix, config, weights)
elif config.model_type == "gemma2":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.flash_gemma2_modeling import (
FlashGemma2ForCausalLM,
)
return FlashGemma2ForCausalLM(prefix, config, weights)
elif config.model_type == "gemma3" or config.model_type == "gemma3_text":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.flash_gemma3_modeling import (
FlashGemma3ForCausalLM,
)
return FlashGemma3ForCausalLM(prefix, config, weights)
elif config.model_type == "paligemma":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.flash_gemma_modeling import (
FlashGemmaForCausalLM,
)
return FlashGemmaForCausalLM(prefix, config, weights)
else:
raise RuntimeError(f"Unsupported model type {config.model_type}")
def load_vision_model(prefix, config, weights):
if config.model_type == "clip_vision_model":
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.clip import (
CLIPVisionTransformer,
)
return CLIPVisionTransformer(
prefix=f"{prefix}.vision_model", config=config, weights=weights
)
if (
config.model_type == "siglip_vision_model"
or config.model_type == "gemma3_vision"
):
from text_generation_server.models.custom_modeling.siglip import (
SiglipVisionTransformer,
)
# TODO: ensure that using the prefix doesn't break any existing models
# that rely on the old prefix (update the old models if necessary)
return SiglipVisionTransformer(
prefix=f"{prefix}.vision_model",
config=config,
weights=weights,
)
else:
raise RuntimeError(f"Unsupported model type {config.model_type}")
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling/vlm.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling/vlm.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 1091
}
| 292
|
import os
import torch
from torch.distributed import ProcessGroup
from datetime import timedelta
from loguru import logger
# Tensor Parallelism settings
RANK = int(os.getenv("RANK", "0"))
WORLD_SIZE = int(os.getenv("WORLD_SIZE", "1"))
MEMORY_FRACTION = float(os.getenv("HPU_MEMORY_FRACTION", "0.8"))
class FakeBarrier:
def wait(self):
pass
class FakeGroup(ProcessGroup):
def __init__(self, rank, size):
self._rank = rank
self._size = size
super().__init__(rank, size)
def allreduce(self, *args, **kwargs):
return FakeBarrier()
def allgather(self, inputs, local_tensor, **kwargs):
assert (
len(inputs[0]) == len(local_tensor) == 1
), f"{len(inputs[0])} != {len(local_tensor)} != 1, and the FakeGroup is supposed to join on simple tensors"
for input_ in inputs:
input_[0].data = local_tensor[0].data
return FakeBarrier()
def barrier(self, *args, **kwargs):
return FakeBarrier()
def size(self):
return self._size
def rank(self):
return self._rank
def _get_backend_name(self):
return "fake"
def initialize_torch_distributed():
if WORLD_SIZE == 1:
return FakeGroup(RANK, WORLD_SIZE), RANK, WORLD_SIZE
else:
if os.getenv("DEBUG", None) == "1":
return FakeGroup(RANK, WORLD_SIZE), RANK, WORLD_SIZE
if not torch.distributed.is_initialized():
# Call the init process.
torch.distributed.init_process_group(
backend="hccl",
world_size=WORLD_SIZE,
rank=RANK,
timeout=timedelta(seconds=120),
)
else:
logger.warning("torch.distributed is already initialized.")
return torch.distributed.group.WORLD, RANK, WORLD_SIZE
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/utils/dist.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/utils/dist.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 817
}
| 293
|
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 Authors of "A Watermark for Large Language Models"
# available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10226
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os
import torch
from transformers import LogitsProcessor
from typing import List, Union
GAMMA = float(os.getenv("WATERMARK_GAMMA", 0.5))
DELTA = float(os.getenv("WATERMARK_DELTA", 2.0))
class WatermarkLogitsProcessor(LogitsProcessor):
def __init__(
self,
gamma: float = GAMMA,
delta: float = DELTA,
hash_key: int = 15485863, # just a large prime number to create a rng seed with sufficient bit width
device: str = "cpu",
):
# watermarking parameters
self.gamma = gamma
self.delta = delta
self.rng = torch.Generator(device="cpu")
self.hash_key = hash_key
def _seed_rng(self, input_ids: Union[List[int], torch.LongTensor]):
if isinstance(input_ids, list):
assert (
len(input_ids) >= 1
), "requires at least a 1 token prefix sequence to seed rng"
prev_token = input_ids[-1]
else:
assert len(input_ids) == 1
input_ids = input_ids[0]
assert (
input_ids.shape[-1] >= 1
), "requires at least a 1 token prefix sequence to seed rng"
prev_token = input_ids[-1].item()
self.rng.manual_seed(self.hash_key * prev_token)
def _get_greenlist_ids(
self,
input_ids: Union[List[int], torch.LongTensor],
max_value: int,
device: torch.device,
) -> List[int]:
# seed the rng using the previous tokens/prefix
self._seed_rng(input_ids)
greenlist_size = int(max_value * self.gamma)
vocab_permutation = torch.randperm(max_value, device=device, generator=self.rng)
greenlist_ids = vocab_permutation[:greenlist_size]
return greenlist_ids
@staticmethod
def _calc_greenlist_mask(
scores: torch.FloatTensor, greenlist_token_ids
) -> torch.BoolTensor:
green_tokens_mask = torch.zeros_like(scores)
green_tokens_mask[-1, greenlist_token_ids] = 1
final_mask = green_tokens_mask.bool()
return final_mask
@staticmethod
def _bias_greenlist_logits(
scores: torch.Tensor, greenlist_mask: torch.Tensor, greenlist_bias: float
) -> torch.Tensor:
scores[greenlist_mask] = scores[greenlist_mask] + greenlist_bias
return scores
def __call__(
self, input_ids: Union[List[int], torch.LongTensor], scores: torch.FloatTensor
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
greenlist_ids = self._get_greenlist_ids(
input_ids, scores.shape[-1], scores.device
)
green_tokens_mask = self._calc_greenlist_mask(
scores=scores, greenlist_token_ids=greenlist_ids
)
scores = self._bias_greenlist_logits(
scores=scores, greenlist_mask=green_tokens_mask, greenlist_bias=self.delta
)
return scores
|
text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/utils/watermark.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/gaudi/server/text_generation_server/utils/watermark.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 1489
}
| 294
|
import os
import pytest
from text_generation_server.generator import NeuronGenerator
from text_generation_server.model import fetch_model, is_cached
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def cached_model_id(neuron_model_config) -> str:
"""
Fixture to provide a cached model ID for testing.
This assumes the model is already cached in the local environment.
"""
export_kwargs = neuron_model_config["export_kwargs"]
os.environ["MAX_BATCH_SIZE"] = str(export_kwargs["batch_size"])
os.environ["MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS"] = str(export_kwargs["sequence_length"])
os.environ["HF_AUTO_CAST_TYPE"] = export_kwargs["auto_cast_type"]
os.environ["HF_NUM_CORES"] = str(export_kwargs["num_cores"])
yield neuron_model_config["model_id"]
os.environ.pop("MAX_BATCH_SIZE", None)
os.environ.pop("MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS", None)
os.environ.pop("HF_AUTO_CAST_TYPE", None)
os.environ.pop("HF_NUM_CORES", None)
def test_model_is_cached(cached_model_id):
assert is_cached(cached_model_id), f"Model {cached_model_id} is not cached"
def test_fetch_cached_model(cached_model_id: str):
model_path = fetch_model(cached_model_id)
assert os.path.exists(
model_path
), f"Model {cached_model_id} was not fetched successfully"
assert os.path.isdir(model_path), f"Model {cached_model_id} is not a directory"
def test_generator_from_cached_model(cached_model_id: str):
generator = NeuronGenerator.from_pretrained(model_id=cached_model_id)
assert generator is not None, "Generator could not be created from cached model"
assert generator.model is not None, "Generator model is not initialized"
assert generator.tokenizer is not None, "Generator tokenizer is not initialized"
|
text-generation-inference/backends/neuron/tests/server/test_cached_model.py/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/neuron/tests/server/test_cached_model.py",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 635
}
| 295
|
use clap::{Parser, Subcommand};
use text_generation_router::{server, usage_stats};
use text_generation_router_v3::{connect_backend, V3Error};
use thiserror::Error;
/// App Configuration
#[derive(Parser, Debug)]
#[clap(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Args {
#[command(subcommand)]
command: Option<Commands>,
#[clap(default_value = "128", long, env)]
max_concurrent_requests: usize,
#[clap(default_value = "2", long, env)]
max_best_of: usize,
#[clap(default_value = "4", long, env)]
max_stop_sequences: usize,
#[clap(default_value = "5", long, env)]
max_top_n_tokens: u32,
#[clap(long, env)]
max_input_tokens: Option<usize>,
#[clap(long, env)]
max_total_tokens: Option<usize>,
#[clap(default_value = "1.2", long, env)]
waiting_served_ratio: f32,
#[clap(default_value = "4096", long, env)]
max_batch_prefill_tokens: u32,
#[clap(long, env)]
max_batch_total_tokens: Option<u32>,
#[clap(default_value = "20", long, env)]
max_waiting_tokens: usize,
#[clap(long, env)]
max_batch_size: Option<usize>,
#[clap(default_value = "0.0.0.0", long, env)]
hostname: String,
#[clap(default_value = "3000", long, short, env)]
port: u16,
#[clap(default_value = "9000", long, short, env)]
prometheus_port: u16,
#[clap(default_value = "/tmp/text-generation-server-0", long, env)]
master_shard_uds_path: String,
#[clap(default_value = "bigscience/bloom", long, env)]
tokenizer_name: String,
#[clap(long, env)]
tokenizer_config_path: Option<String>,
#[clap(long, env)]
revision: Option<String>,
#[clap(long, env, value_enum)]
trust_remote_code: bool,
#[clap(default_value = "2", long, env)]
validation_workers: usize,
#[clap(long, env)]
api_key: Option<String>,
#[clap(long, env)]
json_output: bool,
#[clap(long, env)]
otlp_endpoint: Option<String>,
#[clap(default_value = "text-generation-inference.router", long, env)]
otlp_service_name: String,
#[clap(long, env)]
cors_allow_origin: Option<Vec<String>>,
#[clap(long, env)]
ngrok: bool,
#[clap(long, env)]
ngrok_authtoken: Option<String>,
#[clap(long, env)]
ngrok_edge: Option<String>,
#[clap(long, env, default_value_t = false)]
disable_grammar_support: bool,
#[clap(default_value = "4", long, env)]
max_client_batch_size: usize,
#[clap(default_value = "on", long, env)]
usage_stats: usage_stats::UsageStatsLevel,
#[clap(default_value = "2000000", long, env)]
payload_limit: usize,
}
#[derive(Debug, Subcommand)]
enum Commands {
PrintSchema,
}
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), RouterError> {
// Get args
let args = Args::parse();
// Pattern match configuration
let Args {
command,
max_concurrent_requests,
max_best_of,
max_stop_sequences,
max_top_n_tokens,
max_input_tokens,
max_total_tokens,
waiting_served_ratio,
max_batch_prefill_tokens,
max_batch_total_tokens,
max_waiting_tokens,
max_batch_size,
hostname,
port,
prometheus_port,
master_shard_uds_path,
tokenizer_name,
tokenizer_config_path,
revision,
trust_remote_code,
validation_workers,
api_key,
json_output,
otlp_endpoint,
otlp_service_name,
cors_allow_origin,
ngrok,
ngrok_authtoken,
ngrok_edge,
disable_grammar_support,
max_client_batch_size,
usage_stats,
payload_limit,
} = args;
if let Some(Commands::PrintSchema) = command {
use utoipa::OpenApi;
let api_doc = text_generation_router::server::ApiDoc::openapi();
let api_doc = serde_json::to_string_pretty(&api_doc).unwrap();
println!("{}", api_doc);
std::process::exit(0);
};
text_generation_router::logging::init_logging(otlp_endpoint, otlp_service_name, json_output);
// Validate args
if validation_workers == 0 {
return Err(RouterError::ArgumentValidation(
"`validation_workers` must be > 0".to_string(),
));
}
if let Some(max_batch_size) = max_batch_size {
if max_batch_size == 0 {
return Err(RouterError::ArgumentValidation(
"`max_batch_size` must be > 0".to_string(),
));
}
}
let (backend, backend_info) = connect_backend(
max_input_tokens,
max_total_tokens,
master_shard_uds_path,
waiting_served_ratio,
max_batch_prefill_tokens,
max_batch_total_tokens,
max_waiting_tokens,
max_batch_size,
)
.await?;
// Validate remaining args now that the backend is known
let support_chunking = backend_info.support_chunking;
let max_batch_total_tokens = backend_info.max_batch_total_tokens;
if max_input_tokens.is_none() {
tracing::info!(
"Maximum input tokens defaulted to {}",
backend_info.max_input_tokens
);
}
if max_total_tokens.is_none() {
tracing::info!(
"Maximum total tokens defaulted to {}",
backend_info.max_total_tokens
);
}
let max_input_tokens = backend_info.max_input_tokens;
let max_total_tokens = backend_info.max_total_tokens;
if max_input_tokens >= max_total_tokens {
return Err(RouterError::ArgumentValidation(
"`max_input_tokens` must be < `max_total_tokens`".to_string(),
));
}
if max_input_tokens as u32 > max_batch_prefill_tokens && !support_chunking {
return Err(RouterError::ArgumentValidation(format!("`max_batch_prefill_tokens` must be >= `max_input_tokens`. Given: {max_batch_prefill_tokens} and {max_input_tokens}")));
}
if max_batch_prefill_tokens > max_batch_total_tokens {
return Err(RouterError::ArgumentValidation(format!("`max_batch_prefill_tokens` must be <= `max_batch_total_tokens`. Given: {max_batch_prefill_tokens} and {max_batch_total_tokens}")));
}
if max_total_tokens as u32 > max_batch_total_tokens {
return Err(RouterError::ArgumentValidation(format!("`max_total_tokens` must be <= `max_batch_total_tokens`. Given: {max_total_tokens} and {max_batch_total_tokens}")));
}
// Run server
server::run(
backend,
max_concurrent_requests,
max_best_of,
max_stop_sequences,
max_top_n_tokens,
max_input_tokens,
max_total_tokens,
validation_workers,
api_key,
tokenizer_name,
tokenizer_config_path,
revision,
trust_remote_code,
hostname,
port,
cors_allow_origin,
ngrok,
ngrok_authtoken,
ngrok_edge,
disable_grammar_support,
max_client_batch_size,
usage_stats,
payload_limit,
prometheus_port,
)
.await?;
Ok(())
}
#[derive(Debug, Error)]
enum RouterError {
#[error("Argument validation error: {0}")]
ArgumentValidation(String),
#[error("Backend failed: {0}")]
Backend(#[from] V3Error),
#[error("WebServer error: {0}")]
WebServer(#[from] server::WebServerError),
#[error("Tokio runtime failed to start: {0}")]
Tokio(#[from] std::io::Error),
}
|
text-generation-inference/backends/v3/src/main.rs/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/backends/v3/src/main.rs",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 3468
}
| 296
|
[tool.poetry]
name = "text-generation"
version = "0.7.0"
description = "Hugging Face Text Generation Python Client"
license = "Apache-2.0"
authors = ["Olivier Dehaene <olivier@huggingface.co>"]
maintainers = ["Olivier Dehaene <olivier@huggingface.co>"]
readme = "README.md"
homepage = "https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference"
repository = "https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference"
[tool.poetry.dependencies]
python = "^3.9"
pydantic = "> 2, < 3"
aiohttp = "^3.11"
huggingface-hub = ">= 0.12, < 1.0"
[tool.poetry.group.dev.dependencies]
pytest = "^8"
pytest-asyncio = "^0.26"
pytest-cov = "^6.0.0"
[tool.pytest.ini_options]
asyncio_mode = "auto"
[build-system]
requires = ["poetry-core>=1.0.0"]
build-backend = "poetry.core.masonry.api"
[tool.isort]
profile = "black"
|
text-generation-inference/clients/python/pyproject.toml/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/clients/python/pyproject.toml",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 344
}
| 297
|
# Text Generation Inference Architecture
This document aims at describing the architecture of Text Generation Inference (TGI), by describing the call flow between the separate components.
A high-level architecture diagram can be seen here:
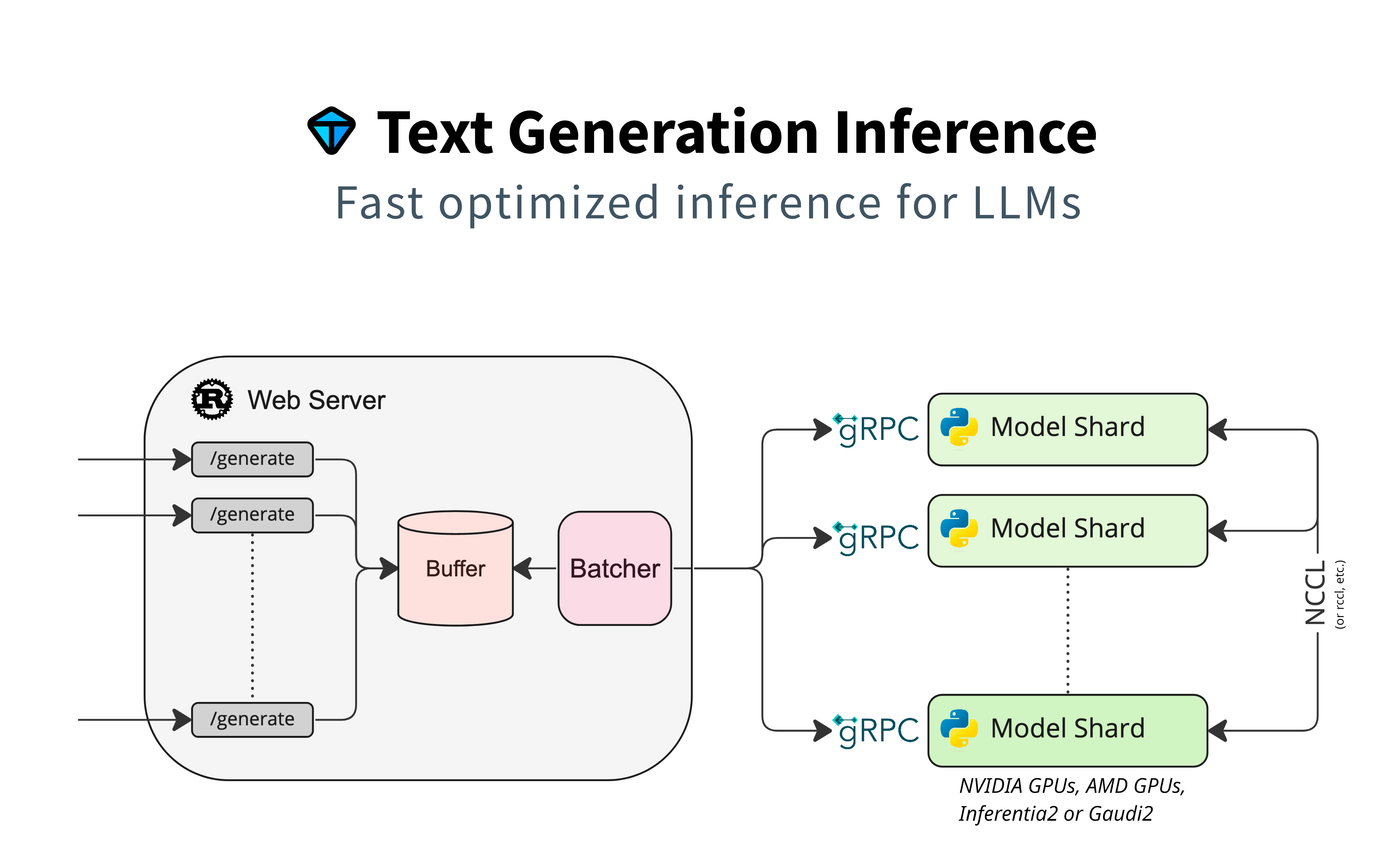
This diagram shows well there are these separate components:
- **The router**, also named `webserver`, that receives the client requests, buffers them, creates some batches, and prepares gRPC calls to a model server.
- **The launcher** is a helper that will be able to launch one or several model servers (if model is sharded), and it launches the router with the compatible arguments.
- **The model server**, responsible for receiving the gRPC requests and to process the inference on the model. If the model is sharded across multiple accelerators (e.g.: multiple GPUs), the model server shards might be synchronized via NCCL or equivalent.
Note that for other backends (eg. TRTLLM) the model server and launcher are specific to the backend.
The router and the model server can be two different machines, they do not need to be deployed together.
## The Router
This component is a rust web server binary that accepts HTTP requests using the custom [HTTP API](https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference/), as well as OpenAI's [Messages API](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/messages_api).
The router receives the API calls and handles the "baches" logic (and introduction to batching can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/router/README.md)).
It uses different strategies to reduce latency between requests and responses, especially oriented to decoding latency. It will use queues, schedulers, and block allocators to achieve that and produce batched requests that it will then be sent to the model server.
### Router's command line
The router command line will be the way to pass parameters to it (it does not rely on configuration file):
```
Text Generation Webserver
Usage: text-generation-router [OPTIONS]
Options:
--max-concurrent-requests <MAX_CONCURRENT_REQUESTS>
[env: MAX_CONCURRENT_REQUESTS=] [default: 128]
--max-best-of <MAX_BEST_OF>
[env: MAX_BEST_OF=] [default: 2]
--max-stop-sequences <MAX_STOP_SEQUENCES>
[env: MAX_STOP_SEQUENCES=] [default: 4]
--max-top-n-tokens <MAX_TOP_N_TOKENS>
[env: MAX_TOP_N_TOKENS=] [default: 5]
--max-input-tokens <MAX_INPUT_TOKENS>
[env: MAX_INPUT_TOKENS=] [default: 1024]
--max-total-tokens <MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS>
[env: MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS=] [default: 2048]
--waiting-served-ratio <WAITING_SERVED_RATIO>
[env: WAITING_SERVED_RATIO=] [default: 1.2]
--max-batch-prefill-tokens <MAX_BATCH_PREFILL_TOKENS>
[env: MAX_BATCH_PREFILL_TOKENS=] [default: 4096]
--max-batch-total-tokens <MAX_BATCH_TOTAL_TOKENS>
[env: MAX_BATCH_TOTAL_TOKENS=]
--max-waiting-tokens <MAX_WAITING_TOKENS>
[env: MAX_WAITING_TOKENS=] [default: 20]
--max-batch-size <MAX_BATCH_SIZE>
[env: MAX_BATCH_SIZE=]
--hostname <HOSTNAME>
[env: HOSTNAME=] [default: 0.0.0.0]
-p, --port <PORT>
[env: PORT=] [default: 3000]
--master-shard-uds-path <MASTER_SHARD_UDS_PATH>
[env: MASTER_SHARD_UDS_PATH=] [default: /tmp/text-generation-server-0]
--tokenizer-name <TOKENIZER_NAME>
[env: TOKENIZER_NAME=] [default: bigscience/bloom]
--tokenizer-config-path <TOKENIZER_CONFIG_PATH>
[env: TOKENIZER_CONFIG_PATH=]
--revision <REVISION>
[env: REVISION=]
--validation-workers <VALIDATION_WORKERS>
[env: VALIDATION_WORKERS=] [default: 2]
--json-output
[env: JSON_OUTPUT=]
--otlp-endpoint <OTLP_ENDPOINT>
[env: OTLP_ENDPOINT=]
--otlp-service-name <OTLP_SERVICE_NAME>
[env: OTLP_SERVICE_NAME=]
--cors-allow-origin <CORS_ALLOW_ORIGIN>
[env: CORS_ALLOW_ORIGIN=]
--ngrok
[env: NGROK=]
--ngrok-authtoken <NGROK_AUTHTOKEN>
[env: NGROK_AUTHTOKEN=]
--ngrok-edge <NGROK_EDGE>
[env: NGROK_EDGE=]
--messages-api-enabled
[env: MESSAGES_API_ENABLED=]
--disable-grammar-support
[env: DISABLE_GRAMMAR_SUPPORT=]
--max-client-batch-size <MAX_CLIENT_BATCH_SIZE>
[env: MAX_CLIENT_BATCH_SIZE=] [default: 4]
-h, --help
Print help
-V, --version
Print version
```
## The Model Server
The model server is a python server, capable of starting a server waiting for gRPC requests, loads a given model, perform sharding to provide [tensor parallelism](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/tensor_parallelism), and stays alive while waiting for new requests.
The model server supports models instantiated using Pytorch and optimized for inference mainly on CUDA/ROCM.
### Model Server Variants
Several variants of the model server exist that are actively supported by Hugging Face:
- By default, the model server will attempt building [a server optimized for Nvidia GPUs with CUDA](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/installation_nvidia). The code for this version is hosted in the [main TGI repository](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference).
- A [version optimized for AMD with ROCm](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/installation_amd) is hosted in the main TGI repository. Some model features differ.
- A [version optimized for Intel GPUs](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/installation_intel) is hosted in the main TGI repository. Some model features differ.
- The [version for Intel Gaudi](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/installation_gaudi) is maintained on a forked repository, often resynchronized with the main [TGI repository](https://github.com/huggingface/tgi-gaudi).
- A [version for Neuron (AWS Inferentia2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/installation_inferentia) is maintained in the main TGI repository. Some model features differ.
- A version for Google TPUs is maintained as part of [Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu/tree/main/text-generation-inference).
Not all variants provide the same features, as hardware and middleware capabilities do not provide the same optimizations.
### Command Line Interface
The official command line interface (CLI) for the server supports three subcommands, `download-weights`, `quantize` and `serve`:
- `download-weights` will download weights from the hub and, in some variants it will convert weights to a format that is adapted to the given implementation;
- `quantize` will allow to quantize a model using the `qptq` package. This feature is not available nor supported on all variants;
- `serve` will start the server that load a model (or a model shard), receives gRPC calls from the router, performs an inference and provides a formatted response to the given request.
Serve's command line parameters on the TGI repository are these:
```
Usage: cli.py serve [OPTIONS] MODEL_ID
╭─ Arguments ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ * model_id TEXT [default: None] [required] │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ --revision TEXT [default: None] │
│ --sharded --no-sharded [default: no-sharded] │
│ --quantize [bitsandbytes|bitsandbytes [default: None] │
│ -nf4|bitsandbytes-fp4|gptq │
│ |awq|eetq|exl2|fp8] │
│ --speculate INTEGER [default: None] │
│ --dtype [float16|bfloat16] [default: None] │
│ --trust-remote-code --no-trust-remote-code [default: │
│ no-trust-remote-code] │
│ --uds-path PATH [default: │
│ /tmp/text-generation-serve… │
│ --logger-level TEXT [default: INFO] │
│ --json-output --no-json-output [default: no-json-output] │
│ --otlp-endpoint TEXT [default: None] │
│ --otlp-service-name TEXT [default: │
│ text-generation-inference...│
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
```
Note that some variants might support different parameters, and they could possibly accept more options that can be passed on using environment variables.
## Call Flow
Once both components are initialized, weights downloaded and model server is up and running, router and model server exchange data and info through the gRPC call. There are currently two supported schemas, [v2](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/proto/generate.proto) and [v3](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/proto/v3/generate.proto). These two versions are almost identical, except for:
- input chunks support, for text and image data,
- paged attention support
Here's a diagram that displays the exchanges that follow the router and model server startup.
```mermaid
sequenceDiagram
Router->>Model Server: service discovery
Model Server-->>Router: urls for other shards
Router->>Model Server: get model info
Model Server-->>Router: shard info
Router->>Model Server: health check
Model Server-->>Router: health OK
Router->>Model Server: warmup(max_input_tokens, max_batch_prefill_tokens, max_total_tokens, max_batch_size)
Model Server-->>Router: warmup result
```
After these are done, the router is ready to receive generate calls from multiple clients. Here's an example.
```mermaid
sequenceDiagram
participant Client 1
participant Client 2
participant Client 3
participant Router
participant Model Server
Client 1->>Router: generate_stream
Router->>Model Server: prefill(batch1)
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch1, timings
Router-->>Client 1: token 1
Router->>Model Server: decode(cached_batch1)
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch1, timings
Router-->>Client 1: token 2
Router->>Model Server: decode(cached_batch1)
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch1, timings
Router-->>Client 1: token 3
Client 2->>Router: generate_stream
Router->>Model Server: prefill(batch2)
Note right of Model Server: This stops previous batch, that is restarted
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch2, timings
Router-->>Client 2: token 1'
Router->>Model Server: decode(cached_batch1, cached_batch2)
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch1, timings
Router-->>Client 1: token 4
Router-->>Client 2: token 2'
Note left of Client 1: Client 1 leaves
Router->>Model Server: filter_batch(cached_batch1, request_ids_to_keep=batch2)
Model Server-->>Router: filtered batch
Router->>Model Server: decode(cached_batch2)
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch2, timings
Router-->>Client 2: token 3'
Client 3->>Router: generate_stream
Note right of Model Server: This stops previous batch, that is restarted
Router->>Model Server: prefill(batch3)
Note left of Client 1: Client 3 leaves without receiving any batch
Router->>Model Server: clear_cache(batch3)
Note right of Model Server: This stops previous batch, that is restarted
Router->>Model Server: decode(cached_batch3)
Note right of Model Server: Last token (stopping criteria)
Model Server-->>Router: generations, cached_batch3, timings
Router-->>Client 2: token 4'
```
|
text-generation-inference/docs/source/architecture.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/docs/source/architecture.md",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 5182
}
| 298
|
# External Resources
- Adyen wrote a detailed article about the interplay between TGI's main components: router and server.
[LLM inference at scale with TGI (Martin Iglesias Goyanes - Adyen, 2024)](https://www.adyen.com/knowledge-hub/llm-inference-at-scale-with-tgi)
|
text-generation-inference/docs/source/conceptual/external.md/0
|
{
"file_path": "text-generation-inference/docs/source/conceptual/external.md",
"repo_id": "text-generation-inference",
"token_count": 83
}
| 299
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.