question
large_stringlengths 265
13.2k
|
|---|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Mishka is trying really hard to avoid being kicked out of the university. In particular, he was doing absolutely nothing for the whole semester, miraculously passed some exams so that just one is left.
There were $n$ classes of that subject during the semester and on $i$-th class professor mentioned some non-negative integer $a_i$ to the students. It turned out, the exam was to tell the whole sequence back to the professor.
Sounds easy enough for those who attended every class, doesn't it?
Obviously Mishka didn't attend any classes. However, professor left some clues on the values of $a$ to help out students like Mishka: $a$ was sorted in non-decreasing order ($a_1 \le a_2 \le \dots \le a_n$); $n$ was even; the following sequence $b$, consisting of $\frac n 2$ elements, was formed and given out to students: $b_i = a_i + a_{n - i + 1}$.
Professor also mentioned that any sequence $a$, which produces sequence $b$ with the presented technique, will be acceptable.
Help Mishka to pass that last exam. Restore any sorted sequence $a$ of non-negative integers, which produces sequence $b$ with the presented technique. It is guaranteed that there exists at least one correct sequence $a$, which produces the given sequence $b$.
-----Input-----
The first line contains a single integer $n$ ($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the length of sequence $a$. $n$ is always even.
The second line contains $\frac n 2$ integers $b_1, b_2, \dots, b_{\frac n 2}$ ($0 \le b_i \le 10^{18}$) — sequence $b$, where $b_i = a_i + a_{n - i + 1}$.
It is guaranteed that there exists at least one correct sequence $a$, which produces the given sequence $b$.
-----Output-----
Print $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($0 \le a_i \le 10^{18}$) in a single line.
$a_1 \le a_2 \le \dots \le a_n$ should be satisfied.
$b_i = a_i + a_{n - i + 1}$ should be satisfied for all valid $i$.
-----Examples-----
Input
4
5 6
Output
2 3 3 3
Input
6
2 1 2
Output
0 0 1 1 1 2
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Alice and Bob are playing a fun game of tree tag.
The game is played on a tree of n vertices numbered from 1 to n. Recall that a tree on n vertices is an undirected, connected graph with n-1 edges.
Initially, Alice is located at vertex a, and Bob at vertex b. They take turns alternately, and Alice makes the first move. In a move, Alice can jump to a vertex with distance at most da from the current vertex. And in a move, Bob can jump to a vertex with distance at most db from the current vertex. The distance between two vertices is defined as the number of edges on the unique simple path between them. In particular, either player is allowed to stay at the same vertex in a move. Note that when performing a move, a player only occupies the starting and ending vertices of their move, not the vertices between them.
If after at most 10^{100} moves, Alice and Bob occupy the same vertex, then Alice is declared the winner. Otherwise, Bob wins.
Determine the winner if both players play optimally.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1 ≤ t ≤ 10^4). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains five integers n,a,b,da,db (2≤ n≤ 10^5, 1≤ a,b≤ n, a≠ b, 1≤ da,db≤ n-1) — the number of vertices, Alice's vertex, Bob's vertex, Alice's maximum jumping distance, and Bob's maximum jumping distance, respectively.
The following n-1 lines describe the edges of the tree. The i-th of these lines contains two integers u, v (1≤ u, v≤ n, u≠ v), denoting an edge between vertices u and v. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree structure.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n across all test cases does not exceed 10^5.
Output
For each test case, output a single line containing the winner of the game: "Alice" or "Bob".
Example
Input
4
4 3 2 1 2
1 2
1 3
1 4
6 6 1 2 5
1 2
6 5
2 3
3 4
4 5
9 3 9 2 5
1 2
1 6
1 9
1 3
9 5
7 9
4 8
4 3
11 8 11 3 3
1 2
11 9
4 9
6 5
2 10
3 2
5 9
8 3
7 4
7 10
Output
Alice
Bob
Alice
Alice
Note
In the first test case, Alice can win by moving to vertex 1. Then wherever Bob moves next, Alice will be able to move to the same vertex on the next move.
<image>
In the second test case, Bob has the following strategy to win. Wherever Alice moves, Bob will always move to whichever of the two vertices 1 or 6 is farthest from Alice.
<image>
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
During their New Year holidays, Alice and Bob play the following game using an array $a$ of $n$ integers:
Players take turns, Alice moves first.
Each turn a player chooses any element and removes it from the array.
If Alice chooses even value, then she adds it to her score. If the chosen value is odd, Alice's score does not change.
Similarly, if Bob chooses odd value, then he adds it to his score. If the chosen value is even, then Bob's score does not change.
If there are no numbers left in the array, then the game ends. The player with the highest score wins. If the scores of the players are equal, then a draw is declared.
For example, if $n = 4$ and $a = [5, 2, 7, 3]$, then the game could go as follows (there are other options):
On the first move, Alice chooses $2$ and get two points. Her score is now $2$. The array $a$ is now $[5, 7, 3]$.
On the second move, Bob chooses $5$ and get five points. His score is now $5$. The array $a$ is now $[7, 3]$.
On the third move, Alice chooses $7$ and get no points. Her score is now $2$. The array $a$ is now $[3]$.
On the last move, Bob chooses $3$ and get three points. His score is now $8$. The array $a$ is empty now.
Since Bob has more points at the end of the game, he is the winner.
You want to find out who will win if both players play optimally. Note that there may be duplicate numbers in the array.
-----Input-----
The first line contains an integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$) — the number of test cases. Then $t$ test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains an integer $n$ ($1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of elements in the array $a$.
The next line contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le 10^9$) — the array $a$ used to play the game.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ over all test cases does not exceed $2 \cdot 10^5$.
-----Output-----
For each test case, output on a separate line:
"Alice" if Alice wins with the optimal play;
"Bob" if Bob wins with the optimal play;
"Tie", if a tie is declared during the optimal play.
-----Examples-----
Input
4
4
5 2 7 3
3
3 2 1
4
2 2 2 2
2
7 8
Output
Bob
Tie
Alice
Alice
-----Note-----
None
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
problem
AOR Ika wants to create a strong password that consists only of lowercase letters. AOR Ika-chan, who was given an example of $ N $ of dangerous passwords by a friend, decided to create a password that meets all of the following conditions.
1. The length is at least one character.
2. Different from any contiguous substring of any dangerous password.
3. This is the shortest character string that meets the conditions 1 and 2.
4. This is the character string that comes to the beginning when arranged in lexicographic order while satisfying the conditions 1, 2, and 3.
Write a program to generate a strong password on behalf of AOR Ika-chan.
input
Input is given from standard input in the following format.
$ N $
$ S_1 $
$ \ vdots $
$ S_N $
* The first line is given the integer $ N $, which represents the number of strings.
* The string $ S_i $ is given to the $ N $ line from the second line.
* $ | S_i | $ is the length of the string, which is one or more characters.
* Satisfy $ 1 \ le N \ le 100,000 $.
* $ 1 \ le \ sum_ {1 \ le i \ le N} | S_i | \ le 400,000 $.
* The string contains only lowercase letters.
output
Print the answer in one line. Also, output a line break at the end.
Example
Input
5
password
login
admin
root
master
Output
b
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
A factory produces thimbles in bulk. Typically, it can produce up to a thimbles a day. However, some of the machinery is defective, so it can currently only produce b thimbles each day. The factory intends to choose a k-day period to do maintenance and construction; it cannot produce any thimbles during this time, but will be restored to its full production of a thimbles per day after the k days are complete.
Initially, no orders are pending. The factory receives updates of the form di, ai, indicating that ai new orders have been placed for the di-th day. Each order requires a single thimble to be produced on precisely the specified day. The factory may opt to fill as many or as few of the orders in a single batch as it likes.
As orders come in, the factory owner would like to know the maximum number of orders he will be able to fill if he starts repairs on a given day pi. Help the owner answer his questions.
Input
The first line contains five integers n, k, a, b, and q (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ b < a ≤ 10 000, 1 ≤ q ≤ 200 000) — the number of days, the length of the repair time, the production rates of the factory, and the number of updates, respectively.
The next q lines contain the descriptions of the queries. Each query is of one of the following two forms:
* 1 di ai (1 ≤ di ≤ n, 1 ≤ ai ≤ 10 000), representing an update of ai orders on day di, or
* 2 pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ n - k + 1), representing a question: at the moment, how many orders could be filled if the factory decided to commence repairs on day pi?
It's guaranteed that the input will contain at least one query of the second type.
Output
For each query of the second type, print a line containing a single integer — the maximum number of orders that the factory can fill over all n days.
Examples
Input
5 2 2 1 8
1 1 2
1 5 3
1 2 1
2 2
1 4 2
1 3 2
2 1
2 3
Output
3
6
4
Input
5 4 10 1 6
1 1 5
1 5 5
1 3 2
1 5 2
2 1
2 2
Output
7
1
Note
Consider the first sample.
We produce up to 1 thimble a day currently and will produce up to 2 thimbles a day after repairs. Repairs take 2 days.
For the first question, we are able to fill 1 order on day 1, no orders on days 2 and 3 since we are repairing, no orders on day 4 since no thimbles have been ordered for that day, and 2 orders for day 5 since we are limited to our production capacity, for a total of 3 orders filled.
For the third question, we are able to fill 1 order on day 1, 1 order on day 2, and 2 orders on day 5, for a total of 4 orders.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Let's play the game using a bag containing several cards with integers written on it. In each game, participants first declare one of their favorite number n. Then, take out an appropriate number of cards from the bag at a time, and if the sum of the numbers written on those cards is equal to n, you will receive a luxurious prize. After each game, the cards will be returned to the bag.
Create a program that inputs the information of m types of cards in the bag and the number declared by the participants in g games, and outputs how many combinations of cards can receive luxury products in each game. please.
Input
A sequence of multiple datasets is given as input. The end of the input is indicated by a single line of zeros. Each dataset is given in the following format:
m
a1 b1
a2 b2
::
am bm
g
n1
n2
::
ng
The number of card types m (1 ≤ m ≤ 7) on the first line, the integer ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100) written on the i-type card on the following m line, and the number bi (1 ≤ bi ≤ 10) Are given with a space delimiter.
The next line is given the number of games g (1 ≤ g ≤ 10), and the next g line is given the integer ni (1 ≤ ni ≤ 1,000) declared in game i.
The number of datasets does not exceed 100.
Output
For each input dataset, the i line prints the number of card combinations that will give you a gorgeous prize in Game i.
Example
Input
5
1 10
5 3
10 3
25 2
50 2
4
120
500
100
168
7
1 10
3 10
5 10
10 10
25 10
50 10
100 10
3
452
574
787
0
Output
16
0
12
7
9789
13658
17466
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Three friends are going to meet each other. Initially, the first friend stays at the position $x = a$, the second friend stays at the position $x = b$ and the third friend stays at the position $x = c$ on the coordinate axis $Ox$.
In one minute each friend independently from other friends can change the position $x$ by $1$ to the left or by $1$ to the right (i.e. set $x := x - 1$ or $x := x + 1$) or even don't change it.
Let's introduce the total pairwise distance — the sum of distances between each pair of friends. Let $a'$, $b'$ and $c'$ be the final positions of the first, the second and the third friend, correspondingly. Then the total pairwise distance is $|a' - b'| + |a' - c'| + |b' - c'|$, where $|x|$ is the absolute value of $x$.
Friends are interested in the minimum total pairwise distance they can reach if they will move optimally. Each friend will move no more than once. So, more formally, they want to know the minimum total pairwise distance they can reach after one minute.
You have to answer $q$ independent test cases.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains one integer $q$ ($1 \le q \le 1000$) — the number of test cases.
The next $q$ lines describe test cases. The $i$-th test case is given as three integers $a, b$ and $c$ ($1 \le a, b, c \le 10^9$) — initial positions of the first, second and third friend correspondingly. The positions of friends can be equal.
-----Output-----
For each test case print the answer on it — the minimum total pairwise distance (the minimum sum of distances between each pair of friends) if friends change their positions optimally. Each friend will move no more than once. So, more formally, you have to find the minimum total pairwise distance they can reach after one minute.
-----Example-----
Input
8
3 3 4
10 20 30
5 5 5
2 4 3
1 1000000000 1000000000
1 1000000000 999999999
3 2 5
3 2 6
Output
0
36
0
0
1999999994
1999999994
2
4
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The only difference between easy and hard versions is constraints.
The BerTV channel every day broadcasts one episode of one of the $k$ TV shows. You know the schedule for the next $n$ days: a sequence of integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le k$), where $a_i$ is the show, the episode of which will be shown in $i$-th day.
The subscription to the show is bought for the entire show (i.e. for all its episodes), for each show the subscription is bought separately.
How many minimum subscriptions do you need to buy in order to have the opportunity to watch episodes of purchased shows $d$ ($1 \le d \le n$) days in a row? In other words, you want to buy the minimum number of TV shows so that there is some segment of $d$ consecutive days in which all episodes belong to the purchased shows.
-----Input-----
The first line contains an integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10000$) — the number of test cases in the input. Then $t$ test case descriptions follow.
The first line of each test case contains three integers $n, k$ and $d$ ($1 \le n \le 2\cdot10^5$, $1 \le k \le 10^6$, $1 \le d \le n$). The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le k$), where $a_i$ is the show that is broadcasted on the $i$-th day.
It is guaranteed that the sum of the values of $n$ for all test cases in the input does not exceed $2\cdot10^5$.
-----Output-----
Print $t$ integers — the answers to the test cases in the input in the order they follow. The answer to a test case is the minimum number of TV shows for which you need to purchase a subscription so that you can watch episodes of the purchased TV shows on BerTV for $d$ consecutive days. Please note that it is permissible that you will be able to watch more than $d$ days in a row.
-----Example-----
Input
4
5 2 2
1 2 1 2 1
9 3 3
3 3 3 2 2 2 1 1 1
4 10 4
10 8 6 4
16 9 8
3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 8 9 7 9 3
Output
2
1
4
5
-----Note-----
In the first test case to have an opportunity to watch shows for two consecutive days, you need to buy a subscription on show $1$ and on show $2$. So the answer is two.
In the second test case, you can buy a subscription to any show because for each show you can find a segment of three consecutive days, consisting only of episodes of this show.
In the third test case in the unique segment of four days, you have four different shows, so you need to buy a subscription to all these four shows.
In the fourth test case, you can buy subscriptions to shows $3,5,7,8,9$, and you will be able to watch shows for the last eight days.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Let us remind you part of the rules of Codeforces. The given rules slightly simplified, use the problem statement as a formal document.
In the beginning of the round the contestants are divided into rooms. Each room contains exactly n participants. During the contest the participants are suggested to solve five problems, A, B, C, D and E. For each of these problem, depending on when the given problem was solved and whether it was solved at all, the participants receive some points. Besides, a contestant can perform hacks on other contestants. For each successful hack a contestant earns 100 points, for each unsuccessful hack a contestant loses 50 points. The number of points for every contestant is represented by the sum of points he has received from all his problems, including hacks.
You are suggested to determine the leader for some room; the leader is a participant who has maximum points.
Input
The first line contains an integer n, which is the number of contestants in the room (1 ≤ n ≤ 50). The next n lines contain the participants of a given room. The i-th line has the format of "handlei plusi minusi ai bi ci di ei" — it is the handle of a contestant, the number of successful hacks, the number of unsuccessful hacks and the number of points he has received from problems A, B, C, D, E correspondingly. The handle of each participant consists of Latin letters, digits and underscores and has the length from 1 to 20 characters. There are the following limitations imposed upon the numbers:
* 0 ≤ plusi, minusi ≤ 50;
* 150 ≤ ai ≤ 500 or ai = 0, if problem A is not solved;
* 300 ≤ bi ≤ 1000 or bi = 0, if problem B is not solved;
* 450 ≤ ci ≤ 1500 or ci = 0, if problem C is not solved;
* 600 ≤ di ≤ 2000 or di = 0, if problem D is not solved;
* 750 ≤ ei ≤ 2500 or ei = 0, if problem E is not solved.
All the numbers are integer. All the participants have different handles. It is guaranteed that there is exactly one leader in the room (i.e. there are no two participants with the maximal number of points).
Output
Print on the single line the handle of the room leader.
Examples
Input
5
Petr 3 1 490 920 1000 1200 0
tourist 2 0 490 950 1100 1400 0
Egor 7 0 480 900 950 0 1000
c00lH4x0R 0 10 150 0 0 0 0
some_participant 2 1 450 720 900 0 0
Output
tourist
Note
The number of points that each participant from the example earns, are as follows:
* Petr — 3860
* tourist — 4140
* Egor — 4030
* c00lH4x0R — - 350
* some_participant — 2220
Thus, the leader of the room is tourist.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
# Scenario
*Now that the competition gets tough it will* **_Sort out the men from the boys_** .
**_Men_** are the **_Even numbers_** and **_Boys_** are the **_odd_**  
___
# Task
**_Given_** an *array/list [] of n integers* , **_Separate_** *The even numbers from the odds* , or **_Separate_** **_the men from the boys_**  
___
# Notes
* **_Return_** *an array/list where* **_Even numbers_** **_come first then odds_**
* Since , **_Men are stronger than Boys_** , *Then* **_Even numbers_** in **_ascending order_** While **_odds in descending_** .
* **_Array/list_** size is *at least **_4_*** .
* **_Array/list_** numbers could be a *mixture of positives , negatives* .
* **_Have no fear_** , *It is guaranteed that no Zeroes will exists* . 
* **_Repetition_** of numbers in *the array/list could occur* , So **_(duplications are not included when separating)_**.
____
# Input >> Output Examples:
```
menFromBoys ({7, 3 , 14 , 17}) ==> return ({14, 17, 7, 3})
```
## **_Explanation_**:
**_Since_** , `{ 14 }` is the **_even number_** here , So it **_came first_** , **_then_** *the odds in descending order* `{17 , 7 , 3}` .
____
```
menFromBoys ({-94, -99 , -100 , -99 , -96 , -99 }) ==> return ({-100 , -96 , -94 , -99})
```
## **_Explanation_**:
* **_Since_** , `{ -100, -96 , -94 }` is the **_even numbers_** here , So it **_came first_** in *ascending order *, **_then_** *the odds in descending order* `{ -99 }`
* **_Since_** , **_(Duplications are not included when separating)_** , *then* you can see **_only one (-99)_** *was appeared in the final array/list* .
____
```
menFromBoys ({49 , 818 , -282 , 900 , 928 , 281 , -282 , -1 }) ==> return ({-282 , 818 , 900 , 928 , 281 , 49 , -1})
```
## **_Explanation_**:
* **_Since_** , `{-282 , 818 , 900 , 928 }` is the **_even numbers_** here , So it **_came first_** in *ascending order* , **_then_** *the odds in descending order* `{ 281 , 49 , -1 }`
* **_Since_** , **_(Duplications are not included when separating)_** , *then* you can see **_only one (-282)_** *was appeared in the final array/list* .
____
____
___
# [Playing with Numbers Series](https://www.codewars.com/collections/playing-with-numbers)
# [Playing With Lists/Arrays Series](https://www.codewars.com/collections/playing-with-lists-slash-arrays)
# [Bizarre Sorting-katas](https://www.codewars.com/collections/bizarre-sorting-katas)
# [For More Enjoyable Katas](http://www.codewars.com/users/MrZizoScream/authored)
___
## ALL translations are welcomed
## Enjoy Learning !!
# Zizou
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Vasya used to be an accountant before the war began and he is one of the few who knows how to operate a computer, so he was assigned as the programmer.
We all know that programs often store sets of integers. For example, if we have a problem about a weighted directed graph, its edge can be represented by three integers: the number of the starting vertex, the number of the final vertex and the edge's weight. So, as Vasya was trying to represent characteristics of a recently invented robot in his program, he faced the following problem.
Vasya is not a programmer, so he asked his friend Gena, what the convenient way to store n integers is. Gena used to code in language X-- and so he can use only the types that occur in this language. Let's define, what a "type" is in language X--:
* First, a type is a string "int".
* Second, a type is a string that starts with "pair", then followed by angle brackets listing exactly two comma-separated other types of language X--. This record contains no spaces.
* No other strings can be regarded as types.
More formally: type := int | pair<type,type>. For example, Gena uses the following type for graph edges: pair<int,pair<int,int>>.
Gena was pleased to help Vasya, he dictated to Vasya a type of language X--, that stores n integers. Unfortunately, Gena was in a hurry, so he omitted the punctuation. Now Gena has already left and Vasya can't find the correct punctuation, resulting in a type of language X--, however hard he tries.
Help Vasya and add the punctuation marks so as to receive the valid type of language X--. Otherwise say that the task is impossible to perform.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), showing how many numbers the type dictated by Gena contains.
The second line contains space-separated words, said by Gena. Each of them is either "pair" or "int" (without the quotes).
It is guaranteed that the total number of words does not exceed 105 and that among all the words that Gena said, there are exactly n words "int".
Output
If it is possible to add the punctuation marks so as to get a correct type of language X-- as a result, print a single line that represents the resulting type. Otherwise, print "Error occurred" (without the quotes). Inside the record of a type should not be any extra spaces and other characters.
It is guaranteed that if such type exists, then it is unique.
Note that you should print the type dictated by Gena (if such type exists) and not any type that can contain n values.
Examples
Input
3
pair pair int int int
Output
pair<pair<int,int>,int>
Input
1
pair int
Output
Error occurred
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Polycarpus adores TV series. Right now he is ready to finish watching a season of a popular sitcom "Graph Theory". In total, the season has n episodes, numbered with integers from 1 to n.
Polycarpus watches episodes not one by one but in a random order. He has already watched all the episodes except for one. Which episode has Polycaprus forgotten to watch?
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100000) — the number of episodes in a season. Assume that the episodes are numbered by integers from 1 to n.
The second line contains n - 1 integer a_1, a_2, ..., a_{n} (1 ≤ a_{i} ≤ n) — the numbers of episodes that Polycarpus has watched. All values of a_{i} are distinct.
-----Output-----
Print the number of the episode that Polycarpus hasn't watched.
-----Examples-----
Input
10
3 8 10 1 7 9 6 5 2
Output
4
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Famous Brazil city Rio de Janeiro holds a tennis tournament and Ostap Bender doesn't want to miss this event. There will be n players participating, and the tournament will follow knockout rules from the very first game. That means, that if someone loses a game he leaves the tournament immediately.
Organizers are still arranging tournament grid (i.e. the order games will happen and who is going to play with whom) but they have already fixed one rule: two players can play against each other only if the number of games one of them has already played differs by no more than one from the number of games the other one has already played. Of course, both players had to win all their games in order to continue participating in the tournament.
Tournament hasn't started yet so the audience is a bit bored. Ostap decided to find out what is the maximum number of games the winner of the tournament can take part in (assuming the rule above is used). However, it is unlikely he can deal with this problem without your help.
Input
The only line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 1018) — the number of players to participate in the tournament.
Output
Print the maximum number of games in which the winner of the tournament can take part.
Examples
Input
2
Output
1
Input
3
Output
2
Input
4
Output
2
Input
10
Output
4
Note
In all samples we consider that player number 1 is the winner.
In the first sample, there would be only one game so the answer is 1.
In the second sample, player 1 can consequently beat players 2 and 3.
In the third sample, player 1 can't play with each other player as after he plays with players 2 and 3 he can't play against player 4, as he has 0 games played, while player 1 already played 2. Thus, the answer is 2 and to achieve we make pairs (1, 2) and (3, 4) and then clash the winners.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Did you know that there are over 40,000 varieties of Rice in the world ? There are so many dishes that can be prepared with Rice too. A famous chef from Mumbai, Tid Gusto prepared a new dish and named it 'Tid Rice'. He posted the recipe in his newly designed blog for community voting, where a user can plus (+) or minus (-) the recipe. The final score is just the sum of all votes, where (+) and (-) are treated as +1 and -1 respectively. But, being just a chef ( and not a codechef ) he forgot to take care of multiple votes by the same user.
A user might have voted multiple times and Tid is worried that the final score shown is not the correct one. Luckily, he found the user logs, which had all the N votes in the order they arrived. Remember that, if a user votes more than once, the user's previous vote is first nullified before the latest vote is counted ( see explanation for more clarity ). Given these records in order ( and being a codechef yourself :) ), calculate the correct final score.
------ Input ------
First line contains T ( number of testcases, around 20 ). T cases follow. Each test case starts with N ( total number of votes, 1 ≤ N ≤ 100 ). Each of the next N lines is of the form "userid vote" ( quotes for clarity only ), where userid is a non-empty string of lower-case alphabets ( 'a' - 'z' ) not more than 20 in length and vote is either a + or - . See the sample cases below, for more clarity.
------ Output ------
For each test case, output the correct final score in a new line
----- Sample Input 1 ------
3
4
tilak +
tilak +
tilak -
tilak +
3
ratna +
shashi -
ratna -
3
bhavani -
bhavani +
bhavani -
----- Sample Output 1 ------
1
-2
-1
----- explanation 1 ------
Case 1 : Initially score = 0. Updation of scores in the order of user tilak's votes is as follows,
( + ): +1 is added to the final score. This is the 1st vote by this user, so no previous vote to nullify. score = 1
( + ): 0 should be added ( -1 to nullify previous (+) vote, +1 to count the current (+) vote ). score = 1
( - ) : -2 should be added ( -1 to nullify previous (+) vote, -1 to count the current (-) vote ). score = -1
( + ): +2 should be added ( +1 to nullify previous (-) vote, +1 to count the current (+) vote ). score = 1
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Amicable numbers are two different numbers so related that the sum of the proper divisors of each is equal to the other number. (A proper divisor of a number is a positive factor of that number other than the number itself. For example, the proper divisors of 6 are 1, 2, and 3.)
For example, the smallest pair of amicable numbers is (220, 284); for the proper divisors of 220 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 11, 20, 22, 44, 55 and 110, of which the sum is 284; and the proper divisors of 284 are 1, 2, 4, 71 and 142, of which the sum is 220.
Derive function ```amicableNumbers(num1, num2)``` which returns ```true/True``` if pair ```num1 num2``` are amicable, ```false/False``` if not.
See more at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amicable_numbers
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
One day Vasya decided to have a look at the results of Berland 1910 Football Championship’s finals. Unfortunately he didn't find the overall score of the match; however, he got hold of a profound description of the match's process. On the whole there are n lines in that description each of which described one goal. Every goal was marked with the name of the team that had scored it. Help Vasya, learn the name of the team that won the finals. It is guaranteed that the match did not end in a tie.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of lines in the description. Then follow n lines — for each goal the names of the teams that scored it. The names are non-empty lines consisting of uppercase Latin letters whose lengths do not exceed 10 symbols. It is guaranteed that the match did not end in a tie and the description contains no more than two different teams.
Output
Print the name of the winning team. We remind you that in football the team that scores more goals is considered the winner.
Examples
Input
1
ABC
Output
ABC
Input
5
A
ABA
ABA
A
A
Output
A
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Your friend has invited you to a party, and tells you to meet them in the line to get in. The one problem is it's a masked party. Everyone in line is wearing a colored mask, including your friend. Find which people in line could be your friend.
Your friend has told you that he will be wearing a `RED` mask, and has **TWO** other friends with him, both wearing `BLUE` masks.
Input to the function will be an array of strings, each representing a colored mask. For example:
```python
line = ['blue','blue','red','red','blue','green']
```
The output of the function should be the number of people who could possibly be your friend.
```python
friend_find(['blue','blue','red','red','blue','green','chipmunk']) # return 1
```
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Monocarp wrote down two numbers on a whiteboard. Both numbers follow a specific format: a positive integer $x$ with $p$ zeros appended to its end.
Now Monocarp asks you to compare these two numbers. Can you help him?
-----Input-----
The first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$) — the number of testcases.
The first line of each testcase contains two integers $x_1$ and $p_1$ ($1 \le x_1 \le 10^6; 0 \le p_1 \le 10^6$) — the description of the first number.
The second line of each testcase contains two integers $x_2$ and $p_2$ ($1 \le x_2 \le 10^6; 0 \le p_2 \le 10^6$) — the description of the second number.
-----Output-----
For each testcase print the result of the comparison of the given two numbers. If the first number is smaller than the second one, print '<'. If the first number is greater than the second one, print '>'. If they are equal, print '='.
-----Examples-----
Input
5
2 1
19 0
10 2
100 1
1999 0
2 3
1 0
1 0
99 0
1 2
Output
>
=
<
=
<
-----Note-----
The comparisons in the example are: $20 > 19$, $1000 = 1000$, $1999 < 2000$, $1 = 1$, $99 < 100$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
There are N points on the 2D plane, i-th of which is located on (x_i, y_i).
There can be multiple points that share the same coordinate.
What is the maximum possible Manhattan distance between two distinct points?
Here, the Manhattan distance between two points (x_i, y_i) and (x_j, y_j) is defined by |x_i-x_j| + |y_i-y_j|.
-----Constraints-----
- 2 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq x_i,y_i \leq 10^9
- All values in input are integers.
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
x_1 y_1
x_2 y_2
:
x_N y_N
-----Output-----
Print the answer.
-----Sample Input-----
3
1 1
2 4
3 2
-----Sample Output-----
4
The Manhattan distance between the first point and the second point is |1-2|+|1-4|=4, which is maximum possible.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Twilight Sparkle once got a crystal from the Crystal Mine. A crystal of size n (n is odd; n > 1) is an n × n matrix with a diamond inscribed into it.
You are given an odd integer n. You need to draw a crystal of size n. The diamond cells of the matrix should be represented by character "D". All other cells of the matrix should be represented by character "*". Look at the examples to understand what you need to draw.
-----Input-----
The only line contains an integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 101; n is odd).
-----Output-----
Output a crystal of size n.
-----Examples-----
Input
3
Output
*D*
DDD
*D*
Input
5
Output
**D**
*DDD*
DDDDD
*DDD*
**D**
Input
7
Output
***D***
**DDD**
*DDDDD*
DDDDDDD
*DDDDD*
**DDD**
***D***
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Take an input string and return a string that is made up of the number of occurences of each english letter in the input followed by that letter, sorted alphabetically. The output string shouldn't contain chars missing from input (chars with 0 occurence); leave them out.
An empty string, or one with no letters, should return an empty string.
Notes:
* the input will always be valid;
* treat letters as **case-insensitive**
## Examples
```
"This is a test sentence." ==> "1a1c4e1h2i2n4s4t"
"" ==> ""
"555" ==> ""
```
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Sagheer is walking in the street when he comes to an intersection of two roads. Each road can be represented as two parts where each part has 3 lanes getting into the intersection (one for each direction) and 3 lanes getting out of the intersection, so we have 4 parts in total. Each part has 4 lights, one for each lane getting into the intersection (l — left, s — straight, r — right) and a light p for a pedestrian crossing. [Image]
An accident is possible if a car can hit a pedestrian. This can happen if the light of a pedestrian crossing of some part and the light of a lane that can get to or from that same part are green at the same time.
Now, Sagheer is monitoring the configuration of the traffic lights. Your task is to help him detect whether an accident is possible.
-----Input-----
The input consists of four lines with each line describing a road part given in a counter-clockwise order.
Each line contains four integers l, s, r, p — for the left, straight, right and pedestrian lights, respectively. The possible values are 0 for red light and 1 for green light.
-----Output-----
On a single line, print "YES" if an accident is possible, and "NO" otherwise.
-----Examples-----
Input
1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1
Output
YES
Input
0 1 1 0
1 0 1 0
1 1 0 0
0 0 0 1
Output
NO
Input
1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0
1 0 1 0
Output
NO
-----Note-----
In the first example, some accidents are possible because cars of part 1 can hit pedestrians of parts 1 and 4. Also, cars of parts 2 and 3 can hit pedestrians of part 4.
In the second example, no car can pass the pedestrian crossing of part 4 which is the only green pedestrian light. So, no accident can occur.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Mobile Display Keystrokes
Do you remember the old mobile display keyboards? Do you also remember how inconvenient it was to write on it?
Well, here you have to calculate how much keystrokes you have to do for a specific word.
This is the layout:
Return the amount of keystrokes of input str (! only letters, digits and special characters in lowercase included in layout without whitespaces !)
e.g:
mobileKeyboard("123") => 3 (1+1+1)
mobileKeyboard("abc") => 9 (2+3+4)
mobileKeyboard("codewars") => 26 (4+4+2+3+2+2+4+5)
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
A prime number n (11, 19, 23, etc.) that divides by 4 and has 3 has an interesting property. The results of calculating the remainder of the square of a natural number (1, 2, ..., n -1) of 1 or more and less than n divided by n are the same, so they are different from each other. The number is (n -1) / 2.
The set of numbers thus obtained has special properties. From the resulting set of numbers, choose two different a and b and calculate the difference. If the difference is negative, add n to the difference. If the result is greater than (n -1) / 2, subtract the difference from n.
For example, when n = 11, the difference between 1 and 9 is 1 − 9 = −8 → −8 + n = −8 + 11 = 3. The difference between 9 and 1 is also 9 −1 = 8 → n − 8 = 11 − 8 = 3, which is the same value 3. This difference can be easily understood by writing 0, 1, ···, n -1 on the circumference and considering the shorter arc between the two numbers. (See the figure below)
<image>
The "difference" in the numbers thus obtained is either 1, 2, ..., (n -1) / 2, and appears the same number of times.
[Example] When n = 11, it will be as follows.
1. Calculate the remainder of the square of the numbers from 1 to n-1 divided by n.
12 = 1 → 1
22 = 4 → 4
32 = 9 → 9
42 = 16 → 5
52 = 25 → 3
62 = 36 → 3
72 = 49 → 5
82 = 64 → 9
92 = 81 → 4
102 = 100 → 1
2. Calculation of "difference" between a and b
1. Calculate the difference between different numbers for 1, 3, 4, 5, 9 obtained in 1.
2. If the calculation result is negative, add n = 11.
3. In addition, if the result of the calculation is greater than (n-1) / 2 = 5, subtract from n = 11.
3. Find the number of appearances
Count the number of occurrences of the calculation results 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
From these calculation results, we can see that 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 appear four times. This property is peculiar to a prime number that is 3 when divided by 4, and this is not the case with a prime number that is 1 when divided by 4. To confirm this, a program that takes an odd number n of 10000 or less as an input, executes the calculation as shown in the example (finds the frequency of the difference of the square that is too much divided by n), and outputs the number of occurrences. Please create.
Input
Given multiple datasets. One integer n (n ≤ 10000) is given on one row for each dataset. The input ends with a line containing one 0.
Output
For each data set, output the frequency of occurrence in the following format.
Number of occurrences (integer) of (a, b) where the difference between the squares of the remainder is 1
The number of occurrences (integer) of (a, b) where the difference between the squares of the remainder is 2
::
::
The number of occurrences (integer) of (a, b) where the difference between the squares of the remainder is (n-1) / 2
Example
Input
11
15
0
Output
4
4
4
4
4
2
2
4
2
4
4
2
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
At a geometry lesson Bob learnt that a triangle is called right-angled if it is nondegenerate and one of its angles is right. Bob decided to draw such a triangle immediately: on a sheet of paper he drew three points with integer coordinates, and joined them with segments of straight lines, then he showed the triangle to Peter. Peter said that Bob's triangle is not right-angled, but is almost right-angled: the triangle itself is not right-angled, but it is possible to move one of the points exactly by distance 1 so, that all the coordinates remain integer, and the triangle become right-angled. Bob asks you to help him and find out if Peter tricks him. By the given coordinates of the triangle you should find out if it is right-angled, almost right-angled, or neither of these.
Input
The first input line contains 6 space-separated integers x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 — coordinates of the triangle's vertices. All the coordinates are integer and don't exceed 100 in absolute value. It's guaranteed that the triangle is nondegenerate, i.e. its total area is not zero.
Output
If the given triangle is right-angled, output RIGHT, if it is almost right-angled, output ALMOST, and if it is neither of these, output NEITHER.
Examples
Input
0 0 2 0 0 1
Output
RIGHT
Input
2 3 4 5 6 6
Output
NEITHER
Input
-1 0 2 0 0 1
Output
ALMOST
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
AquaMoon and Cirno are playing an interesting game with arrays. Cirno has prepared two arrays $a$ and $b$, both consist of $n$ non-negative integers. AquaMoon can perform the following operation an arbitrary number of times (possibly zero):
She chooses two indices $i$ and $j$ ($1 \le i, j \le n$), then decreases the $i$-th element of array $a$ by $1$, and increases the $j$-th element of array $a$ by $1$. The resulting values at $i$-th and $j$-th index of array $a$ are $a_i - 1$ and $a_j + 1$, respectively. Each element of array $a$ must be non-negative after each operation. If $i = j$ this operation doesn't change the array $a$.
AquaMoon wants to make some operations to make arrays $a$ and $b$ equal. Two arrays $a$ and $b$ are considered equal if and only if $a_i = b_i$ for all $1 \leq i \leq n$.
Help AquaMoon to find a sequence of operations that will solve her problem or find, that it is impossible to make arrays $a$ and $b$ equal.
Please note, that you don't have to minimize the number of operations.
-----Input-----
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \leq t \leq 100$) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer $n$ ($1 \leq n \leq 100$).
The second line of each test case contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($0 \leq a_i \leq 100$). The sum of all $a_i$ does not exceed $100$.
The third line of each test case contains $n$ integers $b_1, b_2, \dots, b_n$ ($0 \leq b_i \leq 100$). The sum of all $b_i$ does not exceed $100$.
-----Output-----
For each test case print "-1" on the only line if it is impossible to make two arrays equal with some sequence of operations.
Otherwise, print an integer $m$ ($0 \leq m \leq 100$) in the first line — the number of operations. Then print $m$ lines, each line consists of two integers $i$ and $j$ — the indices you choose for the operation.
It can be proven that if it is possible to make two arrays equal with some sequence of operations, there exists a sequence with $m \leq 100$.
If there are multiple possible solutions, you can print any.
-----Examples-----
Input
4
4
1 2 3 4
3 1 2 4
2
1 3
2 1
1
0
0
5
4 3 2 1 0
0 1 2 3 4
Output
2
2 1
3 1
-1
0
6
1 4
1 4
1 5
1 5
2 5
2 5
-----Note-----
In the first example, we do the following operations:
$i = 2$, $j = 1$: $[1, 2, 3, 4] \rightarrow [2, 1, 3, 4]$;
$i = 3$, $j = 1$: $[2, 1, 3, 4] \rightarrow [3, 1, 2, 4]$;
In the second example, it's impossible to make two arrays equal.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Tanya has $n$ candies numbered from $1$ to $n$. The $i$-th candy has the weight $a_i$.
She plans to eat exactly $n-1$ candies and give the remaining candy to her dad. Tanya eats candies in order of increasing their numbers, exactly one candy per day.
Your task is to find the number of such candies $i$ (let's call these candies good) that if dad gets the $i$-th candy then the sum of weights of candies Tanya eats in even days will be equal to the sum of weights of candies Tanya eats in odd days. Note that at first, she will give the candy, after it she will eat the remaining candies one by one.
For example, $n=4$ and weights are $[1, 4, 3, 3]$. Consider all possible cases to give a candy to dad: Tanya gives the $1$-st candy to dad ($a_1=1$), the remaining candies are $[4, 3, 3]$. She will eat $a_2=4$ in the first day, $a_3=3$ in the second day, $a_4=3$ in the third day. So in odd days she will eat $4+3=7$ and in even days she will eat $3$. Since $7 \ne 3$ this case shouldn't be counted to the answer (this candy isn't good). Tanya gives the $2$-nd candy to dad ($a_2=4$), the remaining candies are $[1, 3, 3]$. She will eat $a_1=1$ in the first day, $a_3=3$ in the second day, $a_4=3$ in the third day. So in odd days she will eat $1+3=4$ and in even days she will eat $3$. Since $4 \ne 3$ this case shouldn't be counted to the answer (this candy isn't good). Tanya gives the $3$-rd candy to dad ($a_3=3$), the remaining candies are $[1, 4, 3]$. She will eat $a_1=1$ in the first day, $a_2=4$ in the second day, $a_4=3$ in the third day. So in odd days she will eat $1+3=4$ and in even days she will eat $4$. Since $4 = 4$ this case should be counted to the answer (this candy is good). Tanya gives the $4$-th candy to dad ($a_4=3$), the remaining candies are $[1, 4, 3]$. She will eat $a_1=1$ in the first day, $a_2=4$ in the second day, $a_3=3$ in the third day. So in odd days she will eat $1+3=4$ and in even days she will eat $4$. Since $4 = 4$ this case should be counted to the answer (this candy is good).
In total there $2$ cases which should counted (these candies are good), so the answer is $2$.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains one integer $n$ ($1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of candies.
The second line of the input contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le 10^4$), where $a_i$ is the weight of the $i$-th candy.
-----Output-----
Print one integer — the number of such candies $i$ (good candies) that if dad gets the $i$-th candy then the sum of weights of candies Tanya eats in even days will be equal to the sum of weights of candies Tanya eats in odd days.
-----Examples-----
Input
7
5 5 4 5 5 5 6
Output
2
Input
8
4 8 8 7 8 4 4 5
Output
2
Input
9
2 3 4 2 2 3 2 2 4
Output
3
-----Note-----
In the first example indices of good candies are $[1, 2]$.
In the second example indices of good candies are $[2, 3]$.
In the third example indices of good candies are $[4, 5, 9]$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Description overhauled by V
---
I've invited some kids for my son's birthday, during which I will give to each kid some amount of candies.
Every kid hates receiving less amount of candies than any other kids, and I don't want to have any candies left - giving it to my kid would be bad for his teeth.
However, not every kid invited will come to my birthday party.
What is the minimum amount of candies I have to buy, so that no matter how many kids come to the party in the end, I can still ensure that each kid can receive the same amount of candies, while leaving no candies left?
It's ensured that at least one kid will participate in the party.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Ilya lives in a beautiful city of Chordalsk.
There are $n$ houses on the street Ilya lives, they are numerated from $1$ to $n$ from left to right; the distance between every two neighboring houses is equal to $1$ unit. The neighboring houses are $1$ and $2$, $2$ and $3$, ..., $n-1$ and $n$. The houses $n$ and $1$ are not neighboring.
The houses are colored in colors $c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_n$ so that the $i$-th house is colored in the color $c_i$. Everyone knows that Chordalsk is not boring, so there are at least two houses colored in different colors.
Ilya wants to select two houses $i$ and $j$ so that $1 \leq i < j \leq n$, and they have different colors: $c_i \neq c_j$. He will then walk from the house $i$ to the house $j$ the distance of $(j-i)$ units.
Ilya loves long walks, so he wants to choose the houses so that the distance between them is the maximum possible.
Help Ilya, find this maximum possible distance.
-----Input-----
The first line contains a single integer $n$ ($3 \leq n \leq 300\,000$) — the number of cities on the street.
The second line contains $n$ integers $c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_n$ ($1 \leq c_i \leq n$) — the colors of the houses.
It is guaranteed that there is at least one pair of indices $i$ and $j$ so that $1 \leq i < j \leq n$ and $c_i \neq c_j$.
-----Output-----
Print a single integer — the maximum possible distance Ilya can walk.
-----Examples-----
Input
5
1 2 3 2 3
Output
4
Input
3
1 2 1
Output
1
Input
7
1 1 3 1 1 1 1
Output
4
-----Note-----
In the first example the optimal way is to walk from the first house to the last one, where Ilya can walk the distance of $5-1 = 4$ units.
In the second example the optimal way is to either walk from the first house to the second or from the second to the third. Both these ways have the distance of $1$ unit.
In the third example the optimal way is to walk from the third house to the last one, where Ilya can walk the distance of $7-3 = 4$ units.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The bear has a string s = s_1s_2... s_{|}s| (record |s| is the string's length), consisting of lowercase English letters. The bear wants to count the number of such pairs of indices i, j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ |s|), that string x(i, j) = s_{i}s_{i} + 1... s_{j} contains at least one string "bear" as a substring.
String x(i, j) contains string "bear", if there is such index k (i ≤ k ≤ j - 3), that s_{k} = b, s_{k} + 1 = e, s_{k} + 2 = a, s_{k} + 3 = r.
Help the bear cope with the given problem.
-----Input-----
The first line contains a non-empty string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 5000). It is guaranteed that the string only consists of lowercase English letters.
-----Output-----
Print a single number — the answer to the problem.
-----Examples-----
Input
bearbtear
Output
6
Input
bearaabearc
Output
20
-----Note-----
In the first sample, the following pairs (i, j) match: (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8), (1, 9).
In the second sample, the following pairs (i, j) match: (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8), (1, 9), (1, 10), (1, 11), (2, 10), (2, 11), (3, 10), (3, 11), (4, 10), (4, 11), (5, 10), (5, 11), (6, 10), (6, 11), (7, 10), (7, 11).
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
In 2937, DISCO creates a new universe called DISCOSMOS to celebrate its 1000-th anniversary.
DISCOSMOS can be described as an H \times W grid. Let (i, j) (1 \leq i \leq H, 1 \leq j \leq W) denote the square at the i-th row from the top and the j-th column from the left.
At time 0, one robot will be placed onto each square. Each robot is one of the following three types:
* Type-H: Does not move at all.
* Type-R: If a robot of this type is in (i, j) at time t, it will be in (i, j+1) at time t+1. If it is in (i, W) at time t, however, it will be instead in (i, 1) at time t+1. (The robots do not collide with each other.)
* Type-D: If a robot of this type is in (i, j) at time t, it will be in (i+1, j) at time t+1. If it is in (H, j) at time t, however, it will be instead in (1, j) at time t+1.
There are 3^{H \times W} possible ways to place these robots. In how many of them will every square be occupied by one robot at times 0, T, 2T, 3T, 4T, and all subsequent multiples of T?
Since the count can be enormous, compute it modulo (10^9 + 7).
Constraints
* 1 \leq H \leq 10^9
* 1 \leq W \leq 10^9
* 1 \leq T \leq 10^9
* H, W, T are all integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
H W T
Output
Print the number of ways to place the robots that satisfy the condition, modulo (10^9 + 7).
Examples
Input
2 2 1
Output
9
Input
869 120 1001
Output
672919729
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Kamil likes streaming the competitive programming videos. His MeTube channel has recently reached 100 million subscribers. In order to celebrate this, he posted a video with an interesting problem he couldn't solve yet. Can you help him?
You're given a tree — a connected undirected graph consisting of n vertices connected by n - 1 edges. The tree is rooted at vertex 1. A vertex u is called an ancestor of v if it lies on the shortest path between the root and v. In particular, a vertex is an ancestor of itself.
Each vertex v is assigned its beauty x_v — a non-negative integer not larger than 10^{12}. This allows us to define the beauty of a path. Let u be an ancestor of v. Then we define the beauty f(u, v) as the greatest common divisor of the beauties of all vertices on the shortest path between u and v. Formally, if u=t_1, t_2, t_3, ..., t_k=v are the vertices on the shortest path between u and v, then f(u, v) = \gcd(x_{t_1}, x_{t_2}, ..., x_{t_k}). Here, \gcd denotes the greatest common divisor of a set of numbers. In particular, f(u, u) = \gcd(x_u) = x_u.
Your task is to find the sum
$$$ ∑_{u is an ancestor of v} f(u, v). $$$
As the result might be too large, please output it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Note that for each y, \gcd(0, y) = \gcd(y, 0) = y. In particular, \gcd(0, 0) = 0.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The following line contains n integers x_1, x_2, ..., x_n (0 ≤ x_i ≤ 10^{12}). The value x_v denotes the beauty of vertex v.
The following n - 1 lines describe the edges of the tree. Each of them contains two integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ n, a ≠ b) — the vertices connected by a single edge.
Output
Output the sum of the beauties on all paths (u, v) such that u is ancestor of v. This sum should be printed modulo 10^9 + 7.
Examples
Input
5
4 5 6 0 8
1 2
1 3
1 4
4 5
Output
42
Input
7
0 2 3 0 0 0 0
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
3 7
Output
30
Note
The following figure shows all 10 possible paths for which one endpoint is an ancestor of another endpoint. The sum of beauties of all these paths is equal to 42:
<image>
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Pasha got a very beautiful string s for his birthday, the string consists of lowercase Latin letters. The letters in the string are numbered from 1 to |s| from left to right, where |s| is the length of the given string.
Pasha didn't like his present very much so he decided to change it. After his birthday Pasha spent m days performing the following transformations on his string — each day he chose integer a_{i} and reversed a piece of string (a segment) from position a_{i} to position |s| - a_{i} + 1. It is guaranteed that 2·a_{i} ≤ |s|.
You face the following task: determine what Pasha's string will look like after m days.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains Pasha's string s of length from 2 to 2·10^5 characters, consisting of lowercase Latin letters.
The second line contains a single integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 10^5) — the number of days when Pasha changed his string.
The third line contains m space-separated elements a_{i} (1 ≤ a_{i}; 2·a_{i} ≤ |s|) — the position from which Pasha started transforming the string on the i-th day.
-----Output-----
In the first line of the output print what Pasha's string s will look like after m days.
-----Examples-----
Input
abcdef
1
2
Output
aedcbf
Input
vwxyz
2
2 2
Output
vwxyz
Input
abcdef
3
1 2 3
Output
fbdcea
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
FizzBuzz is a game in which integers of 1 or more are spoken in order according to the following rules.
* "Fizz" when divisible by 3
* "Buzz" when divisible by 5
* "FizzBuzz" when divisible by both 3 and 5
* At other times, that number
An example of the progress of the game is shown below.
1, 2, Fizz, 4, Buzz, Fizz, 7, 8, Fizz, Buzz, 11, Fizz, 13, 14, FizzBuzz, 16,…
The character string obtained by combining the obtained remarks into one character string is called FizzBuzz String. Since the index s is given, output 20 characters from the s character of the FizzBuzz String. However, the index may start from 1, and the length of the obtained character string may be sufficiently large (s + 20 or more).
Constraints
* s is an integer
* 1 ≤ s ≤ 1018
Input
Input is given in the following format
> s
>
Output
Output 20 characters from the s character of FizzBuzz String on one line
Examples
Input
1
Output
12Fizz4BuzzFizz78Fiz
Input
20
Output
zzBuzz11Fizz1314Fizz
Input
10000000000
Output
93FizzBuzz1418650796
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Sometimes some words like "localization" or "internationalization" are so long that writing them many times in one text is quite tiresome.
Let's consider a word too long, if its length is strictly more than 10 characters. All too long words should be replaced with a special abbreviation.
This abbreviation is made like this: we write down the first and the last letter of a word and between them we write the number of letters between the first and the last letters. That number is in decimal system and doesn't contain any leading zeroes.
Thus, "localization" will be spelt as "l10n", and "internationalization» will be spelt as "i18n".
You are suggested to automatize the process of changing the words with abbreviations. At that all too long words should be replaced by the abbreviation and the words that are not too long should not undergo any changes.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100). Each of the following n lines contains one word. All the words consist of lowercase Latin letters and possess the lengths of from 1 to 100 characters.
Output
Print n lines. The i-th line should contain the result of replacing of the i-th word from the input data.
Examples
Input
4
word
localization
internationalization
pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis
Output
word
l10n
i18n
p43s
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Iahub and Sorin are the best competitive programmers in their town. However, they can't both qualify to an important contest. The selection will be made with the help of a single problem. Blatnatalag, a friend of Iahub, managed to get hold of the problem before the contest. Because he wants to make sure Iahub will be the one qualified, he tells Iahub the following task.
You're given an (1-based) array a with n elements. Let's define function f(i, j) (1 ≤ i, j ≤ n) as (i - j)^2 + g(i, j)^2. Function g is calculated by the following pseudo-code:
int g(int i, int j) {
int sum = 0;
for (int k = min(i, j) + 1; k <= max(i, j); k = k + 1)
sum = sum + a[k];
return sum;
}
Find a value min_{i} ≠ j f(i, j).
Probably by now Iahub already figured out the solution to this problem. Can you?
-----Input-----
The first line of input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100000). Next line contains n integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] ( - 10^4 ≤ a[i] ≤ 10^4).
-----Output-----
Output a single integer — the value of min_{i} ≠ j f(i, j).
-----Examples-----
Input
4
1 0 0 -1
Output
1
Input
2
1 -1
Output
2
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Taro had his own personal computer and set a password for login. However, Taro inadvertently forgot the password. Then, remembering that there was a piece of paper with the password written down, Taro found the paper and was surprised to see it. The paper was cut and there were only fragments, and there were some stains that made it unreadable. Taro decided to guess the password by referring to the memo.
Constraints
* The length of the character strings A and B is 1 to 1000 characters.
* The length of the B string does not exceed the length of the A string.
Input
String A
String B
Output
Output "Yes" or "No" on one line.
Examples
Input
ABCDE
ABC
Output
Yes
Input
KUSATSU
KSATSU
Output
No
Input
ABCABC
ACBA_B
Output
No
Input
RUPCUAPC
__PC
Output
Yes
Input
AIZU
_A
Output
No
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
There is one card each with the numbers from "1" to "10", for a total of 10 cards. This card has numbers on the front and nothing on the back. Using this card, you and your opponent will play the game according to the following rules.
1. You and your opponent are dealt a total of two cards, one face up and one back up. You can see the numbers on the front card of your opponent, but not the numbers on the back card.
2. You win when the total number of cards dealt is 20 or less and greater than the total number of your opponent. For example, if your card is "7" "8" (15 total) and your opponent's card is "9" "10" (19 total), your opponent wins.
3. You and your opponent can draw up to one more card. You don't have to pull it.
Now, as a guide to deciding whether to draw one more card, consider the probability that the total will be 20 or less when you draw a card, and if that probability is 50% or more, draw a card. When calculating this probability, you can use the information of your two cards and the card on the opponent's table for a total of three cards. In other words, you don't draw those cards because you only have one for each card.
A program that reads your two cards and your opponent's front card, and outputs YES if there is a 50% or greater probability that the total will be 20 or less when you draw one more card, otherwise it will output NO. Please create.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets. Given that the number on your first card is C1, the number on your second card is C2, and the number on your opponent's face card is C3, each dataset is given in the following format: ..
C1 C2 C3
Output
Print YES or NO on one line for each dataset.
Example
Input
1 2 3
5 6 9
8 9 10
Output
YES
YES
NO
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The map of Bertown can be represented as a set of $n$ intersections, numbered from $1$ to $n$ and connected by $m$ one-way roads. It is possible to move along the roads from any intersection to any other intersection. The length of some path from one intersection to another is the number of roads that one has to traverse along the path. The shortest path from one intersection $v$ to another intersection $u$ is the path that starts in $v$, ends in $u$ and has the minimum length among all such paths.
Polycarp lives near the intersection $s$ and works in a building near the intersection $t$. Every day he gets from $s$ to $t$ by car. Today he has chosen the following path to his workplace: $p_1$, $p_2$, ..., $p_k$, where $p_1 = s$, $p_k = t$, and all other elements of this sequence are the intermediate intersections, listed in the order Polycarp arrived at them. Polycarp never arrived at the same intersection twice, so all elements of this sequence are pairwise distinct. Note that you know Polycarp's path beforehand (it is fixed), and it is not necessarily one of the shortest paths from $s$ to $t$.
Polycarp's car has a complex navigation system installed in it. Let's describe how it works. When Polycarp starts his journey at the intersection $s$, the system chooses some shortest path from $s$ to $t$ and shows it to Polycarp. Let's denote the next intersection in the chosen path as $v$. If Polycarp chooses to drive along the road from $s$ to $v$, then the navigator shows him the same shortest path (obviously, starting from $v$ as soon as he arrives at this intersection). However, if Polycarp chooses to drive to another intersection $w$ instead, the navigator rebuilds the path: as soon as Polycarp arrives at $w$, the navigation system chooses some shortest path from $w$ to $t$ and shows it to Polycarp. The same process continues until Polycarp arrives at $t$: if Polycarp moves along the road recommended by the system, it maintains the shortest path it has already built; but if Polycarp chooses some other path, the system rebuilds the path by the same rules.
Here is an example. Suppose the map of Bertown looks as follows, and Polycarp drives along the path $[1, 2, 3, 4]$ ($s = 1$, $t = 4$):
When Polycarp starts at $1$, the system chooses some shortest path from $1$ to $4$. There is only one such path, it is $[1, 5, 4]$; Polycarp chooses to drive to $2$, which is not along the path chosen by the system. When Polycarp arrives at $2$, the navigator rebuilds the path by choosing some shortest path from $2$ to $4$, for example, $[2, 6, 4]$ (note that it could choose $[2, 3, 4]$); Polycarp chooses to drive to $3$, which is not along the path chosen by the system. When Polycarp arrives at $3$, the navigator rebuilds the path by choosing the only shortest path from $3$ to $4$, which is $[3, 4]$; Polycarp arrives at $4$ along the road chosen by the navigator, so the system does not have to rebuild anything.
Overall, we get $2$ rebuilds in this scenario. Note that if the system chose $[2, 3, 4]$ instead of $[2, 6, 4]$ during the second step, there would be only $1$ rebuild (since Polycarp goes along the path, so the system maintains the path $[3, 4]$ during the third step).
The example shows us that the number of rebuilds can differ even if the map of Bertown and the path chosen by Polycarp stays the same. Given this information (the map and Polycarp's path), can you determine the minimum and the maximum number of rebuilds that could have happened during the journey?
-----Input-----
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $m$ ($2 \le n \le m \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of intersections and one-way roads in Bertown, respectively.
Then $m$ lines follow, each describing a road. Each line contains two integers $u$ and $v$ ($1 \le u, v \le n$, $u \ne v$) denoting a road from intersection $u$ to intersection $v$. All roads in Bertown are pairwise distinct, which means that each ordered pair $(u, v)$ appears at most once in these $m$ lines (but if there is a road $(u, v)$, the road $(v, u)$ can also appear).
The following line contains one integer $k$ ($2 \le k \le n$) — the number of intersections in Polycarp's path from home to his workplace.
The last line contains $k$ integers $p_1$, $p_2$, ..., $p_k$ ($1 \le p_i \le n$, all these integers are pairwise distinct) — the intersections along Polycarp's path in the order he arrived at them. $p_1$ is the intersection where Polycarp lives ($s = p_1$), and $p_k$ is the intersection where Polycarp's workplace is situated ($t = p_k$). It is guaranteed that for every $i \in [1, k - 1]$ the road from $p_i$ to $p_{i + 1}$ exists, so the path goes along the roads of Bertown.
-----Output-----
Print two integers: the minimum and the maximum number of rebuilds that could have happened during the journey.
-----Examples-----
Input
6 9
1 5
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
2 6
6 4
4 2
4
1 2 3 4
Output
1 2
Input
7 7
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 1
7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Output
0 0
Input
8 13
8 7
8 6
7 5
7 4
6 5
6 4
5 3
5 2
4 3
4 2
3 1
2 1
1 8
5
8 7 5 2 1
Output
0 3
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
For a given array $a_1, a_2, a_3, ... , a_N$ of $N$ elements and $Q$ integers $x_i$ as queries, for each query, print the number of combinations of two integers $(l, r)$ which satisfies the condition: $1 \leq l \leq r \leq N$ and $a_l + a_{l+1} + ... + a_{r-1} + a_r \leq x_i$.
Constraints
* $1 \leq N \leq 10^5$
* $1 \leq Q \leq 500$
* $1 \leq a_i \leq 10^9$
* $1 \leq x_i \leq 10^{14}$
Input
The input is given in the following format.
$N$ $Q$
$a_1$ $a_2$ ... $a_N$
$x_1$ $x_2$ ... $x_Q$
Output
For each query, print the number of combinations in a line.
Example
Input
6 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
6 9 12 21 15
Output
9
12
15
21
18
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Currently, XXOC's rap is a string consisting of zeroes, ones, and question marks. Unfortunately, haters gonna hate. They will write $x$ angry comments for every occurrence of subsequence 01 and $y$ angry comments for every occurrence of subsequence 10. You should replace all the question marks with 0 or 1 in such a way that the number of angry comments would be as small as possible.
String $b$ is a subsequence of string $a$, if it can be obtained by removing some characters from $a$. Two occurrences of a subsequence are considered distinct if sets of positions of remaining characters are distinct.
-----Input-----
The first line contains string $s$ — XXOC's rap ($1 \le |s| \leq 10^5$). The second line contains two integers $x$ and $y$ — the number of angry comments XXOC will recieve for every occurrence of 01 and 10 accordingly ($0 \leq x, y \leq 10^6$).
-----Output-----
Output a single integer — the minimum number of angry comments.
-----Examples-----
Input
0?1
2 3
Output
4
Input
?????
13 37
Output
0
Input
?10?
239 7
Output
28
Input
01101001
5 7
Output
96
-----Note-----
In the first example one of the optimum ways to replace is 001. Then there will be $2$ subsequences 01 and $0$ subsequences 10. Total number of angry comments will be equal to $2 \cdot 2 + 0 \cdot 3 = 4$.
In the second example one of the optimum ways to replace is 11111. Then there will be $0$ subsequences 01 and $0$ subsequences 10. Total number of angry comments will be equal to $0 \cdot 13 + 0 \cdot 37 = 0$.
In the third example one of the optimum ways to replace is 1100. Then there will be $0$ subsequences 01 and $4$ subsequences 10. Total number of angry comments will be equal to $0 \cdot 239 + 4 \cdot 7 = 28$.
In the fourth example one of the optimum ways to replace is 01101001. Then there will be $8$ subsequences 01 and $8$ subsequences 10. Total number of angry comments will be equal to $8 \cdot 5 + 8 \cdot 7 = 96$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Pasha has many hamsters and he makes them work out. Today, n hamsters (n is even) came to work out. The hamsters lined up and each hamster either sat down or stood up.
For another exercise, Pasha needs exactly $\frac{n}{2}$ hamsters to stand up and the other hamsters to sit down. In one minute, Pasha can make some hamster ether sit down or stand up. How many minutes will he need to get what he wants if he acts optimally well?
-----Input-----
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200; n is even). The next line contains n characters without spaces. These characters describe the hamsters' position: the i-th character equals 'X', if the i-th hamster in the row is standing, and 'x', if he is sitting.
-----Output-----
In the first line, print a single integer — the minimum required number of minutes. In the second line, print a string that describes the hamsters' position after Pasha makes the required changes. If there are multiple optimal positions, print any of them.
-----Examples-----
Input
4
xxXx
Output
1
XxXx
Input
2
XX
Output
1
xX
Input
6
xXXxXx
Output
0
xXXxXx
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
During the quarantine, Sicromoft has more free time to create the new functions in "Celex-2021". The developers made a new function GAZ-GIZ, which infinitely fills an infinite table to the right and down from the upper left corner as follows:
[Image] The cell with coordinates $(x, y)$ is at the intersection of $x$-th row and $y$-th column. Upper left cell $(1,1)$ contains an integer $1$.
The developers of the SUM function don't sleep either. Because of the boredom, they teamed up with the developers of the RAND function, so they added the ability to calculate the sum on an arbitrary path from one cell to another, moving down or right. Formally, from the cell $(x,y)$ in one step you can move to the cell $(x+1, y)$ or $(x, y+1)$.
After another Dinwows update, Levian started to study "Celex-2021" (because he wants to be an accountant!). After filling in the table with the GAZ-GIZ function, he asked you to calculate the quantity of possible different amounts on the path from a given cell $(x_1, y_1)$ to another given cell $(x_2, y_2$), if you can only move one cell down or right.
Formally, consider all the paths from the cell $(x_1, y_1)$ to cell $(x_2, y_2)$ such that each next cell in the path is located either to the down or to the right of the previous one. Calculate the number of different sums of elements for all such paths.
-----Input-----
The first line contains one integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 57179$) — the number of test cases.
Each of the following $t$ lines contains four natural numbers $x_1$, $y_1$, $x_2$, $y_2$ ($1 \le x_1 \le x_2 \le 10^9$, $1 \le y_1 \le y_2 \le 10^9$) — coordinates of the start and the end cells.
-----Output-----
For each test case, in a separate line, print the number of possible different sums on the way from the start cell to the end cell.
-----Example-----
Input
4
1 1 2 2
1 2 2 4
179 1 179 100000
5 7 5 7
Output
2
3
1
1
-----Note-----
In the first test case there are two possible sums: $1+2+5=8$ and $1+3+5=9$. [Image]
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Peter has a sequence of integers a_1, a_2, ..., a_{n}. Peter wants all numbers in the sequence to equal h. He can perform the operation of "adding one on the segment [l, r]": add one to all elements of the sequence with indices from l to r (inclusive). At that, Peter never chooses any element as the beginning of the segment twice. Similarly, Peter never chooses any element as the end of the segment twice. In other words, for any two segments [l_1, r_1] and [l_2, r_2], where Peter added one, the following inequalities hold: l_1 ≠ l_2 and r_1 ≠ r_2.
How many distinct ways are there to make all numbers in the sequence equal h? Print this number of ways modulo 1000000007 (10^9 + 7). Two ways are considered distinct if one of them has a segment that isn't in the other way.
-----Input-----
The first line contains two integers n, h (1 ≤ n, h ≤ 2000). The next line contains n integers a_1, a_2, ..., a_{n} (0 ≤ a_{i} ≤ 2000).
-----Output-----
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem modulo 1000000007 (10^9 + 7).
-----Examples-----
Input
3 2
1 1 1
Output
4
Input
5 1
1 1 1 1 1
Output
1
Input
4 3
3 2 1 1
Output
0
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Hearing that energy drinks increase rating in those sites, Takahashi decides to buy up M cans of energy drinks.
There are N stores that sell energy drinks. In the i-th store, he can buy at most B_i cans of energy drinks for A_i yen (the currency of Japan) each.
What is the minimum amount of money with which he can buy M cans of energy drinks?
It is guaranteed that, in the given inputs, a sufficient amount of money can always buy M cans of energy drinks.
-----Constraints-----
- All values in input are integers.
- 1 \leq N, M \leq 10^5
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^9
- 1 \leq B_i \leq 10^5
- B_1 + ... + B_N \geq M
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M
A_1 B_1
A_2 B_2
\vdots
A_N B_N
-----Output-----
Print the minimum amount of money with which Takahashi can buy M cans of energy drinks.
-----Sample Input-----
2 5
4 9
2 4
-----Sample Output-----
12
With 12 yen, we can buy one drink at the first store and four drinks at the second store, for the total of five drinks. However, we cannot buy 5 drinks with 11 yen or less.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Petya loves lucky numbers. We all know that lucky numbers are the positive integers whose decimal representations contain only the lucky digits 4 and 7. For example, numbers 47, 744, 4 are lucky and 5, 17, 467 are not.
One day Petya encountered a tree with n vertexes. Besides, the tree was weighted, i. e. each edge of the tree has weight (a positive integer). An edge is lucky if its weight is a lucky number. Note that a tree with n vertexes is an undirected connected graph that has exactly n - 1 edges.
Petya wondered how many vertex triples (i, j, k) exists that on the way from i to j, as well as on the way from i to k there must be at least one lucky edge (all three vertexes are pairwise distinct). The order of numbers in the triple matters, that is, the triple (1, 2, 3) is not equal to the triple (2, 1, 3) and is not equal to the triple (1, 3, 2).
Find how many such triples of vertexes exist.
Input
The first line contains the single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of tree vertexes. Next n - 1 lines contain three integers each: ui vi wi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, 1 ≤ wi ≤ 109) — the pair of vertexes connected by the edge and the edge's weight.
Output
On the single line print the single number — the answer.
Please do not use the %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit numbers in С++. It is recommended to use the cin, cout streams or the %I64d specificator.
Examples
Input
4
1 2 4
3 1 2
1 4 7
Output
16
Input
4
1 2 4
1 3 47
1 4 7447
Output
24
Note
The 16 triples of vertexes from the first sample are: (1, 2, 4), (1, 4, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 1, 4), (2, 3, 1), (2, 3, 4), (2, 4, 1), (2, 4, 3), (3, 2, 4), (3, 4, 2), (4, 1, 2), (4, 1, 3), (4, 2, 1), (4, 2, 3), (4, 3, 1), (4, 3, 2).
In the second sample all the triples should be counted: 4·3·2 = 24.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Pig is visiting a friend.
Pig's house is located at point 0, and his friend's house is located at point m on an axis.
Pig can use teleports to move along the axis.
To use a teleport, Pig should come to a certain point (where the teleport is located) and choose where to move: for each teleport there is the rightmost point it can move Pig to, this point is known as the limit of the teleport.
Formally, a teleport located at point x with limit y can move Pig from point x to any point within the segment [x; y], including the bounds. [Image]
Determine if Pig can visit the friend using teleports only, or he should use his car.
-----Input-----
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100) — the number of teleports and the location of the friend's house.
The next n lines contain information about teleports.
The i-th of these lines contains two integers a_{i} and b_{i} (0 ≤ a_{i} ≤ b_{i} ≤ m), where a_{i} is the location of the i-th teleport, and b_{i} is its limit.
It is guaranteed that a_{i} ≥ a_{i} - 1 for every i (2 ≤ i ≤ n).
-----Output-----
Print "YES" if there is a path from Pig's house to his friend's house that uses only teleports, and "NO" otherwise.
You can print each letter in arbitrary case (upper or lower).
-----Examples-----
Input
3 5
0 2
2 4
3 5
Output
YES
Input
3 7
0 4
2 5
6 7
Output
NO
-----Note-----
The first example is shown on the picture below: [Image]
Pig can use the first teleport from his house (point 0) to reach point 2, then using the second teleport go from point 2 to point 3, then using the third teleport go from point 3 to point 5, where his friend lives.
The second example is shown on the picture below: [Image]
You can see that there is no path from Pig's house to his friend's house that uses only teleports.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
In graph theory, a graph is a collection of nodes with connections between them.
Any node can be connected to any other node exactly once, and can be connected to no nodes, to some nodes, or to every other node.
Nodes cannot be connected to themselves
A path through a graph is a sequence of nodes, with every node connected to the node following and preceding it.
A closed path is a path which starts and ends at the same node.
An open path:
```
1 -> 2 -> 3
```
a closed path:
```
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1
```
A graph is connected if there is a path from every node to every other node.
A graph is a tree if it is connected and there are no closed paths.
Your job is to write a function 'isTree', which returns true if a graph is a tree, and false if it is not a tree.
Graphs will be given as an array with each item being an array of integers which are the nodes that node is connected to.
For example, this graph:
```
0--1
| |
2--3--4
```
has array:
```
[[1,2], [0,3], [0,3], [1,2,4], [3]]
```
Note that it is also not a tree, because it contains closed path:
```
0->1->3->2->0
```
A node with no connections is an empty array
Note that if node 0 is connected to node 1, node 1 is also connected to node 0. This will always be true.
The order in which each connection is listed for each node also does not matter.
Good luck!
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The weather is fine today and hence it's high time to climb the nearby pine and enjoy the landscape.
The pine's trunk includes several branches, located one above another and numbered from 2 to y. Some of them (more precise, from 2 to p) are occupied by tiny vile grasshoppers which you're at war with. These grasshoppers are known for their awesome jumping skills: the grasshopper at branch x can jump to branches $2 \cdot x, 3 \cdot x, \ldots, \lfloor \frac{y}{x} \rfloor \cdot x$.
Keeping this in mind, you wisely decided to choose such a branch that none of the grasshoppers could interrupt you. At the same time you wanna settle as high as possible since the view from up there is simply breathtaking.
In other words, your goal is to find the highest branch that cannot be reached by any of the grasshoppers or report that it's impossible.
-----Input-----
The only line contains two integers p and y (2 ≤ p ≤ y ≤ 10^9).
-----Output-----
Output the number of the highest suitable branch. If there are none, print -1 instead.
-----Examples-----
Input
3 6
Output
5
Input
3 4
Output
-1
-----Note-----
In the first sample case grasshopper from branch 2 reaches branches 2, 4 and 6 while branch 3 is initially settled by another grasshopper. Therefore the answer is 5.
It immediately follows that there are no valid branches in second sample case.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Ivan had string s consisting of small English letters. However, his friend Julia decided to make fun of him and hid the string s. Ivan preferred making a new string to finding the old one.
Ivan knows some information about the string s. Namely, he remembers, that string ti occurs in string s at least ki times or more, he also remembers exactly ki positions where the string ti occurs in string s: these positions are xi, 1, xi, 2, ..., xi, ki. He remembers n such strings ti.
You are to reconstruct lexicographically minimal string s such that it fits all the information Ivan remembers. Strings ti and string s consist of small English letters only.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of strings Ivan remembers.
The next n lines contain information about the strings. The i-th of these lines contains non-empty string ti, then positive integer ki, which equal to the number of times the string ti occurs in string s, and then ki distinct positive integers xi, 1, xi, 2, ..., xi, ki in increasing order — positions, in which occurrences of the string ti in the string s start. It is guaranteed that the sum of lengths of strings ti doesn't exceed 106, 1 ≤ xi, j ≤ 106, 1 ≤ ki ≤ 106, and the sum of all ki doesn't exceed 106. The strings ti can coincide.
It is guaranteed that the input data is not self-contradictory, and thus at least one answer always exists.
Output
Print lexicographically minimal string that fits all the information Ivan remembers.
Examples
Input
3
a 4 1 3 5 7
ab 2 1 5
ca 1 4
Output
abacaba
Input
1
a 1 3
Output
aaa
Input
3
ab 1 1
aba 1 3
ab 2 3 5
Output
ababab
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Kolya is developing an economy simulator game. His most favourite part of the development process is in-game testing. Once he was entertained by the testing so much, that he found out his game-coin score become equal to 0.
Kolya remembers that at the beginning of the game his game-coin score was equal to n and that he have bought only some houses (for 1 234 567 game-coins each), cars (for 123 456 game-coins each) and computers (for 1 234 game-coins each).
Kolya is now interested, whether he could have spent all of his initial n game-coins buying only houses, cars and computers or there is a bug in the game. Formally, is there a triple of non-negative integers a, b and c such that a × 1 234 567 + b × 123 456 + c × 1 234 = n?
Please help Kolya answer this question.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 10^9) — Kolya's initial game-coin score.
-----Output-----
Print "YES" (without quotes) if it's possible that Kolya spent all of his initial n coins buying only houses, cars and computers. Otherwise print "NO" (without quotes).
-----Examples-----
Input
1359257
Output
YES
Input
17851817
Output
NO
-----Note-----
In the first sample, one of the possible solutions is to buy one house, one car and one computer, spending 1 234 567 + 123 456 + 1234 = 1 359 257 game-coins in total.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
There are N cities and M roads.
The i-th road (1≤i≤M) connects two cities a_i and b_i (1≤a_i,b_i≤N) bidirectionally.
There may be more than one road that connects the same pair of two cities.
For each city, how many roads are connected to the city?
-----Constraints-----
- 2≤N,M≤50
- 1≤a_i,b_i≤N
- a_i ≠ b_i
- All input values are integers.
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M
a_1 b_1
:
a_M b_M
-----Output-----
Print the answer in N lines.
In the i-th line (1≤i≤N), print the number of roads connected to city i.
-----Sample Input-----
4 3
1 2
2 3
1 4
-----Sample Output-----
2
2
1
1
- City 1 is connected to the 1-st and 3-rd roads.
- City 2 is connected to the 1-st and 2-nd roads.
- City 3 is connected to the 2-nd road.
- City 4 is connected to the 3-rd road.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Naturally, the magical girl is very good at performing magic. She recently met her master wizard Devu, who gifted her R potions of red liquid,
B potions of blue liquid, and G potions of green liquid.
-
The red liquid potions have liquid amounts given by r[1], ..., r[R] liters.
-
The green liquid potions have liquid amounts given by g[1], ..., g[G] liters.
-
The blue liquid potions have liquid amounts given by b[1], ..., b[B] liters.
She want to play with the potions by applying magic tricks on them. In a single magic trick, she will choose a particular color. Then she will pick all the potions of the chosen color and decrease the amount of liquid in them to half (i.e. if initial amount
of liquid is x, then the amount after decrement will be x / 2 where division is integer division, e.g. 3 / 2 = 1 and 4 / 2 = 2).
Because she has to go out of station to meet her uncle Churu, a wannabe wizard, only M minutes are left for her. In a single minute, she can perform at most one magic trick. Hence, she can perform at most M magic tricks.
She would like to minimize the maximum amount of liquid among all of Red, Green and Blue colored potions. Formally Let v be the maximum value of amount of liquid in any potion. We want to minimize the value of v.
Please help her.
-----Input-----
First line of the input contains an integer T denoting the number of test cases.
Then for each test case, we have four lines.
The first line contains four space separated integers R, G, B, M. The next 3 lines will describe the amount of different color liquids (r, g, b), which are separated by space.
-----Output-----
For each test case, print a single integer denoting the answer of the problem.
-----Constraints-----
- 1 ≤ T ≤ 1000
- 1 ≤ R, G, B, M ≤ 100
- 1 ≤ r[i], g[i], b[i] ≤ 10^9
-----Example-----
Input:
3
1 1 1 1
1
2
3
1 1 1 1
2
4
6
3 2 2 2
1 2 3
2 4
6 8
Output:
2
4
4
-----Explanation-----
Example case 1. Magical girl can pick the blue potion and make its liquid amount half. So the potions will now have amounts 1 2 1. Maximum of these values is 2. Hence answer is 2.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
There are N towns numbered 1, 2, \cdots, N.
Some roads are planned to be built so that each of them connects two distinct towns bidirectionally. Currently, there are no roads connecting towns.
In the planning of construction, each town chooses one town different from itself and requests the following: roads are built so that the chosen town is reachable from itself using one or more roads.
These requests from the towns are represented by an array P_1, P_2, \cdots, P_N. If P_i = -1, it means that Town i has not chosen the request; if 1 \leq P_i \leq N, it means that Town i has chosen Town P_i.
Let K be the number of towns i such that P_i = -1. There are (N-1)^K ways in which the towns can make the requests. For each way to make requests, find the minimum number of roads needed to meet all the requests, and print the sum of those (N-1)^K numbers, modulo (10^9+7).
Constraints
* 2 \leq N \leq 5000
* P_i = -1 or 1 \leq P_i \leq N.
* P_i \neq i
* All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
P_1 P_2 \cdots P_N
Output
For each way to make requests, find the minimum number of roads needed to meet all the requests, and print the sum of those (N-1)^K numbers, modulo (10^9+7).
Examples
Input
4
2 1 -1 3
Output
8
Input
2
2 1
Output
1
Input
10
2 6 9 -1 6 9 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output
527841
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Nastya came to her informatics lesson, and her teacher who is, by the way, a little bit famous here gave her the following task.
Two matrices $A$ and $B$ are given, each of them has size $n \times m$. Nastya can perform the following operation to matrix $A$ unlimited number of times: take any square square submatrix of $A$ and transpose it (i.e. the element of the submatrix which was in the $i$-th row and $j$-th column of the submatrix will be in the $j$-th row and $i$-th column after transposing, and the transposed submatrix itself will keep its place in the matrix $A$).
Nastya's task is to check whether it is possible to transform the matrix $A$ to the matrix $B$.
$\left. \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline 6 & {3} & {2} & {11} \\ \hline 5 & {9} & {4} & {2} \\ \hline 3 & {3} & {3} & {3} \\ \hline 4 & {8} & {2} & {2} \\ \hline 7 & {8} & {6} & {4} \\ \hline \end{array} \right.$ Example of the operation
As it may require a lot of operations, you are asked to answer this question for Nastya.
A square submatrix of matrix $M$ is a matrix which consist of all elements which comes from one of the rows with indeces $x, x+1, \dots, x+k-1$ of matrix $M$ and comes from one of the columns with indeces $y, y+1, \dots, y+k-1$ of matrix $M$. $k$ is the size of square submatrix. In other words, square submatrix is the set of elements of source matrix which form a solid square (i.e. without holes).
-----Input-----
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $m$ separated by space ($1 \leq n, m \leq 500$) — the numbers of rows and columns in $A$ and $B$ respectively.
Each of the next $n$ lines contains $m$ integers, the $j$-th number in the $i$-th of these lines denotes the $j$-th element of the $i$-th row of the matrix $A$ ($1 \leq A_{ij} \leq 10^{9}$).
Each of the next $n$ lines contains $m$ integers, the $j$-th number in the $i$-th of these lines denotes the $j$-th element of the $i$-th row of the matrix $B$ ($1 \leq B_{ij} \leq 10^{9}$).
-----Output-----
Print "YES" (without quotes) if it is possible to transform $A$ to $B$ and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
-----Examples-----
Input
2 2
1 1
6 1
1 6
1 1
Output
YES
Input
2 2
4 4
4 5
5 4
4 4
Output
NO
Input
3 3
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 4 7
2 5 6
3 8 9
Output
YES
-----Note-----
Consider the third example. The matrix $A$ initially looks as follows.
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3\\ 4 & 5 & 6\\ 7 & 8 & 9 \end{bmatrix} $$
Then we choose the whole matrix as transposed submatrix and it becomes
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 7\\ 2 & 5 & 8\\ 3 & 6 & 9 \end{bmatrix} $$
Then we transpose the submatrix with corners in cells $(2, 2)$ and $(3, 3)$.
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 7\\ 2 & \textbf{5} & \textbf{8}\\ 3 & \textbf{6} & \textbf{9} \end{bmatrix} $$
So matrix becomes
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 7\\ 2 & 5 & 6\\ 3 & 8 & 9 \end{bmatrix} $$
and it is $B$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
For an array of non-negative integers $a$ of size $n$, we construct another array $d$ as follows: $d_1 = a_1$, $d_i = |a_i - a_{i - 1}|$ for $2 \le i \le n$.
Your task is to restore the array $a$ from a given array $d$, or to report that there are multiple possible arrays.
-----Input-----
The first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 100$) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains one integer $n$ ($1 \le n \le 100$) — the size of the arrays $a$ and $d$.
The second line contains $n$ integers $d_1, d_2, \dots, d_n$ ($0 \le d_i \le 100$) — the elements of the array $d$.
It can be shown that there always exists at least one suitable array $a$ under these constraints.
-----Output-----
For each test case, print the elements of the array $a$, if there is only one possible array $a$. Otherwise, print $-1$.
-----Examples-----
Input
3
4
1 0 2 5
3
2 6 3
5
0 0 0 0 0
Output
1 1 3 8
-1
0 0 0 0 0
-----Note-----
In the second example, there are two suitable arrays: $[2, 8, 5]$ and $[2, 8, 11]$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Given an integer a as input, print the value a + a^2 + a^3.
-----Constraints-----
- 1 \leq a \leq 10
- a is an integer.
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
a
-----Output-----
Print the value a + a^2 + a^3 as an integer.
-----Sample Input-----
2
-----Sample Output-----
14
When a = 2, we have a + a^2 + a^3 = 2 + 2^2 + 2^3 = 2 + 4 + 8 = 14.
Print the answer as an input. Outputs such as 14.0 will be judged as incorrect.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The only difference between easy and hard versions is the size of the input.
You are given a string $s$ consisting of $n$ characters, each character is 'R', 'G' or 'B'.
You are also given an integer $k$. Your task is to change the minimum number of characters in the initial string $s$ so that after the changes there will be a string of length $k$ that is a substring of $s$, and is also a substring of the infinite string "RGBRGBRGB ...".
A string $a$ is a substring of string $b$ if there exists a positive integer $i$ such that $a_1 = b_i$, $a_2 = b_{i + 1}$, $a_3 = b_{i + 2}$, ..., $a_{|a|} = b_{i + |a| - 1}$. For example, strings "GBRG", "B", "BR" are substrings of the infinite string "RGBRGBRGB ..." while "GR", "RGR" and "GGG" are not.
You have to answer $q$ independent queries.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains one integer $q$ ($1 \le q \le 2000$) — the number of queries. Then $q$ queries follow.
The first line of the query contains two integers $n$ and $k$ ($1 \le k \le n \le 2000$) — the length of the string $s$ and the length of the substring.
The second line of the query contains a string $s$ consisting of $n$ characters 'R', 'G' and 'B'.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ over all queries does not exceed $2000$ ($\sum n \le 2000$).
-----Output-----
For each query print one integer — the minimum number of characters you need to change in the initial string $s$ so that after changing there will be a substring of length $k$ in $s$ that is also a substring of the infinite string "RGBRGBRGB ...".
-----Example-----
Input
3
5 2
BGGGG
5 3
RBRGR
5 5
BBBRR
Output
1
0
3
-----Note-----
In the first example, you can change the first character to 'R' and obtain the substring "RG", or change the second character to 'R' and obtain "BR", or change the third, fourth or fifth character to 'B' and obtain "GB".
In the second example, the substring is "BRG".
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Nearly each project of the F company has a whole team of developers working on it. They often are in different rooms of the office in different cities and even countries. To keep in touch and track the results of the project, the F company conducts shared online meetings in a Spyke chat.
One day the director of the F company got hold of the records of a part of an online meeting of one successful team. The director watched the record and wanted to talk to the team leader. But how can he tell who the leader is? The director logically supposed that the leader is the person who is present at any conversation during a chat meeting. In other words, if at some moment of time at least one person is present on the meeting, then the leader is present on the meeting.
You are the assistant director. Given the 'user logged on'/'user logged off' messages of the meeting in the chronological order, help the director determine who can be the leader. Note that the director has the record of only a continuous part of the meeting (probably, it's not the whole meeting).
-----Input-----
The first line contains integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 10^5) — the number of team participants and the number of messages. Each of the next m lines contains a message in the format: '+ id': the record means that the person with number id (1 ≤ id ≤ n) has logged on to the meeting. '- id': the record means that the person with number id (1 ≤ id ≤ n) has logged off from the meeting.
Assume that all the people of the team are numbered from 1 to n and the messages are given in the chronological order. It is guaranteed that the given sequence is the correct record of a continuous part of the meeting. It is guaranteed that no two log on/log off events occurred simultaneously.
-----Output-----
In the first line print integer k (0 ≤ k ≤ n) — how many people can be leaders. In the next line, print k integers in the increasing order — the numbers of the people who can be leaders.
If the data is such that no member of the team can be a leader, print a single number 0.
-----Examples-----
Input
5 4
+ 1
+ 2
- 2
- 1
Output
4
1 3 4 5
Input
3 2
+ 1
- 2
Output
1
3
Input
2 4
+ 1
- 1
+ 2
- 2
Output
0
Input
5 6
+ 1
- 1
- 3
+ 3
+ 4
- 4
Output
3
2 3 5
Input
2 4
+ 1
- 2
+ 2
- 1
Output
0
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Little Susie loves strings. Today she calculates distances between them. As Susie is a small girl after all, her strings contain only digits zero and one. She uses the definition of Hamming distance:
We will define the distance between two strings s and t of the same length consisting of digits zero and one as the number of positions i, such that s_{i} isn't equal to t_{i}.
As besides everything else Susie loves symmetry, she wants to find for two strings s and t of length n such string p of length n, that the distance from p to s was equal to the distance from p to t.
It's time for Susie to go to bed, help her find such string p or state that it is impossible.
-----Input-----
The first line contains string s of length n.
The second line contains string t of length n.
The length of string n is within range from 1 to 10^5. It is guaranteed that both strings contain only digits zero and one.
-----Output-----
Print a string of length n, consisting of digits zero and one, that meets the problem statement. If no such string exist, print on a single line "impossible" (without the quotes).
If there are multiple possible answers, print any of them.
-----Examples-----
Input
0001
1011
Output
0011
Input
000
111
Output
impossible
-----Note-----
In the first sample different answers are possible, namely — 0010, 0011, 0110, 0111, 1000, 1001, 1100, 1101.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Section numbers are strings of dot-separated integers. The highest level sections (chapters) are numbered 1, 2, 3, etc. Second level sections are numbered 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, etc. Next level sections are numbered 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.2, 1.2.1, 1.2.2, erc. There is no bound on the number of sections a document may have, nor is there any bound on the number of levels.
A section of a certain level may appear directly inside a section several levels higher without the levels between. For example, section 1.0.1 may appear directly under section 1, without there being any level 2 section. Section 1.1 comes after section 1.0.1. Sections with trailing ".0" are considered to be the same as the section with the trailing ".0" truncated. Thus, section 1.0 is the same as section 1, and section 1.2.0.0 is the same as section 1.2.
```if:python
Write a function `compare(section1, section2)` that returns `-1`, `0`, or `1` depending on whether `section1` is before, same as, or after `section2` respectively.
```
```if:javascript
Write a function `cmp(section1, section2)` that returns `-1`, `0`, or `1` depending on whether `section1` is before, same as, or after `section2` respectively.
```
```if:haskell
Write a function `cmp section1 section2` that returns `LT`, `EQ` or `GT` depending on whether `section1` is before, same as, or after `section2` respectively.
```
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You are given an array $a$ consisting of $n$ integers.
You can remove at most one element from this array. Thus, the final length of the array is $n-1$ or $n$.
Your task is to calculate the maximum possible length of the strictly increasing contiguous subarray of the remaining array.
Recall that the contiguous subarray $a$ with indices from $l$ to $r$ is $a[l \dots r] = a_l, a_{l + 1}, \dots, a_r$. The subarray $a[l \dots r]$ is called strictly increasing if $a_l < a_{l+1} < \dots < a_r$.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains one integer $n$ ($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of elements in $a$.
The second line of the input contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le 10^9$), where $a_i$ is the $i$-th element of $a$.
-----Output-----
Print one integer — the maximum possible length of the strictly increasing contiguous subarray of the array $a$ after removing at most one element.
-----Examples-----
Input
5
1 2 5 3 4
Output
4
Input
2
1 2
Output
2
Input
7
6 5 4 3 2 4 3
Output
2
-----Note-----
In the first example, you can delete $a_3=5$. Then the resulting array will be equal to $[1, 2, 3, 4]$ and the length of its largest increasing subarray will be equal to $4$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
For a non-negative integer K, we define a fractal of level K as follows:
* A fractal of level 0 is a grid with just one white square.
* When K > 0, a fractal of level K is a 3^K \times 3^K grid. If we divide this grid into nine 3^{K-1} \times 3^{K-1} subgrids:
* The central subgrid consists of only black squares.
* Each of the other eight subgrids is a fractal of level K-1.
For example, a fractal of level 2 is as follows:
A fractal of level 2
In a fractal of level 30, let (r, c) denote the square at the r-th row from the top and the c-th column from the left.
You are given Q quadruples of integers (a_i, b_i, c_i, d_i). For each quadruple, find the distance from (a_i, b_i) to (c_i, d_i).
Here the distance from (a, b) to (c, d) is the minimum integer n that satisfies the following condition:
* There exists a sequence of white squares (x_0, y_0), \ldots, (x_n, y_n) satisfying the following conditions:
* (x_0, y_0) = (a, b)
* (x_n, y_n) = (c, d)
* For every i (0 \leq i \leq n-1), (x_i, y_i) and (x_{i+1}, y_{i+1}) share a side.
Constraints
* 1 \leq Q \leq 10000
* 1 \leq a_i, b_i, c_i, d_i \leq 3^{30}
* (a_i, b_i) \neq (c_i, d_i)
* (a_i, b_i) and (c_i, d_i) are white squares.
* All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Q
a_1 \ b_1 \ c_1 \ d_1
:
a_Q \ b_Q \ c_Q \ d_Q
Output
Print Q lines. The i-th line should contain the distance from (a_i, b_i) to (c_i, d_i).
Example
Input
2
4 2 7 4
9 9 1 9
Output
5
8
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
We saw the little game Marmot made for Mole's lunch. Now it's Marmot's dinner time and, as we all know, Marmot eats flowers. At every dinner he eats some red and white flowers. Therefore a dinner can be represented as a sequence of several flowers, some of them white and some of them red.
But, for a dinner to be tasty, there is a rule: Marmot wants to eat white flowers only in groups of size k.
Now Marmot wonders in how many ways he can eat between a and b flowers. As the number of ways could be very large, print it modulo 1000000007 (10^9 + 7).
-----Input-----
Input contains several test cases.
The first line contains two integers t and k (1 ≤ t, k ≤ 10^5), where t represents the number of test cases.
The next t lines contain two integers a_{i} and b_{i} (1 ≤ a_{i} ≤ b_{i} ≤ 10^5), describing the i-th test.
-----Output-----
Print t lines to the standard output. The i-th line should contain the number of ways in which Marmot can eat between a_{i} and b_{i} flowers at dinner modulo 1000000007 (10^9 + 7).
-----Examples-----
Input
3 2
1 3
2 3
4 4
Output
6
5
5
-----Note----- For K = 2 and length 1 Marmot can eat (R). For K = 2 and length 2 Marmot can eat (RR) and (WW). For K = 2 and length 3 Marmot can eat (RRR), (RWW) and (WWR). For K = 2 and length 4 Marmot can eat, for example, (WWWW) or (RWWR), but for example he can't eat (WWWR).
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
## Task:
You have to create a function `isPronic` to check whether the argument passed is a Pronic Number and return true if it is & false otherwise.
### Description:
`Pronic Number` -A pronic number, oblong number, rectangular number or heteromecic number, is a number which is the product of two consecutive integers, that is, n(n + 1).
> The first few Pronic Numbers are - 0, 2, 6, 12, 20, 30, 42...
### Explanation:
0 = 0 × 1 // ∴ 0 is a Pronic Number
2 = 1 × 2 // ∴ 2 is a Pronic Number
6 = 2 × 3 // ∴ 6 is a Pronic Number
12 = 3 × 4 // ∴ 12 is a Pronic Number
20 = 4 × 5 // ∴ 20 is a Pronic Number
30 = 5 × 6 // ∴ 30 is a Pronic Number
42 = 6 × 7 // ∴ 42 is a Pronic Number
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
What are you doing at the end of the world? Are you busy? Will you save us?
<image>
Nephren is playing a game with little leprechauns.
She gives them an infinite array of strings, f0... ∞.
f0 is "What are you doing at the end of the world? Are you busy? Will you save us?".
She wants to let more people know about it, so she defines fi = "What are you doing while sending "fi - 1"? Are you busy? Will you send "fi - 1"?" for all i ≥ 1.
For example, f1 is
"What are you doing while sending "What are you doing at the end of the world? Are you busy? Will you save us?"? Are you busy? Will you send "What are you doing at the end of the world? Are you busy? Will you save us?"?". Note that the quotes in the very beginning and in the very end are for clarity and are not a part of f1.
It can be seen that the characters in fi are letters, question marks, (possibly) quotation marks and spaces.
Nephren will ask the little leprechauns q times. Each time she will let them find the k-th character of fn. The characters are indexed starting from 1. If fn consists of less than k characters, output '.' (without quotes).
Can you answer her queries?
Input
The first line contains one integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 10) — the number of Nephren's questions.
Each of the next q lines describes Nephren's question and contains two integers n and k (0 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1018).
Output
One line containing q characters. The i-th character in it should be the answer for the i-th query.
Examples
Input
3
1 1
1 2
1 111111111111
Output
Wh.
Input
5
0 69
1 194
1 139
0 47
1 66
Output
abdef
Input
10
4 1825
3 75
3 530
4 1829
4 1651
3 187
4 584
4 255
4 774
2 474
Output
Areyoubusy
Note
For the first two examples, refer to f0 and f1 given in the legend.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
A palindrome is a word, phrase, number, or other sequence of characters which reads the same backward as forward. Examples of numerical palindromes are:
2332
110011
54322345
You'll be given 2 numbers as arguments: ```(num,s)```. Write a function which returns an array of ```s``` number of numerical palindromes that come after ```num```. If ```num``` is a palindrome itself, it should be included in the count.
Return "Not valid" instead if any one of the inputs is not an integer or is less than 0.
For this kata, single digit numbers will NOT be considered numerical palindromes.
```
palindrome(6,4) => [11,22,33,44]
palindrome(59,3) => [66,77,88]
palindrome(101,2) => [101,111]
palindrome("15651",5) => "Not valid"
palindrome(1221,"8") => "Not valid"
```
```Haskell
In Haskell, the return type is a Maybe which returns Nothing if either of the inputs is negative."
```
Other Kata in this Series:
Numerical Palindrome #1
Numerical Palindrome #1.5
Numerical Palindrome #2
Numerical Palindrome #3
Numerical Palindrome #3.5
Numerical Palindrome #4
Numerical Palindrome #5
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
< PREVIOUS KATA
NEXT KATA >
###Task:
You have to write a function `pattern` which returns the following Pattern(See Examples) upto (3n-2) rows, where n is parameter.
* Note:`Returning` the pattern is not the same as `Printing` the pattern.
####Rules/Note:
* The pattern should be created using only unit digits.
* If `n < 1` then it should return "" i.e. empty string.
* `The length of each line is same`, and is equal to the length of longest line in the pattern i.e. `length = (3n-2)`.
* Range of Parameters (for the sake of CW Compiler) :
+ `n ∈ (-∞,50]`
###Examples:
+ pattern(5) :
11111
22222
33333
44444
1234555554321
1234555554321
1234555554321
1234555554321
1234555554321
44444
33333
22222
11111
+ pattern(11):
11111111111
22222222222
33333333333
44444444444
55555555555
66666666666
77777777777
88888888888
99999999999
00000000000
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
1234567890111111111110987654321
00000000000
99999999999
88888888888
77777777777
66666666666
55555555555
44444444444
33333333333
22222222222
11111111111
>>>LIST OF ALL MY KATAS<<<
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The cows have just learned what a primitive root is! Given a prime p, a primitive root $\operatorname{mod} p$ is an integer x (1 ≤ x < p) such that none of integers x - 1, x^2 - 1, ..., x^{p} - 2 - 1 are divisible by p, but x^{p} - 1 - 1 is.
Unfortunately, computing primitive roots can be time consuming, so the cows need your help. Given a prime p, help the cows find the number of primitive roots $\operatorname{mod} p$.
-----Input-----
The input contains a single line containing an integer p (2 ≤ p < 2000). It is guaranteed that p is a prime.
-----Output-----
Output on a single line the number of primitive roots $\operatorname{mod} p$.
-----Examples-----
Input
3
Output
1
Input
5
Output
2
-----Note-----
The only primitive root $\operatorname{mod} 3$ is 2.
The primitive roots $\operatorname{mod} 5$ are 2 and 3.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Problem Statement
In the headquarter building of ICPC (International Company of Plugs & Connectors), there are $M$ light bulbs and they are controlled by $N$ switches. Each light bulb can be turned on or off by exactly one switch. Each switch may control multiple light bulbs. When you operate a switch, all the light bulbs controlled by the switch change their states. You lost the table that recorded the correspondence between the switches and the light bulbs, and want to restore it.
You decided to restore the correspondence by the following procedure.
* At first, every switch is off and every light bulb is off.
* You operate some switches represented by $S_1$.
* You check the states of the light bulbs represented by $B_1$.
* You operate some switches represented by $S_2$.
* You check the states of the light bulbs represented by $B_2$.
* ...
* You operate some switches represented by $S_Q$.
* You check the states of the light bulbs represented by $B_Q$.
After you operate some switches and check the states of the light bulbs, the states of the switches and the light bulbs are kept for next operations.
Can you restore the correspondence between the switches and the light bulbs using the information about the switches you have operated and the states of the light bulbs you have checked?
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets. The number of dataset is no more than $50$ and the file size is no more than $10\mathrm{MB}$. Each dataset is formatted as follows.
> $N$ $M$ $Q$
> $S_1$ $B_1$
> :
> :
> $S_Q$ $B_Q$
The first line of each dataset contains three integers $N$ ($1 \le N \le 36$), $M$ ($1 \le M \le 1{,}000$), $Q$ ($0 \le Q \le 1{,}000$), which denote the number of switches, the number of light bulbs and the number of operations respectively. The following $Q$ lines describe the information about the switches you have operated and the states of the light bulbs you have checked. The $i$-th of them contains two strings $S_i$ and $B_i$ of lengths $N$ and $M$ respectively. Each $S_i$ denotes the set of the switches you have operated: $S_{ij}$ is either $0$ or $1$, which denotes the $j$-th switch is not operated or operated respectively. Each $B_i$ denotes the states of the light bulbs: $B_{ij}$ is either $0$ or $1$, which denotes the $j$-th light bulb is off or on respectively.
You can assume that there exists a correspondence between the switches and the light bulbs which is consistent with the given information.
The end of input is indicated by a line containing three zeros.
Output
For each dataset, output the correspondence between the switches and the light bulbs consisting of $M$ numbers written in base-$36$. In the base-$36$ system for this problem, the values $0$-$9$ and $10$-$35$ are represented by the characters '0'-'9' and 'A'-'Z' respectively. The $i$-th character of the correspondence means the number of the switch controlling the $i$-th light bulb. If you cannot determine which switch controls the $i$-th light bulb, output '?' as the $i$-th character instead of the number of a switch.
Sample Input
3 10 3
000 0000000000
110 0000001111
101 1111111100
2 2 0
1 1 0
2 1 1
01 1
11 11 10
10000000000 10000000000
11000000000 01000000000
01100000000 00100000000
00110000000 00010000000
00011000000 00001000000
00001100000 00000100000
00000110000 00000010000
00000011000 00000001000
00000001100 00000000100
00000000110 00000000010
0 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
2222221100
??
0
1
0123456789A
Example
Input
3 10 3
000 0000000000
110 0000001111
101 1111111100
2 2 0
1 1 0
2 1 1
01 1
11 11 10
10000000000 10000000000
11000000000 01000000000
01100000000 00100000000
00110000000 00010000000
00011000000 00001000000
00001100000 00000100000
00000110000 00000010000
00000011000 00000001000
00000001100 00000000100
00000000110 00000000010
0 0 0
Output
2222221100
??
0
1
0123456789A
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Polycarp wants to train before another programming competition. During the first day of his training he should solve exactly $1$ problem, during the second day — exactly $2$ problems, during the third day — exactly $3$ problems, and so on. During the $k$-th day he should solve $k$ problems.
Polycarp has a list of $n$ contests, the $i$-th contest consists of $a_i$ problems. During each day Polycarp has to choose exactly one of the contests he didn't solve yet and solve it. He solves exactly $k$ problems from this contest. Other problems are discarded from it. If there are no contests consisting of at least $k$ problems that Polycarp didn't solve yet during the $k$-th day, then Polycarp stops his training.
How many days Polycarp can train if he chooses the contests optimally?
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains one integer $n$ ($1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of contests.
The second line of the input contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of problems in the $i$-th contest.
-----Output-----
Print one integer — the maximum number of days Polycarp can train if he chooses the contests optimally.
-----Examples-----
Input
4
3 1 4 1
Output
3
Input
3
1 1 1
Output
1
Input
5
1 1 1 2 2
Output
2
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
We have a string S consisting of lowercase English letters.
If the length of S is at most K, print S without change.
If the length of S exceeds K, extract the first K characters in S, append ... to the end of them, and print the result.
-----Constraints-----
- K is an integer between 1 and 100 (inclusive).
- S is a string consisting of lowercase English letters.
- The length of S is between 1 and 100 (inclusive).
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
K
S
-----Output-----
Print a string as stated in Problem Statement.
-----Sample Input-----
7
nikoandsolstice
-----Sample Output-----
nikoand...
nikoandsolstice has a length of 15, which exceeds K=7.
We should extract the first 7 characters in this string, append ... to the end of them, and print the result nikoand....
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You want to build a fence that will consist of $n$ equal sections. All sections have a width equal to $1$ and height equal to $k$. You will place all sections in one line side by side.
Unfortunately, the ground beneath the fence is not flat. For simplicity, you can think that the ground level under the $i$-th section is equal to $h_i$.
You should follow several rules to build the fence:
the consecutive sections should have a common side of length at least $1$;
the first and the last sections should stand on the corresponding ground levels;
the sections between may be either on the ground level or higher, but not higher than $k - 1$ from the ground level $h_i$ (the height should be an integer);
One of possible fences (blue color) for the first test case
Is it possible to build a fence that meets all rules?
-----Input-----
The first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $n$ and $k$ ($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$; $2 \le k \le 10^8$) — the number of sections in the fence and the height of each section.
The second line of each test case contains $n$ integers $h_1, h_2, \dots, h_n$ ($0 \le h_i \le 10^8$), where $h_i$ is the ground level beneath the $i$-th section.
It's guaranteed that the sum of $n$ over test cases doesn't exceed $2 \cdot 10^5$.
-----Output-----
For each test case print YES if it's possible to build the fence that meets all rules. Otherwise, print NO.
You may print each letter in any case (for example, YES, Yes, yes, yEs will all be recognized as positive answer).
-----Examples-----
Input
3
6 3
0 0 2 5 1 1
2 3
0 2
3 2
3 0 2
Output
YES
YES
NO
-----Note-----
In the first test case, one of the possible fences is shown in the picture.
In the second test case, according to the second rule, you should build both sections on the corresponding ground levels, and since $k = 3$, $h_1 = 0$, and $h_2 = 2$ the first rule is also fulfilled.
In the third test case, according to the second rule, you should build the first section on height $3$ and the third section on height $2$. According to the first rule, the second section should be on the height of at least $2$ (to have a common side with the first section), but according to the third rule, the second section can be built on the height of at most $h_2 + k - 1 = 1$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
## Task
To charge your mobile phone battery, do you know how much time it takes from 0% to 100%? It depends on your cell phone battery capacity and the power of the charger. A rough calculation method is:
```
0% --> 85% (fast charge)
(battery capacity(mAh) * 85%) / power of the charger(mA)
85% --> 95% (decreasing charge)
(battery capacity(mAh) * 10%) / (power of the charger(mA) * 50%)
95% --> 100% (trickle charge)
(battery capacity(mAh) * 5%) / (power of the charger(mA) * 20%)
```
For example: Your battery capacity is 1000 mAh and you use a charger 500 mA, to charge your mobile phone battery from 0% to 100% needs time:
```
0% --> 85% (fast charge) 1.7 (hour)
85% --> 95% (decreasing charge) 0.4 (hour)
95% --> 100% (trickle charge) 0.5 (hour)
total times = 1.7 + 0.4 + 0.5 = 2.6 (hour)
```
Complete function `calculateTime` that accepts two arguments `battery` and `charger`, return how many hours can charge the battery from 0% to 100%. The result should be a number, round to 2 decimal places (In Haskell, no need to round it).
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Kavi has 2n points lying on the OX axis, i-th of which is located at x = i.
Kavi considers all ways to split these 2n points into n pairs. Among those, he is interested in good pairings, which are defined as follows:
Consider n segments with ends at the points in correspondent pairs. The pairing is called good, if for every 2 different segments A and B among those, at least one of the following holds:
* One of the segments A and B lies completely inside the other.
* A and B have the same length.
Consider the following example:
<image>
A is a good pairing since the red segment lies completely inside the blue segment.
B is a good pairing since the red and the blue segment have the same length.
C is not a good pairing since none of the red or blue segments lies inside the other, neither do they have the same size.
Kavi is interested in the number of good pairings, so he wants you to find it for him. As the result can be large, find this number modulo 998244353.
Two pairings are called different, if some two points are in one pair in some pairing and in different pairs in another.
Input
The single line of the input contains a single integer n (1≤ n ≤ 10^6).
Output
Print the number of good pairings modulo 998244353.
Examples
Input
1
Output
1
Input
2
Output
3
Input
3
Output
6
Input
100
Output
688750769
Note
The good pairings for the second example are:
<image>
In the third example, the good pairings are:
<image>
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You are given an array of integers. Vasya can permute (change order) its integers. He wants to do it so that as many as possible integers will become on a place where a smaller integer used to stand. Help Vasya find the maximal number of such integers.
For instance, if we are given an array $[10, 20, 30, 40]$, we can permute it so that it becomes $[20, 40, 10, 30]$. Then on the first and the second positions the integers became larger ($20>10$, $40>20$) and did not on the third and the fourth, so for this permutation, the number that Vasya wants to maximize equals $2$. Read the note for the first example, there is one more demonstrative test case.
Help Vasya to permute integers in such way that the number of positions in a new array, where integers are greater than in the original one, is maximal.
-----Input-----
The first line contains a single integer $n$ ($1 \leq n \leq 10^5$) — the length of the array.
The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($1 \leq a_i \leq 10^9$) — the elements of the array.
-----Output-----
Print a single integer — the maximal number of the array's elements which after a permutation will stand on the position where a smaller element stood in the initial array.
-----Examples-----
Input
7
10 1 1 1 5 5 3
Output
4
Input
5
1 1 1 1 1
Output
0
-----Note-----
In the first sample, one of the best permutations is $[1, 5, 5, 3, 10, 1, 1]$. On the positions from second to fifth the elements became larger, so the answer for this permutation is 4.
In the second sample, there is no way to increase any element with a permutation, so the answer is 0.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Have you ever tasted Martian food? Well, you should.
Their signature dish is served on a completely black plate with the radius of R, flat as a pancake.
First, they put a perfectly circular portion of the Golden Honduras on the plate. It has the radius of r and is located as close to the edge of the plate as possible staying entirely within the plate. I. e. Golden Honduras touches the edge of the plate from the inside. It is believed that the proximity of the portion of the Golden Honduras to the edge of a plate demonstrates the neatness and exactness of the Martians.
Then a perfectly round portion of Pink Guadeloupe is put on the plate. The Guadeloupe should not overlap with Honduras, should not go beyond the border of the plate, but should have the maximum radius. I. e. Pink Guadeloupe should touch the edge of the plate from the inside, and touch Golden Honduras from the outside. For it is the size of the Rose Guadeloupe that shows the generosity and the hospitality of the Martians.
Further, the first portion (of the same perfectly round shape) of Green Bull Terrier is put on the plate. It should come in contact with Honduras and Guadeloupe, should not go beyond the border of the plate and should have maximum radius.
Each of the following portions of the Green Bull Terrier must necessarily touch the Golden Honduras, the previous portion of the Green Bull Terrier and touch the edge of a plate, but should not go beyond the border.
To determine whether a stranger is worthy to touch the food, the Martians ask him to find the radius of the k-th portion of the Green Bull Terrier knowing the radii of a plate and a portion of the Golden Honduras. And are you worthy?
Input
The first line contains integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 104) — amount of testcases.
Each of the following t lines contain three positive integers: the radii of the plate and a portion of the Golden Honduras R and r (1 ≤ r < R ≤ 104) and the number k (1 ≤ k ≤ 104).
In the pretests 1 ≤ k ≤ 2.
Output
Print t lines — the radius of the k-th portion of the Green Bull Terrier for each test. The absolute or relative error of the answer should not exceed 10 - 6.
Examples
Input
2
4 3 1
4 2 2
Output
0.9230769231
0.6666666667
Note
Dish from the first sample looks like this:
<image>
Dish from the second sample looks like this:
<image>
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Appleman has a tree with n vertices. Some of the vertices (at least one) are colored black and other vertices are colored white.
Consider a set consisting of k (0 ≤ k < n) edges of Appleman's tree. If Appleman deletes these edges from the tree, then it will split into (k + 1) parts. Note, that each part will be a tree with colored vertices.
Now Appleman wonders, what is the number of sets splitting the tree in such a way that each resulting part will have exactly one black vertex? Find this number modulo 1000000007 (10^9 + 7).
-----Input-----
The first line contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10^5) — the number of tree vertices.
The second line contains the description of the tree: n - 1 integers p_0, p_1, ..., p_{n} - 2 (0 ≤ p_{i} ≤ i). Where p_{i} means that there is an edge connecting vertex (i + 1) of the tree and vertex p_{i}. Consider tree vertices are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
The third line contains the description of the colors of the vertices: n integers x_0, x_1, ..., x_{n} - 1 (x_{i} is either 0 or 1). If x_{i} is equal to 1, vertex i is colored black. Otherwise, vertex i is colored white.
-----Output-----
Output a single integer — the number of ways to split the tree modulo 1000000007 (10^9 + 7).
-----Examples-----
Input
3
0 0
0 1 1
Output
2
Input
6
0 1 1 0 4
1 1 0 0 1 0
Output
1
Input
10
0 1 2 1 4 4 4 0 8
0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1
Output
27
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You are a given an array $a$ of length $n$. Find a subarray $a[l..r]$ with length at least $k$ with the largest median.
A median in an array of length $n$ is an element which occupies position number $\lfloor \frac{n + 1}{2} \rfloor$ after we sort the elements in non-decreasing order. For example: $median([1, 2, 3, 4]) = 2$, $median([3, 2, 1]) = 2$, $median([2, 1, 2, 1]) = 1$.
Subarray $a[l..r]$ is a contiguous part of the array $a$, i. e. the array $a_l,a_{l+1},\ldots,a_r$ for some $1 \leq l \leq r \leq n$, its length is $r - l + 1$.
-----Input-----
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $k$ ($1 \leq k \leq n \leq 2 \cdot 10^5$).
The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($1 \leq a_i \leq n$).
-----Output-----
Output one integer $m$ — the maximum median you can get.
-----Examples-----
Input
5 3
1 2 3 2 1
Output
2
Input
4 2
1 2 3 4
Output
3
-----Note-----
In the first example all the possible subarrays are $[1..3]$, $[1..4]$, $[1..5]$, $[2..4]$, $[2..5]$ and $[3..5]$ and the median for all of them is $2$, so the maximum possible median is $2$ too.
In the second example $median([3..4]) = 3$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Snuke lives at position x on a number line.
On this line, there are two stores A and B, respectively at position a and b, that offer food for delivery.
Snuke decided to get food delivery from the closer of stores A and B.
Find out which store is closer to Snuke's residence.
Here, the distance between two points s and t on a number line is represented by |s-t|.
-----Constraints-----
- 1 \leq x \leq 1000
- 1 \leq a \leq 1000
- 1 \leq b \leq 1000
- x, a and b are pairwise distinct.
- The distances between Snuke's residence and stores A and B are different.
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
x a b
-----Output-----
If store A is closer, print A; if store B is closer, print B.
-----Sample Input-----
5 2 7
-----Sample Output-----
B
The distances between Snuke's residence and stores A and B are 3 and 2, respectively.
Since store B is closer, print B.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
### What is simplifying a square root?
If you have a number, like 80, for example, you would start by finding the greatest perfect square divisible by 80. In this case, that's 16. Find the square root of 16, and multiply it by 80 / 16. Answer = 4 √5.
##### The above example:
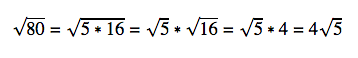
### Task:
Your job is to write two functions, `simplify`, and `desimplify`, that simplify and desimplify square roots, respectively. (Desimplify isn't a word, but I couldn't come up with a better way to put it.) `simplify` will take an integer and return a string like "x sqrt y", and `desimplify` will take a string like "x sqrt y" and return an integer. For `simplify`, if a square root cannot be simplified, return "sqrt y".
_Do not modify the input._
### Some examples:
```python
simplify(1) #=> "1"
simplify(2) #=> "sqrt 2"
simplify(3) #=> "sqrt 3"
simplify(8) #=> "2 sqrt 2"
simplify(15) #=> "sqrt 15"
simplify(16) #=> "4"
simplify(18) #=> "3 sqrt 2"
simplify(20) #=> "2 sqrt 5"
simplify(24) #=> "2 sqrt 6"
simplify(32) #=> "4 sqrt 2"
desimplify("1") #=> 1
desimplify("sqrt 2") #=> 2
desimplify("sqrt 3") #=> 3
desimplify("2 sqrt 2") #=> 8
desimplify("sqrt 15") #=> 15
desimplify("4") #=> 16
desimplify("3 sqrt 2") #=> 18
desimplify("2 sqrt 5") #=> 20
desimplify("2 sqrt 6") #=> 24
desimplify("4 sqrt 2") #=> 32
```
Also check out my other creations — [Square Roots: Approximation](https://www.codewars.com/kata/square-roots-approximation), [Square and Cubic Factors](https://www.codewars.com/kata/square-and-cubic-factors), [Keep the Order](https://www.codewars.com/kata/keep-the-order), [Naming Files](https://www.codewars.com/kata/naming-files), [Elections: Weighted Average](https://www.codewars.com/kata/elections-weighted-average), [Identify Case](https://www.codewars.com/kata/identify-case), [Split Without Loss](https://www.codewars.com/kata/split-without-loss), [Adding Fractions](https://www.codewars.com/kata/adding-fractions),
[Random Integers](https://www.codewars.com/kata/random-integers), [Implement String#transpose](https://www.codewars.com/kata/implement-string-number-transpose), [Implement Array#transpose!](https://www.codewars.com/kata/implement-array-number-transpose), [Arrays and Procs #1](https://www.codewars.com/kata/arrays-and-procs-number-1), and [Arrays and Procs #2](https://www.codewars.com/kata/arrays-and-procs-number-2).
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Simple transposition is a basic and simple cryptography technique. We make 2 rows and put first a letter in the Row 1, the second in the Row 2, third in Row 1 and so on until the end. Then we put the text from Row 2 next to the Row 1 text and thats it.
Complete the function that receives a string and encrypt it with this simple transposition.
## Example
For example if the text to encrypt is: `"Simple text"`, the 2 rows will be:
Row 1
S
m
l
e
t
Row 2
i
p
e
t
x
So the result string will be: `"Sml etipetx"`
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You have received data from a Bubble bot. You know your task is to make factory facilities, but before you even start, you need to know how big the factory is and how many rooms it has. When you look at the data you see that you have the dimensions of the construction, which is in rectangle shape: N x M.
Then in the next N lines you have M numbers. These numbers represent factory tiles and they can go from 0 to 15. Each of these numbers should be looked in its binary form. Because from each number you know on which side the tile has walls. For example number 10 in it's binary form is 1010, which means that it has a wall from the North side, it doesn't have a wall from the East, it has a wall on the South side and it doesn't have a wall on the West side. So it goes North, East, South, West.
It is guaranteed that the construction always has walls on it's edges. The input will be correct.
Your task is to print the size of the rooms from biggest to smallest.
Input
The first line has two numbers which are N and M, the size of the construction. Both are integers:
n (1 ≤ n ≤ 10^3)
m (1 ≤ m ≤ 10^3)
Next N x M numbers represent each tile of construction.
Output
Once you finish processing the data your output consists of one line sorted from biggest to smallest room sizes.
Example
Input
4 5
9 14 11 12 13
5 15 11 6 7
5 9 14 9 14
3 2 14 3 14
Output
9 4 4 2 1
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Example
Input
2 2 2 1
0 0 0
Output
24
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Recently Vova found $n$ candy wrappers. He remembers that he bought $x$ candies during the first day, $2x$ candies during the second day, $4x$ candies during the third day, $\dots$, $2^{k-1} x$ candies during the $k$-th day. But there is an issue: Vova remembers neither $x$ nor $k$ but he is sure that $x$ and $k$ are positive integers and $k > 1$.
Vova will be satisfied if you tell him any positive integer $x$ so there is an integer $k>1$ that $x + 2x + 4x + \dots + 2^{k-1} x = n$. It is guaranteed that at least one solution exists. Note that $k > 1$.
You have to answer $t$ independent test cases.
-----Input-----
The first line of the input contains one integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$) — the number of test cases. Then $t$ test cases follow.
The only line of the test case contains one integer $n$ ($3 \le n \le 10^9$) — the number of candy wrappers Vova found. It is guaranteed that there is some positive integer $x$ and integer $k>1$ that $x + 2x + 4x + \dots + 2^{k-1} x = n$.
-----Output-----
Print one integer — any positive integer value of $x$ so there is an integer $k>1$ that $x + 2x + 4x + \dots + 2^{k-1} x = n$.
-----Example-----
Input
7
3
6
7
21
28
999999999
999999984
Output
1
2
1
7
4
333333333
333333328
-----Note-----
In the first test case of the example, one of the possible answers is $x=1, k=2$. Then $1 \cdot 1 + 2 \cdot 1$ equals $n=3$.
In the second test case of the example, one of the possible answers is $x=2, k=2$. Then $1 \cdot 2 + 2 \cdot 2$ equals $n=6$.
In the third test case of the example, one of the possible answers is $x=1, k=3$. Then $1 \cdot 1 + 2 \cdot 1 + 4 \cdot 1$ equals $n=7$.
In the fourth test case of the example, one of the possible answers is $x=7, k=2$. Then $1 \cdot 7 + 2 \cdot 7$ equals $n=21$.
In the fifth test case of the example, one of the possible answers is $x=4, k=3$. Then $1 \cdot 4 + 2 \cdot 4 + 4 \cdot 4$ equals $n=28$.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You are given a string of length N. Calculate the number of distinct substrings of S.
Constraints
* 1 \leq N \leq 500,000
* S consists of lowercase English letters.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S
Output
Print the answer.
Examples
Input
abcbcba
Output
21
Input
mississippi
Output
53
Input
ababacaca
Output
33
Input
aaaaa
Output
5
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Snuke has decided to use a robot to clean his room.
There are N pieces of trash on a number line. The i-th piece from the left is at position x_i. We would like to put all of them in a trash bin at position 0.
For the positions of the pieces of trash, 0 < x_1 < x_2 < ... < x_{N} \leq 10^{9} holds.
The robot is initially at position 0. It can freely move left and right along the number line, pick up a piece of trash when it comes to the position of that piece, carry any number of pieces of trash and put them in the trash bin when it comes to position 0. It is not allowed to put pieces of trash anywhere except in the trash bin.
The robot consumes X points of energy when the robot picks up a piece of trash, or put pieces of trash in the trash bin. (Putting any number of pieces of trash in the trash bin consumes X points of energy.) Also, the robot consumes (k+1)^{2} points of energy to travel by a distance of 1 when the robot is carrying k pieces of trash.
Find the minimum amount of energy required to put all the N pieces of trash in the trash bin.
Constraints
* 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^{5}
* 0 < x_1 < ... < x_N \leq 10^9
* 1 \leq X \leq 10^9
* All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N X
x_1 x_2 ... x_{N}
Output
Print the answer.
Examples
Input
2 100
1 10
Output
355
Input
5 1
1 999999997 999999998 999999999 1000000000
Output
19999999983
Input
10 8851025
38 87 668 3175 22601 65499 90236 790604 4290609 4894746
Output
150710136
Input
16 10
1 7 12 27 52 75 731 13856 395504 534840 1276551 2356789 9384806 19108104 82684732 535447408
Output
3256017715
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The winner of the card game popular in Berland "Berlogging" is determined according to the following rules. If at the end of the game there is only one player with the maximum number of points, he is the winner. The situation becomes more difficult if the number of such players is more than one. During each round a player gains or loses a particular number of points. In the course of the game the number of points is registered in the line "name score", where name is a player's name, and score is the number of points gained in this round, which is an integer number. If score is negative, this means that the player has lost in the round. So, if two or more players have the maximum number of points (say, it equals to m) at the end of the game, than wins the one of them who scored at least m points first. Initially each player has 0 points. It's guaranteed that at the end of the game at least one player has a positive number of points.
Input
The first line contains an integer number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000), n is the number of rounds played. Then follow n lines, containing the information about the rounds in "name score" format in chronological order, where name is a string of lower-case Latin letters with the length from 1 to 32, and score is an integer number between -1000 and 1000, inclusive.
Output
Print the name of the winner.
Examples
Input
3
mike 3
andrew 5
mike 2
Output
andrew
Input
3
andrew 3
andrew 2
mike 5
Output
andrew
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Problem statement
2D, who is good at cooking, is trying to make lunch. Cooking requires all N ingredients a_ {0}, a_ {1},…, a_ {N−1}.
Now, 2D's refrigerator doesn't contain any ingredients, so I have to go to the supermarket to buy it. At the supermarket, you can buy the material a_ {i} for the price x_ {i} yen.
2D is also a wizard and can use M types of magic. The i-th magic can be changed to the material t_ {i} by applying it to the material s_ {i}, and conversely to s_ {i} by applying it to the material t_ {i}. In addition, you can repeatedly use multiple spells on a single material. For example, you can get r from p using the magic of changing from p to q and the magic of changing from q to r.
2D decided to use the power of magic to prepare the materials as cheaply as possible. Find the minimum sum of the prices of the ingredients that 2D needs to buy to complete the dish.
input
The input is given in the following format.
N
a_ {0} x_ {0}
...
a_ {N−1} x_ {N−1}
M
s_ {0} t_ {0}
...
s_ {M−1} t_ {M−1}
Constraint
* All numbers are integers
* All material names consist of at least 1 and no more than 10 lowercase letters.
* If i ≠ j, then a_ {i} ≠ a_ {j}
* 1 \ ≤ x_ {i} \ ≤ 1,000
* 1 \ ≤ N \ ≤ 5,000
* 0 \ ≤ M \ ≤ {\ rm min} (N (N−1) / 2, 1000)
* s_ {i} ≠ t_ {i}
* There is no duplication in the pair of s_ {i}, t_ {i}
* s_ {i}, t_ {i} are included in a_ {0},…, a_ {N−1}
output
Print the answer in one line.
sample
Sample input 1
2
tako 2
yaki 1
1
tako yaki
You can magically turn a cheap yaki into a tako, so buy two yaki.
Sample output 1
2
Sample input 2
Five
a 1
b 2
c 2
d 4
e 3
Five
b a
a c
c d
e b
c b
Sample output 2
Five
As shown below, all materials can be changed from a.
* a: a as it is
* b: a-> c-> b
* c: a-> c
* d: a-> c-> d
* e: a-> b-> e
<image>
Example
Input
2
tako 2
yaki 1
1
tako yaki
Output
2
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Your friend gave you a dequeue D as a birthday present.
D is a horizontal cylinder that contains a row of N jewels.
The values of the jewels are V_1, V_2, ..., V_N from left to right. There may be jewels with negative values.
In the beginning, you have no jewel in your hands.
You can perform at most K operations on D, chosen from the following, at most K times (possibly zero):
- Operation A: Take out the leftmost jewel contained in D and have it in your hand. You cannot do this operation when D is empty.
- Operation B: Take out the rightmost jewel contained in D and have it in your hand. You cannot do this operation when D is empty.
- Operation C: Choose a jewel in your hands and insert it to the left end of D. You cannot do this operation when you have no jewel in your hand.
- Operation D: Choose a jewel in your hands and insert it to the right end of D. You cannot do this operation when you have no jewel in your hand.
Find the maximum possible sum of the values of jewels in your hands after the operations.
-----Constraints-----
- All values in input are integers.
- 1 \leq N \leq 50
- 1 \leq K \leq 100
- -10^7 \leq V_i \leq 10^7
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N K
V_1 V_2 ... V_N
-----Output-----
Print the maximum possible sum of the values of jewels in your hands after the operations.
-----Sample Input-----
6 4
-10 8 2 1 2 6
-----Sample Output-----
14
After the following sequence of operations, you have two jewels of values 8 and 6 in your hands for a total of 14, which is the maximum result.
- Do operation A. You take out the jewel of value -10 from the left end of D.
- Do operation B. You take out the jewel of value 6 from the right end of D.
- Do operation A. You take out the jewel of value 8 from the left end of D.
- Do operation D. You insert the jewel of value -10 to the right end of D.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
A permutation p of size n is an array such that every integer from 1 to n occurs exactly once in this array.
Let's call a permutation an almost identity permutation iff there exist at least n - k indices i (1 ≤ i ≤ n) such that p_{i} = i.
Your task is to count the number of almost identity permutations for given numbers n and k.
-----Input-----
The first line contains two integers n and k (4 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 4).
-----Output-----
Print the number of almost identity permutations for given n and k.
-----Examples-----
Input
4 1
Output
1
Input
4 2
Output
7
Input
5 3
Output
31
Input
5 4
Output
76
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
problem
You are a traveler traveling on the JOI Highway. The JOI Highway is a road that extends straight from east to west, and there are n post towns on the JOI Highway. Numbered. The westernmost post town on the JOI highway is post town 1, and the easternmost post town is post town n.
You have decided to depart from post town 1 and embark on an m-day journey. Your itinerary is determined according to the sequence a1, a2, ..., am as follows. It is a non-zero integer that represents how to move the eyes. If the post town you depart on day i is post town k, then on day i you move straight from post town k to post town k + ai. Means to do.
The number of post towns n, the number of days of travel m, the information on the distance between post towns, and the sequence a1, a2, ... Create a program that finds the remainder by dividing the sum by 100000 = 105.
Diagram corresponding to the input / output example
<image>
output
The output consists of one line containing the remainder of your total distance traveled in the m-day journey divided by 100000 = 105.
Input / output example
Input example 1
7 5
2
1
1
3
2
1
2
-1
3
2
-3
Output example 1
18
On the first day you move from post town 1 to post town 3. On the second day you move from post town 3 to post town 2. And on the third day you move from post town 2 to post town 5. Move, move from post town 5 to post town 7 on the 4th day, move from post town 7 to post town 4 on the 5th day. Your total travel distance in a 5-day trip is 18.
The above question sentences and the data used for the automatic referee are the question sentences created and published by the Japan Committee for Information Olympics and the test data for scoring.
input
The integers n and m are separated by blanks on the first line. N (2 ≤ n ≤ 100000 = 105) is the number of post towns on the JOI highway, and m (1 ≤ m ≤ 100000 = 105) is Represents the number of days of travel.
The following n − 1 line represents the distance between post towns on the JOI highway. I + 1st line (1 ≤ i ≤ n − 1) is a positive integer si that represents the distance between post town i and post town i + 1. (1 ≤ si ≤ 100) is written.
The following m line contains a sequence of movements for m days. Line i + n (1 ≤ i ≤ m) contains a non-zero integer ai that represents your movement method for day i. Has been.
In the scoring data, it does not move west of post town 1 or east of post town n.
Of the scoring data, 50% of the points are satisfied with n ≤ 100 and m ≤ 100.
Example
Input
7 5
2
1
1
3
2
1
2
-1
3
2
-3
Output
18
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Petya loves lucky numbers very much. Everybody knows that lucky numbers are positive integers whose decimal record contains only the lucky digits 4 and 7. For example, numbers 47, 744, 4 are lucky and 5, 17, 467 are not.
Petya calls a mask of a positive integer n the number that is obtained after successive writing of all lucky digits of number n from the left to the right. For example, the mask of number 72174994 is number 7744, the mask of 7 is 7, the mask of 9999047 is 47. Obviously, mask of any number is always a lucky number.
Petya has two numbers — an arbitrary integer a and a lucky number b. Help him find the minimum number c (c > a) such that the mask of number c equals b.
Input
The only line contains two integers a and b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 105). It is guaranteed that number b is lucky.
Output
In the only line print a single number — the number c that is sought by Petya.
Examples
Input
1 7
Output
7
Input
100 47
Output
147
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
You are given a string S of length N and another string T of length M. These strings consist of lowercase English letters.
A string X is called a good string when the following conditions are all met:
* Let L be the length of X. L is divisible by both N and M.
* Concatenating the 1-st, (\frac{L}{N}+1)-th, (2 \times \frac{L}{N}+1)-th, ..., ((N-1)\times\frac{L}{N}+1)-th characters of X, without changing the order, results in S.
* Concatenating the 1-st, (\frac{L}{M}+1)-th, (2 \times \frac{L}{M}+1)-th, ..., ((M-1)\times\frac{L}{M}+1)-th characters of X, without changing the order, results in T.
Determine if there exists a good string. If it exists, find the length of the shortest such string.
Constraints
* 1 \leq N,M \leq 10^5
* S and T consist of lowercase English letters.
* |S|=N
* |T|=M
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M
S
T
Output
If a good string does not exist, print `-1`; if it exists, print the length of the shortest such string.
Examples
Input
3 2
acp
ae
Output
6
Input
6 3
abcdef
abc
Output
-1
Input
15 9
dnsusrayukuaiia
dujrunuma
Output
45
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
# Task
You are given a string consisting of `"D", "P" and "C"`. A positive integer N is called DPC of this string if it satisfies the following properties:
```
For each i = 1, 2, ... , size of the string:
If i-th character is "D", then N can be divided by i
If i-th character is "P", then N and i should be relatively prime
If i-th character is "C", then N should neither be divided by i
nor be relatively prime with i```
Your task is to find the smallest DPC of a given string, or return `-1` if there is no such. The result is guaranteed to be `<= 10^9`.
# Example
For `s = "DDPDD"`, the result should be `20`.
`"DDPDD"` means `N` should `divided by 1,2,4,5`, and `N,3` should be relatively prime. The smallest N should be `20`.
# Input/Output
- `[input]` string `s`
The given string
- `[output]` an integer
The smallest DPC of `s` or `-1` if it doesn't exist.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Kilani is playing a game with his friends. This game can be represented as a grid of size $n \times m$, where each cell is either empty or blocked, and every player has one or more castles in some cells (there are no two castles in one cell).
The game is played in rounds. In each round players expand turn by turn: firstly, the first player expands, then the second player expands and so on. The expansion happens as follows: for each castle the player owns now, he tries to expand into the empty cells nearby. The player $i$ can expand from a cell with his castle to the empty cell if it's possible to reach it in at most $s_i$ (where $s_i$ is player's expansion speed) moves to the left, up, right or down without going through blocked cells or cells occupied by some other player's castle. The player examines the set of cells he can expand to and builds a castle in each of them at once. The turned is passed to the next player after that.
The game ends when no player can make a move. You are given the game field and speed of the expansion for each player. Kilani wants to know for each player how many cells he will control (have a castle their) after the game ends.
-----Input-----
The first line contains three integers $n$, $m$ and $p$ ($1 \le n, m \le 1000$, $1 \le p \le 9$) — the size of the grid and the number of players.
The second line contains $p$ integers $s_i$ ($1 \le s \le 10^9$) — the speed of the expansion for every player.
The following $n$ lines describe the game grid. Each of them consists of $m$ symbols, where '.' denotes an empty cell, '#' denotes a blocked cell and digit $x$ ($1 \le x \le p$) denotes the castle owned by player $x$.
It is guaranteed, that each player has at least one castle on the grid.
-----Output-----
Print $p$ integers — the number of cells controlled by each player after the game ends.
-----Examples-----
Input
3 3 2
1 1
1..
...
..2
Output
6 3
Input
3 4 4
1 1 1 1
....
#...
1234
Output
1 4 3 3
-----Note-----
The picture below show the game before it started, the game after the first round and game after the second round in the first example:
[Image]
In the second example, the first player is "blocked" so he will not capture new cells for the entire game. All other player will expand up during the first two rounds and in the third round only the second player will move to the left.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Our master carpenter is designing a condominium called Bange Hills Mansion. The condominium is constructed by stacking up floors of the same height. The height of each floor is designed so that the total height of the stacked floors coincides with the predetermined height of the condominium. The height of each floor can be adjusted freely with a certain range.
The final outcome of the building depends on clever height allotment for each floor. So, he plans to calculate possible combinations of per-floor heights to check how many options he has.
Given the height of the condominium and the adjustable range of each floor’s height, make a program to enumerate the number of choices for a floor.
Input
The input is given in the following format.
$H$ $A$ $B$
The input line provides the height of the condominium $H$ ($1 \leq H \leq 10^5$) and the upper and lower limits $A$ and $B$ of the height adjustable range for one floor ($1 \leq A \leq B \leq H$). All data are given as integers.
Output
Output the number of possible height selections for each floor in a line.
Examples
Input
100 2 4
Output
2
Input
101 3 5
Output
0
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Vladik often travels by trains. He remembered some of his trips especially well and I would like to tell you about one of these trips:
Vladik is at initial train station, and now n people (including Vladik) want to get on the train. They are already lined up in some order, and for each of them the city code a_{i} is known (the code of the city in which they are going to).
Train chief selects some number of disjoint segments of the original sequence of people (covering entire sequence by segments is not necessary). People who are in the same segment will be in the same train carriage. The segments are selected in such way that if at least one person travels to the city x, then all people who are going to city x should be in the same railway carriage. This means that they can’t belong to different segments. Note, that all people who travel to the city x, either go to it and in the same railway carriage, or do not go anywhere at all.
Comfort of a train trip with people on segment from position l to position r is equal to XOR of all distinct codes of cities for people on the segment from position l to position r. XOR operation also known as exclusive OR.
Total comfort of a train trip is equal to sum of comfort for each segment.
Help Vladik to know maximal possible total comfort.
-----Input-----
First line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5000) — number of people.
Second line contains n space-separated integers a_1, a_2, ..., a_{n} (0 ≤ a_{i} ≤ 5000), where a_{i} denotes code of the city to which i-th person is going.
-----Output-----
The output should contain a single integer — maximal possible total comfort.
-----Examples-----
Input
6
4 4 2 5 2 3
Output
14
Input
9
5 1 3 1 5 2 4 2 5
Output
9
-----Note-----
In the first test case best partition into segments is: [4, 4] [2, 5, 2] [3], answer is calculated as follows: 4 + (2 xor 5) + 3 = 4 + 7 + 3 = 14
In the second test case best partition into segments is: 5 1 [3] 1 5 [2, 4, 2] 5, answer calculated as follows: 3 + (2 xor 4) = 3 + 6 = 9.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
The Smart Beaver from ABBYY decided to have a day off. But doing nothing the whole day turned out to be too boring, and he decided to play a game with pebbles. Initially, the Beaver has n pebbles. He arranges them in a equal rows, each row has b pebbles (a > 1). Note that the Beaver must use all the pebbles he has, i. e. n = a·b.
<image> 10 pebbles are arranged in two rows, each row has 5 pebbles
Once the Smart Beaver has arranged the pebbles, he takes back any of the resulting rows (that is, b pebbles) and discards all other pebbles. Then he arranges all his pebbles again (possibly choosing other values of a and b) and takes back one row, and so on. The game continues until at some point the Beaver ends up with exactly one pebble.
The game process can be represented as a finite sequence of integers c1, ..., ck, where:
* c1 = n
* ci + 1 is the number of pebbles that the Beaver ends up with after the i-th move, that is, the number of pebbles in a row after some arrangement of ci pebbles (1 ≤ i < k). Note that ci > ci + 1.
* ck = 1
The result of the game is the sum of numbers ci. You are given n. Find the maximum possible result of the game.
Input
The single line of the input contains a single integer n — the initial number of pebbles the Smart Beaver has.
The input limitations for getting 30 points are:
* 2 ≤ n ≤ 50
The input limitations for getting 100 points are:
* 2 ≤ n ≤ 109
Output
Print a single number — the maximum possible result of the game.
Examples
Input
10
Output
16
Input
8
Output
15
Note
Consider the first example (c1 = 10). The possible options for the game development are:
* Arrange the pebbles in 10 rows, one pebble per row. Then c2 = 1, and the game ends after the first move with the result of 11.
* Arrange the pebbles in 5 rows, two pebbles per row. Then c2 = 2, and the game continues. During the second move we have two pebbles which can be arranged in a unique way (remember that you are not allowed to put all the pebbles in the same row!) — 2 rows, one pebble per row. c3 = 1, and the game ends with the result of 13.
* Finally, arrange the pebbles in two rows, five pebbles per row. The same logic leads us to c2 = 5, c3 = 1, and the game ends with the result of 16 — the maximum possible result.
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Solve the programming task below in a Python markdown code block.
Our world is one-dimensional, and ruled by two empires called Empire A and Empire B.
The capital of Empire A is located at coordinate X, and that of Empire B is located at coordinate Y.
One day, Empire A becomes inclined to put the cities at coordinates x_1, x_2, ..., x_N under its control, and Empire B becomes inclined to put the cities at coordinates y_1, y_2, ..., y_M under its control.
If there exists an integer Z that satisfies all of the following three conditions, they will come to an agreement, but otherwise war will break out.
- X < Z \leq Y
- x_1, x_2, ..., x_N < Z
- y_1, y_2, ..., y_M \geq Z
Determine if war will break out.
-----Constraints-----
- All values in input are integers.
- 1 \leq N, M \leq 100
- -100 \leq X < Y \leq 100
- -100 \leq x_i, y_i \leq 100
- x_1, x_2, ..., x_N \neq X
- x_i are all different.
- y_1, y_2, ..., y_M \neq Y
- y_i are all different.
-----Input-----
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M X Y
x_1 x_2 ... x_N
y_1 y_2 ... y_M
-----Output-----
If war will break out, print War; otherwise, print No War.
-----Sample Input-----
3 2 10 20
8 15 13
16 22
-----Sample Output-----
No War
The choice Z = 16 satisfies all of the three conditions as follows, thus they will come to an agreement.
- X = 10 < 16 \leq 20 = Y
- 8, 15, 13 < 16
- 16, 22 \geq 16
Read the inputs from stdin solve the problem and write the answer to stdout (do not directly test on the sample inputs). Enclose your code within ```python delimiters.
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.