[**🇨🇳中文**](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/blob/main/README.md) | [**🌐English**](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/blob/main/README_EN.md) | [**📖文档/Docs**](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki) | [**🤖模型/Models**](https://huggingface.co/shibing624)
-----------------
# MedicalGPT: Training Medical GPT Model
[](https://huggingface.co/shibing624)
[](https://star-history.com/#shibing624/MedicalGPT&Timeline)
[](CONTRIBUTING.md)
[](LICENSE)
[](requirements.txt)
[](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/issues)
[](#Contact)
## 📖 Introduction
**MedicalGPT** training medical GPT model with ChatGPT training pipeline, implemantation of Pretraining,
Supervised Finetuning, Reward Modeling and Reinforcement Learning.
 Training MedicalGPT model:
- Stage 1:PT(Continue PreTraining), Pre-training the LLaMA model on massive domain document data to inject domain knowledge
- Stage 2: SFT (Supervised Fine-tuning) has supervised fine-tuning, constructs instruction fine-tuning data sets, and performs instruction fine-tuning on the basis of pre-trained models to align instruction intentions
- Stage 3: RM (Reward Model) reward model modeling, constructing a human preference ranking data set, training the reward model to align human preferences, mainly the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless"
- Stage 4: RL (Reinforcement Learning) is based on human feedback reinforcement learning (RLHF), using the reward model to train the SFT model, and the generation model uses rewards or penalties to update its strategy in order to generate higher quality, more in line with human preferences text
## ▶️ Demo
- Hugging Face Demo: doing
We provide a simple Gradio-based interactive web interface. After the service is started, it can be accessed through a browser, enter a question, and the model will return an answer. The command is as follows:
```shell
python scripts/gradio_demo.py --base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir --lora_model path_to_lora_dir
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format, or use the HF Model Hub model call name
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is located, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If the lora weights have been merged into the pre-trained model, delete the --lora_model parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
## 🚀 Training Pipeline
### Stage 1: Continue Pretraining
Based on the llama-7b model, use medical encyclopedia data to continue pre-training, and expect to inject medical knowledge into the pre-training model to obtain the llama-7b-pt model. This step is optional
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_pt.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 2: Supervised FineTuning
Based on the llama-7b-pt model, the llama-7b-sft model is obtained by using medical question-and-answer data for supervised fine-tuning. This step is required
Supervised fine-tuning of the base llama-7b-pt model to create llama-7b-sft
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_sft.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 3: Reward Modeling
RM(Reward Model): reward model modeling
In principle, we can directly use human annotations to fine-tune the model with RLHF.
However, this will require us to send some samples to humans to be scored after each round of optimization. This is expensive and slow due to the large number of training samples required for convergence and the limited speed at which humans can read and annotate them.
A better strategy than direct feedback is to train a reward model RM on the human annotated set before entering the RL loop. The purpose of the reward model is to simulate human scoring of text.
The best practice for building a reward model is to rank the prediction results, that is, for each prompt (input text) corresponding to two results (yk, yj), the model predicts which score the human annotation is higher.
The RM model is trained by manually marking the scoring results of the SFT model. The purpose is to replace manual scoring. It is essentially a regression model used to align human preferences, mainly based on the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless".
Based on the llama-7b-sft model, the reward preference model is trained using medical question and answer preference data, and the llama-7b-reward model is obtained after training. This step is required
Reward modeling using dialog pairs from the reward dataset using the llama-7b-sft to create llama-7b-reward:
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rm.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 4: Reinforcement Learning
The purpose of the RL (Reinforcement Learning) model is to maximize the output of the reward model. Based on the above steps, we have a fine-tuned language model (llama-7b-sft) and reward model (llama-7b-reward).
The RL loop is ready to execute.
This process is roughly divided into three steps:
1. Enter prompt, the model generates a reply
2. Use a reward model to score responses
3. Based on the score, a round of reinforcement learning for policy optimization (PPO)
Training MedicalGPT model:
- Stage 1:PT(Continue PreTraining), Pre-training the LLaMA model on massive domain document data to inject domain knowledge
- Stage 2: SFT (Supervised Fine-tuning) has supervised fine-tuning, constructs instruction fine-tuning data sets, and performs instruction fine-tuning on the basis of pre-trained models to align instruction intentions
- Stage 3: RM (Reward Model) reward model modeling, constructing a human preference ranking data set, training the reward model to align human preferences, mainly the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless"
- Stage 4: RL (Reinforcement Learning) is based on human feedback reinforcement learning (RLHF), using the reward model to train the SFT model, and the generation model uses rewards or penalties to update its strategy in order to generate higher quality, more in line with human preferences text
## ▶️ Demo
- Hugging Face Demo: doing
We provide a simple Gradio-based interactive web interface. After the service is started, it can be accessed through a browser, enter a question, and the model will return an answer. The command is as follows:
```shell
python scripts/gradio_demo.py --base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir --lora_model path_to_lora_dir
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format, or use the HF Model Hub model call name
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is located, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If the lora weights have been merged into the pre-trained model, delete the --lora_model parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
## 🚀 Training Pipeline
### Stage 1: Continue Pretraining
Based on the llama-7b model, use medical encyclopedia data to continue pre-training, and expect to inject medical knowledge into the pre-training model to obtain the llama-7b-pt model. This step is optional
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_pt.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 2: Supervised FineTuning
Based on the llama-7b-pt model, the llama-7b-sft model is obtained by using medical question-and-answer data for supervised fine-tuning. This step is required
Supervised fine-tuning of the base llama-7b-pt model to create llama-7b-sft
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_sft.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 3: Reward Modeling
RM(Reward Model): reward model modeling
In principle, we can directly use human annotations to fine-tune the model with RLHF.
However, this will require us to send some samples to humans to be scored after each round of optimization. This is expensive and slow due to the large number of training samples required for convergence and the limited speed at which humans can read and annotate them.
A better strategy than direct feedback is to train a reward model RM on the human annotated set before entering the RL loop. The purpose of the reward model is to simulate human scoring of text.
The best practice for building a reward model is to rank the prediction results, that is, for each prompt (input text) corresponding to two results (yk, yj), the model predicts which score the human annotation is higher.
The RM model is trained by manually marking the scoring results of the SFT model. The purpose is to replace manual scoring. It is essentially a regression model used to align human preferences, mainly based on the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless".
Based on the llama-7b-sft model, the reward preference model is trained using medical question and answer preference data, and the llama-7b-reward model is obtained after training. This step is required
Reward modeling using dialog pairs from the reward dataset using the llama-7b-sft to create llama-7b-reward:
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rm.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 4: Reinforcement Learning
The purpose of the RL (Reinforcement Learning) model is to maximize the output of the reward model. Based on the above steps, we have a fine-tuned language model (llama-7b-sft) and reward model (llama-7b-reward).
The RL loop is ready to execute.
This process is roughly divided into three steps:
1. Enter prompt, the model generates a reply
2. Use a reward model to score responses
3. Based on the score, a round of reinforcement learning for policy optimization (PPO)
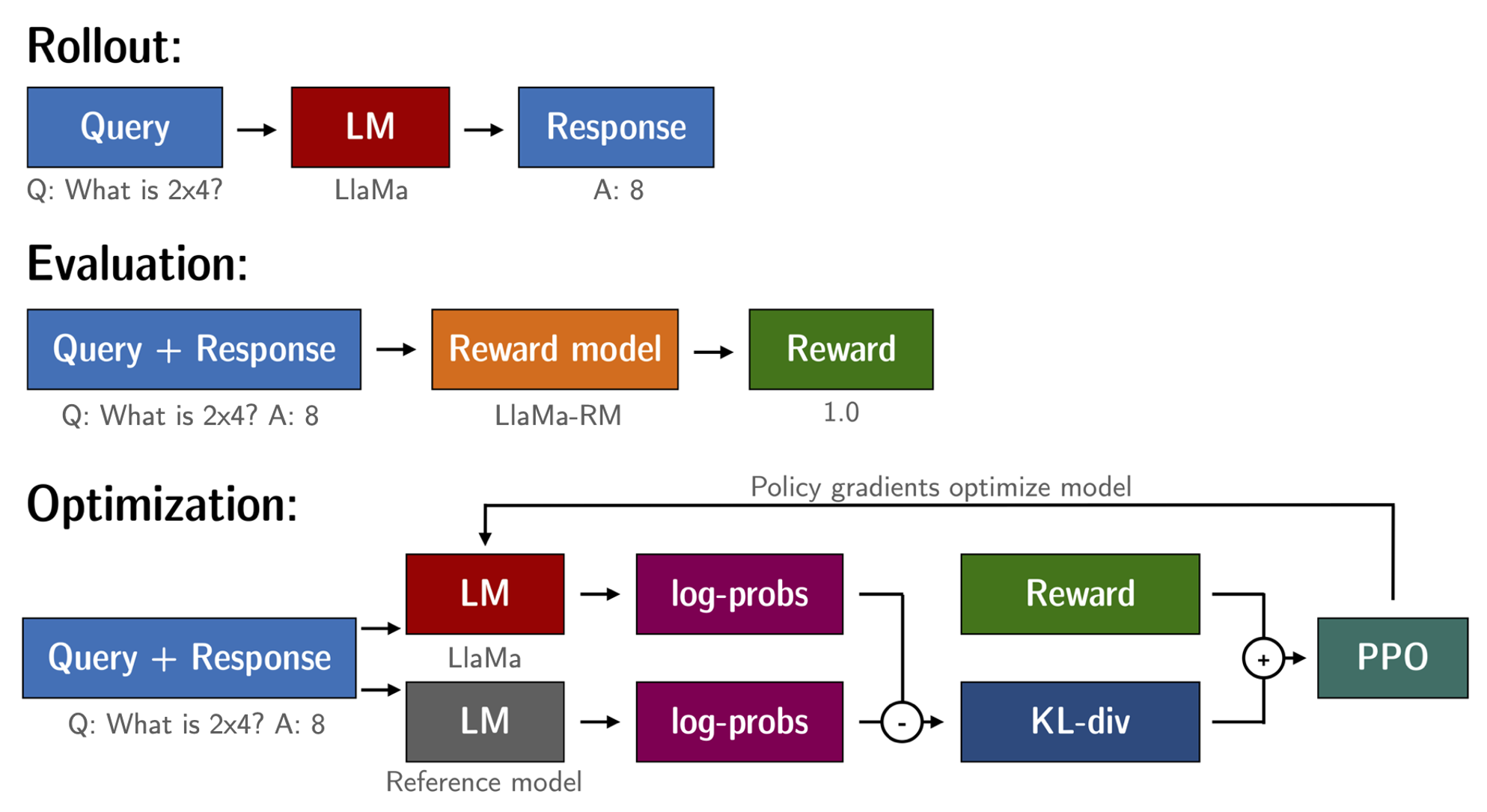 Reinforcement Learning fine-tuning of llama-7b-sft with the llama-7b-reward reward model to create llama-7b-rl
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rl.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
## 🔥 Inference
After the training is complete, now we load the trained model to verify the effect of the model generating text.
```shell
python scripts/inference.py \
--base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir \
--lora_model path_to_lora \
--with_prompt \
--interactive
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: Directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is decompressed, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If you have incorporated LoRA weights into the pre-trained model, you can not provide this parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--with_prompt`: Whether to merge the input with the prompt template. Be sure to enable this option if loading an Alpaca model!
- `--interactive`: start interactively for multiple single rounds of question and answer
- `--data_file {file_name}`: Start in non-interactive mode, read the contents of file_name line by line for prediction
- `--predictions_file {file_name}`: In non-interactive mode, write the predicted results to file_name in json format
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
#### Inference Examples
Reinforcement Learning fine-tuning of llama-7b-sft with the llama-7b-reward reward model to create llama-7b-rl
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rl.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
## 🔥 Inference
After the training is complete, now we load the trained model to verify the effect of the model generating text.
```shell
python scripts/inference.py \
--base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir \
--lora_model path_to_lora \
--with_prompt \
--interactive
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: Directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is decompressed, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If you have incorporated LoRA weights into the pre-trained model, you can not provide this parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--with_prompt`: Whether to merge the input with the prompt template. Be sure to enable this option if loading an Alpaca model!
- `--interactive`: start interactively for multiple single rounds of question and answer
- `--data_file {file_name}`: Start in non-interactive mode, read the contents of file_name line by line for prediction
- `--predictions_file {file_name}`: In non-interactive mode, write the predicted results to file_name in json format
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
#### Inference Examples
| Human | Assistant |
| ----- | ------ |
| How to make yourself energetic, list 5 suggestions | Here are some suggestions to keep you energetic:
1. Get enough sleep. Make sure to get enough sleep every night.
2. Exercise more. Doing moderate aerobic exercise, such as jogging and swimming, can help improve your energy and stamina. 3. Eat healthy food. Choose protein-rich foods such as chicken, fish, and eggs, as well as fresh fruits and vegetables. 4. Reduce caffeine intake. Try to avoid drinking caffeinated beverages or eating caffeinated foods during the day.
5. Relax. Try meditation, yoga, or other forms of relaxation to reduce stress and anxiety. |
## 📚 Dataset
- 2.4 million Chinese medical datasets (including pre-training, instruction fine-tuning and reward datasets): [shibing624/medical](https://huggingface.co/datasets/shibing624/medical)
**Attach links to some general datasets and medical datasets**
- Belle dataset of 500,000 Chinese ChatGPT commands: [BelleGroup/train_0.5M_CN](https://huggingface.co/datasets/BelleGroup/train_0.5M_CN)
- Belle dataset of 1 million Chinese ChatGPT commands: [BelleGroup/train_1M_CN](https://huggingface.co/datasets/BelleGroup/train_1M_CN)
- Alpaca dataset of 50,000 English ChatGPT commands: [50k English Stanford Alpaca dataset](https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca#data-release)
- Alpaca dataset of 20,000 Chinese GPT-4 instructions: [shibing624/alpaca-zh](https://huggingface.co/datasets/shibing624/alpaca-zh)
- Guanaco dataset with 690,000 Chinese instructions (500,000 Belle + 190,000 Guanaco): [Chinese-Vicuna/guanaco_belle_merge_v1.0](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Chinese-Vicuna/guanaco_belle_merge_v1.0)
- 220,000 Chinese medical dialogue datasets (HuatuoGPT project): [FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT-sft-data-v1](https://huggingface.co/datasets/FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT-sft-data-v1)
## ✅ Todo
1. [ ] Added multi-round dialogue data fine-tuning method
2. [x] add reward model finetuning
3. [x] add rl finetuning
4. [x] add medical reward dataset
5. [x] add llama in8/int4 training
6. [ ] add all training and predict demo in colab
## ☎️ Contact
- Issue (suggestion)
: [](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/issues)
- Email me: xuming: xuming624@qq.com
- WeChat Me: Add me* WeChat ID: xuming624, Remarks: Name-Company Name-NLP* Enter the NLP exchange group.
 ## ⚠️ Limitations, Restrictions of Use and Disclaimer
The SFT model trained based on the current data and the basic model still has the following problems in terms of effect:
1. Wrong answers that contradict the facts may be generated on the factual instructions.
2. Unable to identify harmful instructions well, resulting in harmful speech.
3. The ability of the model still needs to be improved in some scenarios involving reasoning, code, and multiple rounds of dialogue.
Based on the limitations of the above models, we require developers to only use our open source model weights and subsequent derivatives generated by this project for research purposes, and not for commercial use, and other purposes that will cause harm to society.
This project can only be used for research purposes, and the project developer is not responsible for any harm or loss caused by the use of this project (including but not limited to data, models, codes, etc.). For details, please refer to [Disclaimer](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/blob/main/DISCLAIMER).
The license agreement for the project code is [The Apache License 2.0](/LICENSE), the code is free for commercial use, and the model weights and data can only be used for research purposes. Please attach MedicalGPT's link and license agreement in the product description.
## 😇 Citation
If you used MedicalGPT in your research, please cite as follows:
```latex
@misc{MedicalGPT,
title={MedicalGPT: Training Medical GPT Model},
author={Ming Xu},
year={2023},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT}},
}
```
## 😍 Contribute
The project code is still very rough. If you have improved the code, you are welcome to submit it back to this project. Before submitting, please pay attention to the following two points:
- Add corresponding unit tests in `tests`
- Use `python -m pytest` to run all unit tests to ensure that all unit tests are passed
Then you can submit a PR.
## 💕 Acknowledgements
- [tloen/alpaca-lora](https://github.com/tloen/alpaca-lora/blob/main/finetune.py)
- [ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca](https://github.com/ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca)
Thanks for their great work!
## ⚠️ Limitations, Restrictions of Use and Disclaimer
The SFT model trained based on the current data and the basic model still has the following problems in terms of effect:
1. Wrong answers that contradict the facts may be generated on the factual instructions.
2. Unable to identify harmful instructions well, resulting in harmful speech.
3. The ability of the model still needs to be improved in some scenarios involving reasoning, code, and multiple rounds of dialogue.
Based on the limitations of the above models, we require developers to only use our open source model weights and subsequent derivatives generated by this project for research purposes, and not for commercial use, and other purposes that will cause harm to society.
This project can only be used for research purposes, and the project developer is not responsible for any harm or loss caused by the use of this project (including but not limited to data, models, codes, etc.). For details, please refer to [Disclaimer](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/blob/main/DISCLAIMER).
The license agreement for the project code is [The Apache License 2.0](/LICENSE), the code is free for commercial use, and the model weights and data can only be used for research purposes. Please attach MedicalGPT's link and license agreement in the product description.
## 😇 Citation
If you used MedicalGPT in your research, please cite as follows:
```latex
@misc{MedicalGPT,
title={MedicalGPT: Training Medical GPT Model},
author={Ming Xu},
year={2023},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT}},
}
```
## 😍 Contribute
The project code is still very rough. If you have improved the code, you are welcome to submit it back to this project. Before submitting, please pay attention to the following two points:
- Add corresponding unit tests in `tests`
- Use `python -m pytest` to run all unit tests to ensure that all unit tests are passed
Then you can submit a PR.
## 💕 Acknowledgements
- [tloen/alpaca-lora](https://github.com/tloen/alpaca-lora/blob/main/finetune.py)
- [ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca](https://github.com/ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca)
Thanks for their great work!

 Training MedicalGPT model:
- Stage 1:PT(Continue PreTraining), Pre-training the LLaMA model on massive domain document data to inject domain knowledge
- Stage 2: SFT (Supervised Fine-tuning) has supervised fine-tuning, constructs instruction fine-tuning data sets, and performs instruction fine-tuning on the basis of pre-trained models to align instruction intentions
- Stage 3: RM (Reward Model) reward model modeling, constructing a human preference ranking data set, training the reward model to align human preferences, mainly the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless"
- Stage 4: RL (Reinforcement Learning) is based on human feedback reinforcement learning (RLHF), using the reward model to train the SFT model, and the generation model uses rewards or penalties to update its strategy in order to generate higher quality, more in line with human preferences text
## ▶️ Demo
- Hugging Face Demo: doing
We provide a simple Gradio-based interactive web interface. After the service is started, it can be accessed through a browser, enter a question, and the model will return an answer. The command is as follows:
```shell
python scripts/gradio_demo.py --base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir --lora_model path_to_lora_dir
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format, or use the HF Model Hub model call name
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is located, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If the lora weights have been merged into the pre-trained model, delete the --lora_model parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
## 🚀 Training Pipeline
### Stage 1: Continue Pretraining
Based on the llama-7b model, use medical encyclopedia data to continue pre-training, and expect to inject medical knowledge into the pre-training model to obtain the llama-7b-pt model. This step is optional
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_pt.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 2: Supervised FineTuning
Based on the llama-7b-pt model, the llama-7b-sft model is obtained by using medical question-and-answer data for supervised fine-tuning. This step is required
Supervised fine-tuning of the base llama-7b-pt model to create llama-7b-sft
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_sft.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 3: Reward Modeling
RM(Reward Model): reward model modeling
In principle, we can directly use human annotations to fine-tune the model with RLHF.
However, this will require us to send some samples to humans to be scored after each round of optimization. This is expensive and slow due to the large number of training samples required for convergence and the limited speed at which humans can read and annotate them.
A better strategy than direct feedback is to train a reward model RM on the human annotated set before entering the RL loop. The purpose of the reward model is to simulate human scoring of text.
The best practice for building a reward model is to rank the prediction results, that is, for each prompt (input text) corresponding to two results (yk, yj), the model predicts which score the human annotation is higher.
The RM model is trained by manually marking the scoring results of the SFT model. The purpose is to replace manual scoring. It is essentially a regression model used to align human preferences, mainly based on the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless".
Based on the llama-7b-sft model, the reward preference model is trained using medical question and answer preference data, and the llama-7b-reward model is obtained after training. This step is required
Reward modeling using dialog pairs from the reward dataset using the llama-7b-sft to create llama-7b-reward:
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rm.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 4: Reinforcement Learning
The purpose of the RL (Reinforcement Learning) model is to maximize the output of the reward model. Based on the above steps, we have a fine-tuned language model (llama-7b-sft) and reward model (llama-7b-reward).
The RL loop is ready to execute.
This process is roughly divided into three steps:
1. Enter prompt, the model generates a reply
2. Use a reward model to score responses
3. Based on the score, a round of reinforcement learning for policy optimization (PPO)
Training MedicalGPT model:
- Stage 1:PT(Continue PreTraining), Pre-training the LLaMA model on massive domain document data to inject domain knowledge
- Stage 2: SFT (Supervised Fine-tuning) has supervised fine-tuning, constructs instruction fine-tuning data sets, and performs instruction fine-tuning on the basis of pre-trained models to align instruction intentions
- Stage 3: RM (Reward Model) reward model modeling, constructing a human preference ranking data set, training the reward model to align human preferences, mainly the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless"
- Stage 4: RL (Reinforcement Learning) is based on human feedback reinforcement learning (RLHF), using the reward model to train the SFT model, and the generation model uses rewards or penalties to update its strategy in order to generate higher quality, more in line with human preferences text
## ▶️ Demo
- Hugging Face Demo: doing
We provide a simple Gradio-based interactive web interface. After the service is started, it can be accessed through a browser, enter a question, and the model will return an answer. The command is as follows:
```shell
python scripts/gradio_demo.py --base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir --lora_model path_to_lora_dir
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format, or use the HF Model Hub model call name
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is located, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If the lora weights have been merged into the pre-trained model, delete the --lora_model parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
## 🚀 Training Pipeline
### Stage 1: Continue Pretraining
Based on the llama-7b model, use medical encyclopedia data to continue pre-training, and expect to inject medical knowledge into the pre-training model to obtain the llama-7b-pt model. This step is optional
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_pt.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 2: Supervised FineTuning
Based on the llama-7b-pt model, the llama-7b-sft model is obtained by using medical question-and-answer data for supervised fine-tuning. This step is required
Supervised fine-tuning of the base llama-7b-pt model to create llama-7b-sft
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_sft.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 3: Reward Modeling
RM(Reward Model): reward model modeling
In principle, we can directly use human annotations to fine-tune the model with RLHF.
However, this will require us to send some samples to humans to be scored after each round of optimization. This is expensive and slow due to the large number of training samples required for convergence and the limited speed at which humans can read and annotate them.
A better strategy than direct feedback is to train a reward model RM on the human annotated set before entering the RL loop. The purpose of the reward model is to simulate human scoring of text.
The best practice for building a reward model is to rank the prediction results, that is, for each prompt (input text) corresponding to two results (yk, yj), the model predicts which score the human annotation is higher.
The RM model is trained by manually marking the scoring results of the SFT model. The purpose is to replace manual scoring. It is essentially a regression model used to align human preferences, mainly based on the "HHH" principle, specifically "helpful, honest, harmless".
Based on the llama-7b-sft model, the reward preference model is trained using medical question and answer preference data, and the llama-7b-reward model is obtained after training. This step is required
Reward modeling using dialog pairs from the reward dataset using the llama-7b-sft to create llama-7b-reward:
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rm.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
### Stage 4: Reinforcement Learning
The purpose of the RL (Reinforcement Learning) model is to maximize the output of the reward model. Based on the above steps, we have a fine-tuned language model (llama-7b-sft) and reward model (llama-7b-reward).
The RL loop is ready to execute.
This process is roughly divided into three steps:
1. Enter prompt, the model generates a reply
2. Use a reward model to score responses
3. Based on the score, a round of reinforcement learning for policy optimization (PPO)
 Reinforcement Learning fine-tuning of llama-7b-sft with the llama-7b-reward reward model to create llama-7b-rl
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rl.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
## 🔥 Inference
After the training is complete, now we load the trained model to verify the effect of the model generating text.
```shell
python scripts/inference.py \
--base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir \
--lora_model path_to_lora \
--with_prompt \
--interactive
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: Directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is decompressed, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If you have incorporated LoRA weights into the pre-trained model, you can not provide this parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--with_prompt`: Whether to merge the input with the prompt template. Be sure to enable this option if loading an Alpaca model!
- `--interactive`: start interactively for multiple single rounds of question and answer
- `--data_file {file_name}`: Start in non-interactive mode, read the contents of file_name line by line for prediction
- `--predictions_file {file_name}`: In non-interactive mode, write the predicted results to file_name in json format
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
#### Inference Examples
Reinforcement Learning fine-tuning of llama-7b-sft with the llama-7b-reward reward model to create llama-7b-rl
```shell
cd scripts
sh run_rl.sh
```
[Training Detail wiki](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/wiki/Training-Details)
## 🔥 Inference
After the training is complete, now we load the trained model to verify the effect of the model generating text.
```shell
python scripts/inference.py \
--base_model path_to_llama_hf_dir \
--lora_model path_to_lora \
--with_prompt \
--interactive
```
Parameter Description:
- `--base_model {base_model}`: Directory to store LLaMA model weights and configuration files in HF format
- `--lora_model {lora_model}`: The directory where the LoRA file is decompressed, and the name of the HF Model Hub model can also be used. If you have incorporated LoRA weights into the pre-trained model, you can not provide this parameter
- `--tokenizer_path {tokenizer_path}`: Store the directory corresponding to the tokenizer. If this parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --lora_model; if the --lora_model parameter is not provided, its default value is the same as --base_model
- `--with_prompt`: Whether to merge the input with the prompt template. Be sure to enable this option if loading an Alpaca model!
- `--interactive`: start interactively for multiple single rounds of question and answer
- `--data_file {file_name}`: Start in non-interactive mode, read the contents of file_name line by line for prediction
- `--predictions_file {file_name}`: In non-interactive mode, write the predicted results to file_name in json format
- `--use_cpu`: use only CPU for inference
- `--gpus {gpu_ids}`: Specifies the number of GPU devices used, the default is 0. If using multiple GPUs, separate them with commas, such as 0,1,2
#### Inference Examples
 ## ⚠️ Limitations, Restrictions of Use and Disclaimer
The SFT model trained based on the current data and the basic model still has the following problems in terms of effect:
1. Wrong answers that contradict the facts may be generated on the factual instructions.
2. Unable to identify harmful instructions well, resulting in harmful speech.
3. The ability of the model still needs to be improved in some scenarios involving reasoning, code, and multiple rounds of dialogue.
Based on the limitations of the above models, we require developers to only use our open source model weights and subsequent derivatives generated by this project for research purposes, and not for commercial use, and other purposes that will cause harm to society.
This project can only be used for research purposes, and the project developer is not responsible for any harm or loss caused by the use of this project (including but not limited to data, models, codes, etc.). For details, please refer to [Disclaimer](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/blob/main/DISCLAIMER).
The license agreement for the project code is [The Apache License 2.0](/LICENSE), the code is free for commercial use, and the model weights and data can only be used for research purposes. Please attach MedicalGPT's link and license agreement in the product description.
## 😇 Citation
If you used MedicalGPT in your research, please cite as follows:
```latex
@misc{MedicalGPT,
title={MedicalGPT: Training Medical GPT Model},
author={Ming Xu},
year={2023},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT}},
}
```
## 😍 Contribute
The project code is still very rough. If you have improved the code, you are welcome to submit it back to this project. Before submitting, please pay attention to the following two points:
- Add corresponding unit tests in `tests`
- Use `python -m pytest` to run all unit tests to ensure that all unit tests are passed
Then you can submit a PR.
## 💕 Acknowledgements
- [tloen/alpaca-lora](https://github.com/tloen/alpaca-lora/blob/main/finetune.py)
- [ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca](https://github.com/ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca)
Thanks for their great work!
## ⚠️ Limitations, Restrictions of Use and Disclaimer
The SFT model trained based on the current data and the basic model still has the following problems in terms of effect:
1. Wrong answers that contradict the facts may be generated on the factual instructions.
2. Unable to identify harmful instructions well, resulting in harmful speech.
3. The ability of the model still needs to be improved in some scenarios involving reasoning, code, and multiple rounds of dialogue.
Based on the limitations of the above models, we require developers to only use our open source model weights and subsequent derivatives generated by this project for research purposes, and not for commercial use, and other purposes that will cause harm to society.
This project can only be used for research purposes, and the project developer is not responsible for any harm or loss caused by the use of this project (including but not limited to data, models, codes, etc.). For details, please refer to [Disclaimer](https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT/blob/main/DISCLAIMER).
The license agreement for the project code is [The Apache License 2.0](/LICENSE), the code is free for commercial use, and the model weights and data can only be used for research purposes. Please attach MedicalGPT's link and license agreement in the product description.
## 😇 Citation
If you used MedicalGPT in your research, please cite as follows:
```latex
@misc{MedicalGPT,
title={MedicalGPT: Training Medical GPT Model},
author={Ming Xu},
year={2023},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/shibing624/MedicalGPT}},
}
```
## 😍 Contribute
The project code is still very rough. If you have improved the code, you are welcome to submit it back to this project. Before submitting, please pay attention to the following two points:
- Add corresponding unit tests in `tests`
- Use `python -m pytest` to run all unit tests to ensure that all unit tests are passed
Then you can submit a PR.
## 💕 Acknowledgements
- [tloen/alpaca-lora](https://github.com/tloen/alpaca-lora/blob/main/finetune.py)
- [ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca](https://github.com/ymcui/Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca)
Thanks for their great work!