 - A Visual Analysis of BERT
- A Visual Analysis of BERT
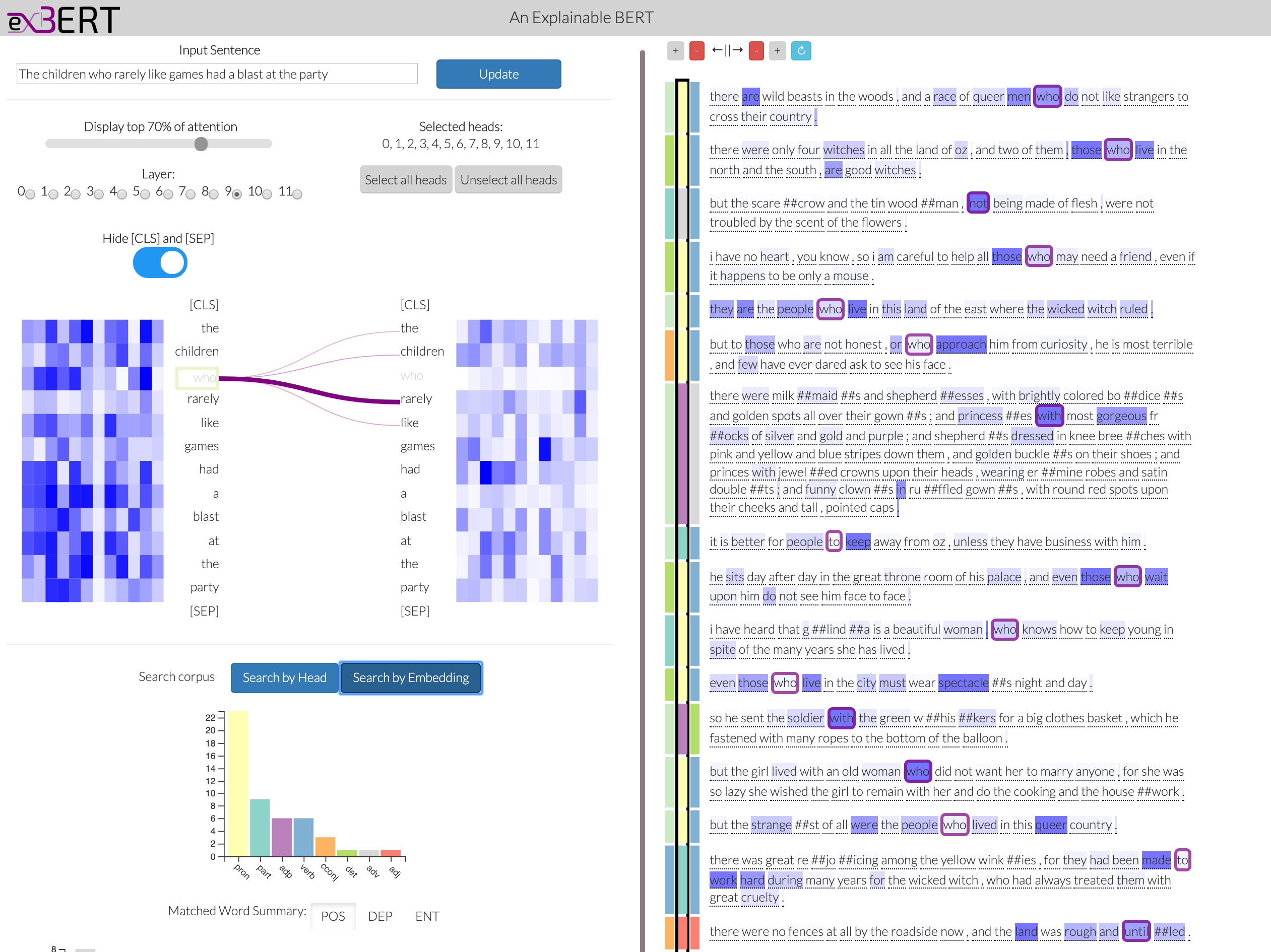
Large language models can produce powerful contextual representations that lead to improvements across many NLP tasks. Since these models are typically guided by a sequence of learned self attention mechanisms and may comprise undesired inductive biases, it is paramount to be able to explore what the attention has learned. While static analyses of these models lead to targeted insights, interactive tools are more dynamic and can help humans better gain an intuition for the model-internal reasoning process.
We present exBERT , an interactive tool named after the popular BERT language model, that provides insights into the meaning of the contextual representations by matching a human-specified input to similar contexts in a large annotated dataset. By aggregating the annotations of the matching similar contexts, exBERT helps intuitively explain what each attention-head has learned.
Large language models can produce powerful contextual representations that lead to improvements across many NLP tasks. Though these models can comprise undesired inductive biases, it is challenging to identify what information they encode in their learned representations.
Since the model-internal reasoning process is often guided by a sequence of learned self-attention mechanisms, it is paramount to be able to explore what the attention has learned. While static analyses for this can lead to targeted insights, interactive tools can be more dynamic and help humans gain an intuition for the model-internal reasoning process. We present exBERT, a tool that helps to gain insights into the meaning of the contextual representations. exBERT matches a human-specified input to similar contexts in a large annotated dataset. By aggregating these annotations across all similar contexts, exBERT can help to explain what each attention-head has learned.
Thanks to Jesse Vig for feedback. Please let us know what you think by commenting below!
We care about your privacy, but know that your activity on the site may be monitored. For more information, check out the links below.
