# Train DCGAN on your custom data
This folder contains a script to train [DCGAN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434) for unconditional image generation, leveraging the [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/) ecosystem for processing your data and pushing the model to the Hub.
The script leverages 🤗 Datasets for loading and processing data, and 🤗 Accelerate for instantly running on CPU, single, multi-GPUs or TPU, also supporting fp16/mixed precision.

## Launching the script
To train the model with the default parameters (5 epochs, 64x64 images, etc.) on [MNIST](https://huggingface.co/datasets/mnist), first run:
```bash
accelerate config
```
and answer the questions asked about your environment. Next, launch the script as follows:
```bash
accelerate launch train.py
```
This will create a local "images" directory, containing generated images over the course of the training.
To train on another dataset available on the hub, simply do (for instance):
```bash
python train.py --dataset cifar-10
```
In case you'd like to tweak the script to your liking, first fork the "community-events" [repo](https://github.com/huggingface/community-events) (see the button on the top right), then clone it locally:
```bash
git clone https://github.com//community-events.git
```
and edit to your liking.
## Training on your own data
You can of course also train on your own images. For this, one can leverage Datasets' [ImageFolder](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/v2.0.0/en/image_process#imagefolder). Make sure to authenticate with the hub first, by running the `huggingface-cli login` command in a terminal, or the following in case you're working in a notebook:
```python
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()
```
Next, run the following in a notebook/script:
```python
from datasets import load_dataset
# first: load dataset
# option 1: from local folder
dataset = load_dataset("imagefolder", data_dir="path_to_folder")
# option 2: from remote URL (e.g. a zip file)
dataset = load_dataset("imagefolder", data_files="URL to .zip file")
# next: push to the hub (assuming git-LFS is installed)
dataset.push_to_hub("huggan/my-awesome-dataset")
```
You can then simply pass the name of the dataset to the script:
```bash
accelerate launch train.py --dataset huggan/my-awesome-dataset
```
## Pushing model to the Hub
You can push your trained generator to the hub after training by specifying the `push_to_hub` flag, along with a `model_name` and `pytorch_dump_folder_path`.
```bash
accelerate launch train.py --push_to_hub --model_name dcgan-mnist
```
This is made possible by making the generator inherit from `PyTorchModelHubMixin`available in the `huggingface_hub` library.
This means that after training, generating a new image can be done as follows:
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage
from huggingface_hub import PyTorchModelHubMixin
class Generator(nn.Module, PyTorchModelHubMixin):
def __init__(self, num_channels=3, latent_dim=100, hidden_size=64):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
# input is Z, going into a convolution
nn.ConvTranspose2d(latent_dim, hidden_size * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_size * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (hidden_size*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(hidden_size * 8, hidden_size * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_size * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (hidden_size*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d(hidden_size * 4, hidden_size * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_size * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (hidden_size*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_size),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (hidden_size) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d(hidden_size, num_channels, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# state size. (num_channels) x 64 x 64
)
def forward(self, noise):
pixel_values = self.model(noise)
return pixel_values
model = Generator.from_pretrained("huggan/dcgan-mnist")
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu
model.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
z = torch.randn(1, 100, 1, 1, device=device)
pixel_values = model(z)
# turn into actual image
image = pixel_values[0]
image = (image + 1) /2
image = ToPILImage()(image)
image.save("generated.png")
```
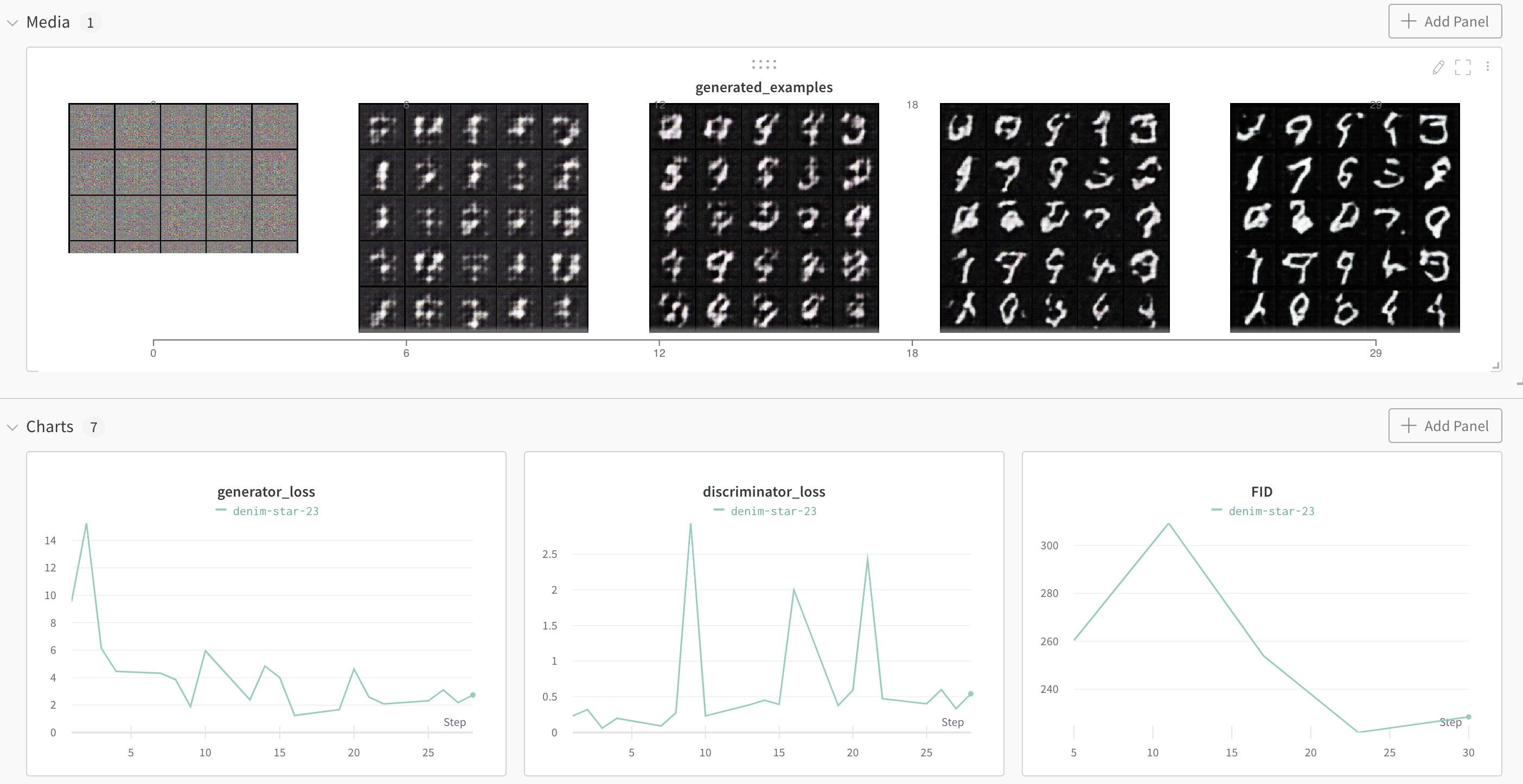
## Weights and Biases integration
You can easily add logging to [Weights and Biases](https://wandb.ai/site) by passing the `--wandb` flag:
```bash
accelerate launch train.py --wandb
````
You can then follow the progress of your GAN in a browser:
# Citation
This repo is entirely based on PyTorch's official [DCGAN tutorial](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html), but with added HuggingFace goodies.


