---
license: apache-2.0
metrics:
- mse
---
# PatchTSMixer model pre-trained on ETTh1 dataset
The [`PatchTSMixer`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/patchtsmixer) is a lightweight and fast multivariate time series forecasting model with state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets.
In this context, we offer a pre-trained `PatchTSMixer` model encompassing all seven channels of the `ETTh1` dataset.
This particular pre-trained model produces a Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 0.37 on the `test` split of the `ETTh1` dataset when forecasting 96 hours into the future with a historical data window of 512 hours.
For training and evaluating a `PatchTSMixer` model, you can refer to [this notebook](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
## Model Details
The PatchTSMixer model was proposed in [TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09364.pdf) by Vijay Ekambaram, Arindam Jati, Nam Nguyen, Phanwadee Sinthong and Jayant Kalagnanam.
PatchTSMixer is a lightweight time-series modeling approach based on the MLP-Mixer architecture. In [this HuggingFace implementation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/patchtsmixer), we provide PatchTSMixer’s capabilities to effortlessly facilitate lightweight mixing across patches, channels, and hidden features for effective multivariate time-series modeling. It also supports various attention mechanisms starting from simple gated attention to more complex self-attention blocks that can be customized accordingly. The model can be pretrained and subsequently used for various downstream tasks such as forecasting, classification and regression.
### Model Description
TSMixer is a lightweight neural architecture exclusively composed of multi-layer perceptron (MLP) modules designed for multivariate forecasting and representation learning on patched time series. Our model draws inspiration from the success of MLP-Mixer models in computer vision. We demonstrate the challenges involved in adapting Vision MLP-Mixer for time series and introduce empirically validated components to enhance accuracy. This includes a novel design paradigm of attaching online reconciliation heads to the MLP-Mixer backbone, for explicitly modeling the time-series properties such as hierarchy and channel-correlations. We also propose a Hybrid channel modeling approach to effectively handle noisy channel interactions and generalization across diverse datasets, a common challenge in existing patch channel-mixing methods. Additionally, a simple gated attention mechanism is introduced in the backbone to prioritize important features. By incorporating these lightweight components, we significantly enhance the learning capability of simple MLP structures, outperforming complex Transformer models with minimal computing usage. Moreover, TSMixer’s modular design enables compatibility with both supervised and masked self-supervised learning methods, making it a promising building block for time-series Foundation Models. TSMixer outperforms state-of-the-art MLP and Transformer models in forecasting by a considerable margin of 8-60%. It also outperforms the latest strong benchmarks of Patch-Transformer models (by 1-2%) with a significant reduction in memory and runtime (2-3X).
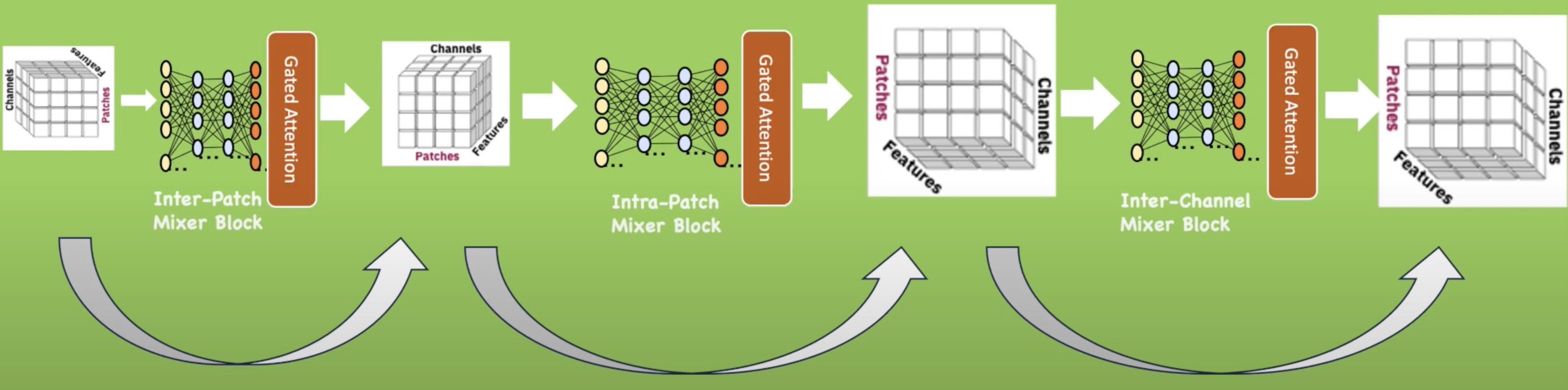 ### Model Sources
- **Repository:** [PatchTSMixer Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/patchtsmixer)
- **Paper:** [PatchTSMixer KDD 2023 paper](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3580305.3599533)
- **Demo:** [Get started with PatchTSMixer](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Uses
This pre-trained model can be employed for fine-tuning or evaluation using any Electrical Transformer dataset that has the same channels as the `ETTh1` dataset, specifically: `HUFL, HULL, MUFL, MULL, LUFL, LULL, OT`. The model is designed to predict the next 96 hours based on the input values from the preceding 512 hours. It is crucial to normalize the data. For a more comprehensive understanding of data pre-processing, please consult the paper or the demo.
## How to Get Started with the Model
Use the code below to get started with the model.
[Demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Training Details
### Training Data
[`ETTh1`/train split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Training Hyperparameters
Please refer to the [PatchTSMixer paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09364.pdf).
## Evaluation
### Testing Data, Factors & Metrics
#### Testing Data
[`ETTh1`/test split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Metrics
Mean Squared Error (MSE).
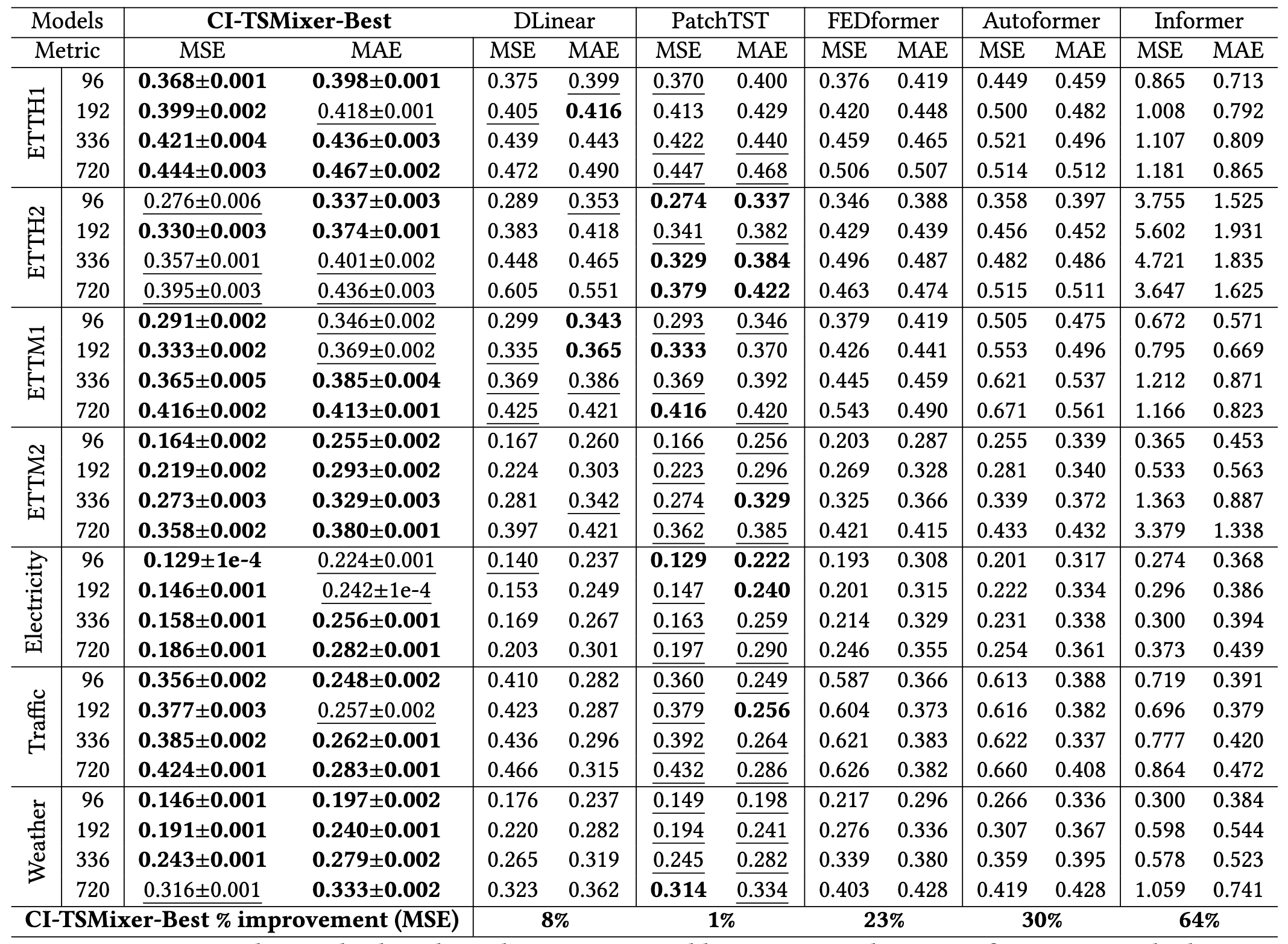
### Results
### Model Sources
- **Repository:** [PatchTSMixer Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/patchtsmixer)
- **Paper:** [PatchTSMixer KDD 2023 paper](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3580305.3599533)
- **Demo:** [Get started with PatchTSMixer](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Uses
This pre-trained model can be employed for fine-tuning or evaluation using any Electrical Transformer dataset that has the same channels as the `ETTh1` dataset, specifically: `HUFL, HULL, MUFL, MULL, LUFL, LULL, OT`. The model is designed to predict the next 96 hours based on the input values from the preceding 512 hours. It is crucial to normalize the data. For a more comprehensive understanding of data pre-processing, please consult the paper or the demo.
## How to Get Started with the Model
Use the code below to get started with the model.
[Demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Training Details
### Training Data
[`ETTh1`/train split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Training Hyperparameters
Please refer to the [PatchTSMixer paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09364.pdf).
## Evaluation
### Testing Data, Factors & Metrics
#### Testing Data
[`ETTh1`/test split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Metrics
Mean Squared Error (MSE).
### Results
 #### Hardware
1 NVIDIA A100 GPU
#### Software
PyTorch
## Citation
**BibTeX:**
```
@article{ekambaram2023tsmixer,
title={TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting},
author={Ekambaram, Vijay and Jati, Arindam and Nguyen, Nam and Sinthong, Phanwadee and Kalagnanam, Jayant},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364},
year={2023}
}
```
**APA:**
```
Ekambaram, V., Jati, A., Nguyen, N., Sinthong, P., & Kalagnanam, J. (2023). TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364.
```
#### Hardware
1 NVIDIA A100 GPU
#### Software
PyTorch
## Citation
**BibTeX:**
```
@article{ekambaram2023tsmixer,
title={TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting},
author={Ekambaram, Vijay and Jati, Arindam and Nguyen, Nam and Sinthong, Phanwadee and Kalagnanam, Jayant},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364},
year={2023}
}
```
**APA:**
```
Ekambaram, V., Jati, A., Nguyen, N., Sinthong, P., & Kalagnanam, J. (2023). TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364.
``` ### Model Sources
- **Repository:** [PatchTSMixer Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/patchtsmixer)
- **Paper:** [PatchTSMixer KDD 2023 paper](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3580305.3599533)
- **Demo:** [Get started with PatchTSMixer](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Uses
This pre-trained model can be employed for fine-tuning or evaluation using any Electrical Transformer dataset that has the same channels as the `ETTh1` dataset, specifically: `HUFL, HULL, MUFL, MULL, LUFL, LULL, OT`. The model is designed to predict the next 96 hours based on the input values from the preceding 512 hours. It is crucial to normalize the data. For a more comprehensive understanding of data pre-processing, please consult the paper or the demo.
## How to Get Started with the Model
Use the code below to get started with the model.
[Demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Training Details
### Training Data
[`ETTh1`/train split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Training Hyperparameters
Please refer to the [PatchTSMixer paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09364.pdf).
## Evaluation
### Testing Data, Factors & Metrics
#### Testing Data
[`ETTh1`/test split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Metrics
Mean Squared Error (MSE).
### Results
### Model Sources
- **Repository:** [PatchTSMixer Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/patchtsmixer)
- **Paper:** [PatchTSMixer KDD 2023 paper](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3580305.3599533)
- **Demo:** [Get started with PatchTSMixer](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Uses
This pre-trained model can be employed for fine-tuning or evaluation using any Electrical Transformer dataset that has the same channels as the `ETTh1` dataset, specifically: `HUFL, HULL, MUFL, MULL, LUFL, LULL, OT`. The model is designed to predict the next 96 hours based on the input values from the preceding 512 hours. It is crucial to normalize the data. For a more comprehensive understanding of data pre-processing, please consult the paper or the demo.
## How to Get Started with the Model
Use the code below to get started with the model.
[Demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb)
## Training Details
### Training Data
[`ETTh1`/train split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Training Hyperparameters
Please refer to the [PatchTSMixer paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09364.pdf).
## Evaluation
### Testing Data, Factors & Metrics
#### Testing Data
[`ETTh1`/test split](https://github.com/zhouhaoyi/ETDataset/blob/main/ETT-small/ETTh1.csv).
Train/validation/test splits are shown in the [demo](https://github.com/IBM/tsfm/blob/main/notebooks/hfdemo/patch_tsmixer_getting_started.ipynb).
#### Metrics
Mean Squared Error (MSE).
### Results
 #### Hardware
1 NVIDIA A100 GPU
#### Software
PyTorch
## Citation
**BibTeX:**
```
@article{ekambaram2023tsmixer,
title={TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting},
author={Ekambaram, Vijay and Jati, Arindam and Nguyen, Nam and Sinthong, Phanwadee and Kalagnanam, Jayant},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364},
year={2023}
}
```
**APA:**
```
Ekambaram, V., Jati, A., Nguyen, N., Sinthong, P., & Kalagnanam, J. (2023). TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364.
```
#### Hardware
1 NVIDIA A100 GPU
#### Software
PyTorch
## Citation
**BibTeX:**
```
@article{ekambaram2023tsmixer,
title={TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting},
author={Ekambaram, Vijay and Jati, Arindam and Nguyen, Nam and Sinthong, Phanwadee and Kalagnanam, Jayant},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364},
year={2023}
}
```
**APA:**
```
Ekambaram, V., Jati, A., Nguyen, N., Sinthong, P., & Kalagnanam, J. (2023). TSMixer: Lightweight MLP-Mixer Model for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09364.
```